Page 1

IGW/100
Linux Security Gateway
Hardware Reference
SSV Embedded Systems
Heisterbergallee 72
D-30453 Hannover
Phone +49-(0)511-40000-0
Fax +49-(0)511-40000-40
e-mail: sales@ist1.de
Manual Revision: 1.0
Date: 2004-07-18
For further information regarding our products please visit us at www.ssv-comm.de
Page 2

IGW/100 – Content
SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
2
CONTENT
1 INTRODUCTION .................................................................................................4
1.1 Conventions used in this Document.......................................................................... 4
1.2 Checklist.................................................................................................................. 4
1.3 Features IGW/100 .................................................................................................... 5
1.4 Features DIL/NetPC ADNP/1520 ............................................................................. 5
2 IGW/100 OVERVIEW ..........................................................................................6
3 IGW/100 COMPONENTS.....................................................................................7
3.1 10/100Mbps Ethernet (LAN 1) ................................................................................. 7
3.2 10Mbps Ethernet (LAN 2 and LAN 3) ...................................................................... 7
3.3 Power Connector...................................................................................................... 7
3.4 CF LED ................................................................................................................... 8
3.5 Power LED .............................................................................................................. 8
3.6 Reset Button ............................................................................................................ 8
3.7 COM1 Serial Interface ............................................................................................. 8
3.8 DIL/NetPC ADNP/1520 ........................................................................................... 8
3.9 JTAG Interface – JP2 ............................................................................................... 8
3.10 RCM Jumper – JP1 .................................................................................................. 8
3.11 CompactFlash Slot ................................................................................................... 9
3.12 Base Address LAN 2 – JP3....................................................................................... 9
3.13 Base Address LAN 3 – JP4....................................................................................... 9
4 THE IGW/100 IN USE........................................................................................10
4.1 Mounting the IGW/100 on a DIN-Rail.................................................................... 10
4.2 Mounting the IGW/100 on a Wall........................................................................... 10
4.3 Providing with Power............................................................................................. 11
4.4 COM1 Serial Link.................................................................................................. 11
4.5 Ethernet Link ......................................................................................................... 12
4.6 Setting the LAN 1 Base Address ............................................................................ 13
4.7 Setting the LAN 2 and LAN 3 Base Address........................................................... 13
APPENDIX 1: PIN ASSIGNMENT – 128-PIN QIL CONNECTOR ........................................14
A1.1 Pin Assignment – 128-pin QIL Connector (1. Part) ............................................. 14
A1.2 Pin Assignment – 128-pin QIL Connector (2. Part) ............................................. 15
A1.3 Pin Assignment – 128-pin QIL Connector (3. Part) ............................................. 16
A1.4 Pin Assignment – 128-pin QIL Connector (4. Part) ............................................. 17
APPENDIX 2: PIN ASSIGNMENT OF COMPONENTS.............................................. 18
A2.1 COM1 Connector................................................................................................ 18
A2.2 10/100 Mbps Ethernet Connector ........................................................................ 18
A2.3 Power Connector ................................................................................................ 18
A2.4 CompactFlash Slot (1. Part) ................................................................................ 19
A2.5 CompactFlash Slot (2. Part) ................................................................................ 20
Page 3

IGW/100 – Content
SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
3
LIST OF FIGURES .................................................................................................. 21
LIST OF TABLES ....................................................................................................21
LIST OF APPENDIXES ...........................................................................................21
CONTACT ..............................................................................................................22
TRADEMARK ANNOTATIONS.................................................................................22
DOCUMENT HISTORY ...........................................................................................22
Page 4
IGW/100 – Introduction
SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
4
1 INTRODUCTION
The focus of the IGW/100 is on safe communication via Ethernet technology. The
IGW/100 offers therefore three LAN-ports, which are ready to go. One
10/100Mbps LAN-port and two 10Mbps ports are available to integrate the
IGW/100 into various industrial solutions. Of course the purpose of this Gateway
is not limited only to communicating via Ethernet. With the modular DIL/NetPC
ADNP/1520 inside the IGW/100 there are plenty of ideas to realize.
This document describes how to start with the IGW/100. For further information
about the individual components of this product you may follow the links from
our website at http://www.ssv-comm.de.
Our Website contains a lot of technical information, which will be updated in
regular periods.
1.1 Conventions used in this Document
Convention Usage
italic
Filenames, Internet addresses like e.g. www.ssv-comm.de
bold italic
User inputs, command lines and pathnames
bold
Important terms
Table 1-1: Convention usage
1.2 Checklist
Compare the content of your IGW/100 package with the standard checklist below.
If any item is missing or appears to be damaged, please contact SSV Embedded
Systems.
Standard Items
9 IGW/100 Security Gateway with DIL/NetPC ADNP/1520 inside
9 Power supply
9 Null modem cable
9 32MB CompactFlash card
9 User manual
9 Support CD-ROM
Page 5

