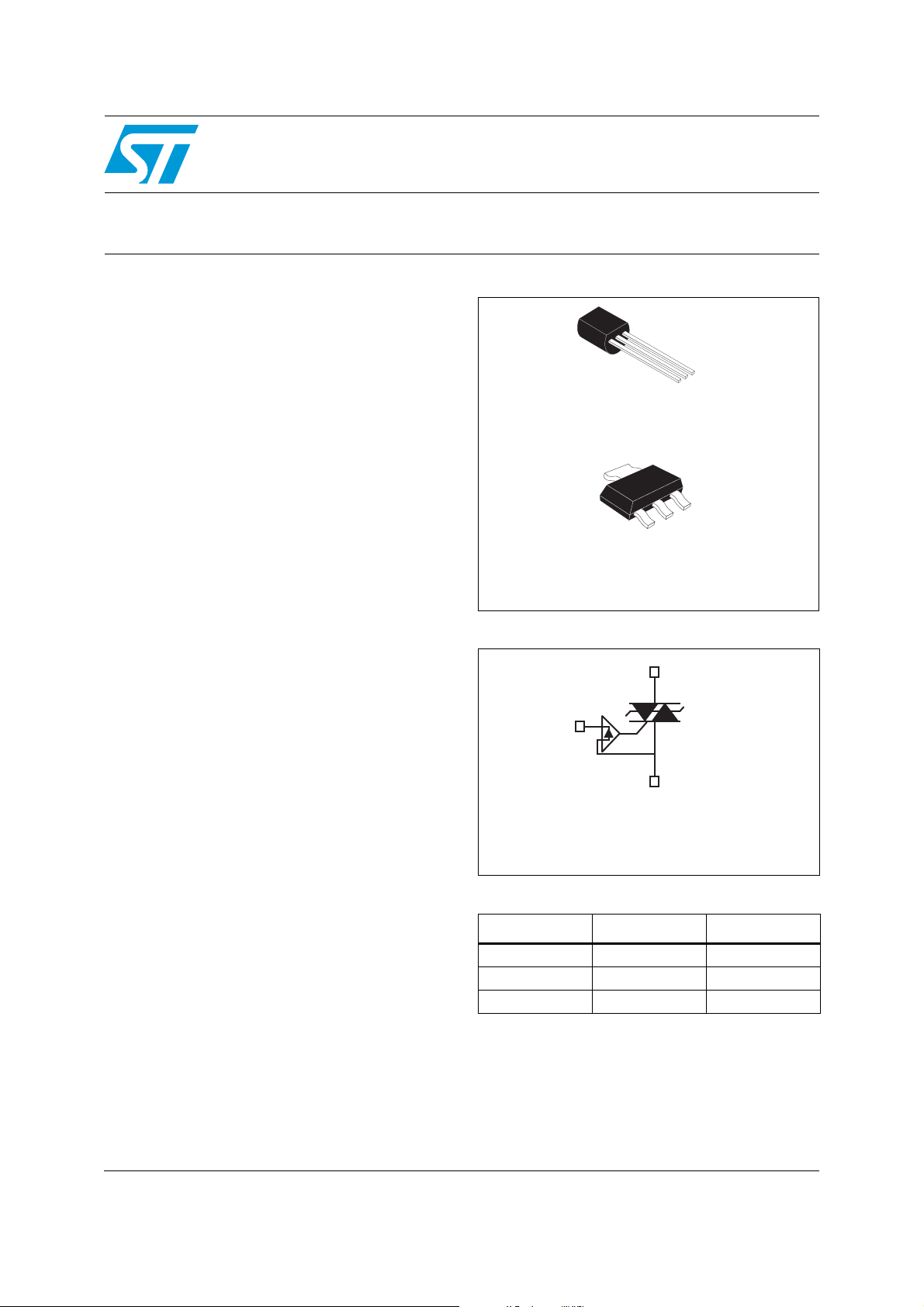
Overvoltage protected AC switch (ACS™)
COM
OUT
COM
G
COM
OUT
G
SOT-223
ACS108-6SN
ACS108-8SN
TO-92
ACS108-6SA
ACS108-8SA
OUT
COM
G
COM Common drive reference to connect
to the mains
OUT Output to connect to the load.
