
AN2715
Application note
IBIS models for signal integrity
simulation of SPEAr600 applications
Introduction
This application note is intended for hardware developers that are using the SPEAr600
embedded MPU in their target design.
The IBIS models are mandatory to run signal integrity simulation in the application PCB.
PCB simulation is very important to make sure that the layout of the PCB does not introduce
any functional problems or timing marginality in high speed interfaces like DDR2 and
Ethernet.
The IBIS models provided for SPEAr600 are organized in a model library containing several
models for each I/O pin (or for a functional group of I/Os). Each I/O pin or functional group of
I/O has a set of models; each model corresponds to a certain operating mode of the I/O
pads.
The operating modes are programmable and are defined by a proper setting of two
registers, one in the miscellaneous register block and the other one in the memory controller
block of the SPEAr600 device (for more details please refer to the miscellaneous registers
and memory controller sections of the SPEAr600 user manual).
This document explains how to select the correct model from the library sp600_v13.ibs after
reading the register settings or knowing the operating mode from the SPEAr600 user
manual.
Note: The registers referred to in this document are described in detail in the SPEAr600 user
manual.
December 2009 Doc ID 14454 Rev 1 1/12
www.st.com
PL_CLK & PL_GPIO IBIS model selection AN2715
1 PL_CLK & PL_GPIO IBIS model selection
The I/O signals of the PL_CLK & PL_GPIO interface form two main groups. Please refer to
the following table for the I/O signals and the associated model name.
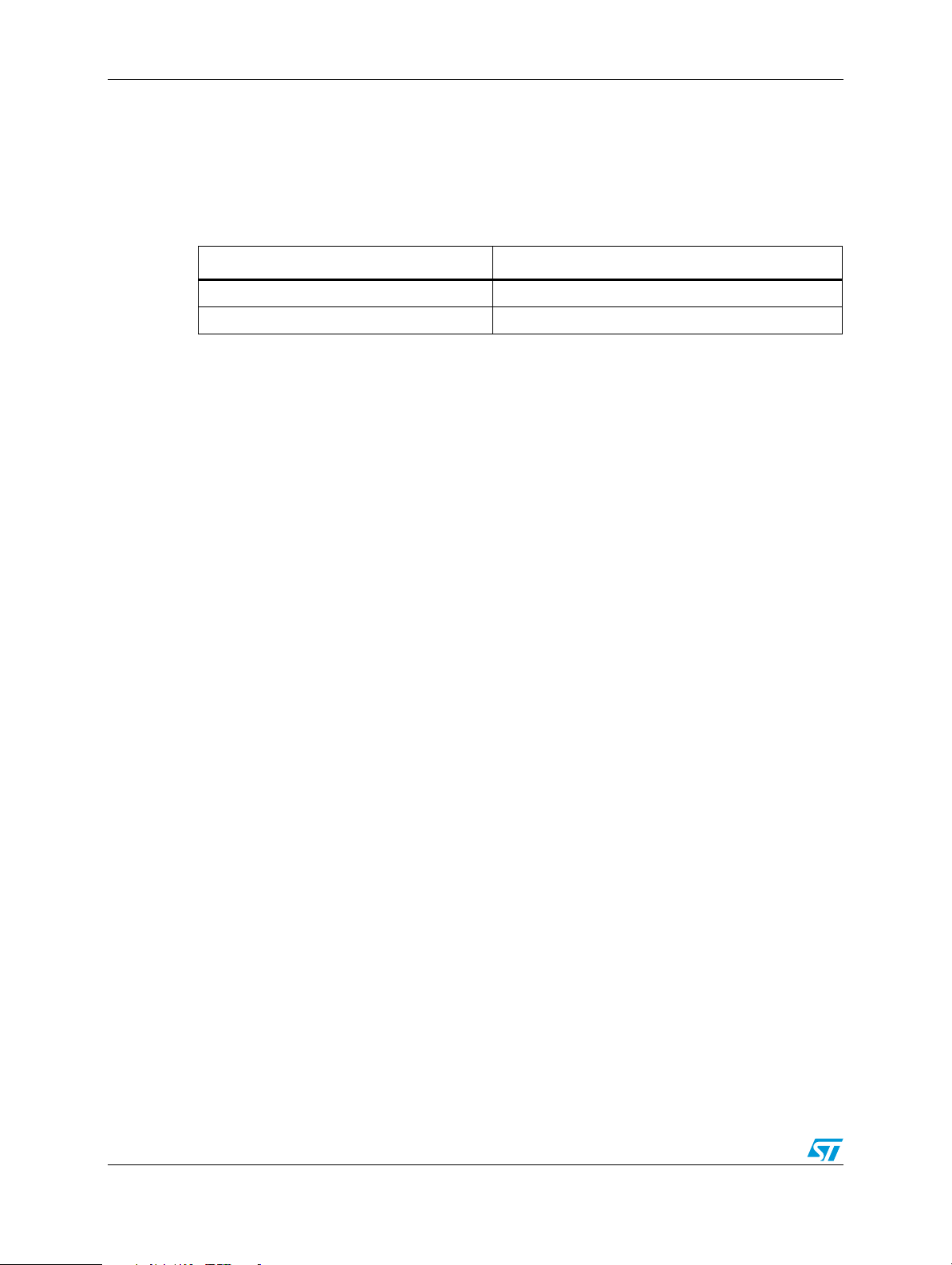
Table 1. Relation between the PL_.... block signals and the used model
PL_.... block signal name IBIS model group name
