Page 1

6" x 12" SURFACE GRINDER
MODEL SB1023
© November, 2009 by South Bend Lathe Co. For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09
Page 2

For your convenience, any updates to this manual will be available to download free of charge
through our website at:
www.southbendlathe.com
Scope of Manual
This manual helps the reader understand the machine, how to prepare it for operation, how to control
it during operation, and how to keep it in good working condition. We assume the reader has a basic
understanding of how to operate this type of machine, but that the reader is not familiar with the
controls and adjustments of this specific model. As with all machinery of this nature, learning the
nuances of operation is a process that happens through training and experience. If you are not an
experienced operator of this type of machinery, read through this entire manual, then learn more
from an experienced operator, schooling, or research before attempting operations. Following this
advice will help you avoid serious personal injury and get the best results from your work.
We've made every effort to be accurate when documenting this machine. However, errors sometimes
happen or the machine design changes after the documentation process—so the manual may not
exactly match your machine. If a difference between the manual and machine leaves you in doubt,
contact our customer service for clarification.
We highly value customer feedback on our manuals. If you have a moment, please share your
experience using this manual. What did you like about it? Is there anything you would change to
make it better? Did it meet your expectations for clarity, professionalism, and ease-of-use?
South Bend Lathe, Inc.
C
/O Technical Documentation Manager
P.O. Box 2027
Bellingham, WA 98227
Email: manuals@southbendlathe.com
Manual Feedback
Updates
Customer Service
We stand behind our machines. If you have any service questions, parts requests or general questions
about the machine, feel free to contact us.
South Bend Lathe Co.
P.O. Box 2027
Bellingham, WA 98227
Phone: (360) 734-1540
Parts Department: (417) 886-2954
Fax: (360) 676-1075 (International)
Fax: (360) 734-1639 (USA Only)
Email: cs@southbendlathe.com
Page 3

Table of Contents
INTRODUCTION ...............................................................2
About This Machine .............................................2
Capabilities .........................................................2
Features .............................................................. 2
Identification ........................................................3
Machine Specifications ........................................ 4
SAFETY ................................................................................6
Understanding Risks of Machinery .................... 6
Basic Machine Safety ..........................................6
Additional Surface Grinder Safety .....................8
PREPARATION .................................................................9
Preparation Overview ..........................................9
Things You'll Need ...............................................9
Unpacking .......................................................... 10
Inventory ............................................................10
Cleaning & Protecting ....................................... 11
Location ..............................................................12
Lifting & Moving ................................................13
Leveling & Mounting ......................................... 13
Leveling ............................................................ 13
Assembly ............................................................14
Power Connection .............................................. 15
SB1023 110V (Prewired) ....................................15
SB1023 (220V Option) .......................................15
220V Conversion for SB1023 .............................. 15
Initial Lubrication .............................................16
Test Run ............................................................. 16
Inspections & Adjustments ............................... 16
Using the Surface Grinder ................................29
Grinding Tips ................................................... 29
MAINTENANCE ............................................................. 30
Maintenance Schedule .......................................30
Lubrication ......................................................... 30
Handwheel Backlash Adjustment ....................32
Column & Table Gib Adjustment .....................32
SERVICE........................................................................... 33
Machine Storage ................................................ 33
Short-term storage (less than year) .................... 33
Long-term storage (more than a year) ................33
TROUBLESHOOTING .................................................34
ELECTRICAL ................................................................... 36
Electrical Safety Instructions ...........................36
SB1023 Wiring Diagram 110V ..........................37
SB1023 Wiring Diagram 220V ..........................38
PARTS................................................................................39
Motor & Spindle ................................................. 39
Column ............................................................... 40
Table ...................................................................41
Column & Table Parts List ...............................42
Stand ..................................................................43
Machine Labels .................................................44
WARRANTY & RETURNS .......................................... 45
OPERATION .................................................................... 17
Operation Overview ........................................... 17
Controls .............................................................. 18
Wheel Selection .................................................. 19
Abrasive Type ....................................................19
Grit Size ............................................................ 19
Grade ................................................................19
Removing & Installing Grinding Wheels .........20
Removing & Installing Wheel & Hub ...............22
Wheel Inspection ................................................24
Ring Test ............................................................ 25
Wheel Dressing .................................................. 25
Wheel Balancing ................................................ 26
Magnetic Chuck ................................................. 28
Setup for a Typical Grinding Operation ........... 28
Grinder Operation .............................................28
Page 4

Model SB1023
INTRODUCTION
INTRODUCTION
About This Machine
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
Capabilities
This 6 x 12" Surface Grinder allows you to
smooth the surface of metallic workpieces. It
utilizes a table that moves on a horizontal plane
and a grinding wheel that moves along a vertical
axis. By mounting a workpiece to the table, then
moving the table and the grinding wheel during
the grinding process, extremely small amounts of
material can be removed to create high-tolerance
flat surfaces.
One example of this type of work may occur
when the table surface of a metalworking or
woodworking machine needs to be made perfectly
flat. By removing the table from the machine and
processing it with a surface grinder, a perfectly
flat surface can be created.
Another example of this type of work often
occurs in the automotive industry. When a head
gasket needs replacing, it is common practice
to resurface the engine head to make sure it is
perfectly flat, in case any warping has occurred.
The head can be precisely ground using a surface
grinder.
Features
Now that you know the basics of what this
machine can do, take a minute to consider its
features.
The SB1023 is equipped with easy-to-reach
front-mounted handwheels for controlling table
movement.
The table travels in the longitudinal direction
on a ball-bearing supported table, driven by a
rack-and-pinion mechanism. The stand doubles
as a storage cabinet where you can keep the
necessary tools and extra grinding wheels right
where you need them.
The included diamond dresser is used to true the
grinding wheel, ensuring high-precision results.
Aside from these features, we designed this
machine to be extremely solid and durable.
With thick, hardened steel ways, cast-iron
construction, and Allen Bradley electrical
components, this South Bend surface grinder is
built to last.
-2-
Page 5

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1023
INTRODUCTION
Identification
Elevation
Handwheel
Grinding Wheel
& Guard
Cross Travel
Handwheel
Longitudinal Travel
Handwheel
Travel Stops
Cross Travel
Lock Knob
Operation
Controls
Electrical
Box
Storage
Cabinet
Figure 1. Identification.
Serious personal injury could occur if
you connect the machine to power before
completing the setup process. DO NOT
connect power until instructed to do so later
in this manual.
Untrained users have an increased risk
of seriously injuring themselves with this
machine. Do not operate this machine until
you have understood this entire manual and
received proper training.
-3-
Page 6
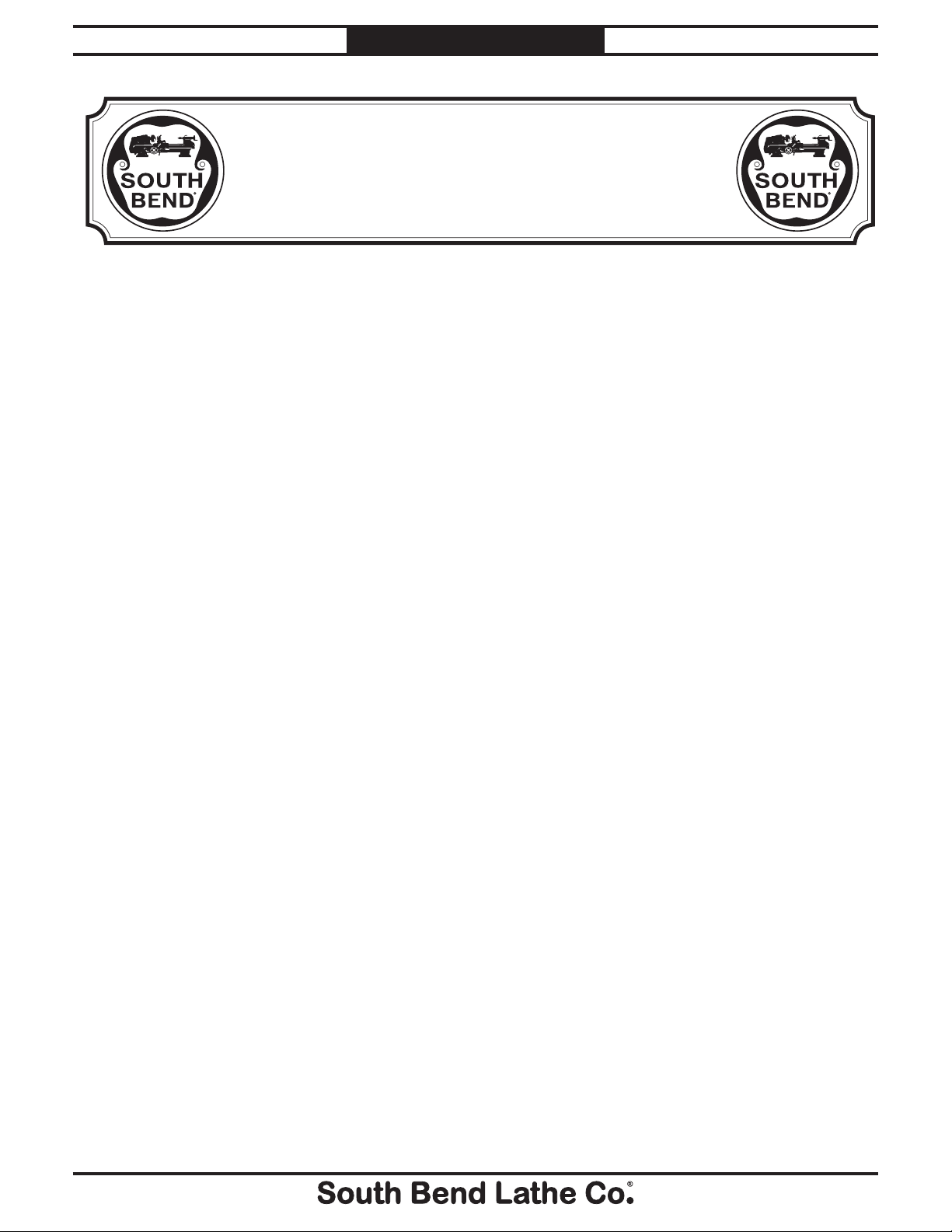
Model SB1023
Model SB1023
6" x 12" Surface Grinder
Product Dimensions:
Weight .......................................................................................................................................................................... 540 lbs.
Length/Width/Height ................................................................................................................................ 50
3
⁄4" x 361⁄2" x 66"
Footprint (Length/Width) ........................................................................................................................................... 24" x 24"
Shipping Dimensions:
Type .................................................................................................................................................................... Wooden Crate
Content ........................................................................................................................................................................ Machine
Weight ........................................................................................................................................................................... 690 lbs.
Length/Width/Height ....................................................................................................................................... 41" x 29" x 65"
Electrical:
Required Power Source .................................................................................................. 110V or 220V, Single Phase, 60 Hz
Switch ............................................................................................ Allen/Bradley Magnetic Contactor w/Thermal Overload
Switch Voltage .................................................................................................................................................................. 110V
Cord Length ......................................................................................................................................................................... 62"
Cord Gauge ................................................................................................................................................................14 Gauge
Recommended Circuit Size ..........................................................................................................................................15 Amp
Plug Included .......................................................................................................................................................................Yes
Plug Type ..................................................................................................................................................................110V 5-15
Motors:
Spindle Motor
Type ............................................................................................................................TEFC Capacitor Start Induction
Horsepower .............................................................................................................................................................
3
⁄4 HP
Voltage ............................................................................................................................................................110V/220V
Prewired ..................................................................................................................................................................110V
Phase .......................................................................................................................................................... Single-Phase
Amps ................................................................................................................................................................9.5/5 Amp
Speed ............................................................................................................................................................... 3450 RPM
Cycle .......................................................................................................................................................................60 Hz
Number Of Speeds .........................................................................................................................................................1
Power Transfer ..................................................................................................................................... Integral Spindle
Bearings ................................................................................................................... Shielded and Permanently Sealed
P.O. Box 2027, Bellingham, WA 98227 U.S.A.
PHONE: (360) 734-1540 •
© South Bend Lathe Co.
www.southbendlathe.com
Machine Specifications
INTRODUCTION
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
Machine Specifications
-4-
Page 7

