现货库存、技术资料、百科信息、热点资讯,精彩尽在鼎好!
Multi-mode controller for SMPS with PFC front-end
Features
■ Selectable multi-mode operation:
fixed frequency or quasi-resonant
■ On-board 700 V high-voltage start-up
■ Advanced light load management
■ Low quiescent current (< 3 mA)
■ Adaptive UVLO
■ Line feedforward for constant power capability
vs. mains voltage
■ Pulse-by-pulse OCP, shutdown on overload
(latched or autorestart)
■ Transformer saturation detection
■ Switched supply rail for PFC controller
■ Latched or autorestart OVP
■ Brownout protection
■ -600/+800 mA totem pole gate driver with
active pull-down during UVLO
■ SO16N package
L6566A
SO16N
Applications
■ Notebook, TV &LCD monitors adapters
■ High power chargers
■ PDP/LCD TV
■ Consumer appliances, like DVD, VCR, set-top
box
■ IT equipment, games, aux. power supplies
■ Power supplies in excess of 150 W
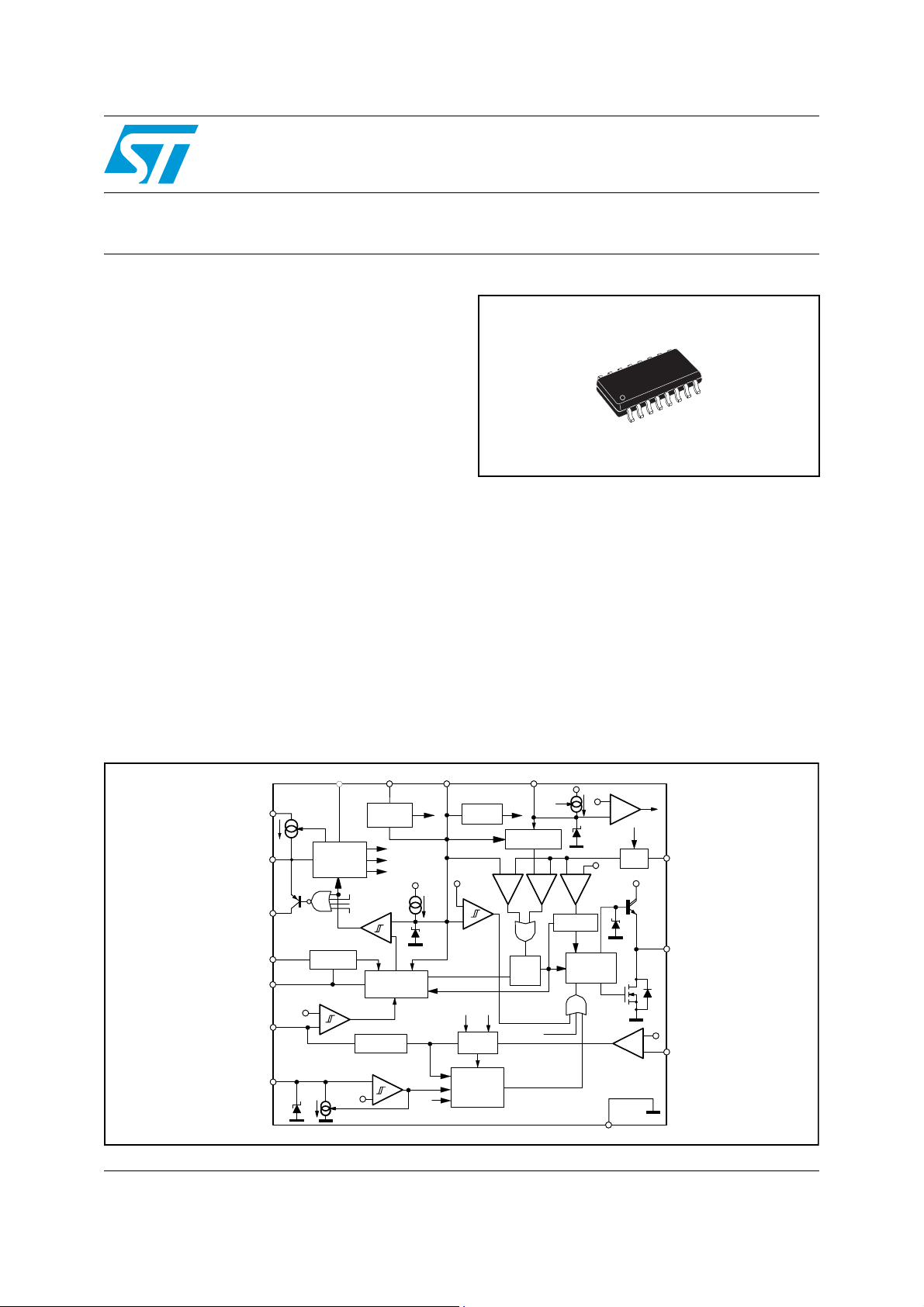
Figure 1. Block diagram
Vcc_PFC
OSC
MODE/S C
ZCD
AC_OK
VREF
10
1
HV
I
charge
V
CC
5
6
13
12
100 mV
11
16
50 mV
3 V
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
ADAPTIVE UVLO
UVLO_SHF
OSCILLATOR
+
15 µA
&
OCP2
IC_LATCH
AC_ FAIL
ZERO CURRENT
DETECTOR
OVERVOLTAGE
0.450V
0.485V
SS
14
SOFT-START
&
FAULT MNGT
Ref er ence
voltages
Internal supply
UVL O
+
MODE SELECTIO N
&
TURN-ON LOGIC
PROTECTION
-
+
August 2007 Rev 1 1/51
COMP
915
TIME
OUT
LOW CLA MP
& DISABLE
Vth
V
CC
400 uA
+
-
5.7V
BURST-MODE
TIME
OVPL
OUT
OVP
LATCH
IC_LATCH
AC_FAIL
UVLO
DISABLE
VFF
OFF2
LINE VOLTAGE
FEEDFORWARD
+-
OCPPWM
R
Q
S
OFF2
OVP
+-
V
CC
+-
Hiccup-mode
OCP logic
OCP2
DRIVER
7.7V
1 mA
GND
6.4V
3
1.5 V
OVPL
+
Q
V
CC
14V
LEB
CS
7
4
GD
4.5V
+
DIS
8
www.st.com
51

Contents L6566A
Contents
1 Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2 Pin settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.1 Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.2 Pin description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
3 Electrical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
3.1 Maximum rating . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
3.2 Thermal data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
4 Electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
5 Application information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
5.1 High-voltage start-up generator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
5.2 Zero current detection and triggering block; oscillator block . . . . . . . . . . 21
5.3 Burst-mode operation at no load or very light load . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
5.4 Adaptive UVLO . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
5.5 PWM control block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
5.6 PWM comparator, PWM latch and voltage feedforward blocks . . . . . . . . 27
5.7 Hiccup-mode OCP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
5.8 PFC interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
5.9 Latched disable function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
5.10 Soft-start and delayed latched shutdown upon overcurrent . . . . . . . . . . . 33
5.11 OVP block . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
5.12 Brownout protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
5.13 Slope compensation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
5.14 Summary of L6566A power management functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
2/51

L6566A Contents
6 Application examples and ideas . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
7 Package mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
8 Order codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
9 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
3/51

List of tables L6566A
List of tables
Table 2. Pin functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Table 3. Absolute maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Table 4. Thermal data. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Table 5. Electrical characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Table 6. L6566A light load management features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Table 7. L6566A protections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Table 8. External circuits that determine IC behavior upon OVP and OCP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Table 9. SO16N mechanical data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Table 10. Order codes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Table 11. Document revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
4/51

L6566A List of figures
List of figures
Figure 1. Block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Figure 2. Typical system block diagram. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Figure 3. Pin connection (through top view) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Figure 4. Multi-mode operation with QR option active . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Figure 5. High-voltage start-up generator: internal schematic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Figure 6. Timing diagram: normal power-up and power-down sequences . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Figure 7. Timing diagram showing short-circuit behavior (SS pin clamped at 5V). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Figure 8. Zero current detection block, triggering block, oscillator block and related logic . . . . . . . . 20
Figure 9. Drain ringing cycle skipping as the load is gradually reduced . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Figure 10. Operation of ZCD, triggering and Oscillator blocks (QR option active). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Figure 11. Load-dependent operating modes: timing diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Figure 12. Addition of an offset to the current sense lowers the burst-mode operation threshold. . . . 25
Figure 13. Adaptive UVLO block. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Figure 14. Possible feedback configurations that can be used with the L6566A. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Figure 15. Externally controlled burst-mode operation by driving pin COMP: timing diagram. . . . . . . 27
Figure 16. Typical power capability change vs input voltage in QR flyback converters . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Figure 17. Left: Overcurrent setpoint vs. VFF voltage; right: Line Feedforward function block . . . . . . 29
Figure 18. Hiccup-mode OCP: timing diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Figure 19. Possible interfaces between the L6566A and a PFC controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Figure 20. Operation after latched disable activation: timing diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Figure 21. Soft-start pin operation under different operating conditions and settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Figure 22. OVP Function: internal block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Figure 23. OVP function: timing diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Figure 24. Maximum allowed duty cycle vs. switching frequency for correct OVP detection. . . . . . . . 37
Figure 25. Brownout protection: internal block diagram and timing diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Figure 26. Ac voltage sensing with the L6566A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Figure 27. Slope compensation waveforms . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Figure 28. Typical low-cost application schematic . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Figure 29. Typical full-feature application schematic (QR operation) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Figure 30. Typical full-feature application schematic (FF operation) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Figure 31. Frequency foldback at light load (FF operation) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Figure 32. Latched shutdown upon mains overvoltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
5/51

