Page 1

Using the STM32F101xx and STM32F103xx DMA controller
1 Introduction
This application note describes how to use the STM32F101xx and STM32F103xx direct
memory access (DMA) controller. The STM32F101xx and STM32F103xx DMA controller,
the Cortex™-M3 core, the advanced microcontroller bus architecture (AMBA) bus and the
memory system contribute to provide a high data bandwidth and to develop very-low latency
response time software.
This application note also describes how to take full advantage of these features and ensure
correct response times for different peripherals and subsystems.
The STM32F101xx and STM32F103xx will be referred to as STM32F10xxx, and the DMA
controller as DMA throughout the document.
AN2548
Application note
April 2009 Doc ID 13529 Rev 3 1/14
www.st.com
Page 2

Contents AN2548
Contents
1 Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
2 DMA controller description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
2.1 Main features . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3
3 Performance considerations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
3.1 Round robin priority scheme . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
3.2 Multi-layer structure and bus stealing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
3.3 DMA latency . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
3.4 Databus bandwidth limitation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
3.5 Choosing channel priority . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3.5.1 Application requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
3.5.2 Internal data bandwidth . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
4 DMA programming examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
4.1 Example of ADC continuous data acquisition with SPI transfer . . . . . . . . 11
4.2 ADC continuous data acquisition with direct SPI transfer . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
4.3 GPIO fast data transfer with DMA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
5 Revision history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
2/14 Doc ID 13529 Rev 3
Page 3

AN2548 DMA controller description
2 DMA controller description
The DMA is an AMBA advanced high-performance bus (AHB) module that features two
AHB ports: a slave port for DMA programming and a master port that allows the DMA to
initiate data transfers between different slave modules.
The DMA allows data transfers to take place in the background, without the intervention of
the Cortex-M3 processor. During this operation, the main processor can execute other tasks
and it is only interrupted when a whole data block is available for processing. Large amounts
of data can be transferred with no major impact on the system performance.
The DMA is mainly used to implement central data buffer storage (usually in system SRAM)
for different peripheral modules. This solution is less expensive in terms of silicon and power
consumption compared to a distributed solution where each peripheral needs to implement
it own local data storage.
The STM32F10xxx DMA controller takes full advantage of the Cortex-M3 Harvard
architecture and the multilayer bus system in order to ensure very low latency both for DMA
transfers and for CPU execution/interrupt event detection/service.
Depending on the sales type used, one or two DMA controllers are implemented
.
2.1 Main features
The DMA(s) offer(s):
● Twelve DMA channels (7 for DMA1 and 5 for DMA2) supporting unidirectional data
transfers from source to destination
● Hardware- and software-programmable channel priority for each DMA
● Memory-to-memory, memory-to-peripheral, peripheral-to-memory and peripheral-to-
peripheral transfers (memory can be SRAM or Flash)
● Control of hardware/software transfers
● Automatic increment of peripheral and memory pointers
● Programmable data size
● Automatic bus-error management
● Non-circular/circular mode
● Transfer of up to 65536 data tokens
The DMA aims to offer a relatively large data buffer to all peripherals. This buffer is usually
located in system SRAM.
