Page 1

AN2658
Application note
Using the analog to digital converter of the STM8S microcontroller
Introduction
The purpose of this application note is to explain how to use the Analog to Digital Converter
implemented in many of the STM8S microcontroller family devices. It provides useful
information on how to configure the ADC registers and microcontroller resources and use
the ADC in different modes.
The STM8 firmware library, containing source code of all the examples described in this
application note, can be downloaded from the STMicroelectronics website: www.st.com.
July 2009 Doc ID 14152 Rev 2 1/23
www.st.com
Page 2

Contents AN2658
Contents
1 ADC hardware description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
1.1 General properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
1.2 ADC operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
2 Summary of features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.1 Resolution . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.2 Clock selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
2.3 Conversion triggers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.4 ADC speed/sampling time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.5 Voltage reference . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.6 Input analog channel selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
2.7 Data storage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2.8 Extended functions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2.8.1 Buffers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2.8.2 Buffer overrun flag . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
2.8.3 Analog watchdog . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
2.8.4 Scan mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
2.8.5 Bandgap reference channel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
3 Configuring ADC registers for conversion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
3.1 Selecting the operating mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
3.1.1 Single conversion mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
3.1.2 Continuous conversion mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
3.1.3 Conversion on external trigger . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
3.1.4 Scan conversion mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
3.2 Conversion speed selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
3.3 Analog input selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
3.4 Storing converted values . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
3.5 Analog watchdog function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
3.6 ADC interrupt management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
4 Practical application . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
4.1 Areas of use . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
2/23 Doc ID 14152 Rev 2
Page 3

AN2658 Contents
4.2 Hardware connection examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
4.3 Methods for precision improvement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
5 Design recommendations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
6 Displaying the ADC conversion result using LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
6.1 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
6.2 Hardware description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
6.3 Firmware description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
7 ADC conversion triggered by TIM1 timer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
7.1 Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
7.2 Hardware description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
7.3 Firmware description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
8 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Doc ID 14152 Rev 2 3/23
Page 4

