Page 1

MI.61xx
fast 8 bit arbitrary waveform generator
D/A converter board
for PCI bus
Hardware Manual
Driver Manual
English version October 5, 2004
SPECTRUM SYSTEMENTWICKLUNG MICROELECTRONIC GMBH · AHRENSFELDER WEG 13-17 · 22927 GROSSHANSDORF · GERMANY
PHONE: +49 (0)4102-6956-0 · FAX: +49 (0)4102-6956-66 · E-MAIL: info@spec.de · INTERNET: http://www.spec.de
Page 2

(c) SPECTRUM SYSTEMENTWICKLUNG MICROELECTRONIC GMBH
AHRENSFELDER WEG 13-17, 22927 GROSSHANSDORF, GERMANY
SBench is a registered trademark of Spectrum Systementwicklung Microelectronic GmbH.
Microsoft, Visual C++, Visual Basic, Windows, Windows 98, Windows NT, Window 2000 and Windows XP are tradenarks/registered
trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
LabVIEW, DASYLab, Diadem and LabWindows/CVI are tradenarks/registered trademarks of National Instruments Corporation.
MATLAB is a tradenark/registered trademark of The Mathworks, Inc.
Agilent VEE, VEE Pro and VEE OneLabare tradenarks/registered trademarks of Agilent Technologies, Inc.
FlexPro is a registered trademark of Weisang GmbH & Co. KG.
Page 3

Introduction....................................................................................................................... 6
Preface ............................................................................................................................................................................... 6
General Information ............................................................................................................................................................. 6
Different models of the MI.61xx series .................................................................................................................................... 7
Additional options................................................................................................................................................................ 8
Extra I/O (Option -XMF).................................................................................................................................................. 8
Extra I/O (Option -XIO)................................................................................................................................................... 8
Starhub ......................................................................................................................................................................... 9
The Spectrum type plate ...................................................................................................................................................... 10
Hardware information......................................................................................................................................................... 11
Block diagram.............................................................................................................................................................. 11
Technical Data ............................................................................................................................................................. 11
Dynamic Parameters ..................................................................................................................................................... 12
Order information......................................................................................................................................................... 12
Hardware Installation ..................................................................................................... 13
System Requirements .......................................................................................................................................................... 13
Warnings.......................................................................................................................................................................... 13
ESD Precautions ........................................................................................................................................................... 13
Cooling Precautions...................................................................................................................................................... 13
Sources of noise ........................................................................................................................................................... 13
Installing the board in the system.......................................................................................................................................... 13
Installing a single board without any options.................................................................................................................... 13
Installing a board with digital inputs/outputs.................................................................................................................... 14
Installing a board with extra I/O (Option -XMF) ............................................................................................................... 14
Installing multiple boards synchronized by starhub............................................................................................................ 15
Installing multiple synchronized boards ........................................................................................................................... 16
Software Driver Installation............................................................................................. 17
Interrupt Sharing ................................................................................................................................................................ 17
Windows 98 ..................................................................................................................................................................... 18
Installation ................................................................................................................................................................... 18
Version control ............................................................................................................................................................. 18
Driver - Update............................................................................................................................................................. 19
Windows 2000 ................................................................................................................................................................. 20
Installation ................................................................................................................................................................... 20
Version control ............................................................................................................................................................. 20
Driver - Update............................................................................................................................................................. 21
Windows XP...................................................................................................................................................................... 22
Installation ................................................................................................................................................................... 22
Version control ............................................................................................................................................................. 22
Driver - Update............................................................................................................................................................. 23
Windows NT..................................................................................................................................................................... 24
Installation ................................................................................................................................................................... 24
Adding boards to the Windows NT driver ....................................................................................................................... 24
Driver - Update............................................................................................................................................................. 24
Linux................................................................................................................................................................................. 25
Overview .................................................................................................................................................................... 25
Installation ................................................................................................................................................................... 25
Software ......................................................................................................................... 27
Software Overview............................................................................................................................................................. 27
First Test with SBench.......................................................................................................................................................... 27
C/C++ Driver Interface....................................................................................................................................................... 28
Header files ................................................................................................................................................................. 28
Microsoft Visual C++ .................................................................................................................................................... 28
Linux Gnu C................................................................................................................................................................. 28
Other Windows C/C++ compilers ................................................................................................................................. 29
National Instruments LabWindows/CVI........................................................................................................................... 29
Driver functions ............................................................................................................................................................ 29
Delphi (Pascal) Programming Interface .................................................................................................................................. 32
Type definition ............................................................................................................................................................. 32
Include Driver............................................................................................................................................................... 32
Examples..................................................................................................................................................................... 32
Driver functions ............................................................................................................................................................ 32
Visual Basic Programming Interface ...................................................................................................................................... 34
Include Driver............................................................................................................................................................... 34
Visual Basic Examples................................................................................................................................................... 34
VBA for Excel Examples ................................................................................................................................................ 34
Driver functions ............................................................................................................................................................ 34
3
Page 4

Programming the Board .................................................................................................. 36
Overview .......................................................................................................................................................................... 36
Register tables ................................................................................................................................................................... 36
Programming examples....................................................................................................................................................... 36
Error handling.................................................................................................................................................................... 36
Initialization....................................................................................................................................................................... 37
Starting the automatic initialization routine ...................................................................................................................... 37
PCI Register ................................................................................................................................................................. 37
Hardware version......................................................................................................................................................... 38
Date of production........................................................................................................................................................ 38
Serial number .............................................................................................................................................................. 38
Maximum possible sample rate ...................................................................................................................................... 38
Installed memory .......................................................................................................................................................... 38
Installed features and options ......................................................................................................................................... 39
Used interrupt line ........................................................................................................................................................ 39
Used type of driver ....................................................................................................................................................... 39
Powerdown and reset ......................................................................................................................................................... 40
Analog Outputs ............................................................................................................... 41
Channel Selection .............................................................................................................................................................. 41
Important note on channels selection............................................................................................................................... 41
Disabling the outputs..................................................................................................................................................... 41
Setting up the outputs.......................................................................................................................................................... 42
Output Amplifiers ......................................................................................................................................................... 42
Output offset ................................................................................................................................................................ 42
Maximum Output Range................................................................................................................................................ 43
Output Filters ............................................................................................................................................................... 43
Standard generation modes ............................................................................................ 44
General description............................................................................................................................................................ 44
Singleshot mode........................................................................................................................................................... 44
Continuous Mode ......................................................................................................................................................... 44
Posttrigger Mode.......................................................................................................................................................... 44
Programming..................................................................................................................................................................... 44
Partitioning the memory................................................................................................................................................. 44
Starting without interrupt (classic mode)........................................................................................................................... 46
Starting with interrupt driven mode ................................................................................................................................. 46
Data organization ........................................................................................................................................................ 47
Writing data with SpcSetData........................................................................................................................................ 47
Sample format.............................................................................................................................................................. 48
FIFO Mode....................................................................................................................... 49
Overview .......................................................................................................................................................................... 49
General Information...................................................................................................................................................... 49
Background FIFO Write................................................................................................................................................. 49
Speed Limitations.......................................................................................................................................................... 49
Programming..................................................................................................................................................................... 50
Software Buffers ........................................................................................................................................................... 50
Buffer processing.......................................................................................................................................................... 51
FIFO mode .................................................................................................................................................................. 52
Example FIFO generation mode ..................................................................................................................................... 52
Data organization ........................................................................................................................................................ 52
Sample format.............................................................................................................................................................. 53
Clock generation ............................................................................................................. 54
Overview .......................................................................................................................................................................... 54
Internally generated sample rate .......................................................................................................................................... 54
Standard internal sample rate ........................................................................................................................................ 54
Using plain quartz with no PLL........................................................................................................................................ 55
Direct external clock ..................................................................................................................................................... 56
External clock with divider ............................................................................................................................................. 57
Trigger modes and appendant registers .......................................................................... 58
General Description............................................................................................................................................................ 58
Software trigger ................................................................................................................................................................. 58
External TTL trigger ............................................................................................................................................................. 58
Edge triggers ............................................................................................................................................................... 59
Option Multiple Replay.................................................................................................... 61
Output modes .................................................................................................................................................................... 61
Standard Mode............................................................................................................................................................ 61
FIFO Mode .................................................................................................................................................................. 61
Trigger modes.................................................................................................................................................................... 61
4
Page 5

Option Gated Replay....................................................................................................... 63
Output modes .................................................................................................................................................................... 63
Standard Mode............................................................................................................................................................ 63
FIFO Mode .................................................................................................................................................................. 63
Trigger modes.................................................................................................................................................................... 63
General information and trigger delay ............................................................................................................................ 63
Allowed trigger modes .................................................................................................................................................. 64
Example program............................................................................................................................................................... 64
Option Extra I/O ............................................................................................................. 65
Digital I/Os....................................................................................................................................................................... 65
Channel direction ......................................................................................................................................................... 65
Transfer Data ............................................................................................................................................................... 65
Analog Outputs.................................................................................................................................................................. 66
Programming example ........................................................................................................................................................ 66
Synchronization (Option) ................................................................................................. 67
The different synchronization options .................................................................................................................................... 67
Synchronization with option cascading ........................................................................................................................... 67
Synchronization with option starhub ............................................................................................................................... 67
The setup order for the different synchronization options ......................................................................................................... 68
Setup Order for use with standard (non FIFO) mode and equally clocked boards ................................................................. 68
Setup synchronization for use with FIFO mode and equally clocked boards ......................................................................... 72
Additions for synchronizing different boards .................................................................................................................... 74
Additions for equal boards with different sample rates ...................................................................................................... 76
Resulting delays using different boards or speeds ............................................................................................................. 76
Appendix ........................................................................................................................ 77
Error Codes....................................................................................................................................................................... 77
Pin assignment of the multipin connector ............................................................................................................................... 78
Extra I/O with external connector(Option -XMF) ............................................................................................................... 78
Pin assignment of the multipin cable ..................................................................................................................................... 78
Pin assignment of the internal multipin connector .................................................................................................................... 79
Extra I/O with internal connector (Option -XIO)................................................................................................................ 79
5
Page 6

Preface Introduction
Introduction
Preface
This manual provides detailed information on the hardware features of your Spectrum instrumentation board. This information includes technical data, specifications, block diagram and a connector description.
In addition, this guide takes you through the process of installing your board and also describes the installation of the delivered driver package
for each operating system.
Finally this manual provides you with the complete software information of the board and the related driver. The reader of this manual will
be able to integrate the board in any PC system with one of the supported bus and operating systems.
Please note that this manual provides no description for specific driver parts such as those for LabVIEW or MATLAB. These drivers are provided by special order.
For any new information on the board as well as new available options or memory upgrades please contact our webside
http://www.spectrum-instrumentation.com. You will also find the current driver package with the latest bug fixes and new features on our site.
Please read this manual carefully before you install any hardware or software. Spectrum is not responsible
for any hardware failures resulting from incorrect usage.
General Information
The MI.61xx series contains 2 different versions of arbitrary waveform generators for the PCI bus. With these boards it is possible to generate
free definable waveforms on several channels synchronously. There are up to four channels on one board with a maximum sample rate of
125 MS/s. The internal standard Syncbus allows the setup of synchronous multi channel systems with higher channel numbers. It is also possible to combine the arbitrary waveform generator with other boards of the MI product family like analogue or digital acquisition boards.
With the up to 512 MSample (512 MByte) large on-board memory long waveform could be generated even with high sample rates. The
memory can also be used as a FIFO buffer to make continuous data transfer from PC memory or hard disk.
Application examples: Automatic test systems, Synthesizer, Supersonics, Signal generators.
6 MI.61xx Manual
Page 7

Introduction Different models of the MI.61xx series
Different models of the MI.61xx series
The following overwiew shows the different available models of the MI.61xx series. They differ in the number mounted generation modules
and the number of available channels. You can also see the model dependant allocation of the output connectors.
• MI.6110
• MI.6111
(c) Spectrum GmbH 7
Page 8
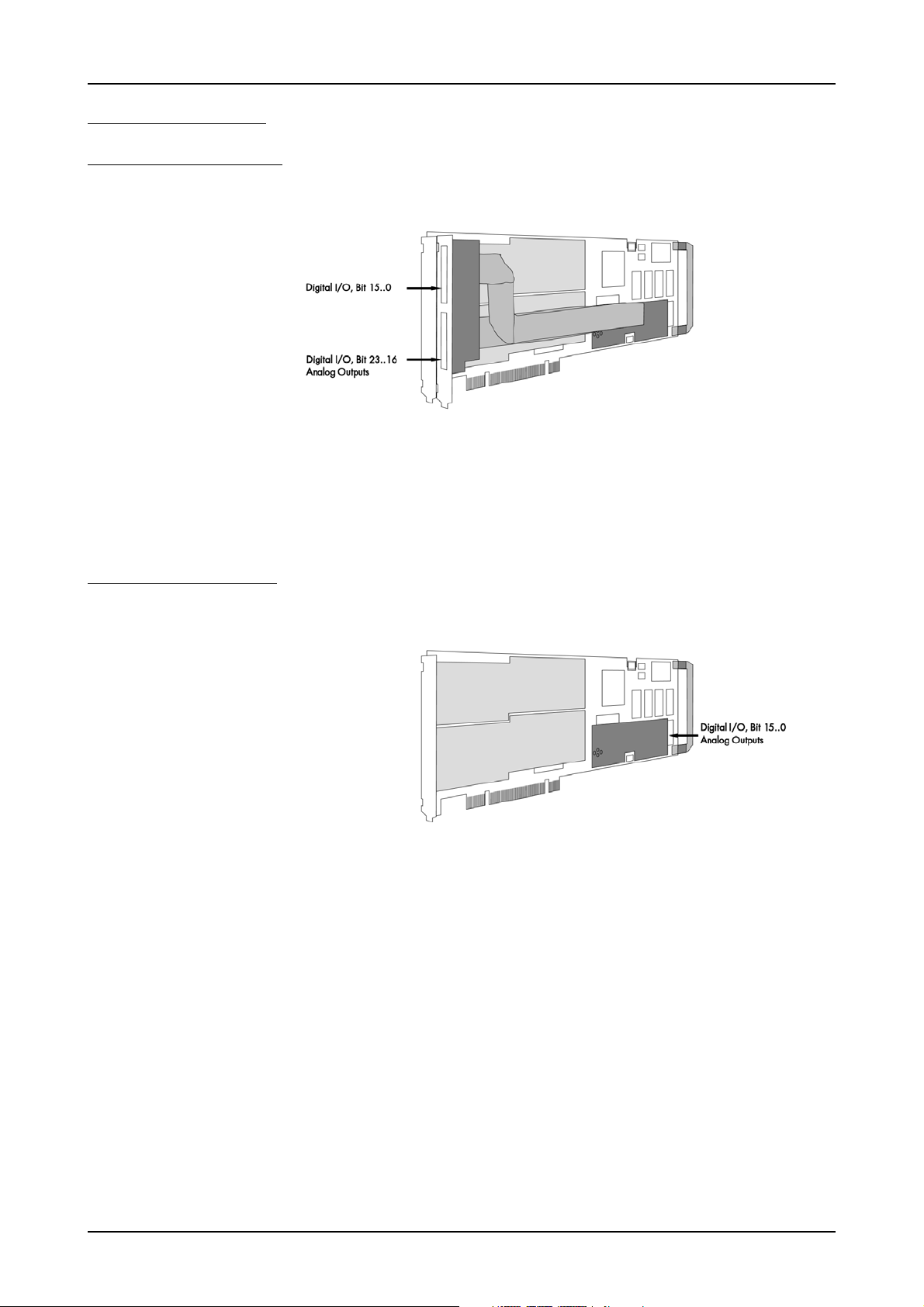
Additional options Introduction
Additional options
Extra I/O (Option -XMF)
With this simple-to-use enhancement
it is possible to control a wide range
of external instruments or other
equipment. Therefore you have 24
digital I/O and the 4 analog outputs
available.
The extra I/O option is useful if an
external amplifier should be controlled, any kind of signal source must
be programmed, an antenna must
be adjusted, a status information
from external machine has to be obtained or different test signals have
to be routed to the board.
The additional inputs and outputs
are mounted on an extra bracket.
The figure shows the allocation of
the two connectors. The shown option is mounted exemplarily on a board with two modules. Of course you can also combine this option as
well with a board that is equipped with only one module.
It is not possible to use this option together with the star hub or timestamp option, because there is just space for
one piggyback module on the on-board expansion slot.
Extra I/O (Option -XIO)
With this simple-to-use enhancement
it is possible to control a wide range
of external instruments or other
equipment. Therefore you have 16
digital I/O and the 4 analog outputs
available.
The extra I/O option is useful if an
external amplifier should be controlled, any kind of signal source must
be programmed, an antenna must
be adjusted, a status information
from external machine has to be obtained or different test signals have
to be routed to the board.
The additional inputs and outputs
are not mounted on an extra brakket, but are available on an internal
connector. The figure shows the position of this connector on the bottom side of the extra I/O piggy-back module. The shown option is mounted exemplarily on a board with two modules. Of course you can also combine this option as well with a board that is equipped with only
one module.
It is not possible to use this option together with the star hub or timestamp option, because there is just space for
one piggyback module on the on-board expansion slot.
8 MI.61xx Manual
Page 9

Introduction Additional options
Starhub
The star hub module allows the synchronisation of up to 16 MI boards.
It is possible to synchronise boards
of the same type with each other as
well as different types.
The module acts as a star hub for
clock and trigger signals. Each
board is connected with a small cable of the same length, even the master board. That minimises the clock
skew between the different boards.
The figure shows the piggyback module mounted on the base board
schematically without any cables to
achieve a better visibility.
Any board could be the clock master and the same or any other
board could be the trigger master. All trigger modes that are available on the master board are also available if the synchronisation star hub
is used.
The cable connection of the boards is automatically recognised and checked by the driver at load time. So no care must be taken on how to
cable the boards. The programming of the star hub is included in the standard board interface and consists of only 3 additional commands.
It is not possible to use this option together with the timestamp or extra I/O option, because the is just space for one
piggyback module on the on-board expansion slot.
(c) Spectrum GmbH 9
Page 10
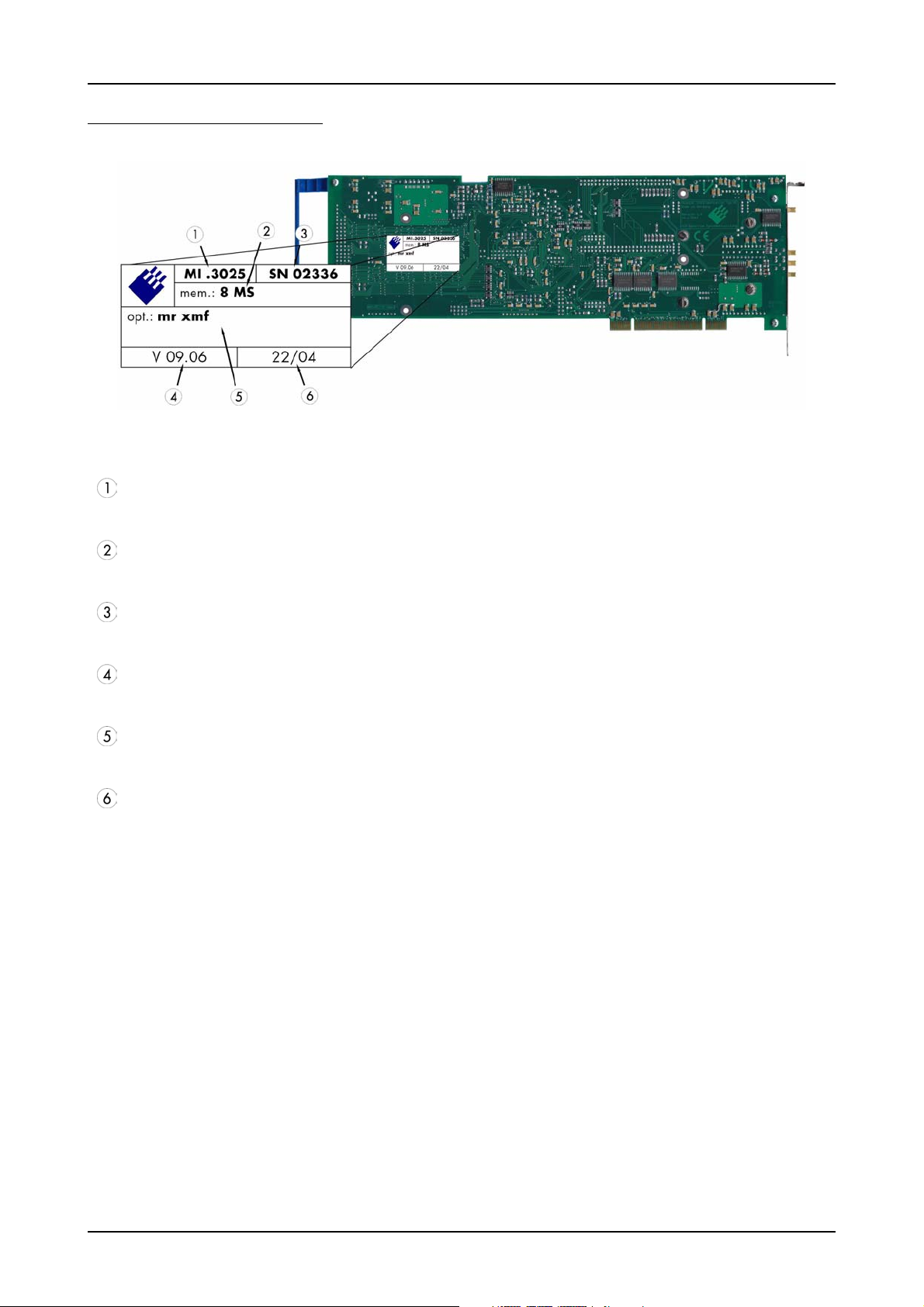
The Spectrum type plate Introduction
The Spectrum type plate
The Spectrum type plate, which consists of the following components, can be found on all of our boards.
The board type, consisting of the two letters describing the bus (in this case MI for the PCI bus) and the model number.
The size of the on-board installed memory in MSamples. In this example there are 8 MS (16 MByte) installed.
The serial number of your Spectrum board. Every board has a unique serial number.
The board revision, consisting of the base version and the module version.
A list of the installed options. A complete list of all available options is shown in the order information. In this example the options
’Multiple recording’ and ’Extra I/O with external outputs’ are installed.
The date of production, consisting of the calendar week and the year.
Please always supply us with the above information, especially the serial number in case of support request. That
allows us to answer your questions as soon as possible. Thank you.
10 MI.61xx Manual
Page 11
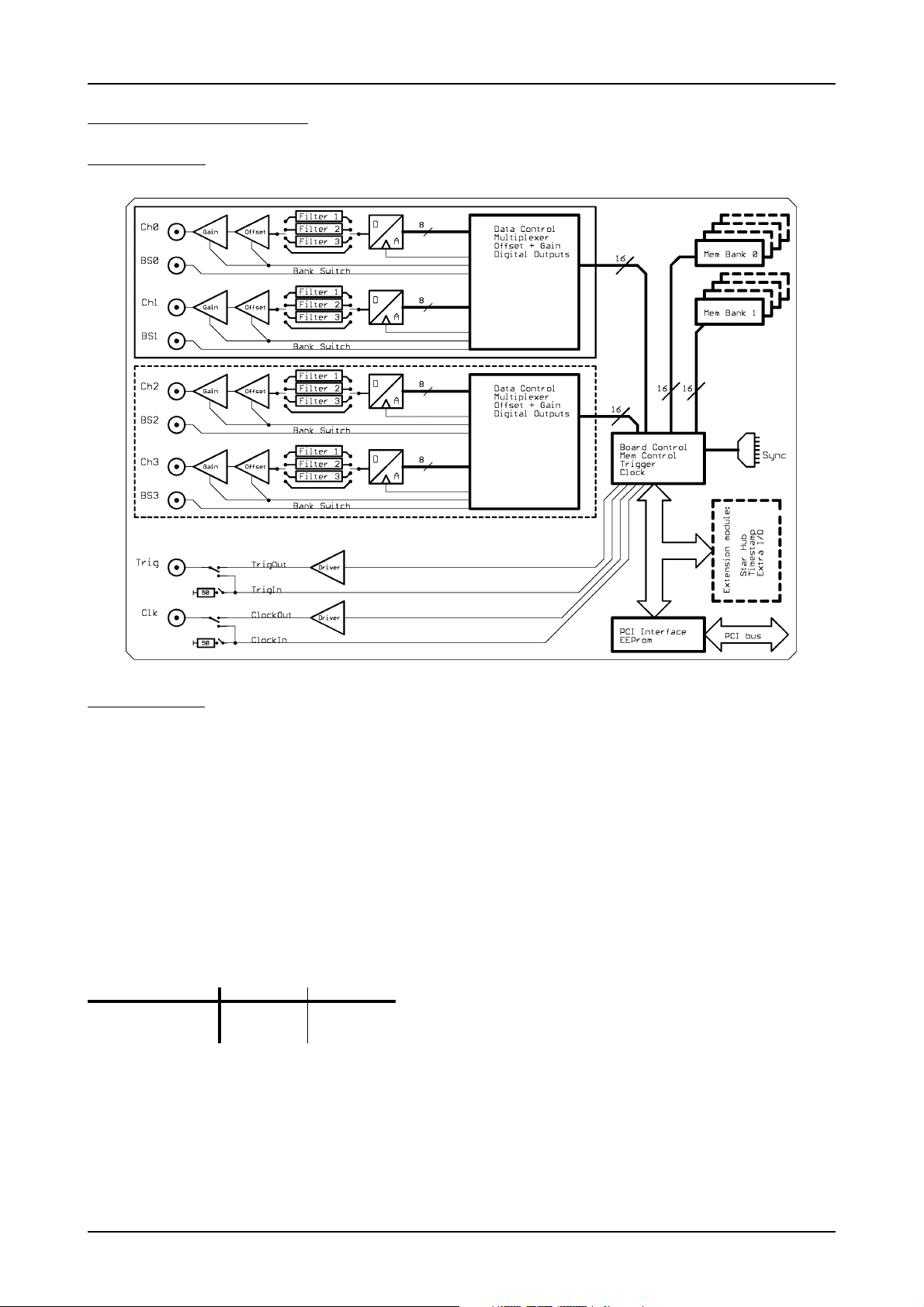
Introduction Hardware information
Hardware information
Block diagram
Technical Data
Resolution 8 Bit Dimension 312 mm x 107 mm
Integral linearity (DAC) ± 1.5 LSB typ. Width (Standard) 1 full size slot
Differential linearity (DAC) ± 1.0 LSB typ. Width (with star hub option) 2 full size slots
Output resistance < 1 Ohm Analogue connector 3 mm SMB male
Max output swing in 50 Ohm ± 3 V (offset + amplitude) Warm up time 10 minutes
Max slew rate (no filter) > 0.9 V/ns Operating temperature 0°C - 50°C
Multi: Trigger to 1st sample delay fixed Storage temperature -10°C - 70°C
Multi: Recovery time < 20 samples Humidity 10% to 90%
Ext. clock: delay to internal clock 42 ns ± 2 ns Offset stepsize < 2 mV
Trigger output delay 1 Sample Amplitude stepsize < 1 mV
Crosstalk @ 1 MHz signal ±3 V < -80 dB
Min internal clock 1 kS/s Power consumption 5 V @ full speed max 3.7 A (18.5 Watt)
Min external clock DC Power consumption 5 V @ power down max 2.3 A (11.5 Watt)
max internal clock 125 MS/s 125 MS/s
max external clock 125 MS/s 125 MS/s
-3 dB bandwidth no filter > 60 MHz > 60 MHz
MI.6110 MI.6111
(c) Spectrum GmbH 11
Page 12
Hardware information Introduction
Dynamic Parameters
Test - Samplerate 125 MS/s 125 MS/s
Filter 3
Characteristics 5th order Butterworth
-3 dB bandwidth 25 MHz 25 MHz
SNR ±1 V in 50 ohm -49 dB
THD ±1 V in 50 ohm -42 dB
Filter 2
Characteristics 4th order Butterworth
-3 dB bandwidth 5 MHz 5 MHz
SNR ±1 V in 50 ohm -42 dB
THD ±1 V in 50 ohm -67 dB
Filter 1
Characteristics 4th order Butterworth
-3 dB bandwidth 500 kHz 500 kHz
SNR ±1 V in 50 ohm -72 dB
THD ±1 V in 50 ohm -54 dB
Dynamic parameters are measured at ± 1 V output level and 50 Ohm termination with a spectrum analyser. The samplerate selected is the maximum possible samplerate. Signal frequency is equal to the cut-off frequency of the filter. SNR and RMS noise parameters may differ depending on the quality of the used PC. SNR = Signal to Noise Ratio, THD = Total Harmonic Distortion
MI.6110 MI.6111
Order information
Order No Description Order No Description
MI6110 MI.6111 with 16 MSample memory and drivers/SBench 5.x MI61xx-32M Option: 32 MSample mem instead of 16 MSample standard mem
MI6111 MI.6111 with 16 MSample memory and drivers/SBench 5.x MI61xx-64M Option: 64 MSample mem instead of 16 MSample standard mem
MI6xxx-mr Option Multiple Replay: Memory segmentation MI61xx-256M Option: 256 MSample mem instead of 16 MSample standard mem
MI6xxx-gs Option Gated Sampling: Gate signal controls replay MI61xx-512M Option: 512 MSample mem instead of 16 MSample standard mem
MI6xxx-cs Synchronisation of 2 - 4 boards, one option per system MI61xx-up Additional handling costs for later memory upgrade
MI61xx-128M Option: 128 MSample mem instead of 16 MSample standard mem
MI6xxx-smod Star Hub: Synchronisation of 2 - 16 boards, one option per system MI61xx-dl DASYLab driver for MI.61xx series
MIxxxx.xio Extra I/O, internal connector: 16 DI/O, 4 Analog out MI61xx-hp VEE driver for MI.61xx series
MIxxxx-xmf Extra I/O, external connector: 24 DI/O, 4 Analog out, incl. cable MI61xx-lv LabVIEW driver for MI.61xx series
Cab-3f-9m-80 Adapter cable: SMB female to BNC male 80 cm Cab-3f-9f-80 Adapter cable: SMB female to BNC female 80 cm
Cab-3f-9m-200 Adapter cable: SMB female to BNC male 200 cm Cab-3f-9f-200 Adapter cable: SMB female to BNC female 200 cm
MATLAB MATLAB driver for all MI.xxxx, MC.xxxx and MX.xxxx series.
12 MI.61xx Manual
Page 13

