SpiderCloud Radio Node - SCRN-220 Hardware Installation Guide
SpiderCloud Wireless, Inc. Proprietary and Confidential
Step 3 With two user-provided screws, attach the mount bracket assembly to a wall or ceiling. The
screw holes are sized for an M4 (#10) or larger screw. Ensure the screws have a snug fit
onto the studs, sheetrock, anchor, or other material you are bolting onto and that you
match the screw head with the appropriate cutout hole size on the bracket.
If needed, use a flat washer between the bracket and screw head to ensure a secure
fastening.
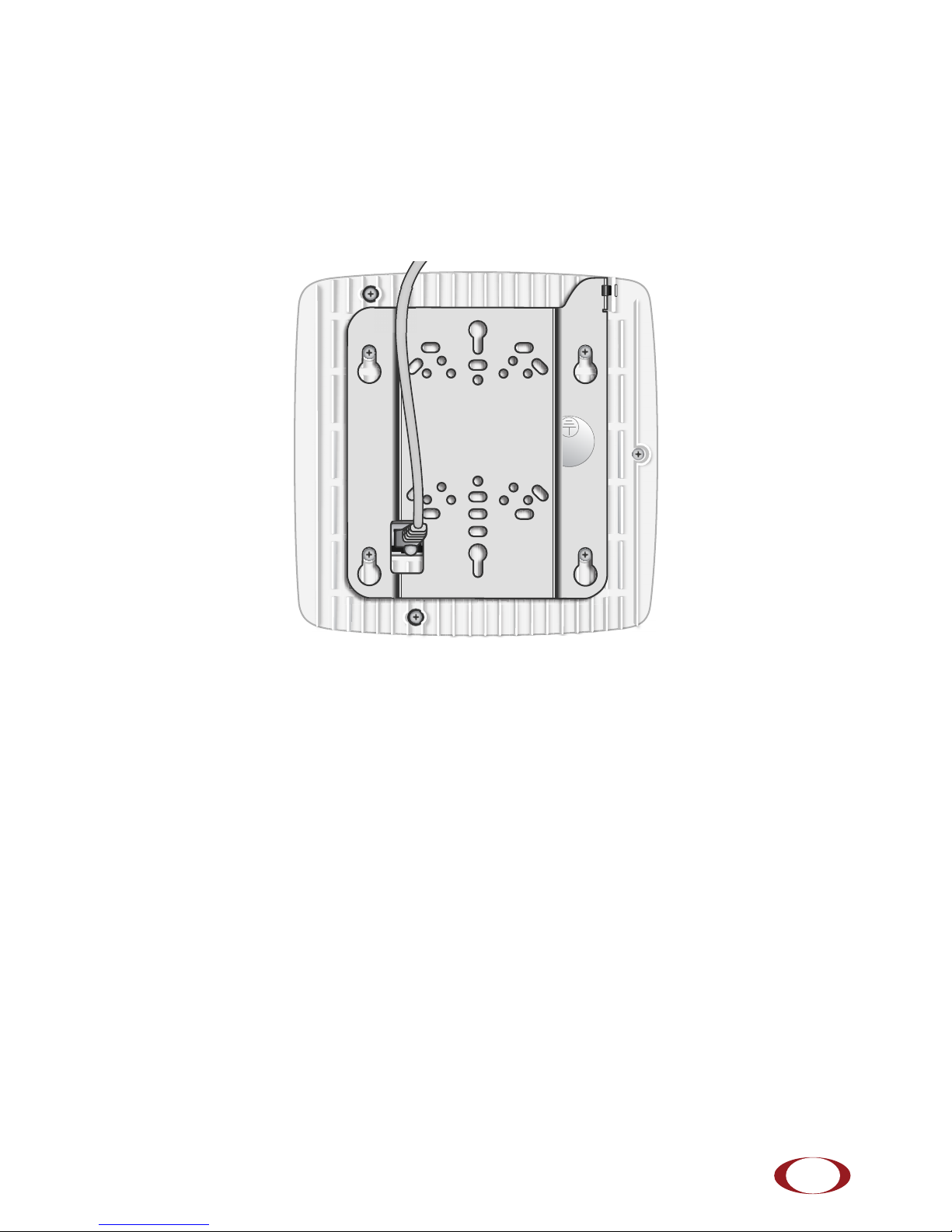
Step 4 Insert the RJ-45 connector into the Ethernet port as shown in Figure 13:
Figure 13 Route and Terminate the Cable
Step 5 Insert the radio node into the mount bracket.
Step 6 Push as much cable back through the wall or ceiling as possible. The mount bracket
assembly has room for some cable slack.
Installing the Radio Node (Method 2)
Use this method with the 1.25 inch bracket when routing an exposed Ethernet cable directly to the radio
node.
To route the cable openly and mount the radio node
Step 1 With two user-provided screws, attach the mount bracket assembly to a wall or ceiling. The
screw holes are sized for an M4 (#10) or larger screw. Ensure the screws have a snug fit
onto the studs, sheetrock, anchor, or other material you are bolting onto and that you
match the screw head with the appropriate cutout hole size on the bracket.
17

