Page 1

Spicer
®
Single Drive Axles
Service Manual
S140 Series
AXSM0030
September 2013
Page 2
General Information
General Information
The description and specifications contained in this service
publication are current at the time of printing.
Dana reserves the right to discontinue or to modify its models
and/or procedures and to change specifications at any time
without notice.
Important Notice
This symbol is used throughout this
manual to call attention to procedures
where carelessness or failure to follow
specific instructions may result in
personal injury and/or component
damage.
Departure from the instructions, choice
of tools, materials and recommended
parts mentioned in this publication
may jeopardize the personal safety
of the service technician or vehicle
operator.
Any reference to brand name in this publication is made
simply as an example of the types of tools and materials
recommended for use and should not be considered an
endorsement. Equivalents, if available, may be used.
WARNING: Failure to follow indicated
procedures creates a high risk of personal
injury to the servicing technician.
CAUTION: Failure to follow indicated
procedures may cause component
damage or malfunction.
IMPORTANT: Highly recommended
procedures for proper service of this unit.
NOTE: Additional service information not
NOTE:
covered in the service procedures.
TIP: Helpful removal and installation
procedures to aid in the service of this unit.
Refer to the OEM vehicle specifications
OEM
Always use genuine Spicer replacement parts.
i
Page 3

General Information
General Information ..........................................................i
Introduction .....................................................................1
Ring Gear and Pinion .......................................................3
Inspection ........................................................................4
Prepare the Parts for Inspection ......................................5
Differential Carrier Assembly ...........................................8
Differential Carrier Assembly -
Parts Exploded View ....................................................9
Remove Differential Carrier ............................................ 10
Install Differential Carrier ............................................... 11
Remove Wheel Differential ............................................. 12
Pinion - Parts Exploded View ......................................... 13
Pinion Removal .............................................................. 14
Drive Pinion ...................................................................15
Pinion Installation ..........................................................16
Wheel Differential Assembly - Parts Exploded ...............18
Disassemble, Overhaul, and
Assemble Wheel Differential ..................................... 19
Measure and Adjust Carrier Assembly ...........................24
Adjust Ring and Pinion Tooth Contact Pattern ............... 26
Install Axle Housing Breather .........................................28
Wheel End Seal - Parts Exploded View ......................... 29
Remove and Overhaul Wheel End Seal .......................... 30
Adjust Wheel Bearing.....................................................31
Wheel End .................................................................... 33
Lubricate Wheel End ..................................................... 34
Lubrication ................................................................... 36
Change Lube ................................................................ 38
Proper Vehicle Towing ....................................................39
Torque Chart ................................................................. 40
Page 4
Introduction
Introduction
Dana Commercial Vehicle Division, presents this publication to aid in maintenance and overhaul of Spicer single drive axles.
Instructions contained cover the models listed. Their design is common, with differences in load capacity. Capacity variations
are achieved by combining basic differential carrier assemblies with different axle housings, axle shafts and wheel equipment.
Model Listing
Rear Axle Load Capacity
S19-140 19,000
S17-140 17,000
Model Information
S 19 - 1 4 0 L
S - S i n gle R e a r Axle
G A W R at in g x 1000 l bs .
Gea r Ty p e
1 - S t a n d a r d S i n gle R e d u c t i o n
2 - D u a l R a n g e
3 - Pla n e t a r y Do uble R ed uc ti on
4 - C o n t r olled Tr act io n Differ en tial
5 - H elical R e d u c t i o n
O p t i o n s
L - L imit e d - S lip
W - W i d e -t r ack
F - Rolled Ove r
R - P a r k i n g B r ake
D e s i g n L evel
H ead A s s e mbl y S e r i e s
1
Page 5
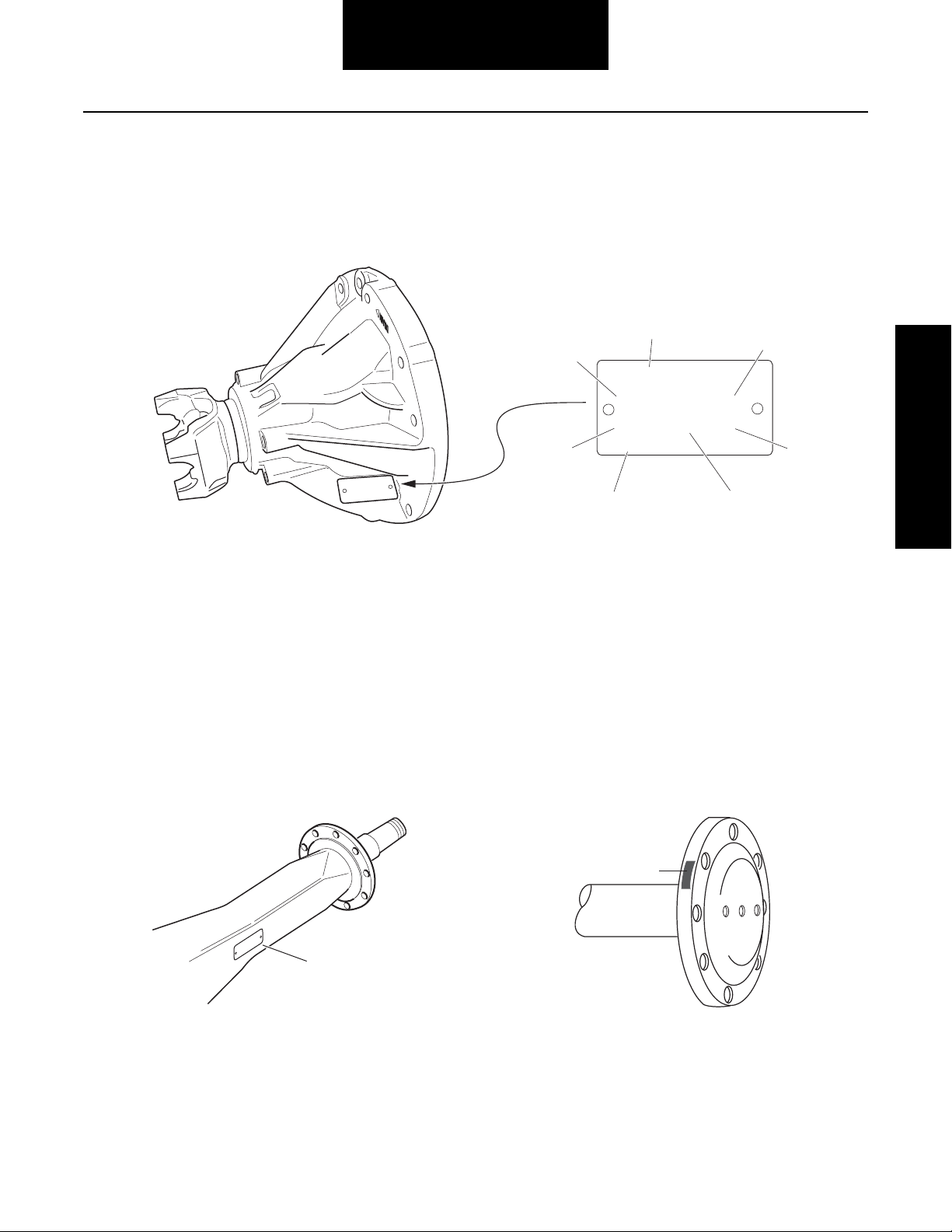
Model Identification
Drive Axle
Introduction
®
Spicer
CUST. PART NO.
SPEC. SERIAL NO.
MODEL PART NO. RATIO
MADE IN:
1 - Country of origin
2 - Axle model identification
3 - Specification number assigned to the axle built by Spicer.
Identifies all component parts of the axle including special
OEM requirements such as yokes or flanges.
4 - OEM part number assigned to the axle build
5 - Carrier assembly serial number assigned by the
manufacturing plant
6 - Axle gear ratio
7 - Carrier assembly production or service part number
Part Identification
Axle Housing Axle Shaft
4
3
CUST. PART NO.
SPEC. SERIAL NO.
MODEL PART NO. RATIO
2
MADE IN:
1
Spicer
7
5
®
Introduction
6
®
Spicer
PT. NO.
HSG. CAP. LBS.
. I.D. NO.
ADE IN
HSG
HOUSING M
1
1 - ID Tag 2 - Axle shaft part number
2
2
Page 6
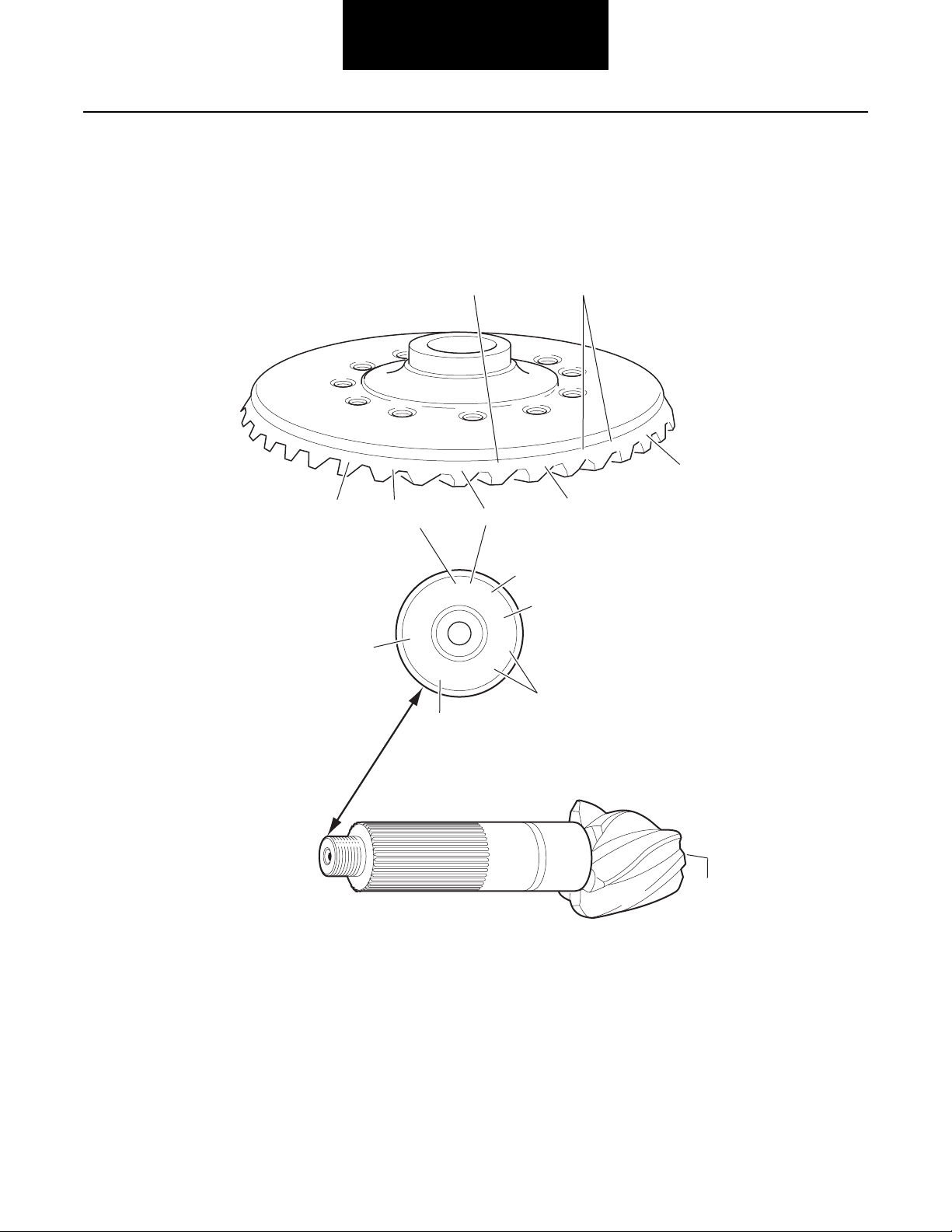
Introduction
Ring Gear and Pinion
Note: Ring gear and drive pinion are matched parts and must be replaced in sets.
127381
1
3
L7038
G
17
OF
4
6
SPICER
7
8
41-8
NL2
5
2
8
8-41
127428
127
6
0H
17
G
127
7
SPICER
3
1
1 - Part number
2 - Number of ring gear teeth
3 - Manufacturing numbers
3
6-39
JD77
85405
86
4
4 - Matching gear set number
5 - Number of pinion teeth
7 - Indicates genuine Spicer parts
8 - Heat Code
6 - Date code
Page 7

