Carbon AIS Aids to Navigation Transceiver
Installation and operation manual

Table of contents
1 Glossary............................................................................................... 4
2 Notices .................................................................................................5
2.1 Safety warnings ................................................................................................................................. 5
2.2 General notices.................................................................................................................................. 5
2.3 Regulatory information....................................................................................................................... 5
3 Introduction .........................................................................................7
3.1 About AIS........................................................................................................................................... 7
3.2 System overview................................................................................................................................ 8
3.3 Supported AIS messages .................................................................................................................. 9
4 AIS AtoN product variants ............................................................... 11
5 Installation ........................................................................................12
5.1 What’s in the box ............................................................................................................................. 13
5.2 Preparing for installation .................................................................................................................. 14
5.3 Attaching the bird deterrent ............................................................................................................ 14
5.4 Mounting the transceiver ................................................................................................................. 15
5.5 Transceiver connections.................................................................................................................. 17
5.6 Connecting power............................................................................................................................ 22
5.7 Installing and connecting the VHF antenna .................................................................................... 23
5.8 Installing and connecting an external GNSS antenna ..................................................................... 24
6 Connecting external sensors and systems.................................... 25
6.1 Basic transceiver interfacing............................................................................................................ 25
6.2 Advanced transceiver interfacing..................................................................................................... 26
7 Configuration using proAtoN ..........................................................30
7.1 proAtoN Installation ......................................................................................................................... 30
7.2 Application layout............................................................................................................................. 30
7.3 Transceiver configuration ................................................................................................................ 32
7.4 Transceiver diagnostics ................................................................................................................... 40
7.5 Other features.................................................................................................................................. 43
8 Operation ...........................................................................................44
8.1 Standby operation............................................................................................................................ 44
9 Data messages and data sources ...................................................45
9.1 Product variants without the extended sensor interface .................................................................. 45
9.2 Variants with the extended sensor interface.................................................................................... 46
10 Manual configuration........................................................................ 50
10.1 Basic Type 1 AIS AtoN configuration (FATDMA operation) ............................................................ 50
10.2 NMEA0183 / IEC61162 configuration sentences ............................................................................ 50
10.3 Proprietary configuration sentences ................................................................................................ 57
11 Technical specification ....................................................................59
11.1 Applicable equipment standards...................................................................................................... 59
Page 1

11.2 AIS Transceiver specification .......................................................................................................... 59
11.3 Configuration interface specification ................................................................................................ 62
11.4 Drawings and dimensions................................................................................................................ 63
12 Firmware upgrade procedure ..........................................................66
Page 2

List of figures
Figure 1 The AIS network ........................................................................................................................... 7
Figure 2 Typical AIS AtoN system .............................................................................................................. 8
Figure 3 Typical AIS AtoN system connections ........................................................................................ 12
Figure 4 What’s in the box - typical configuration ..................................................................................... 13
Figure 5 Attaching the bird deterrent ........................................................................................................ 14
Figure 6 Using the mounting bracket........................................................................................................ 15
Figure 7 Mounting to a metal plate ........................................................................................................... 16
Figure 8 Removing the connector cover................................................................................................... 17
Figure 9 Transceiver connector locations ................................................................................................. 18
Figure 10 Cable routing .............................................................................................................................. 18
Figure 11 Connecting power....................................................................................................................... 22
Figure 12 VHF antenna connection ............................................................................................................ 23
Figure 13 Internal GPS antenna location.................................................................................................... 24
Figure 14 Isolated digital input reference circuit ......................................................................................... 28
Figure 15 Relay drive output reference circuit ............................................................................................ 29
Figure 16 proAtoN application layout.......................................................................................................... 30
Figure 17 proAtoN tab synchronisation icons ............................................................................................. 31
Figure 18 proAtoN message schedule tab layout ....................................................................................... 33
Figure 19 Example FATDMA schedule....................................................................................................... 35
Figure 20 Example RATDMA schedule ...................................................................................................... 36
Figure 21 Virtual AtoN configuration tab layout .......................................................................................... 37
Figure 22 Alert messages configuration tab layout..................................................................................... 38
Figure 23 Status input configuration tab layout........................................................................................... 40
Figure 24 Transceiver mounting bracket dimensions ................................................................................. 63
Figure 25 Transceiver general assembly.................................................................................................... 64
Figure 26 Transceiver dimensions.............................................................................................................. 65
Figure 27 vxsend utility screenshot............................................................................................................. 66
Page 3
1 Glossary
AIS Automatic Identification System
AtoN Aid to Navigation
BIIT Built In Integrity Test
FATDMA Fixed Access Time Division Multiple Access
Glossary
GLONASS
GNSS
GPS Global Positioning System
IALA International Association of Lighthouse Authorities
IEC International Electrotechnical commission
ITU International Telecommunication Union
MID (in the context of
MMSI)
MMSI Maritime Mobile Service Identity
NMEA National Marine Electronics Association
RACON A radar transponder used to mark navigational hazards.
RATMDA Random Access Time Division Multiple Access
Global Navigation Satellite System (term specific to the satellite navigation
system operated by the Russian Federation)
Global Navigation Satellite system (general term used to refer to any satellite
navigation system)
Maritime Identification Digits
RS232 Serial data communications standard - see TIA-232-F
RS422 Serial data communications standard see TIA-422-B
SART Search And Rescue Transponder
SDI-12 Serial Data Interface at 1200 Baud
USB Universal Serial Bus
UTC Coordinated Universal Time
VDL VHF Data Link
VHF Very High Frequency
VSWR Voltage Standing Wave Ratio
Page 4

Notices
!
This equipment must be installed in accordance with the instructions provided in this
manual. Failure to do so will seriously affect its performance and reliability. It is strongly
recommended that a trained technician installs and configures this product.
This equipment is intended as an aid to navigation and is not a replacement for proper
navigational judgement. Information provided by the equipment must not be relied upon as
accurate. User decisions based upon information provided by the equipment are done so
entirely at the users own risk.
!
!
!
The accuracy of a GNSS position fix is variable and affected by factors such as the antenna
positioning, how many satellites are used to determine a position and for how long satellite
information has been received.
2Notices
When reading this manual please pay particular attention to warnings marked with the
warning triangle symbol shown on the left. These are important messages for safety,
installation and usage of the transceiver.
2.1 Safety warnings
2.2 General notices
2.2.1 Position source
All marine Automatic Identification System (AIS) transceivers utilise a satellite based location system such as
the Global Positioning Satellite (GPS) network. The general term for satellite based location systems is Global
Navigation Satellite System or GNSS. This manual refers to either GNSS or GPS depending on context.
2.2.2 Product category
This product is categorised as 'exposed' in accordance with the definitions provided in IEC 60945.
2.2.3 Disposal of the product and packaging
Please dispose of this product in accordance with the European WEEE Directive or with the applicable local
regulations for disposal of electrical equipment. Every effort has been made to ensure the packaging for the
product is recyclable. Please dispose of the packaging in an environmentally friendly manner.
2.2.4 Accuracy of this manual
This manual is intended as a guide to the installation, setup and use of this product. Every effort has been made
to ensure the accuracy of this manual, however due to continuous product development this manual may not
be accurate in all respects, therefore no guarantee is offered. If you are in any doubt about any aspect of this
product, please contact your supplier.
The part number and revision number of this manual are shown on the rear cover.
2.3 Regulatory information
2.3.1 Declaration of conformity - R&TTE
The manufacturer of this product declares that this product is in compliance with the essential requirements
and other provisions of the R&TTE directive. The declaration of conformity is provided with the product
document pack. The product carries the CE mark, notified body number and alert symbol as required by the
R&TTE directive. The product is intended for sale in the following member states: Great Britain, France, Spain,
Sweden, Austria, Netherlands, Portugal, Denmark, Norway, Belgium, Italy, Finland, Ireland, Luxembourg,
Germany and Czech Republic.
Page 5

