SpectraLink NetLink e340, NetLink i640, NetLink h340 Configuration And Administration Manual
Page 1

NetLink e340/h340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP
Configuration and Administration
Part Number: 72-1084-02
Issue E
Page 2
SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
Notice
SpectraLink Corporation has prepared this document for use by SpectraLink personnel and clients. The
drawings and specifications contained herein are the property of SpectraLink and shall be neither reproduced in
whole or in part without the prior written approval of SpectraLink, nor be implied to grant any license to make,
use, or sell equipment manufactured in accordance herewith.
SpectraLink reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information contained in this
document without prior notice, and the reader should in all cases consult SpectraLink to determine whether
any such changes have been made.
The terms and conditions governing the sale of SpectraLink hardware products and the licensing of
SpectraLink software consist solely of those set forth in the written contracts between SpectraLink and its
customers. No representation or other affirmation of fact contained in this document including but not limited
to statements regarding capacity, response-time performance, suitability for use, or performance of products
described herein shall be deemed to be a warranty by SpectraLink for any purpose, or give rise to any liability of
SpectraLink whatsoever.
In no event shall SpectraLink be liable for any incidental, indirect, special, or consequential damages
whatsoever (including but not limited to lost profits) arising out of or related to this document, or the
information contained in it, even if SpectraLink has been advised, knew, or should have known of the
possibility of such damages.
Trademark Information
SpectraLink
LinkPlus
Link Wireless Telephone System
NetLink Telephony Gateway
NetLink Wireless Telephone
NetLink SVP Server
SpectraLink Voice Priority
ccLink Wireless Telephone System
NetLink e340 Wireless Telephone
NetLink h340 Wireless Telephone
NetLink i640 Wireless Telephone
Are trademarks and registered trademarks of SpectraLink Corporation.
All other trademarks used herein are the property of their respective owners.
SpectraLink Corporation
5755 Central Avenue
Boulder, CO 80301
Within the United States, dial
303.440.5330 or
toll free 800.676.5465
Outside the U.S., dial
+1.303.440.5330
www.spectralink.com
Copyright © 1998 to 2005 SpectraLink Corporation. All rights reserved
Information in this document is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the
part of SpectraLink Corporation. The software described in this document is furnished under a license and/or
copyright and may only be used with the terms of SpectraLink’s software license agreement as found in this
manual or at www.spectralink.com/software.php. The software may be used only in accordance with the terms
of the agreement. No part of this manual, or the software described herein, may be reproduced or transmitted
in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying and recording, for any purpose
except for the sole intent to operate the product or without the express written permission of SpectraLink
Corporation.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 2
Page 3

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
Table of Contents
1. About This Document 4
1.1 Referenced Documents 4
1.2 Customer Support Hotline 4
1.3 Icons and Conventions 4
2. NetLink e340/h340/i640 Wireless Telephone Overview 5
2.1 QoS and Security 5
2.2 Quick Start Guide 6
2.3 System Diagram 7
2.4 System Components 8
3. The NetLink Wireless Telephone 10
3.1 Specifications 10
3.2 The Display 11
3.3 Startup Sequence 13
3.4 Handset Modes 14
3.5 NetLink Wireless Telephone Displays 15
4. NetLink Wireless Telephone Configuration 16
4.1 The Admin Menu 16
4.2 User-defined Preferences 25
5. License Management 31
5.1 Requirements 31
5.2 Configuration Process 31
6. Mitel Networks VoIP Integration Factors 33
7. Feature Programming 35
7.1 Feature Assignment 36
7.2 Feature Access 37
8. Testing a Handset 40
9. Diagnostic Tools 41
9.1 Run Site Survey 41
9.2 Diagnostics Mode 43
9.3 Syslog Mode 46
10. Certifying the NetLink Wireless Telephones 48
10.1 Conducting a Site Survey 48
11. Software Maintenance 49
11.1 Upgrading NetLink Wireless Telephones 49
12. Troubleshooting NetLink Wireless Telephone Problems 51
12.1 Access Point Problems 51
12.2 Configuration Problems 51
12.3 NetLink Wireless Telephone Status Messages 52
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 3
Page 4
SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
1. About This Document
This document explains how to configure and maintain the SpectraLink
e340/h340/i640 Wireless Telephone within the Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200
Integrated Communications Platform (ICP).
1.1 Referenced Documents
NetLink SVP Server: Installation, Configuration, and Administration within IP environments
(72-0178-01)
NetLink Wireless Telephone WLAN Compatibility List (72-9000-00)
Access Point Configuration Note (72-99xx-00 where xx indicates a number
corresponding to the type of access point.)
Above documents are available at
http://www.spectralink.com/service/manuals.html.
Open Application Interface (OAI) Specification (72-0052-00)
Above document available by request from SpectraLink Customer Service.
1.2 Customer Support Hotline
SpectraLink wants you to have a successful installation. If you have questions please
contact our Customer Support Hotline at (800) 775-5330. The Hotline is open
Monday through Friday, 5:00 AM to 7:00 PM Mountain Time.
1.3 Icons and Conventions
This manual uses the following icons and conventions.
Caution! Follow these instructions carefully to avoid danger.
Note these instructions carefully.
NORM
This typeface indicates a key, label, or button on the NetLink Telephony
Gateway.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 4
Page 5

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
2. NetLink e340/h340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Overview
The NetLink e340/h340/i640 Wireless Telephone is a mobile handset for workplace
IP telephone systems. NetLink Wireless Telephones operate over an 802.11b
wireless Ethernet LAN providing users a wireless voice over IP (VoIP) extension. By
seamlessly integrating with the Mitel IP telephony system, NetLink Wireless
Telephone users are provided with high-quality mobile voice communications
throughout the workplace. The NetLink Wireless Telephone gives users the freedom
to roam throughout the workplace while providing all the features and functionality
of an IP desk phone.
The NetLink e340/h340/i640 Wireless Telephone provides a wireless extension to
the Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP VoIP solutions. The NetLink Wireless
Telephone supports the MiNET protocol, a proprietary protocol developed by Mitel
Networks for communication between a Mitel Networks IP phone and a Mitel
Networks PBX.
The NetLink Wireless Telephones reside on the wireless LAN with other wireless
devices using Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) radio technology. The
handset radio transmits and receives packets at up to 11Mb/s.
2.1 QoS and Security
The NetLink SVP Server is an Ethernet LAN device that works with the access
points (APs) to provide QoS on the wireless LAN. Voice packets to and from the
NetLink Wireless Telephones are intercepted by the NetLink SVP Server and
encapsulated for prioritization as they are routed to and from an IP telephony server
or gateway. See the NetLink SVP Server: Installation, Configuration and Administration
document for detailed information about this device.
The NetLink e340/h340/i640 Wireless Telephone supports Wired Equivalent
Privacy (WEP) as defined by the 802.11 specification. SpectraLink offers the product
with both 40-bit and 128-bit encryption.
NetLink Wireless Telephones support basic WMM™ (Wi-Fi Multimedia) if also
supported by the AP as part of the 802.11e protocol. If the AP supports WMM, the
handset automatically discovers and uses it. WMM does not replace the NetLink
SVP Server.
NetLink Wireless Telephones also support the 802.11i protocol including Wi-Fi
Protected Access (WPA™ and WPA2™)—PSK. As vendors introduce access points
that are eligible to become Wi-Fi CERTIFIED™ for WPA-PSK and/or WPA2PSK, SpectraLink will determine their compatibility with the NetLink Wireless
Telephones and include them on the NetLink Wireless Telephone Access Point
Compatibility Table.
The latest software versions are required to support the features described
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 5
in this document.
Page 6

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
2.2 Quick Start Guide
1. A wireless LAN must be properly configured and operational through the use of
802.11b APs listed on the NetLink Wireless Telephone Access Point Compatibility
matrix.
2. A TFTP Server must be available on the network in order to load the
appropriate software into the NetLink Wireless Telephones. See the License
Management section for detailed instructions for loading software on NetLink
Wireless Telephones.
3. The supported Mitel Networks VoIP solution must be connected to your
network and completely operational.
4. The NetLink SVP Server, which facilitates the QoS on the wireless LAN for the
NetLink Wireless Telephones, must be on the same subnet as the NetLink
Wireless Telephones and have the proper versions of software.
Ensure you have the following versions for the SVP Server:
173 svp100.toc
174 zvmlinux
175 flashfs
5. Visit http://www.spectralink.com/service/software.php to download the latest
NetLink Wireless Telephone and any updates to the NetLink SVP Server
software.
6. Install the correct NetLink Wireless Telephone software and any updates to the
NetLink SVP Server software per Section 5.2 Configuration Process for the NetLink
Wireless Telephones and per NetLink SVP Server Installation, Setup and Maintenance
section 6.1 Software Updates for the NetLink SVP Server. Ensure the software is
properly loaded on the TFTP server.
7. Configure your NetLink Wireless Telephone to ensure that it is associated with
the wireless LAN, has the appropriate software, and has the correct IP address
for the supported Mitel Networks IP telephony system. See the License
Management section and the NetLink Wireless Telephone Configuration section for
detailed instructions for loading software onto and configuring NetLink Wireless
Telephones.
IP multicast addresses are used by the NetLink i640 Wireless Telephone.
This requires that multicasting be enabled on the subnet used for the
NetLink Wireless Telephones and SVP Server.
Routers are typically configured with filters to prevent multicast traffic
from flowing outside of specific domains. The wireless LAN can be placed
on a separate VLAN or subnet to reduce the effects of broadcast and
multicast traffic from devices in other network segments.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 6
Page 7
SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
A
p
A
p
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
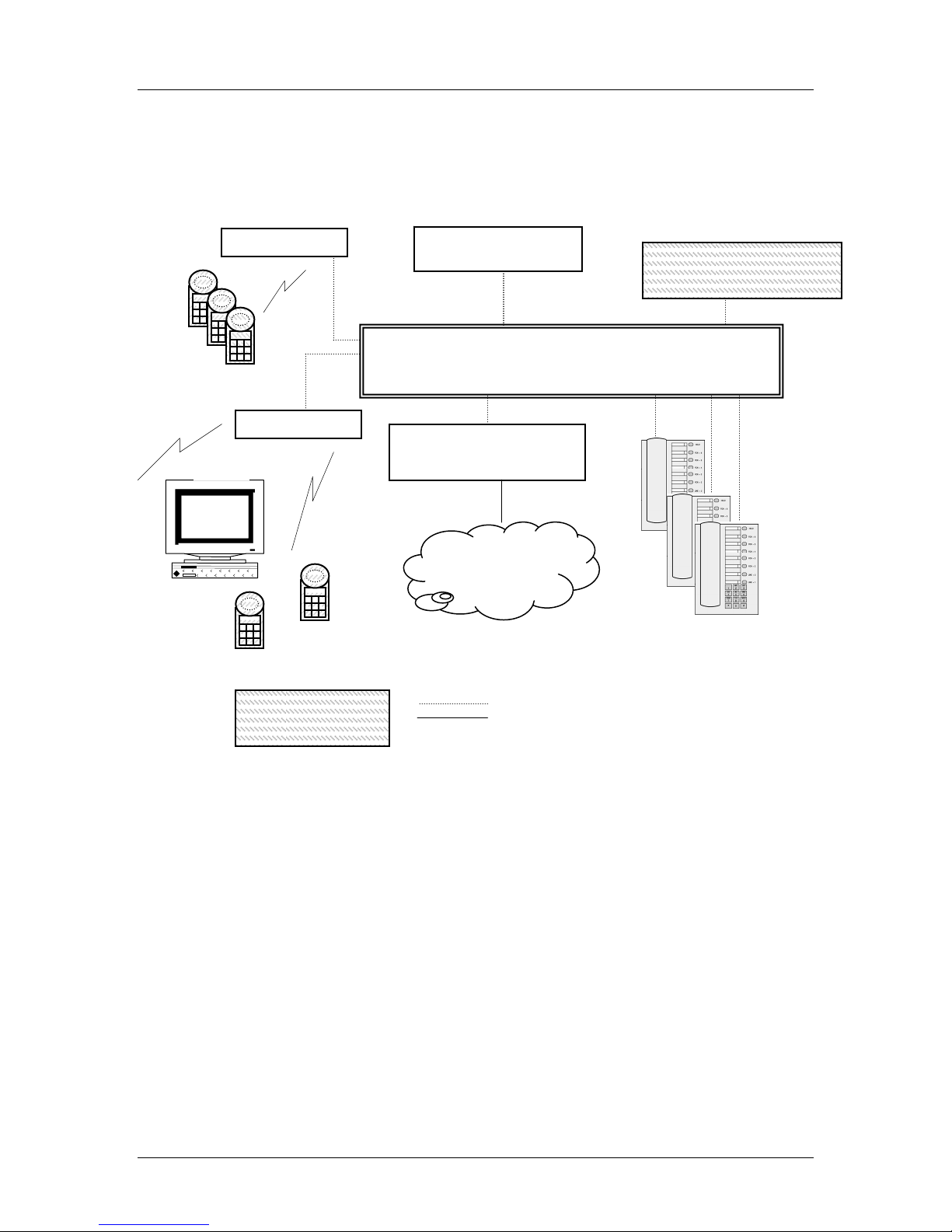
2.3 System Diagram
The following diagram shows the NetLink components residing on a network with
the Mitel Networks IP telephony system, APs, and wireless LAN Ethernet Switched
Hub:
NetLink
Wireless
Tele
hones
optional
Wireless
POS
ccess Point
ccess Point
NetLink
Wireless
Tele
hones
TFTP Server
Ethernet switch
Mitel ICP Platform
PSTN
or
PBX
NetLink SVP Server
Mitel IP
Phones
Device supplied by
SpectraLink
Ethernet cable
Phone cable
Mitel Networks IP telephony server architecture example
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 7
Page 8