Description L6566A
1 Description
The L6566A is an extremely versatile current-mode primary controller IC specifically
designed for high-performance offline flyback converters operated from front-end Power
Factor Correction (PFC) stages in applications supposed to comply with EN61000-3-2 or
JEITA-MITI regulations.
Both Fixed-frequency (FF) and Quasi-resonant (QR) operation are supported. The user can
pick either of the two depending on application needs.
The device features an externally programmable oscillator: it defines converter's switching
frequency in FF mode and the maximum allowed switching frequency in QR mode.
When FF operation is selected, the IC works like a standard current-mode controller with a
maximum duty cycle limited at 70% min.
QR operation, when selected, occurs and is achieved through a transformer
demagnetization sensing input that triggers MOSFET's turn-on. Under some conditions,
ZVS (Zero-voltage Switching) can be achieved. Converter's power capability rise with the
input voltage is compensated by line voltage feedforward. At medium and light load, as the
QR operating frequency equals the oscillator frequency, a function (valley skipping) is
activated to prevent further frequency rise and keep the operation as close to ZVS as
possible.
With either FF or QR operation, at very light load the IC enters a controlled burst-mode
operation that, along with the built-in non-dissipative high-voltage start-up circuit and a
reduced quiescent current, helps keep low the consumption from the mains and meet
energy saving recommendations.
To allow meeting them in two-stage power-factor-corrected systems as well, the L6566A
provides an interface with the PFC controller that enables to turn off the pre-regulator at light
load.
An innovative adaptive UVLO helps minimize the issues related to the fluctuations of the
self-supply voltage due to transformer's parasitics.
The protection functions included in this device are: not-latched input undervoltage
(brownout), output OVP (auto-restart or latch-mode selectable), a first-level OCP with
delayed shutdown to protect the system during overload or short circuit conditions (autorestart or latch-mode selectable) and a second-level OCP that is invoked when the
transformer saturates or the secondary diode fails short. A latched disable input allows easy
implementation of OTP with an external NTC, while an internal thermal shutdown prevents
IC overheating.
Programmable soft-start, leading-edge blanking on the current sense input for greater noise
immunity, slope compensation (in FF mode only), and a shutdown function for externally
controlled burst-mode operation or remote ON/OFF control complete the equipment of this
device.
6/51
L6566A Description
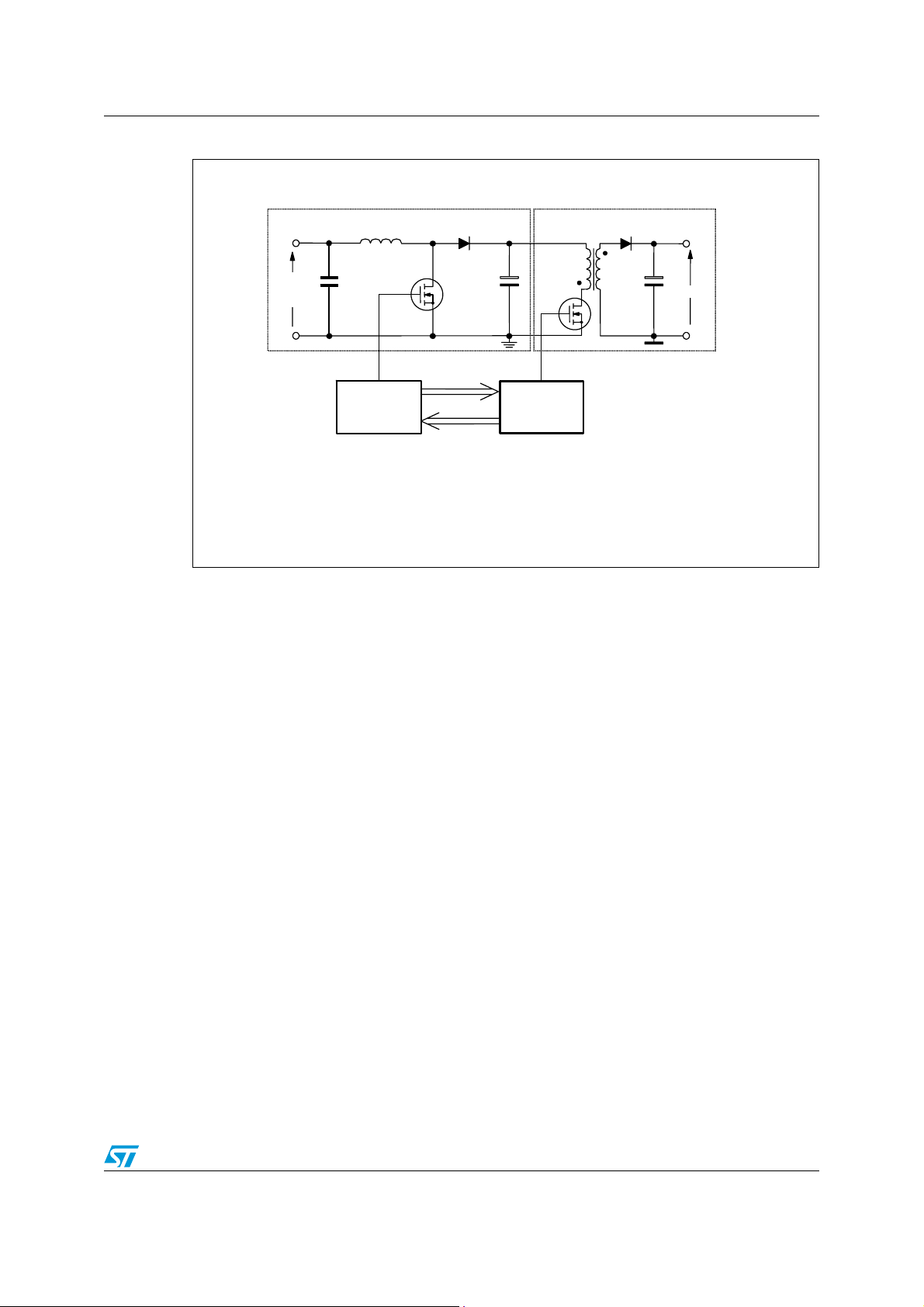
Figure 2. Typical system block diagram
PFC PRE-REGULATOR
Rectified
Mains
Voltage
L6563/A
PFC
FLYBACK DC-DC CONVERTER
PWM/QR controller is turned off in case of PFC's
anomalous operation, for safety
L6566A
PFC is automatically turned off at light
load to ease compliance with
energy saving specifications.
V outdc
7/51
Pin settings L6566A
2 Pin settings
2.1 Connections
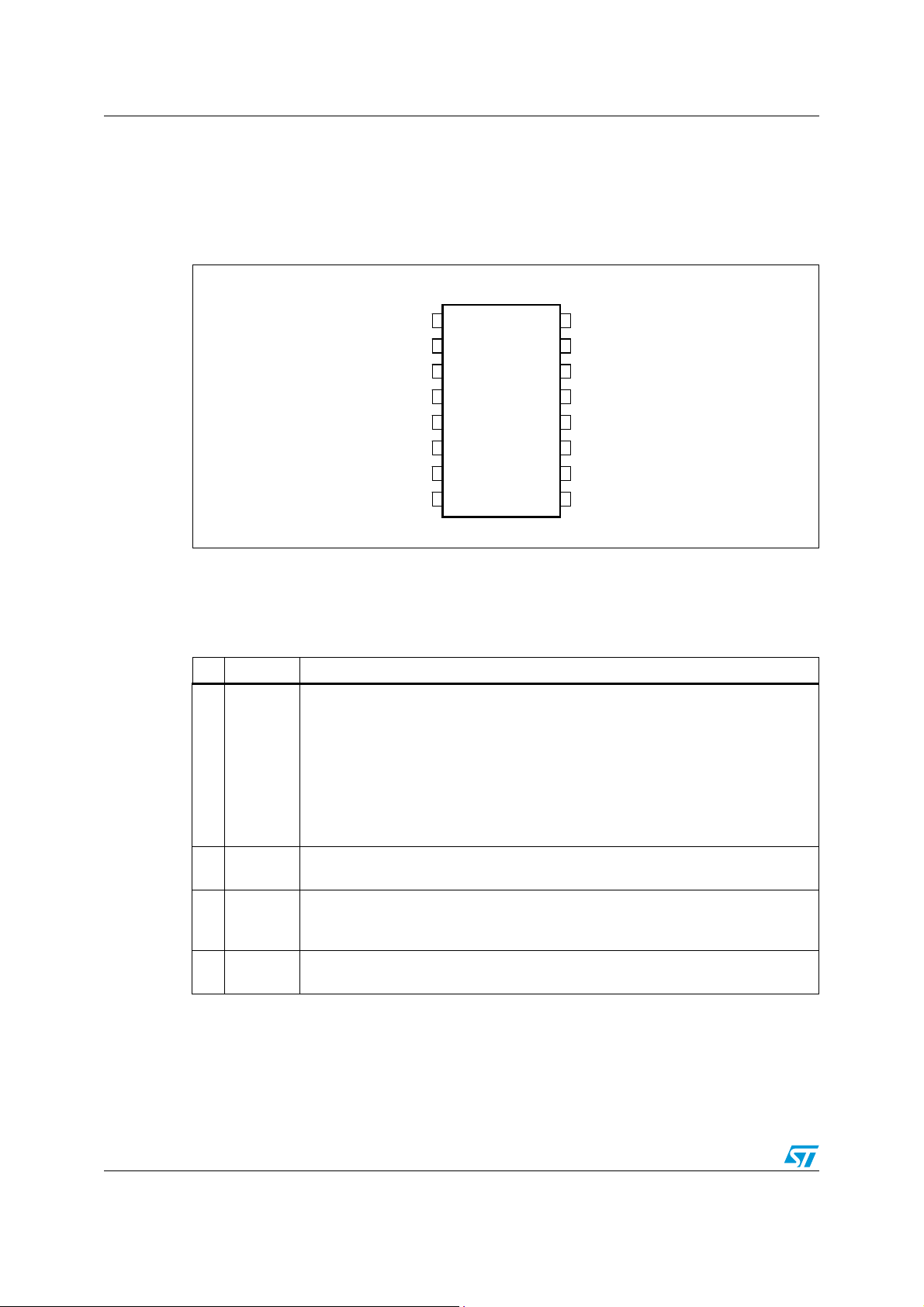
Figure 3. Pin connection (through top view)
1
HVS AC_OK
HVS AC_OK
N.C.
N.C.
GND
GND
GD
GD
Vcc
Vcc
Vcc_PFC
Vcc_PFC
CS
CS
DIS
DIS
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
5
5
6
6
7
7
8
8
16
16
15
15
14
14
13
13
12
12
11
11
10
10
9
9
VFF
VFF
SS
SS
OSC
OSC
MODE/SC
MODE/SC
ZCD
ZCD
VREF
VREF
COMP
COMP
2.2 Pin description
Table 2. Pin functions
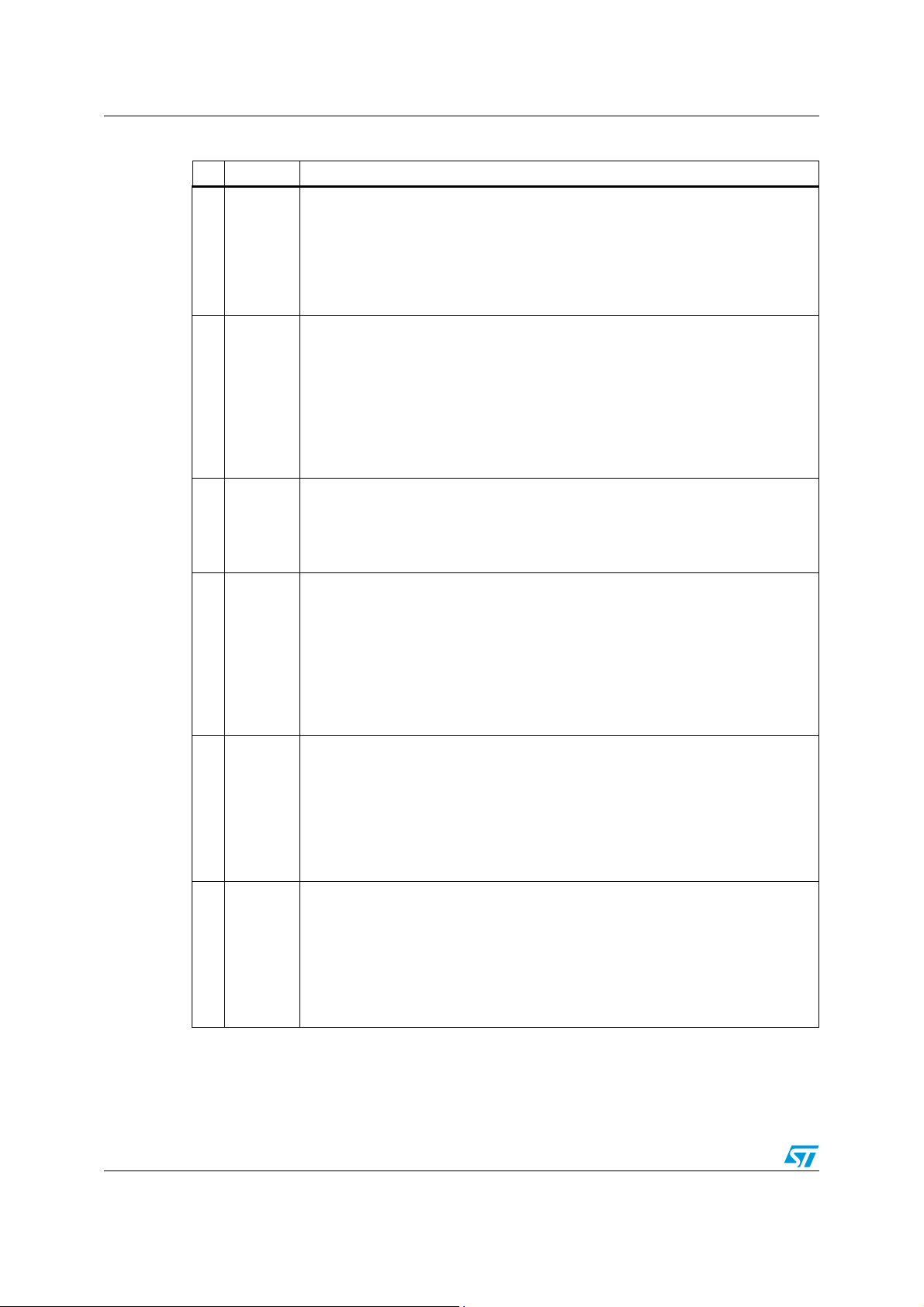
N° Pin Function
High-voltage start-up. The pin, able to withstand 700V, is to be tied directly to the
rectified mains voltage. A 1 mA internal current source charges the capacitor
connected between Vcc pin (5) and GND pin (3) until the voltage on the Vcc pin
reaches the turn-on threshold, then it is shut down. Normally, the generator is re-
1HVS
2N.C.
3GND
4GD
enabled when the Vcc voltage falls below 5V to ensure a low power throughput
during short circuit. Otherwise, when a latched protection is tripped the generator is
re-enabled 0.5V below the turn-on threshold, to keep the latch supplied; or, when
the IC is turned off by pin COMP (9) pulled low the generator is active just below
the UVLO threshold to allow a faster restart.
Not internally connected. Provision for clearance on the PCB to meet safety
requirements.
Ground. Current return for both the signal part of the IC and the gate drive. All of
the ground connections of the bias components should be tied to a track going to
this pin and kept separate from any pulsed current return.
Gate driver output. The totem pole output stage is able to drive power MOSFET’s
and IGBT’s with a peak current capability of 800 mA source/sink.
8/51
L6566A Pin settings
Table 2. Pin functions (continued)
N° Pin Function
Supply Voltage of both the signal part of the IC and the gate driver. The internal
high voltage generator charges an electrolytic capacitor connected between this
pin and GND (pin 3) as long as the voltage on the pin is below the turn-on threshold
5Vcc
6Vcc_PFC
7CS
of the IC, after that it is disabled and the chip is turned on. The IC is disabled as the
voltage on the pin falls below the UVLO threshold. This threshold is reduced at light
load to counteract the natural reduction of the self-supply voltage. Sometimes a
small bypass capacitor (0.1 µF typ.) to GND might be useful to get a clean bias
voltage for the signal part of the IC.
Supply pin output. This pin is intended for supplying the PFC controller IC in
systems comprising a PFC pre-regulator or other compatible circuitry. It is internally
connected to the Vcc pin (5) via a controlled switch. The switch is closed as the IC
starts up and opens when the voltage at pin COMP is lower than a threshold (light
load), whenever the IC is shut down (either latched or not) and during UVLO. If not
used, the pin will be left floating.
Input to the PWM comparator. The current flowing in the MOSFET is sensed
through a resistor, the resulting voltage is applied to this pin and compared with an
internal reference to determine MOSFET’s turn-off. The pin is equipped with 150 ns
min. blanking time after the gate-drive output goes high for improved noise
immunity. A second comparison level located at 1.5V latches the device off and
reduces its consumption in case of transformer saturation or secondary diode short
circuit. The information is latched until the voltage on the Vcc pin (5) goes below
the UVLO threshold, hence resulting in intermittent operation. A logic circuit
improves sensitivity to temporary disturbances.
8DIS
9COMP
10 VREF
IC’s latched disable input. Internally the pin connects a comparator that, when the
voltage on the pin exceeds 4.5V, latches off the IC and brings its consumption to a
lower value. The latch is cleared as the voltage on the Vcc pin (5) goes below the
UVLO threshold, but the HV generator keeps the Vcc voltage high (see pin 1
description). It is then necessary to recycle the input power to restart the IC. For a
quick restart pull pin 16 (AC_OK) below the disable threshold (see pin 16
description).Bypass the pin with a capacitor to GND (pin 3) to reduce noise pick-up.
Ground the pin if the function is not used.
Control input for loop regulation. The pin will be driven by the phototransistor
(emitter-grounded) of an optocoupler to modulate its voltage by modulating the
current sunk. A capacitor placed between the pin and GND (3), as close to the IC
as possible to reduce noise pick-up, sets a pole in the output-to-control transfer
function. The dynamics of the pin is in the 2.5 to 5V range. A voltage below an
internally defined threshold activates burst-mode operation. The voltage at the pin
is bottom-clamped at about 2V. If the clamp is externally overridden and the voltage
is pulled below 1.4V the IC will shut down.
An internal generator furnishes an accurate voltage reference (5V±2%) that can be
used to supply few mA to an external circuit. A small film capacitor (0.1 µF typ.),
connected between this pin and GND (3), is recommended to ensure the stability of
the generator and to prevent noise from affecting the reference. This reference is
internally monitored by a separate auxiliary reference and any failure or drift will
cause the IC to latch off.
9/51
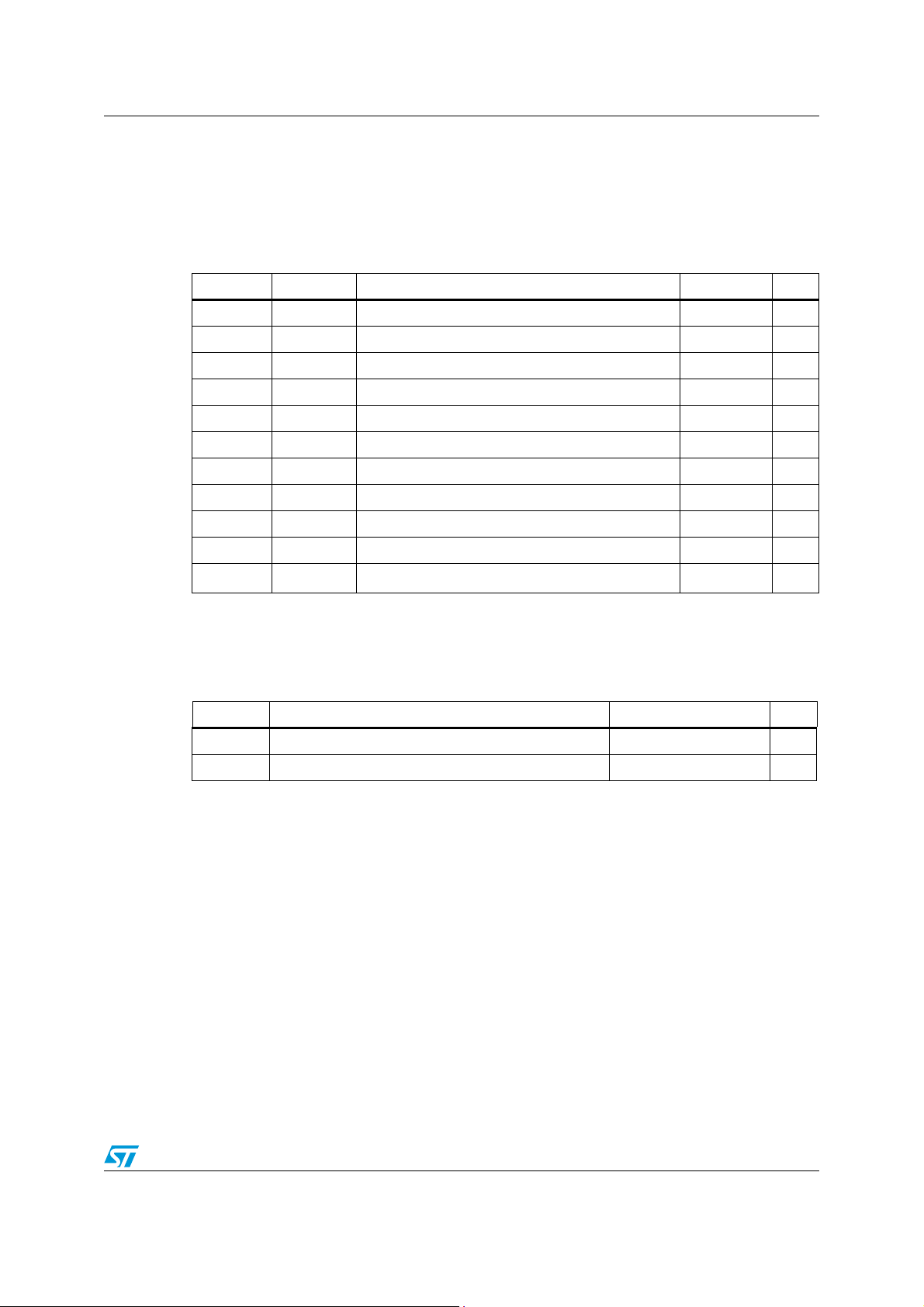
Pin settings L6566A
Table 2. Pin functions (continued)
N° Pin Function
Transformer demagnetization sensing input for quasi-resonant operation and OVP
input. The pin is externally connected to the transformer’s auxiliary winding through
a resistor divider. A negative-going edge triggers MOSFET’s turn-on if QR mode is
11 ZCD
12 MODE/SC
13 OSC
14 SS
15 VFF
selected.
A voltage exceeding 5V shuts the IC down and brings its consumption to a lower
value (OVP). Latch-off or auto-restart mode is selectable externally. This function is
strobed and digitally filtered to increase noise immunity.
Operating mode selection. If the pin is connected to the VREF pin (7) Quasiresonant operation is selected and the oscillator (pin 13, OSC) determines the
maximum allowed operating frequency.
Fixed-frequency operation is selected if the pin is not tied to VREF, in which case
the oscillator determines the actual operating frequency, the maximum allowed
duty cycle is set at 70% min. and the pin delivers a voltage ramp synchronized to
the oscillator when the gate-drive output is high; the voltage delivered is zero while
the gate-drive output is low. The pin is to be connected to pin CS (7) via a resistor
for slope compensation.
Oscillator pin. The pin is an accurate 1 V voltage source, and a resistor connected
from the pin to GND (pin 3) defines a current. This current is internally used to set
the oscillator frequency that defines the maximum allowed switching frequency of
the L6566A, if working in QR mode, or the operating switching frequency if working
in FF mode.
Soft-start current source. At start-up a capacitor Css between this pin and GND
(pin 3) is charged with an internal current generator. During the ramp, the internal
reference clamp on the current sense pin (7, CS) rises linearly starting from zero to
its final value, thus causing the duty cycle to increase progressively starting from
zero as well. During soft-start the Adaptive UVLO function and all functions
monitoring pin COMP are disabled. The soft-start capacitor is discharged whenever
the supply voltage of the IC falls below the UVLO threshold. The same capacitor is
used to delay IC’s shutdown (latch-off or auto-restart mode selectable) after
detecting an overload condition (OLP).
Line voltage feedforward input. The information on the converter’s input voltage is
fed into the pin through a resistor divider and is used to change the setpoint of the
pulse-by-pulse current limitation (the higher the voltage, the lower the setpoint).
The linear dynamics of the pin ranges from 0 to 3V. A voltage higher than 3V makes
the IC stop switching. If feedforward is not desired, tie the pin to GND (pin 3)
directly if a latch-mode OVP is not required (see pin 11, ZCD) or through a resistor
if a latch-mode OVP is required. Bypass the pin with a capacitor to GND (pin 3) to
reduce noise pick-up.
Brownout protection input. A voltage below 0.45V shuts down (not latched) the IC,
lowers its consumption, opens the Vcc_PFC pin (6), and clears the latch set by
latched protections (DIS>4.5V, SS>6.4V, VFF>6.4V). IC’s operation is re-enabled
16 AC_OK
10/51
as the voltage exceeds 0.45V. The comparator is provided with current hysteresis:
an internal 15 µA current generator is ON as long as the voltage on the pin is below
0.45V and is OFF if this value is exceeded. Bypass the pin with a capacitor to GND
(pin 3) to reduce noise pick-up. Tie to Vcc with a 220 to 680 kΩ resistor if the
function is not used.
L6566A Electrical data
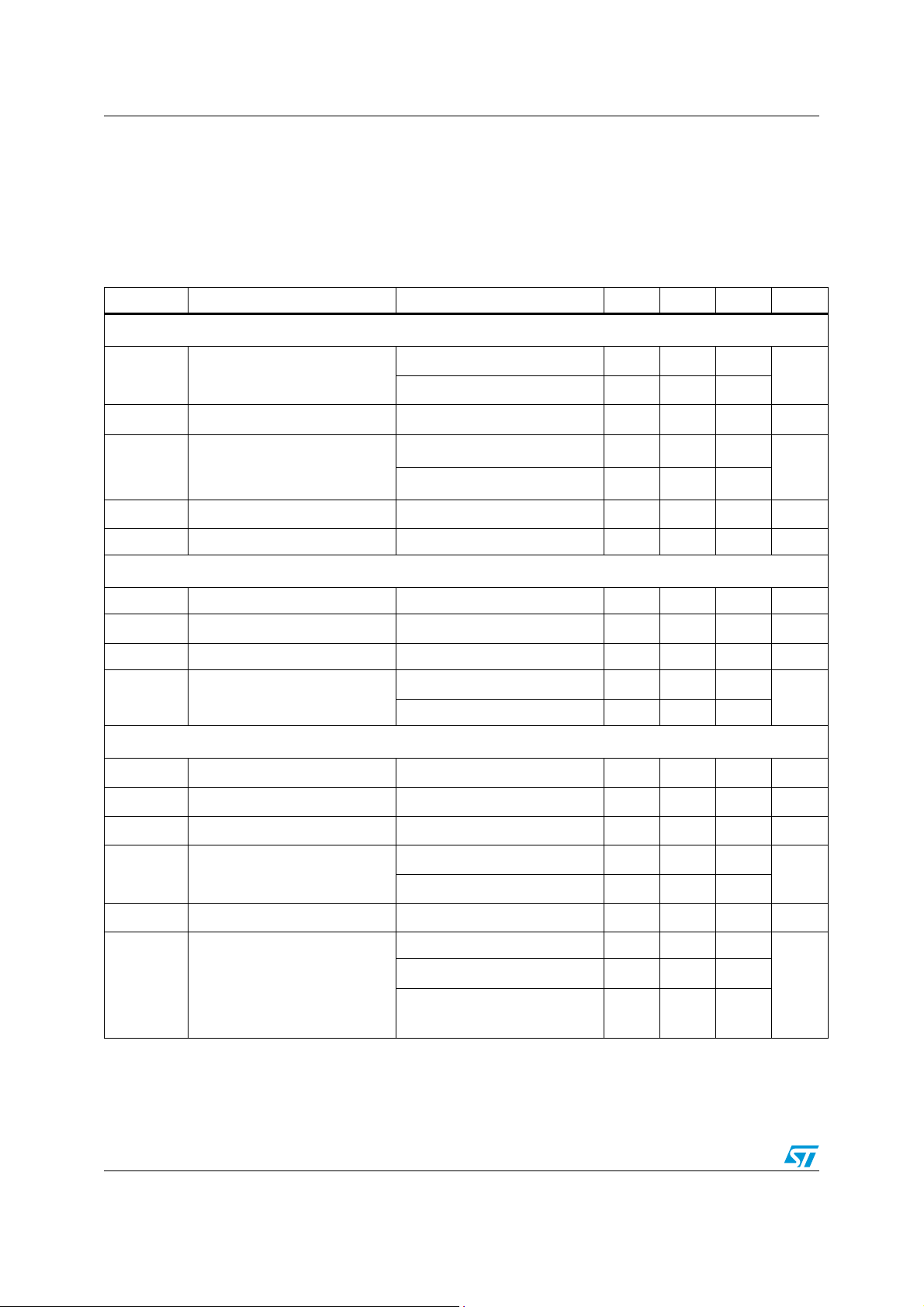
3 Electrical data
3.1 Maximum rating
Table 3. Absolute maximum ratings
Symbol Pin Parameter Value Unit
V
HVS
I
HVS
V
CC
V
Vcc_PFC
I
Vcc_PFC
V
max
V
max
I
ZCD
V
MODE/SC
V
OSC
P
TOT
1 Voltage range (referred to ground) -0.3 to 700 V
1 Start-up current Self-limited
5 IC supply voltage (Icc = 20 mA) Self-limited
6 Voltage range -0.3 to Vcc V
6 Max. source current (continuous) 30 mA
7, 8, 10, 14 Analog inputs & outputs -0.3 to 7 V
9, 15, 16 Maximum pin voltage (Ipin ≤ 1mA) Self-limited
11 Zero current detector max. current ±5 mA
12 Voltage range -0.3 to 5 V
13 Voltage range -0.3 to 3.3 V
Power dissipation @TA = 50°C
0.75 W
3.2 Thermal data
Table 4. Thermal data
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
R
thJA
T
Thermal resistance junction to ambient 120 °C/W
Junction operating temperature range -40 to 150 °C
J
11/51
Electrical characteristics L6566A
4 Electrical characteristics
(TJ = -25 to 125°C, VCC = 12, CO = 1 nF; MODE/SC=V
, RT = 20 kΩ from OSC to GND,
REF
unless otherwise specified).
Table 5. Electrical characteristics
Symbol Parameter Test condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Supply voltage
V
Vcc Operating range after turn-on
V
Vcc
Vcc
Turn-on threshold
On
Turn-off threshold
Off
Hys Hysteresis
V
Zener voltage Icc = 20 mA, IC disabled 23 25 27 V
Z
(1)
(1)
(1)
V
Supply current
I
start-up
I
q
Start-up current Before turn-on, Vcc = 13 V 200 250 µA
Quiescent current
After turn-on, V
Icc Operating supply current MODE/SC open 4 4.6 mA
I
qdis
Quiescent current
IC disabled
IC latched off 440 500
COMP
COMP
V
COMP
V
COMP
COMP
> V
= V
> V
COMPL
COMPO
> V
= V
COMPL
(2)
COMPL
COMPO
ZCD
= V
CS
= 1V
10.6 23
823
13 14 15 V
9.4 10 10.6
7.2 7.6 8.0
4V
2.6 2.8 mA
330 2500
V
V
µA
High-voltage start-up generator
I
V
HV
V
HVstart
I
charge
I
HV, ON
I
HV, OFF
Breakdown voltage
Start voltage
Vcc charge current
ON-state current
OFF-state leakage current
< 100 µA
HV
< 100 µA
I
Vcc
V
HV
V
HV
V
HV
V
HV
> V
Hvstart
> V
Hvstart
> V
Hvstart
= 400 V
Vcc falling 4.4 5 5.6
(1)
V
CCrestart
Vcc restart voltage
IC latched off
(1)
Disabled by
COMP
< V
V
12/51
, Vcc > 3V
, Vcc > 3V
, Vcc = 0
COMPOFF
700 V
65 80 100 V
0.55 0.85 1 mA
1.6
mA
0.8
40 µA
12.5 13.5 14.5
V
9.4 10 10.6
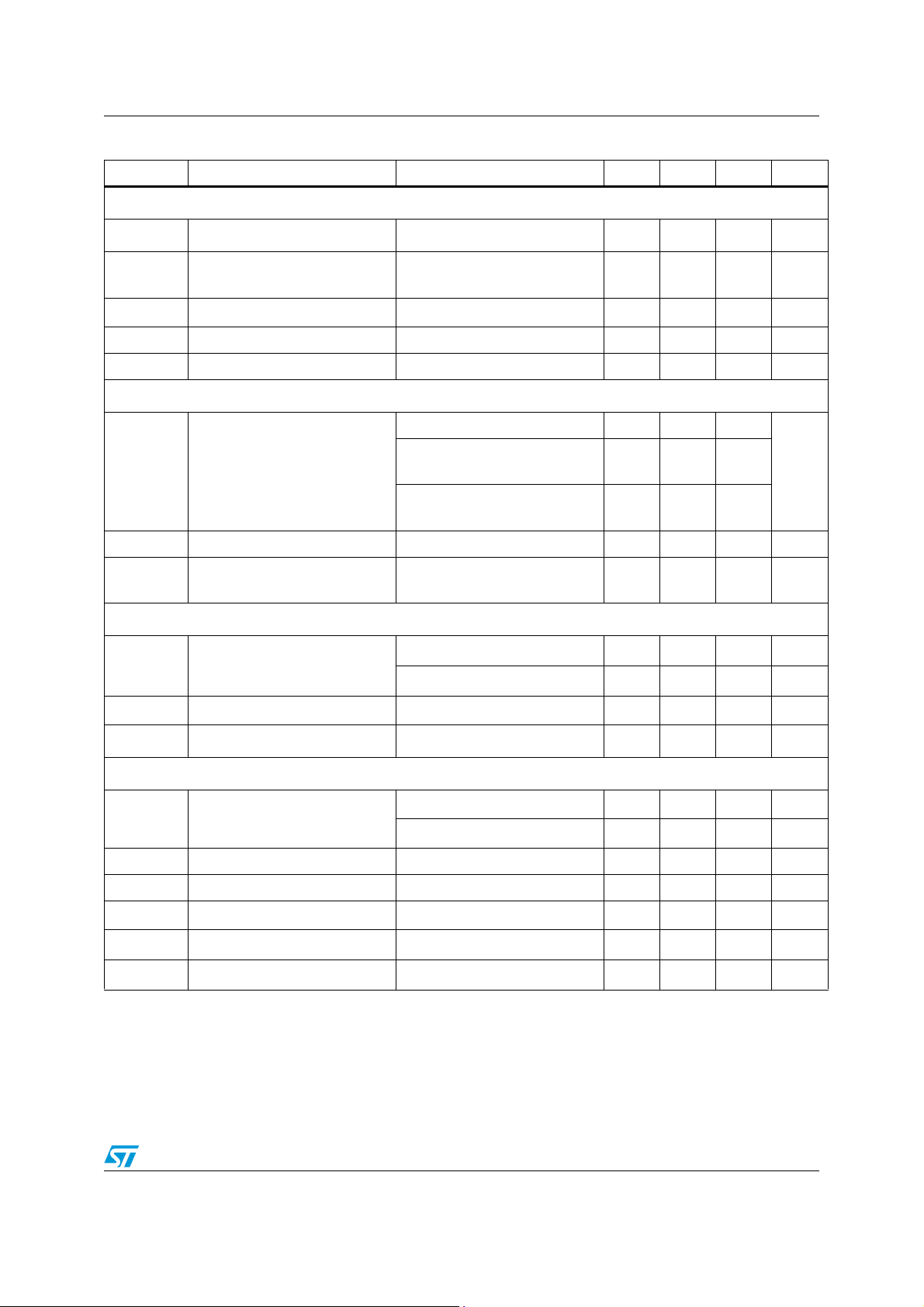
L6566A Electrical characteristics
Table 5. Electrical characteristics (continued)
Symbol Parameter Test condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Reference voltage
V
V
I
REF
REF
REF
Output voltage
To t al va r i at io n
Short circuit current
Sink capability in UVLO Vcc = 6V; Isink = 0.5 mA 0.2 0.5 V
V
OV
Overvoltage threshold 5.3 5.7 V
Internal oscillator
V
D
f
sw
OSC
max
Oscillation frequency
Voltage reference
Maximum duty cycle
Brownout protection
Vth Threshold voltage
I
Hys
V
AC_OK_CL
Current Hysteresis
Clamp level
(1)
TJ = 25 °C; I
I
= 1 to 5 mA,
REF
REF
Vcc= 10.6 to 23 V
= 0
V
REF
= 1 mA
4.95 5 5.05 V
4.9 5.1 V
10 30 mA
Operating range 10 300
TJ = 25°C, V
MODE/SC = Open
Vcc=12 to 23 V, V
MODE/SC = Open
(3)
MODE/SC = Open,
V
= 5 V
COMP
Voltage falling (turn-off)
Voltage rising (turn-on)
Vcc > 5V, V
(1)
I
AC_OK
ZCD
= 0.3V
VFF
= 100µA
= 0,
ZCD
= 0,
95 100 105
93 100 107
0.97 1 1.03 V
70 75 %
0.432 0.450 0.468 V
0.452 0.458 0.518 V
12 15 18 µA
33.153.3 V
kHz
Line voltage feedforward
I
VFF
V
VFF
V
OFF
V
VFFlatch
Kc
K
FF
Input bias current
Linear operation range 0 to 3 V
IC disable voltage 3 3.15 3.3 V
Latch-off/clamp level
Control voltage gain
Feedforward gain
(3)
(3)
V
V
V
V
V
VFF
ZCD
ZCD
VFF
VFF
= 0 to 3 V, V
> V
ZCDth
> V
ZCDth
= 1 V, V
= 1 V, V
COMP
COMP
ZCD
< V
= 4 V
= 4 V
ZCDth
-1 µA
-0.7 -1 mA
6.4 V
0.4 V/V
0.04 V/V
13/51
Electrical characteristics L6566A
Table 5. Electrical characteristics (continued)
Symbol Parameter Test condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Current sense comparator
V
= 0
CS
V
V
V
(1)
I
I
(1)
V
(1)
(1)
V
= V
COMP
COMP
COMP
COMP
SOURCE
V
COMP
COMP
COMPHI
= V
COMPHI
= V
COMPHI
= 0
= -1mA
= 0V
VFF
= 3.3 V
= 2.6 to 4.8 V
MODE/SC = Open
= 2V
COMP
, V
, V
, V
VFF
VFF
VFF
= 0V
= 1.5V
= 3.0V
-1 µA
0.92 1 1.08
0.45 0.5 0.55
00.1
1.4 1.5 1.6 V
5.7 V
2.0 V
4.8 5 5.2 V
320 400 480 µA
25 kΩ
2.52 2.65 2.78
2.7 2.85 3
-3.5 -1.5 mA
V
V
td
V
V
I
CS
t
LEB
(H-L)
CSx
CSdis
Input bias current
Leading edge blanking 150 250 300 ns
Delay to output 100 ns
Overcurrent setpoint
Hiccup-mode OCP level
PWM control
V
COMPHI
V
COMPLO
V
COMPSH
I
COMP
R
COMP
V
COMPBM
Upper clamp voltage
Lower clamp voltage
Linear dynamics upper limit
Max. source current V
Dynamic resistance
Burst-mode threshold
Hys Burst-mode hysteresis 20 mV
I
CLAMPL
V
COMPOFF
Lower clamp capability
Disable threshold Voltage falling 1.4 V
Zero current detector/ overvoltage protection
I
V
ZCDH
V
ZCDL
V
ZCDA
V
ZCDT
I
ZCD
I
ZCDsrc
I
ZCDsnk
T
BLANK1
V
ZCDth
T
BLANK2
Upper clamp voltage
Lower clamp voltage
Arming voltage
Triggering voltage
Internal pull-up
Source current capability
Sink current capability
Turn-on inhibit time After gate-drive going low 2.5 µs
OVP threshold 4.85 5 5.15 V
OVP strobe delay After gate-drive going low 2 µs
= 3 mA
ZCD
= - 3 mA
I
ZCD
(1)
positive-going edge
(1)
negative-going edge
V
V
V
V
< V
COMP
ZCD < 2 V, V
= V
ZCD
= V
ZCD
14/51
COMPSH
ZCDL
ZCDH
COMP
= V
COMPHI
5.4 5.7 6 V
-0.4 V
85 100 115 mV
30 50 70 mV
-1
µA
-130 -100 -70
-3 mA
3mA
L6566A Electrical characteristics
Table 5. Electrical characteristics (continued)
Symbol Parameter Test condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Latched shutdown function
V
I
V
OTP
OTP
Input bias current
Disable threshold
Thermal shutdown
Vth Shutdown threshold 180 °C
Hys Hysteresis 40 °C
VCC_PFC function
DIS
(1)
= 0 to V
OTP
-1 µA
4.32 4.5 4.68 V
I
leak
V
Vcc
V
Vcc_PFC
OFF-state leakage current V
-
ON-state voltage dropout V
Level for pin 6 open and lower
V
COMPO
UVLO off threshold (COMP
voltage falling)
Level for pin 6 closed and higher
V
COMPL
UVLO off threshold (COMP
voltage rising)
T
delay
Pin 6 change of state delay Closed-to-open 10 ms
Mode selection / slope compensation
MODE
SC
SC
Threshold for QR operation 3 V
th
Ramp peak
pk
(MODE/SC = Open)
Ramp starting value
vy
(MODE/SC = Open)
Ramp voltage
(MODE/SC = Open)
Source capability
(MODE/SC = Open)
= 2.5V, V
COMP
= 4V, I
COMP
(3)
(3)
MODE/SC = Open
(3)
(3)
MODE/SC = Open
R
S-COMP
pin high, V
R
S-COMP
VCC_PFC
= 3 kΩ to GND, GD
COMP
= 3 kΩ to GND,
GD pin high
Vcc_PFC
= 5 V
= 0
= 10mA
1µA
0.15 0.3 V
2.61 2.75 2.89 V
3.02 3.15 3.28
2.93.053.2 V
3.41 3.55 3.69
1.7 V
0.3 V
GD pin low 0 V
V
S-COMP = VS-COMPpk
0.8 mA
Soft-start
I
SS1
I
SS2
I
SSdis
V
SSclamp
V
SSDIS
V
SSLAT
Charge current
Discharge current
High saturation voltage
Disable level
Latch-off level
= 25 °C, VSS < 2 V,
T
J
= 4 V
V
COMP
TJ = 25 °C, VSS > 2 V,
=V
V
COMP
V
SS
V
COMP
(1)
V
COMP
V
> 2 V
= 4 V
COMP
=V
COMPHi
=V
COMPHi
COMPHi
15/51
14 20 26
µA
3.5 5 6.5
3.5 5 6.5 µA
2V
4.85 5 5.15 V
6.4 V
Electrical characteristics L6566A
−
−
Table 5. Electrical characteristics (continued)
Symbol Parameter Test condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Gate driver
V
GDH
V
GDL
I
sourcepk
I
sinkpk
t
t
V
GDclamp
Output high voltage
Output low voltage
Output source peak current -0.6 A
Output sink peak current 0.8 A
Fall time 40 ns
f
Rise time 50 ns
r
Output clamp voltage
UVLO saturation Vcc = 0 to V
1. Parameters tracking one another.
2. See Table 6 on page 41 and Table 7 on page 42
3. The Voltage Feedforward block output is given by:
I
GDsource
I
GDsink
I
GDsource
= 5 mA, Vcc = 12V
= 100 mA
= 5mA; Vcc = 20V
ccon, Isink = 1mA 0.9 1.1 V
()
=
9.8 11 V
0.75 V
10 11.3 15 V
VK5.2VKc V
VFFFFCOMPcs
16/51

