
查询M29DW128F供应商
128 Mbit (16Mb x8 or 8Mb x16, Multiple Bank, Page, Boot Block)
Features summary
■ Supply Voltage
–V
–V
–V
■ ASYNCHRONOUS RANDOM/PAGE READ
– Page Width: 8 Words
– Page Access: 25, 30ns
– Random Access: 60, 70ns
■ PROGRAMMING TIME
– 10µs per Byte/Word typical
– 4 Words / 8 Bytes Program
– 32-Word Write Buffer
■ ERASE VERIFY
■ MEMORY BLOCKS
– Quadruple Bank Memory Array:
– Parameter Blocks (at Top and Bottom)
■ DUAL OPERATIONS
– While Program or Erase in one bank, Read
■ PROGRAM/ ERASE SUSPEND and RESUME
MODES
– Read from any Block during Program
– Read and Program another Block during
■ UNLOCK BYPASS PROGRAM
– Faster Production/Batch Programming
■ COMMON FLASH INTERFACE
– 64 bit Security Code
■ 100,000 PROGRAM/ERASE CYCLES per
BLOCK
■ LOW POWER CONSUMPTION
– Standby and Automatic Standby
2.7V to 3.6V for Program, Erase and
CC =
Read
= 1.65V to 3.6V for Input/Output
CCQ
=12V for Fast Program (optional)
PP
16Mbit+48Mbit+48Mbit+16Mbit
in any of the other banks
Suspend
Erase Suspend
M29DW128F
3V Supply, Flash Memory
PRELIMINARY DATA
TSOP56 (NF)
14 x 20mm
BGA
TBGA64 (ZA)
10 x 13mm
■ HARDWARE BLOCK PROTECTION
–V
■ SECURITY FEATURES
– Standard Protection
– Password Protection
■ EXTENDED MEMORY BLOCK
– Extra block used as security block or to
■ ELECTRONIC SIGNATURE
– Manufacturer Code: 0020h
– Device Code: 227Eh + 2220h + 2200h
■ ECOPACK
/WP Pin for fast program and write
PP
protect of the four outermost parameter
blocks
store additional information
®
PACKAGES AVAILABLE
Rev 1.0
August 2005 1/93
This is preliminar y information on a new product now in development or undergoing evaluation. Details are subject to
change without notice.
www.st.com
1

M29DW128F
Contents
1 Summary description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2 Signal descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
2.1 Address Inputs (A0-A22) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
2.2 Data Inputs/Outputs (DQ0-DQ7) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
2.3 Data Inputs/Outputs (DQ8-DQ14) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
2.4 Data Input/Output or Address Input (DQ15A–1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
2.5 Chip Enable (E) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
2.6 Output Enable (G) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
2.7 Write Enable (W) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2.8 V
Write Protect (V
PP/
WP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
PP/
2.9 Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect (RP) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2.10 Ready/Busy Output (RB) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
2.11 Byte/Word Organization Select (BYTE) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
2.12 V
2.13 V
2.14 V
Supply Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
CCQ
Supply Voltage (2.7V to 3.6V) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
CC
Ground . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
SS
3 Bus operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
3.1 Bus Read . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
3.2 Bus Write . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
3.3 Output Disable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
3.4 Standby . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
3.5 Automatic Standby . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
3.6 Special Bus Operations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
3.6.1 Read Electronic Signature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
3.6.2 Verify Extended Block Protection Indicator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
3.6.3 Verify Block Protection Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
3.6.4 Hardware Block Protect . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
3.6.5 Temporary Unprotect of High Voltage Protected Blocks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
4 Hardware Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
2/93

M29DW128F
4.1 Write Protect . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
4.2 Temporary Block Unprotect . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
5 Software Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
5.1 Standard Protection Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
5.1.1 Block Lock/Unlock Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
5.1.2 Non-Volatile Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
5.2 Password Protection Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
5.2.1 Block Lock/Unlock Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
5.2.2 Non-Volatile Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
6 Command Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
6.1 Standard commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
6.1.1 Read/Reset command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
6.1.2 Auto Select command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
6.1.3 Read CFI Query command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
6.1.4 Chip Erase command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
6.1.5 Block Erase command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
6.1.6 Erase Suspend command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
6.1.7 Erase Resume command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
6.1.8 Program Suspend command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
6.1.9 Program Resume command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
6.1.10 Program command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
6.1.11 Verify command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
6.2 Fast Program commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
6.2.1 Write to Buffer and Program command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
6.2.2 Write to Buffer and Program Confirm command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
6.2.3 Write to Buffer and Program Abort and Reset command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
6.2.4 Double Word Program command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
6.2.5 Quadruple Word Program command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
6.2.6 Double Byte Program Command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
6.2.7 Quadruple Byte Program command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
6.2.8 Octuple Byte Program command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
6.2.9 Unlock Bypass command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
6.2.10 Unlock Bypass Program command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
6.2.11 Unlock Bypass Reset command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
3/93

M29DW128F
6.3 Block Protection commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
6.3.1 Enter Extended Block command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
6.3.2 Exit Extended Block command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
6.3.3 Set Extended Block Protection Bit command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
6.3.4 Verify Extended Block Protection Bit command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
6.3.5 Password Program command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
6.3.6 Password Verify command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
6.3.7 Password Protection Unlock command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
6.3.8 Set Password Protection Mode command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
6.3.9 Verify Password Protection Mode command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
6.3.10 Set Standard Protection Mode command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
6.3.11 Verify Standard Protection Mode command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
6.3.12 Set Non-Volatile Modify Protection Bit command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
6.3.13 Verify Non-Volatile Modify Protection Bit command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
6.3.14 Clear Non-Volatile Modify Protection Bits command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
6.3.15 Set Lock Bit command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
6.3.16 Clear Lock Bit command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
6.3.17 Verify Lock Bit command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
6.3.18 Set Lock-Down Bit command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
6.3.19 Verify Lock-Down Bit command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
7 Status Register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
7.1 Data Polling Bit (DQ7) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
7.2 Toggle Bit (DQ6) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
7.3 Error Bit (DQ5) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
7.4 Erase Timer Bit (DQ3) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
7.5 Alternative Toggle Bit (DQ2) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
7.6 Write to Buffer and Program Abort Bit (DQ1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
8 Dual Operations and Multiple Bank architecture . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
9 Maximum Rating . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
10 DC and AC parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
11 Package mechanical . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
4/93

M29DW128F
12 Part numbering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Appendix A Block addresses and Read/Modify Protection groups. . . . . . . . . . 67
Appendix B Common Flash Interface (CFI) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Appendix C Extended Memory Block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
C.1 Factory Locked Section of the Extended Block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
C.2 Customer Lockable Section of the Extended Block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Appendix D High Voltage Block Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
D.1 Programmer Technique . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
D.2 In-System Technique . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Appendix E Flowcharts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
13 Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
5/93

M29DW128F
List of tables
Table 1. Signal Names . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Table 2. Bank Architecture . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Table 3. Bus Operations, 8-bit Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Table 4. Read Electronic Signature, 8-bit Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Table 5. Block Protection, 8-bit Mode. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Table 6. Bus Operations, 16-bit Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Table 7. Read Electronic Signature, 16-bit Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Table 8. Block Protection, 16-bit Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 9. Hardware Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 10. Block Protection Status. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Table 11. Standard Commands, 8-bit Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Table 12. Standard Commands, 16-bit Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Table 13. Fast Program Commands, 8-bit mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Table 14. Fast Program Commands, 16-bit Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Table 15. Block Protection Commands, 8-bit Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Table 16. Block Protection Commands, 16-bit Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Table 17. Protection Command Addresses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Table 18. Program, Erase Times and Program, Erase Endurance Cycles. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Table 19. Status Register Bits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Table 20. Dual Operations Allowed In Other Banks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Table 21. Dual Operations Allowed In Same Bank. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Table 22. Absolute Maximum Ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Table 23. Operating and AC Measurement Conditions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Table 24. Device Capacitance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Table 25. DC Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Table 26. Read AC Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Table 27. Write AC Characteristics, Write Enable Controlled. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Table 28. Write AC Characteristics, Chip Enable Controlled . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Table 29. Toggle and Alternative Toggle Bits AC Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Table 30. Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect AC Characteristics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Table 31. TSOP56 – 56 lead Plastic Thin Small Outline, 14 x 20mm, Package Mechanical Data . . . 64
Table 32. TBGA64 10x13mm - 8x8 active ball array, 1mm pitch, Package Mechanical Data . . . . . . 65
Table 33. Ordering Information Scheme. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Table 34. Block Addresses and Protection Groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Table 35. Query Structure Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Table 36. CFI Query Identification String . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Table 37. CFI Query System Interface Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Table 38. Device Geometry Definition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Table 39. Primary Algorithm-Specific Extended Query Table. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Table 40. Security Code Area. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Table 41. Extended Block Address and Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Table 42. Programmer Technique Bus Operations, 8-bit or 16-bit Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Table 43. Document Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
6/93

M29DW128F
List of figures
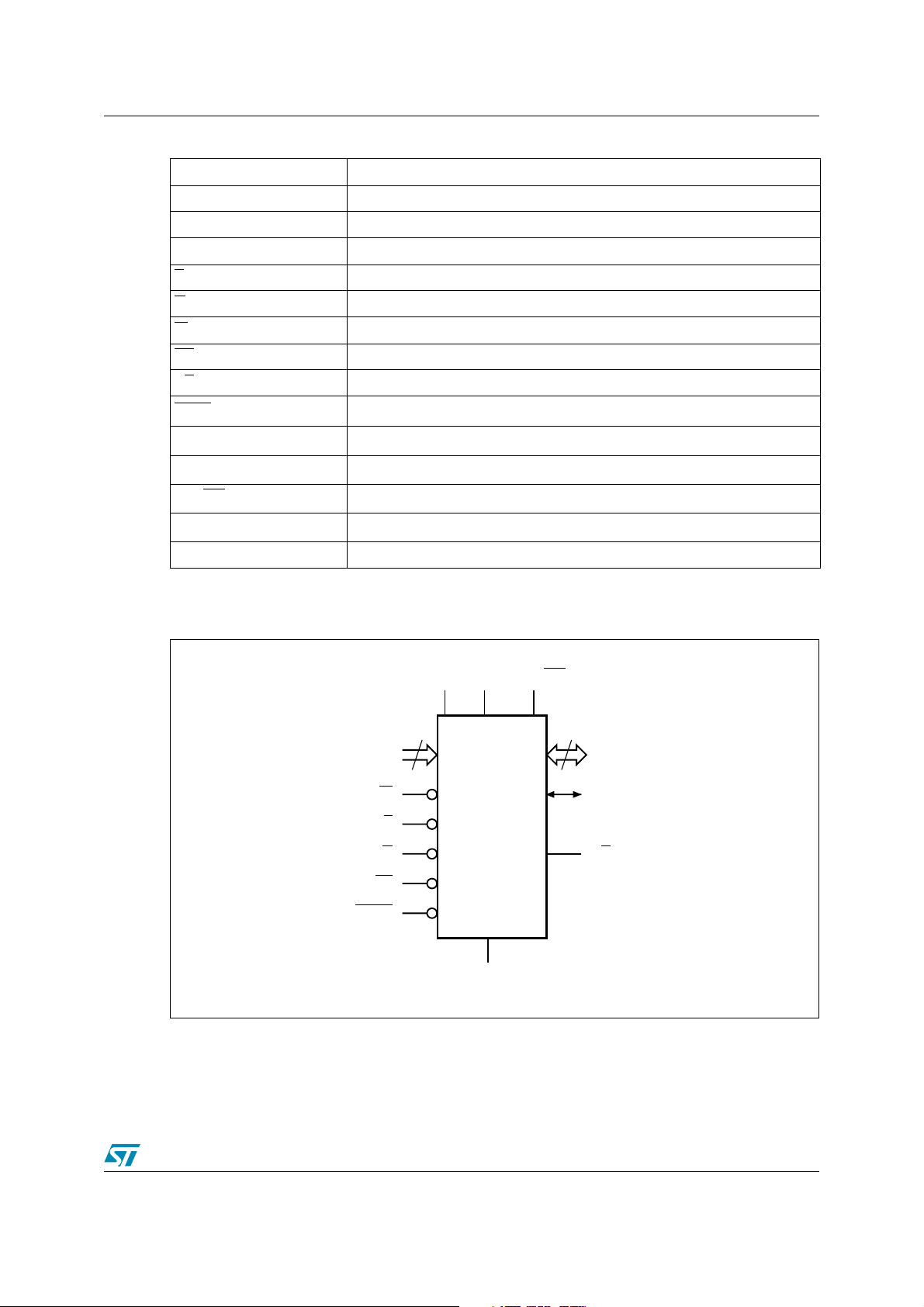
Figure 1. Logic Diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
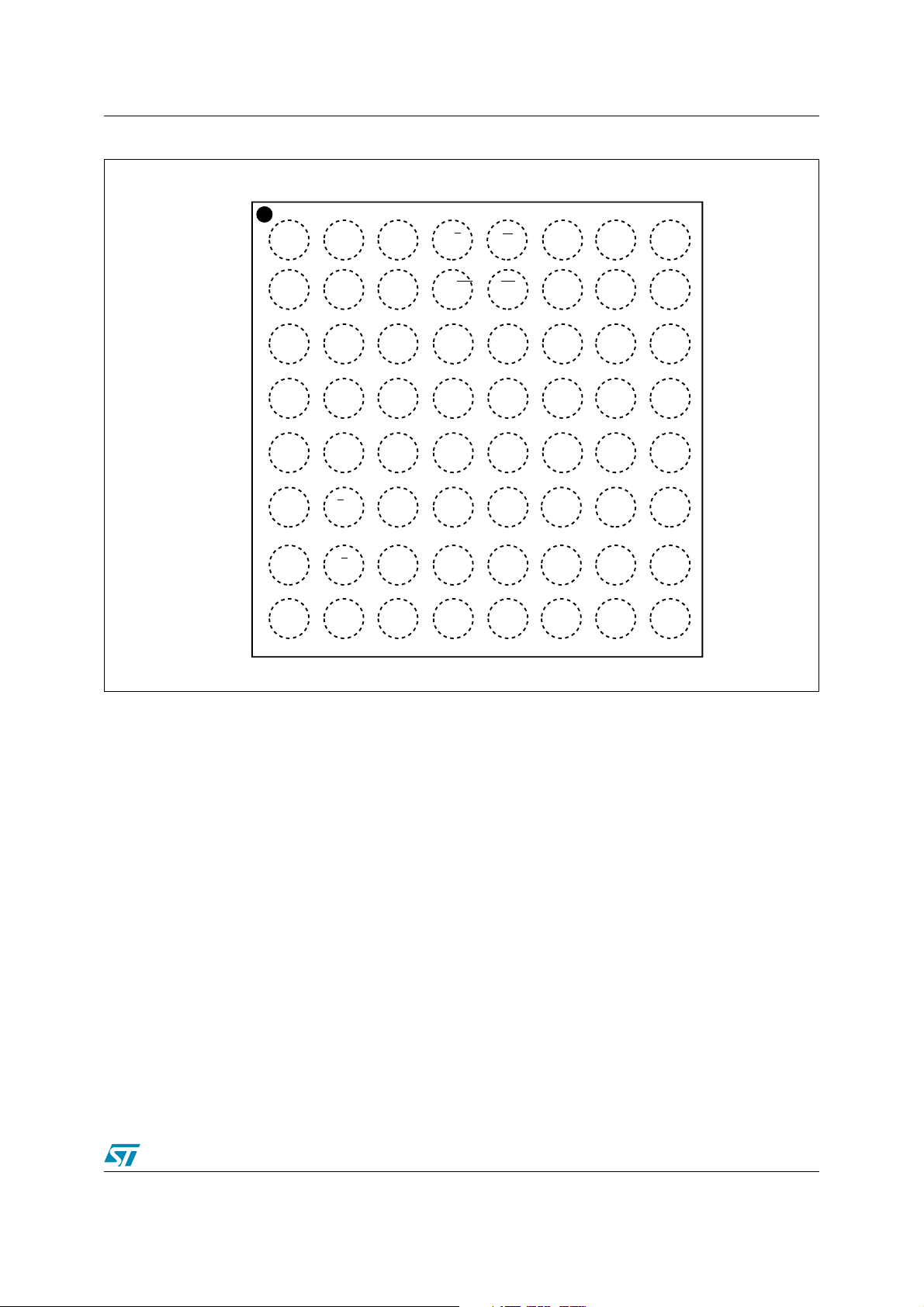
Figure 2. TSOP Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Figure 3. TBGA Connections (Top view through package) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
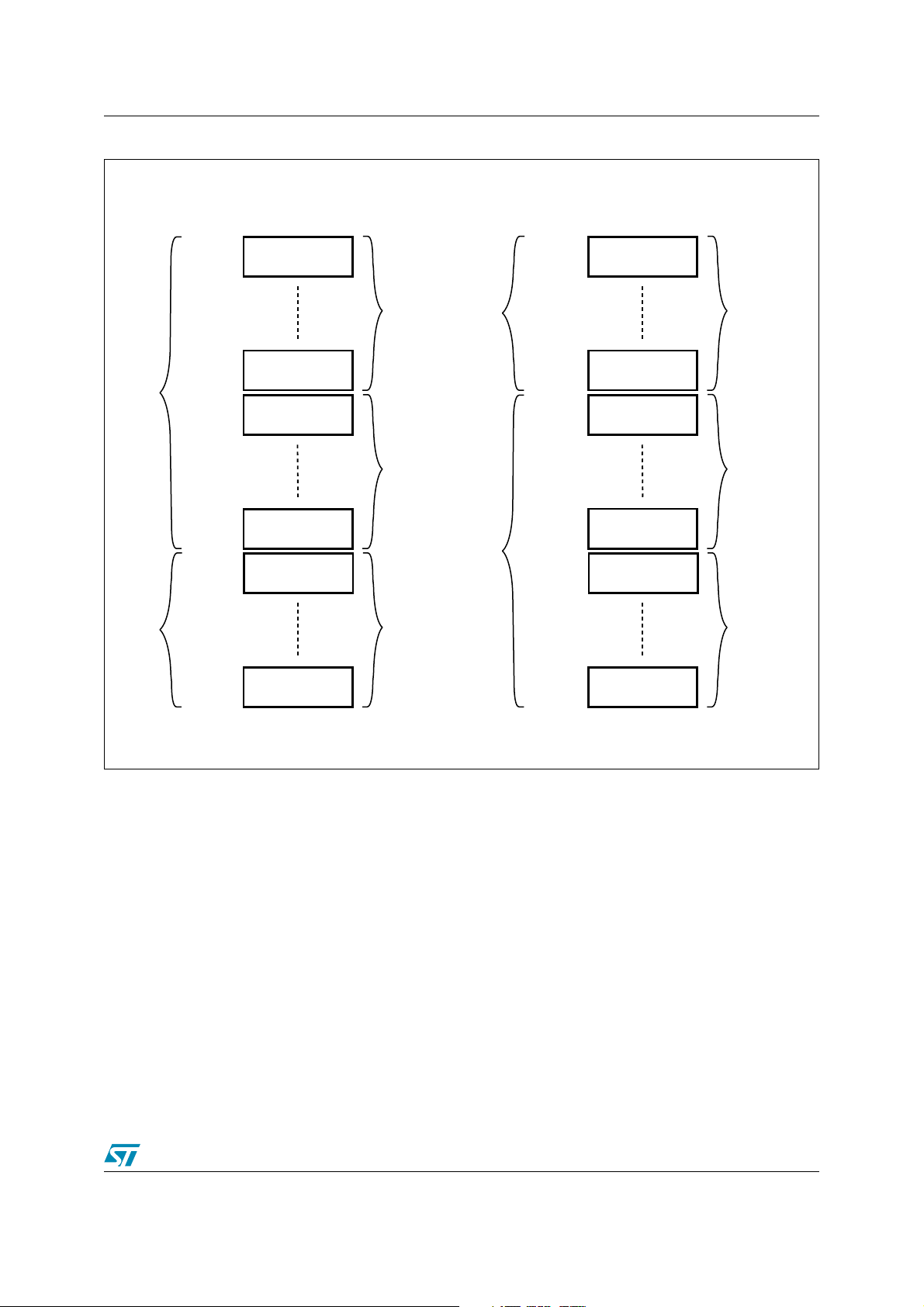
Figure 4. Block Addresses (x8) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Figure 5. Block Addresses (x16) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Figure 6. Block Protection State Diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Figure 7. Software Protection Scheme . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Figure 8. Data Polling Flowchart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Figure 9. Toggle Flowchart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Figure 10. AC Measurement I/O Waveform. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Figure 11. AC Measurement Load Circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Figure 12. Random Read AC Waveforms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Figure 13. Page Read AC Waveforms. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Figure 14. Write AC Waveforms, Write Enable Controlled . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Figure 15. Write AC Waveforms, Chip Enable Controlled . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Figure 16. Toggle and Alternative Toggle Bits Mechanism, Chip Enable Controlled. . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Figure 17. Toggle and Alternative Toggle Bits Mechanism, Output Enable Controlled . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Figure 18. Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect AC Waveforms (No Program/Erase Ongoing). . . . . . . 62
Figure 19. Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect During Program/Erase Operation AC Waveforms . . . . 62
Figure 20. Accelerated Program Timing Waveforms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Figure 21. TSOP56 – 56 lead Plastic Thin Small Outline, 14 x 20mm, Package Outline . . . . . . . . . . 64
Figure 22. TBGA64 10x13mm - 8x8 active ball array, 1mm pitch, Package Outline . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Figure 23. Programmer Equipment Group Protect Flowchart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Figure 24. Programmer Equipment Chip Unprotect Flowchart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Figure 25. In-System Equipment Group Protect Flowchart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Figure 26. In-System Equipment Chip Unprotect Flowchart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Figure 27. Write to Buffer and Program Flowchart and Pseudo Code. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
7/93