Notices
2.3.2 FCC notice
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a class B digital device, pursuant to part
15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference
in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio
communications.
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1)
This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received,
including interference that may cause undesired operation.
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the user's
authority to operate the equipment.
2.3.3 Industry Canada notice
This device complies with Industry Canada licence-exempt RSS standard(s). Operation is subject to the
following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause interference, and
2. This device must accept any interference, including interference that may cause undesired operation
of the device.
This Class B digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Le présent appareil est conforme aux CNR d'Industrie Canada applicables aux appareils radio exempts de
licence. L'exploitation est autorisée aux deux conditions suivantes :
1. L'appareil ne doit pas produire de brouillage, et
2. L'utilisateur de l'appareil doit accepter tout brouillage radioélectrique subi, même si le brouillage est
susceptible d'en compromettre le Fonctionnement.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe B est conforme à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
Page 6
Introduction
3Introduction
3.1 About AIS
The marine Automatic Identification System (AIS) is a location and vessel information reporting system. It
allows vessels equipped with AIS to automatically and dynamically share and regularly update their position,
speed, course and other information such as vessel identity with similarly equipped vessels. Position is derived
from GPS or GLONASS and communication between vessels is by Very High Frequency (VHF) digital
transmissions.
There are a number of types of AIS device as follows:
● Class A transceivers. These are designed to be fitted to commercial vessels such as cargo ships
and large passenger vessels. Class A transceivers transmit at a higher VHF signal power than class
B transceivers and therefore can be received by more distant vessels, they also transmit more
frequently. Class A transceivers are mandatory on all vessels over 300 gross tonnes on international
voyages and certain types of passenger vessels under the SOLAS mandate.
● Inland AIS stations. Similar to class A transceivers with additional features for use on Inland
waterways.
● Class B transceivers. Similar to Class A transceivers in many ways, but are normally lower cost due
to the less stringent performance requirements. Class B transceivers transmit at a lower power and at
a lower reporting rate than Class A transceivers.
● AIS base stations. AIS base stations are used by Vessel Traffic Systems to monitor and control the
transmissions of AIS transceivers.
● Aids to Navigation (AtoN) transceivers. AtoNs are transceivers mounted on buoys or other
hazards to shipping which transmit details of their location to the surrounding vessels.
● AIS receivers. AIS receivers receive transmissions from Class A transceivers, Class B transceivers,
AtoNs and AIS base stations but do not transmit any information about the vessel on which they are
installed.
This product is an AIS Aids to Navigation (AtoN) transceiver.
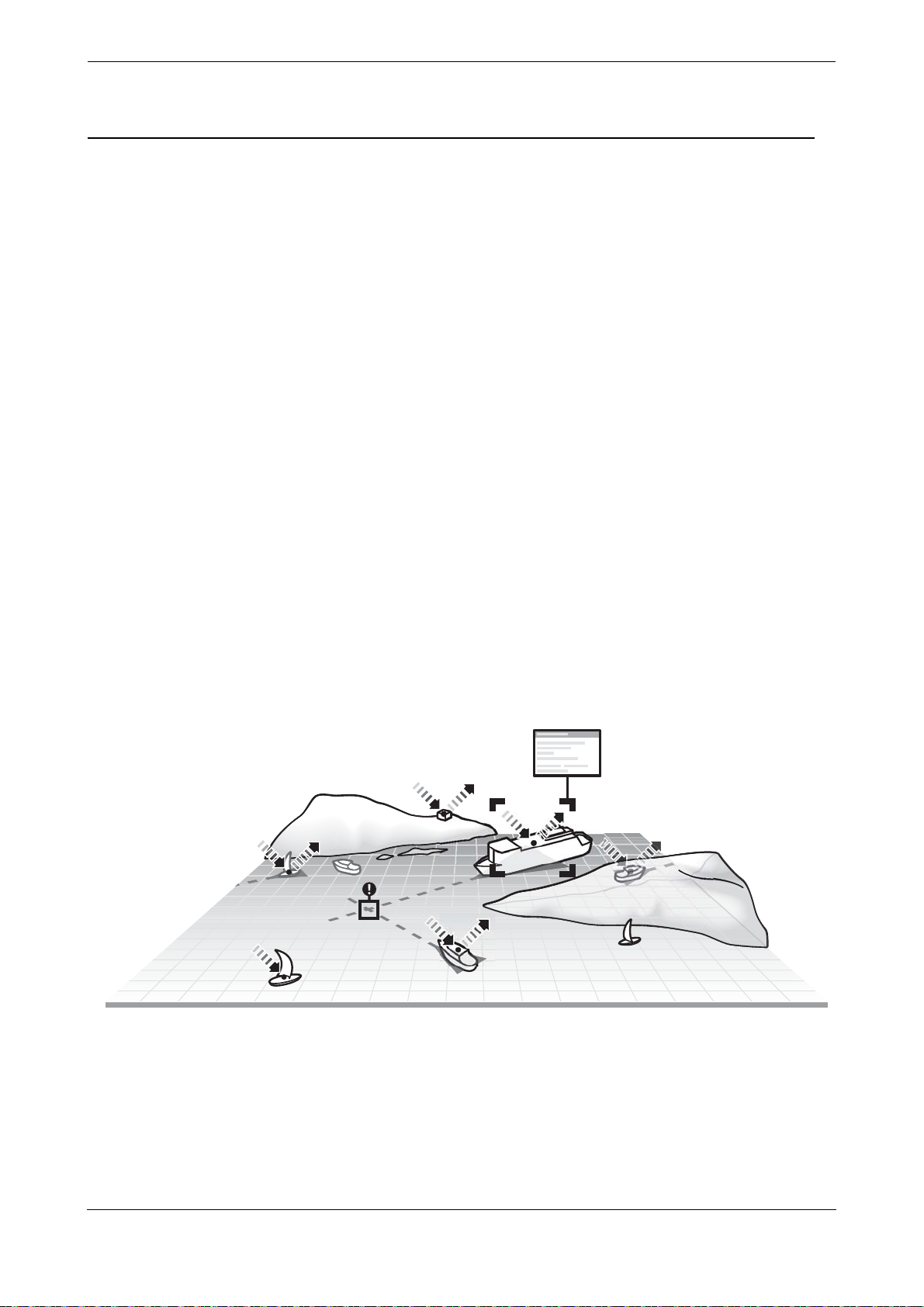
Figure 1 The AIS network
Page 7