Inspection
Inspection
Failure Analysis
Failure analysis is the process of determining the original
cause of a component failure in order to keep it from happening again. Too often, when a failed component is replaced
ut determining its cause, there will be a recurring failure.
witho
If a carrier housing is opened, revealing a ring gear with a broken tooth, it is not enough to settle on the broken tooth as the
cause of the carrier failure.
examined. For a thorough understanding of the failure and
possible insight into related problems, the technician needs to
observe the overall condition of the vehicle.
No one benefits when a failed component goes on the junk
cause unknown. Nothing is more disturbing to a
case of
n.
e
a rebuilt rear axle, mismatched gears may have
pile with th
customer than a repeat failure. Systematically analyzing a failure to prevent a repeat occurrence assures quality
avoiding unnecessary downtime and further expense to the
customer.
The true cause of a failure can be better determined by knowing what to look for, determining how a piece of the equipment was running and learning about previous problems. In
the
been installed. The more successful shops prevent repeat
equipment failures by developing good failure analysis practices. Knowing how to diagnose the cause of a premature failure is one of the prerequisites of
technicia
Other parts
of the carrier must be
ser
vice by
a good heavy-equipment
How to Diagnose a Failure
The following five steps are an effective approach to good failure diagnostics.
1. Document the problem.
2. Make a preliminary investigation.
3. Prepare the parts for inspection.
4. Find the cause of the failure.
5. Correct the cause of the problem.
4. Ask: In what type of service is the truck being used?
5. Ask: Has this particular failure
6.
Ask: How was the truck working p
You need to be a good listener. Sometimes, insignificant or unrelated symptoms can point to the cause of the failure:
7. Ask: Was the vehicle operating at normal temperatures?
8. Ask: Were the gauges showing normal ranges of
operation?
9. Ask: Was there any unusual noise or vibration?
After listening, review the previous repair and maintenance
records. If th
and compare their observations for consistency with the service and maintenance records. Verify the chassis Vehicle
entificat
Id
cation plate, as well as the mileage and hours on the vehicle.
Make a Preliminary Investigation
These steps consist of external inspections and
that will be valuable when combined with the results of the
parts examination.
1. Look for leaks, cracks or other damage that can
2. Make note of obvious leaks around
3. Look for cracks in the carrier housing (harder to see,
4. Does the general mechanical condition of the vehicle
5. Are the tires in good condition and do the
6. If equipped with a torque-limiting device, is it work-
ere is more than one driver, talk to all of them
ion Number (VIN) number from the vehicle identifi-
point to the cause of
A missing fill or drain plug would be an obvious
cause for concern.
metimes visible).
but so
indi
cate proper maintenance or are there signs of
neglect?
match?
ing properly?
the failure.
occurred before?
rior to the failure?
obser
vations
plugs and seals.
sizes
Inspection
Document the Problem
Here are some guidelines for starting to learn about a failure,
including questions to ask:
1.
Talk to the operator of the truck.
2. Look at the service records.
3. Find out when the truck was last serviced.
During the preliminary investigation, wr
of the ordinary for later reference. Items that appear insignificant now may take on more importance when the subassemblies are torn down.
ite down anything out
4
Page 8