IGW/100 – Introduction
SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
5
1.3 Features IGW/100
• 128-pin QIL socket for one DIL/NetPC (like the ADNP/1520)
• One CompactFlash slot
• One 10/100Mbps Ethernet interface (LAN 1)
• Two 10Mbps Ethernet interfaces (LAN 2 and LAN 3)
• RS232 serial interface (COM1)
• Power LED
• Two LAN LEDs on each LAN interface
• One reset switch
• 5V DC power input connector
• Size 162.5 x 106 x 26mm
1.4 Features DIL/NetPC ADNP/1520
• AMD™ SC520 CPU with 133MHz clock speed and FPU
• 16/32/64Mbytes SDRAM memory
• 4/16Mbytes Flash memory
• 10/100Mbps Ethernet interface
• Real time clock
• IDE support
• Two 16C550 UART serial ports
• 20-bit general purpose high-speed parallel I/O
• Seven interrupt inputs, four chip select outputs
• In-system programming features
• 128-pin QIL connector
• 3.3 Volt low power design, single 3.3 V DC supply
• Size 82 x 36mm
Page 6
IGW/100 – IGW/100 Overview
SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
6
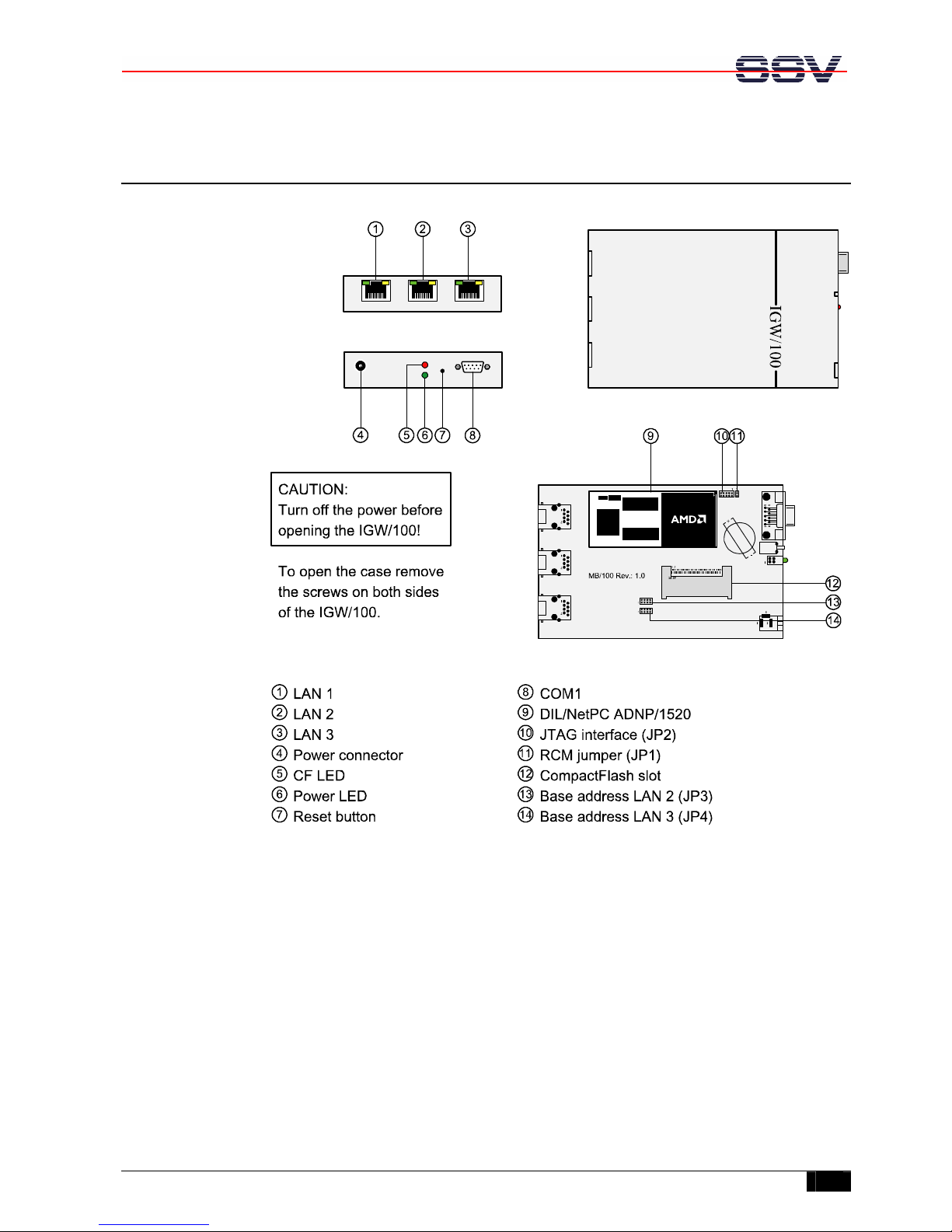
2 IGW/100 OVERVIEW
top view
LAN 1 LAN 2 LAN 3
front view
back view
Power
DC 5V
CF
Power
Reset
RS232
DIL/NetPC ADNP/1520
top view inside
Figure 2-1: Overview of IGW/100
Page 7