ADC hardware description AN2658
1 ADC hardware description
1.1 General properties
STM8 family microcontrollers include one Analog to Digital Converter which has up to 16
multiplexed inputs. Depending on the STM8 device, the ADC can be one of two types:
● A basic ADC type named ADC2
● An extended ADC type named ADC1
The resolution of both ADC types is 10 bits. The number of external analog inputs depends
on the package size of the chosen STM8 family device.
The ADC is a successive approximation Analog to Digital Converter (SAR). Conversion can
be performed in continuous mode or single mode. The analog input channels can be
selected individually or in scan mode. In scan mode, several channels are converted in
sequence, the channel number is incremented for each conversion. The digital result is then
stored in registers. Because the ADC resolution is 10 bits and the ADC data register bit
length is 16, one ADC result is stored in two 8-bit registers. The 10-bit data is either right or
left aligned (this is selectable) in the 16-bit register. Devices with ADC1 can use buffered
mode for data storage. In this case, the values converted by the ADC are stored in N data
buffers (to decrease CPU overhead).
The event used to start conversion can be generated by software or by the STM8
microcontroller's internal timer 1 (any type of timer event can be used). The start of A/D
conversion can also be triggered by an external pin.
The reference voltage for the ADC depends from package. It comes either from an external
source - in this case the reference must be connected to two external pins - or is connected
internally to analog power supply pins. The value of this reference voltage is restricted in its
magnitude - must be from 2.75V up to V
and V
. Resolution can be increased by so-called analog zooming - using a smaller
REF-
. The measured voltage must be between V
DDA
REF+
reference voltage around the range of values to be measured.
Devices with ADC1 have an analog watchdog function. This function compares the
converted data with high and low thresholds and if a threshold is reached then the analog
watchdog flag is set.
If needed, an interrupt can be generated at the end of conversion and if an analog watchdog
event occurred.
The ADC is driven by a clock derived from the MCU master clock through a programmable
divider. This allows you to select the ADC clock speed according to your application
requirements.
4/23 Doc ID 14152 Rev 2
Page 5
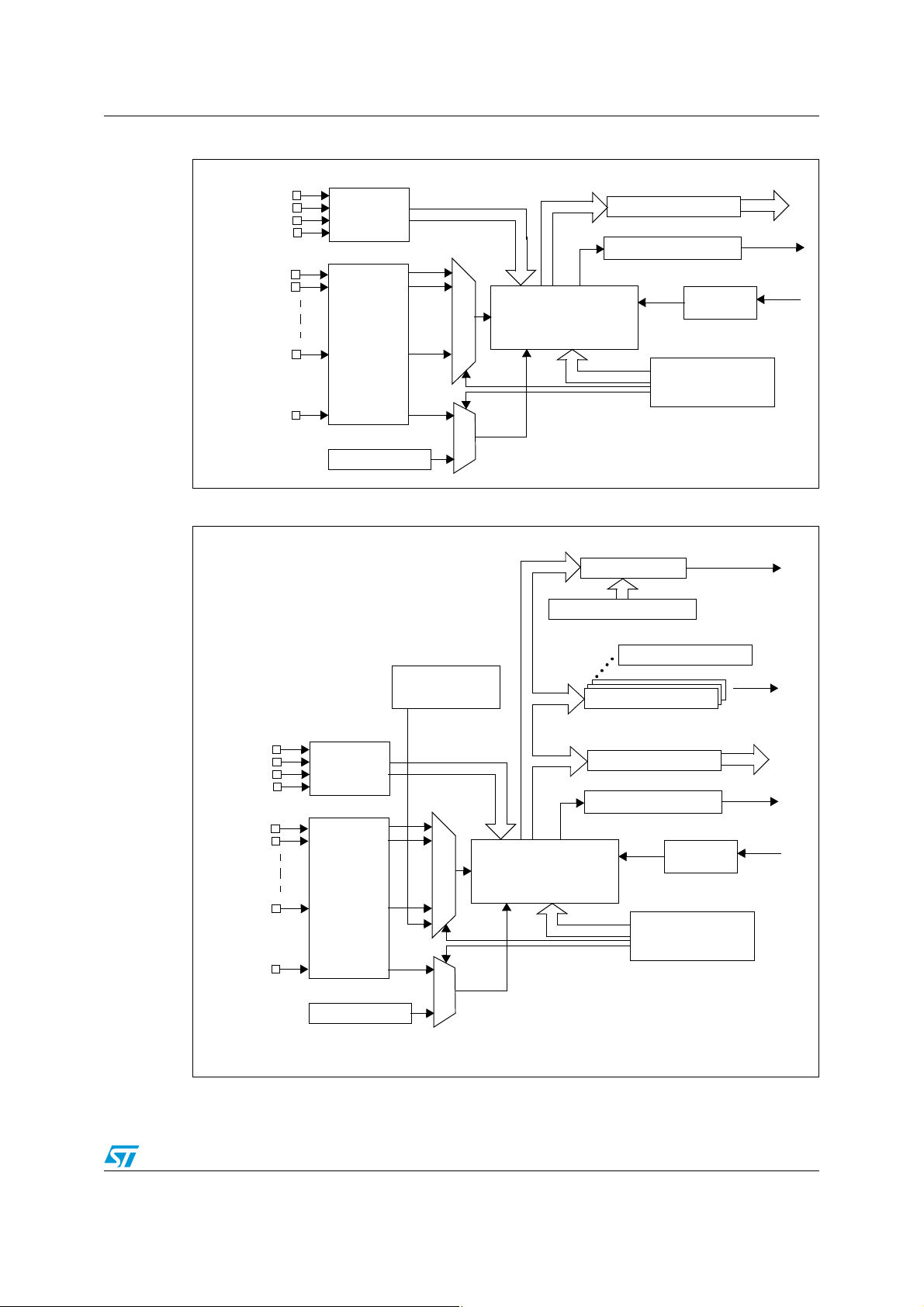
AN2658 ADC hardware description
V
REF+
V
REF-
V
DDA
V
SSA
Power/Analog
pins
AIN0
GPIOs
AIN1
AIN15
ADC_ETR
Timer 1
Analog to digital converter
ADC registers
Clock
End of conversion
Data bus
EOC interrupt
Data register (10-bits)
f
MASTER
f
ADC
prescaler
trigger
V
REF+
V
REF-
V
DDA
V
SSA
Power/Analog
pins
AIN0
GPIOs
AIN1
AIN15
ADC_ETR
Timer 1
Analog to digital converter
ADC registers
Clock
End of conversion
Data bus
Overrun flag
Data register (10-bits)
f
MASTER
f
ADC
prescaler
trigger
Data buffer register 1
Data buffer register n
Bandgap reference
Analog watchdog registers
AWD interrupt
EOC interrupt
U = 1.232V
Analog watchdog
Figure 1. ADC2 block diagram (basic ADC)
Figure 2. ADC1 block diagram (extended ADC)
Doc ID 14152 Rev 2 5/23
Page 6
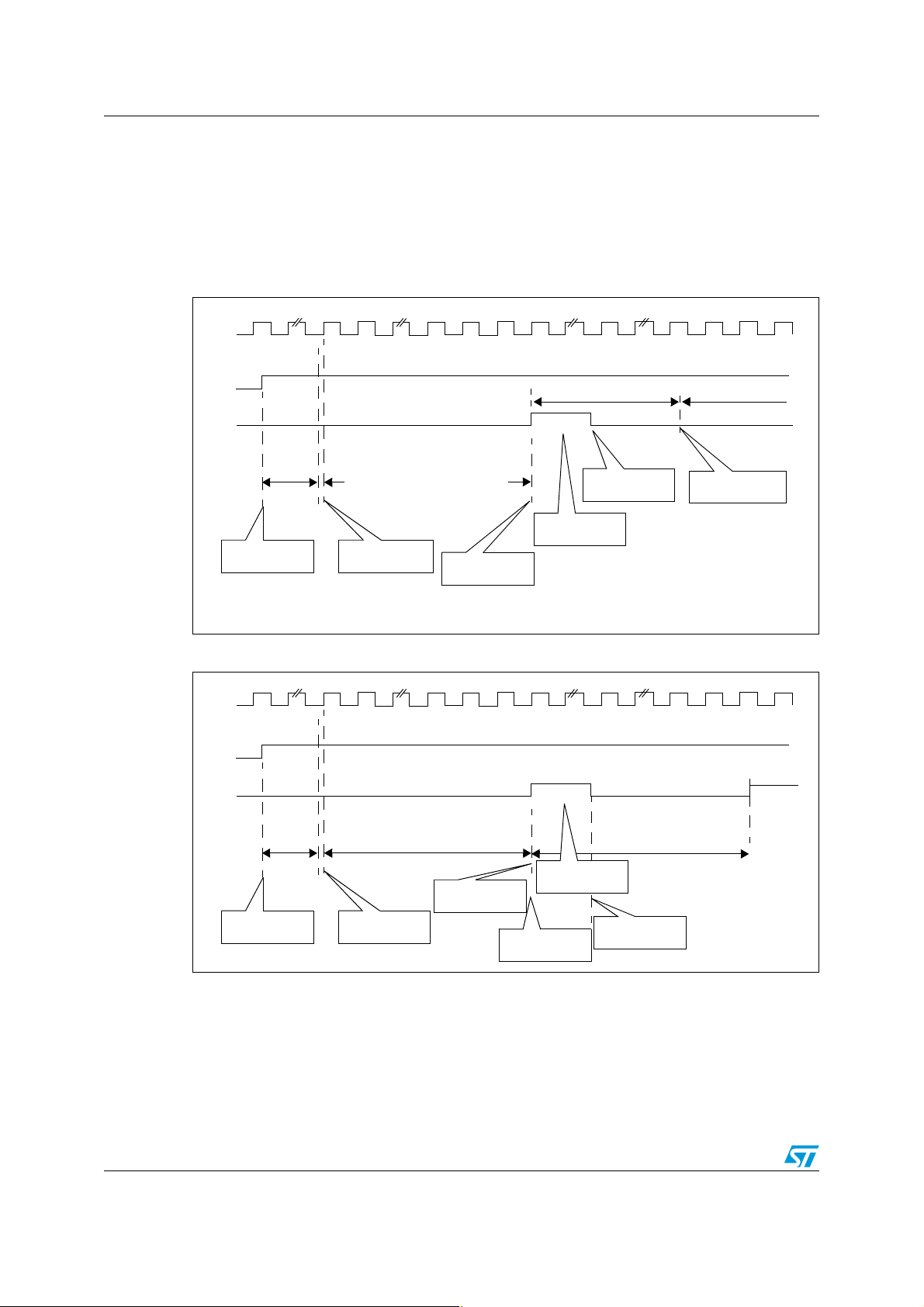
ADC hardware description AN2658
conversion time (14 clocks)
sync clock*
3 clocks sampling time
10 clocks conversion
Power-on ADC
ADON=1
CLK
ADON
EOC
t
STAB (7µs)
Start conversion
ADON=1 or trigger
End of conversion
Software reads
ADC data
Software clears
EOC bit
Start conversion
ADON=1 or trigger
ADC inactive
next conversion
conversion time (14 clocks)
Power-on ADC
ADON=1
CLK
ADON
EOC
t
STAB (7µs)
Start conversion
ADON=1 or trigger
End of conversion
Software clears
EOC bit
Next conversion
starts immediately
next conversion time (14 clocks)
Software reads
ADC data
1.2 ADC operation
The ADC can operate in single or continuous mode. In single mode, the ADC stops after
one conversion. In continuous mode, it continues converting (on the same channel or
different channel).
Figure 3. and Figure 4. describe ADC operation in single and continuous mode.
Figure 3. Single conversion mode
Figure 4. Continuous conversion mode
In devices with ADC1, these two modes can be usefully combined with scan mode and use
of the data buffer registers (buffered mode).
Figure 5. shows all the possible ADC1 operating modes. ADC2 does not support scan and
buffered modes.
6/23 Doc ID 14152 Rev 2
Page 7
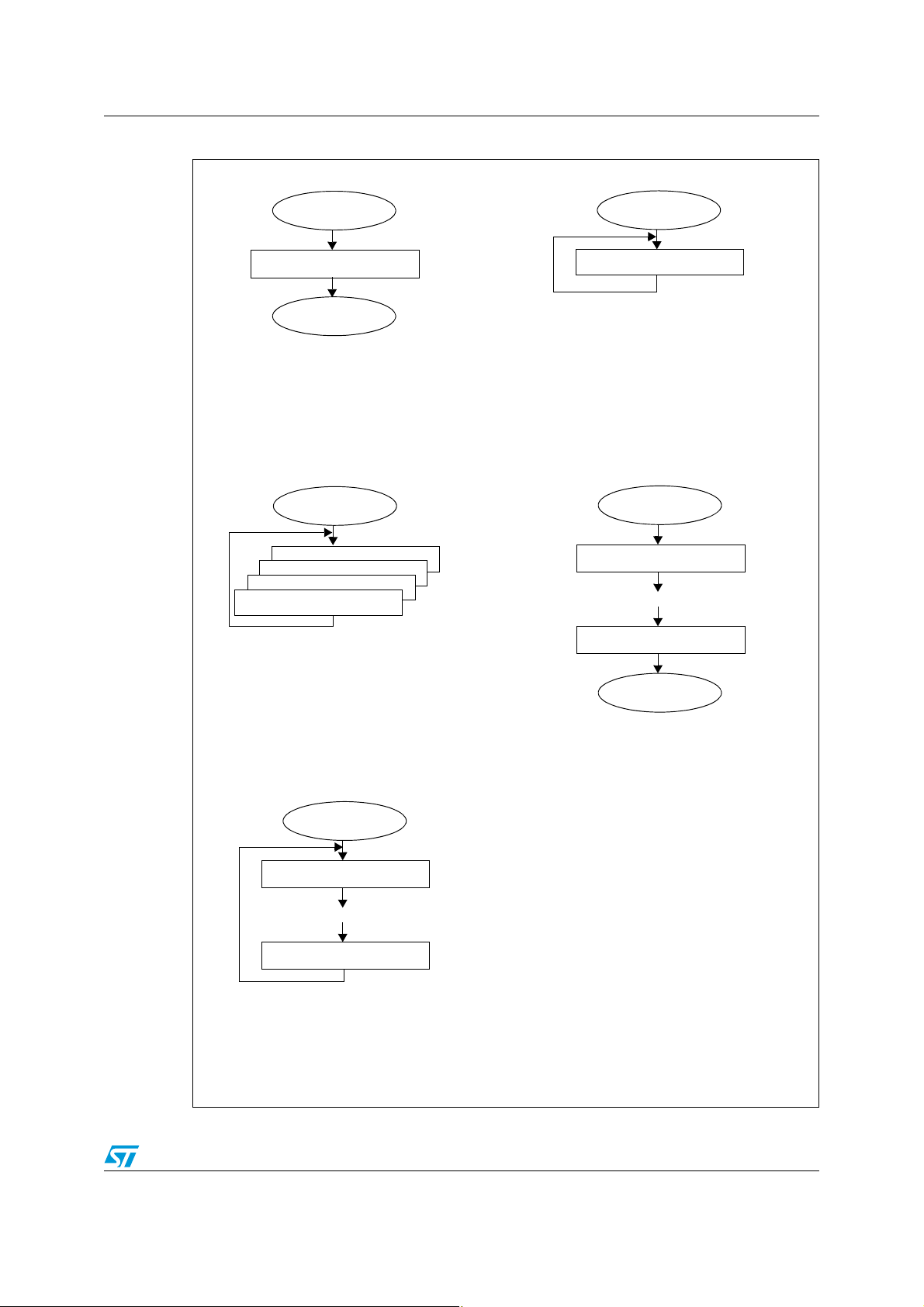
AN2658 ADC hardware description
Start
Stop
Channel 1 conversion
Multiple channels
Scan conversion (buffered)
Start
Channel X conversion
Single channel
Continuous conversion
Start
Channel X conversion
Single channel
Continuous and
Buffered conversion
...
Channel n conversion
Start
Stop
Channel X conversion
Single channel
Single conversion
Channel X conversion
Channel X conversion
Channel X conversion
Start
Channel 1 conversion
Multiple channel
Continuous and
Scan conversion (buffered)
...
Channel n conversion
Figure 5. ADC1 operating modes
Doc ID 14152 Rev 2 7/23
Page 8