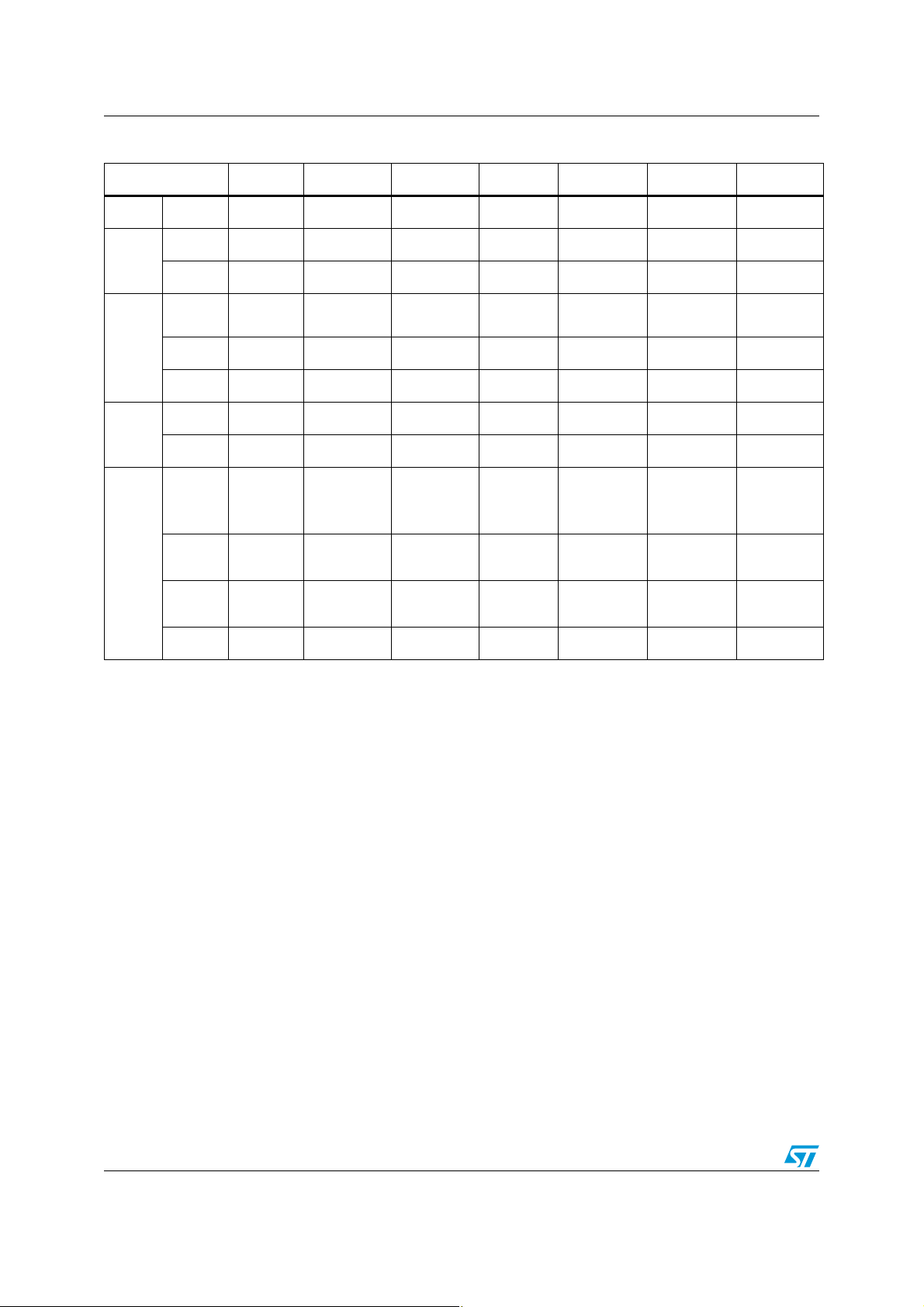
Each channel is assigned to a unique peripheral (data channel) at a given time. Peripherals
connected to the same DMA channel (CH1 to CH7 in Ta b le 1 , CH1 to CH5 in Tab le 2 )
cannot be used simultaneously with active DMA (DMA function active in the peripheral
register).
The different peripherals supporting DMA transfers are shown in Tab le 1 and Ta b le 2 . The
peripherals served by the DMA and the bus system structure are represented in Figure 1.
