Page 1

AN671
Application note
Prevention of data corruption in ST6 on-chip EEPROM
INTRODUCTION
The ST6 Microcontroller has been designed to avoid any potential corruption of data
programmed into its on-chip EEPROM (when available). Data integrity can be ensured as long
as the application designer follows the guidelines provided in this note.
In general, EEPROM data corruption occurs whenever the reset signal is not controlled when
the power supply goes up or down.
This is particularly true with a slow ramp-up and/or slow fall time of the power supply, since the
device may be in a supply voltage area where the device functionality is not guaranteed for a
long time.
If no special care is taken during the power up sequence regarding the reset signal then the
microcontroller core may start writing into the EEPROM. The same behaviour may occur upon
a power down.
Two complementary solutions are possible to prevent from these unwanted actions, a software
solution and a hardware solution.
1 SOFTWARE SOLUTION
This solution only applies to the power down sequence which represents the majority of data
corruption risks.
The solution consists in disabling the enable bit of the EEPROM control register after writing
into the EEPROM and before switching "off" the application; this avoids any spurious writing as
described above.
Note that this bit is automatically reset upon power on, thus the reason why most cases of data
corruption can occur at power down, as the enable bit may have been modified by the user
software.
August 2008 Rev 2
1/4
Page 2
PREVENTION OF DATA CORRUPTION IN ST6 ON-CHIP EEPROM
2 HARDWARE SOLUTION
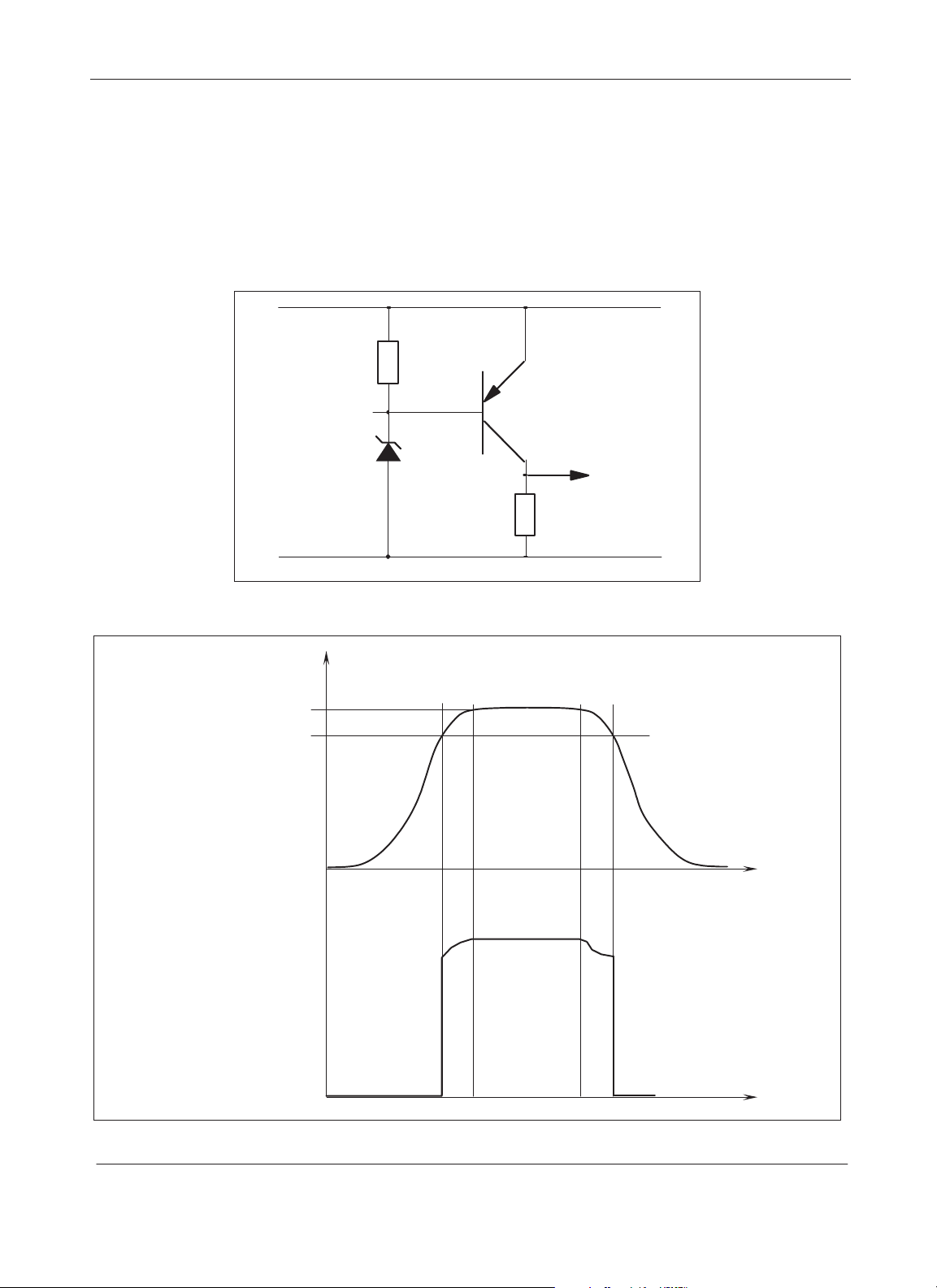
No problems can occur when the device is in the reset state as long as the voltage has not
reached the minimum value at which the CPU performs. A simple level detection circuit which
forces the reset input low before reaching this critical point prevents any unwanted writing into
the EEPROM.
Figure 1. Reset Network
Reset Pin
Figure 2. Supply/ Reset graph
Vdd max.
Min operating voltage
Reset Pin
2/4
Page 3

