Page 1

User Guide
802.11ac Wave 2 Router
Page 2

Table of Contents
2
1 Hardware Setup
1.1 Getting To Know Your WiFi Router.......................................................................................................2
1.2 Unpack WiFi Router’s box.....................................................................................................................3
1.3 Hardware Features....................................................................................................................................4
1.3.1 Front Panel.......................................................................................................................................4
1.3.2 Rear Panel.......................................................................................................................................5
1.4 Position Your WiFi Router......................................................................................................................6
2 Login to your WiFi Router Web GUI
2.1 Login..............................................................................................................................................................7
2.2 Wizard Setup.............................................................................................................................................10
2.3 Basic Setup................................................................................................................................................13
2.3.1 Router...............................................................................................................................................13
2.3.2 WPS Setup.......................................................................................................................15
2.3.3 LAN Setup....................................................................................................................................17
2.3.4 WAN Setup....................................................................................................................................18
2.3.5 Parental Control.........................................................................................................................23
2.3.6 Services.........................................................................................................................................25
2.3.7 System...........................................................................................................................................35
2.4 Advanced Setup.....................................................................................................................................36
2.4.1 Network.........................................................................................................................................36
2.4.2 Services Config..........................................................................................................................66
2.4.3 Security.........................................................................................................................................79
2.4.4 QoS................................................................................................................................................92
2.4.5 Admin..........................................................................................................................................100
2.4.6 Tools.............................................................................................................................................104
.........................................................................................................................2
7
.................................................................7
2.4.7 Status....................................................................................................................................................106
3 FCC Statement
........................................................................................................................113
113
Page 3

1 Hardware Setup
1.1 Getting To Know Your WiFi Router
This product is designed for the In-Home and Business WiFi service for Spectrum customers.
With a custom industrial design, this WiFi Router can be placed in a central location to
deliver superior WiFi network coverage.
WiFi Router provides:
1. High performance:
·
Dual-Core ARM up to 1.7G/1GB DDR RAM.
·
Dual-Band wireless up to AC2350 (2.4G 150M * 4 + 5G 433M * 4).
·
Gigabyte 1 x WAN/ 4x LAN Ethernet ports.
2. High security: Firewall/VPN supported.
3. Easy to setup: Friendly wizard, visual setup & maintenance (Basic Mode), complete
functions (Advanced Mode).
4. USB-based services: File/media/printer sharing.
The WiFi Router is an ideal choice for residential and SMB (Small Business) users who can
enjoy a variety of wireless applications and services.
This chapter contains the following contents:
·
Unpack Your WiFi Router
·
Hardware Features
·
Position Your WiFi Router
2
Page 4

1.2 Unpack WiFi Router’s box
Open the box and remove the WiFi Router, power adapter, Quick Start Guide, WiFi Network
Name and Password Sticker and Ethernet cord.
WiFi Router
Figure 1. Check the package contents
Power Adapter
The box contains the following items:
·
WiFi Router.
·
AC power adapter.
·
Quick Start Guide.
·
WiFi Network Name and Password Sticker.
·
Ethernet cord
If any items are missing or damaged, please contact your Charter Communications. Please
keep original packing materials in case you need to return the product for repairing.
3
Page 5

1.3 Hardware Features
Before setup please take a moment to become familiar with the front Panel and Rear Panel
of your WiFi Router. Pay particular attention to the LED on the front panel. You should know
the surface structure of your WiFi Router only.
1.3.1 Front Panel
The WiFi Router front and back panels feature the status LED and buttons as shown in the
following figure
Figure 2. WiFi Router front view
Front panel LED status
·
Off:
·
Blue Flashing (0.4 second intervals):
·
Blue Pulsing 1 second intervals:
·
Blue solid:
·
Red Flashing:
·
Red and Blue alternate Pulsing:
·
Red solid:
·
LED on front of device will dim to low (65%) when there is no settings activity or
connectivity issues for 120 hours.
·
If any settings are changed or connectivity issues occur LEDs will return to normal (100%)
brightness.
Device off.
Booting up.
Connecting to Internet.
Connected to Internet.
Connectivity issues (no Internet connection).
Updating firmware (or any scenario where
device must not be restarted).
Critical issues (hardware or otherwise).
4
Page 6

1.3.2 Rear Panel
There are Ethernet and USB connections and buttons shown in the following figure.
·
Factory Reset (pinhole):
·
WPS Button:
·
Ethernet (LAN) Port:
·
Internet (WAN) Port:
·
USB (3.0) Port:
·
Power:
Figure 3. WiFi Router rear panel
Press the pinhole and hold over 5 seconds, the WiFi Router will
reset to factory.
Push the button more than 1 second to activate WPS. Reference
2.3.2 WPS Setup.
Connect Ethernet cables for LAN (local area network)
connections, e.g. network switch, hub, personal computer or
Internet devices.
Connect Ethernet cable for WAN (Wide Area Network)
connection to modem. This connects the Ethernet and other
access lines e.g. modem.
Connect a USB Printer, U-Disk or USB drive. For printer and
folder sharing, reference 2.3.6 Services.
Use the bundled AC adapter to connect your WiFi Router to a
power source.
5
Page 7

1.4 Position Your WiFi Router
The WiFi Router lets you access your network from virtually anywhere within the operating
range of your wireless network. However, the wireless communicating distance varies
significantly due to placement of the WiFi Router. For example, the thickness and number of
walls the wireless signal passes through can limit the range. For best results, WiFi Router is
likely to be place like this:
·
Near the center of the area where your computers and other devices operate, and
preferably within line of sight to your wireless devices.
·
So it is accessible to an AC power outlet and near Ethernet cables for wired computers.
·
In an elevated location such as a shelf, keeping the number of walls and ceilings between
the WiFi Router and your other devices to a minimum.
·
Away from electrical devices that are potential sources of interference. Equipment
that might cause interference includes ceiling fans, home security systems, microwaves,
computers, the base of a cordless phone, or a 2.4 GHz cordless phone.
·
Away from any large metal surfaces, such as a solid metal door or aluminum studs. Large
expanses of other materials such as glass, insulated walls, fish tanks, mirrors, brick and
concrete can also affect your wireless signal.
6
Page 8
2 Sign-In Your WiFi Router Web GUI
The WiFi Router contains an intuitive graphical user interface (GUI) based on web, which lets
administrator easily configure its features through a web browser.
2.1 Sign-In
1. Open a web browser, then key in the WiFi Router’s default IP address: http://192.168.1.1,
and click Enter key in the keyboard;;
2. On the sign in webpage, type in its Username and password: admin (admin), then click
Login button.
After the administrator has logged into the WiFi Router, some basic information about it will
be displayed in the browser.
7
Page 9