IGW/100 – IGW/100 Components
SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
7
3 IGW/100 COMPONENTS
This chapter describes the components of the IGW/100 shown in chapter 2 and
gives a short overview about their respective functions.
3.1 10/100Mbps Ethernet (LAN 1)
The ADNP/1520 inside of the IGW/100 is using an SMSCTM LAN91C111 chip
that allows Ethernet connectivity with a speed up to 100Mbps. The RJ45 Ethernet
connector LAN 1 on the IGW/100 is connected to the SMSC LAN controller on
the ADNP/1520.
The LAN 1 connector owns two LEDs. One green LED in the upper left which is
on when a LAN link is established. One yellow LED in the upper right corner
shows LAN activity by blinking.
LAN link LAN activity
Figure 3-2: LEDs on LAN 1 connector
3.2 10Mbps Ethernet (LAN 2 and LAN 3)
Next to the LAN 1 port there are two 10Mbps Ethernet ports available – called
LAN 2 and LAN 3. These ports have standard RJ45 interfaces. LAN 2 and LAN 3
are not provided through your ADNP/1520 inside of the IGW/100. Instead they
come along with two Realtek LAN controller chips onboard. Both LAN-ports can
be configured separately via jumper settings (please see chapter 4.7). This concerns the base addresses and interrupts.
Note: The LAN activity LEDs of LAN 2 and LAN 3 are inverted! The LEDs are
on when there is no LAN activity and they are off when there is LAN activity.
LAN link LAN activity
Figure 3-3: LEDs on LAN 2 and LAN 3 connector
3.3 Power Connector
The IGW/100 needs a supply voltage of 5V DC to work. In your IGW/100 package you will find a plug-in power supply unit to provide the system with the necessary power.
Caution:
Providing the IGW/100 with a voltage higher than the regular 5V DC ±10% could
resolve in damaged board components!
Page 8

IGW/100 – IGW/100 Components
SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
8
3.4 CF LED
The red CF LED is located directly above the Power LED. The CF LED flashes
when there is any activity on the CompactFlash slot. Please see chapter ? how to
insert a CompactFlash card.
3.5 Power LED
The green power LED indicates a present supply voltage. This LED is on when
the IGW/100 is provided with 5V DC voltage by power supply. If this LED is off,
check the connection between the power supply and the IGW/100.
3.6 Reset Button
Press the reset button if the system hangs or you need to restart it. Pressing the reset button will only restart the ADNP/1520. To reset connected devices, turn off
power from the system.
3.7 COM1 Serial Interface
The IGW/100 is equipped with a standard RS232 serial interface named COM1.
This interface comes with a 9-pin Sub-D male connector. The pin assignment of
COM1 is identical to the COM port assignment of a PC so it is possible to use a
standard cable.
3.8 DIL/NetPC ADNP/1520
This is the main component of the IGW/100. The DIL/NetPC ADNP/1520 is
equipped an embedded Linux. Please contact SSV for further information.
Please see chapter 2 how to open the IGW/100.
3.9 JTAG Interface – JP2
The JTAG interface JP2 is for service purposes only. For more information contact our support staff.
Please see chapter 2 how to open the IGW/100.
3.10 RCM Jumper – JP1
Use the RCM-jumper JP1 to activate RCM (Remote Console Mode) for the
ADNP/1520. RCM offers the possibility to control the ADNP/1520 via a terminal
program.
Please see chapter 2 how to open the IGW/100.
To enable RCM place a jumper cap on both pins of the RCM-jumper, so that it is
short.
Page 9

