Page 1
Features
L6706
VR11.1 single phase controller with integrated driver
■ 8-bit programmable output up to 1.60000 V -
■ High current embedded driver
■ High output voltage accuracy
■ Programmable droop function
■ Imon output
■ Load transient boost LTB Technology™ to
®
Intel
VR11.1 DAC
minimize the number of output capacitors
■ Full differential current sense across inductor
■ Differential remote voltage sensing
■ Adjustable voltage offset
■ LSLess startup to manage pre-biased output
■ Feedback disconnection protection
■ Preliminary overvoltage protection
■ Programmable overcurrent protection
■ Programmable overvoltage protection
■ Adjustable switching frequency
■ SSEND and OUTEN signal
■ VFQFPN-40 6x6 mm package with exp. pad
VFQFPN-40 6 x 6 mm
Description
The device implements a single phase step-down
controller with integrated high current driver in a
compact 6x6 mm body package with exposed
pad.
The device embeds VR11.x DACs: the output
voltage ranges up to 1.60000 V managing D-VID
with high output voltage accuracy over line and
temperature variations.
Imon capability guarantee full compatibility with
VR11.1 enabling additional power saving
technique.
Programmable droop function allows to supply all
the latest Intel CPU rails.
Applications
■ VTT and VAXG rails
■ CPU power supply
■ High density DC/DC converters
Load transient boost LTB Technology™ reduces
system cost by providing the fastest response to
load transition.
The controller assures fast protection against load
over current and under / over voltage. Feedback
disconnection prevents from damaging the load in
case of disconnections in the system board.
In case of over-current, the system works in
constant current mode until UVP.
Table 1. Device summary
January 2010 Doc ID 15698 Rev 2 1/47
Order codes Package Packing
L6706
Tr ay
VFQFPN-40
L6706TR Tape and reel
www.st.com
47
Page 2

Contents L6706
Contents
1 Principle application circuit and block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
1.1 Principle application circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
1.2 Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2 Pins description and connection diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2.1 Pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2.2 Thermal data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
3 Electrical specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3.1 Absolute maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3.2 Electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
4 Voltage identifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
5 Device description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
6 DAC and current reading . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
7 Differential remote voltage sensing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
8 Voltage positioning . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
8.1 Offset (optional) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
8.2 Droop function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
9 Droop thermal compensation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
10 Output current monitoring (IMON) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
11 Load transient boost technology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
12 Dynamic VID transitions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
13 Enable and disable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
14 Soft-start . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
2/47 Doc ID 15698 Rev 2
Page 3

