Page 1

AN2710
Application note
Safe GPIO port configuration
in STR7xx devices
Introduction
The general purpose I/O (GPIO) ports of STR7xx devices are programmable by firmware in
several modes: input, output, alternate function, output open drain, output push-pull,
bidirectional weak push-pull and high impedance. It is possible to manage the analog input
mode as well.
This application note describes the best way of configuring the GPIO ports.
February 2008 Rev 1 1/30
www.st.com
Page 2

Contents AN2710
Contents
1 STR71x & STR73x I/O ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1.1 Functional description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
1.2 General-purpose I/O (GPIO) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
1.2.1 Alternate function I/O (AF) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1.2.2 Input configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
1.2.3 Input pull-up/pull-down configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
1.2.4 Output configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
1.2.5 Alternate function configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
1.2.6 High impedance-analog input configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
2 STR75x general-purpose I/O ports (GPIO) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.1 Functional description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
2.1.1 General purpose I/O (GPIO) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2.1.2 Alternate functions (AF) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2.1.3 Input configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2.1.4 Output configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
2.1.5 Alternate function configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
2.1.6 Analog input configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
3 STR7x atomic bit set or bit reset (bit-wise write operations) . . . . . . . 19
4 Recommended configuration sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
4.1 From alternate push-pull . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
4.2 From alternate function open drain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
4.3 From output push-pull . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
4.4 From output open drain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
4.5 From input/output . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
4.6 From input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
4.7 From analog input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
5 Conclusion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
6 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
2/30
Page 3

AN2710 List of tables
List of tables
Table 1. STR71x port bit configuration table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Table 2. STR73x port bit configuration table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Table 3. STR75x Port bit configuration table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Table 4. Alternate push-pull to analog input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Table 5. Alternate push-pull to input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Table 6. Alternate push-pull to Input pull-up/pull-down. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Table 7. Alternate push-pull to output open drain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Table 8. Alternate push-pull to output push-pull . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 9. Alternate push-pull to alternate function open drain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 10. Alternate function open drain to analog input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 11. Alternate function open drain to input. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 12. Alternate function open drain to Input pull-up/pull-down. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 13. Alternate function open drain to output open drain. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 14. Alternate function open drain to output push-pull . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Table 15. Alternate function open drain to alternate function push-pull . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 16. Output push-pull to analog Input. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 17. Output push-pull to input. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 18. Output push pull to Input pull-up/pull-down . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 19. Output push-pull to output open drain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 20. Output push-pull to alternate function open drain. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 21. Output push-pull to alternate function push-pull . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Table 22. Output open drain to analog input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Table 23. Output open drain to input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Table 24. Output open drain to Input pull-up/pull-down . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Table 25. Output open drain to output push-pull . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Table 26. Output open drain to alternate function open drain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Table 27. Output open drain to alternate function push-pull. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Table 28. Input pull-up/pull-down to analog input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
Table 29. Input pull-up/pull-down to Input. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Table 30. Input pull-up/pull-down to output open drain. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Table 31. Alternate Input pull-up/pull-down to output open drain sequence. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Table 32. Input pull-up/pull-down to output push-pull . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Table 33. Alternate sequence: Input pull-up/pull-down to output push-pull . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Table 34. Input pull-up/pull-down to alternate function open drain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Table 35. Alternate sequence: Input pull-up/pull-down to alternate function open drain . . . . . . . . . . 24
Table 36. Input pull-up/pull-down to alternate function push-pull . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Table 37. Input to analog input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Table 38. Input to Input pull-up/pull-down. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Table 39. Input to output open drain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Table 40. Alternate Input to output open drain sequence. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Table 41. Input to output push-pull . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Table 42. Input to alternate function open drain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Table 43. Alternate sequence: Input to alternate function open drain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Table 44. Input to alternate function push-pull . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Table 45. Analog input to input . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Table 46. Analog input to Input pull-up/pull-down. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Table 47. Analog input to output push-pull . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Table 48. Analog input to output open drain. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
3/30
Page 4

List of tables AN2710
Table 49. Analog input to alternate function open drain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Table 50. Analog Input to alternate function push-pull . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Table 51. Document revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
4/30
Page 5

