
查询M29W160DB70M1T供应商
FEATURES SUMMARY
■ SINGLE 2.7 to 3.6V SUPPLY VOLTAGE for
PROGRAM, ERASE and READ OPERATIONS
■ ACCESS TIME: 70ns
■ PROGRAMMING TIME
–10µs per Byte/Word typical
■ 35 MEMORYBLOCKS
– 1 Boot Block (Top or Bottom Location)
– 2 Parameter and 32 Main Blocks
■ PROGRAM/ERASE CONTROLLER
– Embedded Program and Erase algorithms
■ ERASE SUSPEND and RESUME MODES
– Read and Program another Block during
Erase Suspend
■ UNLOCKBYPASS PROGRAM COMMAND
– FasterProduction/Batch Programming
■ TEMPORARY BLOCK UNPROTECTION
MODE
■ SECURITY MEMORY BLOCK
■ LOW POWER CONSUMPTION
– Standby and Automatic Standby
■ 100,000 PROGRAM/ERASE CYCLES per
BLOCK
■ ELECTRONIC SIGNATURE
– Manufacturer Code: 0020h
– Top Device Code M29W160DT: 22C4h
– Bottom Device Code M29W160DB: 2249h
M29W160DT
M29W160DB
16 Mbit (2Mb x8 or 1Mb x16, Boot Block)
3V Supply Flash Memory
PRELIMINARY DATA
Figure 1. Packages
44
1
TSOP48 (N)
12 x 20mm
LFBGA48 (ZA)
8 x 6 solder balls
SO44 (M)
FBGA
January 2001
This is preliminary information on a new product now in development or undergoing evaluation. Details are subject to change without notice.
1/29

M29W160DT, M29W160DB
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SUMMARY DESCRIPTION. . . . . . . . ...................................................5
Logic Diagram . .................................................................5
Signal Names . .................................................................5
TSOP Connections . . . .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ............6
SO Connections . . . . . . . . . .......................................................6
LFBGA Connections (Top view through package) . . . . . . . ...............................7
Table 2. Top Boot Block Addresses, M29W160DT. . ....................................8
Table 3. Bottom Boot Block Addresses, M29W160DB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...............8
SIGNAL DESCRIPTIONS . . ..........................................................9
Address Inputs (A0-A19). . . . . . . ...................................................9
Data Inputs/Outputs (DQ0-DQ7). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Data Inputs/Outputs (DQ8-DQ14). . . . . . . . . . . . . . .....................................9
Data Input/Output or Address Input (DQ15A-1). . . . .....................................9
Chip Enable (E). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...............................9
Output Enable (G). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...............................................9
Write Enable (W). . . . . . . . . . . . . ...................................................9
Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect (RP).. . ............................................9
Ready/Busy Output (RB). . . . . . . ...................................................9
Byte/Word Organization Select (BYTE). . . . . . . . . ......................................9
Supply Voltage. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ............................................9
V
CC
Vss Ground.. . ..................................................................9
BUS OPERATIONS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . ..................................................10
Bus Read. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...........................................10
Bus Write. ....................................................................10
Output Disable. . . ..............................................................10
Standby. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ..............................10
Automatic Standby. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .................................10
Special Bus Operations. .........................................................10
Electronic Signature. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Block Protection and Blocks Unprotection. ...........................................10
Table 4. Bus Operations, BYTE = VIL...............................................10
Table 5. Bus Operations, BYTE = VIH...............................................11
COMMAND INTERFACE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...........................................11
Read/Reset Command.. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ....................................11
Auto Select Command. . . . .......................................................11
Program Command. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...................................11
Unlock Bypass Command. . . . . . ..................................................12
Unlock Bypass Program Command. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .................................12
Unlock Bypass Reset Command. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .................................12
Chip Erase Command. . . . . ......................................................12
Block Erase Command.. .........................................................12
2/29

M29W160DT, M29W160DB
Erase Suspend Command. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .......................12
Erase Resume Command. . . . . .. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...........13
Security Data Command. . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...........................................13