1 Summary description M29DW128F
1 Summary description
The M29DW128F is a 128 Mbit (16Mb x8 or 8Mb x16) non-volatile memory that can be read,
erased and reprogrammed. These operations can be performed using a single low voltage (2.7
to 3.6V) supply. V
1.65V. At Power-up the memory defaults to its Read mode.
The M29DW128F features an asymmetrical block architecture, with 16 parameter and 254
main blocks, divided into four Banks, A, B, C and D, providing multiple Bank operations. While
programming or erasing in one bank, read operations are possible in any other bank. The bank
architecture is summarized in Ta bl e 2 . Eight of the Parameter Blocks are at the top of the
memory address space, and eight are at the bottom.
Program and Erase commands are written to the Command Interface of the memory. An onchip Program/Erase Controller simplifies the process of programming or erasing the memory by
taking care of all of the special operations that are required to update the memory contents.
The end of a program or erase operation can be detected and any error conditions identified.
The command set required to control the memory is consistent with JEDEC standards. The
Chip Enable, Output Enable and Write Enable signals control the bus operations of the
memory. They allow simple connection to most microprocessors, often without additional logic.
The device supports Asynchronous Random Read and Page Read from all blocks of the
memory array.
is an additional voltage supply that allows to drive the I/O pins down to
CCQ
The M29DW128F has one extra 256 Byte block (Extended Block) that can be accessed using a
dedicated command. The Extended Block can be protected and so is useful for storing security
information. However the protection is irreversible, once protected the protection cannot be
undone.
Each block can be erased independently, so it is possible to preserve valid data while old data
is erased.
The device features four different levels of hardware and software block protection to avoid
unwanted program or erase (modify). The software block protection features are available in 16
bit memory organization only:
● Hardware Protection:
–The V
/WP provides a hardware protection of the four outermost parameter blocks
PP
(two at the top and two at the bottom of the address space).
–The RP
pin temporarily unprotects all the blocks previously protected using a High
Voltage Block Protection technique (see Appendix D: High Voltage Block Protection).
● Software Protection
– Standard Protection
– Password Protection
The memory is offered in TSOP56 (14 x 20mm) and TBGA64 (10 x 13mm, 1mm pitch)
packages. The 8-bit Bus mode is only available when the M29DW128F is delivered in TSOP56
package. In order to meet environmental requirements, ST offers the M29DW128F in
ECOPACK
®
packages. ECOPACK packages are Lead-free. The category of second Level
Interconnect is marked on the package and on the inner box label, in compliance with JEDEC
Standard JESD97. The maximum ratings related to soldering conditions are also marked on
the inner box label. ECOPACK is an ST trademark. ECOPACK specifications are available at:
www.st.com. The memory is supplied with all the bits erased (set to ’1’).
8/93
M29DW128F 1 Summary description
Table 1. Signal Names
A0-A22 Address Inputs
DQ0-DQ7 Data Inputs/Outputs
DQ8-DQ14 Data Inputs/Outputs
DQ15A–1 Data Input/Output or Address Input
E
Chip Enable
G
W
Output Enable
Write Enable
RP Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect
RB
BYTE
V
CC
V
CCQ
V
/WP VPP/Write Protect
PP
V
SS
Ready/Busy Output
Byte/Word Organization Select
Supply Voltage
Supply Voltage for Input/Outputs
Ground
(1)
NC Not Connected Internally
1. The x8 organization is only available in TSOP56 Package while the x16 organization is available for both
packages.
Figure 1. Logic Diagram
CCQ
VPP/WP
15
DQ0-DQ14
A0-A22
23
V
V
CC
W
RP
BYTE
DQ15A–1
E
G
M29DW128F
V
SS
RB
AI09208
9/93

1 Summary description M29DW128F
Table 2. Bank Architecture
Parameter Blocks Main Blocks
Bank Bank Size
No. of
Blocks
Block Size
No. of
Blocks
Block Size
A 16 Mbit 8 8 KBytes/ 4 KWords 31 64 KBytes/ 32 KWords
B 48 Mbit — — 96 64 KBytes/ 32 KWords
C 48 Mbit — — 96 64 KBytes/ 32 KWords
D 16 Mbit 8 8 KBytes/ 4 KWords 31 64 KBytes/ 32 KWords
Figure 2. TSOP Connections
NC
1
A22
A15 A16
A14
A13
A12
A11
A10
A9
A8
A19
A20
W
RP
A21
14
M29DW128F
15
VPP/WP
RB
A18
A17
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
NC
NC
28 29
56
43
42
NC
NC
BYTE
V
SS
DQ15A–1
DQ7
DQ14
DQ6
DQ13
DQ5
DQ12
DQ4
V
CC
DQ11
DQ3
DQ10
DQ2
DQ9
DQ1
DQ8
DQ0
G
V
SS
E
A0
NC
V
CCQ
10/93
AI09209b
M29DW128F 1 Summary description
Figure 3. TBGA Connections (Top view through package)
V
87
NC
A22
NC
CCQ
V
SS
NC
NC
NC
654321
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
V
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
CCQ
NC
NC
A3
A4
A2
A1 A20
A0
E
G
V
SS
A7
A17
A6
A5
DQ0
DQ8
DQ9
DQ1
V
PP
A18
DQ2
DQ10
DQ11
DQ3
RB
/
WP
W
RP
A21
A19
DQ5
DQ12
V
CC
DQ4
A9
A8
A10
A11
DQ7
DQ14
DQ13
DQ6
A13
A12
A14
A15
A16
NC
DQ15
V
SS
AI09210b
11/93

1 Summary description M29DW128F
Figure 4. Block Addresses (x8)
Bank A
Bank B
000000h
001FFFh
00E000h
00FFFFh
010000h
01FFFFh
1F0000h
1FFFFFh
200000h
20FFFFh
7F0000h
7FFFFFh
8 KBytes
8 KBytes
64 KBytes
64 KBytes
64 KBytes
64 KBytes
Address lines A22-A0, DQ15A-1
Total of 8
Parameter
Blocks
Total of 31
Main Blocks
Total of 96
Main Blocks
(x8)
Bank C
Bank D
800000h
80FFFFh
DF0000h
DFFFFFh
E00000h
E0FFFFh
FE0000h
FEFFFFh
FF0000h
FF1FFFh
FFE000h
FFFFFFh
64 KBytes
Total of 96
Main Blocks
64 KBytes
64 KBytes
Total of 31
Main Blocks
64 KBytes
8 KBytes
Total of 8
Parameter
Blocks
8 KBytes
1. Also see Appendix A and Table 34 for a full listing of the Block Addresses.
12/93
AI08966
M29DW128F 1 Summary description
Figure 5. Block Addresses (x16)
(x16)
Address lines A22-A0
Bank A
Bank B
000000h
000FFFh
007000h
007FFFh
008000h
00FFFFh
0F8000h
0FFFFFh
100000h
107FFFh
3F8000h
3FFFFFh
4 KWords
4 KWords
32 KWords
32 KWords
32 KWord
32 KWords
Total of 8
Parameter
Blocks
Total of 31
Main Blocks
Total of 96
Main Blocks
Bank C
Bank D
400000h
32 KWords
407FFFh
Total of 96
Main Blocks
6F8000h
32 KWords
6FFFFFh
700000h
32 KWords
707FFFh
Total of 31
Main Blocks
7F0000h
32 KWords
7F7FFFh
7F8000h
4 KWords
7F8FFFh
Total of 8
Parameter
Blocks
7FF000h
4 KWords
7FFFFFh
1. Also see Appendix A, Table 34 for a full listing of the Block Addresses.
13/93
AI08967

2 Signal descriptions M29DW128F
2 Signal descriptions
See Figure 1: Logic Diagram, and Table 1: Signal Names, for a brief overview of the signals
connected to this device.
2.1 Address Inputs (A0-A22)
The Address Inputs select the cells in the memory array to access during Bus Read operations.
During Bus Write operations they control the commands sent to the Command Interface of the
Program/Erase Controller.
2.2 Data Inputs/Outputs (DQ0-DQ7)
The Data I/O outputs the data stored at the selected address during a Bus Read operation.
During Bus Write operations they represent the commands sent to the Command Interface of
the internal state machine.
2.3 Data Inputs/Outputs (DQ8-DQ14)
The Data I/O outputs the data stored at the selected address during a Bus Read operation
when BYTE
impedance. During Bus Write operations the Command Register does not use these bits.
When reading the Status Register these bits should be ignored.
is High, VIH. When BYTE is Low, VIL, these pins are not used and are high
2.4 Data Input/Output or Address Input (DQ15A–1)
When the device is in x16 Bus mode, this pin behaves as a Data Input/Output pin (as DQ8DQ14). When the device is in x8 Bus mode, this pin behaves as an address pin; DQ15A–1 Low
will select the LSB of the addressed Word, DQ15A–1 High will select the MSB. Throughout the
text consider references to the Data Input/Output to include this pin when the device operates
in x16 bus mode and references to the Address Inputs to include this pin when the device
operates in x8 bus mode except when stated explicitly otherwise.
2.5 Chip Enable (E)
The Chip Enable pin, E, activates the memory, allowing Bus Read and Bus Write operations to
be performed. When Chip Enable is High, V
, all other pins are ignored.
IH
2.6 Output Enable (G)
The Output Enable pin, G, controls the Bus Read operation of the memory.
14/93

M29DW128F 2 Signal descriptions
2.7 Write Enable (W)
The Write Enable pin, W, controls the Bus Write operation of the memory’s Command Interface.
2.8 V
The VPP/Write Protect pin provides two functions. The VPP function allows the memory to use
an external high voltage power supply to reduce the time required for Program operations. This
is achieved by bypassing the unlock cycles and/or using the multiple Word (2 or 4 at-a-time) or
multiple Byte Program (2, 4 or 8 at-a-time) commands.
The Write Protect function provides a hardware method of protecting the four outermost boot
blocks (two at the top, and two at the bottom of the address space). When V
Low, V
these blocks are ignored while V
When V
the four outermost boot blocks. Program and Erase operations can now modify the data in
these blocks unless the blocks are protected using Block Protection.
Applying V
(including the four outermost parameter blocks) using a High Voltage Block Protection
technique (In-System or Programmer technique). See Table 9: Hardware Protection for details.
When V
mode. When V
Bypass Program operations the memory draws I
circuits. See the description of the Unlock Bypass command in the Command Interface section.
The transitions from V
Never raise V
memory may be left in an indeterminate state.
Write Protect (VPP/WP)
PP/
/Write Protect is
, the memory protects the four outermost boot blocks; Program and Erase operations in
IL
/Write Protect is High, VIH, the memory reverts to the previous protection status of
PP
to the VPP/WP pin will temporarily unprotect any block previously protected
PPH
/Write Protect is raised to V
PP
/Write Protect returns to VIH or VIL normal operation resumes. During Unlock
PP
to VPP and from VPP to VIH must be slower than t
IH
/Write Protect to VPP from any mode except Read mode, otherwise the
PP
/Write Protect is Low, even when RP is at VID.
PP
the memory automatically enters the Unlock Bypass
PP
from the pin to supply the programming
PP
PP
, see Figure 20.
VHVPP
The V
/Write Protect pin must not be left floating or unconnected or the device may become
PP
unreliable. A 0.1µF capacitor should be connected between the V
V
Ground pin to decouple the current surges from the power supply. The PCB track widths
SS
must be sufficient to carry the currents required during Unlock Bypass Program, I
2.9 Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect (RP)
The Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect pin can be used to apply a Hardware Reset to the
memory or to temporarily unprotect all the blocks previously protected using a High Voltage
Block Protection technique (In-System or Programmer technique).
Note that if V
even if RP
A Hardware Reset is achieved by holding Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect Low, V
least t
PLPX
for Bus Read and Bus Write operations after t
Ready/Busy Output section, Table 30: Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect AC Characteristics
and Figure 18 and Figure 19 for more details.
/WP is at VIL, then the four outermost parameter blocks will remain protected
PP
is at VID.
. After Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect goes High, VIH, the memory will be ready
or t
PHEL
15/93
RHEL
/Write Protect pin and the
PP
.
PP
, for at
IL
, whichever occurs last. See the

2 Signal descriptions M29DW128F
Holding RP at VID will temporarily unprotect all the blocks previously protected using a High
Voltage Block Protection technique. Program and erase operations on all blocks will be
possible. The transition from V
to VID must be slower than t
IH
PHPHH
.
2.10 Ready/Busy Output (RB)
The Ready/Busy pin is an open-drain output that can be used to identify when the device is
performing a Program or erase operation. During Program or erase operations Ready/Busy is
Low, V
. Ready/Busy is high-impedance during Read mode, Auto Select mode and Erase
OL
Suspend mode.
After a Hardware Reset, Bus Read and Bus Write operations cannot begin until Ready/Busy
becomes high-impedance. See Table 30: Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect AC Characteristics
and Figure 18 and Figure 19.
The use of an open-drain output allows the Ready/Busy pins from several memories to be
connected to a single pull-up resistor. A Low will then indicate that one, or more, of the
memories is busy.
2.11 Byte/Word Organization Select (BYTE)
It is used to switch between the x8 and x16 Bus modes of the memory when the M29DW128F
is delivered in TSOP56 package. When Byte/Word Organization Select is Low, V
is in x8 mode, when it is High, V
2.12 V
V
powered independently from V
Supply Voltage
CCQ
provides the power supply to the I/O and control pins and enables all Outputs to be
CCQ
, the memory is in x16 mode.
IH
. V
CC
can be tied to VCC or can use a separate supply.
CCQ
2.13 VCC Supply Voltage (2.7V to 3.6V)
VCC provides the power supply for all operations (Read, Program and Erase).
The Command Interface is disabled when the V
Voltage, V
. This prevents Bus Write operations from accidentally damaging the data during
LKO
power up, power down and power surges. If the Program/Erase Controller is programming or
erasing during this time then the operation aborts and the memory contents being altered will
be invalid.
A 0.1µF capacitor should be connected between the V
Ground pin to decouple the current surges from the power supply. The PCB track widths must
be sufficient to carry the currents required during Program and erase operations, I
CC
, the memory
IL
Supply Voltage is less than the Lockout
Supply Voltage pin and the VSS
CC
.
CC2
2.14 VSS Ground
VSS is the reference for all voltage measurements. The device features two VSS pins both of
which must be connected to the system ground.
16/93

M29DW128F 3 Bus operations
3 Bus operations
There are five standard bus operations that control the device. These are Bus Read (Random
and Page modes), Bus Write, Output Disable, Standby and Automatic Standby.
Dual operations are possible in the M29DW128F, thanks to its multiple bank architecture. While
programming or erasing in one banks, read operations are possible in any of the other banks.
Write operations are only allowed in one bank at a time.
See Ta bl e 3 and Ta bl e 6 , Bus Operations, for a summary. Typically glitches of less than 5ns on
Chip Enable, Write Enable, and Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect pins are ignored by the
memory and do not affect bus operations.
3.1 Bus Read
Bus Read operations read from the memory cells, or specific registers in the Command
Interface. To speed up the read operation the memory array can be read in Page mode where
data is internally read and stored in a page buffer. The Page has a size of 8 Words and is
addressed by the address inputs A0-A2.
A valid Bus Read operation involves setting the desired address on the Address Inputs,
applying a Low signal, V
V
. The Data Inputs/Outputs will output the value, see Figure 12: Random Read AC
IH
Wavefor ms, Figure 13: Page Read AC Waveforms, and Table 26: Read AC Characteristics, for
details of when the output becomes valid.
, to Chip Enable and Output Enable and keeping Write Enable High,
IL
3.2 Bus Write
Bus Write operations write to the Command Interface. A valid Bus Write operation begins by
setting the desired address on the Address Inputs. The Address Inputs are latched by the
Command Interface on the falling edge of Chip Enable or Write Enable, whichever occurs last.
The Data Inputs/Outputs are latched by the Command Interface on the rising edge of Chip
Enable or Write Enable, whichever occurs first. Output Enable must remain High, V
the whole Bus Write operation. See Figure 14 and Figure 15, Write AC Waveforms, and
Ta bl e 2 7 and Tab le 2 8, Write AC Characteristics, for details of the timing requirements.
3.3 Output Disable
The Data Inputs/Outputs are in the high impedance state when Output Enable is High, VIH.
3.4 Standby
When Chip Enable is High, VIH, the memory enters Standby mode and the Data Inputs/Outputs
pins are placed in the high-impedance state. To reduce the Supply Current to the Standby
Supply Current, I
level see Table 25: DC Characteristics. During program or erase operations the memory will
continue to use the Program/Erase Supply Current, I
the operation completes.
, Chip Enable should be held within V
CC2
, during
IH
± 0.2V. For the Standby current
CC
, for Program or Erase operations until
CC3
17/93

3 Bus operations M29DW128F
3.5 Automatic Standby
If CMOS levels (VCC ± 0.2V) are used to drive the bus and the bus is inactive for 300ns or more
the memory enters Automatic Standby where the internal Supply Current is reduced to the
Standby Supply Current, I
operation is in progress.
. The Data Inputs/Outputs will still output data if a Bus Read
CC2
3.6 Special Bus Operations
Additional bus operations can be performed to read the Electronic Signature, verify the
Protection Status of the Extended Memory Block (second section), and apply and remove
Block Protection. These bus operations are intended for use by programming equipment and
are not usually used in applications. They require V
3.6.1 Read Electronic Signature
The memory has two codes, the Manufacturer code and the Device code used to identify the
memory. These codes can accessed by performing read operations with control signals and
addresses set as shown in Ta bl e 4 and Ta b le 6 .
These codes can also be accessed by issuing an Auto Select command (see Auto Select
command in Section 6: Command Interface).
to be applied to some pins.
ID
3.6.2 Verify Extended Block Protection Indicator
The Extended Block is divided in two sections of which one is Factory Locked and the second
one is either Customer Lockable or Customer Locked.
The Protection Status of the second section of the Extended Block (Customer Lockable or
Customer Locked) can be accessed by reading the Extended Block Protection Indicator. This is
performed by applying the signals as shown in Ta b le 5 and Ta bl e 8 . The Protection Status of
the Extended Block is then output on bits DQ7 and DQ6 of the Data Input/Outputs. (see Ta bl e 3
and Ta bl e 6, Bus Operations).
The Protection Status of the Extended Block can also be accessed by issuing an Auto Select
command (see Auto Select command in Section 6: Command Interface).
3.6.3 Verify Block Protection Status
The Protection Status of a Block can be directly accessed by performing a read operation with
control signals and addresses set as shown in Ta bl e 5 and Ta bl e 8.
If the Block is protected, then 01h (in x8 mode) is output on Data Input/Outputs DQ0-DQ7,
otherwise 00h is output.
3.6.4 Hardware Block Protect
The VPP/WP pin can be used to protect the four outermost parameter blocks. When VPP/WP is
at V
the four outermost parameter blocks are protected and remain protected regardless of
IL
the Block Protection Status or the Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect pin state.
18/93
M29DW128F 3 Bus operations
3.6.5 Temporary Unprotect of High Voltage Protected Blocks
The RP pin can be used to temporarily unprotect all the blocks previously protected using the
In-System or the Programmer protection technique (High Voltage techniques).
Refer to Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect (RP) in Section 2: Signal descriptions.
Table 3. Bus Operations, 8-bit Mode
Address Inputs Data Inputs/Outputs
A22-A0, DQ15A-1 DQ14-DQ8 DQ7-DQ0
Operation
(1)
E G W RP
VPP/WP
Bus Read
Bus Write
Output Disable X
Standby
1. X = VIL or VIH.
V
ILVILVIHVIH
V
ILVIHVILVIH
V
IHVIHVIH
V
XX
IH
V
IH
V
IH
V
IH
V
V
IH
IH
Table 4. Read Electronic Signature, 8-bit Mode
Read Cycle
(1)
Manufacturer Code
Device Code (Cycle 1)
Device Code (Cycle 2)
Device Code (Cycle 3)
1. X = VIL or VIH.
E G W
V
ILVILVIH
A22-
A10
X
A9 A8
V
ID
X
A7-A6A5-
V
Cell Address Hi-Z Data Output
Command Address Hi-Z Data Input
X Hi-Z Hi-Z
X Hi-Z Hi-Z
Address Inputs
A3 A2 A1 A0
A4
V
X
ILVILVILVIL
VILVILVILV
IL
V
V
IL
IHVIHVIHVIL
V
IHVIHVIHVIH
DQ15A-1DQ14-
XHi-Z20h
XHi-Z7Eh
IH
XHi-Z20h
XHi-Z00h
Data Inputs/
Outputs
DQ8
DQ7-
DQ0
19/93
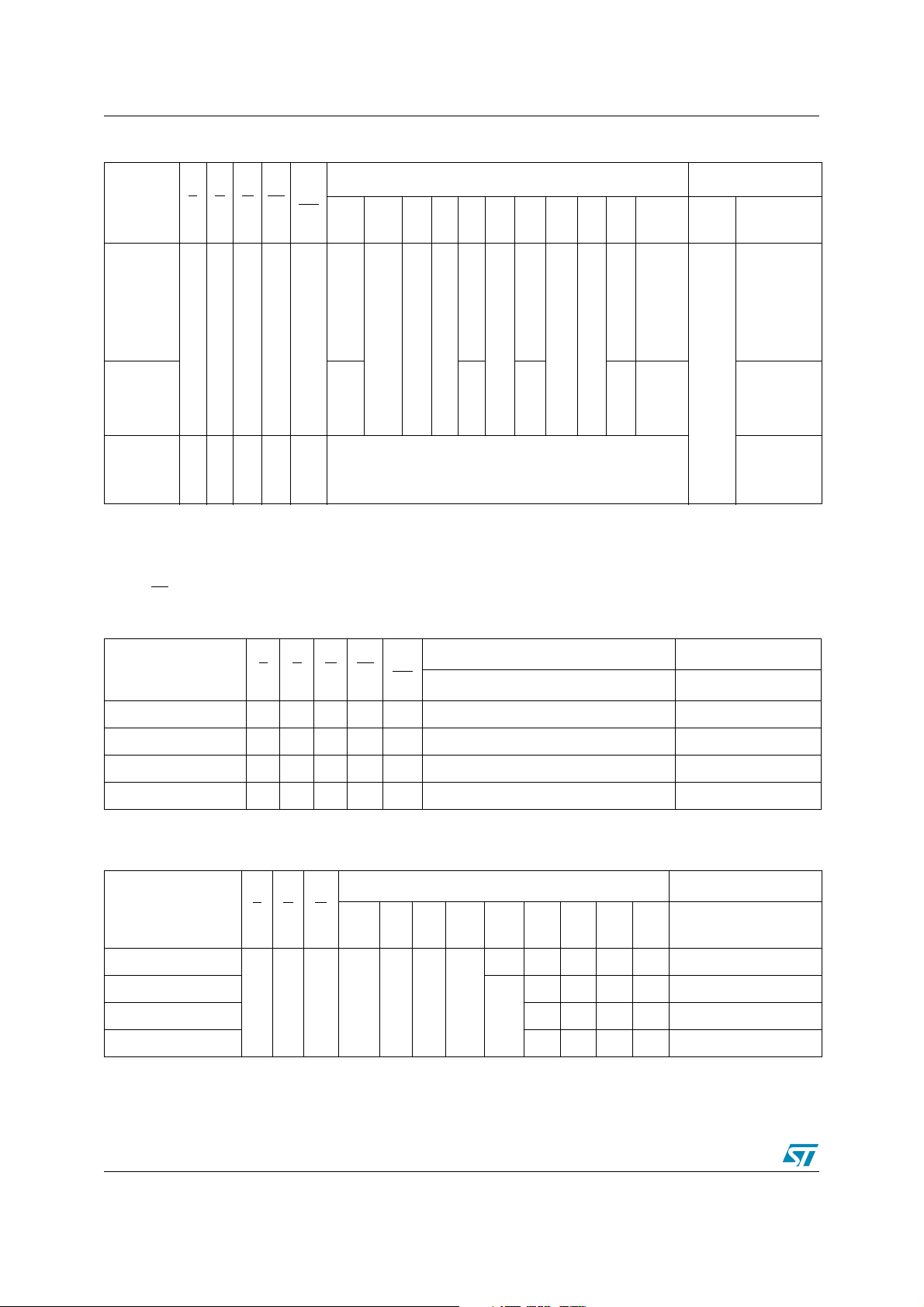
3 Bus operations M29DW128F
Table 5. Block Protection, 8-bit Mode
Operation
(1)
G W RP
E
VPP/
WP
A22-
A12
A11-
A9 A8 A7 A6
A10
Address Inputs
A5-A4A3-
(2)
A2
A1 A0
DQ15A-1DQ14-
Data Inputs/Outputs
DQ8
DQ7-DQ0
Ver if y
Extended
Block
Protection
Indicator
(bits DQ6,
DQ7)
Ver if y Bloc k
Protection
Status
V
ILVILVIHVIHVIH
BA
BKA
X
V
X
X
ID
X
V
IL
V
ILVIH
V
X
IH
Hi-Z
V
IL
V
IL
V
X
IL
(Customer
Lockable)
(Customer
Locked)
(protected)
(unprotected)
Temporary
Block
Unprotect
(4)
XXX
V
X Valid Data Input
ID
1. X = VIL or VIH.
2. BKA Bank Address, BA any Address in the Block.
3. This indicates the protection status of the second section of the Extended Block; the first section of the Extended Block
being always Factory Locked.
4. The RP pin unprotects all the blocks that have been previously protected using a High Voltage protection Technique.
Table 6. Bus Operations, 16-bit Mode
Address Inputs Data Inputs/Outputs
A22-A0 DQ15A-1, DQ14-DQ0
Operation
(1)
E
G W RP
VPP/
WP
80h
C0h
(3)
01h
00h
Bus Read
Bus Write
Output Disable X
Standby
V
ILVILVIHVIHVIH
V
ILVIHVILVIHVIH
V
IHVIHVIHVIH
V
IH
XX
V
IHVIH
1. X = VIL or VIH.
Table 7. Read Electronic Signature, 16-bit Mode
Address Inputs Data Inputs/Outputs
Read Cycle
(1)
Manufacturer Code
Device Code (Cycle 1)
Device Code (Cycle 2)
Device Code (Cycle 3)
1. X = VIL or VIH.
20/93
E
G W
V
ILVILVIH
A22-
A10
X
A9 A8
V
ID
X
A7-A6A5-
V
Cell Address Data Output
Command Address Data Input
X Hi-Z
X Hi-Z
A3 A2 A1 A0 DQ15A-1, DQ14-DQ0
A4
V
X
ILVILVILVIL
VILVILVILV
IL
V
V
IL
IHVIHVIHVIL
V
IHVIHVIHVIH
IH
0020h
227Eh
2220h
2200h
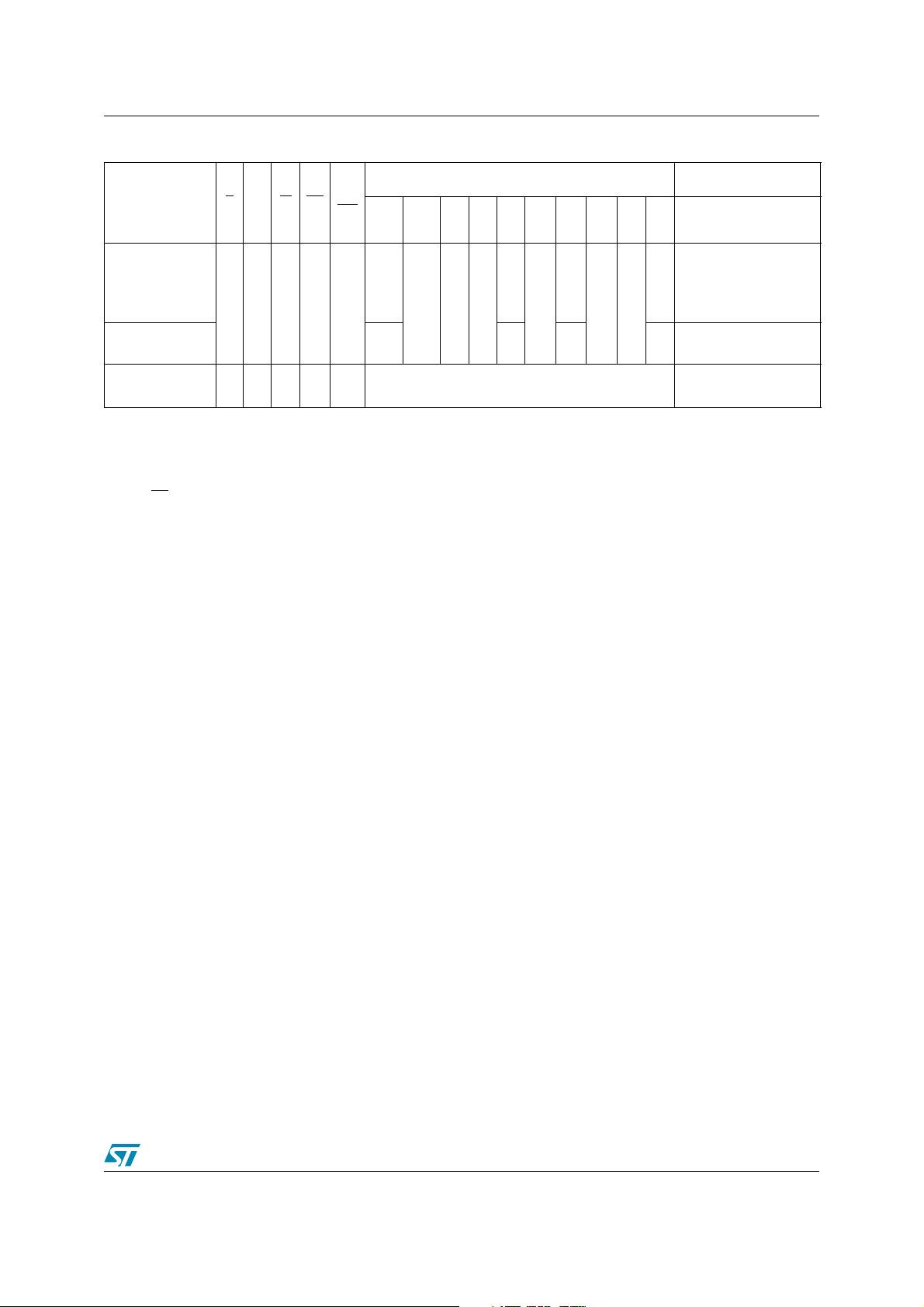
M29DW128F 3 Bus operations
Table 8. Block Protection, 16-bit Mode
Operation
(1)
G
E
W RP
VPP/
WP
A22-
A12
A11-
A9 A8 A7 A6
A10
Address Inputs
(2)
A5-A4A3-
A2
A1 A0 DQ15A-1, DQ14-DQ0
Data Inputs/Outputs
Verify Extended
Block Indicator
(bits DQ6, DQ7)
Verify Block
Protection Status
Temporary Block
Unprotect
(4)
V
ILVILVIHVIHVIH
XXX
V
ID
BA
BKA
X
V
X
X
ID
V
IL
X
V
IL
V
ILVIH
V
IL
V
IH
V
IL
X Valid Data Input
0080h
(Customer Lockable)
00C0h
(Customer Locked)
0001h (protected)
0000h (unprotected)
1. X = VIL or VIH.
2. BKA Bank Address, BA Any Address in the Block.
3. This indicates the protection status of the second section of the Extended Block; the first section of the Extended Block
being always Factory Locked.
4. The RP pin unprotects all the blocks that have been previously protected using a High Voltage protection Technique.
(3)
21/93