Summary of features AN2658
2 Summary of features
Table 1. below summarizes the main features of the STM8 ADC.
Table 1. STM8 ADC features
Feature STM8 ADC
Resolution 10-bit
Clock speed f
Triggers Software, timer or external pin trigger
Operating modes Single or continuous mode
Conversion speed (14 clocks) 2.33 µs @ 6 MHz f
Reference voltage
Number of input channels Up to 16 channels
= 1 to 4 or 6 MHz (refer to datasheet)
ADC
ADC
and V
V
REF+
2.75 V ÷ V
Note: In some packages V
external pins:
REF-
range, analog zooming possible
DDA
and V
REF+
REF-
these cases the reference voltages are V
VSS)
are not available, in
or V
DDA
DD and VSSA
or
Data format Optional left or right alignment
Buffers
(1)
Special functions
1. Available only on ADC1 (extended ADC type)
2.1 Resolution
The STM8 ADC converter has 10-bit resolution. A special extra feature of the STM8 is that,
to read the conversion results faster, and if you can accept lower resolution; you can read
only 8 of the 10 bits, provided that you select the appropriate register alignment.
The register for configuring right or left data alignment is ADC_CR2.
2.2 Clock selection
The A/D conversion speed is given by the ADC clock signal. This clock speed must be
between 1 MHz and 4 or 6 MHz (refer to datasheet). The ADC clock frequency is selected
by dividing the frequency of the master clock.
The register for clock speed selection is ADC_CR1.
(1)
Up to 16 data buffer registers (depending on the number of
channels)
Scan mode, analog watchdog, buffer overrun flag, bandgap
reference voltage channel
8/23 Doc ID 14152 Rev 2
Page 9