Doc ID 13529 Rev 3 3/14
Page 4
DMA controller description AN2548
Table 1. Peripherals served by DMA1 and channel allocation
Peripherals CH1 CH2 CH3 CH4 CH5 CH6 CH7
ADC ADC1 ADC1
SPI1 SPI1_RX SPI1_TX
SPI
SPI2 SPI2_RX SPI2_TX
USART1_
TX
USART1_RX
USART
USART1
USART2 USART2_RX USART2_TX
USART3 USART3_TX USART3_RX
2
I
2
I
C
C1 I2C1_TX I2C1_RX
2
I
C2 I2C2_TX I2C2_RX
TIM1_CH4
TIM1 TIM1_CH1 TIM1_CH2
TIM1_TRIG
TIM1_UP TIM1_CH3
TIM1_COM
TIM
TIM2 TIM2_CH3 TIM2_UP TIM2_CH1
TIM3 TIM3_CH3
TIM3_CH4
TIM3_UP
TIM3_CH1
TIM3_TRIG
TIM2_CH2
TIM2_CH4
TIM4 TIM4_CH1 TIM4_CH2 TIM4_CH3 TIM4_UP
4/14 Doc ID 13529 Rev 3
Page 5
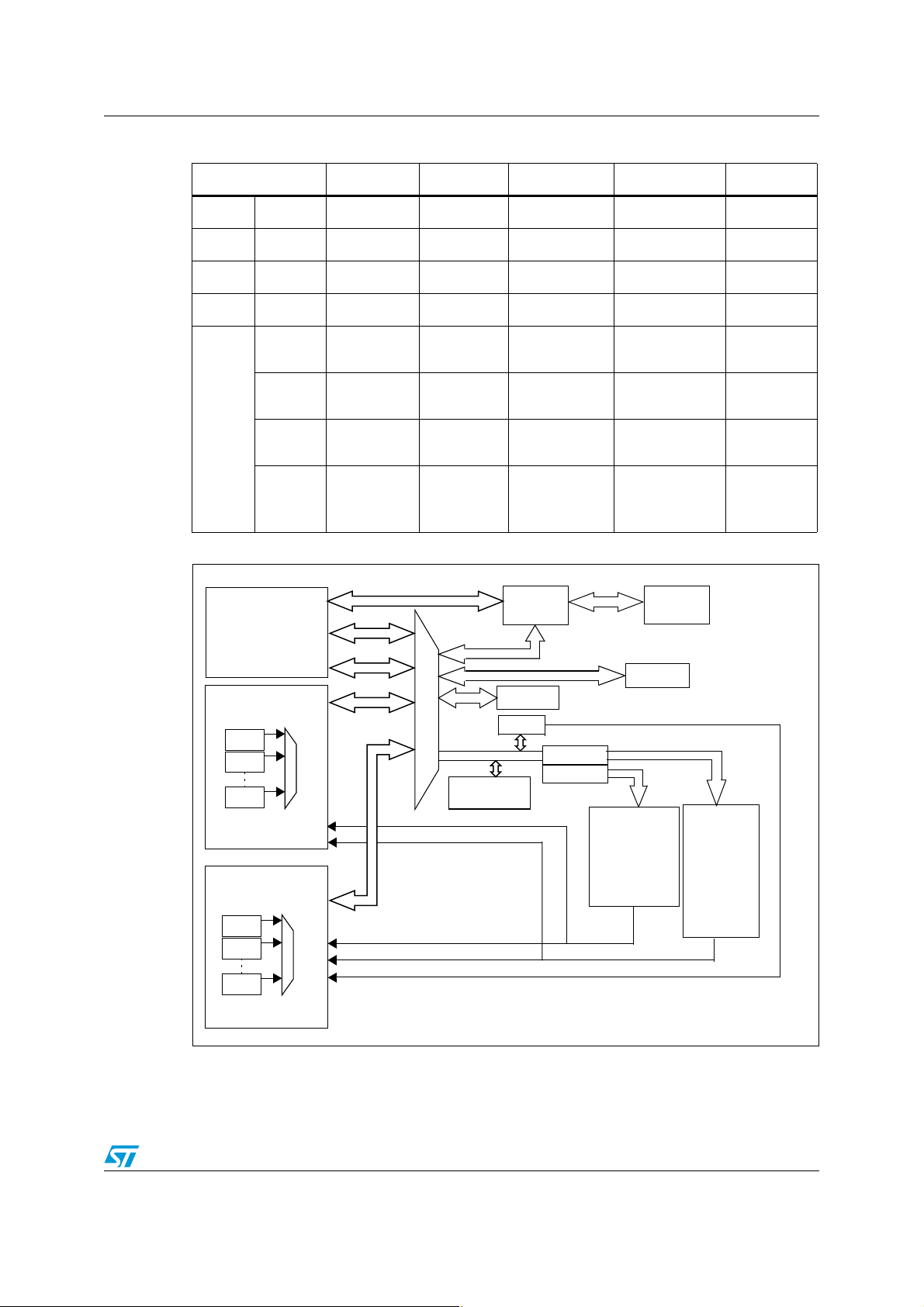
AN2548 DMA controller description
FLITF
Ch.1
Ch.2
Ch.7
Cor tex-M3
DMA1
ICode
DCode
System
AHB system bus
DMA Request
APB 1
Flash
Bridge 2
Bridge 1
Ch.1
Ch.2
Ch.5
DMA2
SRAM
FSMC
SDIO
APB2
DMA request
ADC3
GPIOC
USART1
TIM8
SPI1
TIM1
ADC2
ADC1
GPIOG
GPIOF
GPIOE
GPIOD
GPIOB
GPIOA
EXTI
AFIO
DAC SPI3/I2S
TIM2
PWR
BKP
bxCAN
USB
I2C2
I2C1
UART5
UART4
USART3
USART2
SPI2/I2S
IWDG
WWDG
RTC
TIM7
TIM6
TIM5
TIM4
TIM3
ai14800c
Bus matrix
DMA
DMA
Reset & clock
control (RCC)
Table 2. Peripherals served by DMA2 and channel allocation
Peripherals CH1 CH2 CH3 CH4 CH5
ADC ADC3 ADC3
SPI SPI/I2S3 SPI/I2S3_RX SPI/I2S3_TX
USART USART4 USART1_TX USART1_RX
SDIO SDIO SDIO
TIM5
TIM6
TIM5_CH4
TIM5_TRIG
TIM5_CH3
TIM5_UP
TIM6_UP/
DAC_Channel1
TIM
TIM7
TIM8_CH4
TIM8_TRIG
TIM8_COM
TIM8
TIM8_CH3
TIM8_UP
Figure 1. Bus system and peripherals supporting DMA
TIM5_CH2 TIM5_CH1
TIM7_UP/
DAC_Channel2
TIM8_CH1 TIM8_CH2
Doc ID 13529 Rev 3 5/14
Page 6

Performance considerations AN2548
3 Performance considerations
The STM32F10xxx’s three master modules are the Cortex-M3 processor and the two
DMAs. They are connected to the slave buses, the Flash memory bus, the SRAM bus, the
FSMC bus and the AHB system bus, through a bus matrix. The AHB system bus is in turn
connected to the two APB buses that serve all the embedded peripherals (see Figure 1) but
one –the SDIO peripheral which is directly connected to the AHB system bus.
The bus matrix has two main features that allow to maximize the system performance and
reduce the latency:
● Round-robin priority scheme
● Multi-layer structure and bus stealing