IGW/100 – IGW/100 Components
SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
9
If you remove the jumper cap or place the jumper cap on just one pin, the jumper
is not set and you can not use RCM.
RCM disabled (JP1 not set)
RCM enabled (JP1 set)
jumper cap
Figure 3-1: RCM-jumper in detail
If the RCM jumper is set you will see some boot messages on the serial port
COM1. If the RCM jumper is not set, these messages are blocked.
3.11 CompactFlash Slot
With the CompactFlash slot you can use CF cards with the IGW/100.
Please see chapter 2 how to open the IGW/100.
Note: The CompactFlash slot works only with CF cards in True-IDE-Mode.
The CF cards must be hardwired as master.
Please see chapter A2.4 and A2.5 for the complete pinout of the CompactFlash
slot.
3.12 Base Address LAN 2 – JP3
The Jumper field JP3 allows you to change the base address for LAN 2. The default base address for LAN 2 is 340h. For detailed information please refer to
chapter 4.7.
Please see chapter 2 how to open the IGW/100.
3.13 Base Address LAN 3 – JP4
The Jumper field JP4 allows you to change the base address for LAN 3. The default base address for LAN 3 is 360h. Please refer to chapter 4.7 for detailed information.
Please see chapter 2 how to open the IGW/100.
Page 10

IGW/100 – The IGW/100 in use
SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
10
4 THE IGW/100 IN USE
4.1 Mounting the IGW/100 on a DIN-Rail
To mount the IGW/100 on a DIN-rail is very simple. To click the IGW/100 on the
DIN-rail, just hinge the device into the upper edge of the DIN rail. Then press it
downwards to compress the spring inside the DIN-rail mounting unit (1). After
this, push the IGW/100 against the DIN-rail as to snap it on.
Figure 4-1: Mounting the IGW/100 on a DIN-rail
To snap the IGW/100 off, pull the plastic disassembling lever on the bottom of the
IGW/100 downwards and remove the device from the DIN-rail.
4.2 Mounting the IGW/100 on a Wall
Mounting the IGW/100 on a wall is very simple. First fix the wall mounting units
on the case with the two screws on each side of the IGW/100. Now you can screw
the IGW/100 on a wall.
Figure 4-2: Fixing the wall mounting units on the IGW/100
Page 11

IGW/100 – The IGW/100 in use
SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
11
4.3 Providing with Power
The IGW/100 needs a supply voltage of 5V DC to work. In your package you will
find a plug-in power supply unit to provide the system with the necessary power.
After the connection of all cables the IGW/100 is ready to run.
Figure 4-3: Power supply connection
Caution:
Providing the IGW/100 with a voltage higher than the regular 5V DC ±10% could
resolve in damaged board components.
SSV recommends to power off the IGW/100 every time you alter or modify board
configurations like jumper settings or cable connections.
4.4 COM1 Serial Link
COM1 is mostly used for basic communication with the IGW/100 and follows the
RS232 protocol. The interface has a 9-pin Sub-D male connector. When using a
remote terminal on this port, make sure the RCM jumper is set (please see chap-
ter 3.10).
For a basic communication with the IGW/100 use a null modemcable on port
COM1. This cable comes along with your IGW/100 package. Please connect the
IGW/100 with the COM port of your development system by using this cable.
Figure 4-4: Serial link
Page 12