L6566A Application information
5 Application information
The L6566A is a versatile peak-current-mode PWM controller specific for offline flyback
converters. The device allows either Fixed-Frequency (FF) or Quasi-Resonant (QR)
operation, selectable with the pin MODE/SC (12): forcing the voltage on the pin over 3V (e.g.
by tying it to the 5V reference externally available at pin VREF, 10) will activate QR
operation, otherwise the device will be FF-operated.
Irrespective of the operating option selected by pin 12, the device is able to work in different
modes, depending on the converter's load conditions. If QR operation is selected (see
Figure 4):
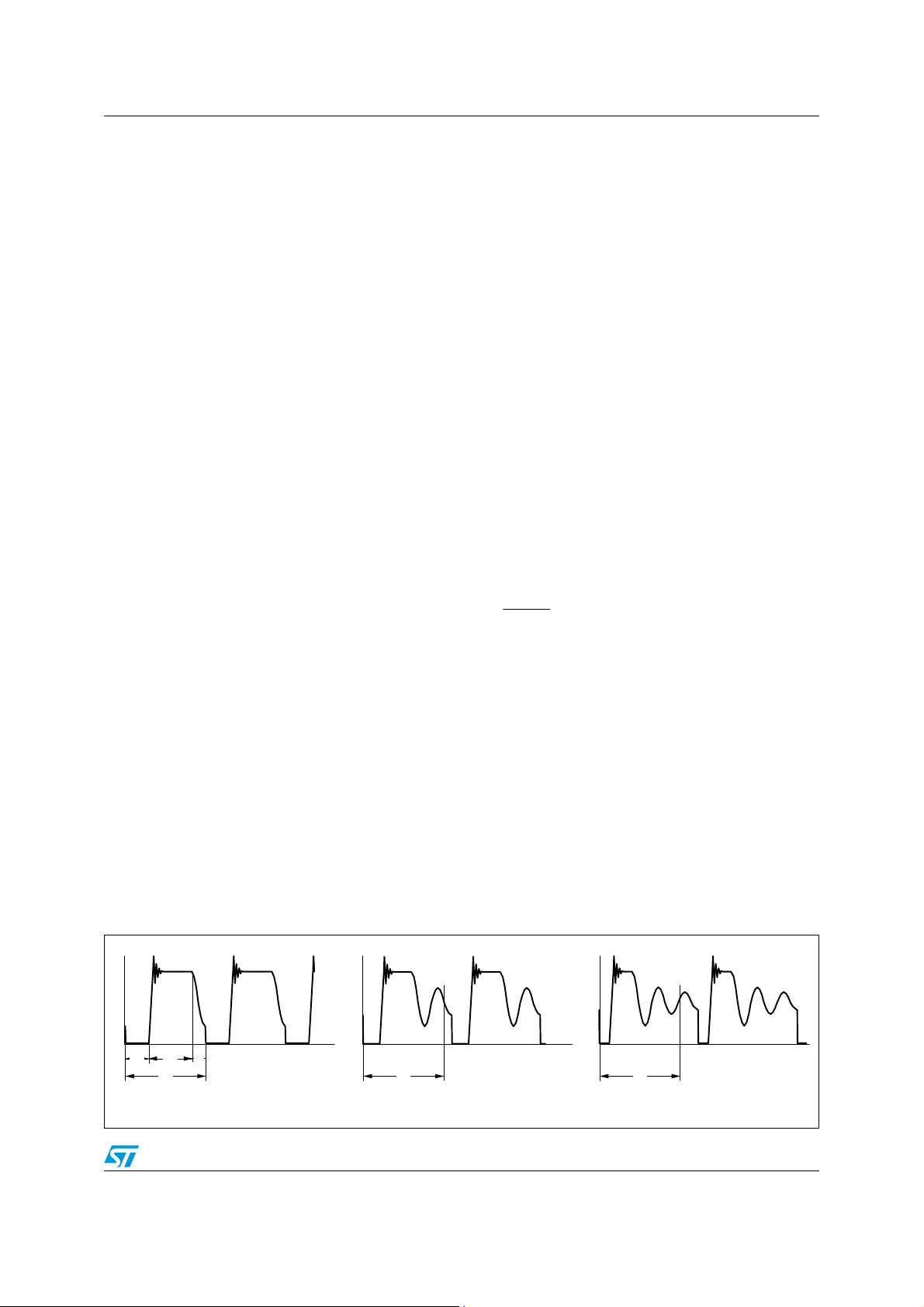
1. QR mode at heavy load. Quasi-resonant operation lies in synchronizing MOSFET's
turn-on to the transformer's demagnetization by detecting the resulting negative-going
edge of the voltage across any winding of the transformer. Then the system works
close to the boundary between discontinuous (DCM) and continuous conduction
(CCM) of the transformer. As a result, the switching frequency will be different for
different line/load conditions (see the hyperbolic-like portion of the curves in
Minimum turn-on losses, low EMI emission and safe behavior in short circuit are the
main benefits of this kind of operation.
2. Valley-skipping mode at medium/ light load. The externally programmable oscillator of
the L6566A, synchronized to MOSFET's turn-on, enables the designer to define the
maximum operating frequency of the converter. As the load is reduced MOSFET's turnon will not any more occur on the first valley but on the second one, the third one and
so on. In this way the switching frequency will no longer increase (piecewise linear
portion in
Figure 4).
3. Burst-mode with no or very light load. When the load is extremely light or disconnected,
the converter will enter a controlled on/off operation with constant peak current.
Decreasing the load will then result in frequency reduction, which can go down even to
few hundred hertz, thus minimizing all frequency-related losses and making it easier to
comply with energy saving regulations or recommendations. Being the peak current
very low, no issue of audible noise arises.
Figure 4).
Figure 4. Multi-mode operation with QR option active
f
osc
Valley-skipping
f
sw
0
0
mode
Burst-mode
Quasi-resonant mode
P
in
17/51
Input volta ge
Pinmax

