Page 1

AN3138
Application note
Wrapper in MATLAB for the STEVAL-MKI062V1
Introduction
This application note provides information on the use of the application programming
interface (API) of the iNEMO™ software development kit (SDK), which provides easy-to-use
function calls to obtain data from the sensors or to change settings. The dynamic link library
(DLL) object handles the hardware communication interfacing and is an easy way to achieve
(soft) real-time performance. Typically, this is preferred when you want to access the iNEMO
board (STEVAL-MKI062V1) capabilities directly in the MathWorks™ MATLAB
software.
®
application
Figure 1. iNemo
TM
platform
January 2010 Doc ID 16985 Rev 1 1/16
www.st.com
Page 2

Contents AN3138
Contents
1 Getting started . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1.1 Power-up . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
1.2 MATLAB version . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
2 Application code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
2.1 Package description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
2.2 Generic MATLAB script usage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
2.3 Main functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2.3.1 Connect . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
2.3.2 Start data acquisition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
2.3.3 Acquire data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.3.4 Stop acquisition . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
3 References and related materials . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Appendix A MATLAB script code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
4 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2/16 Doc ID 16985 Rev 1
Page 3

AN3138 Getting started
1 Getting started
1.1 Power-up
The STEVAL-MKI062V1 board can be supplied by USB. Before connecting the board to a
USB port, configure switch S4 as described in the user manual of the board (UM0752).
The STEVAL-MKI062V1 software must be pre-installed on the computer before to using the
MATLAB script described in this application note.
1.2 MATLAB version
MathWorks MATLAB 7.8 (release R2009a and higher) is compatible with the iNEMO SDK
object. Older versions have not been tested.
Doc ID 16985 Rev 1 3/16
Page 4

