Page 1

AN987
APPLICATION NOTE
ST7 SERIAL TEST CONTROLLER PROGRAMMING
by Microcontroller Division Applications
INTRODUCTION
This application note describes:
– The advantages of Serial Test Controller Programming (STCP) vs. programming using an
EPROM programming board (EPB) (see Sec tion 2.1).
– How to implement Serial Test Controller Programming targeting most of the ST7 general pur-
pose microcontrollers (see Section 2.2). These devices include all parts supported by the
ST7 starter kits and ST7 EPBs in the MDT1, MDT2 and MDT4 tool families (see the supported device list in APPENDIX 1).
Note: In this applicatio n note, the term “programming tool” refers to either the EPBs or the
starter kits.
1 PROGRAM M ING TECHNIQU ES
There are two possible ways of programming an ST7 device:
■ Using a programming tool. In this case, the device is first plugged on the programming board
and then programmed. Then, the part is soldered or plugged into a socket on the user board.
This can be done using any of the following ST7 programming tools:
– ST7 Starter Kit
– ST7 EPB (EPROM Programming Board)
– ST7 Gang Programmer
For further details about the above tools, please refer to the user manual supplied with these
devices.
■ Using a Serial Test Controller Programming (STCP) tool. This technique allows a device to
be directly programmed on the user board. This is a two-step procedure where first the
board is first manufactured with a blank ST7, and afterwards the chip is programmed using
a programming tool (Starter Kit or EPB).
This application note describes the STCP method only.
AN987/1000 1/10
1
Page 2

