查询M29W400BB供应商
4 Mbit (512Kb x8 or 256Kb x16, Boot Block)
Low Voltage Single Supply Flash Memory
■ SINGLE 2.7 to 3.6V SUPPLYVOLTAGE for
PROGRAM, ERASE and READ OPERATIONS
■ ACCESS TIME: 5 5ns
■ PROGRAMMING TIME
– 10 µs per Byte/ Word typical
■ 11 MEMORY BLOCKS
– 1 Boot Block (Top or Bot tom Location)
– 2Parameterand8MainBlocks
■ PROGRAM/ERASE CONTROLLER
– Em bedded Byte/Word Program algorithm
– Em bedded Multi-Block/Chip Erase algorithm
– Status Register Polling and Toggle Bits
– Ready/Busy Output Pin
■ ERASE SUSPEND and RESUMEMODES
– Read and Program another Block during
Erase Suspend
■ UNLOCK BYPASS PROGRAM COMMAND
– Fas ter Production/Batch Programming
■ TEMPORARY BLOCK UNPROTECTION
MODE
■ LOW POWER CONSUMPTION
– Standby and Automatic Standby
■ 100,000 PROGRAM/ERASE CYCLES per
BLOCK
■ 20 YEARS DATA RETENTION
– Defec tivity below 1 ppm/year
■ ELECTRONIC SIGNATURE
– Manuf acturer Code: 0020h
– Top Device Co de M29W400BT: 00EEh
– Bottom Device Code M29W400BB: 00EFh
M29W400BT
M29W400BB
TSOP48 (N)
12 x 20mm
44
1
SO44 (M)
Figure 1. Logic Diagram
V
CC
18
A0-A17
W
E
G
RP
M29W400BT
M29W400BB
FBGA
TFBGA48 (ZA)
6 x 8 ball array
15
DQ0-DQ14
DQ15A–1
BYTE
RB
V
SS
AI02934
1/25June 2001
M29W400BT, M29W400BB
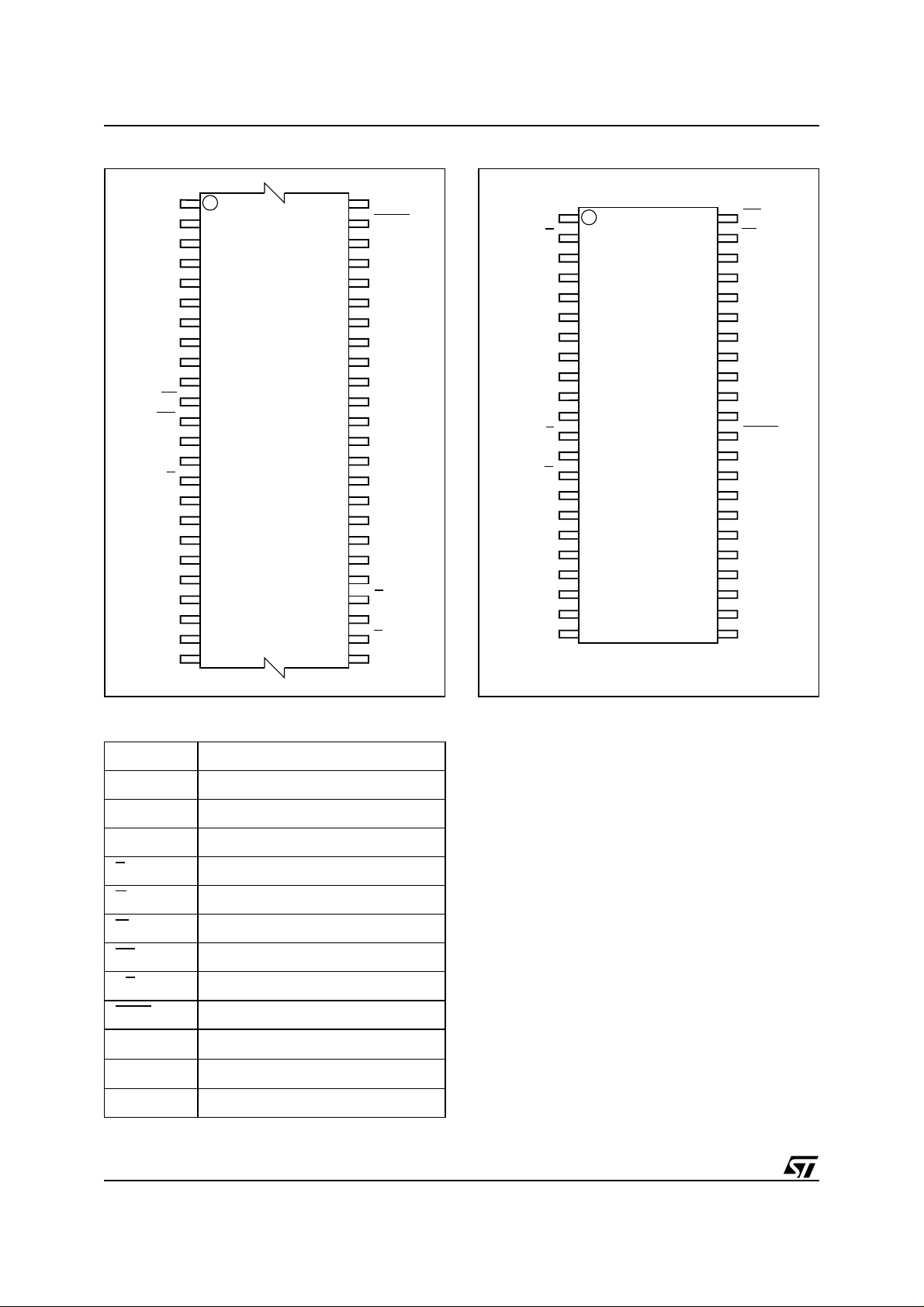
Figure 2. TSOP Connections
A15
A14
A13
A12
A11
A10 DQ14
A9
A8
NC
NC
RP
NC
NC
RB
NC
A17
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
1
W
12
M29W400BT
M29W400BB
13
24 25
48
37
36
AI02935
A16
BYTE
V
SS
DQ15A–1
DQ7
DQ6
DQ13
DQ5
DQ12
DQ4
V
CC
DQ11
DQ3
DQ10
DQ2
DQ9
DQ1
DQ8
DQ0
G
V
SS
E
A0
Figure 3. SO Connections
NC RP
A17 A8
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
A0
V
SS
DQ0
DQ8
DQ9
DQ10
DQ3
DQ11
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
M29W400BT
M29W400BB
12
E
13
14
G
15
16
17DQ1
18
19
20
21
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
2322
AI02936
WRB
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
A16
BYTE
V
SS
DQ15A–1
DQ7
DQ14
DQ6
DQ13
DQ5DQ2
DQ12
DQ4
V
CC
Table 1. Signal Names
A0-A17 Address Inputs
DQ0-DQ7 Data Inputs/Outputs
DQ8-DQ14 Data Inputs/Outputs
DQ15A–1 Data Input/Output or Address Input
E
G
W
RP
RB
BYTE
V
CC
V
SS
NC Not Connected Internally
2/25
Chip Enable
Output Enable
Write Enable
Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect
Ready/Busy Output
Byte/Word Organization Select
Supply Voltage
Ground
SUMMARY DESCRIPTION
The M29W400B is a 4 Mbit (512Kb x8 or 256Kb
x16) non-volatile memory t hat can be read, erased
and reprogrammed. These operations can be performed using a single low voltage (2.7 to 3.6V)
supply. O n power-up the memory d efau lts to its
Read mode where it c an be read in the same way
as a ROM or EPROM. The M29W400B is fully
backward compatible with the M29W400.
The memory is divided into block s that can be
erased independently so it is possible to preserve
valid data while old data is erased. Each block can
be protected independently to prevent accidental
Program or Erase commands from modifying the
memory. Program and Erase com mands are w ritten to the Com mand Interface of the memory. An
on-chip Program/Erase Controller simp lifies the
process of programm ing or erasing the memory by
taking care of all of the spec ial operations that are
required to update the memory contents. The end
of a program or erase operation c an be detected
and any error c onditions identified. The command
set required to contro l the memory is consistent
with J E DE C standards.
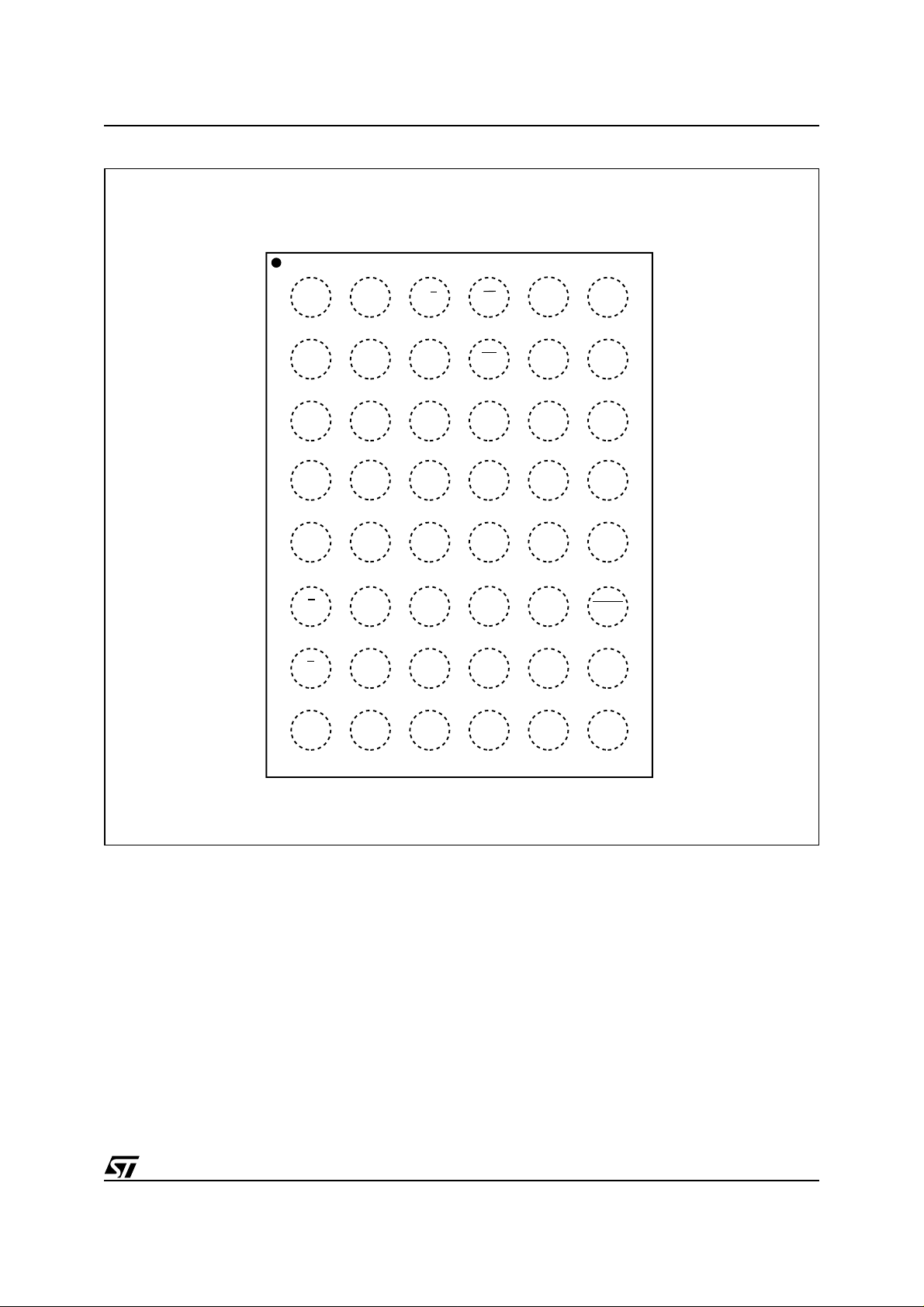
Figure 4. TFBGA Connections (Top view through package)
M29W400BT, M29W400BB
4321
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
A3
A7
A5
DQ0
RB
NCA17A4
NC
DQ10DQ8E
W A13
RP A8
DQ12
V
CC
A9
DQ14
DQ13DQ11DQ9G
65
A12
A14A10NCNCA6A2
A15A11NCA1
A16DQ7DQ5DQ2A0
BYTE
DQ15
A–1
H
SS
DQ3
The blocks in the memory are asymmetrically arranged, see Tables 3 and 4, Block Addresses. The
first or last 64 Kbytes have been divided into four
additional blocks. The 16 Kbyte Boot Block can be
used for small init ialization code t o start the microprocessor, the t wo 8 Kbyte Parame ter Blocks can
be used for parameter storage and the remaining
32K is a small Main Block where the application
may be stored.