Application information L6566A
K
If FF operation is selected:
1. FF mode from heavy to light load. The system operates exactly like a standard current
mode, at a frequency f
determined by the externally programmable oscillator: both
sw
DCM and CCM transformer operation are possible, depending on whether the power
that it processes is greater or less than:
Equation 1
2
sw
⎞
VVin
R
⎟
⎟
VVin
+
R
⎠
Lpf2
Pin
⎛
⎜
⎜
⎝
=
T
where Vin is the input voltage to the converter, VR the reflected voltage (i.e. the
regulated output voltage times the primary-to-secondary turn ratio) and Lp the
inductance of the primary winding. Pin
is the power level that marks the transition from
T
continuous to discontinuous operation mode of the transformer.
2. Burst-mode with no or very light load. This kind of operation is activated in the same
way and results in the same behavior as previously described for QR operation.
The L6566A is specifically designed for flyback converters operated from front-end Power
Factor Correction (PFC) stages in applications supposed to comply with EN61000-3-2 or
JEITA-MITI regulations. Pin 6 (Vcc_PFC) provides the supply voltage to the PFC control IC.
5.1 High-voltage start-up generator
Figure 5 shows the internal schematic of the high-voltage start-up generator (HV generator).
It is made up of a high-voltage N-channel FET, whose gate is biased by a 15 MΩ resistor,
with a temperature-compensated current generator connected to its source.
Figure 5. High-voltage start-up generator: internal schematic
L6566A
Vcc_O
15 M
Ω
HV_EN
CONTROL
3
GND
HV
1
I
HV
Vcc5
I
charge
18/51