ST7 SERIAL TEST CON TR OLLER PROGR AMM IN G
2 SERIAL TEST CONTROLLER PROGRAMMING
2.1 ADVANTAGES
The advantages of STCP are numerous:
■ Time to market
To reduce manufacturing cycle times, a user board can be designed to be generic,
supporting several functions. These functions can be enabled or disabled by software
according to customer requirements. In this case, STCP allows application boards to be
manufactured in one shot and programmed w ith different functions according to customer
needs and orders.
■ Cost reduction
Software updates may be necessary in some cases because of a bug correction or a newly
implemented feature. The STCP is a flexible and painless way of performing such
modifications and at a lower cost. There is no need to add any sockets to the board or to
unsolder and change components in order to upgrade the application.
■ Security
Because STCP offers an easy w ay to custom ise the user’s program, or part of it, it can be
used to insert different key codes for each board. This could be used, for example, i n a door
lock sys te m.
■ Flexibility
For example, STCP can be used to allow calibration procedures to be performed directly in
the field.
2.2 USER BOARD S PECIFICATION
The user has to design his layout in order to support two modes: programming mode and user
mode.
Figure 1. shows the user board divided into two blocks:
■ Block 1:
Includes all the components that play a role during programming mode:
– Connector J1, which links the user board to the programming tool.
– The ST72 MCU, which is the device to be programmed.
– Jumpers W1 to Wn, whose purpose is to isolate the pins used for programming the ST72
from the other components in Block 2. In some application configurations, isolation resistors (47 kΩ) can be used instead of jumpers.
■ Block 2:
This block consists of all the other components soldered on the user board.
2/10
2
Page 3
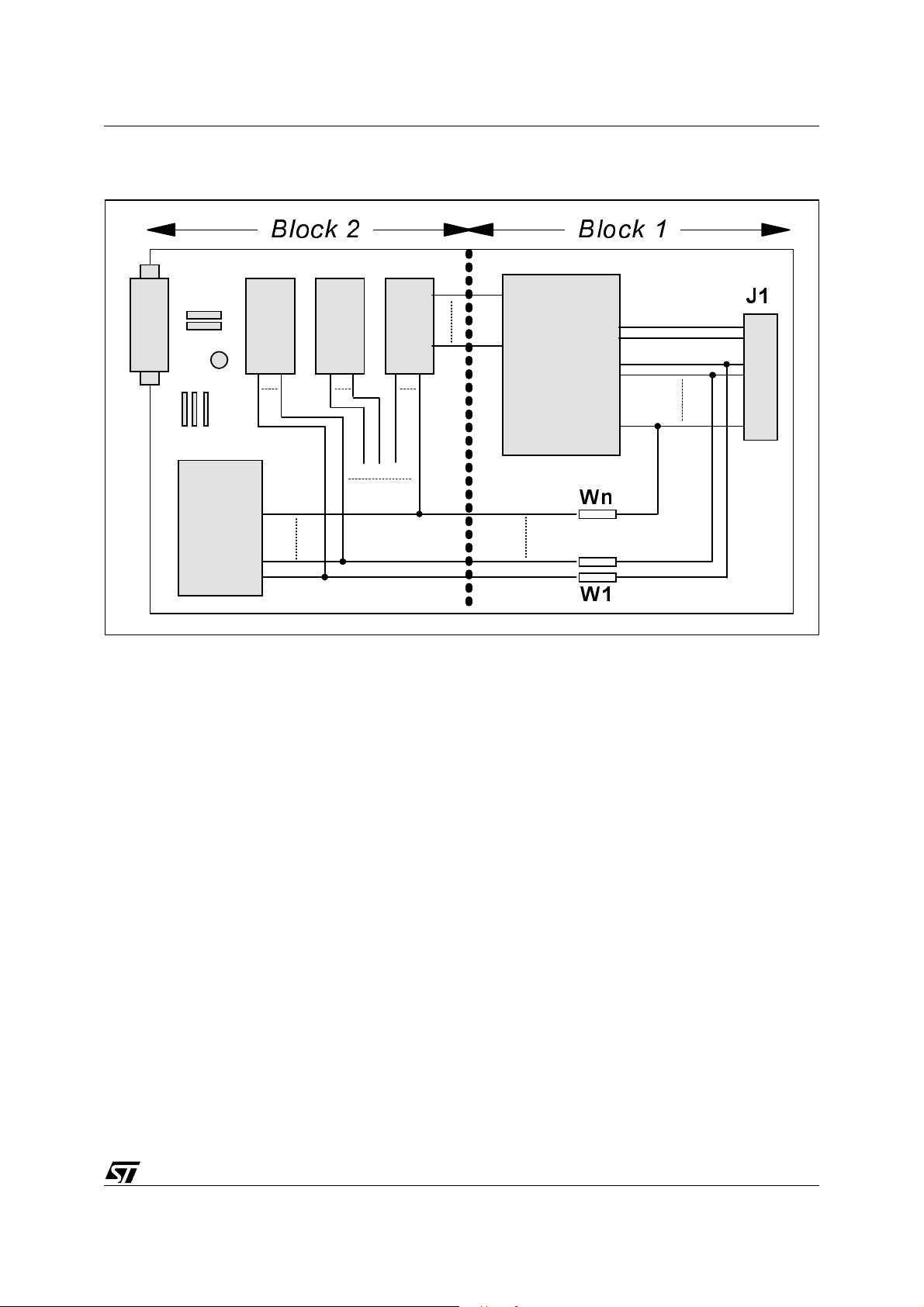
Figure 1. User Board
ST7 SERIAL TEST CONTROLLER PROGRAMMING
%ORFN %ORFN
-
67
:Q
:
Now, let’s define the pins used for pr ogrammin g the ST7. T hese pins a re put tog ether in the
W1 connector implemented in all the ST programming tool boards (see Section 3 APPENDIX
1 for the pin connector assignment).
All the ST7 programming tools referred to in this note (ST7 starter kits and ST7 EPBs in the
MDT1, MDT3 and MDT4 tool families) use a programming technique called JTAG (Joint Test
Action Group).
These programming tools control 11 pins:
■ 5 JTAG pins and 3 test mode pins, which are used for loading the software code into the
ST7. These pins are:
– Pin TCK: the test clock (input),
– Pin TMS: the Test Mode Select (input, weak pull-up),
– Pin TRST0: the Reset (Input, weak pull-up, active low)
– Pin TDI: the Test Data In (input, weak pull-up). This is the serial data input, sampled on
the rising edge of TCK.
– Pin TDO: the Test Data Out (tri-state output). This is the serial data output, updated on the
falling edge of TCK.
– Pins M0, M1 and M2: These 3 pins are used to force the test modes.
Depending on the d evice selected, t hese 8 pins will be as sociated with different p in num -
bers (see APPENDIX 1).
3/10
Page 4