Table 6. Security Memory Block Addresses . . . .......................................13
Table 7. Commands, 16-bit mode, BYTE = VIH.......................................14
Table 8. Commands, 8-bit mode, BYTE = VIL.........................................15
Table 9. Program, Erase Times and Program, Erase Endurance Cycles . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
STATUS REGISTER . . . . . . . . . . . . . ..................................................16
Data Polling Bit (DQ7). . . . . ......................................................16
Toggle Bit (DQ6).. . . . . . .........................................................16
Error Bit (DQ5). . . ..............................................................16
Erase Timer Bit (DQ3). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .................................17
Alternative Toggle Bit (DQ2).. . . ...................................................17
Table 10. Status Register Bits. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...................................17
Figure 6. Data Polling Flowchart . ..................................................18
Figure 7. Data Toggle Flowchart. . . . .. . . ...........................................18
MAXIMUM RATING. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...........................................18
Absolute Maximum Ratings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .................................18
DC and AC PARAMETERS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ..............................19
Operating and AC Measurement Conditions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
AC Measurement I/O Waveform . ..................................................19
AC Measurement Load Circuit . . ..................................................19
Capacitance. . . . . . . . . . . . .......................................................19
DC Characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...........................................20
Read Mode AC Waveforms. ......................................................21
Read AC Characteristics .........................................................21
Write AC Waveforms, Write Enable Controlled. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ...........22
Write AC Characteristics, Write Enable Controlled . . ...................................22
Write AC Waveforms, Chip Enable Controlled . . . . ....................................23
Write AC Characteristics, Chip Enable Controlled . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .......................23
Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect AC Waveforms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ..............24
Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect AC Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ..................24
PACKAGE MECHANICAL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
TSOP48 - 48 lead Plastic Thin Small Outline, 12 x 20mm, Package Outline . . . . . . ...........25
TSOP48 - 48 lead Plastic Thin Small Outline, 12 x 20mm, Package Mechanical Data . . . . . . . . . 25
SO44 - 44 lead Plastic Small Outline, 525 mils body width, Package Outline . . . . . . . . . . . . ....26
LFBGA48 - 8 x 6 balls, 0.80 mm pitch, Bottom View Package Outline......................27
LFBGA48 - 8 x 6 balls, 0.80mm pitch, Package Mechanical Data . . . ......................27
PART NUMBERING . . . . . . . . . ......................................................28
Ordering Information Scheme . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ....................................28
3/29

M29W160DT, M29W160DB
REVISION HISTORY. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ....................................28
Document Revision History .......................................................28
4/29
SUMMARY DESCRIPTION
The M29W160D is a 16 Mbit (2Mb x8 or 1Mbx16)
non-volatile memory that can be read, erased and
reprogrammed. These operations can be performed using a single low voltage (2.7 to 3.6V)
supply. On power-up the memory defaults to its
Read mode where it can be read in the same way
as a ROM or EPROM.
The memory is divided into blocks that can be
erased independently so it is possible to preserve
valid data while old data is erased. Each block can
be protected independently to prevent accidental
Program or Erase commands from modifying the
memory. Program and Erase commands are written to the Command Interface of the memory. An
on-chip Program/Erase Controller simplifies the
process ofprogramming or erasing the memory by
taking care of all of the specialoperations that are
required to update the memory contents.
The end of a program or erase operation can be
detected and any error conditions identified. The
M29W160DT, M29W160DB
command set required to control the memory is
consistent with JEDEC standards.
The blocks in the memory are asymmetrically arranged,see Tables2 and3, BlockAddresses. The
first or last 64 Kbytes have been divided into four
additional blocks. The 16 Kbyte Boot Block can be
used for smallinitialization code to startthe microprocessor, the two 8 Kbyte Parameter Blocks can
be used for parameter storage and the remaining
32K is a small Main Block where the application
may be stored.
Chip Enable, Output Enableand Write Enable signals control the bus operation of the memory.
They allow simple connection to most microprocessors, often without additional logic.