3.1 Round robin priority scheme
The NVIC and Cortex-M3 processor implement a high-performance very low latency
interrupt scheme. All Cortex-M3 instructions are either executed in a single cycle or are
interruptible at cycle level. In order to preserve this advantage at system level, the DMA and
bus matrix ensure that the DMA does not block the bus for a long time. The round-robin
priority scheme ensures that the CPU can access any slave bus during every third cycle, if
needed. As a consequence, the maximum bus system latency for the first data, seen from
the CPU, is of one bus cycle (maximum two APB clock cycles).
3.2 Multi-layer structure and bus stealing
The multi-layer structure allows the two/three masters to perform data transfers concurrently
as long as they are addressing different slave modules. On top of the Cortex-M3 Harvard
architecture, this structure enhances data transfer parallelism, thus contributing to reduce
the execution time and optimize the DMA efficiency. As instruction fetches from the Flash
memory are performed through a completely independent bus, the DMA and CPU only
compete for data access through a given slave bus.
In addition, the STM32F10xxx DMA uses one single bus cycle for data transfers (bus
stealing) while other DMA controllers operate in burst mode. When using the bus-stealing
access mechanism, the maximum time during which the CPU is stalled awaiting for data is
very small (1 bus cycle). CPU accesses to SRAM are naturally interleaved with DMA
accesses, the CPU accesses taking place in parallel with the DMA access to the peripheral
through the APB bus. Even though further data accesses may be faster when using DMA
with burst mode (during the periods when the DMA performs peripheral data transfer), the
long period of time during which the CPU is stalled is seldom recovered. Refer to Figure 2
for a comparison between bus stealing and burst mode mechanisms.
The extreme case occurs when the CPU copies data from memory to memory. In this case
the software execution is delayed by the time taken by the whole DMA transfer. However,
most of the time, the CPU performs data processing. Data accesses are less frequent
(register store/load) allowing natural interleaving of DMA and CPU accesses.