IGW/100 – The IGW/100 in use
SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
12
4.5 Ethernet Link
The Ethernet link on port LAN 1 requires a patch cable that is 100Mbps compliant, i.e. a CAT5 cable. For Ethernet links on ports LAN 2 and 3 the patch cable
must be 10Mbps compliant. Furthermore one hub or switch and an Ethernet LAN
adapter for your development system are needed.
The figures 4-5 and 4-6 show the connections with port LAN 1. Connections to
the port LAN 2 and LAN 3 can be made equivalently.
Please refer to chapter 4.7 for the LAN 2 and LAN 3 jumper settings.
Figure 4-5: Ethernet link on LAN 1 with hub or switch
If you want to connect your development system directly to the IGW/100 place a
crossover cable between these two systems as shown below.
Figure 4-6: Ethernet link on LAN 1 with crossover cable
Page 13

IGW/100 – The IGW/100 in use
SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
13
4.6 Setting the LAN 1 Base Address
The LAN 1 port base address is fixed on 300h. This setting can not be changed.
4.7 Setting the LAN 2 and LAN 3 Base Address
By default the base address for LAN 2 is set to 340h. The default base address of
LAN 3 is set to 360h. Please make sure that the base addresses of LAN 2 and
LAN 3 are not set to an equal value – LAN 2 and LAN 3 must be set to different
base addresses.
Please see chapter 2 how to open the IGW/100.
To change the LAN 2 or LAN 3 base address the jumpers JP3 and JP4 have to be
set like shown in table 4-1. The example below shows the jumper position to set
the base address on 340h. Please refer to table 4-1 to configure LAN 2 and LAN 3
on other base addresses.
jumper cap
Figure 4-7: LAN base address jumper in detail
Default Base Address Pins 1 and 2 Pins 3 and 4
LAN 1 (fixed) 300h open open
320h
close
open
LAN 2
340h open
close
LAN 3
360h
close close
380h open open
3A0h
close
open
3C0h open
close
3E0h
close close
200h open open
220h
close
open
240h open
close
260h
close close
280h open open
2A0h
close
open
2C0h open
close
2E0h
close close
Table 4-1: Jumper positions for base addresses LAN 2 and LAN 3
Page 14

IGW/100 – Appendix 1: Pin Assignment – 128-Pin QIL Connector
SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
14
APPENDIX 1: PIN ASSIGNMENT – 128-PIN QIL CONNECTOR
A1.1 Pin Assignment – 128-pin QIL Connector (1. Part)
Pin Name Group Function
1 PA0 PIO Parallel I/O, port A, bit 0*
2 PA1 PIO Parallel I/O, port A, bit 1*
3 PA2 PIO Parallel I/O, port A, bit 2*
4 PA3 PIO Parallel I/O, port A, bit 3*
5 PA4 PIO Parallel I/O, port A, bit 4*
6 PA5 PIO Parallel I/O, port A, bit 5*
7 PA6 PIO Parallel I/O, port A, bit 6*
8 PA7 PIO Parallel I/O, port A, bit 7*
9 PB0 PIO Parallel I/O, port B, bit 0*
10 PB1 PIO Parallel I/O, port B, bit 1*
11 PB2 PIO Parallel I/O, port B, bit 2*
12 PB3 PIO Parallel I/O, port B, bit 3*
13 PB4 PIO Parallel I/O, port B, bit 4*
14 PB5 PIO Parallel I/O, port B, bit 5*
15 PB6 PIO Parallel I/O, port B, bit 6*
16 PB7 PIO Parallel I/O, port B, bit 7*
17 PC0 PIO Parallel I/O, port C, bit 0*
18 PC1 PIO Parallel I/O, port C, bit 1*
19 PC2 PIO Parallel I/O, port C, bit 2*
20 PC3 PIO Parallel I/O, port C, bit 3*
21 RXD1 SIO COM1 serial port, RXD pin
22 TXD1 SIO COM1 serial port, TXD pin
23 CTS1 SIO COM1 serial port, CTS pin
24 RTS1 SIO COM1 serial port, RTS pin
25 DCD1 SIO COM1 serial port, DCD pin
26 DSR1 SIO COM1 serial port, DSR pin
27 DTR1 SIO COM1 serial port, DTR pin
28 RI1 SIO COM1 serial port, RI pin
29 RESIN RESET Reset input
30 TX+ LAN Ethernet interface, TX+ pin
31 TX- LAN Ethernet interface, TX- pin
32 GND ---- Ground
Table A1-1: ADNP/1520 pinout – pin 1 to 32
The PIO pins 1 to 20 are driven by an in-system programmable (ISP) high density
PLD (ispMACH256 or similar). It is possible to change the function of these pins
over the ADNP/1520 JTAG interface. Please contact our support staff for more information.
Page 15