AN2710 List of figures
List of figures
Figure 1. Basic structure of an I/O port bit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Figure 2. Input configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
Figure 3. Input pull-up/pull-down configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Figure 4. Output configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Figure 5. Alternate function configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Figure 6. High impedance-analog input configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Figure 7. Basic structure of an I/O port bit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Figure 8. Input floating/pull-up/pull-down configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Figure 9. Output configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Figure 10. Alternate function configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Figure 11. High impedance-analog input configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
5/30
Page 6
STR71x & STR73x I/O ports AN2710
1 STR71x & STR73x I/O ports
1.1 Functional description
Each of the general purpose I/O ports has three 16-bit Configuration registers (PC0, PC1,
PC2) and one 16-bit Data register (PD).
Subject to the specific hardware characteristics of each I/O port listed in the “Pin
description” table provided in the relevant STR7x datasheet, each port bit can be individually
configured as an input, output, alternate function, etc.
Each I/O port bit is freely programmable, however the I/O port registers have to be accessed
as 16-bit words. 32-bit or byte access is not allowed.
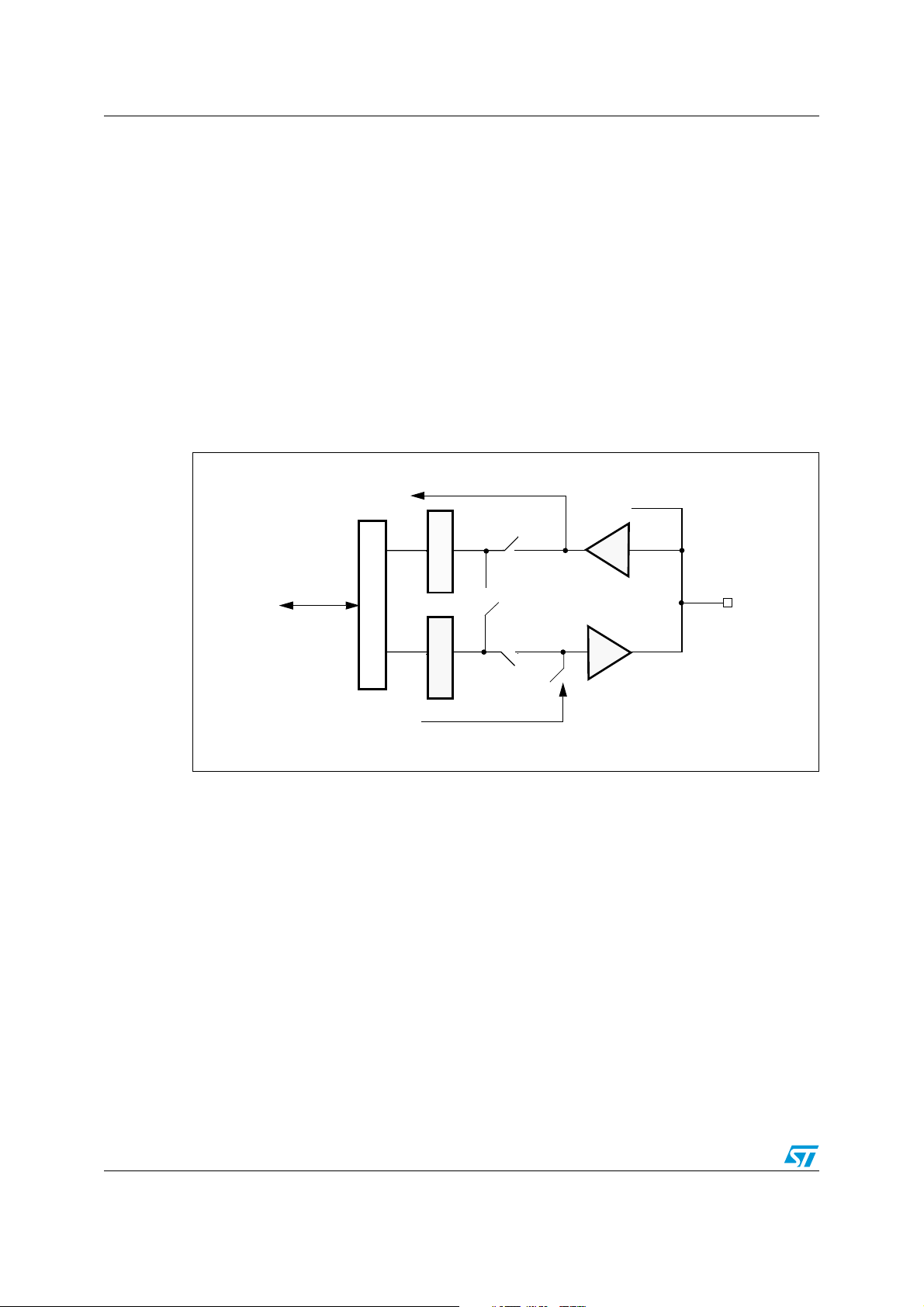
Figure 1 shows the basic structure of an I/O port bit.
Figure 1. Basic structure of an I/O port bit
To on-chip peripheral
Read/Write
I/O Data register
From on-chip peripheral
Alternate function (IN)
Input latch
Output latch
Alternate function (OUT)
TTL
CMOS
Analog input
Push-pull
Tristate
Open drain
Weak push-p ull
I/O pin
ai14915
6/30
Page 7
AN2710 STR71x & STR73x I/O ports
Table 1. STR71x port bit configuration table
Port Configuration
Registers (bit)
(1)
Val ues
PC0(n) 01010101
PC1(n) 00110011
PC2(n) 00001111
Configuration HiZ/AIN IN IN IPUPD OUT OUT AF AF
Output TRI TRI TRI WP OD PP OD PP
Input AIN TTL CMOS CMOS NA NA CMOS CMOS
1. AF = alternate function, AIN = analog input, HiZ = high impedance, IN = input, IPUPD = input pull-up/pulldown, OD = open drain, OUT = output, PP = push-pull, TRI = tristate, TTL = TTL input levels, WP = weak
push-pull.
NA = not applicable. In Output mode, a read access the port will get the output latch value). See Figure 4.
Table 2. STR73x port bit configuration table
(1)
Port
Configuration
Val ues
Registers (bit)
PC0(n) 01 0 10101
PC1(n) 00 1 10011
PC2(n) 00 0 01111
Configuration HiZ/AIN IN
Output TRI TRI WP
reserved
Input - TTL TTL TTL TTL TTL TTL
1. AF = alternate function, AIN = analog input, HiZ = high impedance, IN = input, IPUPD = input pull-up/pulldown, OD = open drain, OUT = output, PP = push-pull, TRI = tristate, TTL = TTL input levels, WP = weak
push-pull.
2. Depending on the PD(n) value, it behaves as weak pull-up (PD=1) or weak pull-down (PD=0)
1.2 General-purpose I/O (GPIO)
At reset the I/O ports are configured as general-purpose (memory mapped I/O).
When the user writes to the I/O Data register, the data are always loaded into the output
latch. The output latch holds the data to be output while the input latch captures the data
present on the I/O pin.
A read access to the I/O Data register reads the input latch or the output latch depending on
whether the port bit is configured as an input or an output.
IPUPD OUT OUT AF AF
(2)
OD PP OD PP
7/30
Page 8
STR71x & STR73x I/O ports AN2710
1.2.1 Alternate function I/O (AF)
The alternate functions for each pin are listed in the datasheet. Configuring a port bit as
alternate function will disconnect the output latch and connect the pin to the output signal of
an on-chip peripheral.
● For alternate function inputs, the port must be configured in Input mode and the input
pin must be driven externally.
Note: It is also possible to emulate the AFI input pin by firmware by programming the GPIO
controller. In this case, the port should be configured in Alternate Function Output mode.
And obviously, the corresponding port should not be driven externally as it will be driven by
the firmware using the GPIO controller.
● For AF output or input-output, the port bit must be in AF configuration.
External interrupts/wakeup lines
Some ports have external interrupt capability (see datasheet). To use external interrupts, the
port must be configured in input mode. For more information on interrupts and wakeup lines,
refer to the reference manual.
1.2.2 Input configuration
When the I/O port is programmed as Input:
● The output buffer is forced tristate
● The data present on the I/O pin are sampled into the input latch with every clock cycle
● A read access to the Data register gets the value in the input latch.
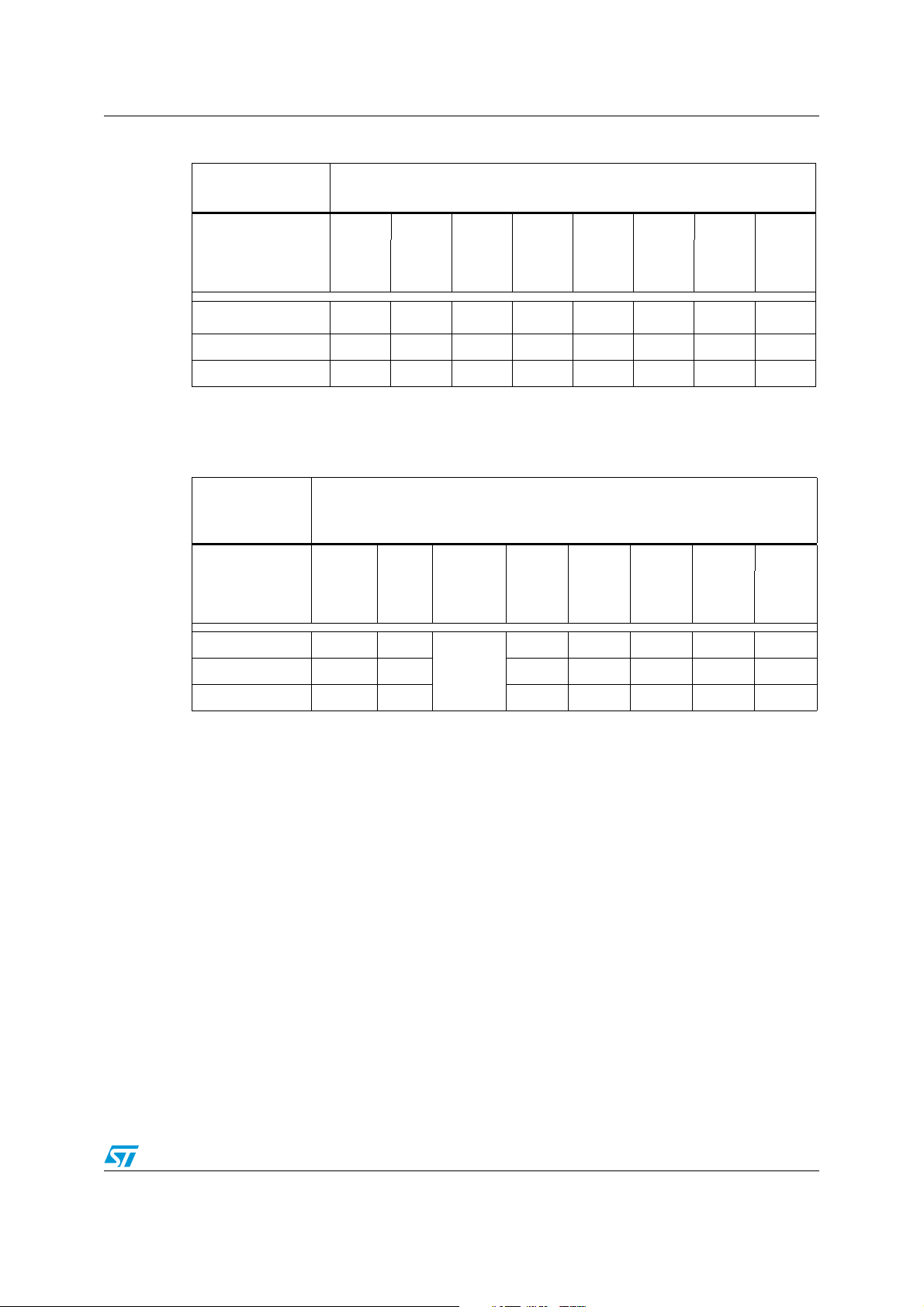
Figure 2 shows the input configuration of the I/O port bit.
Figure 2. Input configuration
Alternate function (IN)
Input latch
I/O Data register
Output latch
Alternate function (OUT)
1. For STR73x only.
TTL
CMOS
Analog input
(1)
Tristate
I/O pin
ai14916
8/30
Page 9
AN2710 STR71x & STR73x I/O ports
1.2.3 Input pull-up/pull-down configuration
When the I/O port is programmed as input pull-up/pull-down:
● The output buffer is turned on in weak push-pull configuration and the firmware can
write the appropriate level into the output latch to activate the weak pull-up or pull-down
as required.
● The data in the output latch drive the I/O pin (a logic zero activates a weak pull-down, a
logic one activates a weak pull-up).
● A read access to the I/O Data register gets the input latch value.
Figure 3 shows the Input pull-up/pull-down configuration of the I/O port.
Figure 3. Input pull-up/pull-down configuration
I/O port Data register
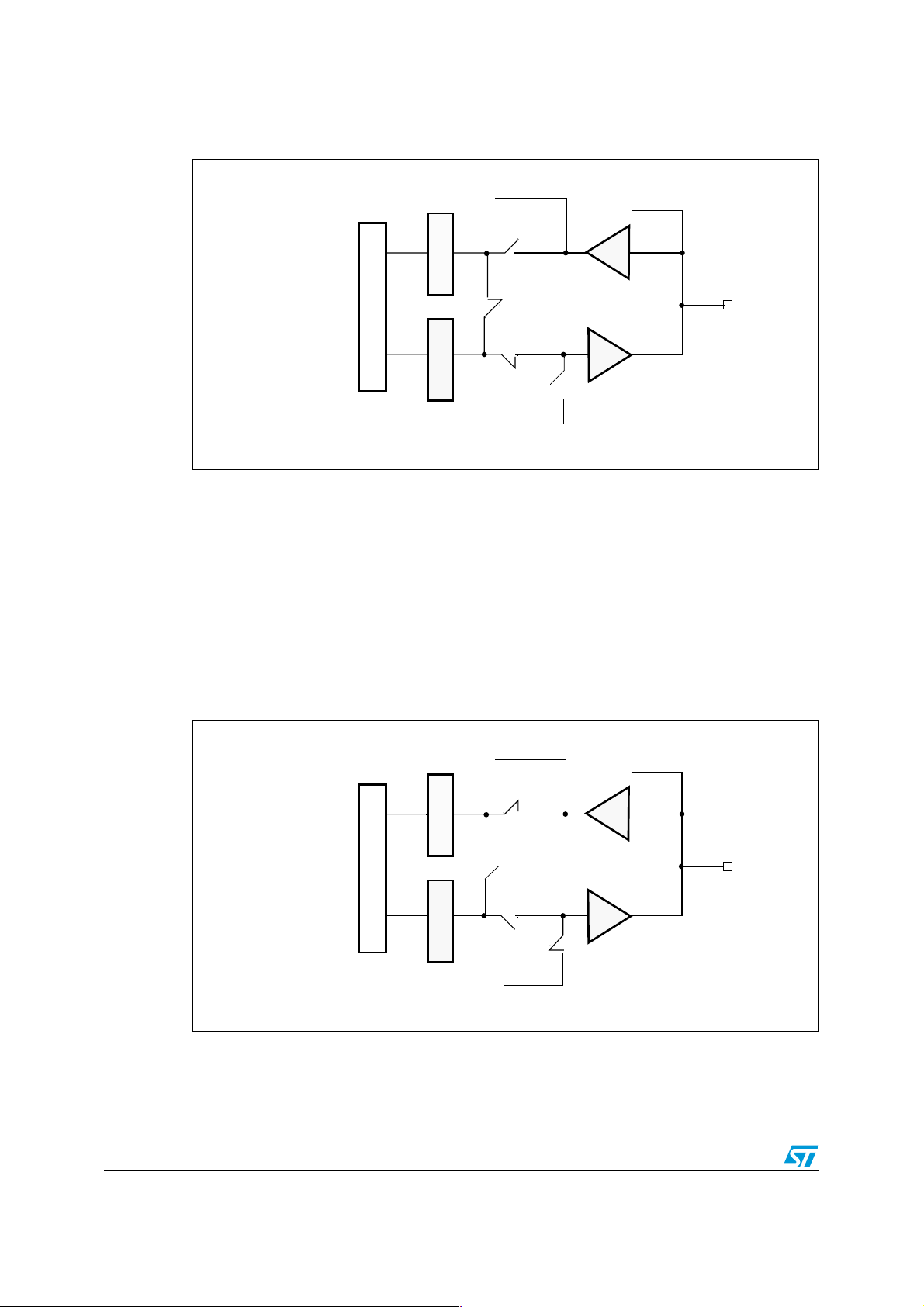
1.2.4 Output configuration
When the I/O port is programmed as output:
● The output buffer is turned on in open drain or push-pull configuration
● The data in the output latch drive the I/O pin
● A read access to the I/O Data register gets the output latch value.
Figure 4 shows the output configuration of the I/O port bit.
Input latch
Output latch
Alternate function (IN)
Alternate function (OUT)
PU
PD
Analog input
When AIEN = 1
I/O pin
Weak push-pull
ai14917
9/30
Page 10
STR71x & STR73x I/O ports AN2710
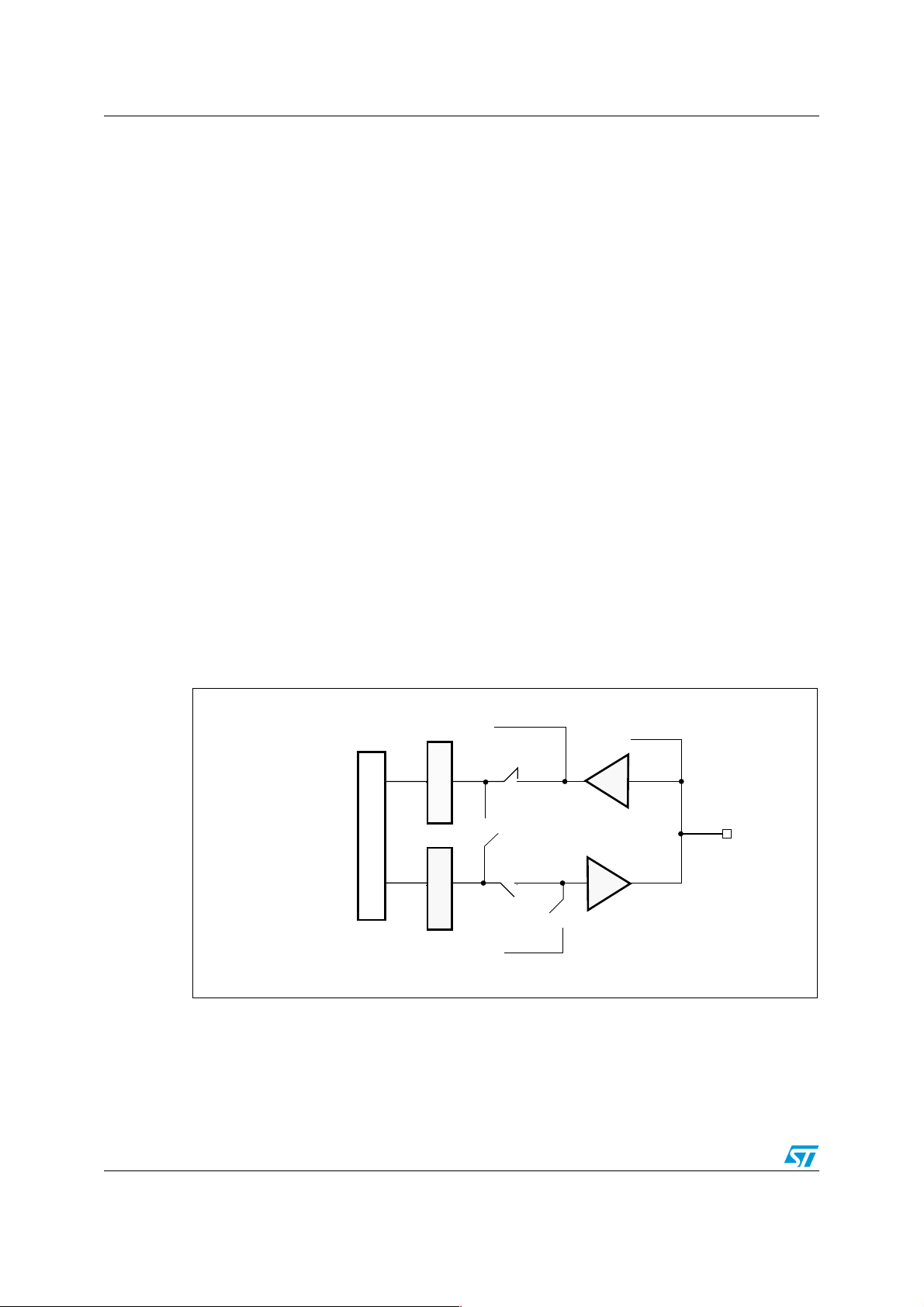
Figure 4. Output configuration
Alternate function (IN)
Input latch
I/O Data register
Output latch
1.2.5 Alternate function configuration
When the I/O port is programmed as alternate function:
● The output buffer is turned on in open drain or push-pull configuration
● The output buffer is driven by the signal coming from the peripheral (alternate function
out)
● The data present on the I/O pin are sampled into the input latch with every clock cycle
● A read access to the Data register gets the value in the Input Latch.
Analog input
I/O pin
Open drain
Push-pull
Alternate function (OUT)
ai14918
Figure 5 shows the Alternate function configuration of the I/O port bit.
Figure 5. Alternate function configuration
Alternate function (IN)
Input latch
I/O Data register
Output latch
Alternate function (OUT)
Analog input
Open drain
Push-pull
I/O pin
ai14919
10/30
Page 11