DQ4
DQ6DQ1V
V
SS
AI03988
Chip Enab le, Output Enable and Write Enable signals control the bus operation of the memory.
They allo w simple connection to most microprocessors, often without additional logic.
The memory is offered in TSOP48 (12 x 20mm),
TFBGA48 (0.8mm pitch) and SO44 packages and
it is supplied with all the bits erased (set to ’1’).
3/25
M29W400BT, M29W400BB
Table 2. Absolute Maximum Ratings
(1)
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
T
A
T
BIAS
T
STG
(2)
V
IO
V
CC
V
ID
Note: 1. Except for the rating "Operating Temperature Range", stresses above those listed in the Table "Absolute Maximum Ratings" may
cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation of the device at these or any other conditions
above those indicated in the Operating sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to A bsolute Maximum Rating conditionsforextended periodsmayaffect device reliability.Refer alsotothe STMicroelectronics SUREProgram and otherrelevant quality documents.
2. Minimum Voltage may undershoot to –2V during transition and for less than 20ns during transitions.
Table 3. Top Boot Block Addresses
M29W400BT
Size
#
(Kbytes)
10 16 7C000h-7FFFFh 3E000h-3FFFFh
9 8 7A000h-7BFFFh 3D000h-3DFFFh
8 8 78000h-79FFFh 3C000h-3CFFFh
Ambient Operating Temperature (Temperature Range Option 1) 0 to 70 °C
Ambient Operating Temperature (Temperature Range Option 6) –40 to 85 °C
Temperature Under Bias –50 to 125 °C
Storage Temperature –65 to 150 °C
Input or Output Voltage –0.6 to 4 V
Supply Voltage –0.6 to 4 V
Identification Voltage –0.6 to 13.5 V
Table 4. Bottom Boo t B l ock Addresses
M29W400BB
Address Range
(x8)
Address Range
(x16)
#
(Kbytes)
Size
Address Range
(x8)
Address Range
(x16)
10 64 70000h-7FFFFh 38000h-3FFFFh
9 64 60000h-6FFFFh 30000h-37FFFh
8 64 50000h-5FFFFh 28000h-2FFFFh
7 32 70000h-77FFFh 38000h-3BFFFh
6 64 60000h-6FFFFh 30000h-37FFFh
5 64 50000h-5FFFFh 28000h-2FFFFh
4 64 40000h-4FFFFh 20000h-27FFFh
3 64 30000h-3FFFFh 18000h-1FFFFh
2 64 20000h-2FFFFh 10000h-17FFFh
1 64 10000h-1FFFFh 08000h-0FFFFh
0 64 00000h-0FFFFh 00000h-07FFFh
7 64 40000h-4FFFFh 20000h-27FFFh
6 64 30000h-3FFFFh 18000h-1FFFFh
5 64 20000h-2FFFFh 10000h-17FFFh
4 64 10000h-1FFFFh 08000h-0FFFFh
3 32 08000h-0FFFFh 04000h-07FFFh
2 8 06000h-07FFFh 03000h-03FFFh
1 8 04000h-05FFFh 02000h-02FFFh
0 16 00000h-03FFFh 00000h-01FFFh
4/25

M29W400BT, M29W400BB
SIGNAL DESCRIPTIONS
See Figure 1, Logic Diagram, and T able 1, Signal
Names, for a brief overview of the signals connected to this device.
Address Inputs (A0-A17). The Address Inputs
select the cells in the memory array to access during Bus Read operations. During Bus W r ite operations they control the commands sent to the
Command Interface of the internal state machine.
Data I np uts/Ou tputs (DQ0-DQ7). TheDataInputs/Outputs output the data stored at the selected
address during a Bus Read op eration. During Bus
Write op erations they represent the commands
sent to the Command Interface of the internal state
machine.
Data I np uts/Ou tputs (DQ8-DQ14). The Data Inputs/Outputs output the data stored at the selected
address during a Bus Read operation when BYTE
is High, VIH. When BYTE is Low, VIL, these pins
are not used and are hi gh im pedance. During Bus
Write operations the Command Register does not
use thes e bits. When reading the Status R egister
these bits should be ignored.
Data Input/Output or Address Input (DQ15A-1).
When B Y TE
is High, VIH, this pin behaves as a
Data Input/Output pin (as DQ8-DQ14). When
BYTE
is Low, VIL, this pin behaves as an address
pin; DQ15A–1 L ow will select the LSB of the Word
on the other addresses, DQ15A–1 High will select
the M SB. Throughout the text c onsider references
to the Data Input/Output to include this pin when
is High and references to the Address In-
BYTE
puts to include this pin when BYTE
is Low except
when stated explicitly otherwise.
Chip Enable (E
). The Chip Enable, E, activates
thememory,allowingBusReadandBusWriteoperations to be performed. When Chip Enable is
High, V
Output Enable (G
, all other pins are ignored.
IH
). T he Output Enable, G, con-
trols the Bus Read operation of the memory.
WriteEnable(W
). The Write Enable, W, controls
the Bus W rite operation of th e memory’s Command Interface.
Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect (RP
). The Re-
set/Block Temporary Unprotect pin can be us ed to
apply a Hardware Res et to the memory or to temporarily unprotect all Blocks that h ave been protected.
A Hardware Reset is ac hieved by holding Reset/
Block Temporary Unprotect Low, V
. After Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect
t
PLPX
goes High, V
, the memory will be read y for Bus
IH
Read and Bus Write operations after t
, for at least
IL
PHEL
or
t
, whichever occurs last. See the Ready/Busy
RHEL
Output section, Table 17 and Figure 12, Reset/
Temporary Unprotect A C Characteristics for more
details.
Holding RP
at VIDwill temporarily unprotect the
protected Blocks in the memory. Program and
Erase operations on all blocks will b e possible.
The transition from V
t
PHPHH
.
Ready/Busy Output (RB
to VIDmust be slower than
IH
). The Ready/Busy pin
is an open-drain output that can be used to identify
when the memory array can be read. Ready/Busy
is high-imp edance during Read mode, Auto Select
mode and Erase Suspend mode.
After a Hardware Reset, Bus Read and B us Write
operations cannot begin until Ready /Bus y becomes hi gh-impedance. See Table 17 and Figure
12, R es et /T emporary Unprotect AC Characteristics.
During Program or Erase operations Re ady /Busy
is Low, V
. Ready/Busy will remain Low during
OL
Read/Reset commands or Hardware Resets until
the memory is ready to ente r Read mode.
The use of an open-drain output allows the Ready/
Busy pins from several memories to be connected
to a single pull-up resistor. A Low will then indicate
that one, or more, of the memories is busy.
Byte/Word Organization Select (BYTE). The Byte/
Word Organization Selec t pin is used to switch between the 8-bit and 16-bit Bus modes of the memory. When Byte/Word Organization Select is Low,
, the memory is in 8-bit mode, when it is High,
V
IL
V
, the mem ory is in 16-bit mode.
IH
Supply Voltage. The VCCSupply Voltage
V
CC
supplies the power for all operations (Read, Program, Erase etc.).
The Command Interface is disabled when the V
CC
Supply Voltage is less than the Lockout Voltage,
V
. This prevents Bus Write operations from ac-
LKO
cidentally damaging the data during power up,
power down and power surges. If the Program/
Erase Controller is program min g or erasing during
this time then the operation aborts an d the memory contents being altered will be invalid.
A 0.1µF capacitor should be c onnec ted between
the V
Supply Voltage pin and the VSSGround
CC
pin to decouple the current s urges from the power
supply. The PCB track widths must be sufficient to
carry the c urrent s required during program and
erase operations,I
Ground. The VSSGround is the reference for
V
SS
CC3
.
all voltage measurements.
5/25
M29W400BT, M29W400BB
BUS OPERATIONS
Thereare five standard bus operations that control
the device. These are Bus Read, Bus Write, OutPut Disable, Standby and Automat ic Standby. See
Tables 5 and 6, Bus Operations, for a summary.
Typically glitches of less than 5ns on Chip Enable
or Write Enable are ig nored by the memory and do
not affect bus operations.
Bus Read. B us Read operations read from the
memory cells, or specific registers in the Command Interface. A valid Bus Read ope ra tion involves setting the desired address on the Address
Inputs, applying a Low sig nal, V
, to Chip Enable
IL
and Output Enable and keeping Write Enable
High, V
. The Data Inputs/Outputs will output the
IH
value, see Figure 9, Read Mode AC Waveforms,
and Table 14, Read AC Charac teristics, for details
of when the output becom es valid.
Bus Write. Bus Write op erations write to the
Command Interface. A valid Bus Write o peration
begins by setting the desired address on the Address Inputs. The Addres s Inputs are latched by
the Command Interface on the falling edge of Chip
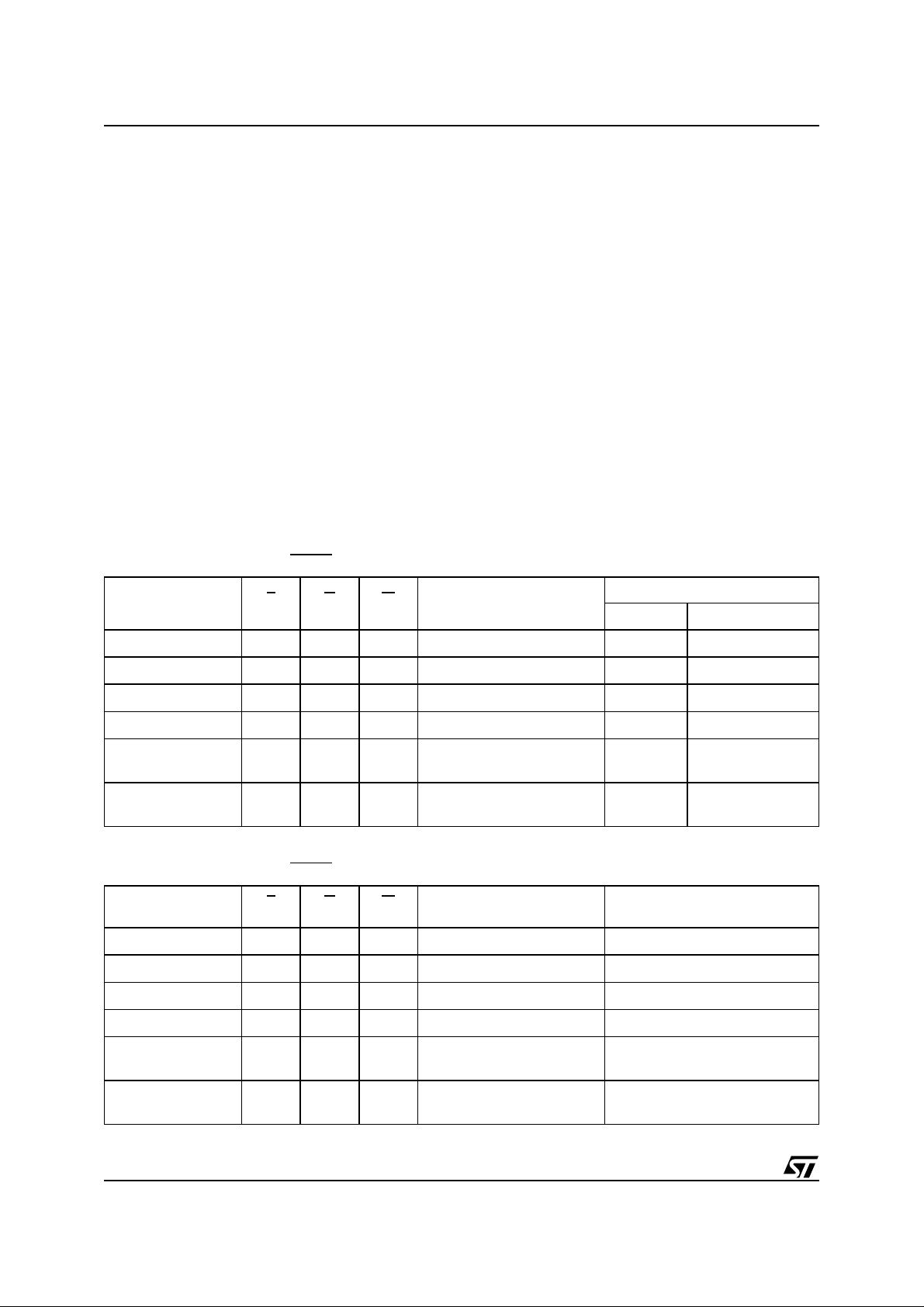
Table 5. Bus Operations, BYTE
Operation E G W
=V
IL
Enable or Write Enable, whichever occurs last.