L6566A Application information
With reference to the timing diagram of Figure 6, when power is first applied to the converter
the voltage on the bulk capacitor (Vin) builds up and, at about 80V, the HV generator is
enabled to operate (HV_EN is pulled high) so that it draws about 1 mA. This current, minus
the device’s consumption, charges the bypass capacitor connected from pin Vcc (5) to
ground and makes its voltage rise almost linearly.
Figure 6. Timing diagram: normal power-up and power-down sequences
Vin
V
HVstart
Vcc
(pin 5)
Vcc
Vcc
Vcc
restart
ON
OFF
regulation is lost here
t
Vcc_PFC
(pin 6)
GD
(pin 4)
HV_EN
Vcc_OK
charge
I
0.85 mA
light load
Power-on Power-off
heavy load
Normal
operation
t
t
t
t
t
As the Vcc voltage reaches the start-up threshold (14V typ.) the low-voltage chip starts
operating and the HV generator is cut off by the Vcc_OK signal asserted high. The device is
powered by the energy stored in the Vcc capacitor until the self-supply circuit (typically an
auxiliary winding of the transformer and a steering diode) develops a voltage high enough to
sustain the operation. The residual consumption of this circuit is just the one on the 15 MΩ
resistor (≈ 10 mW at 400 Vdc), typically 50-70 times lower, under the same conditions, as
compared to a standard start-up circuit made with external dropping resistors.
At converter power-down the system will lose regulation as soon as the input voltage is so
low that either peak current or maximum duty cycle limitation is tripped. Vcc will then drop
and stop IC activity as it falls below the UVLO threshold (10V typ.). The Vcc_OK signal is
de-asserted as the Vcc voltage goes below a threshold Vcc
HV generator can now restart. However, if Vin < Vin
, as illustrated in Figure 6, HV_EN is
start
located at about 5V. The
restart
de-asserted too and the HV generator is disabled. This prevents converter’s restart attempts
and ensures monotonic output voltage decay at power-down in systems where brownout
protection (see the relevant section) is not used.
The low restart threshold Vcc
ensures that, during short circuits, the restart attempts of
restart
the device will have a very low repetition rate, as shown in the timing diagram of
page 20
, and that the converter will work safely with extremely low power throughput.
19/51
Figure 7 on

Application information L6566A
Figure 7. Timing diagram showing short-circuit behavior (SS pin clamped at 5V)
Vcc
(pin 5)
Vcc
Vcc
restart
Vcc
GD
(pin 4)
Vcc_OK
charge
I
0.85 mA
ON
OFF
Short circuit occurs here
< 0.03T
T
rep
rep
t
t
t
t
Figure 8. Zero current detection block, triggering block, oscillator block and related
logic
COMP
915
L6566A
line
FFWD
VFF
+Vin
ZCD
11
MONO
STABLE
BLANKING
TIME
Reset
4:1
Counter
R
Z1
R
Z2
100 mV
50 mV
5V
+
Strobe
+
-
5.7V
S/H
blanking
START
TURN-ON
LOGIC
OSCILLATOR
FAULT
PWM
CS
7
GD
R
Q
S
13
OSC
R
T
DRIVER
4
Q
Rs
20/51
L6566A Application information
V
5.2 Zero current detection and triggering block; oscillator block
The Zero Current Detection (ZCD) and Triggering blocks switch on the external MOSFET if
a negative-going edge falling below 50 mV is applied to the input (pin 11, ZCD). To do so the
triggering block must be previously armed by a positive-going edge exceeding 100 mV.
This feature is typically used to detect transformer demagnetization for QR operation, where
the signal for the ZCD input is obtained from the transformer’s auxiliary winding used also to
supply the L6566A. The triggering block is blanked for T
turn-off to prevent any negative-going edge that follows leakage inductance
demagnetization from triggering the ZCD circuit erroneously.
The voltage at the pin is both top and bottom limited by a double clamp, as illustrated in the
internal diagram of the ZCD block of
Figure 8 on page 20. The upper clamp is typically
located at 5.7 V, while the lower clamp is located at -0.4V. The interface between the pin and
the auxiliary winding will be a resistor divider. Its resistance ratio will be properly chosen
Section 5.11: OVP block on page 35”) and the individual resistance values (R
(see “
will be such that the current sourced and sunk by the pin be within the rated capability of the
internal clamps (±3 mA).
At converter power-up, when no signal is coming from the ZCD pin, the oscillator starts up
the system. The oscillator is programmed externally by means of a resistor (R
from pin OSC (13) to ground. With good approximation the oscillation frequency f
= 2.5 µs after MOSFET’s
BLANK
, RZ2)
Z1
) connected
T
will be:
osc
Equation 2
3
102f⋅
≈
(with f
osc
in kHz and RT in kW). As the device is turned on, the oscillator starts immediately;
osc
R
T
at the end of the first oscillator cycle, being zero the voltage on the ZCD pin, the MOSFET
will be turned on, thus starting the first switching cycle right at the beginning of the second
oscillator cycle. At any switching cycle, the MOSFET is turned off as the voltage on the
current sense pin (CS, 7) hits an internal reference set by the Line Feedforward block, and
the transformer starts demagnetization. If this completes (hence a negative-going edge
appears on the ZCD pin) after a time exceeding one oscillation period T
previous turn-on, the MOSFET will be turned on again - with some delay to ensure minimum
voltage at turn-on – and the oscillator ramp will be reset. If, instead, the negative-going edge
appears before T
after T
will turn-on the MOSFET and synchronize the oscillator. In this way one or more
osc
drain ringing cycles will be skipped (“valley-skipping mode”,
frequency will be prevented from exceeding f
Figure 9. Drain ringing cycle skipping as the load is gradually reduced
DS
has elapsed, it will be ignored and only the first negative-going edge
osc
Figure 9) and the switching
.
osc
V
DS
V
DS
osc
=1/f
from the
osc
T
T
FW
osc
T
V
Pin = Pin'
(limit condition)
T
ON
t
T
osc
in''
< P
in'
Pin= P
t
T
osc
in'''
Pin= P
< P
in''
t
21/51

Application information L6566A
Note: When the system operates in valley skipping-mode, uneven switching cycles may be
observed under some line/load conditions, due to the fact that the OFF-time of the MOSFET
is allowed to change with discrete steps of one ringing cycle, while the OFF-time needed for
cycle-by-cycle energy balance may fall in between. Thus one or more longer switching
cycles will be compensated by one or more shorter cycles and vice versa. However, this
mechanism is absolutely normal and there is no appreciable effect on the performance of
the converter or on its output voltage.
If the MOSFET is enabled to turn on but the amplitude of the signal on the ZCD pin is
smaller than the arming threshold for some reason (e.g. a heavy damping of drain
oscillations, like in some single-stage PFC topologies, or when a turn-off snubber is used),
MOSFET’s turn-on cannot be triggered. This case is identical to what happens at start-up:
at the end of the next oscillator cycle the MOSFET will be turned on, and a new switching
cycle will take place after skipping no more than one oscillator cycle.
The operation described so far does not consider the blanking time T
turn off, and actually T
does not come into play as long as the following condition is
BLANK
after MOSFET’s
BLANK
met:
Equation 3
T
BLANK
1D −≤
T
osc
where D is the MOSFET duty cycle. If this condition is not met, things do not change
substantially: the time during which MOSFET’s turn-on is inhibited is extended beyond T
by a fraction of T
lower than the programmed value f
earlier than expected. However this is quite unusual: setting f
phenomenon can be observed at duty cycles higher than 60%. See
on page 35
for further implications of T
. As a consequence, the maximum switching frequency will be a little
BLANK
and valley-skipping mode may take place slightly
osc
= 150 kHz, the
osc
Section 5.11: OVP block
.
BLANK
osc
If the voltage on the COMP pin (9) saturates high, which reveals an open control loop, an
internal pull-up keeps the ZCD pin close to 2V during MOSFET's OFF-time to prevent noise
from false triggering the detection block. When this pull-up is active, the ZCD pin might not
be able to go below the triggering threshold, which would stop the converter. To allow autorestart operation, however ensuring minimum operating frequency in these conditions, the
oscillator frequency that retriggers MOSFET's turn-on is that of the external oscillator
divided by 128. Additionally, to prevent malfunction at converter's start-up, the pull-up is
disabled during the initial soft-start (see the relevant section). However, to ensure a correct
start-up, at the end of the soft-start phase the output voltage of the converter must meet the
condition:
Equation 4
Vout >
where Ns is the turn number of the secondary winding, Naux the turn number of the
auxiliary winding and I
22/51
the maximum pull-up current (130 µA).
ZCD
Ns
Naux
IR
ZCD1Z

L6566A Application information
The operation described so far under different operating conditions for the converter is
illustrated in the timing diagrams of
Figure 10.
If the FF option is selected the operation will be exactly equal to that of a standard currentmode PWM controller. It will work at a frequency fsw = fosc; both DCM and CCM
transformer's operation are possible, depending on the operating conditions (input voltage
and output load) and on the design of the power stage. The MOSFET is turned on at the
beginning of each oscillator cycle and is turned off as the voltage on the current sense pin
reaches an internal reference set by the Line Feedforward block. The maximum duty cycle is
limited at 70% minimum. The signal on the ZCD pin in this case is used only for detecting
feedback loop failures (see
Figure 10. Operation of ZCD, triggering and Oscillator blocks (QR option active)
ZCD
(pin 11)
100 mV
50 mV
Oscillator
ramp
Section 5.11: OVP block on page 35).
ZCD
(pin 11)
100 mV
50 mV
Oscillator
ramp
ZCD
(pin 11)
100 mV
50 mV
Oscillator
ramp
ZCD
blanking
time
Arm /Trigger
ON-enable
PWM latch
Set
PWM latch
Reset
GD
(pin 4)
armed trigger
a) full load
ZCD
blanking
time
Arm/Trigger
ON-enable
PWM latch
Set
PWM latch
Reset
GD
(pin 4)
b) light load
ZCD
blanking
time
Arm /Trigger
ON-enable
PWM latch
Set
PWM latch
Reset
GD
(pin 4)
c) start - up
23/51

Application information L6566A
5.3 Burst-mode operation at no load or very light load
When the voltage at the COMP pin (9) falls 20 mV below a threshold fixed internally at a
value, V
COMPBM
the MOSFET kept in OFF state and its consumption reduced at a lower value to minimize
Vcc capacitor discharge.
The control voltage now will increase as a result of the feedback reaction to the energy
delivery stop (the output voltage will be slowly decaying), the threshold will be exceeded and
the device will restart switching again. In this way the converter will work in burst-mode with
a nearly constant peak current defined by the internal disable level. A load decrease will
then cause a frequency reduction, which can go down even to few hundred hertz, thus
minimizing all frequency-related losses and making it easier to comply with energy saving
regulations. This kind of operation, shown in the timing diagrams of
others previously described, is noise-free since the peak current is low.
If it is necessary to decrease the intervention threshold of the burst-mode operation, this can
be done by adding a small DC offset on the current sense pin as shown in
page 25
.
Note: The offset reduces the available dynamics of the current signal; thereby, the value of the
sense resistor must be determined taking this offset into account.
Figure 11. Load-dependent operating modes: timing diagrams
, depending on the selected operating mode, the L6566A is disabled with
Figure 11 along with the
Figure 12 on
COMP
(pin 9)
V
COMPBM
f
osc
sw
f
GD
(pin 4)
MODE/SC=Open
MODE/SC=VREF
FF Mode Burst-mode FF Mode
QR Mode
Burst-mode
V alley-skipping Mode
20 mV
hyster.
t
MODE/SC=Open
MODE/SC=VREF
t
t
QR Mode
24/51

L6566A Application information
COMP
Figure 12. Addition of an offset to the current sense lowers the burst-mode operation
threshold
5.4 Adaptive UVLO
A major problem when optimizing a converter for minimum no-load consumption is that the
voltage generated by the auxiliary winding under these conditions falls considerably as
compared even to a few mA load. This very often causes the supply voltage Vcc of the
control IC to drop and go below the UVLO threshold so that the operation becomes
intermittent, which is undesired. Furthermore, this must be traded off against the need of
generating a voltage not exceeding the maximum allowed by the control IC at full load.
To help the designer overcome this problem, the device, besides reducing its own
consumption during burst-mode operation, also features a proprietary adaptive UVLO
function. It consists of shifting the UVLO threshold downwards at light load, namely when
the voltage at pin COMP falls below a threshold V
Interface"), so as to have more headroom. To prevent any malfunction during transients from
minimum to maximum load the normal (higher) UVLO threshold is re-established when the
voltage at pin COMP exceeds V
Vcc has exceeded the normal UVLO threshold (see
ensures that at full load the MOSFET will be driven with a proper gate-to-source voltage.
Figure 13. Adaptive UVLO block
9
V
COMPL
V
COMPO
(*) Vc c
OFF2
Vcc_PFC
Vcc_PFC
-
+
< Vcc
is selected when Q is high
OFF1
6
logic
R
S Q
Vcso= V ref
R
R + Rc
Vref
10
L6566A
4
Rc
R
7
3
Rs
internally fixed (see "PFC
COMPO
(see "Chapter 5.8: PFC interface on page 31") and
COMPL
Figure 13). The normal UVLO threshold
VCOMP
Vcc
5
+
-
UVLO
+
SW
-
Vcc
Vcc
OFF1
OFF2
(*)
L6566A
(pin 9)
V
COMPL
V
COMPO
Vcc
(pin 5)
VccOFF 1
Vcc
Vcc_PFC
(pin 6)
t
OFF2
Q
Tdelay
t
t
t
25/51