Application code AN3138
2 Application code
2.1 Package description
Example codes are provided in the subfolder:
\STMicroelectronics\iNEMO Application\Redist
(the folder name could be different on your computer)
This subfolder contains:
● iNEMO_SDK.chm
– help file for the software development kit
● iNEMO_SDK.dll
– dynamic link library for the SDK
● iNEMO_SDL.h
– header file for the iNEMO SDK dll
● iNEMO_SDK_Wrapper.cs
– wrapper file in C#
● PL_001.dll - PL_001
– dynamic link library
● iNEMO_easy_script.m
– MATLAB example (included in Appendix A)
The iNEMO_easy_script.m file contains all the step-by-step instructions needed to use the
iNEMO SDK API in MATLAB. The explanations in the sections that follow may be used as a
guide for this file.
2.2 Generic MATLAB script usage
To load the dynamic link library within MATLAB, the load library instruction must be used
with the syntax:
[notfound, warnings] = loadlibrary('shrlib', 'hfile')
where the hfile and shrlib are the filenames of the DLL and header files, respectively (names
are case-sensitive). The name used in the load library must be in the same case as the file
on your system. In the present case:
[notfound, warnings] = loadlibrary('iNEMO_SDK.dll', 'iNEMO_SDK.h');
Once the iNEMO_SDK object is loaded, its functions can be listed easily with the
instructions:
libfunctions('iNEMO_SDK')
or
libfunctionsview('iNEMO_SDK')
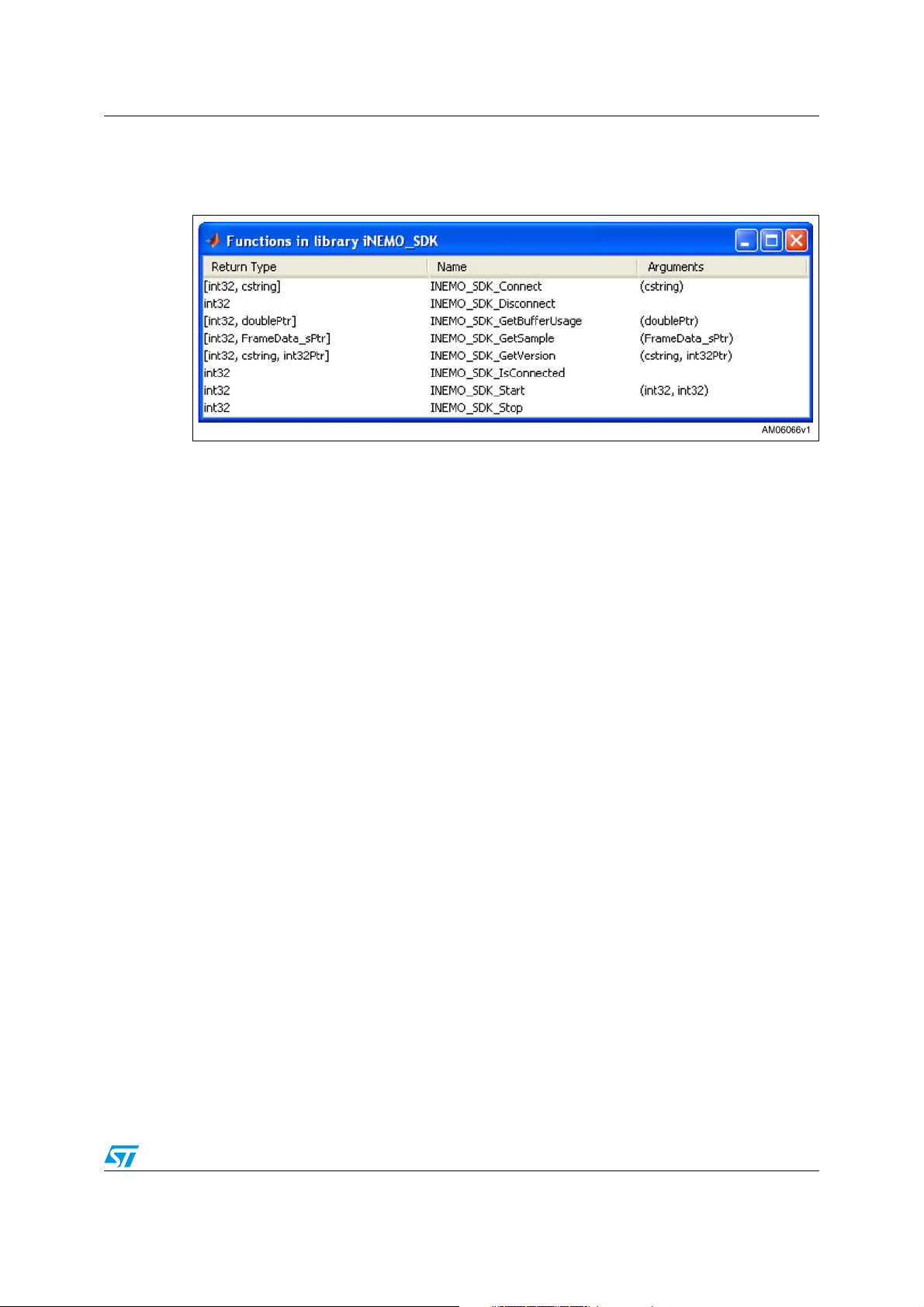
Using one of these functions, the MATLAB displays the window in Figure 2 with all the
available functions that can be executed by using the calllib function:
[ret_1, …] = calllib('iNEMO_SDK', function_name, arg_1, arg_2, …);
4/16 Doc ID 16985 Rev 1
Page 5
AN3138 Application code
The function_name (case-sensitive) should be one of the functions listed in Figure 2. arg_n
are the arguments of the functions, and ret_n are the function results.
Figure 2. Window displaying accessible functions
Finally, to release the iNEMO_SDK from the MATLAB environment, the following function
call must be used:
Unloadlibrary('iNEMO_SDK')
Note: Improper use of function sequence calls may cause MATLAB to release the object
incorrectly, resulting in error messages or unexpected behavior of the MATLAB
environment. Shutting down MATLAB will always release the iNEMO_SDK object.
Moreover, to restart the iNEMO board in the initial state, it is recommended to disconnect
and then reconnect the board.
2.3 Main functions
The iNEMO software development kit (SDK) allows implementation of the following actions:
● Connect the iNEMO board (STEVAL-MKI062V1) through USB virtual COM
● Start data acquisition
● Acquire data
● Stop acquisition
● Disconnect the iNEMO board
2.3.1 Connect
Once the iNEMO_SDK library is loaded, the first instruction to be used is:
calllib('iNEMO_SDK', 'INEMO_SDK_Connect', sCOM);
where sCOM should be a string in the format 'PL_001:COMx, BD115200'. COMx indicates
the virtual COM port used by the iNEMO_SDK.
Doc ID 16985 Rev 1 5/16
Page 6

