Page 1

ToxiLtd®
Single Gas
Detector
Reference Manual
Sperian Instrumentation
651 South Main Street
Middletown, CT 06457
(800) 711-6776
(860) 344-1079
Fax (860) 344-1068
Part number 13-266
Version 2.00
23AUG2007
0
Page 2

THE TOXILTD® PERSONAL PORTABLE GAS DETECTORS HAVE
BEEN DESIGNED FOR THE DETECTION AND MEASUREMENT OF
POTENTIALLY HAZARDOUS ATMOSPHERIC CONDITIONS.
IN ORDER TO ASSURE THAT THE USER IS PROPERLY WARNED OF
POTENTIALLY DANGEROUS ATMOSPHERIC CONDITIONS, IT IS
ESSENTIAL THAT THE INSTRUCTIONS IN THIS REFERENCE MANUAL
BE READ, FULLY UNDERSTOOD, AND FOLLOWED.
Sperian Instrumentation Part Number 13-266
Sperian Protection Instrumentation, LLC
No page or part of this operation manual may be reproduced in
any form without written permission of the copyright owner
Sperian Instrumentation reserves the right to correct
ToxiLtd® Reference Manual
Version 2.00
Copyright 2007
by
Middletown, Connecticut 06457
All rights reserved.
shown above.
typographical errors.
1
Page 3

Table of Contents
Certifications........................................................................................ 3
ATEX Label Requirement.................................................................... 3
Warnings and Cautions ...................................................................... 3
A. Signal Words .........................................................................................................3
B. Warnings................................................................................................................4
1. Overview......................................................................................... 5
1.1 Methods of sampling .......................................................................................... 5
1.2 Sensors..............................................................................................................5
1.2.1 Sensor ranges and resolutions................................................................... 5
1.2.2 ToxiLtd O
1.2.3 F1: Missing sensor during startup............................................................... 5
1.3 Alarm logic......................................................................................................... 6
1.3.1 Gas alarms................................................................................................. 6
1.3.2 Silence warning alarms .............................................................................. 6
1.3.3 Calibration due notices............................................................................... 6
1.3.4 Low battery alarms ..................................................................................... 6
1.4 Design components ........................................................................................... 6
1.5 Standard accessories.........................................................................................7
1.6 Value pack kits................................................................................................... 7
2. Field Operation .............................................................................. 7
2.1 Turning the ToxiLtd on ....................................................................................... 7
2.1.1 O
2.1.2 Toxic version start up sequence................................................................. 7
2.1.3 Start up sequence ......................................................................................7
2.2 Functions ...........................................................................................................8
2.2.1 View max gas readings ..............................................................................8
2.2.2 View alarm levels ....................................................................................... 8
2.3 Calibration due notices.......................................................................................9
2.4 Low battery alarms............................................................................................. 9
2.5 Turning the ToxiLtd off ....................................................................................... 9
2.6 Sampling.......................................................................................................... 10
2.6.1 Sample draw kit usage .............................................................................10
version start up sequence......................................................................7
2
3. Calibration.................................................................................... 10
3.1 Verification of accuracy .................................................................................... 10
3.1.1 Verifying accuracy and response: ToxiLtd O
3.1.2 Verifying toxic sensor performance...........................................................11
3.2 Effect of contaminants on ToxiLtd sensors.......................................................11
3.2.1 Effects of contaminants on oxygen sensors..............................................11
3.2.2 Effects of contaminants on toxic gas sensors........................................... 11
3.3 Fresh air/zero calibration..................................................................................12
3.4 Functional (bump) testing for ToxiLtd with toxic gas sensor..............................12
3.5 Span Calibration for ToxiLtd with toxic gas sensor ...........................................13
3.6 Failure to calibrate............................................................................................14
3.6.1 Fresh air/zero calibration failure................................................................14
3.6.1.1 Reason for fresh air/zero calibration failures....................................................14
3.6.2 Span calibration failure............................................................................. 14
3.6.2.1 Sensor out of range (no CAL)..........................................................................14
3.6.2.2 No gas............................................................................................................14
warm-up phase .........................................................................5
2
...........................................10
2
2
Page 4
3.6.2.3 Causes for span cal failure.............................................................................. 14
3.6.3 Forced fresh air/zero calibration ...............................................................14
3.7 Fresh air/zero calibration in a contaminated atmosphere .................................15
4. Event logging............................................................................... 15
4.1 Initiating communications................................................................................. 15
Appendices ........................................................................................ 16
Appendix A: Sensor Cross-Sensitivity Chart................................................................ 16
Appendix B: Default toxic sensor calibration gas settings ............................................ 16
Appendix C: Calibration Frequency ............................................................................. 17
Sperian Instrumentation Warranty Gas Detection Products ........ 18
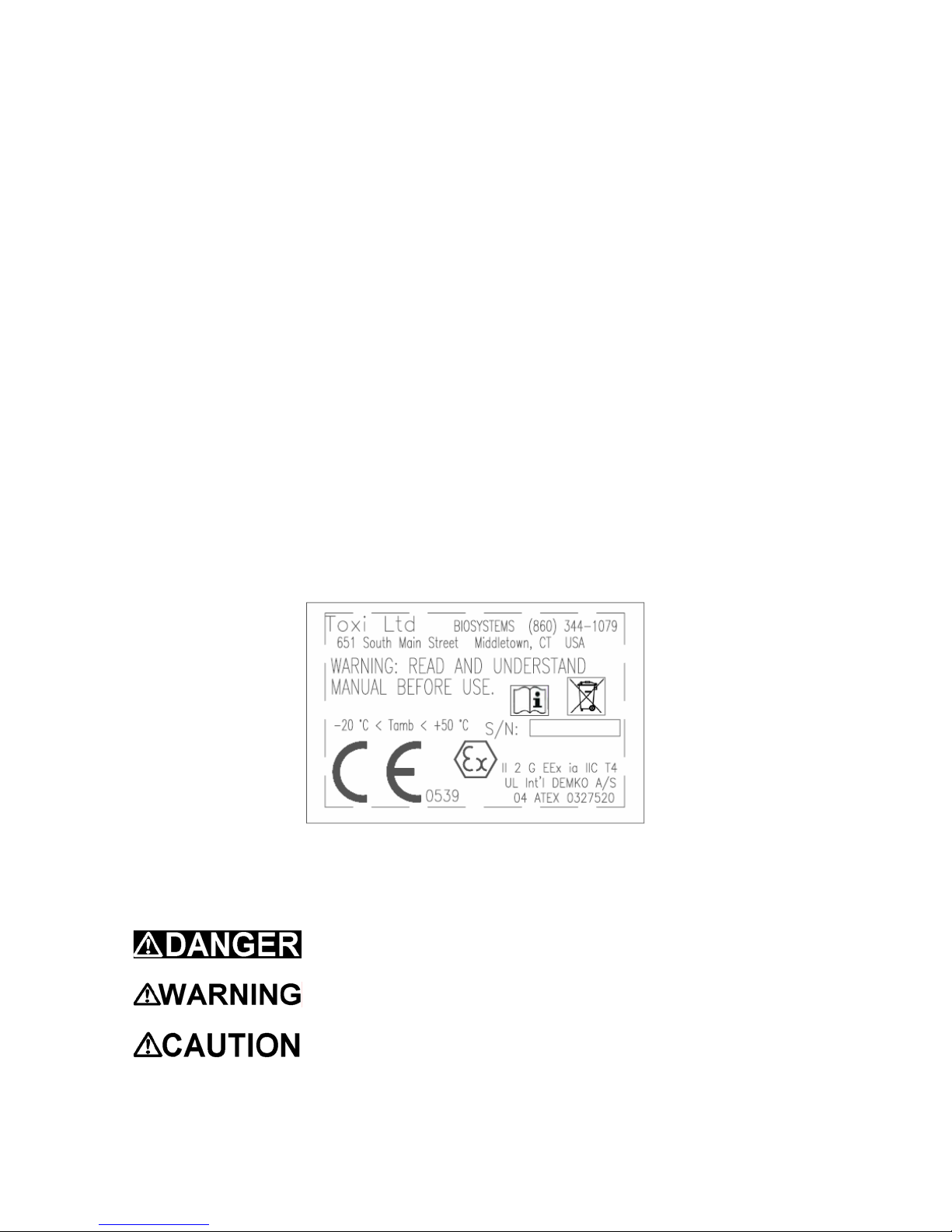
Certifications
The ToxiLtd® carries the following certifications:
UL and c-UL, Class I, Division 1, Groups A,B,C,D, Temp Code T4.
UL Class II, Division 1, Groups E,F,G
ATEX Certification:
II 2 G EEx ia IIC T4
UL International DEMKO A/S 04 ATEX 0327520
IECEx Ex ia IIC T4
CQST (China)
ATEX Label Requirement
Warnings and Cautions
A. Signal Words
The following signal words, as defined by ANSI Z535.4-1998, are used in the ToxiLtd
Operator’s Guide.
indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not
avoided, will result in death or serious injury.
indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not
avoided, could result in death or serious injury.
indicates a potentially hazardous situation, which if not
avoided, may result in moderate or minor injury.
CAUTION used without the safety alert symbol indicates a potentially
hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may result in property damage.
3
Page 5