L6706 Contents
14.1 Low-side-less startup . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
15 Output voltage monitor and protections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
15.1 Undervoltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
15.2 Preliminary overvoltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
15.3 Over voltage and programmable OVP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
15.4 Overcurrent protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
15.5 Feedback disconnection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
16 Oscillator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
17 Driver section . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
18 System control loop compensation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
19 Power dissipation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
20 Layout guidelines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
20.1 Power components and connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
20.2 Small signal components and connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
20.3 Embedding L6706 - Based VR . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
21 Package mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
22 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Doc ID 15698 Rev 2 3/47
Page 4
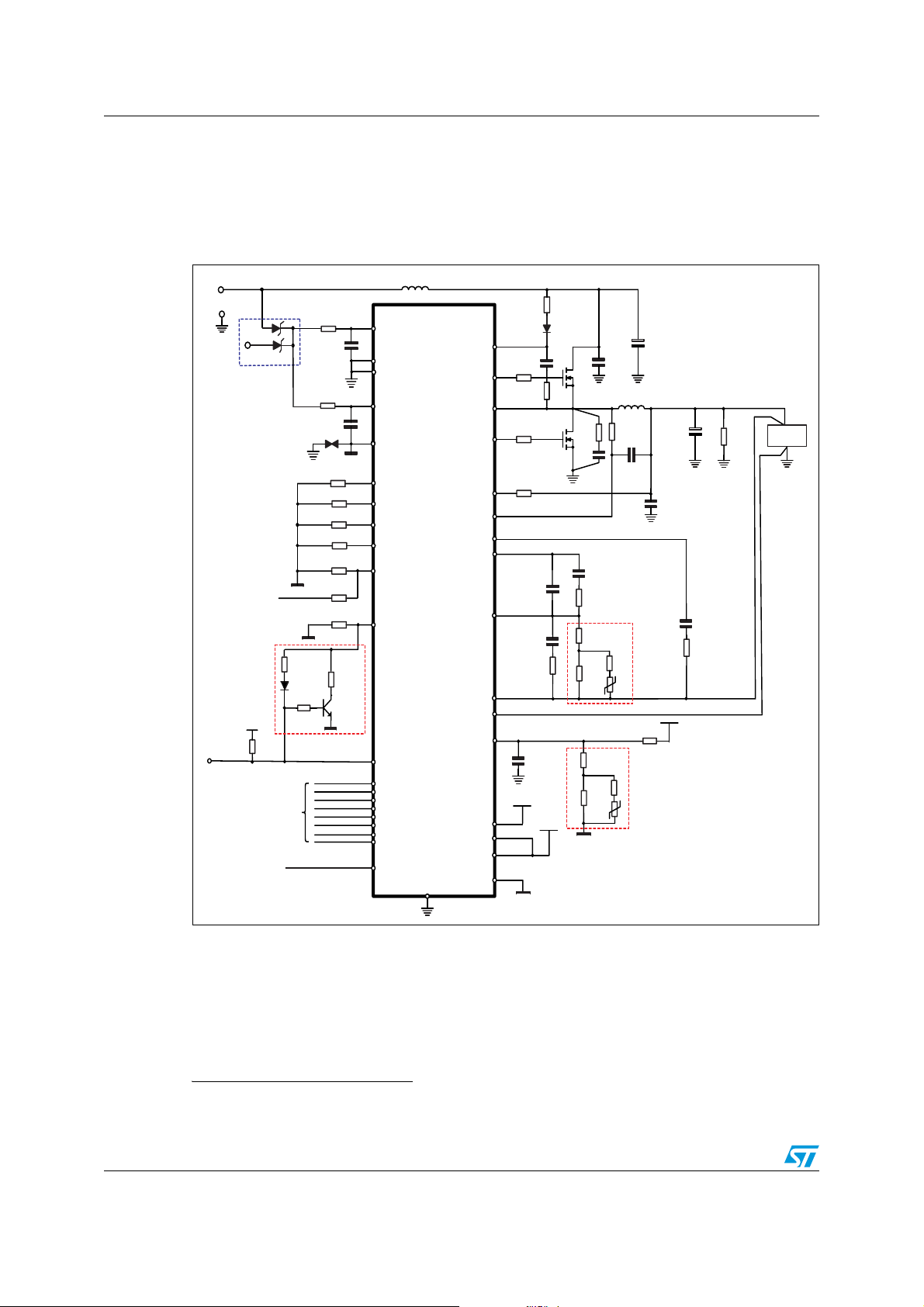
Principle application circuit and block diagram L6706
1 Principle application circuit and block diagram
1.1 Principle application circuit
Figure 1. Principle application circuit
L
V
IN
= 12V
GND
SS_END
IN
5V
SB
Optional:Pre-OVP
Optional:
See DS
VTT
1k
V
cc
To Vcc
R
SSOSC
D
10k
VID bus from CPU
To Enable circuitry
L6706 REF.SCH
R
OVP
R
OCSET
R
OFFSET
R
LTBGAIN
R
OSC_SGND
R
OSC_VCC
R
SS_FLIM
R
Q
FLIMT
35
37
1
3
2
12
13
11
10
14
15
29
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
16
IN
VCCDR
PGND
DGND
VCC
SGND
OVPSEL
OCSET
OFFSET
LTBGAIN
OSC/FAULT
SSOSC/FLIMIT
SSEND
VID7
VID6
VID5
VID4
VID3
VID2
VID1
VID0
OUTEN
EXPAD
UGATE
PHASE
L6706
41
BOOT
LGATE
COMP
VSEN
IMON
INT1
INT3
INT4
INT2
CS-
CS+
LTB
FB
FBG
(a)
38
40
39
36
18
Rg
HS1
LS1
V
IN
17
L1
R
C
220nF
C
IN
Vcc_core
C
OUT
LOAD
R
OUT
GND_core
8
4
C
F
C
P
R
5
C
i
R
i
6
F
R
FB
R
FB1
R
FB2
R
FB3
Optional:
See DS
C
LTB
R
LTB
NTC
7
9
CI
MON
R
1
R
+3V3
19
+12V
31
33
28
2
R
3
NTC
R
IMON_OS
R
IMON_TOT
Optional:
See DS
+3V3
a. Refer to the application note for the reference schematic.
4/47 Doc ID 15698 Rev 2
Page 5
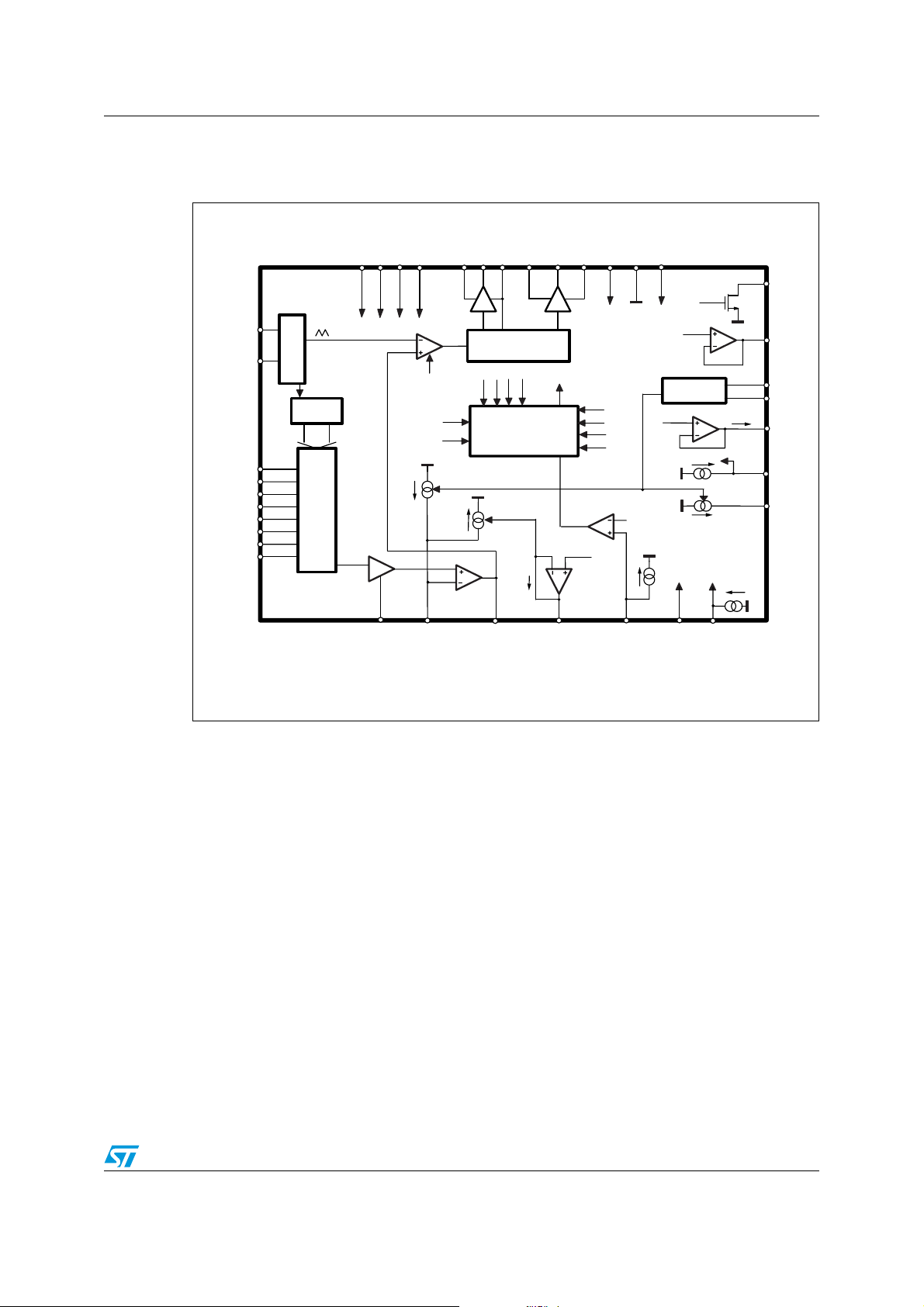
L6706 Principle application circuit and block diagram
1.2 Block diagram
Figure 2. Block diagram
OSC / FAULT
SSOSC/
FLIMT
VID0
VID1
VID2
VID3
VID4
VID5
VID6
VID7
OSCILLATOR
DIGITAL
SOFT START
DAC
WITH DYNAMIC
VID CONTROL
GND DROP
RECOVERY
INT1
INT2
FBG
INT3
VREF
INT4
BOOT
UGATE
PHASE
VCCDR
LGATE
PGND
VCC
SGND
DGND
SSEND
50uA
INFO
+.1240V
CH CURRENT
READING
+.1240V
20uA
LTB
LTB
OUTEN
OUTEN
I
DROOP
I
OVP
10uA
LTBGAIN
CS-
CS+
OCSET
OCSET
OVPSEL
IMON
LOGIC PWM
ADAPTIVE ANTI
CROSS CONDUCTION
PWM
LTB
INT1
INT2
SSOSC
OUTEN
DROOP
I
CONTROL LOGIC
AND PROTECTIONS
DELIVERED CURRENT
OFFSET
I
ERROR
AMPLIFIER
FB
COMP
INT3
L6706
INT4
OFFSET
I
PWM1
OFFSET
VCC
VCCDR
OCSET
INFO
OVP
COMPARATOR
+.1240V
+175mV
1.800V / OVP
VSEN
Doc ID 15698 Rev 2 5/47
Page 6
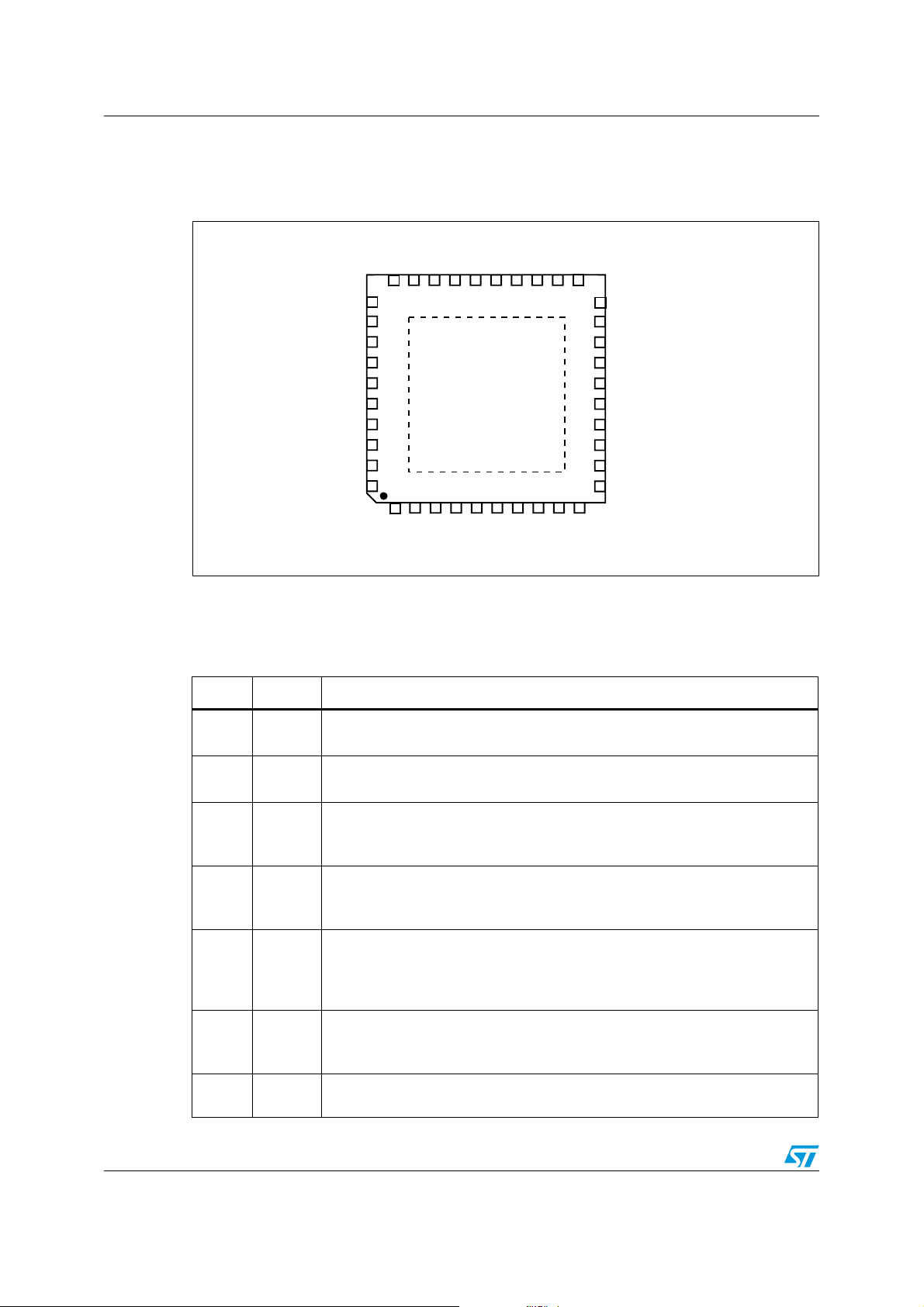
Pins description and connection diagrams L6706
2 Pins description and connection diagrams
Figure 3. Pins connection (top view)
SSEND
INT2
VID7
VID6
VID5
VID4
VID3
VID2
10
VID1
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
VID0
INT1
CS-
CS+
OUTEN
SSOSC/FLIMIT
OSC/FAULT
OCSET
OVPSEL
OFFSET
INT3
N.C.
INT4
N.C.
VCCDR
LGATE
PGND
PHASE
UGATE
BOOT
N.C.
27 26 25 24 23 22 21
28
30
29
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
123456789
L6706
2.1 Pin description
Table 2. Pin description
N° Name Description
1DGND
2SGND
3VCC
4COMP
5FB
Digital GND.
It must be connected to PGND (power ground).
All the internal references are referred to this pin.
Connect it to the PCB signal ground.
Device supply voltage pin.
The operative supply voltage is 12 V ±15%. Filter with 1 x 1 µF MLCC capacitor
vs. SGND.
Error amplifier output.
Connect with an R
pulling down this pin.
Error amplifier inverting input pin.
Connect with a resistor R
current proportional to the load current is sourced from this pin in order to
implement the droop effect. See “Droop function” Section for details.
SGND
DGND
VCC
FB
COMP
VSEN
FBG
LT B
IMON
LTBGAIN
- CF//CP vs. FB pin. The device cannot be disabled by
F
vs. VSEN and with an RF - CF//CP vs. COMP pin. A
FB
6 VSEN
Output voltage monitor, manages OVP/UVP protections and FB disconnection.
Connect to the positive side of the load to perform remote sense. See “Layout
guidelines” Section for proper layout of this connection.
7FBG
Connect to the negative side of the load to perform remote sense. See “Layout
guidelines” Section for proper layout of this connection.
6/47 Doc ID 15698 Rev 2
Page 7
L6706 Pins description and connection diagrams
Table 2. Pin description (continued)
N° Name Description
Load transient boost pin.
- C
Internally fixed at 2 V, connecting a R
8LTB
load transient boost technology™: as soon as the device detects a transient
load it turns on the PHASE. Short to SGND to disable the function.See “Load
transient boost technology” Section for details.
Current monitor output pin.
9IMON
A current proportional to the load current is sourced from this pin. Connect
through a resistor R
pin voltage is clamped to 1.1 V max.
Load transient boost technology™ gain pin.
10 LTBGAIN
Internally fixed at 1.24 V, connecting a R
setting the GAIN of the LTB action. See See “Load transient boost technology”
Section for details.
Offset programming pin.
Internally fixed at 1.240 V, connecting a R
11 OFFSET
setting a current that is mirrored into FB pin in order to program a positive offset
according to the selected RFB. Short to SGND to disable the function.
See “Offset (optional)” Section for details.
Over voltage programming pin.
Internally pulled up by 20 µA (min) to 3.3 V. Leave floating to use built-in
12 OVPSEL
protection thresholds (OVPTH= VID + 175 mV typ). Connect to SGND through a
R
voltage according to the R
OVP” Section for details.
LT B
LTBGAIN
OFFSET
vs. V
resistor vs SGND allows
LT B
to SGND (or FBG) to implement a load indicator. The
MON
resistor and filter with 100 pF (max) to set the OVP threshold to a fixed
OVP
resistor.See “Over voltage and programmable
OVP
allows to enable the
OUT
resistor vs. SGND allows
Over current setting, psi action pin.
13 OCSET
Connect to SGND through a R
resistor to set the OCP threshold. See
OCSET
“Overcurrent protection” Section for details.
Oscillator, fault pin.
. Frequency is programmed
SW
14
OSC/
FAULT
It allows programming the switching frequency F
according to the resistor connected from the pin vs. SGND or VCC with a gain
of 9.1 kHz/µA (see relevant section for details). Leaving the pin floating
programs a switching frequency of 200 kHz. The pin is forced high (3.3 V typ) to
signal an OVP/UVP fault: to recover from this condition, cycle VCC or the
OUTEN pin. See “Oscillator” Section for details.
Soft-start oscillator pin.
By connecting a resistor RSS to GND, it allows programming the soft-start time.
will proportionally change with a gain of 25 [µs / kΩ]. The
SS
to the programmed VID code. The pin is kept to a
BOOT
has to be considered also when the
BOOT
15
SSOSC/
FLIMIT
Soft-start time T
same slope implemented to reach V
reference moves from V
fixed 1.240 V. See “Soft-start” Section for details. It also allows to select
maximum LTB frequency. See “Load transient boost technology” Sectionfor
details.
Doc ID 15698 Rev 2 7/47
Page 8
Pins description and connection diagrams L6706
Table 2. Pin description (continued)
N° Name Description
Output enable pin.
Internally pulled up by 10 µA (typ) to 3 V. Forced low, the device stops
16 OUTEN
17 CS+
18 CS-
operations with all MOSFETs OFF: all the protections are disabled except for
preliminary over voltage. Leave floating, the device starts-up implementing softstart up to the selected VID code. Cycle this pin to recover latch from
protections; filter with 1 nF (typ) vs. SGND.
Current sense positive input.
Connect through an R-C filter to the phase-side of the output inductor.
See Section 20: Layout guidelines on page 43 for proper layout of this
connection.
Current sense negative input.
Connect through a Rg resistor to the output-side of the output inductor.
See Section 20: Layout guidelines on page 43 for proper layout of this
connection.
19 INT1
20 to 27
28 INT2
VID0 to
VID7
Test mode pin.
It must be left unconnected or connected to 3.3 V.
Voltage identification pins. (not internally pulled up).
Connect to SGND to program a '0' or connect to the external Pull-up resistor to
program a '1'. They allow programming output voltage as specified in Ta bl e 7 .
Test mode pin.
It must be connected to SGND.
Soft-start end signal.
29 SSEND
Open drain output sets free after SS has finished and pulled low when
triggering any protection. Pull up to a voltage lower than 3.3 V, if not used it can
be left floating.
30 N.C. Not internally connected.
31 INT3
Test mode pin.
It must be connected to 12 V.
32 N.C. Not internally connected.
33 INT4
Test mode pin.
It must be connected to 12 V.
34 N.C. Not internally connected.
LS driver supply.
35 VCCDR
VCDDR pin voltage has to be the same of VCC pin.
Filter with 1 x 1 µF MLCC capacitor vs. PGND.
36 LGATE
37 PGND
LS driver output.
A small series resistor helps in reducing device-dissipated power.
Power ground pin (LS drivers return path).
Connect to power ground plane.
HS driver return path.
38 PHASE
It must be connected to the HS MOSFET source and provides return path for
the HS driver.
8/47 Doc ID 15698 Rev 2
Page 9
L6706 Pins description and connection diagrams
Table 2. Pin description (continued)
N° Name Description
HS driver output.
39 UGATE
It must be connected to the HS MOSFET gate. A small series resistors helps in
reducing device-dissipated power.
HS driver supply.
40 BOOT
Connect through a capacitor (100 nF typ.) to PHASE and provide necessary
Bootstrap diode. A small resistor in series to the boot diode helps in reducing
Boot capacitor overcharge.
Exposed pad connects the silicon substrate. As a consequence it makes a
good thermal contact with the PCB to dissipate the power necessary to drive
the external MOSFETs.
Connect it to the power ground plane using 4.3 x 4.3 mm square area on the
PA D
Thermal
PA D
PCB and with nine vias, to improve thermal conductivity.
2.2 Thermal data
Table 3. Thermal data
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
R
thJA
R
thJC
T
MAX
T
stg
T
J
Thermal resistance junction to ambient
(Device soldered on 2s2p PC board)
35 °C / W
Thermal resistance junction to case 1 °C / W
Maximum junction temperature 150 °C
Storage temperature range -40 to 150 °C
Junction temperature range -10 to 125 °C
Doc ID 15698 Rev 2 9/47
Page 10
Electrical specifications L6706
3 Electrical specifications
3.1 Absolute maximum ratings
Table 4. Absolute maximum ratings
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
V
CC, VCCDR
V
BOOT
V
PHASE
V
UGATE
V
PHASE
V
PHASE
To P GN D 1 5 V
Boot voltage 15 V
15 V
LGATE to PGND -0.3 to Vcc+0.3 V
All other pins to PGND -0.3 to 3.6 V
Negative peak voltage to PGND; T < 400 ns
VCC = VCCDR = 12 V
Positive voltage to PGND
VCC = VCCDR = 12 V
Positive peak voltage to PGND; T < 200 ns
VCC = VCCDR = 12 V
-8 V
26 V
30 V
Maximum withstanding voltage range test condition:
CDF-AEC-Q100-002- “human body model”
+/- 1750 V
acceptance criteria: “normal performance”
10/47 Doc ID 15698 Rev 2
Page 11
L6706 Electrical specifications
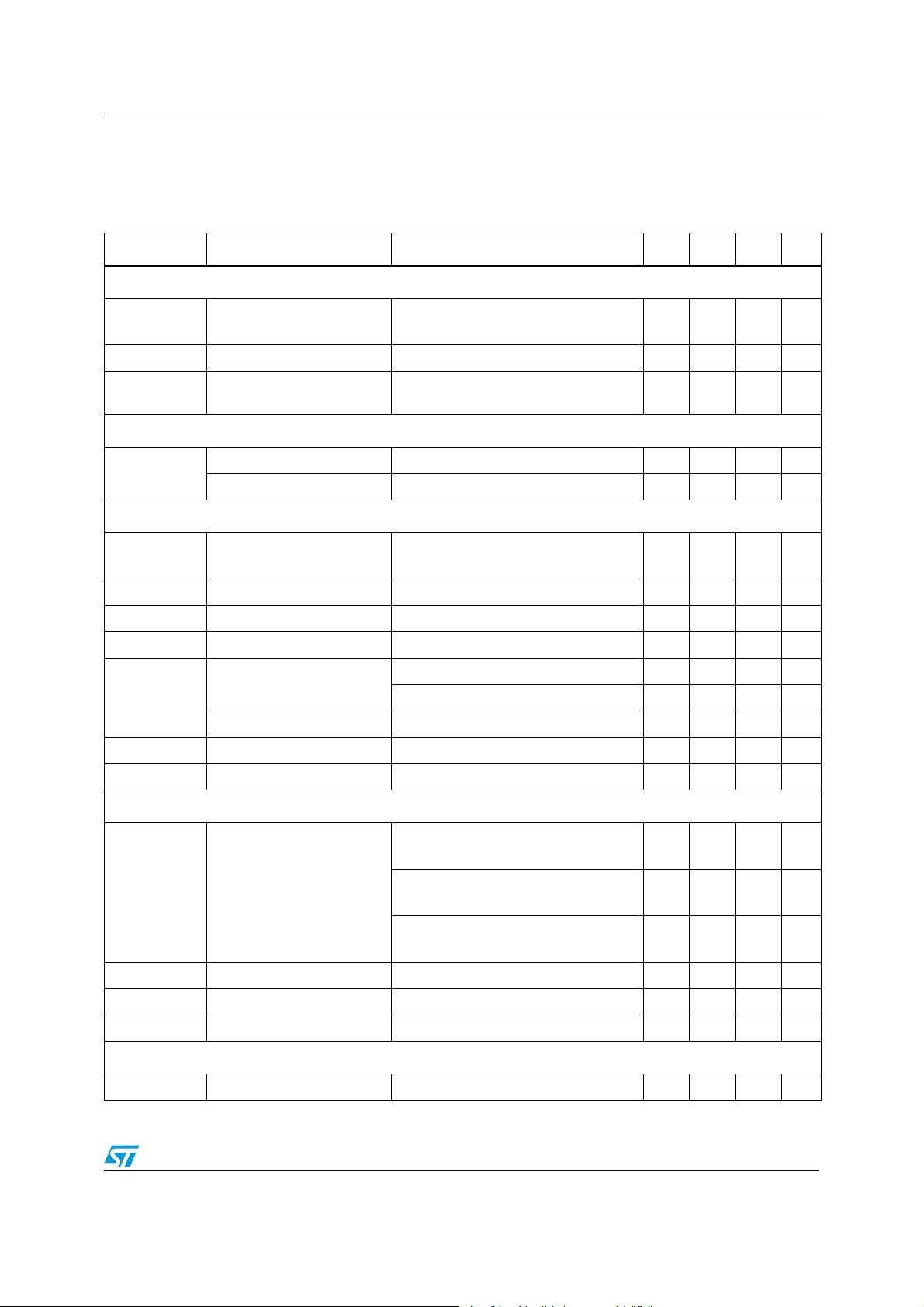
3.2 Electrical characteristics
VCC = 12 V ± 15%, TJ = 0 °C to 70 °C unless otherwise specified
Table 5. Electrical characteristics
Symbol Parameter Test conditions Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Supply current and power-on
I
CC
I
CCDR
I
BOOT
VCC supply current
VCCDR supply current LGATE = OPEN, VCCDR = 12 V 5 7 mA
BOOT supply current
UGATE and LGATE open;
VCC = VBOOT = 12 V
UGATE = OPEN, PHASE to PGND;
VCC = BOOT = 12 V
23 27 mA
23mA
Power-on
VCC turn-ON VCC rising; VCCDR = VCC 3.7 4.0 V
UVLO
VCC
VCC turn-OFF VCC falling; VCCDR = VCC 3.3 3.5 V
Oscillator and inhibit
F
OSC
TD
TD
TD
Initial accuracy
1
2
3
SS delay time 1 1.5 ms
SS TD2 time R
SS TD3 time 50 200 μs
OSC = OPEN
OSC = OPEN; TJ = 0 to 125 °C
= 20 kΩ 500 μs
SSOSC
180
175
200
200
Rising thresholds voltage 0.80 0.85 0.90 V
Output enable
OUTEN
Hysteresis 100 mV
Output pull-up current OUTEN to SGND 10 μA
ΔVosc Ramp amplitude 1.5 V
FAULT Voltage at pin OSC/FAULT OVP and UVP Active 3.3 V
220
225
kHz
kHz
Reference and DAC
K
V
VID
VID
Error amplifier
VID
BOOT
IH
IL
A
0
Output voltage accuracy
VID = 1.000 V to VID = 1.600 V
FB = VOUT; FBG = GNDOUT
VID = 0.800 V to VID = 1.000 V
FB = VOUT; FBG = GNDOUT
VID = 0.500 V to VID = 0.800 V
FB = VOUT; FBG = GNDOUT
-0.5 - 0.5 %
-5 - +5 mV
-8 - +8 mV
Boot voltage 1.081 V
Input low 0.35 V
VID thresholds
Input high 0.8 V
EA DC gain 130 dB
Doc ID 15698 Rev 2 11/47
Page 12
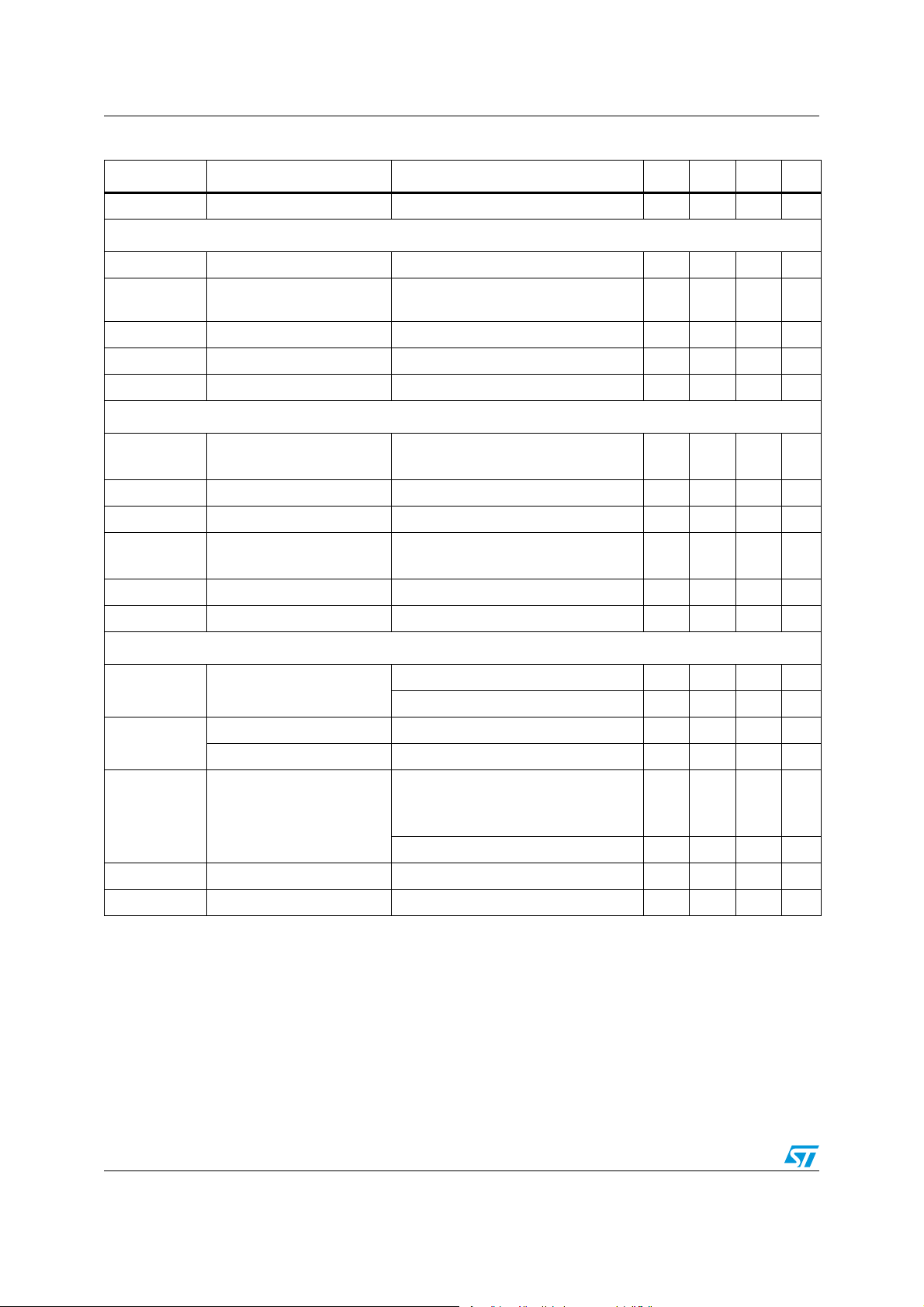
Electrical specifications L6706
Table 5. Electrical characteristics (continued)
Symbol Parameter Test conditions Min. Typ. Max. Unit
SR EA slew-rate COMP = 10 pF to SGND 25 V/μs
Differential current sensing and offset
V
OCSET
K
IDROOP
K
IOFFSET
I
OFFSET
V
OFFSET
Gate drivers
t
RISE UGATE
I
UGATE
R
UGATE
t
RISE LGATE
I
LGATE
R
LGATE
Protections
OVP
Programmable
OVP
OCSET pin voltage 1.120 1.260 1.400 mV
Droop current deviation from
nominal value
Offset current accuracy I
Rg = 1 kΩ; I
= 50 μA to 250 μA-5-5%
OFFSET
= 25 μA; -2 - +2 μA
DROOP
OFFSET current range 0 250 μA
OFFSET pin bias I
High side rise time
BOOT-PHASE = 12 V;
C
= 0 to 250 μA1.240V
OFFSET
to PHASE = 3.3 nF
UGATE
20 ns
High side source current BOOT-PHASE = 12 V 1.5 A
High side sink resistance BOOT-PHASE = 12 V 1.8 Ω
Low side rise time
VCCDR = 12 V;
C
to PGND = 5.6 nF
LGATE
25 ns
Low side source current VCCDR = 12 V 2 A
Low side sink resistance VCCDR = 12 V 1.2 Ω
Over voltage protection
(VSEN rising)
current OVP = SGND 20 22 24 μA
I
OVP
Before V
BOOT
Above VID (after TD
) 150 175 200 mV
3
1.24 1.300 V
Comparator offset voltage OVP = 1.800 V -20 0 20 mV
UVLO
OVP
Pre-OVP
Preliminary over voltage
protection
VCC> UVLO
VSEN rising
Hysteresis 350 mV
UVP Under voltage threshold VSEN falling; below VID 550 600 650 mV
V
SSEND
SS_END voltage low I = -4 mA 0.4 V
12/47 Doc ID 15698 Rev 2
< VCC < UVLO
and OUTEN = SGND
VCC
VCC
1.750 1.800 1.850 V
Page 13
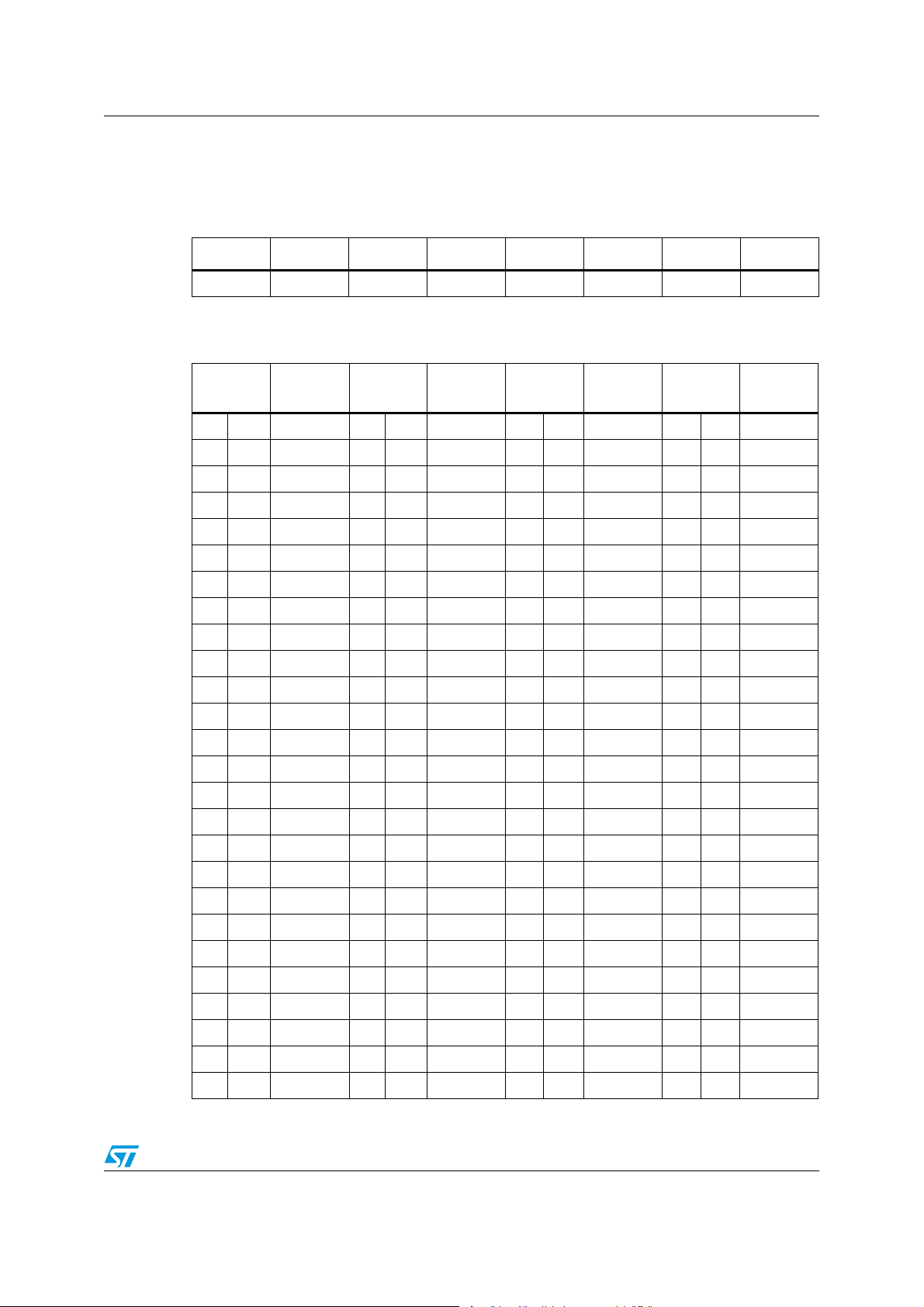
L6706 Voltage identifications
4 Voltage identifications
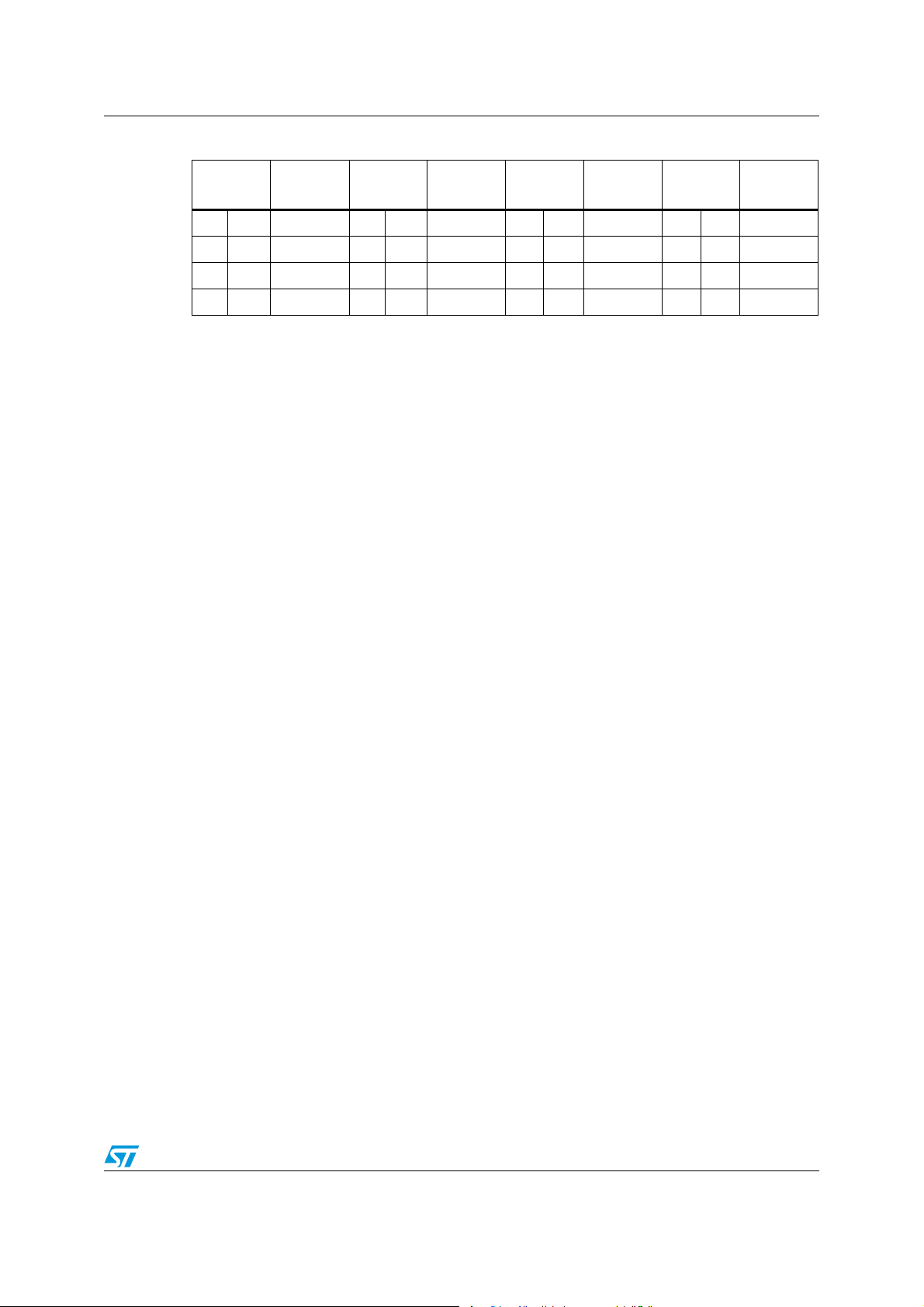
Table 6. Voltage Identification (VID) mapping Intel VR11.x
VID7 VID6 VID5 VID4 VID3 VID2 VID1 VID0
800 mV 400 mV 200 mV 100 mV 50 mV 25 mV 12.5 mV 6.25 mV
Table 7. Voltage Identification (VID) Intel VR11.x
HEX code
Output
voltage
(1)
HEX code
Output
voltage
HEX code
(1)
(1)
Output
voltage
HEX code
(1)
Output
voltage
0 0 OFF 4 0 1.21250 8 0 0.81250 C 0 0.41250
0 1 OFF 4 1 1.20625 8 1 0.80625 C 1 0.40625
0 2 1.60000 4 2 1.20000 8 2 0.80000 C 2 0.40000
0 3 1.59375 4 3 1.19375 8 3 0.79375 C 3 0.39375
0 4 1.58750 4 4 1.18750 8 4 0.78750 C 4 0.38750
0 5 1.58125 4 5 1.18125 8 5 0.78125 C 5 0.38125
0 6 1.57500 4 6 1.17500 8 6 0.77500 C 6 0.37500
0 7 1.56875 4 7 1.16875 8 7 0.76875 C 7 0.36875
0 8 1.56250 4 8 1.16250 8 8 0.76250 C 8 0.36250
0 9 1.55625 4 9 1.15625 8 9 0.75625 C 9 0.35625
0 A 1.55000 4 A 1.15000 8 A 0.75000 C A 0.35000
0 B 1.54375 4 B 1.14375 8 B 0.74375 C B 0.34375
0 C 1.53750 4 C 1.13750 8 C 0.73750 C C 0.33750
0 D 1.53125 4 D 1.13125 8 D 0.73125 C D 0.33125
0 E 1.52500 4 E 1.12500 8 E 0.72500 C E 0.32500
0 F 1.51875 4 F 1.11875 8 F 0.71875 C F 0.31875
(1)
1 0 1.51250 5 0 1.11250 9 0 0.71250 D 0 0.31250
1 1 1.50625 5 1 1.10625 9 1 0.70625 D 1 0.30625
1 2 1.50000 5 2 1.10000 9 2 0.70000 D 2 0.30000
1 3 1.49375 5 3 1.09375 9 3 0.69375 D 3 0.29375
1 4 1.48750 5 4 1.08750 9 4 0.68750 D 4 0.28750
1 5 1.48125 5 5 1.08125 9 5 0.68125 D 5 0.28125
1 6 1.47500 5 6 1.07500 9 6 0.67500 D 6 0.27500
1 7 1.46875 5 7 1.06875 9 7 0.66875 D 7 0.26875
1 8 1.46250 5 8 1.06250 9 8 0.66250 D 8 0.26250
1 9 1.45625 5 9 1.05625 9 9 0.65625 D 9 0.25625
Doc ID 15698 Rev 2 13/47
Page 14
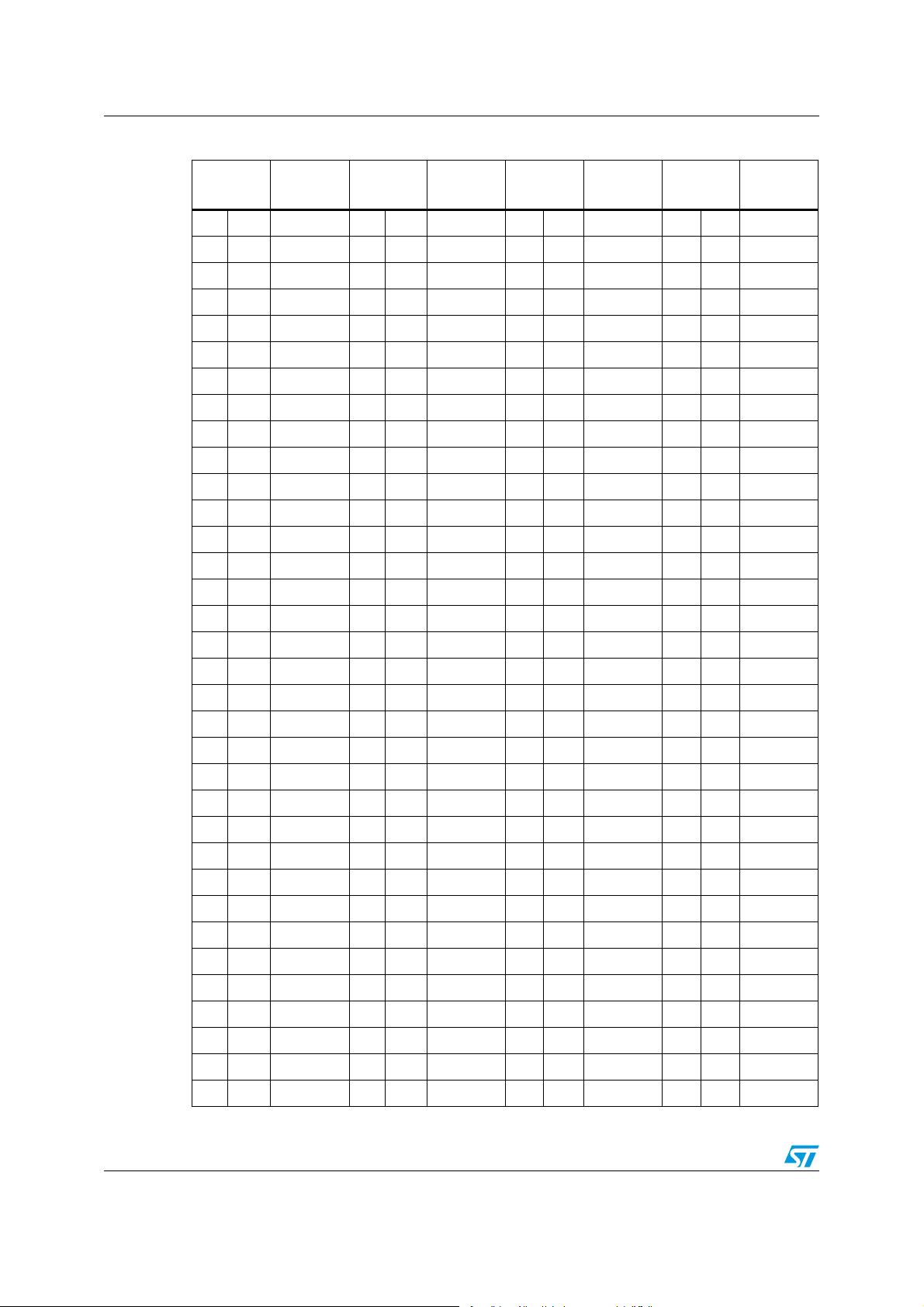
Voltage identifications L6706
Table 7. Voltage Identification (VID) Intel VR11.x
HEX code
Output
voltage
(1)
HEX code
Output
voltage
HEX code
(1)
(1)
(continued)
Output
voltage
HEX code
(1)
Output
voltage
1 A 1.45000 5 A 1.05000 9 A 0.65000 D A 0.25000
1 B 1.44375 5 B 1.04375 9 B 0.64375 D B 0.24375
1 C 1.43750 5 C 1.03750 9 C 0.63750 D C 0.23750
1 D 1.43125 5 D 1.03125 9 D 0.63125 D D 0.23125
1 E 1.42500 5 E 1.02500 9 E 0.62500 D E 0.22500
1 F 1.41875 5 F 1.01875 9 F 0.61875 D F 0.21875
2 0 1.41250 6 0 1.01250 A 0 0.61250 E 0 0.21250
2 1 1.40625 6 1 1.00625 A 1 0.60625 E 1 0.20625
2 2 1.40000 6 2 1.00000 A 2 0.60000 E 2 0.20000
2 3 1.39375 6 3 0.99375 A 3 0.59375 E 3 0.19375
2 4 1.38750 6 4 0.98750 A 4 0.58750 E 4 0.18750
2 5 1.38125 6 5 0.98125 A 5 0.58125 E 5 0.18125
2 6 1.37500 6 6 0.97500 A 6 0.57500 E 6 0.17500
2 7 1.36875 6 7 0.96875 A 7 0.56875 E 7 0.16875
2 8 1.36250 6 8 0.96250 A 8 0.56250 E 8 0.16250
2 9 1.35625 6 9 0.95625 A 9 0.55625 E 9 0.15625
2 A 1.35000 6 A 0.95000 A A 0.55000 E A 0.15000
(1)
2 B 1.34375 6 B 0.94375 A B 0.54375 E B 0.14375
2 C 1.33750 6 C 0.93750 A C 0.53750 E C 0.13750
2 D 1.33125 6 D 0.93125 A D 0.53125 E D 0.13125
2 E 1.32500 6 E 0.92500 A E 0.52500 E E 0.12500
2 F 1.31875 6 F 0.91875 A F 0.51875 E F 0.11875
3 0 1.31250 7 0 0.91250 B 0 0.51250 F 0 0.11250
3 1 1.30625 7 1 0.90625 B 1 0.50625 F 1 0.10625
3 2 1.30000 7 2 0.90000 B 2 0.50000 F 2 0.10000
3 3 1.29375 7 3 0.89375 B 3 0.49375 F 3 0.09375
3 4 1.28750 7 4 0.88750 B 4 0.48750 F 4 0.08750
3 5 1.28125 7 5 0.88125 B 5 0.48125 F 5 0.08125
3 6 1.27500 7 6 0.87500 B 6 0.47500 F 6 0.07500
3 7 1.26875 7 7 0.86875 B 7 0.46875 F 7 0.06875
3 8 1.26250 7 8 0.86250 B 8 0.46250 F 8 0.06250
3 9 1.25625 7 9 0.85625 B 9 0.45625 F 9 0.05625
3 A 1.25000 7 A 0.85000 B A 0.45000 F A 0.05000
3 B 1.24375 7 B 0.84375 B B 0.44375 F B 0.04375
14/47 Doc ID 15698 Rev 2
Page 15
L6706 Voltage identifications
Table 7. Voltage Identification (VID) Intel VR11.x
HEX code
Output
voltage
(1)
HEX code
Output
voltage
HEX code
(1)
(1)
(continued)
Output
voltage
HEX code
(1)
Output
voltage
3 C 1.23750 7 C 0.83750 B C 0.43750 F C 0.03750
3 D 1.23125 7 D 0.83125 B D 0.43125 F D 0.03125
3 E 1.22500 7 E 0.82500 B E 0.42500 F E OFF
3 F 1.21875 7 F 0.81875 B F 0.41875 F F OFF
1. According to INTEL specs, the device automatically regulates output voltage 19 mV lower to avoid any
external offset to modify the built-in 0.5% accuracy improving TOB performances. Output regulated voltage
is than what extracted from the table lowered by 19 mV.
(1)
Doc ID 15698 Rev 2 15/47
Page 16