ST7 SERIAL TEST CON TR OLLER PROGR AMM IN G
If these pins need to be tied to VDD or VSS, or if they are us ed by the user’s application, they
must be isolated from the user circuitry during programming. To do so, a jumper can be
added for each of the eight pins (see Figure 2.).
Note: Isolation resistors (47 kΩ) can be used instead of jumpers only if these pins are used
by the application as input (without Pull-up, without pull-down, or analog input configuration).
■ 3 system pins, VPP/TEST, RESET and OSCIN, which must be connec ted as follows:
– The VPP/TEST pin must not be directly connected to GND/V
on the application board
SS
in order to avoi d any confl ict with the programming voltage. T his pin should be pulled down
by a 10 kΩ resistor (see Figure 2.).
– The RESET
pin controls the entry into programming mode. This pin must be connected to
a 10 kΩ pull-up resistor and a 1 nF c apacitor connected to GND ( see Figure 2.) to av oid
any direct connections to V
. This pin can be connected to a 47 kΩ isolation resistor if an
SS
external reset is provided by the application board.
– The OSCIN pin synchronizes the programming operation using a clock generated by the
programming tool. The OSCIN pin can be directly connected to the J1 connector. No isolation is needed as long as a quartz crystal or ceramic resonator is used in the application.
If an external clock generator is used in the application, it must be disconnected during
STC programming.
Note: The OSCOUT pin does not need to be disconnected during the programming phase
as long as a crystal, a ceramic resonator or an external clock source is used to drive the
internal oscillator (user mode only).
■ The V
and VSS power supply pins. The use of the VDD connection is optional, depending
DD
on whether the application board supply can be disconnected or not.
If the application board supply is disconnected, the chip can be supplied through the
programming tool (as long as the total current load does not exceed 100 mA and the
capacitive load is less than 50 µF). In this case, only 1 jumper needs to be added in order to
disconnect the VPP pin from the user circuitry during the programming sequence. No jumper
is needed for V
(see Figure 2.).
SS
If you want to use the application board power supply, its voltage must be 5 V, so that logic
levels are compatible with those of the programming tool.
Note: In any case, the ground from the application board and the ground from the
programming tool must be connected together (see Figure 2.).
4/10
Page 5

Figure 2. Block 1
ST7 SERIAL TEST CONTROLLER PROGRAMMING
To
block2
VDD appli
To
block2
10 kΩ
10 kΩ
M0
M1
M2
/TEST
V
PP
V
DD
Reset
OSCIN
OSCOUT
V
SS
Tck
Tms
Trst0
Tdi
Tdo
J1
Jumper or 47 kΩ isolation resistor
(depending on the application configuration, refer to the note on page 3).
Jumper use to disconnect the Application board supply if it is not 5 V.
If the application board supply can be used, remove this jumper and
remove the connection between pin VDD and connector J1.
The ST7 programming tool is connected to the user board via connector J1.
5/10
Page 6

