
AN4043
Application note
SLLIMM™-nano
small low-loss intelligent molded module
Introduction
In recent years the variable speed motor control market has required high performance
solutions able to satisfy the increasing energy saving requirements, compactness, reliability,
and system costs in home appliances, such as dish washers, refrigerator compressors, air
conditioning fans, draining and recirculation pumps, and in low power industrial applications,
such as small fans, pumps and tools, etc. To meet these market needs, STMicroelectronics
has developed a new family of very compact, high efficiency, dual-in-line intelligent power
modules, with optional extra features, called small low-loss intelligent molded module nano
(SLLIMM™-nano).
The SLLIMM-nano product family combines optimized silicon chips, integrated in three main
inverter blocks:
● power stage
– six very fast IGBTs
– six freewheeling diodes
● driving network
– three high voltage gate drivers
– three gate resistors
– three bootstrap diodes
● protection and optional features
– op amp for advanced current sensing
– comparator for fault protection against overcurrent and short-circuit
– smart shutdown function
– dead time, interlocking function and undervoltage lockout.
Thanks to its very good compactness, the fully isolated SLLIMM-nano package (NDIP) is
the ideal solution for applications requiring reduced assembly space, without sacrificing
thermal performance and reliability.
Compared to discrete-based inverters, including power devices, and driver and protection
circuits, the SLLIMM-nano family provides a high integrated level that means simplified
circuit design, reduced component count, lower weight, and high reliability.
The aim of this application note is to provide a detailed description of SLLIMM-nano
products, providing guidelines to motor drive designers for an efficient, reliable, and fast
design when using the new ST SLLIMM-nano family.
April 2012 Doc ID 022726 Rev 1 1/60
www.st.com

Contents AN4043
Contents
1 Inverter design concept and SLLIMM-nano solution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
1.1 Product synopsis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1.2 Product line-up and nomenclature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1.3 Internal circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
1.4 Absolute maximum ratings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2 Electrical characteristics and functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
2.1 IGBTs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
2.2 Freewheeling diodes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
2.3 High voltage gate drivers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
2.3.1 Logic inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
2.3.2 High voltage level shift . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
2.3.3 Undervoltage lockout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
2.3.4 Dead time and interlocking function management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
2.3.5 Comparators for fault sensing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
2.3.6 Short-circuit protection and smart shutdown function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
2.3.7 Timing chart of short-circuit protection and smart shutdown function . . 23
2.3.8 Current sensing shunt resistor selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
2.3.9 RC filter network selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
2.3.10 Op amps for advanced current sensing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
2.3.11 Bootstrap circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
2.3.12 Bootstrap capacitor selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
2.3.13 Initial bootstrap capacitor charging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
3 Package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
3.1 Package structure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
3.2 Package outline and dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
3.3 Input and output pins description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
4 Power losses and dissipation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
4.1 Conduction power losses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
4.2 Switching power losses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
4.3 Thermal impedance overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
2/60 Doc ID 022726 Rev 1

AN4043 Contents
4.4 Power loss calculation example . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
5 Design and mounting guidelines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
5.1 Layout suggestions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
5.1.1 General suggestions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
5.2 Mounting instructions and cooling techniques . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
6 General handling precaution and storage notices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
6.1 Packaging specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
7 References . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
8 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Doc ID 022726 Rev 1 3/60

List of tables AN4043
List of tables
Table 1. SLLIMM-nano line-up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Table 2. Inverter part . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Table 3. Control part of the STGIPN3H60 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Table 4. Supply voltage and operation behavior . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Table 5. Total system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Table 6. Integrated pull-up/down resistor values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Table 7. Interlocking function truth table of the STGIPN3H60A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Table 8. Interlocking function truth table of the STGIPN3H60 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 9. Outline drawing of NDIP-26L package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Table 10. Input and output pins . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Table 11. Cauer and Foster RC thermal network elements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Table 12. Document revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
4/60 Doc ID 022726 Rev 1

AN4043 List of figures
List of figures
Figure 1. Inverter motor drive block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Figure 2. Discrete-based inverter vs. SLLIMM-nano solution comparison. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Figure 3. SLLIMM block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Figure 4. SLLIMM-nano nomenclature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Figure 5. Internal circuit of the STGIPN3H60A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Figure 6. Internal circuit of the STGIPN3H60 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Figure 7. Stray inductance components of output stage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Figure 8. High voltage gate drive die image . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Figure 9. High voltage gate driver block diagram . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Figure 10. Logic input configuration for the STGIPN3H60A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Figure 11. Logic input configuration for the STGIPN3H60. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Figure 12. Timing chart of undervoltage lockout function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Figure 13. Timing chart of dead time function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Figure 14. Smart shutdown equivalent circuitry . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Figure 15. Timing chart of smart shutdown function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Figure 16. Examples of SC protection circuit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Figure 17. Example of SC event . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Figure 18. 3-phase system . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Figure 19. General advanced current sense scheme and waveforms. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Figure 20. Bootstrap circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Figure 21. Bootstrap capacitor vs. switching frequency. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Figure 22. Initial bootstrap charging time. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Figure 23. Images and internal view of NDIP-26L package. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Figure 24. Outline drawing of NDIP-26L package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Figure 25. Pinout (top view) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Figure 26. Typical IGBT power losses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Figure 27. IGBT and diode approximation of the output characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
Figure 28. Typical switching waveforms of the STGIPN3H60 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Figure 29. R
Figure 30. Thermal impedance Z
Figure 31. Cauer RC equivalent circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Figure 32. Foster RC equivalent circuit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Figure 33. Maximum I
Figure 34. General suggestions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Figure 35. Example 1 on a possible wrong layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Figure 36. Example 2 on a possible wrong layout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Figure 37. Cooling technique: copper plate on the PCB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Figure 38. Cooling technique: heatsink bonded on the package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Figure 39. Cooling technique: heatsink bonded on the PCB . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Figure 40. Packaging specifications of NDIP-26L package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
equivalent thermal circuit. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
th(j-a)
current vs. fsw simulated curves . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
C(RMS)
curve for a single IGBT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
th(j-a)
Doc ID 022726 Rev 1 5/60
Inverter design concept and SLLIMM-nano solution AN4043
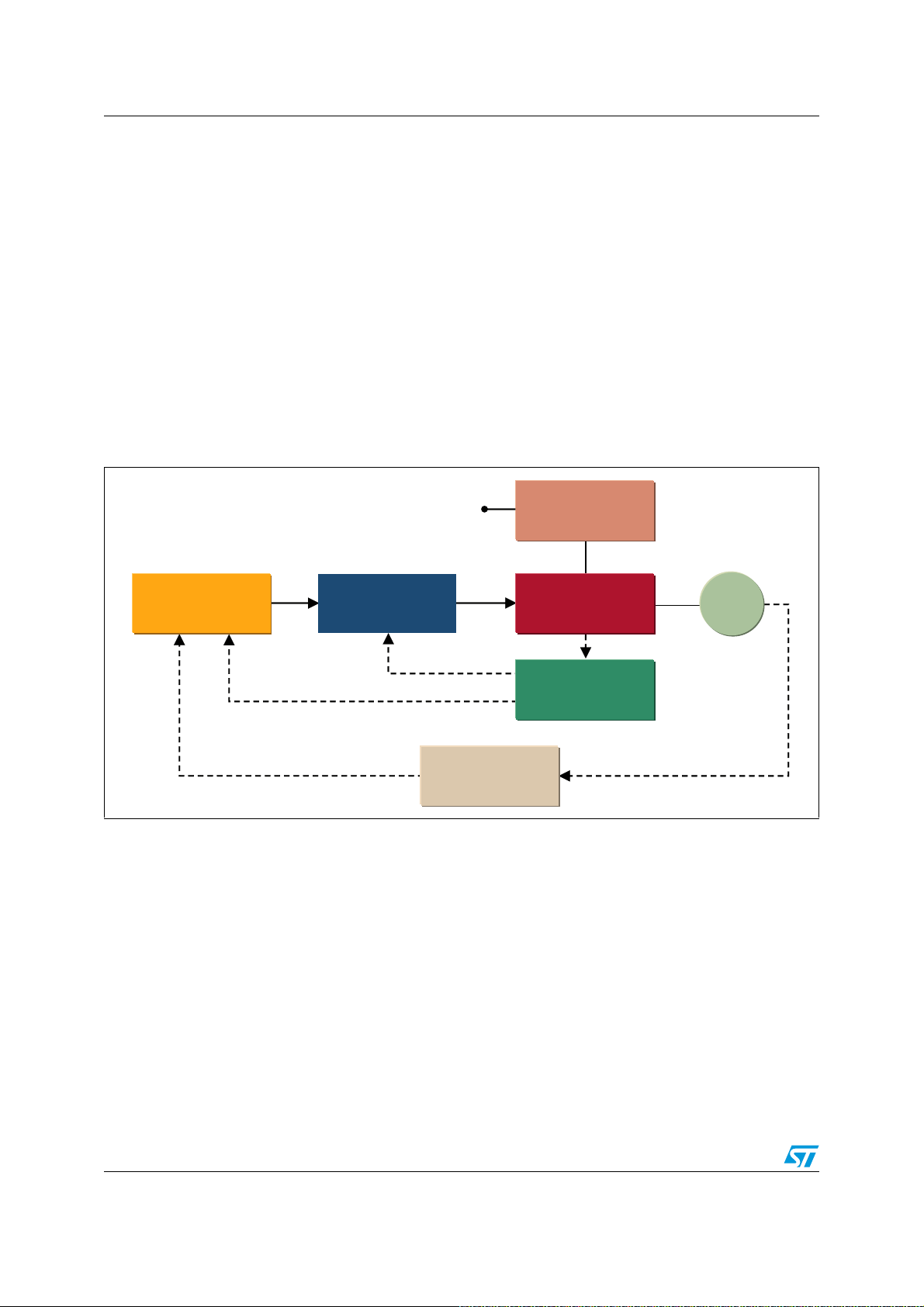
1 Inverter design concept and SLLIMM-nano solution
Motor drive applications, ranging from a few tens of watts to mega watts, are mainly based
on the inverter concept thanks to the fact that this solution can meet efficiency, reliability,
size, and cost constraints required in a number of markets.
As shown in
Figure 1
, an inverter for motor drive applications is basically composed of a
power stage, mainly based on IGBTs and freewheeling diodes; a driving stage, based on
high voltage gate drivers; a control unit, based on microcontrollers or DSPs; some optional
sensors for protection and feedback signals for controls.
The approach of this solution with discrete devices produces high manufacturing costs
associated with high reliability risks, bigger size and higher weight, a considerable number
of components and the significant stray inductances and dispersions in the board layout.
Figure 1. Inverter motor drive block diagram
0DLQV
0LFURFRQWUROOHU
*DWHGULYHU 3RZHUVWDJH
%ULGJHUHFWLILHU
0
6HQVRUV
)HHGEDFN
In recent years, the use of intelligent power modules has rapidly increased thanks to the
benefits of greater integration levels. The new ST SLLIMM-nano family is able to replace
more than 20 discrete devices in a single package.
discrete-based inverter and the SLLIMM-nano solution, the advantages of SLLIMM-nano
can be easily understood and can be summarized in a significantly improved design time,
reduced manufacturing efforts, higher flexibility in a wide range of applications, and
increased reliability and quality level.
In addition, the optimized silicon chips in both control and power stages and the optimized
board layout provide maximized efficiency, reduced EMI and noise generation, higher levels
of protection, and lower propagation delay time.
6/60 Doc ID 022726 Rev 1
Figure 2
!-V
shows a comparison between a
AN4043 Inverter design concept and SLLIMM-nano solution
Figure 2. Discrete-based inverter vs. SLLIMM-nano solution comparison
LYHFRPSRQHQWV
3DVV
'LRG
5HVLVWRUV
HV
+9JDWHGULYHUV ,*%7V):'V
1.1 Product synopsis
The SLLIMM-nano family has been designed to satisfy the requirements of a wide range of
final applications up to 100 W (in free air), such as:
● dish washers
● refrigerator compressors
● air conditioning fans
● draining and recirculation pumps
● low power industrial applications
● small fans, pumps and tools.
(DV\OD\RXW
DQGGHVLJQ
+LJKTXDOLW\
DQGUHOLDELOLW\
5HGXFHGWRWDO
V\VWHPFRVW
D
D
Q
Q
6//,00
6//,00
+LJK
FRPSDFWQHVV
5HGXFHG(0,
DQGQRLVH
QR
QR
$GYDQFHG
SUR
WHFWLRQ
IXQFWLRQ
,PSURYHG
HIILFLHQF\
!-V
The main features and integrated functions can be summarized as follows:
● 600 V, 3 A ratings
● 3-phase IGBT inverter bridge including:
– six low-loss IGBTs
– six low forward voltage drop and soft recovery freewheeling diodes
● three control ICs for gate driving and protection including:
– smart shutdown function
– comparator for fault protection against overcurrent and short-circuit
– op amp for advanced current sensing
– three integrated bootstrap diodes
– interlocking function
– undervoltage lockout
● open emitter configuration for individual phase current sensing
● very compact and fully isolated package
● integrated gate resistors for IGBT switching speed optimum setting
● gate driver proper biasing.
Doc ID 022726 Rev 1 7/60
Inverter design concept and SLLIMM-nano solution AN4043
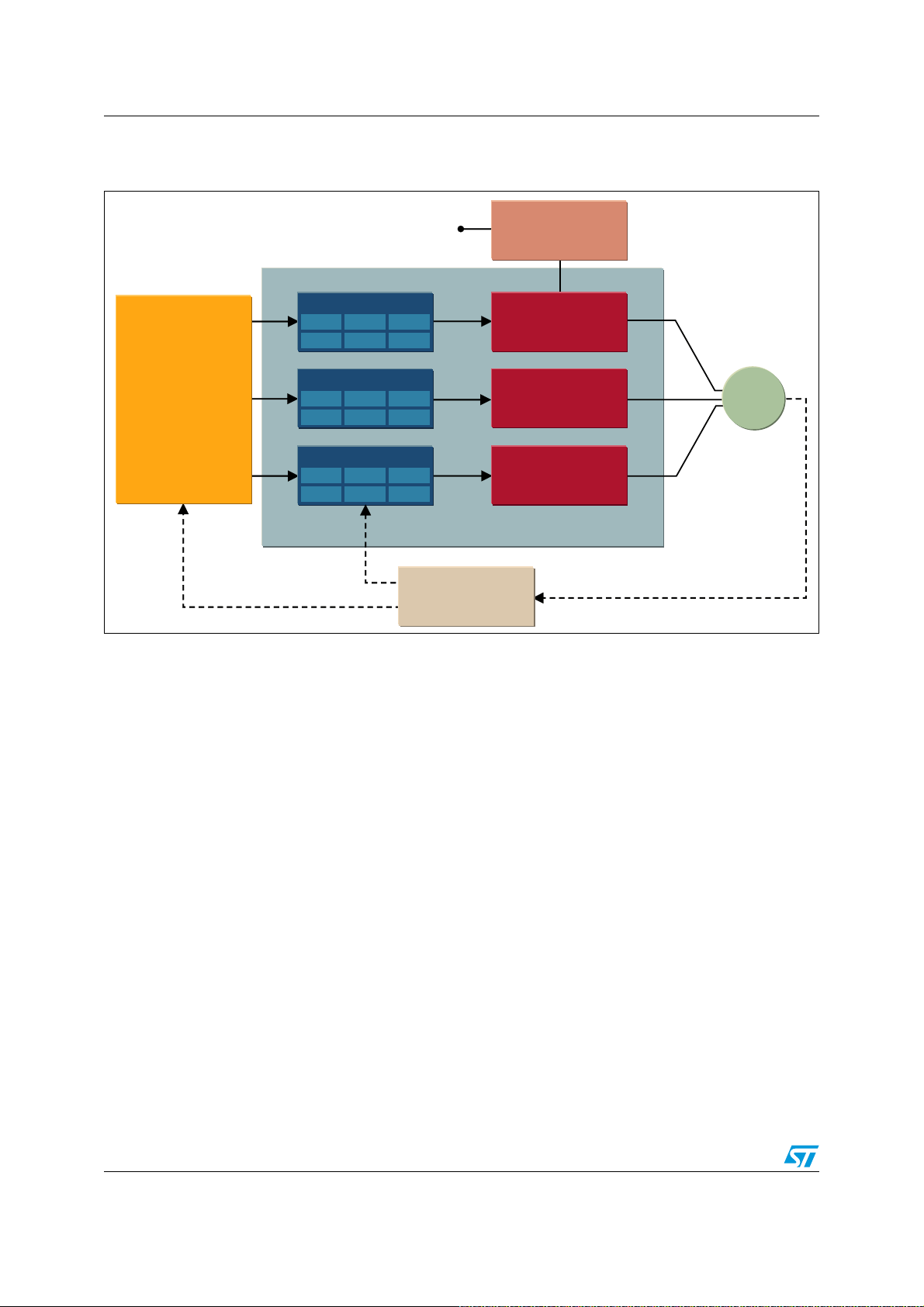
Figure 3
Figure 3. SLLIMM block diagram
shows the block diagram of the SLLIMM-nano included in the inverter solution.
*DWHGULYHU
89/2
'HDGWLPH
&RPSDUDWRU
6KXW'RZQ
*DWHGULYHU
89/2
0LFURFRQWUROOHU
'HDGWLPH
&RPSDUDWRU
6KXW'RZQ
*DWHGULYHU
89/2
'HDGWLPH
&RPSDUDWRU
6KXW'RZQ
/HYHO
6KLIW
6PDUW
/HYHO
6KLIW
6PDUW
/HYHO
6KLIW
6PDUW
0DLQV
%RRWVWUDS
GLRGH
2S$PS
%RRWVWUDS
GLRGH
2S$PS
%RRWVWUDS
GLRGH
2S$PS
)HHGEDFN
%ULGJHUHFWLILHU
+DOIEULGJH
+DOIEULGJH
+DOIEULGJH
6//,00QDQR
0
!-V
The power devices (IGBTs and freewheeling diodes), incorporated in the half bridge block,
are tailored for a motor drive application delivering the greatest overall efficiency, thanks to
the optimized trade-off between conduction and switching power losses and very low EMI
generation, as a result of reduced dV/dt and di/dt.
The IC gate drivers have been selected in order to meet two levels of functionality, giving
users more freedom to choose: a basic version which includes the essential features for a
cost-effective solution and a fully featured version which provides advanced options for a
sophisticated control method.
The fully isolated NDIP package offers a high compactness level, very useful in those
applications with reduced space, ensuring at the same time, high thermal performance and
reliability levels.
8/60 Doc ID 022726 Rev 1
AN4043 Inverter design concept and SLLIMM-nano solution
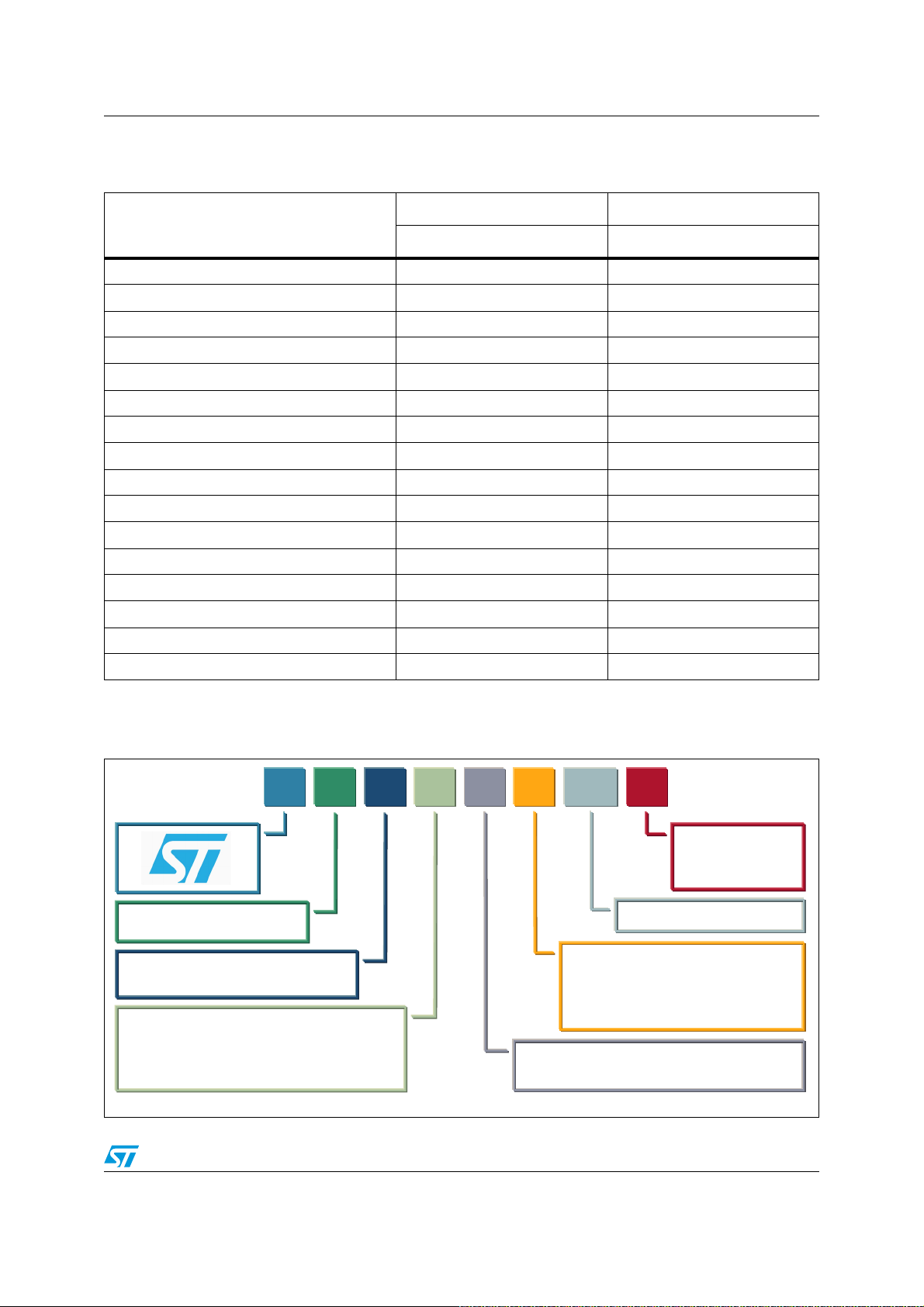
1.2 Product line-up and nomenclature
Table 1. SLLIMM-nano line-up
Basic version Fully featured version
Features
STGIPN3H60A STGIPN3H60
Voltage (V) 600 600
Current @ T
R
max. (°C/W) 50 50
thJA
Package type NDIP-26L NDIP-26L
Package size (mm) X, Y, Z 29.5x12.5x3.1 29.5x12.5x3.1
Integrated bootstrap diode Yes Yes
SD function No Yes
Comparator for fault protection No Yes (1 pin)
Smart shutdown function No Yes
Op amps for advanced current sensing No Yes
Interlocking function Yes Yes
Undervoltage lockout Yes Yes
Open emitter configuration Yes (3 pins) Yes (3 pins)
3.3 / 5 V input interface compatibility Yes Yes
High-side IGBT input signal Active high Active high
Low-side IGBT input signal Active high Active low
= 25 °C (A) 3 3
C
Figure 4. SLLIMM-nano nomenclature
67 * ,3 LLL]] Z YYY [
,*%7
,30
,00 6//,00QDQR
6//
3DFNDJH
1 1',3/PROGHG6//,00QDQR
6
6',3/PROGHG6//,00
/ 6',3/PROGHG6//,00
2SWLRQ
$ %DVLFYHUVLRQ
«
9
YROWDJHGLYLGHGE\
&(6
7HFKQRORJ\
+ 9HU\IDVW
. 6KRUWFLUFXLWUXJJHG
: 8OWUDIDVW
1RPLQDOFXUUHQW
FXUUHQWDW7& &
,
&
!-V
Doc ID 022726 Rev 1 9/60
Inverter design concept and SLLIMM-nano solution AN4043
1.3 Internal circuit
Figure 5. Internal circuit of the STGIPN3H60A
10/60 Doc ID 022726 Rev 1