PREVENTION OF DATA CORRUPTION IN ST6 ON-CHIP EEPROM
3 SUMMARY
Using both solutions shown in this note avoids any potential for data corruption during the
power supply rise/fall time.
The software solution is inexpensive and must be systematically used. The hardware solution
costs little and should be used whenever the power supply is particularly slow (rise/fall time >
100ms) or if the supply comes from the mains through a single resistor and diode network.
3/4
Page 4

PREVENTION OF DATA CORRUPTION IN ST6 ON-CHIP EEPROM
Revision history
segnahc fo noitpircseD noisiveRetaD
14991-yraurbeF
05-Aug-2008
Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”)
reserve the right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services
described herein at any time, without notice.
All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST
assumes no liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and services described herein.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted under this document. If any
part of this document refers to any third party products or services it shall not be deemed a license grant by ST for the use of such
third party products or services, or any intellectual property contained therein or considered as a warranty covering the use in any
manner whatsoever of such third party products or services or any intellectual property contained therein.
2
Please Read Carefully:
go and disclaimer modifiedoL
esaeler laitinI
UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE
LAWS OF ANY JURISDICTION), OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY
RIGHT.
UNLESS EXPRESSLY APPROVED IN WRITING BY AN AUTHORIZED ST REPRESENTATIVE, ST PRODUCTS ARE NOT
RECOMMENDED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN MILITARY, AIR CRAFT, SPACE, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE
SUSTAINING APPLICATIONS, NOR IN PRODUCTS OR SYSTEMS WHERE FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION MAY RESULT IN
PERSONAL INJURY, DEATH, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE. ST PRODUCTS WHICH ARE NOT
SPECIFIED AS "AUTOMOTIVE GRADE" MAY ONLY BE USED IN AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS AT USER’S OWN RISK.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the statements and/or technical features set forth in this document shall
immediately void any warranty granted by ST for the ST product or service described herein and shall not create or extend in any
manner whatsoever, any liability of ST.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of ST in various countries.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners.
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy -
Japan - Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
Information in this document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied.
© 2008 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
STMicroelectronics group of companies
www.st.com
4/4
 Loading...
Loading...