Introduction
3.2 System overview
This AIS AtoN is a self contained device supporting both Type 1 (transmit only) and Type 3 (transmit and
receive) operation. It is designed for installation in exposed locations on physical AtoN structures. The AIS
AtoN can be supplied with an optional sensor interface platform which interfaces to sensors (such as weather
instruments) and transmits measured data via AIS messages to surrounding vessels and shore stations.
The AIS AtoN has an exceptionally low power consumption making it suitable for installation on floating Aids
to Navigation with solar charged power systems. The lowest power consumption is achieved when operating
as a Type 1 AIS AtoN transmitting only position information. Further description of Type 1 and Type 3 operation
is provided below.
Figure 2 Typical AIS AtoN system
3.2.1 Type 1 AIS AtoN
A Type 1 AIS AtoN is a transmit only device using the FATDMA (Fixed Access Time Division Multiple Access)
access scheme. This requires that the AIS AtoN is configured with fixed AIS time slots in which it will transmit
AIS messages. Mobile AIS stations operating in the area where a Type 1 AIS AtoN is installed need to be aware
of the time slots allocated to the AIS AtoN. The slots allocated to the AIS AtoN are 'reserved' by AIS Base
Station transmissions covering the area in which the AIS AtoN is installed.
This mode of operation therefore requires that an AIS base station is operating in the same area as the AIS
AtoN and is configured to make the necessary slot reservations.
3.2.2 Type 3 AIS AtoN
A Type 3 AIS AtoN has transmit and receive capability and can therefore use either the FATDMA or RATDMA
(Random Access Time Division Multiple Access) access schemes. The RATDMA scheme allows the AIS AtoN
to internally allocate slots for transmission of AIS messages without reservation from an AIS Base Station.
AIS receive capability also allows a Type 3 AIS AtoN to be configured and queried for status via AIS messages
sent from a shore station (known as VDL configuration). An extension of VDL configuration is 'Chaining' where
configuration and query commands are passed along a 'chain' of AIS AtoN stations to a distant station beyond
the range of direct communication with a shore station.
3.2.3 GNSS systems
The AIS AtoN includes an internal GNSS receiver supporting the GPS system as standard.
Page 8
Introduction
3.3 Supported AIS messages
The transceiver supports the following AIS message types.
ITU-R
M.1371-4
Message
number
6 Binary addressed message
7 Binary acknowledge message
8 Binary broadcast message Transmitted
12
Description
Addressed safety related
message
Transmitted /
Received by
AtoN
Transceiver
Transmitted
and received
Transmitted
and received
Transmitted
Application
The transceiver uses message 6 to send
binary data (relating to connected
sensors and systems) to a specific shore
station. The transceiver can also receive
addressed binary messages for the
purpose of configuration and control.
This message is transmitted to
acknowledge receipt of a binary
message. The transceiver can also
receiver acknowledgements relating to
its own addressed binary transmissions.
The transceiver uses message 8 to
broadcast binary data (relating to
connected sensors and systems) to all
other AIS stations in range.
The transceiver can be configured to
transmit an addressed safety related
message to a specific shore station to
alert the operator to an off position,
vessel proximity or built in test failure
condition.
13
14
17
Acknowledgement of received
addressed safety related
message
Safety related broadcast
message
DGNSS broadcast binary
message
Received
Transmitted
Received
The transceiver receives message 13 in
acknowledgement of its transmission of
message 12.
The transceiver can be configured to
transmit a broadcast safety related
message to all AIS stations in range to
warn of an off position, vessel proximity
or built in test failure condition.
The transceiver can receive and process
DGNSS corrections provided from a
shore station using message #17. The
content of these messages can be used
to improve the accuracy of the on board
GPS receiver.
Page 9
Introduction
ITU-R
M.1371-4
Message
number
20 Data link management message Received
21 Aids to Navigation report Transmitted
25 Single slot binary message
Description
Transmitted /
Received by
AtoN
Transceiver
Transmitted
and received
Application
When operating as a Type 3 transceiver
slot reservations made by a shore
station using message 20 will be
observed by the transceiver.
This is the primary message transmitted
by the transceiver. It contains the
position, identification and status of the
transceiver.
This message can be used for remote
(over the air) configuration of the
transceiver and configuration of a ‘chain’
of transceivers.
Page 10

AIS AtoN product variants
!
A system of icons is used throughout this manual to highlight which AIS AtoN configurations
a particular section, paragraph or illustration applies to. Sections without any icons apply to
all configurations.
T1
T1+S
T3
T3+S
4 AIS AtoN product variants
The transceiver is available in four variants with different AIS functionality and facilities for connection of
external equipment. This manual describes features and functions for all possible product configurations.
The configuration of the AIS AtoN as Type 1 or Type 3 is selected when ordering the device. The possible
configurations are listed below.
● Type 1 without sensor interfaces
● Type 1 with sensor interfaces
● Type 3 without sensor interfaces
● Type 3 with sensor interfaces
Page 11

Installation
T1
T1+S
T3
T3+S
VHF antenna
Lantern (optional)
12/24V DC supply
GPS antenna (optional)
Meteorological sensors
(optional)
Other sensors and
monitoring equipment
(optional)
AIS AtoN
5 Installation
The AIS AtoN transceiver has been designed for ease of installation. The transceiver is self contained requiring
only an external VHF antenna and power source for a basic installation. A typical system and connection
diagram is provided in Figure 3.
Figure 3 Typical AIS AtoN system connections
The main installation and commissioning steps are:
1. Mount the transceiver in a suitable location on the physical Aid to Navigation
2. Install a VHF antenna according to the manufacturers instructions
3. Connect any sensor interfaces and lamp / RACON monitoring signals
4. Connect power to the transceiver
5. Configure and commission the transceiver via USB (note that this step can be carried out on shore
prior to installation in a remote location)
Page 12

Installation
Product manual
AIS AtoN Transceiver
Power and data cable
Bird deterant components
Product CD
or
T1+S
5.1 What’s in the box
Figure 4 shows the typical items included with the AIS AtoN transceiver. Note that the box contents vary with
the specific product configuration. The following section gives a brief overview of each item. Please ensure all
items are present and if any are missing please contact your supplier.
Figure 4 What’s in the box - typical configuration
● AIS AtoN transceiver
The main transceiver (incorporating internal GPS antenna).
● Bird deterrent spikes
Can be affixed to the top of the transceiver if required.
● Mounting bracket and fixings
Stainless steel bracket for mounting the transceiver to the physical AtoN structure.
● Power and interface cable
A 2m (6.6ft) long cable to supply power to the transceiver. This cable also carries some data interfaces
and status signals for connection to external equipment. Depending on the supplied configuration a
connector shell may be provided in place of the assembled cable.
● USB configuration cable
A 2m (6.6ft) long USB cable for connection to a PC when configuring the transceiver.
● Sensor interface cables
T3+S
2m (6.6ft) long cables for interfacing the transceiver to external sensors and systems. These cables
are optional items and supplied only with transceiver configurations that include a sensor interface.
Depending on the supplied configuration a connector shell may be provided in place of the assembled
cable.
● User manual
This document.
● Support tools CD
CD containing transceiver PC configuration and diagnostic tools.
Page 13