The memory is offered in TSOP48 (12 x 20mm),
SO44 and LFBGA48 (0.8mm pitch) packages and
it is supplied with all the bits erased (set to ’1’).
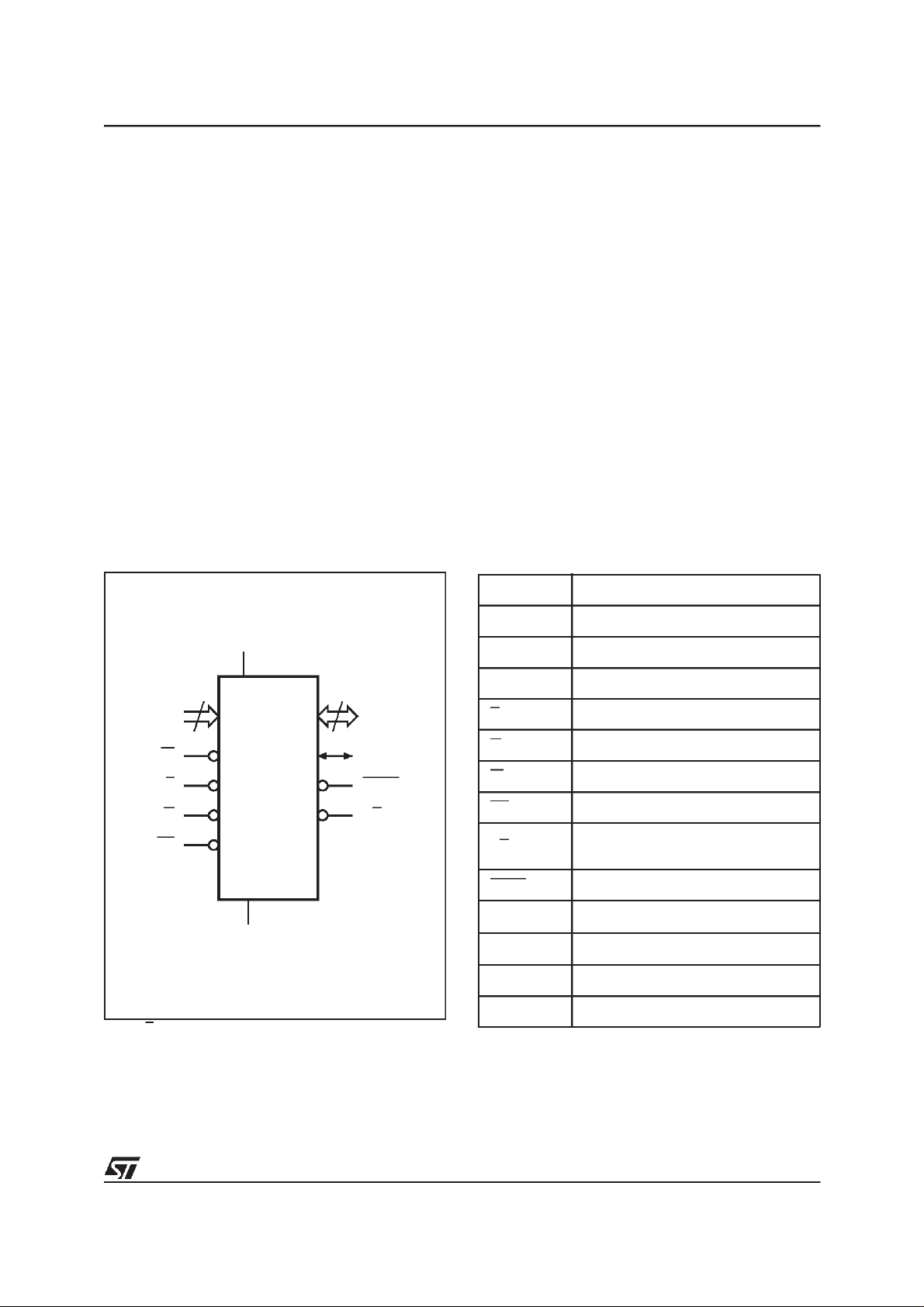
Figure 2. Logic Diagram
V
CC
20
A0-A19
W
E
G
RP
Note: RB not available on SO44 package.