On the right top side, there are two command buttons: Change Password and Logout. Please
click the Logout button when administrator intends to leave the Web GUI.
When the Change Password button has been clicked, the browser will navigate to the
corresponding webpage.
8
Page 10
On this page, user should just type in new password in New Password and Retype New
Password, then click Apply button. Web GUI user sign in password will be changed.
9
Page 11
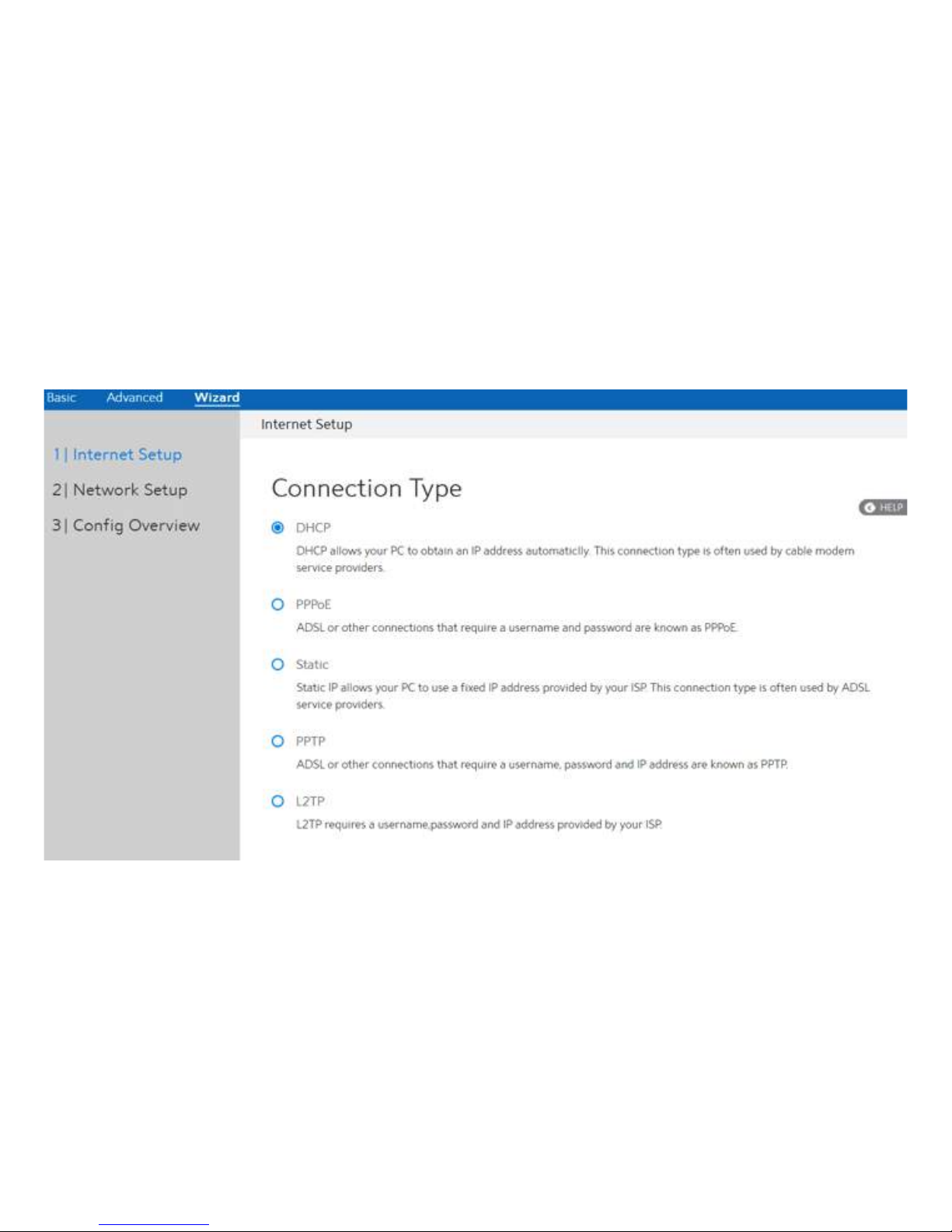
2.2 Wizard Setup
The wizard can navigate the administrator to configure basic settings for the WiFi Router,
which makes the set up of the WiFi Router much easier.
Internet Setup
After the administrator has clicked the Wizard button, the Internet Setup page will be
displayed.
Connection Type:
There are 5 kinds of connection types: DHCP, PPPoE, Static, PPTP and L2TP.
1. DHCP: Enable WiFi Router to obtain IP addresses automatically. This setting is the default
for Spectrum services. More types of settings, reference 2.3.4 WAN Setup.
10
Page 12
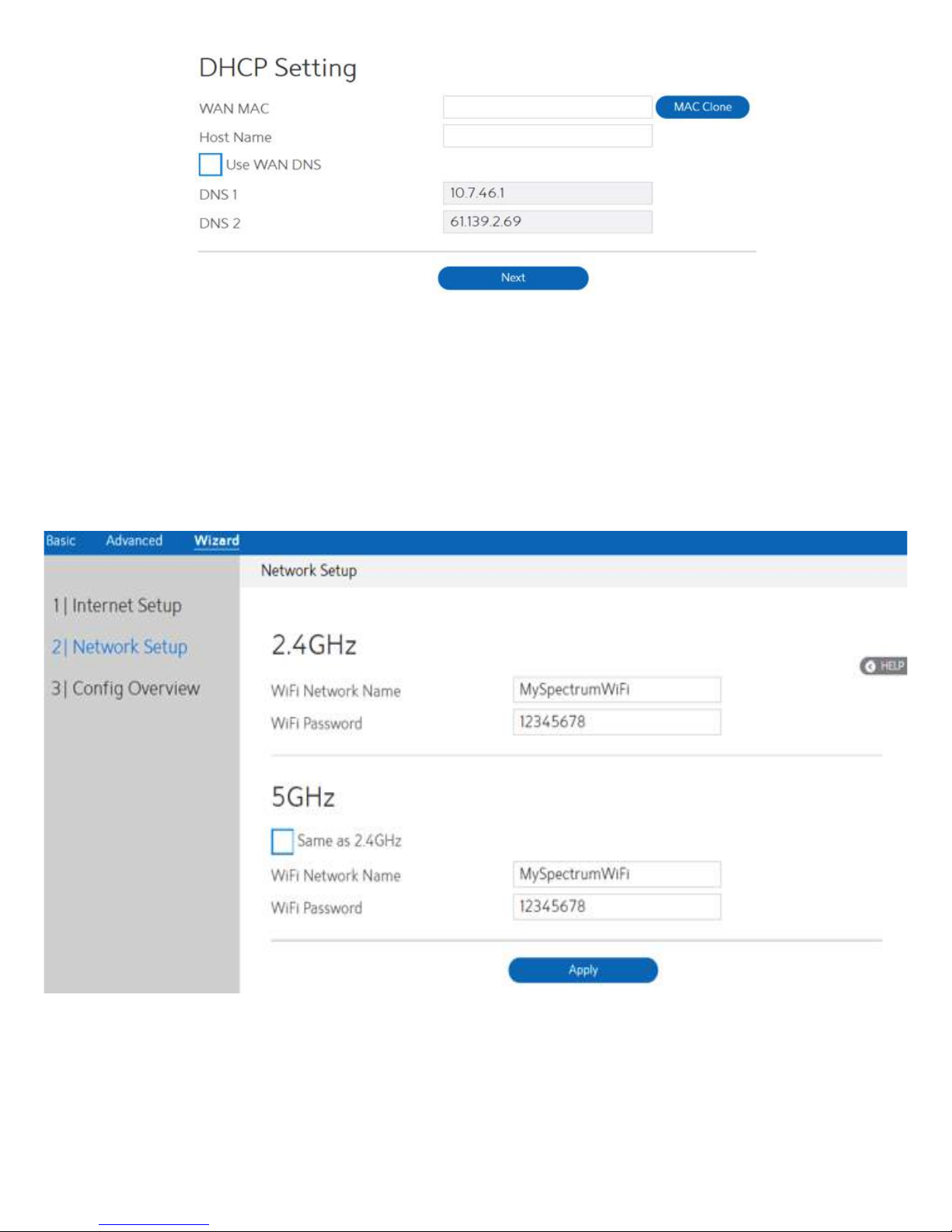
·
WAN MAC:
·
Host Name:
·
DNS 1 & DNS 2:
·
Click Next.
MAC address of WAN port.
This field allows lets administrator provide a name for WiFi Router.
Either of them indicates the IP address of a DNS Server.
Network Setup
After you have clicked Next icon in Internet Setup page, you comes here.
1. WiFi Network Name:
Name for a wireless network, that’s to say it’s used to identify a
wireless network. WiFi devices automatically detect all networks
within its communication range. These are defaulted from the printed
WiFi network name on the back of the WiFi Router. You can change
them here, but they would no longer match the sticker on your WiFi
Router.
11
Page 13
2. WiFi Password:
A password used by WiFi Router to authenticate wireless connections.
These are defaulted from the printed WiFi password on the back of the
WiFi Router. You can change it here, but they would no longer match the
sticker on your router.
3. When done, click Apply.
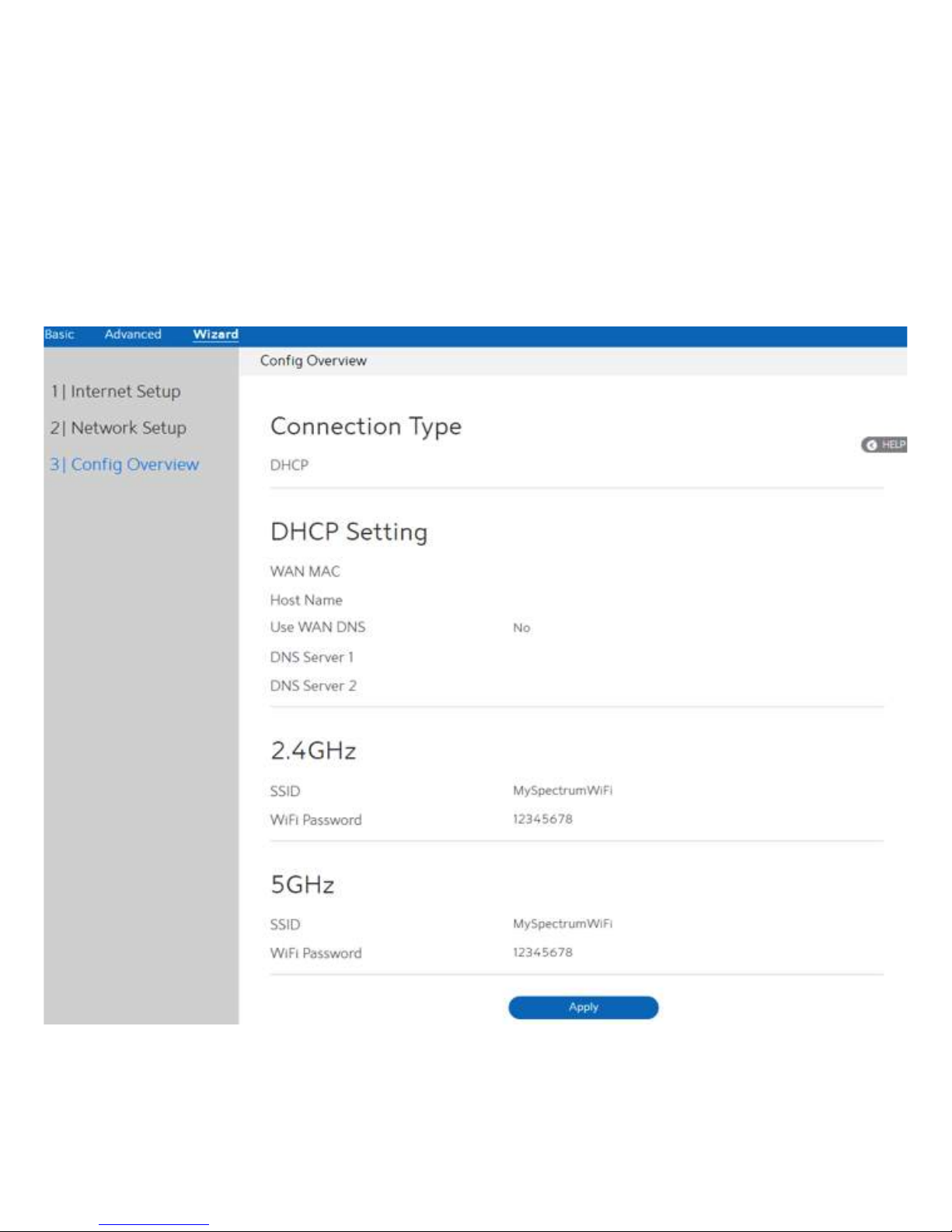
Config Overview
After click the Apply icon, administrator comes to Config Overview page, which displays a
summary of configuration information. If the settings are all correct, administrator should
click Apply icon.
12
Page 14
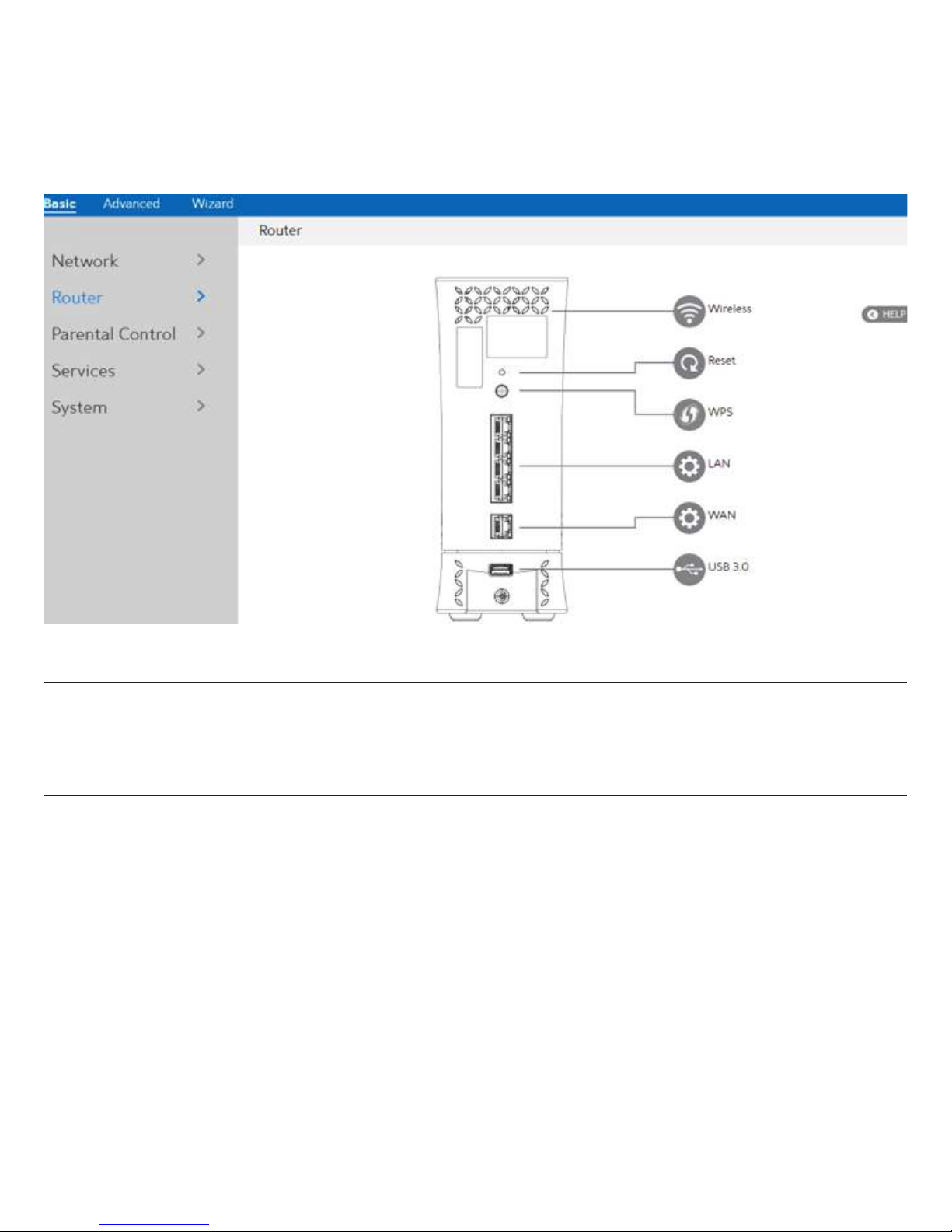
2.3 Basic Setup
2.3.1 Router
From the navigation panel, go to Basic > Router.
NOTE: Click Reset Icon in the Web GUI is used to restart the WiFi Router. The WiFi Router
hardware Factory Reset (pinhole) was pressed and hold over 5 seconds, it will reset
to factory.
13
Page 15
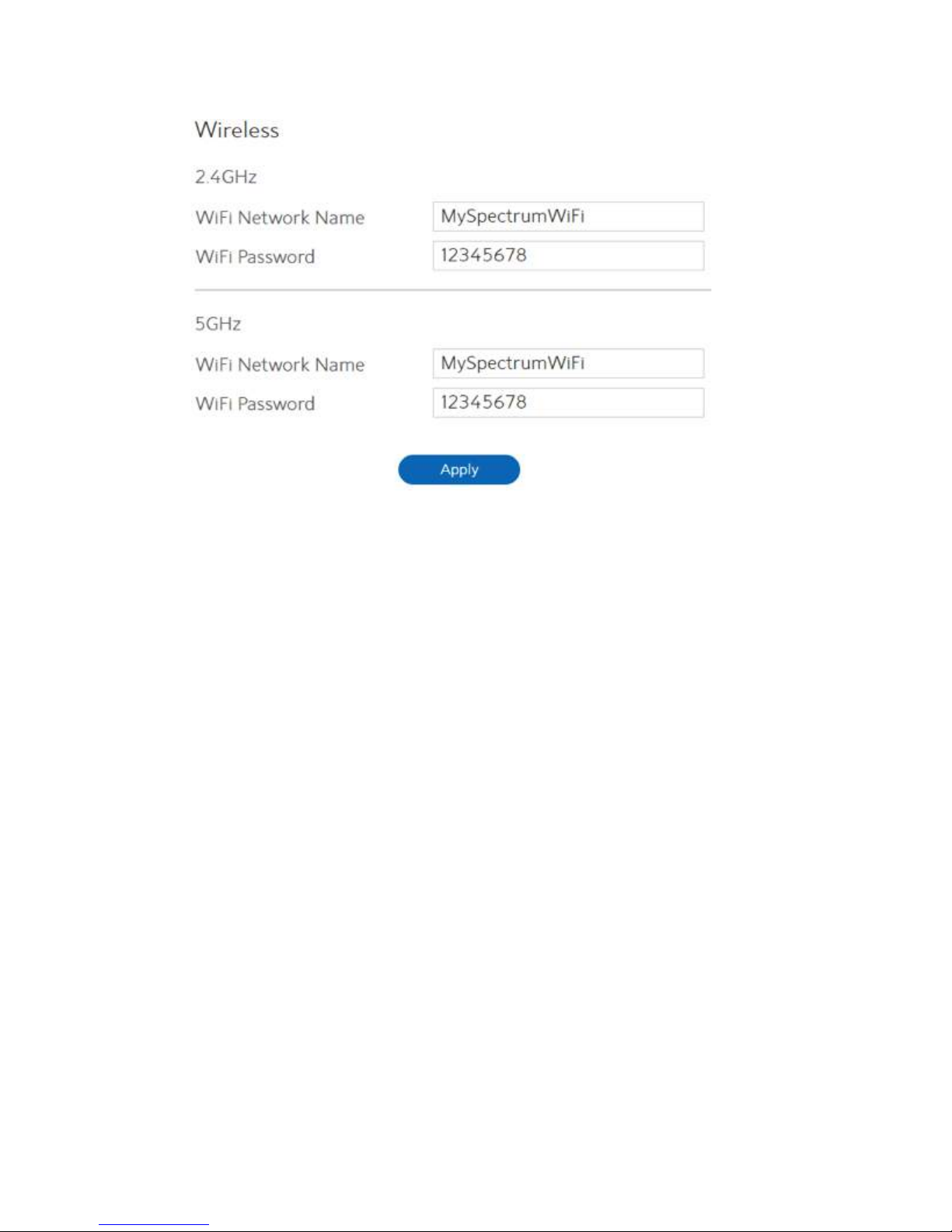
Wireless:
This module is implemented to configure some basic settings for
WiFi Router’s wireless connection.
1. WiFi Network Name:
2. WiFi Password:
3. Click Apply.
A unique name that identifies the wireless network. Wireless device
can automatically detect all networks within its communication
range. The maximum length of a network name (SSID) is 32
characters.
A string used for connection authentication. Its length ranges from 0
to 63 characters (letters, numbers or a combination) or from 8 to 64
hex digits.
14
Page 16
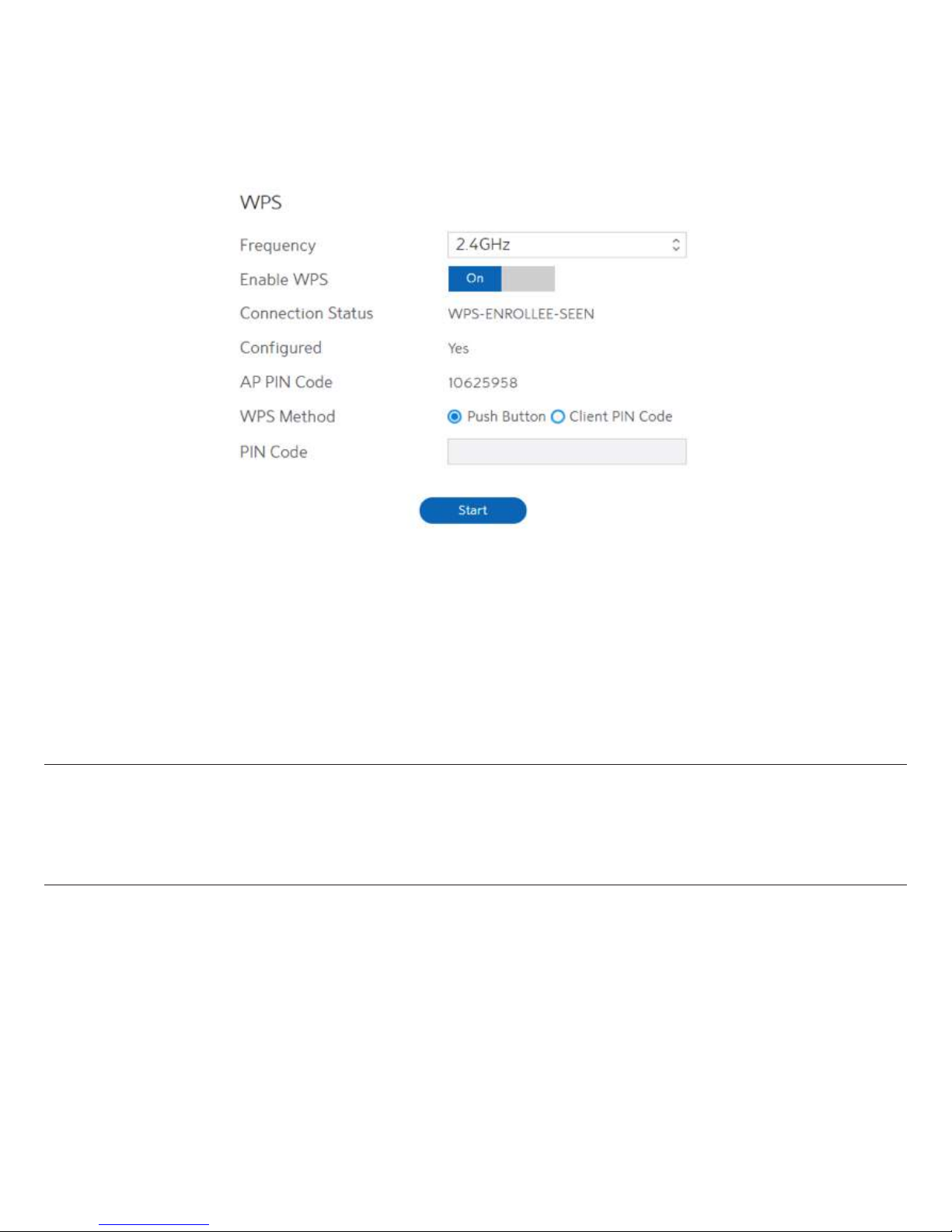
2.3.2 WPS Setup
WPS (WiFi Protected Setup) is a wireless security standard that lets the device easily
connect a WiFi network. You can trigger the WPS function via the PIN code or WPS button.
Steps to enable WPS (WiFi Protected Setup):
1. From the navigation panel, go to Basic > Router.
2. Frequency:
Selecting operating band (2.4 GHz or 5 GHz) for WPS function. Each
one is enabled separately.
3. Enable WPS:
Selecting [On] to run WPS, which simplifies the process of connecting
any device to the WiFi network.
NOTE: Authentication methods supported by WPS are: Open system, WPA-Personal and
WPA2-Personal. Not supported methods are: Shared Key, WPA-Enterprise, WPA2 Enterprise and RADIUS.
15
Page 17