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
2.4 System Components
NetLink e340/h340 Wireless Telephone: The NetLink e340/h340 Wireless
Telephone is a lightweight, durable handset specifically designed for mobile
workplace use within a facility using the supported Mitel Networks IP telephony
system and 802.11b APs in a wireless LAN.
NetLink i640 Wireless Telephone: The NetLink i640 Wireless Telephone offers a
durable design with push-to-talk functionality.
Handset functionality is provided by emulating the Mitel Networks 5220 IP Phone.
Among other features, the handset can receive calls directly, receive transferred calls,
transfer calls to other extensions, and make outside and long distance calls (subject
to the restrictions applied in your facility.) The handsets are to be used on-premises;
they are not cellular or satellite phones.
NetLink e340/h340/i640 Wireless Telephones use Direct Sequence Spread
Spectrum radio technology (DSSS) to transmit audio packets over wireless LAN APs
that support SpectraLink Voice Priority (SVP).
NetLink SVP Server: SpectraLink Voice Priority (SVP) is the SpectraLink quality of
service (QoS) mechanism that is implemented in the handset and AP to enhance
voice quality over the wireless network. SVP gives preference to voice packets over
data packets on the wireless medium, increasing the probability that all voice packets
are transmitted efficiently and with minimum or no delay. SVP is fully compatible
with the IEEE 802.11b standards.
The NetLink SVP Server is an Ethernet LAN appliance that works with the AP to
provide QoS on the wireless LAN. All MiNET packets to and from the NetLink
e340/h340/i640 Wireless Telephones pass through the NetLink SVP Server and are
encapsulated for prioritization as they are routed to and from the supported Mitel
Networks VoIP solution or other handset.
Mitel Networks IP System: Mitel Networks 3300 or SX-200 ICP VoIP solution.
Access Points: (APs) are supplied by third party vendors and provide the
connection between the wired Ethernet LAN and the wireless (802.11b) LAN. APs
must be positioned in all areas where NetLink Wireless Telephones will be used. The
number and placement of APs will affect the coverage area and capacity of the
wireless system. Typically, the requirements for use of NetLink e340/h340/i640
Wireless Telephones are similar to that of wireless data devices.
APs must utilize SpectraLink Voice Priority (SVP). Contact SpectraLink, or a
certified SpectraLink distributor, for information about APs that support SVP.
Ethernet Switch: Interconnects multiple network devices, including the NetLink
SVP Server, the supported Mitel Networks IP telephony system, Mitel Networks IP
Phones and the APs. Ethernet switches provide the highest performance networks,
which can handle combined voice and data traffic, and are required when using the
NetLink e340/h340/i640 Wireless Telephones.
Although a single Ethernet switch network is recommended, the handsets and the
NetLink SVP Server can operate in larger, more complex networks, including
networks with multiple Ethernet switches, routers, VLANs, and/or multiple subnets,
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 8
Page 9

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
as long as the SVP Server and APs are on the same subnet. However, in such
networks, it is possible for the QoS features of the NetLink SVP Server to be
compromised, and voice quality may suffer. Any network that consists of more than
a single Ethernet switch should be thoroughly tested to ensure any quality issues are
detected.
Note that the NetLink e340/h340/i640 Wireless Telephones cannot actively roam
from one subnet to another. If routers and multiple subnets are in use, the NetLink
Wireless Telephones must only use APs attached to a single subnet, or be powered
off and back on to switch to a different subnet.
Mitel Networks IP Phone: The wired LAN desksets provided by Mitel Networks
for use with the supported Mitel Networks IP telephony system.
TFTP Server: Required in the system to distribute software to the handsets. May be
on a different subnet than the supported Mitel Networks IP telephony device(s) and
APs.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 9
Page 10

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
3. The NetLink Wireless Telephone
NetLink e340/h3401 Wireless Telephone NetLink i640 Wireless Telephone
3.1 Specifications
Radio frequency: 2.4000 – 2.4835 GHz
Transmission type: Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS)
Transmit data rate: Up to 11 Mb/s
Radio QoS: SpectraLink Voice Priority (SVP)
Wireless security: Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP), 40-bit and 128-bit, Cisco FSR; WPA-PSK,
WPA2-PSK
FCC certification: Part 15.247
Management: DHCP, TFTP
Voice encoding: G.711 (A- and mu-law), G.729
VoIP Protocols: MiNET
Transmit power: 100 mW peak, < 10 mW average
Display: Pixel-based (up to 4-line x 18-character) alphanumeric, plus line and status
indicators.
e340/h340 dimensions: 5.5” x 2.0” x 0.9” (14.0 x 5.1 x 2.3 cm)
i640 dimensions: 5.9” x 2.2” x 1.0” (15.0 x 5.6 x 2.5 cm)
e340/h340 weight: 4.2 ounces (119.0 g)
i640 weight: 6.0 ounces (170.1 g)
Battery capacity: 4 hours talk time, 80 hours standby (30 hours standby if push to talk (PTT) is
enabled)
1
The NetLink e340 Wireless Telephone is shown. The NetLink h340 Wireless Telephone’s specifications are
identical to the NetLink e340 Wireless Telephone’s specifications.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 10
Page 11

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
3.2 The Display
Alphanumeric
Display information provided by the supported Mitel Networks VoIP solution when
the handset is off-hook will be passed directly to the handset display. The handset
will display up to 18 characters of each line. Certain characters may be used by the
supported Mitel IP PBX solution that are not implemented in the handset, such as
definable or special characters.
Press the FCN key while off hook to scroll through features and emulated keys. Press
the LINE key while off hook to scroll through the line/memory keys.
Signal Strength
The signal strength icon indicates the strength of the signal from the AP and can
assist the user in determining if the handset is moving out of range. It is always
present on the display in the upper left corner.
Battery Charge
The battery icon indicates the amount of charge remaining in the Battery Pack. There
are three levels and when only one level remains, the Battery Pack needs to be
charged. It is always present on the display in the upper right corner.
Voicemail
The voicemail icon is activated when a new voice mail message is received if the
feature is supported by the phone emulation. It appears to the right of the signal
strength icon.
Download
Indicates that the handset is downloading code. This icon only appears while the
handset is running the over-the-air downloader. It appears to the right of the signal
strength icon in the same location as the Voicemail icon.
Line Indicators
The line indicators on the handset will convert to a solid or flashing number to
mimic the icons next to line keys on the Mitel Networks 5220. The text that appears
next to the line keys on the 5220 IP Phone is accessed on the handset by pressing the
LINE key.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 11
Page 12

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
Ringing and Tones
The ringing types are programmed by the handset user into the handset and are not
accessible or changeable by the supported Mitel Networks VoIP solution. When Ring
Cadence is set to PBX and whenever possible, the audible and vibrating ringer on the
handset will follow the MiNET cadence commands provided by the supported Mitel
Networks VoIP solution.
Audio Features
Speakerphone features such as paging, hands-free mode and voice announce are not
available on the handset. The telephony switch should not be programmed to
support such features on the handset.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 12
Page 13
SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
3.3 Startup Sequence
The handset goes through an initialization sequence at startup. The line icons 1-9
display and count down as the handset steps through this sequence. This is usually
very rapid. If there is any difficulty at any step that prevents initialization from
continuing, an error message will display and the related icon(s) will stay on. Please
see the error table at the back of this document for instructions on how to handle
error messages that occur during initialization.
Icon The icon(s) shown in bold turns off when:
123456789 The handset has located and authenticated and associated with at least one AP, and is
proceeding to bring up higher-layer networking functions.
12345678 The handset is either configured for Static IP, or if configured for DHCP the DHCP discovery
process has started.
1234567 If DHCP is configured, a DHCP response was received which contains a good DNS server
configuration.
123456 Note: Only valid on non-SRP protocol. Indicates one of the following:
Static IP configuration, or
SVP Server address found in DHCP response, or
SVP Server address found via DNS lookup.
12345 All networking functions are complete (notably, DHCP) and the handset is proceeding with
establishing the SRP link to the SVP Server.
1234 The SRP link is established, all network stack initialization is complete, proceeding with
application-specific initialization.
123 The link between the handset and the PBX is established.
12 The handset has registered to the PBX.
12
Please Enter PIN
1 The handset has received a definition string for each of the 14 programmable buttons. If the
(no icons)
Requested if PIN had not previously been entered, if PIN has been cleared, or if MAC address
not entered in the DN con-figuration table on the PBX.
The PIN may be up to 18 characters. The first few are a secret number defined at the PBX, the
rest are the extension of this handset. User must enter a valid PIN number and press the
Send softkey. Alternately, the handset may be configured in the DN configuration table on
the PBX.
Note: there is no timeout and the user must reboot if an invalid PIN is entered.
handset hangs up at this point, there has been an undetected error in the retrieval process
and the handset will need to be rebooted.
Initialization is complete. The handset is in standby mode ready to receive and place calls.
EXT. XXXXX
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 13
Page 14

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
3.4 Handset Modes
Standby (on-hook)
In the standby mode the handset is waiting for an incoming call or for the user to
place an outgoing call. The extension number is shown on the display and there is no
dial tone. In this mode, the handset is conserving battery power and wireless LAN
bandwidth.
When an incoming call occurs the handset will ring until the call is answered by
pressing the Start Call key or the End Call key is pressed to silence the ringing.
Predial
To place a call using predialing (cell phone dialing), dial the number while in standby
mode and then press Start Call. This transitions the handset to active off-hook mode
and the number is immediately called.
Active (off-hook)
To place a call, press the Start Call key. This transitions the Wireless Telephone to
active off-hook mode. There is a dial tone, the Wireless Telephone is in
communication with the PBX, and the display shows information as it is received
from the PBX. The user may place a call or press the FCN or LINE key to access
operations.
The Wireless Telephone is also in the active mode when a call is received.
When an incoming call occurs during an active call the handset will play the second
line ringing sound until the call is answered, the caller hangs up, or the call transfers
to voicemail. If End Call is pressed, the first call is terminated and the handset reverts
to a full ring.
The active modes utilize the most bandwidth and battery power. To conserve these
resources, return the handset to the standby mode when a call is completed by
pressing the End Call key.
Active (on-hook)
To transition from the standby mode to the active on-hook mode, press the MENU
key. In this mode, the handset displays the text display as seen on an idle 5220 IP
phone, usually the date and time. There is no dial tone. The user may press the
FCN
or LINE key to access all operations available from the active off-hook mode.
When an incoming call occurs the handset will ring loudly until the call is answered
or the End Call key is pressed. If an active key is pressed, the ring will convert to the
second-line ringing sound.
If there is no activity for 45 seconds, to conserve bandwidth and battery power the
handset will return to the standby mode.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 14
Page 15

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
3.5 NetLink Wireless Telephone Displays
Status display area
Displays information from the PBX in one line of text and displays available softkeys
on the second line. Muted is displayed when local muting is activated. The PBX text
may be truncated as the 5220 IP phone has 20 characters and the Wireless
Telephone display area is 18 characters.
LINE display
Pressing the LINE key from the active mode displays a list of line appearances
extracted from the programmable keys list. The line appearances are also mapped to
corresponding line icons. If more than nine lines are mapped to a handset, the
remaining line appearances will show up on the FCN list.
MENU display
Pressing the MENU key from the active state displays the descriptive text of four
softkeys. The first three are defined by the PBX. The fourth key is normally the
Superkey, but changes to HOLD when audio is flowing and SEND when a PIN number
is being set.
FCN display
Pressing the FCN key from the active state displays the list of six predefined fixed
function keys that emulate the fixed keys on the 5220 IP phone. Additionally, up to
13 programmable keys that are not on the LINE list may be displayed and up to 12
keys defined by an OAI server. The programmable key items that appear on this list
each have a state indicator in the second column of the display that shows a plus sign
if the associated feature is active. This second column is blank if the associated
feature is not active. The plus sign emulates a lit or blinking LED on a deskset.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 15
Page 16