ST7 SERIAL TEST CON TR OLLER PROGR AMM IN G
2.3 PROGRAMMING PROCEDURE
Depending on the device you need to program, use one of these ST7 programming tools:
■ ST7 MDT1-KIT or ST7 MDT1- EPB. They cover the following devices:
– ST72101G1 or G2
– ST72212G2
– ST72213G1
– ST72251G1 or G2
■ ST7 MDT2-KIT or ST7 MDT4- EPB. They cover the following devices:
– ST72121J2 or J4
– ST72311J2 or J4
– ST72311N2 or N4
– ST72331J2 or J4
– ST72331N2 or N4
■ ST7 MDT4-KIT or ST7 MDT4-EPB. They cover the following devices:
– ST72272K2 or K4
– ST72372J4
– ST72371N4
– ST72671N4 or N6
After selecting the appropriate programming tool, proceed as follows:
1. On the application board, remove all jumpers.
2. Locate the 16 pin connector W1 (8x2 header HE10) on the programming tool which contains the 12 signals necessary for performing STCP (see Section 3 APPENDIX 1 for the pin
identification).Then connect the W1 connector of the pr ogramming tool to the application
board connector (J1 in Figure 1.).
3.Using the parallel interface cable, connect the PC parallel port to the parallel connector of
the programming tool.
4.Power on the PC and the board. On the programming tool, LED 1 must light up.
5.Start the Windows EPROMer, target the programming tool, then the correct device. Open
the file containing the code to program. And... program your device!
6. Close the operating software, power down the programming tool, disconnect the application board from the programming tool and replace any jumpers that were disconnected on
the application board. Your application is now ready to run!
6/10
Page 7

ST7 SERIAL TEST CONTROLLER PROGRAMMING
3 APPENDIX 1
The following table lists the devices supported by this application note and the specific starter
kit required for each sales type.
Sales Type Starter Kit supporting the device
ST72x101G1
ST72x101G2
ST72x212G2
ST72x213G1
ST72x251G1
ST72x251G2
ST72x121J2
ST72x121J4
ST72x311J2
ST72x311J4
ST72x311N2
ST72x311N4
ST72x331J2
ST72x331J4
ST72x331N2
ST72x331N4
ST72x272K2
ST72x272K4
ST72x371N4
ST72x372J4
ST72x671N4
ST72x671N6
ST7 MDT1 Starter kit or EPB
ST7 MDT2 Starter kit or EPB
ST7 MDT4 Starter kit or EPB
x = T, if the device is an OTP,
E, if the device is an EPROM.
7/10
Page 8

ST7 SERIAL TEST CON TR OLLER PROGR AMM IN G
4 APPENDIX 2
This appendix provides t he required i nformati on for pr ogrammin g a device suppor ted by the
MDT1, MD T2 and MD T4 E PBs or s ta rter k its. T he fiv e JT AG pins an d t hree test mod e p ins
(M0, M1 and M2) with their associated pin numbers are specified for each device.
4.1 ST7 MDT1 EPB OR STARTER KIT
ST7 Device Pin Numbers
JTDI
JTCK
JTRST
JTMS
Sales type EPROM E2RAM Package
ST72x101G1 4K - 256
ST72x101G2 8K - 256
ST72x212G2 8K - 256
ST72x213G1 4K - 256
ST72x251G1 4K - 256
ST72x251G2 8K - 256
SO28
SDIP322226232724282529141691110121113263011
SO28
SDIP322226232724282529141691110121113263011
SO28
SDIP322226232724282529141691110121113263011
SO28
SDIP322226232724282529141691110121113263011
SO28
SDIP322226232724282529141691110121113263011
SO28
SDIP322226232724282529141691110121113263011
PA3
PA2
PA1
Programming tool W1 connector 5 1 9 3 7 12 10 8 16 4 2 N.C 15
JTDO
PA0
PC3M2PB2M1PB1M0PB0
Vpp Reset Oscin Vdd Vss
22283227
31
22283227
31
22283227
31
22283227
31
22283227
31
22283227
31
x = T, if the device is an OTP,
E, if the device is an EPROM,
N.C., means not connected.
8/10
Page 9