AN2658 Summary of features
2.3 Conversion triggers
ADC conversion can be triggered by a Timer1 TRGO (trigger output) event or by a rising
edge on the ADC_ETR external pin. Conversion can also be triggered by software, by
setting the ADON bit.
The register for trigger selection is ADC_CR2.
2.4 ADC speed/sampling time
The ADC speed (and also sampling time) influences the measurement precision and must
be chosen depending on the output impedance of the measured voltage source and the
required conversion precision. The sampling time cannot be set independently from the
ADC clock.
The ADC speed can be chosen from f
MASTER
microcontroller internal clock. The maximum speed of ADC conversion in the STM8 ADC is
2.33 µS.
The register for selecting the ADC clock division factor is ADC_CR1.
2.5 Voltage reference
The ADC reference voltage must be connected to the external pins or in most packages is
connected internally to analog power supply. The reference voltage must be within the
analog power supply range and the minimum reference voltage value is 2.75V.
2.6 Input analog channel selection
The STM8 ADC has up to 16 analog inputs connected to GPIO input pins. There are fewer
analog inputs on some devices (this depends on the device package). Pins with ADC
function must be configured as floating input and the input Schmidt trigger on these pins
should be disabled (this reduces power consumption).
The register for selecting the input analog channel is ADC_CSR.
/2 down to f
MASTER
/18 where f
MASTER
is the
Doc ID 14152 Rev 2 9/23
Page 10