SpiderCloud Radio Node - SCRN-220 Hardware Installation Guide
SpiderCloud Wireless, Inc. Proprietary and Confidential
If needed, use a flat washer between the bracket and screw head to ensure a secure
fastening. Figure 14 shows the 1.25-inch mount bracket.
Figure 14 1.25-Inch Mount Bracket
Step 2 Insert the RJ-45 connector through the rectangular bracket opening into the Ethernet port
as shown in Figure 15:
Figure 15 Route and Terminate the Cable
Step 3 Insert the radio node into the mount bracket.
18

SpiderCloud Radio Node - SCRN-220 Hardware Installation Guide
Note
SpiderCloud Wireless, Inc. Proprietary and Confidential
Completing the Installation
Step 1 Attach a padlock or cable tie wrap into the provided slot to secure the unit to the mount
bracket.
Figure 16 Padlock and Lock Holes
The lock in the above figure is shown schematically. The orientation is for illustration
purposes (not accurate) since the bracket is typically wall or ceiling mounted.
Step 2 The radio node boots up and attempts to connect to the services node. Refer to Boot
Sequence and Services Node Communication on page 20 for more information.
Detaching the Radio Node from the Mount Bracket
To remove the radio node from the bracket assembly
Step 1 If needed, remove the padlock or cable tie wrap securing the radio node.
Step 2 Slide the radio node out of the mount bracket.
Step 3 Detach the RJ-45 clip from the Ethernet port and remove the cable from cable brackets
and cable opening.
19
SpiderCloud Radio Node - SCRN-220 Hardware Installation Guide
USB CONSOLE
LK AT LK AT LK ATLK AT LK AT LK AT LK AT LK AT
81234567
LNK ACT
MGMT
POWER STATUS 1 2
SIM 0 SIM 1
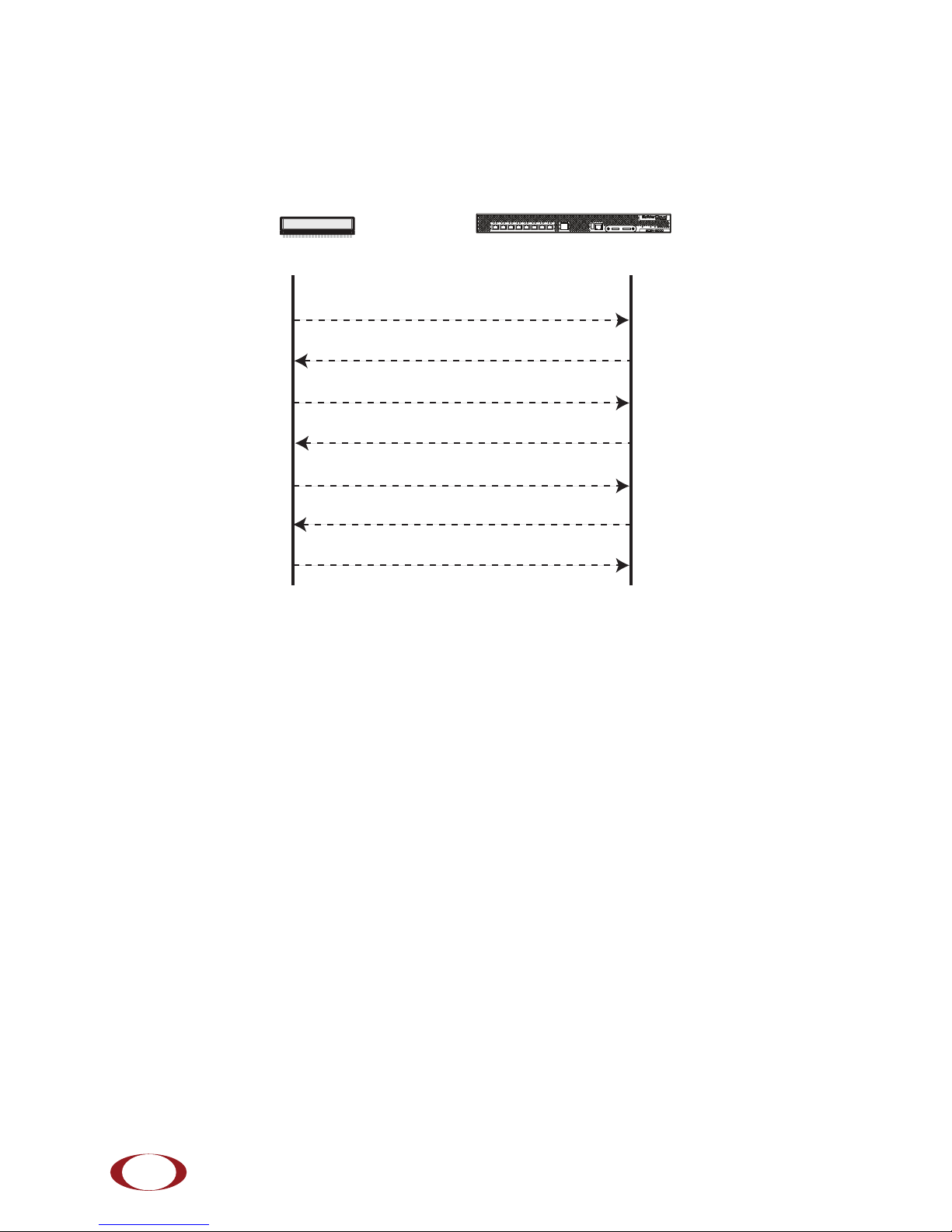