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
4. NetLink Wireless Telephone Configuration
The NetLink e340/h340/i640 Wireless Telephones should be provisioned in the
supported Mitel Networks VoIP solution in the same manner as the Mitel Networks
5220 Internet Telephones. Each handset may be configured for site-specific
requirements by opening the Admin menu and selecting options or entering specific
information. Any settings entered in the Admin menu must conform to system
settings. Only the handset being configured is affected by the Admin menu settings.
The handset user may select several usability options from the Standby menu,
described below in the User-defined Preferences section. This information is also
provided in the end-user manual.
The NetLink Configuration Cradle is an accessory device designed to automate
configuration of e340/h340, and i640 models of the NetLink Wireless Telephone.
The Configuration Cradle is connected to a PC via a serial cable. A downloadable
Configuration Cradle program runs on the PC and enables the system administrator
to establish and store configuration options for system, group and user levels. A
configuration plan may be set up in the program and downloaded into a handset or a
configured handset may be placed in the cradle and its configuration may be
uploaded and edited or saved.
Please see your service representative or contact SpectraLink Customer Service for
more information about this time-saving device
4.1 The Admin Menu
The Admin menu contains configuration options that are stored locally (on each
handset). Every handset is independent and if the default settings are not desired, the
Admin options must be set in each handset requiring different settings.
Opening the Admin Menu
1. With the handset powered OFF, simultaneously press and hold the Power On and
Power Off keys.
2. Release the Power On key, wait for a single beep, then release the Power Off key.
The Admin menu displays.
If an Admin password has been set, the display will require its entry before
opening the Admin menu. If no password is set, the display will proceed
directly into the Admin menu.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 16
Page 17

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
Entering and editing Admin menu options
An asterisk (*) next to an option indicates that it is selected. Use the Up, Down, and
Select side buttons and the softkeys to navigate and select:
Up/Down buttons: Display previous/next menu item.
Select button: Selects the menu item or option.
OK softkey Selects the menu item or option.
Save softkey: Saves the entry.
Bksp softkey: Backspaces to allow editing of entry.
Cncl softkey: Cancels edit and returns to previous menu level.
Up softkey: Returns to previous menu level.
Exit softkey: Exits the menu (at the top level).
End Call key: Exits to standby state (from any level)
Alphanumeric String Entry
1. Press the first digit/letter. The digit displays. Press the key again to scroll through
the letters associated with that key.
Example: if you press 2 repeatedly, you will see 2, A, B, and C, a, b, and c.
The following table shows which key will allow you to enter non-numeric
characters or other characters not represented on the keypad.
To Enter Press
. - _ ! # $ % & ‘ ( ) * + , : ; / \ = @ ~ 1
Space 0
Q,q 7
Z,z 9
2. When the correct entry displays, press the Right Arrow key to move on to the
next character. Repeat for each digit/letter of the entry. To erase, press the Left
Arrow key or
Bksp softkey to erase the previous character.
3. Press the Save softkey to save the entry and return to the menu.
Press the Cncl softkey to abort and return to the menu without saving any
changes.
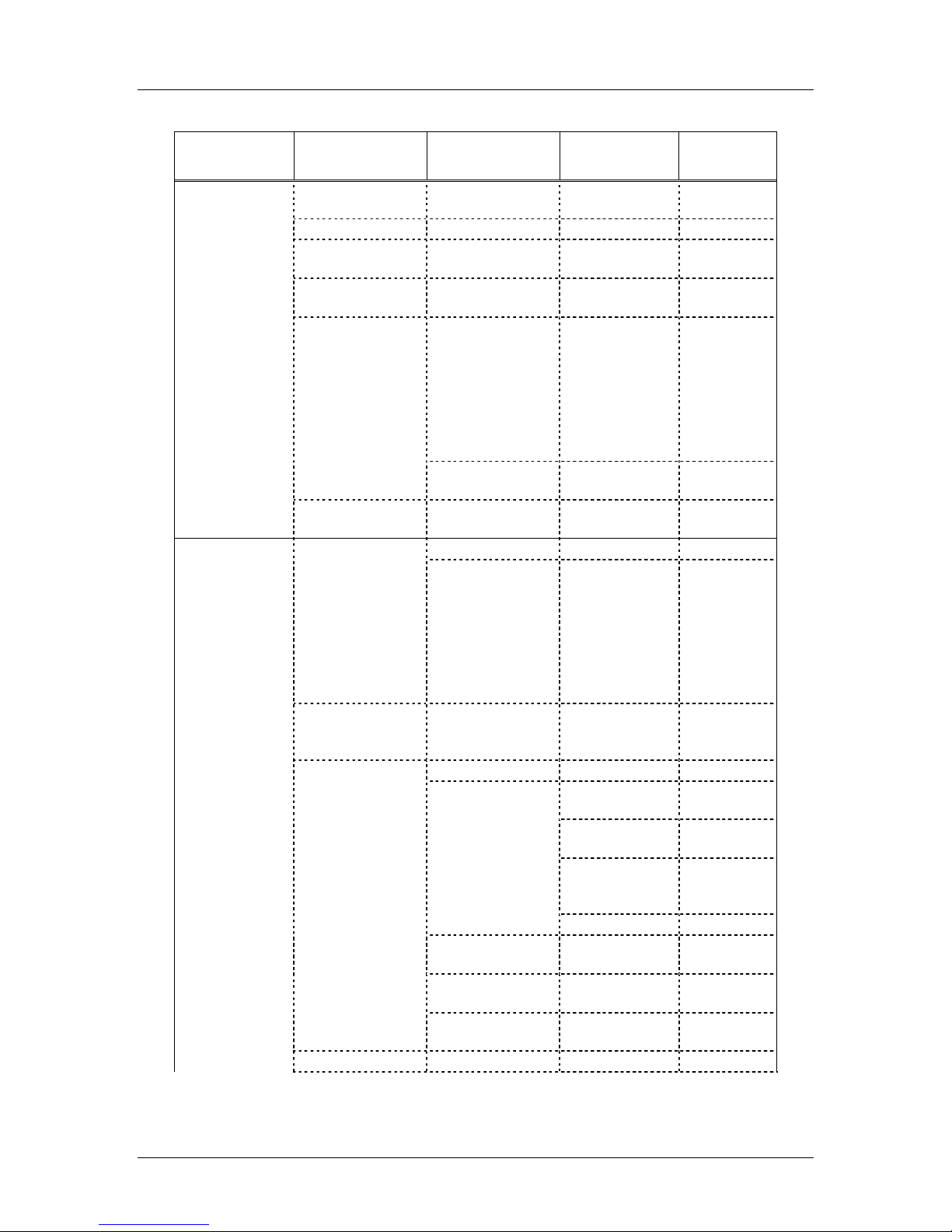
The following table lists the Admin menu items. The default settings are shown
in the table below with an * prior to the option. Detailed descriptions of each
item appear below the table.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 17
Page 18
SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
Admin menu
Admin Menu
Items
Phone Config License Option Set Current [List per
Clear PIN Number
5220 Emulation *Disable 5220
OAI On/Off *Enable OAI
Push-to-talk *Allowed Channels *Channel 1
Allow/Disallow *Allow PTT
Admin Password Enter Admin P.W. Re-enter
Network Config IP Addresses *Use DHCP
Static IP Phone IP
ESS ID *Learn Once
Security *None
WEP Authentication Open System
WEP On/Off WEP Off
Key Information Default Key
Rotation Secret
Cisco FSR Username
WPA-PSK Passphrase
WPA2-PSK Passphrase
Reg. Domain: None
nd
2
Level 3rd Level 4th Level 5th Level
download]
Enable 5220
Disable OAI
*Channel 2
*Channel 3
*Channel 4
*Channel 5
*Channel 6
*Channel 7
*Channel 8
Disallow PTT
Password
TFTP Server IP
Default Gateway
Subnet Mask
Syslog Server IP
SVP IP Addr
RTC IP Addr
OAI Server IP
Learn Always
Static Entry
Shared Key
WEP On
Key Length
Key 1-4
Password
Direct Entry
Direct Entry
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 18
Page 19

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
Admin Menu
Items
Transmit Power *Maximum
Diagnostics Run Site Survey
Diagnostics Mode Diagnostics On
Syslog Mode *Disabled
Restore Defaults
* default setting
† 50 mW and 30 mW only appear if Regulatory Domain is set to None or 01.
Phone Config
License Option
nd
2
Level 3rd Level 4th Level 5th Level
50 mW †
30 mW †
20 mW
15 mW
10 mW
5 mW
*Diagnostics Off
Errors
Events
Full
License Option lets you select the VoIP protocol that your site is licensed to
download and run. The MiNET protocol to use for the NetLink e340/h340 and
i640 Wireless Telephones requires License Option 014. Any other protocol will
cause the handset to malfunction.
Clear PIN Number
The PIN number is saved in the handset’s local memory. If it is necessary to change
the PIN number assigned to this handset, clear the existing number through this
Admin menu option and power cycle the handset. The PBX will request a PIN
number when the handset is powered on, just as it does with the 5220 IP Phone.
Enter the PIN number and press the Send softkey. The new PIN number will be
sent to the PBX. If the new PIN is accepted by the PBX, it will tell the handset to
save the PIN in its local memory.
5220 Emulation
Disable 5220 is the default and should be used if configuring for the SX-200 ICP or
the 3300 ICP is using software version 5.1 or greater. With this revision, the Mitel
Networks system became capable of recognizing NetLink Wireless Telephones. If
the 3300 ICP software version in use is below 5.1, select Enable 5220 to allow Mitel
Networks to recognize the NetLink Wireless Telephone as a 5220 IP Phone.
OAI On/Off
SpectraLink’s Open Application Interface (OAI) enables third-party computer
applications to display alphanumeric messages on the handset display and take input
from the handset keypad. Refer to the Open Application Interface (OAI) Specification
documentation for information about administering the OAI Gateway and the
services it can provide.
If you have an OAI Gateway installed in your system, OAI may be optionally
enabled in each handset. You may select whether the handset should attempt to
connect to the SpectraLink OAI Gateway by choosing either the Enable or Disable
options in this menu.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 19
Page 20

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
If OAI is enabled, and an OAI IP address is available to the telephone (either via
DHCP or Static IP configuration), the telephone will communicate with the OAI
Server at power on, and periodically while it is powered on. If you don’t have a
SpectraLink OAI Gateway installed at your site, you should disable the OAI feature
to preserve network bandwidth and battery life.
Push-to-talk
All eight push-to-talk channels are allowed by default. To toggle the allowed status of
any channel, select Allowed Channels, scroll to the channel to be disallowed and press
the Select side button. Allowed channels are displayed with an * in the left column.
Only those channels allowed in the Admin menu will appear on the Standby menu
where they can be enabled or disabled by the end user. To disallow push-to-talk
entirely, select Allow/Disallow, scroll to and select Disallow PTT.
Admin Password
The Admin Password controls access to the administration functions in the Admin
menu. The password must be set in each handset for which controlled access is
desired. Handsets are shipped without any Admin menu password. Data entry for
the password uses the alphanumeric string entry technique. Type the password and
press the Save softkey. A confirmation prompt will appear. Type the password again
and press the Save softkey. If the passwords match, the Admin password has been
set.
Network Config
IP Addresses
There are two modes in which the handset can operate: DHCP enabled or Static IP.
Select the mode from the IP address menu:
* Use DHCP: Will use Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol to assign an IP
address each time the handset is turned on. If DHCP is enabled, the handset also
receives all other IP address configurations from the DHCP server.
Static IP: Allows you to manually set a fixed IP address. If selected, the handset
will prompt for the IP addresses of each configurable network component.
When entering addresses, enter the digits only, including leading zeroes. No
periods are required.
Regardless of the mode in which the handset is operating, the following
components must be configured in the system:
Phone IP: The IP address of the handset. This is automatically assigned if DHCP
is used. If using Static IP configuration, you must obtain a unique IP address for
each phone from your network administrator.
TFTP Server IP: The IP address of a TFTP server on your network which holds
software images for updating the handsets. If this feature is configured (not set
to 0.0.0.0 or 255.255.255.255) either via Static IP configuration or using DHCP
option 66 (TFTP Server), or the Boot server/next server (siaddr) field, the
handset will check for newer software each time it is powered on or comes back
If you Save with no entry, the password is erased and the display will not
require it before displaying the Admin menu.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 20
Page 21