The Data Inputs/Outputs are latched by the Command Interface on the rising edge of Chip Enable
orWrite Enable, whichever occurs first.Output Enable must rem ain High, V
, during the whole Bus
IH
Write operation. See Figures 10 and 11, Write AC
Waveforms, and Tab les 15 and 16, Write AC
Characteristics, for details of the timi ng requirements.
Output Disable. The Dat a Inputs/Outputs are in
the high im pedance state when Output E nable is
High, V
.
IH
Standby. When Chip Enable is High, V
memory enters St andby mode and th e Data Inputs/Outputs pins are placed in the high-impedance state. To reduce the Supply Current to t he
Standby Supply Current, I
be held within V
±0.2V. For the Standby current
CC
, Chip Enable should
CC2
level see Table 13 , DC Charac teristics.
During program or erase operations the memory
will continue to use the Program/Erase Supply
Current, I
, for P r ogram or Erase operations un-
CC3
til the operation completes.
Address Inputs
DQ15A–1, A0-A17
Data Inputs/Outputs
DQ14-DQ8 DQ7-DQ0
,the
IH
Bus Read
Bus Write
Output Disable X
Standby
Read Manufacturer
Code
Read Device Code
Note: X = VILor VIH.
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
V
IH
X X X Hi-Z Hi-Z
V
IL
V
IL
Table 6. Bus Operations, BYTE =V
Operation E
Bus Read
Bus Write
Output Disable X
Standby
Read Manufacturer
Code
Read Device Code
Note: X = VILor VIH.
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
V
IL
G W
V
IL
V
IH
V
IH
X X X Hi-Z
V
IL
V
IL
V
Cell Address Hi-Z Data Output
IH
V
Command Address Hi-Z Data Input
IL
V
X Hi-Z Hi-Z
IH
A0 = VIL,A1=VIL,A9=VID,
V
IH
Others V
A0=VIH,A1=VIL,A9=VID,
V
IH
Others VILor V
IH
or V
IL
IH
IH
Address Inputs
A0-A17
V
Cell Address Data Output
IH
V
Command Address Data Input
IL
V
X Hi-Z
IH
A0 = VIL,A1=VIL,A9=VID,
V
IH
Others V
A0=VIH,A1=VIL,A9=VID,
V
IH
Others V
or V
IL
IH
or V
IL
IH
Hi-Z 20h
Hi-Z
EEh (M29W400BT)
EFh (M29W400BB)
Data Inputs/Outputs
DQ15A–1, DQ14-DQ0
0020h
00EEh (M29W400BT)
00EFh (M29W400BB)
6/25

M29W400BT, M29W400BB
Automatic Standby. If CMOS levels (VCC±0.2V)
are used to drive the bus and the bus is inactive for
150ns or more t he memory enters Automatic
Standby where the internal Supply Current is reduced to t he Standby Supply Current, I
CC2
.The
Data Inputs/Outputs will still o utpu t data if a Bus
Read operation is in progress.
Special Bus Operations
Additional bus operations can be performed to
read the Electronic Signature and also to apply
and remove Block Protection. Thes e bus operations are intended for use by programming equipment and are not usually used in applications.
They require V
to be applie d to some pin s.
ID
Electronic Signature. The memory has two
codes, the manufacturer code and the device
code, that can be read to identify the memory.
These codes can be read by applying the signals
listed in Tables 5 and 6, Bus Operations.
Block Protection and Blocks Unprotection. Each
block can be separately protected against accidental Program or Erase. Protected blocks can be
unprotected to allow data to be changed.
There are two methods available for protec ting
and unprotecting the blocks, one for use on programming equipment and the other for in-system
use. For further inform ation refer to Appl icati on
Note A N 1122, Applying Protection and Unprotection to M29 Series Flash.
COMMAND INTERFACE
All Bus Write operations t o the memory are interpreted by t he Comman d Interface. Com mands
consist of one or more sequential Bus Write operations. Failure to observe a valid sequence of Bus
Write operations wil l result in the memory returning t o Re ad mode. The long command sequences
are imposed to maximize dat a security.
The address used for the co mm ands changes depending on whether the memory is in 16-bit or 8bit mode. See either Table 7, or 8, depending on
the configuration that is being used, for a summary of the comm ands .
Read/Reset Command. The Rea d/Reset command returns the memory to its Read mode where
it behaves like a ROM or EPROM. It also resets
the errors in the Status Register. Either one or
three Bus Write operations can be used to issue
the Read/Reset command.
If the Read/Reset co mm and is issued during a
Block Erase operation or following a Programming
or Erase error then the memory will take up to
10µs to abort. During the abort period no valid data
can be read from the memory. Issuing a Read/Reset c ommand during a Block Erase operation wi ll
leave invalid data in the m emory.
Auto Select Command. The Aut o Selec t command is used to read the Manufacturer C ode, the
Device Code and t he Block Protection Stat us.
Three consecutive Bus Write operations are required to issue the Auto Select command. Once
the Auto Select command is issued the memory
remains in Auto Select mode until another command is issued.
From the Auto Select mode the Manufacturer
Code can be read using a Bus Read operation
with A0 = V
may be set to either V
and A1 = VIL. Th e other address bits
IL
or VIH. The Manufacturer
IL
Code for STMicroelectronics is 0020h.
The D evice Code can be read using a Bus Read
operation with A0 = V
address bits may be set to either V
and A1 = VIL. The other
IH
or VIH.The
IL
Device Code for the M29W400BT is 00EEh and
for the M29W400BB is 00EFh.
The Block Protection Status of each block can be
read using a Bus Read op eration with A0 = V
A1 = V
, and A12-A17 specifying the address of
IH
IL
the bl oc k. The other address bits may be set to either V
or VIH. If the addressed block is protected
IL
then 01h is output on Dat a Inputs/Outputs D Q0DQ7, otherwise 00h is output.
Program Command. The Program command
can be used to program a value to one address in
the memory array at a time. The command requires four Bus Write operations, the final write operation latches t he address and data in the internal
state machine and starts t he Program/Erase Controller.
If the address fa lls in a protected bloc k then the
Program command i s ignored, the d ata remains
unchanged. The Status R egister is never read and
no error condition is given.
During the program operation the memory will ignore all commands. It is not possible to issue any
command to abort or paus e the operation. Typical
program times are given in Table 9. Bus Read operations during the program operation will output
the Status Register on the Data Inputs/Outputs.
See the section on the Status Register for more
details.
After the program operation has completed the
memory will return to the Read mode, unless an
error has occurred. When an error occurs the
memory will continue t o output the Status Register. A Read/Reset command must be issued to reset the error condition and return t o Read mode.
Note that the Program command cannot change a
bit set at ’0’ back to ’1. One of the Er as e Commands must be used to s et all the bit s in a block or
in the whole mem ory from ’ 0’ to ’1’.
,
7/25
M29W400BT, M29W400BB
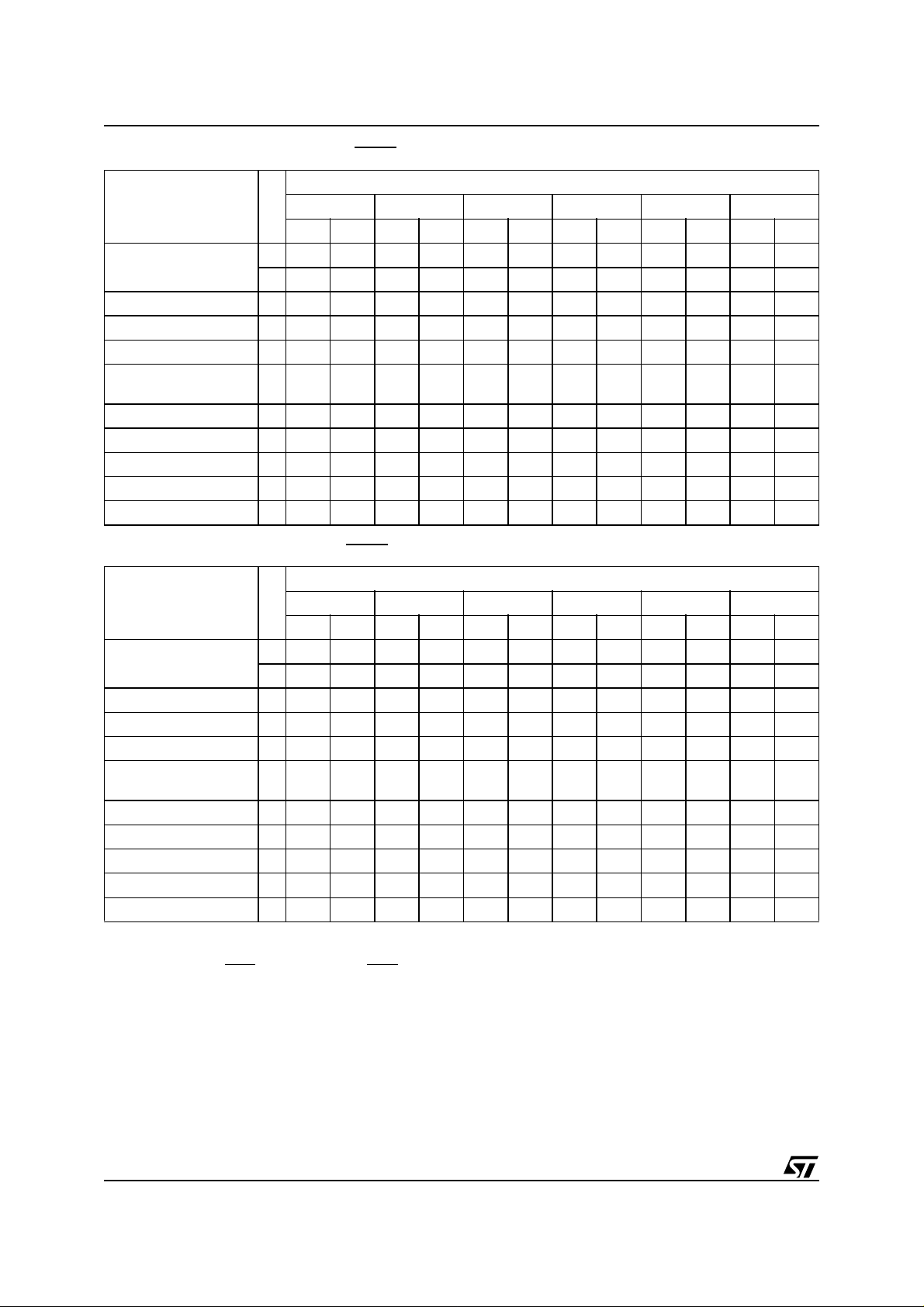
Table 7. Commands, 16-bit mode, BYTE =V
IH
Bus Write Operations
Command
Read/Reset
1X F0
3 555 AA 2AA 55 X F0
1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 6th
Length
Addr Data Addr Data Addr Data Addr Data Addr Data Addr Data
Auto Select 3 555 AA 2AA 55 555 90
Program 4 555 AA 2AA 55 555 A0 PA PD
Unlock Bypass 3 555 AA 2AA 55 555 20
Unlock Bypass
Program
2X A0PAPD
Unlock Bypass Reset 2 X 90 X 00
Chip Erase 6 555 AA 2AA 55 555 80 555 AA 2AA 55 555 10
Block Erase 6+ 555 AA 2AA 55 555 80 555 AA 2AA 55 BA 30
Erase Suspend 1 X B0
Erase Resume 1 X 30
Table 8. Commands, 8-bit mode, BYTE =V
IL
Bus Write Operations
Command
Read/Reset
1X F0
3 AAA AA 555 55 X F0
1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 6th
Length
Addr Data Addr Data Addr Data Addr Data Addr Data Addr Data
Auto Select 3 AAA AA 555 55 AAA 90
Program 4 AAA AA 555 55 AAA A0 PA PD
Unlock Bypass 3 AAA AA 555 55 AAA 20
Unlock Bypass
Program
2X A0PAPD
Unlock Bypass Reset 2 X 90 X 00
Chip Erase 6 AAA AA 555 55 AAA 80 AAA AA 555 55 AAA 10
Block Erase 6+ AAA AA 555 55 AAA 80 AAA AA 555 55 BA 30
Erase Suspend 1 X B0
Erase Resume 1 X 30
Note: X Don’t Care, PA Program Address, PD Program Data, BA Any address in the Block.