PL_CLK[4:1] PL_CLK
PL_GPIO[83:0] PL_GPIO
2/12 Doc ID 14454 Rev 1
AN2715 GMAC IBIS model selection
2 GMAC IBIS model selection
The I/O signals of the GMAC interface form two main groups. Please refer to the following
table for the I/O signals and the associated model name.
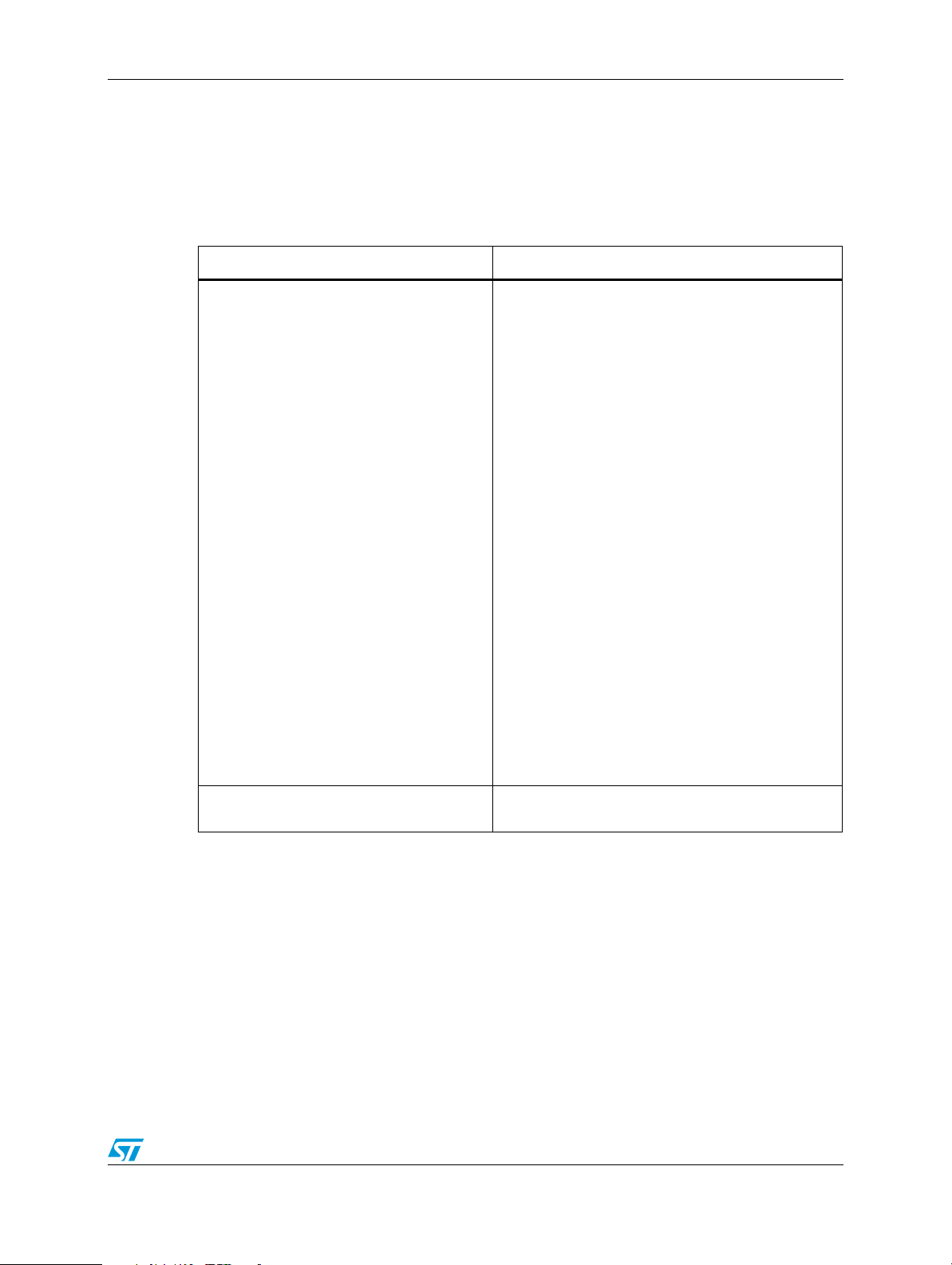
Table 2. Relation between the GMAC block signals and the used model
GMAC block signal name IBIS model group name
GMII_TXCLK
GMII_TXCLK125
MII_TXCLK
TXD_0
TXD_1
TXD_2
TXD_3
GMII_TXD_4
GMII_TXD_5
GMII_TXD_6
GMII_TXD_7
TX_ER
TX_EN
RX_ER
RX_DV
RX_CLK
RXD_0
RXD_1
RXD_2
RXD_3
GMII_RXD_4
GMII_RXD_5
GMII_RXD_7
GMII_RXD_6
COL
CRS
MDIO
MDC
GMAC_HF
GMAC_LF
Doc ID 14454 Rev 1 3/12
SMI IBIS model selection AN2715
3 SMI IBIS model selection
The I/O signals of the SMI interface form two main groups. Please refer to the following table
for the SMI interface I/O signals and the associated model name.