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
into range of your network. This check takes only a second and ensures that all
handsets in your network are kept up-to-date with the same version of software.
Default Gateway and Subnet Mask: Used to identify subnets, when using a complex
network which includes routers. Both of these must be configured either with an
IP address under Static IP (not set to 000.000.000.000 or 255.255.255.255) or
with DHCP for the handset to contact any network components on a different
subnet. If configured on the DHCP server, use option 3 for the Default Gateway
and option 1 for the Subnet Mask. Contact your network administrator for the
proper settings for your network.
Note that the handsets cannot “roam” across subnets, since they cannot
change their IP address while operational. Ensure that all your access
points are attached to the same subnet for proper operation. The handset
can change subnets if DHCP is enabled and the handset is powered off
then back on when within range of access points on the new subnet.
Syslog Server IP: The IP address of the syslog server. See the Diagnostics section
for more information.
SVP Server IP: The IP address of the NetLink SVP Server. If using Static IP
configuration, this is simply the IP address of the NetLink SVP Server. Note that
the NetLink SVP Server must be statically configured to have a permanent IP
address. If DHCP is being used, the handset will try the following, in order: the
DHCP option 151, then a DNS lookup of “SLNKSVP2” if the DHCP options 6
(DNS Server) and 15 (Domain Name) are configured.
ESSID
RTC IP Addr: The IP address of the primary Mitel Networks device. If using Static
IP configuration, this is simply the IP address of the device. If DHCP is being
used, the handset will try to obtain the device’s IP address and port information
using the following DHCP options: 129.
OAI Server IP: The IP address of the SpectraLink OAI Gateway (if applicable). If
using Static IP configuration, this is simply the IP address of the SpectraLink
OAI Gateway. If DHCP is being used, the handset will try the DHCP option
152.
Select the option that will enable the handset to acquire APs with the correct ESSID
(Extended Service Set ID, aka SSID) each time it is turned on.
Note about Automatic Learn options: Broadcast ESSID must be enabled in the
access points for ESSID learning to function. Refer to the Configuration Note for your
access point or call your access point vendor for specifics. Overlapping wireless
systems complicate the use of ESSID learning as the handset in an overlapping area
could receive conflicting signals. If this is the situation at your site, use Static Entry
or Learn Once in an area without overlapping ESSIDs.
* Learn Once: Allows the handset to scan all ESSIDs for a DHCP server and/or
TFTP server. Once either is found, the handset retains the ESSID from
whichever access point it associates with at that point. When overlapping
wireless systems exist, the Learn Once feature allows the handset to use only the
ESSID established at first learn at all subsequent power ons. This ESSID is
retained by the handset until the ESSID option is reselected.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 21
Page 22

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
Learn Always: Allows the handset to automatically learn the ESSID at each power
on or loss of contact with the wireless LAN (out of range). This may be useful if
the handset will be used at more than one site.
Static Entry: If your access points do not accept broadcast ESSID or if there are
overlapping wireless systems in use at the site, enter the correct ESSID manually.
Security
Security
*
NONE disables any 802.11 encryption or security authentication mechanisms.
For WEP, WPA-PSK and WPA2 PSK set each of the following options to
match exactly the settings in your APs.
Encryption codes display as they are entered. For security reasons codes
will not display when a user returns to the Admin menu, Encryption
options.
WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is a wireless encryption protocol that encrypts data
frames on the wireless medium allowing for greater security in the wireless network.
If WEP is required at this site, you must configure each handset to correspond with
the encryption protocol set up in the access points. Select the entries from the
options below to enable the handset to acquire the system.
Authentication
Select either
WEP On/Off
Select either
Open System or Shared Key.
WEP Off or WEP On.
Key Information
Default Key: Enter the key # specified for use by the handsets. This will be 1
through 4.
Key Length: Select either 40-bit or 128-bit depending on the key length
specified for use at this location.
Key 1-4: Scroll to the key option that corresponds to the Default Key that was
entered above. Enter the encryption key as a sequence of hexadecimal
characters. (Use the 2 and 3 keys to access hexadecimal digits A-F, use the
Right Arrow key to advance to the next digit, and the Left Arrow key to
backspace.) For 40-bit keys you will need to enter 10 digits, for 128-bit keys
you will need to enter 26 digits. The display will scroll as needed.
Rotation Secret: This is used for proprietary WEP key rotation. Refer to your
custom document if this feature is supported in your system.
Cisco FSR (Fast Secure Roaming) In order to provide the highest level of security
without compromising voice quality on Cisco Aironet wireless LAN access points,
SpectraLink and Cisco Systems have cooperated to implement the Fast Secure
Roaming mechanism. FSR is designed to minimize call interruptions for NetLink
Wireless Telephone users as they roam throughout a facility. Existing Aironet 350,
1100, and 1200 APs may require a firmware upgrade to support FSR. Cisco FSR
requires advanced configuration of the Cisco access points in your site. See your
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 22
Page 23

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
Cisco representative for detailed documentation on configuring your access points
and other required security services on your wired network. To configure Cisco FSR
in your NetLink Wireless Telephone, you must enter a Radius Server username and
password into each handset.
Username: Enter a username that matches an entry on your Radius server.
Usernames are alphanumeric strings, and can be entered using the alphanumeric
string entry technique.
Password: Enter the password that corresponds to this Username.
WPA-PSK: The security features of WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access) using PSK (Pre-
Shared Key) are available and may be used if supported by the access points in the
facility. Select either Passphrase and enter a passphrase between eight and 63
characters in length or Direct Entry and enter the 256-bit key code.
WPA2-PSK: The security features of WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access) using PSK (Pre-
Shared Key) are available and may be used if supported by the access points in the
facility. Select either
Passphrase and enter a passphrase between eight and 63
characters in length or Direct Entry and enter the 256-bit key code.
Consult the Configuration Note for the access points (APs) installed in your
facility for information on which of the WPA versions are recommended
by SpectraLink engineering. Configure the recommended version on the
AP and select the corresponding option on the Admin menu.
Regulatory Domain
The Regulatory Domain will default to North America on the handset display. FCC
requirements dictate that the menu for changing the domain be available by
password, which in our case is the LINE key. To change the domain, press LINE and
then enter the digits that represent the site’s domain. Note that both digits must be
entered.
01 - North America
02 - Europe (except Spain and France); Japan (channels 1-13)
04 - Spain
05 – France
As of this writing, Spain and France are adopting the general European
Regulatory rules. Check with your wireless LAN administrator or
supplier for which domain to enter in these countries.
Transmit Power
Available transmit power is regulated by domain. The Regulatory Domain setting
above affects the options available for this setting. The default setting is Maximum
which in North America is 100 mW. The Maximum in other domains is 30 mW.
Transmit Power may be set to a lower number if necessary by selecting one of the
other levels. If changed from the default, ensure the Transmit Power setting is the
same on all handsets and all APs.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 23
Page 24

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
Diagnostics
Run Site Survey
The Site Survey mode is activated by selecting this option. Site survey starts running
immediately upon selecting this option. See the Diagnostic Tools section for more
information about Site Survey.
Diagnostics Mode
See the Diagnostic Tools section for a detailed explanation of the Diagnostics Mode
options.
Syslog Mode
See the Diagnostic Tools section for a detailed explanation of the Syslog Mode options.
Restore Defaults
The Restore Defaults option will set all user and administrative parameters except
License Options to their factory defaults.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 24
Page 25

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
4.2 User-defined Preferences
The following user-defined preferences are also covered in the NetLink
e340/h340/i640 Wireless Telephone user guide. The system administrator can refer
to this list for more information about customizing handset settings.
To configure the following options, the handset must acquire the system (no error
message may display) and be at the extension display. This is the standby state. While
in the standby state, press and hold FCN briefly to open the user options menu. Use
the following keys to display and select options:
Up/Down buttons: Display previous/next menu item.
Select button: Selects the menu item or option.
OK softkey: Selects the menu item or option.
Save softkey: Saves the entry.
Bksp softkey: Backspaces to allow editing of entry.
Cncl softkey: Cancels edit and return to previous menu level.
Up softkey: Returns to previous menu level.
Exit softkey: Exits the menu (at the top level).
End Call key: Exits to standby state (from any level).
Standby menu
Standby menu item 2nd Level 3rd Level 4th Level
Lock Keys
Language [List per download]
Ring Options Telephone Ring Ring Cadence Off
*PBX
Continuous
Short Pulse
Long Pulse
Ring Tone *Tone 1
Tone 2
Tone 3
Tone 4
Tone 5
Ring Volume+ Bars
Vibrate Cadence *Off
PBX
Continuous
Short Pulse
Long Pulse
Ring Delay** *No Delay
5 Second Delay
10 Second Delay
Auxiliary Ring 1
Auxiliary Ring 2
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 25
Page 26

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
Standby menu item 2nd Level 3rd Level 4th Level
Phone Options Noise Mode *Normal
High
Severe
Key Tones *Enable Tones
Disable Tones
Warning Tones *Enable warnings
Disable warnings
Display Contrast Contrast %
Keypad Autolock *Disable
5 seconds
10 seconds
20 seconds
System Info Phone IP Addr
Server IP Addr
Firmware Version
Identification *No ID Entered
New ID
Mitel Options Current RTC IP
Current TCP Port
Current RTP Port
Push-to-talk+ Channel Current Channel: X
Enable/Disable PTT Enabled
Audio Volume Bars
Tone Volume Bars
* Default setting
**Option appears when Ring Cadence and Vibrate Cadence are both set to a value other than “Off”
+These options are available only on the NetLink i640 Wireless Telephone
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
New Channel = ?
*PTT Disabled
Main Menu: Scroll through the list of options by pressing the Up and Down side
buttons. Select an option by pressing the Select side button.
Lock Keys
Language
Ring Options
Phone Options
System Info
Identification
Mitel Options
Push-to-talk [i640]
OK Exit
Lock Keys: When enabled, the Keypad Lock option will lock the keypad immediately.
If the keypad is locked, it may be unlocked by the end user pressing the Unlk softkey
and then the # key.
Language: If the system supports multiple languages, the language option will list
what languages are available. Select the language from the list.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 26
Page 27

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
Ring Options: The Ring Option allows the user to set the ring for three separate
functions. Telephone ring is used for usual telephony functions. The Auxiliary Rings
may be used to set different ringing patterns for OAI applications.
Telephone Ring
Auxiliary Ring 1
Auxiliary Ring 2
OK Up
Telephone Ring: Telephone Ring allows the user to set a distinctive ring style, volume
and sequence. Select from an audible ring or a vibrate-only ring or a vibrate ring
along with or followed by an audible ring.
Ring Cadence
Ring Tone
Ring Volume [i640]
Vibrate Cadence
Ring Delay
OK Up
Ring Cadence: The cadence is the rhythm of the ring. It may be set to a pre-
programmed ring cadence or it may be set to obtain its cadence from the Call Agent.
The PBX option is designed to utilize any distinctive rings sent by the Call Agent
while allowing the user to set unique rings for auxiliary applications.
Off
PBX
Continuous
Short Pulse
Long Pulse
OK Up
Off: silent
PBX: Call Agent determines ring cadence (e.g. the Call Agent
may send rings that differentiate between internal and
external calls.)
Continuous: rings continually until answered
Short Pulse: rings in short bursts
Long Pulse: rings in long bursts
Ring Tone: select from five available tones (scroll to Tone 5 option). The Play softkey
allows the user to preview the tone before selecting. If Ring Cadence is turned off,
the Ring Tone option will not appear on the menu.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 27
Tone 1
Tone 2
Tone 3
Tone 4
Tone 5
OK Play Up
Page 28

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
Ring Volume: NetLink i640 Wireless Telephone only. The user may select a volume
level by pressing the Up and Down side buttons and then pressing the OK softkey. The
graduated volume bar indicates the levels. This setting may be overridden by
adjusting volume while the handset is ringing.
Vibrate Cadence: Vibrate Cadence options are the same as for Ring Cadence
Ring Delay: Ring Delay determines how long the vibrate cadence will play before the
audible ring starts. If Ring Cadence and Vibrate Cadence are turned off, the Ring
Delay option will not appear on the menu.
No Delay
5 Second Delay
10 Second Delay
OK UP
Auxiliary Ring 1 and Ring 2: Auxiliary rings are designed to be utilized by OAI
applications, enabling the user to set a distinctive ring for these applications.
Phone Options
Noise
Mode: Provides options that describe the noise level in your environment.
Selecting the correct option will adjust the handset to account for background noise.
Select Normal for most office environments; High for moderate background noise; or
Severe for extremely noisy conditions. Use of the non-Normal modes is not
recommended unless you are in a loud environment or you may find it difficult to be
heard on your handset.
Key Tones: Key tones may be turned on or off and determine if tones play when keys
are pressed. Key tones are enabled by default.
Warning Tones: The handset plays various warning tones such as system up or down,
out of range, etc. These tones may be turned on or off and are enabled by default.
Display Contrast: The display may need to be adjusted for different lighting situations.
Contrast may be set by pressing the Up and Down side buttons until the desired
contrast is displayed and then pressing the
Keypad Autolock: The handset may be set to lock the keypad automatically when in
OK softkey.
standby mode. The automatic locking function of the keypad may be disabled (the
default) or adjusted for a 5, 10 or 20 second delay before locking.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 28
Page 29