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1023
Main Specifications:
Operation Information
Maximum Distance Wheel To Table........................................................................................................................ 8
1
⁄4"
Maximum Distance Table To Spindle Center .......................................................................................................... 12"
Long Stroke ................................................................................................................................................................ 14"
Maximum Grinding Width ....................................................................................................................................... 8
7
⁄8"
Spindle Taper ............................................................................................................................................... 5
1
⁄2 Degrees
Spindle Speed ................................................................................................................................................. 3450 RPM
Hub Diameter ............................................................................................................................................................ 1
1
⁄4"
Grinding Wheel Diameter ........................................................................................................................................... 7"
Grinding Wheel Width................................................................................................................................................
1
⁄2"
Grinding Wheel Bore ................................................................................................................................................ 1
1
⁄4"
Floor To Table Height ................................................................................................................................................ 40"
Column Width ........................................................................................................................................................... 5
1
⁄8"
Column Length ......................................................................................................................................................... 5
1
⁄8"
Vertical Handwheel Graduation ........................................................................................................................ 0.0005"
Vertical Handwheel Revolution ............................................................................................................................. 0.05"
Crossfeed Handwheel Graduation ....................................................................................................................... 0.001"
Crossfeed Handwheel Revolution ............................................................................................................................ 0.1"
Longitudinal Travel ................................................................................................................................................... 14"
Cross Travel .............................................................................................................................................................. 8
7
⁄8"
Table
Table Length ........................................................................................................................................................... 12
1
⁄8"
Table Width ............................................................................................................................................................. 5
15
⁄16"
Table Thickness ........................................................................................................................................................ 2.2"
T-Slot Width ................................................................................................................................................................
1
⁄2"
T-Slot Height ...............................................................................................................................................................
3
⁄4"
Stud Size ......................................................................................................................................................................
1
⁄2"
Construction
Base Construction Material ......................................................................................................... Meehanite Cast Iron
Body Construction Material ......................................................................................................... Meehanite Cast Iron
Table Construction Material ........................................................................................................ Meehanite Cast Iron
Paint .................................................................................................................................................................Urethane
Spindle Bearing Type ........................................................................................ Angular Contact, P5 Class (ABEC-5)
Other Specifications:
Country Of Origin ........................................................................................................................................................ Taiwan
Warranty .........................................................................................................................................................................1 Year
Serial Number Location ................................................................................................. Machine Data Label, Cabinet Door
Assembly Time............................................................................................................................................................... 1 Hour
Features:
Allen-Bradley Electrical Components
Storage Cabinet
Grinding Wheel Included
Swedish SKF Bearings
Steel Ball Bearing Slideways for Super Smooth and Precise Operation
Excellent South Bend Uncompromising Quality
Diamond Wheel Dressing Tool w/Base
Balancing Arbor and Hub
Hub Puller
Toolbox w/Tools Included
INTRODUCTION
-5-
Page 8

Model SB1023
Operating all machinery and machining equipment can be dangerous or relatively safe depending
on how it is installed and maintained, and the operator's experience, common sense, risk awareness,
working conditions, and use of personal protective equipment (safety glasses, respirators, etc.).
The owner of this machinery or equipment is ultimately responsible for its safe use. This
responsibility includes proper installation in a safe environment, personnel training and usage
authorization, regular inspection and maintenance, manual availability and comprehension,
application of safety devices, integrity of cutting tools or accessories, and the usage of approved
personal protective equipment by all operators and bystanders.
The manufacturer of this machinery or equipment will not be held liable for injury or property
damage from negligence, improper training, machine modifications, or misuse. Failure to read,
understand, and follow the manual and safety labels may result in serious personal injury, including
amputation, broken bones, electrocution, or death.
The signals used in this manual to identify hazard levels are defined as follows:
Death or catastrophic
harm WILL occur.
Moderate injury or fire
MAY occur.
Death or catastrophic
harm COULD occur.
Machine or property
damage may occur.
1. Owner’s Manual: All machinery and
machining equipment presents serious
injury hazards to untrained users. To
reduce the risk of injury, anyone who uses
THIS item MUST read and understand
this entire manual before starting.
2. Personal Protective Equipment:
Operating
or servicing this item may expose the user
to flying debris, dust, smoke, dangerous
chemicals, or loud noises. These hazards
can result in eye injury, blindness, longterm respiratory damage, poisoning,
cancer, reproductive harm or hearing loss.
Reduce your risks from these hazards
by wearing approved eye protection,
respirator, gloves, or hearing protection.
3. Trained/Supervised Operators Only:
Untrained users can seriously injure
themselves or bystanders. Only allow
trained and properly supervised personnel
to operate this item. Make sure safe
operation instructions are clearly
understood. If electrically powered, use
padlocks and master switches, and remove
start switch keys to prevent unauthorized
use or accidental starting.
4. Guards/Covers:
Accidental contact with
moving parts during operation may cause
severe entanglement, impact, cutting,
or crushing injuries. Reduce this risk by
keeping any included guards/covers/doors
installed, fully functional, and positioned
for maximum protection.
SAFETY
SAFETY
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
Understanding Risks of Machinery
Basic Machine Safety
-6-
Page 9

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1023
5. Entanglement: Loose clothing, gloves,
neckties, jewelry or long hair may
get caught in moving parts, causing
entanglement, amputation, crushing,
or strangulation. Reduce this risk by
removing/securing these items so they
cannot contact moving parts.
6. Mental Alertness: Operating this item
with reduced mental alertness increases
the risk of accidental injury. Do not let a
temporary influence or distraction lead to a
permanent disability! Never operate when
under the influence of drugs/alcohol, when
tired, or otherwise distracted.
7. Safe Environment:
Operating electrically
powered equipment in a wet environment
may result in electrocution; operating near
highly flammable materials may result in a
fire or explosion. Only operate this item in
a dry location that is free from flammable
materials.
8. Electrical Connection: With electically
powered equipment, improper connections
to the power source may result in
electrocution or fire. Always adhere to all
electrical requirements and applicable
codes when connecting to the power source.
Have all work inspected by a qualified
electrician to minimize risk.
9. Disconnect Power: Adjusting or servicing
electrically powered equipment while it
is connected to the power source greatly
increases the risk of injury from accidental
startup. Always disconnect power
BEFORE any service or adjustments,
including changing blades or other tooling.
10. Secure Workpiece/Tooling:
Loose
workpieces, cutting tools, or rotating
spindles can become dangerous projectiles
if not secured or if they hit another object
during operation. Reduce the risk of this
hazard by verifying that all fastening
devices are properly secured and items
attached to spindles have enough clearance
to safely rotate.
11. Chuck Keys or Adjusting Tools:
Tools used
to adjust spindles, chucks, or any moving/
rotating parts will become dangerous
projectiles if left in place when the machine
is started. Reduce this risk by developing
the habit of always removing these tools
immediately after using them.
12. Work Area:
Clutter and dark shadows
increase the risks of accidental injury.
Only operate this item in a clean, nonglaring, and well-lighted work area.
13. Properly Functioning Equipment:
Poorly
maintained, damaged, or malfunctioning
equipment has higher risks of causing
serious personal injury compared to
those that are properly maintained.
To reduce this risk, always maintain
this item to the highest standards and
promptly repair/service a damaged or
malfunctioning component. Always follow
the maintenance instructions included in
this documentation.
14. Unattended Operation:
Electrically
powered equipment that is left unattended
while running cannot be controlled and is
dangerous to bystanders. Always turn the
power OFF before walking away.
15. Health Hazards: Certain cutting fluids
and lubricants, or dust/smoke created
when cutting, may contain chemicals
known to the State of California to cause
cancer, respiratory problems, birth defects,
or other reproductive harm. Minimize
exposure to these chemicals by wearing
approved personal protective equipment
and operating in a well ventilated area.
16. Difficult Operations:
Attempting
difficult operations with which you are
unfamiliar increases the risk of injury.
If you experience difficulties performing
the intended operation, STOP! Seek an
alternative method to accomplish the
same task, ask a qualified expert how the
operation should be performed, or contact
our Technical Support for assistance.
SAFETY
-7-
Page 10

Model SB1023
SAFETY
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
Additional Surface Grinder Safety
1. Eye Protection: Grinding causes small
particles to become airborne at a high
rate of speed. ALWAYS wear eye
protection when using this machine.
2. Wheel Speed Rating: Wheels operated at
a faster speed than rated for may break
or fly apart. Before mounting a new
wheel, be sure the wheel
RPM rating is equal or higher than the
speed of the grinder.
3. Wheel Flanges: Only use the flanges
included with the grinder when
mounting wheels. Other flanges may
not properly secure the wheel and could
cause the wheel to fly off or break apart.
4. Ring Test: Perform a "ring test" on
grinding wheels before installation to
ensure that they are safe to use. A wheel
that does not pass the ring test may
break or fly apart during operation.
5. Starting Grinder: If a wheel IS damaged,
it will usually fly apart shortly after
start-up. To protect yourself, always
stand to the side of the grinder when
turning it ON and allow it to gain full
speed before standing in front of it.
7. Workpiece Contact: A heavy impact on a
grinding wheel can cause it to break or fly
apart, causing serious personal injuries.
Avoid jamming the workpiece into the
wheel to reduce this risk.
8. Hand/Wheel Contact: Grinding wheels
have the capability of removing a lot
of skin fast. Make sure the workpiece
is securely clamped to the table, then
position your hands a safe distance away
when grinding. Avoid wearing gloves as
they may get caught in the grinding wheel
and cause even more serious entanglement
injuries.
9. Cracked Wheel: Cracked wheels may break
and fly apart during operation. Replace
cracked wheels immediately!
10. Fire Hazard: DO NOT connect a surface
grinder to a dust collection system that is
used with woodworking machines. Sparks
emitted from the grinding process may
ignite wood particles, resulting in fire or
explosion. Only use a metal-specific dust
collection system with this machine.
6. Lung Protection: Grinding produces
hazardous dust, which may cause longterm respiratory problems if breathed.
Always wear a NIOSH approved dust
mask or respirator when grinding.
-8-
Page 11