Prepare the Parts for Inspection
Inspection
After the preliminary investigation, locate the failure and prepare the part for examination. In carrier failure analysis, it may
be necessar
y to disassemble the unit.
1. When disassembling subassemblies and parts, do
not clean the parts immediately since
destroy some of the evidence.
2. When tearing down the drive axle, do it in the recom-
ded manner. Minimize any further damage to the
men
unit.
Ask more questions when examining the interior of
3.
the carrier
specifications regarding quality, quantity and viscosity? As soon as you have located the failed part, take
time
. Does the lubricant meet the manufacturer
to analyze
the data.
cleaning may
Find the Cause of the Failure
Here begins the real challenge to determine the exact cause of
the failure. Keep in mind that there is no benefit to replacing a
failed part without determining the cause of the failure. For
example, after examining a failed part and finding that the fail-
o
ure is caused by a lack of lubricati
there was an external leak. Obviously, if there is an external
leak, just replacing the failed gear is not going to correct the
situation.
Another important consideration is
type of failure which can be a valuable indicator for the cause
of failure. The following pages show different types of failures
and possible causes. Use this as a guide in determining types
of failures and in correcting problems.
n, you must determine if
to determine the
specific
Correct the Cause of the Problem
Once the cause of the problem has been determined, refer to
the appropriate service manual to perform the repairs.
5
Page 9
Inspection
Inspection
Clean
1. Wash steel parts with ground or polished surfaces in
solvent. There are many suita
vents available. Kerosene and diesel fuel are acceptable.
WARNING
Gasoline is not an acceptable solvent because of its
em
e combustibility. It is unsafe in the workshop envi-
extr
ronment.
2. Wash castings or other rough parts in solvent or
clean in hot solution tanks usi
tions.
Note: If a
hot solution tank is used, make sure parts are
heated
thoroughly before rinsing.
3. Rinse thoroughly to remove all traces of the cleaning
ion.
solut
4.
Dry parts immediately with clean rags.
5. Oil parts.
• If parts are to be reused immediately: Lightly oil.
• If parts are to be stored: Coat
sion resistant paper and store in a clean, dry place.
ble commercial sol-
ng mild alkali solu-
with oil, wrap in
corro-
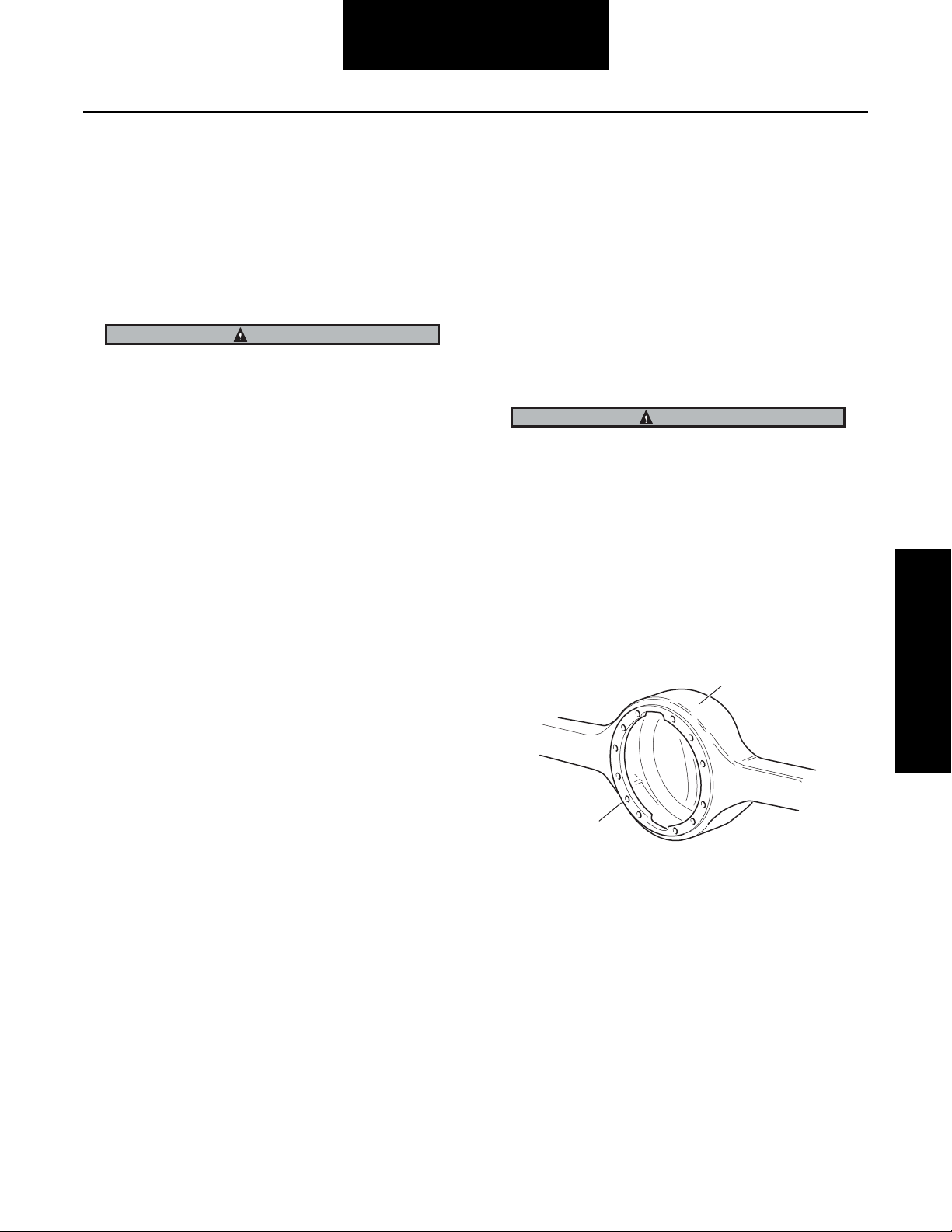
Inspect Axle Housing
Axle housing inspection and repairs are limited to the following checks or repairs.
• Visually inspect axle housing for cracks, nicks and
burrs on
• Check carrier bolt holes and studs for foreign material.
• Replace damaged fasteners. Look for loose bolts
cross-threaded holes
Any damage which affects the alignment or structural integrity of the housing requires housing replacement. Do not
r by bending or straightening. This process can affect
repai
the material’s properties and cause it to fail completely
under load.
• Check all seals and gaskets.
Note: Replace
ket compound (included in many repair kits). The compound provides a more effective seal against lube
seepage and is easier to remove from
when replacing parts.
machined surfaces.
conventional
or
CAUTION
gaskets with silicone rubber gas-
mating surfaces
1
Inspection
2
1 - Axle housing
2 - Machined surface
6
Page 10