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
System Info
Phone IP Addr
Server IP Addr: Displays the IP address of the NetLink SVP Server and the OAI
: Displays the IP address currently assigned to the handset.
Server (if installed).
Firmware Version: displays the software version running the handset. The MAC
address is the hardware identification number and is set at the factory. Three code
numbers correspond to the three files that each version uses.
(MAC address)
(downloader code) (functional code)
(phintl file)
OK Up
Downloader: pd11gl3.bin
Functional: pd11mtd3.bin
Phintl: pi110001.bin
Identification: permits an alphanumeric entry that will appear on the standby display
under the extension number. Use the alphanumeric entry technique described in the
Admin menu section and enter up to 16 characters.
Mitel Options: This option displays the ports being utilized for receiving data at the
handset.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 29
Page 30

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
Push-to-talk: The NetLink i640 Wireless Telephone incorporates PTT functionality.
PTT may be allowed or disallowed in the Admin menu. If allowed, the user may
enable or disable locally, and may set the channel, tone volume and audio volume.
The menu for push-to-talk does not appear if PTT is disallowed on the Admin menu
or if no channel is enabled on the Admin menu.
Channel
Enable/Disable
Audio Volume
Tone V olume
OK Up
Channel: The user may enable any PTT channel that has been allowed in the Admin
menu by entering the corresponding number from the keypad. If PTT has been
enabled in this handset, the default channel is the lowest allowed channel as set in
the Admin menu.
Current Channel: X
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
New Channel = ?
Up
Enable/Disable: The user may enable or disable PTT on this handset. PTT is disabled
by default.
PTT Enabled
PTT Disabled
OK Up
Audio Volume, Tone Volume: The user may select volume levels by pressing the Up and
Down side buttons and then pressing the OK softkey. The graduated volume bar
indicates the levels. The Audio Volume setting may be overridden by adjusting
volume while the handset is in a push-to-talk call.
If PTT is allowed in the Admin menu and enabled by the user, Battery
Pack life when the handset is in standby mode is decreased to about 30
hours.
(Additional options may be present. Contact your system administrator for information.)
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 30
Page 31

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
5. License Management
NetLink Wireless Telephones support a number of different IP protocol
integrations. All NetLink e340/h340/i640 Wireless Telephones are shipped from
SpectraLink with a generic software load that allows them to associate to a wireless
LAN and download their functional software from a TFTP server. The handsets
will not function properly without downloading appropriate software.
The following details the process to properly configure NetLink e340/h340/i640
Wireless Telephones and download software via over-the-air file transfer.
5.1 Requirements
• A wireless LAN must be properly configured and operational through the use of
802.11b wireless access points.
• A TFTP Server must be available on the network in order to load the
appropriate software into the handsets.
• Finally, ensure that the Battery Pack on the handset is fully charged.
5.2 Configuration Process
1. Download the latest NetLink e340/h340/i640 Wireless Telephone IP software
from http://www.spectralink.com/service/software.php
For the SBC HIPCS solution, software is pre-loaded onto an SBC TFTP
2. Load the latest version of the MiNET code and place it on the TFTP Server and
3. If statically assigning IP addresses, ensure that the Phone IP address, TFTP
4. Ensure the handset has properly configured ESSID and Reg Domain
server. It is not necessary to update the software from the SpectraLink
website.
ensure the TFTP Server is started. The five files that are needed must be named:
slnk_cfg.cfg
pd11g13.bin
pd11mtd.bin
pd11mtd3.bin
pi110001.bin
Server IP, Subnet Mask, and Default Gateway information are accurate in the
Admin menu. If using a DHCP Server, ensure that appropriate options are set
for the TFTP Server. See the NetLink Wireless Telephone Configuration section for
detailed configuration instructions.
Information within the Admin menu. If you are accepting broadcast ESSIDs at
your access points, the handset will automatically learn the ESSID information
when powering on. See NetLink Wireless Telephone Configuration section for detailed
configuration instructions.
5. Using the Admin menu on the handset, ensure the License Option menu option
is set to 014. This ensures the handset will check for the proper MiNET files
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 31
Page 32

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
each time it powers on. See NetLink Wireless Telephone Configuration section
for detailed configuration instructions.
6. Power cycle the handset.
7. The MiNET code will now download to the handset. The status bar will
increment fully across the display for each function that is being performed in
the download process. Upon completion of the update process, the handset will
re-boot with the new firmware.
8. If the handset is statically configured, you may now enter the SVP IP address and
RTC address as detailed in the NetLink Wireless Telephone Configuration section
above.
9. Register the handset with the supported Mitel Networks VoIP solution as if it
were a SpectraLink NetLink phone and properly label the handset with the
appropriate extension.
For future software upgrades, simply update the files that are stored on the
TFTP Server. Each time the handset is powered up, it will check with the
TFTP Server to ensure it has the proper software version.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 32
Page 33

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
6. Mitel Networks VoIP Integration Factors
This section describes the mapping between the emulated Mitel Networks 5220 IP
Phone and the NetLink e340/h340/i640 Wireless Telephone.
Voice Messaging Access
Voicemail access is obtained through the Message key which is assigned on the
handset to FCN + 3.
CODECs
The NetLink e340/h340/i640 Wireless Telephone is compatible with the G.711 and
G.729a/ab CODECs. There is no setting required on the handset.
DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a standardized protocol that
enables clients to be dynamically assigned with various configuration parameters,
such as an IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and other critical network
configuration information. DHCP servers centrally manage such configuration data,
and are configured by network administrators with settings that are appropriate for a
given network environment. The handset will search for Mitel Networks server
configuration in the vendor specific and site-specific options listed in the table
below. The handset will use the following DHCP options if DHCP use is enabled:
Option Meaning
1 Subnet Mask
3 Default Gateway
6 DNS Server
15 Domain Name
66 TFTP Server
151 NetLink SVP Server
152 SpectraLink OAI Gateway
128 Mitel TFTP Server address (not currently used by
handset)
129 Mitel PBX RTC IP address
130 String containing “MITEL IP PHONE”
siaddr Boot server or next server
TFTP
The handset uses TFTP to update the handset software over the 802.11b wireless
LAN.
DNS
Domain Name System (DNS), an industry-standard protocol, locates computers on
an IP-based network. IP networks rely on number-based addresses to move
information on the network. However, users are better at remembering friendly
names than number-based addresses, so, it is necessary to translate user-friendly
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 33
Page 34

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
names into addresses that the network can recognize. The handset will use DNS to
automatically translate names into IP addresses for these components: TFTP Server
and the NetLink SVP Server.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 34
Page 35

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
7. Feature Programming
Softkey A Softkey B Softkey C
Fcn6 Fcn1
Fcn2Softkey D
14 13
12
Programmable
10
Line or Feature
8
6
4
Fcn4
keys
Fcn3
11
9
7
5
3
Line12
The SpectraLink NetLink Wireless Telephone model in the Mitel Networks 3300
and SX-200 ICP is similar to the 5220 IP Phone.
The button mapping from the Mitel Networks 5220 IP Phone to the NetLink
Wireless Telephone is designed to preserve nearly all of the functionality of the 5220
IP Phone within a small, mobile device. All telephone functions and messaging
features are supported if possible. Speakerphone functions are not supported.
The handset has four softkeys to the 5220’s three softkeys. The last or rightmost
softkey on the handset, known as Softkey D, emulates the Hold key on the 5220.
The other three softkeys emulate the functions of the three softkeys of the 5220.
The handset uses “shortcut keys” to emulate the feature keys on the 5220. Pressing
LINE, FCN, or MENU plus a shortcut key will activate the assigned line appearance or
feature.
Feature key number 1 on the 5220 is the Line 1 key in the handset. All other feature
keys may be programmed to either line appearances or features. When the handset
becomes active, it requests a label for each of the feature keys from the PBX which
tells it whether the feature key is assigned to a feature or to a line appearance. If the
key is assigned to a line appearance, the handset lists the line extension plus any
shortcut key on the Line Appearance display, visible when the
the key is assigned to a feature, the handset lists it and any shortcut key on the
Feature display, visible when the
feature key order. Its shortcut key is determined by this order. OAI programming
will override any shortcut keys assigned by the handset.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 35
LINE key is pressed. If
FCN key is pressed. Each line or feature appears in
Page 36

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
7.1 Feature Assignment
The table below shows how the keys of the 5220 IP Phone are mapped to key
sequences on the handset.
5220 key Feature
Trans/Conf Transfer or conference FCN + 1
Cancel Cancel FCN + 2
Message Voicemail FCN + 3
Redial Redial FCN + 4
Mute/Unmute FCN + 5
Programmable Feature Key 2-14
Programmable to either line
appearances or features.
Feature Key #1 Line appearance Line + 1
If a line, the line extension
If a feature, the feature name
appears on the Feature menu with
a shortcut key
assignment to a feature key.
appears on the Line Appearance
list, with a line number that
corresponds to the order of
assignment to a feature key.
2 in the order of
handset
Shortcut & Key Sequence
FCN + 7
8
9
*
0
#
Line + 2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
Softkey1 Phonebook (Phbk) Softkey A
Softkey2 Programmable Softkey B
Softkey3 Programmable Softkey C
Superkey Superkey FCN + 6
(Superkey)
Hold (in call) Hold Softkey D
(toggles between
Superkey and Hold)
If an Open Application Interface (OAI) is operational, a function key
sequence will be assigned in the OAI configuration and will override any
function sequence established in the PBX.
2
Note: There may be more features programmed than there are available shortcut keys. In this situation, the
feature may be activated by using the Up, Down, Select buttons on the side of the Wireless Telephone.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 36
Page 37

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
7.2 Feature Access
In its standby state, the handset displays the extension assigned to this handset. The
active state is initiated by pressing either the Start Call key or the MENU key. When the
active state is initiated, the handset contacts the PBX and displays the data provided
– the time, date, default line icon, any voicemail icon, and softkey and feature key
labels. If the Start Call key has been pressed, the handset is off-hook and there is a
dial tone. If the MENU key is pressed, there is no dial tone; pressing MENU again will
bring up the Menu display.
While in the active state, you may switch to any display – Line, Feature, or Menu –
by pressing its corresponding key. Pressing a softkey will activate the feature
displayed.
The handset emulates the operation of the 5220 IP Phone including:
Line Appearances
While off hook, press the LINE key to view the shortcut keys and assigned extensions
for line appearances. There are nine possible line appearances that correspond to the
nine indicators at the top of the handset display. When a line is in use, the indicator
converts to the line number and a + will appear after the shortcut key on the list,
emulating a lit LED. Press the LINE key again to display the second page of the list if
more than four line keys have been programmed. To use an extension, press the
corresponding shortcut key. You may also use the Up, Down, and Select side buttons
to scroll through the displays and activate the line appearances on this list. Up and
down arrows on the display indicate additional items may be viewed by using the side
buttons. Press the End Call key to exit the Line Appearance list.
superkey, local muting, timed reminder, ringer adjust (via superkey),
forwarding (via superkey), hot desk, auto answer (via superkey), and
resiliency. Some or all of these features may be implemented locally.
Menu Display
The softkey labels on the handset are truncated to four characters. The complete text
for each softkey may be displayed by pressing the MENU key from the standby state.
The shortcut key assigned to the softkey feature and the complete text for each of
the softkeys displays.
Activate the softkey features while in the Menu display by pressing the softkey,
pressing the shortcut key, or using the
through and activate the features on this list. Up and down arrows on the display
indicate additional items may be viewed by using the side buttons. Press the End Call
key to exit the Menu display.
Feature List
The 5220 IP Phone has several fixed feature keys. The NetLink implementation
supports five fixed features that are suitable to a mobile user through the Function
(
FCN) key on the handset. When FCN is pressed, the display lists the first four fixed
features and the assigned shortcut key. Pressing FCN repeatedly will display the
remaining items on the list as programmed to the 5220 keys. These display in the
order programmed to the corresponding keys on the 5220, along with any shortcut
key, as available. A “+” will appear after the shortcut key, which emulates a lit LED
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 37
Up, Down, and Select side buttons to scroll
Page 38