Summary of features AN2658
D1 D0
D1 D0
D3 D2D5 D4D7 D6
D9 D8
D9 D8 D3 D2D5 D4D7 D6
ADC_DRH
70
ADC_DRL
70
ADC_DRH
70
ADC_DRL
70
Left alignment mode:
Right alignment mode:
2.7 Data storage
The 10 bits of ADC converted data are stored in two 8-bit registers (and in ADC1 type also
in the buffer registers - see Figure 6.: Data alignment).
The STM8 ADC has selectable data alignment. You can choose to left or right align the 10bit ADC result in the two 8-bit data registers.
You must read the data registers in a particular order to ensure that the data retrieved from
the registers is consistent (resulting from the same conversion). When the first data register
is read, the second data register is latched so it can be read later and to prevent it being
overwritten by the next conversion. The order in which you must read the data registers
depends on the alignment mode. In right alignment mode, the LSB must be read first and
then the MSB. In left alignment mode, the MSB must be read first and then the LSB.
Figure 6. Data alignment
2.8 Extended functions
These extended functions are present only in devices with ADC1.
2.8.1 Buffers
Devices with ADC1 have a set of registers for data storage which are used when buffered
mode is enabled. The converted data are stored cyclically in these registers (ring buffer).
This makes data storage and collection more efficient (less CPU load and less data buffer
overrun issues).
The number of data buffer registers is equal to the number of ADC1 input channels and
depends on the STM8 device type.
2.8.2 Buffer overrun flag
10/23 Doc ID 14152 Rev 2
This flag is set when the values in the ADC1 data buffer registers are overwritten before
being read by the CPU. The user firmware can use this flag detect an overrun event and can
then perform appropriate actions (for example restart A/D conversion).
Page 11