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1023
The purpose of the preparation section is to help
you prepare your machine for operation.
The typical preparation process is as follows:
1. Unpack the machine and inventory the
contents of the box/crate.
2. Clean the machine and its components.
3. Identify an acceptable location for the
machine and move it to that location.
4. Level the machine and either bolt it to the
floor or place it on mounts.
5. Assemble the loose components and make
any necessary adjustments or inspections to
ensure the machine is ready for operation.
6. Connect the machine to the power source.
7. Test run the machine to make sure it
functions properly and is ready for operation.
PREPARATION
Preparation Overview
PREPARATION
Things You'll Need
During the setup process, operation, and
maintenance of your machine, you'll need the
following items:
For Lifting
• Aforkliftorotherpowerliftingdevice
rated for the weight of the machine.
• LiftingStrap or Chain (rated for at least
1500 lbs.)
For Power Connection
• Amachinepowerconnectionthatmeets
federal, state, and local electrical codes.
An electrician may be required.
For Assembly
• Assistant
• Cotton Rags
• Mineral Spirits
• SafetyGlasses
• Wrench 14mm
• Wrench 19mm
• Oil Can with any General Machine Oil
-9-
Page 12
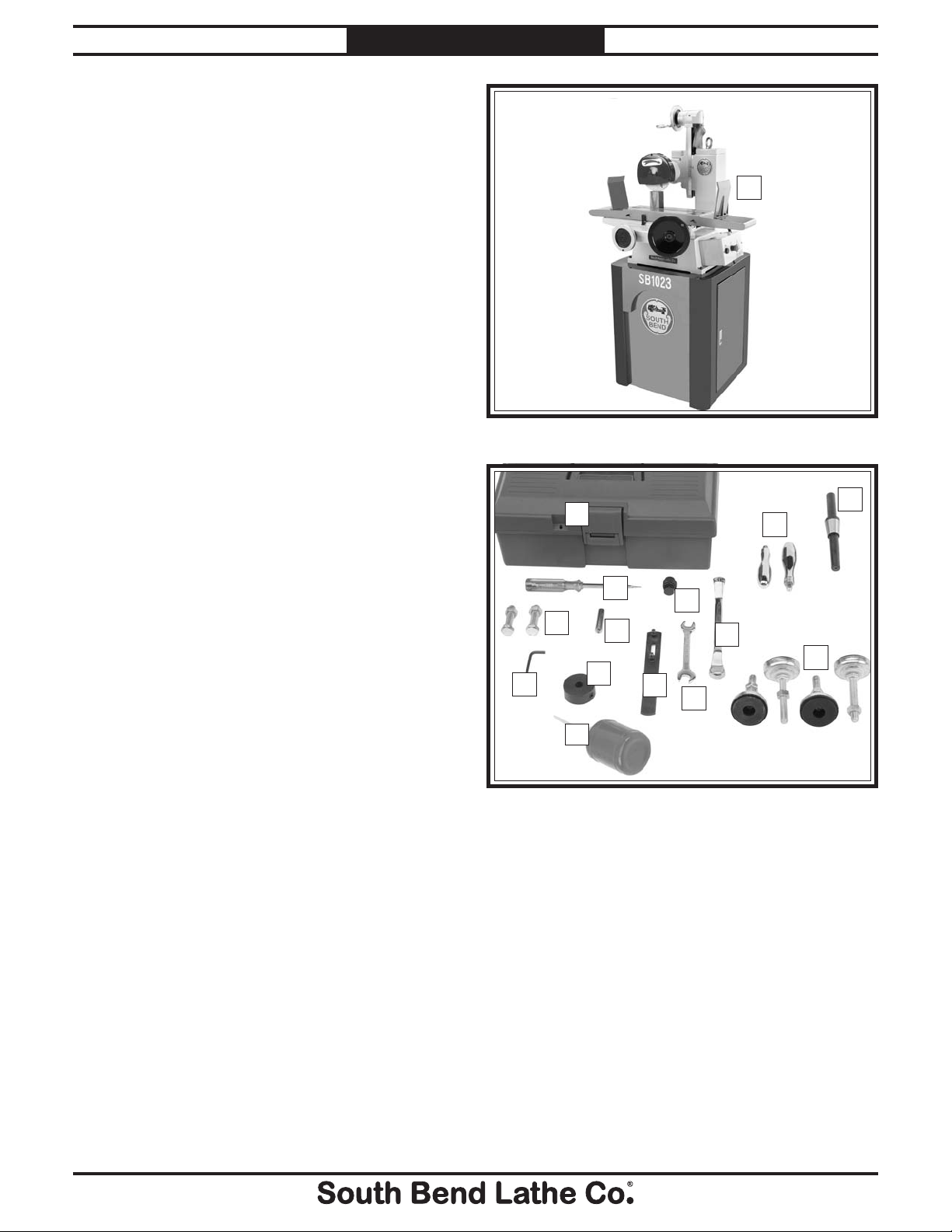
Model SB1023
This item was carefully packaged to prevent
damage during transport. If you discover any
damage, please immediately call Customer
Service at (360) 734-1540 for advice. You may
need to file a freight claim, so save the containers
and all packing materials for possible inspection
by the carrier or its agent.
PREPARATION
Unpacking
Inventory
Main Inventory: (Figure 2) Qty
A. Machine w/Wheel Installed ...........................1
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
A
Tool Box Inventory: (Figure 3) Qty
B. Tool Box ..........................................................1
C. Phillips Head Screwdriver #2 ........................1
D. Hub Puller ...................................................... 1
E. Handles ........................................................... 2
F. Balancing Arbor ............................................. 1
G. Machine Foot Assemblies .............................. 5
H. Box-End Wrench 14 x 17mm ......................... 1
I. Open-End Wrench 12 x 14mm ......................1
J. Adjustable Spanner Wrench ......................... 1
K. Diamond Dresser ........................................... 1
L. Diamond Dresser Base ..................................1
M. Chuck Mounting Hex Bolts
w/Nuts ............................................................2
N. Hex Wrench 4mm .......................................... 1
O. Bottle for Oil ................................................... 1
1
⁄2-12 x 2"
N
Figure 2. Main inventory.
B
M
C
K
L
D
H
J
I
O
Figure 3. Small parts inventory.
F
E
G
-10-
Page 13
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1023
The unpainted surfaces are coated at the factory
with a heavy-duty rust preventative that
prevents corrosion during shipment and storage.
The benefit of this rust preventative is that it
works very well. The downside is that it can be
time-consuming to thoroughly remove.
Be patient and do a careful job when cleaning
and removing the rust preventative. The time
you spend doing this will reward you with
smooth-sliding parts and a better appreciation
for the proper care of the unpainted surfaces.
Although there are many ways to successfully
remove the rust preventative, we have cleaned
thousands of machines and found the following
process to be the best balance between efficiency
and minimized exposure to toxic fumes or
chemicals.
Before cleaning, gather the following:
• Disposablerags
• Cleaner/degreaser (certain citrus-based
degreasers work extremely well and they
have non-toxic fumes)
• Safetyglasses&disposablegloves
Note: Automotive degreasers, mineral spirits, or
WD•40canbeusedtoremoverustpreventative.
Before using these products, though, test them
on an inconspicuous area of a painted area to
make sure they will not damage it.
Basic steps for removing rust preventative:
1. Put on safety glasses and disposable gloves.
2. Coatallsurfacesthathaverustpreventative
with a liberal amount of your cleaner or
degreaser and let them soak for a few
minutes.
3. Wipe off the surfaces. If your cleaner or
degreaser is effective, the rust preventative
will wipe off easily.
Note: To clean off thick coats of rust preventative
on flat surfaces, such as beds or tables, use
aPLASTICpaintscrapertoscrapeoffthe
majority of the coating before wiping it off
withyourrag.(Donotuseametalscraperor
it may scratch the surface.)
4. Repeat Steps 2–3 as necessary until clean,
then coat all unpainted surfaces with a
quality metal protectant or light oil to
prevent rust.
GAS
Gasoline and petroleum
products have low flash
points and can explode
or cause fire if used for
cleaning. Avoid using these
products to remove rust
preventative.
Many cleaning solvents are
toxic if inhaled. Minimize
your risk by only using
these products in a well
ventilated area.
Avoid chlorine-based solvents, such as
acetone or brake parts cleaner that may
damage painted surfaces. Always follow the
manufacturer’s instructions when using any
type of cleaning product.
PREPARATION
Cleaning & Protecting
-11-
Page 14
Model SB1023
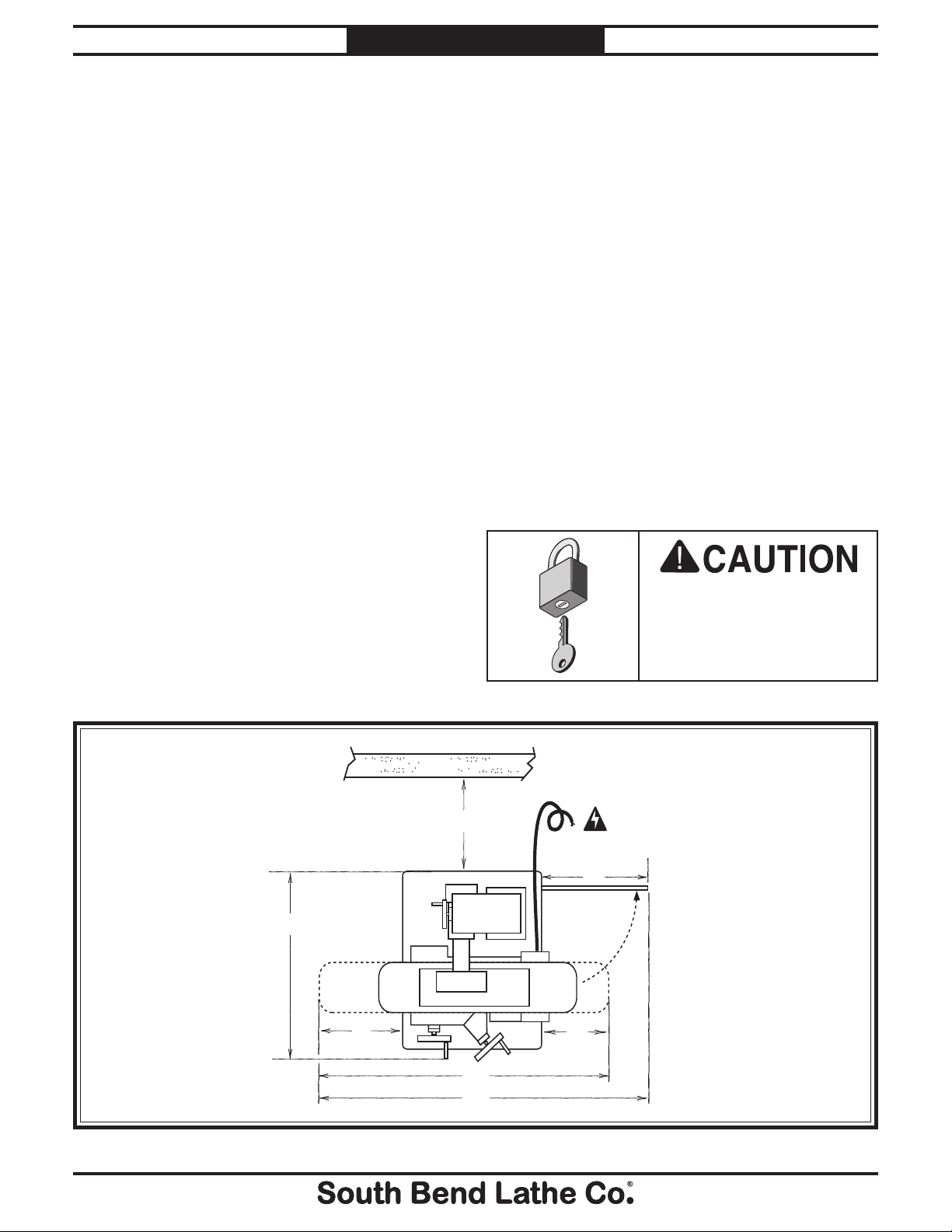
30"
Power
Connection
17"
10"
68"
14"
Wall
24"
72"
Weight Load
Refer to the Machine Specifications for the
weight of your machine. Make sure that the
surface upon which the machine is placed will
bear the weight of the machine, additional
equipment that may be installed on the machine,
and the heaviest workpiece that will be used.
Additionally, consider the weight of the operator
and any dynamic loading that may occur when
operating the machine.
Space Allocation
Consider the largest size of workpiece that will
be processed through this machine and provide
enough space around the machine for adequate
operator material handling or the installation
of auxiliary equipment. With permanent
installations, leave enough space around
the machine to open or remove doors/covers
as required by the maintenance and service
described in this manual.
Physical Environment
The physical environment where your machine
is operated is important for safe operation and
longevity of parts. For best results, operate this
machine in a dry environment that is free from
excessive moisture, hazardous or flammable
chemicals, airborne abrasives, or extreme
conditions. Extreme conditions for this type
of machinery are generally those where the
ambient temperature is outside the range of 41°–
104°F; the relative humidity is outside the range
of 20–95% (non-condensing); or the environment
is subject to vibration, shocks, or bumps.
Electrical Installation
Place this machine near an existing power
source. Make sure all power cords are protected
from traffic, material handling, moisture,
chemicals, or other hazards. Make sure to leave
access to a means of disconnecting the power
source or engaging a lockout/tagout device.
Lighting
Lighting around the machine must be adequate
enough that operations can be performed
safely. Shadows, glare, or strobe effects that
may distract or impede the operator must be
eliminated.
Children or untrained
people may be seriously
injured by this machine.
Only install in an access
restricted location.
Location
PREPARATION
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
-12-
Figure 4. Space required for full range of movement.
Page 15
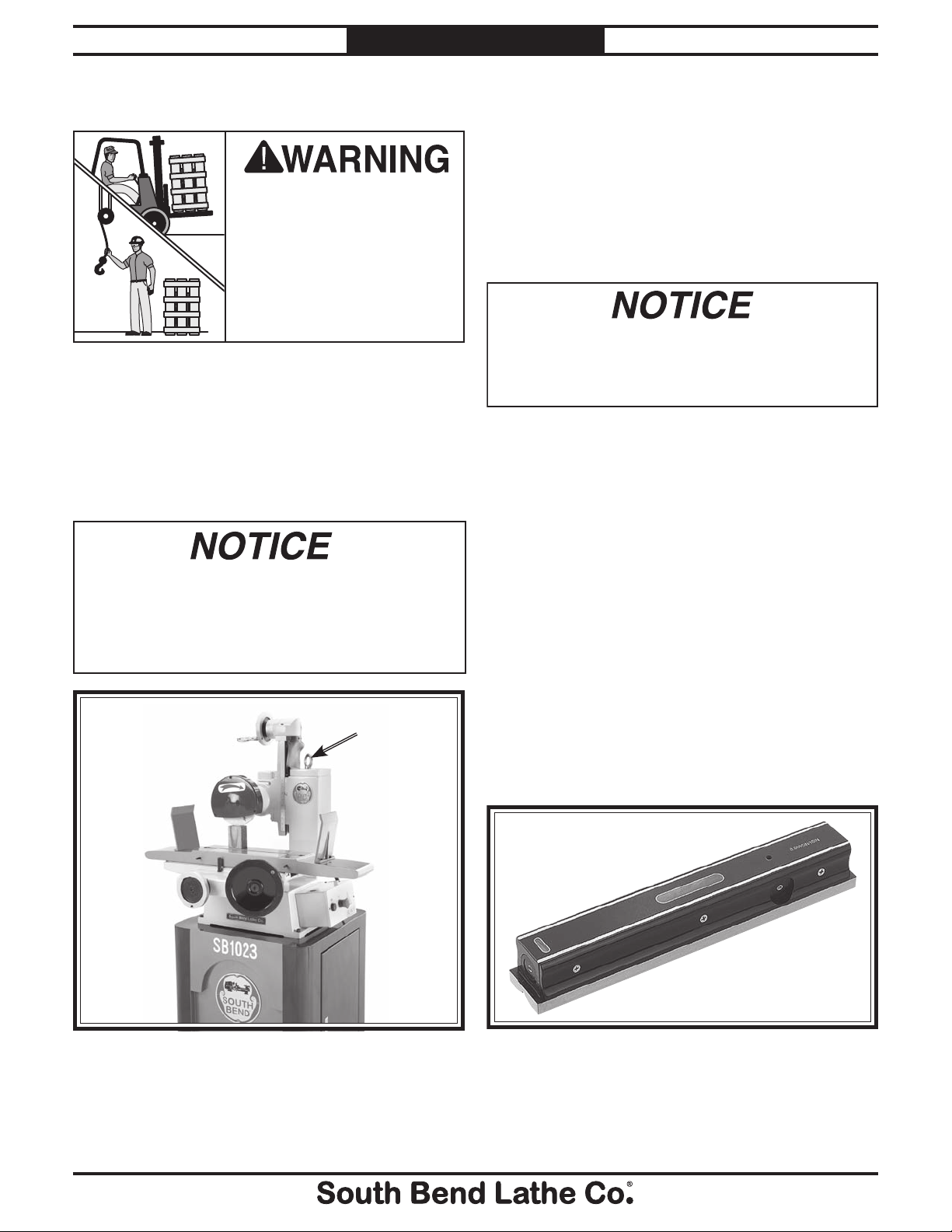
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1023
Leveling machinery helps precision components,
such as bed ways, remain straight and flat
during the lifespan of the machine. Components
on an unleveled machine may slowly twist due to
the dynamic loads placed on the machine during
operation.
For best results, use a precision level that
is at least 12" long and sensitive enough to
show a distinct movement when a 0.003" shim
(approximately the thickness of one sheet of
standard newspaper) is placed under one end of
the level.
See the figure below for an example of a high
precision level.
We strongly recommend securing your
machine to the floor if it is hardwired to the
power source. Consult with your electrician to
ensure compliance with local codes.
Generally, you can either bolt your machine
to the floor or mount it on machine mounts.
Although not required, we recommend that you
secure the machine to the floor and level it while
doing so. Because this is an optional step and
floor materials may vary, hardware for securing
the machine to the floor is not included.
PREPARATION
Lifting & Moving
This machine and its
parts are heavy! Serious
personal injury may occur
if safe moving methods are
not used. To reduce the
risk of a lifting or dropping
injury, ask others for help
and use power equipment.
Unbolt the machine from the pallet and make
sure that the table is locked in place. Connect a
chain or lifting strap to the lifting hook on the
machine (Figure 5), use a hoist or forklift to lift
the machine off the pallet, and move it to the
suitable location. All hoisting equipment and
straps must be rated to lift at lease 1500 lbs.
Leveling & Mounting
Leveling
Never attempt to move this machine without
first locking the table in place. If the machine
is slightly tilted, the table could uncontrollably
slide, fall off of the machine and cause
machine damage or severe injury.
Figure 5. Lifting location.
Figure 6. Example of a precision level.
-13 -
Page 16