B. Warnings
1.
The ToxiLtd personal, portable gas detectors have been
designed for the detection of either oxygen deficiencies or specific toxic gas
accumulations. An alarm condition indicates the presence of a potentially lifethreatening hazard and should be taken very seriously.
2.
In the event of an alarm condition it is important to follow
established procedures. The safest course of action is to immediately leave the
affected area, and to return only after further testing determines that the area is
once again safe for entry. Failure to immediately leave the area may result in
serious injury or death.
3.
The accuracy of ToxiLtd instruments equipped with a toxic
gas sensor should be checked periodically with known concentration calibration
gas. Failure to check accuracy can lead to inaccurate and potentially dangerous
readings. ToxiLtd instruments equipped with an oxygen sensor should be
periodically calibrated in fresh air.
4.
A ToxiLtd equipped with a toxic gas sensor that fails
calibration may not be used until testing with known concentration test gas
determines that accuracy has been restored, and the instrument is once again fit
for use. Instruments equipped with an oxygen sensor that fail calibration may
not be used until testing with fresh air determines that accuracy has been
restored and the instrument is once again fit for use. An instrument that cannot
be calibrated or is found to be out of tolerance must be replaced immediately.
5.
Do not reset the calibration gas concentration setpoints in
the ToxiLtd unless the concentrations of your calibration gas differ from the
concentrations of the calibration gas that is normally supplied by Sperian for use
in calibrating the ToxiLtd.
6.
Use of non-standard calibration gas and/or calibration kit
components when calibrating the ToxiLtd can lead to dangerously inaccurate
readings and may void the standard Sperian warranty.
Sperian offers calibration kits and long-lasting cylinders of test gas specifically
developed for easy calibration. Customers are strongly urged to use only
Sperian calibration materials when calibrating the ToxiLtd.
7.
8.
Substitution of components may impair intrinsic safety.
For safety reasons the ToxiLtd must be operated by
qualified personnel only. Read, understand and follow the directions set forth in
this reference manual before operating the ToxiLtd.
The ToxiLtd has been tested for intrinsic safety in
9.
Explosive Gas/AIR (max. 21.0% O
).
2
10.
parts inside of the instrument.
Do not open the ToxiLtd. There are no user serviceable
4
Page 6
1. Overview
The ToxiLtd is a single sensor gas
detector that is designed to detect either
oxygen (O
gases. The ToxiLtd’s sensor type is
shown on the front of the instrument and
is also shown on the display during the
startup sequence.
ToxiLtd gas detectors are disposable
instruments that are designed to operate
for 2 full years from the date of activation.
ToxiLtd models equipped with a toxic gas
sensor (CO, H
activated within 6 months of the
manufacturing date. Oxygen versions
must be activated within 1 month of the
manufacturing date. If the instrument is
not turned on by the “must be activated by
date”, the instrument will activate itself
and the 2-year countdown will begin
automatically.
Upon delivery, the screen of the ToxiLtd
will be blank except for the negated horn
icon.
If the “must be activated by date” has
passed and the instrument has activated
itself, the instrument will show three lines
on the screen with the negated horn icon.
Contact Sperian or your distributor if
three lines are displayed when you first
receive the detector.
The ToxiLtd is delivered with a preinstalled lithium thionyl chloride (LiSOCl
battery capable of powering the
instrument for the full 2 years of the
instrument’s operating life. After the 2year instrument life cycle is up, the
instrument will turn itself off.
Note: Early production runs of the
oxygen version of the ToxiLtd were
referred to as the “OxyLtd”. The
instructions contained in this manual
that refer to the ToxiLtd Oxygen (O
) or one of a variety of toxic
2
S or SO2) must be
2
)
2
)
2
are valid for the OxyLtd with similar
instrument firmware.
1.1 Methods of sampling
The ToxiLtd may be used in diffusion
mode, or with the manual sample draw kit
that is available separately. In either
mode, the atmosphere must reach the
sensor for the instrument to register a
reading. In diffusion mode, the
atmosphere reaches the sensor by
diffusing through the sensor port on the
front of the instrument. Normal air
movements are enough to carry the
sample to the sensor. During remote
sampling, the gas sample is drawn into
the sensor compartment through the
probe assembly and a length of tubing.
See section 2.6 for more details on
sampling the atmosphere.
1.2 Sensors
Toxic sensor versions of the ToxiLtd use
an electrochemical toxic gas sensor. The
ToxiLtd O
uses a galvanic oxygen
2
sensor. Both types of sensor have been
designed to minimize the effects of
common interfering gases. These
sensors provide accurate, dependable
readings for gases commonly
encountered in industrial applications.
1.2.1 Sensor ranges and resolutions.
Sensor Range Resolution
CO 0-1000 PPM 5 PPM
H2S 0 -200 PPM 2 PPM
SO2 0 – 20 PPM 0.1 PPM
O2 0-30%/Vol. 0.2%/Vol.
1.2.2 ToxiLtd O2 warm-up phase
The ToxiLtd O
requires a one-hour
2
warm-up phase from the moment of
activation until actual use. See section
2.1.1 for further details.
1.2.3 F1: Missing sensor during
startup
If the ToxiLtd fails to detect the sensor
during startup, it will show “F 1” with the
caution symbol following the software
version screen at startup. This is covered
in greater detail in section 2.1.3.
5
Page 7