AN2658 Summary of features
ADC_HTR
ADC_LTR
t
V
in
AWD flag is set
AWD interrupt
2.8.3 Analog watchdog
The analog watchdog compares the last converted value with high and low thresholds.
When a threshold is reached then a flag is set and interrupt can be generated.
This is a useful way of checking for critical analog values without CPU intervention.
Figure 7. Analog watchdog operation
2.8.4 Scan mode
Scan mode allows AD conversion to be performed on consecutive channels. When one AD
conversion is performed on the n-th channel, then channel n+1 is selected as input channel
and the next AD conversion is performed on this channel.
The sequence of channels to be converted starts from channel 1 (always 1) to a selectable
channel N. Channel N is set by programming the input channel selection bits.
If continuous mode is used together with scan mode, then the channels are cyclically
repeated, from the N-th channel back to channel 1 etc.
2.8.5 Bandgap reference channel
Some devices with ADC1 have a bandgap voltage block which is connected to an input
channel (usually the last channel). The purpose of this voltage block is to provide a stable,
precise voltage reference for ADC calibration. Calibration can may be needed because the
analog supply (V
The method of using the bandgap voltage for improving ADC accuracy is based on
periodically performing an ADC conversion of the bandgap voltage input, then calculating an
offset from the result and applying this offset to the results on the other channels.
(postprocessing).
Refer to the device datasheet to determine if a bandgap reference channel is present in the
STM8 device you are using.
DDA
and V
, depends on an external power source.
SSA)
Doc ID 14152 Rev 2 11/23
Page 12

Configuring ADC registers for conversion AN2658
3 Configuring ADC registers for conversion
3.1 Selecting the operating mode
The ADC converter can operate in different modes according to application requirements.
The following sections list the various operating modes, the register settings required to use
the ADC in each mode and the practical uses in each case.
3.1.1 Single conversion mode
In this mode, the ADC performs only one conversion. Conversion start is triggered either by
software writing to the ADON bit or by a signal from Timer1 or from an external signal on the
ADC_ETR pin (rising edge).
There must be a new start of conversion generated before the next single conversion (either
by external trigger or by software).
Register settings:
ADC_CR1: CONT = 0
ADC_CR3: DBUF = 0 or 1 (data buffer registers not used or used)
Practical use: This mode can be used to collect an analog value from an external sensor
(for example to read a temperature periodically).
3.1.2 Continuous conversion mode
In this mode, the ADC performs conversions cyclically. When one conversion has finished,
then the next conversion starts immediately. Data must be collected from the data registers
before they are overwritten by the next conversions.
Register settings:
ADC_CR1: CONT = 1
ADC_CR3: DBUF = 0 or 1 (data buffer registers “not used” or “used”)
Practical use: To collect a set of analog values from an external analog signal (for example
to read an AC voltage waveform).
3.1.3 Conversion on external trigger
Conversion can be started by writing to the ADON control bit or by external trigger. The
external trigger source event can be a Timer1 TRGO event or a rising edge on the external
ADC_ETR pin.
Register settings:
ADC_CR2: EXTSEL and EXTTRIG bits
ADC_CR3: DBUF = 0 or 1 (data buffer registers “not used” or “used”)
Practical use: To measure analog values at regular intervals (timer trigger) or when a user
input occurs (external pin trigger - pushbutton).
3.1.4 Scan conversion mode
In this mode, the ADC performs a sequence of conversions from channel 1 up to a selected
channel number. When one conversion has finished, then the next conversion starts
immediately on the next channel. Data are stored incrementally in data buffer registers
12/23 Doc ID 14152 Rev 2
Page 13

AN2658 Configuring ADC registers for conversion
ADC_DBx (if DBUF bit is set) from which they must be retrieved before they are overwritten
by the next set of conversions (especially if continuous mode is also selected).
Register settings:
ADC_CR2: SCAN bit
ADC_CR3: DBUF = 0 or 1 (data buffer registers “not used” or “used”)
Practical use: To collect a set of analog values from different inputs in one shot (for
example to read a sample of several AC voltage waveforms almost simultaneously).
3.2 Conversion speed selection
The total conversion speed of an ADC depends proportionally on the ADC clock frequency,
the sampling time duration and on the ADC resolution. The ADC clock speed must be
selected by selecting the division factor to be applied to the internal master clock. The
sampling time is not customizable and depends on the ADC clock (3 ADC clocks).
Register settings:
ADC_CR1: SPSEL[2:0] bits
3.3 Analog input selection
The device has up to 16 external analog inputs connected to GPIO input pins. Pins to be
used as ADC input function must be configured as floating inputs and the input Schmitt
triggers on these pins should be disabled to avoid unnecessary power consumption. If the
application changes the analog input channel during conversion then the current conversion
is stopped and the next conversion starts on the new channel.
If scan mode is selected then the channel bits define the top channel in the scan sequence
(from channel 1 to the top channel).
Register settings:
ADC_CSR: CH[3:0] bits
3.4 Storing converted values
The converted ADC value is stored in the ADC_DRH and ADC_DRL registers. If buffered
mode is selected then data are stored cyclically in the data buffer registers ADC_DBxRH
and ADC_DBxRL (x= 0..N, N is device dependent, refer to the datasheet).
Because the converted value has a 10 bit length and the data registers have 2x8 bit length,
it is possible to select left or right alignment of the conversion result in the data registers. In
left alignment the 8 most significant bits are stored in a single register, in right alignment the
8 least significant bits are stored in a single register. This can be chosen to suit the
application. Data register reading is buffered - when the first register is read, the second
register is automatically stored in a shadow register to be read later. This prevents reading
data register values from 2 different conversions.
The first register to be read depends on the data alignment. You must read the MSB first in
left alignment mode and read LSB first in right alignment mode.
Doc ID 14152 Rev 2 13/23
Page 14