Device description L6706
5 Device description
L6706 is single phase PWM controller with embedded high current drivers providing
complete control logic and protections for a high performance step-down DC-DC voltage
regulator optimized for advanced microprocessor power supply.
L6706 is a dual-edge asynchronous PWM controller featuring load transient boost LTB
Technology™: the device turns on the phase as soon as a load transient is detected
allowing to minimize system cost by providing the fastest response to load transition. Load
transition is detected (through LTB pin) measuring the derivate dV/dt of the output voltage
and the dV/dt can be easily programmed extending the system design flexibility. Moreover,
load transient boost (LTB) Technology™ gain can be easily modified in order to keep under
control the output voltage ring back.
LTB Technology™ can be disabled and in this condition the device works as a dual-edge
asynchronous PWM.
L6706 permits easy system design by allowing current reading across inductor in fully
differential mode. Also a sense resistor in series to the inductor can be considered to
improve reading precision.
The controller allows compatibility with both Intel VR11.0 and VR11.1 processors
specifications, also performing D-VID transitions accordingly.
The device is VR11.1 compatible implementing IMON signal.
Low-side-less startup allows soft-start over pre-biased output avoiding dangerous current
return through the main inductor as well as negative spike at the load side.
L6706 provides a programmable over-voltage protection to protect the load from dangerous
over stress, latching immediately by turning ON the lower driver and driving high the
OSC/FAULT pin. Furthermore, preliminary OVP protection also allows the device to protect
load from dangerous OVP when VCC is not above the UVLO threshold or OUTEN is low.
The overcurrent protection is externally adjustable through a single resistor. The device
keeps constant the peak of the inductor current ripple working in constant current mode until
the latched UVP.
A compact 6 x 6 mm body VFQFPN-40 package with exposed thermal pad allows
dissipating the power to drive the external MOSFET through the system board.
16/47 Doc ID 15698 Rev 2
Page 17