1.3 Alarm logic
1.3.1 Gas alarms
When an alarm set point is exceeded a
loud audible alarm sounds, the bright red
LED alarm light flashes and the display
will indicate whether it is a warning alarm
or a more serious danger alarm. If the
ToxiLtd is equipped with the optional
vibrating alarm, it will also be activated
during an alarm condition.
For oxygen sensor-equipped instruments,
the warning alarm is sounded for oxygen
enrichment and the danger alarm is
sounded for oxygen deficiency.
Instruments equipped with a toxic gas
sensor have two ascending alarm set
points. The lower alarm set point is the
warning alarm, while the higher alarm set
point is the danger alarm.
Sensor Warning Alarm Danger Alarm
CO 35 PPM 100 PPM
H2S 10 PPM 20 PPM
SO2 2 PPM 5 PPM
O2 23.5%/Vol. 19.5%/Vol.
Default Warning and Danger Alarm Settings
In the event of an
alarm condition it is important to follow
established procedures. The safest
course of action is to immediately
leave the affected area, and to return
only after further testing determines
that the area is once again safe for
entry. Failure to immediately leave the
area may result in serious injury or
death.
1.3.2 Silence warning alarms
The ToxiLtd’s audible and vibrating (if so
equipped) alarms can be turned off during
an alarm condition by pressing the MODE
button if this function has been enabled
with BioTrak software. The visual warning
alarm light and readings will continue to
indicate the alarm.
1.3.3 Calibration due notices
The ToxiLtd includes calibration due
notices that are displayed when the
instrument is due for calibration.
For more information on the calibration
due notices, see section 2.3 below.
1.3.4 Low battery alarms
The battery in the ToxiLtd is designed to
power the instrument for a full two years
from the date of activation. In the unlikely
event that the battery runs out of power
prior to the completion of the 2-year
operational lifespan, the ToxiLtd includes
two battery warning alarms that are
activated when the battery voltage is
reduced to specific levels.
For more details on the battery alarm,
see section 2.4 below.
1.4 Design components
Case: The instrument is enclosed in a
solid PC (polycarbonate) case with TPE
(rubber) overmold.
Front face: The front face of the
instrument houses the LCD display,
MODE button, sensor port, LED and
audible alarm port.
LCD display: The liquid crystal display
(LCD) displays gas readings, messages
and other information.
Visual alarm (LED) / IrDA port: A bright
red LED (Light-Emitting Diode) alarm light
provides a visual indication of the alarm
state. The LED also functions as the IrDA
port.
MODE button: The large push-button on
the front of the instrument is called the
MODE button. The MODE button is used
to turn the ToxiLtd on and off, to view the
MAX screen and to initiate the automatic
calibration sequence.
Figure 1. Exterior front view.
Sensor port: The sensor port is located
at the upper left corner of the instrument.
A filter prevents unwanted contaminants
from entering the sensor.
Audible alarm orifice: A cylindrical
resonating chamber contains the loud
audible alarm.
6
Page 8

Bottom surface: The belt clip attaches to
the bottom surface of the instrument.
1.5 Standard accessories
Standard accessories with every ToxiLtd
include installed sensor and battery,
reference manual and calibration/sample
draw adapter.
1.6 Value pack kits
ToxiLtd value packs include all standard
accessories, calibration fittings, 34-liter
cylinder of calibration gas, and fixed flow
rate regulator in a foam-lined, hard-shell
carrying case.
2. Field Operation
Field operation of the ToxiLtd is controlled
entirely through the MODE button, which
is located on the front of the instrument.
The MODE button is used to turn the
ToxiLtd on and off (if desired), to access
MAX gas readings for the current session
and to initiate the fresh air/zero and span
calibration sequences.
2.1 Turning the ToxiLtd on
The ToxiLtd is effectively disabled when it
leaves the Sperian Factory. Upon arrival,
the screen will be blank other than the
negated horn icon.
Note: If the ToxiLtd arrives with three
lines showing on the screen, it is an
indication that the “must be activated
by date” has passed and the
instrument has already turned itself on.
Contact Sperian or your distributor for
further instructions.
The ToxiLtd is a disposable instrument.
Once activated, it will operate
continuously for 24 months. In the
unlikely event that the battery runs out of
power prior to the completion of the 2-year
operating cycle, the ToxiLtd must be
returned to Sperian or an authorized
service center for the installation of a new
battery.
There are no user serviceable parts
inside of the ToxiLtd.
To initialize the ToxiLtd press and hold
the MODE button for 5 seconds until the
instrument chirps, then release the MODE
button.
2.1.1 O
ToxiLtd O
version start up sequence
2
models require a one-hour
2
warm-up period prior to use. Once the
MODE button is pressed and held for 5
seconds, the instrument will begin a 60minute countdown. The instrument will be
ready to use in 60 minutes.
When the warm-up period concludes, the
instrument will show three dashes with
the negated horn symbol.
Once three lines are shown, press and
hold the MODE button for 1 second to
start the instrument. The start-up
sequence will begin. Proceed to section
2.1.3.
2.1.2 Toxic version start up sequence
ToxiLtd models equipped with a toxic gas
sensor do not require a warm up period.
Upon arrival, press and hold the MODE
button for 5 seconds. The ToxiLtd will
immediately proceed to the start-up
sequence.
2.1.3 Start up sequence
During the start-up sequence, the
instrument performs an electronic self test
that will take approximately 30 seconds to
complete. During the self-test sequence,
the audible alarm will “chirp” and all
sections of the display will be lit.
The ToxiLtd will then display the “on”
screen followed by software version.
7
Page 9