Application information L6566A
5.5 PWM control block
The device is specific for secondary feedback. Typically, there is a TL431 on the secondary
side and an optocoupler that transfers output voltage information to the PWM control on the
primary side, crossing the isolation barrier. The PWM control input (pin 9, COMP) is driven
directly by the phototransistor's collector (the emitter is grounded to GND) to modulate the
duty cycle (
In applications where a tight output regulation is not required, it is possible to use a primarysensing feedback technique. In this approach the voltage generated by the self-supply
winding is sensed and regulated. This solution, shown in
is cheaper because no optocoupler or secondary reference is needed, but output voltage
regulation, especially as a result of load changes, is quite poor. Ideally, the voltage
generated by the self-supply winding and the output voltage should be related by the
Naux/Ns turn ratio only. Actually, numerous non-idealities, mainly transformer's parasitics,
cause the actual ratio to deviate from the ideal one. Line regulation is quite good, in the
range of ± 2%, whereas load regulation is about ±5% and output voltage tolerance is in the
range of ±10%.
The dynamics of the pin is in the 2.5 to 5V range. The voltage at the pin is clamped
downwards at about 2 V. If the clamp is externally overridden and the voltage on the pin is
pulled below 1.4V the L6566A will shut down. This condition is latched as long as the device
is supplied. While the device is disabled, however, no energy is coming from the self-supply
circuit, thus the voltage on the Vcc capacitor will decay and cross the UVLO threshold after
some time, which clears the latch and lets the HV generator restart. This function is
intended for an externally controlled burst-mode operation at light load with a reduced
output voltage, a technique typically used in multi-output SMPS, such as those for CRT TVs
or monitors (see the timing diagram
Figure 14, left-hand side circuit).
Figure 14, right-hand side circuit,
Figure 15 on page 27).
Figure 14. Possible feedback configurations that can be used with the L6566A
L6566A
9
COMP
TL431
Secondary feedback Primary feedback
Vout
L6566A
COMP
5 Vcc
9
Cs
N
aux
26/51

L6566A Application information
Figure 15. Externally controlled burst-mode operation by driving pin COMP: timing
diagram
Vcc
(pin 5)
Vcc
Vcc
restart
Vcc
COMP
(pin 9)
GD
(pin 4)
Vcc_OK
charge
I
0.85 mA
Vcc_PFC
(pin 6)
Vout
Standby is commanded here
ON
OFF
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
5.6 PWM comparator, PWM latch and voltage feedforward blocks
The PWM comparator senses the voltage across the current sense resistor Rs and, by
comparing it to the programming signal delivered by the feedforward block, determines the
exact time when the external MOSFET is to be switched off. Its output resets the PWM
latch, previously set by the oscillator or the ZCD triggering block, which will assert the gate
driver output low. The use of PWM latch avoids spurious switching of the MOSFET that
might result from the noise generated ("double-pulse suppression").
Cycle-by-cycle current limitation is realized with a second comparator (OCP comparator)
that senses the voltage across the current sense resistor Rs as well and compares this
voltage to a reference value V
the circuit schematic in
Figure 17 on page 29). In this way, if the programming signal
delivered by the feedforward block and sent to the PWM comparator exceeds V
the OCP comparator to reset first the PWM latch instead of the PWM comparator. The value
of Vcsx, thereby, determines the overcurrent setpoint along with the sense resistor Rs.
The power that QR flyback converters with a fixed overcurrent setpoint (like fixed-frequency
systems) are able to deliver changes with the input voltage considerably. Obviously, this is
not a problem if the flyback converter runs off a fixed voltage bus generated by the PFC preregulator; however, with a tracking boost PFC (a "boost follower" PFC), the regulated output
voltage at maximum mains voltage can be even twice the value at minimum mains voltage.
In this case the issue is still there, although not as big as without PFC and wide-range
mains. With a 1:2 voltage change, the maximum transferable power at maximum line can be
50% higher than at minimum line, as shown by the upper curve in the diagram of
The L6566A has the Line Feedforward function available to solve this issue.
. Its output is or-ed with that of the PWM comparator (see
CSX
, it will be
CSX
Figure 16.
27/51

Application information L6566A
Figure 16. Typical power capability change vs input voltage in QR flyback converters
2.5
2
in
inmin
@ V
1.5
@ V
inlim
P
inlim
P
1
0.5
11.522.5 33.54
system not
compensated
system optimally
compensated
in
V
inmin
V
k = 0
k = k
k
opt
It acts on the overcurrent setpoint Vcsx, so that it is a function of the converter’s input voltage
Vin (output of the PFC pre-regulator) sensed through a dedicated pin (15, VFF): the higher
the input voltage, the lower the setpoint. This is illustrated in the diagram on the left-hand
side of
and V
Figure 17 on page 29: it shows the relationship between the voltage on the pin VFF
csx (with the error amplifier saturated high in the attempt of keeping output voltage
regulation):
Equation 5
csx
V
VFF
1V
3
k
1
Vin
−=−=
3
Note: If the voltage on the pin exceeds 3V switching ceases but the soft-start capacitor is not
discharged. The schematic in Figure 17 on page 29 shows also how the function is included
in the control loop.
With a proper selection of the external divider R1-R2, i.e. of the ratio k = R2 / (R1+R2), it is
possible to achieve the optimum compensation described by the lower curve in the diagram
of
Figure 16.
The optimum value of k, k
, which minimizes the power capability variation over the input
opt
voltage range, is the one that provides equal power capability at the extremes of the range.
The exact calculation is complex, and non-idealities shift the real-world optimum value from
the theoretical one. It is therefore more practical to provide a first cut value, simple to be
calculated, and then to fine tune experimentally.
Assuming that the system operates exactly at the boundary between DCM and CCM, and
neglecting propagation delays, the following expression for k
can be found:
opt
Equation 6
V
opt
3k
⋅=
R
()
⋅++⋅
VVVVV
Rmaxinmininmaxinminin
Experience shows that this value is typically lower than the real one. Once the maximum
peak primary current, I
PKpmax
, occurring at minimum input voltage Vinmin has been found,
the value of Rs can be determined from (2):
28/51

L6566A Application information
V
Equation 7
k
opt
1Rs−
=
V
minin
3
I
maxPKp
The converter is then tested on the bench to find the output power level Pout
regulation is lost (because overcurrent is being tripped) both at Vin = Vin
Vin = Vin
Figure 17. Left: Overcurrent setpoint vs. VFF voltage; right: Line Feedforward function block
[V]
csx
1.2
1
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.2
0
00.511.522.533.5
If Pout
increasing; if Pout
V
@ Vin
lim
max
VFF
[V]
.
V
COMP
= Upper clamp
> Pout
max
lim
@ Vin
@ Vin
lim
max
min
< Pout
PFC Outp ut Bus
To PFC's OV
sensi ng
COMP
R1B
R2
9
R1A
15
L6566A
Optional for
OVP settings
VFF CS
VOLTAGE
FEED
FORWARD
Vcsx
1.5 V
Rs
7
+
PWM
+
OCP
+
Hiccup
-
Clock/ZCD
the system is still undercompensated and k needs
@ Vin
lim
the system is overcompensated and k
min
min
R
S
lim
and
Q
DISABLE
where
DRIVER
needs decreasing. This will go on until the difference between the two values is acceptably
low. Once found the true k
in this way, it is possible that Pout
opt
turns out slightly different
lim
from the target; to correct this, the sense resistor Rs needs adjusting and the above tuning
process will be repeated with the new Rs value. Typically a satisfactory setting is achieved in
no more than a couple of iterations.
4
GD
In applications where this function is not wanted, e.g. because the PFC stage regulates at a
fixed voltage, the VFF pin can be simply grounded, directly or through a resistor (see
“
Chapter 5.11: OVP block on page 35”). The overcurrent setpoint will be then fixed at the
maximum value of 1V. If a lower setpoint is desired to reduce the power dissipation on Rs,
the pin can be also biased at a fixed voltage using a divider from VREF (pin 10).
If the FF option is selected the Line Feedforward function can be still used to compensate for
the total propagation delay Td of the current sense chain (internal propagation delay td
(H-L)
plus the turn-off delay of the external MOSFET), which in standard current mode PWM
controllers is done by adding an offset on the current sense pin proportional to the input
voltage. In that case the divider ratio k, which will be much smaller as compared to that used
with the QR option selected, can be calculated with the following equation:
Equation 8
Td
3k
=
opt
29/51
LpRs

Application information L6566A
where Lp is the inductance of the primary winding. In case a constant maximum power
capability vs. the input voltage is not required, the VFF pin can be grounded, directly or
through a resistor (see
setpoint at 1V, or biased at a fixed voltage through a divider from VREF to get a lower
setpoint.
It is possible to bypass the pin to ground with a small film capacitor (e.g. 1-10 nF) to ensure
a clean operation of the IC even in a noisy environment.
The pin is internally forced to ground during UVLO, after activating any latched protection
and when pin COMP is pulled below its low clamp voltage (see
block on page 26
Section 5.11: OVP block on page 35 ), hence fixing the overcurrent
Section 5.5: PWM control
).
5.7 Hiccup-mode OCP
A third comparator senses the voltage on the current sense input and shuts down the device
if the voltage on the pin exceeds 1.5 V, a level well above that of the maximum overcurrent
setpoint (1V). Such an anomalous condition is typically generated by either a short circuit of
the secondary rectifier or a shorted secondary winding or a hard-saturated flyback
transformer.
To distinguish an actual malfunction from a disturbance (e.g. induced during ESD tests), the
first time the comparator is tripped the protection circuit enters a “warning state”. If in the
next switching cycle the comparator is not tripped, a temporary disturbance is assumed and
the protection logic will be reset in its idle state; if the comparator will be tripped again a real
malfunction is assumed and the L6566A will be stopped. Depending on the time relationship
between the detected event and the oscillator, occasionally the device could stop after the
third detection.
This condition is latched as long as the device is supplied. While it is disabled, however, no
energy is coming from the self-supply circuit; hence the voltage on the Vcc capacitor will
decay and cross the UVLO threshold after some time, which clears the latch. The internal
start-up generator is still off, then the Vcc voltage still needs to go below its restart voltage
before the Vcc capacitor is charged again and the device restarted. Ultimately, this will result
in a low-frequency intermittent operation (Hiccup-mode operation), with very low stress on
the power circuit. This special condition is illustrated in the timing diagram of
Figure 18.
30/51

L6566A Application information
t
Figure 18. Hiccup-mode OCP: timing diagram
Vcc
(pin 5)
Vcc
Vcc
restart
Vcc
ON
OFF
Secondary diode is shorted here
CS
V
(pin 7)
GD
(pin 4)
OCP latch
Vcc_OK
Vcc_PFC
(pin 6)
1.5 V
5.8 PFC interface
The device is specifically designed to minimize converter’s losses under light or no-load
conditions, and a special function has been provided to help the designer meet energy
saving requirements even in power-factor-corrected systems where a PFC pre-regulator
precedes the isolated DC-DC converter.
Actually EMC regulations require compliance with low-frequency harmonic emission limits
at nominal load; no limit is envisaged when the converter operates with a light load. Then
the PFC pre-regulator can be turned off, thus saving the no-load consumption of this stage
(0.5÷1W).
t
t
t
t
t
To do so, the L6566A provides the Vcc_PFC pin (6): this pin is internally connected to the
Vcc pin (5) via a PNP transistor, normally closed, that opens when the voltage V
below V
COMPO
, a threshold internally set at a value depending on whether QR operation or
COMP
falls
FF operation is selected. This pin is intended for supplying the PFC controller of the preregulator as shown in
Figure 16 on page 28. The switch is thermally protected, so that the
IC will stop if an external failure causes the pin to be overloaded for too long time or shorted
to ground.
31/51

Application information L6566A
Figure 19. Possible interfaces between the L6566A and a PFC controller
Vcc
5
Vcc_PFC6
L6566A
Vcc
5
22 k
Vcc_PFC6
L6566A
Ω
4.7k
Vcc
L6561
L6562
L6563
RUN
10
Ω
L6563
To prevent intermittent operation of the PFC stage, some hysteresis is provided: if the
internal switch is open, it will be closed (which will re-enable the PFC pre-regulator) when
COMP
exceeds V
COMP
must stay below V
V
transients V
the Vcc_PFC pin to open. Entering burst-mode (V
COMPL
> V
. Additionally, to reject V
COMPO
for more than 1024 oscillator cycles in order for
COMPO
COMP
< V
undershoots during
COMP
COMPBM
) will open Vcc_PFC
immediately.
Besides pin 6 going open, when V
COMP
below to compensate for the drop of the voltage delivered by the self-supply circuit that
occurs at light load (see
Section 5.4: Adaptive UVLO on page 25).
5.9 Latched disable function
The device is equipped with a comparator having the non-inverting input externally available
at the pin DIS (8) and with the inverting input internally referenced to 4.5V. As the voltage on
the pin exceeds the internal threshold, the device is immediately shut down and its
consumption reduced to a low value.
The information is latched and it is necessary to let the voltage on the Vcc pin go below the
UVLO threshold to reset the latch and restart the device. To keep the latch supplied as long
as the converter is connected to the input source, the HV generator is activated periodically
so that Vcc oscillates between the start-up threshold V
HV generator in this way cuts its power dissipation approximately by three (as compared to
the case of continuous conduction) and keeps peak silicon temperature close to the average
value.
To let the L6566A restart it is then necessary to disconnect the converter from the input
source. Pulling pin 16 (AC_OK) below the disable threshold (see
protection on page 38
latch can be cleared and a quicker restart is allowed as the input source is removed. This
operation is shown in the timing diagram of
) will stop the HV generator until Vcc falls below Vcc
falls below V
Figure 20.
COMPO
ccON
the UVLO threshold is set 2.4 V
and V
- 0.5V. Activating the
ccON
Section 5.12: Brownout
, so that the
restart
This function is useful to implement a latched overtemperature protection very easily by
biasing the pin with a divider from VREF, where the upper resistor is an NTC physically
located close to a heating element like the MOSFET, or the transformer. The DIS pin is a
high impedance input, thus it is prone to pick up noise, which might give origin to undesired
latch-off of the device. It is possible to bypass the pin to ground with a small film capacitor
(e.g. 1-10 nF) to prevent any malfunctioning of this kind.
32/51

