Page 1

14" METAL CUTTING BANDSAW
MODEL SB1021 - SINGLE PHASE
MODEL SB1022 - THREE PHASE
Copyright © August, 2009 For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09
Page 2

Scope of Manual
This manual helps the reader understand the machine, how to prepare it for operation, how to control
it during operation, and how to keep it in good working condition. We assume the reader has a basic
understanding of how to operate this type of machine, but that the reader is not familiar with the
controls and adjustments of this specific model. As with all machinery of this nature, learning the
nuances of operation is a process that happens through training and experience. If you are not an
experienced operator of this type of machinery, read through this entire manual, then learn more
from an experienced operator, schooling, or research before attempting operations. Following this
advice will help you avoid serious personal injury and get the best results from your work.
Manual Feedback
We've made every effort to be accurate when documenting this machine. However, errors sometimes
happen or the machine design changes after the documentation process—so the manual may not
exactly match your machine. If a difference between the manual and machine leaves you in doubt,
contact our customer service for clarification.
We highly value customer feedback on our manuals. If you have a moment, please share your
experience using this manual. What did you like about it? Is there anything you would change to
make it better? Did it meet your expectations for clarity, professionalism, and ease-of-use?
South Bend Lathe, Inc.
C
/O Technical Documentation Manager
P.O. Box 2027
Bellingham, WA 98227
Email: manuals@southbendlathe.com
Updates
For your convenience, any updates to this manual will be available to download free of charge
through our website at:
www.southbendlathe.com
Customer Service
We stand behind our machines. If you have any service questions, parts requests or general questions
about the machine, feel free to contact us.
South Bend Lathe Co.
P.O. Box 2027
Bellingham, WA 98227
Phone: (360) 734-1540
Parts Department: (417) 886-2954
Fax: (360) 676-1075 (International)
Fax: (360) 734-1639 (USA Only)
Email: cs@southbendlathe.com
Page 3
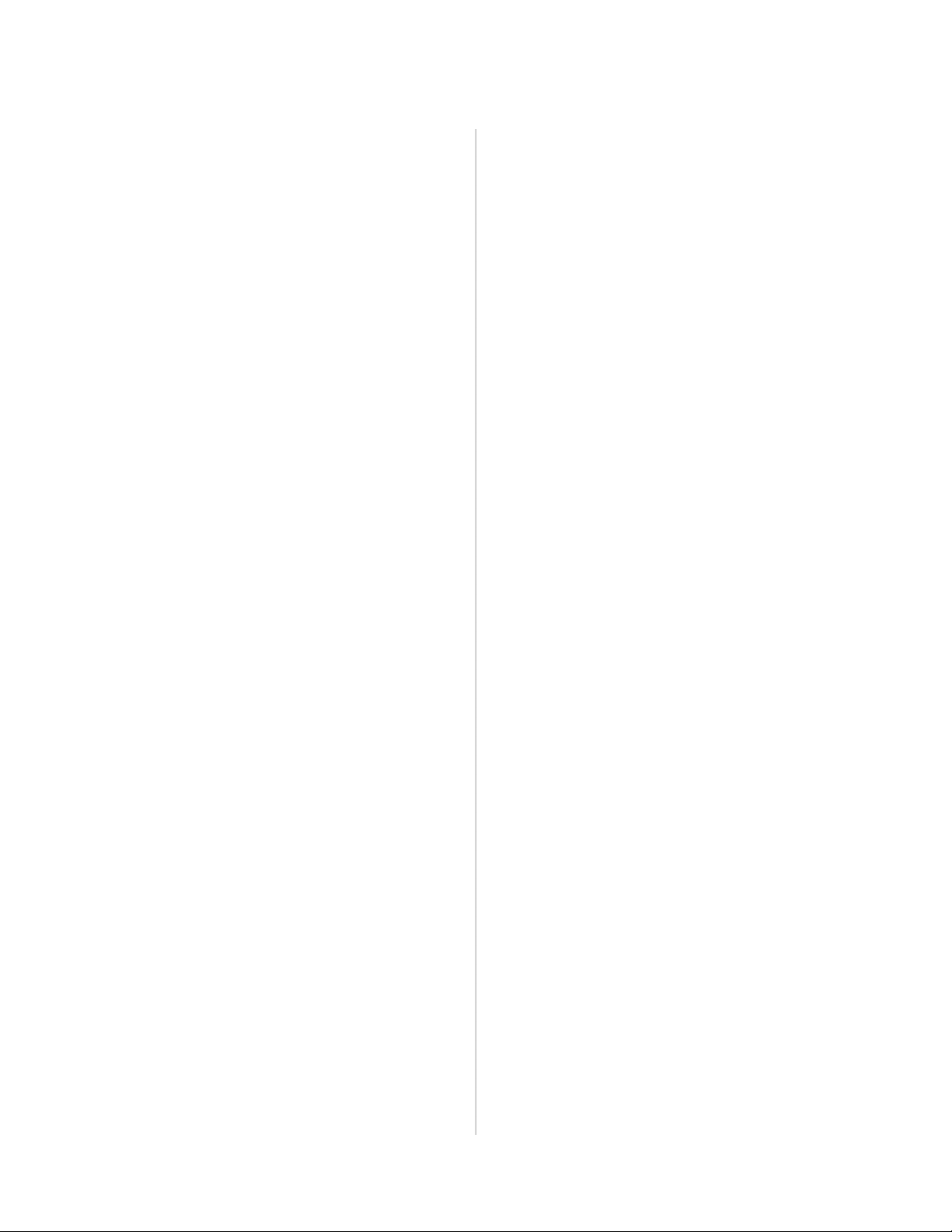
Table of Contents
INTRODUCTION ...............................................................2
About This Machine .............................................2
Capabilities ......................................................... 2
Features .............................................................. 2
Identification ........................................................ 3
Machine Specifications ........................................ 4
SAFETY ................................................................................8
Understanding Risks of Machinery .................... 8
Basic Machine Safety ..........................................8
Additional Metal Cutting Bandsaw Safety ......10
PREPARATION .............................................................. 11
Preparation Overview ........................................ 11
Things You'll Need .............................................11
Unpacking ..........................................................11
Cleaning & Protecting ....................................... 12
Location .............................................................. 13
Lifting & Moving ................................................14
Leveling & Mounting ......................................... 14
Leveling ............................................................14
Bolting to Concrete Floors ..................................15
Machine Mounts ................................................ 15
Assembly ............................................................15
Initial Lubrication .............................................15
Inspections & Adjustments ............................... 15
Power Connection .............................................. 16
220V Conversion for SB1021 .............................. 16
SB1021 110V (Prewired) Power Source ..............16
SB1021 (220V) Power Source .............................16