If the sensor has become disconnected or
removed from the
instrument during
shipping, the screen
will show “F 1” with the
caution symbol
following the software
version screen.
If “F 1” is shown, the
instrument will
automatically shut
down and show three
lines on the screen.
If “F 1” is shown and the ToxiLtd shuts
itself down, contact Sperian or your local
distributor for further information.
Once the sensor is recognized, the serial
number screens will be shown. Note that
the 6 digit serial number is shown on two
screens. In this case, the instrument
serial number is 123456.
The sensor type will be shown next.
During the display of the warning alarm
level, the LED alarm
light will flash twice and
the audible warning
alarm will sound twice.
The audible warning
alarm is slow and
warbling.
During the display of
the danger alarm level,
the LED visual alarm
will flash twice and the
audible danger alarm
will sound twice. The audible danger
alarm is louder and a higher frequency
than the warning alarm.
Following the danger alarm level, the
ToxiLtd will begin standard operation and
will display the number of months
remaining in the 24-month lifecycle of the
instrument. During an alarm condition,
the instrument will display the current gas
reading.
For the first full month of use following
initialization the display
will show 23 full
months remaining.
Once the instrument
determines that there
are 90 days of
operation remaining,
the instrument will
indicate 90 days and
proceed to count the
days down until the instrument reaches 0
days and turns itself off.
2.2 Functions
As stated above, the ToxiLtd will show the
amount of time remaining in the product’s
lifecycle during normal operation unless
there is an alarm present. The ToxiLtd
will display gas readings while it is in
alarm.
2.2.1 View max gas readings
From the months remaining or the current
gas readings screen, press the MODE
button once to view the MAX gas values
screen. The MAX figure represents the
highest gas value reading that has been
recorded by the
instrument during the
current operating session
or during the last 24
hours of operation.
Note: To reset the max readings level,
fresh air/zero calibrate the instrument
as discussed in section 3.3.
The MAX screen will be shown for 5
seconds. The instrument will then
automatically return to the months or days
remaining screen (unless an alarm
condition is present).
2.2.2 View alarm levels
To view the current gas alarm levels, from
the current gas reading screen, press and
hold the MODE button for about 5
seconds until the display test screen is
shown.
8
Page 10

Release the MODE button. The software
will proceed through the software version
and serial number screens before
showing the alarm levels.
The instrument will then return to normal
operation and display the months
remaining screen.
2.3 Calibration due notices
When the calibration due notice is
enabled and the ToxiLtd is due for fresh
air calibration “0-CAL
will be displayed at the
bottom of the current
gas readings screen
along with the
triangular warning
symbol.
When the calibration due notice is
enabled and the ToxiLtd is due for span
calibration the calibration bottle icon will
be displayed at the
bottom of the current
gas readings screen
along with the warning
symbol.
The bump test due notice is designed for
instruments that are processed in an IQ
Express Dock. When the bump test due
notice is enabled and the ToxiLtd is due
for a bump test, the calibration bottle icon
will be displayed at the
bottom of the current
gas readings screen
without the triangular
warning symbol.
Note: If an IQ Express Dock is
unavailable, a manual span calibration
will also reset the bump test due
notice.
The default fresh air/zero calibration
interval for the O
thirty days. Different versions of software
may have different calibration intervals.
version of the ToxiLtd is
2
2.4 Low battery alarms
When the ToxiLtd determines that there
are less than 7 days of battery life
remaining, the battery icon will be lit.
Note that “MONTHS”
or “DAYS” and the
number of months or
days of operating life
remaining are still
shown when the
battery icon is lit.
When the ToxiLtd determines that there
are less than 8 hours of battery life
remaining, the battery icon and the
triangular warning symbol on the LCD will
be shown. At this point the audible alarm
will begin to chirp once per minute.
When the battery reaches a level where it
can no longer power the instrument, the
ToxiLtd will sound the
high/danger audible
alarm while displaying
OFF with the danger,
caution and battery
icons.
Press MODE to turn the instrument off. If
the MODE button is not pressed, the
instrument will remain in alarm for as long
as it can before shutting itself down. The
following screen will be shown after the
instrument is shut down.
In the event that the
instrument actually shuts
itself down due to low
battery levels, it will
automatically launch the
IrDA connection subroutine so that data in
the instrument may be downloaded to
BioTrak.
2.5 Turning the ToxiLtd off
To turn the ToxiLtd off, press and hold the
MODE button. After 5 seconds, the
instrument will light up all segments on
the display. After 3 more seconds, the
display will show “IrDA”. Continue to hold
the MODE button for an additional 15
seconds after “IrDA” is
shown. The following
screen will be shown
after the instrument is
shut down.
Note: Turning the ToxiLtd off will have
no effect on the operational life of the
instrument. The ToxiLtd will operate
9
Page 11