The inherent parallelism of the STM32F10xxx bus structure, associated with the DMA busstealing mechanism ensure that the CPU is not stuck for long periods of time waiting to read
data from the SRAM. DMAs with bus stealing mechanism consequently use the bus in a
more efficient way, thus significantly contributing to reduce the total software execution time.
6/14 Doc ID 13529 Rev 3
Page 7

AN2548 Performance considerations
ai14152
SR AM
APB
DMA DMA
CPU rq1
CPU
CPU
DMA data transfers using bus stealing
SRAM
APB
CPU rq1
DMA CPU
CPU rq2
CPU stall
....
End of SW execution
CPU
CPU stall
CPU rq3
DMA
DMA
CPU rq2
CPU rq3 CPU rq4
DMA data transfers using burst mode
DMA DMADMA DMACPUCPU CPU
....
DMA
CPU rq4
DMA
DMA
....
tStAt
Acc
t+
SRAM
+=
Figure 2. Bus stealing vs. burst mode for DMA transfer
3.3 DMA latency
Three operations are required to perform a DMA data transfer from peripheral to SRAM
memory. When storing ADC continuous conversion data in SRAM, the following steps must
be followed:
1. DMA request arbitration & address computation
2. Reading data from the peripheral (DMA source)
3. Writing loaded data in SRAM (DMA destination)
When transferring data from SRAM to peripheral (for example SPI transmission), the
operations are performed in the opposite order:
1. DMA request arbitration & address computation
2. Reading data from SRAM memory (DMA source)
3. Writing data to the peripheral through the APB bus (DMA destination)
The service time per channel, t
, is given by the equation below:
S
where:
● t
● t
is the arbitration time
A
t
= 2 AHB clock cycle
A
is the peripheral access time
ACC
t
= 1 AHB clock cycle (bus matrix arbitration)
ACC
+ 2 APB clock cycles (effective data transfer)
+ 1 AHB clock cycle (bus synchronization)
● t
is the SRAM read or write access time
SRAM
t
SRAM
+ 1 AHB clock cycles (single read/write operation) or 2 AHB clock cycles in case of
SRAM read-after-write access.
= 1 AHB clock cycle (bus matrix arbitration)
Doc ID 13529 Rev 3 7/14
Page 8

Performance considerations AN2548
t
TStAtAcc
t+
SRAM
tBFt+
Ack
++=
f
AHB
2N
2
23++ 2N
2
2+B
max
N2N1 N
1
1
16
------
f
AHBBmax
When the DMA is idle or after the third operation has completed on one channel, the DMA
compares the priorities of all pending DMA requests (software and hardware priorities, in
this order). The highest priority channel is served next and the DMA jumps to execute the
second operation. While a channel is being served (operation 2 or 3 ongoing), no other
channel can be served whatever its priority.
As a results, when at least two DMA channels are enabled, the DMA latency for the highest
priority channel is the sum of the ongoing transfer time (without the arbitration phase) and
the transfer time for the next DMA channel to be served (highest pending priority).
For the case where only one DMA channel is active, a new request cannot be treated before
completely closing the previous one (DMA rq/ack handshake). For this the total service time,
t
, must be used:
TS
, where:
–t
–t
is the bus free time (bus left free for CPU access)
BF
t
= 1 AHB clock cycle
BF
is the DMA acknowledge time (closing the handshake between peripheral &
Ack
DMA)
t
= 1 AHB clock cycle
Ack
3.4 Databus bandwidth limitation
The data bus bandwidth limitation is mainly due to the fact that the APB buses are slower
than the system SRAM and the AHB bus. Two conditions must be respected for the highest
priority DMA channel (see Figure 3).
1. When more than one DMA channel is enabled, the required data bandwidth for the
highest priority channel on the APB bus must be lower than 25% of the maximum APB
transfer rate. The complete duration of an APB bus transfer must be taken into account.
It is equal to 2 APB clock cycles plus 2 AHB clock cycles for arbitration/synchronization.
2. Even though the high speed/high priority DMA transfers usually take place on APB2
which is the faster APB bus, the CPU and other DMA channels may access peripherals
on APB1. As 3 out of 4 remaining APB transfers may be performed on APB1, the
minimum possible APB2 frequency depends on the fastest DMA channel data
bandwidth.