G Gate input to connect to the controller
through gate resistor
Features
■ Enables equipment to meet IEC 61000-4-5
surge with overvoltage crowbar technology
■ High noise immunity against static dV/dt and
IEC 61000-4-4 burst
■ Needs no external protection snubber or
varistor
■ Reduces component count by up to 80% and
Interfaces directly with the micro-controller
■ Common package tab connection supports
connection of several alternating current
switches on the same cooling pad
■ V
gives headroom before clamping then
CL
crowbar action
ACS108
Datasheet production data
Applications
■ Alternating current on/off static switching in
Figure 1. Functional diagram
appliances and industrial control systems
■ Driving low power high inductive or resistive
loads like:
– relay, valve, solenoid, dispenser,
– pump, fan, low power motor, door lock
–lamp
Description
The ACS108 belongs to the AC switch range (built
with A. S. D.
switch can control a load of up to 0.8 A. The
ACS108 switch includes an overvoltage crowbar
structure to absorb the inductive turn-off energy,
and a gate level shifter driver to separate the
digital controller from the main switch. It is
triggered with a negative gate current flowing out
of the gate pin.
July 2012 Doc ID 6518 Rev 3 1/13
This is information on a product in full production.
®
technology). This high performance
Table 1. Device summary
Symbol Value Unit
I
T(RMS)
, V
V
DRM
RRM
I
GT
®: A.S.D. is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics
TM: ACS is a trademark of STMicroelectronics
0.8 A
600 and 800 V
10 mA
www.st.com
13
Characteristics ACS108
1 Characteristics
Table 2. Absolute maximum ratings (T
= 25 °C, unless otherwise specified)
amb
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
T
= 64 °C 0.45 A
TO-92
I
T(RMS)
On-state rms current (full sine wave)
SOT-223
S = 5 cm
I
TSM
dI/dt
V
I
V
P
G(AV)
T
1. According to test described by IEC 61000-4-5 standard and Figure 18
Table 3. Electrical characteristics (Tj = 25 °C, unless otherwise specified)
Non repetitive surge peak on-state current
(full cycle sine wave, Tj initial = 25 °C)
2
t I²t Value for fusing tp = 10 ms 1.1 A2s
I
Critical rate of rise of on-state current
I
= 2xIGT, tr 100 ns
G
Non repetitive mains peak mains voltage
PP
Peak gate current tp = 20 µs Tj = 125 °C 1 A
GM
Peak positive gate voltage Tj = 125 °C 10 V
GM
(1)
Average gate power dissipation Tj = 125 °C 0.1 W
Storage junction temperature range
stg
T
Operating junction temperature range
j
F = 60 Hz t = 16.7 ms 13.7
F = 50 Hz t = 20 ms 13
F = 120 Hz T
amb
T
= 76 °C
lead
T
= 76 °C
amb
2
= 104 °C
T
tab
= 125 °C 100 A/µs
j
-40 to +150
-30 to +125
0.8 A
2kV
A
°C
Symbol Test conditions Quadrant Value Unit
(1)
I
GT
V
GT
V
GD
I
H
I
L
dV/dt
V
OUT
V
OUT
I
= 100 mA Max. 10 mA
OUT
IG = 1.2 x I
V
OUT
V
OUT
= 12 V, RL = 33
= V
, RL = 3.3 kTj = 125 °C II - III Min. 0.15 V
DRM
GT
= 402 V, gate open, Tj = 125 °C Min. 2000 V/µs
= 536 V, gate open, Tj = 125 °C Min. 400 V/µs
(dI/dt)c Without snubber (15 V/µs), T
= 125 °C, turn-off time 20 ms Min. 2 A/ms
j
II - III Max. 10 mA
II - III Max. 1 V
Max. 25 mA
ICL = 0.1 mA, tp = 1 ms, ACS108-6 Min. 650 V
V
CL
1. Minimum IGT is guaranteed at 10% of IGT max
= 0.1 mA, tp = 1 ms, ACS108-8 Min. 850 V
I
CL
2/13 Doc ID 6518 Rev 3
ACS108 Characteristics
P (W)
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
0.0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8
α = 180°
I (A)
T(RMS)
180°
I (A)
T(RMS)
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
0 25 50 75 100 125
α =180°
SOT-223
T°C
C
Table 4. Static electrical characteristics
Symbol Parameter and test conditions Value Unit
(1)
V
I
TM
V
R
I
DRM
I
RRM
(1)
t0
(1)
D
= 1.1 A, tp = 500 µs Tj = 25 °C Max. 1.3 V
TM
Threshold voltage Tj = 125 °C Max. 0.85 V
Dynamic resistance T
V
OUT
= V
DRM
= V
RRM
= 125 °C Max. 300 m
j
Tj = 25 °C
2µA
Max.