Hardware Installation System Requirements
Hardware Installation
System Requirements
All Spectrum MI.xxxx instrumentation boards are compliant to the PCI standard and require in general one free full length slot. Depending
on the installed options additional free slots can be necessary.
Warnings
ESD Precautions
The boards of the MI.xxxx series contain electronic components that can be damaged by electrostatic discharge (ESD).
Before installing the board in your system or even before touching it, it is absolutely necessary to bleed of
any electrostatic electricity.
Cooling Precautions
The boards of the MI.xxxx series operate with components having very high power consumption at high speeds. For this reason it is absolutely
required to cool this board sufficiently. It is strongly recommended to install an additional cooling fan producing a stream of air across the
boards surface. In most cases professional PC-systems are already equipped with sufficient cooling power. In that case please make sure that
the air stream is not blocked.
During longer pauses between the single measurements the power down mode should be called to reduce the heat production.
Sources of noise
The boards of the MI.xxxx series should be placed far away from any noise producing source (like e.g. the power supply). It should especially
be avoided to place the board in the slot directly adjacent to another fast board (like the graphics controller).
Installing the board in the system
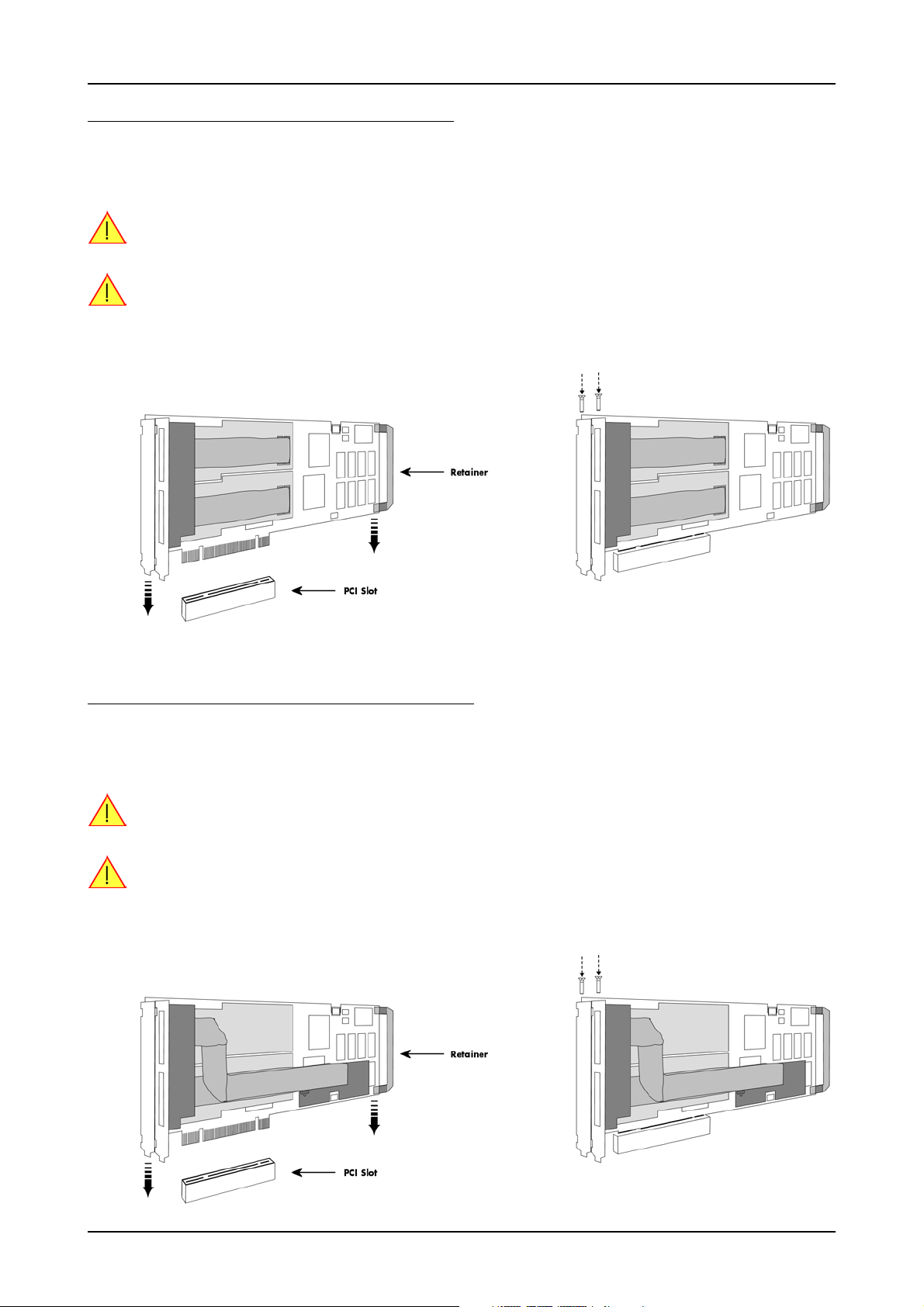
Installing a single board without any options
Before installing the board you first need to unscrew and remove the dedicated blind-bracket usually mounted to cover unused slots of your
PC. Please keep the screw in reach to fasten your Spectrum board afterwards. All Spectrum boards require a full length PCI slot with a track
at the backside to guide the board by it’s retainer. Now insert the board slowly into your computer. This is done best with one hand each at
both fronts of the board.
While inserting the board take care not to tilt the retainer in the track.
Please be very carefully when inserting the board in the PCI slot, as most of the mainboards are mounted
with spacers and therefore might be damaged if they are exposed to high preasure.
After the board’s insertion fasten the screw of the bracket carefully, without overdoing.
(c) Spectrum GmbH 13
Page 14
Installing the board in the system Hardware Installation
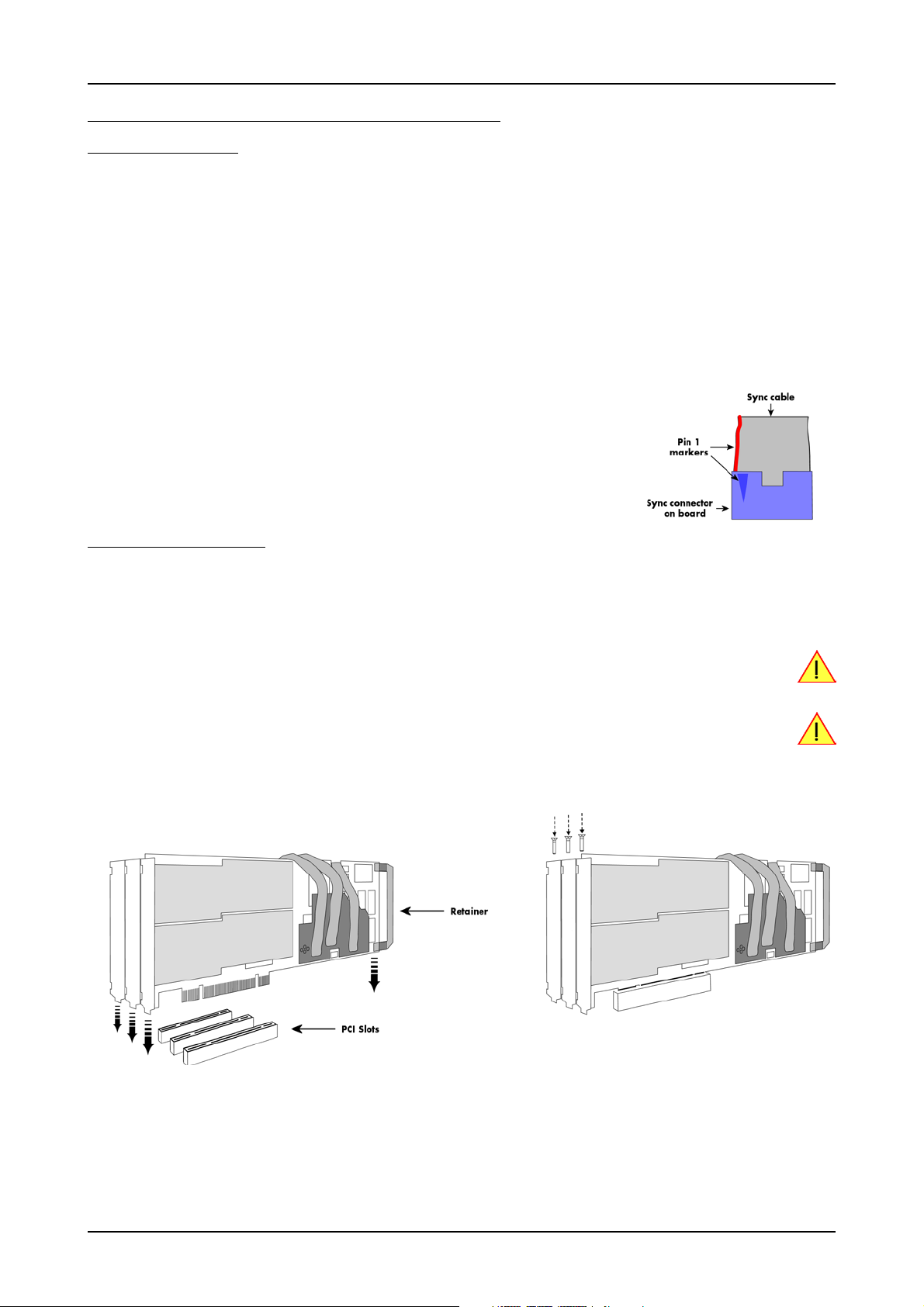
Installing a board with digital inputs/outputs
Before installing the board you first need to unscrew and remove the dedicated blind-brackets usually mounted to cover unused slots of your
PC. Please keep the screws in reach to fasten your Spectrum board and the extra bracket afterwards. All Spectrum boards require a full length
PCI slot with a track at the backside to guide the board by it’s retainer. Now insert the board and the extra bracket slowly into your computer.
This is done best with one hand each at both fronts of the board.
While inserting the board take care not to tilt the retainer in the track.
Please be very carefully when inserting the board in the PCI slot, as most of the mainboards are mounted
with spacers and therefore might be damaged they are exposed to high preasure.
After the board’s insertion fasten the screws of both brackets carefully, without overdoing. The figure shows an example of a board with two
installed modules.
Installing a board with extra I/O (Option -XMF)
Before installing the board you first need to unscrew and remove the dedicated blind-brackets usually mounted to cover unused slots of your
PC. Please keep the screws in reach to fasten your Spectrum board and the extra bracket afterwards. All Spectrum boards require a full length
PCI slot with a track at the backside to guide the board by it’s retainer. Now insert the board and the extra bracket slowly into your computer.
This is done best with one hand each at both fronts of the board.
While inserting the board take care not to tilt the retainer in the track.
Please be very carefully when inserting the board in the PCI slot, as most of the mainboards are mounted
with spacers and therefore might be damaged they are exposed to high preasure.
After the board’s insertion fasten the screws of both brackets carefully, without overdoing. The figure shows an example of a board with two
installed modules.
14 MI.61xx Manual
Page 15
Hardware Installation Installing the board in the system
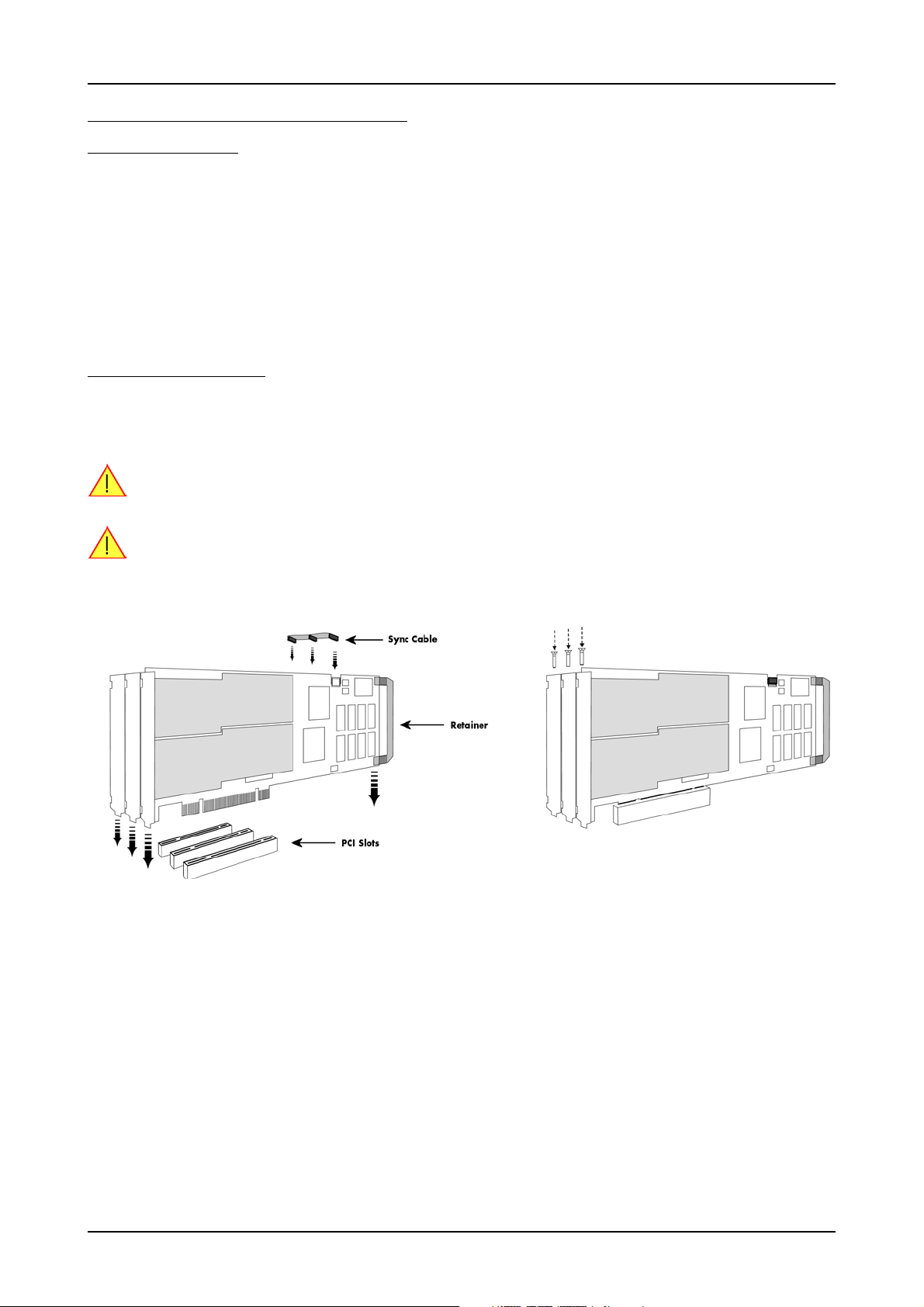
Installing multiple boards synchronized by starhub
Hooking up the boards
Before mounting several synchronized boards for a multi channel system into the PC you can hook up the boards with their synchronization
cables first. If there is enough space in your computer’s case (e.g. a big tower case) you can also mount the boards first and hook them up
afterwards. Spectrum ships the boards together with the needed amount of synchronization cables. All of them are matched to the same
length, to achieve a zero clock delay between the boards.
Only use the included flat ribbon cables.
All of the boards, including the board that carrys the starhub piggy-back module, must be wired to the starhub as the figure is showing exemplarily for three synchronized boards.
It does not matter which of the 16 connectors on the starhub module you use for which board. The software driver will detect the types and
order of the synchronized boards automatically. The figure shows the three cables mounted next to each other only to achieve a better visibility.
As some of the synchronization cables are not secured against wrong plugging you should take
care to have the pin 1 markers on the multiple connectors and the cable on the same side, as the
figure on the right is showing.
Mounting the wired boards
Before installing the boards you first need to unscrew and remove the dedicated blind-brackets usually mounted to cover unused slots of your
PC. Please keep the screws in reach to fasten your Spectrum boards afterwards. All Spectrum boards require a full length PCI slot with a track
at the backside to guide the board by it’s retainer. Now insert the board and the extra bracket slowly into your computer. This is done best
with one hand each at both fronts of the board. Please keep in mind that the board carrying the starhub piggy-back module requires the width
of two slots.
While inserting the boards take care not to tilt the retainers in the tracks.
Please be very carefully when inserting the boards in the PCI slots, as most of the mainboards are mounted
with spacers and therefore might be damaged if they are exposed to high preasure.
After the boards insertion fasten the screws of all brackets carefully, without overdoing. The figure shows an example of three boards with
two installed modules.
(c) Spectrum GmbH 15
Page 16
Installing the board in the system Hardware Installation
Installing multiple synchronized boards
Hooking up the boards
Before mounting several synchronized boards for a multi channel system into the PC you can hook up the boards with the synchronization
cable first. If there is enough space in your computer’s case (e.g. a big tower case) you can also mount the boards first and hook them up
afterwards. Spectrum ships the boards together with the needed synchronization cable.
All of the possible four boards must be wired with the delivered synchronization cable. The figure is showing an example of three synchronized boards.
The outer boards have a soldered termination for the sync bus. These boards are marked with an additional sticker.
Only mount the cluster of synchronized boards in a row with the dedicated boards on the outer sides.
Mounting the wired boards
Before installing the boards you first need to unscrew and remove the dedicated blind-brackets usually mounted to cover unused slots of your
PC. Please keep the screws in reach to fasten your Spectrum boards afterwards. All Spectrum boards require a full length PCI slot with a track
at the backside to guide the board by it’s retainer. Now insert the boards slowly into your computer. This is done best with one hand each
at both fronts of the board.
While inserting the boards take care not to tilt the retainers in the tracks.
Please be very carefully when inserting the boards in the PCI slots, as most of the mainboards are mounted
with spacers and therefore might be damaged if they are exposed to high preasure.
After the boards insertion fasten the screws of all brackets carefully, without overdoing. The figure shows an example of three boards with
two installed modules.
16 MI.61xx Manual
Page 17