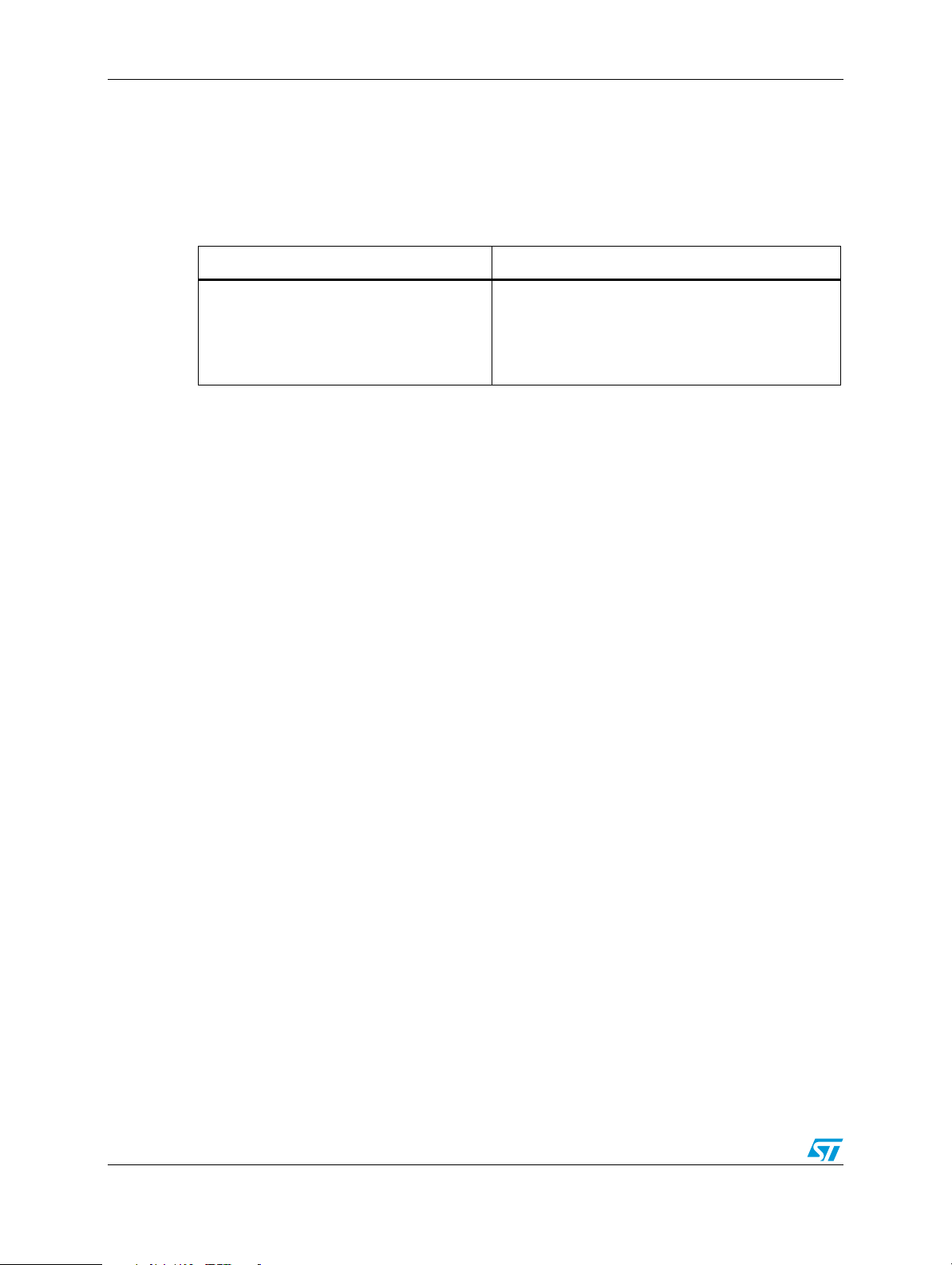
Table 3. Relation between the SMI block signals and the used model
SMI block signal name IBIS model group name
SMI_CLK
SMIDATAIN
SMIDATAOUT
SMICS_0
SMICS_1
PL_GPIO
4/12 Doc ID 14454 Rev 1

AN2715 LVDS IBIS model selection
4 LVDS IBIS model selection
The I/O signals of the LVDS interface form two main groups. Please refer to the following
table for the I/O signals and the associated model name.
Table 4. Relation between the LVDS block signals and the used model
LVD S bl o ck signal name IBIS model group name
PH0
PH0n
PH1
PH1n
PH2
PH2n
PH3
PH3n
PH4
PH4n
PH5
PH5n
PH6
PH6n
PH7
PH7n
PH8
PH8n
LVDS_OUT
LV DS _ IN
Doc ID 14454 Rev 1 5/12

DDR IBIS model selection AN2715
5 DDR IBIS model selection
The I/O signals of the DDR interface form three main groups. Each group has one set of
models associated.
Please refer to the following table for the I/O signals and the assocated model names.