= 125 °C 0.2 mA
T
j
1. For both polarities of OUT referenced to COM
Table 5. Thermal resistance
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
R
R
th (j-l)
th (j-t)
Junction to lead (AC) TO-92 Max. 60
Junction to tab (AC) SOT-223 Max. 25
°C/W
TO-92 Max. 150
R
th (j-a)
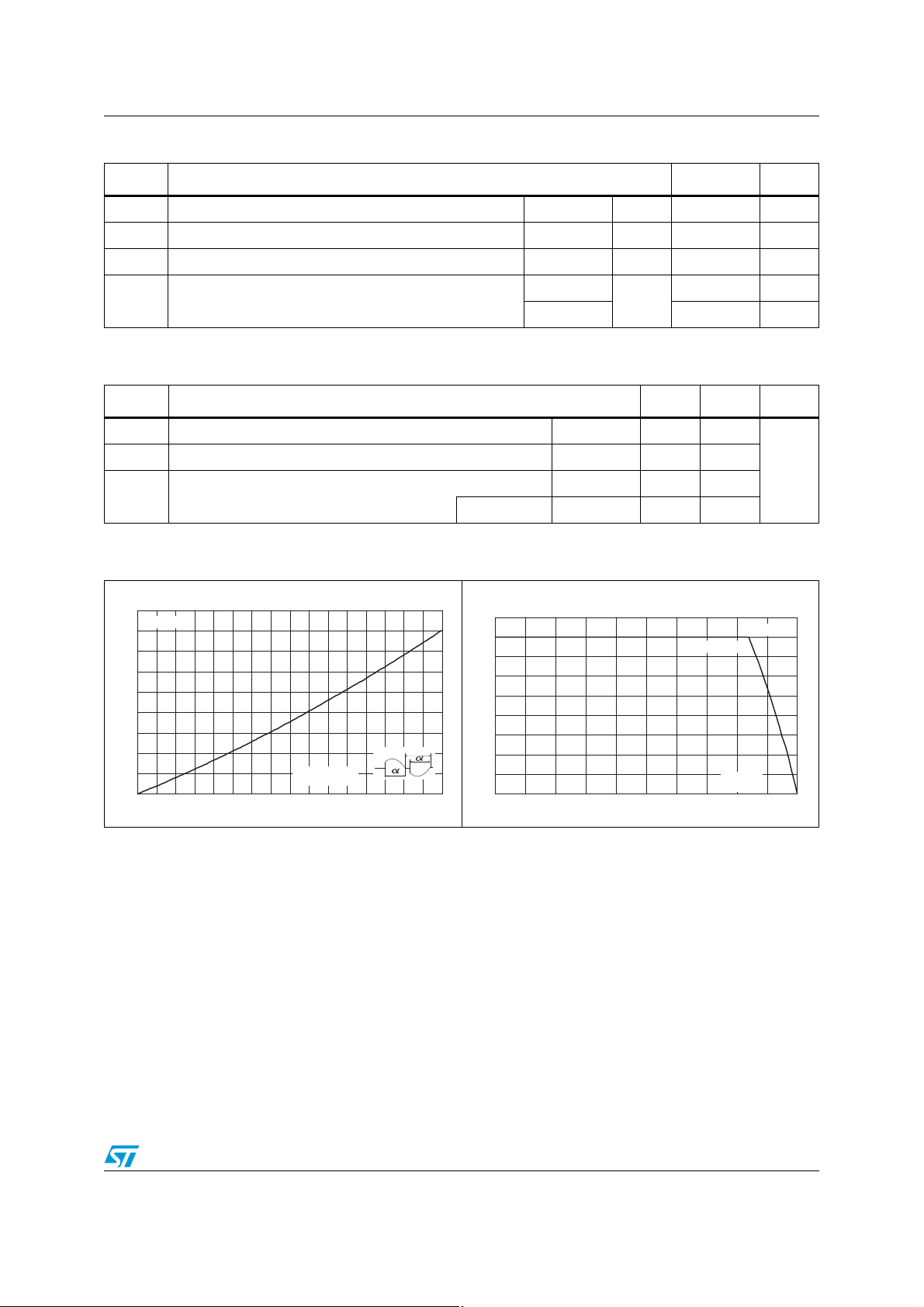
Figure 2. Maximum power dissipation versus
Junction to ambient
on-state rms current
S = 5 cm² SOT-223 Max. 60
Figure 3. On-state rms current versus case
temperature (SOT223)
Doc ID 6518 Rev 3 3/13
Characteristics ACS108
I (A)
T(RMS)
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
0.9
0 25 50 75 100 125
Single layer Printed
circuit board FR4
Natural convection
TO-9 2
SOT-223
α =180°
T°C
C
K=[Z
th(j-a)/Rth(j-a)
]
0.01
0.10
1.00
1.0E-03 1.0E-02 1.0E-01 1.0E+00 1.0E+01 1.0E+02 1.0E+03
Z
th(j-a)
SOT-223
Copper surface
area = 5cm²
TO-9 2
SOT-223
t (s)
P
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
IH,IL[Tj]/IH,IL[Tj=25 °C]
I
H
I
L
Tj(°C)
IGT,VGT[Tj]/IGT,VGT,[Tj=25 °C]
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
3.5
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
IGTQ2
VGTQ2-Q3
IGTQ3
Tj(°C)
I
TSM
(A)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
1 10 100 1000
Non repetitive
T
j
initial=25 °C
TO- 92
Repetitive
T
lead
= 76
°
C
SOT-223
Repetitive
T
tab
= 104°C
One cycle
t=20ms
Number of cycles
I
TSM
(A), I²t (A²s)
1.E-01
1.E+00
1.E+01
1.E+02
1.E+03
0.01 0.10 1.00 10.00
I
TSM
I²t
Sinusoidal pulse,
tp< 10 ms
Tjinitial = 25 °C
(ms)t
p
Figure 4. On-state rms current versus