Installation
T1
T1+S
T3
T3+S
T1
T1+S
T3+S
5.2 Preparing for installation
In addition to the items provided with the transceiver the following items will be required to complete the
installation.
5.2.1 Tools and wiring accessories
The following tools and wiring accessories are required for installation:
● A PoziDriv® screwdriver for assembly of the bird deterrent.
● A 5mm hex key for assembly of the enclosure to the mounting bracket, and assembly of the
connector cover.
● A 10mm spanner for installation of the mounting bracket u-bolts.
● Suitable power supply cable (0.75mm2 conductor cross section for power supply connections).
● 5A rated fuse or breaker appropriate to the electrical installation.
● Zip ties to secure cables during installation.
● Self amalgamating tape to seal any coaxial cable joints.
5.2.2 VHF antenna and cable
Connection of a suitable VHF antenna will be required for the AIS AtoN transceiver to operate. A robust marine
band VHF antenna suited to the environment in which the AtoN will operate should be selected. The antenna
cable should be terminated with a male N type connector. Any joins in the antenna cable should be made with
co-axial connectors and sealed appropriately. It is recommended that RG-213 cable (or equivalent) is used to
connect the VHF antenna.
5.3 Attaching the bird deterrent
The bird deterrent spikes are attached to the top of the transceiver using the fixing cap and screw provided.
The bird deterrent is optional and if not required the fixing cap can be attached without the spikes.
Figure 5 Attaching the bird deterrent
T3
Page 14

Installation
T1
T1+S
T3+S
5.4 Mounting the transceiver
The transceiver can be mounted to a physical aid to navigation using either the supplied mounting bracket or
directly to a metal plate with appropriate cut outs.
The installation location should provide a clear sky view to the internal GPS antenna which is located beneath
the bird deterrent fixing point. Consideration should also be given to cable routing when selecting an installation
location.
Overall dimensions for the transceiver are provided in Figure 26.
5.4.1 Using the mounting bracket
The supplied mounting bracket can be used to install the transceiver to a vertical or horizontal pole with
diameter between 1 inch and 2 inches using the supplied 'U' bolts, or to a flat surface using standard bolts (not
supplied). The fixing holes in the supplied bracket are also compatible with Stauff
series, Group 7). A detailed drawing of the mounting bracket can be found in Figure 24.
The transceiver is attached to the mounting bracket using the four M4 nuts and bolts supplied.
T3
®
pipe clamps (standard
Figure 6 Using the mounting bracket
Page 15

Installation
5.4.2 Mounting to a metal plate
The transceiver can be mounted directly to a metal plate with a 150mm diameter cut out and fixing points
located to match the details for the mounting bracket provided in Figure 24.
The transceiver should be secured to the plate using four M4 fixing bolts.
Figure 7 Mounting to a metal plate
Page 16

Installation
T1
T1+S
T3
T3+S
!
Note that all connecting cables must be routed through the connector cover during
installation. The supplied sealing caps must be fitted to any unused connections.
2
1
3
5.5 Transceiver connections
The transceiver connections are protected by the connector cover. To access the connections first remove the
cover as illustrated in Figure 8.
The function of each connector is identified in Figure 9 Note that the sensor interface connectors X and Y are
only functional in product configurations including sensor interfacing. The function and pin allocation for each
connector is described in the following sections.
Figure 8 Removing the connector cover
Page 17

Installation
VHF antenna
Sensor interface connector X
Sensor interface connector Y
Ground stud
Power and transceiver
data connector (W)
External GPS antenna
Figure 9 Transceiver connector locations
The transceiver incorporates cable routing and retention features in a screw fit component beneath the
connectors. Cables should be routed through the channels provided as illustrated in Figure 10.
Figure 10 Cable routing
Page 18

Installation
T1
T1+S
T3
T3+S
!
Power connections should be kept as short as possible in order to minimise voltage drop. The
cable used to connect power to the connector pins A and C should have conductors with a
cross sectional area of 0.75mm
2
.
5.5.1 Power and transceiver interface connector
This connector provides power to the transceiver along with interface connections for basic transceiver
connectivity. The connector is a Souriau UTS714D19PW32 with type W keying and the mating half is
UTS6JC14E19SW. This connector is IP68 rated when mated or unmated.
Pin
ID
A VIN- Transceiver power input return / 0V connection
B USER_PWR 3.3V DC output to supply interface circuits. Maximum output current
C VIN+ Transceiver power input connection (10 to 32VDC)
D NMEA0183_TX1_A Transceiver NMEA0183 port 1 TX A+ signal
E NMEA0183_TX1_B Transceiver NMEA0183 port 1 TX B- signal
F NMEA0183_RX1_B Transceiver NMEA0183 port 1 RX B- signal
G NMEA0183_RX1_A Transceiver NMEA0183 port 1 RX A+ signal
H NMEA0183_RX2_A Transceiver NMEA0183 port 2 RX A+ signal
J NMEA0183_RX2_B Transceiver NMEA0183 port 2 RX B- signal
K USER_IO_0 Transceiver user IO signal 0 (Light on/off input)
L USER_IO_1 Transceiver user IO signal 1 (Light health input)
M USER_IO_2 Transceiver user IO signal 2 (Racon health input)
N GND Signal ground
Signal name Function & Notes
200mA.
P RELAY_DR_1 Relay drive output 1*
R RELAY_DR_2 Relay drive output 2*
S GND Signal ground
T USER_IO_3 Transceiver user IO signal 3
U USER_IO_4 Transceiver user IO signal 4
V USER_WKUP External wakeup input**
* Only available when configuration includes a sensor interface, otherwise these pins are not connected.
** Use only under direction of your supplier
The transceiver may be supplied with an optional pre-wired power and transceiver interface cable. Please refer
to the cable drawing supplied with the transceiver to identify the individual wire colours relating to the signals
described above.
Page 19