4 Hardware Protection M29DW128F
4 Hardware Protection
The M29DW128F features hardware protection/unprotection. Refer to Ta bl e 9 for details on
hardware block protection/unprotection using V
4.1 Write Protect
The VPP/WP pin protects the four outermost parameter blocks (refer to Section 2: Signal
descriptions for a detailed description of the signals).
4.2 Temporary Block Unprotect
When held at VID, the Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect pin, RP, will temporarily unprotect all
the blocks previously protected using a High Voltage Block Protection technique.
Table 9. Hardware Protection
VPP/WP
RP Function
/WP and RP pins.
PP
V
IH
V
IL
V
ID
VIH or V
1. The temporary unprotection is valid only for the blocks that have been protected using the High Voltage
Protection Technique (see Appendix D: High Voltage Block Protection). The blocks protected using a software
protection method (Standard, Password) do not follow this rules.
V
ID
PPH
V
ID
VIH or V
ID
4 outermost parameter blocks protected from
Program/Erase operations
All blocks temporarily unprotected except the 4
outermost blocks
All blocks temporarily unprotected
All blocks temporarily unprotected
(1)
(1)
(1)
22/93

M29DW128F 5 Software Protection
5 Software Protection
The M29DW128F has two different Software Protection modes: the Standard Protection mode
and the Password Protection mode.
On first use all parts default to the Standard Protection mode and the customer is free to
activate the Standard or the Password Protection mode.
The desired protection mode is activated by setting one of two one-time programmable bits, the
Standard Protection Mode Lock bit or the Password Protection Mode Lock bit. Programming
the Standard and the Password Protection Mode Lock bit to ‘1’ will permanently activate the
Standard Protection mode and the Password Protection mode, respectively. These two bits are
one-time programmable and non-volatile, once the Protection mode has been programmed, it
cannot be changed and the device will permanently operate in the selected Protection mode. It
is recommended to activate the desired Software Protection mode when first programming the
device.
The device is shipped with all blocks unprotected. The Block Protection Status can be read by
issuing the Auto Select command (see Table 10: Block Protection Status).
The Standard and Password Protection modes offer two levels of protection, a Block Lock/
Unlock protection and a Non-Volatile protection.
For the four outermost parameter blocks, an even higher level of block protection can be
achieved by locking the blocks using the Non-Volatile Protection and then by holding the V
WP
pin Low.
5.1 Standard Protection Mode
5.1.1 Block Lock/Unlock Protection
It is a flexible mechanism to protect/unprotect a block or a group of blocks from program or
erase operations.
A volatile Lock bit is assigned to each block or group of blocks. When the lock bit is set to ‘1’ the
associated block or group of blocks is protected from program/erase operations, when the Lock
bit is set to ‘0’ the associated block or group of blocks is unprotected and can be programmed
or erased.
The Lock bits can be set (‘1’) and cleared (‘0’) individually as often as required by issuing a Set
Lock Bit command and Clear Lock bit command, respectively.
After a Power-up or Hardware Reset, all the Lock bits are cleared to ‘0’ (block unlocked).
5.1.2 Non-Volatile Protection
A Non-Volatile Modify Protection bit is assigned to each block or group of blocks.
PP
/
When a Non-Volatile Modify Protection bit is set to ‘1’ the associated block or group of blocks is
protected, preventing any program or erase operations in this block or group of blocks.
The Non-Volatile Modify Protection bits are set individually by issuing a Set Non-Volatile Modify
Protection Bit command. They are non-volatile and will remain set through a hardware reset or
a power-down/power-up sequence.
23/93

5 Software Protection M29DW128F
The Non-Volatile Modify Protection bits cannot be cleared individually, they can only be cleared
all at the same time by issuing a Clear Non-Volatile Modify Protection Bits command.
However if any one of the Non-Volatile Modify Protection bits has to be cleared, care should be
taken to preprogram to ‘1’ all the Non-Volatile Modify Protection Bits prior to issuing the Clear
Non-Volatile Modify Protection bits in order to prevent the over-erasure of previously cleared
Non Volatile Modify Protection bits. It is crucial to prevent over-erasure because the process
may lead to permanent damage to the Non-Volatile Modify Protection Bits and the device does
not have any built-in means of preventing over-erasure.
The device features a volatile Lock-Down bit which can be used to prevent changing the state
of the Non-Volatile Modify Protection bits. When set to ‘1’, the Non-Volatile Modify Protection
bits can no longer be modified; when set to ‘0’, the Non-Volatile Modify Protection bits can be
set and reset using the Set Non-Volatile Modify Protection Bit command and the Clear NonVolatile Modify Protection Bits command, respectively.
The Lock-Down bit is set by issuing the Set Lock-Down Bit Command. It is not cleared using a
command, but through a hardware reset or a power-down/power-up sequence.
The parts are shipped with the Non-Volatile Modify Protection bits set to ‘0’.
Locked blocks and Non-Volatile Locked blocks can co-exist in the same memory array.
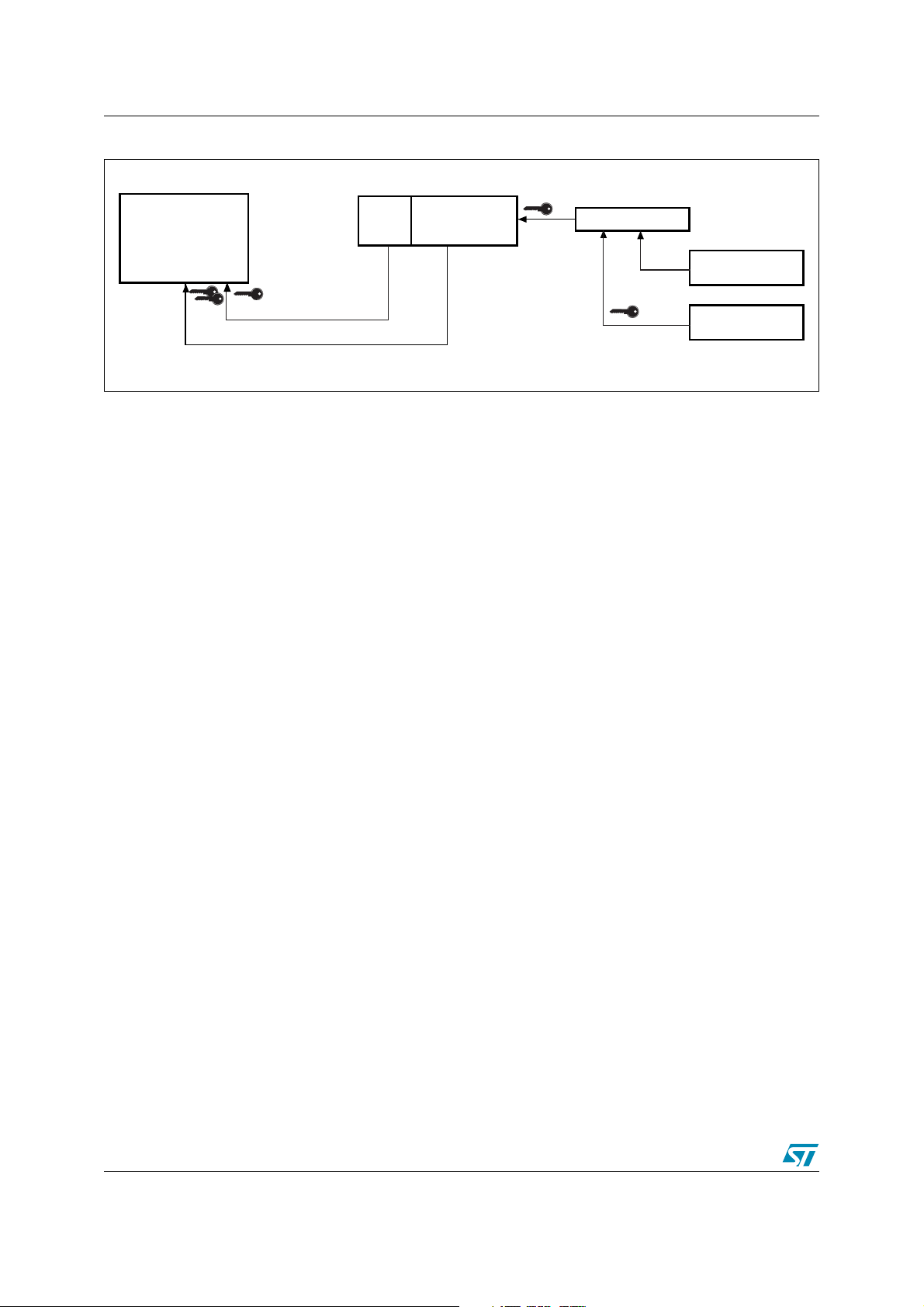
Refer to Table 10: Block Protection Status and Figure 7: Software Protection Scheme for details
on the block protection mechanism.
5.2 Password Protection Mode
The Password Protection mode provides a more advanced level of software protection than the
Standard Protection mode.
Prior to entering the Password Protection mode, it is necessary to set a password and to verify
it (see Password Program command and Password Verify command). The Password Protection
mode is then activated by programming the Password Protection Mode Lock bit to ‘1’. The
Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect pin, RP
This operation is not reversible and once the bit is programmed the device will permanently
remain in the Password Protection mode.
The Password Protection mode uses the same protection mechanisms as the Standard
Protection mode (Block Lock/Unlock, Non-Volatile Protection).
5.2.1 Block Lock/Unlock Protection
The Block Lock/Unlock Protection operates exactly in the same way as in the Standard
Protection mode.
5.2.2 Non-Volatile Protection
The Non-Volatile Protection is more advanced in the Password Protection mode.
In this mode, the Lock-Down bit cannot be cleared through a hardware reset or a power-down/
power-up sequence.
, can be at VID or at VIH.
The Lock-Down bit is cleared by issuing the Password Protection Unlock command along with
the correct password.
24/93
M29DW128F 5 Software Protection
Once the correct Password has been provided, the Lock-Down bit is cleared and the NonVolatile Modify Protection bits can be set or reset using the appropriate commands (the Set
Non-Volatile Modify Protection Bit command or the Clear Non-Volatile Modify Protection Bits
command, respectively).
If the Password provided is not correct, the Lock-Down bit remains locked and the state of the
Non-Volatile Modify Protection bits cannot be modified.
The Password is a 64-bit code located in the memory space. It must be programmed by the
user prior to selecting the Password Protection mode. The Password is programmed by issuing
a Password Program command and checked by issuing a Password Verify command. The
Password should be unique for each part.
Once the device is in Password Protection mode, the Password can no longer be read or
retrieved. Moreover, all commands to the address where the password is stored, are disabled.
Refer to Table 10: Block Protection Status and Figure 7: Software Protection Scheme for details
on the block protection scheme.
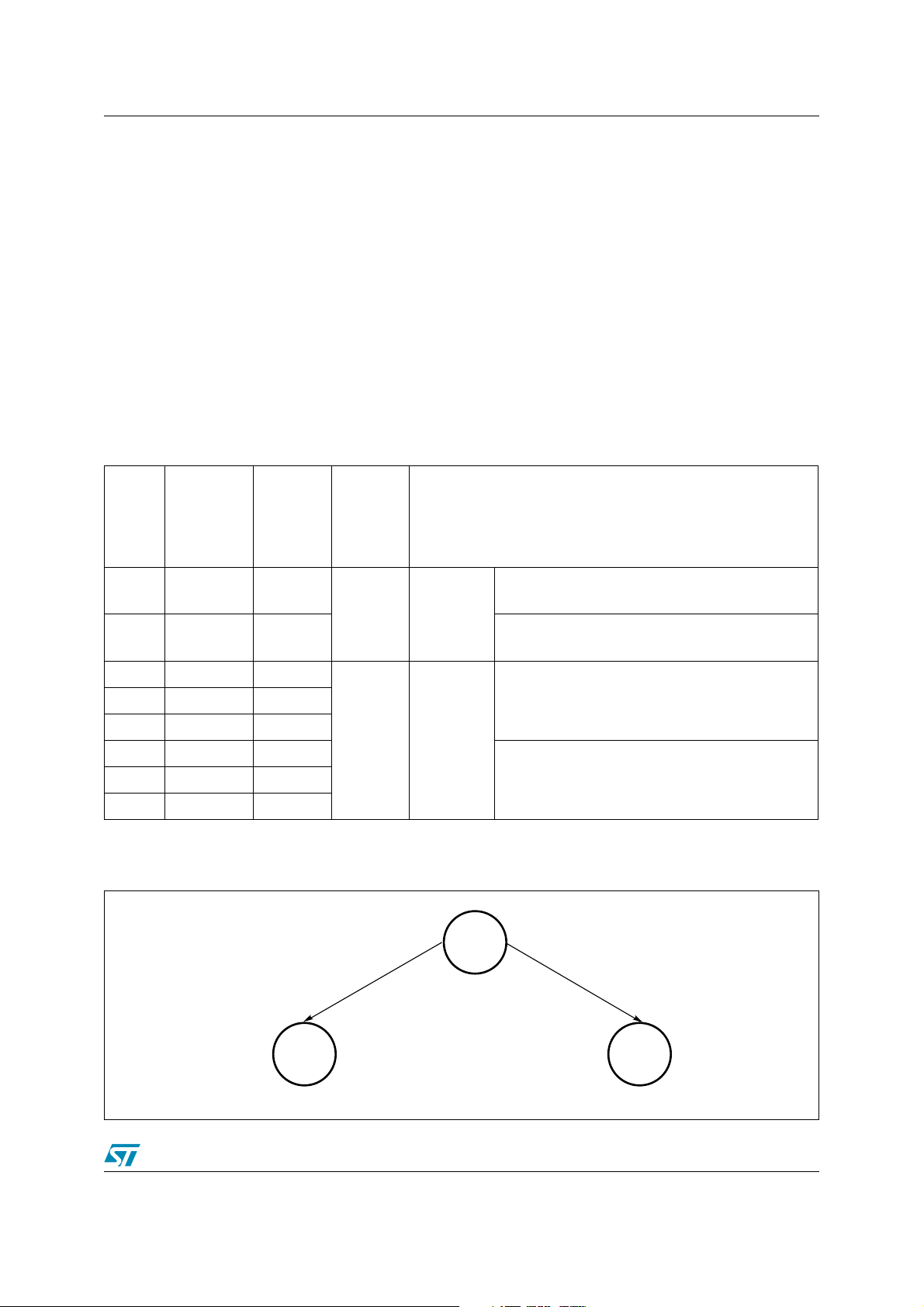
Table 10. Block Protection Status
Non-
Volatile
Lock
Bit
Volatile
Modify
Protection
Bit
Lock-
Down bit
Block
Protectio
n Status
Block Protection Status
00 0
00 1
00h
Block
Unprotected
Non-Volatile Modify Protection bit can be
modified
(1)
Non-Volatile Modify Protection bit cannot be
modified
(1)
01 0
10 0
11 0
01 1
10 1
01h
Block
Program/
Erase
Protected
Non-Volatile Modify Protection bit can be
modified
(1)
Non-Volatile Modify Protection bit cannot be
modified
(1)
11 1
1. The Lock bit can always be modified by issuing a Clear Lock Bit command or by taking the device through a Power-up or
Hardware Reset.
Figure 6. Block Protection State Diagram
Default:
Standard
Set Standard Protection
Mode
Protection
Set Password Protection
Mode
Standard
Protection
Password
Protection
ai11503
25/93
5 Software Protection M29DW128F
Figure 7. Software Protection Scheme
Parameter Block or
Up to 4 Main Blocks
Lock Bit
Block Lock/Unlock Protection
Non-Volatile Protection
Non-Volatile Modify
Protection Bit
Lock-Down bit
Standard Protection
mode
Password Protection
mode
AI11504
26/93