L6566A Application information
Figure 20. Operation after latched disable activation: timing diagram
DIS
(pin 8)
4.5V
Vcc
Vcc
(pin 5)
Vcc
ON
-0.5
Vcc
restart
Vcc
GD
(pin 4)
HV generator is turned on
ON
OFF
Restart is quicker
Disable latch is reset here
HV generator turn-on is di sabled here
t
t
Vcc_PFC
(pin 6)
Vin
HVstart
V
AC_OK
(pin 16)
Vth
Input s o urce is removed here
t
t
t
t
5.10 Soft-start and delayed latched shutdown upon overcurrent
At device start-up, a capacitor (Css) connected between the SS pin (14) and ground is
charged by an internal current generator, I
During this ramp, the overcurrent setpoint progressively rises from zero to the value
imposed by the voltage on the VFF pin (15, see “
Feedforward blocks
”); MOSFET’s conduction time increases gradually, hence controlling the
start-up inrush current. The time needed for the overcurrent setpoint to reach its steady
state value, referred to as soft-start time, is approximately:
Equation 9
, from zero up to about 2V where it is clamped.
SS1
PWM Comparator, PWM Latch and Voltage
V
VFF
3
⎞
⎟
⎟
⎠
During the ramp (i.e. until V
⎛
Css
T
SS
I
1SS
= 2 V) all the functions that monitor the voltage on pin COMP
SS
VFFcsx
Css
⎜
−==
)V(V
1
⎜
I
⎝
1SS
are disabled.
The soft-start pin is also invoked whenever the control voltage (COMP) saturates high,
which reveals an open-loop condition for the feedback system. This condition very often
occurs at start-up, but may be also caused by either a control loop failure or a converter
overload/short circuit. A control loop failure results in an output overvoltage that is handled
by the OVP function of the L6566A (see next section). In case of QR operation, a short
circuit causes the converter to run at a very low frequency, then with very low power
capability. This makes the self-supply system that powers the device unable to keep it
33/51

Application information L6566A
V
operating, so that the converter will work intermittently, which is very safe. In case of
overload the system has a power capability lower than that at nominal load but the output
current may be quite high and overstress the output rectifier. In case of FF operation the
capability is almost unchanged and both short circuit and overload conditions are more
critical to handle.
The L6566A, regardless of the operating option selected, makes it easier to handle such
conditions: the 2V clamp on the SS pin is removed and a second internal current generator
I
= I
SS2
allowed to reach 2 V
resulting behavior will be identical to that under short circuit illustrated in
page 19
See
/4 keeps on charging Css. As the voltage reaches 5V the device is disabled, if it is
SS1
over 5V, the device will be latched off. In the former case the
BE
Figure 6 on
; in the latter case the result will be identical to that of Figure 20 on page 33.
Section 5.9: Latched disable function on page 32 for additional details.
A diode, with the anode to the SS pin and the cathode connected to the VREF pin (10) is the
simplest way to select either auto-restart mode or latch-mode behavior upon overcurrent. If
the overload disappears before the Css voltage reaches 5V the I
off and the voltage gradually brought back down to 2V. Refer to the
examples and ideas on page 44
section (Figure 8 on page 45) for additional hints.
generator will be turned
SS2
Section 6: Application
If latch-mode behavior is desired also for converter’s short circuit, make sure that the supply
voltage of the device does not fall below the UVLO threshold before activating the latch.
Figure 21 shows soft-start pin behavior under different operating conditions and with
different settings (latch-mode or autorestart).
Figure 21. Soft-start pin operation under different operating conditions and settings
Vcc
(pin 5)
SS
(pin 14)
COMP
(pin 9)
Vcc falls below UVLO
5V+2Vbe
5V
2V
before latching off
here the IC
shuts down
here the IC
latches off
UVLO
t
t
GD
(pin 4)
cc_PFC
(pin 6)
START-UP TEMPORARY
NORMAL
OPERATION
OVERLOAD
NORMAL
OPERATION
OVERLOAD
SHUTDOWN
LATCHED
AUTORESTART
RESTART
t
t
t
Note: Unlike other PWM controllers provided with a soft-start pin, in the L6566A grounding the SS
pin does not guarantee that the gate driver is disabled.
34/51

L6566A Application information
5.11 OVP block
The OVP function of the L6566A monitors the voltage on the ZCD pin (11) in MOSFET’s
OFF-time, during which the voltage generated by the auxiliary winding tracks converter’s
output voltage. If the voltage on the pin exceeds an internal 5V reference, a comparator is
triggered, an overvoltage condition is assumed and the device is shut down. An internal
current generator is activated that sources 1mA out of the VFF pin (15). If the VFF voltage is
allowed to reach 2 Vbe over 5V, the L6566A will be latched off. See
disable function on page 32
for more details on IC’s behavior under these conditions. If the
impedance externally connected to pin 15 is so low that the 5+2V
reached or if some means is provided to prevent that, the device will be able to restart after
the Vcc has dropped below 5V. Refer to the “Application examples and Ideas” section
(
Table 8 on page 45) for additional hints.
Figure 22. OVP Function: internal block diagram
PWM latch
QQSR
to triggering
Monostabl e
M1
block
ZCD
11
5 V
40k
Ω
5pF
2 µs
-
+
Monostable
M2
COUT
STROBE
0.5 µs
Section 5.9: Latched
threshold cannot be
BE
L6566A
OVP
FF
R Q1
S
2-bit
counter
Counter
reset
Fault
35/51

Application information L6566A
R
R
Figure 23. OVP function: timing diagram
GD
(pin 4)
Vaux
0
ZCD
(pin 11)
5V
COUT
STROBE
COUNTE
RESET
COUNTE
STATUS
FAULT
Vcc_PF C
(pin 6)
OVP
2 µs 0.5 µs
00 00 →11 →22 →00
NORMAL OPER A T I O N TEMPORAR Y DISTURBA NCE FEEDB ACK LOOP FAILURE
11 →22 →33 →40
→
The ZCD pin will be connected to the auxiliary winding through a resistor divider RZ1, RZ2
(see
Figure 8 on page 20). The divider ratio k
OVP
= R
Z2
/ (R
+ RZ2) will be chosen equal
Z1
to:
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
Equation 10
OVP
Ns
Naux
where Vout
=
5
Vout
k
OVP
is the output voltage value that is to activate the protection, Ns the turn
OVP
number of the secondary winding and Naux the turn number of the auxiliary winding. The
value of R
will be such that the current sourced by the ZCD pin be within the rated
Z1
capability of the internal clamp:
Equation 11
Naux
1
≥
3
−
103
⋅
Np
Vin
max
where Vin
max
winding. See
page 21
for additional details.
R
1Z
is the maximum dc input voltage and Ns the turn number of the primary
Section 5.2: Zero current detection and triggering block; oscillator block on
To reduce sensitivity to noise and prevent the latch from being erroneously activated, first
the OVP comparator is active only for a small time window (typically, 0.5 µs) starting 2 µs
after MOSFET’s turn-off, to reject the voltage spike associated to the positive-going edges
of the voltage across the auxiliary winding Vaux; second, to stop the L6566A the OVP
comparator must be triggered for four consecutive switching cycles. A counter, which is
reset every time the OVP comparator is not triggered in one switching cycle, is provided to
this purpose.
36/51

L6566A Application information
≤
+
Figure 22 on page 35 shows the internal block diagram, while the timing diagrams in
Figure 23 on page 36 illustrate the operation.
Note: To use the OVP function effectively, i.e. to ensure that the OVP comparator will be always
interrogated during MOSFET’s OFF-time, the duty cycle D under open-loop conditions must
fulfill the following inequality:
Equation 12
1fTD
sw2BLANK
where T
BLANK2
= 2 µs; this is also illustrated in the diagram of Figure 24.
Figure 24. Maximum allowed duty cycle vs. switching frequency for correct OVP
detection
Dmax
0.8
0.725
0.7
0.6
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
5.1041.1051.5.1052.1052.5.1053.1053.5.1054.10
fsw [Hz]
5
37/51

Application information L6566A
5.12 Brownout protection
Brownout Protection is basically a not-latched device shutdown function activated when a
condition of mains undervoltage is detected. There are several reasons why it may be
desirable to shut down a converter during a brownout condition, which occurs when the
mains voltage falls below the minimum specification of normal operation.
Firstly, a brownout condition may cause overheating of the PFC front-end due to an excess
of RMS current. Secondly, brownout can also cause the PFC pre-regulator to work open
loop. This could be dangerous to the PFC itself and the downstream converter, should the
input voltage return abruptly to its rated value, given the slow response of PFC to transient
events. Finally, spurious restarts may occur during converter power down, hence causing
the output voltage not to decay to zero monotonically.
L6566A shutdown upon brownout is accomplished by means of an internal comparator, as
shown in the block diagram of
input of the comparator, available on the AC_OK pin (16), is supposed to sense a voltage
proportional to either the RMS or the peak mains voltage; the non-inverting input is
internally referenced to 0.485V with 35 mV hysteresis. If the voltage applied on the AC_OK
pin before the device starts operating does not exceed 0.485V or if it falls below 0.45 V while
the device is running, The AC_OK signal goes high, the pin Vcc_PFC is open and the
device shuts down, with the soft-start capacitor discharged and the gate-drive output low.
Additionally, in case the device has been latched off by some protection function (in which
case Vcc is oscillating between V
0.45 V will clear the latch. This feature can be used to allow a quicker restart as the input
source is removed.
Figure 25, which shows the basic circuit usage. The inverting
ccON
and V
- 0.5V) the AC_OK voltage falling below
ccON
Figure 25. Brownout protection: internal block diagram and timing diagram
Sensed
voltage
R
H
R
L
AC_OK
L6566A
16
15 µA
0.485V
0.45V
Vcc
5
-
+
AC_FAIL
Sensed voltage
ON
Vsen
OFF
Vsen
VAC_OK
(pin 16)
AC_FAIL
HYS
I
15 µA
Vcc
(pin 5)
GD
(pin 4)
Vout
Vcc_PFC
(pin 6)
0.485V
t
0.45V
t
t
t
t
t
t
t
38/51
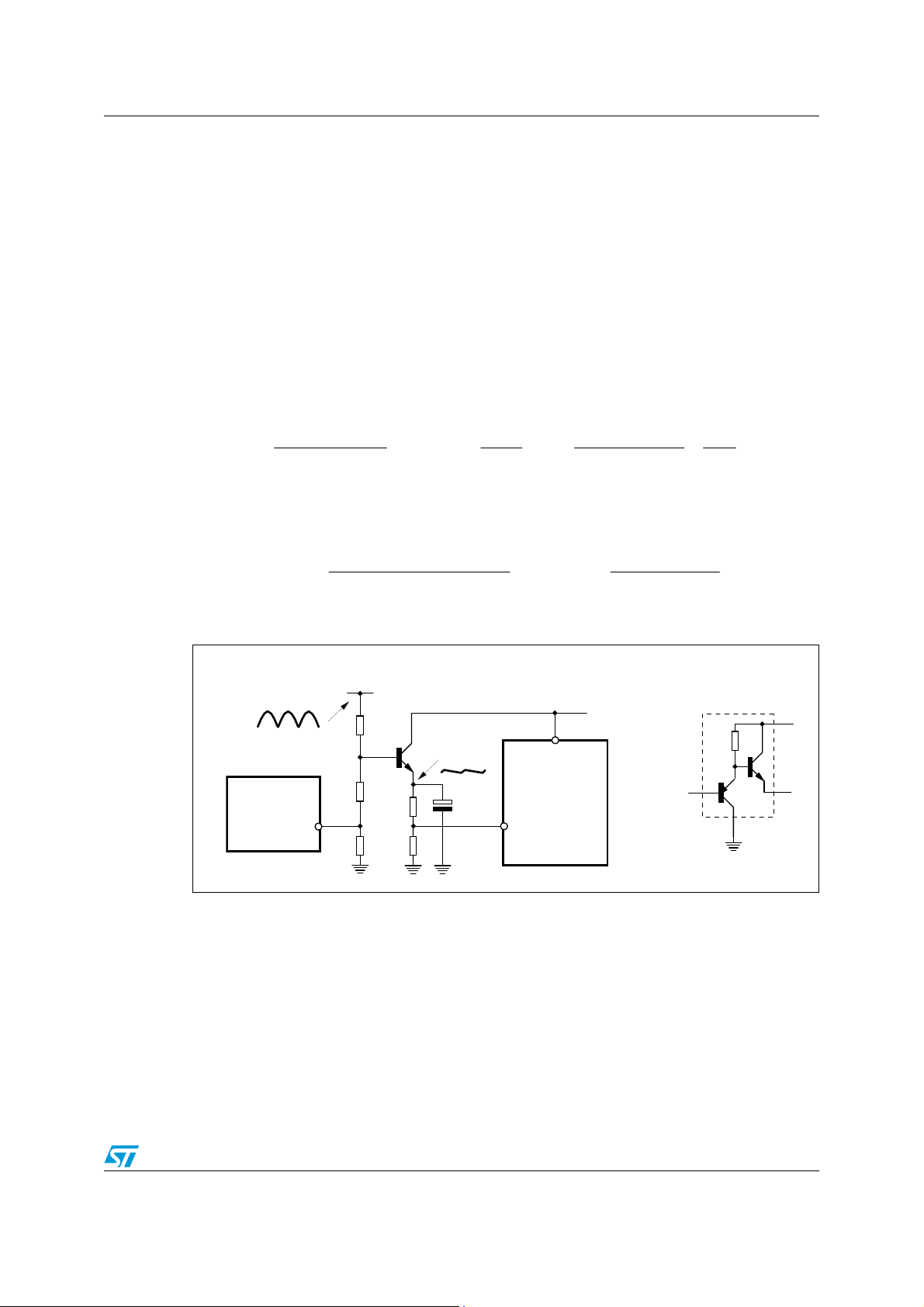
L6566A Application information
−
−
While the brownout protection is active the start-up generator keeps on working but, being
there no PWM activity, the Vcc voltage continuously oscillates between the start-up and the
HV generator restart thresholds, as shown in the timing diagram of
Figure 25 on page 38.
The brownout comparator is provided with current hysteresis in addition to voltage
hysteresis: an internal 15 µA current sink is ON as long as the voltage applied on the
AC_OK pin is such that the AC_FAIL signal is high. This approach provides an additional
degree of freedom: it is possible to set the ON threshold and the OFF threshold separately
by properly choosing the resistors of the external divider (see below). With just voltage
hysteresis, instead, fixing one threshold automatically fixes the other one depending on the
built-in hysteresis of the comparator.
With reference to
the ON (Vsen
Figure 25 on page 38, the following relationships can be established for
) and OFF (Vsen
ON
) thresholds of the sensed voltage:
OFF
Equation 13
ON
485.0Vsen
R
H
1015
485.0
6
−
+⋅=
R
L
which, solved for RH and RL, yield:
Equation 14
Vsen078.1Vsen
⋅−
R
=
H
Figure 26. Ac voltage sensing with the L6566A
Rectified
input voltage
L6561
L6562/A
L6563
MULT
3
−
1015
⋅
Q
R
H
L
R
6
Sensed
voltage:
Vsen < 7V
F
C
AC_OK
OFFON
16
Vcc
5
L6566A
OFF
45.0Vsen
R
RR;
=
HL
45.0
OFF
=
45.0Vsen
−
temper at ure dri ft
45.0
R
LH
For minimum
Q
It is typically convenient not to use additional dividers connected to high-voltage rails
because this could make it difficult to meet no-load consumption targets envisaged by
energy-saving regulations.
Figure 26 shows a simple voltage sensing technique that makes
use of the divider already used by the PFC control chip to sense the ac mains voltage with
just the addition of an extra tap.
The small-signal NPN Q and the capacitor C
of the rms mains voltage can be found across C
make a peak detector, so that the information
F
. Tap’s position determines the dc voltage
F
to be sensed by the AC_OK pin. It is convenient to use a level as high as possible to
minimize the effect of V
changes with temperature. However, it could be necessary to limit
BE
the maximum sensed voltage below 7V to prevent Q’s emitter reverse breakdown; it would
not be destructive because the reverse current would be quite small (the resistors seen by
39/51