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
on the emulated desk phone, indicating that the corresponding feature is turned on.
OAI options appear at the end of the list. All OAI keys will preempt shortcuts
assigned to other keys.
Activate the fixed features on the off-hook handset by pressing FCN + the shortcut
key. You may also use the Up, Down and Select side buttons to scroll through and
activate the features on this list. Up and down arrows on the display indicate
additional items may be viewed by using the side buttons. Press the End Call key to
exit the list.
1 Trans/Conf
2 Cancel
3 Message
4 Redial
5 Mute/Unmute
6 Superkey/Hold
7
8
9
(feature)
(feature)
(feature)
* (OAI)
0 (OAI)
# (OAI)
First
screen
Second
screen
Third
screen
Fourth
screen,
3
etc.
Superkey
The superkey and hold features swap places depending on the mode of the handset.
When in a call, the superkey is menu item FCN + 6 and the Hold feature is available
through softkey Dddd. When not in a call, the superkey (Skey) is available as softkey
Dddd and the Hold feature is displayed as number 6 on the Feature list.
Hot Desking
The Mitel PBX allows configuration of a hot desking feature which allows a handset
to register with the PBX as a different extension. If so configured, a HDsk softkey in
position Cccc will appear on the handset in the active (on-hook) mode. When the
hot desk softkey is pressed, the PBX displays No user logged in and the current
extension. Press the Login softkey (
Logi) and enter the new extension. Press the OK
softkey. The display prompts for a PIN number. Enter the PIN and press the OK
softkey. The handset will display Get button defs as it checks in with the PBX. Once
registration is complete, the new extension will display and the handset will be in
standby mode.
Resiliency
If the primary PBX fails and a secondary PBX is configured, any handset that is
configured to be resilient and powered on at the time of failure will switch to the
backup PBX. During the switchover the handset tries to register with each of the
resiliency IP addresses provided by the primary PBX at power on. These are stored
3
Note: There may be more features programmed than there are available shortcut keys. In this situation, the
feature may be activated by using the Up, Down, Select buttons on the side of the Wireless Telephone.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 38
Page 39

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
in static memory. If the handset is in a call during the failure of the primary PBX, it
will attempt to register with a backup PBX after the call is completed. Note that the
End Call button must be pressed at the end of a call to ensure correct functioning of
this feature.
Paging
The handset does not incorporate speakerphone capabilities and therefore receiving
a page is not supported. The user may send a page if this feature has been
programmed.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 39
Page 40

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
8. Testing a Handset
Verify proper registration and operation of each handset by performing the
following tests on each handset in an active wireless area.
1. Power on the handset by pressing
Power On. You will see a series of messages
displayed as the handset acquires the system. The handset should display the user
extension or dashes if no extension is programmed. Any error messages should
clear.
2. Press the
Start Call key. The extension number should be replaced by information
from the supported Mitel Networks VoIP solution and you should hear dial
tone. Place a call and listen to the audio quality. End the call by pressing the End
Call key.
3. Place a call to the handset and verify ring, answer, clear transmit, and clear
receive audio.
4. Go off-hook and use the FCN key to verify the Features list.
5. Go off-hook and use the LINE key to verify the Line appearances / Line features
list.
6. Press the End Call key. Any line indicators should turn off and the extension
number display will return.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 40
Page 41

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
9. Diagnostic Tools
Site Survey, Diagnostic Mode and Syslog Mode are three diagnostic tools provided
Run
to assist the WLAN administrator in evaluating the functioning of the NetLink
Wireless Telephone and the system surrounding it. Diagnostic Tools are enabled in
the Admin menu.
9.1 Run Site Survey
Site Survey is used to evaluate the facility coverage before certifying that an
installation is complete. It can also be used at any time to evaluate coverage by
testing signal strength, to gain information about an AP, and to scan an area to look
for all APs regardless of ESSID. The information available through site survey
includes:
• ESSID
• Beacon Interval
• Information regarding support of 802.11d, 802.11g, 802.11h, and other 802.11
amendment standards as required.
• Current security configuration
Start the site survey by selecting
Run Site Survey from the Admin menu. The mode
starts immediately.
When the test is started, it is by default in “single ESSID” mode. When the Any soft
key is pressed (softkey A), all APs, regardless of ESSID are displayed, and the
softkey changes to say MyID. Pressing the MyID soft key will revert to the “single
ESSID” mode and change the softkey back to Any.
The display would look like the following for the multiple AP mode.
1 1 1 1 1 1 - 2 2 3 3 4 4 4
1 1 1 1 1 1 - 2 2 3 3 4 4 4
1 1 1 1 1 1 - 2 2 3 3 4 4 4
1 1 1 1 1 1 - 2 2 3 3 4 4 4
A n y
D e t l
Where:
• 111111 = The last three octets of the on-air MAC address for a discovered AP.
• 22 = The signal strength for the specified AP.
• 33 = The channel number of the specified AP.
• 444 = The beacon interval configured on the specified AP.
• Any/MyID = Softkey to toggle between “single ESSID” and “any ESSID”
mode.
• Detl/Smry = Softkey to toggle between the multiple AP (summary) display, and
the single (detail) displays for each AP.
The following screen shows how the display would look when there are three APs
configured with an ESSID that matches that of the handset. The first has a signal
strength of –28dbm, is configured on channel 2, with a beacon interval of 100ms.
The second has a signal strength of –48dbm, is configured on channel 6, with a
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 41
Page 42

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
beacon interval of 200ms. The third has a signal strength of –56dbm, is configured
on channel 11 with a beacon interval of 100ms.
a b 7 b c 8 - 2 8 0 2 1 0 0
2 a e 5 7 8 - 4 8 0 6 2 0 0
2 a e 5 9 6 - 5 6 1 1 1 0 0
A n y
D e t l
When the any ESSID mode is selected, the summary display contains the first six
characters of the APs ESSID instead of the beacon interval as in the example below.
a b 7 b - 2 8 0 2 A L P H A
2 a e 5 - 4 8 0 6 W S M T E S
2 a e 5 - 5 6 1 1 v o i c e
M y I D
D e t l
In detail mode the display would appear as follows. The Left/Right arrow keys will
move between AP indices.
i : b b b b b b s n c h b c n
e e e e e e e e e e e D G H I
r r r r r r r r r r r r r + x x x x
m m m G : g g g g P : p p p p
A n y
S m r y
Where:
• i = Index of selected AP (value will be from 0 to 3 inclusive)
• bbbbbb = The last three octets of the BSSID for a discovered AP.
• sn = Signal strength in –dbm
• ch = Channel
• bcn = Beacon interval
• eeeeeeeeeee = ESSID (Up to first 11 characters)
• DGHI = Standards supported
• rrrrrrrr = Rates supported. Basic rates will have a “b” following the rate.
• + = more rates are supported than those displayed
• xxxx = WMM or UPSD if those QoS methods are supported
• mmm = Security mode
• G:gggg = Group key security
• P:pppp = Pairwise key security
• Any/MyID = Softkey to toggle between “single ESSID” and “any ESSID”
modes.
• Detl/Smry = Softkey to toggle between the multiple AP display (summary), and
the single AP display (detail).
Numbers racing across the handset display indicate AP information is being
obtained. A
Waiting message indicates the system is not configured properly and the
handset cannot find any APs.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 42
Page 43

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
Solving Coverage Issues
Coverage issues are best resolved by adding and/or relocating access points.
Overlap issues may be resolved by reassigning channels to the access points or by
relocating the access points. See the Troubleshooting section Access Point Problems for
more information.
9.2 Diagnostics Mode
The Diagnostics Mode is used to evaluate the overall quality of the link between the
handset, AP, and infrastructure side equipment, such as Call Agent, NetLink SVP
Server, and gateways. Unlike Site Survey, the Diagnostics Mode is used while the
functional code is running, and during a call.
When Diagnostics Mode is turned on in the Admin menu, the handset can display
diagnostic screens any time it is active (in a call).
The display of information is instigated by pressing the MENU key. Only four of the
diagnostic counters listed below can be shown at a time. Pressing the MENU key
multiple times will cycle through the various counters and the normal off hook (Call
Agent) display. The numeric icon at the top of the display indicates what screen
number is being displayed. For example the first time the MENU key is pressed, the 1
icon is shown, and the first four counters are displayed, the next time it is pressed,
the 2 icon is shown, and the next four counters are displayed, the counters will be
cycled through in this fashion until there are no more counters to be displayed. After
all the counters have been displayed, the screen returns to the normal off hook Call
Agent screen.
Note that the normal used of the MENU key is not available if Diagnostics Mode is
enabled.
The information provided by the Diagnostics Mode includes:
Screen 1
• Missed receive packet count since power up (MissedRcvCnt)
• Missed transmit packet count since power up (MissedXmtCnt)
• Receive retry count since power up (RxRetryCount)
• Transmit retry count since power up (TxRetryCount)
M i s s e d R c v C n t n n n n n
M i s s e d X m t C n t n n n n n
R x R e t r y C o u n t n n n n n
T x R e t r y C o u n t n n n n n
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 43
Page 44

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
Screen 2
• Jitter (Jitter), average error or “wobble” in received packet timing, in
microseconds
• Last successful transmit data rate (LastRate)
• Gateway type (GatewyType)
J i t t e r
L a s t R a t e
G a t e w y T y p e
n n n n n
n n n n n
m n e m o
Where:
• mnemo : A mnemonic that indicates what type of gateway is being used
• SawA2: All handsets are rate limited to 2Mb because a 500 series NetLink
handset is on the network.
• 2Mb: non-NetLink SVP Server Gateway system (handsets are limited to 2Mb if
the NetLink SVP Server is not used.)
• 11Mb: Gateway with NetLink SVP Server and no 500 series NetLink Wireless
Telephones. This system can run at the full 11Mb/s speed.
Screen 3
Screen 3 contains a list of the APs that are heard and the following parameters from
each AP:
• Indicator as to whether this is the current AP or an index into the list of other
APs heard
• Last 2 octets of the MAC address of the AP
• Channel number
• Signal strength
• Either the 802.11 Association ID from the current AP or a mnemonic for the
reason code indicating why the handset didn’t hand off to this other AP.
Where:
• C: Indicates the AP that the handset is currently using
• n: Indicates an index into the list of other APs, where n is equal to 1, 2, or 3
• mmmm: This hexadecimal number is the last 2 octets of this AP’s MAC address
• ch: Channel number the AP is configured on
• -ss: Signal strength for the AP in dBm
• aid: The Association ID for the currently associated AP
• mnem: A mnemonic that indicates why the handset didn’t hand off to this other
AP:
Unkn: Reason unknown
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 44
C : m m m m c h - s s a i d
1 : m m m m c h - s s m n e m
2 : m m m m c h - s s m n e m
3 : m m m m c h - s s m n e m
Page 45

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
Weak: Signal Strength too weak
Rate: One or more basic rates not supported
Full: AP can not handle bandwidth requirements
AthT: Authentication Timeout
AscT: Association Timeout
AthF: Authentication Failure
AscF: Association Failure
SecT: Security Handshake Timeout
SecF: Security Handshake Failure
Cnfg: AP not configured correctly for security, QoS mode or infrastructure
network.
Screen 4
• Association count since power up (AssocCount)
• Re-association count since power up (ReAssocCount)
• Association failures since power up (AssocFailure)
• Re-association failures since power up (ReAssocFail)
A s s o c C o u n t
R e A s s o c C o u n t n n n n n
A s s o c F a i l u r e n n n n n
R e A s s o c F a i l
n n n n n
n n n n n
Screen 5
• Security error count since power up (Sec-ErrCount)
• MAC sequence number of frame with last security error (LstSecErrSeq)
S e c - E r r C o u n t n n n n n
L s t S e c E r r S e q n n n n n
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 45
Page 46

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
9.3 Syslog Mode
A syslog server must be present on the network in order for the handset to send the
log messages and have them saved. The syslog server will be found with DHCP
option 7 if the handset is using DHCP. If static addresses are configured, the syslog
server’s IP address can be configured statically in the Admin menu.
If the syslog server address is blank (000.000.000.000 or 255.255.255.255)
Admin menu options:
• *Disabled turns syslog off.
•
• Events logs all errors plus also some other interesting events (see below).
•
The table below lists the syslog messages and which level of logging will produce
them:
or the handset is using DHCP and no option 7 is received from the DHCP
server, the handset will not send any syslog messages.
Errors causes the handset to log only events that we consider to be an error (see
below).
Full logs all the above plus a running stream of other quality information (see
below).
Message type Errors Events Full
Failed Handoff Yes Yes Yes
Successful Handoff No Yes Yes
Security Error Yes Yes Yes
Call Start/End No Yes Yes
Audio stats No No Yes (every 5 secs)
Audio error threshold exceeded Yes Yes Yes
Radio stats No No Yes (every 5 secs)
Radio error threshold exceeded Yes Yes Yes
All syslog messages will include:
• Date and time (to 1/100th of second) since handset power on (currently set to
Jan-1 00:00.00)
• Handset’s MAC address
• Handset’s IP address
• Sequence number
The table below lists the additional items in each Message type:
Failed Handoff
(Sent whenever the handset attempted to
handoff, but failed trying.)
Failed AP MAC
Failed AP signal strength
Current AP MAC
Current AP signal strength
Failure reason
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 46
Page 47