AN4043 Inverter design concept and SLLIMM-nano solution
Figure 6. Internal circuit of the STGIPN3H60
1.4 Absolute maximum ratings
The absolute maximum ratings represent the extreme capability of the device and they can
be normally used as a worst limit design condition. It is important to note that the absolute
maximum value is given according to a set of testing conditions such us temperature,
frequency, voltage, and so on. Device performance can change according to the applied
condition.
Doc ID 022726 Rev 1 11/60
Inverter design concept and SLLIMM-nano solution AN4043
The SLLIMM-nano specifications are described below using the STGIPN3H60 datasheet as
an example. Please refer to the respective product datasheets for a detailed description of
all possible types.
Table 2. Inverter part
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
V
CES
±I
±I
P
TOT
1. Applied between HINU, HINV, HINW; LINU, LINV, LINW and GND.
2. Calculated according to the iterative
3. Pulse width limited by max. junction temperature.
Collector emitter voltage (V
(2)
Each IGBT continuous collector current at TC = 25 °C 3 A
C
(3)
Each IGBT pulsed collector current 18 A
C
Each IGBT total dissipation at TC = 25 °C 8 W
(1)
IN
Equation 1
= 0)
600 V
.
Equation 1
● V
: collector emitter voltage
CES
)T(I
=
CC
⋅
−
TT
−
Cmaxj
))T(IT(@VR
CCmax,j)(max)sat(CE)cj(th
The power stage of the SLLIMM-nano is based on IGBTs (and freewheeling diodes) having
600 V V
rating. Generally, considering the intelligent power module internal stray
CES
inductances during the commutations, which can generate some surge voltages, the
maximum surge voltage between P-N (V
Figure 7
. At the same time, considering also the surge voltage generated by the stray
PN(surge)
) allowed is lower than V
, as shown in
CES
inductance between the device and the DC-link capacitor, the maximum supply voltage (in
steady-state) applied between P-N (V
) must be even lower than V
PN
PN(surge)
. Thanks to the
small package size and the lower working current, this phenomenon is less marked in the
SLLIMM-nano than in a big intelligent power module.
12/60 Doc ID 022726 Rev 1
AN4043 Inverter design concept and SLLIMM-nano solution
Figure 7. Stray inductance components of output stage
7KHUHDOYROWDJHRYHUWKH,*%7
FDQH[FHHGWKHUDWLQJYROWDJH
'XHWRGLGW YDOXHDQGSDUDVLWLF
LQGXFWDQFHWKHRYHUYROWDJHVSLNH
)ODW9
YDOXH
31
FDQDSSHDURQWKH6//,00SLQV
9
9
31VXUJH
31
3
+LJK
GLGW
YDOXH
9
9
EXV
EXV
+9,&
WRPRWRU
&
89:
1
6//,00QDQR
3DUDVLWLFLQGXFWDQFH
GXHWRWKH6//,00LQWHUQDOOD\RXW
● ±I
: each IGBT continuous collector current
C
The allowable DC current continuously flowing at the collector electrode (T
parameter is calculated according to
Table 3. Control part of the STGIPN3H60
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
V
OUT
V
CC
V
CIN
V
OP+
V
OP
V
boot
V
V
SD/OD
dV
OUT
Output voltage applied between OUTU, OUTV, OUTW, and
GND (V
CC
Low voltage power supply -0.3 to 21 V
Comparator input voltage -0.3 to VCC +0.3 V
Op amp non-inverting input -0.3 to V
Op amp inverting input -0.3 to V
Bootstrap voltage -0.3 to 620 V
IN
Logic input voltage applied between HIN, LIN and GND -0.3 to 15 V
Open drain voltage -0.3 to 15 V
/dt Allowed output slew rate 50 V/ns
Equation 1
=15 V)
3DUDVLWLFLQGXFWDQFH
GXHWR3&%OD\RXW
!-V
.
V
-21 to V
boot
= 25 °C). The IC
C
+0.3 V
boot
+0.3 V
CC
+0.3 V
CC
● V
: low voltage power supply
CC
Doc ID 022726 Rev 1 13/60

Inverter design concept and SLLIMM-nano solution AN4043
VCC represents the supply voltage of the control part. A local filtering is recommended to
enhance the SLLIMM-nano noise immunity. Generally, the use of one electrolytic capacitor
(with greater value but not negligible ESR) and one smaller ceramic capacitor (hundreds of
nF), faster than the electrolytic one to provide current, is suggested.
Please refer to
Table 4. Supply voltage and operation behavior
Ta b le 4
in order to properly drive the SLLIMM-nano.
VCC voltage (typ. value)
Operating behavior
STGIPN3H60A STGIPN3H60
< 10 V < 12 V
As the voltage is lower than the UVLO threshold the control circuit is not fully
turned on. A perfect functionality cannot be guaranteed.
12 V – 17 V 13.5 V – 18 V Typical operating conditions
> 18 V > 21 V Control circuit is destroyed
Table 5. Total system
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
T
J
T
C
Operating junction temperature -40 to 150 °C
Module case operation temperature -40 to 125 °C
14/60 Doc ID 022726 Rev 1

AN4043 Electrical characteristics and functions
2 Electrical characteristics and functions
In this section the main electrical characteristics of the power stage are discussed, together
with a detailed description of all the SLLIMM-nano functions.
2.1 IGBTs
The SLLIMM-nano achieves power savings in the inverter stage thanks to the use of IGBTs
manufactured with the proprietary advanced PowerMESH™ process.
These power devices, optimized for the typical motor control switching frequency, offer an
excellent trade-off between voltage drop (V
minimize the two major sources of energy loss, conduction and switching, reducing the
environmental impact of daily-use equipment. A full analysis on the power losses of the
complete system in reported in
2.2 Freewheeling diodes
Turbo 2 ultrafast high voltage diodes have been adequately selected for the SLLIMM-nano
family and carefully tuned to achieve the best t
diodes in order to further improve the total performance of the inverter and significantly
reduce the electromagnetic interference (EMI) in the motor control applications which are
quite sensitive to this phenomena.
Section 4: Power losses and dissipation
) and switching speed (t
CE(sat)
/VF trade-off and softness as freewheeling
rr
), and therefore
fall
.
2.3 High voltage gate drivers
The SLLIMM-nano is equipped with a versatile high voltage gate driver IC (HVIC), designed
using BCD offline (Bipolar, CMOS, and DMOS) technology (see
suited to field oriented control (FOC) motor driving applications, able to provide all the
functions and current capability necessary for high-side and low-side IGBT driving. This
driver can be used in all applications where high voltage shifted control is necessary and it
includes a patented internal circuitry which replaces the external bootstrap diode.
Figure 8
) and particularly
Doc ID 022726 Rev 1 15/60
Electrical characteristics and functions AN4043
Figure 8. High voltage gate drive die image
Each high voltage gate driver chip controls two IGBTs in half bridge topology, offering basic
functions such as dead time, interlocking, integrated bootstrap diode, and also advanced
features such as smart shutdown (patented), fault comparator, and a dedicated high
performance op amp for advanced current sensing. A schematic summary of the features by
device are listed in
Ta bl e 1
.
In this application note the main characteristics of a high voltage gate drive related to the
SLLIMM-nano are discussed. For a greater understanding, please refer to the AN2738
application note.
16/60 Doc ID 022726 Rev 1
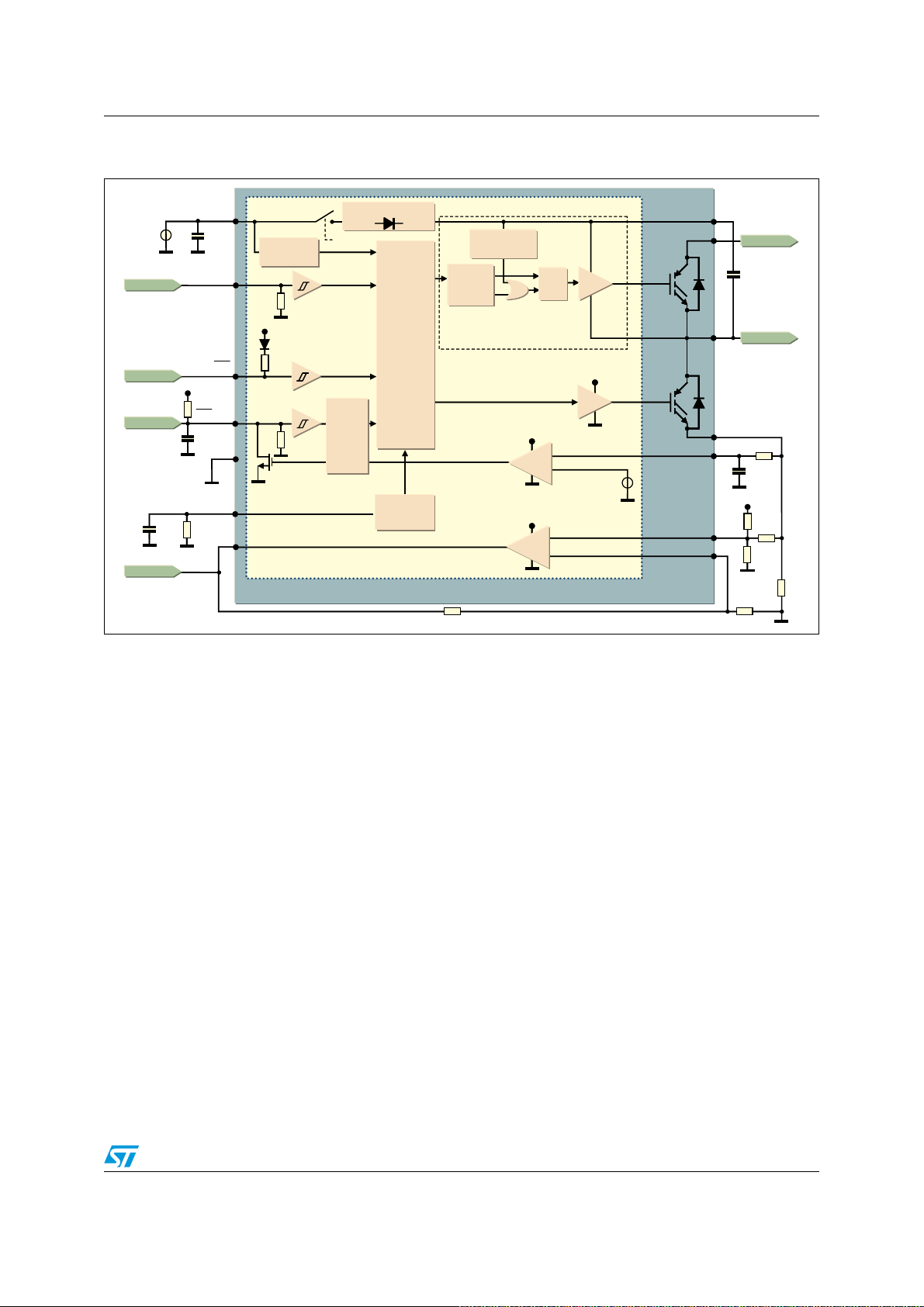
AN4043 Electrical characteristics and functions
Figure 9. High voltage gate driver block diagram
9
&&
IURPP&
IURPP&
IURPWRP&
&
')
WR$'&
9
&&
89
%RRWVWUDSGULYHU%RRWVWUDSGULYHU
IURP/9*
GHWHFWLRQ
+,1
9
/RJLF
6KRRW
WKURXJK
SUHYHQWLRQ
/,1
9
%LDV
5
6'
6'2'
&
6'
*1'
6PDUW
GRZQ
'7
6KXWGRZQ
ODWFK
VKXW
'HDG
WLPH
5
23
')
287
)ORDWLQJVWUXFWXUH
&'6' %6+10
GHWHFWLRQ
/HYHO
VKLIWHU
+9,&
6//,00QDQR
89
78
99
&RPS
9&&9
&&
2SDPS
%227
+9*
6
5
GULYHU
+9*
287
9
3
%227
WR'&OLQN
&
%227
WRPRWRU
89:
9&&9
&&
/9*
GULYHU
/9
*
1
&3
9
5()
!-V
&,1
23
23
&
5
5
6)
9
%LDV
6+817
6)
2.3.1 Logic inputs
The high voltage gate driver IC has two logic inputs, HIN and LIN, to separately control the
high-side and low-side outputs, HVG and LVG. Please refer to
logics by device.
In order to prevent any cross conduction between high-side and low-side IGBT, a safety time
(dead time) is introduced (see
management
All the logic inputs are provided with hysteresis (~1 V) for low noise sensitivity and are
TTL/CMOS 3.3 V compatible. Thanks to this low voltage interface logic compatibility, the
SLLIMM-nano can be used with any kind of high performance controller, such as
microcontrollers, DSPs or FPGAs.
As shown in the block diagrams of
pull-down (or pull-up) resistors in order to set a proper logic level in the case of interruption
in the logic lines. If logic inputs are left floating, the gate driver outputs LVG and HVG are set
to low level. This simplifies the interface circuit by eliminating the six external resistors,
therefore, saving cost, board space and number of components.
for further details).
Ta bl e 1
for the input signal
Section 2.3.4: Dead time and interlocking function
Figure 10
and
Figure 11
, the logic inputs have internal
Doc ID 022726 Rev 1 17/60
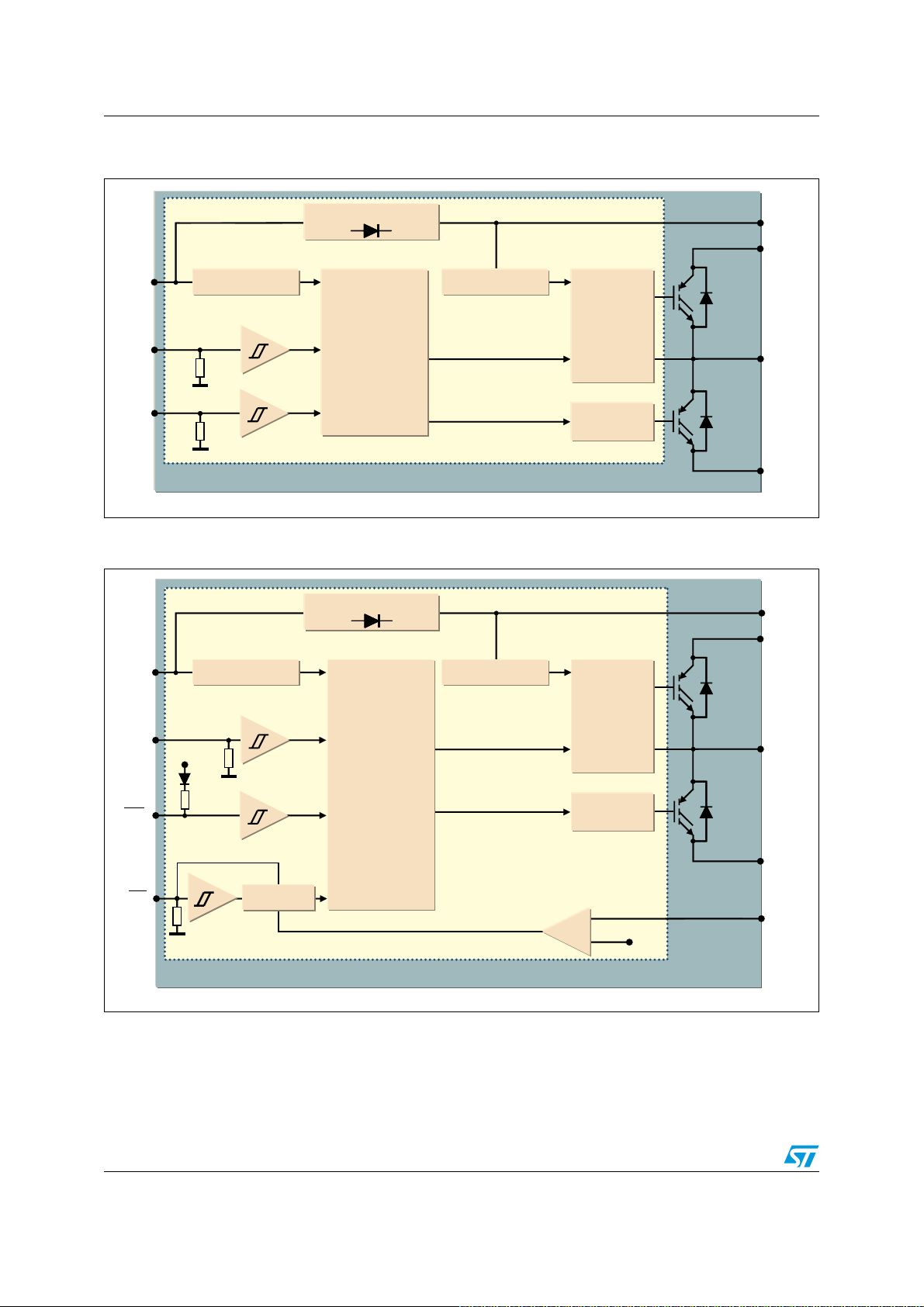
Electrical characteristics and functions AN4043
Figure 10. Logic input configuration for the STGIPN3H60A
9
&&
%RRWVWUDSGULYHU
9
%227
3
89GHWHFWLRQ89GHWHFWLRQ
+LJKVLGH
/RJLF
YHO
OH
VKLIWLQJ
+,1
/,1
RWWKURXJK
6KR
YHQWLRQ
SUH
GUL
YHU
/RZVLGH
GUL
YHU
287
+9,&
6//,00QDQR
1
!-V
Figure 11. Logic input configuration for the STGIPN3H60
%RRWVWUDSGULYHU
9
&&
89GHWHFWLRQ89GHWHFWLRQ
/RJLF
+,1
9
6KR
RWWKURXJK
SUHYHQWLRQ
/,1/,1
6KX
WGRZQ
6'
6PDUW6'
+9,&
6//,00QDQR
+LJKVLGH
OH
YHO
VKLIWLQJ
GUL
YHU
/RZVLGH
YHU
GUL
9
%227
3
287
1
&,1
9
5()
!-V
The typical values of the integrated pull-up/down resistors are shown in
18/60 Doc ID 022726 Rev 1
Ta bl e 6
:

AN4043 Electrical characteristics and functions
Table 6. Integrated pull-up/down resistor values
High-side gate driving
HINU, HINV, HIN
Low-side gate driving
LIN
High-side gate driving
HIN
Low-side gate driving
LIN
SD
Input pin PN Input pin logic Internal pull-up Internal pull-down
W
, LINV, LIN
U
, HINV, HIN
U
, LINV, LIN
U
/ OD shutdown STGIPN3H60 Active low 125 kΩ
W
W
W
STGIPN3H60A Active high 500 kΩ
STGIPN3H60A Active high 500 kΩ
STGIPN3H60 Active high 85 kΩ
STGIPN3H60 Active low 720 kΩ
2.3.2 High voltage level shift
The built-in high voltage level shift allows direct connection between the low voltage control
inputs and the high voltage power half bridge in any power application up to 600 V. It is
obtained thanks to the BCD offline technology which integrates, in the same die bipolar
devices, low and medium voltage CMOS for analog and logic circuitry and high voltage
DMOS transistors with a breakdown voltage in excess of 600 V. This key feature eliminates
the need for external optocouplers, resulting in significant savings regarding component
count and power losses. Other advantages are high-frequency operation and short input-tooutput delays.
2.3.3 Undervoltage lockout
The SLLIMM-nano supply voltage VCC is continuously monitored by an undervoltage
lockout (UVLO) circuitry which turns off the gate driver outputs when the supply voltage
goes below the V
the supply voltage goes above the V
for noise rejection purposes. The high voltage floating supply Vboot is also provided with a
similar undervoltage lockout circuitry. When the driver is in UVLO condition, both gate driver
outputs are set to low level, setting the half bridge power stage output to high impedance.
The timing chart of undervoltage lockout, plotted in
steps:
● t1: when the V
work after the next input signal HIN/LIN is on. The circuit state becomes RESET
● t2: input signal HIN/LIN is on and the IGBT is turned on
● t3: when the V
is detected. The IGBT is turned off in spite of input signal HIN/LIN. The state of the
circuit is now SET
● t4: the gate driver re-starts once the V
threshold
● t5: input signal HIN/LIN is on and the IGBT is turned on again.
CC_thOFF
supply voltage raises the V
CC
supply voltage goes below the V
CC
threshold specified on the datasheet, and turns on the IC when
CC_thON
voltage. A hysteresis of about 1.5 V is provided
Figure 12
CC_thON
supply voltage again raises the V
CC
, is based on the following
threshold, the gate driver starts to
CC_thOFF
threshold, the UVLO event
CC_thON
Doc ID 022726 Rev 1 19/60
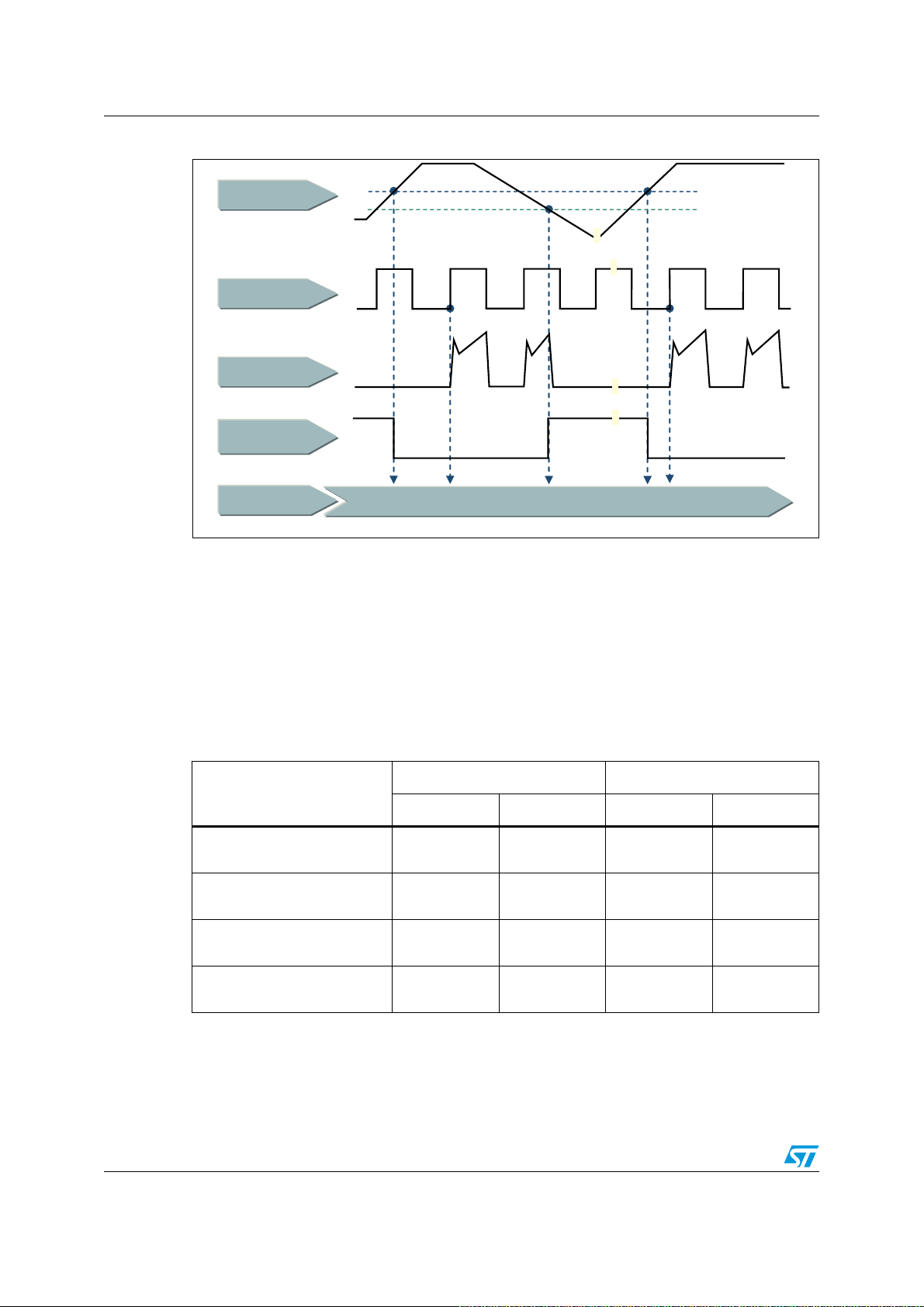
Electrical characteristics and functions AN4043
Figure 12. Timing chart of undervoltage lockout function
s
ͺƚŚKE
9
&&
s
ͺƚŚK&&
§§
§§
+,1/,1
,
&
§§
&LUFXLWVWDWH
7LPH
Z^d
W
W W W
^d
Z^d
2.3.4 Dead time and interlocking function management
In order to prevent any possible cross-conduction between high-side and low-side IGBTs,
the SLLIMM-nano provides both the dead time and the interlocking function. The
interlocking function is a logic operation which sets both the outputs to low level when the
inputs are simultaneously active. The dead time function is a safety time introduced by the
device between the falling edge transition of one driver output and the rising edge of the
other output. If the rising edge set externally by the user occurs before the end of this dead
time, it is ignored and results as delayed until the end of the dead time.
Table 7. Interlocking function truth table of the STGIPN3H60A
) Outputs
I
Condition
Interlocking
half bridge tri-state
Logic input (V
LIN HIN LVG HVG
HHL L
§§
W
!-V
0 “logic state”
half bridge tri-state
1 “logic state”
low-side direct driving
1 “logic state”
high-side direct driving
LLLL
HLHL
LHLH
The dead time is internally set at 320 ns as the typical value of the STGIPN3H60A.
20/60 Doc ID 022726 Rev 1
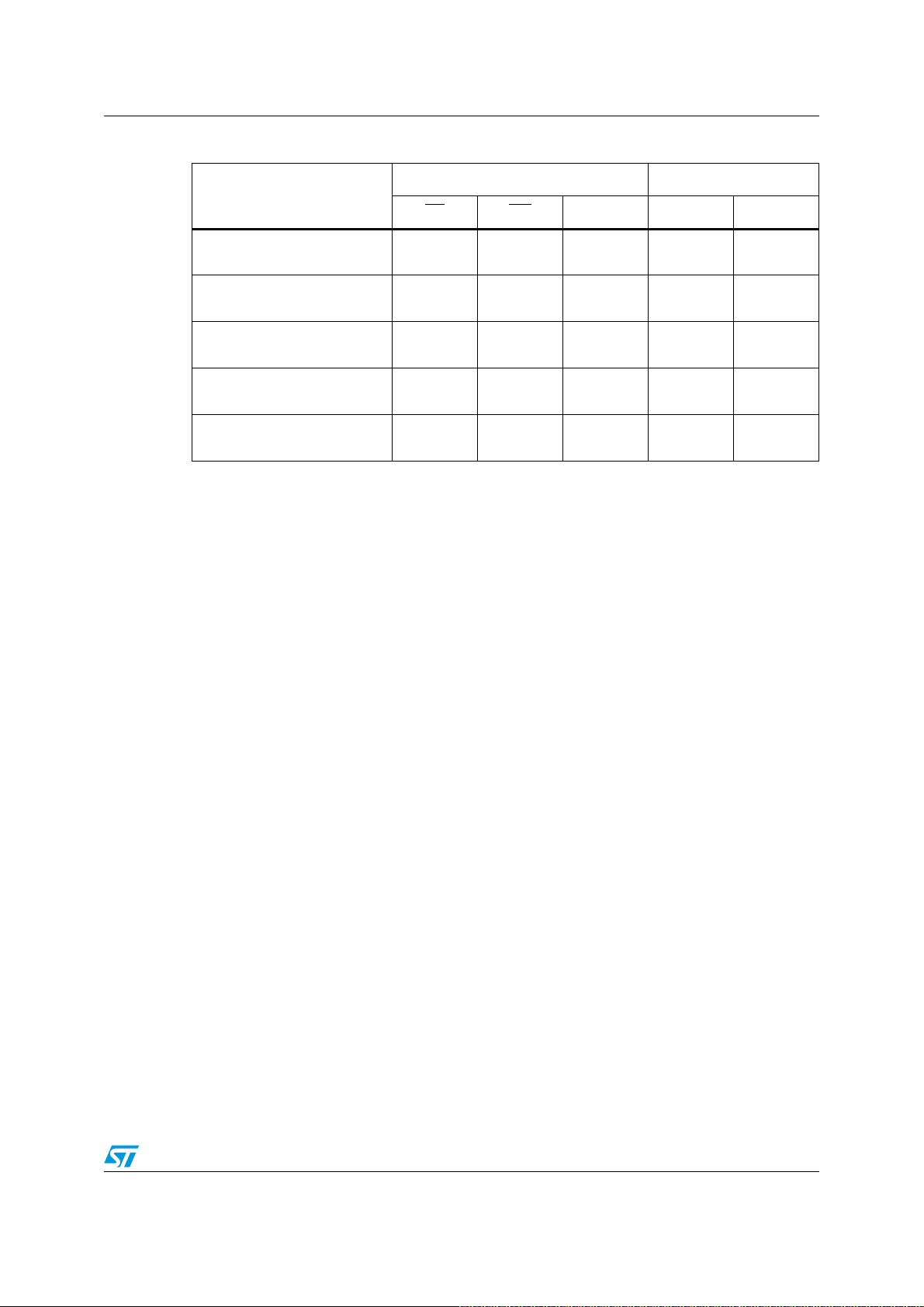
AN4043 Electrical characteristics and functions
Table 8. Interlocking function truth table of the STGIPN3H60
Condition
Shutdown enable
half bridge tri-state
Interlocking
half bridge tri-state
0 “logic state”
half bridge tri-state
1 “logic state”
low-side direct driving
1 “logic state”
high-side direct driving
Note: X: not important.
The dead time is internally set at 180 ns as typical value. In
time and interlocking function management of the STGIPN3H60 is described.
) Outputs
I
SD
Logic input (V
LIN HIN LVG HVG
LXXLL
HLHLL
HHL L L
HLLHL
HHHLH
Figure 13
the details of dead
Doc ID 022726 Rev 1 21/60

Electrical characteristics and functions AN4043
Figure 13. Timing chart of dead time function
LIN
CONTROL SIGNAL EDGES
OVERLAPPED:
INTERLOCKING + DEAD TIME
CONTROL SIGNALS EDGES
SYNCHRONOUS (*):
DEAD TIME
CONTROL SIGNALS EDGES
NOT OVERLAPPED,
BUT INSIDE THE DEAD TIME:
DEAD TIME
CONTROL SIGNALS EDGES
NOT OVERLAPPED,
OUTSIDE THE DEAD TIME:
DIRECT DRIVING
HIN
LVG
HVG
gate driver outputs OFF
(HALF-BRIDGE TRI-STATE)
LIN
HIN
LVG
HVG
gate driver outputs OFF
(HALF-BRIDGE TRI-STATE)
LIN
HIN
LVG
HVG
gate driver outputs OFF
(HALF-BRIDGE TRI-STATE)
LIN
HIN
LVG
HVG
gate driver outputs OFF
(HALF-BRIDGE TRI-STATE)
INTERLOCKING
DTLH
gate driver outputs OFF
(HALF-BRIDGE TRI-STATE)
DTLH DTHL
gate driver outputs OFF
(HALF-BRIDGE TRI-STATE)
DTLH DTHL
gate driver outputs OFF
(HALF-BRIDGE TRI-STATE)
DTLH
gate driver outputs OFF
(HALF-BRIDGE TRI-STATE)
INTERLOCKING
DTHL
DTHL
(*) HIN and LIN can be connected together and driven by just one control signal
2.3.5 Comparators for fault sensing
The SLLIMM-nano STGIPN3H60 integrates one comparator intended for advanced fault
protection, such as overcurrent, overtemperature or any other type of fault measurable via a
voltage signal. The comparator has an internal reference voltage V
datasheet, on its inverting input (see
the C
pin. The comparator input can be connected to an external shunt resistor, in order to
IN
implement a simple overcurrent or short-circuit detection function, as discussed in detail in
Section 2.3.6: Short-circuit protection and smart shutdown function
22/60 Doc ID 022726 Rev 1
Figure 9
), while the non-inverting input is available on
AM10496v1
, specified in the
REF
.