All values in the table are in hexadecimal.
The Command Interface only uses A–1, A0-A10and DQ0-DQ7 to verify the commands; A11-A17, DQ8-DQ14 and DQ15 are Don’t Care.
DQ15A–1 is A–1 when BYTE
Read/Reset. After a Read/Reset command, read the memory as normal until another command is issued.
Auto Select. After an Auto Select command, read Manufacturer ID, Device ID or Block Protection Status.
Program, Unlock Bypass Program, Chip Erase, Block Erase. After these commands read the Status Register until the Program/Erase
Controller completes and the memory returns to Read Mode. Add additional Blocks during Block Erase Command with additional Bus Write
Operations until Timeout Bit is set.
Unlock Bypass. After the Unlock Bypass command issue Unlock Bypass Program orUnlock Bypass Reset commands.
Unlock Bypass Reset. After the Unlock Bypass Reset command read the memory as normal until another command is issued.
Erase Suspend. After the Erase Suspend command read non-erasing memory blocks as normal, issue Auto Select and Program commands
on non-erasing blocks as normal.
Erase Resume. After the Erase Resume command the suspended Erase operation resumes, read the Status Register until the Program/
Erase Controller completes and the memory returns to Read Mode.
is VILor DQ15 when BYTE is VIH.
8/25

M29W400BT, M29W400BB
Unlock Bypass Command. The Unlock Bypass
command is used in conjunction with the Unlock
Bypass Program comm and to program the memory. When the access time to the device is long (as
with some EPROM prog ramm ers ) c ons iderable
time saving can be made by us ing these commands. Three Bus Write operations ar e required
to issue the Unl oc k Bypass c ommand.
Once the Unlock Bypass comm and has been issued the m emory will only accept the Unlock Bypass Program command and the Unlock Bypass
Reset command. The memory can be read as if in
Read mode.
Unlock Bypass P rog ram Command. The Un-
lock Bypas s Program command can be used to
program on e address in memory at a time. The
command requires two Bus Write operations, the
final write operation latches t he address and data
in the internal state machine and starts the Program/Erase Controller.
The Program operation using the Unlock Bypass
Program command behaves identically to the Program o peration using the Program command. A
protected block cannot be programmed; the operation cannot be aborted and the Status Register is
read. Errors must be reset using the Read/Reset
command, which leaves the device in Unlock Bypass Mode. See the Program comm and for details
on the behavior.
Unlock Bypass Reset Command. The Unlock
Bypass Reset command can be used to return to
Read/Reset mode from Unlock Bypass Mode.
Two Bus Write operations are required to issue the
Unlock Bypass R es et command.
Chip Erase Command. The Chip Erase commandcanbeusedtoerasetheentirechip.SixBus
Write operations are required to issue the Chip
Erase Command and start the Program /Erase
Controller.
If any blocks are protected then these are ignored
and all the other blocks are erased. If all of the
blocks are protected the Chip Erase ope ration appears to start but will terminate within about 100µs,
leaving the data unchange d. No error condition is
given when protected blocks are ignored.
During t he erase operat ion the mem ory willignore
all commands. It is not possible to issue any command to abort the operation. Typical chip erase
times are given in Table 9. All Bus Read operations during the Chip E ras e operation will output
the Status R egister on the Data Inputs/Outputs.
See the section on the Status Register for more
details.
After the Chip Erase operation has c ompleted the
memory will return to the Read Mode, unless an
error has occurred. When an error occurs the
memory will continue t o output the Status Register. A Read/Reset command must be issued to reset the error condition and return t o Read Mode.
TheChip Erase Command sets all of the bit s in unprotected blocks of the mem ory to ’1’. All previous
data is lost.
Block Erase Command. TheBlockErasecommandcanbeusedtoerasealistofoneormore
blocks. Six Bus Write operations are required to
select the first block in the list. Each additional
block in the list can be selected by r epeating the
sixth B us Write operation us ing the address of the
additional block. The Block Eras e operation starts
the Program/E rase Controller about 50µs after the
last Bus Write operat ion. Once the Program/Erase
Controller starts it is not possible to select any
more blocks. E ac h additional block must therefore
be selected within 50µs of the last block. The 50µs
timer restarts when an additional block is selected.
The Status R egister can be read after the sixth
Bus Write operation. See the Status Register for
details on how to i dentify if the Program/Erase
Controller has started the Block Erase operation.
If any s elected blocks are protected then these are
ignored and all the ot her selected blocks are
erased. If all of the selected blocks are protected
the Block Erase operation appears to start but will
terminate within about 100µs, leaving the data unchanged. No error condition is given when prot ec ted blocks are ignored.
During the Blo ck Erase operation the memory will
ignore all commands except the Erase Suspend
and Read/Reset commands. Typical bl oc k erase
times are given in Table 9. All Bus Read operations during the Block Erase operation will output
the Status Register on the Data Inputs/Outputs.
See the section on the Status Register for more
details.
After the Block Erase ope ra tion has completed the
memory will return to the Read Mode, unless an
error has occurred. When an error occurs the
memory will continue t o output the Status Register. A Read/Reset command must be issued to reset the error condition and return to Read mode.
The Block Erase Command sets all of t he bits in
the unprotec ted selected blocks to ’1’. All previous
data in the selected blocks is lost.
9/25

M29W400BT, M29W400BB
Erase Suspend Command. The Eras e Su sp end
Command m ay be used to temporarily suspend a
Block Erase operation and return the m emory to
Read mode. The co mm and requires one Bus
Write operation.
The Program/Erase Controller will suspend within
15µs of the Erase Suspend Command being issued. Once the Program/Erase Controller has
stopped t he memory will be set to R ead mode and
the Erase wil l be suspended. If the Erase Suspend
command is issued during the period when the
memory is waiting for an additional block (before
the Program/Erase Controller starts) then the
During Erase Suspend it is possible to Read and
Program cells in blocks that are not being erased;
both Read and Program operations behave as
normal on t hes e blocks. Reading from blocks that
are being erased will output the Status Register. It
is also possibl e to enter the Auto Select mode: the
memory will behave as in the Auto Select mode on
all blocks until a R ead/ Res et command returns the
memory to Eras e Suspend mode.
Erase Resume Com m and . The Erase Resume
command must be used to restart the Program/
Erase Controller from Era se Suspend. An erase
can be suspen ded and resumed more than once.
Erase is su sp ended immediately and will start immediately when the Erase Resume Command is
issued. It will not be possible to select any further
blocks for erasure after the Erase Resume.
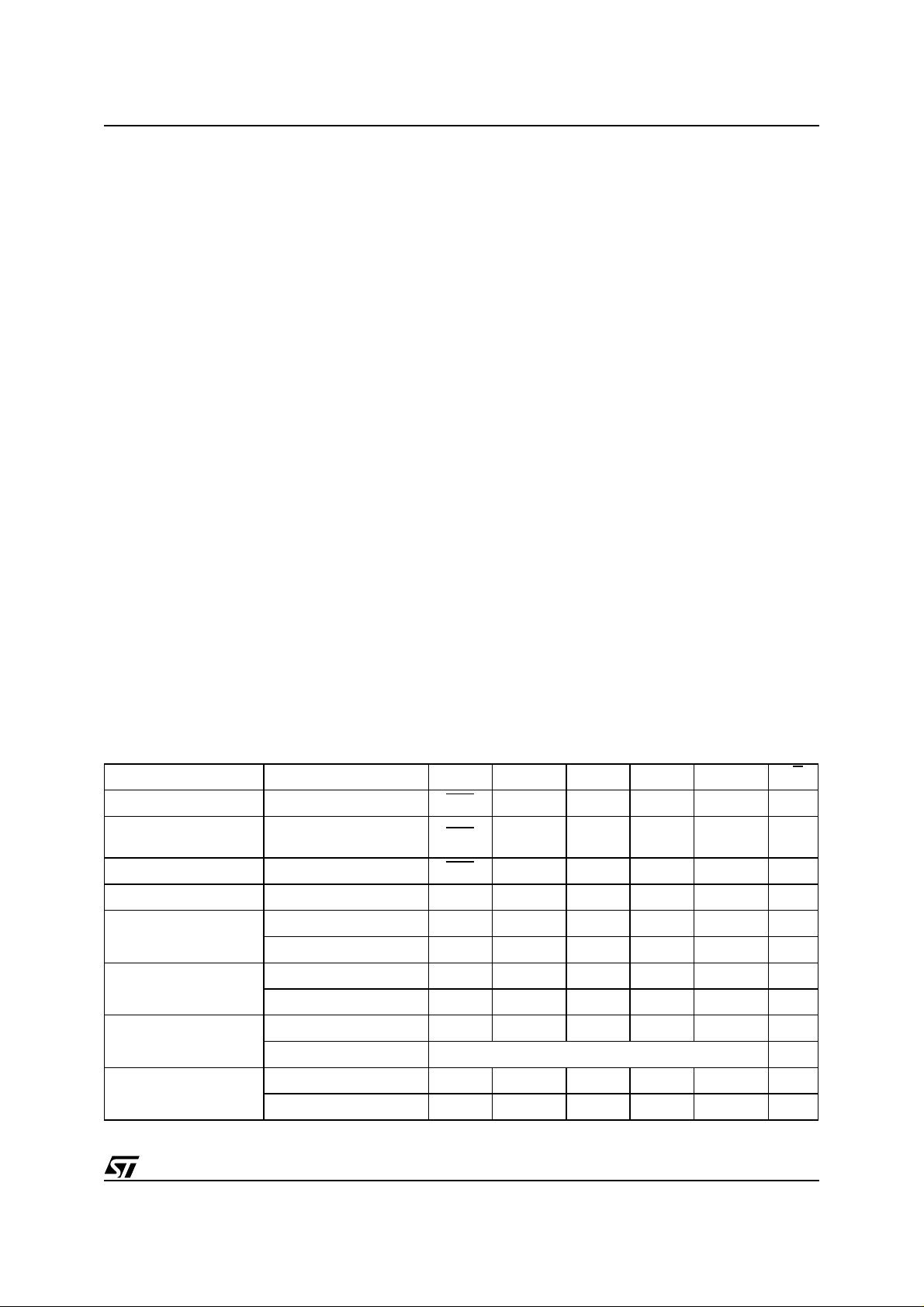
Table 9. Program, Erase Times and Program, Erase Endurance Cycles
= 0 to 70°C or –40 to 85 °C)
(T
A
Parameter Min
Chip Erase (All bits in the memory set to ‘0’) 2.5 2.5 sec
Chip Erase 6 6 35 sec
Block Erase (64 Kbytes) 0.8 0.8 6 sec
Program (Byte or Word) 10 10 200 µs
Typ
(1)
Typical after
100k W/E Cycles
(1)
Max Unit
Chip Program (Byte by Byte) 5.5 5.5 30 sec
Chip Program (Word by Word) 2.8 2.8 15 sec
Program/Erase Cycles (per Block) 100,000 cycles
Note: 1. TA=25°C,VCC=3.3V.