8. PIN Code: The WPS PIN code which clients use to connect with the WiFi Router.
9. In the WPS Method field, select Push Button or Client PIN code. If you select Push Button,
go to step 10. If you select Client PIN code, go to step 11.
10. To set up WPS using the WiFi Router’s WPS button, follow these steps:
a) Click Start or press the WPS button found at the rear of the WiFi Router.
b) Press the WPS button on your wireless device. This is normally identified by the WPS
logo.
11. To set up WPS using the Client’s PIN code, follow these steps:
a) Locate the WPS PIN code in wireless device’s in Web GUI.
b) Key in the Client PIN code on the text box.
12. Click Start.
16
Page 18
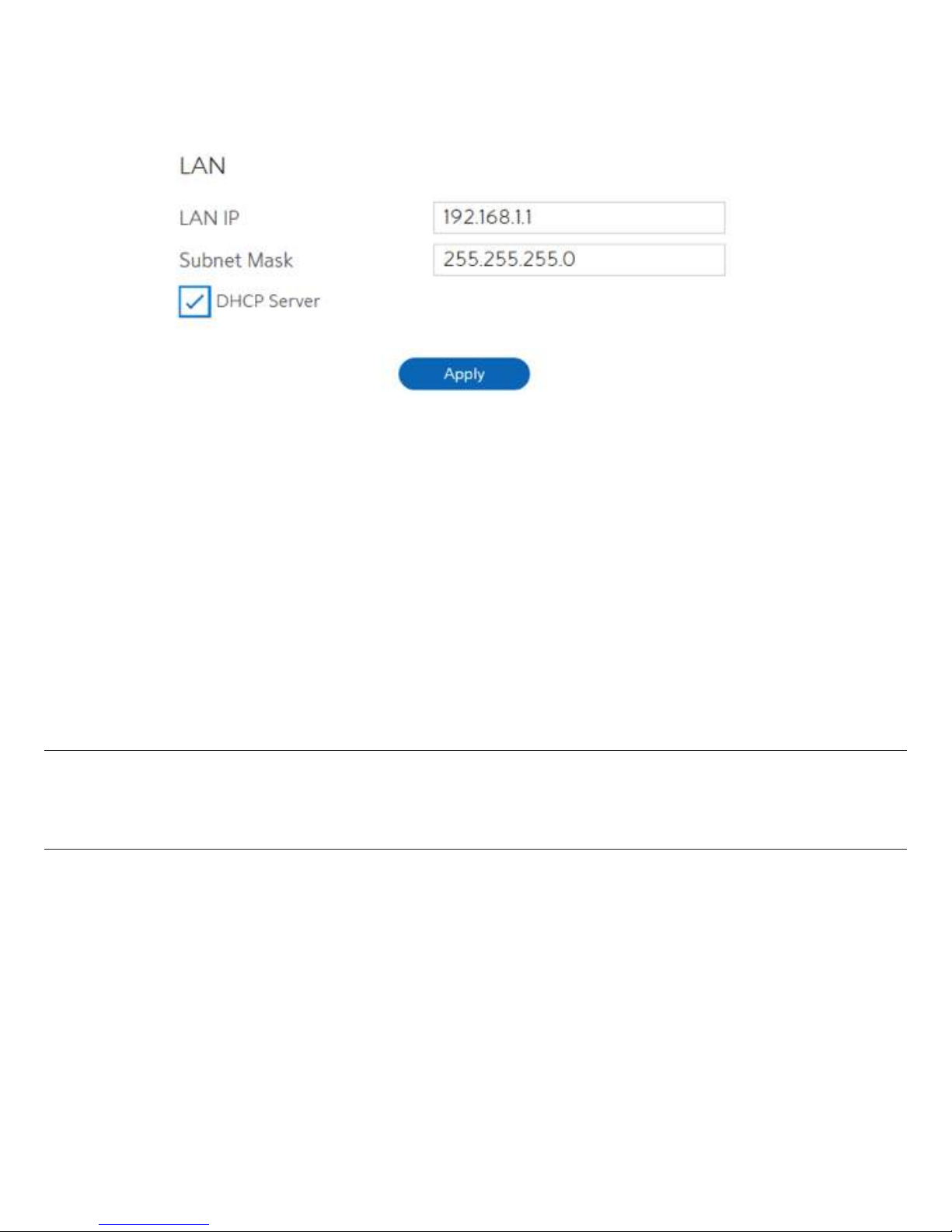
2.3.3 LAN Setup
This module makes it easier for administrator to modify the default LAN IP Address.
Steps to modify LAN IP settings:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Basic > Router.
2. LAN IP:
3. Subnet Mask:
4. DHCP Server:
The LAN IP address of the WiFi Router. Its default value is 192.168.1.1. In
IP-based networks, packets are sent to the network devices' specific IP
addresses.
Subnet mask of WiFi Router. Its default value is 255.255.255.0
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is mostly used to allocate
IP address for LAN-side devices. And a DHCP server can inform LAN-side
devices of DNS server’s address, default gateway IP and etc. This WiFi
Router can allocate 253 IP addresses at most.
NOTE: It’s recommended for administrator to select DHCP Server for LAN IP setting. If not,
administrator has to assign IP address to LAN-side device manually.
5. Click Apply.
17
Page 19
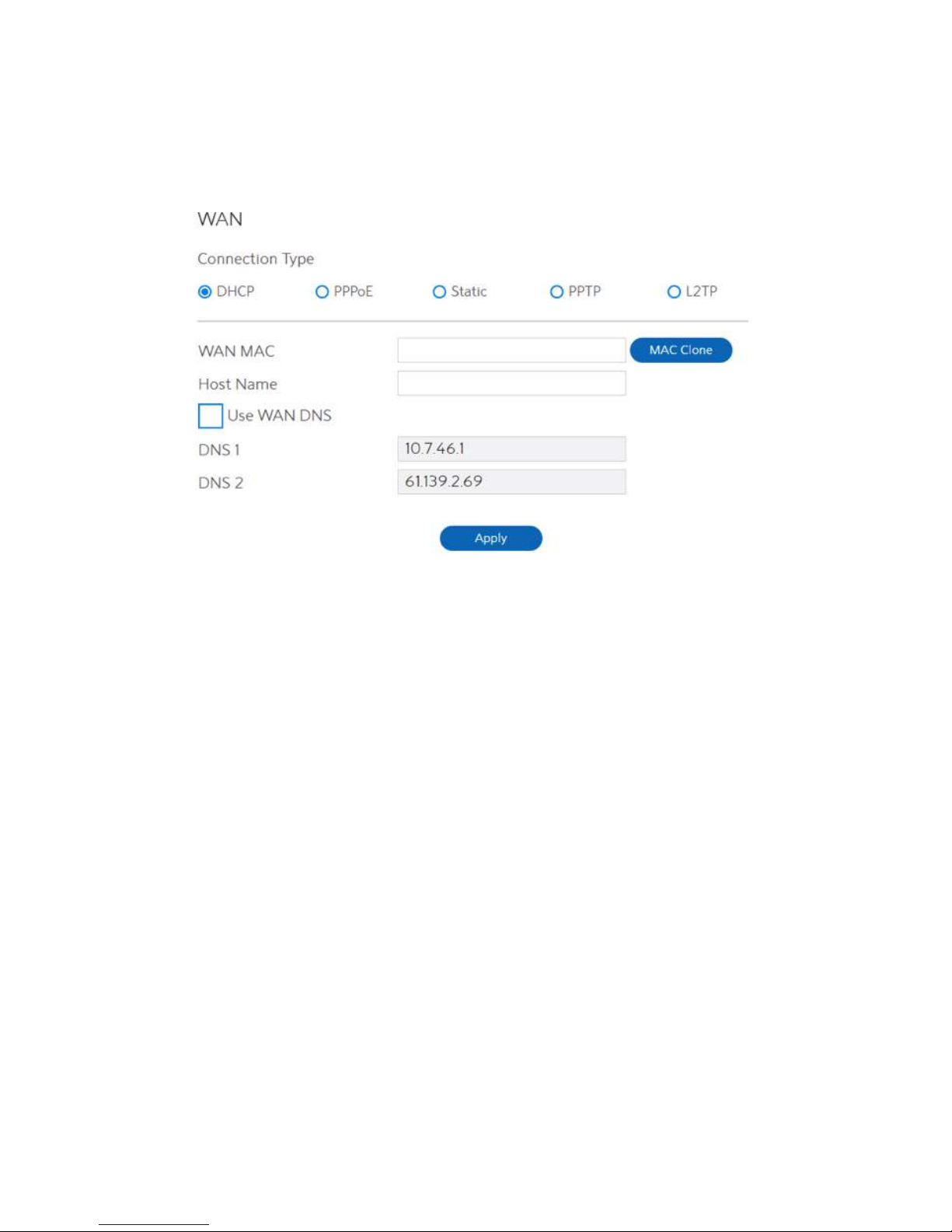
2.3.4 WAN Setup
Click WAN button to configure the WAN connection settings:
1. Connection Type: Choose the Internet Service type. There are five options are DHCP,
PPPoE, Static, PPTP, and L2TP. Consult your ISP if you are unsure what
kind of WAN connection type to select.
2. If you select DHCP:
·
WAN MAC:
MAC (Media Access Control) address is a unique identifier that identifies
your computer or device in the network. ISPs monitor the MAC
addresses of devices that connect to their services, and would disallow
Internet connection for new MAC addresses.
To fix this issue, you can do either of the following:
·
Contact your ISP and request to update the MAC address associated with your ISP
subscription.
·
Clone or change the MAC address of the new device to match the MAC address of the
original device.
·
Host Name: This field lets you provide a host name for WiFi Router. Usually it’s
provided by ISP.
·
DNS 1 & DNS 2: Either of them indicates IP address of a DNS server.
·
Click Apply.
18
Page 20
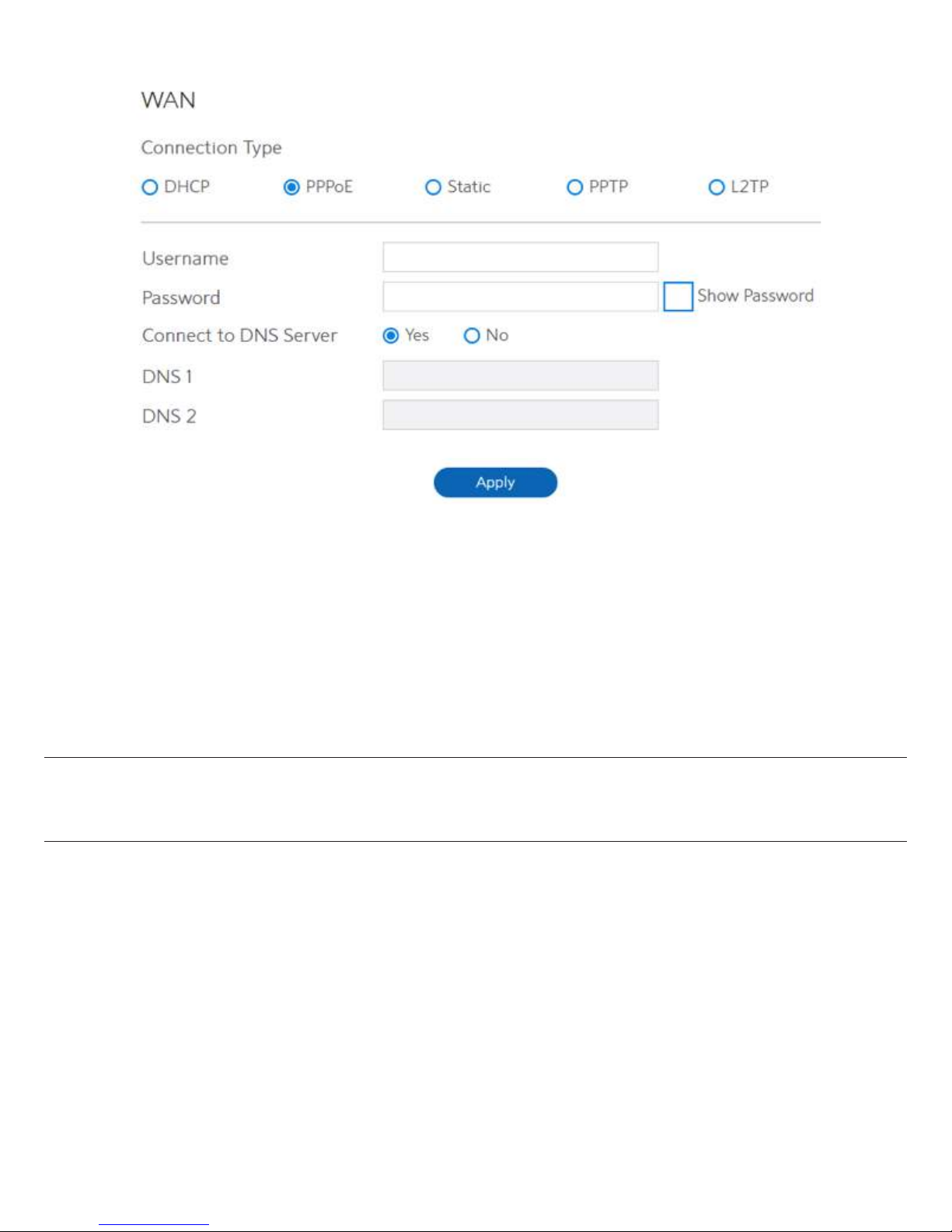
3. If you select PPPoE:
·
Username: This field is only available when you set the WAN Connection Type as PPPoE,
PPTP or L2TP.
·
Password: This field is only available when you set WAN Connection Type as PPPoE, PPTP
or L2TP.
·
DNS1 & DNS2: Either of them indicates IP address of a DNS server that WiFi Router will
contact.
·
Click Apply.
NOTE: All of the parameters mentioned above are provided. If you need assistance, please
contact Charter customer service.
19
Page 21
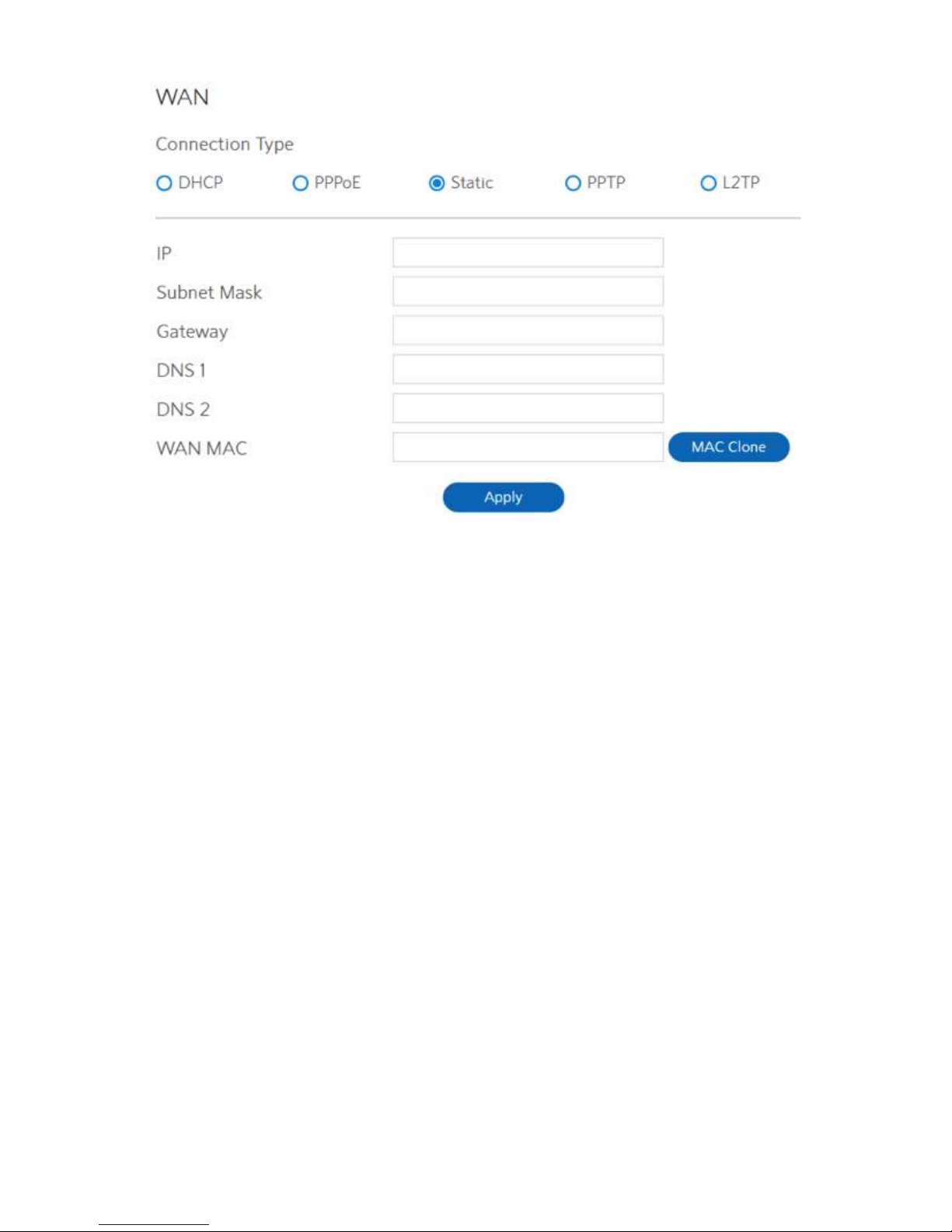
4. If you select Static, below show the steps to set
• IP:
• Subnet Mask:
If WAN connection requires a static IP address, key in the IP address in
this field.
• Gateway:
If WAN connection requires a static IP address, key in the subnet mask in
this field.
• DNS 1 & DNS 2:
If WAN connection requires a static IP address, key in the gateway IP
address in this field.
• WAN MAC:
Either of them indicates IP address of a DNS server.
MAC (Media Access Control) address is a unique identifier that identifies
your computer or device in the network. ISPs monitor the MAC addresses
of devices that connect to their services, and would disallow Internet
connection for new MAC addresses.
To fix this issue, you can do either of the following:
·
Contact your ISP and request to update the MAC address associated with your ISP
subscription.
·
Clone or change the MAC address of the new device to match the MAC address of the
original device.
• Click Apply.
20
Page 22
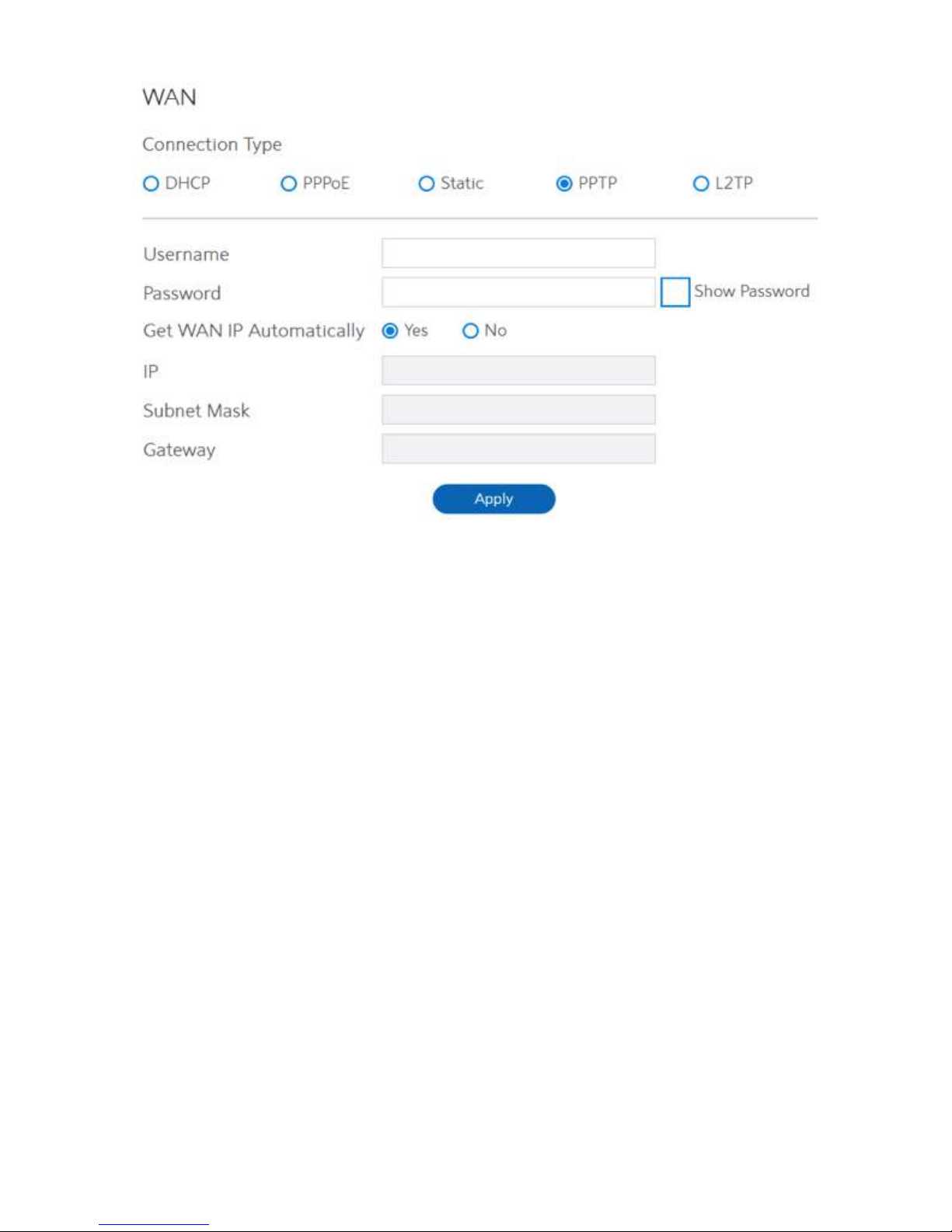
5. If you select PPTP:
• Username:
• Password:
• Get the WAN IP Automatically:
• IP:
• Subnet Mask:
• Gateway:
• Click Apply.
This field is only available when you set the WAN
Connection Type as PPPoE, PPTP or L2TP.
This field is only available when you set WAN Connection
Type as PPPoE, PPTP or L2TP.
Select Yes to get WAN IP automatically and No to enter IP
manually below.
If WAN connection requires a static IP address, key in the
IP address in this field.
If WAN connection requires a static IP address, key in the
subnet mask in this field.
If WAN connection requires a static IP address, key in the
gateway IP address in this field.
21
Page 23
6. If you select L2TP:
Please reference to PPTP above for relevant settings descriptions and enter the required
information.
22
Page 24
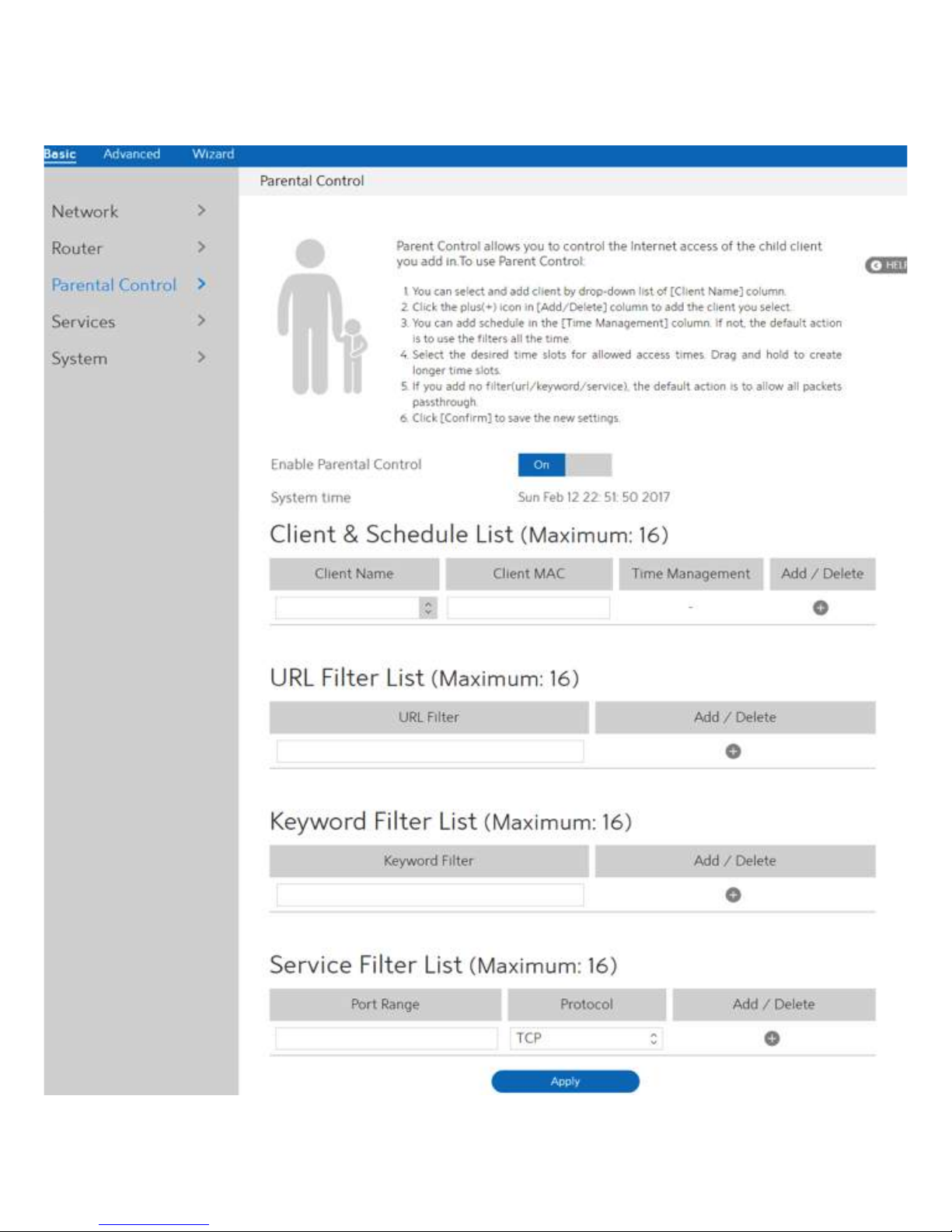
2.3.5 Parental Control
Parental Control lets administrator control the Internet access of the client.
23
Page 25