Application information L6566A
the base terminal are several ten kW) but this could distort the signal on the MULT pin of the
PFC chip and adversely affect the operation of the pre-regulator. C
needs to be quite a big
F
capacitor (in the uF) to have small residual ripple superimposed on the dc level; as a rule-ofthumb, use a time constant (R
+ RH)·CF at least 4-5 times the maximum line cycle period,
L
then fine tune if needed, considering also transient conditions such as mains missing
cycles.
If temperature effects are critical, the NPN Q can be replaced by a PNP-NPN pair arranged
as shown in
Figure 26 on page 39 on the right-hand side; other sensing techniques can be
adopted anyway.
The voltage on the pin is clamped upwards at about 3.15 V; then, if the function is not used
the pin has to be connected to Vcc through a resistor (220 to 680 kΩ).
5.13 Slope compensation
The pin MODE/SC (12), when not connected to VREF, provides a voltage ramp during
MOSFET's ON-time synchronous to that of the internal oscillator sawtooth, with 0.8 mA
minimum current capability. This ramp is intended for implementing additive slope
compensation on current sense. This is needed to avoid the sub-harmonic oscillation that
arises in all peak-current-mode-controlled converters working at fixed frequency in
continuous conduction mode with a duty cycle close to or exceeding 50%.
Figure 27. Slope compensation waveforms
Internal
oscillator
GD
(pin 4)
MODE/SC
(pin 12)
t
t
t
The compensation will be realized by connecting a programming resistor between this pin
and the current sense input (pin 7, CS). The CS pin has to be connected to the sense
resistor with another resistor to make a summing node on the pin. Since no ramp is
delivered during MOSFET OFF-time (see
Figure 27), no external component other than the
programming resistor is needed to ensure a clean operation at light loads.
Note: The addition of the slope compensation ramp will reduce the available dynamics of the
current signal; thereby, the value of the sense resistor must be determined taking this into
account. Note also that the burst-mode threshold (in terms of power) will be slightly
changed.
If slope compensation is not required with FF operation, the pin shall be left floating.
40/51

L6566A Application information
5.14 Summary of L6566A power management functions
It has been seen that the device is provided with a number of power management functions:
multiple operating mode upon loading conditions, protection functions, as well as interaction
with the PFC pre-regulator. To help the designer familiarize with these functions, in the
following tables all of theme are summarized with their respective activation mechanism and
the resulting status of the most important pins. This can be useful not only for a correct use
of the IC but also for diagnostic purposes: especially at prototyping/debugging stage, it is
quite common to bump into unwanted activation of some function, and these tables can be
used as a sort of quick troubleshooting guide.
Table 6. L6566A light load management features
Feature Description
Controlled
Burst
mode
PFC
manage
ment
ON-OFF
operation for
low power
consumption
at light load
PFC off at
light load, on
at heavy load
Caused
by
V
COMP
V
COMPBM -
Hys
V
COMP
V
COMPO
V
COMP
V
COMPL
<
<
<
IC
behavior
Pulse
skipping
operation
V
CC_PFC
0
V
CC_PFC
V
CC
Vcc_restart
=
=
Consump.
(V)
N.A. 1.34mA 5
N.A. 5
(Iqdis,mA)
V
(V)
REF
unchan
unchan
SS
ged
ged
V
COMP
(V)
V
COMPB
to
M-HYS
V
COMPB
M
unchang
ed
OSC
FMOD
(V)
0/1 0
10
V
CC
41/51
Application information L6566A
Table 7. L6566A protections
Vcc
IC Iq
restart
(V)
52.25
(1)
5 1.46 5
(2)
5 1.46 0
5 0.33 0 0 0 0 0 0
(5)
(mA)
VREF
(V)
(6)
(6)
SS
unchanged
VSS
<V
SSLAT
VSS
<V
SSLAT
VCOMP
(6)
V
COMPH
(3)
V
COMPH
(6)
OSC
(V)
FMOD VFF
(V)
0 0 0 unchanged
(6)
i
(5)
i
0 0 unchanged
5 0.33 0 0 0 0 0 unchanged
5 2.5 5 unchanged
unchan
ged
uncha
1
nged
0 unchanged
unchanged
Protection Description Caused by
V
ZCD>VZCDt
for 4
h
consecutive
switching
cycles
OVP
Output
overvoltage
protection
VFF >
VFFlatch
V
COMP
=V
COMPHi
VSS >
OLP
Output
overload
protection
V
SSDIS
V
COMP
=V
COMPHi
VSS >
V
SSLAT
V
COMP
=V
COMPHi
VSS >
Short circuit
protection
Output short
circuit
protection
V
SSDIS
V
COMP
=V
(4)
COMPHi
VSS >
(6)
V
SSLAT
VCS >
V
CSDIS
for 2-3
consecutive
switching
cycles
2nd OCP
Transformer
saturation or
shorted
secondary
diode
protection
Externally
settable
OTP
overtempera
ture
protection
V
DIS>VOTP
Internal
thermal
Tj > 160oC
shutdown
Brownout
Reference
drift
Shutdown1
Mains
undervoltag
e protection
V
drift
REF
protection
Gate driver
disable
V
AC_OK
V
th
V
> VovLatched 13.5 0.33 0 0 0 0 0 0
REF
VFF > V
IC
behavior
Auto
restart
Latched 13.5 0.33 0 0 0 00 0
Auto
restart
Latched 13.5 0.33 0 0 0 0 0 0
Auto
restart
Latched 13.5 0.33 0 0 0 0 0 0
Latched 5 0.33 0 0 0 0 0 0
Latched 13.5 0.33 0 0 0 0 0 0
Auto
restart
Auto
<
restart
Auto
off
restart
42/51

L6566A Application information
Table 7. L6566A protections
Shutdown
Shutdown2
by V
COMP
low
Shutdown
by V
going
cc
ADAPTIVE
UVLO
below V
(lowering of
V
ccoff
threshold at
light load)
1. Use One external diode from V
2. Use one external diode from SS (#14) to V
3. If Css and the Vcc capacitor are such that Vcc falls below UVLO before latch tripping (Figure 21 on page 34)
4. If C
5. When T
and the Vcc capacitor are such that the latch is tripped before V
ss
< 110 oC
J
6. Discharged to zero by V
V
COMP
V
COMPOFF
V
< 9.4V
cc
(
VCOMP
V
ccoff
COMPL
V
< 7.2V
cc
(
VCOMP
V
COMPO
going below UVLO
cc
<
Latched 10 0.33 0 0 0 0 0 0
>
)
Auto
restart
5V
0.18
mA
00 000 0
>
)
(#15) to AC_OK (#16), cathode to AC_OK
FF
(#10), cathode to V
REF
REF
cc
falls below UVLO (Figure 21 on page 34)
It is worth reminding that “Auto-restart” means that the device will work intermittently as long
as the condition that is activating the function is not removed; “Latched” means that the
device is stopped as long as the unit is connected to the input power source and the unit
must be disconnected for some time from the source in order for the device (and the unit) to
restart. Optionally, a restart can be forced by pulling the voltage of pin 16 (AC_OK) below
0.45V.
43/51

Application examples and ideas L6566A
6 Application examples and ideas
8
15
Output capacitor of boost
PFC Pr e - regulator
1012
VREFMODE/ SC
C4 R6
R3 470k
16
IC1
L6566A
OSC
C5
R2
C3
VccAC_OK
HVSFMOD
16
3511
91413
COMP
SS
C6
GND
GD
4
CS
7
ZCD
D2
R4
D3
Optional f or
QR operation
Figure 28. Typical low-cost application schematic
PFC P re-regulator Out put bus
DIS
VFF
Optional f or
QR operation
T1
R1
D1
C2
D4
C8A,B
C7 2.2 nF Y1
Q1
IC3
R5
4
3
TL431
Vout
R7
1
R9
2
C9
R8
R10
Figure 29. Typical full-feature application schematic (QR operation)
R14
PFC controller
R13
R12
PFC Pre-regulator Output bus
C1
Output c ap acit o r of boost
PFC Pre-regulator
10
6
VREF
to mains
volt age sensing
12
MODE/SC
to Vcc pin of
VFF
DIS
NTC2
Vcc_PFC
15
8
C4 R6
AC_OK
IC1
L6566A
13
OSC
T1
R1
D1
R2
HVS
Vcc
ZCD
11
16
C5
5
1
9
14
COMP
SS
GD
4
CS
7
3
GND
C6
C3
R3
R4
D3 1N4148
R18
D2
1N4148
C2
Q1
R5
D4
C8A,B
C7 2.2 nF Y 1
IC3 PC817A
4
3
TL431
Vout
R7
1
R9
2
C9
R8
R10
44/51

L6566A Application examples and ideas
3R15
Figure 30. Typical full-feature application schematic (FF operation)
R1
R12
Table 8. External circuits that determine IC behavior upon OVP and OCP
PFC Pre-regul at o r Out pu t bus
C1
Output capacitor of boost
PFC Pre-re gu la t or
10
VREF
v oltage sensing
6
to mains
13
OSC
to Vcc pin of
PFC controller
VFF
DIS
NTC2
Vcc_PFC
15
8
C4 R6
AC_OK
IC1
L6566A
14
SS
C5
T1
R1
D1
R2
R16
C3
R3
R4
D3 1N4148
R18
HVS
Vcc
ZCD
11
5
1
16
3
9
GNDCOMP
C6
12
4
7
GD
CS
MODE/SC
R17
D2
1N4148
C2
Q1
R5
OVP Latched OVP Auto-restart
AC_OK
R
H
R
L
Diode needed if RL> 4.7 k
OCP Latched
SS VREF
14 10
RH
RFF
VFF
L6566A
15
RL
RFFneeded if RL< 4.7 k
Ω
D4
C8A,B
C7 2.2 nF Y 1
IC3 PC817A
4
3
SS VREF
14 10
16
15
VFF
1
2
TL431
L6566A
Vout
R7
R9
C9
R8
R10
Ω
OCP Auto-restart
1N4148
SS VREF
VFF
14 10
L6566A
15
Ω
R
H
RFF
R
L
RFFneeded if RL< 4. 7 k
1N4148
SS VREF
AC_OK
R
H
14 10
16
L6566A
15
VFF
RL
Diode needed if RL> 4.7 k
Ω
45/51

Application examples and ideas L6566A
Figure 31. Frequency foldback at light load (FF operation)
MODE/SC
12
L6566A
OSC
T
R
R1
Vref
10
COMP
9
13
R2
BC857
Figure 32. Latched shutdown upon mains overvoltage
Vin
Vin
Vcc
L6566A
8
BC857
Vref
10
L6566A
15
VFF
Rq
BC847
5
DIS
8
15
VFF
>10 Rq
DIS
46/51

L6566A Package mechanical data
7 Package mechanical data
In order to meet environmental requirements, ST offers these devices in ECOPACK®
packages. These packages have a Lead-free second level interconnect. The category of
second Level Interconnect is marked on the package and on the inner box label, in
compliance with JEDEC Standard JESD97. The maximum ratings related to soldering
conditions are also marked on the inner box label. ECOPACK is an ST trademark.
ECOPACK specifications are available at: www.st.com.
47/51

Package mechanical data L6566A
Table 9. SO16N mechanical data
mm. inch
Dim.
Min Typ Max Min Typ Max
A 1.75 0.069
a1 0.1 0.25 0.004 0.009
a2 1.6 0.063
b 0.35 0.46 0.014 0.018
b1 0.19 0.25 0.007 0.010
C 0.5 0.020
c1 45° (typ.)
D(1) 9.8 10 0.386 0.394
E 5.8 6.2 0.228 0.244
e 1.27 0.050
e3 8.89 0.350
F(1) 3.8 4.0 0.150 0.157
G 4.60 5.30 0.181 0.208
L 0.4 1.27 0.150 0.050
M 0.62 0.024
S 8°(max.)
Figure 33. Package dimensions
48/51

L6566A Order codes
8 Order codes
Table 10. Order codes
Order codes Package Packaging
L6566A SO16N Tube
L6566ATR SO16N Tape and reel
49/51

Revision history L6566A
9 Revision history
Table 11. Document revision history
Date Revision Changes
20-Aug-2007 1 First release
50/51

L6566A
Please Read Carefully:
Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the
right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any
time, without notice.
All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no
liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and services described herein.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted under this document. If any part of this
document refers to any third party products or services it shall not be deemed a license grant by ST for the use of such third party products
or services, or any intellectual property contained therein or considered as a warranty covering the use in any manner whatsoever of such
third party products or services or any intellectual property contained therein.
UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS
OF ANY JURISDICTION), OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS EXPRESSLY APPROVED IN WRITING BY AN AUTHORIZED ST REPRESENTATIVE, ST PRODUCTS ARE NOT
RECOMMENDED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN MILITARY, AIR CRAFT, SPACE, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE SUSTAINING
APPLICATIONS, NOR IN PRODUCTS OR SYSTEMS WHERE FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY,
DEATH, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE. ST PRODUCTS WHICH ARE NOT SPECIFIED AS "AUTOMOTIVE
GRADE" MAY ONLY BE USED IN AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS AT USER’S OWN RISK.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the statements and/or technical features set forth in this document shall immediately void
any warranty granted by ST for the ST product or service described herein and shall not create or extend in any manner whatsoever, any
liability of ST.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of ST in various countries.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners.
© 2007 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
STMicroelectronics group of companies
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
51/51
 Loading...
Loading...