Inspect Components
Inspect all steel parts for:
• Notches, visible steps or grooves created by wear.
• Pitting or cracking along gear contact lines.
• Scuffing, deformation or discolorations. These are
signs of
related to low lubrication levels or improper lubrication practices.
In addition, inspect the following for damage:
• Differential gearing
• Bearings for loose fit on drive pinion, and differential
bearings.
All fasteners for rounded heads, bends, cracks or
•
dama
excessive heat in the axle
ged threads.
and are usually
Inspection
• Inspect machined surfaces of cast or malleable
parts. They must be free of nicks, burrs
scoring, and wear.
• Look for elongation of drilled holes, wear on surfaces machined for bearing fits and nicks or burrs in
mating surf
aces.
, cracks,
Inspect Primary Gearing
Before reusing a primary gear set, inspect teeth for signs of
excessive wear. Check tooth contact pattern for evidence of
incorrect adjustment.
7
Page 11
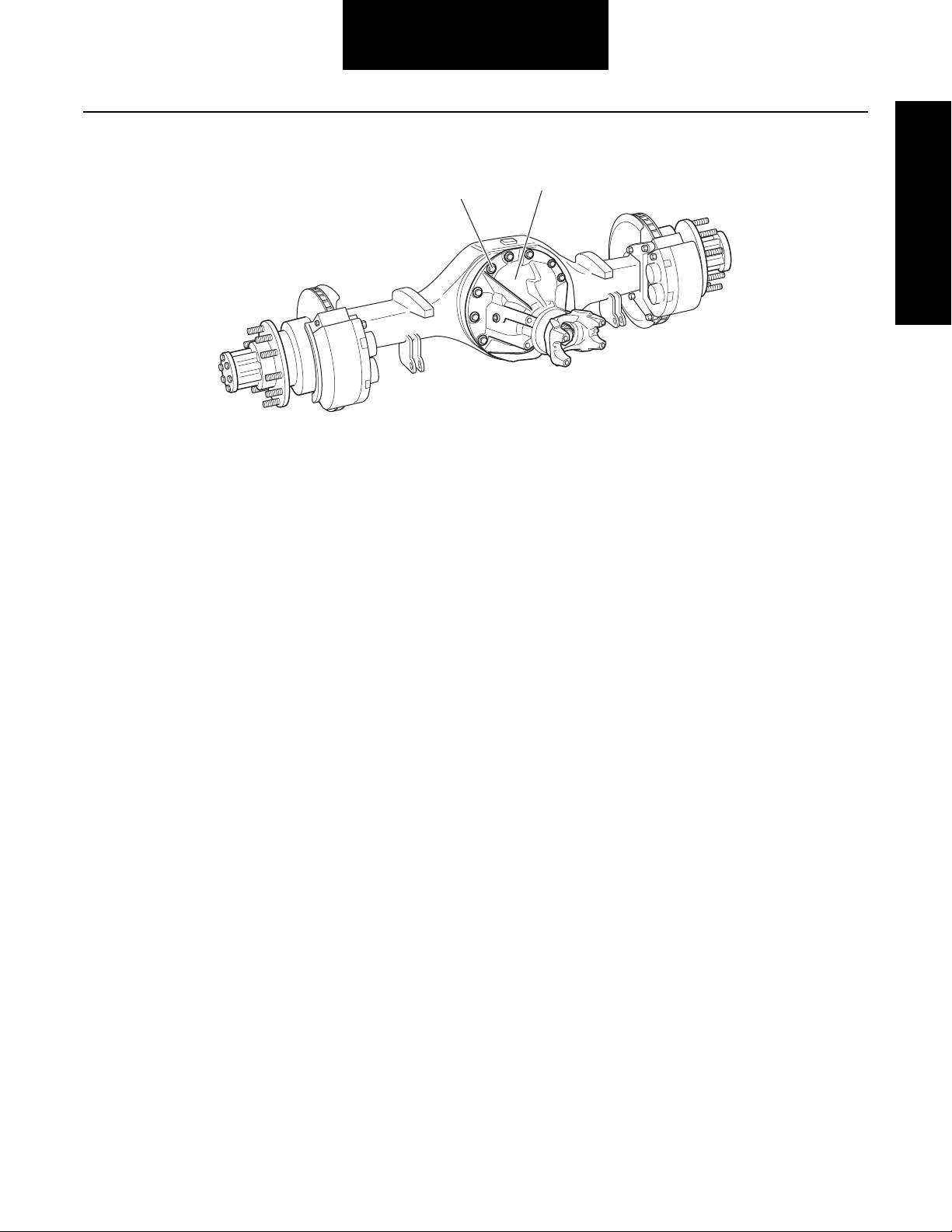
Differential Carrier Assembly
y
Differential Carrier Assembly
1 - Carrier fastener
2 - Carrier assembly
Differential Carrier
1
2
Assembl
8
Page 12
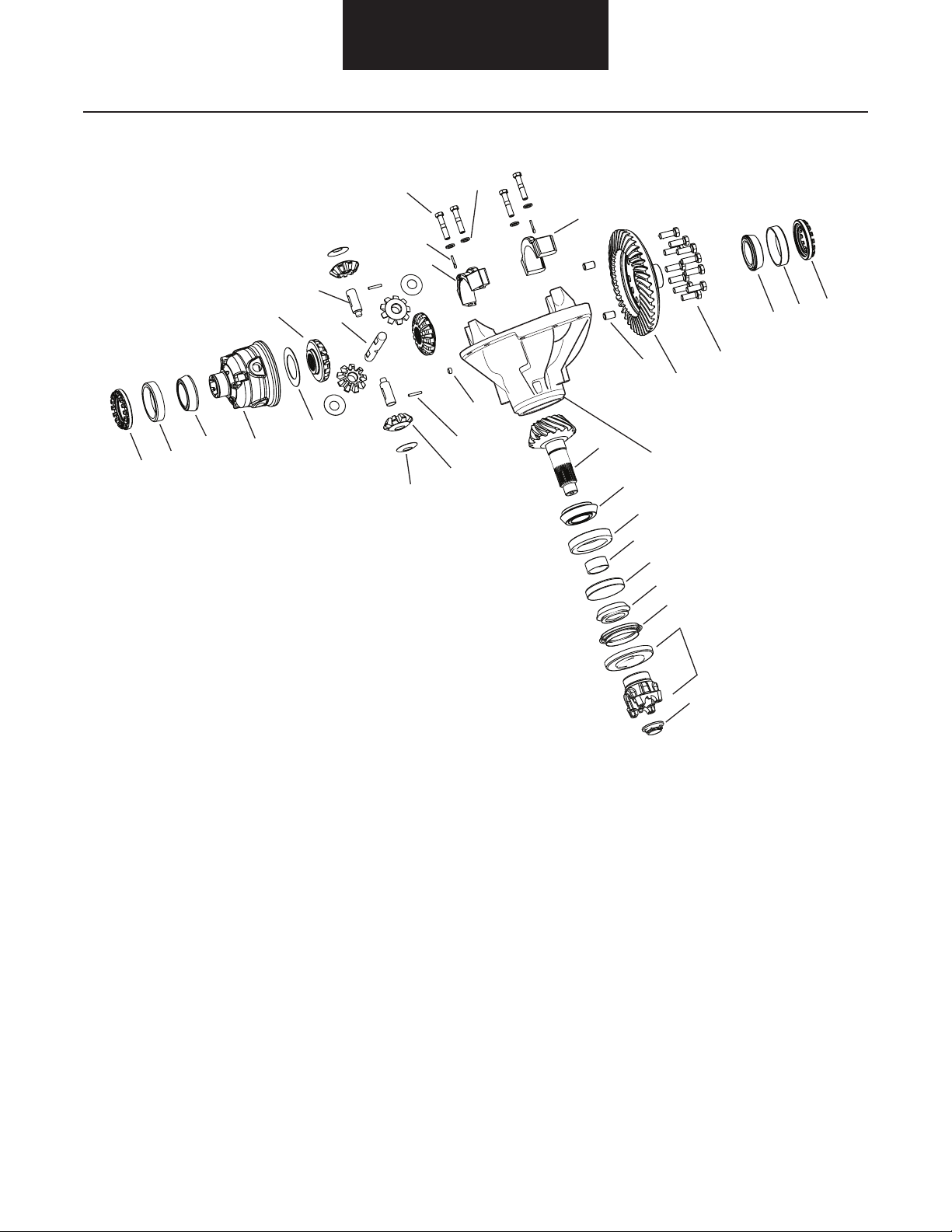
Differential Carrier Assembly
Differential Carrier Assembly - Parts Exploded View
31
30
29
28
19
20B
27
20A
22
17
26
25
18
21
23
32
24
16
15
14
11
9
10
8
7
6
5
4
3
13
12
1 - Pinion Nut
2 - End Yoke and Slinger
3 - Oil Seal
4 - Outer Pinion Bearing Cone
5 - Outer Pinion Bearing Cup
6 - Pinion Spacer
7 - Inner Pinion Bearing Cup
8 - Inner Pinion Bearing Cone
9 - Drive Pinion
10 - Carrier Housing
11 - Diff Case Dowels
12 - Ring Gear
13 - Ring Gear Bolts
14 - Flange Half Bearing Cone
15 - Flange Half Bearing Cup
2
1
16 - Flange Half Bearing Adjuster
17 - Side Pinion Thrust Washer
18 - Side Pinion
19 - Side Gear
20A,B - Differential Shaft
21 - Pin
22 - Capscrew
23 - Flat Washer
24 - Flange Half Cap
25 - Plain Half Cap
26 - Cotter Pin
27 - Side Gear Thrust Washer
28 - Plain Half Diff Case
29 - Plain Half Bearing Cone
30 - Plain Half Bearing Cup
31 - Plain Half Bearing Adjuster
32 - Pipe Plug
9
Page 13
Differential Carrier Assembly
y
Remove Differential Carrier
Standard Differentials
1. Block the vehicle.
2. Drain axle lubricant. Remove bottom two (2) capscrews.
3. Disconnect driveline.
4. Remove axle shafts. (If used, remove lock washers
and tap
Do not lie under carrier after fasteners are removed. Use
transmi
prior to loosening fasteners.
ssion jack to support differential carrier assembly
r dowels.)
e
WARNING
WARNING
CAUTION
CAUTION
Do not strike the shaft head with a steel hammer. Do not
s
use chi
els or wedges to loosen shaft or dowels.
5. Remove carrier capscrews and washers.
6. Remove differential carrier assembly.
Differential Carrier
Assembl
10
Page 14
Differential Carrier Assembly
Install Differential Carrier
IMPORTANTIMPORTANT
Before installing carrier assembly, inspect and thoroughly
clean interior of axle housing using an appropriate solvent
and clean rag.
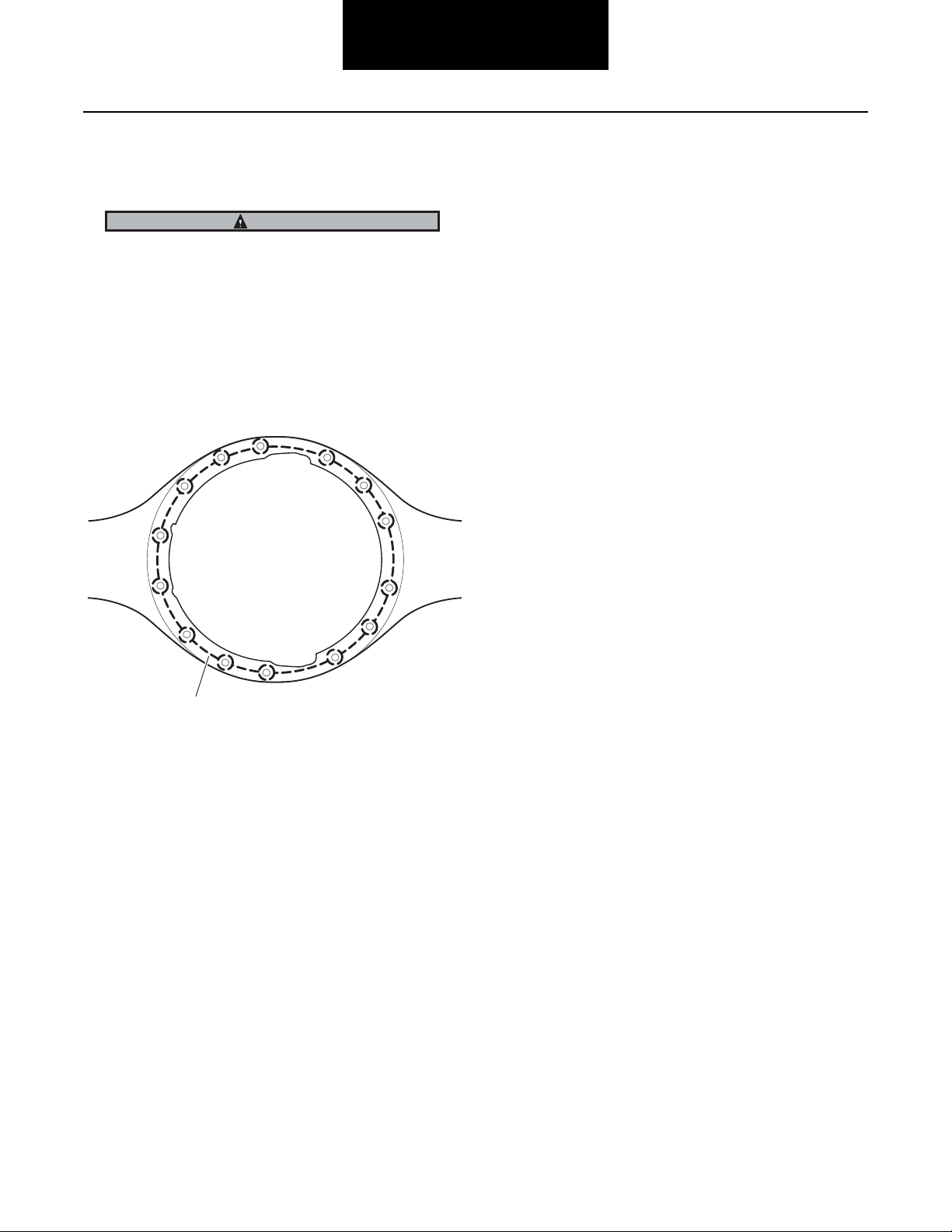
1. Apply Spicer approved RTV compound on axle
housing mating surface as shown in the illustration.
Completely remove all old gasket material prior to
applying new material. Compound will set in 20 minutes. Install carrier before compound sets or reapply.
1
1 - Apply RTV gasket in this pattern
TIP: To assist in installing complete differential carrier use
two pieces of threaded rod (M14 X 2) threaded into carrier
capscrew holes. Rod should be approximately 4" (102 mm)
long. Use these to pilot the carrier into the housing.
2. Install carrier to housing, lock washers and capscrews. Torque to proper specification. Torque to
142–158 lbs. ft. (193–214 N•m).
3. Install axle shafts and axle
d axle lubricant. Fill to bottom of filler hole in car-
4. Ad
rier.
5. Connect main driveline and lubricate joints.
stud nuts.
11
Page 15