10/25
M29W400BT, M29W400BB
STATUS REGISTER
Bus Read operations from any address always
read the Status R egister during Program and
Erase operations. It is also read during Erase Sus pend when an address w ithin a block being erased
is accessed.
The bits in the Status Register are summarized in
Table 10, Status Register Bits.
Data P olling Bit (DQ7). The Data Polling Bit can
be used to identify whether the Program/Erase
Controller has succes sfull y completed its operation or if it has responded to an Erase S us pend.
The Data Polling Bit is output on DQ7 when the
Status Register is read.
During Program operations the Data Polling Bit
outputs the com plement of the bit being programmed to DQ7. After successful completion of
the Program operation the memory returns to
Read mod and Bus Read operations from the address just programmed output DQ7, no t its complemente.
During Erase operations the Data Polling Bit outputs ’0’, the complement of t he eras ed state of
DQ7. After successful completion of the Erase operation the memory returns to Read Mode.
In Erase Suspend m ode the Data Polling Bit will
output a ’1’ during a Bus Read operation within a
block being erased. The Data Polling Bit will
change from a ’0’ to a ’1’ when the Program/Erase
Controller has suspended the Erase operation.
Figure 5, Data Polling Flowchart, gives an example of how to us e the Data Polling Bit. A V alid Ad-
dress is the address being program med or an
address within the block being erased.
Toggle Bit (DQ6). The Toggle Bit can be us ed to
identify wheth er the Program/Erase Controller has
successfully completed its operation or if it has re-
sponded to an Erase Suspend. The Toggle Bit is
output on DQ6 when the Status R egister is read.
During Program and Erase operations the Toggle
Bit changes from ’0’ to ’1’ to ’0’, etc., with succes-
sive Bus Read operations at any address. After
successful completion of the operation the memo-
ry returns to Read mode.
During Eras e Suspend mode the Toggle Bit will
output when addres sing a cell within a block being
erased. The Toggle Bit will stop toggling when the
Program/Erase Controller has suspended the
Erase operation.
Figure 6, Data Toggle Flowchart, gives an exam-
ple of how to use the Data Toggle Bit.
Error B it (DQ5). TheErrorBitcanbeusedto
identify errors detected by the Program/Erase
Controller. The Error Bit is set to ’1’ when a Pro-
gram, Block Er as e or Chip Erase operation fails to
write the correct data to the memory. If the Error
Bit is set a Read/Reset command must be issued
before other commands are issued. The Error bit
is output on DQ5 when the Status Register is read.
Note that the Program command cannot change a
bit set at ’0’ back to ’1’ and attempting to do so may
or may not set D Q5 a t ’1’. In both cases, a succes-
sive Bus Read operation will show the bit is still ’0’.
One of the Erase commands must be used to set
all the bits in a blo ck or in the whole memory from
’0’ to ’1’.
Table 10. Status Register Bits
Operation Address DQ7 DQ6 DQ5 DQ3 DQ2 RB
Program Any Address DQ7 Toggle 0 – – 0
Program During Erase
Suspend
Program Error Any Address DQ7
Chip Erase Any Address 0 Toggle 0 1 Toggle 0
Block Erase before
timeout
Block Erase
Erase Suspend
Erase Error
Note: Unspecified data bits should be ignored.
Any Address DQ7
Erasing Block 0 Toggle 0 0 Toggle 0
Non-Erasing Block 0 Toggle 0 0 No Toggle 0
Erasing Block 0 Toggle 0 1 Toggle 0
Non-Erasing Block 0 Toggle 0 1 No Toggle 0
Erasing Block 1 No Toggle 0 – Toggle 1
Non-Erasing Block Data read as normal 1
Good Block Address 0 Toggle 1 1 No Toggle 0
Faulty Block Address 0 Toggle 1 1 Toggle 0
Toggle 0 – – 0
Toggle 1 – – 0
11/25

M29W400BT, M29W400BB
Figure 5. Data Polling Flowchart
START
READ DQ5 & DQ7
at VALID ADDRESS
DQ7
DATA
NO
DQ5
READ DQ7
at VALID ADDRESS
DQ7
DATA
FAIL PASS
= 1
YES
=
NO
YES
YES
=
NO
AI03598
Figure 6. Data Toggle Flowchart
START
READ
DQ5 & DQ6
READ DQ6
DQ6
=
TOGGLE
NO
DQ5
= 1
READ DQ6
TWICE
DQ6
=
TOGGLE
FAIL PASS
NO
YES
YES
NO
YES
AI01370B
Erase Timer Bit (DQ3). The Erase Timer Bit can
be used to identify the start of P r ogram/Erase
Controller operation during a Block Er ase command. Once the P rogram/E r as e Controller starts
erasing the Erase Timer Bit is set to ’1’. Before the
Program/Erase Contro ller s tarts the Erase Timer
Bit is set to ’0’ and additional b locks to be erased
may be written to the Command I nterface. The
Erase Timer Bit is output on DQ3 when the Status
Register is read.
Alternative Toggle Bit (DQ2). The Alternative
Toggle Bit can be use d to monitor the Program/
Erase c ontroller during E ras e operations. The Alternative T oggle Bit is output on DQ2 when t he
Status Register is read.
During Chip Erase and Block Erase operations t he
Toggle Bit changes from ’0’ to ’1’ to ’0’, etc., with
successive Bus R ead operations from address es
12/25
withintheblocks being erased. Once the operation
completes the memory ret urns to Read mode.
During Erase Suspend the Alternative Toggle Bit
changes from ’0’ to ’1’ to ’0’, etc. with s uc c es s ive
Bus Read operations from addresses within the
blocks being erased. Bus Read operations to ad-
dresses within blocks not being erased will output
the memory cell data as if in Read mode.
After an Eras e operation that c aus es the Error Bit
tobesettheAlternativeToggleBitcanbeusedto
identify which block or blocks have caused the er-
ror. The Alternative Toggle Bit changes from ’0’ to
’1’ to ’0’, etc. with suc c es sive Bus Read Opera-
tions from addresses within blocks that have not
erased correctly. The Alternative Toggle Bit does
not change if the addressed block has erased c or-
rectly.

M29W400BT, M29W400BB
Table 11. AC M easurement Cond ition s
Parameter
55 70 90 / 120
Supply Voltage
V
CC
Load Capacitance (C
)
L
3.0 to 3.6V 2.7 to 3.6V 2.7 to 3.6V
30pF 30pF 100pF
Input Rise and Fall Times ≤ 10ns ≤ 10ns ≤ 10ns
Input Pulse Voltages 0 to 3V 0 to 3V 0 to 3V
Input and Output Timing Ref. Voltages 1.5V 1.5V 1.5V
M29W400B
Figure 7. AC Testing Input Output Waveform
3V
1.5V
0V
AI01417
Figure 8. AC Testing Load Circuit
0.8V
1N914
3.3kΩ
DEVICE
UNDER
TEST
CL = 30pF or 100pF
CL includes JIG capacitance
Table 12. Capacitance
(T
=25°C,f=1MHz)
A
Symbol Parameter Test Condition Min Max Unit
V
V
IN
OUT
=0V
=0V
6pF
12 pF
C
IN
C
OUT
Note: Sampled only, not 100% tested.
Input Capacitance
Output Capacitance
OUT
AI02762
13/25

M29W400BT, M29W400BB
Table 13. DC Characteristics
(T
= 0 to 70°C or –40 to 85 °C)
A
Symbol Parameter Test Condition Min
Typ.
(2)
Max Unit
I
Input Leakage Current
LI
I
I
CC1
I
CC2
I
CC3
V
V
V
V
V
V
LKO
Note: 1. Sampled only, not 100% tested.
Output Leakage Current
LO
Supply Current (Read)
Supply Current (Standby)
(1)
Supply Current (Program/Erase)
Input Low Voltage –0.5 0.8 V
IL
Input High Voltage
IH
Output Low Voltage
OL
Output High Voltage IOH= –100µA
OH
Identification Voltage 11.5 12.5 V
ID
I
Identification Current
ID
Program/Erase Lockout Supply
(1)
Voltage
2. T
=25°C,VCC=3.3V.