L6706 DAC and current reading
6 DAC and current reading
L6706 embeds VRD11.x DAC (see Ta bl e 7 ) that allows to regulate the output voltage with a
tolerance of ±0.5% recovering from offsets and manufacturing variations.
The device automatically introduces a -19 mV (both VRD11.x) offset to the regulated
voltage in order to avoid any external offset circuitry to worsen the guaranteed accuracy
and, as a consequence, the calculated system TOB.
Output voltage is programmed through the VID pins: they are inputs of an internal DAC that
is realized by means of a series of resistors providing a partition of the internal voltage
reference. The VID code drives a multiplexer that selects a voltage on a precise point of the
divider. The DAC output is delivered to an amplifier obtaining the voltage reference (i.e. the
set-point of the error amplifier, V
L6706 embeds a flexible, fully-differential current sense circuitry that is able to read across
inductor parasitic resistance or across a sense resistor placed in series to the inductor
element. The fully-differential current reading rejects noise and allows placing sensing
element in different locations without affecting the measurement's accuracy.
Reading current across the inductor DCR, the current flowing trough phase is read using the
voltage drop across the output inductor or across a sense resistor in its series and internally
converted into a current. The trans-conductance ratio is issued by the external resistor Rg
placed outside the chip between CS- pin toward the reading points.
REF
).
The current sense circuit always tracks the current information, no bias current is sourced
from the CS+ pin: this pin is used as a reference keeping the CS- pin to this voltage. To
correctly reproduce the inductor current an R-C filtering network must be introduced in
parallel to the sensing element.
The current that flows from the CS- pin is then given by the following equation (see
Figure 4):
DCR
1sLDCR()⁄⋅+
-------------
Where I
I
CS-
is the current carried by the relative phase.
PHASE
------------------------------------------ -
⋅=
Rg
1sRC⋅⋅+
I⋅
PHASE
Figure 4. Current reading connections
I
PHASEx
L
PHASE
DCR
R
CS+
C
NO Bias
I
CS-=IINFO
CS-
Rg
Inductor DCR Current Sense
Considering now to match the time constant between the inductor and the R-C filter applied
(Time constant mismatches cause the introduction of poles into the current reading network
Doc ID 15698 Rev 2 17/47
Page 18