Table 5. Relation between the DDR block signals and the used model
DDR block signal name IBIS model group name
DDR_CLKP & DDR_CLKN
DDR_DQS_0 & DDR_nDQS_0
DDR_DQS_1 & DDR_nDQS_1
DDR_ADD[14,12,10,8,6,4,2,0]
DDR_DATA[15,13,11,9,6,4,2,0]
DDR_GATE_0
DDR_DM_1
DDR_CLKEN
DDR_CS_1
DDR_ODT_1
DDR_BA_1
DDR_CAS
DDR_DIFF_[b7:b0] = DDR_DIFF_xxxxxxxx
DDR_G_SIG_[b7:b3 & b1:b0] =
DDR_G_SIG_xxxxxxx
See Note
(1)
DDR_ADD[13,11,9,7,5,3,1]
DDR_DATA[14,12,10,8,7,5,3,1]
DDR_GATE_1
DDR_DM_0
DDR_CS_0
DDR_ODT_0
DDR_BA_0
DDR_BA_2
DDR_RAS
DDR_WE
1. The b2 bit is not present.
DDR_V_SIG_[b7:b3 & b1:b0] =
DDR_V_SIG_xxxxxxx
See Note
(1)
Each model group name contains a set of models depending upon the value of the 8 bits
[b7:b0] for DDR_DIFF and 7 bits [b7:b3 & b1:b0] for DDR_G_SIG and DDR_V_SIG.
In order to determine the value of these 7 or 8 bits, refer to the user manual of the
SPEAr600 device for the following register names:
● SSTLPAD_CFG_CTR
● MEM11_CTL
6/12 Doc ID 14454 Rev 1

AN2715 DDR IBIS model selection
The correlation between bits 0-8 (or 0-7) of the model group names and the bits of each
register is given below:
● Register SSTLPAD_CFG_CTR (Address 0xFCA800F0).
b7 = SSTLPAD_CFG_CTR [15] = dram_type (1 = DDR2 interface)
b6 = SSTLPAD_CFG_CTR [3] = drive_mode_s_w (1 = Weak drive strength)
b5 = SSTLPAD_CFG_CTR [2] = prog_a (slope of the signals. 00 = slower slope)
b4 = SSTLPAD_CFG_CTR [1] = prog_b (slope of the signals. 11 = higher slope)
b3 = Internal level forced to zero.
b2 = Two cases:
– Internal level forced to zero for CLKP or CLKN signals.
– SSTLPAD_CFG_CTR [12] = pseudo_dif_
This is the bit register value for the signals DQS & nDQS (0 = diff. sig.).
● Register MEM11_CTL [1:0] (Address 0xFC60002C) = rtt_pad_terminat[1:0].
The following table is for the DQS, nDQS and DQ signals only. For all the other signals
b1 = b0 = 0 (no ODT).
Table 6. DQS, nDQS and DQ on die termination (ODT)
MEM11_CTL [1] MEM11_CTL [0] B1 B0 Description
000- ODT disabled
0 1 1 1 ODT= 75 Ohm
1 0 1 0 ODT = 150 Ohm
11 Reserved
Note: “-“ means “don’t care”.
5.1 Example
The setting of the registers SSTLPAD_CFG_CTR and MEM11_CTL is normally done at
each system boot-up by the XLOADER part of the boot code.
Let’s assume, as an example, that at the end of the boot operation the application reads
these two registers and finds the following values:
● Register SSTLPAD_CFG_CTR (Address 0xFCA800F0) = 0x0000EAAD.
● Register MEM11_CTL Register (Address 0xFC60002C) = 0x03000002.
The correct model to be selected from the library with the above values is the following:
Table 7. Example of relation between DDR block signals and the used model
DDR block signal name IBIS model used for application board
DDR_CLKP & DDR_CLKN DDR_DIFF_[b7:b0] = DDR_DIFF_11100000
DDR_DQS_0 & nDDR_DQS_0
DDR_DQS_1 & nDDR_DQS_1
If READ => DDR_DIFF_[b7:b0] = DDR_DIFF_11100010
If WRITE => DDR_DIFF_[b7:b0] = DDR_DIFF_11100000
Doc ID 14454 Rev 1 7/12

DDR IBIS model selection AN2715
Table 7. Example of relation between DDR block signals and the used model (continued)
DDR block signal name IBIS model used for application board
DDR_DATA[15,13,11,9,6,4,2,0]
DDR_ADD[14,12,10,8,6,4,2,0]
DDR_GATE_0
DDR_DM_1
DDR_CLKEN
DDR_CS_1
DDR_ODT_1
DDR_BA_1
DDR_CAS
DDR_DATA[14,12,10,8,7,5,3,1]
DDR_ADD[13,11,9,7,5,3,1]
DDR_GATE_1
DDR_DM_0
DDR_CS_0
DDR_ODT_0
DDR_BA_0
DDR_BA_2
DDR_RAS
DDR_WE
If READ => DDR_G_SIG_[b7:b3 & b1:b0] = DDR_G_SIG_1110010
If WRITE => DDR_G_SIG_[b7:b3 & b1:b0] = DDR_G_SIG_1110000
DDR_G_SIG_[b7:b3 & b1:b0] = DDR_G_SIG_1110000
If READ => DDR_V_SIG_[b7:b3 & b1:b0] = DDR_V_SIG_1110010
If WRITE => DDR_V_SIG_[b7:b3 & b1:b0] = DDR_V_SIG_1110000
DDR_V_SIG_[b7:b3 & b1:b0] = DDR_V_SIG_1110000
Note: In Bold the fixed bx bit values for the STM DDR2 application board.