Steps to set parental control function:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Basic > Parental Control.
2. Enable Parental Control:
Select On to enable parental control, Select Off to disable
parental control.
3. Client Name:
Select client from the list. The name in the list stands for the client
that is communicating with the WiFi Router.
4. Client MAC:
MAC address of the selected client.
NOTE: Client Name just makes it easier for administrator to distinguish LAN-side devices. The
Client MAC in fact specify the device with the Client Name.
5. Add/Delete:
6. Time Management:
7. URL Filter List:
8. Add/Delete:
9. Keyword Filter List:
10. Add/Delete:
11. Service Filter List:
12. Add/Delete:
Click or to add/delete the profile.
Click , then setup the client’s schedule timetable to allow or
deny client’s access to Internet.
WiFi Router prevents LAN-side device from accessing the URL
in list. It will filter all Internet WEB URLs which contains the
URLs defined by user. For example, the filter "abc" can filter both
"www.abc.com" and "www.abcd.com"
Click or to add/delete the profile.
WiFi Router prevents LAN-side device from accessing to
webpages contain the keyword in list. It will filter all Internet WEB
URLs which contains the keywords defined by user. For example,
the filter "abc" can filter both "www.abc.com" and "www. abcd.
com"
Click or to add/delete the profile.
WiFi Router prevents LAN-side device from communicating with
remote device with user defined Port Range and Protocol. The
Port Range can be a single port like "xxxx", or a port range like
"xxxx:xxxx".
Click or to add/delete the profile.
13. Click Apply.
24
Page 26
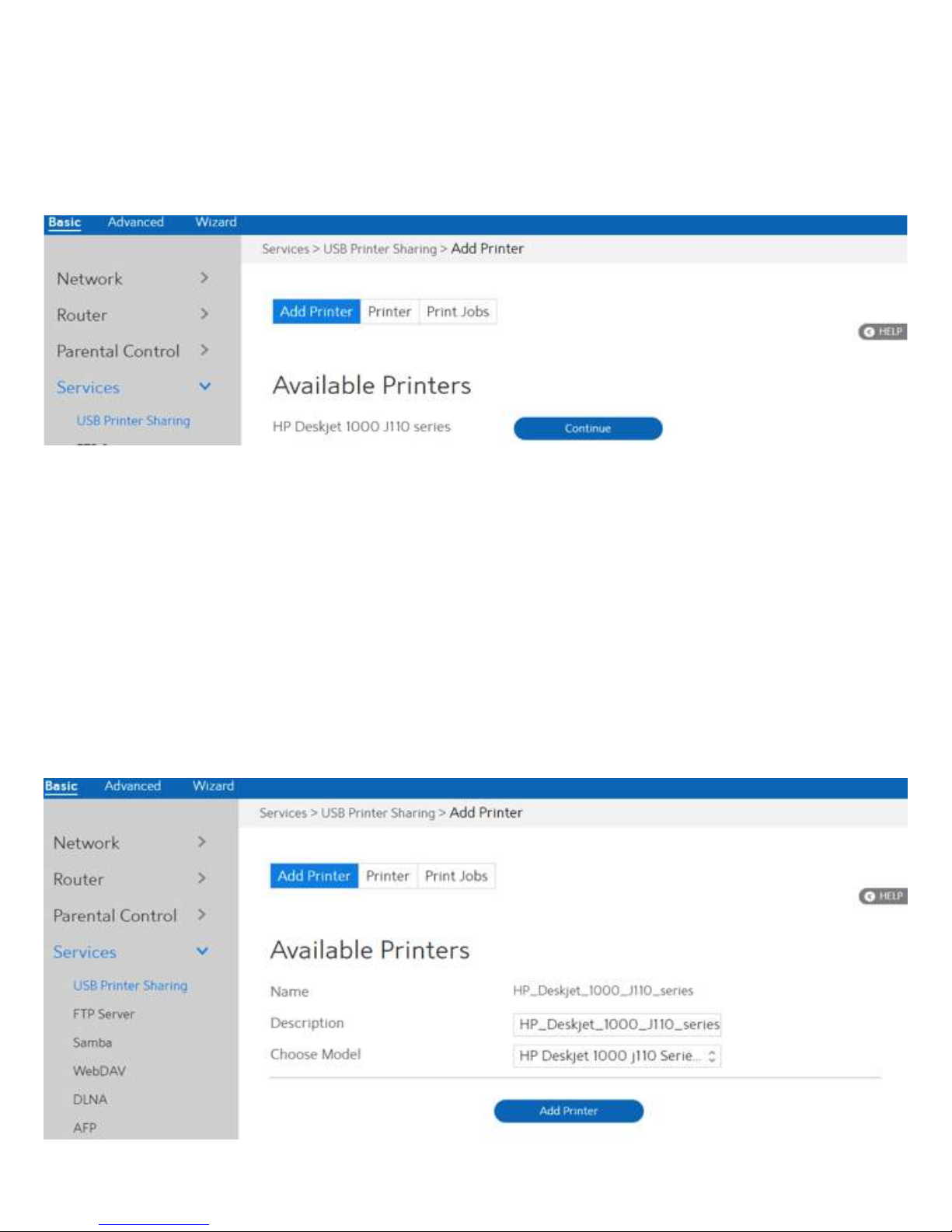
2.3.6 Services
2.3.6.1 USB Printer Sharing
USB Printer sharing lets administrator plug a USB printer to WiFi Router’s USB port and set
up the print server.
Steps to set up USB Printer sharing:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Basic > Service > USB Printer sharing > Add Printer.
2. Plug in the USB interface of the printer to the WiFi Router. Confirm your printer has been
detected and click Continue.
3. Select one of the following modes to install the printer driver, and click Add printer.
·
Auto select: Automatically searches for the appropriate printer driver and installs. If there
is no corresponding printer driver, the system displays add a printer error; please select
the correct printer driver manually.
·
Select printer driver: Manually select the corresponding printer brand and model.
·
Choose PPD File: If the above methods are unable to correctly install the printer driver,
then you can upload a PPD File. Select your PPD file and click the upload button.
25
Page 27
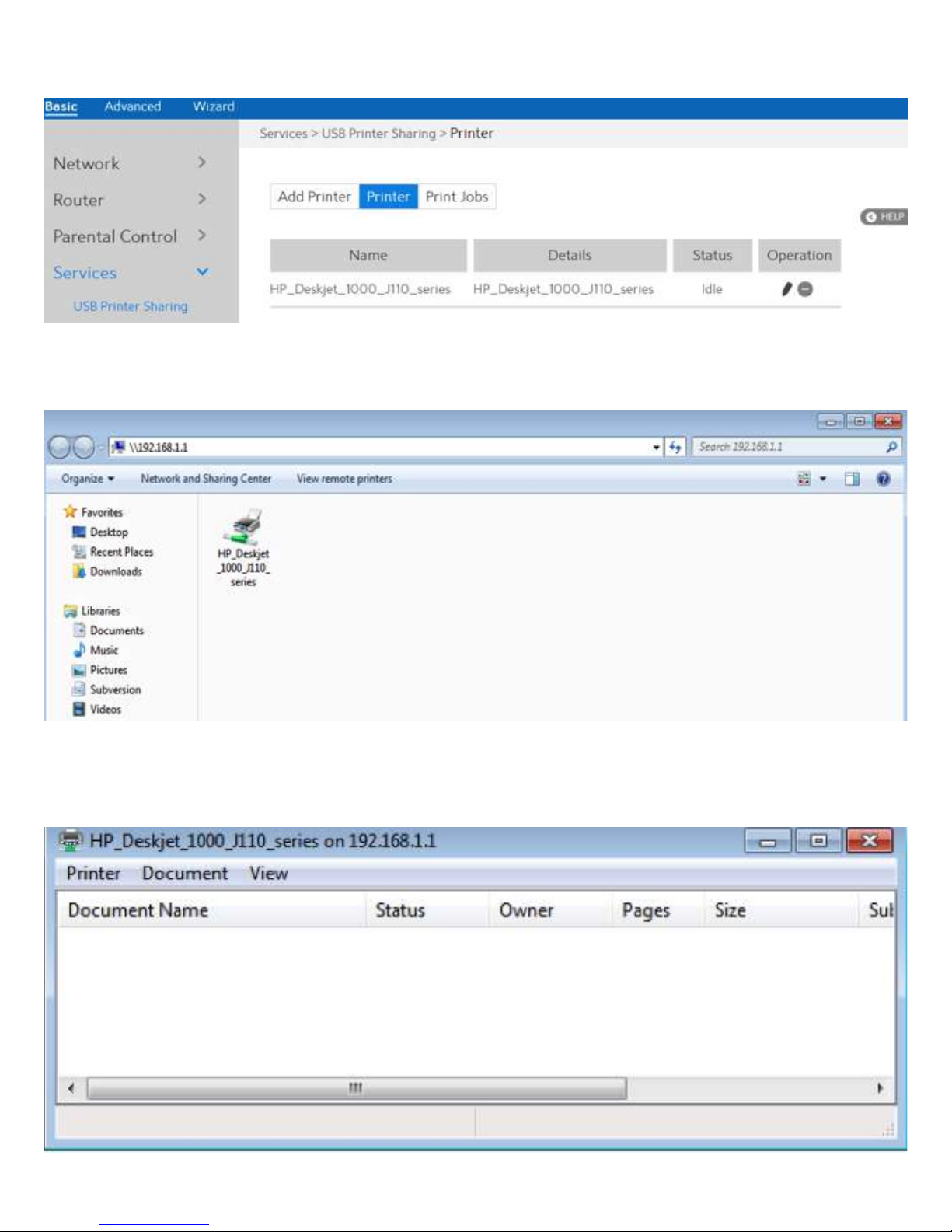
4. Printer tab displays whether your printer is operating correctly with the print server, as
below.
5. To check whether your printer is working correctly or not, input the LAN address (192.168.1.1)
for the printer in Windows Finder.
6. Double-click the printer icon and if you see the status interface as shown below, the
installation was successful. If an error message prompts that the driver cannot be found,
then return to Add Printer settings and select the correct driver.
26
Page 28