DAC and current reading L6706
causing instability. In addition, it is also important for the load transient response and to let
the system show resistive equivalent output impedance), it results:
Where I
L
------------- RC I
DCR
is the current information reproduced internally.
INFO
CS-
DCR
-------------
Rg
⋅=⇒⋅ I
I
PHASE
INFO
I
INFO
DCR
-------------
Rg
⋅=⇒==
I
PHASE
The Rg trans-conductance resistor has to be selected using the following formula, in order
to guarantee the correct functionality of internal current reading circuitry:
MAX
DCR
Where I
OUT
------------------------
Rg
MAX
is the maximum output current, DCR
20μA
I
OUT
MAX⋅=
MAX
the maximum inductor DCR.
18/47 Doc ID 15698 Rev 2
Page 19

L6706 Differential remote voltage sensing
7 Differential remote voltage sensing
The output voltage is sensed in fully-differential mode between the FB and FBG pin.
The FB pin has to be connected through a resistor to the regulation point while the FBG pin
has to be connected directly to the remote sense ground point.
In this way, the output voltage programmed is regulated between the remote sense point
compensating motherboard or connector losses.
Keeping the FB and FBG traces parallel and guarded by a power plane results in common
mode coupling for any picked-up noise.
Figure 5. Differential remote voltage sensing connections
V
PROG
GND DROP
RECOVERY
I
OFFSET
I
DROOP
V
REF
ERROR AMPLIFIER
FBG
FBG
To GND_core
(Remote Sense)
To VCC_core
(Remote Sense)
VSEN
FB
R
FB
R
COMP
F
C
F
C
P
Doc ID 15698 Rev 2 19/47
Page 20

Voltage positioning L6706
DCR
8 Voltage positioning
Output voltage positioning is performed by selecting the internal reference value through
VID pins and by programming the droop function and offset to the reference (see Figure 6
on page 20). The currents sourced/sunk from FB pin cause the output voltage to vary
according to the external R
The output voltage is then driven by the following relationship:
V
OUTIOUT
where:
.
FB
()V
PROGRFBIDROOPIOUT
()I
–[]⋅–=
OFFSET
V
PROG
I
DROOPIOUT
I
OFFSET
VID 19mV–=
()
1.240V
------------------------=
R
OFFSET
-------------
Rg
⋅=
I
OUT
OFFSET function can be disabled shorting to SGND the OFFSET pin.
Figure 6. Voltage positioning (left) and droop function (right)
V
PROG
FBG
FBG
To GND_core
(Remote Sense)
GND DROP
RECOVERY
To VCC_core
(Remote Sense)
I
OFFSET
VSEN
R
FB
ERROR AMPLIFIER
V
REF
I
DROOP
FB
R
F
C
P
COMP
C
F
V
MAX
V
NOM
V
MIN
RESPONSE WITHOUT DROOP
RESPONSE WITH DROOP
ESR Drop
8.1 Offset (optional)
The OFFSET pin allows programming a positive offset (VOS) for the output voltage by
connecting a resistor R
OFFSET
considered in addition to the one already introduced during the production stage (V
VID-19 mV).
OFFSET function can be disabled shorting to SGND the OFFSET pin.
The OFFSET pin is internally fixed at 1.240 V (Tab le 5 ) a current is programmed by
connecting the resistor R
then properly sunk from the FB pin as shown in Figure 7. Output voltage is then
programmed as follow:
20/47 Doc ID 15698 Rev 2
vs. SGND as shown in Figure 7; this offset has to be
OFFSET
between the pin and SGND: this current is mirrored and
PROG
=
Page 21

L6706 Voltage positioning
V
()V
OUTIOUT
PROGRFBIDROOPIOUT
()
1.240V
------------------------–⋅–=
R
OFFSET
where:
1.240V
V
OS
R
FB
------------------------
⋅=
R
OFFSET
Offset resistor can be designed by considering the following relationship (RFB is fixed by the
Droop effect):
1.240V
------------------ -
R
OFFSETRFB
⋅=
V
OS
Offset automatically given by the DAC selection differs from the offset implemented through
the OFFSET pin: the built-in feature is trimmed in production and assures ±0.5% error over
load and line variations
Figure 7. Voltage positioning with positive offset
FB
ERROR AMPLIFIER
V
REF
I
DROOP
FB
R
COMP
F
C
P
C
F
1.240V
OFFSET
OFFSET
I
ROFFSET
V
PROG
FBG
FBG
To GND_core
(Remote Sense)
GND DROP
RECOVERY
To VCC_core
(Remote Sense)
I
OFFSET
VSEN
R
8.2 Droop function
This method “recovers” part of the drop due to the output capacitor ESR in the load
transient, introducing a dependence of the output voltage on the load current: a static error
proportional to the output current causes the output voltage to vary according to the sensed
current.
As shown in Figure 6, the ESR drop is present in any case, but using the droop function the
total deviation of the output voltage is minimized. Moreover, more and more highperformance CPUs require precise load-line regulation to perform in the proper way.
DROOP function is not then required only to optimize the output filter, but also becomes a
requirement of the load.
The device forces a current I
resistor implementing the load regulation dependence. Since I
current information, the output characteristic vs. load current is then given by (neglecting the
OFFSET voltage term):
V
OUT
Where DCR is the inductor parasitic resistance (or sense resistor when used) and I
the output current of the system. The whole power supply can be then represented by a
DROOP
V
PROGRFBIDROOP
⋅– V
, proportional to the read current, into the feedback RFB
depends on the
DROOP
DCR
-------------
REFRFB
⋅⋅– V
Rg
I
OUT
PROGRDROOPIOUT
Doc ID 15698 Rev 2 21/47
⋅–== =
OUT
is
Page 22

Voltage positioning L6706
“real” voltage generator with an equivalent output resistance R
V
. RFB resistor can be also designed according to the R
PROG
Rg
R
FB
R
DROOP
-------------
⋅=
DCR
DROOP
DROOP
and a voltage value of
specifications as follow:
22/47 Doc ID 15698 Rev 2
Page 23

L6706 Droop thermal compensation
9 Droop thermal compensation
Current sense element (DCR inductor) has a non-negligible temperature variation. As a
consequence, the sensed current is subjected to a measurement error that causes the
regulated output voltage to vary accordingly (when droop function is implemented).
To recover from this temperature related error, NTC resistor can be added into feedback
compensation network, as shown in Figure 8.
The output voltage is then driven by the following relationship (neglecting the OFFSET
voltage term):
where R
V
OUT
is the equivalent feedback resistor and it depends on the temperature through
FB
V
PROGRFBIDROOP
⋅()–=
NTC resistor.
Considering the relationships between I
V
(, )[]V
OUTTIOUT
and the I
DROOP
⎛⎞
–=
PROGRFB
⎝⎠
, the output voltage results:
OUT
DCR T[]
----------------------
T[]
⋅⋅
Rg
I
OUT
where T is the temperature.
If the inductor temperature increases the DCR inductor increases and NTC resistor
decreases. As a consequence the equivalent R
resistor decreases keeping constant the
FB
output voltage respect to temperature variation.
NTC resistor must be placed as close as possible to the sense element (phase inductor).
Figure 8. NTC connections for DC load line thermal compensation
V
PROG
GND DROP
RECOVERY
To GND_core
(Remote Sense)
FBG
FBG
To VCC_core
(Remote Sense)
I
OS
R
FB
R
FB3
NTC
R
FB2
I
DROOP
R
V
REF
ERROR AMPLIFIER
FB
R
FB1
COMP
C
F
F
C
P
Doc ID 15698 Rev 2 23/47
Page 24