M29W160DT
M29W160DB
V
SS
15
DQ0-DQ14
DQ15A–1
BYTE
RB
AI03843
Table 1. Signal Names
A0-A19 Address Inputs
DQ0-DQ7 Data Inputs/Outputs
DQ8-DQ14 Data Inputs/Outputs
DQ15A–1 Data Input/Output or Address Input
E Chip Enable
G Output Enable
W Write Enable
RP Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect
RB
BYTE Byte/Word Organization Select
V
CC
V
SS
NC Not Connected Internally
DU Don’t Use as internally connected
Ready/Busy Output
(Not available on SO44 package)
Supply Voltage
Ground
5/29

M29W160DT, M29W160DB
Figure 3. TSOP Connections Figure 4. SO Connections
A15
A14
A13
A12
A11
A10 DQ14
A19
NC
RP
NC
NC
RB
A18
A17
1
A9
A8
W
12
M29W160DT
M29W160DB
13
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
24 25
AI03844
48
37
36
A16
BYTE
V
SS
DQ15A–1
DQ7
DQ6
DQ13
DQ5
DQ12
DQ4
V
CC
DQ11
DQ3
DQ10
DQ2
DQ9
DQ1
DQ8
DQ0
G
V
SS
E
A0
RP
A18
A17 A8
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
A0
V
SS
DQ0
DQ8
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
M29W160DT
E
M29W160DB
12
13
G
14
15
16
17DQ1
DQ9
18
19
DQ10
DQ3
20
21
DQ11
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
2322
AI03845
W
A19
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
A16
BYTE
V
SS
DQ15A–1
DQ7
DQ14
DQ6
DQ13
DQ5DQ2
DQ12
DQ4
V
CC
6/29

Figure 5. LFBGA Connections (Top view through package)
M29W160DT, M29W160DB
654321
A7
A17
A6
A5
DQ0
DQ8
DQ9
DQ1
V
A4
A3
A1
A0
A2
E
G
SS
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
RB
DU
A18
DU
DQ2
DQ10
DQ11
DQ3
W
RP
DU
A19
DQ5
DQ12
V
CC
DQ4
A9
A8
A10
A11
DQ7
DQ14
DQ13
DQ6
A13
A12
A14
A15
A16
BYTE
DQ15
A–1
V
SS
AI02985B
7/29
M29W160DT, M29W160DB
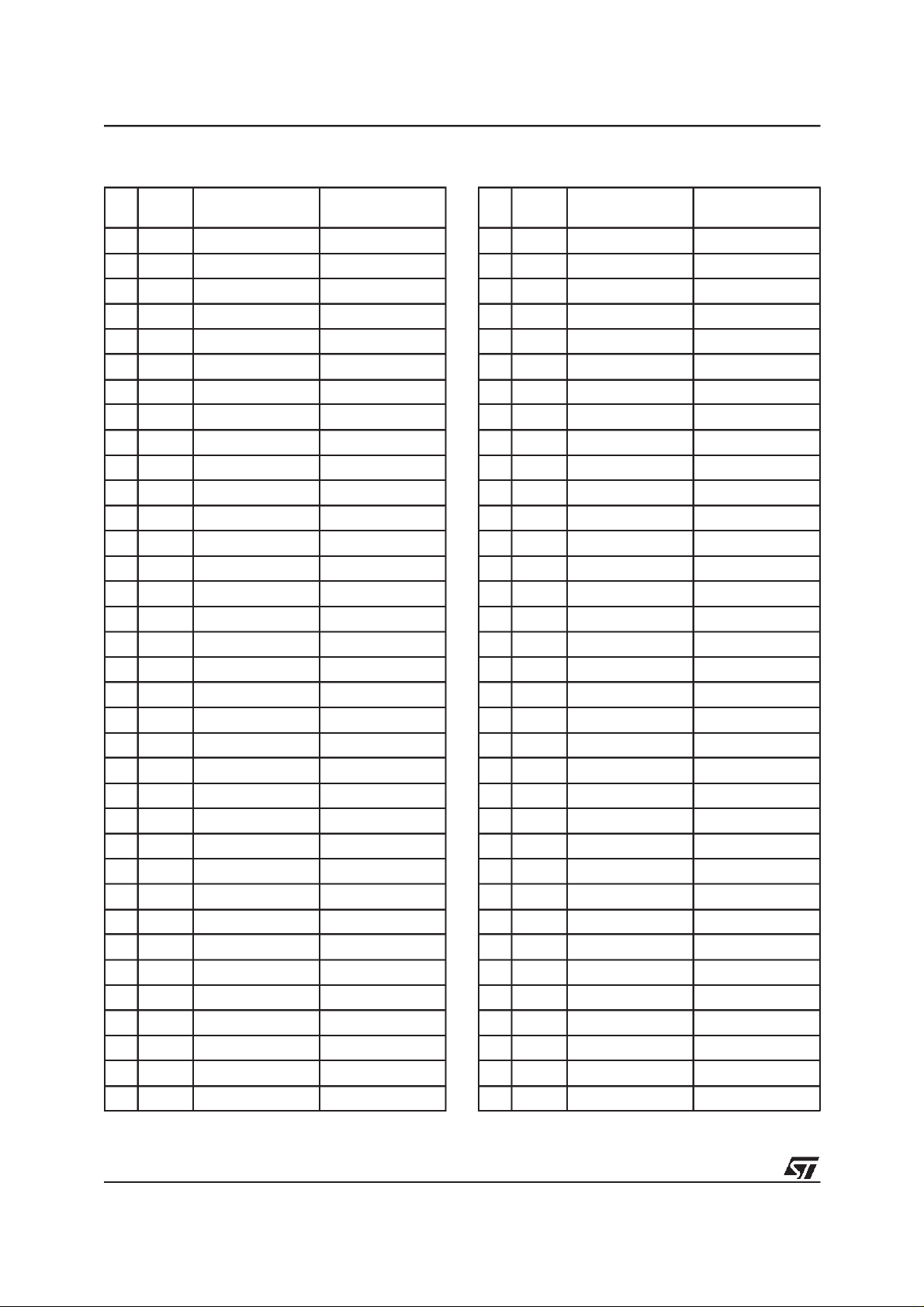