AN4043 Electrical characteristics and functions
2.3.6 Short-circuit protection and smart shutdown function
The fully featured version of the SLLIMM-nano (STGIPN3H60) is able to monitor the output
current and provide protection against overcurrent and short-circuit conditions in a very
short time (comparator triggering to high/low-side driver turn-off propagation delay t
200 ns), thanks to the smart shutdown function. This feature is based on an innovative
patented circuitry which provides an intelligent fault management operation and greatly
reduces the protection intervention delay independently on the protection time duration
which can be set as desired by the device user.
isd
=
As already mentioned in
Figure 9
, the comparator input can be connected to an external shunt resistor, R
order to implement a simple overcurrent detection function. An RC filter network (R
C
) is necessary to prevent erroneous operation of the protection. The output signal of the
SF
comparator is fed to an integrated MOSFET with the open drain available on the SD
pin, shared with the SD
Section 2.3.5: Comparators for fault sensing
and as shown in
SHUNT
SF
, in
and
/ OD
input. When the comparator triggers, the device is set in shutdown
state and all its outputs are set to low level, leaving the half bridge in tri-state. In common
overcurrent protection architectures, the comparator output is usually connected to the SD
input and an external RC network (R
and CSD) is connected to this SD / OD line in order
SD
to provide a mono-stable circuit which implements a protection time when a fault condition
occurs.
Contrary to common fault detection systems, the new smart shutdown structure allows an
immediate turn-off of the output gate driver in the case of fault, without waiting for the
external capacitor to be discharged. This strategy minimizes the propagation delay between
the fault detection event and the actual outputs switch-off. In fact, the time delay between the
fault and outputs disabling is not dependent on the RC value of the external SD circuitry but,
thanks to the new architecture, has a preferential path internally in the driver. Then the
device immediately turns off the driver outputs and latches the turn-on of the open drain
switch, until the SD signal has reached its lower threshold. After the SD signal goes below
the lower threshold, the open drain is switched off (see
Figure 15
).
The smart shutdown system provides the possibility to increase the value of the external RC
network across the SD pin (sized to fix the disable time generated after the fault event) as
much as desired by the user without compromising the intervention time delay of the
SLLIMM-nano protection.
A block diagram of the smart shutdown architecture is depicted in
Doc ID 022726 Rev 1 23/60
Figure 14
.

Electrical characteristics and functions AN4043
Figure 14. Smart shutdown equivalent circuitry
9
/,1
+,1
%LDV
6'
46
4
5
6(7GRPLQDQW))
)6'
&RPS
9
/9 *
+9*
&3
5()
+9,&
6//,00QDQR
([FHSWIRU67*,36.$
In normal operation the outputs follow the commands received from the respective input
signals.
When a fault detection event occurs, the fault signal (FSD) is set to HIGH by the fault
detection circuit output and the FF receives a SET input signal. Consequently, the FF
outputs set the SLLIMM-nano output signals to low level and, at the same time, turn on the
open drain MOSFET which works as active pull-down for the SD
driver outputs stay at low level until the SD
pin has experienced both a falling edge and a
signal. Note that the gate
rising edge, although the fault signal may be returned to low level immediately after the fault
sensing. In fact, even if the FF is reset by the falling edge of the SD
input, the SD signal also
works as enable for the outputs, thanks to the two AND ports. Moreover, once the internal
open drain transistor has been activated, due to the latch, it cannot be turned off until the SD
pin voltage reaches the low logic level. Note that, since the FF is SET dominant, oscillations
of the SD
pin are avoided if the fault signal remains steady at a high level.
!-V
2.3.7 Timing chart of short-circuit protection and smart shutdown function
With reference to
● t1: when the output current is lower than the max. allowed level, the SLLIMM-nano is
working in normal operation
● t2: when the output current reaches the max. allowed level (I
circuit event is detected and the protection is activated.
The voltage across the shunt resistor, and then on the C
the comparator triggers, setting the device in shutdown state and both its outputs are
set to low level leading the half bridge in tri-state.
The smart shutdown switches off the IGBT gate (HVG, LVG) through a preferential path
(200 ns as typical internal delay time) and, at the same time, it switches on the M1
internal MOSFET. The SD signal starts the discharge phase and its value drops with a
time constant
24/60 Doc ID 022726 Rev 1
Figure 15
τ
A
, the short-circuit protection is based on the following steps:
. The time constant τA value is given by:
), the overcurrent/short-
SC
pin, exceeds the V
IN
REF
value,

AN4043 Electrical characteristics and functions
Equation 2
()
● t3: the SD signal reaches the lower threshold V
off the input HIN and LIN. The smart shutdown is disabled (M1 off) and SD can rise up
with a time constant
Equation 3
● t4: when the SD signal reaches the upper threshold V
enabled.
Figure 15. Timing chart of smart shutdown function
/
^
,
&
s
Z&
9
ÂÂ9
6+817
&,1
τ
, given by:
B
5&FLUFXLWWLPH
FRQVWDQW
sd_L_THR
CR ⋅=τ
SDSDB
CR//R ⋅=τ
SDSDOD_ONA
and the control unit switches
sd_H_THR
, the system is re-
7LPH&RQVWDQWV
6'GLVFKDUJHWLPH
W$ 5
21B2'
56'&
6'UHFKDUJHWLPH
W% 56'&
6'
6'
+9*/9*
9
6'
0
+,1/,1
7LPH
VGB+B7+5
9
VGB/B7+5
W
W
W W W
W
2.3.8 Current sensing shunt resistor selection
As previously discussed, the shunt resistors R
pin and ground (see
Figure 9
) are used to realize the overcurrent detection.
When the output current exceeds the short-circuit reference level (I
overtakes the V
value and the short-circuit protection is active. For a reliable and stable
REF
operation the current sensing resistor should be a high quality, low tolerance non-inductive
type. In fact, stray inductance in the circuit, which includes the layout, the RC filter, and also
the shunt resistor, must be minimized in order to avoid undesired short-circuit detection.
For these reasons, the shunt resistor and the filtering components must be placed as close
as possible to the SLLIMM-nano pins, for additional suggestions refer to
suggestions
.
SHUNT
6KXWGRZQFLUFXLW
9
%LDV
5
6'
6'
6'2'
5
21B2'
0
6PDUW
VKXW
GRZQ
IURPWRP&
&
6//,00QDQR
!-V
externally connected between the N
), the CIN signal
SC
Section 5.1: Layout
Doc ID 022726 Rev 1 25/60

Electrical characteristics and functions AN4043
The value of the current sense resistor can be calculated by following different guidelines,
functions of the design specifications, or requirements. A common criterion is presented
here based on the following steps:
● Defining of the overcurrent threshold value (I
). For example, it can be fixed
OC_th
considering the IGBT typical working current in the application and adding 20-30% as
overcurrent.
● Calculation of the shunt resistor value according to the conditioning network. An
example of the conditioning network is shown in
found in the user manuals listed (see
● Selection of the closest shunt resistor commercial value.
● Calculation of the power rating of the shunt resistor, taking into account that this
References
Figure 19
5 and
References
. Further details can be
6).
parameter is strongly temperature dependent. Therefore, the power derating ratio of
the shunt resistor, ΔP(T)%, shown in the manufacturer's datasheet, must be considered
in the calculation as follows:
Equation 4
2
IR
⋅
RMS
)%T(P
Δ
SHUNT
)T(P
=
SHUNT
where I
is the IGBT RMS working current.
RMS
For a proper selection of the shunt resistor, a safety margin of at least 30% is recommended
on the calculated power rating.
2.3.9 RC filter network selection
Two options of shunt (1- or 3-shunt) resistor circuit can be adopted in order to implement
different control techniques and short-circuit protection, as shown in
Figure 16. Examples of SC protection circuit
18
19
1:
&,1
6//,00QDQR
5
5
6)
6+817
&
6)
6//,00QDQR
18
19
1:
&,1
5
6+817B8
5
6+817B9
5
6+817B:
Figure 16
5
6+817
.
5
6)
&
6)
VKXQWUHVLVWRUFLUFXLW VKXQWUHVLVWRUVFLUFXLW
An RC filter network is required to prevent undesired short-circuit operation due to the noise
on the shunt resistor.
26/60 Doc ID 022726 Rev 1
!-V

AN4043 Electrical characteristics and functions
Both solutions allow to detect the total current in all three phases of the inverter. The filter is
based on the R
and CSF network and its time constant is given by:
SF
Equation 5
CRt ⋅=
SFSFSF
In addition to the RC time constant, the turn-off propagation delay of the gate driver, t
isd
(specified in the datasheet) and the IGBT turn-off time (in the range of tens of ns), must be
considered in the total delay time (t
off the IGBT once the short-circuit event is detected. Therefore, the t
), which is the time necessary to completely switch
To ta l
is calculated as
To ta l
follows:
Equation 6
tttt ++=
offisdSFTotal
and the t
is recommended to be set in the range of 1~2 µs.
SF
In the case of a 3-shunt resistor circuit, a specific control technique can be implemented by
using the three shunt resistors (R
SHUNT_U
, R
SHUNT_V
and R
SHUNT_W
) able to monitor each
phase current.
An example of a short-circuit event is shown in
Figure 17
, where it is possible to note the
very fast protection, thanks to the smart shutdown function, against fault events. The main
steps are:
● t1: collector current IC starts to rise. SC event is not detected yet due to the RC
network on the C
● t2: voltage on V
pin.
IN
reaches the V
CIN
. SC event is detected and the smart shutdown
REF
starts to turn off the SLLIMM-nano.
● t3: the SD in activated.
● t4: the SLLIMM-nano is definitively turned off in 580 ns (including the t
d(off)
time of
IGBT) from SC detection.
Finally, the total disable time is t4-t1.
Doc ID 022726 Rev 1 27/60

Electrical characteristics and functions AN4043
Figure 17. Example of SC event
+,1
9
VGB+B7+5
6'
,
&
s
Z&
QV
&,1
([DPSOHRI6&HYHQW
+,1
89:
6//,00QDQR
3
,
&
1
5
6+817
WR'&OLQN
WRPRWRU
&,1
7LPH
,& $'LY &,1 9'LY +,1 9'LY W QV'LY
W
W
W
W
6' 9'LY
2.3.10 Op amps for advanced current sensing
The fully featured version of the SLLIMM-nano (STGIPN3H60) integrates also one
operational amplifier optimized for field oriented control (FOC) applications. In a typical FOC
application the currents in the three half bridges are sensed using a shunt resistor. The
analog current information is transformed into a discontinuous sense voltage signal, having
the same frequency as the PWM signal driving the bridge. The sense voltage is a bipolar
analog signal, whose sign depends on the direction of the current (see
6&HYHQWRQWKH
ZVLGH,*%7
OR
Figure 18
!-V
):
28/60 Doc ID 022726 Rev 1

AN4043 Electrical characteristics and functions
Discontinuous Voltage at f
PWM
frequency
Figure 18. 3-phase system
3-phase driver
Sinusoidal Vector Control
Sensing:
9
6
9
6
9
6
Power
stage
I
SKDVH
PHASE
PRWRU
The sense voltage signals must be provided to an A-D converter. They are usually shifted
and amplified by dedicated op amps in order to exploit the full range of the A-D converter.
The typical scheme and principle waveforms are shown in
Figure 19
:
AM09338v1
Figure 19. General advanced current sense scheme and waveforms
WR'&OLQN
6HQVHYROWDJHVLJQDO
WRPRWRU
6KLIWHGDQGFHQWHUHG
VLJQDO $PSOLILHGVLJQDO )LOWHUHGVLJQDO
9
5()
5
5
9
5
6+817
VHQVH
+DOIEULGJH
FXUUHQWVHQVLQJ
9ROW DJ H
VKLIWLQJ
RIWKH9
5
VHQVH
23
2SDPS
5
23
5
&
9ROWDJHJDLQ
DQGILOWHULQJ
5
287
5
287
UHTXLUHGWR
PDNHWKH
RSDPSVWDEOH
Doc ID 022726 Rev 1 29/60
&
287
&
UHTXLUHGE\WKH$'&
287
IRUVDPSOLQJSXUSRVH
WR$'&
!-V

Electrical characteristics and functions AN4043
ADCs used in vector control applications have a typical full scale range (FSR) of about
3.3 V. The sense signals must be shifted and centered on FSR/2 voltage (about 1.65 V) and
amplified with a gain which provides the matching between the maximum value of the
sensed signal and the FSR of the ADC. Some typical examples of sense network sizing can
be found in the user manuals listed (see
References
5 and
References
6).
2.3.11 Bootstrap circuit
In the 3-phase inverter the emitters of the low-side IGBTs are connected to the negative DC
bus (V
same power supply, while, the emitter of high-side IGBTs is alternately connected to the
positive (V
A bootstrap method is a simple and cheap solution to supply the high voltage section. This
function is normally accomplished by a high voltage fast recovery diode. The SLLIMM-nano
family includes a patented integrated structure that replaces the external diode. It is realized
with a high voltage DMOS driven synchronously with the low-side driver (LVG) and a diode
in series. An internal charge pump provides the DMOS driving voltage.
) as common reference ground, which allows all low-side gate drivers to share the
DC-
) and negative (V
DC+
) DC bus during the running conditions.
DC-
The operation of the bootstrap circuit is shown in
C
is charged, from the VCC supply, when the V
BOOT
Figure 20
OUT
. The floating supply capacitor
voltage is lower than the VCC
voltage (e.g. low-side IGBT is on), through the bootstrap diode and the DMOS path with
reference to the “bootstrap charge current path”. During the high-side IGBT ON phase, the
bootstrap circuit provides the right gate voltage to properly drive the IGBT (see “bootstrap
discharge current path”). This circuit is iterated for all the three half bridges.
Figure 20. Bootstrap circuit
&
%227
89:
3
/HJHQG
%RRWVWUDS
FKDUJH
FXUUHQWSDWK
%RRWVWUDS
GLVFKDUJH
FXUUHQWSDWK
1
ERRWVWUDS
GLRGH
9
&&
FKDUJH
SXPS
9
&&
/,1
'026
9
ERRW
+9*
/9*
9
287
287
ERRW
+9,&
*1'
6//,00QDQR
The value of the C
capacitor should be calculated according to the application
BOOT
condition and must take the following into account:
● voltage across C
must be maintained at a value higher than the undervoltage
BOOT
lockout level for the IC driver. This enables the high-side IGBT to work with a correct
gate voltage (lower dissipation and better overall performances). Please consider that if
30/60 Doc ID 022726 Rev 1
!-V

AN4043 Electrical characteristics and functions
a voltage below the UVLO threshold is applied on the bootstrap channel, the IC
disables itself (no output) without any fault signal.
● the voltage across C
is affected by different components such as drop across the
BOOT
integrated bootstrap structure, drop across the low-side IGBT, and others.
● when the high-side IGBT is on, the C
capacitor discharges mainly to provide the
BOOT
right IGBT gate charge but other phenomena must be considered such as leakage
currents, quiescent current, etc.
2.3.12 Bootstrap capacitor selection
A simple method to properly size the bootstrap capacitor considers only the amount of
charge that is needed when the high voltage side of the driver is floating and the IGBT gate
is driven once. This approach does not take into account either the duty cycle of the PWM,
or the fundamental frequency of the current. Observations on PWM duty cycle, the kind of
modulation (6-step, 12-step and sine-wave) must be considered with their own peculiarity to
achieve the best bootstrap circuit sizing.
During the bootstrap capacitor charging phase, the low-side IGBT is on and the voltage
across C
Equation 7
BOOT
(V
) can be calculated as follows:
CBOOT
where:
V
: supply voltage of gate driver.
CC
V
: bootstrap diode forward voltage drop.
F
V
CE(sat)max
V
RDS(on)
The dimension of the bootstrap capacitance C
drop (ΔV
: maximum emitter collector voltage drop of low-side IGBT.
: DMOS voltage drop.
) to guarantee when the high-side IGBT is on, and must be:
CBOOT
BOOT
Equation 8
under the condition:
Equation 9
VV >
where:
V
GE(min)
V
Considering the factors contributing to V
bootstrap capacitor (during high-side ON phase) is:
: minimum gate emitter voltage of high-side IGBT.
BS_thON
: bootstrap turn-on undervoltage threshold (maximum value, see datasheet).
CBOOT
decreasing, the total charge supplied by the
VVVVV −−−=
max)sat(CE)on(RDSFCCCBOOT
value is based on the minimum voltage
VVVVVV −−−−=Δ
thON_BS(min)CBOOT
max)sat(CE(min)GE)on(RDSFCCCBOOT
Doc ID 022726 Rev 1 31/60
Electrical characteristics and functions AN4043
()
Equation 10
where:
Q
: total IGBT gate charge.
GATE
I
: IGBT gate emitter leakage current.
LKGE
I
: bootstrap circuit quiescent current.
QBO
I
: bootstrap circuit leakage current.
LK
I
I
but can be ignored if other types of capacitors are used).
t
Q
Finally, the minimum size of the bootstrap capacitor is:
Equation 11
For an easier selection of bootstrap capacitor,
(calculated) versus switching frequency (f
corresponding to
cycle δ
: bootstrap diode leakage current.
LKDiode
: bootstrap capacitor leakage current (relevant when using an electrolytic capacitor
LKCap
: high-side ON time.
Hon
: charge required by the internal level shifters.
LS
Q
C
BOOT
Equation 11 Equation 11
sw
for a continuous sinusoidal modulation and a duty
TOT
=
V
Δ
CBOOT
Figure 21
shows the behavior of C
), with different values of ΔV
CBOOT
= 50%.
QtIIIIIQQ +⋅+++++=
LSHonapLKCLKDiodeLKQBOLKGEGATETOT
BOOT
,
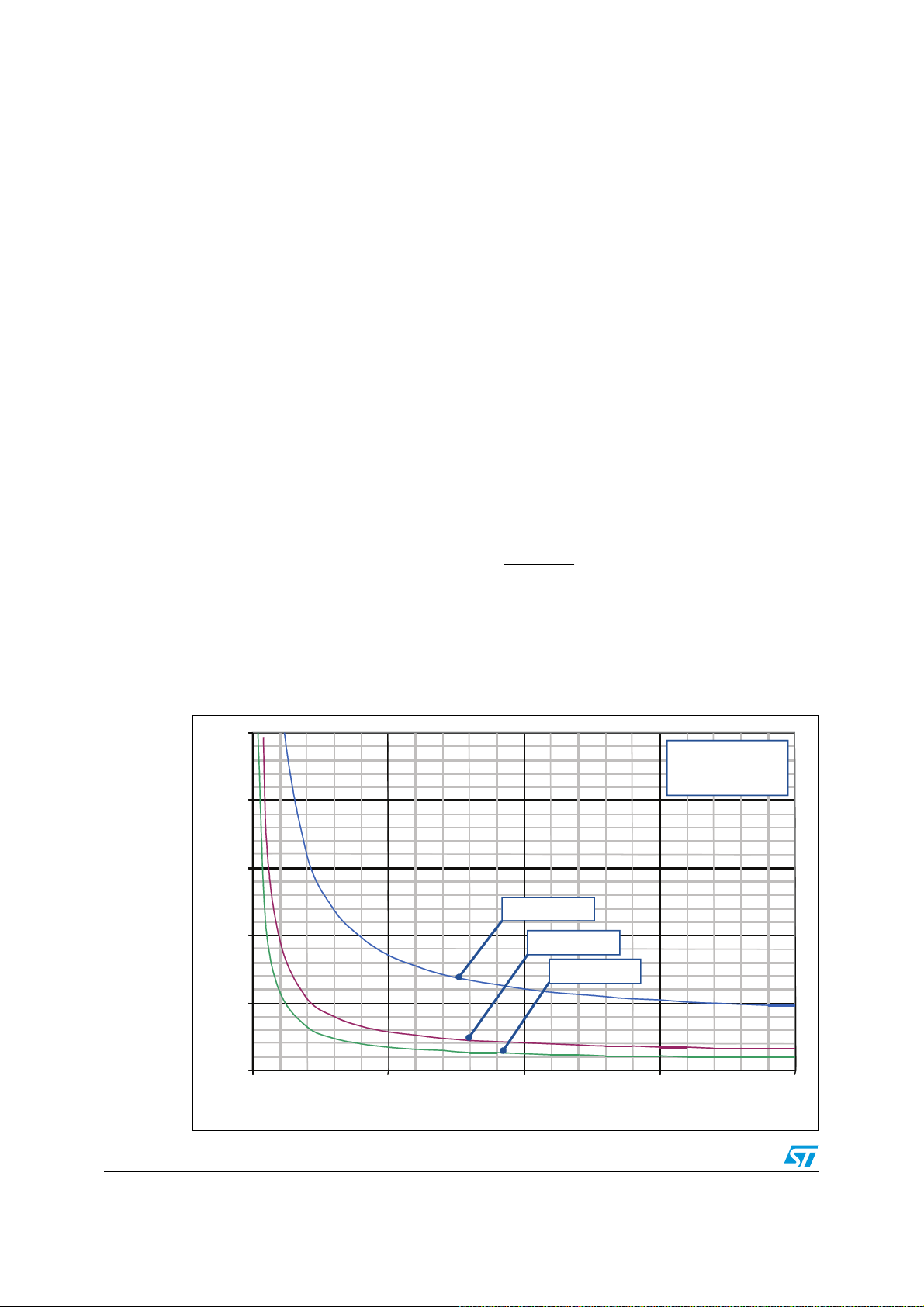
Figure 21. Bootstrap capacitor vs. switching frequency
5
4
(µF)
3
Δ
V
=0.1V
CB OOT
2
BOOT Calculated
C
1
0
0 5 10 15 20
fsw(kHz)
Δ
V
=0.3V
CBOOT
Δ
V
CBOOT
=0.5V
AM11814v1
STGIPN3H60A
STGIPN3H60
δ
= 50%
32/60 Doc ID 022726 Rev 1