A
0V ≤ V
0V ≤ V
E
=VIL,G=VIH, f = 6MHz
E
RP
≤ V
IN
CC
≤ V
OUT
=VCC± 0.2V,
=VCC± 0.2V
CC
Program/Erase
Controller active
I
= 1.8mA
OL
A9 = V
ID
±1
±1
410mA
30 100
20 mA
0.7V
CC
VCC+ 0.3
0.45 V
V
–0.4
CC
100
1.8 2.3 V
µA
µA
µA
V
V
µA
14/25
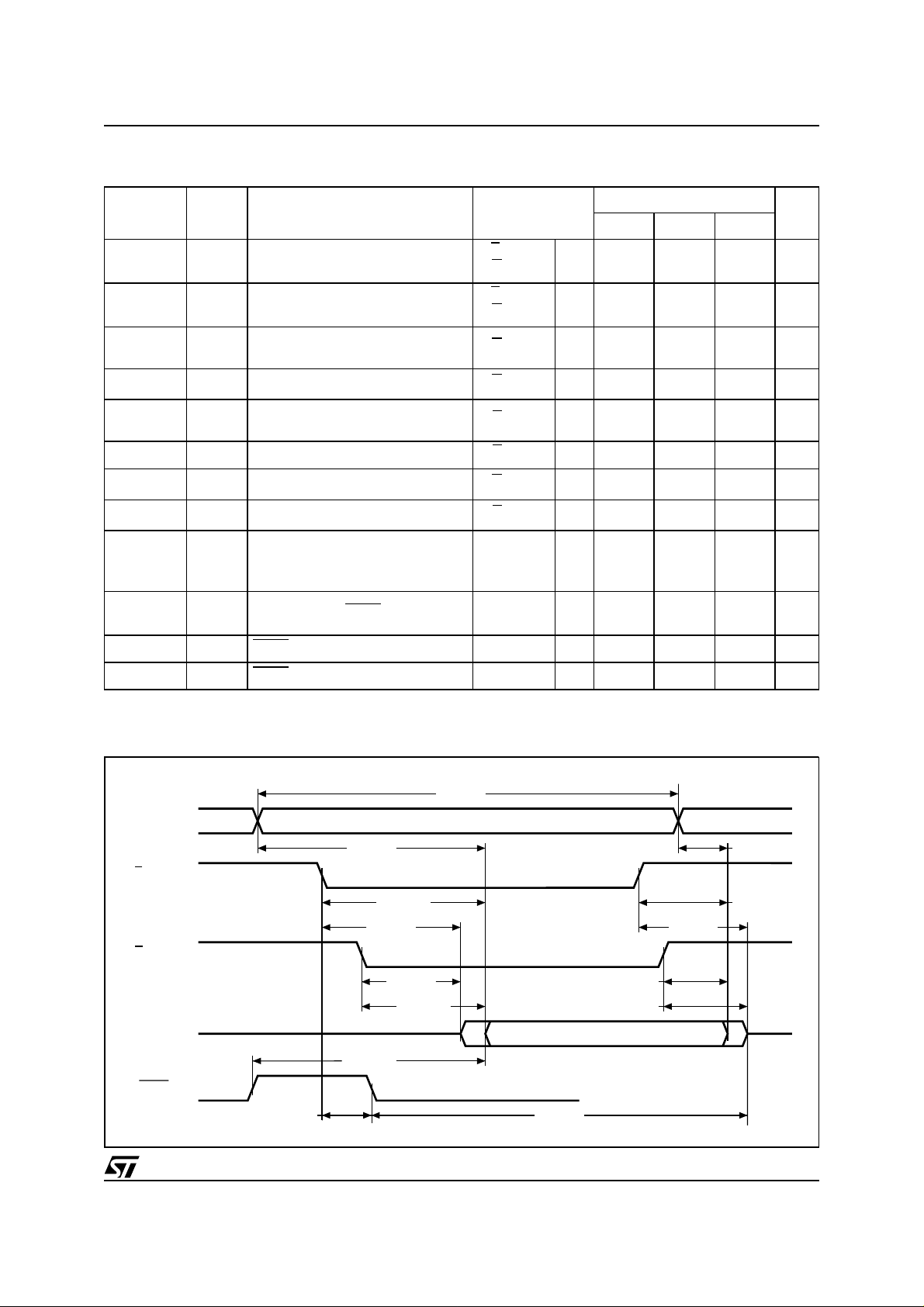
Table 14. Read AC Chara cteri stics
(T
= 0 to 70°C or –40 to 85 °C)
A
Symbol Alt Parameter Test Condition
=VIL,
t
t
t
ELQX
AVAV
AVQV
(1)
t
RC
t
ACC
t
Address Valid to Next Address
Valid
Address Valid to Output Valid
Chip Enable Low to Output
LZ
Transition
E
G =V
E
=VIL,
G =V
=V
G
IL
IL
IL
M29W400BT, M29W400BB
M29W400B
Unit
55 70 90 / 120
Min 55 70 90 ns
Max 55 70 90 ns
Min 0 0 0 ns
t
t
ELQV
(1)
(1)
(1)
t
t
ELFL
t
ELFH
t
FLQZ
t
FHQV
t
GLQX
t
GLQV
t
EHQZ
t
GHQZ
t
EHQX
t
GHQX
t
AXQX
t
ELBL
t
ELBH
t
BLQZ
t
BHQV
Note: 1. Sampled only, not 100% tested.
Chip Enable Low to Output Valid
CE
Output Enable Low to Output
OLZ
Transition
t
Output Enable Low to Output Valid
OE
t
Chip Enable High to Output Hi-Z
HZ
t
Output Enable High to Output Hi-Z
DF
Chip Enable, Output Enable or
t
Address Transition to Output
OH
Transition
Chip Enable to BYTE Low or High Max 5 5 5 ns
BYTE Low to Output Hi-Z Max 25 25 30 ns
BYTE High to Output Valid Max 30 30 40 ns
Figure 9. Read Mode AC W aveforms
A0-A17/
A–1
tAVQV tAXQX
tAVAV
VALID
G
=V
=V
E
E
=V
G
=V
E
=V
Max 55 70 90 ns
IL
Min 0 0 0 ns
IL
Max 30 30 35 ns
IL
Max 20 25 30 ns
IL
Max 20 25 30 ns
IL
Min 0 0 0 ns
E
G
DQ0-DQ7/
DQ8-DQ15
BYTE
tELQV tEHQX
tELQX tEHQZ
tGLQX tGHQX
tGLQV
tBHQV
tELBL/tELBH tBLQZ
tGHQZ
VALID
AI02907
15/25
M29W400BT, M29W400BB
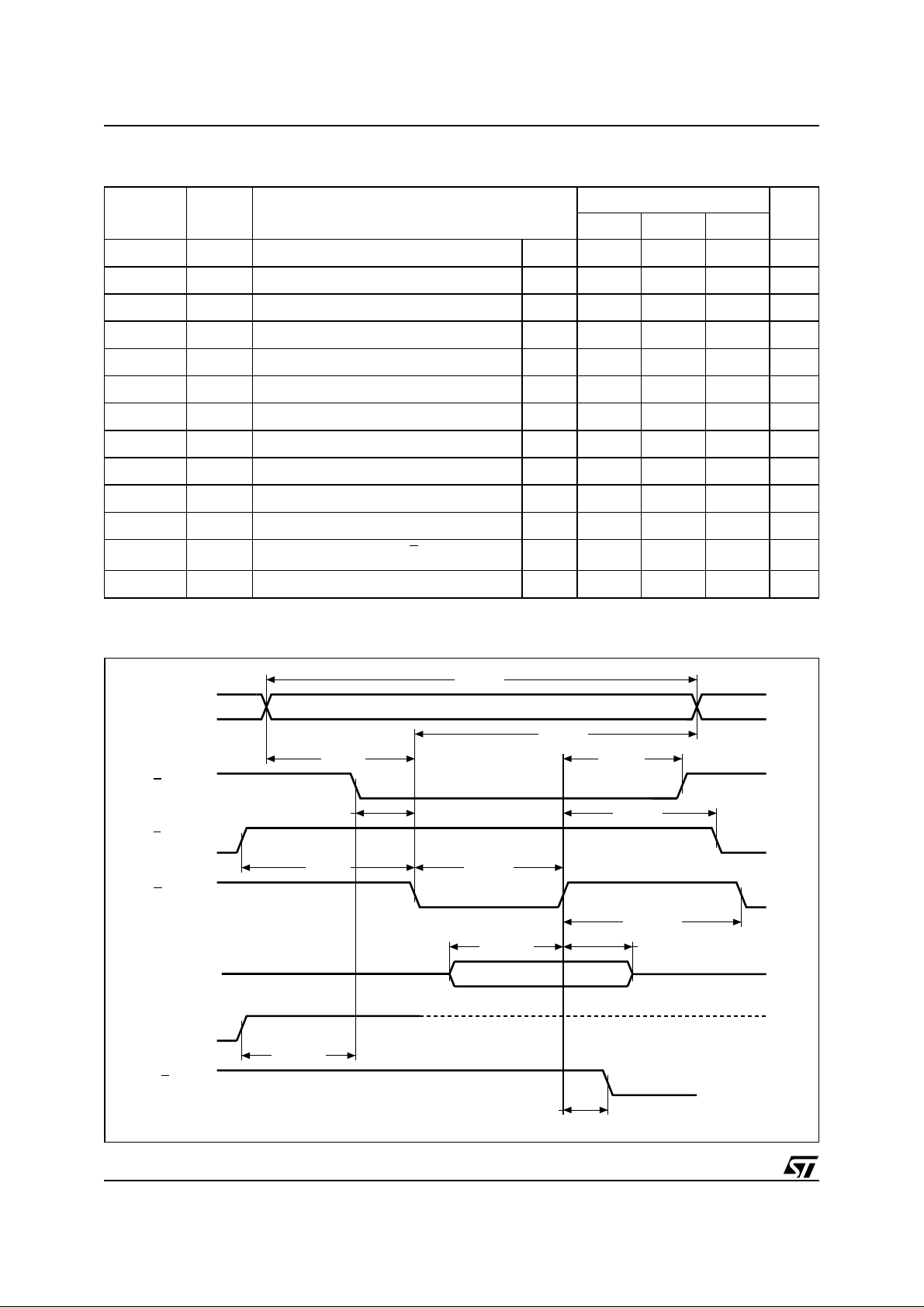
Table 15. Write AC Characteristics, Write Enable Controlled
(T
= 0 to 70°C or –40 to 85 °C)
A
Symbol Alt Parameter
t
AVAV
t
ELWL
t
WLWH
t
DVWH
t
WHDX
t
WHEH
t
WHWL
t
AVWL
t
WLAX
t
GHWL
t
WHGL
(1)
t
WHRL
t
VCHEL
Note: 1. Sampled only, not 100% tested.
t
WC
t
CS
t
WP
t
DS
t
DH
t
CH
t
WPH
t
AS
t
AH
t
OEH
t
BUSY
t
VCS
Address Valid to Next Address Valid Min 55 70 90 ns
Chip Enable Low to Write Enable Low Min 0 0 0 ns
Write Enable Low to Write Enable High Min 40 45 45 ns
Input Valid to Write Enable High Min 25 30 45 ns
Write Enable High to Input Transition Min 0 0 0 ns
Write Enable High to Chip Enable High Min 0 0 0 ns
Write Enable High to Write Enable Low Min 30 30 30 ns
Address Valid to Write Enable Low Min 0 0 0 ns
Write Enable Low to Address Transition Min 40 45 45 ns
Output Enable High to Write Enable Low Min 0 0 0 ns
Write Enable High to Output Enable Low Min 0 0 0 ns
Program/Erase Valid to RB Low Max 30 30 35 ns
VCCHigh to Chip Enable Low
M29W400B
Unit
55 70 90 / 120
Min505050µs
Figure 10. Write AC Waveforms, Write Enab le Controlled
tAVAV
A0-A17/
A–1
E
G
W
DQ0-DQ7/
DQ8-DQ15
V
CC
RB
tAVWL
tELWL
tVCHEL
VALID
tWLWHtGHWL
tDVWH
tWLAX
tWHEH
tWHGL
tWHWL
tWHDX
VALID
16/25
tWHRL
AI01869C
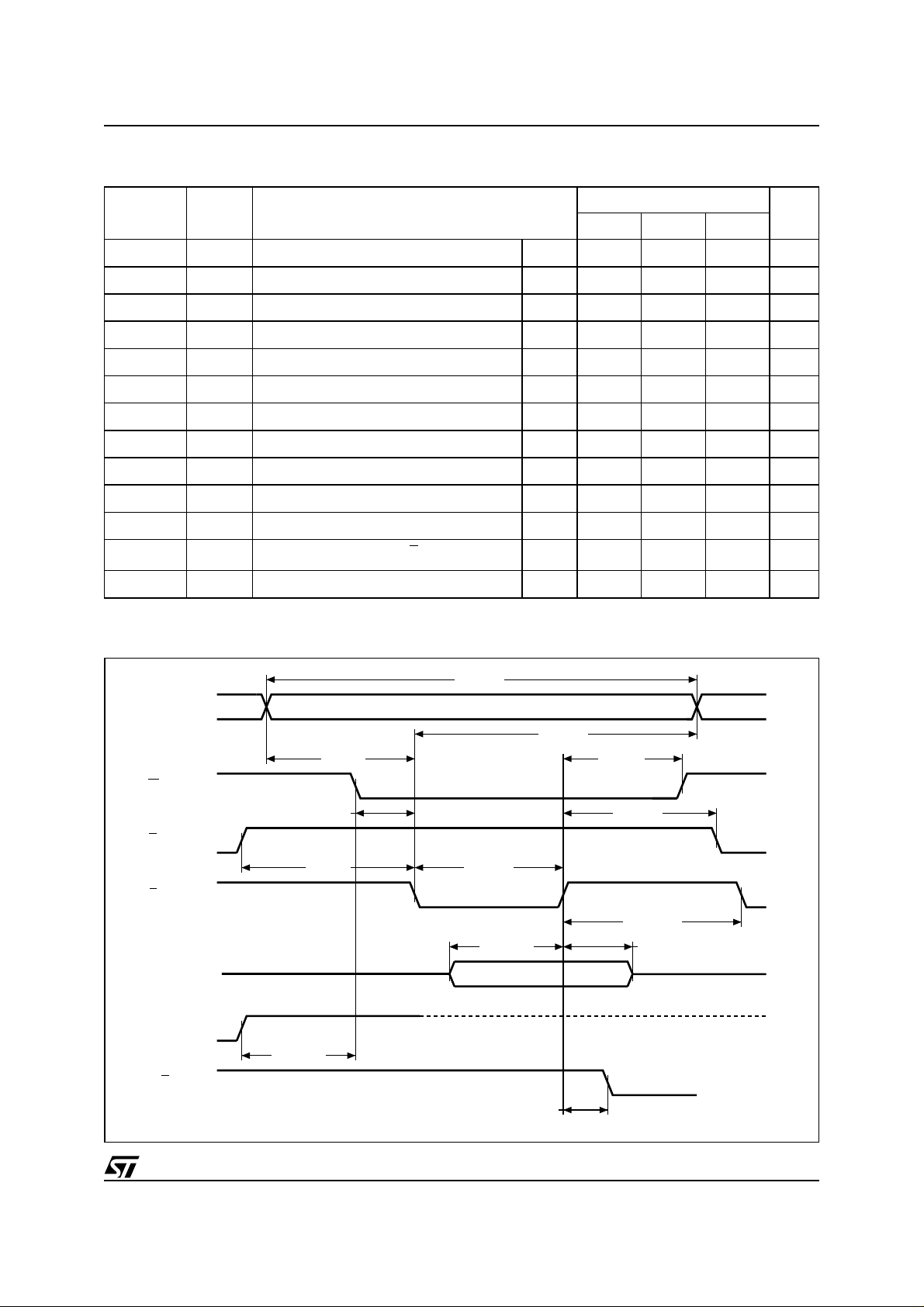
Table 16. Write AC Characteristics, Chip Enable Controlled
(T
= 0 to 70°C or –40 to 85 °C)
A
Symbol Alt Parameter
t
AVAV
t
WLEL
t
ELEH
t
DVEH
t
EHDX
t
EHWH
t
EHEL
t
AVEL
t
ELAX
t
GHEL
t
EHGL
(1)
t
EHRL
t
VCHWL
Note: 1. Sampled only, not 100% tested.