M29DW128F 6 Command Interface
6 Command Interface
All Bus Write operations to the memory are interpreted by the Command Interface. Commands
consist of one or more sequential Bus Write operations. Failure to observe a valid sequence of
Bus Write operations will result in the memory returning to Read mode. The long command
sequences are imposed to maximize data security.
The address used for the commands changes depending on whether the memory is in 16-bit or
8-bit mode.
6.1 Standard commands
See either Ta bl e 1 2, or Tab le 1 1, depending on the configuration that is being used, for a
summary of the Standard commands.
6.1.1 Read/Reset command
The Read/Reset command returns the memory to Read mode. It also resets the errors in the
Status Register. Either one or three Bus Write operations can be used to issue the Read/Reset
command.
The Read/Reset command can be issued, between Bus Write cycles before the start of a
program or erase operation, to return the device to Read mode. If the Read/Reset command is
issued during the time-out of a Block erase operation, the memory will take up to 10µs to abort.
During the abort period no valid data can be read from the memory.
The Read/Reset command will not abort an Erase operation when issued while in Erase
Suspend.
6.1.2 Auto Select command
The Auto Select command is used to read the Manufacturer Code, the Device Code, the
Protection Status of each block (Block Protection Status) and the Extended Block Protection
Indicator. It can be addressed to either Bank.
Three consecutive Bus Write operations are required to issue the Auto Select command. Once
the Auto Select command is issued Bus Read operations to specific addresses output the
Manufacturer Code, the Device Code, the Extended Block Protection Indicator and a Block
Protection Status (see Ta bl e 1 1 and Tab le 1 2 in conjunction with Ta b l e 4 , Ta bl e 5, Ta bl e 7 and
Ta bl e 8 ). The memory remains in Auto Select mode until a Read/Reset or CFI Query command
is issued.
6.1.3 Read CFI Query command
The Read CFI Query Command is used to put the addressed bank in Read CFI Query mode.
Once in Read CFI Query mode Bus Read operations to the same bank will output data from the
Common Flash Interface (CFI) Memory Area. If the read operations are to a different bank from
the one specified in the command then the read operations will output the contents of the
memory array and not the CFI data.
One Bus Write cycle is required to issue the Read CFI Query Command. Care must be taken to
issue the command to one of the banks (A22-A19) along with the address shown in Ta bl e 3 and
27/93

6 Command Interface M29DW128F
Ta bl e 6 . Once the command is issued subsequent Bus Read operations in the same bank
(A22-A19) to the addresses shown in Appendix B: Common Flash Interface (CFI) (A7-A0), will
read from the Common Flash Interface Memory Area.
This command is valid only when the device is in the Read Array or Auto Select mode. To enter
Read CFI query mode from Auto Select mode, the Read CFI Query command must be issued
to the same bank address as the Auto Select command, otherwise the device will not enter
Read CFI Query mode.
The Read/Reset command must be issued to return the device to the previous mode (the Read
Array mode or Auto Select mode). A second Read/Reset command is required to put the
device in Read Array mode from Auto Select mode.
See Appendix B, Ta b le 3 5, Ta b le 3 6 , Tab l e 3 7, Ta b le 3 8 , Ta bl e 3 9 and Tab le 4 0 for details on
the information contained in the Common Flash Interface (CFI) memory area.
6.1.4 Chip Erase command
The Chip Erase command can be used to erase the entire chip. Six Bus Write operations are
required to issue the Chip Erase Command and start the Program/Erase Controller.
If any blocks are protected, then these are ignored and all the other blocks are erased. If all of
the blocks are protected the Chip Erase operation appears to start but will terminate within
about 100µs, leaving the data unchanged. No error condition is given when protected blocks
are ignored.
During the erase operation the memory will ignore all commands, including the Erase Suspend
command. It is not possible to issue any command to abort the operation. Typical chip erase
times are given in Ta bl e 18 . All Bus Read operations during the Chip Erase operation will output
the Status Register on the Data Inputs/Outputs. See the section on the Status Register for
more details.
After the Chip Erase operation has completed the memory will return to the Read mode, unless
an error has occurred. When an error occurs the memory will continue to output the Status
Register. A Read/Reset command must be issued to reset the error condition and return to
Read mode.
The Chip Erase Command sets all of the bits in unprotected blocks of the memory to ’1’. All
previous data is lost.
6.1.5 Block Erase command
The Block Erase command can be used to erase a list of one or more blocks in one or more
Banks. It sets all of the bits in the unprotected selected blocks to ’1’. All previous data in the
selected blocks is lost.
Six Bus Write operations are required to select the first block in the list. Each additional block in
the list can be selected by repeating the sixth Bus Write operation using the address of the
additional block. The Block Erase operation starts the Program/Erase Controller after a timeout period of 50µs after the last Bus Write operation. Once the Program/Erase Controller starts
it is not possible to select any more blocks. Each additional block must therefore be selected
within 50µs of the last block. The 50µs timer restarts when an additional block is selected. After
the sixth Bus Write operation a Bus Read operation within the same Bank will output the Status
Register. See the Status Register section for details on how to identify if the Program/Erase
Controller has started the Block Erase operation.
28/93

M29DW128F 6 Command Interface
If any selected blocks are protected then these are ignored and all the other selected blocks are
erased. If all of the selected blocks are protected the Block Erase operation appears to start but
will terminate within about 100µs, leaving the data unchanged. No error condition is given when
protected blocks are ignored.
During the Block Erase operation the memory will ignore all commands except the Erase
Suspend command and the Read/Reset command which is only accepted during the 50µs
time-out period. Typical block erase times are given in Ta b le 1 8.
After the Erase operation has started all Bus Read operations to the Banks being erased will
output the Status Register on the Data Inputs/Outputs. See the section on the Status Register
for more details.
After the Block Erase operation has completed the memory will return to the Read mode,
unless an error has occurred.
When an error occurs, Bus Read operations to the Banks where the command was issued will
continue to output the Status Register. A Read/Reset command must be issued to reset the
error condition and return to Read mode.
6.1.6 Erase Suspend command
The Erase Suspend command may be used to temporarily suspend a Block or multiple Block
Erase operation. One Bus Write operation specifying the Bank Address of one of the Blocks
being erased is required to issue the command. Issuing the Erase Suspend command returns
the whole device to Read mode.
The Program/Erase Controller will suspend within the Erase Suspend Latency time (see
Ta bl e 1 8 for value) of the Erase Suspend Command being issued. Once the Program/Erase
Controller has stopped the memory will be set to Read mode and the Erase will be suspended.
If the Erase Suspend command is issued during the period when the memory is waiting for an
additional block (before the Program/Erase Controller starts) then the Erase is suspended
immediately and will start immediately when the Erase Resume Command is issued. It is not
possible to select any further blocks to erase after the Erase Resume.
During Erase Suspend it is possible to Read and Program cells in blocks that are not being
erased; both Read and Program operations behave as normal on these blocks. If any attempt is
made to program in a protected block or in the suspended block then the Program command is
ignored and the data remains unchanged. The Status Register is not read and no error
condition is given. Reading from blocks that are being erased will output the Status Register.
It is also possible to issue the Auto Select, Read CFI Query and Unlock Bypass commands
during an Erase Suspend. The Read/Reset command must be issued to return the device to
Read Array mode before the Resume command will be accepted.
During Erase Suspend a Bus Read operation to the Extended Block will output the Extended
Block data. Once in the Extended Block mode, the Exit Extended Block command must be
issued before the erase operation can be resumed.
6.1.7 Erase Resume command
The Erase Resume command is used to restart the Program/Erase Controller after an Erase
Suspend. The command must include the Bank Address of the Erase-Suspended Bank,
otherwise the Program/Erase Controller is not restarted.
The device must be in Read Array mode before the Resume command will be accepted. An
Erase can be suspended and resumed more than once.
29/93

6 Command Interface M29DW128F
6.1.8 Program Suspend command
The Program Suspend command allows the system to interrupt a program operation so that
data can be read from any block. When the Program Suspend command is issued during a
program operation, the device suspends the program operation within the Program Suspend
Latency time (see Ta bl e 1 8 for value) and updates the Status Register bits. The Bank
Addresses of the Block being programmed must be specified in the Program Suspend
command.
After the program operation has been suspended, the system can read array data from any
address. However, data read from Program-Suspended addresses is not valid.
The Program Suspend command may also be issued during a program operation while an
erase is suspended. In this case, data may be read from any addresses not in Erase Suspend
or Program Suspend. If a read is needed from the Extended Block area (One-time Program
area), the user must use the proper command sequences to enter and exit this region.
The system may also issue the Auto Select command sequence when the device is in the
Program Suspend mode. The system can read as many Auto Select codes as required. When
the device exits the Auto Select mode, the device reverts to the Program Suspend mode, and is
ready for another valid operation. See Auto Select command sequence for more information.
6.1.9 Program Resume command
After the Program Resume command is issued, the device reverts to programming. The
controller can determine the status of the program operation using the DQ7 or DQ6 status bits,
just as in the standard program operation. See Write Operation Status for more information.
The system must write the Program Resume command, specifying the Bank addresses of the
Program-Suspended Block, to exit the Program Suspend mode and to continue the
programming operation.
Further issuing of the Resume command is ignored. Another Program Suspend command can
be written after the device has resumed programming.
6.1.10 Program command
The Program command can be used to program a value to one address in the memory array at
a time. The command requires four Bus Write operations, the final Write operation latches the
address and data in the internal state machine and starts the Program/Erase Controller.
Programming can be suspended and then resumed by issuing a Program Suspend command
and a Program Resume command, respectively (see Program Suspend command and
Program Resume command paragraphs).
If the address falls in a protected block then the Program command is ignored, the data remains
unchanged. The Status Register is never read and no error condition is given.
After programming has started, Bus Read operations in the Bank being programmed output the
Status Register content, while Bus Read operations to the other Bank output the contents of
the memory array. See the section on the Status Register for more details. Typical program
times are given in Tab l e 1 8.
After the program operation has completed the memory will return to the Read mode, unless an
error has occurred. When an error occurs Bus Read operations to the Bank where the
command was issued will continue to output the Status Register. A Read/Reset command must
be issued to reset the error condition and return to Read mode.
30/93

M29DW128F 6 Command Interface
One of the Erase Commands must be used to set all the bits in a block or in the whole memory
from ’0’ to ’1’.
6.1.11 Verify command
The Verify command is used to check if a block is blank or in other words, if it has been
successfully erased and all its bits set to ’1’. It reads the value of the Error Bit DQ5. If the Error
Bit is set to ’1’, it indicates that the operation failed.
Three cycles are required to issue a Verify command:
1. The command starts with two unlock cycles.
2. The third Bus Write cycle sets up the Verify command code along with the address of the
block to be checked.
Table 11. Standard Commands, 8-bit Mode
Bus Operations
(1)(2)
Command
Read/Reset
Manufacturer Code
Auto
Select
Program 4 AAA AA 555 55 AAA A0 PA PD
Verify 3 AAA AA 555 55 BA BC
Chip Erase 6 AAA AA 555 55 AAA 80
Block Erase
Erase/Program Suspend 1 BKA B0
Erase/Program Resume 1 BKA 30
Read CFI Query 1
1. Grey cells represent Read cycles. The other cells are Write cycles.
2. X Don’t Care, PA Program Address, PD Program Data, BA Any address in the Block, BKA Bank Address. All values in the
table are in hexadecimal.
3. The Auto Select addresses and data are given in Table 4: Read Electronic Signature, 8-bit Mode, and Table 5: Block
Protection, 8-bit Mode, except for A9 that is ‘Don’t Care’.
Device Code
Extended Block Protection
Indicator
Block Protection Status
1X F0
3 AAA AA 555 55 X F0
3 AAA AA 555 55
6
+
1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 6th
Length
Add Data Add
AAA AA 555 55 AAA 80
(BKA)
AAA
98
Dat
Add Data Add Data Add Data Add Data
a
(BKA)
AAA
90
(3)
(3)
AA
AA 555 55 AAA 10
A
AA
AA 555 55 BA 30
A
31/93

6 Command Interface M29DW128F
Table 12. Standard Commands, 16-bit Mode
Bus Operations
(1)(2)
Command
Read/Reset
Manufacturer Code
Device Code
Auto Select
Program 4 555 AA 2AA 55 555 A0 PA PD
Verify 3 555 AA 2AA 55 BA BC
Chip Erase 6 555 AA 2AA 55 555 80 555 AA 2AA 55 555 10
Block Erase 6+ 555 AA 2AA 55 555 80 555 AA 2AA 55 BA 30
Erase/Program Suspend 1 BKA B0
Erase/Program Resume 1 BKA 30
Read CFI Query 1
1. Grey cells represent Read cycles. The other cells are Write cycles.
2. X Don’t Care, PA Program Address, PD Program Data, BA Any address in the Block, BKA Bank Address. All values in the
table are in hexadecimal.
3. The Auto Select addresses and data are given in Table 7: Read Electronic Signature, 16-bit Mode, and Table 8: Block
Protection, 16-bit Mode, except for A9 that is ‘Don’t Care’.
Extended Block
Protection Indicator
Block Protection Status
1XF0
3 555 AA 2AA 55 X F0
3 555 AA 2AA 55
1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 6th
Length
Add Data Add Data Add Data Add Data Add Data Add Data
(BKA)
555
(BKA)
555
98
90
(3)
(3)
6.2 Fast Program commands
The M29DW128F offers a set of Fast Program commands to improve the programming
throughput:
● Write to Buffer and Program
● Double and Quadruple Word, Program
● Double, Quadruple and Octuple Byte Program
● Unlock Bypass.
See either Ta bl e 1 4, or Tab le 1 3, depending on the configuration that is being used, for a
summary of the Fast Program commands.
When V
Program mode. The user can then choose to issue any of the Fast Program commands. Care
must be taken because applying a V
protected block.
Only one bank can be programmed at any one time. The other bank must be in Read mode or
Erase Suspend.
32/93
is applied to the VPP/Write Protect pin the memory automatically enters the Fast
PPH
to the VPP/WP pin will temporarily unprotect any
PPH

M29DW128F 6 Command Interface
After programming has started, Bus Read operations in the Bank being programmed output the
Status Register content, while Bus Read operations to the other Bank output the contents of
the memory array. Fast program commands can be suspended and then resumed by issuing a
Program Suspend command and a Program Resume command, respectively (see Program
Suspend command and Program Resume command paragraphs.)
After the fast program operation has completed, the memory will return to the Read mode,
unless an error has occurred. When an error occurs Bus Read operations to the Bank where
the command was issued will continue to output the Status Register. A Read/Reset command
must be issued to reset the error condition and return to Read mode. One of the Erase
Commands must be used to set all the bits in a block or in the whole memory from ’0’ to ’1’.
Typical Program times are given in Table 18: Program, Erase Times and Program, Erase
Endurance Cycles.
6.2.1 Write to Buffer and Program command
The Write to Buffer and Program Command makes use of the device’s 64-Byte Write Buffer to
speed up programming. 32 Words/64 Bytes can be loaded into the Write Buffer. Each Write
Buffer has the same A5-A22 addresses.The Write to Buffer and Program command
dramatically reduces system programming time compared to the standard non-buffered
Program command.
When issuing a Write to Buffer and Program command, the V
High, V
or raised to V
IH
PPH
.
PP/WP
pin can be either held
See Ta bl e 1 8 for details on typical Write to Buffer and Program times in both cases.
Five successive steps are required to issue the Write to Buffer and Program command:
1. The Write to Buffer and Program command starts with two unlock cycles.
2. The third Bus Write cycle sets up the Write to Buffer and Program command. The setup
code can be addressed to any location within the targeted block.
3. The fourth Bus Write cycle sets up the number of Words to be programmed. Value n is
written to the same block address, where n+1 is the number of Words to be programmed.
n+1 must not exceed the size of the Write Buffer or the operation will abort.
4. The fifth cycle loads the first address and data to be programmed.
5. Use n Bus Write cycles to load the address and data for each Word into the Write Buffer.
Addresses must lie within the range from the start address+1 to the start address + n-1.
Optimum performance is obtained when the start address corresponds to a 64 Byte
boundary. If the start address is not aligned to a 64 Byte boundary, the total programming
time is doubled.
All the addresses used in the Write to Buffer and Program operation must lie within the same
page.
To program the content of the Write Buffer, this command must be followed by a Write to Buffer
and Program Confirm command.
If an address is written several times during a Write to Buffer and Program operation, the
address/data counter will be decremented at each data load operation and the data will be
programmed to the last word loaded into the Buffer.
Invalid address combinations or failing to follow the correct sequence of Bus Write cycles will
abort the Write to Buffer and Program.
33/93

6 Command Interface M29DW128F
The Status Register bits DQ1, DQ5, DQ6, DQ7 can be used to monitor the device status during
a Write to Buffer and Program operation.
If is not possible to detect Program operation fails when changing programmed data from ‘0’ to
‘1’, that is when reprogramming data in a portion of memory already programmed. The
resulting data will be the logical OR between the previous value and the current value.
A Write to Buffer and Program Abort and Reset command must be issued to abort the Write to
Buffer and Program operation and reset the device in Read mode.
During Write to Buffer and Program operations, the bank being programmed will accept
Program/Erase Suspend commands.
See Appendix E, Figure 27: Write to Buffer and Program Flowchart and Pseudo Code, for a
suggested flowchart on using the Write to Buffer and Program command.
6.2.2 Write to Buffer and Program Confirm command
The Write to Buffer and Program Confirm command is used to confirm a Write to Buffer and
Program command and to program the n+1 Words loaded in the Write Buffer by this command.
6.2.3 Write to Buffer and Program Abort and Reset command
The Write to Buffer and Program Abort and Reset command is used to abort Write to Buffer
and Program command.
6.2.4 Double Word Program command
This is used to write two adjacent Words in x16 mode, simultaneously. The addresses of the
two Words must differ only in A0.
Three bus write cycles are necessary to issue the command:
1. The first bus cycle sets up the command.
2. The second bus cycle latches the Address and the Data of the first Word to be written.
3. The third bus cycle latches the Address and the Data of the second Word to be written and
starts the Program/Erase Controller.
6.2.5 Quadruple Word Program command
This is used to write a page of four adjacent Words, in x16 mode, simultaneously. The
addresses of the four Words must differ only in A1 and A0.
Five bus write cycles are necessary to issue the command:
1. The first bus cycle sets up the command.
2. The second bus cycle latches the Address and the Data of the first Word to be written.
3. The third bus cycle latches the Address and the Data of the second Word to be written.
4. The fourth bus cycle latches the Address and the Data of the third Word to be written.
5. The fifth bus cycle latches the Address and the Data of the fourth Word to be written and
starts the Program/Erase Controller.
6.2.6 Double Byte Program Command
This is used to write two adjacent Bytes in x8 mode, simultaneously. The addresses of the two
Bytes must differ only in DQ15A-1.
34/93

M29DW128F 6 Command Interface
Three bus write cycles are necessary to issue the command:
1. The first bus cycle sets up the command.
2. The second bus cycle latches the Address and the Data of the first Byte to be written.
3. The third bus cycle latches the Address and the Data of the second Byte to be written and
starts the Program/Erase Controller.
6.2.7 Quadruple Byte Program command
This is used to write four adjacent Bytes in x8 mode, simultaneously. The addresses of the four
Bytes must differ only in A0, DQ15A-1.
Five bus write cycles are necessary to issue the command.
1. The first bus cycle sets up the command.
2. The second bus cycle latches the Address and the Data of the first Byte to be written.
3. The third bus cycle latches the Address and the Data of the second Byte to be written.
4. The fourth bus cycle latches the Address and the Data of the third Byte to be written.
5. The fifth bus cycle latches the Address and the Data of the fourth Byte to be written and
starts the Program/Erase Controller.
6.2.8 Octuple Byte Program command
This is used to write eight adjacent Bytes, in x8 mode, simultaneously. The addresses of the
eight Bytes must differ only in A1, A0 and DQ15A-1.
Nine bus write cycles are necessary to issue the command:
1. The first bus cycle sets up the command.
2. The second bus cycle latches the Address and the Data of the first Byte to be written.
3. The third bus cycle latches the Address and the Data of the second Byte to be written.
4. The fourth bus cycle latches the Address and the Data of the third Byte to be written.
5. The fifth bus cycle latches the Address and the Data of the fourth Byte to be written.
6. The sixth bus cycle latches the Address and the Data of the fifth Byte to be written.
7. The seventh bus cycle latches the Address and the Data of the sixth Byte to be written.
8. The eighth bus cycle latches the Address and the Data of the seventh Byte to be written.
9. The ninth bus cycle latches the Address and the Data of the eighth Byte to be written and
starts the Program/Erase Controller.
6.2.9 Unlock Bypass command
The Unlock Bypass command is used in conjunction with the Unlock Bypass Program
command to program the memory faster than with the standard program commands. When the
cycle time to the device is long, considerable time saving can be made by using these
commands. Three Bus Write operations are required to issue the Unlock Bypass command.
Once the Unlock Bypass command has been issued the bank enters Unlock Bypass mode.
When in Unlock Bypass mode, only the Unlock Bypass Program and Unlock Bypass Reset
commands are valid. The Unlock Bypass Program command can then be issued to program
addresses within the bank, or the Unlock Bypass Reset command can be issued to return the
bank to Read mode. In Unlock Bypass mode the memory can be read as if in Read mode.
35/93

6 Command Interface M29DW128F
6.2.10 Unlock Bypass Program command
The Unlock Bypass Program command can be used to program one address in the memory
array at a time. The command requires two Bus Write operations, the final write operation
latches the address and data and starts the Program/Erase Controller.
The Program operation using the Unlock Bypass Program command behaves identically to the
Program operation using the Program command. The operation cannot be aborted, a Bus
Read operation to the Bank where the command was issued outputs the Status Register. See
the Program command for details on the behavior.
6.2.11 Unlock Bypass Reset command
The Unlock Bypass Reset command can be used to return to Read/Reset mode from Unlock
Bypass mode. Two Bus Write operations are required to issue the Unlock Bypass Reset
command. Read/Reset command does not exit from Unlock Bypass mode.
Table 13. Fast Program Commands, 8-bit mode
Bus Write Operations
(1)
Command
Write to Buffer
and Program
Write to Buffer
and Program
Abort and
Reset
Write to Buffer
and Program
Confirm
Double Byte
Program
Quadruple Byte
Program
Octuple Byte
Program
Unlock Bypass 3 AAA AA 555 55 AAA 20
Unlock Bypass
Program
Unlock Bypass
Reset
1. X Don’t Care, PA Program Address, PD Program Data, BA Any address in the Block, BKA Bank Address, WBL Write Buffer Location. All
values in the table are in hexadecimal.
2. The maximum number of cycles in the command sequence is 37. N+1 is the number of Words to be programmed during the Write to Buffer
and Program operation.
3. Each buffer has the same A5-A22 addresses. A0-A4 are used to select a Word within the N+1 Word page.
4. The 6th cycle has to be issued N time. WBL scans the Word inside the page.
5. BA must be identical to the address loaded during the Write to buffer and Program 3rd and 4th cycles.
1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 6th 7th 8th 9th
Length
Add Data Add Data Add Data Add Data Add Data Add Data Add Data Add Data Add Data
N
+5AAA AA 555 55 BA 25 BA
3 AAA AA 555 55 AAA F0
BA
1
3 AAA 50 PA0 PD0 PA1 PD1
5 AAA 56 PA0 PD0 PA1 PD1 PA2 PD2 PA3 PD3
9 AAA 8B PA0 PD0 PA1 PD1 PA2 PD2 PA3 PD3 PA4 PD4 PA5 PD5 PA6 PD6 PA7 PD7
2 X A0 PA PD
2X 90 X 00
29
(5)
PA
(2)
N
(3)
PD
WBL
(4)
PD
36/93