Model SB1023
Foot Stud
Jam Nut
Threaded
Hole
Machine
Foot
PREPARATION
Assembly
After the machine is placed in the final location,
and before the lifting apparatus is removed,
you should install the machine feet. Included
with your machine are four cushioned feet with
built-in adjustment studs (see Figure 7). These
feet are easily installed and provide for accurate
machine leveling.
To install the feet:
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
8. Use a 19mm wrench to tighten the jam nuts
inside of the cabinet and lock the feet studs
into place.
Note: Over the course of the next six months,
periodically verify that the machine is still
level, and re-adjust the feet as required.
9. Rotate the top handwheel counterclockwise
to raise the headstock slightly. Then remove
the wood support block (see Figure 8).
1. Using lifting equipment and wooden blocks,
raise and support the machine base so there
is approximately 5" between the floor and
underside of the base.
2. Remove the jam nuts from the foot studs.
3. Apply any general-purpose automotive
grease to the stud threads.
4. Thread the studs into the machine base
from the bottom up until the studs emerge
from the cabinet floor approximately 2" (see
Figure 7).
Top
Handwheel
Wood Support
Block
Figure 8. Support block.
10. Using a 14mm wrench, install the two
handles into the handwheels (Figure 9).
Figure 7. Machine feet.
5. Thread the jam nuts onto the protruding
studs but do not tighten them at this time.
6. Place the machine onto the floor.
7. Using a precision level on the machine table,
adjust the feet studs, so the machine is level
from side-to-side and front-to-back.
-14-
Figure 9. Headstock height handwheel.
Page 17

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1023
PREPARATION
Power Connection
Electrocution or fire
may occur if machine is
ungrounded, incorrectly
connected to power, or
connected to an undersized
circuit. Use a qualified
electrician to ensure a safe
power connection.
Once your machine is set up and assembled as
previously described in this manual, it is ready to
be connected to the power source.
Note About Extension Cords: Using an
incorrectly sized extension cord may decrease the
life of electrical components on your machine.
SB1023 110V (Prewired)
Required Power Source ........ 110V, 1-Phase, 60Hz
Full Load Amp Draw .............................. 9.5 Amps
Phase ..........................................................1-Phase
Frequency ...................................................... 60 Hz
Minimum Circuit Size ............................. 15 Amps
Included Plug ...................................... NEMA 5-15
Minimum Extension Cord Size ................14 AWG
Maximum Extension Cord Length ................ 50 ft.
220V Conversion for SB1023
Wiring diagrams are provided in the back of
this manual (Page 36) showing the Model
SB1023 wired for both 110V and 220V.
Refer to these diagrams when following this
procedure. Additionally, you must purchase the
220V conversion kit in order to complete the
conversion. Call our parts department at
(417) 886-2954 and order part number
PSB1023180.
To convert the Model SB1023 to operate on
220V power:
1. DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
2. Rewire the motor for 220V, as shown in the
diagram on the inside of the motor junction
box. If there is not a diagram in the junction
box, use the diagram in this manual (Page
36).
3. Replace the contactor on the machine with
the contactor from the 220V conversion kit.
Set the amp dial to 5.5A
4. Replace the power cord plug with a NEMA
6-15 plug.
SB1023 (220V Option)
Required Power Source ........ 220V, 1-Phase, 60Hz
Full Load Amp Draw ................................. 5 Amps
Phase ..........................................................1-Phase
Frequency ...................................................... 60 Hz
Minimum Circuit Size ............................. 15 Amps
Recommended Plug/Receptacle .......... NEMA 6-15
Minimum Extension Cord Size ................16 AWG
Maximum Extension Cord Length ................ 50 ft.
-15 -
Page 18

Model SB1023
PREPARATION
Initial Lubrication
Your machine was lubricated at the factory,
but we strongly recommend that you inspect all
lubrication points yourself and provide additional
lubrication if necessary. Refer to Lubrication on
Page 30 for specific locations.
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
• Investigate and correct strange or
unusual noises or vibrations before
operating the machine further. Always
stop the machine and disconnect it from
power before investigating or correcting
potential problems.
7. Press the STOP button.
Test Run
After all preparation steps have been completed,
the machine and its safety features must be
tested to ensure correct operation. If you discover
a problem with the operation of the machine or
its safety components, do not operate it further
until you have resolved the problem.
Refer to Troubleshooting on Page 34 for
solutions to common problems that may occur
with surface grinders. If you need additional
help, contact our Technical Support at
(360) 734-1540.
To test run your machine:
1. Read and follow the safety instructions
at the beginning of the manual, take the
required safety precautions, and make sure
the machine is set up and adjusted properly.
2. Ring test the grinding wheel, and install the
wheel onto the spindle.
Refer to Ring Test on Page 25, and
Installing & Removing Grinding Wheels
on Page 20 for procedures.
3. Clear away all tools and objects used during
assembly and preparation.
8. WITHOUT resetting the switch, press the
START button. The machine should not
start.
• If the machine does not start, the
STOP button safety feature is working
correctly.
• If the machine does start (with the
stop button pushed in), immediately
disconnect power to the machine. The
STOP button safety feature is not
working correctly. This safety feature
must work properly before proceeding
with regular operations. Call Tech
Support for help.
Inspections &
Adjustments
The following list of adjustments were performed
at the factory before your machine was shipped:
• Ring Test on Page 25
• Wheel Dressing on Page 25
• Wheel Balancing on Page 26
4. Connect the machine to the power source.
5. Push the STOP button in, then twist it
clockwise so it pops out. When the STOP
button pops out, the switch is reset and
ready for operation.
6. Verify that the machine is operating
correctly by pushing the START button.
• When operating correctly, the machine
runs smoothly with little or no vibration
or rubbing noises.
-16 -
• Lubricationon Page 30
• Handwheel Backlash Adjustment on
Page 32
• Column & Table Gib Adjustment on
Page 32
Page 19