The maximum APB clock division factor is given by the equation below:
if
, where:
–f
–N
–B
is the AHB clock frequency,
AHB
and N2 are APB1 and APB2 clock division factors, respectively,
1
is the maximum peripheral data bandwidth on APB2 expressed in
max
transfers/s.
8/14 Doc ID 13529 Rev 3
Page 9

AN2548 Performance considerations
ai14153
APB2
APB1
DMAx DMA1
CPU? DMAy
CPU? CPUDMA1CPU
DMA1 rq1
DMAy rq
DMA1 rq2
Figure 3. APB bus occupation during DMA transfers
1. DMA1 is the highest priority channel.
Doc ID 13529 Rev 3 9/14
Page 10

Performance considerations AN2548
3.5 Choosing channel priority
In order to achieve continuous data transfers to/from a peripheral, the corresponding DMA
channel must be able to sustain the peripheral data rate and ensure that the service latency
is shorter than the period of time between two consecutive data.
The high speed/high bandwidth peripherals must have the highest DMA priorities. This
ensures that the maximum data latency will be respected for these peripherals and
over/under-run conditions will be avoided.
In case of equal bandwidth requirements, it is recommended to assign a higher priority to
the peripherals working in slave mode (which have no control on the data transfer speed)
compared with the ones working in master mode (which may control the data flow).
By default, the channel allocation and hardware priority (from 1 to 7) are set in order to
assign the fastest peripherals to the highest priority channels. However, this may not be true
for some applications. In this case, the user can configure a software priority for each
channel (4 levels – from Very High to Low), which takes precedence over the hardware
priority.
When using several peripherals in parallel (with or without DMA), the user must make sure
that the internal system can sustain the total data bandwidth required for the application. A
compromise must be find between two factors:
● The application requirements for each peripheral
● The internal data bandwidth
3.5.1 Application requirements
As an example, the data bandwidth for an SPI interface is obtained by dividing the baud rate
by the data word length used by the SPI (since one full data needs to be transferred to/from
the SPI before/after each transmission). Let us take the example of an SPI interface
performing 8-bit data transfers at 18 MBaud, and configured to operate in simplex mode. In
this case, the internal data bandwidth requirement are of 2.25 Mtransfers/s.
Note: The data bandwidth can be divided by 2 when using the SPI in 16-bit mode: with the same
baud rate, it only requires a transfer speed of 1.125 Mtransfers/s.
It is strongly recommended, whenever possible, to use the 16-bit mode in order to minimize
bus usage and power consumption.
3.5.2 Internal data bandwidth
The internal data bandwidth depends on:
● The bus frequencies
The available data bandwidth is directly proportional to the bus clock frequency.
● The bus type
AHB data transfers take 2 clock cycles, except for SRAM read-after-write accesses that
take 3 cycles. Data transfers to a peripheral through an APB bus takes 2 APB clock
cycles plus 2 AHB clock cycles dedicated to bus matrix arbitration and data
synchronization.
It is recommended to keep the DMA bus usage below 2/3 in order to maintain the system
and CPU performance at a reasonable level.
10/14 Doc ID 13529 Rev 3
Page 11

AN2548 DMA programming examples
4 DMA programming examples
All the examples described below use the STM32F10xxx Standard peripheral library and
are provided in the firmware package associated with this application note. Both the
package and the application note are available for download from the STMicroelectronics
website: http://www.st.com.
4.1 Example of ADC continuous data acquisition with SPI transfer
The ADC is configured to operate in Continuous Conversion mode. In this mode, it
continuously converts one input channel at the maximum speed. In this mode, the AHB bus
frequency is set to 56 MHz, the ADC prescaler to 4 and the sample time to 13.5 cycles.
These settings are transferred through DMA1 channel 1 into a buffer located in a system
RAM buffer. The data bandwidth for channel 1 is set to 0.54 Mtransfer/s.
After the DMA has filled one half of the buffer with ADC data, the software computes the
peak value and normalizes the digitized data (the peak value is set to 0xFF). The results of
the conversion are then transmitted externally through the SPI interface.
The results of the conversion are then transmitted externally through the SPI1 interface.