M29DW128F 6 Command Interface
Table 14. Fast Program Commands, 16-bit Mode
Bus Write Operations
(1)
Command
Write to Buffer and Program
Write to Buffer and Program Abort and
Reset
Write to Buffer and Program Confirm 1
Double Word Program 3 555 50 PA0 PD0 PA1 PD1
Quadruple Word Program 5 555 56 PA0 PD0 PA1 PD1 PA2 PD2 PA3 PD3
Unlock Bypass 3 555 AA 2AA 55 555 20
Unlock Bypass Program 2 X A0 PA PD
Unlock Bypass Reset 2 X 90 X 00
1. X Don’t Care, PA Program Address, PD Program Data, BA Any address in the Block, BKA Bank Address, WBL Write
Buffer Location. All values in the table are in hexadecimal.
2. The maximum number of cycles in the command sequence is 37. N+1 is the number of Words to be programmed during
the Write to Buffer and Program operation.
3. Each buffer has the same A5-A22 addresses. A0-A4 are used to select a Word within the N+1 Word page.
4. The 6th cycle has to be issued N time. WBL scans the Word inside the page.
5. BA must be identical to the address loaded during the Write to buffer and Program 3rd and 4th cycles.
N+
5
3 555 AA 2AA 55 555 F0
1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 6th
Length
Add Data Add Data Add Data Add Data Add Data Add Data
555 AA 2AA 55 BA 25 BA
(5)
29
BA
(2)
N
(3)
PA
PD
WBL
(4)
6.3 Block Protection commands
PD
Blocks or groups of blocks can be protected against accidental program, erase or read
operations. The Protection Groups are shown in Appendix A, Table 34: Block Addresses and
Protection Groups. The device block protection scheme is shown in Figure 7: Software
Protection Scheme and Figure 6: Block Protection State Diagram. See either Ta bl e 1 5, or
Ta bl e 1 6 , depending on the configuration that is being used, for a summary of the Block
Protection commands.
Only the commands related to the Extended Block Protection are available in both 8 bit and 16
bit memory configuration. The other block protection commands are available in 16-bit
configuration only.
6.3.1 Enter Extended Block command
The M29DW128F has one extra 256-Byte block (Extended Block) that can only be accessed
using the Enter Extended Block command.
Three Bus Write cycles are required to issue the Extended Block command. Once the
command has been issued the device enters the Extended Block mode where all Bus Read or
Program operations are conducted on the Extended Block. Once the device is in the Extended
Block mode, the Extended Block is addressed by using the addresses occupied by the boot
blocks in the other operating modes (see Table 34: Block Addresses and Protection Groups).
The device remains in Extended Block mode until the Exit Extended Block command is issued
or power is removed from the device. After power-up or a hardware reset, the device reverts to
37/93

6 Command Interface M29DW128F
the Read mode where commands issued to the Boot Block Address space will address the
Boot Blocks.
Note that when the device is in the Extended Block mode, the V
fast programming and the Unlock Bypass mode is not available.
The Extended Block cannot be erased, and can be treated as one-time programmable (OTP)
memory. In Extended Block mode only array cell locations (Bank A) with the same addresses
as the Extended Block are not accessible. In Extended Block mode dual operations are allowed
and the Extended Block physically belongs to Bank A.
In Extended Block mode, Erase, Chip Erase, Erase Suspend and Erase resume commands are
not allowed.
To exit from the Extended Block mode the Exit Extended Block command must be issued.
The Extended Block can be protected by setting the Extended Block Protection Bit to ‘1’;
however once protected the protection cannot be undone.
6.3.2 Exit Extended Block command
The Exit Extended Block command is used to exit from the Extended Block mode and return
the device to Read mode. Four Bus Write operations are required to issue the command.
6.3.3 Set Extended Block Protection Bit command
The Set Extended Block Protection Bit command programs the Extended Block Protection bit to
‘1’ thus preventing the second section of the Extended Block from being programmed.
A Read/Reset command must be issued to abort a Set Extended Block Protection Bit
command.
/WP pin cannot be used for
PP
Six successive steps are required to issue the Set Extended Block Protection Bit command.
1. The command starts with two unlock cycles.
2. The third Bus Write cycle sets up the Set Extended Block Protection Bit command.
3. The fourth Bus Write Cycle programs the Extended Block Protection bit to ‘1’.
4. The last two cycles verify the value programmed at the Extended Block Protection bit
address: if bit DQ0 of Data Inputs/Outputs is set to ’1’, it indicates that the Extended Block
Protection bit has been successfully programmed. If DQ0 is ‘0’, the Set Extended Block
Protection Bit command must be issued and verified again.
6.3.4 Verify Extended Block Protection Bit command
The Verify Extended Block Protection Bit command reads the status of the Extended Block
Protection bit on bit DQ0 of the Data Inputs/Outputs. If DQ0 is ‘1’, the second section of the
Extended Block is protected from program operations.
6.3.5 Password Program command
The Password Program Command is used to program the 64-bit Password used in Password
Protection mode.
Four cycles are required to program the Password:
1. The first two cycles are unlock cycles.
2. The third cycle issues the Password Program command.
38/93

M29DW128F 6 Command Interface
3. The fourth cycle inputs the 16-bit data required to program the Password.
To program the 64-bit Password, the complete command sequence must be entered four times
at four consecutive addresses selected by A1 to A0.
Read operations can be used to read the Status Register during a Password Program
operation. All other operations are forbidden.
The Password can be checked by issuing a Password Verify command.
Once Password Program operation has completed, a Read/ Reset command must be issued to
return the device to Read mode. The Password Protection mode can then be selected.
By default, all Password bits are set to ‘1’.
6.3.6 Password Verify command
The Password Verify Command is used to verify the Password used in Password Protection
mode. To verify the 64-bit Password, the complete command sequence must be entered four
times at four consecutive addresses selected by A1 to A0. If the Password Mode Locking Bit is
programmed and the user attempts to verify the Password, the device will output all F’s onto the
I/O data bus. The Password is output regardless of the bank address.
The user must issue a Read/reset command to return the device to Read mode.
Dual operations are not allowed during a Password Verify operation.
6.3.7 Password Protection Unlock command
The Password Protection Unlock command is used to clear the Lock-Down bit in order to
unprotect all Non-Volatile Modify Protection bits when the device is in Password Protection
mode. The Password Protection Unlock command must be issued along with the correct
Password.
The complete command sequence must be entered for each 16 bits of the Password.
There must be a 2µs delay between successive Password Protection Unlock commands in
order to prevent hackers from cracking the Password by trying all possible 64-bit combinations.
If this delay is not respected, the latest command will be ignored.
6.3.8 Set Password Protection Mode command
The Set Password Protection Mode command puts the device in Password Protection mode by
programming the Password Protection Mode Lock bit to ‘1’. This command can be issued either
with the Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect pin, RP
Six cycles are required to issue a Set Password Protection Mode command:
1. The first two cycles are unlock cycles.
2. The third cycle issues the command.
3. The fourth and fifth cycles select the address (see Table 17: Protection Command
Addresses).
4. The last cycle verifies if the operation has been successful. If DQ0 is set to ’1’, the device
has successfully entered the Password Protection mode. If DQ0 is ‘0’, the operation has
failed and the command must be re-issued.
, at VID or at VIH.
There must be a 100µs delay between the fourth and fifth cycles.
39/93

6 Command Interface M29DW128F
Once the Password Protection mode is activated the device will permanently remain in this
mode.
6.3.9 Verify Password Protection Mode command
The Verify Password Protection Mode command reads the status of the Password Protection
Mode Lock Bit. If it is ‘1’, the device is in Password Protection mode.
6.3.10 Set Standard Protection Mode command
The Set Standard Protection Mode command puts the device in Standard Protection mode by
programming the Standard Protection Mode Lock bit to ‘1’.
Six cycles are required to issue the Standard Protection Mode command:
1. The first two cycles are unlock cycles.
2. The third cycle issues the program command.
3. The fourth and fifth cycles select the address (see Table 17: Protection Command
Addresses).
4. The last cycle verifies if the operation has been successful. If DQ0 is set to ’1’, the
Standard Protection Mode has been successfully activated. If DQ0 is ‘0’, the operation has
failed and the command must be re-issued.
There must be a 100µs delay between the fourth and fifth cycles.
Once the Standard Protection mode is activated the device will permanently remain in this
mode.
6.3.11 Verify Standard Protection Mode command
The Verify Standard Protection Mode command reads the status of the Standard Protection
Mode Lock Bit. If it is ‘1’, the device is in Standard Protection mode.
6.3.12 Set Non-Volatile Modify Protection Bit command
A block or group of blocks can be protected from program or erase by issuing a Set Non-Volatile
Modify Protection Bit command along with the block address. This command sets the NonVolatile Modify Protection bit to ‘1’ for a given block or group of blocks.
Six cycles are required to issue the command:
1. The first two cycles are unlock cycles.
2. The third cycle issues the program command.
3. The fourth and fifth cycles select the address (see Table 17: Protection Command
Addresses).
4. The last cycle verifies if the operation has been successful. If DQ0 is set to ’1’, the NonVolatile Modify Protection bit has been successfully programmed. If DQ0 is ‘0’, the
operation has failed and the command must be re-issued.
There must be a 100µs delay between the fourth and fifth cycles.
The Non-Volatile Modify Protection bits are erased simultaneously by issuing a Clear NonVolatile Modify Protection Bits command except if the Lock-Down bit is set to ‘1’.
The Non-Volatile Modify Protection bits can be set a maximum of 100 times.
40/93

M29DW128F 6 Command Interface
6.3.13 Verify Non-Volatile Modify Protection Bit command
The status of a Non-Volatile Modify Protection bit for a given block or group of blocks can be
read by issuing a Verify Non-Volatile Modify Protection Bit command along with the block
address.
6.3.14 Clear Non-Volatile Modify Protection Bits command
This command is used to clear all Non-Volatile Modify Protection bits. No specific block address
is required. If the Lock-Down bit is set to ‘1’, the command will fail.
Six cycles are required to issue a Clear Non-Volatile Modify Protection Bits command:
1. The first two cycles are unlock cycles.
2. The third cycle issues the command.
3. The last three cycles verify if the operation has been successful. If DQ0 is set to ’0’, all
Non-Volatile Modify Protection bits have been successfully cleared. If DQ0 is ‘1’, the
operation has failed and the command must be re-issued.
There must be a 12ms delay between the fourth and fifth cycles.
6.3.15 Set Lock Bit command
The Set Lock Bit command individually sets the Lock bit to ‘1’ for a given block or group of
blocks.
If the Non-Volatile Lock bit for the same block or group of blocks is set, the block is locked
regardless of the value of the Lock bit. (see Table 10: Block Protection Status).
6.3.16 Clear Lock Bit command
The Clear Lock Bit command individually clears (sets to ‘0’) the Lock Bit for a given block or
group of blocks.
If the Non-Volatile Lock bit for the same block or group of blocks is set, the block or group of
blocks remains locked (see Table 10: Block Protection Status).
6.3.17 Verify Lock Bit command
The status of a Lock bit for a given block can be read by issuing a Verify Lock Bit command
along with the block address.
6.3.18 Set Lock-Down Bit command
This command is used to set the Lock-Down bit to ‘1’ thus protecting the Non-Volatile Modify
Protection bits from program and erase.
There is no Unprotect Lock-Down Bit command.
6.3.19 Verify Lock-Down Bit command
This command is used to read the status of the Lock-Down bit. The status is output on bit DQ1.
If DQ1 is ‘1’, all the Non-Volatile Modify Protection bits are protected from program or erase
operations.
41/93

6 Command Interface M29DW128F
Table 15. Block Protection Commands, 8-bit Mode
Bus Operations
(1)(2)
Command
1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 6th
Length
Add Data Add Data Add Data Add Data Add Data Add Data
Set Extended Block Protection Bit 6 AAA AA 555 55 AAA 60 OW 68
Verify Extended Block Protection
Bit
4 AAA AA 555 55 AAA 60 OW DQ0
OW
(3)
48
OW DQ0
Enter Extended Block 3 AAA AA 555 55 AAA 88
Exit Extended Block 4 AAA AA 555 55 AAA 90 X 00
1. OW Extended Block Protection Bit Address (A7-A0=’00011010’), X Don’t Care. All values in the table are in hexadecimal.
2. Grey cells represent Read cycles. The other cells are Write cycles.
3. A 100µs timeout is required between cycles 4 and 5.
Table 16. Block Protection Commands, 16-bit Mode
PW
[0-3]
RPW
[0-3]
RPW
[0]
(1)(2)(3)(4)
PWA
[1]
RPW
[1]
PWA
[2]
RPW
[2]
PWA
[3]
Command
Set Extended
Block
Protection
(5)(6)
Bit
Verify Extended
Block
Protection Bit
Enter Extended
Block
Exit Extended
Block
Password
Program
(5)(7)(8)
Password
(8)(9)
Ver if y
Password
Protection
(7)(10)(11)
Unlock
Set Password
Protection
(5)(6)
Mode
Verify Password
Protection
Mode
Bus Operations
1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 6th 7th
Length
Add Data Add Data Add Data Add Data Add Data Add Data Add Data
6 555 AA 2AA 55 555 60 OW 68 OW 48 OW DQ0
4 555 AA 2AA 55 555 60
OW DQ0
3 555 AA 2AA 55 555 88
4 555 AA 2AA 55 555 90 X 00
4 555 AA 2AA 55 555 38 X[0-3]
4 555 AA 2AA 55 555 C8
7 555 AA 2AA 55 555 28
PWA
[0-3]
PWA
[0]
6 555 AA 2AA 55 555 60 PL 68 PL 48 PL DQ0
4 555 AA 2AA 55 555 60
PL DQ0
RPW
[3]
42/93

M29DW128F 6 Command Interface
Command
Set NonVolatile Modify
Protection Bit
(6)
(5)
Verify NonVolatile Modify
Protection Bit
Clear NonVolatile Modify
Protection
(12)(13)(14)
Bits
Set Lock-Down
bit
Verify Lock-
Down bit
Set Lock Bit
(15)
(7)
Clear Lock
(7)
Bit
Bus Operations
(1)(2)(3)(4)
1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 6th 7th
Length
Add Data Add Data Add Data Add Data Add Data Add Data Add Data
6 555 AA 2AA 55 555 60
4 555 AA 2AA 55 555 60
(BA)/
NVMP
(BA)
NVMP
68
/
48
6 555 AA 2AA 55 555 60 NVMP 60
(BA)/
NVMP
(BA)/
NVMP
(BA)/
NVMP
DQ0
48
40
(BA)/
NVMP
(BA)/
NVMP
DQ0
DQ0
3 555 AA 2AA 55 555 78
4 555 AA 2AA 55 555 58 BA DQ1
4 555 AA 2AA 55 555 48 BA X1h
4 555 AA 2AA 55 555 48 BA X0h
Verify Lock Bit
4 555 AA 2AA 55 555 58
BA DQ0
Set Standard
Protection
(5)(6)
Mode
6 555 AA 2AA 55 555 60 SL 68 SL 48 SL DQ0
Verify Standard
Protection
(5)
Mode
4 555 AA 2AA 55 555 60 SL DQ0
1. Grey cells represent Read cycles. The other cells are Write cycles.
2. SA Protection Group Address, BA Any address in the Block, BKA Bank Address, SL Standard Protection Mode Lock bit
Address, PL Password Protection Mode Lock Bit Address, PW Password Data, PWA Password Address, RPW Password
Data Being Verified, NVMP Non-Volatile Modify Protection Bit Address, OW Extended Block Protection Bit Address, X Don’t
Care. All values in the table are in hexadecimal.
3. Addresses are described in Table 17: Protection Command Addresses.
4. During Unlock and Command cycles, if the lower address bits are 555h or 2AAh then the address bits higher than A11
(except where BA is required) and data bits higher than DQ7 are Don't Care.
5. A Reset Command must be issued to return to the Read mode.
th
6. The 4
Bus Write cycle programs a protection bit (Extended Block Protection bit, Password Protection Mode Lock bit,
Standard Protection Mode Lock bit, and a block NVMP bit). The 5th and 6th cycles verify that the bit has been successively
programmed when DQ0=1. If DQ0=0 in the 6
th
cycle, the program command must be issued again and verified again. A
100µs delay is required between the 4th and the 5th cycle.
7. Data is latched on the rising edge of W
.
8. The entire command sequence must be entered for each portion of the password.
9. The command sequence returns FFh if the Password Protection Mode locking bit is set.
10. The password is written over four consecutive cycles, at addresses [0-3]
11. A 2µs timeout is required between any two portions of the password.
12. A 10ms delay is required between the 4th and the 5th cycle.
13. A 12ms timeout is required between cycles 4 and 5.
43/93

6 Command Interface M29DW128F
14. Cycle 4 erases all Non-Volatile Modify Protection bits. Cycles 5 and 6 verify that the bits have been successfully cleared
when DQ0=0. If DQ0=1 in the 6
erase command, all Non-Volatile Modify Protection bits should be programmed to prevent over erasure.
15. DQ1=1 if the Non-Volatile Modify Protection bit is locked, DQ1 = 0 if it is unlocked.
th
cycle, the erase command must be issued again and verified again. Before issuing the
Table 17. Protection Command Addresses
Bit Condition Address Inputs A7-A0 Other Address Inputs
Password Protection Mode Lock Bit
Address (PL)
RP at V
RP
at V
IH
ID
00001010 X
10001010 X
Standard Protection Mode Lock bit Address (SL) 00010010 X
Non-Volatile Modify Protection Bit Address (NVMP) 01000010
Block Protection Group
Address
Extended Block Protection Bit Address (OW) 00011010 X
Table 18. Program, Erase Times and Program, Erase Endurance Cycles
Parameter Min
Typ
Chip Erase 80
Block Erase (64 KBytes) 0.8
Erase Suspend Latency Time
Byte Program
Word Program
Single or Multiple Byte Program
(1, 2, 4 or 8 Bytes at-a-time)
Write to Buffer and Program
(64 Bytes at-a-time)
Single or Multiple Word Program
(1, 2 or 4 Words at-a-time)
Write to Buffer and Program
(32 Words at-a-time)
VPP/WP =V
/WP=V
V
PP
V
/WP=
PP
V
PPH
/WP=V
V
PP
PPH
IH
IH
10
90
280
10
90
280
Chip Program (Byte by Byte) 80
Chip Program (Word by Word) 40
Chip Program (Quadruple Byte or Double Word) 20
Chip Program (Octuple Byte or Quadruple Word) 10
(1)(2)
Max
400
6
50
200
200
400
200
100
50
(2)
(3)
(4)
(4)
(3)
(3)
(3)
(3)
(3)
(3)
Unit
s
s
µs
µs
µs
µs
µs
s
s
s
s
Program Suspend Latency Time 4 µs
Program/Erase Cycles (per Block) 100,000 cycles
Data Retention 20 years
1. Typical values measured at room temperature and nominal voltages.
2. Sampled, but not 100% tested.
3. Maximum value measured at worst case conditions for both temperature and VCC after 100,00 program/erase cycles.
4. Maximum value measured at worst case conditions for both temperature and VCC.
44/93

M29DW128F 7 Status Register
7 Status Register
The M29DW128F has one Status Register. The Status Register provides information on the
current or previous Program or Erase operations executed in each bank. The various bits
convey information and errors on the operation. Bus Read operations from any address within
the Bank, always read the Status Register during Program and Erase operations. It is also read
during Erase Suspend when an address within a block being erased is accessed.
The bits in the Status Register are summarized in Table 19: Status Register Bits.
7.1 Data Polling Bit (DQ7)
The Data Polling Bit can be used to identify whether the Program/Erase Controller has
successfully completed its operation or if it has responded to an Erase Suspend. The Data
Polling Bit is output on DQ7 when the Status Register is read.
During Program operations the Data Polling Bit outputs the complement of the bit being
programmed to DQ7. After successful completion of the Program operation the memory returns
to Read mode and Bus Read operations from the address just programmed output DQ7, not its
complement.
During Erase operations the Data Polling Bit outputs ’0’, the complement of the erased state of
DQ7. After successful completion of the Erase operation the memory returns to Read mode.
In Erase Suspend mode the Data Polling Bit will output a ’1’ during a Bus Read operation within
a block being erased. The Data Polling Bit will change from a ’0’ to a ’1’ when the Program/
Erase Controller has suspended the Erase operation.
Figure 8: Data Polling Flowchart, gives an example of how to use the Data Polling Bit. A Valid
Address is the address being programmed or an address within the block being erased.
7.2 Toggle Bit (DQ6)
The Toggle Bit can be used to identify whether the Program/Erase Controller has successfully
completed its operation or if it has responded to an Erase Suspend. The Toggle Bit is output on
DQ6 when the Status Register is read.
During a Program/Erase operation the Toggle Bit changes from ’0’ to ’1’ to ’0’, etc., with
successive Bus Read operations at any address. After successful completion of the operation
the memory returns to Read mode.
During Erase Suspend mode the Toggle Bit will output when addressing a cell within a block
being erased. The Toggle Bit will stop toggling when the Program/Erase Controller has
suspended the Erase operation.
Figure 9: Toggle Flowchart, gives an example of how to use the Data Toggle Bit. Figure 16 and
Figure 17 describe Toggle Bit timing waveform.
45/93