y
Remove Wheel Differential
Differential Carrier Assembly
Note: Omit this step if the gear set is to be replaced. If gear
set is to be reused, check tooth contact pattern and ring
gear backlash before disassembling differential carrier.
When checking backlash, a yoke must be installed and
torqued to get an accurate reading. Best results are
obtained when established wear patterns are maintained
in used gearing.
1. Mount differential carrier in repair stand.
,
Note: For easier disassembly
ion (self-locking) nut.
loosen but do not remove pin-
3. Remove capscrews and bearing caps. Back
ing adjusters and remove adjusters and bearing
.
cups
4. Lift ring gear and differential
assembly out of
off bear-
carrier.
Differential Carrier
Assembl
2. Punch mark bearing caps. If reusing
punch mark bearing adjusters for reference during
assembly.
1
1 - Punch Marks
gear set,
also
12
Page 16

Pinion - Parts Exploded View
11
Differential Carrier Assembly
1 - Pinion Nut
2 - End Yoke
3 - Slinger
4 - Oil Seal
5 - Outer Pinion Bearing Cone
6 - Outer Pinion Bearing Cup
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
7 - Pinion Spacer
8 - Inner Pinion Bearing Cup
9 - Inner Pinion Bearing
10 - Drive Pinion
11 - Carrier
13
Page 17

y
Pinion Removal
Differential Carrier Assembly
1. Remove yoke nut.
2. Remove yoke using a yoke puller service tool.
1
1 - Yoke puller
3. Remove oil seal.
4. Place carrier in a press with
threaded end of
pinion
face up.
5. Place a wood block under pinion to avoid damage to
gear teeth.
1
2
3
6. Press pinion through outer bearing and out
of carrier
casting.
7.
Remove bearing preload spacer and save for use in
reassembly.
8.
Remove inner bearing cone from pinion using a
split-type puller.
Use two procedure steps to remove
each bearing.
a. Mount puller vertically to separate the bearing. This
action will force puller
halves under bearing and start
moving bearing off pinion.
b. Mount puller horizontally to press pinion out of bear-
ing.
1
Differential Carrier
Assembl
6
5
4
1 - Press
2 - Outer bearing
3 - Inner bearing
1 - Press
4 - Wood block
9. If bearings are to be replaced, remove bearing cups
5 - Drive pinion
6 - Bearing preload spacer
from carrier
complete.
casting at this time. Pinion removal
14
Page 18

Drive Pinion
Drive Pinion
Rear Axle Pinion Assembly - Parts Exploded View
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
1 - Pinion Nut
2 - End Yoke
3 - Slinger
4 - Oil Seal
5 - Outer Pinion Bearing Cone
2
1
6 - Outer Pinion Bearing Cup
7 - Pinion Spacer
8 - Inner Pinion Bearing Cup
9 - Inner Pinion Bearing Cone
10 - Drive Pinion
15
Page 19

Drive Pinion
Pinion Installation
Final Buildup
Note: Do not install oil seal in carrier until bearing preload is
correctly adjusted.
1. Press inner bearing cone on pinion.
3. Press inner and outer bearing cups into the carrier
until seated. Use
approx.) to make sure that bearing cups are fully
seated in bearing bores. Apply lubricant to both cup
and cone.
4. Place carrier housing in press with the pinion supported by wood block (6" x 6" x 6" [152 x 152 x 152
m
]), so the inner pinion bearing is mated to the
m
cone.
3
a feeler gage (.0015" [.038 mm]
1
2
5
4
Drive Pinion
IMPORTANTIMPORTANT
To prevent bearing damage, use suitable sleeve that only
contacts inn
2. Install preselected bearing spacer.
er race of bearing cone.
1 - Press
2 - Outer pinion bearing
3 - Wood block
4 - Drive pinion
5 - Bearing preload spacer
5. Press outer bearing onto pinion until completely
seated. Rotate carrier during
6. Use torque multiplier and torque pinion nut to 7101040
lbs. ft. (848-1410 N•m).
seating process
.
16
Page 20

Drive Pinion
7. Measure torque to rotate the pinion with an inchpound torque wrench. Torque measurements should
be taken every fourth (4th) revolution and should
read between 34-42 in.lbs. of bearing preload.
Note: If bearing preload does not fall within allowed limits,
preload can be increased by using a thinner spacer and
decreased by using a thicker spacer.
Always measure each spacer before assembly to
ensure correct thickness.
8. Repeat process until torque to rotate is between 3442 in. lbs. After proper preload is achieved, remove
yoke and install new seal with proper service tool.
11. Use a rubber mallet to drive the seal tool in until the
flange bottoms on the housing cover bore face. The
flange will locate the seal at the proper depth.
1
2
3
12. Install end yoke.
Note: Spicer recommends that new torque prevailing
nuts be used.
13. Use torque multiplier and torque pinion nut to 7101040 lbs. ft. (848-1410 N•m).
1 - Seal Driver
2 - Oil Seal
3 - Pinion Cage
CAUTIONCAUTION
Do not use any silicone or permatex-type bore sealant with
this seal.
9. Remove the new seal from its package and install
with the proper driver:
R-Pinion-Use drive #126917 only
WARNINGWARNING
Due to the resiliency of the plastic driver, hammer rebound
may occur when the seal is seated. Kee
rebound path!
mer
p clear of the ham-
10. Handle the seal by its outside diameter avoiding any
contact with the seal lips. During installation, use the
proper driver to make sure that the seal is mounted
properly.
17
Page 21

Wheel Differential Assembly
y
Wheel Differential Assembly - Parts Exploded
9
8
10
9
1
1 - Diff. Case Bearing Adjuster
2 - Diff. Bearing Cup
3 - Diff. Case Bearing Cone
4 - Differential Case
5 - Side Gear Thrust Washer
6 - Side Gear
7 - Differential Shaft
8 - Side Pinion
7
6
6
10
5
9
9
13
14
15
12
16
11
Wheel Differential
Assembl
3
2
4
9 - Side Pinion Thrust Washer
10 - Pin
11 - Ring Gear
12 - Ring Gear Bolt
13 - Ring Gear Bearing Cone
14 - Ring Gear Bearing Cup
15 - Ring Gear Bearing Adjuster
16 - Locating Dowels
18
Page 22

Wheel Differential Assembly
Disassemble, Overhaul, and Assemble Wheel Differential
Disassemble Wheel Differential
1. Remove capscrews fastening ring gear to differential
case.
2. The ring gear to differential case interface is a press
fit. Place the assembly in
ing downward. Support the assembly on eitiher side
of the ring gear
the case holes by hand. Press down on the head of
the capscrew, you may need to press in more than
one position to free the ring gear from the case.
. Thread a capscrew back into one of
a press with the case fac-
CAUTIONCAUTION
The differential case and gears will fall after separation.
Support
ferential or bodily injury.
the case so that it will not cause damage to the dif-
3. Remove the outer side gear.
4. Remove the differential shaft locking pins by turning
the differen
hammer to lightly tap on the side of the case to free
the locking pins.
tial case opening facing down. Use a
IMPORTANTIMPORTANT
Do not press on the wheel differential shaft to free the ring
gear fro
may cause it to bend and/or fatigue.
19
m the case. Pressing on the wheel differential shaft
5. The locking pins are slip fit and should fall from the
case easily
.
Page 23