7. You can view print status information in the Print Jobs tab.
·
Active:
·
Processing:
·
All Jobs:
All active jobs, including processing and pending jobs.
The job currently processing/communicating print data.
All print jobs.
27
Page 29
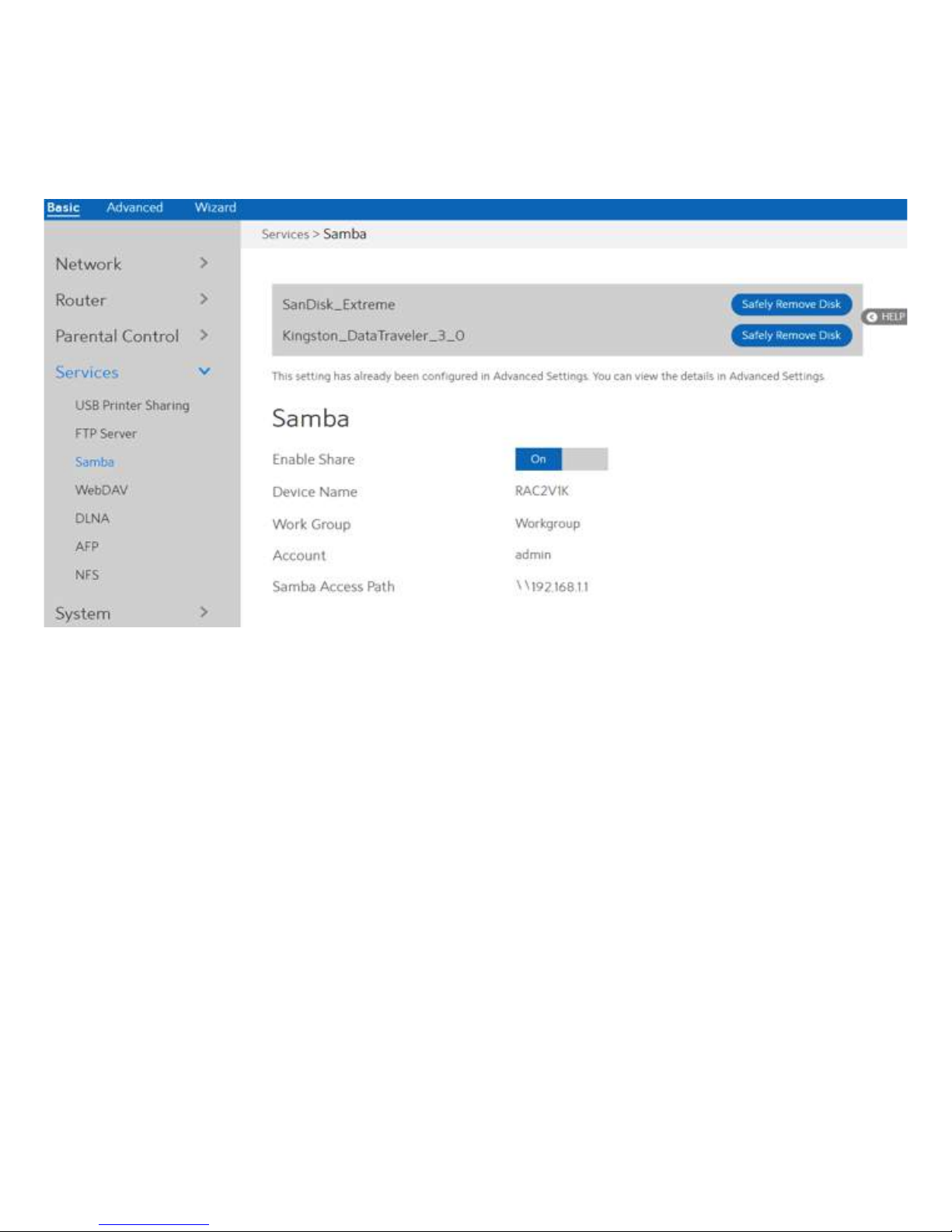
2.3.6.2 FTP Server
FTP Server enables an FTP server to share files from USB disk to other devices via your local
area network or via the Internet. This page shows information about the FTP Server. For set
up FTP Server, go to Advanced > Servers > FTP Server.
Display information on FTP Server:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Basic > Services > FTP Server.
2. Connect an external USB hard disk drive or USB flash drive to your WiFi Router, and your
device will be displayed here.
3. Enable FTP:
Click On/Off to enable/disable Internet access to FTP
service.
4. Maximum number of Connections:
the maximum number of concurrent connections for
the Network Neighborhood or FTP Server.
5. Enable Outside Access:
Select On/Off to enable/disable access to FTP server
by wide area network.
6. Outside Access:
The numbers of external service ports
(default value: 8021).
7. Safely Remove Disk:
Click to safely remove USB devices. When the USB
disk is ejected successfully, the USB status shows 'No
device '.
28
Page 30
2.3.6.3 Samba
Samba Share lets you set up the accounts and permissions for the Samba service. This page
shows information about the Samba Server. For Samba setup go to Advanced > Servers >
Samba.
·
From the navigation panel, go to Basic > Services > Samba.
·
Connect an external USB hard disk drive or USB flash drive to your WiFi Router, and your
device will be displayed here.
·
Enable Share:
·
Device Name:
Click the On/Off to enable/disable Internet access to Samba service.
Enter a name for your device and you can use this name in your web
browser's URL field to quickly access the device as a Network Place
service.
·
Work Group:
·
Safely Remove Disk:
Group name of the WiFi Router in Network Neighborhood.
Click to safely remove the disk. When the USB disk is ejected
successfully, the USB status shows 'No device '.
29
Page 31

2.3.6.4 WebDAV
The client can write operations in WebDAV directory with appropriate permissions. This page
shows information about the WebDAV Server. To set up WebDAV go to Advanced > Servers
> WebDAV.
1. From the navigation panel, go to Basic > Services > WebDAV.
2. Connect an external USB hard disk drive or USB flash drive to your WiFi Router, and your
device will be displayed here.
3. HTTP Access Port:
The port to access the WebDAV server for HTTP protocol in the
local area network (default value: 80).
4. HTTPS Access Port:
The port to access the WebDAV server for HTTPS protocol in the
local area network (default value: 443).
5. Enable Outside Access:
Select On/Off to enable/disable access to WebDAV server by wide
area network.
30
Page 32

6. Outside Access:
7. Outside Access HTTPS:
8. Safely Remove Disk:
The port number of external service ports via HTTP
(default value: 8080).
The port number of external service ports via HTTPS
(default value: 8443).
Click to safely remove the disk. When the USB disk is ejected
successfully, the USB status shows 'No device '.
31
Page 33

2.3.6.5 DLNA
DLNA (Digital Living Network Alliance) lets you share audio, image and video. Your WiFi
Router lets DLNA-supported devices access multimedia files from the USB disk connected
to your WiFi Router. This page shows information about the DLNA Server. To setup DLNA
server, go to Advanced > Servers > DLNA.
Steps to set DLNA:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Basic > Services > DLNA.
2. Connect an external USB hard disk drive or USB flash drive to your WiFi Router, and your
device will be displayed here.
3. Enable DLNA Media Server:
4. Media Server Name:
Switch DLNA media server on or off.
The DLNA server's name, which will be displayed by the
media player such as VLC or Windows Media Player.
5. Safely Remove Disk:
Click to safely remove the disk. When the USB disk is ejected
successfully, the USB status shows 'No device '.
32
Page 34

2.3.6.6 AFP
An AFP server is a kind of network file sharing server based on AFP protocol implementation,
mainly used for file sharing between Linux and MAC systems. This page shows information
about the AFP server. To setup AFP, go to Advanced > Servers > AFP.
Steps to set AFP:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Basic > Services > AFP.
2. Connect an external USB hard disk drive or USB flash drive to your WiFi Router, and your
device will be displayed here.
3. Enable Share:
4. Safely Remove Disk:
Click On/Off to enable/disable AFP service.
Click to safely remove the disk. When the USB disk is ejected
successfully, the USB status shows 'No device '.
33
Page 35

2.3.6.7 NFS
Network File System Server is used to share the USB disk with clients via network. Clients
can mount the remote disk to a local directory for a faster speed than using a Samba server.
This page shows information about the NFS Server. To setup NFS, go to Advanced > Servers
> NFS.
Steps to set NFS:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Basic > Services > NFS.
2. Connect an external USB hard disk drive or USB flash drive to the WiFi Router, then
device’s name will be displayed here.
3. Enable NFS:
Enable or disable NFS service. When disabled, users can't access the
USB storage via the NFS service.
4. Safely Remove Disk:
Click to safely remove the disk. When the USB disk is ejected
successfully, the USB status shows 'No device '.
34
Page 36

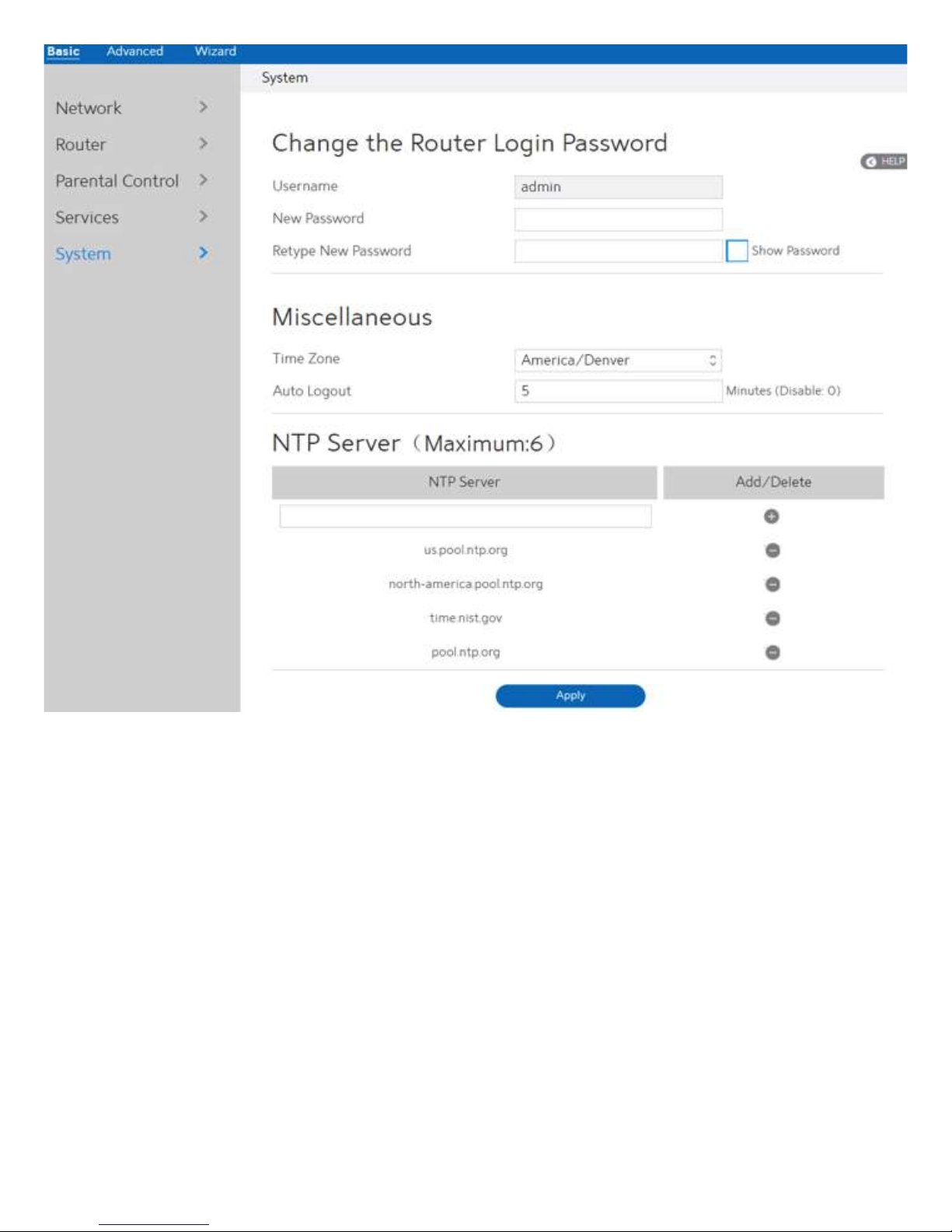
2.3.7 System
This module lets sign in user do some settings, such as changing your own sign in password,
selecting time-zone and adding NTP server. If you changed the password, the user password
to sign in SSH will be changed.
Steps to set the System settings:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Basic > System.
2. Username:
3. New Password:
4. Retype New Password:
5. Time Zone:
6. Auto Logout:
7. NTP Server:
Name used to sign in WiFi Router.
New sign in password for WiFi Router.
Retype new sign in password for WiFi Router.
The time zone used by default.
Auto logout after a specified period of time.
DNS of a NTP (Network Time Protocol) server.
8. Click Apply.
35
Page 37

2.4 Advanced Setup
2.4.1 Network
2.4.1.1 WAN Settings
2.4.1.1.1 Internet Settings
WiFi Router supports several WAN connection types. Select the type from the WAN
Connection Type dropdown menu.
36
Page 38