7 Status Register M29DW128F
7.3 Error Bit (DQ5)
The Error Bit can be used to identify errors detected by the Program/Erase Controller. The Error
Bit is set to ’1’ when a Program, Block Erase or Chip Erase operation fails to write the correct
data to the memory. If the Error Bit is set a Read/Reset command must be issued before other
commands are issued. The Error bit is output on DQ5 when the Status Register is read.
Note that the Program command cannot change a bit set to ’0’ back to ’1’ and attempting to do
so will set DQ5 to ‘1’. A Bus Read operation to that address will show the bit is still ‘0’. One of
the Erase commands must be used to set all the bits in a block or in the whole memory from ’0’
to ’1’.
7.4 Erase Timer Bit (DQ3)
The Erase Timer Bit can be used to identify the start of Program/Erase Controller operation
during a Block Erase command. Once the Program/Erase Controller starts erasing the Erase
Timer Bit is set to ’1’. Before the Program/Erase Controller starts the Erase Timer Bit is set to ’0’
and additional blocks to be erased may be written to the Command Interface. The Erase Timer
Bit is output on DQ3 when the Status Register is read.
7.5 Alternative Toggle Bit (DQ2)
The Alternative Toggle Bit can be used to monitor the Program/Erase controller during Erase
operations. The Alternative Toggle Bit is output on DQ2 when the Status Register is read.
During Chip Erase and Block Erase operations the Toggle Bit changes from ’0’ to ’1’ to ’0’, etc.,
with successive Bus Read operations from addresses within the blocks being erased. A
protected block is treated the same as a block not being erased. Once the operation completes
the memory returns to Read mode.
During Erase Suspend the Alternative Toggle Bit changes from ’0’ to ’1’ to ’0’, etc. with
successive Bus Read operations from addresses within the blocks being erased. Bus Read
operations to addresses within blocks not being erased will output the memory array data as if
in Read mode.
After an Erase operation that causes the Error Bit to be set, the Alternative Toggle Bit can be
used to identify which block or blocks have caused the error. The Alternative Toggle Bit
changes from ’0’ to ’1’ to ’0’, etc. with successive Bus Read Operations from addresses within
blocks that have not erased correctly. The Alternative Toggle Bit does not change if the
addressed block has erased correctly.
Figure 16 and Figure 17 describe Alternative Toggle Bit timing waveform.
7.6 Write to Buffer and Program Abort Bit (DQ1)
The Write to Buffer and Program Abort bit, DQ1, is set to ‘1’ when a Write to Buffer and
Program operation aborts. The Write to Buffer and Program Abort and Reset command must
be issued to return the device to Read mode (see Write to Buffer and Program in COMMANDS
section).
46/93

M29DW128F 7 Status Register
Table 19. Status Register Bits
Operation Address DQ7 DQ6 DQ5 DQ3 DQ2 DQ1 RB
Program Bank Address DQ7 Toggle 0 – – 0 0
Program During Erase
Suspend
Bank Address DQ7 Toggle 0 – – – 0
Write to Buffer and
Program Abort
Bank Address DQ7 Toggle 0 – – 1 0
Program Error Bank Address DQ7 Toggle 1 – – – Hi-Z
Chip Erase Any Address 0 Toggle 0 1 Toggle – Hi-Z
Block Erase before
timeout
Erasing Block 0 Toggle 0 0 Toggle – 0
Non-Erasing Block 0 Toggle 0 0 No Toggle – 0
Erasing Block 0 Toggle 0 1 Toggle – Hi-Z
Block Erase
Non-Erasing Block 0 Toggle 0 1 No Toggle – 0
Erasing Block 1 No Toggle 0 – Toggle – Hi-Z
Erase Suspend
Non-Erasing Block Data read as normal – Hi-Z
Good Block Address 0 Toggle 1 1 No Toggle – 0
Erase Error
Faulty Block Address 0 Toggle 1 1 Toggle – 0
1. Unspecified data bits should be ignored.
2. Figure 16 and Figure 17 describe Toggle and Alternative Toggle Bits timing waveforms.
Figure 8. Data Polling Flowchart
START
READ DQ5 & DQ7
at VALID ADDRESS
DQ7
=
DATA
NO
NO
DQ5 = 1
YES
READ DQ7
at VALID ADDRESS
DQ7
=
DATA
NO
FAIL PASS
47/93
YES
YES
AI07760

7 Status Register M29DW128F
Figure 9. Toggle Flowchart
START
READ DQ6
ADDRESS = BA
READ
DQ5 & DQ6
ADDRESS = BA
NO
ADDRESS = BA
1. BA = Address of Bank being Programmed or Erased.
DQ6
=
TOGGLE
YES
DQ5
= 1
YES
READ DQ6
TWICE
DQ6
=
TOGGLE
YES
FAIL
NO
NO
PASS
AI08929b
48/93

M29DW128F 8 Dual Operations and Multiple Bank architecture
8 Dual Operations and Multiple Bank architecture
The Multiple Bank Architecture of the M29DW128F gives greater flexibility for software
developers to split the code and data spaces within the memory array. The Dual Operations
feature simplifies the software management of the device by allowing code to be executed from
one bank while another bank is being programmed or erased.
The Dual Operations feature means that while programming or erasing in one bank, read
operations are possible in another bank with zero latency.
Only one bank at a time is allowed to be in program or erase mode. However, certain
commands can cross bank boundaries, which means that during an operation only the banks
that are not concerned with the cross bank operation are available for dual operations. For
example, if a Block Erase command is issued to erase blocks in both Bank A and Bank B, then
only Banks C or D are available for read operations while the erase is being executed.
If a read operation is required in a bank, which is programming or erasing, the program or erase
operation can be suspended.
Also if the suspended operation was erase then a program command can be issued to another
block, so the device can have one block in Erase Suspend mode, one programming and other
banks in read mode.
By using a combination of these features, read operations are possible at any moment.
Ta bl e 2 0 and Ta bl e 2 1 show the dual operations possible in other banks and in the same bank.
Note that only the commonly used commands are represented in these tables.
Table 20. Dual Operations Allowed In Other Banks
Commands allowed in another bank
Status of bank
Idle Yes
Programming Yes No No No – – No No
Erasing Yes No No No – – No No
Program
Suspended
Erase Suspended Yes No Yes Yes Yes No -
1. If several banks are involved in a program or erase operation, then only the banks that are not concerned with
the operation are available for dual operations.
2. Read Status Register is not a command. The Status Register can be read during a block program or erase
operation.
3. Only after a program or erase operation in that bank.
4. Only after a Program or Erase Suspend command in that bank.
5. Only a Program Resume is allowed if the bank was previously in Program Suspend mode.
6. Only an Erase Resume is allowed if the bank was previously in Erase Suspend mode.
Read/
Reset
Ye s N o Y e s Ye s N o N o -
Read
Status
Register
(2)
(3)
Ye s
Read
CFI
Query
Ye s Ye s Ye s Ye s
Auto
Select
Program Erase
(1)
Program/
Erase
Suspend
Ye s
(3)
Program
/Erase
Resume
(4)
Ye s
(5)
Ye s
(6)
Ye s
49/93

8 Dual Operations and Multiple Bank architecture M29DW128F
Table 21. Dual Operations Allowed In Same Bank
Commands allowed in same bank
Status of bank
Read/
Reset
Read
Status
Register
(1)
Idle Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Programming No Yes No No – –
Erasing No Yes No No – No
Program
Suspended
Erase Suspended
1. Read Status Register is not a command. The Status Register can be read by addressing the block being
programmed or erased.
2. Only after a program or erase operation in that bank.
3. Only after a Program or Erase Suspend command in that bank.
4. Only a Program Suspend.
5. Only an Erase suspend.
6. Not allowed in the Block or Word that is being erased or programmed.
7. The Status Register can be read by addressing the block being erase suspended.
Ye s
Ye s
(6)
(6)
No Yes Yes No – – Yes
(7)
Ye s
Read
CFI
Query
Select
Ye s Ye s
Auto
Program Erase
Ye s
(6)
No – Yes
Program/
Erase
Suspend
(2)
Ye s
(4)
Ye s
(5)
Ye s
Program/
Erase
Resume
(3)
Ye s
–
–
50/93

M29DW128F 9 Maximum Rating
9 Maximum Rating
Stressing the device above the rating listed in the Absolute Maximum Ratings table may cause
permanent damage to the device. Exposure to Absolute Maximum Rating conditions for
extended periods may affect device reliability. These are stress ratings only and operation of
the device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the Operating sections of
this specification is not implied. Refer also to the STMicroelectronics SURE Program and other
relevant quality documents.
Table 22. Absolute Maximum Ratings
Symbol Parameter Min Max Unit
T
BIAS
T
STG
V
IO
V
CC
V
CCQ
V
ID
(3)
V
PP
1. Minimum voltage may undershoot to –2V during transition and for less than 20ns during transitions.
2. Maximum voltage may overshoot to V
3. VPP must not remain at 12V for more than a total of 80hrs.
Temperature Under Bias –50 125 °C
Storage Temperature –65 150 °C
Input or Output Voltage
(1)(2)
–0.6
VCC +0.6
Supply Voltage –0.6 4 V
Input/Output Supply Voltage –0.6 4 V
Identification Voltage –0.6 13.5 V
Program Voltage –0.6 13.5 V
+2V during transition and for less than 20ns during transitions.
CC
V
51/93

10 DC and AC parameters M29DW128F
10 DC and AC parameters
This section summarizes the operating measurement conditions, and the DC and AC
characteristics of the device. The parameters in the DC and AC characteristics Tables that
follow, are derived from tests performed under the Measurement Conditions summarized in
Table 23: Operating and AC Measurement Conditions. Designers should check that the
operating conditions in their circuit match the operating conditions when relying on the quoted
parameters.
Table 23. Operating and AC Measurement Conditions
M29DW128F
Parameter
Unit60 70
Min Max Min Max
V
Supply Voltage
CC
2.7 3.6 2.7 3.6 V
Ambient Operating Temperature –40 85 –40 85 °C
Load Capacitance (C
)
L
30 30 pF
Input Rise and Fall Times 10 10 ns
Input Pulse Voltages
Input and Output Timing Ref. Voltages
0 to V
CC
/2 VCC/2
V
CC
0 to V
CC
Figure 10. AC Measurement I/O Waveform
V
CC
VCC/2
0V
AI05557
Figure 11. AC Measurement Load Circuit
V
PP
V
CC
V
CC
V
V
0.1µF
0.1µF
CL includes JIG capacitance
52/93
DEVICE
UNDER
TEST
25kΩ
C
25kΩ
L
AI05558

M29DW128F 10 DC and AC parameters
Table 24. Device Capacitance
Symbol Parameter Test Condition Min
Max
(1)
Unit
C
IN
C
OUT
1. Sampled only, not 100% tested.
Input Capacitance
Output Capacitance
VIN = 0V
= 0V
V
OUT
6pF
12 pF
Table 25. DC Characteristics
Symbol Parameter Test Condition Min Max Unit
≤ V
IN
CC
≤ V
OUT
CC
f = 6MHz
= VCC ±0.2V,
= VCC ±0.2V
V
PP
V
IL
VPP/WP =
= 2.7V ±10%
/WP =
or V
V
PPH
±1 µA
±1 µA
10 mA
100 µA
IH
20 mA
20 mA
0.7V
CC
VCC +0.3
11.5 12.5 V
I
CC3
I
CC1
V
I
I
CC2
V
V
I
LI
LO
(1)(2)
IL
IH
PPH
Input Leakage Current
Output Leakage Current
(1)
Supply Current (Read)
0V ≤ V
0V ≤ V
= VIL, G = VIH,
E
E
Supply Current (Standby)
Supply Current (Program/
Erase)
Program/Erase
Controller active
RP
Input Low Voltage –0.5 0.8 V
Input High Voltage
Voltage for V
Acceleration
/WP Program
PP
V
CC
V
I
V
V
V
V
LKO
1. In Dual operations the Supply Current will be the sum of I
2. Sampled only, not 100% tested.
Current for V
PP
Acceleration
Output Low Voltage
OL
Output High Voltage
OH
Identification Voltage 11.5 12.5 V
ID
Program/Erase Lockout
Supply Voltage
/WP Program
PP
=2.7V ±10%
V
CC
= 1.8mA
I
OL
= –100µAV
I
OH
CC
–0.4
15 mA
0.45 V
1.8 2.3 V
(read) and I
CC1
(program/erase).
CC3
53/93
V

10 DC and AC parameters M29DW128F
Figure 12. Random Read AC Waveforms
tAVAV
A0-A22/
A–1
tAVQV tAXQX
E
VALID
G
DQ0-DQ7/
DQ8-DQ15
BYTE
tELQV
tELQX tEHQZ
tGLQX tGHQX
tGLQV
tBHQV
tELBL/tELBH tBLQZ
tEHQX
tGHQZ
VALID
AI08970
54/93

M29DW128F 10 DC and AC parameters
Figure 13. Page Read AC Waveforms
AI08971c
tEHQX
tEHQZ
tGHQX
tGHQZ
VALID VALID VALID
VALID
VALID VALID VALID VALID
VALID VALID VALID VALID
tAVQV
tELQV
tGLQV
VALID
VALID
tAVQV1
VALID VALID VALID
A3-A22
A-1
A0-A2
E
G
DQ0-DQ15
55/93

10 DC and AC parameters M29DW128F
Table 26. Read AC Characteristics
M29DW128F
Symbol Alt Parameter Test Condition
E
t
AVAV
t
AVQ V
t
AVQ V1
(1)
t
ELQX
t
ELQV
(1)
t
GLQX
t
GLQV
(1)
t
EHQZ
(1)
t
GHQZ
t
EHQX
t
GHQX
t
AXQX
t
ELBL
t
ELBH
t
BLQZ
t
BHQV
1. Sampled only, not 100% tested.
2. TSOP56 package only.
t
RC
t
ACC
t
PAG E
t
LZ
t
CE
t
OLZ
t
OE
t
HZ
t
DF
t
OH
t
ELFL
t
ELFH
t
FLQZ
t
FHQV
Address Valid to Next Address Valid
Address Valid to Output Valid
Address Valid to Output Valid (Page)
Chip Enable Low to Output Transition
Chip Enable Low to Output Valid
Output Enable Low to Output
Transition
Output Enable Low to Output Valid
Chip Enable High to Output Hi-Z
Output Enable High to Output Hi-Z
Chip Enable, Output Enable or
Address Transition to Output Transition
Chip Enable to BYTE Low or High
BYTE Low to Output Hi-Z
BYTE High to Output Valid
(2)
(2)
(2)
= VIL,
G = V
E = VIL,
G
= V
E = VIL,
G
= V
= V
G
G = V
= V
E
= V
E
= V
G
= V
E
IL
IL
IL
IL
IL
IL
IL
IL
IL
60 70
Min 60 70 ns
Max 60 70 ns
Max 25 30 ns
Min 0 0 ns
Max 60 70 ns
Min 0 0 ns
Max 20 25 ns
Max 25 25 ns
Max 25 25 ns
Min 0 0 ns
Max 5 5 ns
Max 25 25 ns
Max 30 30 ns
Unit
56/93

M29DW128F 10 DC and AC parameters
Figure 14. Write AC Waveforms, Write Enable Controlled
tAVAV
A0-A22/
A–1
tAVWL
E
VALID
tWLAX
tWHEH
G
W
DQ0-DQ7/
DQ8-DQ15
V
CC
RB
tVCHEL
tELWL
tWLWHtGHWL
tDVWH
tWHRL
tWHGL
tWHWL
tWHDX
VALID
AI08972
57/93

10 DC and AC parameters M29DW128F
Table 27. Write AC Characteristics, Write Enable Controlled
M29DW128F
Symbol Alt Parameter
60 70
Unit
t
AVAV
t
ELWL
t
WLWH
t
DVW H
t
WHDX
t
WHEH
t
WHWL
t
AVW L
t
WLAX
t
GHWL
t
WHGL
(1)
t
WHRL
t
VCHEL
1. Sampled only, not 100% tested.
t
WC
t
CS
t
WP
t
DS
t
DH
t
CH
t
WPH
t
AS
t
AH
t
OEH
t
BUSY
t
VCS
Address Valid to Next Address Valid Min 60 70 ns
Chip Enable Low to Write Enable Low Min 0 0 ns
Write Enable Low to Write Enable High Min 45 45 ns
Input Valid to Write Enable High Min 45 45 ns
Write Enable High to Input Transition Min 0 0 ns
Write Enable High to Chip Enable High Min 0 0 ns
Write Enable High to Write Enable Low Min 30 30 ns
Address Valid to Write Enable Low Min 0 0 ns
Write Enable Low to Address Transition Min 45 45 ns
Output Enable High to Write Enable Low Min 0 0 ns
Write Enable High to Output Enable Low Min 0 0 ns
Program/Erase Valid to RB Low Max 30 30 ns
VCC High to Chip Enable Low
Min 50 50 µs
58/93

M29DW128F 10 DC and AC parameters
3
Figure 15. Write AC Waveforms, Chip Enable Controlled
tAVAV
A0-A22/
A–1
tAVEL
W
VALID
tELAX
tEHWH
G
E
DQ0-DQ7/
DQ8-DQ15
V
CC
RB
tWLEL
tVCHWL
tELEHtGHEL
tDVEH
tEHGL
tEHEL
tEHDX
VALID
tEHRL
AI0897
59/93

10 DC and AC parameters M29DW128F
Table 28. Write AC Characteristics, Chip Enable Controlled
M29DW128F
Symbol Alt Parameter
60 70
Unit
t
AVAV
t
WLEL
t
ELEH
t
DVEH
t
EHDX
t
EHWH
t
EHEL
t
AVEL
t
ELAX
t
GHEL
t
EHGL
(1)
t
EHRL
t
VCHWL
1. Sampled only, not 100% tested.
t
WC
t
WS
t
CP
t
DS
t
DH
t
WH
t
CPH
t
AS
t
AH
t
OEH
t
BUSY
t
VCS
Address Valid to Next Address Valid Min 60 70 ns
Write Enable Low to Chip Enable Low Min 0 0 ns
Chip Enable Low to Chip Enable High Min 45 45 ns
Input Valid to Chip Enable High Min 45 45 ns
Chip Enable High to Input Transition Min 0 0 ns
Chip Enable High to Write Enable High Min 0 0 ns
Chip Enable High to Chip Enable Low Min 30 30 ns
Address Valid to Chip Enable Low Min 0 0 ns
Chip Enable Low to Address Transition Min 45 45 ns
Output Enable High Chip Enable Low Min 0 0 ns
Chip Enable High to Output Enable Low Min 0 0 ns
Program/Erase Valid to RB Low Max 30 30 ns
VCC High to Write Enable Low
Min 50 50 µs
60/93

M29DW128F 10 DC and AC parameters
Figure 16. Toggle and Alternative Toggle Bits Mechanism, Chip Enable Controlled
Address Outside the Bank
being Programmed or Erased
Toggle/
Read Operation Outside the Bank
Being Programmed or Erased
DQ2
A0-A22
(1)
/DQ6
Address Outside the Bank
being Programmed or Erased
E
G
(2)
Read Operation outside the Bank
Being Programmed or Erased
Data Data
Address in the Bank
being Programmed or Erased
tAXEL
tELQV
Toggle/
Alt.Toggle Bit
Read Operation in the Bank
Being Programmed or Erased
tELQV
Alt.Toggle Bit
1. The Toggle bit is output on DQ6.
2. The Alternative Toggle bit is output on DQ2.
3. Refer to Table 26: Read AC Characteristics for the value of t
ELQV
.
Figure 17. Toggle and Alternative Toggle Bits Mechanism, Output Enable Controlled
A0-A22
Address Outside the Bank
being Programmed/Erased
Address in the Bank
being Programmed/Erased
tAXGL
Address Outside the Bank
being Programmed/Erased
AI08914e
G
E
tGLQV
DQ2
(1)
(2)
/DQ6
Read Operation outside Bank
Being Programmed or Erased
Data Data
Being Programmed or Erased
Toggle/
Alt.Toggle Bit
Read Operation in Bank
1. The Toggle bit is output on DQ6.
2. The Alternative Toggle bit is output on DQ2.
3. Refer to Table 26: Read AC Characteristics for the value of t
GLQV
.
Table 29. Toggle and Alternative Toggle Bits AC Characteristics
Symbol Alt Parameter
t
AXEL
t
AXGL
Address Transition to Chip Enable Low Min 10 10 ns
Address Transition to Output Enable Low Min 10 10 ns
tGLQV
Toggle/
Alt.Toggle Bit
Read Operation outside Bank
Being Programmed or Erased
AI08915e
M29DW128F
Unit
60 70
61/93

10 DC and AC parameters M29DW128F
Figure 18. Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect AC Waveforms (No Program/Erase Ongoing)
RB
E, G
tPHEL,
tPHGL
RP
tPLPX
AI11300b
Figure 19. Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect During Program/Erase Operation AC Waveforms
tPLYH
RB
tRHEL, tRHGL
E, G
RP
tPLPX
Table 30. Reset/Block Temporary Unprotect AC Characteristics
Symbol Alt Parameter
(1)
t
PLYH
t
PLPX
t
PHEL,
(1)
t
PHGL
t
RHEL
(1)
t
RHGL
1. Sampled only, not 100% tested.
t
READY
t
t
t
RPD
t
RP Low to Read mode, during Program or
Erase
RP Pulse Width Min 500 ns
RP
RP High to Write Enable Low, Chip Enable
RH
Low, Output Enable Low
RP Low to Standby Mode. Min 20 ns
RB High to Write Enable Low, Chip Enable
RB
Low, Output Enable Low
AI11301b
M29DW128F
Unit
60 70
Max 20 µs
Min 50 ns
Min 0 ns
62/93

M29DW128F 10 DC and AC parameters
Figure 20. Accelerated Program Timing Waveforms
V
VPP/WP
PP
V
or V
IL
IH
tVHVPP
tVHVPP
AI05563
63/93

11 Package mechanical M29DW128F
11 Package mechanical
Figure 21. TSOP56 – 56 lead Plastic Thin Small Outline, 14 x 20mm, Package Outline
A2
1. Drawing is not to scale.
1 N
N/2
DIE
TSOP-b
D1
E
A
D
C
e
B
CP
LA1 α
Table 31. TSOP56 – 56 lead Plastic Thin Small Outline, 14 x 20mm, Package Mechanical Data
millimeters inches
Symbol
Typ M in Max Typ Min Max
A 1.200 0.0472
A1 0.100 0.050 0.150 0.0039 0.0020 0.0059
A2 1.000 0.950 1.050 0.0394 0.0374 0.0413
B 0.220 0.170 0.270 0.0087 0.0067 0.0106
C 0.100 0.210 0.0039 0.0083
CP 0.100 0.0039
D 20.000 19.800 20.200 0.7874 0.7795 0.7953
D1 18.400 18.300 18.500 0.7244 0.7205 0.7283
e 0.500 – – 0.0197 – –
E 14.000 13.900 14.100 0.5512 0.5472 0.5551
L 0.600 0.500 0.700 0.0236 0.0197 0.0276
alpha305305
N56 56
64/93

M29DW128F 11 Package mechanical
Figure 22. TBGA64 10x13mm - 8x8 active ball array, 1mm pitch, Package Outline
D
FD
FE
D1
SD
SE
ddd
A2
A1
BGA-Z23
1. Drawing is not to scale.
E1E
BALL "A1"
A
eb
Table 32. TBGA64 10x13mm - 8x8 active ball array, 1mm pitch, Package Mechanical Data
millimeters inches
Symbol
Typ Min Max Typ Min Max
A 1.200 0.0472
A1 0.300 0.200 0.350 0.0118 0.0079 0.0138
A2 0.800 0.0315
b 0.350 0.500 0.0138 0.0197
D 10.000 9.900 10.100 0.3937 0.3898 0.3976
D1 7.000 – – 0.2756 – –
ddd 0.100 0.0039
e 1.000 – – 0.0394 – –
E 13.000 12.900 13.100 0.5118 0.5079 0.5157
E1 7.000 – – 0.2756 – –
FD 1.500 – – 0.0591 – –
FE 3.000 – – 0.1181 – –
SD 0.500 – – 0.0197 – –
SE 0.500 – – 0.0197 – –
65/93