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
Successful Handoff New AP MAC
New AP signal strength
Old AP MAC
Old AP signal strength
Reason for handoff
Other candidate APs:
MAC
Signal strength
Reason not used
Security Error AP MAC
AP signal strength
Security mode
Error details (mode dependent)
Call Start Call type (telephony, OAI, PTT)
AP MAC
AP signal strength
Call End AP MAC
AP signal strength
Audio stats AP MAC
AP signal strength
Payload size (in msec)
Payloads sent
Payloads received
Payloads missed (not received)
Payloads missed rate (over last 5 seconds)
Payloads late
Payloads late rate (over last 5 seconds)
Average jitter
Audio error threshold exceeded
Same as audio stats
(Sent if payloads missed rate or payloads late
rate exceeds 2%, or if the average jitter is over 2
msec)
Radio stats AP MAC
AP signal strength
Directed packets sent
Directed packets received
Multicast packets sent
Multicast packets received
Broadcast packets sent
Broadcast packets received
TX dropped count
TX drop rate (over last 5 seconds)
TX retry count
TX retry rate (over last 5 seconds)
RX retry count
RX retry rate (over last 5 seconds)
Radio error threshold exceeded
Same as radio stats
(Sent if TX drop rate exceeds 2% or TX or RX
retry rate exceeds 5%)
Messages are formatted like the following example:
Jan 1 00:01:26.72 0090.7a02.2a1b (172.16.0.46) [001a] RStat: AP 00:40:96:48:1D:0C (-56
dBm), Sent 783523, Recvd 791342, MSnt 245, MRcd 5674, BSnt 43, BRcd 10783, TX drop 43
(0.0%), TX retry 578 (1.2%), RX retry 1217 (1.6%)
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 47
Page 48

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
10. Certifying the NetLink Wireless Telephones
Prior to determining that an installation is complete, test the handsets following the
sequence given in the previous Testing a NetLink Wireless Telephone section and
conduct a site survey mode test according to the directions given in the previous
Diagnostic Tools section. Note any areas where coverage is conflicting or inadequate.
Note any system difficulties and work with your wireless LAN and/or LAN system
administrator to determine the cause and possible remedy. See the section NetLink
Wireless Telephone Problems for clues to possible sources of difficulties. If any
adjustments are made to the system, re-test the device in the same vicinity to
determine if the difficulty is resolved.
The installer should not leave the site before performing installation
verification.
These tests must be performed in typical operating conditions, especially if heavy
loads occur. Testing sequence and procedure is different for every installation.
Generally, you should organize the test according to area and volume, placing
numerous calls to others who can listen while you perform coverage tests. Note any
areas with excessive static or clarity problems and report it to a SpectraLink service
engineer.
The coverage test will also require you to put the handset in Site Survey mode and
walk the entire coverage area to verify all access points.
10.1 Conducting a Site Survey
Conduct a Site Survey of the installation, by walking the site looking for interfering
802.11 systems, adequate coverage and channel assignment, and correct AP
configuration.
1. Referring to section 6.1 Run Site Survey, put a handset into Site Survey in the
Any/Smry ESSID mode. Walk throughout the site checking for any expected
APs or other ESSIDs.
2. Then, walk the site again, in MyID/Smry ESSID mode, this time checking that
every location has adequate coverage (there should be at least one AP stronger
than -70dBm in all areas) and has good channel allocation (at any point, the
strongest AP shown should be on a different channel than the next best choice).
3. Finally, use the single AP (MyID/Detl) display to check each AP, to ensure it is
configured for the proper data rates, beacon interval, 802.11 options enabled,
QoS method, and security method.
4. Make any necessary adjustments to AP locations and configurations and repeat
steps 1-3 until the Site Survey shows adequate coverage and correct
configuration at every location.
The installation is not complete until these certification steps have been performed. Do not
hand out handsets at a site that has not been certified.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 48
Page 49

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
11. Software Maintenance
The NetLink e340/h340/i640 Wireless Telephones use proprietary software
programs written and maintained by SpectraLink Corporation. The software versions
that are running on the
the
Power On button.
SpectraLink or its authorized dealer will provide information about software updates
and how to obtain the software.
Downloads are available from http://www.spectralink.com/service/software.php.
11.1 Upgrading NetLink Wireless Telephones
After software updates are obtained from SpectraLink, they must be transferred to
the appropriate location in the LAN to update the code used by the handsets.
NetLink e340/h340/i640 Wireless Telephones allow over-the-air transfer of
software updates from the designated TFTP server to the handsets. The downloader
function in the handset checks its software version every time the handset is turned
on. If there is any discrepancy the handset immediately begins to download the
update.
handsets can be displayed during power on by holding down
Normal Download Messages
When the handset is powered on, it displays a series of messages indicating that it is
searching for new software, checking the versions, and downloading. The normal
message progression is:
Message Description
Checking Code Handset is contacting the TFTP Server to determine if it has a newer version of software that
should be downloaded.
Erasing Memory Handset has determined that a download should occur and is erasing the current software from
memory. This message also displays a progress bar. When the progress bar fills the display line
the erase operation is complete.
Updating Code Handset is downloading new software into memory. The number icons at the bottom of the
display indicate which file number is currently being downloaded. This message also displays a
progress bar. When the progress bar fills the display line the update operation is complete on
that file.
When the update is complete, the handset displays the extension number, and is
ready for use.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 49
Page 50

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
Download Failure or Recovery Messages
The following display messages indicate a failure or recovery situation during the
download process.
Message Description
Server Busy Handset is attempting to download from a TFTP Server that is busy downloading other
phones and refusing additional downloads. The handset will automatically retry the
download every few seconds.
TFTP ERROR(x):yy A failure has occurred during the TFTP download of one of the files. (x) = The file number
which was being downloaded; yy is an error code describing the particular failure. Possible
error codes are:
01 = TFTP server did not find the requested file.
02 = Access violation (reported from TFTP server).
07 = TFTP server reported "No such user" error. Check the TFTP server configuration.
81 = File put into memory did not CRC. The handset will attempt to download the file again.
FF = Timeout error. TFTP server did not respond within a specified period of time.
Erase Failed Download process failed to erase the memory in the handset. This operation will retry.
Waiting Handset has attempted some operation several times and failed, and is now waiting for a
period of time before attempting that operation again.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 50
Page 51

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
12. Troubleshooting NetLink Wireless Telephone Problems
NetLink Wireless Telephones can exhibit transmission problems in several ways.
They can cease functioning properly, display error messages, or display incorrect
data. When using and troubleshooting handsets, consider the following problem
sources to determine the best method of approaching any specific situation.
12.1 Access Point Problems
Most, but not all, handset audio problems have to do with access point range,
positioning and capacity. Performing a Site Survey as described in this document can
isolate the AP causing these types of problems. If the handset itself is suspected,
conduct a parallel Site Survey with a handset that is known to be properly
functioning.
In range/Out of range – service will be disrupted if a user moves outside the area
covered by the wireless LAN access points. Service is restored if the user moves back
within range. If a call drops because a user moves out of range, the handset will
recover the call if the user moves back into range within a few seconds.
Capacity – in areas of heavy use, the call capacity of a particular AP may be filled. If
this happens, the user will hear three chirps from the handset. The user can wait until
another user terminates a call, or move within range of another AP and try the call
again. If a user is on a call and moves into an area where capacity is full, the system
attempts to find another AP. Due to range limitations, this may be the same as
moving out of range.
Transmission Obstructions –prior to system installation, the best location for APs for
optimum transmission coverage was determined. However, small pockets of
obstruction may still be present, or obstructions may be introduced into the facility
after system installation. This loss of service can be restored by moving out of the
obstructed area, or by adding APs.
12.2 Configuration Problems
Certain problems are associated with improper configuration of either the MGCP
system or the handset.
Configuration problems are generally corrected by changing the configuration on the
MGCP system or on the handset. There may also be incorrect programming of the
AP. See the Configuration Note for the AP in use at the site.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 51
Page 52

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
12.3 NetLink Wireless Telephone Status Messages
NetLink Wireless Telephone status messages provide information about the NetLink
e340/h340/i640 Wireless Telephone's communication with the AP and host
telephone system. The following table summarizes the status messages, in
alphabetical order.
Message Description Action
3 chirps Handset is not able to communicate with the
best AP, probably because that AP has no
bandwidth available.
Address Mismatch Handset software download files are
incorrect or corrupted
ASSERT xxx c
Line yyy
Assoc Failed
xxxxxxxxxxxx
Assoc Timeout
xxxxxxxxxxxx
Auth Failed
xxxxxxxxxxxx
The handset has detected a fault from which
it cannot recover.
x…x = AP MAC address.
Handset association was refused by AP;
displays MAC of failing AP.
x…x = AP MAC address.
Handset did not receive association
response from AP; displays MAC of failing AP
x…x = AP MAC address.
Handset authentication was refused by AP;
displays MAC of failing AP
None. This is only a warning, the call will
handoff to the best AP once it becomes
available.
Download new software from the
SpectraLink site per
Maintenance
Record the error code so it can be
reported.
Turn the handset off then on again.
If error persists, try registering a different
handset to this telephone port.
If error still persists, contact SpectraLink
Technical Support and report the error.
Check handset and AP security settings.
Ensure AP is configured per
Note
.
Try another AP.
Check handset and AP security settings.
Ensure AP is configured per
Note
.
Try another AP.
Check handset and AP security settings.
Ensure AP is configured per
Note
.
Try another AP.
Software
.
Configuration
Configuration
Configuration
Auth Timeout
xxxxxxxxxxxx
Bad Code Type xx
Expected Code Type yy
Bad Config Some needed configuration parameter has
Bad ESSID The handset is configured for “static ESSID”
Bad Phintl File Handset software download files are
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 52
x…x = AP MAC address
Handset did not receive authentication
response from AP; displays MAC of failing AP
xx, yy = software license types
Handset software does not match current
handset license selection
not been set
(as opposed to “Learn once” or “Learn
always” and no ESS ID has been entered.
incorrect or corrupted
Check handset and AP security settings.
Ensure AP is configured per
Note
.
Try another AP.
Download new software from the
SpectraLink site per
Maintenance
Check all required handset configuration
parameters for valid settings
Enter an ESSID in the configuration
settings or change to one of the “Learn”
modes.
Download new software from the
SpectraLink site per
Maintenance
.
.
Configuration
Software
Software
Page 53

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
Message Description Action
Bad Program File Handset software download files are
incorrect or corrupted
(battery icon),
Low battery In call: the battery icon displays and a soft
Battery Low,
beep (audio)
Download new software from the
SpectraLink site per
Maintenance
Software
.
beep will be heard when the user is on the
handset and the battery charge is low. User
has 15–30 minutes of battery life left.
The Battery Pack can be changed while the
call is still in progress. Do not press End
Call. Place call on Hold or Park. Quickly
remove the discharged battery and replace
with a charged battery, power on the
handset, and press Start Call to resume
the call in progress.
Not in call: The battery icon displays
whenever the battery charge is low The
message Battery Low and a beep indicate
a critically low battery charge when user is
not on the handset. The handset will not
work until the Battery Pack is charged.
Battery Failure The Battery Pack is not functioning. Replace the Battery Pack with a new or
confirmed SpectraLink Battery Pack. Any
non-Spectra-Link Battery Packs will not
work.
Battery Failed Battery Pack is damaged or incompatible
with handset.
Replace the Battery Pack with a new or
confirmed SpectraLink Battery pack. Any
non-SpectraLink Battery Packs will not
work.
Can’t Renew DHCP
yyy.yyy.yyy.yyy
y…y = DHCP server IP address
DHCP server is not responding to initial
Configuration problem. Check the IP
address configuration in the DHCP server.
renewal attempt
Charging … The handset is charging in the Desktop
No action needed.
Charger.
Charge Complete The handset is now fully charged. No action needed.
Checking Code Handset is contacting the TFTP Server to
determine if it has a newer version of
software that should be downloaded.
None, this message should only last for
approximately one second. If message
remains displayed, power off and contact
customer support for a replacement
phone.
Checking DHCP IP The handset is retrieving DHCP information
None. This is informational only.
from the DHCP server
CRC Code Error The software which has been TFTP
downloaded has a bad redundancy code
check
Try the download again; it is possible the
software was corrupted during download. If
the error repeats, check that the download
image on the TFTP server is not corrupted.
Code Mismatch! The software loaded into the handset is
incorrect for this model handset
Verify the License Management value is
correct. Replace the software image on the
TFTP server with software that is correct for
the handset model.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 53
Page 54