ambient temperature
(free air convection)
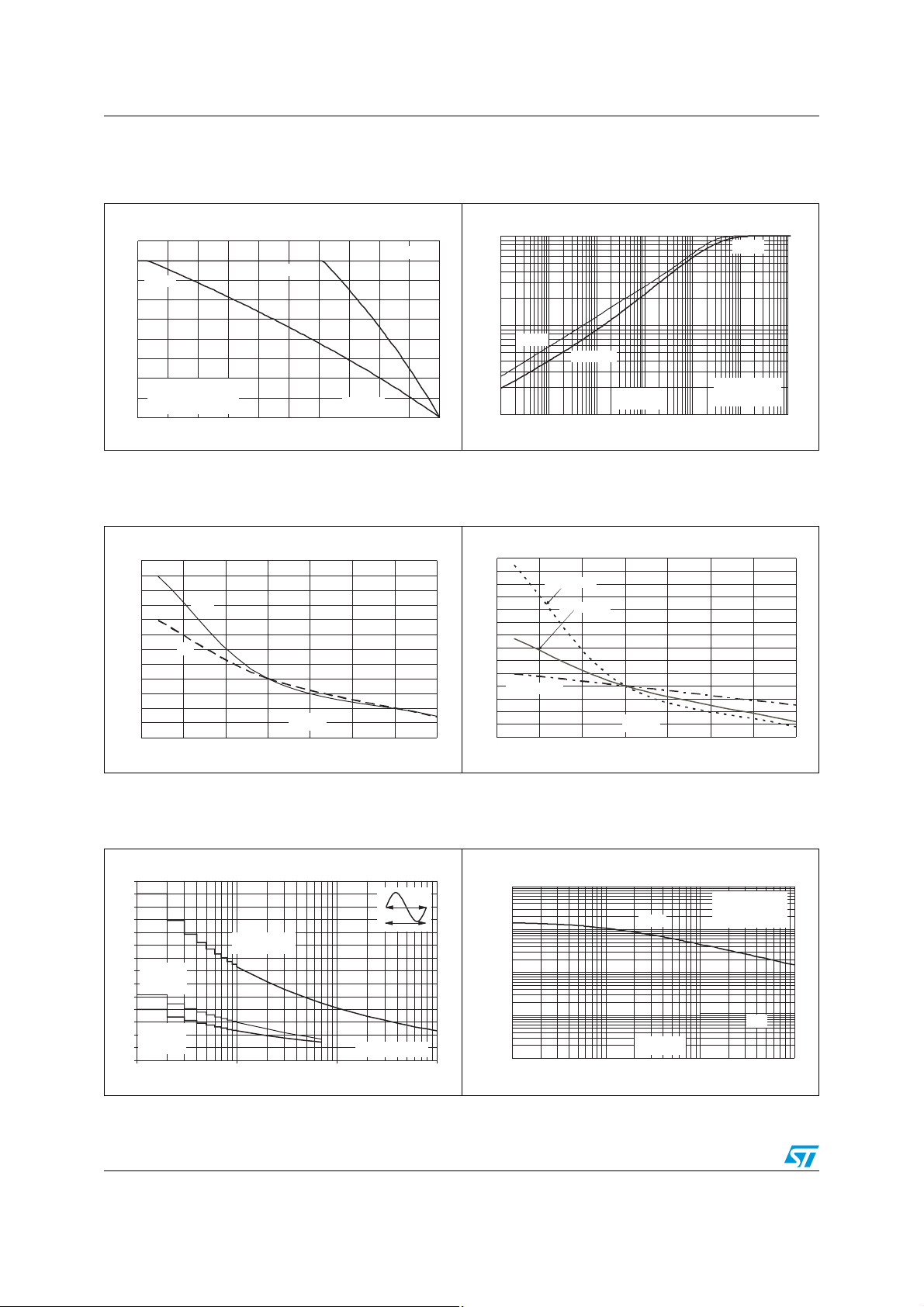
Figure 6. Relative variation of holding and
latching current versus junction
temperature
Figure 5. Relative variation of thermal
impedance junction to ambient
versus pulse duration
Figure 7. Relative variation of IGT and VGT
versus junction temperature
Figure 8. Surge peak on-state current versus
number of cycles
4/13 Doc ID 6518 Rev 3
Figure 9. Non repetitive surge peak on-state
current for a sinusoidal pulse, and
corresponding value of I²t

ACS108 Characteristics
I
TM
(A)
0.10
1.00
10.00
100.00
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5
Tjmax.:
V
to
= 0.85 V
R
d
= 300 m0
Tj=25 °C
Tj=125 °C
VTM(V)
(dI/dt) [T ] / (dI/dt) [T =125 °C]
cc
jj
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
25 35 45 55 65 75 85 95 105 115 125
T (°C)
j
dV/dt [ T
j
]/dV/dt[T
j
=125°C]
0
1
2
3
4
5
25 50 75 100 125
VD=VR=536V
Tj(°C)
1.0E-03
1.0E-02
1.0E-01
1.0E+00
25 50 75 100 125
I
DRM/IRRM
[Tj;V
DRM/VRRM
]/I
DRM/IRRM
[Tj=125°C;800V]
V
DRM=VRRM
=600 V
V
DRM=VRRM
=800 V
Tj(°C)
(dI/dt)
c
[(dV/dt)
c
] / Specified(dI/dt)
c
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
3.5
4.0
4.5
5.0
0.1 1.0 10.0 100.0
Tj =125 °C
(dV/dt)c(V/µs)
R
th(j-a)
(°C/W)
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0
SOT-223
SCU(cm²)
Printed circuit board FR4
copper thickness = 35 µm
Figure 10. On-state characteristics (maximal
values)
Figure 12. Relative variation of static dV/dt
immunity versus junction
temperature
(1)