Software Driver Installation Interrupt Sharing
Software Driver Installation
Before using the board a driver must be installed that matches the operating system. The installation is done in different ways depending on
the used operating system. The driver that is on CD supports all boards of the MI, MC and MX series. That means that you can use the same
driver for all boards of theses families.
Interrupt Sharing
This board uses a PCI interrupt for DMA data transfer and for controlling the FIFO mode. The used interrupt line is allocated by the PC BIOS
at system start and is normally depending on the selected slot. Because there is only a limited number of interrupt lines available on the PCI
bus it can happen that two or more boards must use the same interrupt line. This so called interrupt sharing must be supported by all drivers
of the participating equipment.
Most available drivers and also the Spectrum driver for your board can manage interrupt sharing. But there are also some drivers on the
market that can only use one interrupt exclusively. If this equipment shares an interrupt with the Spectrum board, the system will hang up if
the second driver is loaded (the time is depending on the operating system).
If this happens it is necessary to reconfigure the system in that way that the critical equipment has an exclusive access to an interrupt.
On most systems the BIOS shows a list of all installed PCI boards with their allocated interrupt lines directly after system start. You have to
check whether an interrupt line is shared between two boards. Some BIOS allow the manual allocation of interrupt lines. Have a look in your
mainboard manual for further information on this topic.
Because normally the interrupt line is fixed for one PCI slot it is simply necessary to use another slot for the critical board to force a new
interrupt allocation. You have to search a configuration where all critical boards have only exclusive access to one interrupt.
Depending on the system, using the Spectrum board with a shared interrupt may degrade performance a little. Each interrupt needs to be
checked by two drivers. For this reason when using time critical FIFO mode even the Spectrum board should have an exclusively access to
one interrupt line.
(c) Spectrum GmbH 17
Page 18
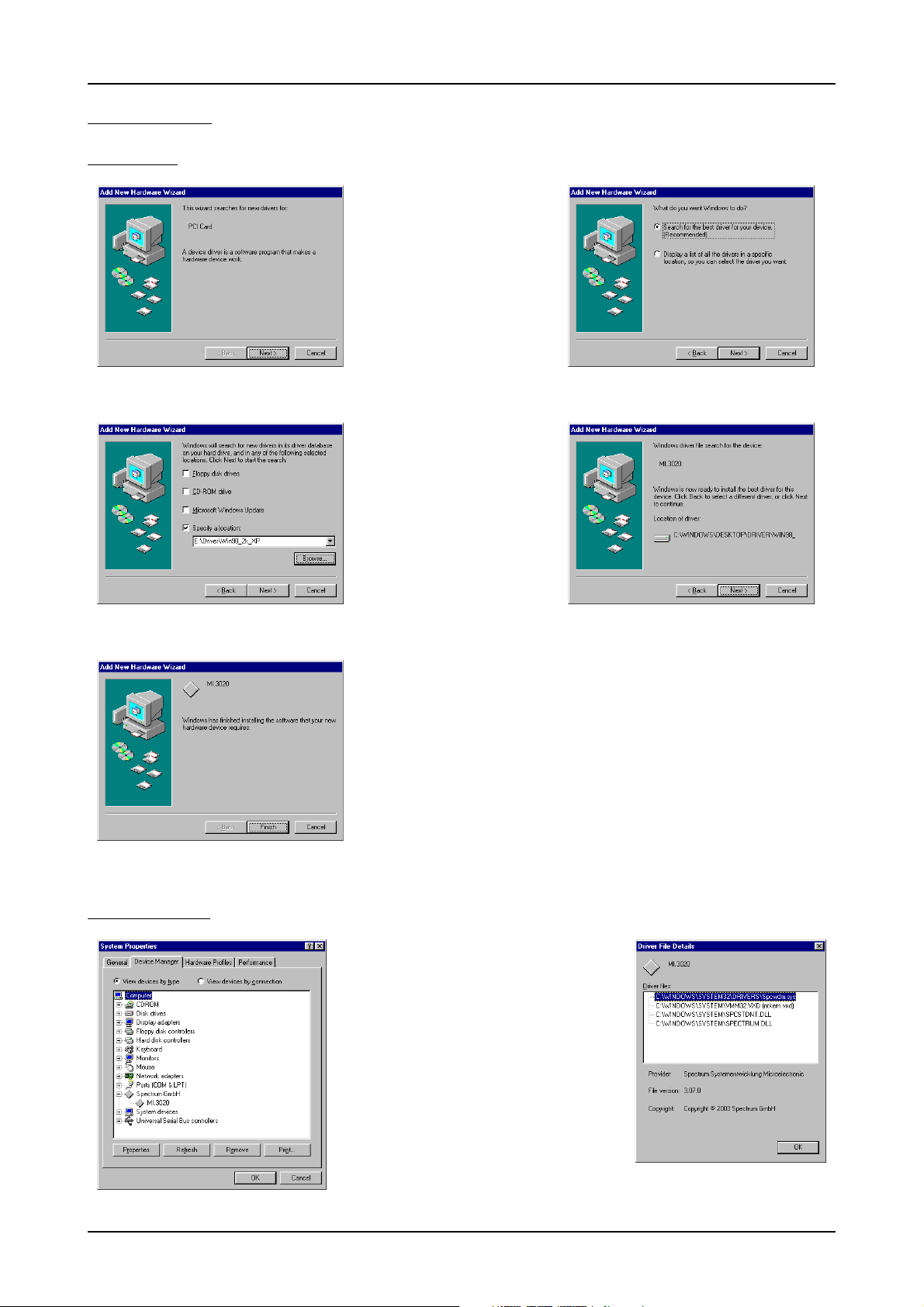
Windows 98 Software Driver Installation
Windows 98
Installation
When installing the board in a Windows 98 system the Spectrum board
will be recognized automatically on
the next start-up.
The system offers the direct installation of a driver for the board.
Let Windows search automatically
for the best driver for your system.
Select the CD that was delivered
with the board as installation source.
The driver files are located on CD in
the directory
\Driver\Win98_2k_XP.
The hardware assistant shows you
the exact board type that has been
found like the MI.3020 in the example. Older boards (before june
2004) show „Spectrum Board“ instead.
Version control
The drivers can be used directly after installation. It is not necessary to restart the system.
The installed drivers are linked in the device manager. Below you’ll see how to examine
the driver version and how to update the driver with a newer version.
If you want to check which driver version is installed
in the system this can be easily done in the device
manager. Therefore please start the device manager
from the control panel and show the properties of the
installed driver.
On the property page Windows 98 shows the date
of the driver.
18 MI.61xx Manual
Page 19
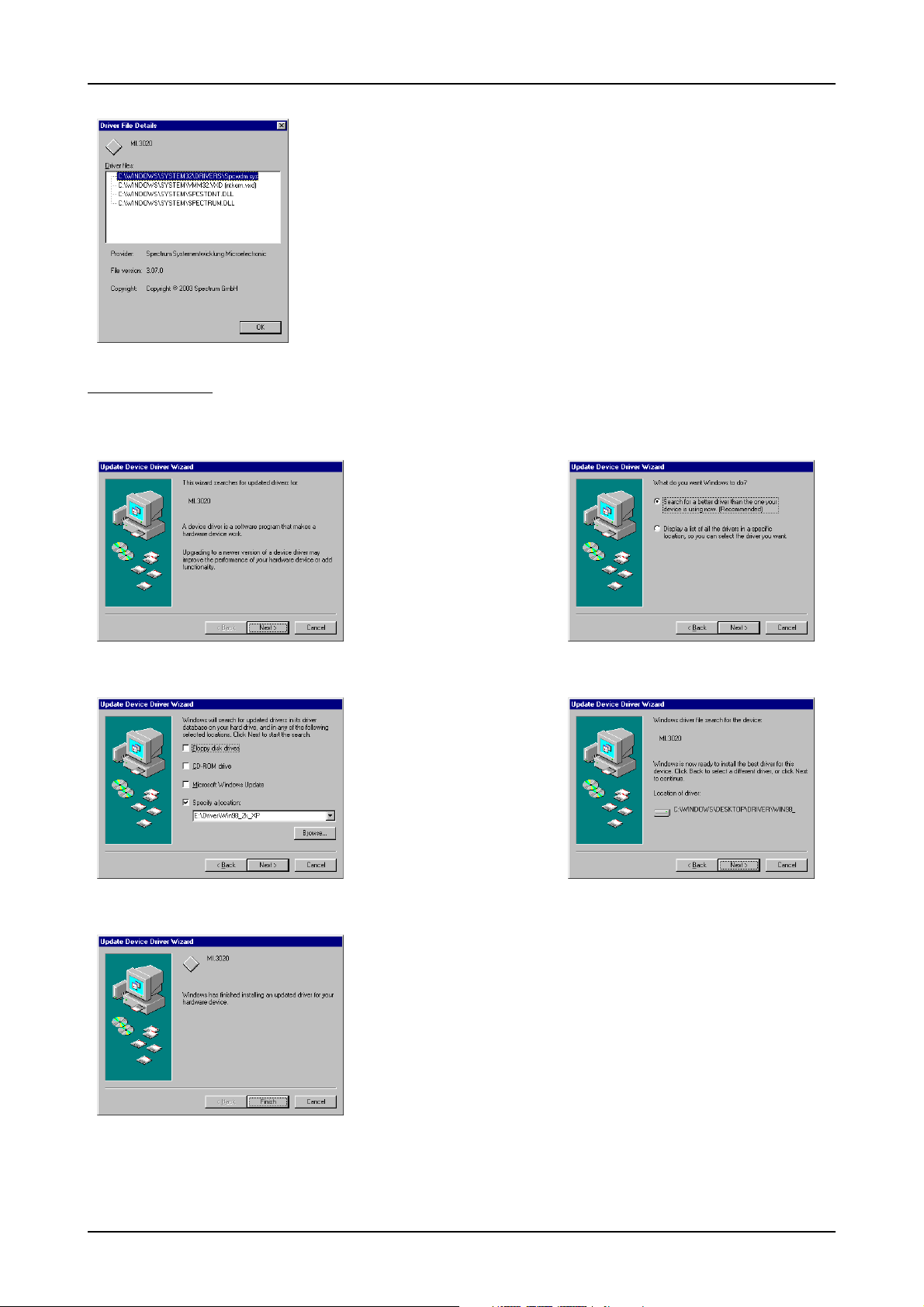
Software Driver Installation Windows 98
After clicking the driver info button the detailed version information of the driver is shown. In the case
of a support question this information must be presented together with the board’s serial number to
the support team to help finding a fast solution.
Driver - Update
If a new driver version is to be installed no Spectrum board should be in use. So please stop and exit all software that could access the boards.
New drivers are available at http://www.spectrum-instrumentation.com. After down loading the driver unzip it to a temporary folder.
A new driver version is directly installed from the device manager.
Therefore please open the properties
page of the driver as shown in the
section before. As next step click on
the update driver button and follow
the steps of the driver installation in
a similar way to the previous board
and driver installation.
Please select the path where the new
driver version was unzipped to. If
you’ve got the new driver version on
CD please select the
\Driver\Win98_2k_XP path on the
CD containing the new driver version.
The new driver version can be used directly after installation without restarting the system.
Please keep in mind to update the driver of all installed Spectrum boards.
(c) Spectrum GmbH 19
Page 20
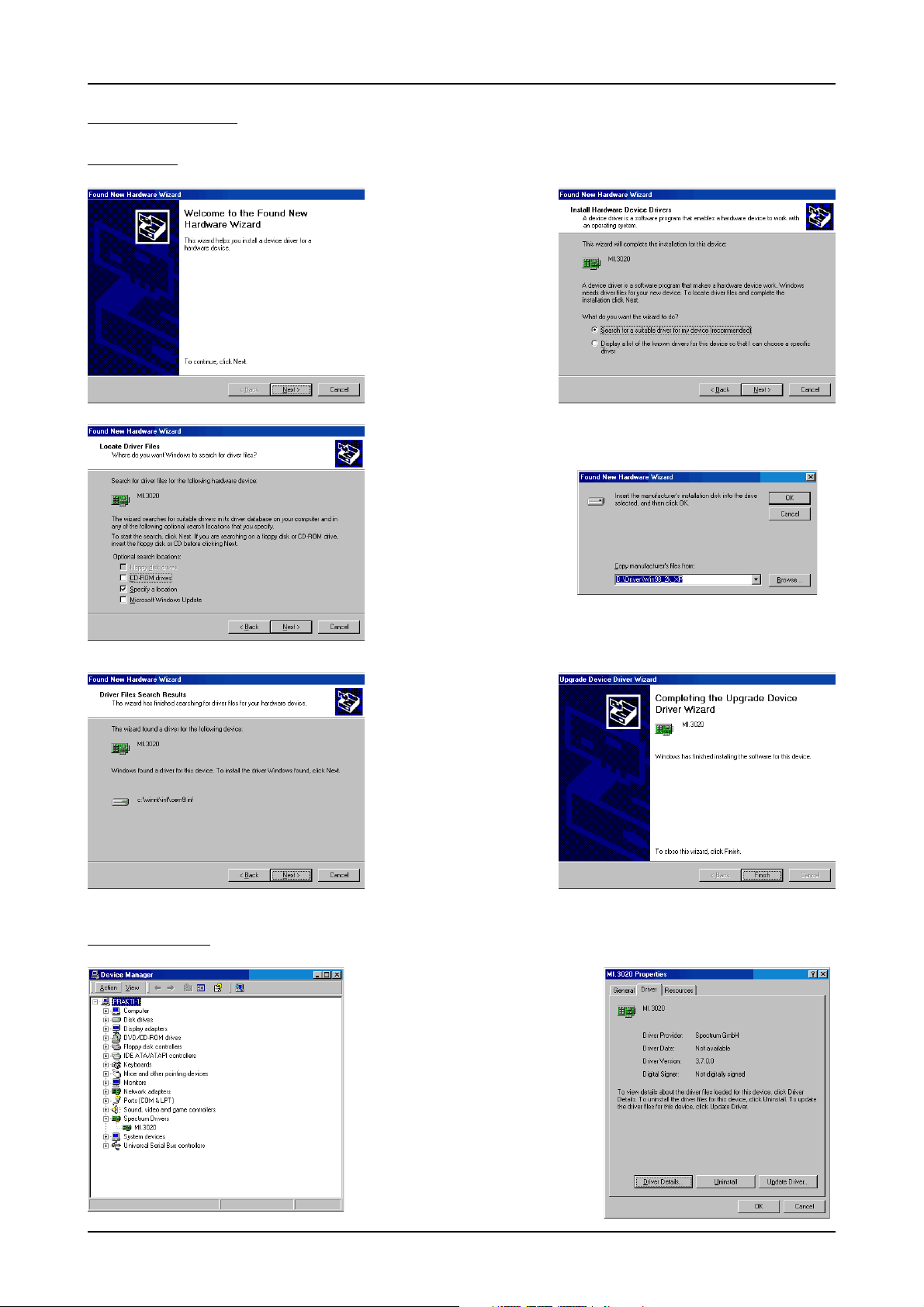
Windows 2000 Software Driver Installation
Windows 2000
Installation
When installing the board in
a Windows 2000 system the
Spectrum board will be recognized automatically on the
next start-up.
The system offers the direct installation of a driver for the
board.
Let Windows search automatically for the best driver for
your system.
Select the CD that was delivered with the board as installation source. The driver files
are located on CD in the directory
\Driver\Win98_2k_XP.
Version control
The hardware assistant
shows you the exact board
type that has been found like
the MI.3020 in the example.
Older boards (before june
2004) show „Spectrum
Board“ instead.
The drivers can be used directly after installation. It is
not necessary to restart the
system. The installed drivers
are linked in the device manager.
Below you’ll see how to examine the driver version and
how to update the driver with
a newer version.
If you want to check which driver version
is installed in the system this can be easily done in the device manager. Therefore please start the device manager
from the control panel and show the
properties of the installed driver.
On the property page Windows 2000
shows the date and the version of the installed driver.
After clicking the driver details button the
detailed version information of the driver
is shown. In the case of a support question this information must be presented together with the board’s serial number to
the support team to help finding a fast solution.
20 MI.61xx Manual
Page 21
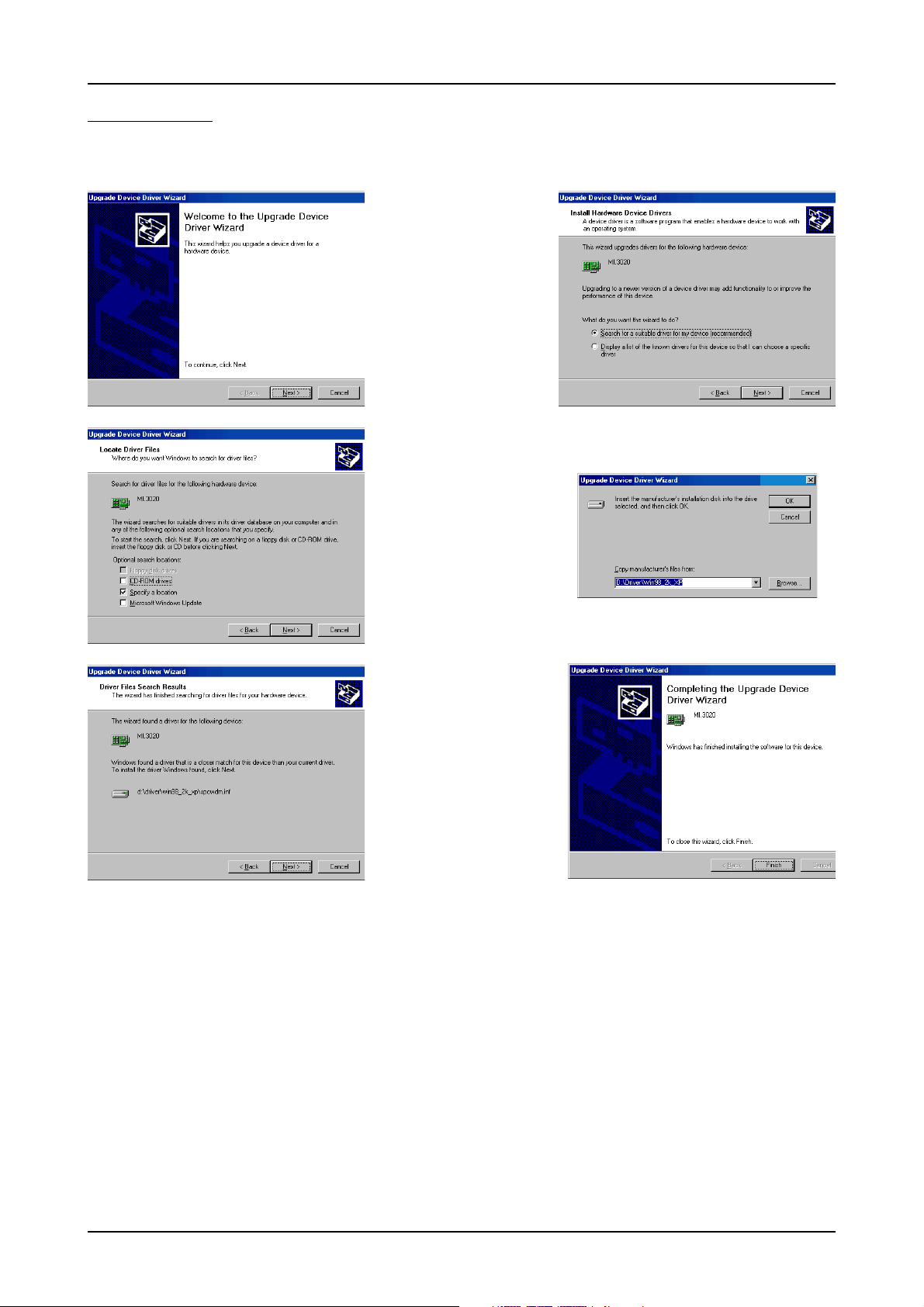
Software Driver Installation Windows 2000
Driver - Update
If a new driver version should be installed no Spectrum board is allowed to be in use by any software. So please stop and exit all software
that could access the boards.
A new driver version is directly installed from the device
manager. Therefore please
open the properties page of
the driver as shown in the section before. As next step click
on the update driver button
and follow the steps of the
driver installation in a similar
way to the previous board
and driver installation.
Please select the path where
the new driver version was
unzipped to. If you’ve got the
new driver version on CD
please select the
\Driver\Win98_2k_XP path
on the CD containing the new
driver version.
The new driver version can
be used directly after installation without restarting the system. Please keep in mind to
update the driver of all installed Spectrum boards.
(c) Spectrum GmbH 21
Page 22
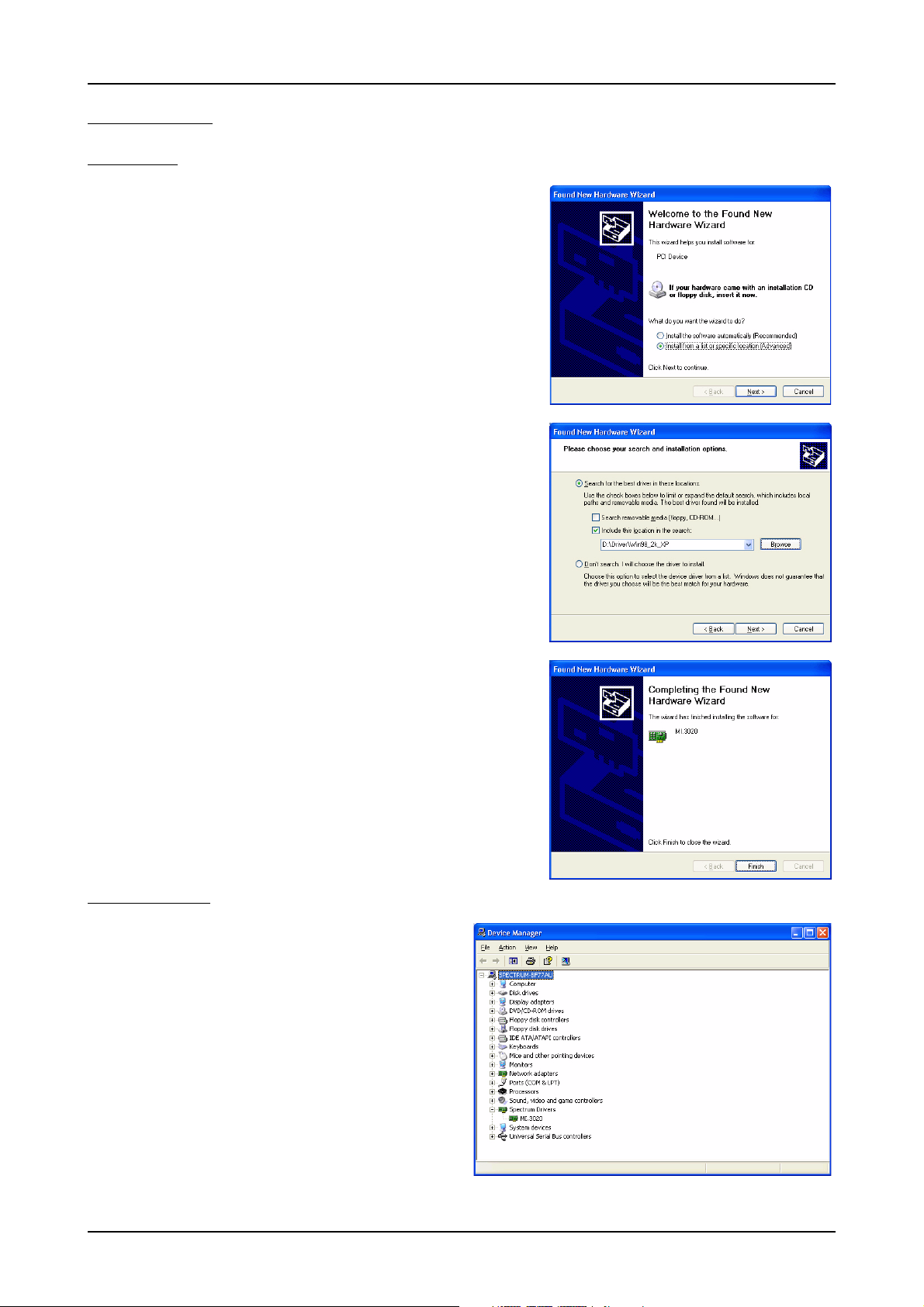
Windows XP Software Driver Installation
Windows XP
Installation
When installing the board in a Windows XP system the Spectrum board will be recognized automatically on the next start-up.
The system offers the direct installation of a driver for the board.
Do not let Windows automatically search for the best driver, because sometimes the driver will not be found on the CD. Please take the
option of choosing a manual installation path instead.
Allow Windows XP to search for the most suitable driver in a specific directory. Select the CD that was delivered with the board as installation source. The driver files
are located on CD in the directory \Driver\Win98_2k_XP.
The hardware assistant shows you the exact board type that has been found like
the MI.3020 in the example. Older boards (before june 2004) show „Spectrum
Board“ instead.
The drivers can be used directly after installation. It is not necessary to restart the
system. The installed drivers are linked in the device manager.
Below you’ll see how to examine the driver version and how to update the driver
with a newer version.
Version control
If you want to check which driver version is installed in the system this
can be easily done in the device manager. Therefore please start the
device manager from the control panel and show the properties of
the installed driver.
22 MI.61xx Manual
Page 23
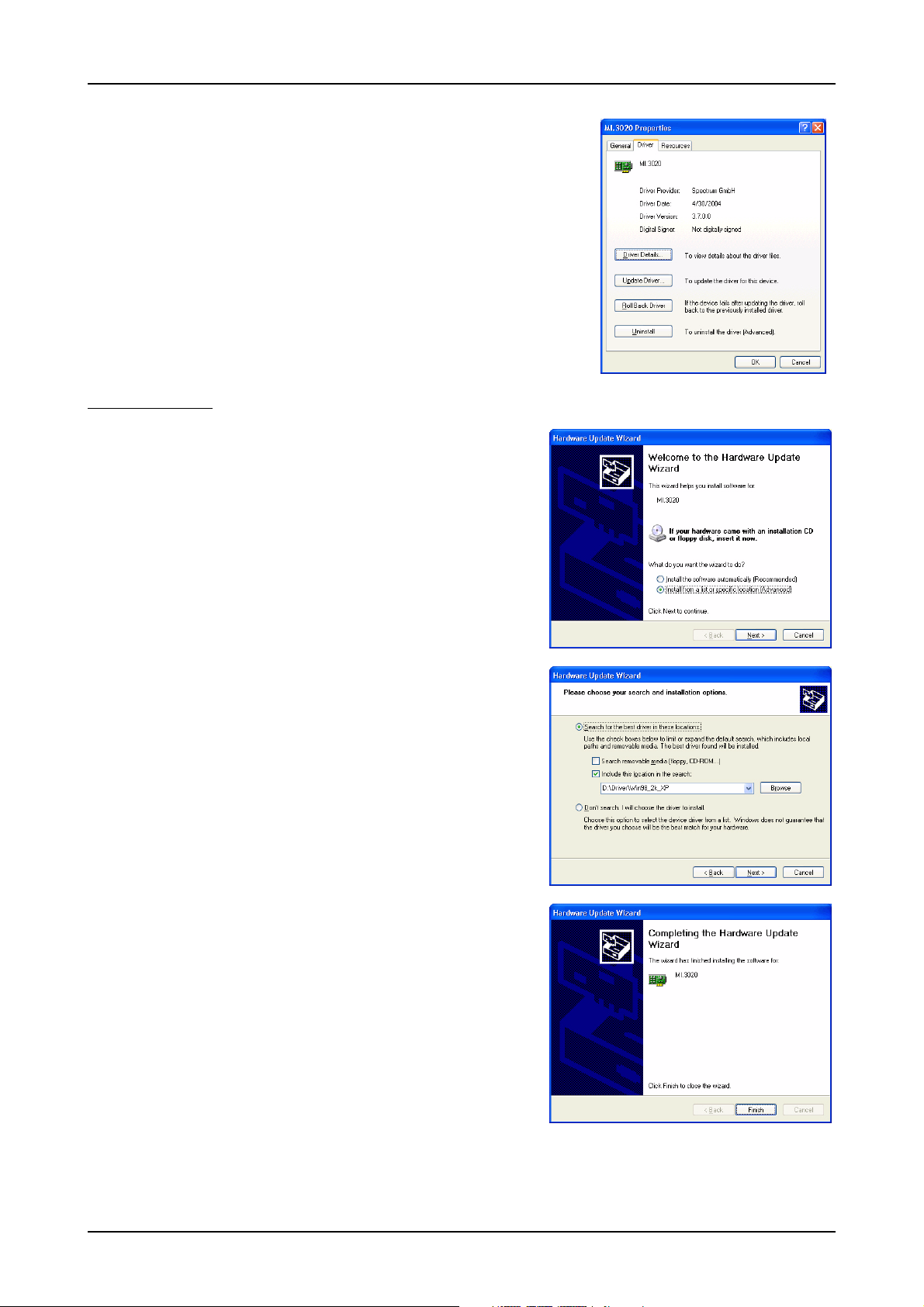
Software Driver Installation Windows XP
On the property page Windows XP shows the date and the version of the installed driver.
After clicking the driver details button the detailed version information of the driver is shown.
In the case of a support question this information must be presented together with the
board’s serial number to the support team to help finding a fast solution.
Driver - Update
If a new driver version should be installed no Spectrum board is allowed to be in
use by any software. So please stop and exit all software that could access the
boards.
A new driver version is directly installed from the device manager. Therefore please
open the properties page of the driver as shown in the section before. As next step
click on the update driver button and follow the steps of the driver installation in a
similar way to the previous board and driver installation.
Please select the path where the new driver version was unzipped to. If you’ve got
the new driver version on CD please select the \Driver\Win98_2k_XP path on the
CD containing the new driver version.
The new driver version can be used directly after installation without restarting the
system. Please keep in mind to update the driver of all installed Spectrum boards.
(c) Spectrum GmbH 23
Page 24

Windows NT Software Driver Installation
Windows NT
Installation
Under Windows NT the
Spectrum driver must be installed manually. The driver is
found on CD in the directory
\Install\WinNTDrv. Please
start the „Setup.exe“ program. The installation is performed totally automatically,
simply click on the „Next“
button. After installtion the system must be rebooted once
(see picture on the right side).
The driver is install to support
device. If more boards are installed in the system the configuration of the driver has to be changed. Please see the following chapter for this
topic.
Adding boards to the Windows NT driver
one PCI/PXI or CompactPCI
The Windows NT driver
must be configured by the
Driver Configuration utility
to support more than one
board. The Driver Configuration utility is automatically installed with the driver.
The Utility can be found in
the start menu as „DrvConfig“.
To add a new card please follow these steps:
• Increase the board number on top of the screen by pressing the right button
• Change the board type from „Not Installed“ to „PCI Board“
• Press the „Apply changes“ button
• Press the „OK“ button
• Restart the system
Driver - Update
If a new driver version should be installed no Spectrum board is allowed to be in use by any software. So please stop and exit all software
that could access the boards.
When updating a system please simply execute the setup file of the new driver version. Afterwards the system has to be rebooted. The driver
configuration is not changed.
24 MI.61xx Manual
Page 25

