Page 1

AN1713
APPLICATION NOTE
SMBus SLAVE DRIVER FOR ST7 I2C PERIPHERAL
by Microcontroller Division Applications
INTRODUCTION
The goal of this application note is to implement the SMBus slave protocol using ST7 I2C. The
software of this application performs all SMBus bus protocols mentioned in SMBus v1.1. The
device chosen here is ST72F264 which has multi-master I2C capability.
The program described in this application note is in C language. The driver is compatible with
Metrowerks and Cosmic compilers.
1 CHARACTERISTICS
The main characteristics of this SMBus slave driver are:
■ SMBus bus protocols: Quick command, Send/ Receive Byte, Write/ Read Byte, Write/ Read
Word, Write/ Read Block, Process Call Word/ Block
■ Slave SMBus addressing
■ CRC-8 Packet Error Checking
For more details please refer to the SMBus specification v1.1.
2 SMBus
The System Management Bus (SM Bus) i s a two-wire interface through which various system
component chips can communicate with each other and with the rest of the system. It is based
on the principles of operation of I2C.
2.1 Similarities of SMBus and I2C
■ 2 wire bus protocol (1 Clk, 1 Data)
■ Master-slave communication, Master provides clock
■ Multi master capability
■ SMBus data format similar to I2C 7-bit addressing format.
AN1713/0803 1/4
1
Page 2
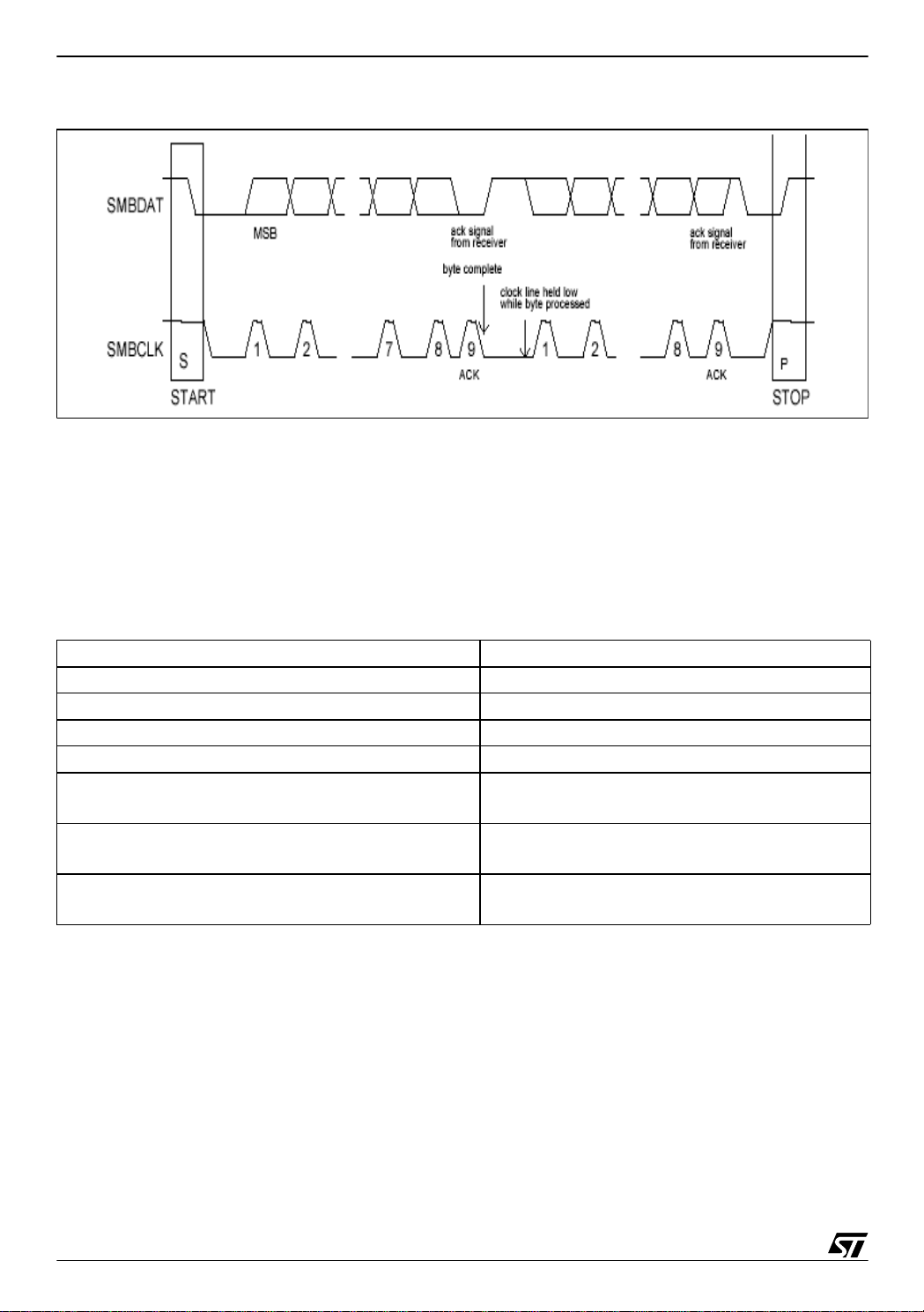
SMBus SLAVE DRIVER FOR ST7 I2C PERIPHERAL
Figure 1. Data transfer format
SMBDAT: SMBus data line
SMBCLK: SMBus clock line
2.2 Differences between SMBus and I2C
The following table describes the differences between SMBus and I2C.
Table 1. SMBus vs I2C
SMBus ST7 I2C
Max. speed 100 kHz Max. speed 400 kHz
Min. clock speed 10 kHz No minimum clock speed
35ms clock low time-out No time-out
Logic levels are fixed Logic levels are VDD dependent
Different address types (reserved, dynamic
etc.)
Different bus protocols (quick command, process call etc.)
Packet error checking (PEC) implemented
7-bit, 10-bit and general call slave address
types
No bus protocols
No packet error checking. Only error status
indication
2.3 SMBus Application
With Sy stem M anag ement B us, a devi ce c an pro vide manufa cture r inform ation, tell t he
system what its model/part number is, save its state for a suspend event, report different types
of errors, accept contr ol param eters, and r eturn its status. SMBus pr ovides a control bus for
system and power management related tasks.
2/4
2
Page 3