Figure 11. Relative variation of critical rate of
decrease of main current versus
junction temperature
Figure 13. Relative variation of leakage
current versus junction
temperature
1. VD = VR = 402 V: Typical values above 5 kV/µs. Beyond equipment capability
Figure 14. Relative variation of critical rate of
decrease of main current (di/dt)c
versus (dV/dt)c
Figure 15. Thermal resistance junction to
ambient versus copper surface
under tab (SOT-223)
Doc ID 6518 Rev 3 5/13

Alternating current mains switch - basic application ACS108
AC Mains
ACS108
Valve
Power supply
MCU
V
dd
V
ss
Rg
220 Ω
I
T
V
T
2 Alternating current mains switch - basic application
The ACS108 switch is triggered by a negative gate current flowing from the gate pin G. The
switch can be driven directly by the digital controller through a resistor as shown in
Figure 16.
Thanks to its overvoltage protection and turn-off commutation performance, the ACS108
switch can drive a small power high inductive load with neither varistor nor additional turn-off
snubber.
Figure 16. Typical application schematic
2.1 Protection against overvoltage: the best choice is ACS
In comparison with standard Triacs the ACS108 is over-voltage self-protected, as specified
by the new parameter V
off of very inductive load, and in case of surge voltage that can occur on the electrical
network.
2.1.1 High inductive load switch-off: turn-off overvoltage clamping
With high inductive and low RMS current loads the rate of decrease of the current is very
low. An overvoltage can occur when the gate current is removed and the OUT current is