for 24 months from the activation date
regardless of whether the instrument is
turned on or off.
2.6 Sampling
The ToxiLtd may be used in either
diffusion or sample-draw mode. In either
mode, the gas sample must enter the
sensor compartment for the instrument to
register a gas reading.
In diffusion mode, the atmosphere
reaches the sensor by diffusing through
the sensor port on the front of the
instrument. Normal air movements are
enough to carry the sample to the sensor.
The sensor reacts quickly to changes in
the concentration of the gas being
measured.
It is also possible to use the ToxiLtd to
sample remote locations with the handaspirated sample-draw kit that is available
separately. During remote sampling, the
gas sample is drawn into the sensor
compartment through the probe assembly
and a length of tubing.
2.6.1 Sample draw kit usage
1. Connect the shorter piece of hose
from the squeeze bulb to the sample
draw adapter. Connect the longer end
of the hose to the sample probe.
2. Attach the sample draw adapter to the
ToxiLtd.
3. Cover the end of the sample draw
probe assembly with a finger, and
squeeze the aspirator bulb. If there
are no leaks in the sample draw kit
components, the bulb should stay
deflated for a few seconds.
4. Insert the end of the sample probe into
the location to be sampled.
5. Squeeze the aspirator bulb several
times to draw the sample from the
remote location to the sensor
compartment. Allow one squeeze of
the bulb for every one foot of sampling
hose for the sample to reach the
sensors. Then continue to squeeze
the bulb for an additional 45 seconds
or until readings stabilize.
6. Note the gas measurement readings.
CAUTION: Hand aspirated remote
sampling only provides continuous
gas readings for the area in which the
probe is located when the bulb is being
continuously squeezed.
Note: Each time a reading is desired, it
is necessary to squeeze the bulb a
sufficient number of times to bring a
fresh sample to the sensor
compartment and to then continue
squeezing the bulb for an additional 45
seconds or until readings stabilize.
3. Calibration
The ToxiLtd features fully automated
calibration functions. Instruments
equipped with an oxygen sensor only
require the fresh air/zero calibration, while
toxic sensor-equipped instruments require
both fresh air/zero and span calibrations.
The MODE button is used to initiate the
automatic calibration sequence.
Calibration adjustments are made
automatically by the instrument.
3.1 Verification of accuracy
Sperian recommends regular verification
of accuracy for all of our gas detection
products in order to maximize worker
safety. For a discussion of Sperian’s
Calibration Recommendations, see
Appendix C.
3.1.1 Verifying accuracy and
response: ToxiLtd O
The ToxiLtd O
uses a galvanic oxygen
2
sensor that puts out a continuous
electrical signal (as long as oxygen is
present), which the detector converts into
a reading. As the oxygen sensor ages,
the output signal tends to diminish
gradually, which can eventually lead to
erroneous readings.
The display on the ToxiLtd O
a reading when it is in alarm, so it is
difficult to know exactly when to fresh
air/zero calibrate the detector. Sperian
recommends that the fresh air/zero
calibration be performed regularly on the
ToxiLtd O
. The fresh air/zero calibration
2
takes less than ten seconds to perform
and does not require an external gas
source when it is performed in a fresh air
environment.
Simply take the ToxiLtd O
where the atmosphere is known to be
fresh and perform a fresh air/zero
calibration adjustment as discussed below
in section 3.3. If fresh air is not available,
see section 3.7 below for instructions on
fresh air calibration in contaminated air.
10
2
only shows
2
to an area
2
Page 12

Sperian also recommends that the
response of the oxygen sensor be
regularly verified by any of the three
following methods:
x Expose the O
sensor to a known
2
concentration of gas containing less
than 19% oxygen. If the descending
oxygen alarm is set to 19.5% the
instrument should go into alarm a few
seconds after the gas reaches the
sensor face.
x Process the ToxiLtd O
in an IQ
2
Express Dock that has a cylinder of
calibration gas containing 18.0%
oxygen (or less) connected to the gas
port and proceed with the oxygen
bump test.
x Breath test: Hold your breath for 10
seconds, then slowly exhale directly
onto the face of the sensor (in the
same way you would to fog up a piece
of glass). If the descending oxygen
alarm is set to 19.5%, the instrument
should go into alarm after a few
seconds.
3.1.2 Verifying toxic sensor
performance
Verification is a two-step procedure for
ToxiLtd instruments equipped with a toxic
gas sensor.
Step one is to take the ToxiLtd to an area
where the atmosphere is known to be
fresh and perform a fresh air/zero
calibration as discussed below in section
3.3. The fresh air/zero calibration takes
less than ten seconds to perform and
does not require an external gas source
when it is performed in a fresh air
environment.
Step two is to test sensor response by
exposing the sensor to a test gas of
known concentration. This is known as a
functional (bump) test. Readings are
considered to be accurate when the
display is between 90%* and 120% of the
expected values as given on the
calibration gas cylinder. If readings are
accurate, there is no need to adjust your
gas detector. See section 3.4 for further
details concerning the functional/bump
test.
If the readings are inaccurate, the
instrument must be span calibrated before
further use as discussed in section 3.5.
The Canadian Standards Association
*
(CSA) requires the instrument to
undergo calibration when the
displayed value during a bump test
fails to fall between 100% and 120% of
the expected value for the gas.
Accuracy of
ToxiLtd instruments equipped with a
toxic gas sensor should be checked
periodically with known concentration
calibration gas. Failure to check
accuracy can lead to inaccurate and
potentially dangerous readings.
See Appendix C for a discussion of
calibration frequency.
3.2 Effect of contaminants on
ToxiLtd sensors
The atmosphere in which the ToxiLtd is
used can have lasting effects on the
sensors. Sensors may suffer losses in
sensitivity leading to degraded
performance if exposed to certain
substances.
There are two basic types of sensors that
may be installed in the ToxiLtd: galvanic
oxygen or electrochemical toxic. Each
type of sensor uses a slightly different
detection principle, so the kinds of
conditions that affect the accuracy of the
sensors vary from one type of sensor to
the next.
3.2.1 Effects of contaminants on
oxygen sensors
Oxygen sensors may be affected by
prolonged exposure to "acid" gases such
as carbon dioxide. The oxygen sensors
used in Sperian instruments are not
recommended for continuous use in
atmospheres containing more than 25%
.
CO
2
3.2.2 Effects of contaminants on
toxic gas sensors
Sperian’s “substance-specific”
electrochemical sensors have been
carefully designed to minimize the effects
of common interfering gases.
“Substance-specific” sensors are
designed to respond only to the gases
that they are supposed to measure. The
higher the specificity of the sensor, the
less likely the sensor will react to other
gases, which may be incidentally present
in the environment. For instance, a
11
Page 13