Output current monitoring (IMON) L6706
DCR
10 Output current monitoring (IMON)
The device sources from IMON pin a current proportional to the load current (the sourced
current is a copy of droop current).
Connect IMON pin through a R
resistor to remote ground (GND Core) to implement a
IMON
load indicator, as shown in Figure 9.
As INTEL VR11.1 specification required, on the IMON voltage as to be added a small
positive offset to avoid under-estimation of the output load (due to elements accuracy).
The voltage across IMON pin is given by the following formula:
V
MONITORING
⋅
IMONROS
-----------------------------------
R
+
IMONROS
⋅ V
I
DROOP
REF
R
IMON
-----------------------------------
⋅+=
R
+
IMONROS
R
where:
-------------
I
I
DROOP
Rg
⋅=
OUT
The IMON pin voltage is clamped to 1.100 V max to preserve the CPU from excessive
voltages as INTEL VR11.1 specification required.
Figure 9. Output monitoring connection (left) and thermal compensation (right)
VREF = +3V3
R
To CPU
IMON_OS
IMON
I
DROOP
CIMON
VREF = +3V3
IMON_OS
R
To CPU
IMON
I
DROOP
CIMON
To GND_core
(Remote Sense)
R
IMON
Current sense element (DCR inductor) has a non-negligible temperature variation. As a
consequence, the sensed current is subjected to a measurement error that causes the
monitoring voltage to vary accordingly.
To recover from this temperature related error, NTC resistor can be added into monitoring
network, as shown in Figure 9.
The monitoring voltage is then driven by the following relationship (neglecting the offset term
for simplicity):
R
⋅
IMONROS
V
where now the R
MONITORING
is the equivalent monitoring resistor and it depends on the
IMON
-----------------------------------
R
+
IMONROS
temperature through NTC resistor.
Considering the relationships between I
24/47 Doc ID 15698 Rev 2
I
⋅
DROOP
DROOP
To GND_core
(Remote Sense)
R
-----------------------------------
R
and the I
R3
NTC
⋅
IMONROS
+
IMONROS
, the voltage results:
OUT
DCR
-------------
⋅⋅==
Rg
R2
R
IMON
R1
I
OUT
Page 25

L6706 Output current monitoring (IMON)
V
MONITORINGTIOUT
(, )[]
R
--------------------------------------------- -
R
IMON
IMON
TR
⋅
OS
TR
+
OS
DCR T[]
----------------------
⋅⋅=
Rg
I
OUT
where T is the temperature.
If the inductor temperature increases the DCR inductor increases and NTC resistor
decreases. As a consequence the equivalent R
resistor decreases keeping constant
IMON
the monitoring voltage respect to temperature variation. NTC resistor must be placed as
close as possible to the sense element (phase inductor).
Doc ID 15698 Rev 2 25/47
Page 26

Load transient boost technology L6706
11 Load transient boost technology
LTB Technology™ further enhances the performances of dual-edge asynchronous systems
by reducing the system latencies and immediately turning ON the phase to provide the
correct amount of energy to the load.
By properly designing the LTB network, as well as the LTB gain, the undershoot and the
ring-back can be minimized also optimizing the output capacitors count.
LTB Technology™ monitors the output voltage through a dedicated pin (see Figure 11)
detecting Load-Transients with selected dV/dt and turning-on immediately the phase.
It then implements a parallel independent loop that (bypassing error amplifier (E/A)
latencies) reacts to load-transients in very short time (< 150 ns).
LTB Technology™ control loop is reported in Figure 10.
Figure 10. LTB Technology™ control loop
LTB Ramp
LTB
LT Detect
ZF(s)
COMP
V
PWM_BOOST
d V
PWM
Ref
FBCOMP
F
C
P
C
F
R
COMP
V
PROG
GND DROP
DROOP
I
Monitor
VSEN
FB
R
RECOVERY
LT Detect
FBG
FB
C
LTB
Z
R
(s)
FB
LTBGAIN
LTBCLTB
L
ESR
C
O
R
LTBGAIN
V
OUT
R
O
The LTB detector is able to detect output load transients by coupling the output voltage
through an R
LT B
- C
network. After detecting a load transient, the LTB ramp is reset and
LT B
then compared with the COMP pin level. The resulting duty-cycle programmed is then ORed with the PWM signal by-passing the main control loop. The phase will then be turned-on
and the EA latencies results bypassed as well.
Short LTB pin to SGND to disable the LTB Technology™: in this condition the device works
as a dual-edge asynchronous PWM controller.
Sensitivity of the load transient detector and the gain of the LTB ramp can be programmed in
order to control precisely both the undershoot and the ring-back.
● Detector design. R
LT B
- C
is design according to the output voltage deviation dV
LT B
which is desired the controller to be sensitive as follow:
dV
R
LTB
26/47 Doc ID 15698 Rev 2
OUT
------------------= C
25μA
LTB
1
-----------------------------------------=
2π R
⋅⋅
LTBFSW
OUT
Page 27

L6706 Load transient boost technology
e
● Gain design. Through the LTBGAIN pin it is possible to modify the slope of the LTB
Ramp in order to modulate the entity of the LTB response once the LT has been
detected. In fact, the response depends on the board design and its parasites requiring
different actions from the controller.
Connect R
LTBGAIN
to SGND using the following relationship in order to select the
default value (slope of the LTB ramp equal to 1/2 of the OSC ramp slope).
2 1240 10
⋅⋅
Fsw kHz[]200–
⎛⎞
------------------------------------------- -
20
+
⎝⎠
10
Where F
R
LTBGAIN
is the selected switching frequency (in kHz).
SW
kΩ[]
------------------------------------------------------------------- -=
LTB Technology™ design tips.
– Decrease R
smaller dV
– Increase C
to increase the system sensitivity making the system sensitive to
LT B
.
OUT
to increase the system sensitivity making the system sensitive to
LT B
higher dV/dt.
– Decrease R
LTBGAIN
to decrease the width of the LTB pulse reducing the system
ring-back or vice versa.
Figure 11. LTB connection (left) and waveform (right)
LT B
R
LT B
C
LT B
To VCC_Cor
3
Doc ID 15698 Rev 2 27/47
Page 28

Dynamic VID transitions L6706
T
12 Dynamic VID transitions
The device is able to manage dynamic VID code changes that allow output voltage
modification during normal device operation.
OVP and UVP signals are masked during every VID transition and they are re-activated
after the transition finishes with a
transition.
When changing dynamically the regulated voltage (D-VID), the system needs to charge or
discharge the output capacitor accordingly. This means that an extra-current I
be delivered, especially when increasing the output regulated voltage and it must be
considered when setting the over current threshold.
This current can be estimated using the following relationships:
15 µs (typ) delay to prevent from false triggering due to the
needs to
D-VID
dV
OU
DVID–
C
OUT
----------------- -
⋅=
dT
VID
where d
is the selected DAC LSB (6.25 mV for VR11.1) and T
VOUT
is the time interval
VID
between each LSB transition (externally driven).
Overcoming the OC threshold during the dynamic VID causes the device to enter the
constant current limitation slowing down the output voltage dV/dt also causing the failure in
the D-VID test. In order to avoid this situation the device automatically increases the OCP
threshold to 150% of the selected OCP threshold during every VID transition (adding an
extra
15 µs of delay).
L6706 checks for VID code modifications (see Figure 12) on the rising edge of an internal
additional DVID-clock and waits for a confirmation on the following falling edge. Once the
new code is stable, on the next rising edge, the reference starts stepping up or down in LSB
increments every VID-clock cycle until the new VID code is reached. During the transition,
VID code changes are ignored; the device re-starts monitoring VID after the transition has
finished on the next rising edge available. VID-clock frequency (F
) is in the range of 1.8
DVI D
MHz to assure compatibility with the specifications.
Note: If the new VID code is more than 1 LSB different from the previous, the device will execute
the transition stepping the reference with the DVID-clock frequency F
until the new code
DVI D
has reached: for this reason it is recommended to carefully control the VID change rate in
order to carefully control the slope of the output voltage.
28/47 Doc ID 15698 Rev 2
Page 29

L6706 Dynamic VID transitions
Figure 12. Dynamic VID transitions
VID Sampled
VID Clock
VID Sampled
VID Stable
VID Sampled
Ref Moved (1)
Ref Moved (2)
Ref Moved (3)
VID Sampled
Ref Moved (4)
VID Sampled
VID Sampled
VID Sampled
Ref Moved (1)
VID Sampled
VID Sampled
VID Stable
Ref Moved (1)
VID Sampled
VID Sampled
VID Stable
Ref Moved (1)
VID Sampled
VID Stable
VID Sampled
Ref Moved (1)
VID Sampled
VID Stable
VID Sampled
VID Sampled
VID Sampled
VID [0,7]
Int. Reference
V
out
T
DVID
T
sw
x 4 Step VID Transition
Vout Slope Controlled by internal
DVID-Clock Oscillator
T
VID
4 x 1 Step VID Transition
Vout Slope Controlled by external
driving circuit (T
t
t
t
t
)
VID
Doc ID 15698 Rev 2 29/47
Page 30

Enable and disable L6706
13 Enable and disable
L6706 has three different supplies: VCC pin to supply the internal control logic, VCCDR to
supply the low side driver and BOOT to supply the high side driver.
If the voltage at pin VCC is not above the turn on threshold specified in the Electrical
characteristics table (see Ta bl e 5 ), the device is shut down: High-side and low-side driver
keep the MOSFETs off to show high impedance to the load.
Once the device is correctly supplied, proper operation is assured and the device can be
driven by the OUTEN pin to control the power sequencing. Setting the pin free, the device
implements a soft-start up to the programmed voltage. Shorting the pin to SGND, it resets
the device (SS_END is shorted to SGND in this condition) from any latched condition and
also disables the device keeping all the MOSFET turned off to show high impedance to the
load.
30/47 Doc ID 15698 Rev 2
Page 31

L6706 Soft-start
14 Soft-start
L6706 implements a soft-start to smoothly charge the output filter avoiding high in-rush
currents to be required to the input power supply. The device increases the reference from
zero up to the programmed value and the output voltage increases accordingly with closed
loop regulation.
The device implements soft-start only when all the power supplies are above their own turnon thresholds and the OUTEN pin is set free.
At the end of the digital soft-start, SS_END signal is set free.
Protections are active during soft-start: Under voltage is enabled when the reference voltage
reaches 0.6 V while over voltage is always enabled.
Figure 13. Soft-start
OUTEN
V
OUT
SS_END
OVP
TD1TD2TD3T
T
SS
T
D4
t
t
t
D5
Once L6706 receives all the correct supplies and enables, it initiates the soft-start phase
with a T
V - 19 mV) in T
= 1.5 ms (typ) delay. After that, the reference ramps up to V
D1
according to the SSOSC settings and waits for T
D2
= 1.081 V (1.100
BOOT
= 200 μsec (typ) during
D3
which the device reads the VID lines. Output voltage will then ramps up to the programmed
value in T
with the same slope as before (See Figure 13).
D4
SSOSC defines the frequency of an internal additional soft-start-oscillator used to step the
reference from zero up to the programmed value; this oscillator is independent from the
main oscillator whose frequency is programmed through the OSC pin.
The current flowing from SSOSC pin before the end of soft-start is used to program the
desiderated soft-start time (T
SS
).
After that the soft-start is finished the current flowing from SSOSC pin is used to program
the maximum LTB switching frequency (F
In the Figure 14 is shown the SSOSC connection in order to select both parameter (T
F
) in independent way.
LIMIT
In particular, it allows to precisely programming the startup time up to V
a fixed voltage independent by the programmed VID. Total soft-start time dependence on
the programmed VID results (see Figure 15).
LIMIT
).
and
SS
(TD2) since it is
BOOT
Note: If during T
voltage will ramp to the programmed voltage starting from V
the programmed VID selects an output voltage lower than V
D3
BOOT
.
Doc ID 15698 Rev 2 31/47
, the output
BOOT
Page 32

Soft-start L6706
-
Figure 14. SSOSC connection
SSOSCSS_END
R
SSOSC
V
Pull-Up
(1.2V)
R
Pull-Up
(1k)
D
R
FLIMIT
R
FLIM_SS
TSSμs[] 200 μs[]
where T
is the time spent to reach the programmed voltage VSS and R
SS
to SSEND Logic
R
SSOSC
⎧
⎪
⎪
+=
⎨
⎪
⎪
⎩
Soft Start time and FLIMIT
selected in indipendent way.
kΩ[]TD2μs[]40 10
40 10
⋅
40 10
⋅
kΩ[]
3–
kΩ[]
3–
R
SSOSC
---------------------------------- -
R
SSOSC
---------------------------------- -
⋅⋅ ⋅=
---------------------------------------------- -
⋅⋅if V
1.24 V
---------------------------------------------- -
1.24 V
1.24
1.24
Rb(10k)
1.24 V
3–
---------------------------------------------- -
V[]–
DIODE
V[]–
DIODE
Q
Soft Start time depends
on selected FLIMIT.
V[]–
DIODE
1.24
V
SS
------------------
V
BOOT
V
SS
1
------------------+⋅⋅if VSSV
V
BOOT
connected between SSOSC and SSEND (through a signal diode) in kΩ.
Figure 15. Soft-start time (T
) when using R
SS
, diode versus SSEND
SSOSC
>()
SSVBOOT
<()
BOOT
the resistor
SSOSC
Use the following relationship to select the maximum LTB switching frequency:
kΩ[]
where F
has to be higher than the FSW switching frequency.
LIMIT
32/47 Doc ID 15698 Rev 2
FLIMIT
---------------------------------
F
LIMIT
kHz[]
4
⋅
2.11 10
1.24 V
----------------------------------------------
⋅=
CE
1.24
BJT
V[]–
Page 33