lower than I
As shown in Figure 17, at the end of the last conduction half-cycle, the load current
decreases ➀. The load current reaches the holding current level I
➂. The water valve, as an inductive load (up to 15 H), reacts as a current generator and an
overvoltage is created, which is clamped by the ACS ➃. The current flows through the ACS
avalanche and decreases linearly to zero. During this time, the voltage across the switch is
limited to the clamping voltage V
dissipated in the clamping section that is designed for this purpose. When the energy has
been dissipated, the ACS voltage falls back to the mains voltage value (230 V rms, 50 Hz)➄.
.
H
. This feature is useful in two operating conditions: in case of turn-
CL
➁, and the ACS turns off
H
. The energy stored in the inductance of the load is
CL
6/13 Doc ID 6518 Rev 3

ACS108 Alternating current mains switch - basic application
1
2
3
4
5
I
H
V
CL
100 µs/div
I
(5 mA/div)
T
V
(200 V/div)
T
I
H
V
CL
V
I
1
2
3
4
5
I
H
V
CL
V
T
I
T
1
2
3
4
5
Load
220 Ω
ACS108
150 Ω
5 µH
+2 kV surge
generator
C
C
OUT
G
COM
Mains
voltage
230 V rms
50 Hz
I
T
V
T
Figure 17. Switching off of a high inductive load - typical clamping capability of
ACS108 (T
amb
= 25 °C)
2.1.2 Alternating current mains transient voltage ruggedness
The ACS108 switch is able to withstand safely the AC mains transients either by clamping
the low energy spikes or by breaking-over when subjected to high energy shocks, even with
high turn-on current rises.