SB1022 (220V 3-Phase) Power Source ................16
Test Run ............................................................. 17
OP ER ATIO N .................................................................... 18
Operation Overview ........................................... 18
Controls ..............................................................19
Blade Selection ...................................................20
Blade Terminology .............................................20
Blade Length ..................................................... 20
Blade Width ......................................................20
Tooth Set ...........................................................21
Tooth Type ........................................................21
Blade Pitch (TPI) ............................................... 22
Blade Changes ...................................................23
Blade Tensioning ............................................... 23
Blade Breakage .................................................. 24
Blade Care & Break-In ...................................... 24
Blade Care ........................................................24
Blade Break-In .................................................. 24
Blade Speed Chart .............................................25
Chip Inspection Chart ....................................... 25
Positioning Guide Post ...................................... 26
Adjusting Blade Guides ..................................... 26
Tilting Table .......................................................28
Blade Welding ....................................................28
MAINTENANCE ............................................................. 32
Maintenance Schedule .......................................32
Cleaning .............................................................32
Dressing Grinding Wheel .................................. 32
Lubrication ......................................................... 33
V-Belts ................................................................ 34
Speed Hub Belts ................................................ 34
Sprocket Drive Belt ...........................................34
Air Pump Belt ...................................................34
Dressing Rubber Tires ....................................... 34
SERVICE........................................................................... 35
Blade Tracking ................................................... 35
Table Calibration ............................................... 35
Guide Post Alignment........................................36
Pinion Gear Backlash ........................................37
Leadscrew End Play .......................................... 37
TROUBLESHOOTING .................................................38
ELECTRICAL ...................................................................42
Electrical Safety Instructions ...........................42
Wiring Overview ................................................ 43
SB1021/2 Control Panel & Welding Unit ......... 44
SB1021 110V Electrical Panel, Motor & Cord .45
SB1021 220V Electrical Panel, Motor & Cord .46
SB1022 220V Electrical Panel, Motor & Cord .47
Electrical Component Pictures..........................48
PARTS................................................................................49
Lower Frame ......................................................49
Drive System ...................................................... 51
Upper Frame ...................................................... 53
Table & Tensioning System ..............................55
Electrical Cabinet .............................................. 57
Welder & Control Panel ....................................58
Machine Labels .................................................. 60
WARRANTY & RETURNS ..........................................61
Page 4

Model SB1021/SB1022
INTRODUCTION
INTRODUCTION
About This Machine
For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09
Capabilities
This 14" Metal-Cutting Bandsaw allows you to
make exterior and interior contoured or straight
cuts. To better understand these capabilities,
imagine making a "doughnut" out of 1" steel
plate.