AN4043 Electrical characteristics and functions
Considering the limit cases during the PWM control and further leakages and dispersions in
the board layout, the capacitance value to use in the bootstrap circuit must be selected two
or three times higher than the C
calculated in the graph of
BOOT
Figure 21
. The bootstrap
capacitor should be with a low ESR value for a good local decoupling, therefore, in case an
electrolytic capacitor is used, one parallel ceramic capacitor placed directly on the SLLIMMnano pins is strictly recommended.
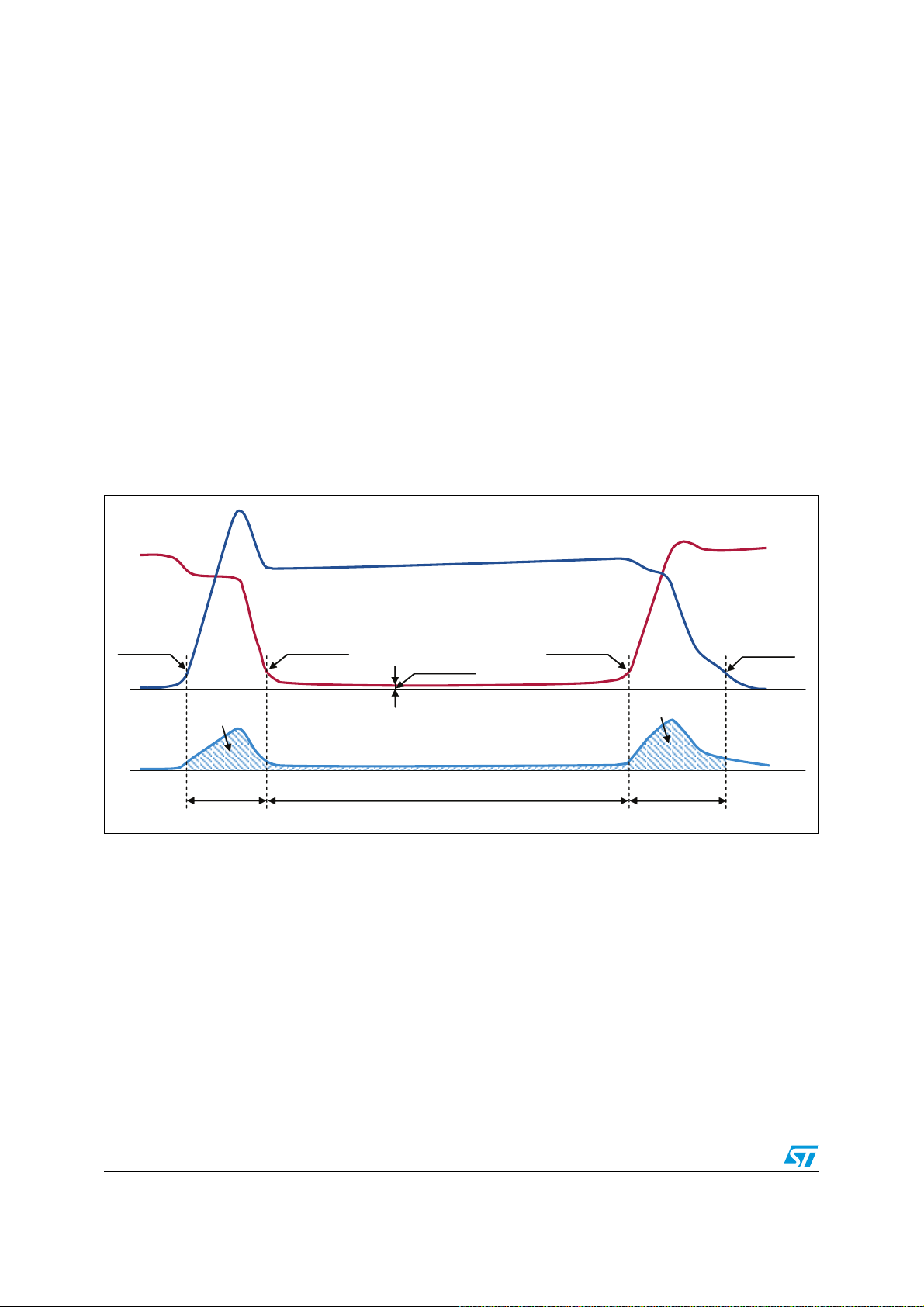
2.3.13 Initial bootstrap capacitor charging
During the startup phase, the bootstrap capacitor must be charged for a suitable time to
complete the initial charging time (t
CHARGE
exceed the turn-on undervoltage threshold V
9Equation 9
. For a normal operation, the voltage across the bootstrap capacitor must never
drop down to the turn-off undervoltage threshold V
conditions. For the period of startup, only the low-side IGBT is switched on and, just after
this phase, the PWM is run, as shown in the following steps of
● t1: the bootstrap capacitor starts to charge through the low-side IGBT (LVG)
● t2: the voltage across the bootstrap capacitor (V
undervoltage threshold V
t3: the bootstrap capacitor is fully charged; this enables the high-side IGBT and the
●
C
capacitor starts to discharge in order to provide the right IGBT gate charge. The
BOOT
BS_thON
bootstrap capacitor recharges during the on-state of the low-side IGBT (LVG).
), which is, at least, the time V
BS_thON
, as already stated in
BS_thOFF
throughout the working
Figure 22
) reaches its turn-on
CBOOT
CBOOT
Equation
:
needs to
Figure 22. Initial bootstrap charging time
9
&&
'&%XV9
The initial charging time is given by
+9*
/9*
9
&%227
7LPH
31
9
%6BWK21
9
%6BWK2))
W
W
Equation 12 Equation 12
reasons, at least three times longer than the calculated value.
W
!-V
and must be, for safety
Doc ID 022726 Rev 1 33/60

Electrical characteristics and functions AN4043
Equation 12
t
CHARGE
≥
BOOT
RC
⋅
⎛
)on(DS
V
⎜
ln*
⎜
V
Δδ
CBOOT
⎝
CC
⎞
⎟
⎟
⎠
where δ is the duty cycle of the PWM signal and R
is 120 Ω typical value, as shown in
DS(on)
the datasheet.
A practical example can be done by considering a motor drive application where the PWM
switching frequency is 16 kHz, with a duty cycle of 50%, and ΔV
a gate driver supply voltage V
capacitance is 1.0 µF, therefore the C
= 17.5 V). From the graph in
CC
can be selected by using a value between 2.0
BOOT
Figure 21
= 0.1 V (that means,
CBOOT
the bootstrap
and 3.0 µF. According to the commercial value the bootstrap capacitor can be 2.2 µF. From
Equation 12Equation 12
, the initial charging time is:
Equation 13
t
CHARGE
≥
6
−
120102.2
⋅⋅
5.0
5.17
⎞
⎛
ln
⋅
⎜
⎜
1.0
⎝
ms7.2
=
⎟
⎟
⎠
For safety reasons, the initial charging time must be at least 8.1 ms.
34/60 Doc ID 022726 Rev 1

AN4043 Package
3 Package
The NDIP is a dual-in-line transfer mold package available in 26-lead version (NDIP-26L)
able to meet demanding cost and size requirements of consumer appliance inverters. It
consists of a copper lead frame with power stage and control stage soldered on it and
housed using the transfer molding process. The excellent thermal properties of the copper
allows good heat spread and heat transfer, furthermore, the thickness and the layout of the
lead frames has been optimized in order to further reduce the thermal resistance.
The package pinout has been designed in order to maximize the distance between the high
voltage and low voltage pins, by placing the relevant pins on the opposite side of the
package. This is mainly useful to keep a safe distance between high voltage and low voltage
pins and for an easy PCB layout.
Finally, thanks to the transfer molding technology and design optimization, the SLLIMMnano offers a high power density level in a very compact package while providing good
thermal propriety, electrical isolation and overall reliable performance.
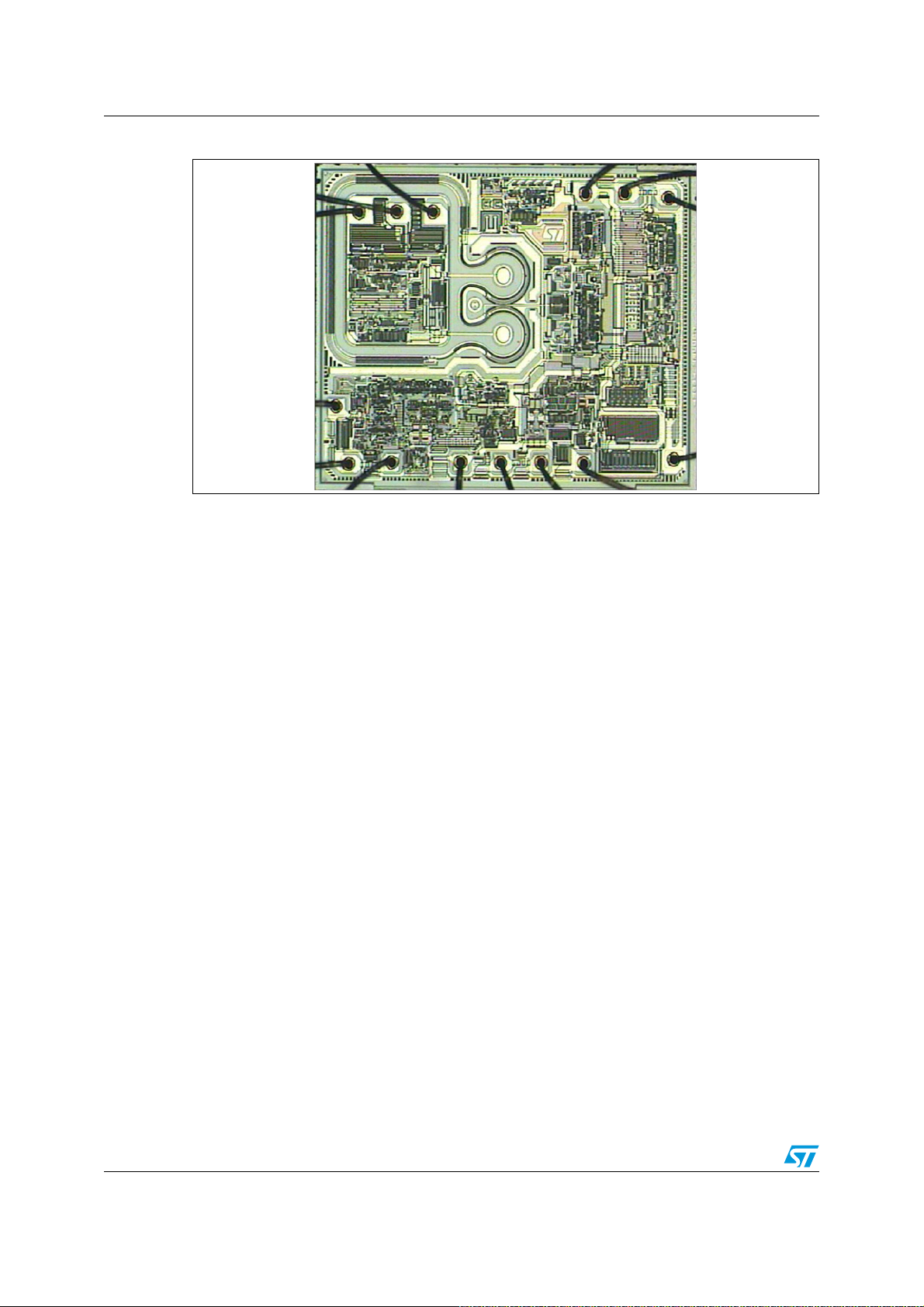
3.1 Package structure
Figure 23
contains the images and an internal structure illustration of the NDIP-26L
package.
Figure 23. Images and internal view of NDIP-26L package
o
n
a
n
-
M
M
I
L
L
S
Top view
SLLIMM-nano
NDIP-26L
IGBT FWDHVIC
Internal view
x = 29.5 mm
y
= 12.5 mm (body only)
1
= 22 mm (including leads)
y
2
z1 = 3.1 mm (body only)
z2 = 7 mm (including leads)
Bottom view
z
x
y
Main dimensions
Doc ID 022726 Rev 1 35/60

Package AN4043
3.2 Package outline and dimensions
Figure 24. Outline drawing of NDIP-26L package
D3
0.075
A2
A
A3
A1
b
e
D
L
A4
0.075
b,b2
b1,b3
c
c1
D1
8278949_A
eB1
eB2
E
b2
D2
e1
AM11815v1
36/60 Doc ID 022726 Rev 1

AN4043 Package
Table 9. Outline drawing of NDIP-26L package
(mm)
Dimension
Min. Typ. Max.
A4.4
A1 0.811.2
A2 3 3.1 3.2
A3 1.7 1.8 1.9
A4 5.7 5.9 6.1
b0.53 0.72
b1 0.52 0.6 0.68
b2 0.83 1.02
b3 0.82 0.9 0.98
c0.46 0.59
c1 0.45 0.5 0.55
D 29.05 29.15 29.25
D1 0.5
D2 0.35
D3 29.55
E 12.35 12.45 12.55
e1.71.81.9
e1 2.4 2.5 2.6
eB1 16.1 16.4 16.7
eB2 21.18 21.48 21.78
L 1.24 1.39 1.54
3.3 Input and output pins description
This paragraph defines the input and output pins of the SLLIMM-nano. For a more accurate
description and layout suggestions, please consult the relevant sections.
Doc ID 022726 Rev 1 37/60