Application code AN3138
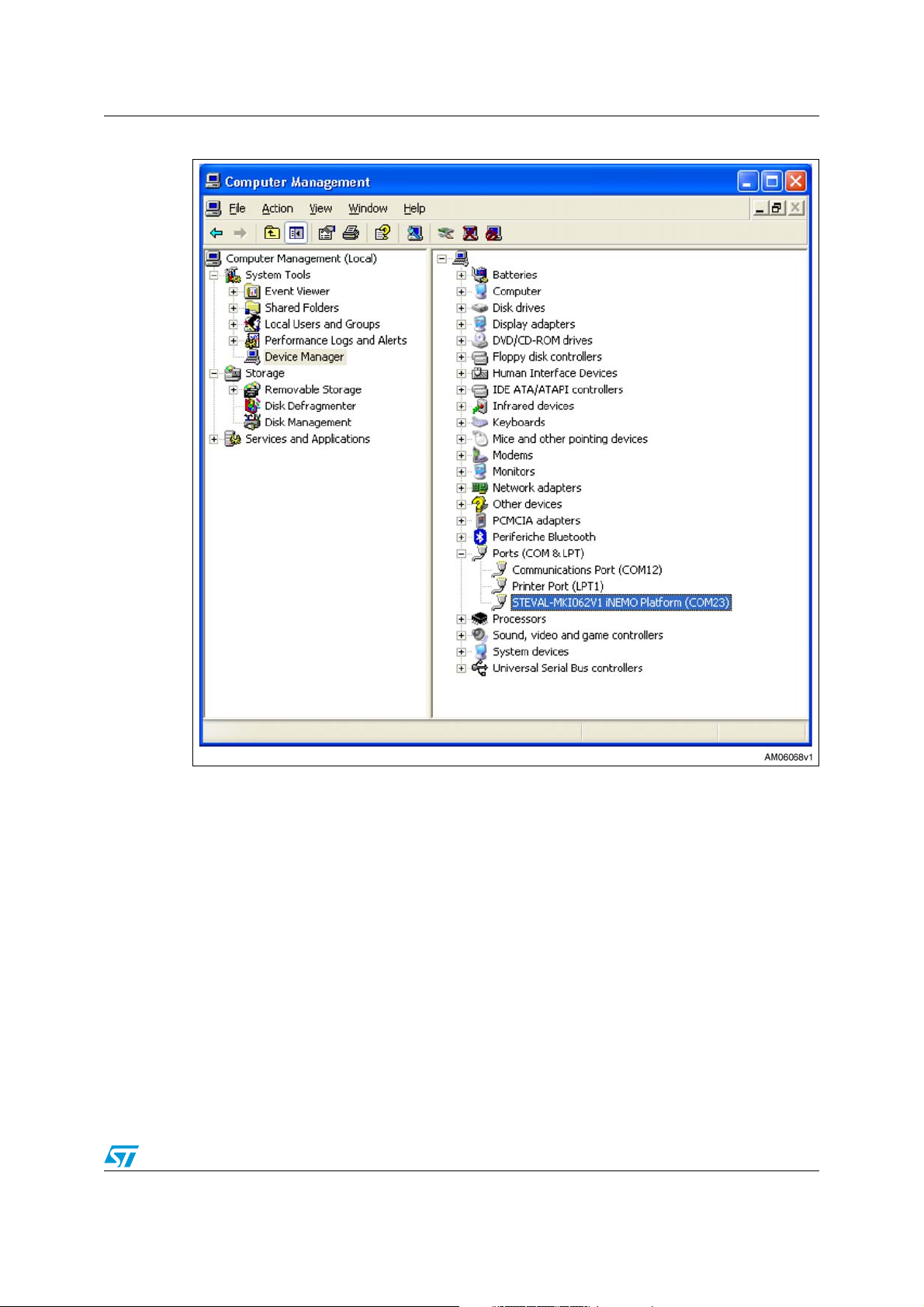
To identify which virtual COM port has been assigned by the PC to the iNEMO board, follow
these steps:
1. On the desktop, right-click the My Computer icon and click on Manage (see Figure 3).
2. In Computer Management window, double-click on System Tools and then Device
Manager to view all the hardware devices installed on the PC.
3. In the right pane, click the “+” sign next to Ports (COM & LPT) to view the list of
available ports. In the list, the STEVAL-MKI062V1 iNEMO Platform (COMx) string
should appear (see Figure 4).
The string contains the number of the COM port used by the board. This number should be
used in the parameter string 'PL_001:COMx, BD115200' of the INEMO_SDK_Connect
function. In the case shown in Figure 4, the parameter string is 'PL_001:COM23,
BD115200'.
Figure 3. First step: identifying the COM port used by the iNEMO board
6/16 Doc ID 16985 Rev 1
Page 7
AN3138 Application code
Figure 4. Second step: identifying the COM port used by iNEMO board
2.3.2 Start data acquisition
The sensor data acquisition phase starts using this function:
calllib('iNEMO_SDK','INEMO_SDK_Start', nFreq, nSamples);
where nFreq is the acquisition frequency (Hz), and nSamples is the number of samples to
be received. If the latter is 0, the iNEMO board sends data in infinite loop mode until an
INEMO_SDK_Stop command is received (Figure 5), otherwise the board sends only a finite
number of samples indicated in the nSamples parameter (Figure 6).
The nFreq parameter accepts the values 1, 10, 25 or 50, while the nSamples parameter
accepts values in the range 0 - 65535. As described above, this parameter is also used to
choose the acquisition mode.
Doc ID 16985 Rev 1 7/16
Page 8