L6706 Soft-start
Note: Connecting SSOSC pin to SGND through only the R
Figure 14), the soft-start time depends on the F
LIMIT
In this case use the following relationship to select F
start time:
2.11 104⋅
-------------------------------- -=
F
LIMIT
5.275 105⋅
-------------------------------- -=
F
LIMIT
when using R
Figure 16. Soft-start time (T
R
SS
FLIM SS–
T
D2
) vs F
kΩ[]
μs[]
LIMIT
FLIM_SS
resistor (blue one network in
selected.
and as a consequence the soft-
LIMIT
kHz[]
kHz[]
FLIM_SS
resistor versus SGND
14.1 Low-side-less startup
In order to avoid any kind of negative undershoot on the load side during startup, L6706
performs a special sequence in enabling LS driver to switch: during the soft-start phase, the
LS driver results disabled (LS = OFF) until the HS starts to switch. This avoid the dangerous
negative spike on the output voltage that can happen if starting over a pre-biased output
(see Figure 17).
This particular feature of the device masks the LS turn-on only from the control loop point of
view: protections are still allowed to turn-ON the LS MOSFET in case of over voltage if
needed.
Figure 17. Low-side-less startup comparison.WITH LS-Less startup
WITHOUT LS-Less startup
V
OUT
LGATE
V
WITH LS-Less startup
OUT
LGATE
Doc ID 15698 Rev 2 33/47
Page 34

Output voltage monitor and protections L6706
15 Output voltage monitor and protections
L6706 monitors through pin VSEN the regulated voltage in order to manage the OVP and
UVP conditions. Protections are active also during soft-start (See “Soft-start” Section) while
they are masked during D-VID transitions with an additional 67µs delay after the transition
has finished to avoid false triggering.
15.1 Undervoltage
If the output voltage monitored by VSEN drops more than 600 mV (typ) below the
programmed reference for more than one clock period, the L6706:
– Permanently turns OFF the MOSFETs
– Drives the OSC/ FAULT pin high (3.3 V typ).
– Power supply or OUTEN pin cycling is required to restart operations.
15.2 Preliminary overvoltage
To provide a protection while VCC is below the UVLO
threshold is fundamental to avoid
VCC
damage to the CPU in case of failed HS MOSFETs. In fact, since the device is supplied from
the 12 V bus, it is basically “blind” for any voltage below the turn-on threshold (UVLO
VCC
). In
order to give full protection to the load, a preliminary-OVP protection is provided while VCC
is within UVLO
and UVLO
VCC
Pre-OVP
.
This protection turns-on the low side MOSFETs as long as the VSEN pin voltage is greater
than 1.800 V with a 350 mV hysteresis. When set, the protection drives the LS MOSFET
with a gate-to-source voltage depending on the voltage applied to VCC. This protection
depends also on the OUTEN pin status as detailed in Figure 18.
A simple way to provide protection to the output in all conditions when the device is OFF
(then avoiding the unprotected red region in Figure 18-Left) consists in supplying the
controller through the 5 V
bus as shown in Figure 18-Right: 5VSB is always present before
SB
+12 V and, in case of HS short, the LS MOSFET is driven with 5V assuring a reliable
protection of the load.
Figure 18. Output voltage protections and typical principle connections
BAT54C
SB
10Ω
2.2Ω
1μF
1μF
VCC
VCCDR
UVLO
UVLO
VCC
OVP
V
cc
(OUTEN = 0)
Preliminary OVP
VSEN Monitored
Preliminary OVP Enabled
VSEN Monitored
(OUTEN = 1)
Programmable OVP
VSEN Monitored
No Protection
Provided
+5V
+12V
34/47 Doc ID 15698 Rev 2
Page 35

L6706 Output voltage monitor and protections
15.3 Over voltage and programmable OVP
Once VCC crosses the turn-ON threshold and the device is enabled (OUTEN = 1), L6706
provides an over voltage protection: when the voltage sensed by VSEN overcomes the OVP
threshold (OVP
– Permanently turns OFF the high-side MOSFETs.
– Permanently turns ON the low-side MOSFET in order to protect the load.
– Drives the OSC/ FAULT pin high (3.3 V typ).
– Power supply or OUTEN pin cycling is required to restart operations.
The OVP threshold can be also programmed through the OVP pin: leaving the pin floating, it
is internally pulled-up and the OVP threshold is set to VID + 175 mV (typ).
), the controller:
TH
Connecting the OVP pin to SGND through a resistor R
voltage present at the pin. Since the OVP pin sources a constant I
, the OVP threshold becomes the
OVP
= 20 µA (Min) current
OVP
(see Ta bl e 5 ), the programmed voltage becomes:
OVP
OVP
THROVP
20μAMIN)()⋅= R
----------------------------------=⇒
OVP
20μAMIN)()
TH
Filter OVP pin with 100 pF (max) vs. SGND.
Table 8. Over voltage protection threshold
OVP pin Thresholds OVP threshold
Floating Tracking OVP
to SGND Fixed OVP
R
OVP
= VID + 175 mV (typ)
TH
= R
TH
* 20 μA (min)
OVP
Over voltage protections is always active during the soft-start, as shown in the following
picture:
Figure 19. OVP threshold during soft-start for tracking (left) and fixed (right) mode
OUTEN
V
OUT
SS_END
OVP
TH
1.240V
t
t
t
VID+150mV(MIN)
OUTEN
V
OUT
SS_END
OVP
TH
t
t
t
ROVP * 22uA(MIN)
15.4 Overcurrent protection
The device limits the peak the inductor current entering in constant current until setting UVP
as below explained.
The over current threshold has to be programmed, by designing the R
shown in the Figure 20, to a safe value, in order to be sure that the device doesn't enter
t
OCSET
t
resistors as
Doc ID 15698 Rev 2 35/47
Page 36

Output voltage monitor and protections L6706
OCP during normal operation of the device. This value must take into consideration also the
extra current needed during the dynamic VID transition I
(see Section 12: Dynamic VID
D-VID
transitions for details):
IOUT
OCP
IOUT
MAX
I
+>
DVID–
The device detects an over current when the I
overcome the threshold I
INFO
OCTH
externally
programmable through OCSET pin.
I
INFO
I
OCTH
OCP
V
OCSET
--------------------- -
R
OCSET
DCR
-------------
Rg
1.260 t yp()
----------------------------==
R
OCSET
OCP
⎛⎞
I
⋅=
OUT
⎝⎠
ΔIL
-------- -+
2
where ΔIL is the inductor ripple current (peak-to-peak).
Since the device always senses the current across the inductor, the I
crossing will
OCTH
happen during the HS conduction time: as a consequence of OCP detection, the device will
turn OFF the HS MOSFET and turns ON the LSMOSFET until I
re-cross the threshold
INFO
or until the next clock cycle. This implies that the device limits the peak of the inductor
current.
In any case, the inductor current won't overcome the I
value and this will represent the
OCP
maximum peak value to consider in the OC design.
The device works in constant-current, and the output voltage decreases as the load
increase, until the output voltage reaches the UVP threshold. When this threshold is
crossed, MOSFETs are turned off and the device stops working. Cycle the power supply or
the OUTEN pin to restart operation.
Figure 20. Overcurrent protection connection
V
OCSET
=1.260V (
TYP)
R
OCSET
OCTH
I
OCSET
Note: In order to avoid the OCP intervention during the DVID, the device automatically increases
the OCP threshold to 150% of the selected OCP threshold during every VID transition
(adding an extra
15 µs of delay).
Since the device reads the current information across inductor DCR, the process spread
and temperature variations of these sensing elements has to be considered. Also the
programmable threshold spread (I
36/47 Doc ID 15698 Rev 2
spread, see Ta bl e 5 ) has to be considered for the R
R
OCSET
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------=
DCR MAX )()
---------------------------------- -
current spread as a consequence of V
OCTH
Rg
V
OCSET
⎛⎞
I
⋅ 77μA+
OUT
⎝⎠
design:
OCSET
MIN()
OCP()
ΔIL
-------- -+
2
OCSET
Page 37

L6706 Output voltage monitor and protections
I
DROOP
15.5 Feedback disconnection
L6706 allows to protect the load from dangerous over voltage also in case of feedback
disconnection. The device is able to recognize both FB pin and FBG pin disconnections, as
shown in the Figure 21.
When VSEN pin is more than 500 mV higher then VPROG, the device recognize a FBG
disconnections. Viceversa, when CS- is more than 700 mV higher then VSEN, the device
recognize a FB disconnection.
In both of the previous condition the device stops switching with the MOSFETs permanently
OFF and drives high the OSC/FAULT pin. The condition is latched until VCC or OUTEN
cycled.
Figure 21. Feedback disconnection
500mV
V
PROG
GND DROP
RECOVERY
FBG
FBG
To GND_core
(Remote Sense)
FBG
DISCONNECTED
To VCC_core
(Remote Sense)
VSEN
V
REF
700mV
I
OS
R
FB
FB
R
AMPLIFIER
F
ERROR
COMP
C
C
P
F
PHASE
CS+ CS-
C
R
L
FB
DISCONNECTED
Rg
DCR
V
OUT
Doc ID 15698 Rev 2 37/47
Page 38

Oscillator L6706
16 Oscillator
The internal oscillator generates the triangular waveform for the PWM charging and
discharging with a constant current an internal capacitor. The current delivered to the
oscillator is typically 25 μA (corresponding to the free running frequency F
and it may be varied using an external resistor (R
) connected between the OSC/FAULT
OSC
pin and SGND or VCC (or a fixed voltage greater than 1.24 V). Since the OSC/FAULT pin is
fixed at 1.240 V, the frequency is varied proportionally to the current sunk (forced) from (into)
the pin considering the internal gain of 10 kHz/μA.
= 200 kHz)
SW
F
SW
F
SW
In particular connecting R
pin), while connecting R
to SGND the frequency is increased (current is sunk from the
OSC
to VCC = 12 V the frequency is reduced (current is forced into
OSC
the pin), according the following relationships:
R
vs. SGND
OSC
3
⋅
kΩ()
kΩ()
R
OSC
OSC
kΩ()⇒+
kΩ()⇒
11.284 103⋅
----------------------------------------------------------- -== =kΩ[]
FSWkHz()200 k Hz()–
9.7916 104⋅
----------------------------------------------------------- -== =kΩ[]
200 k Hz()F
SW
200 kHz()
R
vs. +12V
OSC
12V 1.240 V–
200 k Hz()
----------------------------------- -
1.240V
----------------------------
R
OSC
R
kΩ()
OSC
kHz
---------- -
9.1
⋅+ 200 k Hz()
kΩ()
μA
kHz
---------- -
9.1
⋅– 200 k Hz()
μA
11.284 10
------------------------------- -
R
OSC
9.7916 104⋅
------------------------------- -– R
R
OSC
Maximum programmable switching frequency must be limited to 1 MHz to avoid minimum
Ton limitation. Anyway, device power dissipation must be checked prior to design high
switching frequency systems.
Figure 22. R
vs. switching frequency
OSC
kHz()–
38/47 Doc ID 15698 Rev 2
Page 39

L6706 Driver section
17 Driver section
The integrated high-current driver allow using different types of power MOS (also multiple
MOS to reduce the equivalent R
The driver for the high-side MOSFETs use BOOT pin for supply and PHASE pin for return.
The driver for the low-side MOSFETs use VCCDR pin for supply and PGND pin for return. A
minimum voltage at VCCDR pin is required to start operations of the device.
The controller embodies a sophisticated anti-shoot-through system to minimize low side
body diode conduction time maintaining good efficiency saving the use of Schottky diodes:
when the high-side MOSFET turns off, the voltage on its source begins to fall; when the
voltage reaches 2 V, the low-side MOSFET gate drive is suddenly applied. When the lowside MOSFET turns off, the voltage at LGATE pin is sensed. When it drops below 1V, the
high-side MOSFET gate drive is suddenly applied.
If the current flowing in the inductor is negative, the source of high-side MOSFET will never
drop. To allow the turning on of the low-side MOSFET even in this case, a watchdog
controller is enabled: if the source of the high-side MOSFET doesn't drop, the low side
MOSFET is switched on so allowing the negative current of the inductor to recirculate. This
mechanism allows the system to regulate even if the current is negative.
The BOOT and VCCDR pin are separated from IC's power supply (VCC pin) as well as
signal ground (SGND pin) and power ground (PGND pin) in order to maximize the switching
noise immunity.
), maintaining fast switching transition.
ds(ON)
Doc ID 15698 Rev 2 39/47
Page 40

