Page 1

> Directional Fault Sensing > Smart Tap
APPLICATION GUIDE
Smart Tap
®
Fault Location in
Transmission Networks
Fault location and load restoration in transmission networks.
Faults on tapped transmission lines can result in signicant outage times and customer dissatisfaction. Commonly used
substation based fault locating solutions for tapped transmission lines can be problematic when trying to locate the specic
line segment where the fault occurred. Using Smart Tap technology, the fault location information is reported through the
SCADA system allowing the system operator to determine which line segment has experienced the fault.
For momentary faults, the SCADA fault information can assist the crews in the location and elimination of the source
of the momentary fault. For permanent faults, the operator can isolate the faulted section and minimize outage times.
Information from each line tap provides an indicator of a fault and fault direction, it also provides deterministic information
to allow proper sectionalizing.
For example, in a transmission network with four taps, there are nine
possible sections where the fault could occur.
• Faulted section is not identied
• Trial and error approach required to clear fault
• For permanent faults, breakers are reclosed into fault to locate faulted
section
• The trial and error approach repeated until proper section is
identied
• Not possible to identify sections where momentary faults occur
Smart Tap is an innovative new technology that correctly identies the faulted section for low current momentary
faults and over current permanent faults.
KEY FEATURES
• Detects low current and over current faults
• Detects magnitude and direction of permanent and
momentary faults
• Works on looped transmission lines with radial load taps
• Does not require PTs to determine fault direction
• Direction indication points to faulted section
• Reports information to SCADA operator
• Can be congured for automatic operation
Page 2
APPLICATION GUIDE
MOMENTARY OR PERMANENT FAULT
> Directional Fault Sensing > Smart Tap
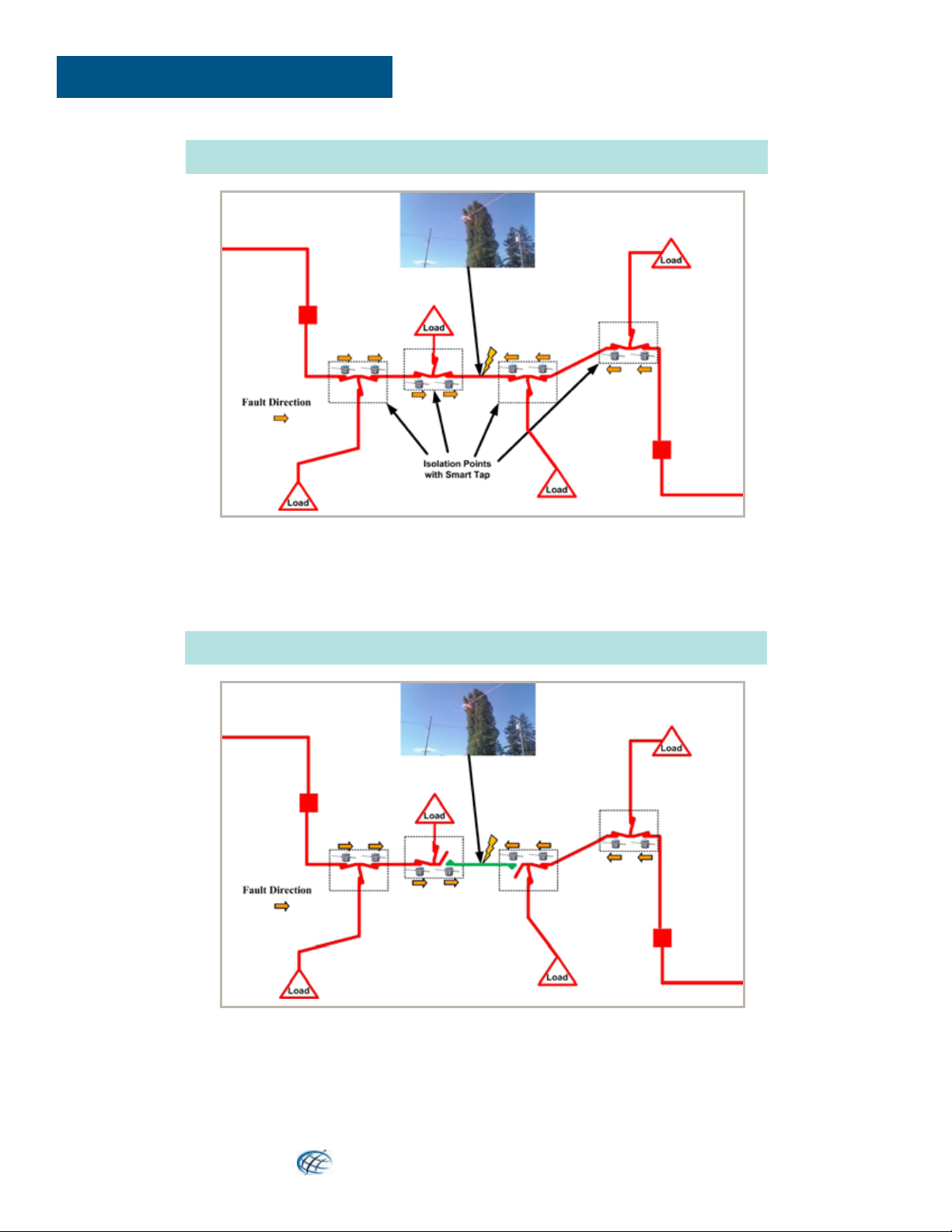
Line fault between two taps. Smart Tap generates fault direction ags at each sensing point. These ags can be sent to the
SCADA system and displayed on the operators single line diagram. These direction indicators represented as arrows on this
diagram point to the faulted line segment.
PERMANENT FAULT
Faulted Line Section Isolated
In the case of a permanent fault, The SCADA operator can open the switches which will isolate the faulted section after
the breakers have locked out for the remote controlled switches. If the switches are manually operated the crews can be
dispatched to the proper section to isolate the fault without the guess work of trying several locations before the proper location
is identied. The power to the customer can be quickly restored while the crews are clearing the source of the fault.
SSIPOWER SENSORS AND AUTOMATION
Page 3