Steps to configure WAN connection settings:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced > Network > WAN > Internet.
2. WAN Connection Type: Choose the Internet Service Provider type. There are 5 options:
DHCP, PPPoE, Static, PPTP and L2TP. If you are unsure which type to select, please
consult your ISP.
3. MTU:
Maximum Transmission Unit value, which defines the
maximum length of a packet.
4. Connect to DNS Server:
Lets WiFi Router get IP address from the DNS Server
automatically. DNS Server is a host on the Internet that
translates Internet names to numeric IP addresses.
5. Get WAN IP Automatically:
Select Yes to get WAN IP automatically and No to enter IP
manually below.
6. IP Address:
If your WAN connection requires a static IP address, key in the
IP address in this field.
7. Subnet Mask:
If your WAN connection requires a static IP address, key in the
subnet mask in this field.
8. Default Gateway:
If your WAN connection requires a static IP address, type in
the gateway IP address in this field.
9. DNS 1 & DNS 2:
10. Authentication:
Either of them indicates an IP address of a DNS server.
Use 802.1x MD5 authentication or not (IEEE 802.1x is an IEEE
Standard for port-based Network Access Control).
11. Username:
12. Password:
13. PPTP Options:
Username for 802.1x MD5 authentication.
Password for 802.1x MD5 authentication.
PPTP Encryption method. Select Auto for automatic Microsoft
Point-to-Point Encryption (MPPE) and select No Encryption
to disable MPPE. Select MPPE 40 for 40-bit MPPE with PPTP
Server and select MPPE 128 for 128-bit MPPE with PPTP
Server.
14.
Access Concentrator Name:
Specifies the Access Concentrator to connect to. If unset,
pppd uses the first discovered one.
15. Additional Pppd Options:
Additional command line arguments to pass to the pppd
daemon.
16. Host Name:
This field lets you provide a host name for your WiFi Router. It
is usually provided by ISP.
17. MAC Address:
MAC address identifies a device in the network. ISPs monitor
the MAC addresses of devices that connect to their services,
and would disallow Internet connection for new MAC
addresses.
To fix this issue, you can do either of the following:
·
Contact your ISP and request to update the MAC address associated with your ISP
subscription.
·
Clone or change the MAC address of the new device to match the MAC address of the
original device.
37
Page 39

18. DHCP Query Frequency:
19. Enable Default Route:
20.VPN Server:
21. Click Apply.
Some ISP blocks MAC addresses if the device makes DHCP
queries too often. To prevent this, change the DHCP Query
Frequency. In the default Aggressive mode, if your WiFi Router
does not get a response from the ISP, it sends another query
after 20 seconds and makes three more attempts. In Normal
mode, if your WiFi Router does not get a response from the ISP,
it makes a second query after 120 seconds and makes two more
attempts.
Whether to create a default route over the tunnel.
IP address or DNS for VPN server.
38
Page 40

2.4.1.1.2 DDNS
DDNS(Dynamic DNS)makes administrator can get access to WiFi Router even though it’s
working within a local network.
Steps to set up DDNS:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced > Network > WAN > DDNS.
2. Enable the DDNS Client:
Yes means enable DDNS function, No means disable DDNS
function.
3. Server:
4. Host Name:
5. Username or E-mail Address:
Select supported DDNS service provider’s URL from the list.
URL that has been registered in the specified Vendor.
User name or email address which has been registered in
the specified vendor.
6. Password or DDNS Key:
Password which has been registered in the specified vendor.
7. Click Apply.
NOTES: DDNS service will not work properly under these conditions:
·
When the WiFi Router is using a private WAN IP address (192.168.x.x, 10.x.x.x, or
172.16.x.x), as indicated by yellow text.
·
The WiFi Router works on a network who uses multiple NAT tables.
39
Page 41

2.4.1.1.3 UPnP
UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) let devices (such as routers, televisions, stereo systems) be
controlled via an IP-based network with or without a central control unit. Under the help of
UPnP, one device can be discovered once it has connected to network, then device can be
remotely configured to support P2P applications, interactive gaming, video conferencing, and
web or proxy servers. Unlike Port forwarding, UPnP automatically configures the WiFi Router
to accept incoming connections and direct requests to a specific PC on the local network.
Steps to set up UPnP:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced > Network > WAN > UPnP.
2. Enable UPnP:
3. Advertisement Period:
Yes means enable UPnP and No means disable it.
WiFi Router will broadcast its UPnP information to all devices
every advertisement-period seconds.
4. Advertisement Time To Live:
Number of hops that an advertisement will be transmitted.
5. Click Apply.
40
Page 42

2.4.1.1.4 Port Triggering
Port triggering mechanism forwards the packets from the Incoming Port to the local client
when the local client makes an outgoing connection through a predetermined port/port
range (Triggering Port).
Steps to set up Port Triggering:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced > Network > WAN > Port Triggering.
2. Enable Port Triggering:
3. Well-Known Applications:
Check to enable or disable Port Triggering.
Select popular games and web services to add to the Port
Triggering List.
4. Description:
5. Triggering Port:
A brief description for application.
When there is incoming data from LAN-side application to this
port, the Port Triggering mechanism will be activated.
6. Local IP:
7. Protocol:
8. Incoming Port:
Local host's IP address.
Select the type of protocol that the application will use.
Defines the range of port. After Port triggering mechanism has
been activated, the data from port within this range will be
forwarded to the corresponding port of the application which
has activated Port triggering mechanism.
9. Operation:
Add, Edit or Delete operation for this item.
10. Click Apply.
NOTE:Triggering Port element in the list is regarded as a triggering, that’s to say when data
comes to this port, the Port Triggering mechanism will be activated.
41
Page 43

2.4.1.1.5 Port Forwarding
Port forwarding lets remote computers access a specific service within a LAN-side network.
It can redirect a network request from one address/ports (Public IP/Port) to another (Local
IP/Port).
Steps to set up Port Forwarding:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced> Network> WAN>Port Forwarding.
2. Click the Add button to add the port forwarding rules.
42
Page 44

3. Well Known Server List:
Select a pre-defined Server list from the drop-down menu and the
Port Forwarding List will be auto-filled.
4. Well Known Game List:
Select a game from the Server list and the Port Forwarding List
will be auto-filled.
5. Services:
6. Public IP:
7. Port Range:
A short description about this service.
IP address of WAN Port.
Defines the range of port in wan side.
NOTE: A network makes use of ports in order to exchange data, with each port assigned a
port number and a specific task. For example, port 80 is used for HTTP. A specific
port can only be used by one application or service at a time. Hence, two PCs
attempting to access data through the same port at the same time would fail. For
example, you cannot set up Port Forwarding for port 100 for two PCs at the same
time.
8. Local IP:
9. Local Port:
The client’s LAN IP address.
Enter a specific port to receive forwarded packets. Leave this field
blank if you want the incoming packets to be redirected to the
specified port range.
10. Protocol:
The required protocol. Refer to the documentation for the service
that you are hosting.
11. Status:
The status of this rule, on or off.
12. Operation: Edit or Delete operation for this rule.
13. Click Apply
Steps to check whether Port Forwarding module has been activated successfully:
·
Ensure that your server or application is set up and running.
·
You will need a client outside your LAN which has Internet access (referred to as
“Internet client”). This client should not be connected to the WiFi Router.
·
On the Internet client, use the WiFi Router’s WAN IP to access the server. If port
forwarding has been successful, you should be able to access available/specified files
or applications.
Differences between port triggering and port forwarding:
·
Port triggering will work even without setting up a specific LAN IP address. Unlike port
forwarding, which requires a static LAN IP address, port triggering allows dynamic
port forwarding using the WiFi Router. Predetermined port ranges are configured to
accept incoming connections for a limited period of time. Port triggering lets multiple
computers run applications that would normally require manually forwarding the same
ports to each PC on the network.
·
Port triggering is more secure than port forwarding since the incoming ports are
not open all the time. They are opened only when an application is making an outgoing
connection through the triggering port.
43
Page 45

2.4.1.1.6 DMZ
Virtual DMZ module exposes one client to the Internet, allowing this client to receive all
inbound packets directed to a Local Area Network. For IPv4, inbound traffic from the Internet
is usually discarded and routed to a specific client only if port forwarding or a port trigger
has been configured on the network. For IPv6, inbound traffic from the Internet is usually
discarded and routed to a specific client address or a prefix only the ipv6 firewall have the
rules to let them in. In a DMZ configuration, one network client receives all inbound packets.
CAUTION: Opening all of the client’s ports to Internet makes the network vulnerable to
outside attacks. Please be aware of the security risks involved in using DMZ.
Steps to set up DMZ:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced > Network > WAN > DMZ.
2. Enable ipv4 DMZ:
3. IP Address of Exposed Station:
Check to enable or disable DMZ.
LAN IP address of a client who can provide DMZ service.
This makes the device with this IP address expose to
Internet. Make sure that the server client has a static IP
address.
4. Enable IPv6 DMZ:
5.
IPv6 Address of Exposed Station
Check to enable or disable IPv6 DMZ.
The client's LAN IPv6 address that will provide the DMZ
:
service and be exposed on the Internet.
44
Page 46

6. IPv6 prefix for DMZ setting: The IPv6 DMZ address must be in the range of IPv6 prefix.
Show it for user to set valid DMZ address.
7. Click Apply.
45
Page 47

2.4.1.1.7 NAT Pass Through
NAT Pass Through lets a Virtual Private Network (VPN) connection pass through the WiFi
Router to the network server.
Steps to set up NAT Pass Through:
1. To configure NAT Pass Through settings, go to Advanced > Network > WAN > NAT Pass
Through.
2. PPTP Passthrough:
Enable or disable. Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is a
method for implementing virtual private networks.
3. L2TP Passthrough:
Enable or disable. In computer networking, Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol
(L2TP) is a tunneling protocol used to support virtual private
networks (VPNs) or as part of the delivery of services by ISPs. It does
not provide any encryption or confidentiality by itself.
4. IPSec Passthrough:
Enable or disable. Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) is a protocol suite
for securing Internet Protocol (IP) communications by authenticating
and encrypting each IP packet of a communication session.
5. SSL Passthrough:
Secure Sockets Layer(SSL) is cryptographic protocols that provide
communications security over a computer network.
6. RTSP Passthrough:
Enable or disable. The Real Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP) is a
network control protocol designed for use in entertainment and
communications systems to control streaming media servers.
46
Page 48

7. H.323 Passthrough:
Enable or disable. H.323 is a recommendation from the ITU
Telecommunication Standardization Sector (ITU-T) that defines the
protocols to provide audio-visual communication sessions on any
packet network.
8. SIP Passthrough:
Enable or disable. The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is a
communications protocol for signaling and controlling multimedia
communication sessions. The most common applications of SIP are
in Internet telephony for voice and video calls, as well as instant
messaging all over Internet Protocol (IP) networks.
9. NORM Passthrough:
Enable or disable. NACK-Oriented Reliable Multicast (NORM)
Transport Protocol, which can provide end-to-end reliable transport
of bulk data objects or streams over generic IP multicast routing and
forwarding services.
10. Enable PPPoE Relay:
PPPoE relay lets devices in LAN establish an individual PPPoE
connection that passes through NAT.
11. When done, click Apply.
47
Page 49

2.4.1.2 LAN Settings
2.4.1.2.1 LAN
The LAN IP module lets administrator modify LAN-side IP address of the router.
Steps to modify the LAN IP settings:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced > Network > LAN > LAN IP.
2. IP Address:
3. Subnet Mask:
4. Click Apply.
NOTE: Any change to the LAN IP module will affect router’s DHCP settings.
The LAN IP address of WiFi Router. The default value is 192.168.1.1. In IPbased networks, data packets are sent to the network devices' specific IP
addresses.
The LAN subnet mask of WiFi Router. Its default value is 255.255.255.0
48
Page 50

2.4.1.2.2 DHCP Server
DHCP server can assign each client an IP address and informs the client of DNS server’s IP,
default gateway’s IP and etc. This WiFi Router can allocate up to 253 IP addresses for LANside devices.
Steps to configure the DHCP server:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced > Network > LAN > DHCP Server.
2. Enable DHCP Server:
Enable DHCP server function which lets WiFi Router act as a DHCP
server to automatically assign IP addresses to network clients. If this
function is disabled, administrator has to manually set LAN devices.
49
Page 51

3. Domain Name:
4. IP Pool Starting Address:
5. IP Pool Ending Address:
6. Lease Time:
7. Default Gateway:
8. DNS Server:
9. WINS Server:
10. Enable Manual:
11. MAC:
12. IP:
13. Add/Delete:
14. Click Apply.
Domain Name for clients who request IP Address from DHCP
Server. This field only contains alphanumeric characters and
dash symbols.
Starting address that can be allocated to LAN-side devices.
Ending address that can be allocated to LAN-side devices.
Defines the time that LAN-side devices can use the assigned IP
address. When the lease time expires, the network client will
either send renew or rebind message to a DHCP server.
IP address of the gateway for LAN.
IP address of a DNS server. DNS Server is used to resolve a DNS
into a numerical IP Address. By default, the WiFi Router will act
as a DNS server.
Windows Internet Naming Service manages interactions of
each PC with the Internet. If you use a WINS server, enter the IP
Address of server here.
Assign fixed IP address for clients.
MAC address of LAN-side device.
IP address within DHCP IP Pool for an-side device.
Add/Delete static IP.
NOTES:
• We recommend that administrator use an IP address format of 192.168.1.xxx (where xxx
can be any number between 2 and 254) when specifying an IP address range.
• An IP Pool Starting Address should not be greater than the IP Pool Ending Address.
50
Page 52

2.4.1.3 Wireless Settings
2.4.1.3.1 Basic
Basic settings allow you to set up the basic wireless settings.
Steps to set up the basic wireless settings:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced > Network > Wireless > Basic.
2. Frequency:
3. SSID Enable:
4. WiFi Network Name:
5. Hide SSID:
6. Security Setting:
7. WPA Encryption:
Select the frequency band to configure.
Switch the SSID on/off (enable/disable).
A name whose length is less than 32 characters is used to identify
a wireless network. WiFi devices automatically detect all networks
within its communication range.
If [Yes] is selected, network name (SSID) does not show in site
surveys by wireless mobile clients and they can only connect to WiFi
Router by manually enteringnetwork name (SSID).
This field enables authentication methods for wireless clients.
Enable WPA Encryption to encrypt data.
51
Page 53

8. WiFi Password:
9.
Protected Management Frames:
10. Max Clients:
11. Password Rotation Interval:
12. Click Apply.
Requires a password of 8-63 characters (letters,
numbers or a combination) or 8 - 64 hex digits to start
the encryption process.
Protected Management Frames is a feature to protect
some types of management frames like deauthorization,
disassociation and action frames.
The maximum number of clients allowed.
This field specifies the interval (in seconds) after which
a WPA group password is changed. Enter [0] (zero)
to indicate that a periodic key-change is not required.
Please input the value between 600 to 86400 (seconds).
52
Page 54

2.4.1.3.2 WPS
WPS (WiFi Protected Setup) is a wireless security standard that lets you easily connect
devices to a wireless network. You can trigger the WPS function via the PIN code or WPS
button. Reference 2.3.2 WPS Setup
53
Page 55

2.4.1.3.3 ACL
ACL can be used to allow or disallow one device to associate to the AP/ Router.
Steps to set up the ACL:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced > Network > Wireless > ACL.
2. Frequency:
In the frequency field, select the frequency band that you want to
use for the ACL settings.
3. WiFi Network Name:
A name whose length is less than 32 characters is used to identify a
wireless network.
4. Enable MAC Filter:
5. MAC Filter Mode:
Enable MAC filter or disable.
Select Accept to allow devices in the MAC filter list to associate to
the AP/ Router, select Reject to prevent devices in the MAC filter list
from associating to the AP /Router.
6. MAC Filter List:
Enter the MAC address of the wireless device. MAC filtering lets users
either limit specific MAC addresses from associating with the AP/
router, or specifically indicates which MAC addresses can associate
with the AP/router.
7. When done, click Apply.
54
Page 56