Configuring ADC registers for conversion AN2658
Right alignment has the advantage of fast read access when measuring low level signals. In
cases where the result does not affect the high order bits, you can read only the least
significant byte.
Practical usage: Left alignment is useful for fast read access to the conversion result in 8bit resolution.
Register settings:
ADC_CR3: DBUF bit
ADC_CR2: ALIGN bit
ADC_CR3: OVR bit
3.5 Analog watchdog function
The converted ADC sample is compared with the high and low analog watchdog threshold
registers. If the threshold is reached then the AWD flag is set and another status bit in the
analog watchdog status register to indicate the channel on which the event occurred. The
analog watchdog function can be enabled for selected channels only by setting the
corresponding bits in the ADC_AWCRx control registers.
Register settings:
ADC_HTRH, ADC_HTRL, ADC_LTRH, ADC_LTRL - high and low thresholds
ADC_AWCRH, ADC_AWCRL - control registers
ADC_AWSRH, ADC_AWSRL - status registers
ADC_CSR: AWDIE and AWD bits
3.6 ADC interrupt management
ADC interrupt source(s) are selectable from one or more of the following events:
● End of conversion (EOC) in non buffered mode: generated after each AD conversion
● End of conversion (EOC) in buffered mode: generated after data buffer registers are full
● Analog watchdog alert: when converted values reach the high or low threshold values
Event-driven programming can be used for efficiency or for special software requirements.
With this technique, when the main program is running, it is notified of state changes by
events. You can enable the ADC interrupt to give the main program fast asynchronous event
notification at the end of conversion(s). This means the main program does not need to poll
the ADC conversion status flags but only has to process the ADC data results (for example
after storing a set of conversions in a buffer). The reception of the ADC converted data
values is performed by an interrupt routine in the background. In addition, the analog
watchdog interrupt can be used for monitoring a given analog range on the measured
channels.
Register settings:
ADC_CSR: AWDIE, EOCIE bits
14/23 Doc ID 14152 Rev 2
Page 15

AN2658 Practical application
STM8
V
REF-
V
SS
AINx
U
IN
4 Practical application
4.1 Areas of use
● Temperature measurement:
– Process calibration
– Device thermal protection
– Fan control
● Power supply measurement:
– Auto save configuration
– Battery charging/protection
● Measurement of physical values in other types of application:
– Automation: from sensors with analog outputs
– Household: automatic lights dimmers, weather stations, thermometers, security
sensors, …
– Industry: lights, thermostats, humidity control, …
– Electrical quantity measurements: voltage, current, capacity, resistance, …
4.2 Hardware connection examples
Figure 8. Simple unipolar DC signal measurement
Doc ID 14152 Rev 2 15/23
Page 16

Practical application AN2658
STM8
V
REF-
V
SS
AINx
U
IN
+
-
R1
R2
STM8
V
REF-
V
SS
AINx
U
IN
-
+
R2
R4
R1
R3
STM8
V
REF-
V
SS
AINx
U
IN
DC
filter
Figure 9. External preamplifier usage (with high impedance input)
Figure 10. Differential DC signal measurement with preamplifier
Figure 11. AC signal (FFT) measurement
16/23 Doc ID 14152 Rev 2
Page 17

AN2658 Practical application
STM8
V
REF-
V
SS
AINx
U
IN =
(V
REF+
, V
REF-
)
V
REF+
U
REF
STM8
V
REF-
V
SS
AIN1
U
IN0
AIN0
AINx
U
IN1
U
INx
Figure 12. Analog zooming
Figure 13. Multiple channel measurement (in scan mode for example)
Doc ID 14152 Rev 2 17/23
Page 18

Practical application AN2658
4.3 Methods for precision improvement
● Averaging samples:
– Averaging decreases speed but can give improved accuracy
● Analog zooming (use appropriate V
– Select reference voltage between input signal ranges
– Gives full ADC range - min. voltage per bit
● White noise added to measured signal: wobbling of input signal over several bits gives
possibility to use averaging (if input signal is very stable)
– White noise gives independence from sampling frequency
● Digital filtering (50/60 Hz suppression from DC value)
– Set proper sampling frequency (The trigger from Timer1 is useful in this case)
● Perform software post processing on sampled data (comb filter)
● Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) for AC measurements:
– To show harmonic parts in measured signal
– Slower due to more computational power requirements
● Calibration of ADC: offset, gain, bit weight calibration
– Decreases internal ADC errors
– Internal ADC structure must be known
● Good hardware design:
– Grounding
– Reference voltage filtering
– Power supply filtering
– Preamplifier usage
– Frequency independence
–…
voltage and V
REF
REF
offset):
Refer to AN2719 for more details.
18/23 Doc ID 14152 Rev 2
Page 19