AN2710 STR71x & STR73x I/O ports
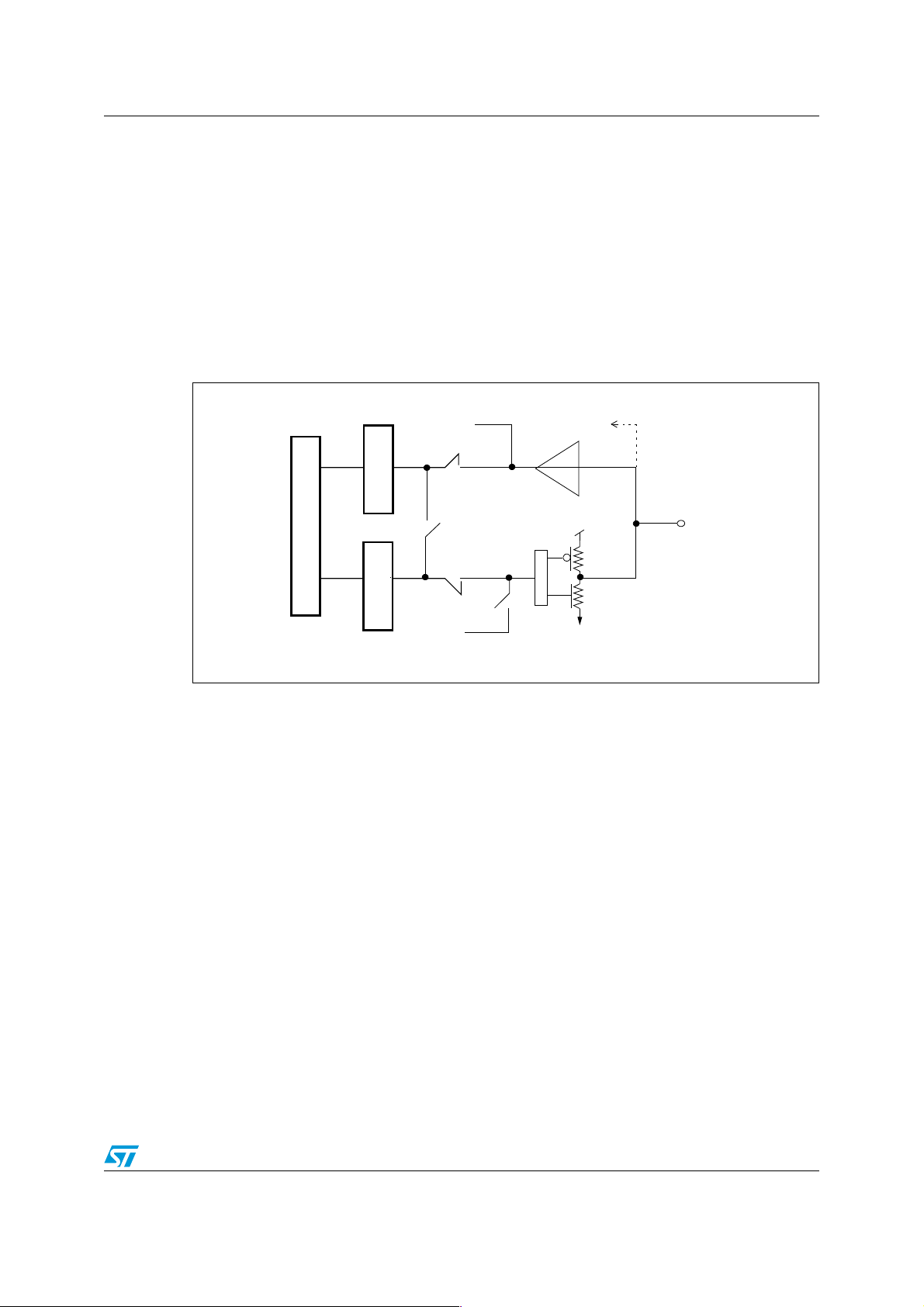
1.2.6 High impedance-analog input configuration
When the I/O port is programmed as high impedance-analog input configuration:
● The output buffer is forced tristate
● The input buffer is disabled (the alternate function input is forced to a constant value)
● The analog input can be input to an analog peripheral
● A read access to the I/O Data register gets the output latch value
Figure 6 shows the high impedance-analog input configuration of the I/O port bit.
Figure 6. High impedance-analog input configuration
Analog input
Input latch
I/O pin
I/O Port Data register
Output latch
Alternate function (OUT)
Tristate
ai14920
Refer to the STR71x and STR73x reference manuals for the I/O port register description.
11/30
Page 12