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
Message Description Action
DCA Timeout The handset has detected a fault for which it
cannot recover, possibly due to a failure to
acquire any network.
Turn the handset off then on again. If error
persists, contact SpectraLink Technical
Support and report the error.
DHCP Error (1-5) DHCP Error 1 The handset cannot locate a DHCP server.
It will try every 4 seconds until a server is
located.
DHCP Error 2 The handset has not received a response
from the server for a request to an IP
address. It will retry until a server is found.
DHCP Error 3 The server refuses to lease the handset an
IP address. It will keep trying.
DHCP Error 4 The server offered the handset a lease that
is too short. The minimum lease time is 10
minutes but SpectraLink engineers
recommend at least one hour minimum
lease time. The handset will stop trying.
Reconfigure the server and power cycle the
handset.
DHCP Error 5 Failure during WEP Key rotation process
(proprietary feature).
DHCP Lease Exp
yyy.yyy.yyy.yyy
y…y = DHCP Server IP address DHCP is not
responding to renewal attempts (at least one
renewal succeeded)
The handset failed to renew its DHCP
lease, either because the DHCP server is
not running, or because the configuration
has been changed by the administrator.
The handset will attempt to negotiate a
new lease, which will either work, or
change to one of the above DHCP errors (1-
4).
DHCP NACK error
yyy.yyy.yyy.yyy
y…y = DHCP server IP address
DHCP server explicitly refused renewal
DL Not On Sector Handset software download files are
incorrect or corrupted
DO NOT POWER OFF The handset is in a critical section of the
software update
Duplicate IP The handset has detected another device
with its same IP address
Erase Failed Download process failed to erase the
memory in the handset.
The DHCP lease currently in use by the
handset is no longer valid, which forces the
handset to restart. This problem should
resolve itself on the restart. If it does not,
the problem is in the DHCP server.
Download new software from the
SpectraLink site per
Maintenance
Software
.
None. Do not remove the battery or
attempt to power off the phone while this is
displayed. Doing so may require the phone
to be returned to SpectraLink to be
recovered.
If using DHCP, check that the DHCP server
is properly configured to avoid duplicate
addresses.
If using Static IP, check that the handset
was assigned a unique address
Operation will retry but may eventually
report the error "int. error: 0F" Power cycle
the phone.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 54
Page 55

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
Message Description Action
Erasing Memory Handset has determined that a download
should occur and is erasing the current
software from memory.
None. When the progress bar fills the
display line the erase operation is
complete.
Do not turn the handset off during this
operation.
Far End TCP Close The handset has lost communication with the
PBX.
No action necessary. After about 20
seconds, the handset will re-initialize and
reconnect to either the same PBX or to
another PBX if it has been instructed to do
so or the first PBX fails to respond.
Files Too Big Handset software download files are
incorrect or corrupted
Download new software from the
SpectraLink site per
Maintenance
Software
.
Flash Config Error Handset internal configuration is corrupt. Perform "Restore Defaults" operation via
administrator menus [or reprogram with
Configuration Cradle]
Forced Redirect The PBX has told the handset to re-register
No action necessary.
with another PBX.
Get Button Defs The Handset is attempting to get definitions
No action necessary.
from the PBX of how the user-programmable
keys are currently programmed.
Initializing … The handset is performing power on
None. This is informational only.
initialization
Internal Err. # # The handset has detected a fault from which
it cannot recover.
Invalid Redirect The PBX has told the handset to re-attempt
registration with another PBX. The reason
code in the redirect message is invalid.
Multiple GW Res More than one NetLink SVP Server has
responded
Multiple SVP Reg
yyy.yyy.yyy.yyy
y…y = SVP IP address
Handset received responses from multiple
SVP Servers; displays IP address of one
responding SVP Server
Must Upgrade SW! Handset software is incompatible with
hardware.
Record the error code so it can be
reported.
Turn the handset off then on again.
If error persists, try registering a different
handset to this telephone port.
If error still persists, contact SpectraLink
Technical Support and report the error.
No action necessary.
Caused by two or more handsets sharing
the same IP address. Assign unique IP
addresses to each phone.
This can happen if the handset has been
re-configured to use a different SVP server
and then powered-up before the previous
server has had time to determine that the
handset is no longer connected to it. The
problem should go away after about 30
seconds.
Download new software from the
SpectraLink site per
Maintenance
Software
.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 55
Page 56

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
Message Description Action
Net Busy
xxxxxxxxxxxx
x…x = AP MAC address
Handset cannot obtain sufficient bandwidth
Try the call again later.
to support a call; displays MAC of failing AP.
No DHCP Server Handset is unable to contact the DHCP
server.
Check that DNCP is operational and
connected to WLAN or use Static IP
configuration in the handset.
No ESSID Attempted to run site survey application
without an ESSID set.
Let handset come completely up.
Statically configure an ESSID in the Admin
menu.
No Func Code Handset software download files are
incorrect or corrupted
No Host IP The handset is configured for “static IP” (as
opposed to “use DHCP”) and no valid host IP
address (the handset’s IP address) has been
Reconfigure the handset to gain access to
the WLAN and download new code.
Enter a valid IP address in the
configuration settings or change to “use
DHCP”.
entered.
No IP Address Invalid IP Check the IP address of the handset and
re-configure if required.
No Net Access Cannot authenticate / associate with AP Verify the AP configuration.
Verify that all the WEP settings in the
handset match those in the APs.
No Net Found
No APs
Handset cannot find any Access Points
This indicates any of the following:
No radio link Verify that the AP is turned on.
No ESSID – Auto-learn not supported (or)
incorrect ESSID
Verify the ESSID of the wireless LAN and
enter or Autolearn it again if required.
AP does not support appropriate data rates Check the AP configuration against
Configuration Note for AP.
Out of range Try getting closer to an AP. Check to see if
other handsets are working within the
same range of an AP. If so, check the
ESSID of this handset.
Incorrect Security settings Verify that all the Security settings in the
handset match those in the APs
No Net Found
xxxxxxxxxxxx yy
x…x = AP MAC address
yy = AP signal strength
Handset cannot find a suitable access point;
displays MAC and signal strength of “best”
non-suitable AP found.
Check AP and handset network settings
such as ESSID, Security, Reg domain and
Tx power.
Ensure APs are configured per
Configuration Note
.
Try Site Survey mode to determine more
specific cause.
No PBX IP Addr The Handset could not locate the Mitel PBX. If the handset is operating in static IP
mode, make sure that the PBX IP address
has been entered in the administrative
menus under RTC IP Addr. In DHCP mode,
ensure that the system administrator has
properly entered the DHCP option
parameters at the DHCP server.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 56
Page 57

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
Message Description Action
No PBX Response The handset has exceeded its retransmission
limit with no ACK response from Call Agent.
Verify that Call Agent IP address and port
are properly configured.
No Reg Domain Regulatory Domain Not Set Configure the Regulatory Domain of the
handset
No SVP IP The handset is configured for “static IP” (as
opposed to “use DHCP”) and no valid
NetLink SVP Server address has been
Enter a valid NetLink SVP server IP address
in the configuration setting or change to
“use DHCP.”
entered.
No SVP Response
yyy.yyy.yyy.yyy
y…y = SVP Server IP address
Handset has lost contact with the SVP Server.
This may be caused by bad radio reception
or a problem with the NetLink SVP Server.
The handset will keep trying to fix the
problem for 20 seconds, and the message
may clear by itself. If it does not, the
handset will restart. Report this problem to
the system administrator if it keeps
happening.
No SVP Server Handset can’t locate NetLink SVP Server IP address configuration of NetLink SVP
Server is wrong or missing.
NetLink SVP Server is not working Check error status screen on NetLink SVP
Server.
No LAN connection at the NetLink SVP Server Verify NetLink SVP Server connection to
LAN.
No SVP Server
No DNS Entry
Handset unable to perform DNS lookup for
SVP Server, server had no entry for SVP
Server
No SVP Server
No DNS IP
Handset unable to perform DNS lookup for
SVP Server, no IP address for DNS server
No SW Found A required software component has not been
identified.
The network administrator must verify that
a proper IP address has been entered for
the SVP Server DHCP option.
The network administrator must verify
proper DHCP server operation.
Check that the handset license type has a
corresponding entry in the slnk_cfg.cfg
file.
Check that the pd11mgd.bin and
pi110000.bin entries exist in under this
license type in the slnk.cfg.cfg file.
Not Installed! A required software component is missing Check that all required software files are
on the TFTP server, if over-the-air
downloading is being used. If the error
repeats, contact SpectraLink Technical
Support.
Press END Call The far end of a call has hung up. Hang up the near end.
Register to PBX The handset is attempting to register to the
PBX.
If this message persists, verify that the
handset is properly provisioned on the PBX
and that the 5220 Emulation mode is set
properly in the administrative menus.
Restart Command The Handset received a restart command
from the supported Mitel Networks VoIP
None. The Handset will automatically
restart in a few seconds.
solution.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 57
Page 58

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
Message Description Action
Select License The correct protocol has not been selected
from the license set.
Server Busy Handset is attempting to download from a
TFTP Server that is busy downloading other
devices and refusing additional downloads.
Skt Open Fail Socket open fail. Occurs when the Handset
tries to connect to the PBX but there is no
response. If resiliency is active, the handset
will keep trying.
Storing Config Handset is storing changes to handset
configuration.
SVP Service Rej. The NetLink SVP Server has rejected a
request from the handset
System Busy
yyy.yyy.yyy.yyy
y…y = SVP Server IP Address
SVP Server has reached call capacity.
Using the administrative menus, select one
license from the set to allow the phone to
download the appropriate software.
None, the handset will automatically retry
the download every few seconds.
If the PBX is inoperative and resiliency is
not active or the handset cannot locate a
backup PBX, turn off the handset and
repair the primary PBX. Note that it may be
advisable to reconfigure the backup PBX to
be the primary PBX if the repair is more
time-consum-ing than the reconfiguration.
None. Informational only. The handset may
display this briefly following a
configuration change or software
download.
The handset will restart and attempt to reregister with the SVP Server, which should
fix the problem. Report to your
administrator if it keeps happening.
All call paths are in use, try the call again
in a few minutes.
System Locked
(with Busy Tone)
NetLink SVP Server is locked Try call again later, system has been
locked for maintenance
System Gateway is locked Try the call again, system has been locked
for maintenance
TCP Rcv Timeout If the PBX has failed, this message may
display briefly as the handset tries to connect
to the backup PBX in a resilient setting. This
Wait for the handset to cycle through
attempts to connect to the backup PBX.
See SKT Open Fail above.
message may be replaced by the SKT Open
Fail message if the handset is unsuccessful
at connecting with the backup PBX or if
resiliency is not programmed.
TFTP ERROR(x):yy A failure has occurred during a TFTP software
download. (x) = The file number which was
being downloaded; yy is an error code
describing the particular failure. Possible
error codes are:
01 = TFTP server did not find the requested
file.
02 = Access violation (reported from TFTP
Error code 01, 02 or 07 - check the TFTP
server configuration.
Error code 81, the handset will attempt to
download the file again.
For other messages, power off the handset,
then turn it on again to retry the download.
If the error repeats, note it and contact
SpectraLink Technical Support.
server).
07 = TFTP server reported "No such user"
error.
81 = File put into memory did not CRC.
FF = Timeout error. TFTP server did not
respond within a specified period of time.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 58
Page 59

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
Message Description Action
Too Many Errors The handset continues to reset and cannot
be recovered.
Unknown
A phrase is missing from your phintl file. Download new software from the
xx:yy:zz
Updating … The handset is internally updating its
software images
Updating Code… Handset is downloading new software into
memory. The number icons at the bottom of
the display indicate which file number is
currently being downloaded. This message
also displays a progress bar. When the
progress bar fills the display line the update
operation is complete on that file.
Waiting… Handset has attempted some operation
several times and failed
Watchdog Timeout The handset failed to hear from the
supported Mitel Networks VoIP solution
within the watchdog timeout interval.
Wrong Code Type The software loaded into the handset is
incorrect for this model phone
Fatal error. Return handset to SpectraLink.
SpectraLink site per
Maintenance
Software
.
None. The handset may do this briefly after
a download. This is informational only.
None. When the progress bar fills the
display line the update operation is
complete on that file.
Do not turn the handset off during this
operation.
None. The handset is waiting for a
specified period of time before attempting
that operation again.
Verify the supported Mitel Networks VoIP
solution is operational and connected to
the network.
Replace the software image on the TFTP
server with software that is correct for the
phone model.
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 59
Page 60

SpectraLink Corporation Configuration and Administration—NetLink e340/i640 Wireless Telephone
Mitel Networks 3300 and SX-200 ICP and 5220 IP Phone emulation
Index
Access point
Coverage, 43
Coverage test, 48
Access point, description, 8
Automatic Learn, 21, 22
Capacity, 51
Checking code, 49
Customer Support Hotline, 4
Download messages
Failure or Recover, 50
Normal, 49
Erasing memory, 49
handset
Status messages, 56
High noise option, 28
Hotline, 4
NetLink SVP Server, 8
OAI On/Off, 19
Obstructions, 51
Out of range, 51
Preferences, user-defined, 25
Regulatory Domain, 23
Restore Defaults, 24
Site Certification, 48
Status messages, 52
Switched Hub, description, 9
Transmission obstructions, 51
Updating code, 49
User Preferences, 25
Wireless Telephone
Configuration problems, 51
Display IP address of, 29
Problems with, 51
Status messages, 52
Wireless Telephone, description, 8
PN: 72-1084-02-E.doc Page 60
 Loading...
Loading...