Application code AN3138
Figure 5. Finite loop mode algorithm
Figure 6. Infinite loop mode algorithm
8/16 Doc ID 16985 Rev 1
Page 9

AN3138 Application code
2.3.3 Acquire data
The'INEMO_SDK_Start' instruction starts an internal process of the dynamic link library
which collects the data from the iNEMO board in a FIFO (first-input, first-output) list. To
obtain the data from this list the following instruction must be used:
[i32, pFD] = calllib('iNEMO_SDK', 'INEMO_SDK_GetSample', pFD);
where pFD is a C-language structure is organized as follows:
typedef struct
{
SampleTimeStamp // timestamp (milliseconds from start)
Accelerometer // Accelerometer component (X, Y, Z) in mg unit
Gyroscope // Gyroscope component (X, Y1, Y2, Z) in dps unit
Magnetometer // Magnetometer component (X, Y, Z) in mGa unit
Pressure // Pressure value in 1/10 of mbar unit
Temperature // Temperature value in 1/10 of ºC unit
}
Note: The FIFO filling is dictated by the frequency indicated in the nFreq parameter, since the use
of the INEMO_SDK_GetSample instruction must be in accordance with this frequency.
Otherwise, a faster INEMO_SDK_GetSample returns an empty pFD structure and a tooslow INEMO_SDK_GetSample returns too-old values.
To verify the effectiveness of the pFD structure, it is recommended to check the returned
value i32, which could be:
0 INEMO_SDK_ERROR_NONE = No error
4 INEMO_SDK_ERROR_STACK_EMPTY = The stack of data is empty
2.3.4 Stop acquisition
To stop the data acquisition process, use this instruction:
calllib('iNEMO_SDK', 'iNEMO_SDK_Stop');
This instruction does not delete the FIFO data, since the acquired data are still available to
be viewed or processed.
Finally, to correctly detach the virtual COM port used on the USB link, is recommended to
use the disconnect instruction:
calllib('iNEMO_SDK', 'INEMO_SDK_Disconnect')
Section Appendix A: MATLAB script code contains the MATLAB script code.
Doc ID 16985 Rev 1 9/16
Page 10