STR75x general-purpose I/O ports (GPIO) AN2710
2 STR75x general-purpose I/O ports (GPIO)
2.1 Functional description
Each of the general-purpose I/O ports has three 32-bit configuration registers (PC0, PC1,
PC2), a 32-bit Data register (PD) and a 32-bit mask register (PM).
Subject to the specific hardware characteristics of each I/O port listed in the datasheet, each
port bit of the general-purpose I/O (GPIO) ports, can be individually configured by firmware
in several modes:
● Input floating
● Input pull-up
● Input pull-down
● Analog input
● Output open-drain
● Output push-pull
● Alternate function
Each I/O port bit is freely programmable, however the I/O port registers have to be accessed
as 32-bit words (half-word or byte accesses are not allowed). The purpose of the mask
register is to allow atomic read/modify accesses (or bitwise write accesses) to any of the
GPIO registers. In this way, there is no risk of an IRQ occurring between a read access and
a modify access.
Figure 7 shows the basic structure of an I/O port bit.
Figure 7. Basic structure of an I/O port bit
ON/OFF
Analog
switch
ON/OFF
TTL Schmitt
trigger
Output
control
To on-chip
peripheral
Read/Write
From on-chip
peripheral
Analog input
Alternate function input
Input data latch
I/O Data register
Output data latch
Alternate function output
Input driver
Output driver
AFOEN
ON/OFF
ON/OFF
V
DD_IO
P-MOS
N-MOS
V
SS
V
DD_IO
Pull
up
Pull
down
V
SS
Push-pull,
Open-drain or
disabled
V
DD_IO
V
Protection
diode
Protection
diode
SS
I/O pin
ai14922
12/30
Page 13