Software Driver Installation Linux
Linux
Overview
The Spectrum boards are delivered with drivers for linux. It is necessary to install them manually following the steps explained afterwards.
The linux drivers can be found on CD in the directory /Driver/linux. As linux is an open source operating system there are several distributions
in use world-wide that are compiled with different kernel settings. As we are not able to install and maintain hundreds of different distributions
and versions we had to focus on some common used linux distributions.
However if your distribution does not work with one of these pre-compiled kernel modules or you have a specialized kernel installed (like a
SMP kernel) you can get the linux driver sources directly from us. With this sources it’s no problem to compile and use the linux driver on your
system. Please contact your local distributor to get the sources. The Spectrum linux drivers are compatible with kernel versions 2.4 and 2.6.
On this CD you’ll find pre-compiled linux kernel modules for the following versions:
SuSE version 8.0 Kernel 2.4.18 directory /Driver/linux/suse80 SuSE version 8.2 Kernel 2.4.20 directory /Driver/linux/suse82
SuSE version 9.0 Kernel 2.4.21 directory /Driver/linux/suse90 SuSE version 9.1 Kernel 2.6.4 directory /Driver/linux/suse91
Redhat version 9.0 Kernel 2.4.20 directory /Driver/linux/redhat90
Installation
Login as root.
It is necessary to have the root rights for installing a driver.
Select the right driver from the CD.
Refer to the list shown above. If your distribution is not listed there please select the module that most closely matches your installed kernel
version. Copy the driver kernel module spc.o from the CD directory to your hard disk. Be sure to use a hard disk directory that is a accessible
by all users who should work with the board.
First time load of the driver
The linux driver is shipped as the loadable module spc.o. The driver includes all Spectrum PCI, PXI and CompactPCI boards. The boards are
recognized automatically after driver loading.Load the driver with the insmod command:
linux:~ # insmod spc.o
The insmod command may generate a warning that the driver module was compiled for another kernel version. In that case you may try to
load the driver module with the force parameter and test the board very carefully.
linux:~ # insmod -f spc.o
If the kernel module could not be loaded in your linux installation it is necessary to compile the driver directly on your system. Please contactSpectrum to get the needed source files including the compilation description.
Depending on the used linux distribution the insmod command generates a message telling the driver version and the board types and serial
numbers that have been found. If your distribution does not show this message it is possible to view them with the dmesg command:
linux:~ # dmesg
... some other stuff
spc driver version: 3.07 build 0
sp0: MI.3020 sn 01234
In the example we show you the output generated by a MI.3020. All other board types are similar to this output but showing the correct
board type.
Examine the major number of the driver
For accessing the device driver it is necessary to know the major number of the device. This number is listed in the /proc/devices list. The
device driver is called "spec" in this list. Normally this number is 254 but this depends on the device drivers that have been installed before.
linux:~ # cat /proc/devices
Character devices:
...
171 ieee1394
180 usb
188 ttyUSB
254 spec
Block devices:
1 ramdisk
2 fd
...
(c) Spectrum GmbH 25
Page 26

Linux Software Driver Installation
Installing the device
You connect a device to the driver with the mknod command. The major number is the number of the driver as shown in the last step, the
minor number is the index of the board starting with 0. This step must only be done once for the system where the boards are installed in.
The device will remain in the file structure even if the board is de-installed from the system.
The following command makes a device for the first Spectrum board the driver has found:
linux:~ # mknod /dev/spc0 c 254 0
Make sure that the users who work with the driver have full rights access for the device. Therefore you should give all persons all rights to the
device:
linux:~ # chmod a+w /dev/spc0
Now it is possible to access the board using this device.
Driver info
Information about the installed boards could be found in the /proc/spectrum file. All PCI, PXI and CompactPCI boards show the basic information found in the EEProm there. This is an example output generated by a MI.3020:
linux:~ # cat /proc/spectrum
Spectrum driver information
--------------------------Driver Version: 3.07 build 0
Board#0: MI.3020
serial number: 01234
production month: 05/2004
version: 9.6
samplerate: 100 MHz
installed memory: 16 MBytes
Automatic load of the driver
It is necessary to load the kernel driver module after each start of the system before using the boards. Therefore you may add the „insmod
spc.o“ command in one of the start-up files. Or you may load the kernel driver module manually whenever you need access to the board.
26 MI.61xx Manual
Page 27

Software Software Overview
Software
This chapter gives you an overview about the structure of the drivers and the software, where to find and how to use the examples. It detailed
shows how the drivers are included under different programming languages and where the differences are when calling the driver functions
from different programming languages.
This manual only shows the use of the standard driver API. For further information on programming drivers
for third-party software like LabVIEW, MATLAB, DASYLab or VEE an additional manual is required that is delivered with the ordered driver option.
Software Overview
The Spectrum drivers offer you a common and fast API for using all of the board hardware features. This API is nearly the same on all operating
systems. Based on this API one can write your own programs using any programming language that can access the driver API. This manual
detailed describes the driver API allowing you to write your own programs.
The optional drivers for third-party products like LabVIEW or DASYLab are also based on this API. The special functionality of these drivers
is not subject of this manual and is described on separate manuals delivered with the driver option.
First Test with SBench
After installation of the board and the drivers it can be useful to first test the board function with
a ready to run software before starting with programming. A full version of SBench 5.x is delivered with the board on CD. The program supports all actual acquisition, generator and digital I/O boards from Spectrum. Depending on the used board and the software setup, one
could use SBench as a digital storage oscilloscope, a spectrum analyser, a logic analyser or
simply as a data recording front end. Different export and import formats allow the use of
SBench together with a variety of other programs.
On the CD you’ll find an install version of SBench in the directory /Install/SBench. There’s also
a pre-installed program version on CD that can be started directly from CD without installing
to hard disk. This file can be found in the /Programs/SBench5 directory. Also on CD is a program description that shows in detail how SBench works and what settings have to be done to
use SBench in one of the different modes. The manual is found in the path /Internet/english/
swmanuals/SBench.
The current version of SBench can be down loaded free of charge directly from the Spectrum
website http://www.spectrum-instrumentation.com. Please go to the download section and get the latest version there.
SBench is designed to run under Windows 98, Windows ME, Windows NT, Windows 2000 and Windows XP.
It does not run under Linux. At the moment there is no graphical ready-to-run software for Linux available.
Please use the driver examples to examine whether the board is correctly installed under Linux.
(c) Spectrum GmbH 27
Page 28

C/C++ Driver Interface Software
C/C++ Driver Interface
C/C++ is the main programming language for which the drivers have been build up. Therefore the interface to C/C++ is the best match. All
the small examples of the manual showing different parts of the hardware programming are done with C.
Header files
The basic task before using the driver is to include the header files that are delivered on CD together with the board. The header files are
found in the directory /Driver/header_c. Please don’t change them in any way because they are updated with each new driver version to
include the new registers and new functionality.
dlltyp.h Includes the platform specific definitions for data types and function declarations. All data types are based on this definitions. The use of this typ definition file
regs.h Defines all registers and commands which are used in the Spectrum driver for the different boards. The registers a board uses are described in the board spe-
spectrum.h Defines the functions of the driver. All definitions are taken from the file dlltyp.h. The functions itself are described below.
spcerr.h Lists all and describes all error codes that can be given back by any of the driver functions. The error codes and their meaning are described in detail in the
errors.h Only there for backward compatibility with older program versions. Please use spcerr.h instead.
allows the use of examples and programs on different platforms without changes to the program source.
cific part of the documentation.
appendix of this manul.
Example for including the header files:
// ----- driver includes ----#include "dlltyp.h"
#include "spectrum.h"
#include "spcerr.h"
#include "regs.h"
Microsoft Visual C++
Include Driver
The driver files can be easily included in Microsoft C++ by simply using the library file that is delivered together with the drivers. The library
file can be found on the CD in the path /Driver/Win98_2k_XP. Please include the library file Spectrum.lib in your Visual C++ project. All
functions described below are now available in your program.
Examples
Examples can be found on CD in the path /Examples/vc. There is one subdirectory for each board family. You’ll find board specific examples
for that family there. The examples are bus type independent. As a result that means that the MI30xx directory contains examples for the
MI.30xx, the MC.30xx and the MX.30xx families. The example directories contain a running project file for Microsoft Visual C++ that can
be directly loaded and compiled.
There are also some more board independent examples in the directory MIxxxx. These examples show different aspects of the boards like
programming options or synchronization and have to be combined with one of the board specific example.
Linux Gnu C
Include Driver
The interface of the linux drivers is a little bit different from the windows interface. To make the access easier and to have more similar examples we added an include file that re maps the standard driver functions to the linux specific functions. This include file is found in the path /
Examples/linux/spcioctl.inc. All examples are based on this file.
Example for including Linux driver:
// ----- driver includes ----#include "dlltyp.h"
#include "regs.h"
#include "errors.h"
// ----- include the easy ioctl commands from the driver ----#include "../spcioctl.inc"
Examples
Examples can be found on CD in the path /Examples/linux. There is one subdirectory for each board family. You’ll find board specific examples for that family there. The examples are bus type independent. As a result that means that the MI30xx directory contains examples for
the MI.30xx, the MC.30xx and the MX.30xx families. The examples are simple one file programs and can be compiled using the Gnu C
compiler gcc. It’s not necessary to use a makefile for them.
28 MI.61xx Manual
Page 29

Software C/C++ Driver Interface
Other Windows C/C++ compilers
Include Driver
To access the driver, the driver functions must be loaded from the driver dll. This can be easily done by standard windows functions. There
is one example in the directory /Examples/other that shows the process. After loading the functions from the dll one can proceed with the
examples that are given for Microsoft Visual C++.
Example of function loading:
// definition of external function that has to be loaded from DLL
typedef int16 (SPCINITPCIBOARDS) (int16* pnCount, int16* pnPCIVersion);
typedef int16 (SPCSETPARAM) (int16 nNr, int32 lReg, int32 lValue);
typedef int16 (SPCGETPARAM) (int16 nNr, int32 lReg, int32* plValue);
...
SPCINITPCIBOARDS* pfnSpcInitPCIBoards;
SPCSETPARAM* pfnSpcSetParam;
SPCGETPARAM* pfnSpcGetParam;
...
// ----- Search for dll ----hDLL = LoadLibrary ("spectrum.dll");
// ----- Load functions from DLL ----pfnSpcInitPCIBoards = (SPCINITPCIBOARDS*) GetProcAddress (hDLL, "SpcInitPCIBoards");
pfnSpcSetParam = (SPCSETPARAM*) GetProcAddress (hDLL, "SpcSetParam");
pfnSpcGetParam = (SPCGETPARAM*) GetProcAddress (hDLL, "SpcGetParam");
National Instruments LabWindows/CVI
Include Drivers
To use the Spectrum driver under LabWindows/CVI it is necessary to first load the functions from the driver dll. This is more or less similar to
the above shown process with the only difference that LabWindows/CVI uses it’s own library handling functions instead of the windows
standard functions.
Example of function loding under LabWindows/CVI:
// ----- load the driver entries from the DLL ----DriverId = LoadExternalModule ("spectrum.lib");
// ----- Load functions from DLL ----SpcInitPCIBoards = (SPCINITPCIBOARDS*) GetExternalModuleAddr (DriverId, "SpcInitPCIBoards", &Status);
SpcSetParam = (SPCSETPARAM*) GetExternalModuleAddr (DriverId, "SpcSetParam", &Status);
SpcGetParam = (SPCGETPARAM*) GetExternalModuleAddr (DriverId, "SpcGetParam", &Status);
Examples
Examples for LabWindows/CVI can be found on CD in the directory /Examples/cvi. Theses examples show mainly how to include the driver
in a LabWindows/CVI environment and don’t use any special functions of the boards. The examples have to be merged with the standard
windows examples described under Visual C++.
Driver functions
The driver contains five functions to access the hardware.
Function
This function initializes all installed PCI, PXI and CompactPCI boards. The boards are recognized automatically. All installation parameters
are read out from the hardware and stored in the driver. The number of PCI boards will be given back in the value Count and the version of
the PCI bus itself will be given back in the value PCIVersion.
SpcInitPCIBoard
Function SpcInitPCIBoards:
int16 SpcInitPCIBoards (int16* count, int16* PCIVersion);
Under Linux this function is not available. Instead one must open and close the driver with the standard file
functions open and close. The functionality behind this function is the same as the SpcInitPCIBoards function.
Using the Driver under Linux:
hDrv = open ("/dev/spc0", O_RDWR);
...
close (hDrv);
(c) Spectrum GmbH 29
Page 30

C/C++ Driver Interface Software
Function SpcSetParam
All hardware settings are based on software registers that can be set by the function SpcSetParam. This function sets a register to a defined
value or executes a command. The board must first be initialized. The available software registers for the driver are listed in the board specific
part of the documentation below.
The value „nr“ contains the index of the board that you want to access, the value „reg“ is the register that has to be changed and the value
„value“ is the new value that should be set to this software register. The function will return an error value in case of malfunction.
Function SpcSetParam
int16 SpcSetParam (int16 nr, int32 reg, int32 value);
Under Linux the value „nr“ must contain the handle that was retrieved by the open function for that specific
board. The values is then not of the type „int16“ but of the type „handle“.
Function
SpcGetParam
The function SpcGetParam reads out software registers or status information. The board must first be initialized. The available software registers for the driver are listed in the board specific part of the documentation below.
The value „nr“ contains the index of the board that you want to access, the value „reg“ is the register that has to be read out and the value
„value“ is a pointer to a value that should contain the read parameter after function call. The function will return an error value in case of
malfunction.
Function SpcGetParam
int16 SpcGetParam (int16 nr, int32 reg, int32* value);
Under Linux the value „nr“ must contain the handle that was given back by the open function of that specific
board. The values is then not of the type „int16“ but of the type „handle“.
Function
SpcSetData
Writes data to the board for a specific memory channel. The board must first be initialized. The value „nr“ contains the index of the board
that you want to access, the „ch“ parameter contains the memory channel. „start“ and „len“ define the position of data to be written. „data“
is a pointer to the array holding the data. The function will return an error value in case of malfunction.
This function is only available on generator or i/o boards. The function is not available on acquisition boards.
Function SpcSetData (Windows)
int16 SpcSetData (int16 nr, int16 ch, int32 start, int32 len, dataptr data);
Under Linux the additional parameter nBytesPerSample must be used for this function. For all boards with 8 bit resolution the parameter is
„1“, for all boards with 12, 14 or 16 bit resolution this parameter has to be „2“. Under Linux the value „hDrv“ must contain the handle that
was given back by the open function of that specific board.
Function SpcSetData (Linux)
int32 SpcSetData (int hDrv, int32 lCh, int32 lStart, int32 lLen, int16 nBytesPerSample, dataptr pvData)
Function
SpcGetData
Reads data from the board from a specific memory channel. The board must first be initialized. The value „nr“ contains the index of the board
that you want to access, the „ch“ parameter contains the memory channel. „start“ and „len“ define the position of data to be read. „data“
is a pointer to the array that should hold the data. The function will return an error value in case of malfunction.
This function is only available on acquisition or i/o boards. The function is not available on generator boards.
Function SpcGetData
int16 SpcGetData (int16 nr, int16 ch, int32 start, int32 len, dataptr data);
30 MI.61xx Manual
Page 31

Software C/C++ Driver Interface
Under Linux the additional parameter nBytesPerSample must be used for this function. For all boards with 8 bit resolution the parameter is
„1“, for all boards with 12, 14 or 16 bit resolution this parameter has to be „2“. Under Linux the value „hDrv“ must contain the handle that
was given back by the open function of that specific board.
Function SpcGetData (Linux)
int32 SpcGetData (int hDrv, int32 lCh, int32 lStart, int32 lLen, int16 nBytesPerSample, dataptr pvData)
(c) Spectrum GmbH 31
Page 32

Delphi (Pascal) Programming Interface Software
Delphi (Pascal) Programming Interface
Type definition
All Spectrum driver functions are using pre-defined variable types to cover different operating systems and to use the same driver interface
for all programming languages. Under Delphi it is necessary to define these types once. This is also shown in the examples delivered on CD.
Delphi type definition:
type
int8 = shortint;
pint8 = ^shortint;
int16 = smallint;
pint16 = ^smallint;
int32 = longint;
pint32 = ^longint;
data = array[1..MEMSIZE] of smallint;
dataptr = ^data;
In the example shown above the size of data is defined to „smallint“. This definition is only valid for boards
that have a sample resolution of 12, 14 or 16 bit. On 8 bit boards this has to be a „shortint“ type.
Include Driver
To include the driver functions into delphi it is necessary to first add them to the implementation section of the program file. There the name
of the function and the location in the dll is defined:
Driver implementation:
function SpcSetData (nr,ch:int16; start,len:int32; data:dataptr): int16; cdecl; external 'SPECTRUM.DLL';
function SpcGetData (nr,ch:int16; start,len:int32; data:dataptr): int16; cdecl; external 'SPECTRUM.DLL';
function SpcSetParam (nr:int16; reg,value: int32): int16; cdecl; external 'SPECTRUM.DLL';
function SpcGetParam (nr:int16; reg:int32; value:pint32): int16; cdecl; external 'SPECTRUM.DLL';
function SpcInitPCIBoards (count,PCIVersion: pint16): int16; cdecl; external 'SPECTRUM.DLL';
Examples
Examples for Delphi can be found on CD in the directory /Examples/delphi. There is one subdirectory for each board family. You’ll find
board specific examples for that family there. The examples are bus type independent. As a result that means that the MI30xx directory contains examples for the MI.30xx, the MC.30xx and the MX.30xx families. The example directories contain a running project file for Borland
Delphi that can be directly loaded and compiled.
Driver functions
The driver contains five functions to access the hardware.
Function SpcInitPCIBoard
This function initializes all installed PCI, PXI and CompactPCI boards. The boards are recognized automatically. All installation parameters
are read out from the hardware and stored in the driver. The number of PCI boards will be given back in the value Count and the version of
the PCI bus itself will be given back in the value PCIVersion.
Function SpcSetParam
All hardware settings are based on software registers that can be set by the function SpcSetParam. This function sets a register to a defined
value or executes a command. The board must first be initialized. The available software registers for the driver are listed in the board specific
part of the documentation below.
The value „nr“ contains the index of the board that you want to access, the value „reg“ is the register that has to be changed and the value
„value“ is the new value that should be set to this software register. The function will return an error value in case of malfunction.
Function SpcGetParam
The function SpcGetParam reads out software registers or status information. The board must first be initialized. The available software registers for the driver are listed in the board specific part of the documentation below.
The value „nr“ contains the index of the board that you want to access, the value „reg“ is the register that has to be read out and the value
„value“ is a pointer to a value that should contain the read parameter after function call. The function will return an error value in case of
malfunction.
Function SpcSetData
Writes data to the board for a specific memory channel. The board must first be initialized. The value „nr“ contains the index of the board
that you want to access, the „ch“ parameter contains the memory channel. „start“ and „len“ define the position of data to be written. „data“
is a pointer to the array holding the data. The function will return an error value in case of malfunction.
32 MI.61xx Manual
Page 33

Software Delphi (Pascal) Programming Interface
This function is only available on generator or i/o boards. The function is not available on acquisition boards.
Function SpcGetData
Reads data from the board from a specific memory channel. The board must first be initialized. The value „nr“ contains the index of the board
that you want to access, the „ch“ parameter contains the memory channel. „start“ and „len“ define the position of data to be read. „data“
is a pointer to the array that should hold the data. The function will return an error value in case of malfunction.
This function is only available on acquisition or i/o boards. The function is not available on generator boards.
(c) Spectrum GmbH 33
Page 34

Visual Basic Programming Interface Software
Visual Basic Programming Interface
The Spectrum boards can be used together with Microsoft Visual Basic as well as with Microsoft Visual Basic for Applications. This allows
per example the direct access of the hardware from within Microsoft Excel. The interface between the programming language and the driver
is the same for both.
Include Driver
To include the driver functions into Basic it is necessary to first add them to the module definition section of the program file. There the name
of the function and the location in the dll is defined:
Module definition:
Public Declare Function SpcInitPCIBoards Lib "SpcStdNT.dll" Alias "_SpcInitPCIBoards@8" (ByRef Count As Integer,
ByRef PCIVersion As Integer) As Integer
Public Declare Function SpcInitBoard Lib "SpcStdNT.dll" Alias "_SpcInitBoard@8" (ByVal Nr As Integer, ByVal Typ
As Integer) As Integer
Public Declare Function SpcGetParam Lib "SpcStdNT.dll" Alias "_SpcGetParam@12" (ByVal BrdNr As Integer, ByVal
RegNr As Long, ByRef Value As Long) As Integer
Public Declare Function SpcSetParam Lib "SpcStdNT.dll" Alias "_SpcSetParam@12" (ByVal BrdNr As Integer, ByVal
RegNr As Long, ByVal Value As Long) As Integer
Public Declare Function SpcGetData8 Lib "SpcStdNT.dll" Alias "_SpcGetData@20" (ByVal BrdNr As Integer, ByVal
Channel As Integer, ByVal Start As Long, ByVal Length As Long, ByRef data As Byte) As Integer
Public Declare Function SpcSetData8 Lib "SpcStdNT.dll" Alias "_SpcSetData@20" (ByVal BrdNr As Integer, ByVal
Channel As Integer, ByVal Start As Long, ByVal Length As Long, ByRef data As Byte) As Integer
Public Declare Function SpcGetData16 Lib "SpcStdNT.dll" Alias "_SpcGetData@20" (ByVal BrdNr As Integer, ByVal
Channel As Integer, ByVal Start As Long, ByVal Length As Long, ByRef data As Integer) As Integer
Public Declare Function SpcSetData16 Lib "SpcStdNT.dll" Alias "_SpcSetData@20" (ByVal BrdNr As Integer, ByVal
Channel As Integer, ByVal Start As Long, ByVal Length As Long, ByRef data As Integer) As Integer
The module definition is already done for the examples and can be found in the Visual Basic examples directory. Please simply use the file
declnt.bas.
Visual Basic Examples
Examples for Visual Basic can be found on CD in the directory /Examples/vb. There is one subdirectory for each board family. You’ll find
board specific examples for that family there. The examples are bus type independent. As a result that means that the MI30xx directory contains examples for the MI.30xx, the MC.30xx and the MX.30xx families. The example directories contain a running project file for Visual
Basic that can be directly loaded.
VBA for Excel Examples
Examples for VBA for Excel can be found on CD in the directory /Examples/excel. The example here simply show the access of the driver
and make a very small demo acquisition. It is necessary to combine these examples with the Visual Basic examples to have full board functionality.
Driver functions
The driver contains five functions to access the hardware.
Function SpcInitPCIBoard
This function initializes all installed PCI, PXI and CompactPCI boards. The boards are recognized automatically. All installation parameters
are read out from the hardware and stored in the driver. The number of PCI boards will be given back in the value Count and the version of
the PCI bus itself will be given back in the value PCIVersion.
Function SpcInitPCIBoard:
Function SpcInitPCIBoards (ByRef Count As Integer, ByRef PCIVersion As Integer) As Integer
Function SpcSetParam
All hardware settings are based on software registers that can be set by the function SpcSetParam. This function sets a register to a defined
value or executes a command. The board must first be initialized. The available software registers for the driver are listed in the board specific
part of the documentation below.
The value „nr“ contains the index of the board that you want to access, the value „reg“ is the register that has to be changed and the value
„value“ is the new value that should be set to this software register. The function will return an error value in case of malfunction.
Function SpcSetParam:
Function SpcSetParam (ByVal BrdNr As Integer, ByVal RegNr As Long, ByVal Value As Long) As Integer
34 MI.61xx Manual
Page 35

Software Visual Basic Programming Interface
Function SpcGetParam
The function SpcGetParam reads out software registers or status information. The board must first be initialized. The available software registers for the driver are listed in the board specific part of the documentation below.
The value „nr“ contains the index of the board that you want to access, the value „reg“ is the register that has to be read out and the value
„value“ is a pointer to a value that should contain the read parameter after function call. The function will return an error value in case of
malfunction.
Function SpcGetParam:
Function SpcGetParam (ByVal BrdNr As Integer, ByVal RegNr As Long, ByRef Value As Long) As Integer
Function SpcSetData
Writes data to the board for a specific memory channel. The board must first be initialized. The value „nr“ contains the index of the board
that you want to access, the „ch“ parameter contains the memory channel. „start“ and „len“ define the position of data to be written. „data“
is a pointer to the array holding the data. The function will return an error value in case of malfunction.
Function SpcSetData:
Function SpcSetData8 (ByVal BrdNr As Integer, ByVal Channel As Integer, ByVal Start As Long, ByVal Length As
Long, ByRef data As Byte) As Integer
Function SpcSetData16 (ByVal BrdNr As Integer, ByVal Channel As Integer, ByVal Start As Long, ByVal Length As
Long, ByRef data As Integer) As Integer
It is necessary to select the function with the matching data width from the above mentioned data write functions. Use the SpcSetData8 function for boards with 8 bit resolution and use the SpcSetData16 function for
boards with 12, 14 and 16 bit resolution.
This function is only available on generator or i/o boards. The function is not available on acquisition boards.
Function SpcGetData
Reads data from the board from a specific memory channel. The board must first be initialized. The value „nr“ contains the index of the board
that you want to access, the „ch“ parameter contains the memory channel. „start“ and „len“ define the position of data to be read. „data“
is a pointer to the array that should hold the data. The function will return an error value in case of malfunction.
Function SpcGetData:
Function SpcGetData8 (ByVal BrdNr As Integer, ByVal Channel As Integer, ByVal Start As Long, ByVal Length As
Long, ByRef data As Byte) As Integer
Function SpcGetData16 (ByVal BrdNr As Integer, ByVal Channel As Integer, ByVal Start As Long, ByVal Length As
Long, ByRef data As Integer) As Integer
It is necessary to select the function with the matching data width from the above mentioned data read functions. Use the SpcGetData8 function for boards with 8 bit resolution and use the SpcGetData16 function for
boards with 12, 14 and 16 bit resolution.
This function is only available on acquisition or i/o boards. The function is not available on generator boards.
(c) Spectrum GmbH 35
Page 36

Overview Programming the Board
Programming the Board
Overview
The following chapters show you in detail how to program the different aspects of the board. For every topic there’s a small example. For
the examples we focussed on Visual C++. However as shown in the last chapter the differences in programming the board under different
programming languages are marginal. This manual describes the programming of the whole hardware family. Some of the topics are similar
for all board versions. But some differ a little bit from type to type. Please check the given tables for these topics and examine carefully which
settings are valid for your special kind of board.
Register tables
The programming of the boards is totally software register based. All software registers are described in the following form:
The name of the software register as found in the regs.h file.
Could directly be used by C and
C++ compiler
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_COMMAND 0 r/w Command register of the board.
SPC_START 10 Starts the board with the current register settings.
SPC_STOP 20 Stops the board manually.
Any constants that can be used to
program the register directly are
shown inserted beneath the register
table.
If no constants are given below the register table, the dedicated register is used as a switch. All such registers
are activated if written with a “1“ and deactivated if written with a “0“.
The decimal value of the software register.
Also found in the regs.h file. This value must
be used with all programs or compilers that
cannot use the header file directly.
The decimal value of the constant. Also
found in the regs.h file. This value must be
used with all programs or compilers that
cannot use the header file directly.
Describes whether
the register can be
read (r) and/or written (w).
Short description of
the use of this constant.
Short description of the functionality of the register. A more detailled description is found
above or below this register.
Programming examples
In this manual a lot of programming examples are used to give you an impression on how the actual mentioned registers can be set within
your own program. All of the examples are located in a seperated colored box to indicate the example and to make it easier to differ it from
the describing text.
All of the examples mentioned throughout the manual are basically written using the Visual C++ compiler for Windows. If you use Linux there
are some changes in the funtion’s parameter lists as mentioned in the relating software chapter.
To keep the examples as compatible as possible for users of both operational systems (Windows and Linux) all the functions that
contain either a board number (Windows) or a handle (Linux) use the common parameter name ’hDrv’. Windows users simply have
to set the parameter to the according board number (as the example below is showing), while Linux uses can easily use the handle
that is given back for the according board by the initialization function.
// Windows users must set hDrv to the according board number before.
// Assuming that there is only one Spectrum board installed you’ll
// have to set hDrv like this:
hDrv = 0;
SpcGetParam (hDrv, SPC_LASTERRORCODE, &lErrorCode); // Any command just to show the hDrv usage
Error handling
If one action caused an error in the driver this error and the register and value where it occurs will be saved.
The driver is then locked until the error is read out using the SPC_LASTERRORCODE function. All other functions
will lead to the same errorcode unless the error is cleared by reading SPC_LASTERRORCODE.
36 MI.61xx Manual
Page 37