Table 2. Top Boot Block Addresses,
M29W160DT
Size
#
(Kby t es)
34 16 1FC000h-1FFFFFh FE000h-FFFFFh
33 8 1FA000h-1FBFFFh FD000h-FDFFFh
32 8 1F8000h-1F9FFFh FC000h-FCFFFh
31 32 1F0000h-1F7FFFh F8000h-FBFFFh
30 64 1E0000h-1EFFFFh F0000h-F7FFFh
29 64 1D0000h-1DFFFFh E8000h-EFFFFh
28 64 1C0000h-1CFFFFh E0000h-E7FFFh
27 64 1B0000h-1BFFFFh D8000h-DFFFFh
26 64 1A0000h-1AFFFFh D0000h-D7FFFh
25 64 190000h-19FFFFh C8000h-CFFFFh
24 64 180000h-18FFFFh C0000h-C7FFFh
23 64 170000h-17FFFFh B8000h-BFFFFh
22 64 160000h-16FFFFh B0000h-B7FFFh
21 64 150000h-15FFFFh A8000h-AFFFFh
20 64 140000h-14FFFFh A0000h-A7FFFh
19 64 130000h-13FFFFh 98000h-9FFFFh
18 64 120000h-12FFFFh 90000h-97FFFh
17 64 110000h-11FFFFh 88000h-8FFFFh
16 64 100000h-10FFFFh 80000h-87FFFh
15 64 0F0000h-0FFFFFh 78000h-7FFFFh
14 64 0E0000h-0EFFFFh 70000h-77FFFh
13 64 0D0000h-0DFFFFh 68000h-6FFFFh
12 64 0C0000h-0CFFFFh 60000h-67FFFh
11 64 0B0000h-0BFFFFh 58000h-5FFFFh
10 64 0A0000h-0AFFFFh 50000h-57FFFh
9 64 090000h-09FFFFh 48000h-4FFFFh
8 64 080000h-08FFFFh 40000h-47FFFh
7 64 070000h-07FFFFh 38000h-3FFFFh
6 64 060000h-06FFFFh 30000h-37FFFh
5 64 050000h-05FFFFh 28000h-2FFFFh
4 64 040000h-04FFFFh 20000h-27FFFh
3 64 030000h-03FFFFh 18000h-1FFFFh
2 64 020000h-02FFFFh 10000h-17FFFh
1 64 010000h-01FFFFh 08000h-0FFFFh
0 64 000000h-00FFFFh 00000h-07FFFh
AddressRange
(x8)
Addres sRange
(x16)
Table 3. Bottom Boot Block Addresses,
M29W160DB
Size
#
(Kbytes)
34 64 1F0000h-1FFFFFh F8000h-FFFFFh
33 64 1E0000h-1EFFFFh F0000h-F7FFFh
32 64 1D0000h-1DFFFFh E8000h-EFFFFh
31 64 1C0000h-1CFFFFh E0000h-E7FFFh
30 64 1B0000h-1BFFFFh D8000h-DFFFFh
29 64 1A0000h-1AFFFFh D0000h-D7FFFh
28 64 190000h-19FFFFh C8000h-CFFFFh