AN2710 STR75x general-purpose I/O ports (GPIO)
Table 3. STR75x Port bit configuration table
Input
Output
Configuration mode Input buffer
Input floating (reset state) Input floating I/O pin don’t care 0 0 1
Input floating Input Floating I/O pin don’t care 0 1 0
Input pull-down TTL Pull-Down I/O pin 0 0 1 1
Input pull-up TTL Pull-Up I/O pin 1 0 1 1
Analog input AIN 0 don’t care 0 0 0
Output open-drain TTL floating I/O pin 0 or 1 1 0 0
Output push-pull not used
Alternate function open-drain TTL floating I/O pin don’t care 1 1 0
Alternate function push-pull TTL floating I/O pin don’t care 1 1 1
2.1.1 General purpose I/O (GPIO)
During and just after reset the alternate functions are not active and the I/O ports are
configured in Input Floating mode (PxC2=0, PxC1=0, PxC0=1).
PxD Register
Read
access
last value
written
PxC2
Write
access
0 or 1 1 0 1
Register
PxC1
Register
Register
PxC0
When configured as output, the value written to the I/O Data register is loaded into the
output latch. The output latch holds the data to be output. It is possible to use the output
driver in Push-Pull or Open-Drain mode (only the N-MOS is activated when outputting 0).
The input latch captures the data present on the I/O pin at every APB clock cycle.
A read access to the I/O Data register reads the input latch or the output latch depending on
whether the port bit is configured as input or output Open-Drain or Push-Pull.
All GPIO pins features weak internal pull-up and pull-down resistors which can or not be
activated when configured as inputs.
In all low-power modes, except for the Standby mode, GPIO states are preserved. In
Standby mode, all GPIOs are put in high impedance with the exception of the WKP_STDBY
pin which is kept in input mode.
Note: Care must be taken when configuring an I/O port from one mode to another, because an
unexpected intermediate state could disturb the application. Program the registers using
only intermediate states that do not disturb your application. For instance, it is important to
know that in "analog input" mode, the Schmitt trigger output is forced to '0'.
2.1.2 Alternate functions (AF)
It is necessary to program the Port Bit Configuration Register before using a default
alternate function.
● For alternate function inputs, the port must be configured in Input mode (floating, pull-
up or pull-down) and the input pin must be driven externally
Note: It is also possible to emulate the AFI input pin by firmware by programming the GPIO
controller. In this case, the port should be configured in Alternate Function Output mode.
13/30
Page 14