Programming the Board Initialization
This means as a result that it is not necessary to check each driver call for an error but to check for an error before the board is started to see
whether all settings have been valid.
By reading all the error information one can easily examine where the error occured. The following table shows all the error related registers
that can be read out.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_LASTERRORCODE 999999 r Error code of the last error that occured. The errorcodes are found in spcerr.h. If this register is read,
SPC_LASTERRORREG 999998 r Software register that causes the error.
SPC_LASTERRORVALUE 999997 r The value that has been written to the faulty software register.
the driver will be unlocked.
The error codes are described in detail in the appendix. Please refer to this error description and the description of the software register to examine the cause for the error message.
Example for error checking:
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_MEMSIZE, -345); // faulty command
if (SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_COMMAND, SPC_START) != ERR_OK) // try to start and check for an error
{
SpcGetParam (hDrv, SPC_LASTERRORCODE, &lErrorCode); // read out the error information
SpcGetParam (hDrv, SPC_LASTERRORREG, &lErrorReg);
SpcGetParam (hDrv, SPC_LASTERRORVALUE, &lErrorValue);
printf („Error %d when writing Register %d with Value %d !\n“, lErrorCode, lErrorReg, &lErrorValue);
}
This short program then would generate a printout as:
Error 101 when writing Register 10000 with Value -345 !
Initialization
Starting the automatic initialization routine
Before you can access the boards in your program, you have to initialize them first. Therefore the Spectrum function SpcInitPCIBoards is used.
If it is called, all Spectrum boards in the host system are initialized automatically. If no errors occured during the initialization, the returned
value is 0 (ERR_OK). In any other cases something has gone wrong. Please see appendix for explanations of the different error codes.
If the process of initializing the boards was successful, the function returns the total number of Spectrum boards that have been found in your
system. The third return value is the revision of the PCI Bus, the Spectrum boards are installed in.
The following example shows how to start the initialization of the board and check for errors.
// ----- Initialization of PCI Bus Boards-----------------------------------if (SpcInitPCIBoards (&nCount, &nPCIBusVersion) != ERR_OK)
return;
if (nCount == 0)
{
printf ("No Spectrum board found\n");
return;
}
PCI Register
These registers are set by the driver after the PCI initialization. The information is found in the on-board ROM, and can easily be read out by
your own application software. All of the following PCI registers are read only. You get access to all registers by using the Spectrum function
SpcGetParam with one of the following registers.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_PCITYP 2000 r Type of board as listed in the table below
One of the following values are returned, when reading this register.
Boardtype Value hexade-
TYP_MI6110 6110 24848 TYP_MI6111 6111 24849
zimal
Value dezimal Boardtype Value hexade-
(c) Spectrum GmbH 37
zimal
Value dezimal
Page 38

Initialization Programming the Board
Hardware version
Since all of the MI, MC and MX boards from Spectrum are modular boards, they consist of one base board and one or two (only PCI and
CompactPCI) piggy-back modules. This register SPC_PCIVERSION gives information about the revision of either the base board and the modules. Normally you do not need this information but if you have a support question, please provide the revision together with it.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_PCIVERSION 2010 r Board revision: bit 15..8 show revision of the base card, bit 7..0 the revision of the modules
If your board has a piggy-back expansion module mounted (MC und MI series boards only) you can get the hardwareversion with the following register.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_PCIEXTVERSION 2011 r Board’s expansion module hardware revision as integer value.
Date of production
This register informs you about the production date, which is returned as one 32 bit longword. The upper word is holding the information
about the year, while the lower byte informs about the month. The second byte (counting from below) is not used. If you only need to know
the production year of your board you have to mask the value accordingly. Normally you do not need this information, but if you have a
support question, please provide the revision within.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_PCIDATE 2020 r Production date: year in bit 31..16, month in bit 7..0, bit 15..8 are not used
Serial number
This register holds the information about the serial number of the board. This numer is unique and should always be sent together with a
support question. Normally you use this information together with the register SPC_PCITYP to verify that multiple measurements are done with
the exact same board.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_PCISERIALNO 2030 r Serial number of the board
Maximum possible sample rate
This register gives you the maximum possible samplerate the board can run however. The information provided here does not consider any
restrictions in the maximum speed caused by special channel settings. For detailed information about the correlation between the maximum
samplerate and the number of activated chanels please refer th the according chapter.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_PCISAMPLERATE 2100 r Maximum samplerate in Hz as a 32 bit integer value
Installed memory
This register returns the size of the installed on-board memory in bytes as a 32 bit integer value. If you want to know the ammount of samples
you can store, you must regard the size of one sample of your Spectrum board. All 8 bit boards can store only sample per byte, while all
other boards with 12, 14 and 16 bit use two bytes to store one sample.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_PCIMEMSIZE 2110 r Instaleld memory in bytes as a 32 bit integer value
The following example is written for a „two bytes“ per sample board (12, 14 or 16 bit board).
SpcGetParam (hDrv, SPC_PCIMEMSIZE, &lInstMemsize);
printf ("Memory on board: %ld MBytes (%ld MSamples)\n", lInstMemsize /1024 / 1024, lInstMemsize /1024 / 1024 /2);
38 MI.61xx Manual
Page 39

Programming the Board Initialization
Installed features and options
The SPC_PCIFEATURES register informs you about the options, that are installed on the board. If you want to know about one option being
installed or not, you need to read out the 32 bit value and mask the interesting bit.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_PCIFEATURES 2120 r PCI feature register. Holds the installed features and options as a bitfield, so the return value must be
PCIBIT_MULTI 1 Is set if the Option Multiple Recording / Multiple Replay is installed.
PCIBIT_DIGITAL 2 Is set if the Option Digital Inputs / Digital Outputs is installed.
PCIBIT_GATE 32 Is set if the Option Gated Sampling / Gated Replay is installed.
PCIBIT_SYNC 512 Is set if the Option Synchronization is installed for that certain board, regardless what kind of synchronization you
PCIBIT_TIMESTAMP 1024 Is set if the Option Timestamp is installed.
PCIBIT_STARHUB 2048 Is set on the board, that carrys the starhub piggy-back module. This flag is set in addition to the PCIBIT_SYNC flag
PCIBIT_XIO 8192 Is set if the Option Extra I/O is installed.
use. Boards without this option cannot be synchronized with other boards.
mentioned above. If on no synchronized board the starhub option is installed, the boards are synchronized with the
cascading option.
masked with one of the masks below to get information about one certain feature.
The following example demonstrates how to read out the information about one feature.
SpcGetParam (hDrv, SPC_PCIFEATURES, &lFeatures);
if (lFeatures & PCIBIT_DIGITAL)
printf("Option digital inputs is installed on your board");
Used interrupt line
This register holds the information of the actual used interrupt line for the board. This information is sometimes more easy in geting the interrupt
line of one specific board then using the hardware setups of your operating system.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_PCIINTERRUPT 2300 r The used interrupt line of the board.
Used type of driver
This register holds the information about the driver that is actually used to access the board. Although most users will use the boards within
a Windows system and most Windows users will use the WDM driver, it can be sometimes necessary of knowing the type of driver.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_GETDRVTYPE 1220 r Gives information about what type of driver is actually used
DRVTYP_DOS 0 DOS driver is used
DRVTYP_LINUX 1 Linux driver is used
DRVTYP_VXD 2 Windows VXD driver is used (only Windows 95)
DRVTYP_NTLEGACY 3 Windows NT Legacy driver is used (only Windows NT)
DRVTYP_WDM 4 Windows WDM driver is used (only Windows 98/ME/2000/XP). This is the most common Windows driver.
Driver version
This register informs Windows users about the actual used driver DLL. This information can also be obtained from the device manager. Please
refer to the „Driver Installation“ chapter. Linux users will get the revision of their kernel driver instead, because linux does not use any DLL.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_GETDRVVERSION 1200 r Gives information about the driver DLL version
Kernel Driver version
This register informs OS independent about the actual used kernel driver. Windows users can also get this information from the device manager. Plese refer to the „Driver Installation“ chapter. Linux users can get the driver version by simply accessing the following register for the
kernel driver.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_GETKERNELVERSION 1210 r Gives information about the kernel driver version.
(c) Spectrum GmbH 39
Page 40

Powerdown and reset Programming the Board
Example program for the board initialization
The following example is only an exerpt to give you an idea on how easy it is to initialize a Spectrum board.
// ----- Initialization of PCI Bus Boards ----------------------------------if (SpcInitPCIBoards (&nCount, &nPCIBusVersion) != ERR_OK)
return;
if (nCount == 0)
{
printf ("No Spectrum board found\n");
return;
}
// ----- request and print Board type and some information -----------------SpcGetParam (hDrv, SPC_PCITYP, &lBrdType);
SpcGetParam (hDrv, SPC_PCIMEMSIZE, &lInstMemsize);
SpcGetParam (hDrv, SPC_PCISERIALNO, &lSerialNumber);
// ----- print the board type depending on bus. Board number is always the lower 16 bit of type ----switch (lBrdType & TYP_SERIESMASK)
{
case TYP_MISERIES:
printf ("Board found: MI.%x sn: %05d\n", lBrdType & 0xffff, lSerialNumber);
break;
case TYP_MCSERIES:
printf ("Board found: MC.%x sn: %05d\n", lBrdType & 0xffff, lSerialNumber);
break;
case TYP_MXSERIES:
printf ("Board found: MX.%x sn: %05d\n", lBrdType & 0xffff, lSerialNumber);
break;
}
printf ("Memory on board: %ld MBytes (%ld MSamples)\n", lInstMemsize /1024/1024, lInstMemsize /1024/1024 /2);
printf ("Serial Number: %05ld\n", lSerialNumber);
Powerdown and reset
Every Spectrum board can be set to powerdown mode by software. In this mode the board is therefore consuming less power than in normal
operation mode. The amount of saved power is board dependant. Please refer to the technical data section for details. The board can be set
to normal mode again either by performing a reset as mentioned below or by starting the board as described in the according chapters later
in this manual.
If the board is set to powerdown mode or a reset is performed the data in the on-board will be no longer
valid and cannot be read out or replayed again.
Performing a board reset or powering down the board can be easily done by the related board commands mentioned in the following table.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_COMMAND 0 r/w Command register of the board.
SPC_POWERDOWN 30 Sets the board to powerdown mode. The data in the on-board memory is no longer valid and cannot be read out or
SPC_RESET 0 A software and hardware reset is done for the board. All settings are set to the default values. The data in the board’s
replayed again. The board can be set to normal mode again by the reset command or by starting the boards.
on-board memory will be no longer valid.
40 MI.61xx Manual
Page 41

Analog Outputs Channel Selection
Analog Outputs
Channel Selection
One key setting that influences all other possible settings is the channel enable register. An unique feature of the Spectrum boards is the
possibility to program the number of channels you want to use. All on-board memory can then be used by these activated channels.
This description shows you the channel enable register for the complete board family. However your specific board may have less channels
depending on the board type you purchased and did not allow you to set the maximum number of channels shown here.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_CHENABLE 11000 r/w Sets the channel enable information for the next board run.
CHANNEL0 1 Activates channel 0
CHANNEL1 2 Activates channel 1
CHANNEL2 4 Activates channel 2
CHANNEL3 8 Activates channel 3
The channel enable register is set as a bitmap. That means one bit of the value corresponds to one channel to be activated. To activate more
than one channel the values have to be combined by a bitwise OR.
Example showing how to activate 4 channels:
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_CHENABLE, CHANNEL0 | CHANNEL1 | CHANNEL2 | CHANNEL3);
The following table shows all allowed settings for the channel enable register.
Channels to activate
Ch0 Ch1 Ch2 Ch3 Values to program Value as hex Value as decimal
X CHANNEL0 1h 1
X X CHANNEL0 | CHANNEL1 3h 3
X X CHANNEL0 | CHANNEL2 5h 5
X X X X CHANNEL0 | CHANNEL1 | CHANNEL2 | CHANNEL3 Fh 15
Any channel activation mask that is not shown here is not valid. If programming another channel activation
the driver automatically remaps this to the best matching activation mask. You can read out the channel enable register to see what channel activation mask the driver has set.
Reading out the channel enable register can be done directely after setting it or later like this:
SpcGetParam (hDrv, SPC_CHENABLE, &lActivatedChannels);
printf ("Activated channels are: %ld \n", lActivatedChannels);
Important note on channels selection
As some of the manuals passages are used in more than one hardware manual most of the registers and
channel settings throughout this handbook are described for the maximum number of possible channels that
are available on one board of the actual series. There can be less channels on your actual type of board or
bus-system. Please refer to the table above to get the actual number of available channels.
Disabling the outputs
In contrast to simply not using one or more channels by setting the channel enable registers accordingsly, the outputs can also be set to a
high impedance state(tristate). Because of the internal structure the outputs can only be disabled per module by the registers shown in the
table below.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_DISABLEMOD0 203000 r/w Disables the outputs of module 0 (channel 0 and channel 1). Outputs will go to high impedance.
SPC_DISABLEMOD1 203010 r/w Disables the outputs of module 1 (channel 2 and channel 3). Outputs will go to high impedance.
(c) Spectrum GmbH 41
Page 42

Setting up the outputs Analog Outputs
Setting up the outputs
Output Amplifiers
This arbitrary waveform generator board uses separate output amplifiers for each channel. This gives you the possibility to seperately
set up the channel outputs to best suit your application
The output amplifiers can easily be set by the corresponding amplitude registers.
The table below shows the available registers to set up the output
amplitude for your type of board.
Register Value Direction Description Amplitude range
SPC_AMP0 30010 r/w Defines the amplitude of channel0. 100 mV up to 3000 mV
SPC_AMP1 30110 r/w Defines the amplitude of channel1. 100 mV up to 3000 mV
SPC_AMP2 30210 r/w Defines the amplitude of channel2. 100 mV up to 3000 mV
SPC_AMP3 30310 r/w Defines the amplitude of channel3. 100 mV up to 3000 mV
The amplitude can be changed at any time even if the board is running and outputting a signal to the con-
nectors. The board will not be stopped when changing these settings.
Output offset
In many applications an output of symmetrical signals is required. But in some cases, depending on
your application, it can be necessary to generate
signals that are not symmetrical.
For such cases you can adjust the offset of the outputs for each channel seperately.
The figure at the right shows some examples, how
to set up the offset in combination with different amplitudes.
Register Value Direction Description Offset range
SPC_OFFS0 30000 r/w Defines the output’s offset and therfore shifts the output of channel0. ± 3000 mV in steps of 1 mV
SPC_OFFS1 30100 r/w Defines the output’s offset and therfore shifts the output of channel1. ± 3000 mV in steps of 1 mV
SPC_OFFS2 30200 r/w Defines the output’s offset and therfore shifts the output of channel2. ± 3000 mV in steps of 1 mV
SPC_OFFS3 30300 r/w Defines the output’s offset and therfore shifts the output of channel3. ± 3000 mV in steps of 1 mV
The offset settings can be changed at any time even if the board is running and outputting a signal to the
connectors. The board will not be stopped when changing these settings.
42 MI.61xx Manual
Page 43

Analog Outputs Setting up the outputs
Maximum Output Range
In order not to generate distorted signals it is necessary to keep the total output range as a combination of the set amplitude and offset within a range
of ±3000 mV.
If this limit is exceeded a heavy distorted signal will
be seen and the signals waveform will be cut off at
the maximum range of +3000 mV or at the minimum range of -3000 mV.
To avoid heavily distorted output signals please make sure to keep the signals in a range of ±3000 mV.
To give you an example how the registers of the amplitude and the offset are to be used, the following example shows a setup to match all
of the three signals shown in the offset figure.
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_AMP0 , 1000); // Set up amplitude of channel0 to ± 1.0 V
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_AMP1 , 1000); // Set up amplitude of channel1 to ± 1.0 V
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_AMP2 , 1500); // Set up amplitude of channel2 to ± 1.5 V
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_OFFS0, 0); // Set the output offsets
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_OFFS1, 500);
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_OFFS2, -500);
Output Filters
Every output of your Spectrum D/A board is equipped with a bypass
path and three fixed filters that can be used for signal smoothing.
The filters are located in the signal chain between the output amplification section and the DAC, as shown in the right figure. Depending
on your type of board these filters are of differerent filter types and
have different cut off frequencies, as shown below. As well as the setting for amplitude and offset, the settings for the filters can be changed
at any time. The board will not be stopped for changing the different
filters. You can choose between the different filters easily by setting the
dedicated filter registers. The registers and the possible values are shown in the table below.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_FILTER0 30080 r/w Sets the signal filter of channel0.
SPC_FILTER1 30180 r/w Sets the signal filter of channel1.
SPC_FILTER2 30280 r/w Sets the signal filter of channel2.
SPC_FILTER3 30380 r/w Sets the signal filter of channel3.
0 No filter is used on the corresponding channel.
1 Filter 1 is used on the corresponding channel. The type of filter depends on the type of board and is shown below.
2 Filter 2 is used on the corresponding channel. The type of filter depends on the type of board and is shown below.
3 Filter 3 is used on the corresponding channel. The type of filter depends on the type of board and is shown below.
Filter Specifications MI.6110 MI.6111
filter 0 No filter will be used.
filter 1 -3 dB bandwidth 25 MHz
filter 2 -3 dB bandwidth 5 MHz
filter 3 -3 dB bandwidth 500 kHz
(c) Spectrum GmbH 43
Page 44

General description Standard generation modes
Standard generation modes
General description
The generated data is replayed from the on-board memory. These modes allows generating waveforms at very high sample rates without the
need to transfer the data into the board’s on-board memory at high speed. These modes are running totally independent from the PC and
don’t need any processing power after being started.
Singleshot mode
The singleshot mode is the most simple output mode for the
Spectrum boards. It simply replays the programmed data
once after detecting the trigger event. The amount of memory
to be replayed can be programmed by software. Any trigger
source can be used to start the output. If output should be started immediately one can simply use the software trigger capabilities of the board.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_SINGLESHOT 41000 r/w Write a „1“ to enable the singleshot mode (a „0“ disables it)
Continuous Mode
After detetcting the trigger event the programmed data is replayed continuously. On reaching end of the programmed
memory size the output starts again with the first sample. There’s no gap in output when switching from the last sample to
the first sample. The output runs until the users stops it by software. If not stopped the continuous output runs independent
of any other PC components until the system is shut off.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_SINGLESHOT 41000 r/w Write a „0“ to disable the singleshot mode
SPC_OUTONTRIGGER 41100 r/w Write a „1“ to enable the continuous mode
Posttrigger Mode
The posttrigger mode is normally only used when starting the
output board together with an acquisiton board.
The data is written to a programmed amount of the on-board
memory (memsize). After starting the board the output will immediately start and continue to loop. At this point the mode is
similar to the continuous mode explained above. After detecting a rigger event, a certain programmed amount of data is
replayed (posttrigger) and then the replay finishes automatically.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_SINGLESHOT 41000 r/w Write a „0“ to disable the singleshot mode
SPC_OUTONTRIGGER 41100 r/w Write a „0“ to disable the continuous mode
Programming
Partitioning the memory
The memory size register defines the length of the data to be replayed. Depending on the mode used this data is replayed once or continuously.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_MEMSIZE 10000 r/w Sets the memory size in samples per channel.
SPC_POSTTRIGGER 10100 r/w Sets the number of samples to be replayed after the trigger event has been detected.
The maximum memsize that can be use for replaying is of course limited by the installed amount of memory and by the number of channels
to be replayed. The following table gives you an overview on the maximum memsize in relation to the installed memory.
44 MI.61xx Manual
Page 45

Standard generation modes Programming
Maximum memsize
ch0 ch1 ch2 ch3
x 1/1 1/1
xx 1/21/2
xxn.a.1/2
xxxxn.a.1/4
6110
6111
How to read this table: If you have installed the standard amount of 8 MSample on your 6111 board and you want to replay all four channels,
you have a total maximum memory of 16 MSample * 1/4 = 4 MSample per channel for your data.
The maximum settings for the post counter are limited by the hardware, because the post counter has a limited range for counting. The settings
depend on the number of activated channels, as the table below is showing.
Maximum posttrigger in MSamples
ch0 ch1 ch2 ch3
x 256 256
x x 128 128
xxn.a.256
xxxxn.a.128
6110
6111
The amount of memory that can be either set for the used memsize and postcounter values can only be set by certain steps. These steps are
results of the internal memory organization. For this reason these steps also define the minimum size for the data memory and the postcounter.
The values depend on the number of activated channels and on the type of board being used. The minimum stepsizes for setting up the memsize and the postcounter are shown in the table below.
Minimum and stepsize of memsize and posttrigger in samples
ch0 ch1 ch2 ch3
x6464
xx 32 32
xxn.a.64
xxxxn.a.32
6110
6111
(c) Spectrum GmbH 45
Page 46

Programming Standard generation modes
Starting without interrupt (classic mode)
Command register
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_COMMAND 0 r/w Command register of the board.
SPC_START 10 Starts the board with the current register settings.
SPC_STOP 20 Stops the board manually.
In this mode the board is started by writing the SPC_START value to the command register. All settings like for example the size of memory
and postcounter, the number of activated channels and the trigger settings must have been programmed before. If the start command has
been given, the setup data is transferred to the board and the board will start.
If your board has relays to switch between different settings a programmed time will be waited to prevent having the influences of the relays
settling time in the signal. For additional information please first see the chapter about the relay settling time. You can stop the board at any
time with the command SPC_STOP. This command will stop immediately.
Once the board has been started, it is running totally independent from the host system. Your program has full CPU time to do any calculations
or display. The status register shown in the table below shows the current status of the board. The most simple programming loop is simply
waiting for the status SPC_READY. This status shows that the board has stopped automatically.
The read only status register can be read out at any time, but it is mostly used for polling on the board’s status after the board has been
started. However polling the status will need CPU time.
Status
register
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_STATUS 10 r Status register, of the board.
SPC_RUN 0 Indicates that the board has been started and is waiting for a triggerevent.
SPC_TRIGGER 10 Indicates that the board is running and a triggerevent has been detected.
SPC_READY 20 Indicates, that the board has stopped.
The following shortened excerpt of a sample program gives you an example of how to start the board in classic mode and how to poll for
the SPC_READY flag. It is assumed that all board setup has been done before.
// ----- start the board ----nErr = SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_COMMAND, SPC_START);
// Here you can check for driver errors as mentioned in the relating chapter
// ----- Wait for Status Ready (polling for SPC_READY in a loop) ----do
{
SpcGetParam (hDrv, SPC_STATUS, &lStatus);
}
while (lStatus != SPC_READY);
printf ("Board has stopped\n");
Starting with interrupt driven mode
In contrast to the classic mode, the interrupt mode has no need for polling for the board’s status. Starting your board in the interrupt driven
mode does in the main not differ from the classic mode. But there has to be done some additional programming to prevent the program from
hanging. The SPC_STARTANDWAIT command doesn’t return until the board has stopped. Big advantage of this mode is that it doesn’t waste
any CPU time for polling. The driver is just waiting for an interrupt and the System has full CPU time for other jobs. To benefit from this mode
it is necessary to set up a program with at least two different tasks: One for starting the board and to be blocked waiting for an interrupt. The
other one to make any kind of calculations or display activities.
Command register
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_COMMAND 0 r/w Command register, of the board.
SPC_STARTANDWAIT 11 Starts the board with the current register settings in the interrupt driven mode.
SPC_STOP 20 Stops the board manually.
If the board is started in the interrupt mode the task calling the start function will not return until the board
has finished. If no trigger event is found or the external clock is not present, this function will wait until the
program is terminated from the taskmanager (Windows) or from another console (Linux).
46 MI.61xx Manual
Page 47

Standard generation modes Programming
To prevent the program from this deadlock, a second task must be used which can send the SPC_STOP signal to stop the board. Another
possibility, that does not require the need of a second task is to define a timeout value.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_TIMEOUT 295130 r/w Defines a time in ms after which the function SPC_STARTANDWAIT terminates itself.
This is the easiest and safest way to use the interrupt driven mode. If the board started in the interrupts mode it definitely will not return until
either the recording has finished or the timeout time has expired. In that case the function will return with an error code. See the appendix
for details.
The following excerpt of a sample program gives you an example of how to start the board in the interrupt driven mode. It is assumed that
all board setup has been done before.
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_TIMEOUT, 1000); // Define the timeout to 1000 ms = 1 second
nErr = SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_COMMAND, SPC_STARTANDWAIT); // Starts the board in the interrupt driven mode
if (nErr == ERR_TIMEOUT) // Checks for the timeout
printf ("No trigger found. Timeout has expired.\n");
An example on how to get a second task that can do some monitoring on the running task and eventually send the SPC_STOP command can
be found on the Spectrum driver CD that has been shipped with your board. The latest examples can also be down loaded via our website
at http://www.spectrum-instrumentation.com.
Data organization
In standard mode tha data is organized on the board in two memory channels, named memory channel 0 and memory channel 1. The data
in memory is organized depending on the used channels and the type of board. This is a result of the internal hardware structure of the board.
Ch0 Ch1 Ch2 Ch3 Sample ordering in standard mode on memory channel 0 Sample ordering in standard mode on memory channel 1
X A0A1A2A3A4A5A6A7A8A9
X X A0 B0 A1 B1 A2 B2 A3 B3 A4 B4
X X A0A1A2A3A4A5A6A7A8A9B0 B1 B2 B3B4B5 B6 B7 B8 B9
X X X X A0 B0 A1 B1 A2 B2 A3 B3 A4 B4 C0 D0 C1 D1 C2 D2 C3 D3 C4 D4
The samples are re-named for better readability. A0 is sample 0 of channel 0, C4 is sample 4 of channel 2, ...
Writing data with SpcSetData
The function SpcSetData enables you to write data to the on-board memory before starting the generation. Depending on your operation
system, the function is called with a different amount of parameters. Please refer to the relating chapter earlier in this manual. The examples
in this section are written in Visual C++ for Windows, so the examples differ a little bit for the use with linux.
As the data is written individually for every memory channel, it is important to know where the data has to be stored. Please refer to the data
organization section, to get the information you need first.
The function SpcSetData has two parameters that allow you to write in any position of the replay memory. That can be very helpful if only
parts of the signal should be exchanged. However the user must make sure that the complete replay memory is filled with appropriate data.
The value ’start’ as a 32 bit integer value
This value defines the start of the memory area to be written in samples. This result is, that you do not need to care for the number of bytes a
single sample contains. If you want to write the whole memory at once this value must be set to 0.
The value ’len’ as a 32 bit integer value
This value defines the number of samples that are written, beginning with the first sample defined by the ’start’ value mentioned above. If you
want to write the whole on-board memory you need to set up that value to the memsize you have set the board up to before acquisition. This
memsize must be a total memsize for all channels that are generated from that memory channel. As a result that means if generating two
channels from memory channel 0 the „len“ value must be set to „2 * memsize“.
Multiplexed data
Depending on the activated channels and the board type several channels could be stored in one memory channel. As a result that means
that „start“ and „len“ parameter have to be multiplied by the number of channels per memory channel (module). If for example two channels
have are replayed from one memory channel a call like:
SpcSetData (hDrv, 0, 2 * 4096, 2 * 2048, Data);
writes data of both channels to memory channel 0 starting at sample position 4k and a length of 2k. The Data array must be of course hold
data of both channels (in that case 2 * 2k = 4k of data) multiplexed as shown above.
(c) Spectrum GmbH 47
Page 48