2.4.1.3.4 Radio
Administrator can set some advanced feature for radio of the WiFi Router.
55
Page 57

Steps to set Radio:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced > Network > Wireless > Radio.
2. Frequency:
3. Enable Wireless Scheduler:
4. Date to Enable (Weekdays):
5. Time of Day To Enable:
6. Date to Enable (Weekend):
7. Time of Day To Enable:
8. Enable Radio:
Selecting the frequency band that the WiFi Router is running.
Switch wireless schedule on or not.
Select weekdays to enable Wi-Fi.
Set weekday time to enable Wi-Fi.
Select weekend days to enable Wi-Fi.
Set weekend time to enable WiFi.
Select [Yes] to enable wireless radio (wireless network).
Select [No] to disable wireless radio (wireless network).
9. Wireless Mode:
10. Channel Bandwidth:
11. Control Channel:
12. Enable TX Bursting:
Select a Wireless Mode of your 802.11n interface.
Sets manual channel bandwidth.
The radio channel for wireless connection operation.
TX Bursting improves transmission speed between WiFi
Router and 802.11g devices.
13. Tx Power Adjustment:
Set the capability for transmission power. The maximum
value is 100%. You can save power and increase security if
you don’t require full wireless range.
NOTE: Increasing the Transmission Power adjustment values may affect the stability of the
wireless network.
14. OBSS RSSI:
Configure OBSS RSSI threshold. If OBSS RSSI is greater than
configured value, then only move to 20 Mhz.
15. RTS Threshold:
Select a lower value for RTS (Request to Send) Threshold to
improve wireless communication in a busy or noisy wireless
network with high network traffic and numerous wireless
devices.
16. Fragmentation Threshold:
Set the fragmentation threshold, which is the maximum
fragment size.
17. Beacon Interval:
Beacon Interval means the period of time between one
beacon and the next one. The default value is 100 (the unit is
millisecond, or 1/1000 second). Lower the Beacon Interval to
improve transmission performance in unstable environment
or for roaming clients, but it will be power consuming.
18. HT AMPDU Factor:
Enables or disables Tx AMPDU aggregation for the entire
interface. Receiving aggregate frames will still be performed,
but no aggregate frames will be transmitted if this is
disabled.
19. VHT AMPDU Factor:
Set VHT capability field, Maximum A-MPDU length exponent.
Value range is 0 to 7. Maximum A-MPDU length exponent
indicates the maximum length of A-MPDU that the station
can receive.
56
Page 58

20. DCS Enable:
21. Radio Resource Management:
22. When done, click Apply.
Enable or disable DCS function which is a feature to
detect and avoid CW interference.
Enables or disables 802.11k
57
Page 59

2.4.1.3.5 Advanced
The Professional module provides advanced configuration options.
NOTE: We recommend that administrators use the default settings.
58
Page 60

In this module, administrator can configure the followings:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced > Network > Wireless > advanced.
2. Frequency:
3. WiFi Network Name:
Select the frequency band to configure professional settings.
A name whose length is less than 32 characters is used to
identify a wireless network.
4. Enable TX STBC:
Enables or disables the Space Time Coding Block (STBC)
feature, as described in 802.11n specification, in transmitting
(TX) direction.
5. Enable RX STBC:
Enables or disables the Space Time Coding Block (STBC)
feature, as described in 802.11n specification, in receiving(RX)
direction.
6. Set AP Isolated:
Prevent wireless devices from communicating with each other
via WiFi Router. This feature is useful if many guests frequently
join or leave your network. Select [Yes] to enable this feature or
select [No] to disable.
7. Multicast Rate (Mbps):
8. Short Guard Interval:
Setting transmission rate for multicast.
Defines the length of time that the WiFi Router spends for CRC
(Cyclic Redundancy Check). CRC is a method of detecting
errors during data transmission. Select Enable for a busy
wireless network with high network traffic.
9. DTIM Interval:
DTIM (Delivery Traffic Indication Message) Interval or Data
Beacon Rate is the time interval before a signal is sent to a
wireless device in sleep mode indicating that a data packet is
awaiting delivery. The default value is three milliseconds.
10. WMM:
Enables or disables WMM capabilities in the driver. The WMM
capabilities perform special processing for multimedia stream
data including voice and video data.
11. Enable WMM APSD:
Enable WMM APSD (WiFi Multimedia Automatic Power Save
Delivery) to improve power management between wireless
devices. Select Disable to switch off WMM APSD.
12. Turbo QAM:
256-QAM (MCS 8/9) support. Wireless Mode must be set to
auto.
13. Universal Beamforming:
For legacy wireless network adapters which do not support
beamforming, the WiFi Router estimates the channel and
determines the steering direction to improve the downlink
speed. (Also known as Implicit Beamforming.)
14. Click Apply.
59
Page 61

2.4.1.4 IPv6
The module is used to set some basic functions related to IPv6. For IPv6 service is not yet
widely available, contact your ISP to make sure whether IPv6 service is provided.
60
Page 62

Steps to set up IPv6:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced > Network > IPv6.
2. Connection Type:
Select IPv6 connection type to configure Disable,
Native, Static IPv6.
3. WAN IPv6 Address:
4. WAN Prefix Length:
5. WAN IPv6 Gateway:
6. WAN IPv6 MTU:
Set the wan interface’s ipv6 address.
Set the wan interface’s ipv6 prefix length.
Set the wan interface’s ipv6 gateway
Set the WAN interface’s IPv6 MTU
(Maximum Transmission Unit).
7. User Class Option:
The user class option (15) of ORO that DHCPv6
clients send to the DHCPv6 server by solicit
message.
8. Auto Configuration:
The wan interface’s address assign type (SLAAC). Enable: WAN
interface can get ipv6 address by SLAAC. Disable:
WAN interface gets the ipv6 address only by stateful.
9. Enable LAN:
Enable/Disable WiFi Router allocating IPv6
addresses for LAN-side devices.
10. Simultaneous:
The mode which hosts connected to the LAN
11. LAN IPv6 Address:
12. LAN Prefix Length:
13. LAN IPv6 Prefix:
14. Enable Pool Setting For Lan Host:
15. DHCP Pool Start:
16. DHCP Pool End:
17. PD-Valid Lifetime:
18. PD-Preferred Lifetime:
interface can get IPv6 addresses. When enabled,
hosts get IPv6 address by simultaneous Stateless
and Stateful (requires address between DHCP
pool start and end values). When disabled, hosts
do not get IPv6 addresses simultaneously, and a
mode must be selected instead (SLAAC + RDNSS,
SLAAC+Stateless DHCPv6, Stateful DHCPv6).
Set LAN interface’s IPv6 address.
Set LAN interface’s IPv6 prefix length.
Set LAN interface’s prefix.
Enable to set DHCP pool start and end values for
client IPv6 address assign range, it’s disable by
default.
DHCPv6 address setting address pool start.
DHCPv6 address setting address pool end.
Prefix delegation for valid lifetime.
Prefix delegation for preferred lifetime.
19. LAN IPv6 MTU:
20. Connect to DNS Server Automatically:
21. IPv6 DNS Server 1:
Set MTU for LAN-side devices.
Choose to get the DNS from manually from
uplink.
IPv6 address for DNS server.
61
Page 63

22. IPv6 DNS Server 2: IPv6 address for DNS server.
23. IPv6 DNS Server 3: IPv6 address for DNS server.
24. Port Ranges Valid for Port Forwarding: The "port ranges" are set by Map-T mode, and
the port setting for port forwarding must be in
these ranges.
25. Click Apply.
62
Page 64

2.4.1.5 Parental Control
Refer to 2.3.5 Parental Control for relevant setting descriptions.
2.4.1.6 Multicast
Enable multicast. The sender and receiver achieve a point to multipoint connection.
Steps to set up Multicast:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced > Network > Multicast.
2. IPv4 Multicast Route: Select an IPv4 Multicast Route.
* IGMP Proxy: IGMP Proxy enables hosts in a unidirectional link routing
(UDLR) environment that are not directly connected to a
downstream WiFi Router to join a multicast group sourced
from an upstream network.
* PIM: PIM-Source-specific multicast (SSM) is used in IPv4/IPv6
and is a method of delivering multicast packets in which the
only packets that are delivered to a receiver are those
originating from a specific source address requested by the
receiver. By limiting the source, SSM reduces demands on
the network and improves security.
3. IPv6 Multicast Route: Select an IPv6 Multicast Route.
* MLD Proxy: The MLD proxy is used in IPv6 environments. This feature
enables a device
to learn proxy group membership information, and forward
multicast packets based upon that information. If a device
is acting as RP for route proxy entries, MLD membership
reports for these entries can be generated on user specified
proxy interface.
63
Page 65

4. Enable IGMP/MLD Snooping: Check [Yes] to enable snooping and Check [No] to disable
snooping. IGMP/MLD snooping is the process of listening to
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) / Multicast
Listener Discovery (MLD) network traffic. The feature lets a
network switch listen in on the IGMP/MLD conversation
between hosts and WiFi Routers.
5. When done, click Apply.
64
Page 66

2.4.1.7 Routing
This module can be used to build a static NAT table between WAN IP address and LAN IP
address.
Steps to set up Routing:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced > Network > Routing.
2. Enable 1:1 NAT: Check [Yes] to enable this function, check [No] to disable this function.
3. Name: A brief description for application.
4. Public IP: IP address from Charter supplied public IP subnets.
5. Local IP: Key in the client’s LAN IP address, not limited to the subnet for the directly
connected LAN interface
6. Click On/Off to enable/disable Internet access to FTP service.
7. Click to add this item to the 1:1 NAT List.
8. Click Apply.
NOTE: This module only works only when WAN port is in static mode!
65
Page 67

2.4.2 Services Config
2.4.2.1 USB Printer sharing
Refer to 2.3.6.1 USB Printer sharing for relevant setting descriptions.
2.4.2.2 FTP Server
FTP Server enables an FTP server to share files from USB disk to other devices via your local
area network or via the Internet.
To set up FTP Server:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced > Services > FTP Server.
2. Connect an external USB hard disk drive or USB flash drive to the WiFi Router, and your
device will be displayed here.
66
Page 68

3. Click On/Off to enable/disable Internet access to FTP service.
To create a new account:
1. Add new account.
2. In the Account and Password fields, key in the name and password of your network client.
Retype the password to confirm. Click Add to add the account to the list.
To add a folder:
1. Add new folder.
2. Enter a folder name. The folder that you created will be added to the folder list.
To set up permissions on the folder for FTP server:
1. From the list of folders, choose one of the shared folders and select the type of access
permission that you want to assign for specific users:
·
R/W: Select this option to assign read/write access.
·
R: Select this option to assign read-only access.
·
No: Select this option if you do not want to share a specific file folder.
2. Click Save Permission to apply the changes.
Refer to the following descriptions:
·
Maximum number of Connections: The maximum number of concurrent connections
for the Network Neighborhood or FTP Server.
·
Enable Outside Access: Select On/Off to enable/disable to access FTP server by wide
area network.
·
Outside Access: The numbers of external service ports (default value: 8021).
·
·
Anonymous Login: Enable/disable anonymous access to the FTP server.
Safely Remove Disk: Click to safely remove disk. When the USB disk is ejected
successfully, the USB status shows “No device”.
·
Click Save Permission.
67
Page 69

2.4.2.3 Samba
Samba Share lets you set up the accounts and permissions for the Samba service.
To set up Samba:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced > Services > Samba Server.
2. Connect an external USB hard disk drive or USB flash drive to the WiFi Router, and your
device will be displayed here.
3. Click On/Off to enable/disable Internet access to Samba service.
To create a new account:
1. Add new account.
2. In the Account and Password fields, key in the name and password of your network client.
Retype the password to confirm. Click Add to add the account to the list.
68
Page 70

To add a folder:
1. Add new folder.
2. Enter a folder name. The folder that you created will be added to the folder list.
To set up permissions on the folder for Samba server:
1. From the list of folders, choose one of the shared folders and add the share name, and
choose the type of access permission that you want to assign for specific users:
·
R/W: Select this option to assign read/write access.
·
R: Select this option to assign read-only access.
·
No: Select this option if you do not want to share a specific file folder.
2. Click Save Permission to apply the changes
Refer to the following descriptions:
·
Device Name: Enter a name for your device and you can use this name in your web
browser's URL field to quickly access the device as a Network Place service.
·
Work Group: Group name of the cascade in Network Neighborhood.
·
Note: The standard input characters include letters (A-Z, a-z), digits (0-9).
The hyphen (-) and under line (_) characters may also be used, but
the hyphen (-) can't be as the first character.
·
Guest Login: By enabling [Guest Login], any user in your local network can access
your network place (Samba) without authentication.
·
Safely Remove Disk: Click to safely remove the disk. When the USB disk is ejected
successfully, the USB status shows 'No device '.
·
Click Save Permission.
69
Page 71

2.4.2.4 WebDAV
The client can write operation in WebDAV directory with appropriate permissions.
To set up WebDAV:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced > Services > WebDAV Server.
2. Connect an external USB hard disk drive or USB flash drive to your WiFi Router, and your
device will be displayed here.
3. Click On/Off to enable/disable Internet access via WebDAV.
To create a new account:
1. Add new account.
2. In the Account and Password fields, key in the name and password of your network client.
Retype the password to confirm. Click Add to add the account to the list.
70
Page 72

To add a folder:
1. Add new folder.
2. Enter a folder name. The folder that you created will be added to the folder list.
To set up permissions on the folder for WebDAV server:
1. From the list of folders, choose one of the shared folders and add the share name, then
choose the type of access permission that you want to assign for specific users:
·
·
R/W: Select this option to assign read/write access.
R: Select this option to assign read-only access.
2. Click Save Permission to apply the changes.
Refer to the following for the descriptions of the fields:
·
Enable Outside Access: Select On/Off to enable/ disable access to WebDAV server by
WAN (wide area network).
·
Outside Access: The port number of external service ports via HTTP (default value: 8080).
·
Outside Access HTTPS: The port number of external service ports via HTTPS
(default value: 8443).
·
Safely Remove Disk: Click to safely remove the disk. When the USB disk is ejected
successfully, the USB status shows 'No device '.
·
Click Save Permission.
71
Page 73

2.4.2.5 DLNA
DLNA (Digital Living Network Alliance) lets you share audio, image and video. Your WiFi
Router lets DLNA-supported devices access multimedia files from the USB disk connected to
your WiFi Router.
To set up DLNA:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced > Services > DLNA Server.
2. Enable DLNA Media Server: Switch DLNA media on or off.
3. Media Server Name: The DLNA server's name, which will be displayed by the media
player, such as VLC or windows media player.
4. Media Server Path Setting: The methods of setting the folders' path which will be shared.
There are two methods to be chose, "All Disks Shared" means
share all of the mounted disks' all media; "Manual Media
Server Path" means set the folders to be shared manually,
When Manual is selected you must enter additional
information in " Manual Media Server Path".
5. Manual Media Server Path: Set the folders to be shared and the media type that will be
shared by the DLNA server.
6. Media Server Directory: The folders that will be shared by the DLNA.
72
Page 74

7. Shared Content Type: The media type that will be shared by the DLNA server: audio,
image, video.
8. Safely Remove Disk: Click to safely remove the disk. When the USB disk is ejected
successfully, the USB status shows 'No device '.
9. Click Apply.
73
Page 75

2.4.2.6 AFP
An AFP server is a kind of network file sharing server based on AFP protocol implementation,
mainly used for file sharing between Linux and MAC systems.
To set up AFP:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced > Services > AFP Server.
2. Connect an external USB hard disk drive or USB flash drive to your WiFi Router, and your
device will be displayed here.
3. Click the On/Off to enable/disable Internet access via AFP.
To create a new account:
1. Add new account.
2. In the Account and Password fields, key in the name and password of your network
client. Retype the password to confirm. Click Add to add the account to the list.
To add a folder:
1. Add new folder.
2. Enter a folder name. The folder that you created will be added to the folder list.
74
Page 76

To set up permissions on the folder for AFP server:
1. From the list of folders, choose one of the shared folder and add the share name, and
choose the type of access permission that you want to assign for specific users:
·
RW: Select this option to assign read/write access.
·
R: Select this option to assign read-only access.
·
No: Select this option if you do not want to share a specific file folder.
2. Click Save Permission to apply the changes.
Refer to the following for the descriptions of the fields:
·
Guest Login: By enabling [Guest Login], any user in your local network can access
your network place (AFP) without authentication.
·
Safely Remove Disk: Click to safely remove the disk. When the USB disk is ejected
successfully, the USB status shows 'No device '.
·
Click Save Permission.
75
Page 77