Wheel Differential Assembly
y
6. Remove the half shafts first and then remove their
side pinions and thrust washers.
Half
Differential
Shaft
7. Remove the full shaft, side pinions and thrust washers.
9. Remove bearing cones from ring
gear and differential case in two steps:
A. Mount puller vertically to split bearing. This action
will start moving the bearing off case and gear.
B. Mount puller horizontally to remove cone.
Wheel Differential
Assembl
8. Remove inner side gear and thrust washer.
20
Page 24

Wheel Differential Assembly
Assemble Wheel Differential
10. Press new bearing cone on the differential case.
11. Place thrust washer on the side gear. Lubricate both
sides of the thrust
washer before installing.
13. Start the full differential shaft into
the shaft bores in
the case that does not have a locking pin hole.
Side Pinion
and Thrust
Washer
Full
Differential
Shaft
Locking
Pin Holes
14. Install a side pinion and thrust washer and push the
shaft t
hrough the side pinion.
Side Pinion
and Thrust
Washer
12. Install the side gear and thrust washer in the differential case.
15. Install the side pinion and thrust washer to the other
full
side of the
shaft.
16. Install a side pinion and thrust washer on the half
shaft side.
Side Pinion
and Thrust
Washer
21
Page 25

Wheel Differential Assembly
y
17. Install the half shaft so that the pin is facing upward
and push it in until it stops.
Half
Differential
Shaft
Pin Hole
Facing
Upward
18. The end of the half shaft should fit into the slot of
the full shaft at the same time as the hole in the case
lines up with the hole in the half shaft.
Align Pin
Holes
Fit End
Into Slot
Note: No thrust washer is us
ed at this location.
21. Lower the ring gear onto the case assembly aligning
the locking dowels.
Wheel Differential
Assembl
19. Install the locking pins to both sides of the
tial case.
differen-
22. Install and hand-tighten all new ring gear capscrews.
Locking
Pin
20. Install outer side gear.
22
Page 26

Wheel Differential Assembly
23. The interface of the ring gear to differential case is a
press fit. Put the assembly in a press with the ring
gear facing upward. Make certain that the ring gear
is flush and square to the differential case before
pressing. Press until ring gear bottoms out on the
case.
IMPORTANTIMPORTANT
DO NOT use the capscrews to draw the ring gear into place.
Only use a press.
tool should have a slit cut if the ID is the same as the
bearing boss OD.
25. Tighten and torque ring gear capscrews in an altering pattern. 435-465 lbs. ft. (589-630 N•m).
nat
26. Install differential case assembly into carrier. Be
careful no
ing the assembly.
t to damage the differential bearings lower-
24. Press new ring gear bearing cone.
IMPORTANTIMPORTANT
When pressing differential case bearing cones, note that
bearing is beyond flush with the top of the case. The
the
cone must be fully seated. To prevent bearing damage, use
suitable sleeve that only contacts the inner race of the
cone. A used bearing race would be a suitable tool. This
27. Lubricate the differential bearings and install bearing
and differential bearing adjusters.
cups
23
Page 27

Wheel Differential Assembly
y
Measure and Adjust Carrier Assembly
Adjust Backlash and Preload
1. Turn the flange half-bearing adjuster in until the ring
gear contacts the pinion (zero backlash) then back
the adjuster out two (2) notches from the adjuster
lugs.
1
1 - Flange half
2 - Plain half
2. Tighten the plain half-adjuster until the bearing cup
just starts to turn, this is a zero bearing preload.
4. Use a rubber mallet to make certain that both bearing adjusters are fully seated.
5. Measure backlash. Make sure it is within specification of .008"–.018” (.15-.46 mm).
TIP: To give yourself room to adjust contact pattern, set it
ween .012"–.014” (.30-.36 mm).
bet
2
Wheel Differential
Assembl
Tighten the plain half-adjuster two lug notches. Start
3.
e notch at the top, count two notches coun-
with th
terclockwise on the adjuster, turn the adjuster so
that the notch is
two-notch preload.
1 - Lugs
2 - One notch
facing straight up. You now have a
2
1
24
Page 28

Wheel Differential Assembly
Change Backlash Setting
If you have too much backlash, the ring gear needs to move
closer to the pinion. Back off the plain half-adjuster, counting
the number of notches you back it off (each notch equals
about .003" [.08 mm] of backlash).
IMPORTANTIMPORTANT
In order to maintain the differential bearing preload, you
l
need to turn the flange half-bearing adjuster the same
wil
amount in the same direction. If you need more backlash,
reverse this procedure.
1. Install carrier bearing caps and torque carrier
bolts to 350-428 lbs. ft. (475-580 N•m).
2. Recheck backlash: If the bearing adjusters were not
in straight or
a. Used Gearing:
before disassembly.
b. New Gearing: Backlash
.008” and .018" (.15-.46 mm).
fully seated, the backlash will change.
Reset to backlash recorded
should be between
cap
Measure Ring Gear Runout
Measure Ring Gear Total
1. Measure ring gear total radial runout. (Indicator
reading shou
2. Measure ring gear total backface runout.
read
ing should not exceed .010" [.25 mm]).
ld not exceed .010" [.25 mm]).
(Indicator
3. Check ring gear tooth contact pattern. Paint ring
teeth and check tooth contact pattern. Correct tooth
patterns, see "Adjust Tooth Contact Pattern."
4. Install bearing adjuster cotter pins.
25
gear
Page 29

Adjust Tooth Contact Pattern
Adjust Ring and Pinion Tooth Contact Pattern
Used Gearing - Correct Pattern
2
1
1 - Face width
2 - Tooth depth
3 - Heel
4 - Top land
5 - Root
6 - Toe
1. Identify if new or used gearing.
2. Check tooth contact pattern (new or use
New Gearing - Correct Pattern
• Paint six ring gear teeth 180° apart and roll the
to obtain a contact pattern. The correct pattern is
slightly below center on the ring gear tooth with
lengthwise contact up off the toe. The length of the
pattern in an unloaded condition is approximately
one-half (1/2) to two-thirds
(2/3) of the ring gear tooth in most models and
ios.
rat
The pattern could vary in length and should cover
•
half (1/2) of the tooth or
tern should be evenly centered between tooth top
land and
root and should be up off the tooth toe.
more (face width). The pat-
3
4
5
6
d gearing).
gear
• Used gearing will not usually display the square,
even contact pattern found in new gear sets. The
will normally have a “pocket” at the heal end of
gear
the gear tooth. The more use a gear has had, the
more the line becomes the dominant characteristic
of the pattern.
• Adjust used gear sets to display the same contact
obser
pattern
tern is up off the toe and centers evenly along the
face width between the top
the length and shape of the pattern are highly variable and is considered acceptable as long as it does
t run
no
1 - Pattern along the face width could be longer
Adjust Contact Pattern
• If necessary, adjust the contact pattern by changing
the ring
•
Ring gear position controls the backlash. This
adjust
width of the gear tooth.
Note: This is a shimless pinion designed carrier
shows an
sure the inner pinion cup is fully seated. Use a feeler
gauge.
ved before disassembly. A correct pat-
land and root. Otherwise,
off the tooth at any point.
gear position.
ment moves the contact pattern along the face
. If the pattern
incorrect pinion cone position, check to make
Adjust Tooth Contact
Pattern
26
Page 30

Adjust Tooth Contact Pattern
Adjust Ring Gear Position (Backlash)
If the ring gear pattern shows incorrect face width contact,
change backlash by
If the pattern is too close to the edge of the tooth toe, move the
ring gear away
1. Loosen the bearing adjuster on the teeth side of the
ring
adjusting the ring gear.
from the pinion to increase backlash.
gear several notches.
2.
Loosen the opposite adjuster one notch.
3. Return to adjuster on teeth side of the ring gear and
tigh
ten adjuster until it contacts the bearing cup.
4. Continue tightening the same adjuster two (2) or
three (3) notches and recheck backlash.
If
the pattern is concentrated at the heel (too far up the tooth),
the
move
ring gear toward the pinion to decrease backlash.
5. Loosen the bearing adjuster on the teeth side of the
ring gear several notches.
Tighten the opposite adjuster one notch.
6.
7. Return to adjuster on teeth side of ring gear and
tigh
ten adjuster until it contacts the bearing cup.
8. Continue tightening the same adjuster two (2) or
three (3) notches and recheck backlash.
27
Page 31

Install Axle Housing Breather
1. Install fitting in breather hole.
2. Tighten fitting finger tight.
Housing Breather
4. Insert hose onto fitting, long end down.
3. Torque to 5 lbs. ft. (7 N•m) and align the nose of the
breather to the
rear.
5. Push hose firmly against fitting. Rotate hose to point
wn.
do
Housing Breather
28
Page 32