IGW/100 – Appendix 1: Pin Assignment – 128-Pin QIL Connector
SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
15
A1.2 Pin Assignment – 128-pin QIL Connector (2. Part)
Pin Name Group Function
33 RX+ LAN Ethernet interface, RX+ pin
34 RX- LAN Ethernet interface, RX- pin
35 RESOUT RESET Reset output
36 VBAT PSP SC520 real time clock battery input
37 CLKOUT PSP Clock output (default 1.8432 MHz)
38 TXD2 PSP COM2 serial port, TXD pin
39 RXD2 PSP COM2 serial port, RXD pin
40 INT5 PSP Programmable interrupt input 5
41 INT4 PSP Programmable interrupt input 4
42 INT3 PSP Programmable interrupt input 3
43 INT2 PSP Programmable interrupt input 2
44 INT1 PSP Programmable interrupt input 1
45 CS4 PSP Programmable chip select output 4
46 CS3 PSP Programmable chip select output
47 CS2 PSP Programmable chip select output 2
48 CS1 PSP Programmable chip select output 1
49 IOCHRDY PSP I/O channel ready
50 IOR PSP I/O read signal, I/O expansion bus
51 IOW PSP I/O write signal, I/O expansion bus
52 SA3 PSP System expansion bus, address bit 3
53 SA2 PSP System expansion bus, address bit 2
54 SA1 PSP System expansion bus, address bit 1
55 SA0 PSP System expansion bus, address bit 0
56 SD7 PSP System expansion bus, data bit 7
57 SD6 PSP System expansion bus, data bit 6
58 SD5 PSP System expansion bus, data bit 5
59 SD4 PSP System expansion bus, data bit 4
60 SD3 PSP System expansion bus, data bit 3
61 SD2 PSP System expansion bus, data bit 2
62 SD1 PSP System expansion bus, data bit 1
63 SD0 PSP System expansion bus, data bit 0
64 Vcc PSP 3.3V power input
Table A1-2: ADNP/1520 pinout – pin 33 to 64
Page 16

IGW/100 – Appendix 1: Pin Assignment – 128-Pin QIL Connector
SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
16
A1.3 Pin Assignment – 128-pin QIL Connector (3. Part)
Pin Name Group Function
65 SBHE PSP System byte high enable, sys. exp. bus
66 IOCS16 PSP I/O chip select 16, sys. expansion bus
67 MEMCS16 PSP Memory chip select 16, sys. exp. bus
68 MEMW PSP Memory write signal, sys. expansion
69 MEMR PSP Memory read signal, sys. expansion bus
70 BALE PSP bus address latch enable, sys. exp. bus
71 AEN PSP Address enable signal, sys. expansion
72 Reserved PSP Reserved. don’t use
73 RCME PSP Remote Console Mode enable
74 Reserved PSP Reserved. don’t use
75 Reserved PSP Reserved. don’t use
76 Reserved PSP Reserved. don’t use
77 Reserved PSP Reserved. don’t use
78 Reserved PSP Reserved. don’t use
79 Reserved PSP Reserved. don’t use
80 Reserved PSP Reserved. don’t use
81 Reserved PSP Reserved. don’t use
82 Reserved PSP Reserved. don’t use
83 Reserved PSP Reserved. don’t use
84 Reserved PSP Reserved. don’t use
85 INT6 PSP Programmable interrupt input 6
86 INT7 PSP Programmable interrupt input 7
87 IDERES PSP IDE interface reset output
88 IDECS0 PSP IDE interface chip select 0
89 IDECS1 PSP IDE interface chip select 1
90 Reserved PSP Reserved. don’t use
91 Reserved PSP Reserved. don’t use
92 Reserved PSP Reserved. don’t use
93 Reserved PSP Reserved. don’t use
94 Reserved PSP Reserved. don’t use
95 Reserved PSP Reserved. don’t use
96 GND --- Ground
Table A1-3: ADNP/1520 pinout – pin 65 to 96
Page 17