Package AN4043
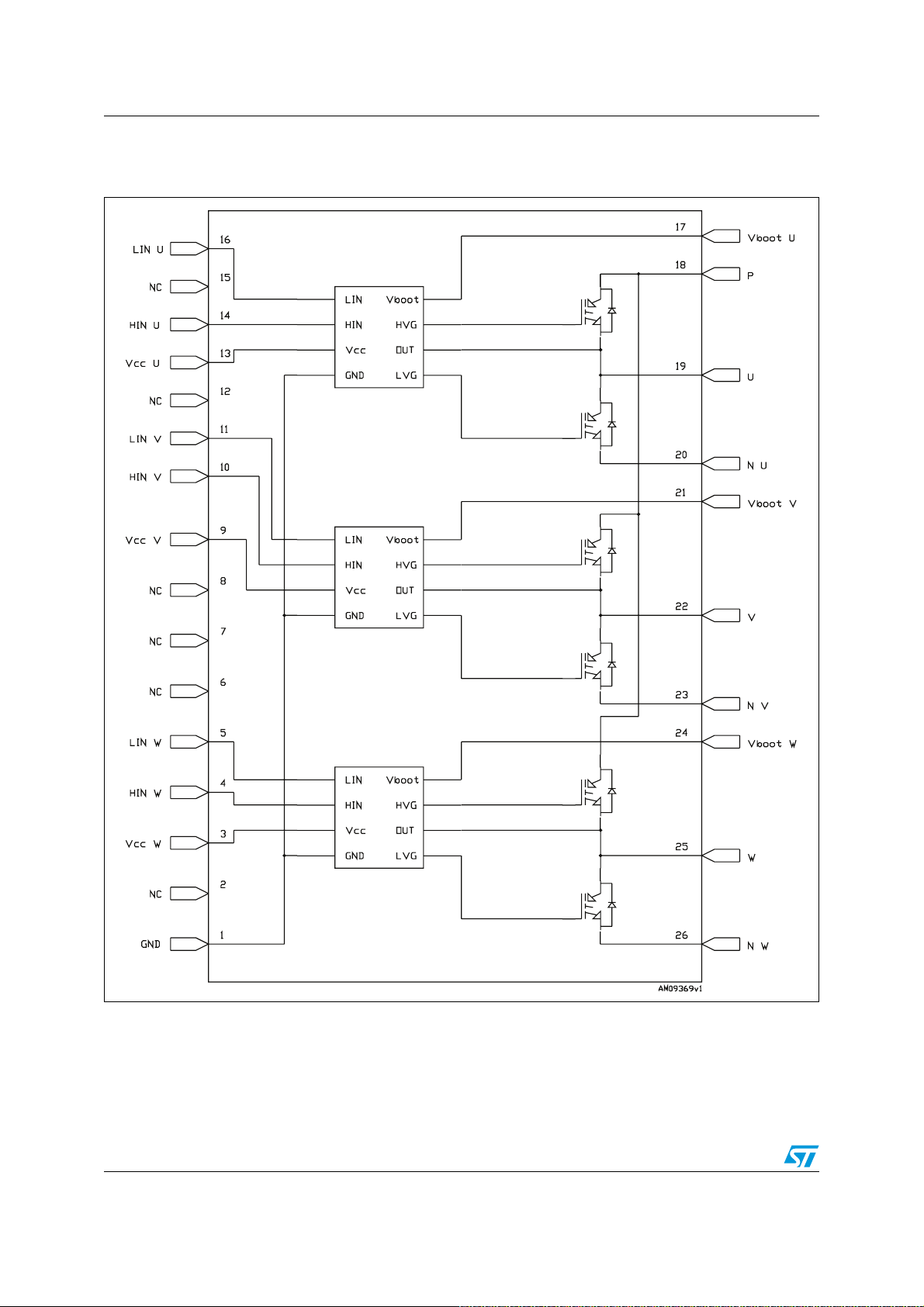
Figure 25. Pinout (top view)
Table 10. Input and output pins
Name Description
Pin #
STGIPN3H60A STGIPN3H60 STGIPN3H60A STGIPN3H60
1 GND Ground
2NC SD
3V
4HIN
5LIN
CC W
W
W
/ OD Not connected
LIN
W
Low voltage power supply W phase
High-side logic input for W phase
Low-side logic input for W
phase (active high)
Shutdown logic input (active low) /
open drain (comparator output)
Low-side logic input for W phase
(active low)
6NC OP+Not connected Op amp non inverting input
7NC OP
8NC OP
9V
10 HIN
11 LIN
CC V
V
V
LIN
OUT
-
V
Not connected Op amp output
Not connected Op amp inverting input
Low voltage power supply V phase
High-side logic input for V phase
Low-side logic input for V
phase (active high)
Low-side logic input for V phase
(active low)
12 NC CIN Not connected Comparator input
13 V
14 HIN
CC U
U
15 NC SD
/ OD Not connected
Low voltage power supply U phase
High-side logic input for U phase
Shutdown logic input (active low) /
open drain (comparator output)
16 LIN
U
17 V
bootU
LIN
U
Low-side logic input for U
phase (active high)
38/60 Doc ID 022726 Rev 1
Low-side logic input for U phase
(active low)
Bootstrap voltage for U phase

AN4043 Package
Table 10. Input and output pins (continued)
Name Description
Pin #
STGIPN3H60A STGIPN3H60 STGIPN3H60A STGIPN3H60
18 P Positive DC input
19 U U phase output
20 N
21 V
22 V V phase output
23 N
24 V
25 W W phase output
26 N
U
bootV
V
bootW
W
Negative DC input for U phase
Bootstrap voltage for V phase
Negative DC input for V phase
Bootstrap voltage for W phase
Negative DC input for W phase
High-side bias voltage pins /high-side bias voltage reference
Pins: V
● The bootstrap section is designed to realize a simple and efficient floating power
bootU
-U, V
bootV
-V, V
bootW
-W
supply, in order to provide the gate voltage signal to the high-side IGBTs
● The SLLIMM-nano family integrates the bootstrap diodes. This helps users to save
costs, board space, and number of components
● The advantage of the ability to bootstrap the circuit scheme is that no external power
supplies are required for the high-side IGBTs
● Each bootstrap capacitor is charged from the VCC supply during the on-state of the
corresponding low-side IGBT
● To prevent malfunction caused by noise and ripple in supply voltage, a good quality
(low ESR, low ESL) filter capacitor should be mounted close to these pins
● The value of bootstrap capacitors is strictly related to the application conditions. Please
consult
Section 2.3.11: Bootstrap circuit
for more information.
Gate driver bias voltage
Pins: V
●
● To prevent malfunction caused by noise and ripple in the supply voltage, a good quality
, V
CC U
CC V
, V
CC W
Control supply pins for the built-in ICs
(low ESR, low ESL) filter capacitor should be mounted close to these pins.
Gate drive supply ground
Pin: GND
● Ground reference pin for the built-in ICs
● To avoid noise influence, the main power circuit current should not be allowed to flow
through this pin (see
Section 5.1: Layout suggestions
).
Doc ID 022726 Rev 1 39/60
Package AN4043
Signal input
Pins: HIN
● These pins control the operation of the built-in IGBTs.
● The signal logic of HIN
, HINV, HINW; LINU, LINV, LINW; LINU, LINV, LIN
U
, HINV, HINW, LINU, LINV, and LINW pins is active high. The
U
W
IGBT associated with each of these pins is turned on when a sufficient logic (higher
than a specific threshold) voltage is applied to these pins.
● The signal logic of LIN
, LINV, LINW pins is active low. The IGBT associated with each
U
of these pins is turned on when a logic voltage (lower than a specific threshold voltage)
is applied to these pins.
● The wiring of each input should be as short as possible to protect the SLLIMM-nano
against noise influence. RC coupling circuits should be adopted for the prevention of
input signal oscillation. Suggested values are R
=100Ω and C=1nF.
Internal comparator non-inverting (only for the STGIPN3H60)
Pin: CIN
● The current sensing shunt resistor, connected on each phase leg, may be used by the
internal comparator (pin CIN) to detect short-circuit current
● The shunt resistor should be selected to meet the detection levels matched for the
specific application
● An RC filter (typically ~1 µs) should be connected to the CIN pin to eliminate noise
● The connection length between the shunt resistor and CIN pin should be minimized
● If a voltage signal, higher than the specified V
the SLLIMM-nano automatically shuts down and the SD
(see datasheet), is applied to this pin,
REF
/ OD pin is pulled down (to
inform the microcontroller).
Shutdown / open drain (only for the STGIPN3H60)
Pins: SD
● There are two available pins of SD / OD which are exactly the same. They are placed
/ OD
on the opposite ends of the package in order to offer higher flexibility to the PCB layout.
It is sufficient to use only one of the two pins for the proper functioning of the device.
● The SD / OD pins work as enable/disable pins.
● The signal logic of SD / OD pins are active low. The SLLIMM-nano shuts down if a
voltage lower than a specific threshold is applied to these pins, leading each half bridge
in tri-state.
● The SD / OD status is connected also to the internal comparator status (
Short-circuit protection and smart shutdown function
the SD
● The SD / OD, when pulled down by the comparator, are open drain configured. The SD
/ OD pin is pulled down acting as a FAULT pin.
). When the comparator triggers,
Section 2.3.6:
/ OD voltage should be pulled up to the 3.3 V or 5 V logic power supply through a pullup resistor.
Integrated operational amplifier (only for the STGIPN3H60)
Pins: OP+, OP-, OP
The op amp is completely uncommitted
●
● The op amp performance is optimized for advanced control technique (FOC)
● Thanks to the integrated op amp, it is possible to realize a compact and efficient board
OUT
layout, minimizing the required BOM list.
40/60 Doc ID 022726 Rev 1

AN4043 Package
Positive DC-link
Pin: P
● This is a DC-link positive power supply pin of the inverter and it is internally connected
to the collectors of the high-side IGBTs
● To suppress the surge voltage caused by the DC-link wiring or PCB pattern inductance,
connect a smoothing filter capacitor close to the P pin. Generally a 0.1 or 0.22 µF high
frequency, high voltage non-inductive capacitor is recommended.
Negative DC-link
Pins: N
●
● These pins are connected to the low-side IGBT emitters of each phase
● The power ground of the application should be separated from the logic ground of the
, NV, N
U
W
These are the DC-link negative power supply pins (power ground) of the inverter
system and they should be reconnected at one specific point (star connection).
Inverter power output
Pins: U, V, W
● Inverter output pins for connecting to the inverter load (e.g. motor).
Doc ID 022726 Rev 1 41/60
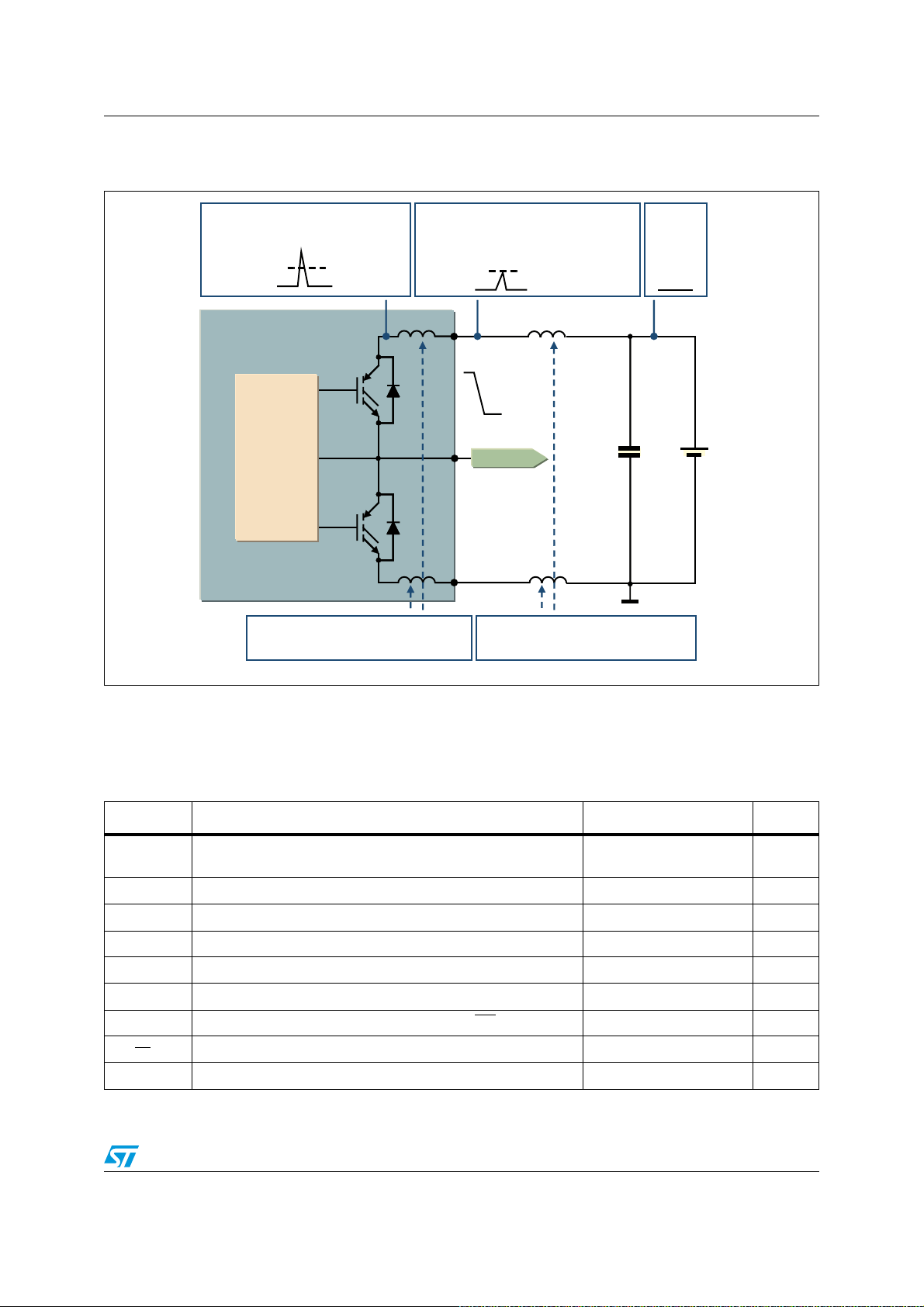
Power losses and dissipation AN4043
4 Power losses and dissipation
The total power losses in an inverter are comprised of conduction losses, switching losses,
and off-state losses and they are essentially generated by the power devices of the inverter
stage, such as the IGBTs and the freewheeling diodes. The conduction losses (P
the on-state losses during the conduction phase. The switching losses (P
) are the
SW
dynamic losses encountered during turn-on and turn-off. The off-state losses, due to the
blocking voltage and leakage current, can be neglected.
Finally, the total power losses are given by:
Equation 14
PPP +≈
swcondtot
COND
) are
Figure 26
shows a typical waveform of an inductive hard switching application such as a
motor drive, where the major sources of power losses are specified.
Figure 26. Typical IGBT power losses
V
10% I
CE
C
E
sw(on)
t
c(on)
I
C
10% V
CE
V
CE(sat)
conduction
4.1 Conduction power losses
10% V
CE
E
sw(off)
t
c(off)
10% I
C
AM09357v1
The conduction losses are caused by IGBT and freewheeling diode forward voltage drop at
rated current. They can be calculated using a linear approximation of the forward
characteristics for both the IGBT and diode, having a series connection of DC voltage
source representing the threshold voltage, V
emitter on-state resistance, R
in
Figure 27
42/60 Doc ID 022726 Rev 1
.
, (and anode cathode on-state resistance, RAK), as shown
CE
for IGBT, (and VFO for diode) and a collector
TO

AN4043 Power losses and dissipation
Figure 27. IGBT and diode approximation of the output characteristics
R
= ΔV
R
= ΔV
AK
AK
R
= ΔV
R
= ΔV
CE
CE
Δ
Δ
I
I
C
C
Δ
Δ
V
V
CE
CE
V
V
TO
TO
CE
CE
/ΔI
/ΔI
C
C
FM
FM
/ΔI
/ΔI
FM
FM
Δ
Δ
I
I
FM
FM
Δ
Δ
V
V
FM
FM
V
V
FO
FO
AM09345v1
Both forward characteristics are temperature dependent, and so must be considered under
a specified temperature.
The linear approximations can be translated for IGBT in the following equation:
Equation 15
iRV)(iv ⋅+=
cCETOcce
and, for freewheeling diode:
Equation 16
iRV)(iv ⋅+=
fmAKFOfmfm
The conduction losses of IGBT and diode can be derived as the time integral of the product
of conduction current and voltage across the devices, as follows:
Equation 17
P
T
1
T
0
(t)dtiv
ccecond_IGBT
T
1
⎛
⎜
∫∫
⎝
T
0
2
⎞
dt(t)iR(t)iV
⋅+⋅=⋅=
⎟
ccecTO
⎠
Equation 18
P
T
1
T
(t)dtiv
ffcond_Diode
0
T
1
⎛
⎜
⎝
∫∫
T
0
2
⎞
⋅+⋅=⋅=
dt(t)iR(t)iV
AKfFO
⎟
f
⎠
where T is the fundamental period.
The different utilization mode of the SLLIMM-nano, modulation technique, and working
conditions make the power losses very difficult to estimate, it is therefore necessary to fix
some starting points.
Doc ID 022726 Rev 1 43/60

Power losses and dissipation AN4043
Assuming that:
1. The application is a variable voltage variable frequency (VVVF) inverter based on
sinusoidal PWM technique.
2. The switching frequency is high and therefore the output currents are sinusoidal.
3. The load is ideal inductive.
Under these conditions, the output inverter current is given by:
Equation 19
()
φ= -θcos Iˆi
where Î is the current peak, θ
stands for ωt and φ is the phase angle between output voltage
and current.
The conduction power losses can be obtained as:
Equation 20
P
cond_IGBT
V
=
2
π
φ+
2
ˆ
⋅
I
π
2
() ()
φ+π−
Equation 21
π
φ+
2
IˆV
()() () ()
π
2
φ+π−
2
d-cos 1
where ξ
P
cond_Diode
=
is the duty cycle for this PWM technique and is given by:
Equation 22
a
=ξ
2
π
φ+
2
2
ˆ
⋅
I
R
CETO
+θφθξ
d-cos
R
AKFO
+θφθξ−
π
2
θ⋅+
cosm1
∫∫
π
2
2
π
φ+
2
2
ˆ
I
∫∫
φ+π−
2
2
φ+π−
2
θφθξ
d-cos
θφθξ−
d-cos 1
and m
Finally, solving
is the PWM amplitude modulation index.
a
Equation 20Equation 20
and
Equation 21Equation 21
Equation 23
VP
TOcond_IGBT
⎛ φ⋅
1
ˆ
⎜
+
⋅=
I
⎜
π
2
⎝
cosm
8
Equation 24
1
⎛
ˆ
⎜
⋅=
I
VP
FOcond_Diode
⎜
π
2
⎝
44/60 Doc ID 022726 Rev 1
cosm
−
8
, we have:
2
ˆ
⎛
⎞
⎠
φ⋅
⎞
⎠
⋅
1
I
R
CEa
+⎟⎟
R
+⎟⎟
⎜
⎜
π
2
⎝
2
ˆ
⋅
I
⎛
AKa
⎜
⎜
π
2
⎝
a
+
8
1
a
−
8
⎞
φ⋅
cosm
⎟
⎟
π
3
⎠
φ⋅
cosm
⎞
⎟
⎟
π
3
⎠