STR75x general-purpose I/O ports (GPIO) AN2710
And obviously, the corresponding port should not be driven externally as it will be driven by
the firmware using the GPIO controller.
● For alternate function outputs, the port must be configured in Alternate Function Output
mode (push-pull or open-drain).
● For bidirectional alternate functions, the port bit must be configured in Alternate
Function Output mode (push-pull or open-drain). In this case the input driver is
configured in input floating mode
Configuring a port bit as Alternate Function Output will disconnect the output latch and
connect the pin to the output signal of an on-chip peripheral.
If firmware configures a GPIO pin as Alternate Function Output, but no peripheral output
alternate function exists for that pin (refer to the datasheet pin description table), its output is
not specified.
Special case of SSP bidirectional alternate functions
When using the SSP, the MISO, MOSI, NSS and SCK alternate functions consist of
bidirectional alternate functions. They must be configured as alternate function output
through the Port Configuration register:
● When configuring the SSP in master mode, the MISO pin is automatically used as an
alternate function input and the output driver is automatically disabled (even if still
programmed as alternated function output in the Port Configuration registers).
In addition, when configured in master mode, the MOSI pin is always driven (never left
Hi-Z) even if the SSP is in idle mode (no transmission)
● When configuring the SSP in slave mode, the MOSI, SCK and NSS pins are
automatically configured as alternate functions inputs and the output drivers are
automatically disabled (even if still programmed as alternated function outputs in the
Port Configuration registers).
In addition, when configured in slave mode, the MISO pin is left Hi-Z when the NSS pin
is high or when the SOD control bit (Slave Output Disable) is set.
Configuring I2C alternate functions
After reset release, the I2C is able to detect a Start condition on the SDA and SCL lines even
2
if the I
reference manual)
Consequently, care must be taken when configuring SDA and SCL as alternate function
open-drain in order not to create parasitic falling edges.
The states to avoid are:
● output 0
● input pull-down
● analog input (because the output of the Schmitt trigger goes to 0)
14/30
C is not configured. (Refer to the SDA/SCL line control section in the STR75x
Page 15

AN2710 STR75x general-purpose I/O ports (GPIO)
Consequently, the configuration must be done in the following order:
1. Reset state: PC2,1,0=001 PD=0: input floating
-> SDA=SCL = '1' due to external pull-up
2. Write PD=1: PC2,1,0=001 PD=1: input floating
-> SDA=SCL = '1' due to external pull-up
3. Write PC1=1: PC2,1,0=011 PD=1: input pull-up
-> SDA=SCL = '1' due to internal and external pup
4. Write PC0=0: PC2,1,0=010 PD=1: input floating
-> SDA=SCL = '1' due to external pull-up
5. Write PC2=1: PC2,1,0=110 PD=1: AF Open Drain
-> SDA=SCL = '1' because the I2C does not drive the line when disabled (I2C PE=0)
2.1.3 Input configuration
When the I/O port is programmed as an input:
● The output buffer is disabled
● The Schmitt trigger Input is activated
● The analog switch is disabled
● The weak pull-up and pull-down resistors are activated or not depending on the input
configuration (pull-up, pull-down or floating):
● The data present on the I/O pin are sampled into the input latch with every APB clock
cycle
● A read access to the Data register gets the value in the input latch.
Figure 8 shows the input configuration of the I/O port bit.
Figure 8. Input floating/pull-up/pull-down configurations
V
DD_IO
ON/OFF
ON/OFF
V
SS
Read/write
ON
Input data latch
Input driver
Output driver
I/O Data register
Output data latch
TTL Schmitt
trigger
pullup
pulldown
V
DD_IO
V
Protection
diode
I/O pi n
Protection
diode
SS
ai14923
15/30
Page 16

STR75x general-purpose I/O ports (GPIO) AN2710
2.1.4 Output configuration
When the I/O port is programmed as an output:
● The output buffer is enabled:
– Open Drain mode: a “0” in the output latch activates the N-MOS while a “1” in the
output latch leaves the port in Hi-Z (the P-MOS is never activated)
– Push-Pull mode: a “0” in the output latch activates the N-MOS while a “1” in the
output latch activates the P-MOS
● The Schmitt trigger input is activated
● The analog switch is disabled
● The weak pull-up and pull-down resistors are disabled
● The data present on the I/O pin is sampled into the input latch with every APB clock
cycle
● A read access to the I/O Data register gets:
– the output latch value in Push-Pull mode (which corresponds to the last data
written)
– the input latch value in Open-Drain mode
Figure 9 shows the output configuration of the I/O port bit.
Figure 9. Output configuration
Input data latch
Read/write
I/O Data register
Output data latch
Input driver
Output driver
ON
TTL Schmitt
trigger
Output
control
V
V
DD_IO
SS
P-MOS
N-MOS
Push-pull or
open-drain
V
DD_IO
V
Protection
diode
Protection
diode
SS
I/O pin
ai14924
16/30
Page 17

AN2710 STR75x general-purpose I/O ports (GPIO)
2.1.5 Alternate function configuration
When the I/O port is programmed as an alternate function:
● The output buffer is turned on in open drain or push-pull configuration
● The output buffer is driven by the signal coming from the peripheral (alternate function
out)
● The Schmitt trigger input is activated
● The analog switch is disabled
● The weak pull-up and pull-down resistors are disabled
● The data present on the I/O pin are sampled into the input latch with every APB clock
cycle
● A read access to the I/O Data register gets:
– the output latch value in Push-Pull mode (which corresponds to the last data
written)
– the input latch value in Open-Drain mode
Figure 10 shows the alternate function configuration of the I/O port bit.
Figure 10. Alternate function configuration
To on-chip
peripheral
From on-chip
peripheral
Alternate Function Input
Read/write
Input data latch
I/O Data register
Output data latch
Alternate Function Output
2.1.6 Analog input configuration
When the I/O port is programmed as an analog input:
● The output buffer is disabled
● The Schmitt trigger input is de-activated, providing zero consumption for every analog
value of the I/O pin. The output of the Schmitt trigger is forced to a constant value (0).
● The weak pull-up and pull-down resistors are disabled
● The analog switch is enabled by the ADC each time a conversion is in progress
● Read access to the I/O Data register gets the input latch value (0)
TTL Schmitt
trigger
Input driver
Output driver
control
Output
ON
V
DD_IO
V
SS
P-MOS
N-MOS
Push-pull or
open-drain
V
DD_IO
V
Protection
diode
Protection
diode
SS
I/O pin
ai14925
Figure 11 shows the high impedance-analog input configuration of the I/O port bit.
17/30
Page 18