IGW/100 – Appendix 1: Pin Assignment – 128-Pin QIL Connector
SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
17
A1.4 Pin Assignment – 128-pin QIL Connector (4. Part)
Pin Name Group Function
97 LANLED PSP LAN interface activity LED
98 Reserved PSP Reserved. don’t use
99 RSTDRV PSP Reset output, System expansion bus
100 SA23 PSP System expansion bus, address bit 23
101 SA22 PSP System expansion bus, address bit 22
102 SA21 PSP System expansion bus, address bit 21
103 SA20 PSP System expansion bus, address bit 20
104 SA19 PSP System expansion bus, address bit 19
105 SA18 PSP System expansion bus, address bit 18
106 SA17 PSP System expansion bus, address bit 17
107 SA16 PSP System expansion bus, address bit 16
108 SA15 PSP System expansion bus, address bit 15
109 SA14 PSP System expansion bus, address bit 14
110 SA13 PSP System expansion bus, address bit 13
111 SA12 PSP System expansion bus, address bit 12
112 SA11 PSP System expansion bus, address bit 11
113 SA10 PSP System expansion bus, address bit 10
114 SA9 PSP System expansion bus, address bit 9
115 SA8 PSP System expansion bus, address bit 8
116 SA7 PSP System expansion bus, address bit 7
117 SA6 PSP System expansion bus, address bit 6
118 SA5 PSP System expansion bus, address bit 5
119 SA4 PSP System expansion bus, address bit 4
120 SD15 PSP System expansion bus, data bit 15
121 SD14 PSP System expansion bus, data bit 14
122 SD13 PSP System expansion bus, data bit 13
123 SD12 PSP System expansion bus, data bit 12
124 SD11 PSP System expansion bus, data bit 11
125 SD10 PSP System expansion bus, data bit 10
126 SD9 PSP System expansion bus, data bit 9
127 SD8 PSP System expansion bus, data bit 8
128 Vcc --- 3.3V power input
Table A1-4: ADNP/1520 pinout - pin 97 to 128
Page 18

IGW/100 – Appendix 2: Pin Assignment of Components
SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
18
APPENDIX 2: PIN ASSIGNMENT OF COMPONENTS
A2.1 COM1 Connector
Top view Pin Name Function
1 DCD COM1 serial port, DCD pin
2 RXD COM1 serial port, RXD pin
3 TXD COM1 serial port, TXD pin
4 DTR COM1 serial port, DTR pin
5 GND Ground
6 DSR COM1 serial port, DSR pin
7 RTS COM1 serial port, RTS pin
8 CTS COM1 serial port, CTS pin
9 RI COM1 serial port, RI pin
Table A2-1: Pinout COM1 connector
Note: All COM1-port signals are on RS232 level. There is no TTL level available
on these port.
A2.2 10/100 Mbps Ethernet Connector
Top view Pin Name Function
1 TX+ 10/100 Mbps LAN, TX+ pin
2 TX- 10/100 Mbps LAN, TX- pin
3 RX+ 10/100 Mbps LAN, RX+ pin
4 --- Not connected
5 --- Not connected
6 RX- 10/100 Mbps LAN, RX- pin
7 --- Not connected
8 --- Not connected
Table A2-2: Pinout 10/100 Mbps Ethernet connector
A2.3 Power Connector
Top view Pin Name Function
1 Vcc Power In
2 GND Ground
3 GND Ground
Table A2-3: Pinout power connector
Page 19

IGW/100 – Appendix 2: Pin Assignment of Components
SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
19
A2.4 CompactFlash Slot (1. Part)
Top view Pin Name Function
1 GND Ground
2 D3 D3
3 D4 D4
4 D5 D5
5 D6 D6
6 D7 D7
7 CS0# IDE_CS0#
8 A10 Ground
9 ATASEL# Ground
10 A9 Ground
11 A8 Ground
12 A7 Ground
13 Vcc Power
14 A6 Ground
15 A5 Ground
16 A4 Ground
17 A3 Ground
18 A2 S_A2
19 A1 S_A1
20 A0 S_A0
21 D0 S_D0
22 D1 S_D1
23 D2 S_D2
24 IOCS16# Misc 25
25 CD2# CF_CD2#
Table A2-4: Pinout CompactFlash slot – pin 1 to 25
Note: The CompactFlash slot works only with CF cards in True-IDE-Mode. The
CF cards must be hardwired as master.
Page 20