AN4043 Power losses and dissipation
and therefore, the conduction power losses of one device (IGBT and diode) are:
Equation 25
PPP +=
cond_Diodecond_IGBTcond
Of course, the total conduction losses per inverter are six times this value.
4.2 Switching power losses
The switching loss is the power consumption during the turn-on and turn-off transients. As
already shown in
(t
) and turn-off (t
on
the collector current and collector-emitter voltage for the switching period. However, the
dynamic performance is strictly related to many parameters such as voltage, current and
temperature, so it is necessary to use the same assumptions of conduction power losses
(
Section 4.1: Conduction power losses
Under these conditions, the switching energy losses are given by:
Equation 26
Figure 26
). Experimentally, it can be calculated by the time integral of product of
off
, it is given by the pulse of power dissipated during the turn-on
) to simplify the calculations.
()
onon
φ=θ -θcos Eˆ)(E
Equation 27
()
φ=θ -θcos Eˆ)(E
and Îc, θ stands for ωt and φ is
jmax
where Ê
and Ê
on
offoff
are the maximum values taken at T
off
the phase angle between output voltage and current.
Finally, the switching power losses per device depend on the switching frequency (f
) and
sw
they are calculated as follows:
Equation 28
π
φ+
2
1
∫
2
π
π
φ+
2
df)EE(
=θ⋅+
swDiodeIGBTsw
π
f)EE(
⋅+
swDiodeIGBT
are the total switching energy for the IGBT and the freewheeling
where E
IGBT
P
and E
=
Diode
diode, respectively. Also in this case, the total switching losses per inverter are six times this
value.
Figure 28
shows the real turn-on and turn-off waveforms of the STGIPN3H60 under the
following conditions:
● V
= 300 V, IC = 0.5 A, Tj = 100 °C with inductive load on full bridge topology, taken on
PN
the low-side IGBT.
The green plots represent instantaneous power as a result of IC (in red) and V
(in yellow)
CE
waveforms multiplication, during the switching transitions. The areas under these plots are
the switching energies computed by graphic integration thanks to the digital oscilloscope.
Doc ID 022726 Rev 1 45/60
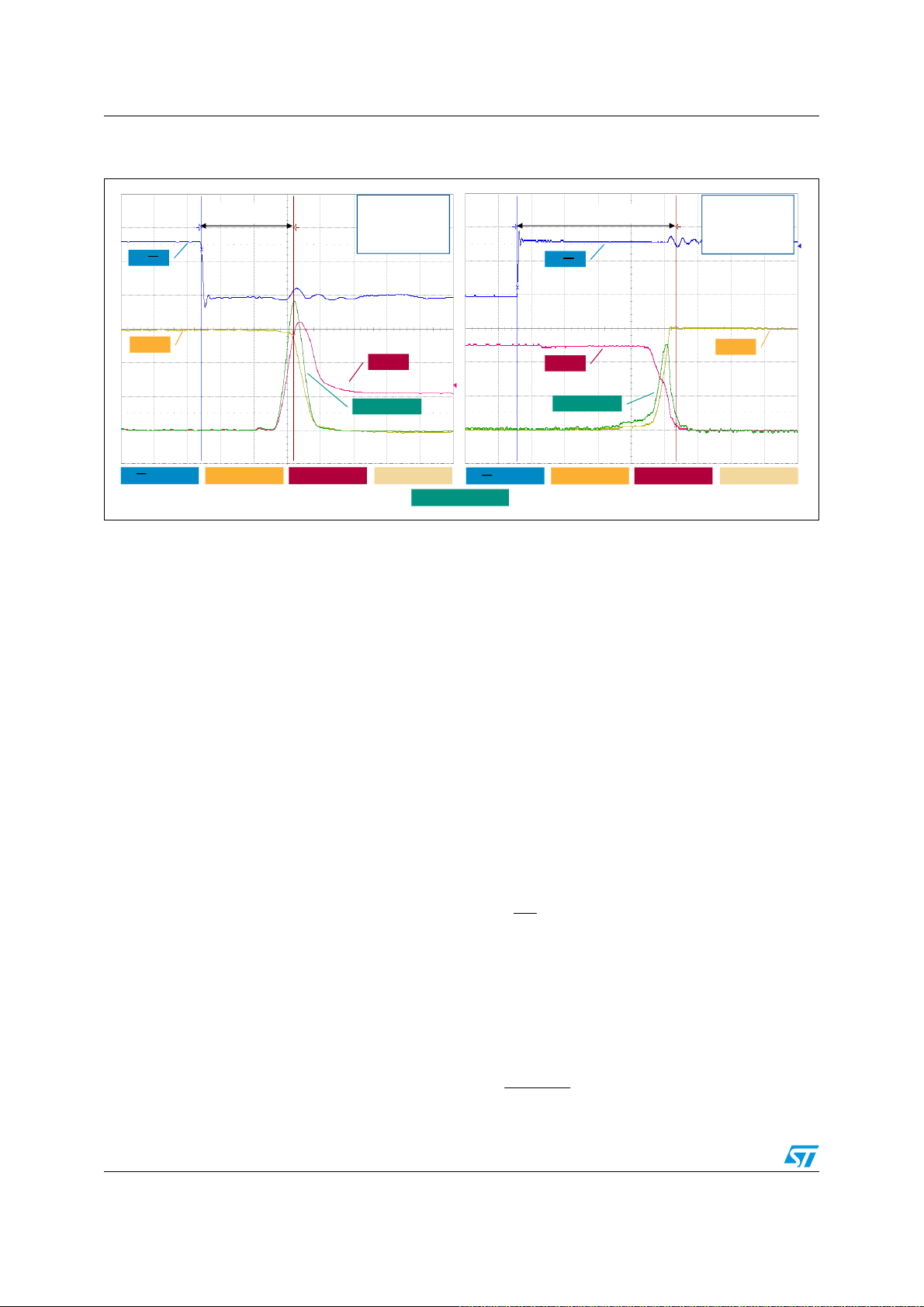
Power losses and dissipation AN4043
Figure 28. Typical switching waveforms of the STGIPN3H60
t
= 270ns
on
V
LIN
Tur n on
STGIPN3H60
Low side
Tj=100°C
t
= 905ns
off
V
LIN
Tur n off
STGIPN3H60
Low side
Tj=100°C
V
CE
V
= 2V/Div IC= 500mA/DivVCE= 100V/Div t = 100ns/Div
LIN
(*) E
and E
on
are the areas under the red plots
off
I
C
Eon=23.5μJ(*)
V
LIN
E = ∫ (VCE· IC) dt
4.3 Thermal impedance overview
During operation, power losses generate heat which elevates the temperature in the
semiconductor junctions contained in the SLLIMM-nano, limiting its performance and
lifetime. To ensure safe and reliable operation, the junction temperature of power devices
must be kept below the limits defined in the datasheet, therefore, the generated heat must
be conducted away from the power chips and into the environment using an adequate
cooling system.
The SLLIMM-nano was designed to drive electric motors up to 100 W without any heatsink.
Therefore, the thermal aspect of the system is one of the key factors in designing high
efficiency and high reliability equipment. In this environment the package and its thermal
resistance play a fundamental role.
V
I
C
E
=5.1μJ(*)
off
= 2V/Div IC= 200mA/DivVCE= 100V/Div t = 200ns/Div
CE
AM11816v1
Thermal resistance quantifies the capability of a given thermal path to transfer heat in
steady-state and it is generically given as the ratio between the temperature increase above
the reference and the relevant power flow:
Equation 29
Δ
R
=
th
Δ
The thermal resistance specified in the datasheet is the junction-ambient R
commonly used with natural and forced convection air cooled systems and it is defined as
the difference in temperature between junction and ambient reference divided by the power
dissipation per device:
Equation 30
=
a)th(j-
46/60 Doc ID 022726 Rev 1
T
P
which is
th(j-a)
TTR−
ambj
P
D
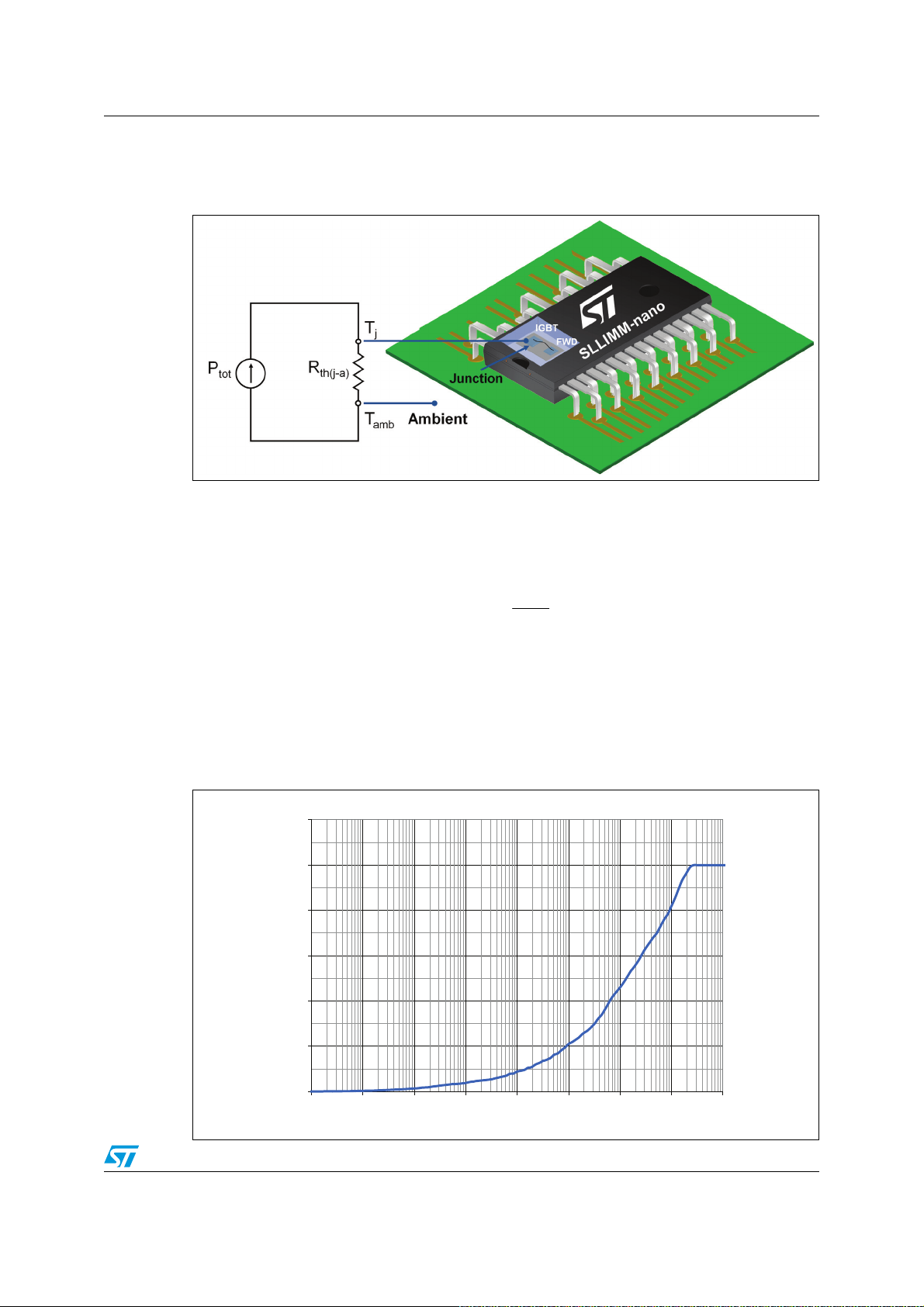
AN4043 Power losses and dissipation
Figure 29
ambient R
Figure 29. R
As the power loss P
shows an equivalent circuit of the thermal resistance between junction and
.
th(j-a)
equivalent thermal circuit
th(j-a)
is cyclic, also the transient thermal impedance must be considered. It
tot
is defined as the ratio between the time dependent temperature increase above the
reference, ΔT(t), and the relevant heat flow:
Equation 31
)t(T
Δ
)t(Z
=
th
P
Δ
AM11817v1
Contrary to that already seen regarding the thermal resistance, the thermal impedance is
typically represented by an RC equivalent circuit. For pulsed power loss, the thermal
capacitance effect delays the rise in junction temperature and therefore the advantage of
this behavior is the short-term overload capability of the SLLIMM-nano.
For example,
Figure 30
shows thermal impedance from a junction to ambient curve for a
single IGBT of the SLLIMM-nano.
Figure 30. Thermal impedance Z
60
50
40
30
(°C/W)
th(j-a)
Z
20
10
0
1.E-05 1.E-04 1.E-03 1.E-02 1.E-01 1.E+00 1.E+01 1.E+02 1.E+03
curve for a single IGBT
th(j-a)
SLLIMM-nano Z
time (sec)
th(j-a)
AM11818v1
Doc ID 022726 Rev 1 47/60

Power losses and dissipation AN4043
More generally, in the case of the device, power is time dependent too. The device
temperature can be calculated by using the convolution integral method applied to
31Equation 31
, as follows:
Equation
Equation 32
t
ττ⋅τ−=Δ
th
∫
0
d)(P)t(Z)t(T
An alternative method, very useful for the simulator tools, is the transient thermal impedance
model, which provides a simple method to estimate the junction temperature rise under a
transient condition.
By using the thermo-electrical analogy, the transient thermal impedance Z
can be
th(t)
transformed into an electrical equivalent RC network. The number of RC sections increases
the model details, therefore a twelfth order model, for Z
, based on the Cauer and Foster
th(j-a)
networks, has been used in order to improve the accuracy of both models.
Figure 31
and
Figure 32
show the general Cauer and Foster RC equivalent circuit used for
the thermal impedance model.
Figure 31. Cauer RC equivalent circuit
7
M
3
WRW
W
=WKW
R1
C1 C2 C3 Cn
R2
R3
7
Rn
DPE
AM11819v1
Figure 32. Foster RC equivalent circuit
7
M
R1
R2
R3
Rn
3
WRW
W
=WKW
C1
C2 C3 Cn
Temperatures inside the electrical RC network represent voltages, power flows represent
currents, electrical resistances and capacitances represent thermal resistances and
capacitances respectively. The case temperature is represented with a DC voltage source
and it can be interpreted as the initial junction temperature.
Transient thermal impedance models are derived by curve fitting an equation to the
measured data. Values for the individual resistors and capacitors are the variables from that
equation and are defined in
Ta bl e 1 1
, for both Z
models.
48/60 Doc ID 022726 Rev 1
Cauer and Foster thermal impedance
th(j-a)
7
DPE
AM11820v1

AN4043 Power losses and dissipation
Table 11. Cauer and Foster RC thermal network elements
Element Z
R1 (°C/W) 8.96E-01 1.81E-01
R2 (°C/W) 9.37E-01 1.71E-01
R3 (°C/W) 5.92E-01 8.12E-02
R4 (°C/W) 1.37E-02 5.11E-02
R5 (°C/W) 2.11E-02 1.86E-01
R6 (°C/W) 2.84E+00 6.58E-01
R7 (°C/W) 1.26E-01 5.00E-04
R8 (°C/W) 4.48E-02 6.95E-02
R9 (°C/W) 4.06E-01 5.14E-01
R10 (°C/W) 4.93E+00 4.43E+00
R11 (°C/W) 9.38E+00 7.90E+00
R12 (°C/W) 2.99E+01 3.58E+01
C1 (W·sec/°C) 6.25E-04 1.55E-01
C2 (W·sec/°C) 3.81E-03 1.67E-01
C3 (W·sec/°C) 4.69E-03 1.19E+00
C4 (W·sec/°C) 2.41E-03 9.09E-01
Cauer Network Z
th(j-a)
Foster Network
th(j-a)
C5 (W·sec/°C) 4.39E-03 1.84E-02
C6 (W·sec/°C) 3.27E-03 1.07E-03
C7 (W·sec/°C) 1.82E-02 1.77E-03
C8 (W·sec/°C) 1.32E-02 8.80E-02
C9 (W·sec/°C) 3.63E-03 1.19E-02
C10 (W·sec/°C) 6.72E-02 4.74E-02
C11 (W·sec/°C) 2.75E-02 2.35E-01
C12 (W·sec/°C) 2.22E+00 1.75E+00
4.4 Power loss calculation example
As a result of power loss calculation and thermal aspects, fully treated in the previous
sections, it is possible to simulate the maximum I
curves for a VVVF inverter using a 3-phase sinusoidal PWM and a six-step 120° switching
modulation to synthesize sinusoidal output currents.
The curves graphed in
nano in safety conditions, when the junction temperature rises to the maximum junction
temperature of 150 °C for three ambient temperatures (25, 50 and 75 °C), which is a typical
operating condition to guarantee the reliability of the system. These curves, functions of the
motor drive typology and control scheme, are simulated under the following conditions:
● V
= 300 V, ma = 0.8, cos = 0.6, Tj = 150 °C, Tc = 100 °C, f
PN
R
, typical V
th(j-c)
Figure 33
CE(sat)
represent the maximum current managed by the SLLIMM-
and E
values.
tot
current versus switching frequency
C(RMS)
= 60 Hz, max. value of
SINE
Doc ID 022726 Rev 1 49/60
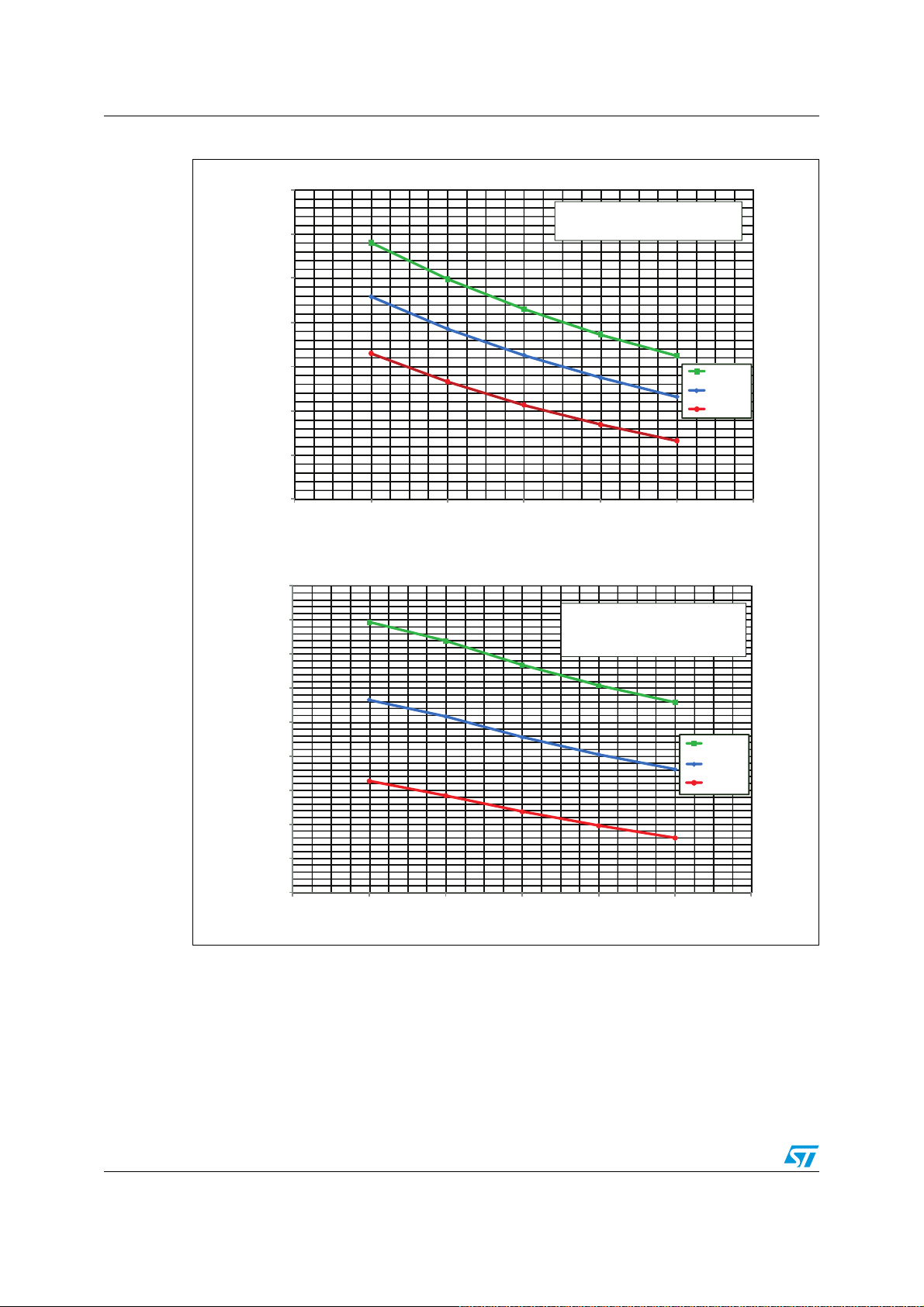
Power losses and dissipation AN4043
Figure 33. Maximum I
0.9
0.8
0.7
(A)
0.6
C(RMS)
I
0.5
0.4
0.3
0.2
04812162024
1.5
current vs. fsw simulated curves
C(RMS)
3-phase sinusoidal PWM
f
(kHz)
sw
Six -step 120 ° switching
AM11821v1
VPN= 300 V, Modulation Index = 0.8,
PF = 0.6, T
= 150 °C, f
j
sine
= 60 Hz
Ta = 25°C
Ta = 50 ° C
Ta = 75°C
AM11822v1
1.4
1.3
1.2
1.1
(A)
1
C(RMS)
I
0.9
0.8
0.7
0.6
04812162024
f
(kHz)
sw
VPN= 300 V, Modulation Index = 0.8,
PF = 0.6, T
= 150 °C, f
j
duty-cycle=60%
sine
= 60 Hz,
Ta = 25°C
Ta = 50 °C
Ta = 75°C
50/60 Doc ID 022726 Rev 1