Installation
T1
T1+S
T3
T3+S
T1+S
T3+S
5.5.2 USB connector
The USB connector provides USB interfaces for configuration of the transceiver and sensor interface (if
provided). Only the supplied USB interface cable should be used to connect the transceiver to a PC during
configuration. For further information on configuration of the transceiver and sensor interfaces refer to section
7. The USB connector should be left disconnected in the final installation and protected with the blanking cap
supplied.
5.5.3 Sensor interface connector X
This connector provides a range of sensor interface connections. The connector is a Souriau
UTS714D19PW32 with type X keying and the mating half is UTS6JC14E19SX. This connector is IP68 rated
when mated or unmated.
Pin
allocation
A ISENSE- Lamp current sense loop return (max 5A)
B ISENSE+ Lamp current sense loop input (max 5A)
C AN_1+ Non-isolated analogue input 1 positive connection
D S_RS422_TX1_A Sensor interface RS422 port TX A+ signal
E S_RS422_TX1_B Sensor interface RS422 port TX B- signal
F S_RS422_RX1_A Sensor interface RS422 port RX A+ signal
G S_RS422_RX1_B Sensor interface RS422 port RX B- signal
H S_RS232_TX1 Sensor interface RS232 port 1 TX
J S_RS232_RX1 Sensor interface RS232 port 1 RX
K ISO_DI1+ Isolated digital input 1 positive
L ISO_DI1- Isolated digital input 1 negative
M ISO_DI2+ Isolated digital input 2 positive
N ISO_DI2- Isolated digital input 2 negative
Signal name Function & Notes
P AN_1- Non-isolated analogue input 1 negative connection
R S_DIG_IO_1 Non-isolated digital IO 1
S S_RS422_GND Senor interface RS422 port ground
T GND Signal ground
U S_DIG_IO_3 Non-isolated digital IO 3
V S_DIG_IO_2 Non-isolated digital IO 2
The transceiver may be supplied with an optional pre-wired sensor interface cable. Please refer to the cable
drawing supplied with the transceiver to identify the individual wire colours relating to the signals described
above.
Page 20

Installation
T1+S
T3+S
5.5.4 Sensor interface connector Y
This connector provides a range of sensor interface connections. The connector is a Souriau
UTS714D19PW32 with type Y keying and the mating half is UTS6JC14E19SY . This connector is IP68 rated
when mated or unmated.
Pin
allocation
A S_RS232_TX2 Sensor interface RS232 port 2 TX
B S_RS232_RX2 Sensor interface RS232 port 2 RX
C S_DIG_IO_4 Non-isolated digital IO 4
D EXT_WAKEUP External wake up input
E SDI_DATA SDI Bus data signal
F ISO_DI_3+ Isolated digital input 3 positive
G ISO_DI_3- Isolated digital input 3 negative
H ISO_DI_4+ Isolated digital input 4 positive
J ISO_DI_4- Isolated digital input 4 negative
K ISO_DI_5+ Isolated digital input 5 positive
L ISO_DI_5- Isolated digital input 5 negative
M ISO_AN_1+ Isolated analogue input 1 positive
N ISO_AN_1- Isolated analogue input 1 negative
Signal name Function & Notes
P ISO_AN_2+ Isolated analogue input 2 positive
R ISO_AN_2- Isolated analogue input 2 negative
S AN_2+ Non-isolated analogue input 2 positive connection
T AN_2- Non-isolated analogue input 2 negative connection
U AN_3+ Non-isolated analogue input 3 positive connection
V AN_3- Non-isolated analogue input 3 negative connection
The transceiver may be supplied with an optional pre-wired sensor interface cable. Please refer to the cable
drawing supplied with the transceiver to identify the individual wire colours relating to the signals described
above.
5.5.5 VHF antenna connector
The VHF antenna connector is a female 'N' type co-axial connector. The antenna ground is galvanically
isolated from the AIS AtoN system ground. The connector and mating half must be sealed with self
amalgamating tape once mated. A lighting protector should be installed in line with the VHF antenna connector.
The recommended lighting protector is Huber+Suhner part number 3401.17.C with gas discharge tube
9071.99.0547.
5.5.6 External GNSS antenna connector
The external GNSS antenna connector is a female 'TNC' co-axial connector. An external GNSS antenna can
be connected here if the installation prohibits use of the internal GPS antenna. The connector and mating half
must be sealed with self amalgamating tape once mated.
Page 21

Installation
T1
T1+S
T3+S
Red
Black
Power supply +
Power supply –
Refer to section 5.8 for further detail on the selection and installation of an external GNSS antenna. If the
External GNSS antenna connector is not used it must be protected with the supplied blanking cap.
5.5.7 Earth connection stud
The earth connection stud is an M4 stud connected to the VHF antenna ground. This point should be connected
to a common grounding point for lighting protection. Note that the ground stud is galvanically isolated from the
incoming transceiver and power supply.
5.6 Connecting power
The transceiver requires a nominal 12VDC or 24VDC supply and will operate between 10V and 32VDC. The
peak current drawn when operating from 12VDC is 3A and when operating from 24VDC is 2.5A. Power should
be connected using either the supplied moulded interface connector and cable, or the appropriate Souriau
connector mating half. It is recommended that 5A rated fuses are installed in line with the power supply positive
and negative connections.
T3
Figure 11 Connecting power
Overall power consumption is dependent on the configuration of the transceiver messaging and sensor
interface. Minimum power consumption figures are provided in section 11.
Page 22

Installation
T1
T1+S
T3+S
!
The performance and reliability of the VHF antenna is essential to correct operation of the
transceiver. Ensure that a high quality antenna suitable for use in harsh environmental
conditions is selected. Ensure all co-axial connections are well made and watertight.
!
The VHF antenna should be installed according to the manufacturer's instructions.
VHF antenna
GPS antenna (optional)
AIS AtoN
5.7 Installing and connecting the VHF antenna
The VHF antenna should have the following specification:
● Centre frequency 159MHz
● VSWR < 2.0
● Impedance 50 Ohms
● Power handling 12.5 Watts
● Gain 3dBi or 6dBi
It is recommended that high quality RG213 or RG214 co-axial cable is used to connect the VHF antenna to the
transceiver. The antenna cable should be as short as possible and no more than 30 metres (100 feet) in length.
When selecting the installation location for the VHF antenna:
● Install the antenna as high as possible on the physical aid to navigation
● Keep the antenna away from any large vertical metallic structures.
● Install the antenna as far away as possible from any other VHF antennas
T3
Figure 12 VHF antenna connection
Page 23

Installation
T1
T1+S
T3+S
!
The performance and reliability of the GNSS antenna is essential to correct operation of the
transceiver. Ensure that a high quality antenna suitable for use in harsh environmental
conditions is selected. Ensure all co-axial connections are well made and watertight.
!
The GNSS antenna should be installed according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Internal GPS antenna location
5.8 Installing and connecting an external GNSS antenna
The transceiver has an internal GPS antenna that is suitable for most applications and installation locations.
The location of the internal GPS antenna is shown in Figure 13.
T3
Figure 13 Internal GPS antenna location
If the installation requires an external GNSS antenna it should be specified as follows:
● Centre frequency 1575.42MHz for GPS operation.
● Active antenna with overall gain of at least 20dB
● Bias voltage 3.3V
● Impedance 50 Ohms
● VSWR <2.0
When installing the transceiver (using the internal GPS antenna) or an external GNSS antenna:
● Make sure the antenna has a clear view of the sky with no overhead obstructions
● Position the antenna as far as possible from any VHF or other transmitting antennas
● Position the antenna as high as possible on the physical aid to navigation.
It is recommended that high quality RG213 or RG214 co-axial cable is used to connect the GNSS antenna to
the transceiver. The antenna cable should be as short as possible and no more than 10 metres (30 feet) in
length.
Page 24