Data are transferred from the SRAM buffer using DMA1 channel 3 to SPI1 data register. To
achieve the maximum DMA transfer speed of 0.875 Mtransfers/s, the SPI1 interface is
configured in 16-bit master transmit mode, and 14 MBaud transfer speed.
However, as SPI1 operates in master mode, and the SPI1 effective data transfer speed is
limited by the data availability rate of 1 Mtransfers/s, the priorities are configured as
following:
● Channel1 (ADC): VeryHigh
● Channel3 (SPI1_TX): High.
4.2 ADC continuous data acquisition with direct SPI transfer
This example implements almost the same function as the previous one, without data
normalization. As the data are not used internally by the CPU, the bus occupation can be
reduced by half by transferring directly data from the ADC converter to the SPI data register.
As a consequence, only DMA1 channel 1 is used. The destination memory address for this
channel is set to the SPI data register, without the need of an intermediate SRAM buffer.
Doc ID 13529 Rev 3 11/14
Page 12

DMA programming examples AN2548
4.3 GPIO fast data transfer with DMA
This example shows how to use different peripherals for DMA request and data transfer.
This mechanism allows to implement simple fast parallel synchronous interfaces without
using the CPU (for example a camera interface).
Timer 3 and DMA1 channel 6 connected to TIM3_TRIG are used to implement this data
acquisition interface. An 16-bit parallel data is available on the GPIO port and an external
clock signal applied on the external trigger input of Timer 3. On the rising edge of the
external trigger, the timer generates a DMA request. As the GPIO data register address is
set to DMA1 channel 6 peripheral address, the DMA controller reads the data from the
GPIO port on each DMA request, and stores it into an SRAM buffer.
12/14 Doc ID 13529 Rev 3
Page 13

AN2548 Revision history
5 Revision history
Table 3. Document revision history
Date Revision Changes
29-June-2007 1 Initial release.
Minor text modifications in Section 2.1: Main features.
Updated DMA/CPU clock cycle information with bus matrix
arbitration and APB bridge data in Section 3.3: DMA latency
and Section 3.4: Databus bandwidth limitation.
Updated relation between internal data bandwidth and bus
10-Dec-2007 2
30-Apr-2009 3
type in Section 3.5.2: Internal data bandwidth.
Updated Section 4.1: Example of ADC continuous data
acquisition with SPI transfer.
Changed DMA channel 4 into DMA channel 6, Timer 1 into
Timer 3 and 8-bit data into 16-bit data in Section 4.3: GPIO
fast data transfer with DMA.
Document updated to cover the case where the device has
two DMA controllers (Table 2: Peripherals served by DMA2
and channel allocation added, Figure 1: Bus system and
peripherals supporting DMA updated).
Updated DMA/CPU clock cycle information with latency vs.
total service time in Section 3.3: DMA latency and Section 3.4:
Databus bandwidth limitation.
Small text changes.
Doc ID 13529 Rev 3 13/14
Page 14

AN2548
Please Read Carefully:
Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the
right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any
time, without notice.
All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no
liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and services described herein.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted under this document. If any part of this
document refers to any third party products or services it shall not be deemed a license grant by ST for the use of such third party products
or services, or any intellectual property contained therein or considered as a warranty covering the use in any manner whatsoever of such
third party products or services or any intellectual property contained therein.
UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS
OF ANY JURISDICTION), OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS EXPRESSLY APPROVED IN WRITING BY AN AUTHORIZED ST REPRESENTATIVE, ST PRODUCTS ARE NOT
RECOMMENDED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN MILITARY, AIR CRAFT, SPACE, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE SUSTAINING
APPLICATIONS, NOR IN PRODUCTS OR SYSTEMS WHERE FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY,
DEATH, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE. ST PRODUCTS WHICH ARE NOT SPECIFIED AS "AUTOMOTIVE
GRADE" MAY ONLY BE USED IN AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS AT USER’S OWN RISK.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the statements and/or technical features set forth in this document shall immediately void
any warranty granted by ST for the ST product or service described herein and shall not create or extend in any manner whatsoever, any
liability of ST.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of ST in various countries.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners.
© 2009 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
STMicroelectronics group of companies
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Philippines - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
14/14 Doc ID 13529 Rev 3
 Loading...
Loading...