Wheel End Seal - Parts Exploded View
Wheel End Seal
1
1 - Installation tool
2 - Seal
3 - Rear hub
2
3
29
Page 33

Remove and Overhaul Wheel End Seal
Wheel End Seal
WARNINGWARNING
Never work under a vehicle supported by only a jack.
Always supp
make sure the vehicle will not roll before releasing the
brakes.
Wheel end seals can be easily damaged during handling.
ve the sea
Lea
damage or contamination.
1. Remove outer nut and locking washer.
2. Remove inner nut.
3. Remove outer bearing and wheel.
4. Remove oil seal.
5. Remove inner bearing.
6. Inspect spindle journal and hu
ort vehicle with stands. Block the wheels and
IMPORTANTWARNING
l in its package until installation to prevent
b bore for scratch
burrs. Recondition with an emery cloth as required.
es or
Install Wheel End Seal
1. Before installation, lubricate the following with the
same
lubricant used in the axle sump.
• Inner bearing.
• Wheel seal (follow the directions pro
the seal supplier).
2. Place seal on installation tool.
3. Drive seal with installation tool onto hub.
vided by
Wheel End Seal
Note: Deep
Always use the seal installation tool specified by the seal
manuf
age the seal and cause premature seal failure.
gouges can be repaired by filling gouge with hard-
ening gas
7. Clean hub cavity and bearing bores before reassem-
8. Clean bearings thoroughly with solvent and examine
acturer. Using an improper tool can distort or dam-
ket cement and smoothing
. Be sure to remove contaminants from all
bly
recesses and corners.
for damage. Replace damaged
IMPORTANTIMPORTANT
with emery cloth.
or worn bearings.
30
Page 34

Adjust Wheel Bearing
Wheel Adjustment Systems
WARNINGWARNING
Do not mix spindle nuts and lock washers from different
systems. Mixing spindle nuts and lock washers can
cause
wheel separation.
Note: The lock
washer
for a four-piece tang/dowel-type wheel
nut system is thinner than the lock washer for a threepiece tang-type wheel nut system and is not designed to
bear against the inner nut.
1. Inspect the spindle and nut threads for
and clean thoroughly or
Note: Proper assembly and
replace as required.
adjustment is
corrosion
not possible if the
spindle or nut threads are corroded.
2. Inspect the tang-type washer (if used).
washer
if the tangs are broken, cracked, or dam-
Replace the
aged.
3. Install the hub and drum on the spindle with care to
prevent damage
or distortion to the wheel seal.
CAUTIONCAUTION
Never use an impact wrench to adjust wheel bearings. A
torqu
e wrench is required to assure the nuts are properly
tightened.
8. Back off the inner nut one full turn. Rotate the wheel
hub.
Retighten the inner nut to 50 lbs. ft. (68 N•m) while
9.
rotatin
g the wheel hub.
10. Back off the inner nut exactly 1/4 turn.
Note: This adjustment procedure allows th
e wheel to rotate
freely with 0.001" -.005” (0.025 mm–0.127 mm) endplay.
Install the correct lock washer for the wheel nut sys-
11.
tem being used.
Three-piece Dowel-type Lock Washer System
WARNINGCAUTION
A wheel dolly is recommended during installation to make
sure that
the wheel seal is not damaged by the weight of the
hub and drum. Never support the hub on the spindle with
just the inner bearing and seal. This can damage the seal
and cause premature failure.
4. Completely fill the hub cavity between the inner and
used
outer bearing races with the same lubricant
in
the axle sump.
5. Before installation, lubricate the outer bearing with
the same lubricant used in the
Note: Lubricate only with clean axle
type used in the
axle sump. Do not pack the bearings
axle sump.
lubricant of the same
with grease before installation. Grease will prevent the
proper circulation of axle lubricant and may cause wheel
seal failure.
6. Install the outer bearing on the spindle.
7. Install the inner nut on the spindle. Tighten the inner
to 20
nut
0 lbs. ft. (271 N•m) while rotating the wheel
hub.
1
2
3
4
1 - Inner nut
2 - Dowel pin
3 - Dowel-type lock washer
4 - Outer nut
• Install the Dowel-type lock washer on the spindle.
Note: If the dowel pin and washer are not
aligned, remove
washer, turn it over and reinstall. If required, loosen the
inner nut just enough for alignment.
IMPORTANTIMPORTANT
Never tighten the inner nut for alignment. This can preload
bearing and cause premature failure.
the
31
Page 35

Wheel Adjustment Systems
y
• Install the outer nut on the spindle and tighten to
350 lbs. ft. (475 N•m).
• Verify end-play, see “Verify Wheel End Play Proce-
dure."
Three-piece Tang-type Lock Washer System
1
2
3
1 - Inner nut
2 - Tang-type lock washer .123” thick
3 - Outer nut
• Install the Tang-type lock washer on the spindle.
IMPORTANTIMPORTANT
Never tighten the inner nut for alignment. This can preload
earing and cause premature failure.
the b
Four-piece Tang/Dowel-type Lock Washer System
3
4
5
1
2
1 - Inner nut
2 - Dowel pin
3 - Dowel-type lock washer
4 - Tang-type lock washer
5 - Outer nut
• Install the Dowel-type lock washer on the spindle.
Note: If the dowel pin and washer are not
washer, turn it over and reinstall. If required, loosen the
inner nut just enough for alignment.
8” thick
.047
aligned, remove
Wheel Adjustment
S
stems
• Install the outer nut on the spindle and tighten to 250
lbs. ft
. (339 N•m).
• Verify end-play, see “Verify Wheel End Play Proce-
dure."
• After verifying end-play, secure wheel nuts by bend-
ing one of the locking washer tangs over the outer
wheel nut and
• Go to step 12.
another tang over the inner wheel nut.
Never tighten the inner nut for alignment. This can preload
bearing and cause premature failure.
the
• Install the Tang-type lock washer on the spindle.
• Install the outer nut on the spindle and tighten to 250
lbs. ft. (
• Verify end-play, see “Verify Wheel End Play Procedure."
• After verifying end-play, secure the ou
bending (180° apart) two opposing tangs of the
locking washer over the outer nut.
12. Install the following:
• New gasket at axle shaft flange.
• Axle shaft.
• Axle flange nuts and tighten to specified torque.
13. Lubricate axle wheel ends.
339 N•m).
IMPORTANTIMPORTANT
ter nut by
32
Page 36

Wheel End
Wheel Adjustment
Verify Wheel End-play Procedure
Verify end-play meets specification using a dial indicator. An
indicator with .001" (.03 mm) resolution is required. Wheel
end-play is the free movement of the tire and wheel assembly
along the spindle
Correct end-play is .001-.005” (.025-.125 mm).
1. Attach a dial indicator with its magnetic base to the
hub
2. Adjust the dial indicator so that its plu
is against the end of the spindle with its line of action
approximately parallel to the axis of the spindle.
3. Grasp the wheel assembly at the 3 o’clock and
9 o’clock positions. Push the wheel assembly in and
out while oscillating
bearing end-play as the total indicator movement.
If end-play is not within specification, readjustment is
quired.
re
axis.
or brake drum as shown below.
nger or pointer
it to seat the bearings. Read
WARNINGCAUTION
Adjust End-play with Wheel Hub
With indicator mounted at bottom, push / pull at sides of
drum.
Readjust Wheel End-play Procedure
Excessive End-play: If end-play is greater than .005"
(.127 mm), remove the outer nut and pull the lock washer
away from
inner nut to the next alignment hole of the dowel-type washer
(if used). Reassemble the washer and retorque the outer nut.
Verify end-play with a dial indicator.
the inner nut, but not off the spindle. Tighten the
Adjust End-play with Tire and Wheel Assembly
Insufficient End-play: If end-play is
outer nut and pull the lock washer away from the inner nut,
but not off the spindle. Loosen the inner nut to the next
adjustment hole of the dowel-type washer (if used). Reassemble the washer and retorque t
with a dial indicator.
Fine Tuning the End-play: If,
ment procedures, end-play is still not within the .001"-.005”
27 mm) range, disassemble and inspect the compo-
(.025-1
ts. If parts are found to be defective, replace the defective
nen
parts, reassemble and repeat
cedure. Verify end-play with a dial indicator.
not present, remove
h
e outer nut. Verify end-play
after per
wheel bearing adjustment pro-
forming the readjust-
the
33
Page 37

Lubricate Wheel End
Wheel Adjustment
IMPORTANTIMPORTANT
Before operating the axle, the wheel hub cavities and bearings must be lubricated to prevent failure.
When wheel ends are serviced, follow Spicer’s wheel
end lubrication procedure before operating the axle.
Spicer axles may be equipped with either of two (2)
wheel-end designs:
• Wheel ends with an oil fill hole.
• Wheel ends without an oil fill hole .
Wheel Ends with an Oil Fill Hole
1. Remove the oil fill plug.
2. Pour half (1/2) a pint of axle sump lubricant into
each hub through the wheel end fill hole.
3. Install oil fill plug and tighten to specified torque.
Wheel End with Oil Fill Hole
1
2
1 - Wheel end oil fill hole
2 - Proper lubricant level
Wheel End without Oil Fill Hole
Wheel End
1 - Lubricant flow from sump
1
34
Page 38