STR75x general-purpose I/O ports (GPIO) AN2710
Figure 11. High impedance-analog input configuration
ON when converting
Analog
switch
OFF
0
TTL Schmitt
trigger
To on-chip
peripheral
Read/write
From on-chip
peripheral
Analog Input
Input data latch
Input driver
I/O Data register
Output data latch
Refer to STR75x reference manual for the I/O port registers description.
V
DD_IO
V
Protection
diode
Protection
diode
SS
I/O pin
ai14926
18/30
Page 19

AN2710 STR7x atomic bit set or bit reset (bit-wise write operations)
3 STR7x atomic bit set or bit reset (bit-wise write
operations)
The bitwise instructions proposed by the "ARM7 Instruction Set" only apply to the internal
ARM7 Ri registers. Consequently, it is not possible to directly perform bitwise write
operations (like a bit set or a bit clear) on an I/O Port register. Three operations are required:
● Load the whole Port Data register into an Ri register
● Modify the Ri register using the bitwise ARM7 instruction
● Store back the whole result from the Ri register into the Port Data Register
Since this is not an atomic operation, an interrupt subroutine (ISR) may happen to be served
between the load access and the store access. If the ISR sets or clears some other Port
register bits, the port might be corrupted when the data are stored back into the Port
register. Consequently, if the interrupt subroutines are susceptible to modify the other bits of
the I/O port being written, it is recommended to disable the interrupts during bitwise write
operations.
With the STR75x, however, this is not needed because it features a Port Mask Register. The
purpose of the Port Mask Register is to allow atomic read/modify accesses (or bitwise write
operations) to any of the GPIO registers. In this case, you simply need to:
● first program the Port Mask Register (PxM) to mask the bits that you do not want
modified
● then, program the port registers (PxC2, PxC1, PxC0 and PxD). The masked bits will
not be modified.
This mask applies to all the Configuration and Data registers (PxC3, PxC1, PxC0 and PxD).
Note: It is recommended that each interrupt subroutine that accesses the port registers stacks the
Port Mask Register. Otherwise, an interrupt occurring between the modification of the PxM
register and a bit manipulation on the PxD registers might lead to a corruption of the port
bits.
19/30
Page 20

Recommended configuration sequence AN2710
4 Recommended configuration sequence
It appears that the safest sequence for writing the Port Configuration registers in most
situations is: PC2 - PC1 - PC0.
Exceptions to this would be in the following transitions:
1. Input/Output to Output open drain
2. Input/Output to Output push-pull
3. Input/Output to Alternate Function open drain
4. Input to Output open drain
5. Input to Alternate Function open drain
In all of these cases the safest sequence for writing the PC registers is: PC0 - PC1 - PC2.
Note: It is possible to have a level change on a pin during transition between open drain and push-
pull output modes. The resulting output level may be determined by the state of the GPIO
output, alternate function output and/or external pull-up/down (if any). The user needs to be
aware of the output state when changing the pin configuration.
4.1 From alternate push-pull
If the port is set to alternate push-pull, use the following sequences to change modes.
Table 4. Alternate push-pull to analog input
PC2 - 0 IPUPD
PC1 - 0 Input
PC0 - 0 No change
1. Input pull-up/pull-down.
Table 5. Alternate push-pull to input
PC2 - 0 IPUPD
PC1 - 0 Input
PC0 - 1 No change
1. Input pull-up/pull-down.
Table 6. Alternate push-pull to Input pull-up/pull-down
PC2 - 0 IPUPD
PC1 - 1 No change
PC0 - 1 No change
1. Input pull-up/pull-down.
Table 7. Alternate push-pull to output open drain
PC2 - 1 No change
(1)
(1)
(1)
PC1 - 0 Output push-pull
PC0 - 0 Output open drain
20/30
Page 21

AN2710 Recommended configuration sequence
Table 8. Alternate push-pull to output push-pull
PC2 - 1 No change
PC1 - 0 Output push-pull
PC0 - 1 No change
Table 9. Alternate push-pull to alternate function open drain
PC2 - 1 No change
PC1 - 1 No change
PC0 - 0 Alternate function open drain
4.2 From alternate function open drain
If the port is set to alternate function open drain, use the following sequences to change
modes.
Table 10. Alternate function open drain to analog input
PC2 - 0 Reserved/Input
PC1 - 0 Analog input
PC0 - 0 No change
Table 11. Alternate function open drain to input
PC2 - 0 Reserved/Input
PC1 - 0 Analog input
PC0 - 1 IN
Table 12. Alternate function open drain to Input pull-up/pull-down
PC2 - 0 Reserved/Input
(1)
PC1 - 1 No change
PC0 - 1 IPUPD
1. Reserved for STR73x only
2. Input pull-up/pull-down.
Table 13. Alternate function open drain to output open drain
(2)
PC2 - 1 No change
PC1 - 0 Output open drain
PC0 - 0 No change
Table 14. Alternate function open drain to output push-pull
PC2 - 1 No change
PC1 - 0 Output open drain
PC0 - 1 Output push pull
21/30
Page 22

Recommended configuration sequence AN2710
Table 15. Alternate function open drain to alternate function push-pull
PC2 - 1 No change
PC1 - 1 No change
PC0 - 1 Alternate function push-pull
4.3 From output push-pull
if the port is set to output push-pull, use the following sequences to change modes.
Table 16. Output push-pull to analog Input
PC2 - 0 Input
PC1 - 0 No change
PC0 - 0 Analog input
Table 17. Output push-pull to input
PC2 - 0 Input
PC1 - 0 No change
PC0 - 1 No change
Table 18. Output push pull to Input pull-up/pull-down
PC2 - 0 Input
PC1 - 1 IPUPD
(1)
PC0 - 1 No change
1. Input pull-up/pull-down.
Table 19. Output push-pull to output open drain
PC2 - 1 No change
PC1 - 0 No change
PC0 - 0 Output open drain
Table 20. Output push-pull to alternate function open drain
PC2 - 1 No change
PC1 - 1 Alternate function push-pull
PC0 - 0 Alternate function open drain
Table 21. Output push-pull to alternate function push-pull
PC2 - 1 No change
PC1 - 1 Alternate function push-pull
PC0 - 1 No change
22/30
Page 23