8/12 Doc ID 14454 Rev 1

AN2715 DDR IBIS model selection
Figure 1. CLKP signal simulation case (for example) with the HyperLynx tool
As shown in the above picture, if the simulation tool supports the model selector function, it’s
pretty easy to select the right model. When you select the pin name of the package (ball
name) to be used in the simulation, the tool points automatically to the signal name and
shows the model group name, listing in a window all the models contained in the group. As
you can see in the model selector windows, all the models with all the available combination
of the 7 or 8 bits are presented.
Knowing the operational mode or the content of the two registers explained in the previous
paragraph, you can select the right model to be used by the simulation. In this specific
example, the selected model is DDR_DIFF_11100000
There are simulation tools that do not support the model selector function. In this case, you
must probably manually remove from the IBIS model library all the models with the bit
settings that are not used in the simulation, only leaving in the library the models with the
combination of bits related to the used operating mode.
Doc ID 14454 Rev 1 9/12

USB IBIS model selection AN2715
6 USB IBIS model selection
All the I/O signals of the USB interface are grouped in one main group.
Please refer to the following table for the I/O signals and the assocated model names.
Table 8. Relation between the USB block signals and the used model
USB block signal name IBIS model group name
USB_DEVICE_DM
USB_DEVICE_DP
USB_HOST2_DM
USB_HOST2_DP
USB_HOST1_DM
USB_HOST1_DP
usb2phy_p3_tx (if transmitter)
usb2phy_p3_rx (if receiver)
10/12 Doc ID 14454 Rev 1

AN2715 Revision history
7 Revision history
Table 9. Document revision history
Date Revision Changes
04-Dec-2009 1 Initial release.
Doc ID 14454 Rev 1 11/12

AN2715
Please Read Carefully:
Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the
right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any
time, without notice.
All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no
liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and services described herein.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted under this document. If any part of this
document refers to any third party products or services it shall not be deemed a license grant by ST for the use of such third party products
or services, or any intellectual property contained therein or considered as a warranty covering the use in any manner whatsoever of such
third party products or services or any intellectual property contained therein.
UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS
OF ANY JURISDICTION), OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS EXPRESSLY APPROVED IN WRITING BY AN AUTHORIZED ST REPRESENTATIVE, ST PRODUCTS ARE NOT
RECOMMENDED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN MILITARY, AIR CRAFT, SPACE, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE SUSTAINING
APPLICATIONS, NOR IN PRODUCTS OR SYSTEMS WHERE FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY,
DEATH, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE. ST PRODUCTS WHICH ARE NOT SPECIFIED AS "AUTOMOTIVE
GRADE" MAY ONLY BE USED IN AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS AT USER’S OWN RISK.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the statements and/or technical features set forth in this document shall immediately void
any warranty granted by ST for the ST product or service described herein and shall not create or extend in any manner whatsoever, any
liability of ST.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of ST in various countries.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners.
© 2009 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
STMicroelectronics group of companies
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Philippines - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
12/12 Doc ID 14454 Rev 1
 Loading...
Loading...