Radio Node Services Node
DHCP Request for IP Address
DHCP Response (RN, IP, Controller IP)
Join Request
Join Response (Join Grant, Redirect, Denied)
Arrival sequence begins
Send SpiderCloud software package
Boot-up, bring up the IPsec tunnel and join the network
SpiderCloud Wireless, Inc. Proprietary and Confidential
Boot Sequence and Services Node Communication
On initial boot, the radio node performs the following boot sequence. When finished, all devices are
reachable. Figure 17 shows the radio node boot sequence:
Figure 17 Radio Node Boot Sequence
Boot Sequence:
1. When the radio node is powered on, the device sends a DHCP Request to the services node
DHCP server to get IP information. The DHCP server is configured on the services node to
respond only to DHCP requests from SpiderCloud Wireless radio nodes. Refer to the SpiderCloud
OS (SCOS) Administrator Guide for more information about the services node DHCP server
configuration.
2. The server responds with the IP addresses of the radio node and the services node (the master of
the radio node).
3. Using its own IP address, the radio node sends a Join Request message to the services node.
The radio node seeks to join the cellular network.
4. The services node responds with a Join Response message indicating whether the radio node is
allowed to join the network or not.
5. The arrival sequence begins. The services node sends the SpiderCloud software image to the
radio node.
6. The radio node boots up the received SpiderCloud software package.
7. The radio node establishes an IPsec tunnel with the services node. Based upon the radio
configuration, the radio node loads the appropriate protocol elements and joins the network.
20