Programming Standard generation modes
Standard mode
Writing data to the memory is really easy, if a replay mode is used, that stores non multiplexed data in the dedicated memory channels. The
next example shows, how to write the data before replaying two channels without multiplexing to both memory channels.
for (i = 0; i < 2; i++) // both memory channels have been used
pbyData[i] = (ptr8) malloc (lMemsize); // allocate memory for the data pointers
// with the maximum size (lMemsize)
// generate or load data into pbyData[0..1]
SpcSetData (hDrv, 0, 0, lMemsize, (dataptr) pbyData[0]); // no multiplexing is necessary on channel 0
SpcSetData (hDrv, 1, 0, lMemsize, (dataptr) pbyData[1]); // neither it is on channel 1
If you use two channels for replay using only one memory channel, the data in the memory channel(s) has to be multiplexed and needs to be
sorted by the user. The following example shows how to sort the data for the replay of two channels using memory channel 0.
for (i = 0; i < 2; i++) // two channels to write to memory channel 0
pbyData[i] = (ptr8) malloc (lMemsize); // allocate memory for the data pointers
// with the maximum size (lMemsize) per channel
// generate or load data into pbyData[0..1]
pbyTmp = (ptr8) malloc (lMemsize * 2); // allocate temporary buffer for copy
for (i = 0; i < lMemsize; i++) // combine data of the two channels
{
pbyTmp[2*i] = pbyData[0][i];
pbyTmp[2*i+1] = pbyData[1][i];
}
SpcSetData (hDrv, 0, 0, 2 * lMemsize, (dataptr) pbyTmp); // write both channels to memory channel 0
free (pbyTmp); // free the temporary buffer
Sample format
The 8 bit samples in twos complement are always stored in memory 16 bit integer values. This leads to a range of possible integer values
from -128…0…+127.
Bit Standard Mode
D7 DAx Bit 7 (MSB)
D6 DAx Bit 6
D5 DAx Bit 5
D4 DAx Bit 4
D3 DAx Bit 3
D2 DAx Bit 2
D1 DAx Bit 1
D0 DAx Bit 0 (LSB)
48 MI.61xx Manual
Page 49

FIFO Mode Overview
FIFO Mode
Overview
General Information
The FIFO mode allows to record data continuously and transfer it online to the PC (acquisition boards) or allows to write
data continuously from the PC to the board (generation
boards). Therefore the on-board memory of the board is used
as a continuous buffer. On the PC the data can be used for
any calculation or can be written to hard disk while recording
is running (acquisition boards) or the data can be read from
hard disk and calculated online before writing it to the board.
FIFO mode uses interrupts and is supported by the drivers on 32 bit operating systems like Window 9x/ME, Windows NT/2000/XP or Linux.
Start of FIFO mode waits for a trigger event. If you wish to start FIFO mode immediately, you may use the software trigger.FIFO mode can
be used together with the options Multiple Recording/Replay and Gated Sampling/Replay. Details on this can be found in the appropriate
chapters about the options.
Background FIFO Write
On the hardware side the memory is split in two buffers of the same length. These buffers can be up to half of the on-board memory in size.
The driver holds up to 256 software buffers of the same length as the hardware buffers. Whenever a hardware buffer is empty and all data
replayed the hardware generates an interrupt and the driver transfers the next software buffer to the empty hardware buffer. The driver is
doing this job automatically in the background. After driver has finsihed transferring the data the application software gets a signal and can
generate data or load the next buffer from hard disk.
After processing the data the application software tells the driver that the data in the software buffer is valid and can again be used for data
generation. This two stages buffering has big advantages when running FIFO mode at the speed limit. The software buffers expand the generation time that can be buffered and protects the whole system against buffer underruns.
Speed Limitations
The FIFO mode is running continuously all the time. Therefore the data must be read out from the board (data acquisition) or written to the
board (data generation) at least with the same speed that it is recorded/replayed. If data is read out from the board or written to the board
more slowly, the hardware buffers will overrun at a certain point and FIFO mode is stopped.
One bottleneck with the FIFO mode is the PCI bus. The standard PCI bus is theoretically capable of transferring data with 33 MHz and 32
Bit. As a result a maximum burst transfer rate of 132 MByte per second can be achieved. As several devices can share the PCI bus this
maximum transfer rate is only available to a short transfer burst until a new bus arbitration is necessray. In real life the continuous transfer
rate is limited to approximately 100-110 MBytes per second. The maximum FIFO speed one can achieve heavily depends on the PC system
and the operating system and varies from system to system.
The maximum sample rate one can run in continuous FIFO mode depends on the number of activated channels:
(c) Spectrum GmbH 49
Page 50

Programming FIFO Mode
1 Channel 100 MS/s [1 Channel] x [1 Byte per sample] * 100 MS/s = 100 MB/s
2 Channels 50 MS/s [2 Channels] x [1 Byte per sample] * 50 MS/s = 100 MB/s
4 Channels 25 MS/s [4 Channels] x [1 Byte per sample] * 25 MS/s = 100 MB/s
8 Channels 12.5 MS/s [8 Channels] x [1 Byte per sample] * 12.5 MS/s = 100 MB/s
Theoretical maximum sample rate PCI Bus Throughput
When using FIFO mode together with one of the options that allow to have gaps in the generation like Multiple Replay or Gated Replay one
can even run the board with higher sample rates. It just has to be sure that the average sample rate (calculated with generation time and
gap) does not exceed the above mentioned sample rate limitations.
The sample rate that can be run in one of these mode is depending on the number of channels that have been activated. Due to the internal
structure of the board this is limited to a internal throughput of 250 MB/s (250 MS/s):
1 Channel 250 MS/s [1 Channel] x [1 Byte per sample] x 250 MS/s = 250 MB/s
2 Channels 125 MS/s [2 Channels] x [1 Byte per sample] x 125 MS/s = 250 MB/s
4 Channels 62.5 MS/s [4 Channels] x [1 Byte per sample] x 62.5 MS/s = 250 MB/s
8 Channels 31.25 MS/s [8 Channels] x [1 Byte per sample] x 31.25 MS/s = 250 MB/s
Maximum sample rate that can be programmed Internal throughput
Programming
The setup of FIFO mode is done with a few additional software registers described in this chapter. All the other settings can be used as described before. In FIFO mode the register SPC_MEMSIZE and SPC_POSTTRIGGER are not used.
Software Buffers
This register defines the number of software buffers that should be used for FIFO mode. The number of hardware buffers is always two and
can not be changed by software.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_FIFO_BUFFERS 60000 r/w Number of software buffers to be used for FIFO mode. Value has to be between 2 and 256
When this manual was printed there are a total of 256 buffers possible. However if there are changes and enhancements to the driver in the
future it will be informative to read out the number of buffers the new driver version can hold.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_FIFO_BUFADRCNT 60040 r Read out the number of available FIFO buffers
The length of each buffer is defined in bytes. This length is used for hardware and software buffers as well. Both have the same length. The
maximum length that can be used is depending on the installed on-board memory.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_FIFO_BUFLEN 60010 r/w Length of each buffer in bytes. Must be a multiple of 1024 bytes.
Each FIFO buffer can be a maximum of half the memory. Be aware that the buffer length is given in overall bytes not in samples. Therefore
the value has to be calculated depending on the activated channels and the resolution of the board:
50 MI.61xx Manual
Page 51

FIFO Mode Programming
Analog acquisition or generation boards
1 Channel 1 x [Samples in Buffer] 1 x 2 x [Samples in Buffer] 1 x 2 x [Samples in Buffer] 1 x 2 x [Samples in Buffer]
8 bit resolution 12 bit resolution 14 bit resolution 16 bit resolution
2 Channels 2 x [Samples in Buffer] 2 x 2 x [Samples in Buffer] 2 x 2 x [Samples in Buffer] 2 x 2 x [Samples in Buffer]
4 Channels 4 x [Samples in Buffer] 4 x 2 x [Samples in Buffer] 4 x 2 x [Samples in Buffer] 4 x 2 x [Samples in Buffer]
8 Channels 8 x [Samples in Buffer] 8 x 2 x [Samples in Buffer] 8 x 2 x [Samples in Buffer] 8 x 2 x [Samples in Buffer]
Buffer length to be programmed in Bytes
Digital I/O (701x or 702x ) or pattern generator boards (72xx)
8 bit mode 16 bit mode 32 bit mode 64 bit mode
[Samples in Buffer] 2 x [Samples in Buffer] 4 x [Samples in Buffer] 8 x [Samples in Buffer]
Buffer length to be programmed in Bytes
Digital I/O board 7005 only
1 Channel 1/8 x [Samples in Buffer] 1/4 x [Samples in Buffer] 1/2 x [Samples in Buffer] [Samples in Buffer] 2 x [Samples in Buffer]
1 bit mode 2 bit mode 4 bit mode 8 bit mode 16 bit mode
Buffer length to be programmed in Bytes
We at Spectrum achieved best results when programming the buffer length to a number of samples that can hold approximately 100 ms of
data. However if going to the limit of the PCI bus with the FIFO mode or when having buffer overruns it can be useful to have larger FIFO
buffers to buffer more data in it.
When the goal is a fast update in FIFO mode smaller buffers and a larger number of buffers can be a better setup.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_FIFO_BUFADR0 60100 r/w 32 bit address of FIFO buffer 0. Must be allocated by application program
SPC_FIFO_BUFADR1 60101 r/w 32 bit address of FIFO buffer 1. Must be allocated by application program
... ...
SPC_FIFO_BUFADR255 60355 r/w 32 bit address of FIFO buffer 255. Must be allocated by application program
The driver handles the programmed number of buffers. To speed up FIFO transfer the driver uses buffers that are allocated and maintained
by the application program. Before starting the FIFO mode the addresses of the allocated buffers must be set to the driver.
Example of FIFO buffer setup. No memory allocation error checking in the example to improve readability:
// ----- setup FIFO buffers ---- SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_FIFO_BUFFERS, 64); // 64 FIFO buffers used in the example
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_FIFO_BUFLEN, 8192); // Each FIFO buffer is 8 kBytes long
// ----- allocate memory for data ---- for (i = 0; i < 64; i++)
pnData[i] = (ptr16) malloc (8192); // memory allocation for 12, 14, 16 bit analog boards
// and digital boards
// pbyData[i] = (ptr8) malloc (8192); // memory allocation for 8 bit analog boards
// ----- tell the used buffer adresses to the driver ---- for (i = 0; i < 64; i++)
nErr = SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_FIFO_BUFADR0 + i, (int32) pnData[i]); // for 12, 14, 16 bit analog boards
// and digital boards only
// nErr = SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_FIFO_BUFADR0 + i, (int32) pbyData[i]); // for 8 bit analog boards only
Buffer processing
The driver counts all the software buffers that have been transferred. This number can be read out from the driver to know the exact amount
of data that has been transferred.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_FIFO_BUFCOUNT 60020 r Number of transferred buffers until now
If one knows before starting FIFO mode how long this should run it is possible to program the numer of buffers that the driver should process.
After transferring this number of buffer the driver will automatically stop. If FIFO mode should run endless a zero must be programmed to this
register. Then the FIFO mode must be stoped by the user.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_FIFO_BUFMAXCNT 60030 r/w Number of buffers to be transferred until automatic stop. Zero runs endless
(c) Spectrum GmbH 51
Page 52

Programming FIFO Mode
FIFO mode
In normal applications the FIFO mode will run in a loop and process one buffer after the other. There are a few special commands and registers for the FIFO mode:
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_COMMAND 0 w Command register. Allowed values for FIFO mode are listed below
SPC_FIFOSTART 12 Starts the FIFO mode and waits for the first interrupt
SPC_FIFOWAIT 13 Waits for the next buffer interrupt
SPC_STOP 20 Stops the FIFO mode
The start command and the wait command both wait for the signal from the driver that the next buffer has to be processed. This signal is
generated by the driver on receiving an interrupt from the hardware. While waiting none of these commands waiste cpu power (no polling
mode). If for any reason the signal is not coming from the hardware (e.g. trigger is not found) the FIFO mode must be stopped from a second
task with a stop command.
This handshake command tells the driver that the application has finished it’s work with the software buffer. The both commands
SPC_FIFOWAIT (SPC_FIFOSTART) and SPC_FIFO_BUFFERS form a simple but powerful handshake protocol between application software
and board driver.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_FIFO_BUFREADY 60050 w FIFO mode handshake. Application has finsihed with that buffer. Value is index of buffer
Backward compatibility: This register replaces the formerly known SPC_FIFO_BUFREADY0 ...
SPC_FIFO_BUFREADY15 commands. It has the same functionality but can handle more FIFO buffers. For back-
ward compatibility the older commands still work but are still limited to 16 buffers.
Example FIFO generation mode
This example shows the main loop of a FIFO generation. The example is a part of the FIFO examples that are available for each board on
CD. The example simply calls a routine for output data calculation and counts the buffers that has been processed.
FIFO generation example:
// ----- fill the first buffers with data ---- for (i=0; i<MAX_BUF; i++)
vCalcOutputData (pnData[i], BUFSIZE);
// ----- start the board ---- nBufIdx = 0;
lCommand = SPC_FIFOSTART;
lBufCount = 0;
printf ("Start\n");
do
{
nErr = SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_COMMAND, lCommand);
lCommand = SPC_FIFOWAIT;
// ----- driver requests next buffer: calculate it or load if from disk ---- printf ("Buffer %d\n", lBufCount);
vCalcOutputData (pnData[nBufIdx], BUFSIZE);
// ----- buffer is ready ---- SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_FIFO_BUFREADY, nBufIdx);
// ----- next Buffer ---- lBufCount++;
nBufIdx++;
if (nBufIdx == MAX_BUF)
nBufIdx = 0;
}
while (nErr == ERR_OK);
Before starting the FIFO output all software buffers must be filled once with data. The driver immediately
transfers data to the hardware after receiving the start command.
Data organization
When using FIFO mode data in memory is organized in some cases a little bit different then in standard mode. This is a result of the internal
hardware structure of the board. The organization of data is depending on the activated channels:
Ch0 Ch1 Ch2 Ch3 Sample ordering in FIFO buffer
X A0A1A2A3A4A5A6A7A8A9A10A11A12A13A14A15A16A17A18A19
X X A0 B0 A1 B1 A2 B2 A3 B3 A4 B4 A5 B5 A6 B6 A7 B7 A8 B8 A9 B9
52 MI.61xx Manual
Page 53

FIFO Mode Programming
Ch0 Ch1 Ch2 Ch3 Sample ordering in FIFO buffer
X X A0B0A1B1A2B2A3B3A4B4A5B5A6B6A7B7A8B8A9B9
X X X X A0 C0 B0 D0 A1 C1 B1 D1 A2 C2 B2 D2 A3 C3 B3 D3 A4 C4 B4 D4
The samples are re-named for better readability. A0 is sample 0 of channel 0, C4 is sample 4 of channel 2, ...
The following example shows how to sort the channel data when using 4 channels in FIFO mode:
for (i = 0; i < lBufferSizeInSamples; i+=4)
{
FIFOBuffer[i + 0] = Data[0][i/4];
FIFOBuffer[i + 2] = Data[1][i/4];
FIFOBuffer[i + 1] = Data[2][i/4];
FIFOBuffer[i + 3] = Data[3][i/4];
}
Sample format
The sample format in FIFO mode does not differ from the one of the standard (non FIFO) mode. Please refer to the relating passage concerning
the sample format in the standard acquisition chapter.
(c) Spectrum GmbH 53
Page 54

Overview Clock generation
Clock generation
Overview
The Spectrum boards offer a wide variety of different clock modes to match all the customers needs. All the clock modes are described in
detail with programming examples below. This chapter simply gives you an overview which clock mode to select:
Standard internal sample rate
PLL with internal 40 MHz reference. This is the easiest way to generate a sample rate with no need for additional external clock signals. The
sample rate has a fine resolution.
Quartz and divider
Internal quarz clock with divider. For applications that need a lower clock jitter than the PLL produces. The possible sample rates are restricted
to the values of the divider.
External reference clock
PLL with external 1 MHz to 125 MHz reference clock. This provides a very good clock accuracy if a stable external reference clock is used.It
also allows the easy synchronization with an external source.
External clock
Any clock can be fed in that matches the specification of the board. The external clock signal can be used to synchronize the board on a
system clock or to feed in an exact matching sample rate.
External clock with divider
The externally fed in clock can be divided to generate a low-jitter sample rate of a slower speed than the external clock available.
There is a more detailed description of the clock generation part available as an application note. There some
more background information and details of the internal structure are explained.
Internally generated sample rate
Standard internal sample rate
The internal sample rate is generated in default mode by a PLL and dividers out of an internal 40 MHz frequency reference. In most cases
the user does not need to care on how the desired sample rate is generated by multiplying and dividing internally. You simply write the
desired sample rate to the according register shown in the table below. If you want to make sure the sample rate has been set correctly you
can also read out the register and the driver will give you back the sample rate that is matching your desired one best.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_SAMPLERATE 20000 w Defines the sample rate in Hz for internal sample rate generation.
r Read out the internal sample rate that is nearest matching to the desired one.
If a sample rate is generated internally, you can additionally enable the clock output. The clock will be available on the external clock connector and can be used to synchronize external equipment with the board.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_EXTERNOUT 20110 r/w Enables the clock output on the external clock connector. Only possible with internal clocking.
Example on writing and reading internal sample rate
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_SAMPLERATE, 1000000); // Set internal sample rate to 1 MHz
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_EXTERNOUT, 1); // enable the clock output of that 1 MHz
SpcGetParam (hDrv, SPC_SAMPLERATE, &lSamplerate); // Read back the sample rate that has been programmed
printf („Samplerate = %d\n“, lSamplerate); // print it. Output should be „Samplerate = 1000000“
Minimum internal sample rate
The minimum internal sample rate is limited on all boards to 1 kHz and the maximum sample rate depends on the specific type of board. The
maximum sample rates for your type of board are shown in the tables below.
54 MI.61xx Manual
Page 55

Clock generation Internally generated sample rate
Maximum internal sample rate in MS/s normal (non FIFO) mode
Remapped channels
ch0 ch1 ch2 ch3
x 125 125
x x 125 125
xxn.a.125
xxxxn.a.125
6110
6111
Maximum internal sample rate in MS/s in FIFO mode
Remapped channels
ch0 ch1 ch2 ch3
x 125 125
x x 125 125
xxn.a.125
xxxxn.a.60
6110
6111
Using plain quartz with no PLL
In some cases it is useful for the application not to have the on-board PLL activated. Although the PLL used on the Spectrum boards is a lowjitter version it still produces more clock jitter than a plain quartz oscillator. For these cases the Spectrum boards have the opportunity to switch
off the PLL by software and use a simple clock divider.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_PLL_ENABLE 20030 r/w A „1“ enables the PLL mode (default) or disables it by writing a 0 to this register
The sample rates that could be set are then limited to the quartz speed divided by one of the below mentioned dividers. The quartz used on
the board is similar to the maximum sample rate the board can achieve. As with PLL mode it’s also possible to set a desired sample rate and
read it back. The result will then again be the best matching sample rate.
Available divider values
1 2 4 8 101620405080100200
400 500 800 1000 2000
External reference clock
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_REFERENCECLOCK 20140 r/w Programs the external reference clock in the range from 1 MHz to 125 MHz.
0 Internal reference is used for internal sample rate generation.
External sample rate in Hz as an integer value External reference is used. You need to set up this register exactly to the frequency of the external fed in clock.
If you have an external clock generator with a extremly stable frequency, you can use it as a reference clock. You can connect it to the external
clock connector and the PLL will be fed with this clock instead of the internal reference. Due to the fact that the driver needs to know the
external fed in frequency for an exact calculation of the sample rate you must set the the SPC_REFERENCECLOCK register accordingly. The
driver automatically sets the PLL to achieve the desired sample rate. Therefore it examines the reference clock and the sample rate registers.
Example of reference clock:
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_EXTERNAL, 0); // Set to internal clock
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_REFERENCECLOCK, 10000000); // Reference clock that is fed in is 10 MHz
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_SAMPLERATE, 25000000); // We want to have 25 MHz as sample rate
Termination of the clock input
If the external connector is used as an input, either for feeding in an external reference clock or for external clocking you can enable a 50
Ohm termination on the board. If the termination is disabled, the impedance is 1 Megaohm. Please make sure that your source is capable
of driving that current and that it still fulfills the clock input specification as given in the technical data section.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_CLOCK50OHM 20120 r/w A „1“ enables the 50 Ohm termination at the external clock connector. Only possible, when using
the external connector as an input.
External clocking
(c) Spectrum GmbH 55
Page 56

Internally generated sample rate Clock generation
Direct external clock
An external clock can be fed in on the external clock connector of the board. This can be any clock, that matches the specification of the
board. The external clock signal can be used to synchronize the board on a system clock or to feed in an exact matching sample rate.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_EXTERNALCLOCK 20100 r/w Enables the external clock input. If external clock input is disabled, internal clock will be used.
The maximum values for the external clock is board dependant and shown in the table below.
Termination of the clock input
If the external connector is used as an input, either for feeding in an external reference clock or for external clocking you can enable a 50
Ohm termination on the board. If the termination is disabled, the impedance is 1 Megaohm. Please make sure that your source is capable
of driving that current and that it still fulfills the clock input specification as given in teh technical data section.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_CLOCK50OHM 20120 r/w A „1“ enables the 50 Ohm termination at the external clock connector. Only possible, when using
Minimum external sample rate
The minimum external sample rate is limited on all boards to 1 MHz and the maximum sample rate depends on the specific type of board.
The maximum sample rates for your type of board are shown in the tables below.
Maximum external samplerate in MS/s
the external connector as an input.
Remapped channels
ch0 ch1 ch2 ch3
x 125 125
x x 125 125
xxn.a.125
xxxxn.a.125
6110
6111
An external sample rate above the mentioned maximum can cause damage to the board.
Ranges for external sample rate
Due to the internal structure of the board it is essential to know for the driver in which clock range the external clock is operating. The external
range register must be set according to the clock that is fed in externally.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_EXTERNRANGE 20130 r/w Defines the range of the actual fed in external clock. Use one of the below mentioned ranges
EXRANGE_SINGLE 2 External Range Single
EXRANGE_BURST_S 4 External Range Burst S
EXRANGE_BURST_M 8 External Range Burst M
EXRANGE_BURST_L 16 External Range Burst X
EXRANGE_BURST_XL 32 External Range Burst XL
The range must not be left by more than 5 % when the board is running. Remember that the ranges depend
on the activated channels as well, so a different board setup for external clocking must always include the
related clock ranges.
This table below shows the ranges that are defined by the different range registers mentioned above. The range depends on the activated
channels and the mode the board is used in. Please be sure to select the correct range. Otherwise it is possible that the board will not run
properly.
ch0 ch1 ch2 ch3 Mode EXRANGE_SINGLE EXRANGE_BURST_S EXRANGE_BURST_M EXRANGE_BURST_L EXRANGE_BURST_XL
X Standard/FIFO < 10 MHz 10 MHz up to max
X X Standard/FIFO < 5 MHz 5 MHz up to max
X X Standard/FIFO < 10 MHz 10 MHz up to max
X X X X Standard only < 5 MHz 5 MHz up to max
X X X X FIFO < 2.5 MHz 2.5 MHz up to 7.5 MHz 7.5 MHz up to 17.5 MHz 17.5 MHz up to 36 MHz > 36 MHz
How to read this table? If you have activated all four channels and are using the board in FIFO mode and your external clock is known to
be around 5 MHz you have to set the EXRANGE_BURST_S for the external range.
56 MI.61xx Manual
Page 57

Clock generation Internally generated sample rate
Example:
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_CHENABLE, CHANNEL0 | CHANNEL1 | CHANNEL2 | CHANNEL3); // activate all 4 channels
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_EXTERNALCLOCK, 1); // activate external clock
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_EXTERNRANGE, EXRANGE_BURST_M); // set external range to Burst M
External clock with divider
The extra clock divider can be used to divide an external fed in clock by a fixed value. The external clock must be > 1 MS/s. This divided
clock is used as a sample clock for the board.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_CLOCKDIV 20040 r/w Extra clock divider for external samplerate. Allowed values are listed below
Available divider values
1 2 4 8 101620405080100200
400 500 800 1000 2000
The clock divider is also used by internal clock generation for all clock rates that are below 1 MS/s sum sample rate per module. If internal clock divider and extra clock divider are used together the resulting clock
divider is one value of the above listed. The driver searches for the best matching divider. Read out the register after all sample rate registers are set to receive the resulting extra clock divider. For correct setting of the clock
divider the sample rate and channel enable information must be set before the clock divider is programmed.
(c) Spectrum GmbH 57
Page 58