Connecting external sensors and systems
T1
T1+S
T3
T3+S
!
Voltages above 3.3V must not be connected to these inputs. An external circuit and isolation
may be required to interface external equipment. Isolated status inputs are available with the
extended sensor interface and are described in section 6.2.
6 Connecting external sensors and systems
The transceiver can be interfaced to external sensors and systems for the transmission of sensor data via the
AIS network. Typically metrological and hydrological sensors are interfaced to the transceiver so that local
conditions can be shared with other AIS users.
The transceiver is available with and without extended sensor interfaces as described in section 4. Section 6.1
describes the interfaces available without the extended sensor interface while section 6.2 describes the
interfaces available with the extended sensor interface.
6.1 Basic transceiver interfacing
This section describes the interfaces available without the extended sensor interface. In this version of the
transceiver only the power and transceiver interface connector is used for connection of external equipment.
The interfaces available are:
● Five user configurable input/output signals
● A bi-directional NMEA0183 port
● An input only NMEA0183 port
The transceiver also has the ability to measure the incoming power supply voltage. This measurement is used
by the transceivers BIIT (Built In Integrity Test) routines and can be used to trigger changes to the transceiver
health flag in AIS message #21 (the AtoN position report) or additional AIS alert messages if so configured.
6.1.1 Basic user configurable input / output signals
The basic user I/O signals are 3.3V logic level signals and configurable as inputs or outputs. These connections
can be configured as inputs and mapped to the AtoN status bits in AIS message #21 (the AtoN position report).
The default mapping of the signals is described in the table below and these connections are available at the
'Power and transceiver interface connector' described in section 5.5.1.
Configuration of the source and other settings for AtoN status information is described in section 6.1.3.
6.1.2 Basic Lamp and RACON status interfacing
Additional circuitry may be required to interface the lamp or RACON status outputs to the transceiver. Please
contact your supplier with details of the lamp or RACON for further information.
The encoding of the connected equipment status to the lamp and RACON status is defined below.
● Light on / off - User IO 0 (logic high input = light on)
● Light health - User IO 1 (logic high input = light error)
● Racon health - User IO 2 (logic high input = RACON operational)
When appropriately configured the status of the lamp and RACON signals will be sampled prior to each AtoN
position report transmission and the status encoded in the message.
6.1.3 AtoN Status source and configuration
AIS AtoN position report messages (AIS message #21) contain status bits describing the status of a connected
lamp and RACON. The general health of the transceiver is also provided as either ‘good health’ or alarm. The
transceiver can be configured to obtain status information from one of three sources:
● Directly from the transceiver basic I/O signals described in 6.1.1
● From the extended sensor interface isolated digital inputs described in 6.2.4
● By input of an ACE (Extended General AtoN Station configuration command) sentence to one of the
transceiver NMEA0183 port. The ACE sentence is described in section
used to supply the status bits for transmission rather than sourcing from the hardware inputs.
Page 25
10.2.2. This sentence can be

Connecting external sensors and systems
T1+S
The source of the status information is configured using either proAtoN (see section 7). The following settings
must also be configured using proAtoN:
● Lamp fitted / not fitted
● Racon fitted / not fitted
● Racon monitored / not monitored
Note that the AIS AtoN ‘health’ bit is generated internally by the transceiver. However, if the ACE sentence is
configured as the source for status information then the AIS AtoN ‘health’ bit is the combination of the internal
transceiver health and the ACE sentence health bit. In this configuration if either the internal transceiver health
or the external health status provided by the ACE sentence is set to ‘1’ (alarm) then the status will be
transmitted as alarm.
6.1.4 Bi-directional NMEA0183 port
The bi-directional NMEA port (port 1) is available at the 'Power and transceiver interface connector' described
in section 5.5.1. This port accepts and outputs NMEA0183/IEC61162-1 sentences for configuration of the
transceiver and communication of binary message payload data (see section 7) to the transceiver for
transmission in AIS messages. Whilst the transceiver is awake own position reports are also output to this port
(as AIVDO messages) and in the case of a Type 3 transceiver remote vessel reports (as AIVDM messages)
are also output.
The electrical and interface specification for this port is as follows:
● Four wire NMEA0183 / IEC61162-1/2 port (RS422 levels)
● Baud rate 38,400baud
● Isolated receiver circuitry, non-isolated transmitter circuitry
Port signal name Function
NMEA0183_TX1_A Transceiver NMEA0183 port 1 TX A+ signal
NMEA0183_TX1_B Transceiver NMEA0183 port 1 TX B- signal
NMEA0183_RX1_B Transceiver NMEA0183 port 1 RX B- signal
NMEA0183_RX1_A Transceiver NMEA0183 port 1 RX A+ signal
6.1.5 Input only NMEA0183 port
The input only NMEA port (port 2) is available at the 'Power and transceiver interface connector' described in
section 5.5.1. The electrical and interface specification for this port is as follows:
● Two wire NMEA0183 / IEC61162-1/2 port (RS422 levels)
● Baud rate 38,400baud
● Isolated receiver circuitry
Port signal name Function
NMEA0183_RX2_A Transceiver NMEA0183 port 2 RX A+ signal
NMEA0183_RX2_B Transceiver NMEA0183 port 2 RX B- signal
6.2 Advanced transceiver interfacing
This section describes the interfaces available with the extended sensor interface. In this version of the
transceiver all three 19 way connectors are used for connection of external equipment. The interfaces available
in addition to those described in section 6.1 are:
● Two fully isolated analogue inputs
T3+S
Page 26

Connecting external sensors and systems
● Three non-isolated analogue inputs
● A lamp current sense loop
● Five isolated digital inputs
● Five non-isolated digital inputs / outputs
● A fully isolated RS422 / NMEA0183 port
● Two RS232 ports
● An SDI-12 serial bus interface (one RS232 port is unavailable if this interface is used)
● Two relay drive outputs
The following sections describe the hardware specification and interface to these inputs. The function of the
sensor interface (in terms of translation of sensor data to AIS messages) is determined by the software
configuration of the AIS AtoN. The default configuration and supported sensors are described in section 8 of
this document. For alternate configurations please refer to the additional documentation supplied with the
product or contact your supplier.
6.2.1 Isolated analogue inputs
The extended sensor interface includes two isolated analogue inputs. These inputs are available at "Sensor
Interface Connector Y" described in section 5.5.4. The electrical and measurement specification of these inputs
is as follows:
● Differential input range ±13.75V
● Impedance 22KΩ
● 16 bit resolution
The voltage to be measured should be applied across the differential positive and negative inputs.
6.2.2 Non-isolated analogue inputs
The extended sensor interface includes three non-isolated analogue inputs. The first of these inputs is available
at the "Sensor Interface Connector X" described in section 5.5.3 and the remaining two inputs at the "Sensor
Interface Connector Y" described in section 5.5.4. The electrical and measurement specification for these
inputs is as follows:
● Differential input range ± 37.2V
● Impedance 620KΩ
● 12 bit resolution
The voltage to be measured should be applied across the differential positive and negative inputs.
6.2.3 Lamp current sense loop
The extended sensor interface includes a lamp current sense loop. This facility is intended for health monitoring
of a lamp on the physical aid to navigation. Connections for the lamp current sense loop are available at
"Sensor Interface Connector X" described in section 5.5.3. The specification of the current sense loop is as
follows:
● Maximum current 5A
● Measurement of currents up to 0.5A
● 12 bit resolution
6.2.4 Isolated digital inputs
The extended sensor interface includes five isolated digital inputs. These inputs are intended for use with status
outputs from external equipment such as lamps, RACONs and power supply monitoring systems. The first two
inputs is available at the "Sensor Interface Connector X" described in section 5.5.3 and the remaining three
inputs at the "Sensor Interface Connector Y" described in section 5.5.4. The specification for these inputs is as
follows:
● Maximum input voltage ±15V
Page 27