AN2710 Recommended configuration sequence
4.4 From output open drain
If the port is set to output open drain, use the following sequences to change modes.
Table 22. Output open drain to analog input
PC2 - 0 Analog input
PC1 - 0 No change
PC0 - 0 No change
Table 23. Output open drain to input
PC2 - 0 Analog input
PC1 - 0 No change
PC0 - 1 Input
Table 24. Output open drain to Input pull-up/pull-down
PC2 - 0 Analog Input
PC1 - 1 Reserved/Input
PC0 - 1 Input/Output
1. Reserved for STR73x only
Table 25. Output open drain to output push-pull
PC2 - 1 No change
PC1 - 0 No change
PC0 - 1 Output push-pull
Table 26. Output open drain to alternate function open drain
PC2 - 1 No change
PC1 - 1 Alternate function push-pull
PC0 - 0 No change
Table 27. Output open drain to alternate function push-pull
PC2 - 1 No change
PC1 - 1 Alternate function open drain
PC0 - 1 Alternate function push-pull
(1)
4.5 From input/output
if the port is set to Input/Output, use the following sequences to change modes.
Table 28. Input pull-up/pull-down to analog input
PC2 - 0 No change
PC1 - 0 Input
PC0 - 0 Analog input
23/30
Page 24

Recommended configuration sequence AN2710
Table 29. Input pull-up/pull-down to Input
PC2 - 0 No change
PC1 - 0 Input
PC0 - 1 No change
Table 30. Input pull-up/pull-down to output open drain
PC2 - 1 Alternate function push-pull
PC1 - 0 Output push-pull
(2)
(1)
PC0 - 0 Output open drain
1. Glitch possible if the alternate function is a test function.
2. Glitch possible if OUTPUT=1 with no external pull-up.
Alternatively, the following sequence can be used:
Table 31. Alternate Input pull-up/pull-down to output open drain sequence
PC0 - 0 Reserved
PC1 - 0 Analog input
PC2 - 1 Output open drain
Table 32. Input pull-up/pull-down to output push-pull
PC2 - 1 Alternate function push-pull
(1)
PC1 - 0 Output push-pull
PC0 - 1 No change
1. Glitch possible if alternate function is a test function.
Alternatively, the following sequence can be used:
Table 33. Alternate sequence: Input pull-up/pull-down to output push-pull
PC0 - 1 No change
PC1 - 0 Input
PC2 - 1 Output push-pull
Table 34. Input pull-up/pull-down to alternate function open drain
PC2 - 1 Alternate function push-pull
(1)
PC1 - 1 No change
PC0 - 0 Alternate function open drain
1. Glitch possible if alternate function is a test function and if OUTPU=1 with no external pull-up.
Alternatively, the following sequence can be used:
Table 35. Alternate sequence: Input pull-up/pull-down to alternate function open
drain
PC0 - 0 Reserved/Input
PC1 - 1 No change
PC2 - 1 Alternate function open drain
24/30
Page 25

AN2710 Recommended configuration sequence
Table 36. Input pull-up/pull-down to alternate function push-pull
PC2 - 1 Alternate function push-pull
PC1 - 1 No change
PC0 - 1 No change
4.6 From input
If the port is set to Input, use the following sequences to change modes.
Table 37. Input to analog input
PC2 - 0 No change
PC1 - 0 No change
PC0 - 0 Analog input
Table 38. Input to Input pull-up/pull-down
PC2 - 0 No change
PC1 - 0 IPUPD
PC0 - 1 No change
Table 39. Input to output open drain
PC2 - 1 Output push-pull
PC1 - 0 No change
(1)
PC0 - 0 Output open drain
1. Glitch possible if OUTPUT =1 with no external pull-up
Alternatively, the following sequence can be used:
Table 40. Alternate Input to output open drain sequence
PC0 - 0 Analog input
PC1 - 0 No change
PC2 - 1 Output open drain
Table 41. Input to output push-pull
PC2 - 1 Alternate function push-pull
PC1 - 0 Output push-pull
PC0 - 1 No change
25/30
Page 26

Recommended configuration sequence AN2710
Table 42. Input to alternate function open drain
PC2 - 1 Output push-pull
PC1 - 1 Alternate function push-pull
PC0 - 0 No change
1. Glitch possible if OUTPUT differs from ALT OUTPUT value
2. Glitch possible if OUTPUT = 1 with no external pull-up
3. Glitch possible if alternate function is a test function
(1)
(2)
(3)
Alternatively, the following sequence can be used:
Table 43. Alternate sequence: Input to alternate function open drain
PC0 - 0 Analog Input
PC1 - 1 Reserved
PC2 - 1 Alternate function open drain
Table 44. Input to alternate function push-pull
PC2 - 1 Output push-pull
PC1 - 1 Alternate function push-pull
PC0 - 1 No change
4.7 From analog input
if the port is set to Analog Input, use the following sequences to change modes.
Table 45. Analog input to input
PC2 - 0 No change
PC1 - 0 No change
PC0 - 1 Input
Table 46. Analog input to Input pull-up/pull-down
PC2 - 0 No change
PC1 - 1 Reserved
PC0 - 1 IPUPD
1. Input pull-up/pull-down.
Table 47. Analog input to output push-pull
PC2 - 1 Output open drain
PC1 - 0 No change
PC0 - 1 Output push-pull
(1)
26/30
Page 27

AN2710 Recommended configuration sequence
Table 48. Analog input to output open drain
PC2 - 1 Output open drain
PC1 - 0 No change
PC0 - 0 No change
Table 49. Analog input to alternate function open drain
PC2 - 1 Output open drain
PC1 - 1 Alternate function push-pull
PC0 - 0 No change
Table 50. Analog Input to alternate function push-pull
PC2 - 1 Output push-pull
PC1 - 1 Alternate function open drain
PC0 - 1 Alternate function push-pull
27/30
Page 28

Conclusion AN2710
5 Conclusion
This application note gives practical information on how to configure the GPIO ports in
STR7xx MCUs. It also provide the safest sequences to change I/O port configurations while
avoiding any unexpected intermediate state that might disturb an application.
28/30
Page 29

AN2710 Revision history
6 Revision history
Table 51. Document revision history
Date Revision Changes
14-Feb-2008 1 Initial release.
29/30
Page 30

AN2710
Please Read Carefully:
Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the
right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any
time, without notice.
All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no
liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and services described herein.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted under this document. If any part of this
document refers to any third party products or services it shall not be deemed a license grant by ST for the use of such third party products
or services, or any intellectual property contained therein or considered as a warranty covering the use in any manner whatsoever of such
third party products or services or any intellectual property contained therein.
UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS
OF ANY JURISDICTION), OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS EXPRESSLY APPROVED IN WRITING BY AN AUTHORIZED ST REPRESENTATIVE, ST PRODUCTS ARE NOT
RECOMMENDED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN MILITARY, AIR CRAFT, SPACE, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE SUSTAINING
APPLICATIONS, NOR IN PRODUCTS OR SYSTEMS WHERE FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY,
DEATH, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE. ST PRODUCTS WHICH ARE NOT SPECIFIED AS "AUTOMOTIVE
GRADE" MAY ONLY BE USED IN AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS AT USER’S OWN RISK.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the statements and/or technical features set forth in this document shall immediately void
any warranty granted by ST for the ST product or service described herein and shall not create or extend in any manner whatsoever, any
liability of ST.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of ST in various countries.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners.
© 2008 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
STMicroelectronics group of companies
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
30/30
 Loading...
Loading...