t
WC
t
WS
t
CP
t
DS
t
DH
t
WH
t
CPH
t
AS
t
AH
t
OEH
t
BUSY
t
VCS
Address Valid to Next Address Valid Min 55 70 90 ns
Write Enable Low to Chip Enable Low Min 0 0 0 ns
Chip Enable Low to Chip Enable High Min 40 45 45 ns
Input Valid to Chip Enable High Min 25 30 45 ns
Chip Enable High to Input Transition Min 0 0 0 ns
Chip Enable High to Write Enable High Min 0 0 0 ns
Chip Enable High to Chip Enable Low Min 30 30 30 ns
Address Valid to Chip Enable Low Min 0 0 0 ns
Chip Enable Low to Address Transition Min 40 45 45 ns
Output Enable High Chip Enable Low Min 0 0 0 ns
Chip Enable High to Output Enable Low Min 0 0 0 ns
Program/Erase Valid to RB Low Max 30 30 35 ns
VCCHigh to Write Enable Low
M29W400BT, M29W400BB
M29W400B
Unit
55 70 90 / 120
Min505050µs
Figure 11. Write AC Waveforms, Chip Enable Controlled
tAVAV
A0-A17/
A–1
W
G
E
DQ0-DQ7/
DQ8-DQ15
V
CC
RB
tAVEL
tWLEL
tVCHWL
VALID
tELEHtGHEL
tDVEH
tELAX
tEHWH
tEHGL
tEHEL
tEHDX
VALID
tEHRL
AI01870C
17/25

M29W400BT, M29W400BB
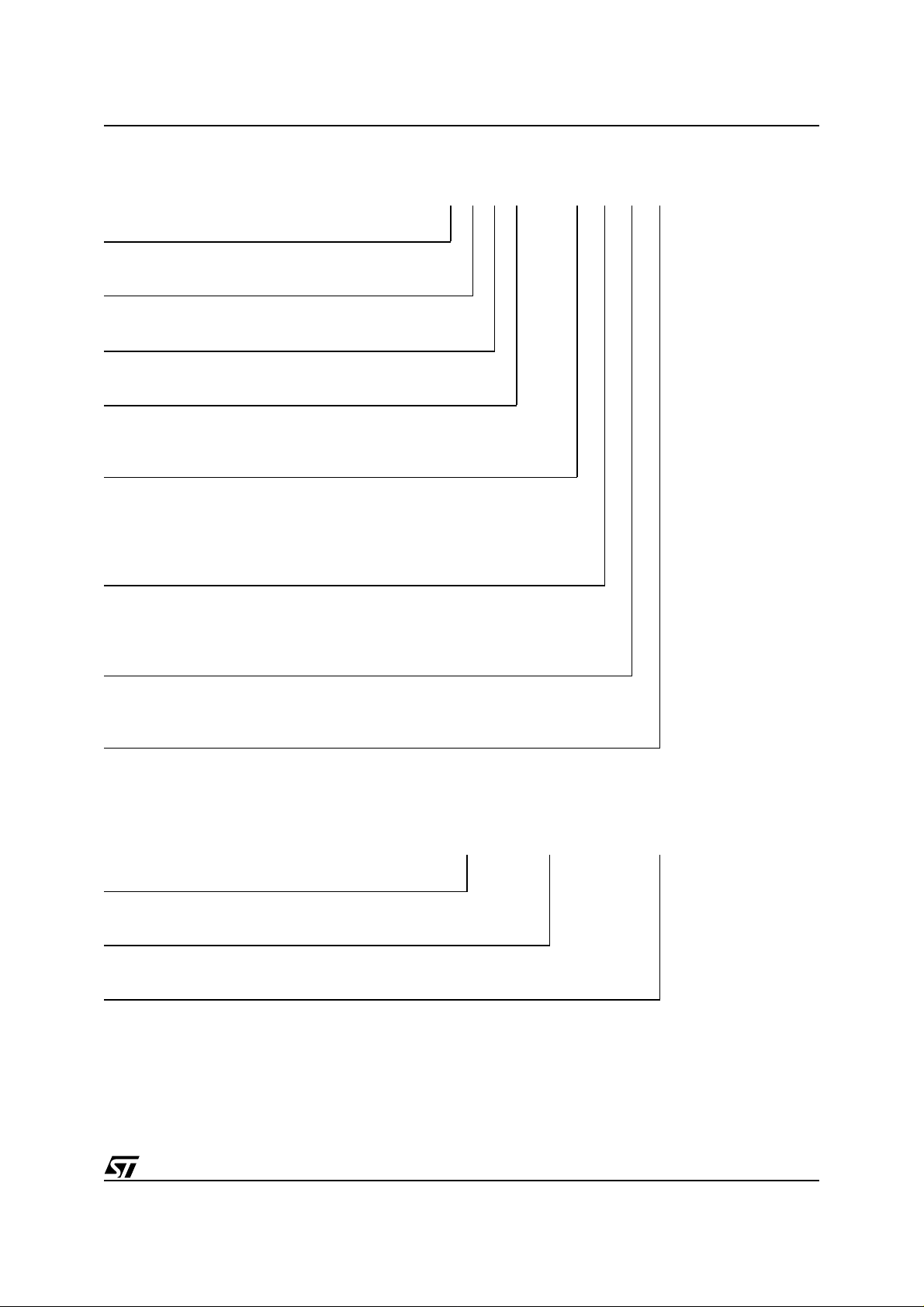
Table 17. Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect AC Character istics
(T
= 0 to 70°C or –40 to 85 °C)
A
Symbol Alt Parameter
(1)
t
PHWL
t
PHEL
(1)
t
PHGL
(1)
t
RHWL
(1)
t
RHEL
(1)
t
RHGL
t
PLPX
(1)
t
PHPHH
(1)
t
PLYH
Note: 1. Sampled only, not 100% tested.
t
t
VIDR
t
READY
Figure 12. Reset/B lock Temporary Unprotect AC Waveforms
RP High to Write Enable Low, Chip Enable
RH
Low, Output Enable Low
RB High to Write Enable Low, Chip Enable
t
RB
Low, Output Enable Low
t
RP Pulse Width Min 500 500 500 ns
RP
RP Rise Time to V
ID
RP Low to Read Mode
Min 50 50 50 ns
Min 0 0 0 ns
Min 500 500 500 ns
Max101010µs
M29W400B
Unit
55 70 90 / 120
W,
RB
RP
E, G
tPHWL, tPHEL, tPHGL
tRHWL, tRHEL, tRHGL
tPLPX
tPHPHH
tPLYH
AI02931
18/25
M29W400BT, M29W400BB
Table 18. Ordering Informa tion Scheme
Example: M29W400BB 55 N 1 T
Device Type
M29
Operating Voltage
W=V
Device Function
400B = 4 Mbit (x8/x16), Boot Block
Array Matrix
T=TopBoot
B = Bottom Boot
Speed
55 = 55 ns
70 = 70 ns
90 = 90 ns
120 = 120 ns
= 2.7 to 3.6V
CC
Package
N = TSOP48: 12 x 20 mm
M = SO44
ZA = TFBGA48: 0.8mm pitch
Temperature Range
1 = 0 to 70 °C
6 = –40 to 85 °C
Option
T = Tape & Reel Packing
Table 19. Daisy Chain Ordering Scheme
Example: M29 DCL1-4 T
Device Type
M29
Daisy Chain
DCL1-4 = Daisy Chain Level 1 for 4 Mbit parts
Option
T = Tape & Reel Packing
Devices are shipped from the fa ctory with the memory c ontent bits erased to ’1’.
For a list of available options (Speed, Package, etc...) or for further information on any as pect of this de-
vice, please contact the ST Sales Of fice nearest to you.