12 Part numbering M29DW128F
12 Part numbering
Table 33. Ordering Information Scheme
Example: M29DW128F 70 NF 1 T
Device Type
M29
Architecture
D = Dual Operation
Operating Voltage
W = V
Device Function
128F = 128 Mbit (x8/x16), Multiple Bank, Page, Boot Block, 16+48+48+16 partitioning,
Flash Memory
Speed
60 = 60ns
70 = 70ns
= 2.7 to 3.6V
CC
Package
NF = TSOP56: 14 x 20 mm
ZA = TBGA64: 10 x13mm, 1mm pitch
Temperature Range
1 = 0 to 70 °C
6 = –40 to 85 °C
Option
Blank = Standard Packing
T = Tape & Reel Packing
E = ECOPACK Package, Standard Packing
F = ECOPACK Package, Tape & Reel 24mm Packing
Note: This product is also available with the Extended Block factory locked. For further details
and ordering information contact your nearest ST sales office.
Devices are shipped from the factory with the memory content bits erased to ’1’.
For a list of available options (Speed, Package, etc.) or for further information on any aspect of
this device, please contact your nearest ST Sales Office.
66/93

M29DW128F 12 Part numbering
Appendix A Block addresses and Read/Modify
Protection groups
Table 34. Block Addresses and Protection Groups
Bank Block
Size
(KBytes/
KWords)
Protection Block
Group
(x8) (x16)
0 8/4 Protection Group
1 8/4 Protection Group
2 8/4 Protection Group
3 8/4 Protection Group
4 8/4 Protection Group
5 8/4 Protection Group
6 8/4 Protection Group
7 8/4 Protection Group
8 64/32
9 64/32 020000h-02FFFFh 010000h–017FFFh
Protection Group
000000h-001FFFh
002000h-003FFFh
004000h-005FFFh
006000h-007FFFh
008000h-009FFFh
00A000h-00BFFFh
00C000h-00DFFFh
00E000h-00FFFFh
010000h-01FFFFh 008000h–00FFFFh
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
000000h–000FFFh
001000h–001FFFh
002000h–002FFFh
003000h–003FFFh
004000h–004FFFh
005000h–005FFFh
006000h–006FFFh
007000h–007FFFh
10 64/32 030000h-03FFFFh 018000h–01FFFFh
11 64/32
040000h-04FFFFh 020000h–027FFFh
12 64/32 050000h-05FFFFh 028000h–02FFFFh
Protection Group
13 64/32 060000h-06FFFFh 030000h–037FFFh
Bank A
14 64/32 070000h-07FFFFh 038000h–03FFFFh
15 64/32
080000h-08FFFFh 040000h–047FFFh
16 64/32 090000h-09FFFFh 048000h–04FFFFh
Protection Group
17 64/32 0A0000h-0AFFFFh 050000h–057FFFh
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
18 64/32 0B0000h-0BFFFFh 058000h–05FFFFh
19 64/32
0C0000h-0CFFFFh 060000h–067FFFh
20 64/32 0D0000h-0DFFFFh 068000h–06FFFFh
Protection Group
21 64/32 0E0000h-0EFFFFh 070000h–077FFFh
22 64/32 0F0000h-0FFFFFh 078000h–07FFFFh
23 64/32
100000h-10FFFFh 080000h–087FFFh
24 64/32 110000h-11FFFFh 088000h–08FFFFh
Protection Group
25 64/32 120000h-12FFFFh 090000h–097FFFh
26 64/32 130000h-13FFFFh 098000h–09FFFFh
67/93

12 Part numbering M29DW128F
Bank Block
27 64/32
28 64/32 150000h-15FFFFh 0A8000h–0AFFFFh
29 64/32 160000h-16FFFFh 0B0000h–0B7FFFh
30 64/32 170000h-17FFFFh 0B8000h–0BFFFFh
31 64/32
32 64/32 190000h-19FFFFh 0C8000h–0CFFFFh
33 64/32 1A0000h-1AFFFFh 0D0000h–0D7FFFh
Bank A
34 64/32 1B0000h-1BFFFFh 0D8000h–0DFFFFh
35 64/32
36 64/32 1D0000h-1DFFFFh 0E8000h–0EFFFFh
37 64/32 1E0000h-1EFFFFh 0F0000h–0F7FFFh
38 64/32 1F0000h-1FFFFFh 0F8000h–0FFFFFh
39 64/32
40 64/32 210000h-21FFFFh 108000h–10FFFFh
41 64/32 220000h-22FFFFh 110000h–117FFFh
Size
(KBytes/
KWords)
Protection Block
Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
(x8) (x16)
140000h-14FFFFh 0A0000h–0A7FFFh
180000h-18FFFFh 0C0000h–0C7FFFh
1C0000h-1CFFFFh 0E0000h–0E7FFFh
200000h-20FFFFh 100000h–107FFFh
42 64/32 230000h-23FFFFh 118000h–11FFFFh
43 64/32
44 64/32 250000h-25FFFFh 128000h–12FFFFh
45 64/32 260000h-26FFFFh 130000h–137FFFh
46 64/32 270000h-27FFFFh 138000h–13FFFFh
47 64/32
48 64/32 290000h-29FFFFh 148000h–14FFFFh
49 64/32 2A0000h-2AFFFFh 150000h–157FFFh
Bank B
50 64/32 2B0000h-2BFFFFh 158000h–15FFFFh
51 64/32
52 64/32 2D0000h-2DFFFFh 168000h–16FFFFh
53 64/32 2E0000h-2EFFFFh 170000h–177FFFh
54 64/32 2F0000h-2FFFFFh 178000h–17FFFFh
55 64/32
56 64/32 310000h-31FFFFh 188000h–18FFFFh
57 64/32 320000h-32FFFFh 190000h–197FFFh
58 64/32 330000h-33FFFFh 198000h–19FFFFh
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
240000h-24FFFFh 120000h–127FFFh
280000h-28FFFFh 140000h–147FFFh
2C0000h-2CFFFFh 160000h–167FFFh
300000h-30FFFFh 180000h–187FFFh
68/93

M29DW128F 12 Part numbering
Bank Block
59 64/32
60 64/32 350000h-35FFFFh 1A8000h–1AFFFFh
61 64/32 360000h-36FFFFh 1B0000h–1B7FFFh
62 64/32 370000h-37FFFFh 1B8000h–1BFFFFh
63 64/32
64 64/32 390000h-39FFFFh 1C8000h–1CFFFFh
65 64/32 3A0000h-3AFFFFh 1D0000h–1D7FFFh
66 64/32 3B0000h-3BFFFFh 1D8000h–1DFFFFh
67 64/32
68 64/32 3D0000h-3DFFFFh 1E8000h–1EFFFFh
69 64/32 3E0000h-3EFFFFh 1F0000h–1F7FFFh
70 64/32 3F0000h-3FFFFFh 1F8000h–1FFFFFh
71 64/32
72 64/32 410000h–41FFFFh 208000h–20FFFFh
73 64/32 420000h–42FFFFh 210000h–217FFFh
Size
(KBytes/
KWords)
Protection Block
Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
(x8) (x16)
340000h-34FFFFh 1A0000h–1A7FFFh
380000h-38FFFFh 1C0000h–1C7FFFh
3C0000h-3CFFFFh 1E0000h–1E7FFFh
400000h–40FFFFh 200000h–207FFFh
74 64/32 430000h–43FFFFh 218000h–21FFFFh
75 64/32
Bank B
76 64/32 450000h–45FFFFh 228000h–22FFFFh
77 64/32 460000h–46FFFFh 230000h–237FFFh
78 64/32 470000h–47FFFFh 238000h–23FFFFh
79 64/32
80 64/32 490000h–49FFFFh 248000h–24FFFFh
81 64/32 4A0000h–4AFFFFh 250000h–257FFFh
82 64/32 4B0000h–4BFFFFh 258000h–25FFFFh
83 64/32
84 64/32 4D0000h–4DFFFFh 268000h–26FFFFh
85 64/32 4E0000h–4EFFFFh 270000h–277FFFh
86 64/32 4F0000h–4FFFFFh 278000h–27FFFFh
87 64/32
88 64/32 510000h–51FFFFh 288000h–28FFFFh
89 64/32 520000h–52FFFFh 290000h–297FFFh
90 64/32 530000h–53FFFFh 298000h–29FFFFh
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
440000h–44FFFFh 220000h–227FFFh
480000h–48FFFFh 240000h–247FFFh
4C0000h–4CFFFFh 260000h–267FFFh
500000h–50FFFFh 280000h–287FFFh
69/93

12 Part numbering M29DW128F
Bank Block
91 64/32
92 64/32 550000h–55FFFFh 2A8000h–2AFFFFh
93 64/32 560000h–56FFFFh 2B0000h–2B7FFFh
94 64/32 570000h–57FFFFh 2B8000h–2BFFFFh
95 64/32
96 64/32 590000h–59FFFFh 2C8000h–2CFFFFh
97 64/32 5A0000h–5AFFFFh 2D0000h–2D7FFFh
98 64/32 5B0000h–5BFFFFh 2D8000h–2DFFFFh
99 64/32
100 64/32 5D0000h–5DFFFFh 2E8000h–2EFFFFh
101 64/32 5E0000h–5EFFFFh 2F0000h–2F7FFFh
102 64/32 5F0000h–5FFFFFh 2F8000h–2FFFFFh
103 64/32
104 64/32 610000h–61FFFFh 308000h–30FFFFh
105 64/32 620000h–62FFFFh 310000h–317FFFh
Size
(KBytes/
KWords)
Protection Block
Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
(x8) (x16)
540000h–54FFFFh 2A0000h–2A7FFFh
580000h–58FFFFh 2C0000h–2C7FFFh
5C0000h–5CFFFFh 2E0000h–2E7FFFh
600000h–60FFFFh 300000h–307FFFh
106 64/32 630000h–63FFFFh 318000h–31FFFFh
107 64/32
Bank B
108 64/32 650000h–65FFFFh 328000h–32FFFFh
109 64/32 660000h–66FFFFh 330000h–337FFFh
110 64/32 670000h–67FFFFh 338000h–33FFFFh
111 64/32
112 64/32 690000h–69FFFFh 348000h–34FFFFh
113 64/32 6A0000h–6AFFFFh 350000h–357FFFh
114 64/32 6B0000h–6BFFFFh 358000h–35FFFFh
115 64/32
116 64/32 6D0000h–6DFFFFh 368000h–36FFFFh
117 64/32 6E0000h–6EFFFFh 370000h–377FFFh
118 64/32 6F0000h–6FFFFFh 378000h–37FFFFh
119 64/32
120 64/32 710000h–71FFFFh 388000h–38FFFFh
121 64/32 720000h–72FFFFh 390000h–397FFFh
122 64/32 730000h–73FFFFh 398000h–39FFFFh
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
640000h–64FFFFh 320000h–327FFFh
680000h–68FFFFh 340000h–347FFFh
6C0000h–6CFFFFh 360000h–367FFFh
700000h–70FFFFh 380000h–387FFFh
70/93

M29DW128F 12 Part numbering
Bank Block
123 64/32
124 64/32 750000h–75FFFFh 3A8000h–3AFFFFh
125 64/32 760000h–76FFFFh 3B0000h–3B7FFFh
126 64/32 770000h–77FFFFh 3B8000h–3BFFFFh
127 64/32
128 64/32 790000h–79FFFFh 3C8000h–3CFFFFh
129 64/32 7A0000h–7AFFFFh 3D0000h–3D7FFFh
Bank B
130 64/32 7B0000h–7BFFFFh 3D8000h–3DFFFFh
131 64/32
132 64/32 7D0000h–7DFFFFh 3E8000h–3EFFFFh
133 64/32 7E0000h–7EFFFFh 3F0000h–3F7FFFh
134 64/32 7F0000h-7FFFFFh 3F8000h-3FFFFFh
135 64/32
136 64/32 810000h–81FFFFh 408000h–40FFFFh
137 64/32 820000h–82FFFFh 410000h–417FFFh
Size
(KBytes/
KWords)
Protection Block
Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
(x8) (x16)
740000h–74FFFFh 3A0000h–3A7FFFh
780000h–78FFFFh 3C0000h–3C7FFFh
7C0000h–7CFFFFh 3E0000h–3E7FFFh
800000h–80FFFFh 400000h–407FFFh
138 64/32 830000h–83FFFFh 418000h–41FFFFh
139 64/32
140 64/32 850000h–85FFFFh 428000h–42FFFFh
141 64/32 860000h–86FFFFh 430000h–437FFFh
142 64/32 870000h–87FFFFh 438000h–43FFFFh
143 64/32
144 64/32 890000h–89FFFFh 448000h–44FFFFh
145 64/32 8A0000h–8AFFFFh 450000h–457FFFh
Bank C
146 64/32 8B0000h–8BFFFFh 458000h–45FFFFh
147 64/32
148 64/32 8D0000h–8DFFFFh 468000h–46FFFFh
149 64/32 8E0000h–8EFFFFh 470000h–477FFFh
150 64/32 8F0000h-8FFFFFh 478000h–47FFFFh
151 64/32
152 64/32 910000h–91FFFFh 488000h–48FFFFh
153 64/32 920000h–92FFFFh 490000h–497FFFh
154 64/32 930000h–93FFFFh 498000h–49FFFFh
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
840000h–84FFFFh 420000h–427FFFh
880000h–88FFFFh 440000h–447FFFh
8C0000h–8CFFFFh 460000h–467FFFh
900000h-90FFFFh 480000h–487FFFh
71/93

12 Part numbering M29DW128F
Bank Block
155 64/32
156 64/32 950000h–95FFFFh 4A8000h–4AFFFFh
157 64/32 960000h–96FFFFh 4B0000h–4B7FFFh
158 64/32 970000h–97FFFFh 4B8000h–4BFFFFh
159 64/32
160 64/32 990000h–99FFFFh 4C8000h–4CFFFFh
161 64/32 9A0000h–9AFFFFh 4D0000h–4D7FFFh
162 64/32 9B0000h–9BFFFFh 4D8000h–4DFFFFh
163 64/32
164 64/32 9D0000h–9DFFFFh 4E8000h–4EFFFFh
165 64/32 9E0000h–9EFFFFh 4F0000h–4F7FFFh
166 64/32 9F0000h–9FFFFFh 4F8000h-4FFFFFh
167 64/32
168 64/32 A10000h–A1FFFFh 508000h–50FFFFh
169 64/32 A20000h–A2FFFFh 510000h–517FFFh
Size
(KBytes/
KWords)
Protection Block
Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
(x8) (x16)
940000h–94FFFFh 4A0000h–4A7FFFh
980000h–98FFFFh 4C0000h–4C7FFFh
9C0000h–9CFFFFh 4E0000h–4E7FFFh
A00000h–A0FFFFh 500000h–507FFFh
170 64/32 A30000h–A3FFFFh 518000h–51FFFFh
171 64/32
Bank C
172 64/32 A50000h–A5FFFFh 528000h–52FFFFh
173 64/32 A60000h–A6FFFFh 530000h–537FFFh
174 64/32 A70000h–A7FFFFh 538000h–53FFFFh
175 64/32
176 64/32 A90000h–A9FFFFh 548000h–54FFFFh
177 64/32 AA0000h–AAFFFFh 550000h–557FFFh
178 64/32 AB0000h–ABFFFFh 558000h–55FFFFh
179 64/32
180 64/32 AD0000h–ADFFFFh 568000h–56FFFFh
181 64/32 AE0000h–AEFFFFh 570000h–577FFFh
182 64/32 AF0000h-AFFFFFh 578000h–57FFFFh
183 64/32
184 64/32 B10000h–B1FFFFh 588000h–58FFFFh
185 64/32 B20000h–B2FFFFh 590000h–597FFFh
186 64/32 B30000h-B3FFFFh 598000h–59FFFFh
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
A40000h–A4FFFFh 520000h–527FFFh
A80000h–A8FFFFh 540000h–547FFFh
AC0000h–ACFFFFh 560000h–567FFFh
B00000h–B0FFFFh 580000h–587FFFh
72/93

M29DW128F 12 Part numbering
Bank Block
187 64/32
188 64/32 B50000h–B5FFFFh 5A8000h–5AFFFFh
189 64/32 B60000h–B6FFFFh 5B0000h–5B7FFFh
190 64/32 B70000h-B7FFFFh 5B8000h–5BFFFFh
191 64/32
192 64/32 B90000h–B9FFFFh 5C8000h–5CFFFFh
193 64/32 BA0000h–BAFFFFh 5D0000h–5D7FFFh
194 64/32 BB0000h–BBFFFFh 5D8000h–5DFFFFh
195 64/32
196 64/32 BD0000h–BDFFFFh 5E8000h–5EFFFFh
197 64/32 BE0000h–BEFFFFh 5F0000h–5F7FFFh
198 64/32 BF0000h–BFFFFFh 5F8000h-5FFFFFh
199 64/32
200 64/32 C10000h–C1FFFFh 608000h–60FFFFh
201 64/32 C20000h–C2FFFFh 610000h–617FFFh
Size
(KBytes/
KWords)
Protection Block
Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
(x8) (x16)
B40000h–B4FFFFh 5A0000h–5A7FFFh
B80000h–B8FFFFh 5C0000h–5C7FFFh
BC0000h–BCFFFFh 5E0000h–5E7FFFh
C00000h–C0FFFFh 600000h–607FFFh
202 64/32 C30000h–C3FFFFh 618000h–61FFFFh
203 64/32
Bank C
204 64/32 C50000h–C5FFFFh 628000h–62FFFFh
205 64/32 C60000h–C6FFFFh 630000h–637FFFh
206 64/32 C70000h-C7FFFFh 638000h–63FFFFh
207 64/32
208 64/32 C90000h–C9FFFFh 648000h–64FFFFh
209 64/32 CA0000h–CAFFFFh 650000h–657FFFh
210 64/32 CB0000h–CBFFFFh 658000h–65FFFFh
211 64/32
212 64/32 CD0000h–CDFFFFh 668000h–66FFFFh
213 64/32 CE0000h–CEFFFFh 670000h–677FFFh
214 64/32 CF0000h-CFFFFFh 678000h–67FFFFh
215 64/32
216 64/32 D10000h–D1FFFFh 688000h–68FFFFh
217 64/32 D20000h–D2FFFFh 690000h–697FFFh
218 64/32 D30000h–D3FFFFh 698000h–69FFFFh
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
C40000h–C4FFFFh 620000h–627FFFh
C80000h–C8FFFFh 640000h–647FFFh
CC0000h–CCFFFFh 660000h–667FFFh
D00000h–D0FFFFh 680000h–687FFFh
73/93

12 Part numbering M29DW128F
Bank Block
219 64/32
220 64/32 D50000h–D5FFFFh 6A8000h–6AFFFFh
221 64/32 D60000h–D6FFFFh 6B0000h–6B7FFFh
222 64/32 D70000h-D7FFFFh 6B8000h–6BFFFFh
223 64/32
224 64/32 D90000h-D9FFFFh 6C8000h–6CFFFFh
225 64/32 DA0000h-DAFFFFh 6D0000h–6D7FFFh
Bank C
226 64/32 DB0000h-DBFFFFh 6D8000h–6DFFFFh
227 64/32
228 64/32 DD0000h-DDFFFFh 6E8000h–6EFFFFh
229 64/32 DE0000h-DEFFFFh 6F0000h–6F7FFFh
230 64/32 DF0000h-DFFFFFh 6F8000h-6FFFFFh
231 64/32
232 64/32 E10000h-E1FFFFh 708000h–70FFFFh
233 64/32 E20000h-E2FFFFh 710000h–717FFFh
Size
(KBytes/
KWords)
Protection Block
Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
(x8) (x16)
D40000h–D4FFFFh 6A0000h–6A7FFFh
D80000h-D8FFFFh 6C0000h–6C7FFFh
DC0000h-DCFFFFh 6E0000h–6E7FFFh
E00000h-E0FFFFh 700000h–707FFFh
234 64/32 E30000h-E3FFFFh 718000h–71FFFFh
235 64/32
236 64/32 E50000h-E5FFFFh 728000h–72FFFFh
237 64/32 E60000h-E6FFFFh 730000h–737FFFh
238 64/32 E70000h-E7FFFFh 738000h–73FFFFh
239 64/32
240 64/32 E90000h-E9FFFFh 748000h–74FFFFh
241 64/32 EA0000h-EAFFFFh 750000h–757FFFh
Bank D
242 64/32 EB0000h-EBFFFFh 758000h–75FFFFh
243 64/32
244 64/32 ED0000h-EDFFFFh 768000h–76FFFFh
245 64/32 EE0000h-EEFFFFh 770000h–777FFFh
246 64/32 EF0000h-EFFFFFh 778000h–77FFFFh
247 64/32
248 64/32 F10000h-F1FFFFh 788000h–78FFFFh
249 64/32 F20000h-F2FFFFh 790000h–797FFFh
250 64/32 F30000h-F3FFFFh 798000h–79FFFFh
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
E40000h-E4FFFFh 720000h–727FFFh
E80000h-E8FFFFh 740000h–747FFFh
EC0000h-ECFFFFh 760000h–767FFFh
F00000h-F0FFFFh 780000h–787FFFh
74/93

M29DW128F 12 Part numbering
Bank Block
251 64/32
252 64/32 F50000h-F5FFFFh 7A8000h–7AFFFFh
253 64/32 F60000h-F6FFFFh 7B0000h–7B7FFFh
254 64/32 F70000h-F7FFFFh 7B8000h–7BFFFFh
255 64/32
256 64/32 F90000h-F9FFFFh 7C8000h–7CFFFFh
257 64/32 FA0000h-FAFFFFh 7D0000h–7D7FFFh
258 64/32 FB0000h-FBFFFFh 7D8000h–7DFFFFh
259 64/32
260 64/32 FD0000h-FDFFFFh 7E8000h–7EFFFFh
261 64/32 FE0000h-FEFFFFh 7F0000h-7F7FFFh
Bank D
262 8/4 Protection Group
263 8/4 Protection Group
264 8/4 Protection Group
265 8/4 Protection Group
266 8/4 Protection Group
267 8/4 Protection Group
268 8/4 Protection Group
269 8/4 Protection Group
1. Parameter Blocks.
Size
(KBytes/
KWords)
Protection Block
Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
Protection Group
(x8) (x16)
F40000h-F4FFFFh 7A0000h–7A7FFFh
F80000h-F8FFFFh 7C0000h–7C7FFFh
FC0000h-FCFFFFh 7E0000h–7E7FFFh
FF0000h-FF1FFFh
FF2000h-FF3FFFh
FF4000h-FF5FFFh
FF6000h-FF7FFFh
FF8000h-FF9FFFh
FFA000h-FFBFFFh
FFC000h-FFDFFFh
FFE000h-FFFFFFh
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
7F8000h-7F8FFFh
7F9000h-7F9FFFh
7FA000h-7FAFFFh
7FB000h-7FBFFFh
7FC000h-7FCFFFh
7FD000h-7FDFFFh
7FE000h-7FEFFFh
7FF000h-7FFFFFh
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
75/93