● Input impedance 1KΩ
ISO_DI+
To proccessor
1K
100K
100n
1n
3V8
GND
GND
1
2
4
3
BAS70-07
PC357N7J000F
ISO_DI-
● Sensitivity 2.5V
Figure 14 Isolated digital input reference circuit
6.2.5 Non-isolated digital inputs/outputs
Connecting external sensors and systems
The extended sensor interface includes six non-isolated logic level digital interfaces. When configured as
inputs the signal level must not exceed 3.3VDC referenced to the transceiver signal ground. The first three
inputs is available at the "Sensor Interface Connector X" described in section 5.5.3 and the remaining three
inputs at the "Sensor Interface Connector Y" described in section 5.5.4. Note that the S_DIG_IO_5 input can
also act to 'wake' the sensor interface system from sleep if so configured.
6.2.6 Isolated RS422 / NMEA0183 port
The extended sensor interface provides a fully isolated NMEA0183 (RS422 level) serial interface for
connection of external equipment. Connections for the isolated NMEA0183 port are available at "Sensor
Interface Connector X" described in section 5.5.3.
The port operates at 38,400baud by default. The data types accepted are determined by the configuration of
the sensor interface.
6.2.7 RS232 ports
The extended sensor interface provides two non-isolated RS232 interfaces for connection of external
equipment. The first of these ports is available at the "Sensor Interface Connector X" described in section 5.5.3
and the second at the "Sensor Interface Connector Y" described in section 5.5.4.
The port operates at 38,400baud by default. The data types accepted are determined by the configuration of
the sensor interface.
RS232 port 2 shares hardware with the SDI-12 interface described in section 6.2.8 and is not available if the
SDI-12 interface enabled by configuration.
6.2.8 SDI-12 interface
The extended sensor interface provides an SDI-12 for interface to external sensors supporting this bus. The
extended sensor interface operates as an SDI-12 bus master. The electrical interface consists of three
connections:
● A serial data line
● A ground line
● A 12-volt line (used to power connected sensors)
For further information on the SDI-12 interface please refer to the specification available at
http://www.sdi-12.org/. Note that the 12V supply line is not provided by the sensor interface.
Page 28

Connecting external sensors and systems
From processor
RELAY_DRIVE
10K
100R
3V8
GND
BSP75NTA
6.2.9 Relay drive outputs
The extended sensor interface provides two open drain relay drive outputs that default to the normally open
state. The outputs are capable of switching 200mA at 60VDC; a circuit diagram of the output driver is provided
in Figure 15.
Note that use of the relay drive outputs is restricted to configurations where the extended sensor interface is
permanently powered on.
Figure 15 Relay drive output reference circuit
6.2.10 Input voltage monitor
The extended sensor interface has the facility to measure the incoming power supply voltage. This can be used
to provide a measurement of the charge state of a battery supply to the transceiver. The voltage measured can
be included in transmitted AIS measurements if so configured. No additional connections are required in order
to make use of this facility.
Page 29

Configuration using proAtoN
T1
T1+S
T3
T3+S
COM Port selection
Read / Write conguration
Conguration tabs
Status bar
7 Configuration using proAtoN
The proAtoN PC application is supplied on the CD packaged with the transceiver. The application provides
features for configuration of the transceiver and confirming correct operation before deployment. The main
features of the application are:
● Configuration of essential transceiver parameters such as MMSI, name and dimensions
● Configuration of reporting schedules
● Configuration of virtual and/or synthetic AtoN reporting schedules
● Configuration of other messaging features
● GNSS diagnostics
● System diagnostics and alarm display
● Configuration of the source for external equipment status information
7.1 proAtoN Installation
proAtoN should be installed from the CD supplied with the transceiver. The steps to complete the installation
are as follows:
1. Insert the CD into your PC
2. Navigate to the proAtoN folder on the CD
3. Double click the ‘setup.exe’ item to start the installation process
4. Follow on screen instructions to complete the installation
Following successful installation the application can be launched from the proAtoN folder in the Windows start
menu.
USB device drivers for the transceiver are installed automatically during installation of proAtoN.
7.2 Application layout
The basic layout of the proAtoN application is provided in Figure 16.
Figure 16 proAtoN application layout
Page 30

Configuration using proAtoN
Green - Tab synchronised
Red - Tab not synchronised
Blue - Synchronisation in progress
Tab edited (sync required)
COM Port selection
When connected via USB the COM port associated with the transceiver will be listed in the selection drop down.
To connect to the transceiver select the ‘AIS AtoN Port’ option from the drop down and click the ‘Connect’
button.
Read / Write configuration
Clicking the left hand button will transfer current configuration information from the transceiver to proAtoN.
Clicking the right hand button will configure the transceiver with the information currently displayed in proAtoN.
It is possible to select transfer of configuration information relating only to the currently selected tab, or to all
tabs by clicking the drop down arrow to the right of each button.
Configuration tabs
The configuration and status of the transceiver is displayed through a number of tabs.
● Real AtoN tab
Configuration of AtoN MMSI, name, type and dimensions.
● Message schedule tab
Configuration of FATDMA or RATDMA message schedules.
● Virtual AtoN tab
Configuration of virtual and/or synthetic AtoN transmissions.
● Status input configuration tab
Configuration of the source for AtoN status information
● Alert messages tab
Configuration of non-periodic messages (e.g., vessel proximity alert messages).
● GPS
Displays signal strength and status information for the transceiver GPS receiver.
● Diagnostics
Displays software version information, alarms and other key status information.
● Serial data
Displays raw IEC61162 (NMEA0183) data output from the transceiver.
When connected to a transceiver a synchronisation status icon is displayed alongside the title of each tab. This
icon indicates the current synchronisation status of the information displayed in that tab with the internal
configuration of the transceiver. The synchronisation status icons are shown in Figure 17.
Figure 17 proAtoN tab synchronisation icons
Synchronisation is achieved by either writing the configuration displayed in proAtoN to the transceiver (click the
write configuration button), or reading the current configuration from the transceiver for display in proAtoN (click
the read configuration button).
Page 31