General Description Trigger modes and appendant registers
Trigger modes and appendant registers
General Description
Concerning the trigger modes of the Spectrum MI, MC and MX D/A boards, you can choose between three external TTL trigger modes and
one internal software trigger. This chapter is about to explain the different trigger modes and setting up the board’s registers for the desired
mode. Every analog Spectrum board has one dedicated SMB connector mounted in it’s bracket for feeding in an external trigger signal or
outputting a trigger signal of an internal trigger event. As only one connector is available for external trigger I/O, it is not possible to forward
the external trigger signal that is fed in to another board. If this is necessary, you need to first split up the external trigger signal.
Software trigger
The software trigger is the easiest way of triggering any Spectrum
board. The acquisition or replay of data will start immediately after starting the board. The only delay results from the time the
board needs for its setup.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_TRIGGERMODE 40000 r/w Sets the triggermode for the board.
TM_SOFTWARE 0 Sets the trigger mode to software, so that the recording/replay starts immediately.
In addition to the softwaretrigger (free run) it is also possible to force a triggerevent by software while the board is waiting for an internal or
external trigger event. Therefore you can use the board command shown in the following table.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_COMMAND 0 r/w Command register of the board.
SPC_FORCETRIGGER 16 Forces a trigger event if the hardware is still waiting for a trigger event. Needs a base board hardware version > 7.x.
Due to the fact that the software trigger is an internal trigger mode, you can optionally enable the external trigger output to generate a high
active trigger signal, which indicates when the data acquisition or replay begins. This can be useful to synchronize external equipment with
your Spectrum board.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_TRIGGEROUT 40100 r/w Defines the data direction of the external trigger connector.
0 The trigger connector is not used and the line driver is disabled.
1 The trigger connector is used as an output that indicates a detected internal trigger event.
Example for setting up the software trigger:
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_TRIGGERMODE, TM_SOFTWARE); // Internal software trigger mode is used
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_TRIGGEROUT , 1 ); // And the trigger output is enabled
External TTL trigger
Enabling the external trigger input is performed by one of the following external trigger modes. The dedicated register for that operation is
shown below.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_TRIGGERMODE 40000 r/w
TM_TTLPOS 20000 Sets the trigger mode for external TTL trigger to detect positive edges.
TM_TTLNEG 20010 Sets the trigger mode for external TTL trigger to detect negative edges
TM_TTLBOTH 20030 Sets the trigger mode for external TTL trigger to detect positive and negative edges
If you choose an external trigger mode the SPC_TRIGGEROUT register will be overwritten and the trigger connector will be used as an input
by default.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_TRIGGEROUT 40100 r/w Defines the data direction of the external trigger connector.
X If external triggermodes are used, this register will have no effect.
58 MI.61xx Manual
Page 59

Trigger modes and appendant registers External TTL trigger
As the trigger connector is used as an input, you can decide whether the input is 50 Ohm terminated or not. If you enable the termination,
please make sure, that your trigger source is capable to deliver the desired current. If termination is disabled, the input is at high impedance.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_TRIGGER50OHM 40110 r/w Sets the 50 Ohm termination, if the trigger connector is used as an input for external trigger signals.
The following short example shows how to set up the board for external positive edge TTL trigger. The trigger input is 50 Ohm terminated.
The different modes for external TTL trigger are to be detailed described in the next few passages.
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_TRIGGERMODE , TM_TTLPOS); // External positive TTL edge trigger
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_TRIGGER50OHM, 1 ); // and the 50 Ohm termination of the trigger input are used
Edge triggers
Positive TTL trigger
This mode is for detecting the rising edges of an external TTL signal. The board will trigger on the first rising edge that is detected after starting the board. The next triggerevent will then be
detected, if the actual recording/replay has finished and the
board is armed and waiting for a trigger again.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_TRIGGERMODE 40000 r/w Sets the triggermode for the board
TM_TTLPOS 20000 Sets the trigger mode for external TTL trigger to detect positive edges
Example on how to set up the board for positive TTL trigger:
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_TRIGGERMODE, TM_TTLPOS); // Setting up external TTL trigger to detect positive edges
Negative TTL trigger
This mode is for detecting the falling edges of an external TTL signal. The board will trigger on the first falling edge that is detected after starting the board. The next triggerevent will then be
detected, if the actual recording/replay has finished and the
board is armed and waiting for a trigger again.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_TRIGGERMODE 40000 r/w Sets the triggermode for the board.
TM_TTLNEG 20010 Sets the trigger mode for external TTL trigger to detect negative edges.
(c) Spectrum GmbH 59
Page 60

External TTL trigger Trigger modes and appendant registers
Positive and negative TTL trigger
This mode is for detecting the rising and falling edges of an external TTL signal. The board will trigger on the first rising or falling
edge that is detected after starting the board. The next triggerevent will then be detected, if the actual recording/replay has finished and the board is armed and waiting for a trigger again.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_TRIGGERMODE 40000 r/w Sets the triggermode for the board.
TM_TTLBOTH 20030 Sets the trigger mode for external TTL trigger to detect positive and negative edges.
60 MI.61xx Manual
Page 61

Option Multiple Replay Output modes
Option Multiple Replay
The option Multiple Replay allows the generation of data blocks with multiple trigger events without restarting the hardware. The on-board
memory will be divided into several segments of the same size. Each segment will be replayed when a trigger event occures.
Output modes
Standard Mode
With every detected trigger event one data block is replayed. The length of one Multiple Replay segment is set by the value of the posttrigger
register. The total amount of samples to be replayed is defined by the memsize register.
In most cases memsize will be set to a a multiple of the segment size (postcounter). The table below shows the register for enabling Multiple
Replay. For detailed information on how to setup and start the standard replay mode please refer to the according chapter earlier in this
manual.
Multiple Replay is not compatible with continuous output.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_MULTI 220000 r/w Enables Multiple Replay mode.
SPC_MEMSIZE 10000 r/w Defines the total amount of samples to be replayed.
SPC_POSTTRIGGER 10100 r/w Defines the size of one Multiple Replay segment.
FIFO Mode
The Multiple Replay in FIFO Mode is similar to the Multiple
Replay in Standard Mode. The segment size is also set by
the postcounter register.
In contrast to the Standard mode you cannot programm a
certain total amount of samples to be replayed. The generation is running until the user stops it. The data is transfered
FIFO block by FIFO block by the driver to the board. These
blocks can be online generated by the user program. This
mode significantly reduces the average data transfer rate
on the PCI bus. This enables you to use faster sample rates then you would be able to in FIFO mode without Multiple Replay.Usually the FIFO
blocks are multiples of the Multiple Replay segments.
The advantage of Multiple Replay in FIFO mode is that you can stream data online from the host system to the board, so you can replay a
huge amount of data from the hard disk. The table below shows the dedicated register for enabling Multiple Replay. For detailed information
how to setup and start the board in FIFO mode please refer to the according chapter earlier in this manual.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_MULTI 220000 r/w Enables Multiple Replay mode.
SPC_POSTTRIGGER 10100 r/w Defines the size of one Multiple Replay segment.
Trigger modes
In Multiple Replay mode all of the board’s trigger modes
are available except the software and pattern trigger. Depending on the different trigger modes, the chosen sample
rate, used channels and activated board synchronization,
(see relevant chapter for details about synchronizing multiple boards) there are different delay times between the trigger event and the first replayed data (see figure).
This internal delay is necessary as the board is equipped
with dynamic RAM, which needs refresh cycles to keep the
data in memory when the board is not replaying.
The delay is fixed for a certain board setup. All possible
delays in samples between the trigger event and the first replayed sample are listed in the table below.
The patterntrigger modes of digital I/O boards cannot be used with multiple replay.
(c) Spectrum GmbH 61
Page 62

Trigger modes Option Multiple Replay
Resulting start delays
Sample rate Output Mode Activated channels external TTL trigger ext. TTL trigger with activated
0 1 2 3
< 5 MHz Standard or FIFO x 8 samples 10 samples
> 5 MHz Standard or FIFO x 24 samples 26 samples
< 2.5 MHz Standard or FIFO x x 5 samples 6 samples
> 2.5 MHz Standard or FIFO x x 14 samples 15 samples
< 5 MHz Standard x x 8 samples 10 samples
> 5 MHz Standard x x 24 samples 26 samples
< 2.5 MHz FIFO x x 5 samples 6 samples
> 2.5 MHz FIFO x x 14 samples 15 samples
< 2.5 MHz Standard x x x x 5 samples 6 samples
> 2.5 MHz Standard x x x x 14 samples 15 samples
< 1.25 MHz FIFO x x x x 3.5 samples (falling clock edge) 3.5 samples (falling clock edge)
> 1.25 MHz FIFO x x x x 8.5 samples (falling clock edge) 8.5 samples (falling clock edge)
synchronization
The following example shows how to set up the board for Multiple Replay in standard mode. The setup would be similar in FIFO mode, but
the memsize register would not be used.
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_MULTI, 1); // Enables Multiple Replay
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_POSTTRIGGER, 1024); // Set the segment size to 1024 samples
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_MEMSIZE, 4096); // Set the total memsize for replaying to 4096 samples
// so that actually four segments will be replayed
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_TRIGGERMODE, TM_TTLPOS); // Set the triggermode to external TTL mode (rising edge)
62 MI.61xx Manual
Page 63

Option Gated Replay Output modes
Option Gated Replay
The option Gated Replay allows the data generation controlled by an external gate signal. Data will only be output, if the programmed gate
condition is true.
Output modes
Standard Mode
Data will be replayed as long as the gate signal fulfills the gate
condition that has had to be programmed before. At the end of
the gate interval the replay will be stopped and the board will
pause until another gates condition is detected. If the total
amount of data to replay has been reached the board stops immediately (see figure). The total amount of samples to be replayed can be defined by the memsize register.
The table below shows the register for enabling Gated Replay.
For detailed information on how to setup and start the standard
generation mode please refer to the relevant chapter earlier in
this manual.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_GATE 220400 r/w Enables Gated Replay mode.
SPC_MEMSIZE 10000 r/w Defines the total amount of samples to replay.
FIFO Mode
The Gated Replay in FIFO Mode is similar to the Gated Replay
in Standard Mode. In contrast to the Standard mode you cannot
program a certain total amount of samples to be replayed. The
generation is running until the user stops it. The data is transfered
to the board FIFO block by FIFO block by the driver. These
blocks can be online generated by the user program.
The advantage of Gated Replay in FIFO mode is that you can
stream data online from the host system to the board, so you can
replay a huge amount of data from the hard disk with a lower
average data rate than in conventional FIFO mode. The table below shows the dedicated register for enabling Gated Replay. For
detailed information how to setup and start the board in FIFO mode please refer to the according chapter earlier in this manual.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_GATE 220400 r/w Enables Gated Replay mode.
Trigger modes
General information and trigger delay
Not all of the board’s trigger modes can be used in combination with Gated Replay. All possible trigger modes are listed below. Depending on the different trigger modes, the
chosen sample rate, the used channels and activated board
synchronization (see according chapter for details about
synchronizing multiple boards) there are different delay
times between the trigger event and the first replayed sample(see figure). This start delay is necessary as the board is
equipped with dynamic RAM, which needs refresh cycles to
keep the data in memory when the board is not replaying.
It is fix for a certain board setup.
All possible start delays in samples between the trigger
event and the first replayed sample are listed in the table
below.
(c) Spectrum GmbH 63
Page 64

Example program Option Gated Replay
Due to the structure of the on-board memory there is
another delay at the end of the gate interval.
Internally a gate-end signal can only be recognized at
an eight samples alignment.
So depending on what time your external gate signal
will leave the programmed gate condition it might happen that at maximum seven more samples are replayed,
before the board pauses (see figure).
The figure on the right is showing this end delay exemplarily for three possible gate signals. As all samples are
counted from zero. The eight samples alignment in the
upper two cases is reached at the end of sample 39,
which is therefore the 40th sample.
Resulting start delays
Sample rate Output Mode Activated channels external TTL trigger ext. TTL trigger with activated
0 1 2 3
< 5 MHz Standard or FIFO x 8 samples 10 samples
> 5 MHz Standard or FIFO x 24 samples 26 samples
< 2.5 MHz Standard or FIFO x x 5 samples 6 samples
> 2.5 MHz Standard or FIFO x x 14 samples 15 samples
< 5 MHz Standard x x 8 samples 10 samples
> 5 MHz Standard x x 24 samples 26 samples
< 2.5 MHz FIFO x x 5 samples 6 samples
> 2.5 MHz FIFO x x 14 samples 15 samples
< 2.5 MHz Standard x x x x 5 samples 6 samples
> 2.5 MHz Standard x x x x 14 samples 15 samples
< 1.25 MHz FIFO x x x x 3.5 samples (falling clock edge) 3.5 samples (falling clock edge)
1.25 MHz FIFO x x x x 8.5 samples (falling clock edge) 8.5 samples (falling clock edge)
>
synchronization
Allowed trigger modes
As mentioned above not all of the possible trigger modes can be used as a gate condition. The following table is showing the allowed trigger modes that can be used and explains the event that has to be detected for gate-start end for gate-end.
External TTL edge trigger
Mode Gate start will be detected on Gate end will be detected on
TM_TTLPOS positive edge on external trigger negative edge on external trigger
TM_TTL_NEG negative edge on external trigger positive edge on external trigger
Example program
The following example shows how to set up the board for Gated Replay in standard mode. The setup would be similar in FIFO mode, but the
memsize register would not be used.
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_GATE, 1); // Enables Gated Repaly
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_MEMSIZE, 4096); // Set the total memsize of generation to 4096 samples
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_TRIGGERMODE, TM_TTLPOS); // Sets the gate condition to external TTL mode, so that
// data is replayed, if the signal is at HIGH level
64 MI.61xx Manual
Page 65

Option Extra I/O Digital I/Os
Option Extra I/O
Digital I/Os
With this simple-to-use enhancement it is possible to control a wide range of external instruments or other equipment. Therefore you have
several digital I/Os and the 4 analog outputs available. All extra I/O lines are completely independent from the board’s function, data direction or sample rate and directly controlled by software (asynchronous I/Os).
The extra I/O option is useful if an external amplifier should be controlled, any kind of signal source must be programmed, an antenna must
be adjusted, a status information from external machine has to be obtained or different test signals have to be routed to the board.
It is not possible to use this option together with the star hub or timestamp option, because there is just space
for one piggyback module on the on-board expansion slot.
Channel direction
Option -XMF (external connector)
The additional inputs and outputs are mounted on an extra bracket.
The direction of the 24 available digital lines can be programmed for every group of eight lines. The table below shows the direction register
and the possible values. To combine the values so simply have to OR them bitwise.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_XIO_DIRECTION 47100 r/w Defines bytewise the direction of the digital I/O lines. The values can be combined by a bitwise OR.
XD_CH0_INPUT 0 Sets the direction of channel 0 (bit D7…D0) to input.
XD_CH1_INPUT 0 Sets the direction of channel 1 (bit D15…D8) to input.
XD_CH2_INPUT 0 Sets the direction of channel 2 (bit D23…D16) to input.
XD_CH0_OUTPUT 1 Sets the direction of channel 0 (bit D7…D0) to output.
XD_CH1_OUTPUT 2 Sets the direction of channel 1 (bit D15…D8) to output.
XD_CH2_OUTPUT 4 Sets the direction of channel 2 (bit D23…D16) to output.
Option -XIO
(internal connector)
The additional inputs and outputs are available through an internal connector directely on the extra I/O piggiback module.
The direction of the 16 available digital lines can be programmed for every group of eight lines. The table below shows the direction register
and the possible values. To combine the values so simply have to OR them bitwise.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_XIO_DIRECTION 47100 r/w Defines bytewise the direction of the digital I/O lines. The values can be combined by a bitwise OR.
XD_CH0_INPUT 0 Sets the direction of channel 0 (bit D7…D0) to input.
XD_CH1_INPUT 0 Sets the direction of channel 1 (bit D15…D8) to input.
XD_CH0_OUTPUT 1 Sets the direction of channel 0 (bit D7…D0) to output.
XD_CH1_OUTPUT 2 Sets the direction of channel 1 (bit D15…D8) to output.
Transfer Data
The outputs can be written or read by a single 32 bit register. If the register is read, the actual pin data will be taken. Therefore reading the
data of outputs gives back the generated pattern. The single bits of the digital I/O lines correspond with the bitnumber of the 32 bit register.
Values written to the most significant byte will be ignored.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_XIO_DIGITALIO 47110 r Reads the data directly from the pins of all digital I/O lines either if they are declared as inputs or
SPC_XIO_DIGITALIO 47110 w Writes the data to all digital I/O lines that are declared as outputs. Bytes that are declared as inputs
outputs.
will ignore the written data.
(c) Spectrum GmbH 65
Page 66

Analog Outputs Option Extra I/O
Analog Outputs
In addition to the digital I/Os there are four analog outputs available. These outputs are directly programmed with the voltage values in mV.
As the analog outputs are driven by a 12 bit DAC, the output voltage can be set in a stepsize of 5 mV. The table below shows the registers,
you must write the desired levels too. If you read these outputs, the actual output level is given back from an internal software register.
Register Value Direction Description Offset range
SPC_XIO_ANALOGOUT0 47120 r/w Defines the output value for the analog output A0. ± 10000 mV in steps of 5 mV
SPC_XIO_ANALOGOUT1 47121 r/w Defines the output value for the analog output A1. ± 10000 mV in steps of 5 mV
SPC_XIO_ANALOGOUT2 47122 r/w Defines the output value for the analog output A2. ± 10000 mV in steps of 5 mV
SPC_XIO_ANALOGOUT3 47123 r/w Defines the output value for the analog output A3. ± 10000 mV in steps of 5 mV
After programming the levels of all analog outputs by the registers above, you have to update the analog outputs. This is done by the register
shown in the table below. To update all of the outputs all you need to do is write a “1“ to the dedicated register.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_XIO_WRITEDACS 47130 w All the analog outputs are simultaniously updated by the programmed levels if a “1“ is written.
Programming example
The following example shows how to use either the digital I/O#s and the analog outputs.
// ----- output 8 bit on D7 to D0 and read 8 bit on D15 to D8 ----SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_XIO_DIRECTION, XD_CH0_OUTPUT | XD_CH1_INPUT); // set directions of digital I/O transfer
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_XIO_DIGITALIO, 0x00005A); // write data to D7-D0
SpcGetParam (hDrv, SPC_XIO_DIGITALIO, &lData); // read data and write values to lData
// ----- write some values to the analog channels. ----SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_XIO_ANALOGOUT0, -2000); // -2000 mV = -2.0 V
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_XIO_ANALOGOUT1, 0); // 0 mV = 0.0 V
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_XIO_ANALOGOUT2, +3500); // 3500 mV = 3.5 V
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_XIO_ANALOGOUT3, +10000); // 10000 mV = 10.0 V
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_XIO_WRITEDACS, 1); // Write data simultaneously to DAC
66 MI.61xx Manual
Page 67

Synchronization (Option) The different synchronization options
Synchronization (Option)
This option allows the connection of multiple boards to generate a multi-channel system. It is possible to synchronize multiple Spectrum boards
of the same type as well as different board types. Therefore the synchronized boards must be linked concerning the board’s system clock and
the trigger signals.
If no synchronization is desired for a certain board you can exclude it by setting the register shown in the following table. This must be done
seperately for every board that should not work synchronized.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_COMMAND 0 r/w Command register of the board
SPC_NOSYNC 120 Disables the synchronization globally.
The different synchronization options
Synchronization with option cascading
With the option cascading up to four Spectrum boards can be synchronized. All boards are connected with one synchronization cable on
their sync-connectors (for details please refer to the chapter about installing the hardware).
As the synchronization lines are organized as a bus topology, there is a need for termination at both ends of the
bus. This is done in factory for the both end-boards. The maximum possible two middle-boards have no termination
on board.
When synchronizing multiple boards, one is set to be the clock master for all the connected boards. All the other
boards are working as clock slaves. It’s also possible to temporarily disable boards from the synchronization.
The same board or another one of the connected boards can be defined as a trigger master for all boards. All
trigger modes of the trigger master board can be used. It is also possible to synchronize the connected boards only
for the samplerate and not for trigger. This can be useful if one generator board is continuously generating a test-
pattern, while the connected acquisition board is triggering for test results or error conditions of the device under test.
For the fact that the termination is set in factory the order of the syncronized boards cannot be changed by
the user. Please refer to the boards type plate for details on the board’s termination. End boards are marked
with the option „cs-end“ while middle boards are marked with the option „cs-mid“
When the boards are synchronized by the option cascading
there will be a delay of about 500 ps between two adjacent
boards.
The figure on the right shows the clocks of three cascaded
boards with two channels each, where one end-board is defined as a clock master. Slave 1 is therefore a middle-board
and Slave 2 is the other end-board. The resulting delay between data of the two end-boards is therefore about 1 ns.
Please keep in mind that the delay between the channels of
two boards is depending on which board is actually set up as
the clock master and what boards are directly adjacent to the
master.
Synchronization with option starhub
With the option starhub up to 16 Spectrum boards can be synchronized. All boards are connected with a seperate synchronization cable
from their sync-connectors to the starhub module, which is a piggy-back module on one Spectrum board (for details please refer to the chapter
about installing the hardware).
When synchronizing multiple boards, one is set to be the clock master for all the connected boards. All the other boards are working as clock
slaves. It’s also possible to temporarily disable the synchronization of one board. This board then runs individually while the other boards
still are synchronized.
The same board or another one of the connected boards can be defined as a trigger master for all boards. All trigger modes of the board
defined as the trigger master can be used. It is also possible to synchronize the connected boards only for the samplerate and not for trigger.
This can be useful, if one generator board is continuously generating a testpattern, while the connected acquisition board is triggering for
test results or error conditions of the device under test.
Additionally you can even define more than one board as a trigger master. The trigger events of all boards are combined by a
logical OR, so that the first board that detects a trigger will start the boards. This OR connection is available starting with starhub
hardware version V4.
(c) Spectrum GmbH 67
Page 68

The setup order for the different synchronization options Synchronization (Option)
When the boards are synchronized by the option starhub there
will be no delay between the connected boards. This is achieved as all boards, including the one the starhub module is
mounted on, are connected to the starhub with cables of the
same length.
The figure on the right shows the clock of three boards with two
channels each that are synchronized by starhub.
The setup order for the different synchronization options
If you setup the boards for the use with synchronization it is important to keep the order within the software
commands as mentioned below to get the boards working correctly.
Depending on if you use the board either in standard or in FIFO mode there are slightly different orders in the setup for the synchronization
option. The following steps are showing the setups either for standard or FIFO mode.
Setup Order for use with standard (non FIFO) mode and equally clocked boards
(1) Set up the board parameters
Set all parameters like for example sample rate, memsize and trigger modes for all the synchronized boards, except the dedicated registers
for the synchronization itself that are shown in the tables below.
All boards must be set to the same settings for the entire clocking registers (see the according chapter for sample rate generation), for the
trigger mode and memory and should be set to the same postcounter size to get the same pretrigger sizes as well.
If you use acquisition boards with different pretrigger sizes, please keep in mind that after starting the board
the pretrigger memory of all boards will be recorded first, before the boards trigger detection is armed. Take
care to prevent boards with a long pretrigger setup time from hangup by adequately checking the board’s
status. Long setup times are needed if either you use a huge pretrigger size and/or a slow sample rate.
If you don’t care it might happen that boards with a small pretrigger are armed first and detect a triggerevent, while one or more boards with
a huge pretrigger are still not armed. This might lead to an endless waiting-state on these boards, which should be avoided.
Example of board setup for three boards
// --------- Set the Handles to fit for Windows driver --------hDrv[0] = 0;
hDrv[1] = 1;
hDrv[2] = 2;
// (1) ----- Setup all boards, shortened here !!!----for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
SpcSetParam (hDrv[i], SPC_MEMSIZE, 1024); // memory in samples per channel
SpcSetParam (hDrv[i], SPC_POSTTRIGGER, 512); // posttrigger in samples
// ...
SpcSetParam (hDrv[i], SPC_SAMPLERATE, 10000000); // set sample rate to all boards
SpcSetParam (hDrv[i], SPC_TRIGGERMODE, TM_SOFTWARE); // set trigger mode to all boards
}
(2) Write Data to on-board memory (output boards only)
If one or more of the synchronized boards are used for generating data (arbitrary waveform generator boards or digital I/O boards with
one or more channels set to output direction) you have to transfer the data to the board’s on-board memory before starting the synchronization.
Please refer to the related chapter for the standard mode in this manual. If none of your synchronized boards is used for generation purposes
you can ignore this step.
Example for data writing
SpcSetData (hDrv[0], 0, 0, 1024, pData[0]);
SpcSetData (hDrv[1], 0, 0, 1024, pData[1]);
SpcSetData (hDrv[2], 0, 0, 1024, pData[2]);
68 MI.61xx Manual
Page 69

Synchronization (Option) The setup order for the different synchronization options
(3) Define the board(s) for trigger master
At least one board must be set as the trigger master to get synchronization running. Every one of the synchronized boards can be programmed
for beeing the trigger master device.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_COMMAND 0 r/w Command register of the board
SPC_SYNCTRIGGERMASTER 101 Defines the according board as the triggermaster.
Example of board #2 set as trigger master
SpcSetParam (hDrv[2], SPC_COMMAND, SPC_SYNCTRIGGERMASTER); // Set board 2 to trigger master
(3a) Define synchronization OR trigger
If you use synchronization with the starhub option you can even set up more than one board as the trigger master. The boards will be combined by a logical OR and therefore the boards will be started if any of the trigger masters has detected a trigger event.
The synchronization OR-trigger is not available when using the cascading option. It is also not available with
starhub option prior to hardware version V4. See the initialization section of this manual to find out how to
determint the hardware version of the starhub.
If you set up the boards for the synchronization OR trigger all boards that are set as trigger master must be programmed to the same triggermode. If the boards are using different trigger modes this will result in a time shift between the boards. It is of course possible to set different
edges or different trigger levels on the channels.
It is only possible to use the synchronization OR trigger if the board carrying the starhub piggy-back module
is one of the boards that is programmed as a trigger master.
To find out what board is carrying the starhub piggy-back module you make use of the board’s feature registers as described in the
chapter about initialising the board.
Example of setting up three boards to be trigger master
SpcSetParam (hDrv[0], SPC_COMMAND, SPC_SYNCTRIGGERMASTER); // Set board 0 to trigger master
SpcSetParam (hDrv[1], SPC_COMMAND, SPC_SYNCTRIGGERMASTER); // Set board 1 to trigger master
SpcSetParam (hDrv[2], SPC_COMMAND, SPC_SYNCTRIGGERMASTER); // Set board 2 to trigger master
(4) Define the remaining boards as trigger slaves
As you can set more than one board as the trigger master (starhub option only) you have to tell the driver additionally which of the boards
are working as trigger slaves.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_COMMAND 0 r/w Command register of the board
SPC_SYNCTRIGGERSLAVE 111 Defines the according board as the trigger slave.
Each of the synchronized boards must be set up either as a trigger master or as a trigger slave to get the
synchronization option working correctly. Therefore it does not matter if you use the cascading or starhub
option.
It is assumed that only one of the three boards (board 2 in this case) is set up as trigger master, as described in (3)
SpcSetParam (hDrv[0], SPC_COMMAND, SPC_SYNCTRIGGERSLAVE); // Setting all the other boards to
SpcSetParam (hDrv[1], SPC_COMMAND, SPC_SYNCTRIGGERSLAVE); // trigger slave is a must !
It sometimes might be necessary to exclude one or more boards from the synchronization trigger. An example for this solution is that one or
more output boards are used for continuously generating test patterns, while one or more acqusition boards are triggering for test results or
error conditions. Therefore it is possible to exclude a board from the triggerbus so that only a synchronization for clock is done and the according boards are just using the trigger events they have detected on their own.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_NOTRIGSYNC 200040 r/w If activated the dedicated board will use its own trigger modes instead of the synchronization trigger.
Even if a board is not using the synchronization trigger, it must have been set as a triggerslave before even
if you exclude the board with the SPC_NOTRIGSYNC register.
(c) Spectrum GmbH 69
Page 70