4.2 ST7 MDT2 EPB OR STARTER KIT
ST7 Device Pin Numbers
Sales type EPROM E
ST72x121J2 8K - 384
ST72x121J4 16K - 512
ST72x311J2 8K - 384
ST72x311J4 16K - 512
ST72x311N2 8K - 384
ST72x311N4 16K - 512
ST72x331J2 8K 256 384
ST72x331J4 16K 256 512
ST72x331N2 8K 256 384
ST72x331N4 16K 256 512
Programming tool W1 connector 5 1 9 3 7 12 10 8 16 4 2
2
RAM Package
TQFP44
SDIP4237303629
TQFP44
SDIP4237303629
TQFP44
SDIP4237303629
TQFP44
SDIP4237303629
TQFP64
SDIP5652405139
TQFP64
SDIP5652405139
TQFP44
SDIP4237303629
TQFP44
SDIP4237303629
TQFP64
SDIP5652405139
TQFP64
SDIP5652405139
ST7 SERIAL TEST CONTROLLER PROGRAMMING
JTDI
JTCK
PA7
JTRST
PA6
PA5
35
28
35
28
35
28
35
28
50
38
50
38
35
28
35
28
50
38
50
38
JTMS
JTDO
PA4
PA3M2PB2M1PB1M0PB0
342731244413402393831393242
342731244413402393831393242
342731244413402393831393242
342731244413402393831393242
493746347556545535341544259
493746347556545535341544259
342731244413402393831393242
342731244413402393831393242
493746347556545535341544259
493746347556545535341544259
Vpp Reset Oscin
35
35
35
35
45
45
35
35
45
45
4.3 ST7 MDT4 EPB OR STARTER KIT
ST7 Device Pin Numbers
JTDI
JTCK
JTRST
JTMS
Sales type EPROM E2RAM Package
ST72x272K2 8K - 384
ST72x272K2 16K - 512
ST72x371N4 16K - 512
ST72x372J4 16K - 512 SDIP42 34 35 36 37 31 2 1 42 41 40 33 25 23
ST72x671N4 16K - 512
ST72x671N6 32K - 1K
SO34
SDIP32292730283129323025243322113432333128268877
SO34
SDIP32292730283129323025243322113432333128268877
TQFP64
SDIP56284629473048314920384334224114056385427451131929
TQFP64
SDIP56284629473048314920384334224114056385427451131929
TQFP64
SDIP56284629473048314920384334224114056385427451131929
PA7
PA6
PA5
Programming tool W1 connector 5 1 9 3 7 12 10 8 16 4 2 N.C 15
x = T, if the device is an OTP,
E, if the device is an EPROM,
N.C., means not connected.
JTDO
PA4
PC6M2DA3M1DA2M0DA1
Vpp Reset Oscin Vdd Vss
9/10
Page 10

ST7 SERIAL TEST CON TR OLLER PROGR AMM IN G
THE PRESENT NOTE WHICH IS FOR GUIDANCE ONLY AIMS AT PROVIDING CUSTOMERS WITH INFORMATION
REGARDING THE IR PRO DUCT S IN OR DER FO R THEM TO SAV E TIME . AS A RES ULT, STMIC ROEL ECTR ONI CS
SHALL NOT BE HELD LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES WITH RESPECT TO
ANY CLAIMS ARISING FROM THE CONTENT OF SUCH A NOTE AND/OR THE USE MADE BY CUSTOMERS OF
THE INFORMATION CONTAINED HEREIN IN CONNEXION WITH THEIR PRODUCTS."
Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, STMicroelectronics assumes no responsibility for the consequences
of use of such information nor for any infringement of patents or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. No license is granted
by implic ation or otherwise under any patent or patent ri ghts of STM i croelectr oni cs. Specifications mentioned in thi s publicati on are subject
to change without notice. This publication supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied. STMicroelectronics products are not
authorized for use as cri tical comp onents in life support dev i ces or systems wi thout the express written approv al of STMicroel e ctronics.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics
Purchase of I
Australi a - Brazil - China - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Italy - Japan - Malaysia - Malt a - Morocco - Singapore - Spain
2
C Components by STMicroelectronics conveys a license under the Philips I2C Patent. Rights to use the se components in an
2
I
C system i s granted pro vid ed that the sy stem conforms to the I2C Standard Specification as defined by Philips.
2000 ST Microelectronics - All Rights Reserved.
STMicroelectronics Group of Compan i es
Sweden - Switzerland - United K i ngdom - U.S. A.
http://www.s t. com
10/10
 Loading...
Loading...