12 Part numbering M29DW128F
Appendix B Common Flash Interface (CFI)
The Common Flash Interface is a JEDEC approved, standardized data structure that can be
read from the Flash memory device. It allows a system software to query the device to
determine various electrical and timing parameters, density information and functions
supported by the memory. The system can interface easily with the device, enabling the
software to upgrade itself when necessary.
When the Read CFI Query command is issued the addressed bank enters Read CFI Query
mode and read operations in the same bank (A22-A19) output the CFI data. Ta bl e 3 5, Tab le 3 6,
Ta bl e 3 7 , Tab le 3 8, Ta b le 3 9 and Ta bl e 4 0 show the addresses (A-1, A0-A10) used to retrieve
the data.
The CFI data structure also contains a security area where a 64 bit unique security number is
written (see Table 40: Security Code Area). This area can be accessed only in Read mode by
the final user. It is impossible to change the security number after it has been written by ST.
Table 35. Query Structure Overview
Address
Sub-section Name Description
x16 x8
10h 20h CFI Query Identification String Command set ID and algorithm data offset
1Bh 36h System Interface Information Device timing & voltage information
27h 4Eh Device Geometry Definition Flash device layout
40h 80h
61h C2h Security Code Area 64 bit unique device number
1. Query data are always presented on the lowest order data outputs.
Primary Algorithm-specific Extended
Query table
Additional information specific to the Primary
Algorithm (optional)
76/93

M29DW128F 12 Part numbering
Table 36. CFI Query Identification String
Address
Data Description Value
x16 x8
10h 20h 0051h “Q”
11h 22h 0052h Query Unique ASCII String "QRY" "R"
12h 24h 0059h "Y"
13h 26h 0002h
14h 28h 0000h
Primary Algorithm Command Set and Control Interface ID code 16 bit
ID code defining a specific algorithm
AMD
Compatible
15h 2Ah 0040h
16h 2Ch 0000h
17h 2Eh 0000h
18h 30h 0000h
19h 32h 0000h
1Ah 34h 0000h
1. Query data are always presented on the lowest order data outputs (DQ7-DQ0) only. DQ8-DQ15 are ‘0’.
Address for Primary Algorithm extended Query table (see Ta bl e 3 9)P = 40h
Alternate Vendor Command Set and Control Interface ID Code
second vendor - specified algorithm supported
Address for Alternate Algorithm extended Query table NA
NA
77/93

12 Part numbering M29DW128F
Table 37. CFI Query System Interface Information
Address
Data Description Value
x16 x8
VCC Logic Supply Minimum Program/Erase voltage
1Bh 36h 0027h
1Ch 38h 0036h
1Dh 3Ah 00B5h
1Eh 3Ch 00C5h
1Fh 3Eh 0004h
20h 40h 0000h
bit 7 to 4BCD value in volts
bit 3 to 0BCD value in 100mV
V
Logic Supply Maximum Program/Erase voltage
CC
bit 7 to 4BCD value in volts
bit 3 to 0BCD value in 100mV
VPP [Programming] Supply Minimum Program/Erase voltage
bit 7 to 4HEX value in volts
bit 3 to 0BCD value in 100mV
[Programming] Supply Maximum Program/Erase voltage
V
PP
bit 7 to 4HEX value in volts
bit 3 to 0BCD value in 10mV
n
Typical timeout per single Byte/Word program = 2
Typical timeout for minimum size write buffer program = 2
µs
n
µs
2.7V
3.6V
11.5V
12.5V
16µs
NA
21h 42h 0009h
22h 44h 0000h
23h 46h 0005h
24h 48h 0000h
25h 4Ah 0004h
26h 4Ch 0000h
1. The values given in the above table are valid for both packages.
Typical timeout per individual block erase = 2n ms
Typical timeout for full Chip Erase = 2n ms
Maximum timeout for Byte/Word program = 2
Maximum timeout for write buffer program = 2n times typical
Maximum timeout per individual block erase = 2n times typical
Maximum timeout for Chip Erase = 2
n
times typical
n
times typical
512ms
NA
512µs
NA
8s
NA
78/93

M29DW128F 12 Part numbering
Table 38. Device Geometry Definition
Address
Data Description Value
x16 x8
27h 4Eh 0018h
0001h
28h 50h
0002h
29h 52h 0000h
2Ah 54h 0006h
2Bh 56h 0000h
2Ch 58h 0003h
2Dh
2Eh
2Fh
30h
31h
32h
33h
34h
35h
36h
37h
38h
39h
3Ah
3Bh
3Ch
5Ah
5Ch
5Eh
60h
62h
64h
66h
68h
6Ah
6Ch
6Eh
70h
72h
74h
76h
78h
0007h
0000h
0020h
0000h
00FDh
0000h
0000h
0001h
0007h
0000h
0020h
0000h
0000h
0000h
0000h
0000h
Device Size = 2
n
in number of Bytes
MBytes
TBGA64
(x16 only)
TSOP56
(x8/x16)
Flash Device Interface Code description
x8, x16
Async.
Both
Packages
Maximum number of Bytes in Multiple-Byte program or Page= 2
(1)
Number of Erase Block Regions
. It specifies the number of regions
n
containing contiguous Erase Blocks of the same size.
Erase Block Region 1 Information
Number of Erase Blocks of identical size = 0007h+1
Erase Block Region 1 Information
Block size in Region 1 = 0020h * 256 Byte
Erase Block Region 2 Information
Number of Erase Blocks of identical size = 00FDh+1
KBytes
254
Erase Block Region 2 Information
Block size in Region 2 = 0100h * 256 Byte
KBytes
Erase Block Region 3 information
Number of Erase Blocks of identical size = 0007h + 1
Erase Block Region 3 information
Block size in region 3 = 0020h * 256 Bytes
KBytes
Erase Block Region 4 information 0
16
64
3
8
8
64
8
8
1. Erase Block Region 1 corresponds to addresses 000000h to 007FFFh; Erase block Region 2 corresponds to addresses
008000h to 3F7FFFh and Erase Block Region 3 corresponds to addresses 3F8000h to 3FFFFFh.
79/93

12 Part numbering M29DW128F
Table 39. Primary Algorithm-Specific Extended Query Table
Address
Data Description Value
x16 x8
40h 80h 0050h
41h 82h 0052h "R"
Primary Algorithm extended Query table unique ASCII string “PRI”
"P"
42h 84h 0049h "I"
43h 86h 0031h Major version number, ASCII "1"
44h 88h 0033h Minor version number, ASCII "3"
Address Sensitive Unlock (bits 1 to 0)
45h 8Ah 000Ch
00 = required, 01= not required
Ye s
Silicon Revision Number (bits 7 to 2)
46h 8Ch 0002h
47h 8Eh 0001h
48h 90h 0001h
49h 92h 0006h
4Ah 94h 00E7
Erase Suspend
00 = not supported, 01 = Read only, 02 = Read and Write
Block Protection
00 = not supported, x = number of sectors in per group
Temporary Block Unprotect
00 = not supported, 01 = supported
Block Protect /Unprotect
06 = M29DW128F
Simultaneous Operations,
x = number of blocks (excluding Bank A)
2
1
Ye s
6
231
4Bh 96h 0000h Burst Mode, 00 = not supported, 01 = supported No
4Ch 98h 0002h Page Mode, 00 = not supported, 02 = 8-Word page Yes
V
Supply Minimum Program/Erase voltage
PP
4Dh 9Ah 00B5h
bit 7 to 4 HEX value in volts
11.5V
bit 3 to 0 BCD value in 100mV
VPP Supply Maximum Program/Erase voltage
4Eh 9Ch 00C5h
bit 7 to 4 HEX value in volts
12.5V
bit 3 to 0 BCD value in 100mV
Top/Bottom Boot Block Flag
00h = Uniform device
01h = 8 x8 KByte Blocks or 4KWords, Top and Bottom Boot with
4Fh 9Eh 0001h
Write Protect
T/B
02h = Bottom boot device
03h = Top Boot Device
04h = Both Top and Bottom
50h A0h 0001h Program Suspend, 00 = not supported, 01 = supported Yes
57h AEh 0004h
58h B0h 0027h
Bank Organization, 00 = data at 4Ah is zero
X = number of banks
Bank A information
X = number of blocks in Bank A
4
39
80/93

M29DW128F 12 Part numbering
Address
Data Description Value
x16 x8
59h B2h 0060h
5Ah B4h 0060h
5Bh B6h 0027h
1. The values given in the above table are valid for both packages.
Bank B information
X = number of blocks in Bank B
Bank C information
X = number of blocks in Bank C
Bank D information
X = number of blocks in Bank D
Table 40. Security Code Area
Address
Data Description
x16 x8
61h C3h, C2h XXXX
62h C5h, C4h XXXX
63h C7h, C6h XXXX
64h C9h, C8h XXXX
64 bit: unique device number
96
96
39
81/93

12 Part numbering M29DW128F
Appendix C Extended Memory Block
The M29DW128F has an extra block, the Extended Block, that can be accessed using a
dedicated command.
This Extended Block is 128 Words in x16 mode and 256 Bytes in x8 mode. It is used as a
security block (to provide a permanent security identification number) or to store additional
information.
The Extended Block is divided into two memory areas of 64 Words each:
● The first one is Factory Locked.
● The second one is Customer Lockable. It is up to the customer to protect it from program
operations. Its status is indicated by bit DQ6 and DQ7. When DQ7 is set to ‘1’ and DQ6 to
‘0’, it indicates that this second memory area is Customer Lockable. When DQ7 and DQ6
are both set to ‘1’, it indicates that the second part of the Extended Block is Customer
Locked and protected from program operations. Bit DQ7 being permanently locked to
either ‘1’ or ‘0’ is another security feature which ensures that a customer lockable device
cannot be used instead of a factory locked one.
Bits DQ6 and DQ7 are the most significant bits in the Extended Block Protection Indicator and
a specific procedure must be followed to read it. See “Section 3.6.2: Verify Extended Block
Protection Indicator” and Ta bl e 5 and Ta bl e 8 , Block Protection, for details of how to read bit
DQ7.
The Extended Block can only be accessed when the device is in Extended Block mode. For
details of how the Extended Block mode is entered and exited, refer to the Program command
and Exit Extended Block command paragraphs, and to Ta bl e 1 5 and Tab le 1 6, Block Protection
Commands.
C.1 Factory Locked Section of the Extended Block
The first section of The Extended Block is permanently protected from program operations and
cannot be unprotected. The Random Number, Electronic Serial Number (ESN) and Security
Identification Number (see Table 41: Extended Block Address and Data) are written in this
section in the factory.
C.2 Customer Lockable Section of the Extended Block
The device is delivered with the second section of the Extended Block "Customer Lockable":
bits DQ7 and DQ6 are set to '1' and '0' respectively. It is up to the customer to program and
protect this section of the Extended Block but care must be taken because the protection is not
reversible.
There are three ways of protecting this section:
● Issue the Enter Extended Block command to place the device in Extended Block mode,
then use the In-System Technique with RP
Technique in Appendix D: High Voltage Block Protection, and to the corresponding
flowcharts Figure 25 and Figure 26 for a detailed explanation of the technique).
● Issue the Enter Extended Block command to place the device in Extended Block mode,
then use the Programmer Technique. Refer to Programmer Technique in Appendix D: High
either at VIH or at VID. Refer to In-System
82/93

M29DW128F 12 Part numbering
Voltage Block Protection, and to the corresponding flowcharts Figure 23 and Figure 24 for
a detailed explanation of the technique).
● Issue a Set Extended Block Protection Bit command to program the Extended Block
Protection Bit to ‘1’ thus preventing the second section of the Extended Block from being
programmed.
Bit DQ6 of the Extended Block Protection Indicator is automatically set to '1' to indicate that the
second section of the Extended Block is Customer Locked.
Once the Extended Block is programmed and protected, the Exit Extended Block command
must be issued to exit the Extended Block mode and return the device to Read mode.
Table 41. Extended Block Address and Data
Device
Address
x8 x16 Factory Locked Customer Lockable
(1)
Data
000000h-
00007Fh
M29DW128F
000080h0000FFh
1. See Table 34: Block Addresses and Protection Groups.
2. ESN = Electronic Serial Number.
000000h-
00003Fh
000040h-
00007Fh
(2)
Random Number, ESN
Security Identification Number
Unavailable
,
Unavailable
Determined by
Customer
83/93

12 Part numbering M29DW128F
Appendix D High Voltage Block Protection
The High Voltage Block Protection can be used to prevent any operation from modifying the
data stored in the memory. The blocks are protected in groups, refer to Appendix A, Ta bl e 34 for
details of the Protection Groups. Once protected, Program and Erase operations within the
protected group fail to change the data.
There are three techniques that can be used to control Block Protection, these are the
Programmer technique, the In-System technique and Temporary Unprotection. Temporary
Unprotection is controlled by the Reset/Block Temporary Unprotection pin, RP
in the Signal Descriptions section.
To protect the Extended Block issue the Enter Extended Block command and then use either
the Programmer or In-System technique. Once protected issue the Exit Extended Block
command to return to read mode. The Extended Block protection is irreversible, once protected
the protection cannot be undone.
D.1 Programmer Technique
The Programmer technique uses high (VID) voltage levels on some of the bus pins. These
cannot be achieved using a standard microprocessor bus, therefore the technique is
recommended only for use in Programming Equipment.
; this is described
To protect a group of blocks follow the flowchart in Figure 23: Programmer Equipment Group
Protect Flowchart. To unprotect the whole chip it is necessary to protect all of the groups first,
then all groups can be unprotected at the same time. To unprotect the chip follow Figure 24:
Programmer Equipment Chip Unprotect Flowchart. Table 42: Programmer Technique Bus
Operations, 8-bit or 16-bit Mode, gives a summary of each operation.
The timing on these flowcharts is critical. Care should be taken to ensure that, where a pause is
specified, it is followed as closely as possible. Do not abort the procedure before reaching the
end. Chip Unprotect can take several seconds and a user message should be provided to show
that the operation is progressing.
D.2 In-System Technique
The In-System technique requires a high voltage level on the Reset/Blocks Temporary
Unprotect pin, RP
components on the microprocessor bus, therefore this technique is suitable for use after the
memory has been fitted to the system.
To protect a group of blocks follow the flowchart in Figure 25: In-System Equipment Group
Protect Flowchart. To unprotect the whole chip it is necessary to protect all of the groups first,
then all the groups can be unprotected at the same time. To unprotect the chip follow Figure 26:
In-System Equipment Chip Unprotect Flowchart.
The timing on these flowcharts is critical. Care should be taken to ensure that, where a pause is
specified, it is followed as closely as possible. Do not allow the microprocessor to service
interrupts that will upset the timing and do not abort the procedure before reaching the end.
Chip Unprotect can take several seconds and a user message should be provided to show that
the operation is progressing.
(1)
. This can be achieved without violating the maximum ratings of the
84/93

M29DW128F 12 Part numbering
Note 1: RP can be either at V
or at V
IH
when using the In-System Technique to protect the
ID
Extended Block.
Table 42. Programmer Technique Bus Operations, 8-bit or 16-bit Mode
Operation E G W
Block (Group) Protect
Chip Unprotect
(1)
V
V
ILVIDVIL
IDVIDVIL
Pulse
Pulse
A9 = VID, A12-A22 Block Address
A0 = VIL, A1 = VIH, A2-A7 = VIL,
Block (Group) Protect
Ver if y
V
V
IL
V
IL
IH
A9 = VID, A12-A22 Block Address
A0 = VIL, A1 = VIH, A2 -A5 = VIL,
Block (Group) Unprotect
Ver if y
1. Block Protection Groups are shown in Appendix D, Table 34.
V
V
IL
V
IL
IH
A9 = V
Address Inputs
A0-A22
Others = X
A6 = V
, A9 = VID, A12 = VIH,
IH
A15 = VIH Others = X
Others = X
A6 = V
ID
, A7 = VIL,
IH
, A12-A22 Block Address
Others = X
Data Inputs/Outputs
DQ15A–1, DQ14-DQ0
X
X
Pass = xx01h
Retry = xx00h.
Pass = xx00h
Retry = xx01h.
85/93

12 Part numbering M29DW128F
Appendix E Flowcharts
Figure 23. Programmer Equipment Group Protect Flowchart
START
ADDRESS =
GROUP ADDRESS
W = V
IH
n = 0
G, A9 = VID,
E = V
IL
Wait 4µs
W = V
IL
Verify Protect Set-upEnd
Wait 100µs
W = V
IH
E, G = VIH, A1 = V
A0, A2 to A7 = V
E = V
IL
Wait 4µs
G = V
IL
Wait 60ns
Read DATA
DATA = 01h
YES
A9 = V
IH
E, G = V
IH
IH
IL
NO
++n
= 25
A9 = V
E, G = V
NO
YES
IH
IH
1. Block Protection Groups are shown in Appendix D, Table 34.
86/93
FAILPASS
AI07756b

M29DW128F 12 Part numbering
Figure 24. Programmer Equipment Chip Unprotect Flowchart
START
PROTECT ALL
GROUPS
n = 0
CURRENT GROUP = 0
A6, A12, A15 = V
E, G, A9 = V
Wait 4µs
W = V
Wait 10ms
W = V
E, G = V
ADDRESS = CURRENT
GROUP ADDRESS
A0, A2, A3, A4, A5, A7 = V
A1, A6 = V
E = V
Wait 4µs
G = V
(1)
IH
ID
IL
IH
IH
IH
IL
IL
IL
INCREMENT
CURRENT GROUP
Verify Unprotect Set-upEnd
NO
++n
= 1000
YES
A9 = V
IH
E, G = V
IH
FAIL PASS
Wait 60ns
Read DATA
DATA = 00h
1. Block Protection Groups are shown in Appendix D, Table 34.
YESNO
LAST
GROUP
A9 = V
E, G = V
NO
YES
IH
IH
AI07757b
87/93

12 Part numbering M29DW128F
Figure 25. In-System Equipment Group Protect Flowchart
START
n = 0
RP = V
ID
Verify Protect Set-upEnd
ADDRESS = GROUP ADDRESS
ADDRESS = GROUP ADDRESS
ADDRESS = GROUP ADDRESS
ADDRESS = GROUP ADDRESS
WRITE 60h
A0, A2, A3, A6 = V
WRITE 60h
A0, A2, A3, A6 = V
Wait 100µs
WRITE 40h
A0, A2, A3, A6 = V
Wait 4µs
READ DATA
A1 = VIH, A0, A2 to A7 = V
DATA = 01h
RP = V
ISSUE READ/RESET
COMMAND
IL,
IL,
IL,
YES
IH
A1 = V
A1 = V
A1 = V
NO
IH
IH
IH
IL
++n
= 25
RP = V
NO
YES
IH
PASS
1. Block Protection Groups are shown in Appendix D, Table 34.
can be either at V
2. RP
IH
or at V
when using the In-System Technique to protect the Extended Block.
ID
88/93
ISSUE READ/RESET
COMMAND
FAIL
AI07758b

M29DW128F 12 Part numbering
Figure 26. In-System Equipment Chip Unprotect Flowchart
START
PROTECT ALL GROUPS
n = 0
CURRENT GROUP = 0
RP = V
ID
WRITE 60h
ANY ADDRESS WITH
A1 = VIH, A0, A2 to A7 = V
WRITE 60h
ANY ADDRESS WITH
A0, A2, A3, A4, A5, A7 = V
A1, A6 = V
Wait 10ms
IL
IL
IH
Verify Unprotect Set-upEnd
WRITE 40h
ADDRESS =
CURRENT GROUP ADDRESS
A1 = VIH, A0, A2 to A7 = V
Wait 4µs
READ DATA
ADDRESS =
CURRENT GROUP ADDRESS
A1 = VIH, A0, A2 to A7 = V
DATA = 00h
NO
++n
= 1000
YES
RP = V
IH
ISSUE READ/RESET
COMMAND
FAIL PASS
IL
IL
YESNO
INCREMENT
CURRENT GROUP
LAST
GROUP
YES
RP = V
IH
ISSUE READ/RESET
COMMAND
NO
AI07759d
1. Block Protection Groups are shown in Appendix D, Table 34.
89/93

12 Part numbering M29DW128F
Figure 27. Write to Buffer and Program Flowchart and Pseudo Code
Start
Write to Buffer F0h
Command,
Block Address
(1)
Write n
Block Address
Write Buffer Data,
Start Address
X=n
,
First Part of the
Write to Buffer and Program Command
NO
DQ1 = 1
X = 0
NO
Abort Write
to Buffer
NO
Write Next Data,
Program Address Pair
X = X-1
Program Buffer
to Flash Block Address
Read Status Register
(DQ1, DQ5, DQ7) at
Last Loaded Address
YES
DQ7 = Data
NO
NO
DQ5 = 1
YES
YES
Write to a Different
Write to Buffer and
(3)
Program Aborted
Block Address
(2)
YES
YES
Check Status Register
(DQ5, DQ7) at
Last Loaded Address
DQ7 = Data
(4)
YES
NO
FAIL OR ABORT
(5)
END
1. n+1 is the number of addresses to be programmed.
2. A Write to Buffer and Program Abort and Reset must be issued to return the device in Read mode.
90/93
AI08968b

M29DW128F 12 Part numbering
3. When the block address is specified, any address in the selected block address space is acceptable. However when
loading Write Buffer address with data, all addresses must fall within the selected Write Buffer page.
4. DQ7 must be checked since DQ5 and DQ7 may change simultaneously.
5. If this flowchart location is reached because DQ5=’1’, then the Write to Buffer and Program command failed. If this
flowchart location is reached because DQ1=’1’, then the Write to Buffer and Program command aborted. In both cases, the
appropriate reset command must be issued to return the device in Read mode: a Reset command if the operation failed, a
Write to Buffer and Program Abort and Reset command if the operation aborted.
6. See Table 11 and Table 12, for details on Write to Buffer and Program command sequence.
91/93

13 Revision History M29DW128F
13 Revision History
Table 43. Document Revision History
Date Version Revision Details
02-Aug-2005 0.1 First Issue derived from the M29DW128F/FS datasheet revision 0.5.
92/93

M29DW128F
Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, STMicroelectronics assumes no responsibility for the consequences
of use of such information nor for any infringement of patents or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. No license is granted
by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of STMicroelectronics. Specifications mentioned in this publication are subject
to change without notice. This publication supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied. STMicroelectronics products are not
authorized for use as critical components in life support devices or systems without express written approval of STMicroelectronics.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics.
All other names are the property of their respective owners
© 2005 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
STMicroelectronics group of companies
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
93/93
 Loading...
Loading...