The setup order for the different synchronization options Synchronization (Option)
After you have excluded one or more of the installed boards from the synchronization trigger it is possible to change the triggermodes
of these boards. So only all the boards that should work synchronously must be set up for the same trigger modes to get the synchro-
nization mode working correctly.
(5) Define the board for clock master
Using the synchronization option requires one board to be set up as the clock master for all the synchronized board. It is not allowed to set
more than one board to clock master.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_COMMAND 0 r/w Command register of the board
SPC_SYNCMASTER 100 Defines the according board as the clock master for operating in standard (non FIFO) mode only.
Example: board number 0 is clock master
SpcSetParam (hDrv[0], SPC_COMMAND, SPC_SYNCMASTER); // Set board 0 to clock master
(6) Define the remaining boards as clock slaves
It is necessary to set all the remaining boards to clock slaves to obtain correct internal driver settings.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_COMMAND 0 r/w Command register of the board
SPC_SYNCSLAVE 110 Defines the according board as a clock slave for operating in standard (non FIFO) mode only.
Settings the remining boards to clock slaves. Board number 0 is clock master in the example
SpcSetParam (hDrv[1], SPC_COMMAND, SPC_SYNCSLAVE); // Setting all the other boards to
SpcSetParam (hDrv[2], SPC_COMMAND, SPC_SYNCSLAVE); // clock slave is a must !
(7) Arm the boards for synchronization
Before you can start every single one of the synchronized boards on their own you have to arm all the synchronized boards before for the
use with synchronization. The synchronization has to be started on the clock master board.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_COMMAND 0 r/w Command register of the board
SPC_SYNCSTART 130 Arms all boards for the use with synchronization.
Example of starting the synchronization. Board number 0 is clock master.
SpcSetParam (hDrv[0], SPC_COMMAND, SPC_SYNCSTART);
(8) Start all of the trigger slave boards
After having armed the synchronized boards, you must start all of the boards that are defined as trigger slaves first.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_COMMAND 0 r/w Command register of the board
SPC_START 10 Starts the board with the current register settings.
SPC_STARTANDWAIT 11 Starts the board with the current register settings in the interrupt driven mode.
For details on how to start the board in the different modes in standard mode (non FIFO) please refer to the according chapter earlier in this
manual.
If using the interrupt driven mode SPC_STARTANDWAIT it is necessary to start each board in it’s own software
thread. This is necessary because the function does not return until the board has stopped again. If not using
different threads this will result in a program deadlock.
Example of starting trigger slave boards. Board number 2 is trigger master.
SpcSetParam (hDrv[0], SPC_COMMAND, SPC_START);
SpcSetParam (hDrv[1], SPC_COMMAND, SPC_START);
70 MI.61xx Manual
Page 71

Synchronization (Option) The setup order for the different synchronization options
(9) Start all of the trigger master boards
After having armed the synchronized boards, you must start all of the boards, that are defined as trigger masters.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_COMMAND 0 r/w Command register of the board
SPC_START 10 Starts the board with the current register settings.
SPC_STARTANDWAIT 11 Starts the board with the current register settings in the interrupt driven mode.
For details on how to start the board in the different modes in standard mode (non FIFO) please refer to the according chapter earlier in this
manual.
If you use the synchronization OR with the starhub option it is important to start the board carrying the starhub piggy-back module as last. Otherwise the trigger masters that are started first might detect trigger
events while other trigger masters haven’t even been started.
To find out what board is carrying the starhub piggy-back module you make use of the board’s feature registers as described in the chapter
about programming the board.
Example of starting the trigger master board
SpcSetParam (hDrv[2], SPC_COMMAND, SPC_START);
(10) Wait for the end of the measurement
After having started the last board, you will have to wait until the measurement is done. Depending if you use the board in standard (non
FIFO) mode interrupt driven or not, you can poll for the board’s status. Please refer to the relating chapter in this manual. It is necessary to
wait until each board returns the status SPC_READY before proceeding.
Example for polling for three synchronzed boards
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++) // For all synchronized boards
do // The status is read out
{
SpcGetParam (hDrv[i], SPC_STATUS, &lStatus); // by polling for SPC_READY
}
while (lStatus != SPC_READY);
}
printf (“All boards have stopped“);
(11) Read data from the on-board memory (acquisition boards only)
If one or more of the synchronized boards are used for recording data (transient recorder boards or digital I/O boards with one or more
channels set to input direction) you have to read out the data from the board’s on-board memory now. Please refer to the related chapter for
the standard (non FIFO) mode in this manual. If none of your synchronized boards is used for recording purposes you can ignore this step.
Example for data reading
SpcGetData (hDrv[0], 0, 0, 1024, pData[0]);
SpcGetData (hDrv[1], 0, 0, 1024, pData[1]);
SpcGetData (hDrv[2], 0, 0, 1024, pData[2]);
(12) Restarting the board for another synchronized run
If you want to restart the synchronized boards with the same settings as before it is sufficient to repeat only the steps starting with (7). This
assumes that on generation boards the output data is not changed as well.
If you want to change the output data of generation boards you’ll have to restart the setup procedure starting with step (2).
If you even want to change any of the boards parameters you’ll have to restart the setup procedure from the first step on.
(c) Spectrum GmbH 71
Page 72

The setup order for the different synchronization options Synchronization (Option)
Setup synchronization for use with FIFO mode and equally clocked boards
Most of the steps are similar to the setup routine for standard synchronization mentioned before. In this passage only the differences between
the two modes are shown. Please have a look at the passage before to see the complete setup procedure. The following steps differ from
standard mode to FIFO mode. All steps that are not mentioned here are similar as described before.
(2) Allocate the FIFO software buffers
If you use the board in FIFO mode additional memory in the PC RAM is needed for software FIFO buffers. For details please refer to the
according chapter for the FIFO mode.
Example of FIFO buffer allocation:
for (i = 0; i < FIFO_BUFFERS; i++)
for (b = 0; b < 3; b++)
{
pnData[b][i] = (ptr16) GlobalAlloc (GMEM_FIXED, FIFO_BUFLEN); // allocate memory
SpcSetParam (b, SPC_FIFO_BUFADR0 + i, (int32) pnData[b][i]); // send the adress to the driver
}
(2a) Write first data for output boards
When using the synchronization FIFO mode with output boards this is the right position to fill the first software buffers with data. As you can
read in the FIFO chapter, output boards need some data to be written to the software FIFO buffers before starting he board.
Example of calulcating and writing output data to software FIFO buffers:
// ----- data calculation routine ----int g_nPos =0; // some global variables
void vCalcOutputData (ptr16 pnData, int32 lBufsize) // function to calculate the
{ // output data. In this case
int i; // a sine function is used.
for (i = 0; i < (lBufsize/2); i++)
pnData[b][i] = (int16) (8191.0 * sin (2 * PI / 500000 * (g_nPos+i)));
g_nPos += lBufsize/2;
}
// ----- main task ----int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
...
for (i =0; i < MAX_BUF; i++) // fill the first buffers with data
for (b = 0; b < 3; b++) // for all installed boards
vCalcOutputData (pnData[b][i], BUFSIZE);
...
}
(5) Define the board for clock master
Using the synchronization option requires one board to be set up as the clock master for all the synchronized board. It is not allowed to set
more than one board to clock master.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_COMMAND 0 r/w Command register of the board
SPC_SYNCMASTERFIFO 102 Defines the according board as the clock master for operating in FIFO mode only.
Example: board number 0 is clock master
SpcSetParam (hDrv[0], SPC_COMMAND, SPC_SYNCMASTERFIFO); // Set board 0 to clock master
(6) Define the remaining boards as clock slaves
It is necessary to set all the remaining boards to clock slaves to obtain correct internal driver settings.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_COMMAND 0 r/w Command register of the board
SPC_SYNCSLAVEFIFO 102 Defines the according board as a clock slave for operating in FIFO mode only.
Settings the remaining boards to clock slaves. Board number 0 is clock master in the example
SpcSetParam (hDrv[1], SPC_COMMAND, SPC_SYNCSLAVEFIFO); // Setting all the other boards to
SpcSetParam (hDrv[2], SPC_COMMAND, SPC_SYNCSLAVEFIFO); // clock slave is a must !
72 MI.61xx Manual
Page 73

Synchronization (Option) The setup order for the different synchronization options
(8) Start all of the trigger slave boards
After having armed the synchronized boards, you must start all of the boards, that are defined as trigger slaves first. This is done with the
FIFOSTART command.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_COMMAND 0 r/w Command register of the board
SPC_FIFOSTART 10 Starts the board with the current register settings in FIFO mode and waits for the first interrupt.
Remember that the FIFO mode is allways interrupt driven. As a result the FIFOSTART function will not return
until the first software buffer is transferred. For that reason it is absolutely necessary to start different threads
for each board that runs synchronuously in FIFO mode. If this is not done a deadlock will occur and the program will not start properly.
(9) Start all of the trigger master boards
After having armed the synchronized boards, you must start all of the boards, that are defined as trigger masters.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_COMMAND 0 r/w Command register of the board
SPC_FIFOSTART 10 Starts the board with the current register settings in FIFO mode and waits for the first interrupt.
This example shows how to set up three boards for synchronization in FIFO mode. Board 0 is clock master and board 2 is trigger master.
// (3) ----- trigger synchronization of trigger master board(s) ---- SpcSetParam (hDrv[2], SPC_COMMAND, SPC_SYNCTRIGGERMASTER); // board 2 set as trigger master
// (4) ----- trigger synchronization of trigger slave boards ---- SpcSetParam (hDrv[0], SPC_COMMAND, SPC_SYNCTRIGGERSLAVE); // as trigger slaves
SpcSetParam (hDrv[1], SPC_COMMAND, SPC_SYNCTRIGGERSLAVE); // as trigger slaves
// (5) ----- synchronization information for clock master board ---- SpcSetParam (hDrv[0], SPC_COMMAND, SPC_SYNCMASTERFIFO);
// (6) ----- synchronization information for clock slave boards ---- SpcSetParam (hDrv[1], SPC_COMMAND, SPC_SYNCSLAVEFIFO);
SpcSetParam (hDrv[2], SPC_COMMAND, SPC_SYNCSLAVEFIFO);
// (7) ----- start the synchronization ---- SpcSetParam (hDrv[0], SPC_COMMAND, SPC_SYNCSTART);
// (8) ----- start the FIFO tasks. Trigger slaves are started first ---- CreateThread (NULL, 0, &dwFIFOTask, (void*) hDrv[0], 0, &dwThreadId[b]);
CreateThread (NULL, 0, &dwFIFOTask, (void*) hDRV[1], 0, &dwThreadId[b]);
// (9) ----- start the trigger master FIFO task ---- CreateThread (NULL, 0, &dwFIFOTask, (void*) hDrv[2], 0, &dwThreadId[hDrv[2]]);
It is assumed, that the created threads start in the same order as they are called from within the program. As described before, starting of
the FIFO mode in synchronization has to be done in different threads to avoid a deadlock. A simple example for a FIFO thread can be found
below.
Example of FIFO task. It simply starts the boards and counts the buffers that have been transfered:
unsigned long __stdcall dwFIFOTask (void* phDrv)
{
int16 hDrv = (int16) phDrv;
int32 lCmd = SPC_FIFOSTART;
int16 nBufIdx = 0, nErr;
int32 lTotalBuf;
lTotalBuf = 0;
do
{
nErr = SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_COMMAND, lCmd); // wait for buffer
lCmd = SPC_FIFOWAIT; // here you can do
printf ("Board %d Buffer %d total buffers: %d\n", nIdx, nBufIdx, lTotalBuf);// e.g. calculations
// just a printf here
SpcSetParam (hDrv, SPC_COMMAND, SPC_FIFO_BUFREADY0 + nBufIdx); // release buffer
nBufIdx++;
lTotalBuf++;
if (nBufIdx == FIFO_BUFFERS)
nBufIdx = 0;
}
while (nErr == ERR_OK);
return 0;
}
(c) Spectrum GmbH 73
Page 74

The setup order for the different synchronization options Synchronization (Option)
Additions for synchronizing different boards
General information
Spectrum boards with different speed grades, different number of channels or even just different clock settings for the same types of boards
can be synchronized as well. To get the boards working together synchronously some extra setups have to be done, which are described in
the following passages.
All clock rates of all synchronized boards are derived from the clock signal that is distributed via the sync bus. This clock is the sum samplerate
of one module of the clock master board. Based on this speed the clock rates of the slave boards can be set. As these clock rates are divided
from the sync clock, the board with the maximum sum sample rate should be set up as clock master.
Calculating the clock dividers
The sum sample rate can easily be calculated by the formula on the right.
The value for the sample rate of board N must contain the actual desired
conversion rate for one channel of board N. Please refer to the dedicated
chapter in the board’s manual to get informed about the relation beween
the board model and the number of actually activated channels per module for the different channel setups.
SumSampleRateNSampleRate=
ActChPerModule
⋅
N
N
As mentioned above the board with the highest sum sample rate must be
set up as the clock master. This maximum sum sample rate is used as the
overall sync speed, which is distributed via the sync bus. If you have cal-
ClockDivider
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------- -=
N
SampleRateNActChPerModule
SyncSpeed
⋅
culated the sync speed you can calculate the clock dividers for the different boards with the formula on the right.
The maximum possible channels per module for all Spectrum boards are
given in the table below.
20xx x 30xx x 31xx x 40xx x 45xx x 60xx x 61xx x 70xx x 72xx x
0x 7005 1
1x 3010 1 3110 2 6110 2 7010 1 7210 1
3011 2 3111 4 6011 2 6111 2 7011 2 7211 1
3012 2 3112 4 6012 2
3013 2
3014 2
3015 1
3016 2
2x 2020 2 3020 1 3120 2 4020 1 4520 2 7020 1 7220 1
2021 2 3021 2 3121 4 4021 2 4521 2 6021 2 7021 2 7221 1
3022 2 3122 4 4022 2 6022 2
3023 2
3024 2
3025 1
3026 2
3027 1
N
3x 3130 2 4030 1 4530 2 6030 1
2031 2 3031 2 3131 4 4031 2 4531 2 6031 1
3132 4 4032 2
2033 2 3033 2 6033 2
6034 2
4x 4540 2
4541 2
74 MI.61xx Manual
Page 75

Synchronization (Option) The setup order for the different synchronization options
Setting up the clock divider
The clock divider can easily be set by the following register. Please keep in mind that the divider must be set for every synchronized board
to have synchronization working correctly. For more details on the board’s clocking modes please refer to the according chapter in this manual.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_CLOCKDIV 20040 r/w Extra clock divider for synchronizing different boards.
Available divider values
1 2 4 8 101620405080100200
400 500 800 1000 2000
Although this setup is looking very complicated at first glance, it is not really difficult to set up different boards to work synchronously with the
same speed. To give you an idea on how to setup the boards the calculations are shown in the following two examples.
Each example contains of a simple setup of two synchronized boards. It is assumed that all of the available channels on the dedicated boards
have been activated.
Example calculation with synchronous speed where slave clock is divided
Board type 3122 3120
Channels available 8 x 12 bit A/D 2 x 12 bit A/D
Desired sample rate 10 MS/s 10 MS/s
Enabled channels per module 4 2
Sum sample rate 40 MS/s 20 MS/s
Therefore this board is set up
to be the clockmaster.
Sync speed 40 MS/s 40 MS/s
Clock divider 1 2
Divided sum clock 40 MS/s 20 MS/s
Enabled channels per module 4 2
Conversion speed 10 MS/s 10 MS/s
Example calculation with synchronous speed where master clock is divided
Board type 3025 3131
Channels available 2 x 12 bit A/D 4 x 12 bit A/D
Desired sample rate 20 MS/s 20 MS/s
Enabled channels per module 1 2
Sum sample rate 20 MS/s 40 MS/s
Therefore this board is set up
to be the clockmaster.
Sync speed 40 MS/s 40 MS/s
Clock divider 2 1
Divided sum clock 20 MS/s 40 MS/s
Enabled channels per module 1 2
Conversion speed 20 MS/s 20 MS/s
(c) Spectrum GmbH 75
Page 76

The setup order for the different synchronization options Synchronization (Option)
Additions for equal boards with different sample rates
In addition to the possibility of synchronizing different types of boards to one synchronous sample rate it can be also useful in some cases to
synchronize boards of the same type, with one working at a divided speed.
In this case you simply set up the fastest board as the clock master and set it’s clock divider to one. Now you can easily generate divided
clock rates on the slave boards by setting their dividers to according values of the divider list.
Please keep in mind that only the dedicated divider values mentioned in the list above can be used to derive
the sample rates of the slave boards.
The following example calculation is explaining that case by using to acquisition boards. One of the boards is running with only a hundreth
of the other sample rate.
Example with equal boards but asynchronous speeds
Board type 3121 3121
Channels available 4 x 12 bit A/D 4 x 12 bit A/D
Desired sample rate 10 MS/s
Enabled channels per module 4 4
Sum sample rate 40 MS/s
This board is set up to be the
clockmaster now.
Sync speed 40 MS/s 40 MS/s
Clock divider (is set to) 1 100
Divided sum clock 40 MS/s 400 kS/s
Enabled channels per module 4 4
Conversion speed 10 MS/s 100 kS/s
Resulting delays using different boards or speeds
Delay in standard (non FIFO) modes
There is a fixed delay between the samples of the different boards depending on the type of board, the selected clock divider and the activated channels. This delay is fixed for data acquisition or generation with the same setup.
If you use generation boards in the single shot mode this delay will be compensated within the software driver automatically.
Delay in FIFO mode
When the FIFO mode is used a delay is occuring between the data of the different boards. This delay is depending on the type of board, the
selected clock divider and the activated channel. You can read out the actual resulting delay from every board with the following register.
Register Value Direction Description
SPC_STARTDELAY 295110 r Start delay in samples for FIFO synchronization only.
The resulting delay between the clock master board and the single clock
slave boards can be easily calculated with the formular mentioned on
the right.
ResultingDelay ClockMasterDelay ClockSlaveDelay
–=
N
76 MI.61xx Manual
Page 77

Appendix Error Codes
Appendix
Error Codes
The following error codes could occur when a driver function has been called. Please check carefully the allowed setup for the register and
change the settings to run the program.
error name value (hex) value (dec.) error description
ERR_OK 0h 0 Execution OK, no error.
ERR_INIT 1h 1 The board number is not in the range of 0 to 15. When initialisation is executed: the board number is yet
ERR_NR 2h 2 The board is not initialised yet. Use the function SpcInitPCIBoards first. If using ISA boards the function SpcI-
ERR_TYP 3h 3 Initialisation only: The type of board is unknown. This is a critical error. Please check whether the board is
ERR_FNCNOTSUPPORTED 4h 4 This function is not supported by the hardware version.
ERR_BRDREMAP 5h 5 The board index remap table in the registry is wrong. Either delete this table or check it craefully for double
ERR_KERNELVERSION 6h 6 The version of the kernel driver is not matching the version of the DLL. Please do a complete reinstallation of
ERR_HWDRVVERSION 7h 7 The hardware needs a newer driver version to run properly. Please install the driver that was delivered toge-
ERR_LASTERR 10h 16 Old Error waiting to be read. Please read the full error information before proceeding. The driver is locked
ERR_ABORT 20h 32 Abort of wait function. This return value just tells that the function has been aborted from another thread.
ERR_BOARDLOCKED 30h 48 Access to the driver already locked by another program. Stop the other program before starting this one.
ERR_REG 100h 256 The register is not valid for this type of board.
ERR_VALUE 101h 257 The value for this register is not in a valid range. The allowed values and ranges are listed in the board spe-
ERR_FEATURE 102h 258 Feature (option) is not installed on this board. It’s not possible to access this feature if it’s not installed.
ERR_SEQUENCE 103h 259 Channel sequence is not allowed.
ERR_READABORT 104h 260 Data read is not allowed after aborting the data acquisition.
ERR_NOACCESS 105h 261 Access to this register denied. No access for user allowed.
ERR_POWERDOWN 106h 262 Not allowed if powerdown mode is activated.
ERR_TIMEOUT 107h 263 A timeout occured while waiting for an interrupt. Why this happens depends on the application. Please
ERR_CHANNEL 110h 272 The channel number may not be accessed on the board: Either it is not a valid channel number or the chan-
ERR_RUNNING 120h 288 The board is still running, this function is not available now or this register is not accessible now.
ERR_ADJUST 130h 304 Automatic adjustion has reported an error. Please check the boards inputs.
ERR_NOPCI 200h 512 No PCI BIOS is found on the system.
ERR_PCIVERSION 201h 513 The PCI bus has the wrong version. SPECTRUM PCI boards require PCI revision 2.1 or higher.
ERR_PCINOBOARDS 202h 514 No SPECTRUM PCI boards found. If you have a PCI board in your system please check whether it is cor-
ERR_PCICHECKSUM 203h 515 The checksum of the board information has failed. This could be a critical hardware failure. Restart the
ERR_DMALOCKED 204h 516 DMA buffer not available now.
ERR_MEMALLOC 205h 517 Internal memory allocation failed. Please restart the system and be sure that there is enough free memory.
ERR_FIFOBUFOVERRUN 300h 768 Driver buffer overrun in FIFO mode. The hardware and the driver have been fast enough but the application
ERR_FIFOHWOVERRUN 301h 769 Hardware buffer overrun in FIFO mode. The hardware transfer and the driver has not been fast enough.
ERR_FIFOFINISHED 302h 770 FIFO transfer has been finished, programmed number of buffers has been transferred.
ERR_FIFOSETUP 309h 777 FIFO setup not possible, transfer rate to high (max 250 MB/s).
ERR_TIMESTAMP_SYNC 310h 784 Synchronisation to external timestamp reference clock failed. At initialisation is checked wether there is a
ERR_STARHUB 320h 800 The autorouting function of the star-hub initialisation has failed. Please check whether all cables are mounted
initialised, the old definition will be used.
nitBoard must be called first.
correctly plug in the slot and whether you have the latest driver version.
values.
the hardware driver. This error normally only occurs if someone copies the dll manually to the system directory.
ther with the board.
until the error information has been read.
Only one program can access the driver at the time.
cific documentation.
check whether the timeout value is programmed too small.
nel is not accessible due to the actual setup (e.g. Only channel 0 is accessible in interlace mode)
rectly plug into the slot connector and whether you have the latest driver version.
system and check the connection of the board in the slot.
software didn’t manage to transfer the buffers in time.
Please check the system for bottlenecks and make sure that the driver thread has enough time to transfer
data.
clock edge present at the input.
correctly.
(c) Spectrum GmbH 77
Page 78

Pin assignment of the multipin connector
Pin assignment of the multipin connector
The 40 lead multipin connector is the main connector for all of Spectrum’s digital boards and is additionally used for different options, like “Extra I/O“ or the additional digital inputs (on analog acquisition
boards only) or additional digital outputs (on analog generation boards only).
The connectors for all the options are mounted on an extra bracket, while the main conncectors for the
digital boards are mounted directly on the board’s bracket. Only in case that a digital board uses more
than two connectors (more than 32 in and/or output bits) an additional bracket will be used for mounting the connectors as well.
The pin assignment depends on what type of board you have and on which of the below mentioned
options are installed.
Extra I/O with external connector(Option -XMF)
B1 B2 B3 B4 B5 B6 B7 B8 B9 B10 B11 B12 B13 B14 B15 B16 B17 B18 B19 B20
D0 GND D1 GND D2 GND D3 GND D4 GND D5 GND D6 GND D7 GND n.c. n.c. n.c. n.c.
A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 A7 A8 A9 A10 A11 A12 A13 A14 A15 A16 A17 A18 A19 A20
D8 GND D9 GND D10 GND D11 GND D12 GND D13 GND D14 GND D15 GND n.c. n.c. n.c. n.c.
B21 B22 B23 B24 B25 B26 B27 B28 B29 B30 B31 B32 B33 B34 B35 B36 B37 B38 B39 B40
D16 GND D17 GND D18 GND D19 GND D20 GND D21 GND D22 GND D23 GND n.c. n.c. n.c. n.c.
A21 A22 A23 A24 A25 A26 A27 A28 A29 A30 A31 A32 A33 A34 A35 A36 A37 A38 A39 A40
A0 GND GND GND A1 GND GND GND A2 GND GND GND A3 GND GND GND n.c. n.c. n.c. n.c.
A3…A0 are the pins for the analog outputs, while D23…D0 are the 24 digital I/Os.
Pin assignment of the multipin cable
The 40 lead multipin cable is used for the additional digital inputs
(on analog acquisition boards only) or additional digital outputs (on
analog generation boards only) as well as for the digital I/O or pattern generator boards.
The flat ribbon cable is shipped with the boards that are equipped
with one or more of the above mentioned options. The cable ends
are assembled with a standard IDC socket connector so you can easily make connections to your type of equipment or DUT (device under test).
The pin assignment is given in the table in the according chapter of
the appendix.
78 MI.61xx Manual
Page 79

Pin assignment of the internal multipin connector
Pin assignment of the internal multipin connector
The 26 lead internal connector is used for
the option “Extra I/O“ (-XIO) without the
external connector described before.
The connector mentioned here is mounted
on the bottom side of the Extra I/O module.
Extra I/O with internal connector (Option -XIO)
Pin2 Pin4 Pin6 Pin8 Pin10 Pin12 Pin14 Pin16 Pin18 Pin20 Pin22 Pin24 Pin26
A2 A0 GND D14 D12 D10 D8 GND D6 D4 D2 D0 GND
Pin1 Pin3 Pin5 Pin7 Pin9 Pin11 Pin13 Pin15 Pin17 Pin19 Pin21 Pin23 Pin25
A3 A1 GND D15 D13 D11 D9 GND D7 D5 D3 D1 GND
A3…A0 are the pins for the analog outputs, while D15…D0 are the 16 digital I/Os.
(c) Spectrum GmbH 79
 Loading...
Loading...