AN4043 Design and mounting guidelines
5 Design and mounting guidelines
This section introduces the main layout suggestions for an optimized design and major
mounting recommendations, to appropriately handle and assemble the SLLIMM-nano
family.
5.1 Layout suggestions
Optimization of PCB layout for high voltage and high switching frequency applications is a
critical point. PCB layout is a complex matter as it includes several aspects, such as length
and width of track and circuit areas, but also the proper routing of the traces and the
optimized reciprocal arrangement of the various system elements in the PCB area.
A good layout can help the application to properly function and achieve the expected
performance. On the other hand, a PCB without a careful layout can generate EMI issues
(both induced and perceived by the application), can provide overvoltage spikes due to
parasitic inductances along the PCB traces, and can produce higher power loss and even
malfunction in the control and sensing stages.
The compactness of the SLLIMM-nano solution, which offers an optimized gate driving
network and reduced parasitic elements, allows users to focus only on certain issues, such
as the ground issue or noise filter. Therefore, in order to avoid all the aforementioned
conditions, the following general guidelines and suggestions must be followed in PCB layout
for 3-phase applications.
5.1.1 General suggestions
● PCB traces should be designed to be as short as possible and the area of the circuit
(power or signal) should be minimized to avoid the sensitivity of such structures to
surrounding noise.
● Ensure a good distance between switching lines with high voltage transitions and the
signal line sensitive to electrical noise. Specifically, the tracks of each OUT phase,
bringing significant currents and high voltages, should be separated from the logic lines
and analog sensing circuit of the op amp and comparator.
● Place the R
nano (N
, NV and NW). Parasitic inductance can be minimized by connecting the
U
ground line (also called driver ground) of the SLLIMM-nano directly to the cold terminal
of sense resistors. Use of a low inductance type resistor, such as an SMD resistor
instead of long-lead type resistors, can help to further decrease the parasitic
inductance.
● Avoid any ground loop. Only a single path must connect two different ground nodes.
● Place each RC filter as close as possible to the SLLIMM-nano pins in order to increase
their efficiency.
● In order to prevent surge destruction, the wiring between the smoothing capacitor and
the P and N pins should be as short as possible. The use of a high frequency, high
voltage non-inductive capacitor about 0.1 or 0.22 µF between the P and N pins is
recommended.
● Fixed voltage tracks, such as GND or HV lines, can be used to shield the logic and
analog lines from the electrical noise produced by the switching lines (e.g. U, V and W).
● Generally it is recommended to connect each half bridge ground in a star configuration
and the three R
resistors as close as possible to the low-side pins of the SLLIMM-
SENSE
SENSE
very close to each other and to the power ground.
Doc ID 022726 Rev 1 51/60
Design and mounting guidelines AN4043
In
Figure 34
, general suggestions for all SLLIMM-nano products are summarized.
Figure 34. General suggestions
Signal ground and power ground must be connected at only one point
(star connections), avoiding long connections.
P lease ensure a safety distances between ground tra cks and noisy tracks
(high volta ge or high frequency signals tracks)
Shunt resistor
GND
from
+15V
power
GND
source
to
V
IN(WL)
V
MCU
IN(WH)
P hase current
to
V
IN(VL)
V
MCU
IN(VH)
V
IN(UL)
to V
DD
Shut down
V
IN(UH)
Layer 1
Place an RC
filter directly
across SD pin
Layer 2
Place an R C filter directly across
the CI N (for each phase) pin to
avoid false short-circuit trigger
SD/OD
V
CC W
HIN
LIN
OP
+
OP
OUT
OP
-
V
CC V
HIN
LIN
CIN
V
CC U
HIN
SD/OD
LIN
W
W
V
BOOTW
N
W
W
N
V
V
V
V
U
U
V
BOOTV
N
U
U
V
BOOTU
P
Bootstrap capacitor should be
located as close as possible
to th e SL L I M M -n a no pi ns
Use of low inductance type resistor,
such as the SMD, ca n help to
further decrease the parasitic
inductance
Power G ND (N)
to mo to r
-
+
Main
electrolytic
capacitor
R educe all distances
between shunt resistors and
SLLIMM-nano power GND
AM11823v1
Special attention must be paid to wrong layouts. In
Figure 35
PCB mistakes are shown.
Figure 35. Example 1 on a possible wrong layout
from
+15V
power
GND
source
to
V
IN(WL)
V
MCU
IN(WH)
P hase current
V
IN(VL)
V
IN(VH)
Shut down
V
to V
V
IN(UL)
IN(UH)
to
MCU
DD
Layer 1
Layer 2
WRONG!
Long distance betwee n CI N filter and
SLLIMM-nano CIN pin. It is important to
minimize this dis tance in order to reduce
the noise impact
GND
SD/OD
V
CC W
HIN
W
LIN
W
OP
+
OP
OUT
OP
-
V
CC V
HIN
V
LIN
V
CIN
V
CC U
HIN
U
SD/OD
LIN
U
V
BOOTW
N
W
W
N
V
V
V
BOOTV
N
U
U
V
P
BOOTU
WRONG!
C I N filte r gr ound is n ot the
same as SLL IMM-nano
ground.
T his may cause noise
and
Shunt resistor
CIN
filter
Figure 36
some common
Power G ND (N)
to mo to r
-
+
Main
electrolytic
capacitor
CIN filter is close to high voltage
Noise influences compara tor
WRONG!
switching track (V
performances
BOOT
).
AM11824v1
52/60 Doc ID 022726 Rev 1

AN4043 Design and mounting guidelines
Figure 36. Example 2 on a possible wrong layout
%XON
FDSDFLWRU
6HQVHUHVLVWRU
FROGWHUPLQDO
*URXQGSDWK
6//,00QDQR
JURX
QG
6//,00QDQR
:521*
U\ODUJHJURXQGORRS
9H
'RHVQRWXVHWKHVXJJHVWHGVWDU
FRQQHFWLRQ
/RQJJURXQGSDWKFRXOGEHDIIHFWHG
E\QRLVHGXHWRKLJKYROWDJH
VZLWFKLQJWUDFNVDQGFRXOGDIIHFW
GULYHURUDSSOLFDWLRQSHUIRUPDQFH
:521*
7KHFROGWHUPLQDORIWKHVHQVH
UHVLVWRULVQRWFKRVHQDVVWDUFHQWUH
:521*
&RQQHFWLRQEHWZHHQWKH
6//,00QDQRDQGJURXQGLVQRW
PLQLPL]HG
!-V
5.2 Mounting instructions and cooling techniques
The SLLIMM-nano is a very compact intelligent power module able to drive electric motors
up to 100 W without any heatsink or cooling system installed on the board. The NDIP is a
transfer mold package with no screw holes, therefore some dedicated cooling techniques
must be adopted if a higher power level is targeted.
One of the easiest methods is based on a natural cooling system and a proper design of the
PCB layout. In this case, the PCB, along with the pads, acts as a heatsink providing paths
for individual packages to effectively transfer heat to the board and the adjacent
environment. Therefore, maximizing the area of the metal traces where the power and
ground pins of the package are located is a valuable method for reducing the thermal
resistance and for leading to an improved power performance.
The pins mainly involved in this phenomenon are the positive DC pin (P) and the phase
output pins (U, V, W), since they are directly connected to the copper lead frame where the
power devices are mounted and IGBTs and diodes are the major source of heat, as already
treated in
thermal performance, such as the area of metal traces, the thickness of the copper plate,
their placement on the board and the distance between the SLLIMM-nano and other heat
Section 4: Power losses and dissipation
Doc ID 022726 Rev 1 53/60
. Several aspects impact on the total

Design and mounting guidelines AN4043
sources. Both sides of the PCB can be used and thermally connected through direct copper
connections or thermal vias in order to increase the heat dissipation and reduce the layout
complexity.
Figure 37
shows an example of a metal trace layout used to dissipate heat on the PCB.
Figure 37. Cooling technique: copper plate on the PCB
AM11826v1
Higher thermal performance can be achieved by using a large and compact external
heatsink, in close contact with the SLLIMM-nano.
The heatsink can be directly fixed on the package thanks to thermal conductive glue or
adhesive foil between the heatsink and the backside of the package, as shown in
Figure 38
.
Figure 38. Cooling technique: heatsink bonded on the package
AM11827v1
An alternative method provides a heatsink (or plate) bonded on the package and fixed on
the PCB through a mounting screw, giving higher mechanical stability, as shown in
Figure 39
. This heatsink installation method requires a uniform layer of thermal grease or
thermal rubber layer and needs a safety distance between the heatsink and the lateral side
of the SLLIMM-nano, where some cut pins appear.
54/60 Doc ID 022726 Rev 1
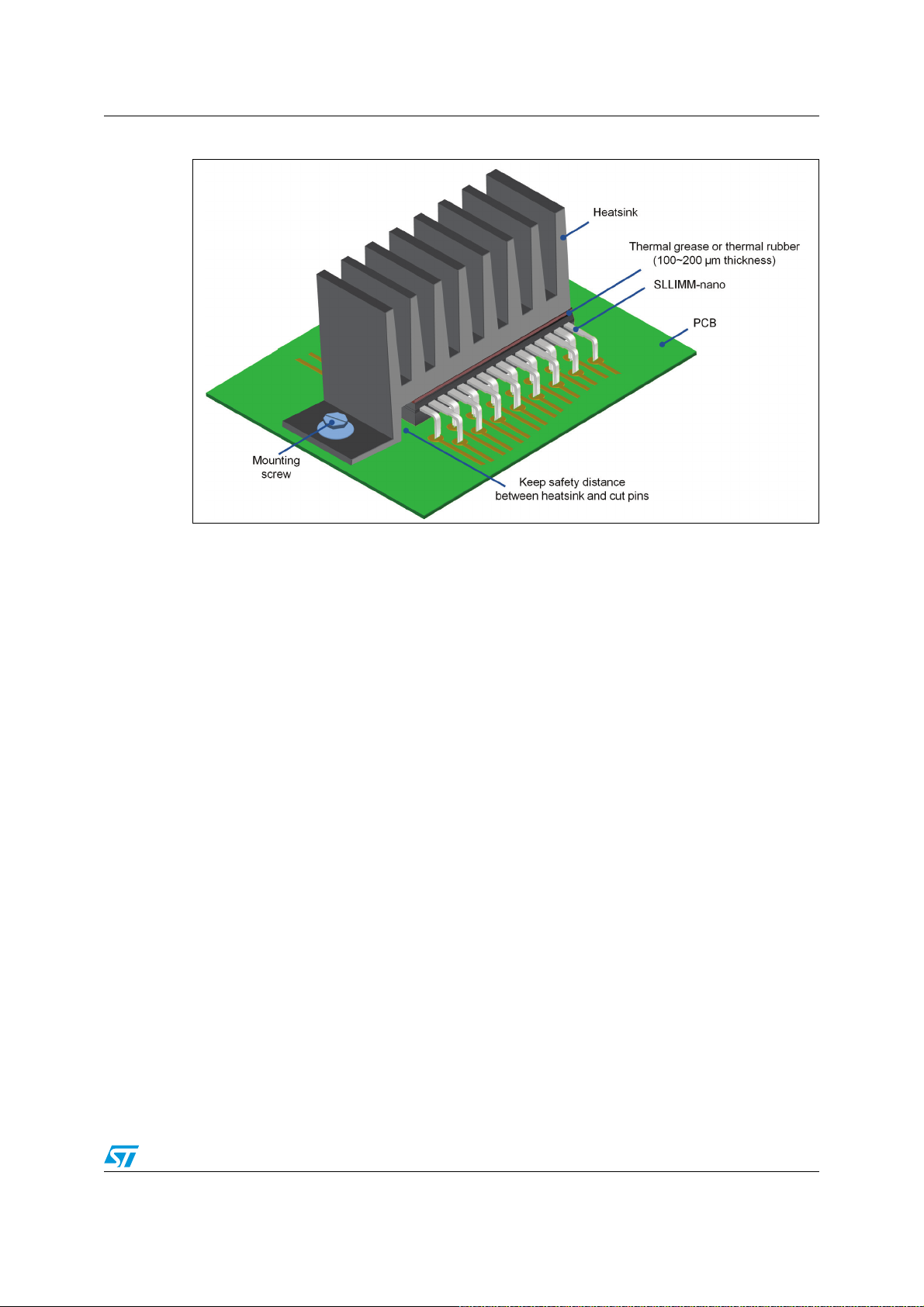
AN4043 Design and mounting guidelines
Figure 39. Cooling technique: heatsink bonded on the PCB
AM11828v1
Finally, a large variety of solutions may exist which take advantage of the metal box in which
the board can eventually be housed.
Nevertheless, whatever the heatsink installation method may be, some precautions should
be observed to maximize the effect of the heatsink. Smoothen the surface by removing burrs
and protrusions; it is essential to ensure an optimal contact between the SLLIMM-nano and
the heatsink. Apply a uniform layer of silicon grease (or thermal conductive glue), from 100
µm up to 200 µm of thickness, between the device and the heatsink to reduce the contact
thermal resistance. Be sure to apply the coating thinly and evenly, taking care to not have
any voids remaining on the contact surface between the SLLIMM-nano and the heatsink.
We recommend using high quality grease with stable performance within the operating
temperature range of the SLLIMM-nano.
Doc ID 022726 Rev 1 55/60

General handling precaution and storage notices AN4043
6 General handling precaution and storage notices
The incidence of thermal and/or mechanical stress to the semiconductor devices due to
improper handling may result in significant deterioration of their electrical characteristics
and/or reliability.
The SLLIMM-nano is an ESD sensitive device and it may be damaged in the case of ESD
shocks. All equipment used to handle power modules must comply with ESD standards
including transportation, storage, and assembly.
Transportation
Be careful when handling the SLLIMM-nano and packaging material. Ensure that the
module is not subjected to mechanical vibration or shock during transport. Do not throw or
drop in order to ensure that the SLLIMM-nano is correctly functioning before boarding. Wet
conditions are dangerous and moisture can also adversely affect the packaging. Hold the
package in such a way as to avoid touching the leads during mounting. Putting package
boxes upside down, leaning them at an angle, or giving them uneven stress may cause the
terminals to be deformed or the resin to be damaged.
Throwing or dropping the packaging boxes may cause the modules to be damaged. Wetting
the packaging boxes may cause the malfunction of modules when operating. Pay attention
when transporting in wet conditions.
Storage
● Do not force or load external pressure on the modules while they are in storage
● Humidity should be kept within the range of 40% to 75%, the temperature should not go
over 35 °C or below 5 °C
● Lead solder ability is degraded by lead oxidation or corrosion. So using storage areas
where there is minimal temperature fluctuation is highly recommended
● The presence of harmful gases or dusty conditions is not acceptable for storage
● Use antistatic containers.
Electrical shock and thermal injury
● Do not touch either module or heatsink when the SLLIMM-nano is operating to avoid
sustaining an electrical shock and/or a burn injury.
56/60 Doc ID 022726 Rev 1

AN4043 General handling precaution and storage notices
6.1 Packaging specifications
Figure 40. Packaging specifications of NDIP-26L package
AM10474v1
8313150_A
ANTISTATIC S 03 PVC
Doc ID 022726 Rev 1 57/60

References AN4043
7 References
1. AN3338 application note
2. STGIPN3H60A datasheet
3. STGIPN3H60 datasheet
4. AN2738 application note
5. UM1483 user manual
6. UM1517 user manual
7. Minimum-Loss Strategy for Three-Phase PWM Rectifier, IEEE, JUNE 1999
Note: SLLIMM™ and PowerMESH™ are trademarks of STMicroelectronics.
58/60 Doc ID 022726 Rev 1

AN4043 Revision history
8 Revision history
Table 12. Document revision history
Date Revision Changes
05-Apr-2012 1 Initial release.
Doc ID 022726 Rev 1 59/60

AN4043
Please Read Carefully:
Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the
right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any
time, without notice.
All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no
liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and services described herein.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted under this document. If any part of this
document refers to any third party products or services it shall not be deemed a license grant by ST for the use of such third party products
or services, or any intellectual property contained therein or considered as a warranty covering the use in any manner whatsoever of such
third party products or services or any intellectual property contained therein.
UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS
OF ANY JURISDICTION), OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS EXPRESSLY APPROVED IN WRITING BY TWO AUTHORIZED ST REPRESENTATIVES, ST PRODUCTS ARE NOT
RECOMMENDED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN MILITARY, AIR CRAFT, SPACE, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE SUSTAINING
APPLICATIONS, NOR IN PRODUCTS OR SYSTEMS WHERE FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY,
DEATH, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE. ST PRODUCTS WHICH ARE NOT SPECIFIED AS "AUTOMOTIVE
GRADE" MAY ONLY BE USED IN AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS AT USER’S OWN RISK.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the statements and/or technical features set forth in this document shall immediately void
any warranty granted by ST for the ST product or service described herein and shall not create or extend in any manner whatsoever, any
liability of ST.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of ST in various countries.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners.
© 2012 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
STMicroelectronics group of companies
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Philippines - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
60/60 Doc ID 022726 Rev 1
 Loading...
Loading...