“substance-specific” carbon monoxide
sensor is deliberately designed not to
respond to other gases that may be
present at the same time, such as
hydrogen sulfide (H
).
(CH
4
Although great care has been taken to
reduce cross-sensitivity, some interfering
gases may still have an effect on toxic
sensor readings. In some cases the
interference may be positive and result in
readings that are higher than actual. In
other cases the interference may be
negative and produce readings that are
lower than actual and may even cause the
instrument to display negative readings for
the target gas.
See Appendix A for cross-sensitivity
data.
3.3 Fresh air/zero calibration
To initiate the fresh air/zero calibration
procedure:
1. From the current gas reading screen,
press the MODE button three times
within two seconds. The ToxiLtd will
briefly display “CAL” and then begin a
5-second countdown with the 0-CAL
icon lit.
S) and methane
2
o
2. Press the MODE button before the
end of the 5-second countdown to
begin the fresh air/zero calibration.
The fresh air/zero calibration has been
successfully initiated when the ToxiLtd
alternates between the following two
screens:
when the instrument returns to the
current gas reading screen.
Note: The maximum reading value
(MAX) will be automatically reset
following a successful fresh air/zero
calibration.
Fresh air/zero
calibrations may only be performed in
an atmosphere that is known to
contain 20.9% oxygen and 0 PPM toxic
gas. Performing fresh air/zero
calibrations in an atmosphere that is
not comprised of 20.9% oxygen and 0
PPM toxic gas may lead to inaccurate
and potentially dangerous readings.
3.4 Functional (bump) testing for
ToxiLtd with toxic gas sensor
The accuracy of the ToxiLtd with a toxic
gas sensor may be verified at any time by
a simple functional (bump) test.
To perform a functional (bump) test, do
the following:
1. Turn the ToxiLtd on and wait at least
three minutes to allow the readings to
fully stabilize.
2. Make sure the instrument is located in
fresh air.
3. Perform a fresh air/zero calibration as
discussed in section 3.3 and allow the
instrument to return to the normal
operation.
l
3. For instruments equipped with a toxic
gas sensor, the fresh air/zero
calibration is complete when the
instrument begins a second 5-second
countdown for the span calibration. If
span calibration is not required, allow
the countdown to reach 0 without
pressing the MODE button.
If the instrument is equipped with an
oxygen sensor, calibration is complete
Figure 3.4: Bump-test/span calibration setup for toxic sensor-equipped instruments.
4. Apply the calibration gas as shown in
figure 3.4.
5. Wait for the readings to stabilize.
Forty-five seconds to one minute is
usually sufficient.
12
Page 14

6. Note the readings. Readings are
considered accurate if they are
between 90%* and 120% of the
expected value. If the readings are
considered accurate, then the
instrument may be used without
further adjustment. If readings are
considered inaccurate, the instrument
must be adjusted using the “span”
calibration procedures discussed in
section 3.5 before further use.
*The Canadian Standards
Association (CSA) considers bump
test readings accurate when the
displayed values fall between 100%
and 120% of the expected value for
the gas. To meet the CSA
requirement, an instrument must
undergo calibration when the
displayed value during a bump test
fails to fall between 100% and 120%
of the expected value for the gas.
3.5 Span Calibration for ToxiLtd
with toxic gas sensor
Span calibration should be performed
when a functional (bump) test has shown
that the instrument’s gas readings are not
between 90%* and 120% of the expected
values as given on the calibration gas
cylinder (as discussed in section 3.4).
*To meet the CSA requirement, an
instrument must undergo calibration when
the displayed value during a bump test
fails to fall between 100% and 120% of
the expected value for the gas.
Prior to performing a span calibration,
perform a fresh air/zero calibration as
discussed in section 3.3. After successful
completion of the fresh air/zero
calibration, the instrument will begin a
second five-second countdown with the
calibration gas bottle icon highlighted.
1. Press the MODE button before the
countdown is complete to initiate the
span calibration. The display will
alternate between “GAS” and the
expected concentration of calibration
gas.
l
2. Apply calibration gas as shown above
in figure 3.4. Once calibration gas is
detected, the readout will change to
show the gas reading. Note that the
negated horn symbol is shown to
indicate that the alarms are not
operating because the instrument is in
calibration mode.
3. The calibration is fully automatic from
this point on. Once the instrument
successfully completes the span
calibration, it will emit three short
beeps and display the maximum span
calibration adjustment value for two
seconds.
Note: The maximum span calibration
adjustment value shown is an
indication of the relative health of the
sensor. As a sensor loses sensitivity,
the maximum adjustment level will
approach the calibration gas
concentration, letting you know when
the sensor is losing sensitivity.
4. The instrument will then return to
normal operation.
Note: Once the calibration cycle is
completed, the ToxiLtd automatically
returns to normal operation and the
gas alarms may be activated.
Disconnect the calibration assembly
immediately after calibration.
Use of nonstandard calibration gas and/or
calibration kit components when
calibrating the ToxiLtd can lead to
inaccurate and potentially dangerous
readings, and may void the standard
Sperian Warranty.
13
Page 15

3.6 Failure to calibrate
3.6.1 Fresh air/zero calibration failure
In the event of fresh air/zero calibration
failure, the “no” and “CAL” screens will be
alternately displayed as shown below with
the “0-CAL” segment lit. The instrument
will then return to the gas reading screen.
l
Following a fresh air/zero calibration
failure, the triangular warning symbol and
“0-CAL” indicator will remain lit until a
successful fresh air/zero calibration is
performed.
3.6.1.1 Reason for fresh air/zero
calibration failures
Fresh air/zero calibration failures often
result from the attempt to calibrate the
instrument in a contaminated atmosphere.
Fresh air/zero calibration failures can also
result from sensor failures.
3.6.2 Span calibration failure
The ToxiLtd is designed to recognize two
distinct types of span calibration failure:
failures that occur due to sensor response
outside the sensor’s normal range for
calibration and failures that occur when
the instrument fails to recognize any
calibration gas whatsoever.
3.6.2.1 Sensor out of range (no
CAL)
If the instrument recognizes calibration
gas, but the sensor response is not within
the range to calibrate the instrument, span
calibration will fail and the “no” and “CAL”
screens will be alternately displayed.
l
After displaying “no” and “CAL” three
times, the instrument will return to the
current gas readings screen and the
warning symbol and the calibration bottle
icon will be shown, which signifies that the
instrument failed the last attempt to span
calibrate.
3.6.2.2 No gas
In the case of a span calibration failure in
which calibration gas is not detected, the
“no” and “GAS” screens will be alternately
displayed as shown below with the
calibration bottle icon highlighted.
l
When the instrument returns to the
current gas readings screen, the warning
symbol and the calibration bottle icon will
be shown, which signifies that the
instrument failed the last attempt to span
calibrate.
3.6.2.3 Causes for span cal failure
Span calibration failures can be caused
by the following:
1. Expired calibration gas.
2. Calibration gas whose concentration
fails to match the concentration
expected by the instrument.
3. Inappropriate regulator. The ToxiLtd
must be calibrated using a 1.0
liter/minute fixed flow regulator.
4. Sensor failure.
3.6.3 Forced fresh air/zero calibration
If a fresh air/zero calibration fails in an
atmosphere known to be fresh, the
ToxiLtd can be forced to fresh air calibrate
as follows.
1. Follow instructions 1 and 2 in section
3.3 to begin the fresh air/zero
calibration sequence.
2. As soon as the alternating right and
left 0’s are shown on the screen,
press and hold the MODE button.
14
Page 16