27 64 180000h-18FFFFh C0000h-C7FFFh
26 64 170000h-17FFFFh B8000h-BFFFFh
25 64 160000h-16FFFFh B0000h-B7FFFh
24 64 150000h-15FFFFh A8000h-AFFFFh
23 64 140000h-14FFFFh A0000h-A7FFFh
22 64 130000h-13FFFFh 98000h-9FFFFh
21 64 120000h-12FFFFh 90000h-97FFFh
20 64 110000h-11FFFFh 88000h-8FFFFh
19 64 100000h-10FFFFh 80000h-87FFFh
18 64 0F0000h-0FFFFFh 78000h-7FFFFh
17 64 0E0000h-0EFFFFh 70000h-77FFFh
16 64 0D0000h-0DFFFFh 68000h-6FFFFh
15 64 0C0000h-0CFFFFh 60000h-67FFFh
14 64 0B0000h-0BFFFFh 58000h-5FFFFh
13 64 0A0000h-0AFFFFh 50000h-57FFFh
12 64 090000h-09FFFFh 48000h-4FFFFh
11 64 080000h-08FFFFh 40000h-47FFFh
10 64 070000h-07FFFFh 38000h-3FFFFh
9 64 060000h-06FFFFh 30000h-37FFFh
8 64 050000h-05FFFFh 28000h-2FFFFh
7 64 040000h-04FFFFh 20000h-27FFFh
6 64 030000h-03FFFFh 18000h-1FFFFh
5 64 020000h-02FFFFh 10000h-17FFFh
4 64 010000h-01FFFFh 08000h-0FFFFh
3 32 008000h-00FFFFh 04000h-07FFFh
2 8 006000h-007FFFh 03000h-03FFFh
1 8 004000h-005FFFh 02000h-02FFFh
0 16 000000h-003FFFh 00000h-01FFFh
Address Range
(x8)
Address Range
(x16)
8/29
SIGNAL DESCRIPTIONS
See Figure 2, Logic Diagram, and Table 1, Signal
Names, fora brief overview ofthesignals connected to this device.
Address Inputs (A0-A19).
The Address Inputs
select the cells in the memoryarray to access during Bus Read operations. During BusWrite operations they control the commands sent to the
Command Interface of the internal state machine.
Data Inputs/Outputs (DQ0-DQ7).
The Data Inputs/Outputs outputthe datastored at the selected
address during a Bus Readoperation. DuringBus
Write operations they represent the commands
sent tothe Command Interface of theinternal state
machine.