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1023
OPERATION
OPERATION
Operation Overview
The purpose of the operation section is to
familiarize you with the basic controls,
terminology, capabilities, and adjustments that
are necessary to use this machine.
To better understand the remaining parts of
this section, please take a moment to read this
overview.
To reduce the risk of
serious injury when using
this machine, read and
understand this entire
manual before beginning
any operations.
Loose hair, clothing, or
jewelry could get caught
in machinery and cause
serious personal injury.
Keep these items away
from moving parts at all
times to reduce this risk.
To complete a typical operation, the operator
does the following:
1. Examines the grinding wheel to make sure it
is suitable for use t
2. Examines the workpiece to make sure it is
properly prepared for grinding.
3. Uses the elevation handwheel to raise
the grinding wheel assembly to provide
clearance for mounting the workpiece.
4. Wipes the table surface clean to remove any
debris that may interfere with the clamping
process.
5. Uses a magnetic chuck to hold the workpiece
to the table, then turns the elevation
handwheel to lower the grinding wheel to
just above the top surface of the workpiece.
6. Turns the grinder ON, then stands aside
while the wheel reaches full speed.
7. Performs the grinding operation.
Note: Because the method for performing
each grinding operation varies, specific
actions are not listed here.
During operation, small
metal chips may become
airborne, leading to serious
eye injury. Wear safety
glasses to reduce this risk.
8. When the grinding operation is complete,
turns the grinder OFF and allows the
grinding wheel to come to a complete stop.
9. Removes the workpiece from the table.
-17-
Page 20

Model SB1023
OPERATION
Controls
Refer to Figures 10–11 and the following
descriptions to become familiar with the basic
controls of this machine.
Longitudinal Travel Handwheel: Moves the
A.
table back and forth along the longitudinal
axis (X-axis).
Center Table Stop: Provides a barrier for
B.
the table stops to limit table movement.
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
G.
Spindle On Button: Supplies power to the
grinding wheel motor.
Emergency Stop (Off) Button: Cuts power
H.
to the grinding wheel motor.
G
Table Stop: Adjusts along the length of the
C.
table to limit longitudinal travel.
Cross Axis Lock Knob: Locks the cross
D.
table movement (Y-Axis).
Elevation Handwheel: Controls vertical
E.
movement of the grinding wheel assembly.
Cross Travel Handwheel: Moves the table
F.
forward and backward along the cross axis
(Y-axis).
E
H
Figure 11. Control panel.
-18 -
C
B
D
F
Figure 10. Basic controls.
A
Page 21

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1023
OPERATION
Wheel Selection
Most grinding wheels from major manufacturers
are marked in a somewhat uniform manner.
Understanding these markings will help you
understand the capabilities of various wheels.
Always refer to the manufacturer’s grinding
recommendations when selecting a wheel for
your project.
The grinding wheel you choose will depend on
several factors related to the operation you plan
to perform. The hardness of the material you
will be grinding and the surface finish you desire
are the two primary factors to consider when
selecting a grinding wheel.
An example of the basic format for wheel
numbering is shown below. The wheel in this
example is a "36A60LV".
Prefix Abrasive
Type
36 A 60 L V
The prefix is a manufacturer-specific designation
and will vary depending on the manufacturer.
Use the charts below as a basic wheel selection
outline for most grinding operations.
Abrasive Type
Grit
Size
Grade Bond
Type
Grit Size
The ideal grit for an operation depends on a
number of considerations. Use the table below to
choose a grit suitable for your desired results.
Results
Operation
Consideration
Material
Removal
Surface Finish Rough Smooth
Workpiece
Hardness
Width of Cut Wide Narrow
Coarse Grit
(10–46)
Increased Decreased
Soft Hard
Fine Grit
(54–180)
Grade
The grade of a wheel is an indicator of its
hardness based on an alphabetical scale in which
A is the softest and Z is the hardest.
Wheel Hardness
Operation
Consideration
Workpiece
Hardness
Width of Cut Wide Narrow
Feed Rate Slow Fast
Wheel Speed Fast Slow
Soft
A–M
Hard Soft
Hard
N–Z
Abrasive
Application
Type
A Aluminum Oxide: For grinding
common steel.
WA White Aluminum Oxide: For
grinding harder metals (heat
treated steel, carbon steel, alloy
steel, etc.).
H For grinding high speed steel.
C Silicon Carbide: For grinding cast
iron and non-ferrous metals.
CG Ceramic Grain: For extremely hard
metals, such as tungsten carbide.
-19 -
Page 22

Model SB1023
OPERATION
Removing & Installing
Grinding Wheels
If you must conduct a ring test, the grinding
wheel must be removed and reinstalled onto the
hub. However, when doing this, remember that
overtightening or rotating the spanner nut in the
incorrect direction can damage threads, crack
the grinding wheel, and make grinding wheel
removal more difficult than necessary.
To remove and install a grinding wheel:
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
4. Position the spanner wrench on the spanner
nut (Figure 14).
Spacer
Washer
Spanner
Nut
1. DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
2. Place a sheet of plywood on top of the table
to protect the table (Figure 12), and open
the grinding wheel cover.
Plywood
Figure 12. Protecting table.
3. Position a 12mm wrench on the spindle shaft
that protrudes from the motor fan cover
(Figure 13).
Figure 14. Wheel spanner nut.
5. Using the wrenches, loosen the spanner nut
in the direction shown in Figure 15.
Hold
Figure 15. Removing spanner nut.
6. Unthread the spanner nut (Figure 16).
-20-
Figure 13. Spindle shaft.
Figure 16. Exposing wheel spacer washer.
Page 23

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1023
OPERATION
7. Remove the grinding wheel, as shown in
Figure 17.
Paper
Washer
Figure 19. Important paper washer.
Figure 17. Removing wheel.
8. Wipe the grinding wheel seat shown in
Figure 18 so no paper is stuck to the seat.
The seat must be clean and free of debris.
Note: Wiping the threads, grinding wheel seat,
and hub with a lightly-oiled rag is acceptable
to prevent rust.
Grinding Wheel
Seat
Note: If you need to replace or install new paper
washers, replacements can be cut out of
any thick construction paper or card stock.
Regular notebook paper or paper from a copy
machine is not acceptable, as it is too thin to
provide the required cushion. Don't forget to
record the wheel type and RPM rating on the
new paper washer.
10. Ring test the grinding wheel, even if it is
new, then if the wheel is free of cracks, slide
the wheel onto the hub. Refer to Ring Test
on Page 25 for details.
11. Complete the preceding steps in the reverse
order to install the grinding wheel.
• After the grinding wheel is installed, you
will have to use the dressing tool to trueup the wheel. Refer to Wheel Dressing
on Page 25 for details.
Figure 18. Wheel mounting hub.
9. Inspect the paper washers for missing pieces
on both sides of the grinding wheel (Figure
19). The paper washers are cushions
between the spacer washer and the grinding
wheel seat. Without the washers, cracks can
spawn from the center of the wheel when the
spanner nut is tightened. Over time, these
cracks can radiate outward and the wheel
may explode possibly causing injury.
• When the wheel runs true, the hub and
grinding wheel must then be removed
and balanced as an assembly since
grinding wheels can have different
densities at various points of the
wheel. The wheel will only deliver
superior results if it is properly truedup and balanced. Refer to Removing
& Installing Wheel & Hub on Page
22 to remove the assembly; and refer
to Wheel Balancing on Page 26 for
specific procedures on balancing.
-21-
Page 24

Model SB1023
OPERATION
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
Removing & Installing
Wheel & Hub
When the wheel has been ring tested, and
dressed, the wheel and hub must be removed and
balanced as an assembly. However, remember
that overtightening or rotating the spindle bolt in
the incorrect direction can damage threads, crack
the grinding wheel, and make grinding wheel
removal more difficult than it needs to be.
When removing and installing the hub onto the
spindle or balancing arbor, keep in mind that the
mating surfaces between these components have
the single most important effect on your final
balancing results. Hubs, spindles, and balancing
arbors can be easily damaged during installation
and removal. Just one grain of sand, small burr,
or hidden ding in either mating surface will
undermine all balancing results. Make sure
that all mating surfaces are carefully stoned to
establish a perfect fit.
NEVER pound on a hub or arbor for any reason.
This will permanently displace metal and change
high tolerance dimensions.
To remove and reinstall the wheel and hub:
1. DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
2. Place a sheet of plywood or similar on top of
table to protect the table (Figure 20), and
open the grinding wheel cover.
Figure 20. Protecting the table.
3. Position the spindle wrench on the spindle
bolt (Figure 21).
NEVER use a hydraulic press to install the
balancing arbor or attempt to use a heat
differential between parts to establish a shrinkfit. This will change high tolerance dimensions.
NEVER twist-fit the hub onto the spindle or
the balancing arbor. Doing this can gall the
tapered surfaces. Instead use a small arbor press
with light pressure to install and remove the
balancing arbor from the hub.
ALWAYS make sure that all mating surfaces
are immaculately cleaned before hub or arbor
installation. Use a lint-free photography lens
cloth that is slightly oiled with a thin machine
oil. For the best fit, the mating surfaces must
be polished without having a wet layer of oil on
them. The oil should only be in the pores of the
metal.
Spindle
Bolt
Figure 21. Retaining fasteners.
-22-
Page 25

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1023
OPERATION
4. Position a 12mm open end wrench on the
spindle shaft that protrudes from the motor
fan cover (Figure 22).
Figure 22. Spindle shaft.
5. Using the wrenches, turn the spindle bolt
clockwise as shown in Figure 23.
Hold
7. Oil the threads and thread the hub puller
(Figure 25) into the hub until it stops.
Hub
Hub
Puller
Figure 25. Hub puller.
8. While holding the wheel and hub from
sliding off of the spindle, tighten the hub
puller bolt until the wheel and hub assembly
are pulled off the spindle as shown in
Figure 26.
Figure 23. Hub removal.
6. Remove the spindle bolt (Figure 24).
Hub
Hold
Figure 26. Pulling wheel hub.
Spindle bolt
Figure 24. Spindle bolt removal.
-23-
Page 26

Model SB1023
9. Set the wrenches aside and carefully remove
the wheel and hub assembly with the hub
puller still installed (Figure 27).
Figure 27. Wheel and hub removal.
10. Unthread the hub puller and set it aside.
11. Wipe the spindle and hub taper (Figure 28),
so the tapers are perfectly clean. Wiping the
threads and tapers with a lightly-oiled rag is
acceptable to prevent rust and still to allow
for a tight fit.
Hub
Taper
OPERATION
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
Wheel Inspection
Do not assume that a wheel is in sound condition
just because it is new—damage can often occur
during shipping, with age, with prolonged
exposure to moisture, or because of improper
storage.
To inspect a wheel for damage:
1. Remove the wheel and look for any cracks,
chips, nicks or dents in the surface of the
wheel. If you see any of these, DO NOT
attempt to use the wheel.
2. Do a ring test. This test will give you an
indication of any internal damage that may
not be obvious during a visual inspection.
3. Inspect the paper washers on both sides
of the grinding wheel (Figure 29). These
washers are cushions between the spacer
washer and the grinding wheel seat. Without
the washers, cracks can be spawned from
the center of the wheel when the spanner
nut is tightened. Over time, these cracks can
radiate outward and the wheel may explode
during operation, possibly causing injury.
Spindle Taper
Figure 28. Spindle taper.
12. To install the grinding wheel and hub,
complete the preceding steps in the reverse
order, but skipping the steps regarding hub
puller usage. After the grinding wheel and
hub are installed, many machinists still
choose to dress the grinding wheel. Refer to
Wheel Dressing on Page 25 for details.
Paper
Washer
Figure 29. Important paper washer.
Note: If you need to replace or install new paper
washers, replacements can be cut out of
any thick construction paper or card stock.
Regular notebook paper or paper from a copy
machine is not acceptable, as it is too thin
to provide the required cushion. Be sure to
transfer any RPM limitations and wheel type
information.
-24-
Page 27