SpiderCloud Radio Node - SCRN-220 Hardware Installation Guide
SpiderCloud Wireless, Inc. Proprietary and Confidential
Radio Node LED Boot Sequence
The radio node state machine is sequential and progresses in the following order:
State 0 -> State 1 -> State 2 -> State 3 -> State 4 -> State 5
A normal boot sequence transitions through all these states sequentially and the LED state transitions
accordingly. If the radio node fails to transition to the next state, the system restarts the boot sequence,
starting with State 0. You can determine the progress during the booting stages by observing the LED color
transitions. On failure, the last LED state will display the state that encountered the failure. Ta bl e 6 shows
the radio node boot sequence and corresponding LED behavior:
Table 6: Radio Node LED Boot Sequence
State LED Color Description Possible Failures and Actions
0. Power On/
Reset
1. DHCP Solid
2. Join Solid
Flashing
Green
Red
Blue
This is the initial state on startup.
The radio node bootup is controlled by
firmware in this state.
It will go through a lamp test in this
state. A lamp test involves cycling
through all LED colors.
The radio node starts by sending out a
DHCP Request.
The radio node moves to the next state
(State 2) upon receiving a DHCP
response and an IP Address.
The radio node has an IP Address and
sends a UDP Join request to the
Serving services node.
The radio node moves to the next state
(State 3) upon getting a JOIN GRANT
from the services node.
This state should be very short
lived and should transition to the
next state immediately.
A radio node should not stay in
this state indefinitely.
Note: Flashing Green is also
used to indicate a radio node
that has been administratively
disabled. This can be
determined from the CLI.
No DHCP Response, IP
Address not allocated.
Check cabling, DHCP Server
configuration.
No IP reachability to the
services node.
Check IP network between
radio node and services node
for routing issues.
3. TFTP Flashing
Blue
The radio node proceeds next to
download the operating system image
from the services node.
The radio node moves to the next state
(State 4) after the image has been
downloaded.
Failure to download TFTP
image.
Check firewall between radio
node and services node.
21

SpiderCloud Radio Node - SCRN-220 Hardware Installation Guide
SpiderCloud Wireless, Inc. Proprietary and Confidential
Table 6: Radio Node LED Boot Sequence (continued)
State LED Color Description Possible Failures and Actions
4. Operating
System Booting
5. Running Solid
Flashing
Green
Green
The radio node loads the operating
system and starts the default platform
applications.
The radio node moves to the next state
(State 5) when it establishes
connectivity with the service node.
The operating system is running. The
radio node continues the startup
sequence, but is now controlled by the
services node.
Failure to start the operating
system.
This normally points to a
software/build issue. Please
contact SpiderCloud support.
The operating system is up and
running on the radio node.
Any subsequent state
transitions can now be tracked
from events and logs on the
services node.
Radio Node LED Management
The LED display is active by default, but can be deactivated in light-sensitive environments as needed.
Even when the display is disabled, the LED will be lighted during the following conditions:
• while the radio node is booting
• if the radio node or cell is in fault state
• if there is an active emergency call
• if the locate radio node feature is active
• if the follow IMSI feature is active
Ta bl e 7 shows the default LED behavior of the radio node:
Table 7: Radio Node LED Behavior
LED Status Flash Rate
Green: slow flashing The radio node or radio is
administratively disabled
Green: fast flashing Booting Approximately 1.4 second on/off cycle
Green: solid Operational
Red: solid Fault
Red: fast flashing One or more emergency UMTS calls
active
Blue: fast flashing Locate radio node enabled* Approximately 1 second on/off cycle
Blue: solid Follow IMSI enabled and that IMSI is
camped on a UMTS cell in the radio
node*
Off Powered off or LED disabled
Approximately ½ second on, 1½ sec. off
Approximately 1 second on/off cycle
22