Data Inputs/Outputs (DQ8-DQ14).
The Data Inputs/Outputs outputthe datastored at the selected
address during a Bus Read operation when BYTE
is High, V
. When BYTE is Low, VIL, these pins
IH
are not used and arehigh impedance. During Bus
Write operations the Command Register does not
use these bits. When reading the Status Register
these bits should be ignored.
Data Input/Output or Address Input (DQ15A-1).
When BYTE is High, VIH, this pin behaves as a
Data Input/Output pin (as DQ8-DQ14). When
BYTE is Low, VIL, this pin behaves asan address
pin; DQ15A–1 Low willselect the LSB of the Word
on the other addresses, DQ15A–1 Highwill select
the MSB. Throughout the text consider references
to the Data Input/Output to include this pin when
BYTE is High and references to the Address Inputs to include this pin when BYTE is Low except
when stated explicitly otherwise.
Chip Enable (E). The Chip Enable, E, activates
the memory,allowing BusRead and Bus Writeoperations to be performed. When Chip Enable is
High, V
, all other pins are ignored.
IH
Output Enable (G). The Output Enable, G, controls the Bus Read operation of the memory.
Write Enable (W). The Write Enable, W, controls
the Bus Write operation of the memory’s Command Interface.
Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect (RP). The
Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect pin can be
used to apply a Hardware Resetto the memory or
to temporarily unprotect all Blocks that have been
protected.
A Hardware Reset is achieved by holding Reset/
Block Temporary Unprotect Low, V
t
. After Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect
PLPX
, for at least
IL
goes High, VIH, the memory will be ready for Bus
Read and Bus Write operations after t
PHEL
or
M29W160DT, M29W160DB
, whicheveroccurs last. See the Ready/Busy
t
RHEL
Output section, Table 18 and Figure 13, Reset/
Temporary Unprotect AC Characteristics for more
details.
Holding RP at VIDwill temporarily unprotect the
protected Blocks in the memory. Program and
Erase operations on all blocks will be possible.
The transition from VIHtoVIDmustbe slower than
t
Ready/Busy Output (RB).
is anopen-drain output that canbe used toidentify
when the memory array can be read. Ready/Busy
is high-impedance during Read mode,Auto Select
mode and Erase Suspend mode.
After a Hardware Reset, Bus Read and Bus Write
operations cannot begin until Ready/Busy becomes high-impedance. See Table 18 and Figure
13, Reset/Temporary Unprotect AC Characteristics.
During Program or Erase operations Ready/Busy
is Low, VOL. Ready/Busy will remain Low during
Read/Reset commands or Hardware Resets until
the memory is ready to enter Read mode.
The use ofan open-drain output allowsthe Ready/
Busy pins from several memories to be connected
to asingle pull-up resistor. A Low will then indicate
that one, or more, of the memories is busy.
Byte/Word Organization Select (BYTE). The
Byte/Word Organization Select pin is used to
switch between the 8-bit and 16-bit Bus modes of
the memory. When Byte/Word Organization Select isLow, V
it is High, VIH, the memory is in 16-bit mode.
V
supplies the power for all operations (Read, Program, Erase etc.).
The Command Interface is disabledwhen the V
Supply Voltage is less than the Lockout Voltage,
V
cidentally damaging the data during power up,
power down and power surges. If the Program/
Erase Controller is programming orerasing during
this time thenthe operation aborts and the memory contents being altered will be invalid.
A 0.1µF capacitor should be connected between
the VCCSupply Voltage pin and the VSSGround
pin to decouplethe current surges from the power
supply. The PCB track widthsmust be sufficient to
carry the currents required during program and
erase operations, I
Vss Ground. The VSSGround is the reference
for all voltage measurements.
.
PHPHH
The Ready/Busy pin
, the memory is in 8-bit mode, when
IL
Supply Voltage. The VCCSupply Voltage
CC
. Thisprevents Bus Write operationsfrom ac-
LKO
.
CC3
CC
9/29
 Loading...
Loading...