The test circuit shown in Figure 18 is representative of the final ACS108 application, and is
also used to test the AC switch according to the IEC 61000-4-5 standard conditions. Thanks
to the load limiting the current, the ACS108 switch withstands the voltage spikes up to 2 kV
above the peak mains voltage. The protection is based on an overvoltage crowbar
technology. Actually, the ACS108 breaks over safely as shown in Figure 19. The ACS108
recovers its blocking voltage capability after the surge (switch off back at the next zero
crossing of the current).
Such non-repetitive tests can be done 10 times on each AC mains voltage polarity.
Figure 18. Overvoltage ruggedness test circuit for resistive and inductive loads,
T
= 25 °C (conditions equivalent to IEC 61000-4-5 standard)
amb
Doc ID 6518 Rev 3 7/13

Alternating current mains switch - basic application ACS108
IT(4 A/div)
V
T
(200 V/div)
I
T max
= 17.2 A
dIT/dt = 1.8 A/µs
500 ns/div
Figure 19. Typical current and voltage waveforms across the ACS108 (+2 kV surge,
IEC 61000-4-5 standard)
8/13 Doc ID 6518 Rev 3

ACS108 Ordering information scheme
ACS 1 08 - 6 S A -TR
AC switch series
Number of switches
Current
Voltage
Sensitivity
Package
Packing
08 = 0.8 A rms
6 = 600 V
8 = 800 V
S = 10 mA
A = TO-92
N = SOT-223
TR = Tape and reel 7” (SOT-223, 1000 pieces) 13” (TO-92, 2000 pieces)
AP = Ammopack (TO-92, 2000 pieces)
Blank = (TO-92, 2500 pieces)bulk
3 Ordering information scheme
Figure 20. Ordering information scheme
Doc ID 6518 Rev 3 9/13

Package information ACS108
A
F
C
B
a
DE
4 Package information
● Epoxy meets UL94, V0
● Lead-free packages
In order to meet environmental requirements, ST offers these devices in different grades of
ECOPACK
specifications, grade definitions and product status are available at: www.st.com
ECOPACK
Table 6. TO-92 dimensions
®
packages, depending on their level of environmental compliance. ECOPACK®
®
is an ST trademark.
.
Dimensions
Ref
Millimeters Inches
Min. Typ. Max. Min. Typ. Max.
A1.35 0.053
B 4.70 0.185
C2.54 0.100
D 4.40 0.173
E 12.70 0.500
F 3.70 0.146
a 0.50 0.019
10/13 Doc ID 6518 Rev 3

ACS108 Package information
A
A1
e1
D
B1
H
E
e
1243
B
V
c
3.25
1.32
7.80
5.16
1.32
2.30 0.95
Table 7. SOT-223 dimensions
Dimensions
Ref.
Millimeters Inches
Min. Typ. Max. Min. Typ. Max.
A1.800.071
A1 0.02 0.10 0.001 0.004
B 0.60 0.70 0.85 0.024 0.027 0.033
B1 2.90 3.00 3.15 0.114 0.118 0.124
c 0.24 0.26 0.35 0.009 0.010 0.014
(1)
6.30 6.50 6.70 0.248 0.256 0.264
D
e 2.3 0.090
e1 4.6 0.181
(1)
3.30 3.50 3.70 0.130 0.138 0.146
E
H 6.70 7.00 7.30 0.264 0.276 0.287
V 10° max
1. Do not include mold flash or protrusions. Mold flash or protrusions shall not exceed 0.15mm (0.006inches)
Figure 21. SOT-223 footprint (dimensions in mm)
Doc ID 6518 Rev 3 11/13

Ordering information ACS108
5 Ordering information
Table 8. Ordering information
Order code Marking Package Weight Base Qty Delivery mode
ACS108-6SA
ACS108-6SA-TR TO-92 0.2 g 2000 Tape and reel
ACS108-6SA-AP TO-92 0.2 g 2000 Ammopack
ACS108-6SN-TR ACS 108 6SN SOT-223 0.11 g 1000 Tape and reel
ACS108-8SA
ACS108-8SA-TR TO-92 0.2 g 2000 Tape and reel
ACS108-8SA-AP TO-92 0.2 g 2000 Ammopack
ACS108-8SN-TR ACS 108 8SN SOT-223 0.11 g 1000 Tape and reel
ACS1 086SA
ACS1 088SA
6 Revision history
04
Table 9. Document revision history
Date Revision Changes
Apr_2004 1
21-Jun-2005 2 Marking information updated from ACSxxxx to ACS1xxx.