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1023
YES
NO
Rotation
Grinding
Wheel
Dressing
Tool
Magnetic Chuck
OPERATION
Ring Test Wheel Dressing
This test will give you an indication of any
internal damage that may not be obvious during
a visual inspection.
To perform a ring test:
1. Make sure the wheel that you test is clean
and dry; otherwise, you may get false
results.
2. Hang the wheel in the air with a piece of
cord or string looped through the hole in the
center, as shown in Figure 30.
Superior grinding results can only be achieved
with a properly balanced and dressed wheel. Do
not assume that a wheel will run true on the
spindle if it is new or has not been separated
from the hub.
Dressing the wheel correctly will save you from
wasting grinding abrasive and shattering the
dressing tool diamond. Additionally, with a
properly balanced and dressed wheel you can
rest assured that if you have finish problems, the
grinding wheel is not the culprit.
Depending on the finish required, varying
degrees of roughness can be obtained. For
example: A fast dressing at a depth of 0.03mm
will prepare a wheel surface for rough cuts, and
slow dressing with multiple light passes of the
diamond at a depth of 0.01mm will prepare the
same wheel for finish cuts.
Positioning is critical for the dressing tool so
you will not shatter the diamond or have poor
dressing results. The dressing tool must be
positioned in the trailing zone of the wheel, as
shown in Figure 31, for best results and safe
use. If the tool is positioned on the leading side
of the wheel, the diamond will be shattered or
even grabbed by the wheel and drawn under the
grinding wheel, causing severe damage or injury.
Paper Washer
Figure 30. Ring test setup and test locations.
3. At the locations shown in Figure 30, gently
tap the wheel with a light non-metallic
device such as the handle of a screwdriver or
a wooden mallet.
An undamaged wheel will emit a clear
metallic ring or “ping” sound in each of these
spots. A damaged wheel will respond with
a dull thud that has no clear tone. If you
determine from the ring test that the wheel
is damaged, DO NOT use it!
Figure 31. Safe tool positioning for wheel dressing.
-25-
Page 28

Model SB1023
OPERATION
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
To dress the grinding wheel:
1. Insert the diamond tipped dressing tool into
its base (Figure 32), and use a 4mm hex
wrench to tighten the locking set screw.
Figure 32. Dressing tool setup.
2. Lower the headstock so the wheel is
approximately 5mm lower than the tip of the
dressing tool.
Wheel Balancing
Static wheel balancing can be difficult and very
time consuming without practice. For accurate
grinding results, wheel balancing is mandatory.
For this balancing procedure, you will need a
wheel balancing fixture. The wheel balancing
fixture shown in Figure 33 is one example of the
many varieties available on the market.
Before proceeding, the grinding wheel must be
ring tested (refer to Page ) and dressed (refer to
Page ).
3. Position the tip of the dressing tool at the
trailing side of the wheel, as shown in
Figure 31, and move the table inward until
the diamond tip of the dressing tool slightly
touches the edge of the grinding wheel.
Verify by manually rotating the wheel and
listening for contact.
4. Turn on the magnetic chuck, and move the
cross slide so the tip is free of the grinding
wheel.
5. Start the grinder, and use the cross slide
handwheel to progressively move the table,
so the diamond sweeps across the wheel at a
depth between 0.01 – 0.03mm.
Figure 33. Wheel on balancing fixture.
If flood coolant was used with the grinding
wheel, run the machine with the grinding wheel
installed for 5-minutes to sling off any residual
coolant that may have settled to the low side of
the wheel. If the paper washers are missing, wet,
or damaged, replace them before proceeding. If
during a period of machine operation, you find
that a finish is becoming poor, redress the wheel.
If that does not correct the problem rebalance
your grinding wheel.
To balance the grinding wheel:
1. DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
2. Set up the wheel balancer as outlined in its
product user manual.
3. Remove the grinding wheel and hub as
a unit from the spindle as outlined in
Removing & Installing Grinding Wheel
Hub on Page 22.
-26-
Page 29

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1023
MAINTENANCE
4. Without letting any of the dogs or the lock
balls they contain fall out of the hub, use
a 2.5mm hex wrench to loosen the dogs
and position them at the 0°, 120°, and 240°
degree locations as indicated by the degree
scale on the hub (Figure 34).
Lock Ball Inside
Degree Scale
Paper Washer
Figure 34. Grinding wheel hub.
Balance Dog
Dog Slot
Hub
Note: Pay special attention to keep the dogs
engaged in the hub slot when they are loose.
If you lose any of the 4mm lock balls, it will
be impossible to continue this procedure
until they are replaced.
5. Using a slightly-oiled lint free cloth, wipe the
mating surfaces of the balancing arbor and
the internal hub taper perfectly clean, and
push the hub and arbor together, as shown
in Figure 35.
7. Spin the wheel so it rotates one full turn and
comes to rest with the heaviest side hanging
down at six o'clock. This may take a few
times to find the exact location.
8. Using a pencil, draw a line at the six o'clock
position to mark the heaviest side of the
wheel.
9. Line up the closest dog with the line you
just drew and lock it in place. This dog will
now be positioned at the heaviest side of the
wheel and will be called dog "A".
10. Using the scale, position the other two "B"
dogs so they are both evenly spaced 120°
degrees apart from dog "A". At this point all
dogs will be 120° apart from one another.
The "B" dogs are the two dogs you will move
to balance the wheel.
11. Rotate the wheel 90° degrees, let go, and
observe the direction that it rotates out of
balance. Move each "B" dog in one degree
increments, toward each other and away
from dog "A" to balance the wheel. For
example, depending on the amount of
balance correction, the distance between
the two "B" dogs will decrease, and the
distance between the "B" dogs and "A" dog
will increase. This step must be repeated
as many times as required until the wheel
will not rock back and forth by itself in any
position.
Figure 35. Installing the balancing arbor.
6. Place the balancing arbor onto the wheel
balancing fixture (Figure 33).
12. When you are satisfied with the wheel
balance, install the grinding wheel on the
machine, and run it for five minutes to verify
the wheel is in balance.
13. If any balance problems are detected, repeat
the balancing procedure.
Note: Some machinists will re-dress the grinding
wheel one last time at this point to ensure
ultra-high grinding precision.
-27-
Page 30

Model SB1023
OPERATION
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
Magnetic Chuck
The Model SB1023 is designed to be used with
a magnetic chuck. The table is equipped with a
T-slot for securing your magnetic chuck. Refer to
your magnetic chuck manufacturer's instruction
manual for proper chuck preparation and
mounting techniques.
A magnetic chuck secures workpieces to the table
without the use of clamps. With proper attention
to preparation of both the workpiece and the
magnetic chuck, a magnetic chuck will provide
ample clamping force on most magnetic metals.
Refer to your magnetic chuck manufacturer's
instruction manual for proper workpiece
mounting techniques.
Setup for a Typical
Grinding Operation
Grinder Operation
Grinding with a surface grinder is a delicate
process that takes practice, skill, and knowledge.
In addition to this, the method used for any one
procedure will depend on a number of factors,
including, but not limited to the material being
ground, the grinding wheel being used, the
quality and calibration of measuring tools, and
the finish that is desired.
For these reasons, specific techniques are not
outlined in this manual. We recommend that you
consult books, trade magazines, metalworking
experts, and other reliable resources for
techniques pertaining to the specific tasks you
wish to perform.
The information that follows serves as a general
outline to help familiarize you with the basic
grinding technique.
Once you have chosen the proper wheel for the
operation and properly installed the magnetic
chuck on the table, use the following procedures
to prepare for a grinding operation.
To prepare for a grinding operation:
1. DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
2. To ensure flat mating surfaces on the
workpiece and the magnetic chuck, surface
grind and stone the top of the chuck and the
bottom of the workpiece.
3. Make sure the magnetic chuck is turned
OFF, then place the workpiece onto the
chuck. Once the workpiece is positioned as
needed, turn the magnetic chuck ON.
4. Make sure the grinding wheel is not
contacting the workpiece, connect the
grinder to power, then turn the motor ON.
-28-
Page 31

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1023
Workpiece
Surfaced Portion
Grinding Wheel
Surfaced Portion
Surfaced Portion
New Portion
Exposed
*Movement exaggerated for clarity
*Movement exaggerated for clarity
Continue/repeat as necessary until desired
results are achieved.
Surfaced Portion
New Portion
Exposed
Surfaced Portion
OPERATION
Using the Surface Grinder
Operation of the grinder is controlled through
the movement of the three handwheels. The
elevation handwheel controls the up and down
movement of the grinding head. It is this axis
that governs the amount of stock removal.
Never attempt to remove too much material in
one pass. The best results are be achieved with
multiple light passes.
The longitudinal travel handwheel rapidly moves
the table from left to right. This allows the
operator to move the workpiece back and forth
underneath the grinding wheel.
The cross travel handwheel controls the frontto-back movement of the table and is only to be
used between longitudinal passes to expose a
new area of the workpiece to the grinding wheel
When grinding, sweep the table back and forth
under the wheel in the longitudinal direction
until no further sparks emerge from the
workpiece, move the table in the cross direction
to expose a new portion of the workpiece to
the wheel, then take another sweep in the
longitudinal direction. Repeat this process until
the entire surface is ground. See Figure 36 for
an illustration of this process.
Grinding Tips
While every grinding operation is unique, there
are a few techniques that apply to most, if not all
grinding operations.
• Duringlongitudinalpasses,tightenthecross
travel lock knob to prevent chatter that may
occur as a result of slight cross movement of
the table.
• Betweenlongitudinalpasses,usethe
squeegee to remove any foreign material
from the workpiece.
Figure 36. Grinding process illustrated.
-29-
Page 32

Model SB1023
!
Maintenance
MAINTENANCE
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
Maintenance Schedule
Always disconnect
machine from power before
performing maintenance or
serious personal injury may
result.
To keep this machine in the best operating
condition, make sure to complete the following maintenance items within the minimum
intervals listed below.
Daily:
• Checkforandcorrectloosemountingbolts.
• Check for and correct damaged or cracked
grinding wheel.
• Check for and correct worn or damaged
wires.
• Clean and protect table.
• Vacuum metal shavings from machine.
• Correct any other unsafe condition.
Lubrication
If this machine is used in a heavy industrial
setting, or in a dirty or damp environment,
increase the lubrication intervals.
To lubricate your machine:
1. DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
2. Clean the upper column leadscrew section
with mineral spirits, dry with a rag, and
relubricate with any standard machine or
multipurpose grade grease (Figure 37).
Leadscrew
Grease Fitting
Bi-weekly
• Remove the table, clean and relubricate the
ways, ball bearings, and rack and pinion.
• Lubricate the column grease fitting with two
pumps of grease.
• Lubricate the table cross way grease fitting
with two pumps of grease.
• Clean and grease all three leadscrews.
Figure 37. Upper column leadscrew and grease fitting.
3. Wipe the column grease fitting clean (see
Figure 37) and pump the fitting with two or
three pumps of grease. Wipe off any grease
that bleeds through the seams.
-30-
Page 33

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1023
MAINTENANCE
4. Clean the lower column leadscrew section
with mineral spirits, dry with a rag, and
relubricate with any standard machine or
multipurpose grade grease (Figure 38).
Figure 38. Lower column leadscrew.
5. Wipe the table cross feed grease fitting clean
(Figure 39), and put two or three pumps
Figure 40. Ball bearing ways.
of grease into it. Wipe off any grease that
bleeds through the seams.
Grease Fitting
Figure 39. Cross way grease fitting.
6. With the help of another person, lift the
table off the ways and set the table upside
down on a workbench (Figures 40-41).
Figure 41. Table ways and rack.
7. Clean the pinion, rack, bearings, ways, and
leadscrew with mineral spirits. Dry all parts,
and re-lubricate with white lithium grease.
8. With the help of your assistant,
CAREFULLY place the table back onto the
ways. DO NOT drop the table or you may
put a nick in a way and ruin it permanently.
-31-
Page 34