Configuration using proAtoN
Status bar
The status bar displays the current connection status of the application (bottom left) and the current GPS time
(if available, bottom right).
7.3 Transceiver configuration
The following sections describe the configuration options available and their effect on the behavior of the
transceiver. Configuration of an AIS AtoN transceiver requires knowledge of the local AIS environment and
may require interaction with shore infrastructure. Familiarity with the current IALA guidelines on the use of AIS
Aids to Navigation (IALA A-126) is assumed.
7.3.1 Configuration of ‘Real’ AtoN parameters
The following parameters associated with the ‘real’ AIS AtoN transceiver should be configured via the ‘Real
AtoN’ tab:
● MMSI
The MMSI number associated with the ‘real’ AtoN. Typically the MMSI number for a ‘real’ AtoN station
follows the format 99MID1XXX where MID is the appropriate national MID and XXX is a number
unique to this station.
● Name
The name of the AtoN station as broadcast to other AIS users. Up to 34 characters are available for
the name.
● Type of AtoN
Select from a list of possible types of AtoN. The types are as defined by IALA in IALA A-126.
● Type of EPFS
Select the type of EPFS (Electronic Position Fixing System) used by the transceiver. The transceiver
is available with either GPS or GLONASS GNSS fitted and the appropriate system should be selected
here. Note this selection does not affect the hardware configuration, only the contents of the ‘Type of
EPFS’ field in transmitted AtoN position reports. Alternatively for a fixed or shore based transceiver a
surveyed position type can be selected. Note that when the surveyed position is selected the
surveyed position is broadcast to other AIS users and GNSS position information is ignored.
● Nominal position
Enter the nominal or charted position of the AtoN. This is the position transmitted to other AIS users
for a fixed AtoN when the ‘Surveyed’ EPFS type is selected. For all other configurations this position
is used to perform ‘off position’ calculations only; the actual GNSS position is broadcast to other
users.
○ The application can average the current GNSS position over 5 minutes and use this value for the
nominal position. Click the ‘Get GNSS position’ button to the right of the latitude and longitude
fields to begin this process.
○ The position accuracy can only be entered when the type of EPFS is set to ‘Surveyed’. The
accuracy should be set in accordance with the accuracy of the surveyed position.
● Off position alternate message enable
The current GNSS position is compared to the nominal position according to the algorithm defined in
IALA A-126 Annex A, Example 1. The off position threshold distance is specified in metres. If the
transceiver determines that it is ‘off position’ then the alternate reporting schedule for message #21
(index 2) is enabled. For example, the alternate reporting schedule could be configured to decrease
the reporting interval if the AtoN has drifted off position. The off position flag in message #21 is set
when off position regardless of this setting.
The transceiver off position algorithm is always operational and compares the current GPS position to
the nominal position of the transceiver.
Page 32

Configuration using proAtoN
!
It is essential that valid nominal position is entered and that a reasonable off position
threshold is entered. If the default nominal position 00° 00’ 00.00”N / 000° 00’ 00.00”E is left
unchanged then the transceiver will always be ‘off position’ resulting in the GPS receiver
being permanently enabled. This will lead to significantly increased power consumption and
the ‘off position’ flag in the Aids to Navigation report will be set.
Add new message
schedules
Current messages
and schedules
Deactivate or remove
selected schedule
● MMSI for addressed messages
This is the destination MMSI used for all addressed message types generated by the transceiver. This
is usually the MMSI of a shore station collecting status information from the transceiver. It is also
possible to enable the acknowledgement of received binary messages (via message #7 or #13).
● Dimensions
The dimensions of the AtoN should be entered to the nearest metre. Guidance on the appropriate
configuration of dimensions for various types of AtoN can be found in IALA A-126.
● Radio channels
Selection of alternative radio channels for AIS transmission and reception is possible, however in
most cases the default channels (AIS1 and AIS2) should be used.
● Transmitter power level
The transmitter power level for the transceiver can be selected as 1W, 2W, 5W or 12.5W. The default
value of 12.5W is appropriate for most scenarios.
7.3.2 Message schedule configuration
The layout of the message schedule tab is described in Figure 18.
Figure 18 proAtoN message schedule tab layout
Default messages
An AIS AtoN position report is made using AIS message #21. This message occupies two AIS slots. The
default configuration shown in proAtoN includes two message #21 schedule configurations. The first
configuration, index 1, is the primary position reporting schedule for the transceiver. The second, index 2, is
the alternate position reporting schedule selected when the ‘off position’ monitor is enabled and the AtoN is
determined to be off position (see section 7.3.1). If the alternate ‘off position’ schedule is not required it can be
deactivated by selecting the associated row in the message schedule table and clicking the ‘Deactivate’ button.
When deactivated the alternate schedule will be greyed out.
Page 33

Configuration using proAtoN
T1
T1+S
T3
T3+S
T3
T3+S
T1
T1+S
T3
T3+S
Adding additional messages to the schedule
Additional binary data messages can be added to the schedule table by selecting the required message type
from the drop down at the top of this tab, then clicking the ‘Add’ button. The available message types are:
● Message #8 - for broadcast of binary data to all other stations in range. The binary data may be
provided by the extended sensor interface (if present) or third party equipment connected to the
transceiver. See section
● Message #6 - for transmission of binary data to an individual destination MMSI. The destination MMSI
is set on the ‘Real AtoN’ tab. The binary data may be provided by the extended sensor interface (if
present) or third party equipment connected to the transceiver. See section
● Message #12 - for transmission of text messages to an individual destination MMSI. The destination
MMSI is set on the ‘Real AtoN’ tab. This schedule is used for transmission of alert messages (see
section
● Message #14 - for broadcast of text messages to all other stations in range. This schedule is used for
transmission of alert messages (see section
Up to four separate schedules are available for each binary message type. Each individual schedule has an
index from 1 to 4 which is used to identify that schedule (for example, message #8 index 2).
Access scheme selection
The TMDA access scheme for each message must be selected as either FATDMA or RATDMA (see section
3.2). The selection is made by selecting the required row in the schedule table, then clicking on the current
access scheme in that row. A drop down menu will then appear in that location allowing selection of the
required access scheme.
● FADTMA
Configuration of an FATDMA schedule continues in section 7.3.3.
● RATDMA
Configuration of an RATMDA schedule continues in section 7.3.4.
7.3.6).
8 for further information.
8 for further information.
7.3.6).
7.3.3 FATDMA Schedule configuration
Using the FATDMA (Fixed Access TDMA) access scheme the actual slot for each transmission made by the
transceiver is specified. There are 2250 slots per minute (or frame) on each AIS channel. The scheduled slots
must be reserved for the transceiver by an AIS base station operating in the same area using AIS message
#20. Further information on FATDMA reservations and slot allocation schemes can be found in IALA A-124,
Appendix 14.
The parameters required for an FATDMA schedule are as follows.
Channel 1 start UTC
This is the hour and minute for transmission on channel 1. This specifies the AIS frame (minute) within a day
in which the start slot for channel 1 resides.
Channel 1 start slot
This is the slot number for the first transmission on channel 1. The slot number can range from -1 (transmission
disabled on this channel) to 2249. Note that each message #21 transmission occupies two slots and associated
base station slot reservations must therefore reserve two slots.
Channel 1 interval
This is the interval in slots between transmissions on channel 1. The interval can range from 0 to 3240000 slots,
which equates to an interval of one day. Typically the interval is set to 13500 slots (6 minutes) on each channel
which results in an overall interval of 3 minutes.
Page 34
 Loading...
Loading...