SpiderCloud Radio Node - SCRN-220 Hardware Installation Guide
SpiderCloud Wireless, Inc. Proprietary and Confidential
* Refer to the SpiderCloud OS (SCOS) Administrator Guide for information about the locate radio node
and follow IMSI features.
To disable the LED display
Step 1 From the Configuration Mode, issue the set System RadioNode LED DefaultMode
Dark command to disable the LED display:
set System RadioNode LED DefaultMode Dark
Step 2 Issue the show System RadioNode LED command to verify the configuration:
show System RadioNode LED
DefaultMode Dark;
To re-enable the LED display
Step 1 From the Configuration Mode, issue the set System RadioNode LED DefaultMode
Standard command to re-enable the LED display:
set System RadioNode LED DefaultMode Standard
Step 2 Issue the show System RadioNode LED command to verify the configuration:
show System RadioNode LED
DefaultMode Standard;
The SpiderCloud Documentation Set
The SpiderCloud documentation set includes:
•The SpiderCloud System Description provides an overview of how the SpiderCloud system fits
within an operator’s network and in an enterprise, describes key features of the system, and
provides specifications for the services and radio nodes.
•The SpiderCloud Feature Description provides high-level descriptions of the E-RAN system
features, their impact on the product components (services nodes and radio nodes),
manageability considerations, and feature benefits.
•The SpiderCloud OS (SCOS) Administrator Guide provides procedures for configuring the
software environment and internetworking between the services node and radio node devices.
•The SpiderCloud Services Node Hardware Installation Guide provides hardware specifications
and installation instructions.
•The SpiderCloud Radio Node Hardware Installation Guide provides hardware specifications and
installation instructions.
•The E-RAN Deployment Planning Guide provides information about planning and dimensioning
E-RAN systems.
•The SpiderCloud OS (SCOS) CLI User Guide provides an introduction to the key features and
functionalities of the SpiderCloud Command Line Interface (CLI).
•The SCOS NB Data Model Reference Guide provides details about the objects and parameters
that comprise the system configuration and operational state.
•The SpiderCloud OS Faults, Conditions, and Events Reference Guide provides details about
all alarms, conditions, and events in the system.
•The SpiderCloud System Commissioning Guide provides information about turning up a
SpiderCloud E-RAN with the Local Configuration Interface (LCI) graphical user interface.
23

SpiderCloud Radio Node - SCRN-220 Hardware Installation Guide
SpiderCloud Wireless, Inc. Proprietary and Confidential
•The Performance Measurements for Dual-Mode Small-Cell E-RANs provides a reference guide
to UMTS and LTE Key Performance Indicators (KPI) that monitor the health and state of the ERAN system.
•The Performance Measurements for LTE Small-Cell E-RANs provides a reference guide to Key
Performance Indicators (KPI) that monitor the health and state of an LTE E-RAN system.
•The SpiderNet Management System Installation and Administration Guide provides information
about installing the SpiderNet network management server and client and using it to remotely
manage E-RAN deployments.
•The E-RAN Troubleshooting Guide provides information about diagnosing and correcting
problems with installing, provisioning, administering, and maintaining SpiderCloud equipment
and services.
•The Troubleshooting E-RAN Systems with SpiderNet provides information about diagnosing
and correcting problems in the SpiderCloud system with the SpiderNet network management
system.
•The SpiderCloud Time Zone Reference Guide provides the information required to configure the
time zone for SpiderCloud services nodes.
•The SpiderCloud Call Performance Event Reporting Guide provides detailed information about
call performance events files including the file format, reported events, and event parameters.
•The SpiderNet NBI Integration Guide provides information about integrating the SpiderNet
network management system into operator’s Northbound Interface (NBI) Operations Support
Systems (OSSs) to surveil SpiderCloud networks.
24

SpiderCloud Radio Node - SCRN-220 Hardware Installation Guide
LTE Band 2
Frequency: 1960 MHz. Peak Gain: 3.21 Dbi.
Frequency: 1960 MHz. Peak Gain: 1.50 Dbi.
0º
Front
90º
Up
90º
0º
Up
SpiderCloud Wireless, Inc. Proprietary and Confidential
Appendix A: LTE Antenna Patterns
25

SpiderCloud Radio Node - SCRN-220 Hardware Installation Guide
LTE Band 4
Frequency: 2145 MHz. Peak Gain: 4.10 Dbi.
Frequency: 2145 MHz. Peak Gain: 2.63 Dbi.
0º
Front
90º
Up
90º
0º
Up
SpiderCloud Wireless, Inc. Proprietary and Confidential
26

SpiderCloud Radio Node - SCRN-220 Hardware Installation Guide
LTE Band 13
0º
Front
90º
Up
90º
0º
Up
SpiderCloud Wireless, Inc. Proprietary and Confidential
27

SpiderCloud Radio Node - SCRN-220 Hardware Installation Guide
SpiderCloud Wireless, Inc. Proprietary and Confidential
28
 Loading...
Loading...