l
3. The forced fresh air/zero calibration is
complete when the instrument emits
three short beeps. Units equipped
with an oxygen sensor will then return
to gas detection mode. Units
equipped with a toxic gas sensor will
then move on the span calibration
procedure.
Performing the
forced fresh air/zero calibration in a
contaminated atmosphere may lead to
inaccurate and potentially dangerous
readings.
3.7 Fresh air/zero calibration in a
contaminated atmosphere
To perform the fresh air/zero calibration in
a contaminated atmosphere, it is
necessary to use special calibration gas,
whose composition is identical to that of
fresh air. Sperian offers the “Zero Air”
calibration gas cylinder as part number
54-9039, which contains 0 PPM toxic gas
and 20.9% oxygen.
1. Apply “Zero Air” calibration gas to the
instrument as shown above in figure
3.4 for at least 15 seconds or until the
readings fully stabilize.
2. Perform the fresh air/zero calibration
procedure as described in section 3.3.
3. Once the fresh air/zero calibration is
complete, disconnect the calibration
assembly and move on to the span
calibration if necessary as described in
section 3.5.
4.1 Initiating communications
To initiate communications, simply hold
the MODE button as if you are turning the
instrument off. The ToxiLtd will briefly
light all segments in the display after
about 5 seconds. Continue to hold the
MODE button for an additional 2-3
seconds until the “IrdA” screen is shown
and the LED/IrDA port blinks. Then
release the MODE button.
Align the infrared port at the top front of
the ToxiLtd with the PC’s infrared port and
proceed with the download. The ToxiLtd
should be located 1-2” (2.5-5cm) from the
IrDA Port.
Position of IrDA Module and ToxiLtd
During download.
If 30 seconds pass and the ToxiLtd has
not detected an infrared interface, it will
return to normal operation.
4. Event logging
Each ToxiLtd includes a built-in event
logger that stores instrument readings and
other data whenever a reading exceeds a
pre-set alarm point.
Incident information can be extracted
through a PC with BioTrak software and a
functioning IrDA port. The ToxiLtd may
also be returned to Sperian to have the
information extracted.
If you need to return the instrument to
Sperian, call Sperian’s Technical Service
Department for a Return Authorization
(RA#) prior to shipping the instrument.
15
Page 17

2
H
2
C
4
H
2
C
3
HCN HCl NH
2
H
2
ClO
2
Calibration Gas Part Number
Default
58 or 103 Liter 34 Liter
Setting
54-9037 54-9058
2
S 54-9034 54-9057
2
16
Cl
2
NO NO
2
S SO
2
CO H
Appendices
Appendix A: Sensor Cross-Sensitivity Chart
The table below provides the cross-sensitivity response of the ToxiLtd toxic gas sensors to common interference gases. The values are ToxiLtd as
a percentage of the primary sensitivity or the reading of the sensor when exposed to 100ppm of the interfering gas at 20ºC. These values are
approximate. The actual values depend on the age and condition of the sensor. Sensors should always be calibrated to the primary gas type.
Cross-sensitive gases should not be used as sensor calibration surrogates without the written consent of Sperian.
SENSOR
100 10 5 10 -15 -5 -15 50 15 3 0 75 250
Carbon
Monoxide
(CO)
0.5 100 20 2 -20 -20 -60 0.2 0 0 0 n/d n/d
S)
ulfide
Hydrogen
(H
2
1 1 100 1 -100 -50 -150 0.2 n/d n/d 0 (+) (+)
ulfur
Dioxide
)
2
(SO
Calibration Gas
Description
ToxiLtd
Appendix B: Default toxic sensor calibration gas settings
n/d = no data, (+) undetermined positive, (-) undetermined negative n/d = no data, (+) undetermined positive, (-) undetermined negative
Part Number
S Hydrogen sulfide 25 PPM H
2
54-45-01 CO Carbon monoxide 50 PPM CO 54-9033 54-9036
54-45-02 H
Sulfur dioxide 10 PPM SO
2
54-45-03 SO
Page 18

Appendix C: Calibration
Frequency
One of the most common
questions that we are asked at
Sperian Instrumentation is: “How
often should I calibrate my gas
detector?”
Sensor Reliability and Accuracy
Today’s sensors are designed to
provide years of reliable service.
In fact, many sensors are
designed so that with normal use
they will only lose 5% of their
sensitivity per year or 10% over a
two-year period. Given this, it
should be possible to use a sensor
for up to two full years without
significant loss of sensitivity.
Verification of Accuracy
With so many reasons why a
sensor can lose sensitivity and
given the fact that dependable
sensors can be key to survival in a
hazardous environment, frequent
verification of sensor performance
is paramount.
There is only one sure way to
verify that a sensor can respond to
the gas for which it is designed.
That is to expose it to a known
concentration of target gas and
compare the reading with the
concentration of the gas. This is
referred to as a “bump” test. This
test is very simple and takes only
a few seconds to accomplish. The
safest course of action is to do
a “bump” test prior to each
day’s use. It is not necessary to
make a calibration adjustment if
the readings fall between 90%*
and 120% of the expected value.
As an example, if a CO sensor is
checked using a gas concentration
of 50 PPM it is not necessary to
perform a calibration unless the
readings are either below 45 PPM
or above 60 PPM.
*The Canadian Standards
Association (CSA) requires the
instrument to undergo
calibration when the displayed
value during a bump test fails to
fall between 100% and 120% of
the expected value for the gas.
Lengthening the Intervals
between Verification of
Accuracy
We are often asked whether there
are any circumstances in which
the period between accuracy
checks may be lengthened.
Sperian Instrumentation is not the
only manufacturer to be asked this
question! One of the professional
organizations to which Sperian
Instrum entation belongs is the
Industrial Safety Equipment
Association (ISEA). The
“Instrument Products” group of this
organization has been very active
in developing a protocol to clarify
the minimum conditions under
which the interval between
accuracy checks may be
lengthened.
A number of leading gas detection
equipment manufacturers have
participated in the development of
the ISEA guidelines concerning
calibration frequency. Sperian
Instrum entation’s procedures
closely follow these guidelines.
If your operating procedures do
not permit daily checking of the
sensors, Sperian Instrumentation
recommends the following
procedure to establish a safe and
prudent accuracy check schedule
for your Sperian instrum ents:
1. During a period of initial use
of at least 10 days in the
intended atmosphere, check
the sensor response daily to
be sure there is nothing in the
atmosphere that is poisoning
the sensor(s). The period of
initial use must be of sufficient
duration to ensure that the
sensors are exposed to all
conditions that might have an
adverse effect on the sensors.
2. If these tests demonstrate
that it is not necessary to
make adjustments, the time
between checks may be
lengthened. The interval
between accuracy checking
should not exceed 30 days.
3. When the interval has been
extended the toxic and
combustible gas sensors
should be replaced
immediately upon warranty
expiration. This will minimize
the risk of failure during the
interval between sensor
checks.
4. The history of the instrument
response between
verifications should be kept.
Any conditions, incidents,
experiences, or exposure to
contaminants that might have
an adverse effect on the
calibration state of the
sensors should trigger
imm ediate re-verification of
accuracy before further use.
5. Any changes in the
environment in which the
instrum ent is being used, or
changes in the work that is
being performed, should
trigger a resum ption of daily
checking.
6. If there is any doubt at any
time as to the accuracy of the
sensors, verify the accuracy
of the sensors by exposing
them to known concentration
test gas before further use.
Gas detectors used for the
detection of oxygen deficiencies,
flammable gases and vapors, or
toxic contaminants must be
maintained and operated properly
to do the job they were designed
to do. Always follow the guidelines
provided by the manufacturer for
any gas detection equipment you
use!
If there is any doubt regarding
your gas detector's accuracy, do
an accuracy check! All it takes is a
few moments to verify whether or
not your instrum ents are safe to
use.
One Button Auto Calibration
While it is only necessary to do a
“bump” test to ensure that the
sensors are working properly, all
current Sperian gas detectors offer
a one-button auto calibration
feature. This feature allows you to
calibrate a Sperian gas detector in
about the same time as it takes to
complete a “bump” test. The use
of automatic bump test and
calibration stations can further
simplify the tasks, while
automatically maintaining records.
Don't take a chance
with your life.
Verify accuracy frequently!
Please read also Sperian
Instrumentation’s application
note: AN20010808 “Use of
‘equivalent’ calibration gas
mixtures”. This application note
provides procedures to ensure
safe calibration of LEL sensors
that are subject to silicone
poisoning.
Biosystems website is located at
http://www.biosystems.com
17
Page 19