IGW/100 – Appendix 2: Pin Assignment of Components
SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
20
A2.5 CompactFlash Slot (2. Part)
Top view Pin Name Function
26 CD1# CF_CD1#
27 D11 S_D11
28 D12 S_D12
29 D13 S_D13
30 D14 S_D14
31 D15 S_D15
32 CS1# IDE_CS1#
33 VS1 --34 IOR# Misc 4
35 IOW# Misc 3
36 WE# Vcc
37 IRQ IDE_IRQ
38 Vcc Power
39 CSEL# Ground
40 VS2 --41 RESET# IDE_RST#
42 IOCHRDY Misc 10
43 INPACK# --44 REG# Vcc 3
45 DASP# IDE_DASP#
46 PDIAG# --47 D8 S_D8
48 D9 S_D9
49 D10 S_D10
50 GND Ground
Table A2-5: Pinout CompactFlash slot – pin 26 to 50
Note: The CompactFlash slot works only with CF cards in True-IDE-Mode. The
CF cards must be hardwired as master.
Page 21

IGW/100 – List of Figures
SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
21
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 2-1: Overview of IGW/100 ..................................................................................................... 6
Figure 3-2: LEDs on LAN 1 connector .............................................................................................. 7
Figure 3-3: LEDs on LAN 2 and LAN 3 connector............................................................................. 7
Figure 3-1: RCM-jumper in detail...................................................................................................... 9
Figure 4-1: Mounting the IGW/100 on a DIN-rail ............................................................................ 10
Figure 4-2: Fixing the wall mounting units on the IGW/100 ............................................................. 10
Figure 4-3: Power supply connection............................................................................................... 11
Figure 4-4: Serial link ..................................................................................................................... 11
Figure 4-5: Ethernet link on LAN 1 with hub or switch .................................................................... 12
Figure 4-6: Ethernet link on LAN 1 with crossover cable ................................................................. 12
Figure 4-7: LAN base address jumper in detail................................................................................. 13
LIST OF TABLES
Table 1-1: Convention usage ............................................................................................................. 4
Table 4-1: Jumper positions for base addresses LAN 2 and LAN 3 ................................................... 13
Table A1-1: ADNP/1520 pinout – pin 1 to 32 .................................................................................. 14
Table A1-2: ADNP/1520 pinout – pin 33 to 64 ................................................................................ 15
Table A1-3: ADNP/1520 pinout – pin 65 to 96 ................................................................................ 16
Table A1-4: ADNP/1520 pinout - pin 97 to 128 ............................................................................... 17
Table A2-1: Pinout COM1 connector...............................................................................................18
Table A2-2: Pinout 10/100 Mbps Ethernet connector........................................................................ 18
Table A2-3: Pinout power connector................................................................................................ 18
Table A2-4: Pinout CompactFlash slot – pin 1 to 25......................................................................... 19
Table A2-5: Pinout CompactFlash slot – pin 26 to 50....................................................................... 20
LIST OF APPENDIXES
Appendix 1: Pin Assignment – 128-Pin QIL Connector ............................................................... 14
Appendix 2: Pin Assignment of Components..................................................................... 18
List of Figures .................................................................................................................. 21
List of Tables.................................................................................................................... 21
Contact ............................................................................................................................. 22
Trademark Annotations..................................................................................................... 22
Document History............................................................................................................. 22
Page 22

IGW/100 – Contact
SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS
22
CONTACT
SSV Embedded Systems
Heisterbergallee 72
D-30453 Hannover
Phone +49-(0)511-40000-0
Fax +49-(0)511-40000-40
e-mail: sales@ist1.de
Internet: www.ssv-comm.de
TRADEMARK ANNOTATIONS
AMD, the AMD logo and combinations thereof are trademarks of Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
Standard Microsystems and SMSC are registered trademarks of Standard Microsystems Corporation.
Other word marks and logos are owned by their respective holders.
DOCUMENT HISTORY
Revision Date Remarks Name
1.0 2004-07-18 first version WBU
This document is written only for the internal application. The content of this document can change any time without announcement. There is taken over no guarantee for the accuracy of the statements.
Copyright © SSV EMBEDDED SYSTEMS 2004. All rights reserved.
INFORMATION PROVIDED IN THIS DOCUMENT IS PROVIDED 'AS IS'
WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND. The user assumes the entire risk as to
the accuracy and the use of this document. Some names within this document can
be trademarks of their respective holders.
 Loading...
Loading...