References and related materials AN3138
3 References and related materials
The following additional information for the STEVAL-MKI062V1 is available on www.st.com:
● STEVAL-MKI062V1 data brief
● User manual UM0752: STEVAL-MKI062V1, iNEMO: iNErtial MOtion demonstration
board based on the MEMS devices and STM32F103Rx
10/16 Doc ID 16985 Rev 1
Page 11

AN3138 MATLAB script code
Appendix A MATLAB script code
% ************* (C) COPYRIGHT 2009 STMicroelectronics *************
% File Name : iNEMO_easy_script.m
% Author : IMS SYSTEMS LAB - ART TEAM
% Version : V 1.0
% Date : 10/27/2009
% Description : iNEMO Demo file for Matlab
%
*******************************************************************
% THE PRESENT FIRMWARE WHICH IS FOR GUIDANCE ONLY AIMS AT PROVIDING
CUSTOMERS
% WITH CODING INFORMATION REGARDING THEIR PRODUCTS IN ORDER FOR THEM
TO SAVE TIME.
% AS A RESULT, STMICROELECTRONICS SHALL NOT BE HELD LIABLE FOR ANY
DIRECT,
% INDIRECT OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES WITH RESPECT TO ANY CLAIMS
ARISING FROM THE
% CONTENT OF SUCH FIRMWARE AND/OR THE USE MADE BY CUSTOMERS OF THE
CODING
% INFORMATION CONTAINED HEREIN IN CONNECTION WITH THEIR PRODUCTS.
%
% THIS SOURCE CODE IS PROTECTED BY A LICENSE.
% FOR MORE INFORMATION PLEASE CAREFULLY READ THE LICENSE AGREEMENT
FILE LOCATED
% IN THE ROOT DIRECTORY OF THIS FIRMWARE PACKAGE.
%
*******************************************************************
% Further Note:
%
% This script has been tested with Mathworks Matlab R2009a
%
%
*******************************************************************
% Press "F5" to run this script, please select correctly the COM
port.
Doc ID 16985 Rev 1 11/16
Page 12

MATLAB script code AN3138
% You should get a single sample from the iNEMO DLL with all data
sensors.
% To view all the methods of the iNEMO software component:
% libfunctions('iNEMO_SDK')
%
% or
%
% libfunctionsview('iNEMO_SDK')
% set up instance of iNEMO in MATLAB
%if (libisloaded('iNEMO_SDK'))
% unloadlibrary('iNEMO_SDK');
%end
% Load the Dll within Matlab
[notfound, warnings] = loadlibrary('iNEMO_SDK.dll', 'iNEMO_SDK.h');
sCOM=input('What COM-port is your iNEMO connected to? <1>','s');
sCOM = strcat('PL_001:COM', sCOM, ', BD115200');
% Connect to iNEMO Board
% Check i32 to manage errors
% cs will return the sCOM string
[i32, cs] = calllib('iNEMO_SDK', 'INEMO_SDK_Connect', sCOM);
% Replace the previous instruction with the following in case you
receive
% an error on this row
%vp = libpointer('voidPtr', [int8(sCOM) 0]);
%[i32, cs] = calllib('iNEMO_SDK', 'INEMO_SDK_Connect', vp)
% Verify if iNEMO Board is Connected
% Check i32 to manage errors (0 not connected, otherwise
connected)
% [i32] = calllib('iNEMO_SDK', 'INEMO_SDK_IsConnected')
12/16 Doc ID 16985 Rev 1
Page 13