Model SB1023
MAINTENANCE
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
Handwheel Backlash
Adjustment
Backlash is the amount of play found in a
leadscrew. Without moving the table, the amount
of backlash can be determined by lightly turning
the handwheel with your fingertips in one
direction until the handwheel stops, noting the
location shown on the handwheel scale. Then the
handwheel is turned in the other direction until
it stops. The distance between both stopping
locations is the amount of backlash. If the
backlash exceeds 0.007", adjust it back into range
the of 0.003" to 0.006".
The backlash adjustment is made by tightening
or loosening the cross-feed leadscrew halfnut
cap screws shown in Figure 42. These screws
draw two halves of the halfnut together against
the leadscrew placing pressure on the threads.
If this fit is too tight, loosen the cap screws, tap
the table a few times with a rubber or wooden
mallet, and turn the handle slowly back-andforth until the handle turns freely. To readjust
the backlash, rock the handle back-and-forth and
tighten the screws slowly until the backlash is
correct.
Column & Table Gib
Adjustment
The gib is a tapered piece of steel that is held in
position by a gib screw. When the screw is turned
clockwise, the gib will be moved to fill the loose
void in the way, thus, removing the play. If more
play is needed, adjust the screws the opposite
direction.
When adjusting the table or column gib screw
(Figure 43), keep in mind that the goal is to
remove sloppiness in the ways without causing
the dovetailed ways to bind or prematurely wear.
A loose gib can cause dimensional problems or a
poor finish on the workpiece.
Note: Avoid the temptation to overtighten
the cap screws at the leadscrew halfnut.
Overtightening will cause excessive wear
to the halfnut and leadscrew. Reducing
backlash to less than 0.003" is impractical
and reduces the life of the gib and the ways.
Gib
Cap Screws
Leadscrew
Gib Screw
Figure 42. Table gib and leadscrew.
and Halfnut
Figure 43. Column gib and leadscrew.
-32-
Page 35

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1023
MAINTENANCE
Service
Machine Storage
Never attempt to move this machine without
first locking the table in place. If the machine
is slightly tilted, the table could uncontrollably
slide and fall off of the machine and cause
machine damage or severe injury.
Machinery can develop serious rust problems and
corrosion damage if it is not properly prepared
for storage. If decommissioning this machine, use
the steps in this section to ensure that it remains
in good condition.
Short-term storage (less than
year)
1. DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
2. Thoroughly clean all unpainted, bare
metal surfaces, then coat them with a rust
preventative oil or wax specifically designed
to protect machinery while in storage. DO
NOT USE MOTOR OIL in storage situations
as it does not sufficiently protect against
rust.
3. Lubricate the machine as outlined in the
Lubrication section on Page 30.
4. Cover and place the machine in an area
that is out of direct sunlight and away
from where paints and thinners are stored,
or where gasses are present. Fumes and
sunlight can bleach or discolor paint and
clear plastic guards.
5. Once or twice a month, depending on
humidity, wipe down the machine as
outlined in Step 2.
Long-term storage
Long-term storage (more than a
year)
1. Empty and flush any cutting fluid pumps,
lines, or tanks.
2. DISCONNECT MACHINE FROM POWER!
3. Thoroughly clean all unpainted, bare metal
surfaces, then coat them with a heavy grease
or rust preventative. Take care to ensure
these surfaces are completely covered but
that the grease or rust preventative is kept
off painted surfaces. Make sure that both
the upper and lower portions of the column
leadscrew are completely coated with white
lithium grease.
4. Remove the table, and then clean and pack
the bearings with white lithium grease.
5. Using mineral spirits, clean and brush the
ways, rack, pinion gear, and the leadscrew
with any quality grease or wax that is
specifically formulated for protecting
machine parts during storage.
6. Open the main electrical box on the machine
and place a few moisture absorbing desiccant
packs at the bottom of the electrical box.
7. Cover and place the machine in an area
that is out of direct sunlight and away
from where paints and thinners are stored,
or where gasses are present. Fumes and
sunlight can bleach or discolor paint and
clear plastic guards.
Note: When the machine is being put back into
service from long-term storage, lubricate
the machine as outlined in the Lubrication
section on Page 30.
6. Every two months, move all handwheels so
the headstock and column move at least once
in their full range of motion. This will keep
the bearings, bushings, gears, and shafts
well lubricated and protected from corrosion,
especially during the winter months.
-33-
Page 36

Model SB1023
TROUBLESHOOTING
If you need replacement parts, or if you are unsure how to do any of the solutions given here, feel free
TROUBLESHOOTING
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
to call us at (360) 734-1540.
Symptom Possible Cause Possible Solution
Machine does not
start.
Motor chatters
during startup or
during operation.
Power supply switched off/has
1.
incorrect voltage.
Blown fuse/tripped circuit breaker
2.
at main panel.
Thermal overload relay has tripped.
3.
Plug or receptacle is corroded or
4.
mis-wired.
Break or short in wiring; or loose
5.
connections.
Motor ON/OFF switch at fault.
6.
Motor connection wired incorrectly.
7.
Contactor not energized/has poor
8.
contacts.
Motor at fault.
9.
Extension cord (if used) is causing
1.
voltage drop.
Low power supply voltage.
2.
Switch power supply on/verify voltage.
1.
Correct the cause of overload, then reset/replace
2.
fuse or breaker.
Allow motor to cool. If necessary, press reset button
3.
inside switch.
Clean/retighten contacts; correct the wiring.
4.
Trace/replace broken or corroded wires; fix loose
5.
connections.
Replace switch.
6.
Wire motor correctly (refer to inside junction box
7.
cover or manual).
Test all legs for power, test field coil and replace if
8.
at fault.
Test for shorted windings, bad bearings and repair
9.
or replace.
Move machine closer to the power source, or use a
1.
larger gauge wire or shorter extension cord.
Have the power supply verified and corrected by an
2.
electrician.
Machine has excessive vibration or
noise.
Machine stalls or
slows when operating.
Handwheel has
excessive backlash,
endplay, binds, or
is difficult to move.
Motor fan rubbing on fan cover.
1.
Motor is loose.
2.
Grinding wheel out of balance.
3.
Motor bearings worn or damaged.
4.
Motor is being overloaded.
1.
Motor at fault.
2.
Leadscrew is dirty or lacks proper
1.
lubrication.
Leadscrew or leadscrew nut worn.
2.
Linkage bolts, pins, and holes are
3.
loose or worn.
Longitudinal feed rack and pinion
4.
are worn.
Fix/replace fan cover; replace loose or damaged fan.
1.
Tighten any loose fasteners.
2.
Dress and balance grinding wheel.
3.
Replace motor bearings or replace motor.
4.
Reduce depth of cut.
1.
Test for shorted windings, bad bearings and repair
2.
or replace.
Clean and lubricate the leadscrew and service oil
1.
system (Page 30).
Adjust or replace leadscrew or leadscrew nut.
2.
Replace linkage bolts, pins, and re-bush any worn
3.
pin holes.
Replace rack and pinion gears.
4.
-34-
Page 37

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1023
TROUBLESHOOTING
Symptom Possible Cause Possible Solution
Vibration when
grinding, poor
surface finish,
or incorrect final
dimensions.
Grinding wheel is out-of-round or is
1.
loaded up with material.
Grinding wheel is out of balance or
2.
damaged.
Missing or torn grinding wheel
3.
paper washers.
Incorrect grinding wheel hardness
4.
or grit rating.
Improperly installed magnetic
5.
chuck.
Workpiece is loose.
6.
Wheel hub not installed onto
7.
spindle shaft correctly.
Loose machine component.
8.
Ways or leadscrews are out of
9.
lubrication or contaminants have
loaded up on the ways.
Headstock is loose.
10.
Grinding wheel has varying
11.
densities, or is of poor quality.
Table and handwheel have lash.
12.
Table is loose.
13.
Grinding operation requires
14.
coolant.
Coolant is incorrect or incorrectly
15.
mixed.
Bad motor or spindle bearings.
16.
Dress grinding wheel to make concentric and to the
1.
required grit level (Page 25).
Remove, and ring test, and balance the grinding
2.
wheel (Page 20 & 26).
Remove and replace paper washers, dress and
3.
rebalance grinding wheel.
Match wheel grade and grit rating with workpiece
4.
hardness.
Stone table and chuck surfaces, and remove all
5.
burrs and foreign material from mating surfaces,
and reinstall the chuck.
Replace or repair chuck for poor holding power.
6.
Remove wheel and hub assembly, stone taper high
7.
spots or dings, and reinstall wheel and hub (Page
22).
Inspect all machine connections, and tighten any
8.
loose fasteners.
Remove table, clean and relubricate the ways and
9.
ball bearings (Page 30).
10. Tighten column gib (Page 32).
Replace grinding wheel with acceptable brand
11.
(Page 20).
12. Adjust cross feed leadscrew halfnut (Page 32).
13. Adjust cross feed gib (Page 32).
Install aftermarket coolant kit.
14.
Refer to coolant manufacturer's workpiece verses
15.
coolant type recommendations and correct coolant.
Replace motor or replace bearings.
16.
-35-
Page 38

Model SB1023
1. Shock Hazard: It is extremely dangerous to
perform electrical or wiring tasks while the
machine is connected to the power source.
Touching electrified parts will result in
personal injury including but not limited to
severe burns, electrocution, or death. For
your own safety, disconnect machine from
the power source before servicing electrical
components or performing any wiring tasks!
2.
Wire Connections: All connections must be
tight to prevent wires from loosening during
machine operation. Double-check all wires
disconnected or connected during any wiring
task to ensure tight connections.
3.
Modifications: Using aftermarket parts or
modifying the wiring beyond what is shown
in the diagram may lead to unpredictable
results, including serious injury or fire.
4.
Motor Wiring: The motor wiring shown
in these diagrams is current at the time of
printing, but it may not match your machine.
Always use the wiring diagram inside the
5.
Circuit Requirements: Connecting the
machine to an improperly sized circuit will
greatly increase the risk of fire. To minimize
this risk, only connect the machine to a
power circuit that meets the minimum
requirements given in this manual.
6.
Capacitors/Inverters: Some capacitors and
power inverters store an electrical charge for
up to 10 minutes after being disconnected
from the power source. To reduce the risk of
being shocked, wait at least this long before
working on capacitors.
7.
Wire/Component Damage: Damaged wires
or components increase the risk of serious
personal injury, fire, or machine damage. If
you notice that any wires or components are
damaged while performing a wiring task,
replace those wires or components before
completing the task.
8.
Experiencing Difficulties: If you are
experiencing difficulties understanding the
information included in this section, contact
The photos and diagrams included in this section are best viewed in color. You can
see them in color at www.southbendlathe.com.
BLACK
WHITE
GREEN
RED
BLUE
BROWN
G RAY
ORANGE
YEL LOW
YEL LOW
GREEN
PURPLE
PINK
LIGHT
BLUE
BLUE
WHITE
TURQUIOSE
NOTICE:
WIRING DIAGRAM COLOR KEY
ELECTRICAL
ELECTRICAL
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
Electrical Safety Instructions
These pages are accurate at the time of printing. In the constant effort to improve, however, we may
make changes to the electrical systems of future machines. Study this section carefully. If you see
differences between your machine and what is shown in this section, call Technical Support at (360)
734-1540 for assistance BEFORE making any changes to the wiring on your machine.
-36-
Page 39

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1023
AMP
10
16
THER MAL
RELAY
Allen Bradley
193TAC
CONTACTOR
Allen Bradley
C09400
1 3 5 7L1 L2 L3 L4
2 4 6 8T1 T2 T3 T4
95 96
10.5A
NONC 97 98
U
U
V
V
2
2
S
S
GND
GND
S
S
R
R
R
R
R
4
4
4
4
4
3
3
3 3
3
Run Capacitor
200MFD
125VAC
GND
V
U 3
1
4
2
Neutral
Hot
Ground
110 VAC
5-15 Plug
(As Recommended)
ON BUTTON
(Viewed From
Behind)
OFF BUTTON
(Viewed From
Behind)
Motor
Control Panel
(Viewed From
Behind)
Electrical Box
2 1
3
4
ELECTRICAL
SB1023 Wiring Diagram 110V
Electrical Box
Spindle
Motor
Control Panel
Figure 44. Spindle motor & pump motor locations.
Figure 45. Electrical box & control panel location.
-37-
Page 40