System control loop compensation L6706
DCR
B
C
--
18 System control loop compensation
The control loop is an average current mode control loop (see Figure 5): the output voltage
is equal to the reference programmed by VID minus the droop function terms.
The system control loop is reported in Figure 24. The current information I
the FB pin flows into R
implementing the dependence of the output voltage from the read
FB
DROOP
current.
Figure 23. Main control loop
PWM
ERROR AMPLIFIER
COMP FB
L
C
OUT
V
REF
I
DROOP
ZF(s) ZFB(s)
R
OUT
The control loop gain results (obtained opening the loop after the COMP pin):
G
LOOP
s()
PWM Z
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------–=
ZPs() ZLs()+[]
F
s() R
DROOPZP
Z
s()
F
-------------- 1
⎛⎞
⎝⎠
As()
1
----------- -+
As()
s()+()⋅⋅
R
⋅+⋅
FB
Where:
DCR is the Inductor parasitic resistance;
sourced by
DROOP
Z
(s) is the impedance resulting by the parallel of the output capacitor (and its ESR) and the
P
-------------
Rg
applied load R
Z
(s) is the compensation network impedance;
F
Z
(s) is the inductor impedance;
L
is the equivalent output resistance determined by the droop function;
R
⋅=
F
;
O
A (s) is the error amplifier gain;
V
3
IN
-- -
-----------------
WM
⋅=
5
is the PWM transfer function where ΔV
ΔV
OS
and has a typical value of 1.5 V.
Removing the dependence from the error amplifier gain, so assuming this gain high enough,
and with further simplifications, the control loop gain results:
ZFs()
---------------
R
FB
ROR
------------------------------------------- -
G
LOOP
s()
--- -
⋅⋅⋅ ⋅–=
5
ΔV
OSC
V
3
IN
----------------------
The system control loop gain (see Figure 23) is designed in order to obtain a high DC gain
to minimize static error and to cross the 0dB axes with a constant -20 dB/dec slope with the
40/47 Doc ID 15698 Rev 2
+
RORL+
DROOP
is the oscillator ramp amplitude
OSC
1sCOR
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- -
s2COL⋅⋅s
L
-------- - COESR⋅ CORL⋅++ 1+⋅+
R
O
DROOP
//ROESR+()⋅⋅+
Page 41

L6706 System control loop compensation
desired crossover frequency ωT. Neglecting the effect of ZF(s), the transfer function has one
zero and two poles; both the poles are fixed once the output filter is designed (LC filter
resonance ω
) and the zero (ω
LC
) is fixed by ESR and the droop resistance.
ESR
Figure 24. Equivalent control loop block diagram (left) and bode diagram (right)
I
DROOP
VREF
PWM
d V
L
OUT
C
ESR
O
V
OUT
R
O
dB
G
(s)
LOOP
FB COMP
R
ZF(s)
F
C
P
R
(s)
Z
FB
FB
To obtain the desired shape an R
implementation. A zero at ω
VSEN
C
F
FBG
- CF series network is considered for the ZF(s)
F
= 1/RFCF is then introduced together with an integrator. This
F
integrator minimizes the static error while placing the zero ω
K
RF[dB]
ω
=
ω
LC
F
ω
ESR
in correspondence with the L-
F
Z
(s)
F
ω
T
C resonance assures a simple -20 dB/dec shape of the gain.
In fact, considering the usual value for the output filter, the LC resonance results to be at
frequency lower than the above reported zero.
Compensation network can be simply designed placing ω
over frequency ω
1/10th of the switching frequency F
as desired obtaining (always considering that ωT might be not higher than
T
RFBΔV
⋅
--------------------------------- -
R
F
V
IN
OSC
SW
):
5
-- -
⋅⋅ ⋅=
3
---------------------------------------------- -
ω
T
R
L
DROOP
= ωLC and imposing the cross-
F
COL⋅
------------------- -=
ESR+()
F
R
F
Moreover, it is suggested to filter the high frequency ripple on the COMP pin adding also a
capacitor between COMP pin and FB pin (it does not change the system bandwidth):
1
-------------------------------------- -=
C
P
⋅⋅
2 π R⋅
FFSW
ω
Doc ID 15698 Rev 2 41/47
Page 42

Power dissipation L6706
19 Power dissipation
L6706 embeds high current MOSFET drivers for both high side and low side MOSFETs: it is
then important to consider the power the device is going to dissipate in driving them in order
to avoid overcoming the maximum junction operative temperature.
Exposed pad needs to be soldered to the PCB power ground plane through several VIAs in
order to facilitate the heat dissipation.
Two main terms contribute in the device power dissipation: bias power and drivers' power.
The first one (P
and it is simply quantifiable as follow (assuming to supply HS and LS drivers with the same
VCC of the device):
) depends on the static consumption of the device through the supply pins
DC
P
DCVCCICCICCDRIBOOT
++()⋅=
Drivers' power is the power needed by the driver to continuously switch on and off the
external MOSFETs; it is a function of the switching frequency and total gate charge of the
selected MOSFETs. It can be quantified considering that the total power P
dissipated to
SW
switch the MOSFETs (easy calculable) is dissipated by three main factors: external gate
resistance (when present), intrinsic MOSFET resistance and intrinsic driver resistance. This
last term is the important one to be determined to calculate the device power dissipation.
The total power dissipated to switch the MOSFETs results:
P
SWFSWQGHSVBOOT
⋅ Q
⋅+()⋅=
GLSVCCDR
External gate resistors helps the device to dissipate the switching power since the same
power P
will be shared between the internal driver impedance and the external resistor
SW
resulting in a general cooling of the device. When driving multiple MOSFETs in parallel, it is
suggested to use one gate resistor for each MOSFET.
Figure 25. L6706 dissipated power (quiescent + switching)
42/47 Doc ID 15698 Rev 2
Page 43

L6706 Layout guidelines
20 Layout guidelines
Since the device manages control functions and high-current drivers, layout is one of the
most important things to consider when designing such high current applications. A good
layout solution can generate a benefit in lowering power dissipation on the power paths,
reducing radiation and a proper connection between signal and power ground can optimize
the performance of the control loops. Two kind of critical components and connections have
to be considered when layouting a VRM based on L6706: power components and
connections and small signal components connections.
20.1 Power components and connections
These are the components and connections where switching and high continuous current
flows from the input to the load. The first priority when placing components has to be
reserved to this power section, minimizing the length of each connection and loop as much
as possible. To minimize noise and voltage spikes (EMI and losses) these interconnections
must be a part of a power plane and anyway realized by wide and thick copper traces: loop
must be anyway minimized. The critical components, i.e. the power transistors, must be
close one to the other. The use of multi-layer printed circuit board is recommended.
Figure 26 shows the details of the power connections involved and the current loops. The
input capacitance (C
), or at least a portion of the total capacitance needed, has to be
IN
placed close to the power section in order to eliminate the stray inductance generated by the
copper traces. Low ESR and ESL capacitors are preferred, MLCC are suggested to be
connected near the HS drain. Use proper VIAs number when power traces have to move
between different planes on the PCB in order to reduce both parasitic resistance and
inductance. Moreover, reproducing the same high-current trace on more than one PCB layer
will reduce the parasitic resistance associated to that connection.
Connect output bulk capacitor as near as possible to the load, minimizing parasitic
inductance and resistance associated to the copper trace also adding extra decoupling
capacitors along the way to the load when this results in being far from the bulk capacitor
bank.
Gate traces must be sized according to the driver RMS current delivered to the power
MOSFET. The device robustness allows managing applications with the power section far
from the controller without losing performances. External gate resistors help the device to
dissipate power resulting in a general cooling of the device. When driving multiple
MOSFETs in parallel, it is suggested to use one resistor for each MOSFET.
20.2 Small signal components and connections
These are small signal components and connections to critical nodes of the application as
well as bypass capacitors for the device supply (see Figure 26). Locate the bypass capacitor
(VCC and bootstrap capacitor) close to the device and refer sensible components such as
frequency set-up resistor R
connect SGND to PGND plane in a single point to avoid that drops due to the high current
delivered causes errors in the device behavior.
, over current resistor R
OSC
. Star grounding is suggested:
OCSET
Remote sensing connection must be routed as parallel nets from the FBG/VSEN pins to the
load in order to avoid the pick-up of any common mode noise. Connecting these pins in
Doc ID 15698 Rev 2 43/47
Page 44

Layout guidelines L6706
points far from the load will cause a non-optimum load regulation, increasing output
tolerance. Locate current reading components close to the device. The PCB traces
connecting the reading point must use dedicated nets, routed as parallel traces in order to
avoid the pick-up of any common mode noise. It's also important to avoid any offset in the
measurement and, to get a better precision, to connect the traces as close as possible to
the sensing elements. Small filtering capacitor can be added, near the controller, between
V
and SGND, on the CS- line to allow higher layout flexibility. Power connections and
OUT
related connections layout.
Figure 26. Power connections and related connections layout
UGATE
PHASE
LGATE
PGND
V
IN
C
IN
L
LOAD
To limit C
BOOT
PHASE
VCC
SGND
Extra-Charge
BOOT
BOOT
C
+Vcc
V
IN
C
IN
L
LOAD
Note: Boot capacitor extra charge. systems that do not use schottky diodes might show big
negative spikes on the phase pin. This spike can be limited as well as the positive spike but
has an additional consequence: it causes the bootstrap capacitor to be over-charged. This
extra-charge can cause, in the worst case condition of maximum input voltage and during
particular transients, that boot-to-phase voltage overcomes the abs. max. ratings also
causing device failures. It is then suggested in this cases to limit this extra-charge by adding
a small resistor in series to the boot diode (see Figure 26) and by using standard and lowcapacitive diodes.
20.3 Embedding L6706 - Based VR
When embedding the VRD into the application, additional care must be taken since the
whole VRD is a switching DC/DC regulator and the most common system in which it has to
work is a digital system such as MB or similar. In fact, latest MB has become faster and
powerful: high speed data bus are more and more common and switching-induced noise
produced by the VRD can affect data integrity if not following additional layout guidelines.
Few easy points must be considered mainly when routing traces in which high switching
currents flow (high switching currents cause voltage spikes across the stray inductance of
the trace causing noise that can affect the near traces):
Keep safe guarding distance between high current switching VRD traces and data buses,
especially if high-speed data bus to minimize noise coupling. Keep safe guard distance or
filter properly when routing bias traces for I/O sub-systems that must walk near the VRD.
Possible causes of noise can be located in the PHASE connection, MOSFET gate drive and
Input voltage path (from input bulk capacitors and HS drain). Also PGND connection must
be considered if not insisting on a power ground plane. These connections must be carefully
kept far away from noise-sensitive data bus. Since the generated noise is mainly due to the
switching activity of the VRM, noise emissions depend on how fast the current switches. To
reduce noise emission levels, it is also possible, in addition to the previous guidelines, to
reduce the current slope by properly tuning the HS gate resistor and the PHASE snubber
network.
44/47 Doc ID 15698 Rev 2
Page 45

L6706 Package mechanical data
21 Package mechanical data
In order to meet environmental requirements, ST offers these devices in different grades of
ECOPACK
specifications, grade definitions and product status are available at: www.st.com.
ECOPACK
®
packages, depending on their level of environmental compliance. ECOPACK®
®
is an ST trademark.
Table 9. VFQFPN-40 mechanical data
mm inch
Dim.
Min. Typ. Max. Min. Typ. Max.
A 0.800 0.900 1.000 0.031 0.035 0.039
A1 0.020 0.050 0.0008 0.0019
b 0.180 0.250 0.300 0.007 0.009 0.012
D 5.900 6.000 6.100 0.232 0.236 0.240
D2 3.950 4.100 4.200 0.155 0.161 0.165
E 5.900 6.000 6.100 0.232 0.236 e 0.240
E2 3.950 4.100 4.200 0.155 0.161 0.165
e 0.500 0.020
L 0.300 0.400 0.500 id 0.012 0.015 0.018
ddd 0.080 0.003
Figure 27. VFQFPN-40 package dimensions
ddd
Doc ID 15698 Rev 2 45/47
Page 46

Revision history L6706
22 Revision history
Table 10. Document revision history
Date Revision Changes
26-May-2009 1 First release
20-Jan-2010 2
Updated Table 2 on page 6, Table4 on page10, Chapter 10 on
page 24, Figure 9 on page 24 and Chapter 16 on page 38
46/47 Doc ID 15698 Rev 2
Page 47

L6706
Please Read Carefully:
Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the
right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any
time, without notice.
All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no
liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and services described herein.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted under this document. If any part of this
document refers to any third party products or services it shall not be deemed a license grant by ST for the use of such third party products
or services, or any intellectual property contained therein or considered as a warranty covering the use in any manner whatsoever of such
third party products or services or any intellectual property contained therein.
UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS
OF ANY JURISDICTION), OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS EXPRESSLY APPROVED IN WRITING BY AN AUTHORIZED ST REPRESENTATIVE, ST PRODUCTS ARE NOT
RECOMMENDED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN MILITARY, AIR CRAFT, SPACE, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE SUSTAINING
APPLICATIONS, NOR IN PRODUCTS OR SYSTEMS WHERE FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY,
DEATH, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE. ST PRODUCTS WHICH ARE NOT SPECIFIED AS "AUTOMOTIVE
GRADE" MAY ONLY BE USED IN AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS AT USER’S OWN RISK.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the statements and/or technical features set forth in this document shall immediately void
any warranty granted by ST for the ST product or service described herein and shall not create or extend in any manner whatsoever, any
liability of ST.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of ST in various countries.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners.
© 2010 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
STMicroelectronics group of companies
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Philippines - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
Doc ID 15698 Rev 2 47/47
 Loading...
Loading...