APPLICATION GUIDE
> Directional Fault Sensing > Smart Tap
FAULT SENSING CHARACTERISTICS OF SMART TAP
Low current faults can trip the breaker and be cleared on the instantaneous
reclose operation. Smart Tap detects the direction of these faults and provides
information to the investigative team on the section where the fault occurred. The
detection of the direction of these kinds of faults is very sensitive due to pre-fault
compensation. Small changes in ground current are detected and the direction of
the fault is calculated. This information is not reported unless the substation circuit
breaker trips and a momentary outage exists.
Over current faults can be detected with sudden changes in line current. Pre-
fault compensation allows the over current set points to be set incrementally above
the short term average load current. These direction indications are only reported if
the substation breaker trips out the line.
Smart Tap detects the direction of low current fauts with
the use of pre-fault compensation system which enables
the detection of faults with magnitude less than the current
unbalance in the network.
Smart Tap can work with a variety of current sensing devices.
Conventional CTs and the SSIPower CMD
to 362 KV. Line post sensor devices can be used at 46 KV and
below.
®
II can be used up
CMD® II Line Post Sensor
CT
Smart Tap does not require the use of high voltage PTs to nd fault direction. Voltage synchronization can
be from any AC power source
APPLICATIONS
Substations and
Switching Stations
Manual and Remote
Controlled Switches
SSIPOWER SENSORS AND AUTOMATION
Circuit Switchers
Page 4

APPLICATION GUIDE
> Directional Fault Sensing > Smart Tap
System Integration Options
SMART TAP OPERATION
The inputs are from any current sensors capable of providing an analog signal of the current and fault current waveforms.
Potential transformer inputs can be accommodated, if desired but are optional. Smart Tap measures and reports fault
information either to a local RTU or through a self contained communication system to a remote location.
SYSTEM INTEGRATION OPTIONS
Smart Tap provides direction information to SCADA. through local RTU and SCADA communication network. Direction
indicators can be displayed on the SCADA diagrams and to provide information to the operator to guide the sectionalizing
switching steps.
SCADA Display with Fault Direction Indication
RTUs or Modems
Smart Tap can be integrated into the substation and
SCADA networks with the use of optional substation
touch screen HMI servers and ICCP servers available
from SSI Power.
Smart Tap
HMI Server
Smart Tap Application Server
ICCP
DNP
30 Georgia Avenue Hampton, GA 30228
P 770-946-4562 F 770-946-8106
sales@southernstatesLLC.com
www.southernstatesLLC.com
Publication No. AG1510-SmartTap-R2 02082013
Printed in USA February 2013 ©2013 Southern States, LLC
Smart Tap
®
is a registered Trademark of SSIPower
 Loading...
Loading...