Model SB1023
THER MAL
RELAY
CONTACTOR
Allen Bradley
C09400
1 3 5 7L1 L2 L3 L4
2 4 6 8T1 T2 T3 T4
95 96 NONC 97 9 8
U
U
V
V
2
2
S
S
GND
GND
S
S
R
R
R
R
R
4
4
4
4
4
3
3
3 3
3
Run Capacitor
200MFD
125VAC
GND
V
U
3
1
4
2
Hot
Hot
Ground
220 VAC
6-15 Plug
(As Recommended)
ON BUTTON
(Viewed From
Behind)
OFF BUTTON
(Viewed From
Behind)
Motor Wired for 220V
Control Panel
(Viewed From
Behind)
Electrical Box
220V Contactor Kit Part No. PSB1023180 / Set to 5.5A
2 1
3
4
AMP
4
6
Allen Bradley
193TAC
5.5A
ELECTRICAL
SB1023 Wiring Diagram 220V
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
-38-
Page 41

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1023
1A *
2A
11A
12
13
14
15
17
16
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
51
51
41
*Only available as a complete assembly
50
51
1
REF PART # DESCRIPTION REF PART # DESCRIPTION
1A PSB1023001A MOTOR & SPINDLE ASSEMBLY 28 PSB1023001A FAN COVER
1 PSB1023001A MOTOR 110/220V 3/4HP 1PH 29 PSB1023001A MOTOR BODY
2A PSB1023002A GRINDING WHEEL COVER ASSEMBLY 30 PSB1023001A MOTOR COIL
11A PSB1023011A WHEEL FLANGE ASSEMBLY 31 PSB1023001A MOTOR ROTOR
12 PSB1023012 GRINDING WHEEL 7"D X 1/2"W X 1-1/4"B 41 P7206 ANGULAR CONTACT BALL BEARING 7206
13 PCAP02M CAP SCREW M6-1 X 20 42 PC200F S CAPACITOR 200M 125V 1-3/8 X 2-3/4
14 PCAP14M CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 20 43 P6202ZZ BALL BEARING 6202ZZ
15 PCAP111M CAP SCREW M12-1.75 X 35 44 PSB1023001A GROMMET
16 PN03M HEX NUT M8-1.25 45 PSB1023001A CONTACT PLATE
17 PLW05M LOCK WASHER 12MM 46 PSB1023001A CENTRIFUGAL SWITCH
21 PSB1023001A SPINDLE 47 PSB1023001A MOTOR FAN
22 PSB1023001A OUTER SPINDLE NUT 48 PSB1023001A JUNCTION BOX
23 PSB1023001A INNER SPINDLE NUT 49 PSB1023001A TERMINAL BLOCK
24 PSB1023001A OUTER SPINDLE SPACER 50 PS22 PHLP HD SCR 10-24 X 5/8
25 PSB1023001A INNER SPINDLE SPACER 51 PS06 PHLP HD SCR 10-24 X 3/8
26 PSB1023001A BEARING SEAT 52 PCAP15M CAP SCREW M5-.8 X 20
27 PSB1023001A CAPACITOR COVER
PARTS
Motor & Spindle
-39-
Page 42

Model SB1023
61
62
63A
64
65
67
68
69
70
71
72
73A
74
75
76
77
78
79
81
82
91
92
93
93
94
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
104
105
106
107
108
108
Column
PARTS
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
-40-
See Column Parts List on Page 42.
Page 43

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1023
111
112
113
115A
116
118A
119
120
160
121
122
123
124
125A
126
127
128
114
128
129
130
131
131
132
133
134
141
142
143
144
144
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
156
157
158
159
162
PARTS
Table
See Table Parts List on Page 42.
-41-
Page 44

Model SB1023
REF PART # DESCRIPTION REF PART # DESCRIPTION
111 PSB1023111 CROSS TRAVEL BASE 134 PSB1023134 COMPRESSION SPRING
112 PSB1023112 TABLE BASE 141 PCAP17M CAP SCREW M4-.7 X 10
113 PSB1023113 LOWER BEARING RACE 142 PCAP16M CAP SCREW M4-.7 X 16
114 PSB1023114 TABLE 143 PCAP33M CAP SCREW M5-.8 X 12
115A PSB1023115A HANDWHEEL INDEX COLLAR ASSEMBLY 144 PCAP24M CAP SCREW M5-.8 X 16
116 PSB1023116 CROSS GIB 145 PCAP02M CAP SCREW M6-1 X 20
118A PSB1023118A CROSS LEADSCREW W/NUT ASSEMBLY 146 PCAP06M CAP SCREW M6-1 X 25
119 PSB1023119 RACK 147 PCAP84M CAP SCREW M10-1.5 X 35
120 PSB1023120 CROSS FEED HELICAL GEAR 148 PSS31M SET SCREW M5-.8 X 8
121 PSB1023121 LONGITUDINAL TRAVEL STOP 149 PSS06M SET SCREW M8-1.25 X 16
122 PSB1023122 LONGITUDINAL SHAFT 150 PFH31M FLAT HD SCR M4-.7 X 8
123 PSB1023123 LONGITUDINAL HANDWHEEL 151 PN11 HEX NUT 3/8-16
124 PSB1023124 HANDWHEEL SPACER 152 PN02 HEX NUT 5/16-18
125A PSB1023125A BEARING CAGE ASSEMBLY 153 PK69M KEY 4 X 4 X 12
126 PSB1023126 FRONT UPPER BEARING RACE 154 PK09 KEY 1/4 X 1/4 X 3/4
127 PSB1023127 REAR UPPER BEARING RACE 155 P6202ZZ BALL BEARING 6202ZZ
128 PSB1023128 SPARK STOP 156 PSB1023156 CROSS HANDWHEEL HANDLE
129 PSB1023129 TRAVEL STOP 157 PRP03M ROLL PIN 5 X 20
130 PSB1023130 GIB ADJUSTMENT SCREW 158 PSB1023097 ZERK FITTING 1/8" PT
131 PSB1023131 BEARING RETAINING PLATE 159 PSB102396 STEEL BALL 8MM
132 PSB1023132 CROSS HANDWHEEL SPACER 160 PSB1023160 TAPER PIN M4 X 40
133 PSB1023133 CROSS FEED HANDWHEEL 162 PSB1023162 KNOB BOLT M8-1.25 X 21
REF PART # DESCRIPTION REF PART # DESCRIPTION
61 PSB1023061 COLUMN BASE 82 PSB1023082 UPPER VERTICAL TRAVEL STOP
62 PSB1023062 COLUMN 91 PK05M KEY 4 X 4 X 10
63A PSB1023063A ELEVATION LEADSCREW W/NUT ASSY 92 PK134M KEY 4 X 4 X 14
64 PSB1023064 BEVEL GEAR 93 P6202ZZ BALL BEARING 6202ZZ
65 PSB1023065 ELEVATION HANDWHEEL SHAFT 94 P51102 THRUST BEARING 51102
67 PSB1023067 COLUMN GIB 95 PSB1023095 HANDWHEEL HANDLE
68 PSB1023068 HANDWHEEL MOUNTING BRACKET 96 PSTB002M STEEL BALL 8MM
69 PSB1023069 PLATE FOR RUBBER COVER 97 PZERK005 ZERK FITTING 1/8" PT
70 PSB1023070 RUBBER COVER 98 PCAP02M CAP SCREW M6-1 X 20
71 PSB1023071 TOP PLATE 99 PCAP14M CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 20
72 PSB1023072 GIB ADJUSTMENT SCREW 100 PCAP01M CAP SCREW M6-1 X 16
73A PSB1023073A HANDWHEEL INDEX COLLAR ASSEMBLY 101 PCAP06M CAP SCREW M6-1 X 25
74 PSB1023074 ELEVATION HANDWHEEL SPACER 102 PCAP37M CAP SCREW M6-1 X 50
75 PSB1023075 HANDWHEEL COLLAR PLATE 103 PCAP16M CAP SCREW M4-.7 X 16
76 PSB1023076 ELEVATION HANDWHEEL 104 PSB1023104 LEADSCREW SPACER
77 PSB1023077 COMPRESSION SPRING 105 PCAP11M CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 16
78 PSB1023078 ELEVATION SCALE 106 PSS06M SET SCREW M8-1.25 X 16
79 PSB1023079 ELEVATION INDICATOR 107 PSB1023107 TAPER PIN M8 X 40
81 PSB1023081 LOWER VERTICAL TRAVEL STOP 108 PCAP38M CAP SCREW M5-.8 X 25
Column Parts List
PARTS
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
Table Parts List
-42-
Page 45

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1023
171
172
173
181
182
183
184
185
176
177
179
178
180
(For 220V Conversion)
177A
REF PART # DESCRIPTION REF PART # DESCRIPTION
171 PSB1023171 GRINDER BASE 179 PSB1023179 O/L RELAY AB 193TAC16 10–16A
172 PSB1023172 COLUMN CAP 180 PSB1023180 220V CONVERSION KIT
173 PSB1023173 ELECTRICAL BOX 181 PCAP31M CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 25
174A PSB1023174A STAND W/DOOR ASSEMBLY 182 PCAP84M CAP SCREW M10-1.5 X 35
176 PSB1023176 ON BUTTON 183 PSB1023183 LIFTING HOOK M12-1.75
177 PSB1023177 OFF BUTTON 184 PN06 HEX NUT 1/2-13
178 PSB1023178 CONTACTOR AB C09-400 110V 185 PSB1023185 ADJUSTING FOOT
PARTS
Stand
-43-
Page 46

Model SB1023
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
314
315
313
REF PART # DESCRIPTION REF PART # DESCRIPTION
301 PSB1023301 CONTROL PANEL LABEL 309 PSB1023309 MACHINE ID LABEL
302 PSB1023302 ROTATION LABEL 310 PSBLABEL02VL DISCONNECT POWER LABEL
303 SB1317 SOUTH BEND NAMEPLATE 1 36MM 311 PSBPAINT02 SB LIGHT BLUE TOUCH-UP PAINT
304 PSBPAINT01 SB GRAY TOUCH-UP PAINT 312 SB1321 SOUTH BEND NAMEPLATE 5 203MM
305 PSB1023305 TABLE TIP LABEL 313 PSBPAINT03 SB DARK BLUE TOUCH-UP PAINT
306 PSBLABEL01VS READ MANUAL LABEL 314 PSB1023314 MODEL NUMBER LABEL
307 PSBLABEL09VS FACESHIELD RESPIRATOR LABEL 315 PSB1023315 SOUTH BEND LOGO RECT
308 PSB1023308 110V 1-PH LABEL
The safety labels provided with your machine are used to make the operator aware of the
machine hazards and ways to prevent injury. The owner of this machine MUST maintain the
original location and readability of these safety labels. If any label is removed or becomes
unreadable, REPLACE that label before using the machine again. Contact South Bend Lathe Co. at
(360) 734-1540 or www.southbendlathe.com to order new labels.
Machine Labels
PARTS
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
-44-
Page 47

WARRANTY & RETURNS
This quality product is warranted by South Bend Lathe Company to the original buyer for one year
from the date of purchase. This warranty does not apply to consumable parts, or defects due to any
kind of misuse, abuse, negligence, accidents, repairs, alterations or lack of maintenance. We do not
reimburse for third party repairs. In no event shall we be liable for death, injuries to persons or
property, or for incidental, contingent, special or consequential damages arising from the use of our
products.
We do not warrant or represent that this machine complies with the provisions of any law, act, code,
regulation, or standard of any domestic or foreign government, industry, or authority. In no event
shall South Bend’s liability under this warranty exceed the original purchase price paid for this
machine. Any legal actions brought against South Bend Lathe Company shall be tried in the State of
Washington, County of Whatcom.
This is the sole written warranty for this machine. Any and all warranties that may be implied by
law, including any merchantability or fitness, for any purpose, are hereby limited to the duration of
this warranty. To take advantage of this warranty, contact us by mail or phone to give us the details
of the problem you are having.
Thank you for your business and continued support.
WARRANTY
Page 48

Printed In Taiwan #CRJB12368
 Loading...
Loading...