AN2658 Design recommendations
5 Design recommendations
The following is a checklist of the main design rules for using the ADC.
● Grounding of analog/digital power:
– Star topology
● V
● V
● Source impedance vs. input impedance knowledge:
● External preamplifier usage:
● Select appropriate ADC mode, speed, trigger
● Software methods: averaging, FFT, …
, V
SSA
filtering:
DDA
– RC, LC filtering
– Avoid noise from noisy digital power
selection - offset, value, precision:
REF
– Reference voltage source precision and stability to meet the required precision in
the application and the and ADC’s capability
– Reference voltage source value and precision according to the expected
measurement range
– Use input buffers for measured signal
– Impedance relation with required conversion speed
– For low (and also high) level signals
– Amplifier speed and precision properties
– Amplifier dependency from frequency
Doc ID 14152 Rev 2 19/23
Page 20

Displaying the ADC conversion result using LEDs AN2658
5 V
10 KΩ
AIN9
STM8
6 Displaying the ADC conversion result using LEDs
6.1 Overview
This section describes how to use the ADC continuous conversion mode and display the
result on LEDs.
The example shows how to use continuous conversion mode and observe the effect of
changing the voltage values on the analog channel and observing the accuracy of the ADC
conversion.
6.2 Hardware description
Figure 14 shows a typical connection between the STM8 AIN9 pin and a potentiometer.
Figure 14. Connection to a potentiometer
6.3 Firmware description
The STM8 firmware library includes the ADC driver that supports the ADC through a set of
functions.
In this example the ADC is configured in continuous conversion mode with interrupt
enabled. In the interrupt routine, the range of the converted value defines the number of
LEDs to light up each time a conversion occurs. Increasing the voltage applied to channel 9
of the ADC, using the potentiometer, increases the number of LEDs that light up (up to 4).
This firmware is provided as ADC example 1 in the STM8 firmware library, available from the
STMicroelectronics microcontroller website.
20/23 Doc ID 14152 Rev 2
Page 21

AN2658 ADC conversion triggered by TIM1 timer
7 ADC conversion triggered by TIM1 timer
7.1 Overview
This section describes how to start and ADC conversion triggered by the TIM1 trigger
output.
There are several ways of starting ADC conversions in the STM8 including any event that
can be generated by the multipurpose timer (TIM1). This gives the you a large choice when
implementing your application.
7.2 Hardware description
Figure 14 shows a typical connection between the STM8 AIN9 pin and a potentiometer. This
allows you to test the ADC by changing the input voltage to be converted. The conversion
result is displayed on four LEDs. This example hardware is implemented in the STM8
evaluation board STM8/128-EVAL.
7.3 Firmware description
The STM8 firmware library includes the ADC driver that supports the ADC through a set of
functions.
ADC is configured in continuous conversion mode with interrupt enabled. The conversion is
triggered by the TIM1 TRGO event. In the interrupt routine, the range of the converted value
defines the number of LEDs to light up each time a conversion occurs.
This firmware is provided as ADC example 2 in the STM8 firmware library, available from the
STMicroelectronics microcontroller website.
Doc ID 14152 Rev 2 21/23
Page 22

Revision history AN2658
8 Revision history
Table 2. Document revision history
Date Revision Changes
28-Oct-2008 1 Initial release.
08-Jul-2009 2 Revised to describe ADC1 and ADC2 specific features.
22/23 Doc ID 14152 Rev 2
Page 23

AN2658
Please Read Carefully:
Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the
right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any
time, without notice.
All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no
liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and services described herein.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted under this document. If any part of this
document refers to any third party products or services it shall not be deemed a license grant by ST for the use of such third party products
or services, or any intellectual property contained therein or considered as a warranty covering the use in any manner whatsoever of such
third party products or services or any intellectual property contained therein.
UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS
OF ANY JURISDICTION), OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS EXPRESSLY APPROVED IN WRITING BY AN AUTHORIZED ST REPRESENTATIVE, ST PRODUCTS ARE NOT
RECOMMENDED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN MILITARY, AIR CRAFT, SPACE, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE SUSTAINING
APPLICATIONS, NOR IN PRODUCTS OR SYSTEMS WHERE FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY,
DEATH, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE. ST PRODUCTS WHICH ARE NOT SPECIFIED AS "AUTOMOTIVE
GRADE" MAY ONLY BE USED IN AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS AT USER’S OWN RISK.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the statements and/or technical features set forth in this document shall immediately void
any warranty granted by ST for the ST product or service described herein and shall not create or extend in any manner whatsoever, any
liability of ST.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of ST in various countries.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners.
© 2009 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
STMicroelectronics group of companies
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Philippines - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
Doc ID 14152 Rev 2 23/23
 Loading...
Loading...