Sperian Instrumentation Warranty Gas Detection Products
General
Sperian Protection Instrumentation, LLC (hereafter Sperian) warrants gas detectors, sensors and
accessories manufactured and sold by Sperian, to be free from defects in materials and workmanship for the
periods listed in the tables below.
Damages to any Sperian products that result from abuse, alteration, power fluctuations including surges and
lightning strikes, incorrect voltage settings, incorrect batteries, or repair procedures not made in accordance
with the Instrument’s Reference Manual are not covered by the Sperian warranty.
The obligation of Sperian under this warranty is limited to the repair or replacement of components deemed
by the Sperian Instrument Service Department to have been defective under the scope of this standard
warranty. To receive consideration for warranty repair or replacement procedures, products must be
returned with transportation and shipping charges prepaid to Sperian at its manufacturing location in
Middletown, Connecticut, or to a Sperian Authorized Warranty Service Center. It is necessary to obtain a
return authorization number from Sperian prior to shipment.
THIS WARRANTY IS EXPRESSLY IN LIEU OF ANY AND ALL OTHER WARRANTIES AND
REPRESENTATIONS, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE WARRANTY OF
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. SPERIAN WILL NOT BE LIABLE FOR LOSS OR DAMAGE OF
ANY KIND CONNECTED TO THE USE OF ITS PRODUCTS OR FAILURE OF ITS PRODUCTS TO
FUNCTION OR OPERATE PROPERLY.
Instrument & Accessory Warranty Periods
Product(s) Warranty Period
PhD5, PhD Lite, PhD Plus, PhD Ultra, Cannonball3, MultiVision,
Toxi, Toxi/Oxy Plus, Toxi/Oxy Ultra, ToxiVision, Ex Chek
ToxiPro®, MultiPro
ToxiLtd®
Toxi3Ltd®
Mighty-Tox
Mighty-Tox 2
Prorated credit is given towards repair or purchase of a new unit
of the same type.
IQ Systems, Series 3000, Airpanel, Travelpanel, ZoneGuard,
Gas9Chek1 and Gas9Chek4
Battery packs and chargers, sampling pumps and other
components, which by their design are consumed or depleted
during normal operation, or which may require periodic
replacement
As long as the instrument is in service
2 years from date of purchase
2 years after activation or 2 years
after the “Must Be Activated By” date,
whichever comes first
3 years after activation or 3 years
after the “Must Be Activated By” date,
whichever comes first
90 days after activation or 90 days
after the “Must Be Activated By” date,
whichever comes first
0 – 6 months of use 100% credit
6 – 12 months of use 75% credit
12 – 18 months of use 50% credit
18 – 24 months of use 25% credit
One year from the date of purchase
One year from the date of purchase
Sensor Warranty Periods
Instrument(s) Sensor Type(s) Warranty Period
PhD Plus, PhD Ultra, PhD5, PhD Lite,
Cannonball3, MultiVision, MultiPro, ToxiVision,
ToxiPro®, Ex Chek
Toxi, Toxi/Oxy Plus, Toxi/Oxy Ultra
All Others All Sensors 1 Year
** Damage to combustible gas sensors by acute or chronic exposure to known sensor poisons such as volatile lead
(aviation gasoline additive), hydride gases such as phosphine, and volatile silicone gases emitted from silicone
caulks/sealants, silicone rubber molded products, laboratory glassware greases, spray lubricants, heat transfer fluids,
waxes & polishing compounds ( neat or spray aerosol s), mold release agen ts for plastics inject ion molding operations,
waterproofing formulations, vinyl & leather preservatives, and hand lotions which may contain ingredients listed as
cyclomethicone, dimethicone and polymethicone (at the discretion of Sperian’s Instrument Service department) void
Sperian Instrumentation’s Standard Warranty as it applies to the replacement of combustible gas sensors.
O2, LEL**, CO, CO+, H2S
& Duo-Tox
All Other Sensors 1 Year
CO, CO+, H2S 2 Years
All Other Sensors 1 Year
2 Years
18
Page 20

®
ToxiLtd
c-UL Version
ATEX / CQST Version
IECEx Version
Gas O2 CO
H
S SO2
2
Firmware Ver. _______
Vibrating Motor
Belt Clip
Serial # ______________
Activation Date
19
 Loading...
Loading...