SMBus SLAVE D RIVER FOR ST7 I2C PER IPH ERAL
Section 3 contains the description of the SMBus driver. These functions available with the
driver configure the ST7 I2C peripheral as an SMBus slave and allow it to communicate with
any SMBus master . Here al l SMBus v1.1 fe atures a re suppo rted. This dr iver can be u sed in
the Smart Battery System and other low-power devices.
For more details about the functions please refer to the SMBS_UM.pdf file.
3 SOFTWARE
The Software and user manual are available in the zip file supplied with this application note.
The User manu al expla ins ho w to us e the S MBus slave fu nct ions. An exam ple is al so pro vided to help the user to write an application using SMBus functions.
The following lists the source files which can be used for the SMBus slave interface. They are
separated into 2 types.
1. User accessible files: Following files can be modified by the user depending on the requirement.
main.c: Contains the Example program for SMBus slave driver co mmunication for Write Word, Write
Block and read word protocols. Here the PEC option is not chosen.
SMBS_config.h: Select the CPU frequency and Packet Error Checking option
2. Non-user accessible files: These files should not be modified by the user.
SMBS.c: Contains source code for all the Slave SMBus functions
SMBS.h: Contains prototypes for all the slave SMBus functions
SMBS_hr.c: Contains all the I2C hardware registers
SMBS_hr.h: Declares all the hardware registers as extern
This software is tested only for write word, read word and write block protocols.
3/4
Page 4

SMBus SLAVE DRIVER FOR ST7 I2C PERIPHERAL
THE PRESENT NOTE WHICH IS FOR GUIDANCE ONLY AIMS AT PROVIDING CUSTOMERS WITH INFORMATION
REGARDING THE IR PRO DUCT S IN OR DER FO R THEM TO SAV E TIME . AS A RES ULT, STMIC ROEL ECTR ONI CS
SHALL NOT BE HELD LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES WITH RESPECT TO
ANY CL AIM S AR IS IN G FR OM T HE CO N TENT OF S UC H A NO TE A ND /O R T HE U SE M AD E BY C US TO ME RS O F
THE INFORMATION CONTAINED HEREIN IN CONNECTION WITH THEIR PRODUCTS.
Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, STMicroelectronics assumes no responsibility for the consequences
of use of such information nor for any infringement of patents or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. No license is granted
by implic ation or otherwise under any patent or patent ri ghts of STM i croelectr oni cs. Spec i fications mentioned i n this publication are subje ct
to change without notice. This publication supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied. STMicroelectronics products are not
authorized for use as cri tical comp onents in life support dev i ces or systems wi thout the express written approv al of STMicroel ectronics.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics
2003 STMicroelectronics - All Rights Reserved.
STMicroelectronics Group of Compan i es
http://www.s t. com
Purchase of I
2
C Components by STMicroelectronics conveys a license under the Philips I2C Patent. Rights to use the se components in an
2
I
C system i s granted pro vi ded that the sy stem conforms to the I2C Standard Specification as defined by Philips.
Australi a - B razil - Canada - China - Finl and - France - Germany - Hong Kong - Ind ia - Israel - Italy - Japan
Malaysi a - M al ta - Morocco - Singapore - Spain - Sw eden - Switz erland - United Kingdom - U.S.A.
4/4
 Loading...
Loading...