AN3138 MATLAB script code
% Request device information from iNEMO
% Check i32 to manage errors (0 no error, otherwise code error)
% cs will contain the string required
% ip32 will contain the number of char returned
sVER = 'iNEMO String - Please do not delete this row';
[i32, cs, ip32] = calllib('iNEMO_SDK', 'INEMO_SDK_GetVersion',
sVER, 30);
% Replace the previous instruction with the following in case you
receive
% an erro on this row
%vp = libpointer('voidPtr', [int8(sVER) 0]);
%[i32, cs, ip32] = calllib('iNEMO_SDK', 'INEMO_SDK_GetVersion', vp,
30)
% Start Data Acquisition
% Input: nFreq the acquisition frequency (Hz). Allowed values are
1, 10,
% 25, 50
% nSamples number of samples to receive. Allowed range
value is
% 0-65535; if 0 the device will send data
in
% continous mode until stop
% Check i32 to manage errors (0 no error, otherwise code error)
nFreq = 10;
nSamples = 100;
[i32]= calllib('iNEMO_SDK','INEMO_SDK_Start', nFreq, nSamples);
% Initialize the FrameData Structure
pFD = struct('SampleTimeStamp',0, ...
'Accelerometer',struct('X',0,'Y',0,'Z',0), ...
'Gyroscope',struct('X',0,'Y1',0,'Y2',0,'Z',0), ...
'Magnetometer', struct('X',0,'Y',0,'Z',0), ...
'Pressure', 0, 'Temperature', 0);
Doc ID 16985 Rev 1 13/16
Page 14

MATLAB script code AN3138
% Add a 5% to the Time Acquisition interval (1/nFreq)
pauseDelay= 1.05/nFreq;
for i=1:nSamples
pause(pauseDelay);
% Get a data Sample, pFD is a pointer to FrameData_t structure
% Check i32 to manage errors (0 no errors, otherwise code
error)
[i32, pFD] = calllib('iNEMO_SDK', 'INEMO_SDK_GetSample', pFD);
% Show the Acquired Data
disp(pFD.SampleTimeStamp);
disp(pFD.Accelerometer);
disp(pFD.Gyroscope);
disp(pFD.Magnetometer);
disp(pFD.Pressure);
disp(pFD.Temperature);
end
% Stop Data Acquisition
% It is mainly needed in case of Continous Acquisition
% Check i32 to manage errors (0 no error, otherwise code error)
% [i32] = calllib('iNEMO_SDK', 'iNEMO_SDK_Stop');
% Disconnect iNEMO Board
% Check i32 to manage errors (0 no error, otherwise code error)
[i32] = calllib('iNEMO_SDK', 'INEMO_SDK_Disconnect')
% when finished with iNEMO SDK, release it from the MATLAB workspace
% unloadlibrary('iNEMO_SDK')
14/16 Doc ID 16985 Rev 1
Page 15

AN3138 Revision history
4 Revision history
Table 1. Document revision history
Date Revision Changes
18-Jan-2010 1 Initial release.
Doc ID 16985 Rev 1 15/16
Page 16

AN3138
Please Read Carefully:
Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the
right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any
time, without notice.
All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no
liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and services described herein.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted under this document. If any part of this
document refers to any third party products or services it shall not be deemed a license grant by ST for the use of such third party products
or services, or any intellectual property contained therein or considered as a warranty covering the use in any manner whatsoever of such
third party products or services or any intellectual property contained therein.
UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS
OF ANY JURISDICTION), OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS EXPRESSLY APPROVED IN WRITING BY AN AUTHORIZED ST REPRESENTATIVE, ST PRODUCTS ARE NOT
RECOMMENDED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN MILITARY, AIR CRAFT, SPACE, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE SUSTAINING
APPLICATIONS, NOR IN PRODUCTS OR SYSTEMS WHERE FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY,
DEATH, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE. ST PRODUCTS WHICH ARE NOT SPECIFIED AS "AUTOMOTIVE
GRADE" MAY ONLY BE USED IN AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS AT USER’S OWN RISK.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the statements and/or technical features set forth in this document shall immediately void
any warranty granted by ST for the ST product or service described herein and shall not create or extend in any manner whatsoever, any
liability of ST.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of ST in various countries.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners.
© 2010 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
STMicroelectronics group of companies
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Philippines - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
16/16 Doc ID 16985 Rev 1
 Loading...
Loading...