11-Jul-2012 3 Removed 500 V devices and added 600 V and 800 V devices.
TO-92 0.2 g 2500 Bulk
TO-92 0.2 g 2500 Bulk
Initial release. This datasheet covers order codes previously
described in the datasheet for ACS108-6S, Doc ID 11962, Rev 3
December 2010.
12/13 Doc ID 6518 Rev 3

ACS108
Please Read Carefully:
Information in this document is provided solely in connection with ST products. STMicroelectronics NV and its subsidiaries (“ST”) reserve the
right to make changes, corrections, modifications or improvements, to this document, and the products and services described herein at any
time, without notice.
All ST products are sold pursuant to ST’s terms and conditions of sale.
Purchasers are solely responsible for the choice, selection and use of the ST products and services described herein, and ST assumes no
liability whatsoever relating to the choice, selection or use of the ST products and services described herein.
No license, express or implied, by estoppel or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted under this document. If any part of this
document refers to any third party products or services it shall not be deemed a license grant by ST for the use of such third party products
or services, or any intellectual property contained therein or considered as a warranty covering the use in any manner whatsoever of such
third party products or services or any intellectual property contained therein.
UNLESS OTHERWISE SET FORTH IN ST’S TERMS AND CONDITIONS OF SALE ST DISCLAIMS ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY WITH RESPECT TO THE USE AND/OR SALE OF ST PRODUCTS INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE (AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS UNDER THE LAWS
OF ANY JURISDICTION), OR INFRINGEMENT OF ANY PATENT, COPYRIGHT OR OTHER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY RIGHT.
UNLESS EXPRESSLY APPROVED IN WRITING BY TWO AUTHORIZED ST REPRESENTATIVES, ST PRODUCTS ARE NOT
RECOMMENDED, AUTHORIZED OR WARRANTED FOR USE IN MILITARY, AIR CRAFT, SPACE, LIFE SAVING, OR LIFE SUSTAINING
APPLICATIONS, NOR IN PRODUCTS OR SYSTEMS WHERE FAILURE OR MALFUNCTION MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY,
DEATH, OR SEVERE PROPERTY OR ENVIRONMENTAL DAMAGE. ST PRODUCTS WHICH ARE NOT SPECIFIED AS "AUTOMOTIVE
GRADE" MAY ONLY BE USED IN AUTOMOTIVE APPLICATIONS AT USER’S OWN RISK.
Resale of ST products with provisions different from the statements and/or technical features set forth in this document shall immediately void
any warranty granted by ST for the ST product or service described herein and shall not create or extend in any manner whatsoever, any
liability of ST.
ST and the ST logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of ST in various countries.
Information in this document supersedes and replaces all information previously supplied.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelectronics. All other names are the property of their respective owners.
© 2012 STMicroelectronics - All rights reserved
STMicroelectronics group of companies
Australia - Belgium - Brazil - Canada - China - Czech Republic - Finland - France - Germany - Hong Kong - India - Israel - Italy - Japan -
Malaysia - Malta - Morocco - Philippines - Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - United Kingdom - United States of America
www.st.com
Doc ID 6518 Rev 3 13/13
 Loading...
Loading...