19/25
M29W400BT, M29W400BB
Table 20. Revision History
Date Version Revision Details
July 1999 -01 First Issue
-02 Chip Erase Max. specification added
Block Erase Max. specification added
9/21/99
10/04/99
-03 FBGA Connections change
1/21/00 -04 FBGA Package removed
2/01/00 -05 TSOP48 Package mechanical data change
-06 Document type: from Preliminary Data to Data Sheet
3/09/00
4/18/00 -07 Status Register section clarification
2/09/01 -08 TFBGA48 package added
-09 TFBGA48 package mechanical outline and data changed
6/21/01
Program Max. specification added
Chip Program Max. specification added
Typ. specification added
I
CC1
I
Typ. specification added
CC2
Test Condition change
I
CC
Status Register bit DQ5 clarification
Data Polling Flowchart diagram change
Data Toggle Flowchart diagram change
Daisy Chain commercial code defined
TFBGA48 Daisy Chain diagrams, Package and PCB Connections added
20/25
M29W400BT, M29W400BB
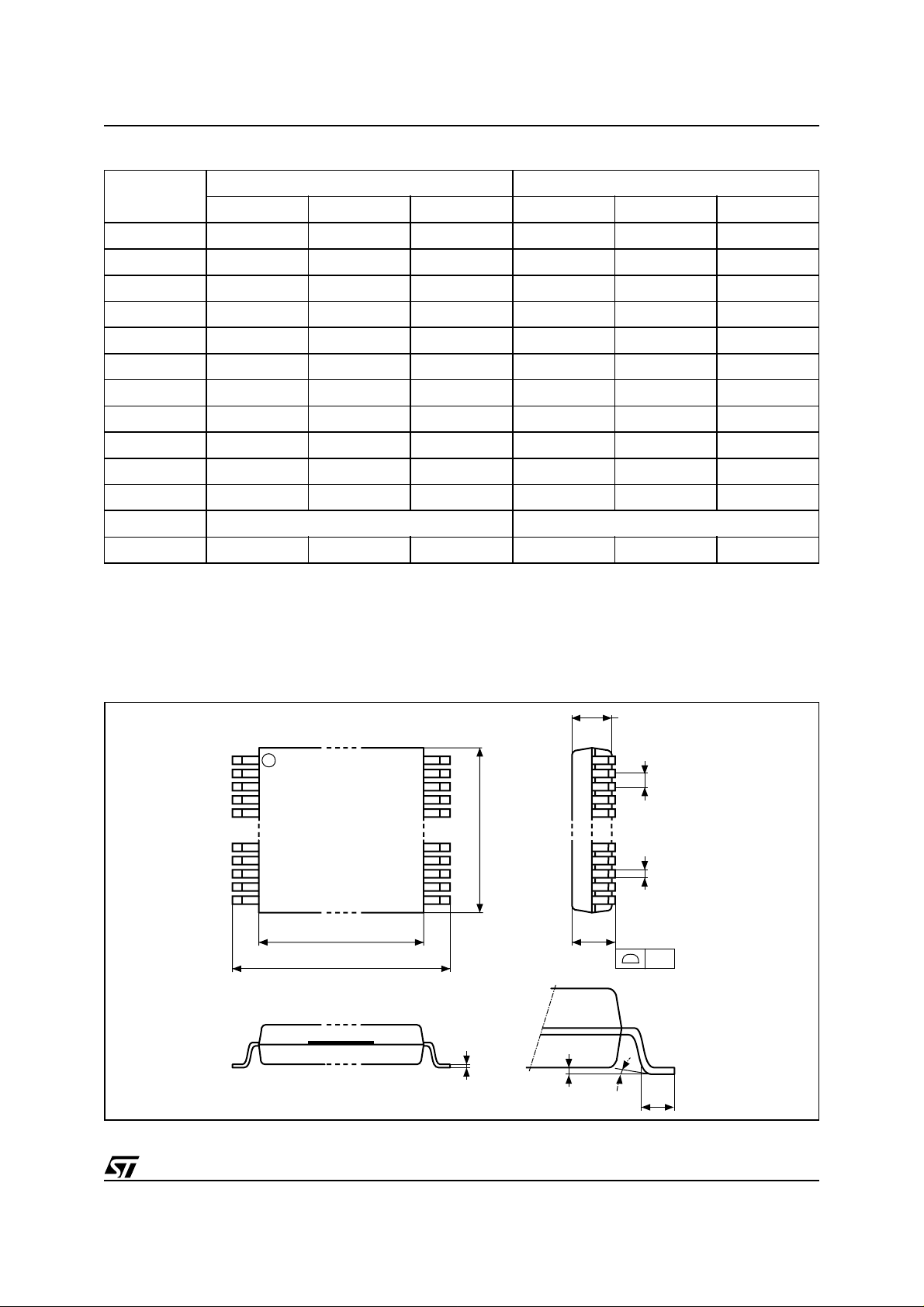
Table 21. TSOP 48 - 48 lead Plastic Thin Smal l Outline, 12 x 20mm , Package Mechanical D ata
Symbol
Typ Min Max Typ Min Max
A 1.20 0.0472
A1 0.05 0.15 0.0020 0.0059
A2 0.95 1.05 0.0374 0.0413
B 0.17 0.27 0.0067 0.0106
C 0.10 0.21 0.0039 0.0083
D 19.80 20.20 0.7795 0.7953
D1 18.30 18.50 0.7205 0.7283
E 11.90 12.10 0.4685 0.4764
e 0.50 – – 0.0197 – –
L 0.50 0.70 0.0197 0.0279
α 0° 5° 0° 5°
N48 48
CP 0.10 0.0039
mm inches
Figure 13. TSOP48 - 48 lead Plastic Thin Small Outline, 12 x 20mm , Package Outline
A2
1 N
e
E
B
N/2
D1
D
DIE
A
CP
C
TSOP-a
Drawing is not to scale.
LA1 α
21/25
M29W400BT, M29W400BB
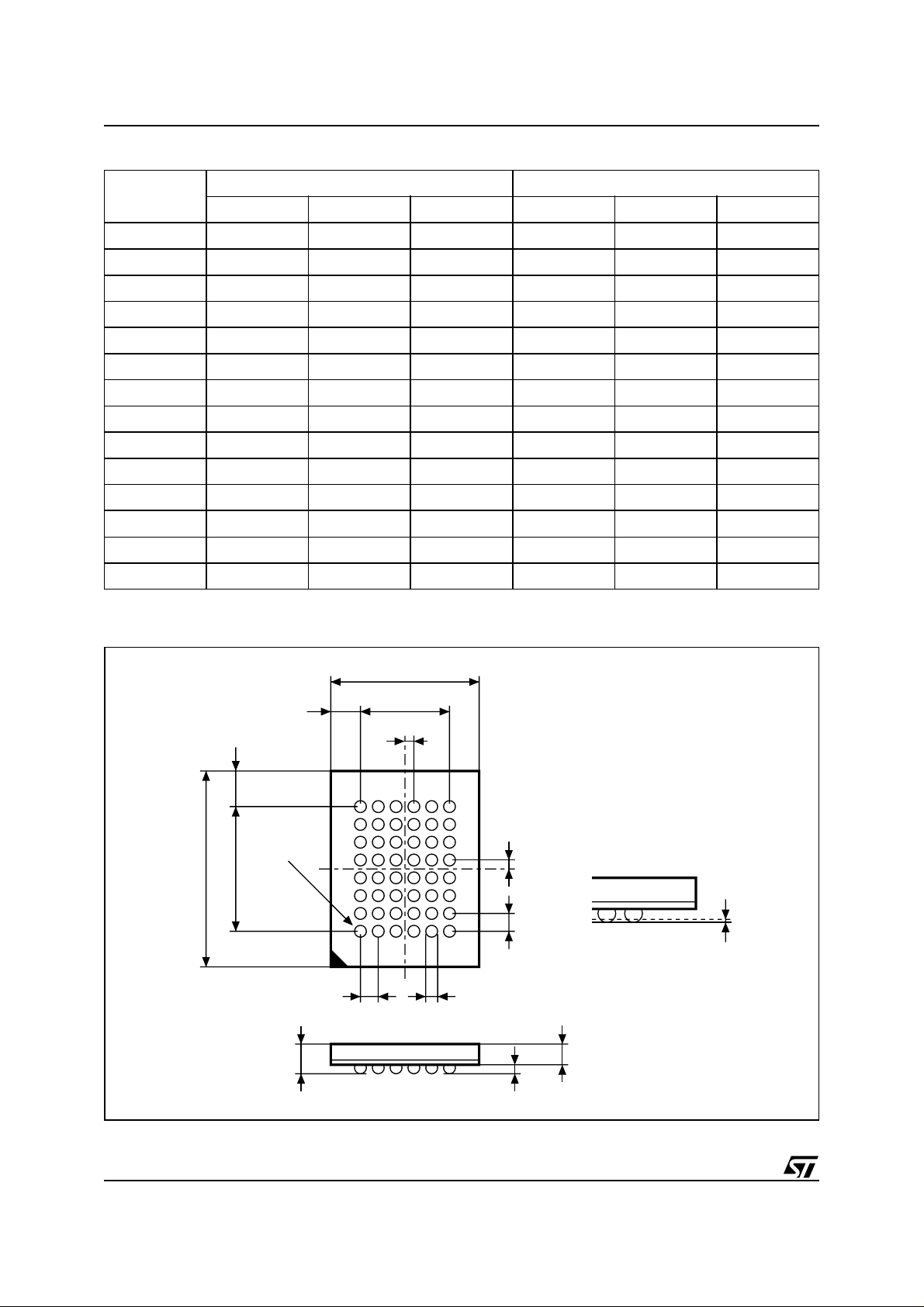
Table 22. TFBGA48 - 6 x 8 bal l array, 0. 8 m m pitch, Package Mechanical Data
Symbol
Typ Min Max Typ Min Max
A 1.200 0.0472
A1 0.200 0.0079
A2 1.000 0.0394
b 0.400 0.350 0.450 0.0157 0.0138 0.0177
D 6.000 5.900 6.100 0.2362 0.2323 0.2402
D1 4.000 – – 0.1575 – –
ddd 0.100 0.0039
E 9.000 8.900 9.100 0.3543 0.3504 0.3583
E1 5.600 – – 0.2205 – –
e 0.800 – – 0.0315 – –
FD 1.000 – – 0.0394 – –
FE 1.700 – – 0.0669 – –
SD 0.400 – – 0.0157 – –
SE 0.400 – – 0.0157 – –
millimeters inches
Figure14.TFBGA48-6x8ballarray,0.8mmpitch,PackageOutline,Bottomview
D
FD
FE
BALL "A1"
E1E
eb
A
D1
SD
SE
e
A2
A1
ddd
Drawing is not to scale.
22/25
BGA-Z00

M29W400BT, M29W400BB
Figure 15. TFBGA48 Daisy Chain - Packag e C onnections (Top view through package)
12 6
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
543
AI04893
Figure 16. TFBGA48 Daisy Chain - PCB Connections (Top view through package)
START
POINT
12 6
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
543
END
POINT
H
AI04892
23/25

M29W400BT, M29W400BB
Table 23. SO44 - 44 lead P lastic Small Outline, 525 mils body width , Package Mechanical Data
Symbol
Typ Min Max Typ Min Max
A 2.42 2.62 0.0953 0.1031
A1 0.22 0.23 0.0087 0.0091
A2 2.25 2.35 0.0886 0.0925
B 0.50 0.0197
C 0.10 0.25 0.0039 0.0098
D 28.10 28.30 1.1063 1.1142
E 13.20 13.40 0.5197 0.5276
e 1.27 – – 0.0500 – –
H 15.90 16.10 0.6260 0.6339
L 0.80 – – 0.0315 – –
α 3° – – 3° – –
N44 44
CP 0.10 0.0039
mm inches
Figure 17. SO44 - 4 4 lead Plastic S m all Outline, 525 mils body w id th, Package Outline
A2
A
C
B
e
CP
D
N
E
H
1
LA1 α
SO-b
Drawing is not to scale.
24/25

M29W400BT, M29W400BB
Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, STMicroelectronics assumes no responsibility for the consequences
of use ofsuchinformation nor for any infringement of patents orotherrights ofthird parties which may result from its use. No license is granted
by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of STMicroelectronics. Specifications mentioned in this publication are subject
to change without notice. This publication supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied. STMicroelectronics products are not
authorized for use as critical components in life support devices or systems without express written approval of STMicroelectronics.
The ST logo is registered trademark of STMicroelectronics
All other names are the property of their respective owners
2001 STMicroelectronics - All Rights Reserved
Australia - Brazil - China - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Italy - Japan - Malaysia - Malta - Morocco -
Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - U.S.A.
STMicroelectronics GROUP OF COMPANIES
www.st.com
25/25

WWW.ALLDATASHEET.COM
Copyright © Each Manufacturing Company.
All Datasheets cannot be modified without permission.
This datasheet has been download from :
www.AllDataSheet.com
100% Free DataSheet Search Site.
Free Download.
No Register.
Fast Search System.
www.AllDataSheet.com
 Loading...
Loading...