Wheel Adjustment
Wheel Ends without Oil Fill Hole
1. With axle level and wheel ends assembled, add lubricant through filler hole in carrier until fluid is
with the bottom of filler hole.
2. Raise the right side of the axle six (6) inches (152
mm) or more.
minute.
3. Lower the right side.
4. Raise the left side of the axle six (6) inches (152
mm) or more.
minute.
5. Lower the left side.
6. With axle on a level surface, add lubricant through
carrier oil filler hole until fluid is level
tom of the hole.
Note: Axles witho
mately 2.5 additional pints of lubricant to bring the lube
level even with
Hold axle in this position for one (1)
Hold axle in this position for one (1)
with the bot-
u
t wheel end fill holes will require approxi-
the bottom of fill hole.
level
1 - Oil will run into wheel end
2 - Oil will run into wheel end
1
2
35
Page 39

Lubrication
Lubrication
The ability of a drive axle to deliver quiet, trouble-free operation over a period of years is largely dependent upon the use
of good-quality gear lubrication in the correct quantity. The
most satisfactory results can be obtained by following the
directions contained in this manual.
The following lubrication instructions represent the most current recommendations from the Axle & Brake Division of Dana.
Approved Lubricants
General - Gear lubrications acceptable under military specifi-
cation (MILSPEC) MIL-L-2105D (Lubricating Oils, Gear, Multipurpose) are approved for use in Spicer Drive Axles.
The MIL-L-2105D specification defines performance and viscosity requirements for multigrade oils. It su
MIL-L-2105B, MIL-L-2105C and cold weather specification
MIL-L-10324A. This specification applies to both petroleumbased and synthetic based gear lubricants if they appear on
the most current “Qualified Products Lis
MIL-L-2105D.
Note: The use of separate oil additives and/or friction modifi-
ers are not approved in Spicer Drive Axles.
persedes both
t” (QPL-2105) for
Recommendations for Viscosity/Ambient
Temperature
The following chart lists the various SAE Grades covered by
MIL-L-2105D and the associated ambient temperature range
from each. Those SAE grades shown with an asterisk (*) are
available in the Spicer family of synthetic gear lubricants.
The lowest ambient temperatures covered by this chart are
-40°F and -40°C. Lubrication recommendations for those
applications which consistently operate below this temperature range must be obtained through Dana by contacting
your local Dana representative.
Grade Ambient Temperature Range
75W -40°F to -15°F (-40°C to -26°C)
75W
-80 -40°F to 80°F (-40°C to 21°C)
75W-90* -40°F to 100°F (-40°C to 38°C)
75W-140 -40°F and
80W-90 -15°F to 100°F (-26°C to 38°C)
above (-40°C and above)
Lubrication
Synthetic Based - Synthetic-based gear lubricants exhibit
superior thermal and oxidation stability, and generally
degrade at a lower rate when compared to petroleum-based
lubricants. The performance characteristics of these lubricants include extended change intervals, improved
omy, better extreme temperature operation, reduced wear and
cleaner component appearance. The family of Spicer gear
lubricants represents a premium quality synthetic lube
which fully meets or exceeds the requirements of
MIL-L-2105D. These products, available in both 75W-90
and 80/W-140, have demonstrated superior performance in
comparison to others qualified under the MILSPEC, as demonstrated by extensive laboratory and field testing. For a complete list of Spicer-approved synthetic lubricants, contact
your local Dana
manual for appropriate phone number.
Makeu
p Lube - Maximu
lube is 10%.
representative. See back cover of this
m amount of non-synthetic makeup
fuel econ-
80W-140* -15°F and above (-26°C and above)
85W-140 10°F and above (-12°C and above)
* Available in the Spicer family of synthetic gear lubricants.
36
Page 40

Lube Change Intervals
Lubrication
This product combines the latest manufacturing and part
washing technology. When filled with a Spicer-approved
synthetic lubricant at the factory, the initial drain is
not required.
Change the lubricant within the first 5,000 miles of operation when not using a Spicer-approved synthetic lubricant
in either a new axle or after a carrier head replacement.
Base subsequent lubricant changes on a combination of
the following chart and user assessment of the application
and operating environment.
Synthetic or
Mineral
Synt
hetic* SHAES-256 SAE 75W-90 500,000 miles [800,000 Km] or
Synthetic** SHAES-256 SAE 75W-90,
Mineral
Base
* Axles using LMS wheel end system
Lubricant SAE Change Interval for Line Haul Change Interval for Voca-
75W-140
MIL-L-2105E/J02360,
API GL-5 Gear Oil,
PRF-2105E
MIL-
75W, 75W-90,
75W-140, 80W90, 85W-140
Severe Service Lubrication Change Intervals - Severe service applications are those where the vehicle consistently
operates at or near its maximum GCW or GVW ratings, dusty
t environments, or consistent operation on grades
or we
greater than 8%.
WAY portion of the chart should be used. Typical applications
are construction, logging, mining and refuse removal.
Note: Clean metallic particles from the magnetic filler plug
and drain plugs. Clean or replace the breather yearly to
avoid lube contamination due to water ingestion.
5 years
250,000 miles (400,000 Km) or
3 years
120,000 miles [193,000 Km] or
1 year
For these applications, the ON/OFF HIGH-
tional
120,000 miles (193,000 Km)
or 1year
60,000 miles [96,500 Km] or 1
year
60,000 miles [96,500 Km] or
1 year
** Axles using adjustable wheel bearing system
37
Page 41

Change Lube
Lubrication
Lubrication
Drain
1. Drain when the lube is at normal operating temperature (150°-200°F [66°-93°C]). It will run
minimize the time necessary to fully drain the axle,
this insures the axle is flushed.
2. Remove the bottom two carrier to h
screws and allow the lube to drain into a suitable
container
Note: Dispose
posal
oils.
Inspect breather for clogging or corrosion. Clean or
3.
repla
.
of all used lubricants properly by following dis-
methods approved for mineral- or synthetic-based
ce as necessar
y.
freely and
ousing cap-
Fill
1. Reinstall bottom two carrier to housing capscrews –
use Loctite 270 and torque to 142–158 lbs. ft. (193214 N•m).
2. Remove the filler hole plug from the side of the carrier and fill the axle with the approved lubricant until
ith the bottom of the hole.
level w
3. If wheel ends were removed, follow instructions in
the wheel end servicing
Always use the filler hole as the final reference. If lube is level
with the bottom
Note: Lube fill capacities are basic guid
based on the angle the axle is installed in a particular
chassis. Torque fill plug to 40–60 lbs. ft. (54–82 N•m).
e axle can be filled through the axle housing breather
TIP: Th
hole
. Fill until lube level is even with the bottom of filler hole in
side of carrier.
of the hole, the axle is properly filled.
section.
e
lines and will vary
Fill
Drain
38
Page 42

Proper Vehicle Towing
Proper Vehicle Towing
Lift the drive wheels completely off of the ground or damage
will occur.
WARNINGWARNING
Do not lift the front wheels (non-drive wheels). This alters
oil’s position in the drive axle, draining it away from the
the
drive pinion and its bearings. If the pinion is rotated under
these conditions for any period of time, bearings will overheat resulting in axle damage or failure.
If it is impossible to lift the drive wheels, remove all axle
shafts to prevent gear
vent loss of lubricant and a possible road hazard. See
lowing section Proper Vehicle Towing with Wheel Differential
Lock for removal procedure.
rotation and cap the
wheel hubs to pre-
the fol-
39
Page 43

Torque Chart
Torque Chart
Location Thread Size Class/Grade Torque Secifications
Pinion End Nut M36 x 1.5 10.9 710-1040 lbs. ft. (848-1410 N•m)
Ring Gear to Diff Case Capscrew M20 x 1.5 10.9 435-465 lbs. ft. (589-630 N•m)
Carrier Cap Capscrew M20 x 2 10.9 350-428 lbs. ft. (475-580 N•m)
Fill Plug 1 x 1.11.5 – 40-60 lbs. ft. (54-81 N•m)
Carrier to Housing Capscrew M14 x 2 10.9 142-158 lbs. ft. (193-214 N•m)
Parking Brake Capscrew M16 x 1.5 10.9 180-220 lbs. ft. (244-298 N•m)
40
Page 44

For spec‘ing or service assistance, call 1-877-777-5360 or visit our website at www.dana.com
Dana Commercial Vehicle Products Group
3939 Technology Drive
Maumee, Ohio, USA 43537
www.dana.com
All applications must be approved by the Application Engineering Department. Specifications and/or design are subject to change without notice or obligation. Printed in USA AXSM-0030 09/13
 Loading...
Loading...