2.4.2.7 NFS
Network File System Server is used to share the USB disk with clients via network. Clients
can mount the remote disk to a local directory for a faster speed than using a Samba server.
To setup NFS:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced > Services > NFS Server.
2. Connect an external USB hard disk drive or USB flash drive to your WiFi Router, and your
device will be displayed here.
3. Enable NFS: Enable or disable NFS service. When disabled, users can't access the USB
storage via the NFS service.
4. Clients: "Clients" are users who can access the shared partition specified. You can
input the proper information into the input field to allow the clients to access
the specified shared partition. The proper permission format is "IP address,
Read and write permission" and if you want to set more than one clients
and with different permission, you can input the information separated by ";".
For read and write permissions, "ro" means "read only" permission and the
"rw" means " read and write" permission. The IP address can be replaced by
"*" and means all IPs. For example,
1) Let the clients with the IP address 192.168.1.2 access the partition
with "read and write" permission.
2) Let two clients access the shared partition. The client with IP
address 192.168.1.2 has "read only" permission, and the client with IP
address 192.168.1.3 has "read and write" permission. >
192.168.1.2,ro;192.168.1.3,rw
76
Page 78

3) Let clients access the destination shared partition with the
"read only" permission. > *,ro
5. Safely Remove Disk: Click to safely remove the disk. When the USB disk is ejected
successfully, the USB status shows 'No device '.
77
Page 79

2.4.3 Security
2.4.3.1 VPN
VPN (Virtual Private Network) provides a secure communication to a remote computer or
remote network using a public network such as the Internet.
2.4.3.1.1 PPTP VPN Server
The VPN server lets administrator get access to home network anytime, anywhere.
NOTE: Before setting up a VPN connection, you need the IP address or domain name of the
VPN server you are trying to access.
Steps to set up access to PPTP VPN server:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced > Security > VPN > PPTP VPN Server.
·
·
settings.
·
name and password for the VPN server and click the
button.
Enable VPN Server: enable or disable PPTP VPN Server.
VPN Details: The details of PPTP VPN Server. Select General or Advanced
Username and Password: The user information of PPTP VPN Server. Input the user
78
Page 80

2. Advanced VPN server settings, as below.
·
Broadcast Support: Turns on broadcast relay to clients from the WiFi
Router.
·
Authorization Mode: Select Authorization Mode.
·
MPPE Encryption: Select MPPE Encryption type.
·
Connect to DNS Server Automatically: DNS of PPTP clients.
·
Connect to WINS Server Automatically: WINS of PPTP clients.
·
MRU/MTU: The Maximum Receive Unit (MRU) or Maximum
Transmission Unit (MTU) sizes are sent to the
client as part of the PPTP parameters to use
during the PPTP session. We recommend that
you do not change MTU or MRU values unless
you are sure the change corrects a known
problem with your PPTP sessions. Incorrect MTU
or MRU values cause traffic through the PPTP
VPN to fail.
·
Client IP Address: The IP address range of PPTP clients.
·
Click Apply.
79
Page 81

2.4.3.1.2 OpenVPN Server
The VPN server lets administrator get access to home network anytime, anywhere.
Steps to set OpenVPN Server:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced > Security > VPN > OpenVPN Server.
·
Enable VPN Server: Enable or disable OpenVPN server function.
·
VPN Details: Enter the details of your VPN server. Select General or Advanced
settings.
·
Username and Password: The user information of OpenVPN server. Input the user
name and password for the VPN server and click the button.
2. Advanced VPN server settings:
80
Page 82

·
Interface Type: "TUN" will create a routed IP tunnel, "TAP" will create
an Ethernet tunnel.
·
Protocol: TCP or UDP server.
·
Server Port: The TCP/UDP port which OpenVPN server will listen
on.
·
Firewall: Firewall configuration for VPN server. Auto will create
complete firewall configurations, External only will
create basic firewall configurations and Custom will not
create any firewall configurations.
·
Authorization Mode: Select Authorization Mode.
81
Page 83

·
Username / Password Auth. Only: Yes requires only username and password for
authentication, No also requires authentication
certificate.
·
Extra HMAC Authorization: If enabled, a tls_auth key will be used on the server.
Every client must also have the key.
·
VPN Subnet / Subnet Mask: VPN subnet and subnet mask settings.
·
Poll Interval: The interval time for crontab of VPN server starting.
·
Push LAN to Clients: Push routes to the client to allow it to reach other
private subnets behind the server.
·
All traffic through VPN: If enabled, this directive will configure all clients to
redirect their default network gateway through the
VPN, causing all IP traffic such as web browsing and
DNS lookups to go through the VPN.
·
Respond to DNS: Push DNS to clients.
·
Encryption Cipher: Select a cryptographic method. This configure item
must be copied to the client configure file as well.
·
Compression: Enable compression on the VPN link. If this function is
enable here, in the client configure administrator also
should enable it.
·
TLS Renegotiation Time: After a period of time, authentication is required again.
·
Manage Client-Specific Options: To assign specific IP addresses to specific clients or if
a connecting client has a private subnet behind it that
should also have VPN access, enable this option.
·
Click Apply.
82
Page 84

2.4.3.1.3 VPN Client
View the VPN server list and add profiles. There are three types of VPN servers: PPTP, L2TP
and Open VPN.
Steps to setup a VPN Client:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced > Security > VPN > VPN Client.
2. VPN Sever list is displayed. Click Add Profile to set up VPN Client.
3. VPN Server List: Current VPN Services which have been configured.
4. VPN Type: Type of VPN Server access such as PPTP, L2TP and OpenVPN.
83
Page 85

5. Enable Default Route:
6. Description:
7. VPN Server:
8. Username:
9. Password:
10. PPTP Options:
Check [Yes] to use default route acquiring from VPN Server.
Check [No] to use general default route.
Enter a description for reference.
VPN Server IP address or URL.
VPN authentication username.
VPN authentication password.
PPTP Encryption method. Select Auto for automatic Microsoft
Point-to-Point Encryption (MPPE) and select No Encryption to
disable MPPE. Select MPPE 40 for 40-bit MPPE with PPTP Server
and select MPPE 128 for 128-bit MPPE with PPTP Server.
11. When done, click Confirm.
84
Page 86

2.4.3.2 IPv4 Firewall
Enable the firewall to protect local area network against attacks from outside. Firewall filters
the incoming and outgoing packets based on rules.
NOTE: Firewall is enable by default.
2.4.3.2.1 Common
Steps to set up basic Firewall settings:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced > Security > IPv4 Firewall > Common.
2. Enable Firewall: Disabling the firewall will deactivate all related
functions.
3. Enable DoS Protection: A "denial-of-service" attack is an explicit attempt
to deny legitimate users from using a service or
computer resource. Enabling this feature can
protect the WiFi Router from DoS attack but it
would increase the WiFi Router's workload.
4. Respond to Ping Request from WAN: This feature lets WiFi Router make a response to
ping request from WAN.
5. Enable IGMP: Check [Yes] to allow IGMP packages to be
transferred to the WiFi Router. Check No to deny
IGMP packages.
6. Click Apply.
85
Page 87

2.4.3.2.2 Net Service Filter
Net Service Filter can work in either White List or Black List mode. When running in White
List mode, it only lets certain packets get through the WiFi Router. While in Black List mode,
it only blocks certain packets passthrough.
Steps to set Net Service Filter:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced> Security> IPv4 Firewall> Net Service Filter.
2. Enable Net Service Filter: Enable or disable this module.
3. Filter Table List: There are two kinds of filter list: White List, Black List. White
List can make WiFi Router serve the specified service defined
in the list, Black List make WiFi Router deny serving the
specified service.
4. Filtered ICMP packet types: This field defines a list of LAN to WAN ICMP packets type
that will be filtered. For example, if you would like to filter
Echo (type 8) and Echo Reply (type 0) ICMP packets, you
need to enter a string with numbers separated by blank, such
as [0 8].
5. Source IP: For source or destination IP address, you can:
(a) enter a specific IP address such as "192.168.122.1";
(b) enter IP addresses within one subnet or within the same IP pool such as "192.168.123.*"
or "192.168.*.*";
(c) enter all IP addresses as "*.*.*.*".
86
Page 88

6. Port Range:
For source or destination port range, you can either:
a) enter a specific port, such as "95";
b) enter ports within a range such as "103:315", ">100", or "<65535".
7. Destination IP: For source or destination IP address, you can:
a) enter a specific IP address such as "192.168.122.1";
b) enter IP addresses within one subnet or within the same IP pool such as "192.168.123.*"
or "192.168.*.*"
c) enter all IP addresses as "*.*.*.*".
8. Port Range:
For source or destination port range, you can either:
a) enter a specific port, such as "95";
b) enter ports within a range, such as "103:315", ">100", or "<65535".
9. Protocol: The protocol of service used to transport the packages. (UDP, TCP)
10. Add/Delete: Click or to add/delete the profile.
11. When done, click Apply.
87
Page 89

2.4.3.2.3 Client ACL
Client ACL can forbid the client from accessing to the WiFi Router. The client in the Client
ACL List can’t visit the resource of WiFi Router and the internet.
Steps to set up Client ACL:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced> Security> IPv4 Firewall> Client ACL.
2. Enable Client ACL: Enable or disable Client ACL function.
3. Client: MAC address of LAN-side devices.
4. Add/Delete: Click or to add/delete the profile.
5. When done, click Apply.
88
Page 90

2.4.3.3 IPv6 Firewall
2.4.3.3.1 Common
Steps to set up common IPv6 Firewall:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced > Security >IPv6 Firewall > Common.
2. Enable Firewall: Enable or disable the IPv6 firewall. When disabled,
all IPv6 packages can input WiFi Router, output
WiFi Router and forward without any limitation.
3. Respond to Ping Request from WAN: This feature lets WiFi Router make a response
to ping request from WAN.
4. Enable MLD: Check [Yes] to allow MLD packages to be
transferred to the WiFi Router.
Check [No] to deny MLD packages.
5. Click Apply.
89
Page 91

2.4.3.3.1 Allow Services
Allow Services allows various types of service rules including protocol like TCP/UDP and
ICMPv6 Message Type. It will allow certain packets and drop the other IPv6 packets from
WAN-side to LAN-side.
Steps to set up IPv6 Firewall:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced > Security > IPv6 Firewall > Allow Services.
2. Enable Allow Services: Enable or disable the IPv6 Allow Services feature. When
Allow Services is enabled, the Allowed Service Rules will
be allowed.
3. Allowed Well-Known Server List: List of well-known servers to be allowed. For example:
ftp, samba.
4. Service Name: The name of the service which will add IPv6 firewall rule.
5. Remote IP/Prefix: IPv6 address or Prefix of a remote server.
6. Local IP/Prefix: IPv6 address or Prefix of a LAN-side client.
7. Port Range: Port range accepts various formats such as Port Range
(300:350), individual ports (566,789) or Mix (1015:1024,
3021).
90
Page 92

8. Protocol: The protocol the service uses to transport the packages e.g. (UDP, TCP).
9. ICMPv6 Message Type: Make WiFi Router process the defined types of ICMPv6 packet
from specified host.
10. Local Host: IPv6 address of the host.
11. Add/Delete: Click or to add/delete the profile.
12. When done, click Apply.
91
Page 93

2.4.4 QoS
QoS(Quality of Service, QoS) module provides different services according to the priority of
applications, users, or data flows. In a word, it can guarantee a certain level of performance
to a data flow.
2.4.4.1 Airtime Fairness
The ATF(Airtime Fairness, ATF) module supports mixing rates of WiFi devices to achieve
better performance in busy/intense environments.
Steps to set ATF:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced > QoS > Airtime Fairness.
2. Enable ATF: Enable or disable. ATF require primarily focuses on scheduling
fairness for transmission of traffic from Access Point (AP), and
efficient WiFi bandwidth utilization.
3. Frequency: In the frequency field, select the frequency band that you want to
use for the ATF settings.
4. ATF Mode:
Airtime Fairness implements 2 scheduling algorithms:
strict-queue and fair-queue algorithm, which are mutually exclusive. Strict-queue
algorithm follows strict airtime allocation as configured by the user and does not try and
utilize any unused bandwidth. Fair-queue algorithm guarantees the configured airtime in
congested environments and it also utilizes any unused bandwidth.
5. WiFi Network Name: Set the network name (SSID) which will be controlled by ATF.
92
Page 94

6. Percentage of Air Time: Set the percentage of SSID which will be used for ATF control.
7. MAC: Select client by MAC address and set the percent which will be
used for ATF control.
8. Click Apply.
93
Page 95

2.4.4.2 Common
Set up queue and down queue type, Decided in the queue page we can operate the type of
queue, and set uplink and downlink limit, Limit our uplink and downlink transmission rate.
Steps to set it:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced > QoS > Common.
2. QoS Enable: Set the switch of CPE QOS function through Web page.
3. WAN Uploading Speed: The speed of the uplink data limit.
4. LAN Downloading Speed: The downstream limit of the subnet LAN.
5. WAN Interface Queue Type: Upstream Qos queue type, should to be set (Strict Priority /
Weighted Round Robin / Weighted Fair Queuing).
6. LAN Interface Queue Type: Downstream Qos queue type, Should to be set (Strict
Priority / Weighted Round Robin / Weighted Fair Queuing),
For Subnet LAN.
7. Click Apply.
94
Page 96

2.4.4.3 Queue
Create an upstream queue and a downstream queue to classify traffic of different types into
the upstream or downstream queue. Up queue and down queue type based on common
page selection. In the queue page on the queue. Add, delete, modify.
2.4.4.3.1 UpStream Queue
Steps to set queue:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced > QoS > Queue > UpStream Queue.
2. Enable: Enables or disables this queue.
3. Weight: Weight of this queue in case of Weighted Round Robin or Weighted Fair
Queuing, but only used for queues of equal precedence.
4. Operation: Add, Edit or Delete operation for this item.
5. Click Apply.
95
Page 97

2.4.4.3.2 DownStream Queue
Steps to set queue:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced > QoS > Queue > DownStream Queue.
2. Enable: Enables or disables this queue.
3. Weight: Weight of this queue in case of Weighted Round Robin or Weighted Fair
Queuing, but only used for queues of equal precedence.
4. Operation: Add, Edit or Delete operation for this item.
5. Click Apply.
96
Page 98

2.4.4.4 Classification
According to the characteristics of the data flow, traffic is classified and then queued to the
specified upstream or downstream queues.
Classification Display page:
Display classification table (Simple information).
Steps to set up Classification:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced > QoS > Classification.
2. Classification is displayed. Click Add to set up.
3. Name: Classification name.
4. Queue Type: The queue that represents the current entry selection.
5. Enable: Display the entry’s status.
6. Edit/Del: Modify or delete this entry.
97
Page 99

7. Enable:
8. Base On:
Disable or enable this classification function.
It is a fast classification, (can be based on Client, Custom, Server,
SSID, APP).
9. Name:
10. Queue Type:
11. Queue Name:
Define this classification alias name.
Select the existing queue (upstream or downstream).
Only display. Indicates the index number of the queue type
selected by the user.
12. Class Interface:
13. Source IP:
This specifies the ingress interface associated with the entry.
Source IP address. An empty string indicates this criterion is not
used for classification.
14. Source MAC Address:
Source MAC Address. An empty string indicates this criterion is
not used for classification.
15. Source Port:
16. Protocol:
17. Dest IP:
Source port number
Protocol
Destination IP address, an empty string indicates this criterion is
not used for classification.
18. Dest MAC Address:
Destination MAC Address. An empty string indicates this criterion
is not used for classification
19. Dest Port:
20. DSCP Check:
21. DSCP Remark:
Destination port number.
DSCP number (0~63), base on it filter.
Remark new DSCP number.
22. When done, click Apply.
98
Page 100

2.4.5 Admin
2.4.5.1 System
The System page lets you configure your WiFi Router settings. If you changed the password,
the user password used to sign in SSH will be changed.
Steps to set System:
1. From the navigation panel, go to Advanced > Admin > System.
2. Username: WiFi Router’s sign in name.
3. New Password: New password.
4. Retype New Password: Retype new password.
99
 Loading...
Loading...