The outside circular shape can be easily cut by
moving the workpiece around the blade, using a
pre-drawn line as a cutting guide.
Cutting the inside hole would normally be a
difficult task with a bandsaw. But this machine
makes it easy. First, the bandsaw blade is cut
with the built-in blade shear. A hole slightly
larger than the blade is then drilled into the
center of the workpiece, so the blade can be
threaded through the hole. The ends of the blade
are then clamped into the built-in welder, welded
back together, annealed, and ground flat with the
built-in grinder. Once the blade is re-installed on
the wheels, it can then be used to cut the interior
hole and complete the doughnut shape. After
completion, the blade is sheared again to remove
it from the workpiece.
Aside from the above capabilities, this machine
can also be used for straight cuts in sheets too
large to fit in the vise of a horizontal metalcutting bandsaw
Features
Now that you know the basics of what this
machine can do, take a minute to consider its
features.
This machine is equipped with a built-in air
blower near the blade guides. This feature keeps
metal chips away from the cutting area, so you
can accurately follow pre-drawn cutting lines
without metal chips getting in the way.
An adjustable work lamp is also provided above
the table to eliminate shadows from the work
area. This is a great feature when doing close up
work near moving blades!
We also equipped this bandsaw with variable
speed, so you can precisely control cutting
results for the type of blade installed and type
of material being cut. This is a great feature to
have when doing precision cutting.
Aside from features, we designed this machine to
be extremely solid and durable. We used heavy
gauge steel for the wheel doors, ridiculously thick
table trunnions and frame castings, USA-made
Allen-Bradley electronics, and Japanese-made
NSK ball bearings.
For example, if you needed to cut a 24" x
24" sheet of 1" steel in half, you can clamp a
straightedge to the bandsaw table, then guide
the sheet along the straightedge to make a nice
straight cut. Cutting this same size of stock on a
horizontal bandsaw would require a very large
machine.
On the other hand, if you need to "resaw" an 8"
x 8" billet into a series of 1" thick plates, clamp
a straightedge 1" away from the blade, raise the
blade guides to accommodate the height of the
billet, and each cut you make will produce an 8"
x 1" plate.
Both of these types of straight cuts can also be
made with the table tilted to 15°, which creates a
beveled cut.
-2-
Page 5
For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09 Model SB1021/SB1022
INTRODUCTION
Identification
Blade Tension Handwheel
Operation
Controls
Welding
Area
Air Blower
Blade
Shear
Table
Grinder
Guide Post
Elevation Knob
Work
Lamp
Electrical
Control Box
Variable Speed
Handwheel
Front View Rear View
Serious personal injury could occur if
you connect the machine to power before
completing the setup process. DO NOT
connect power until instructed to do so later
in this manual.
Table Trunnions
Untrained users have an increased risk
of seriously injuring themselves with this
machine. Do not operate this machine until
you have understood this entire manual and
received proper training.
-3-
Page 6
Model SB1021/SB1022
INTRODUCTION
Machine Specifications
Machine Specifications
Model SB1021 14" Variable Speed
Vertical Metal Cutting Bandsaw
Product Dimensions:
Weight ..........................................................................................................................................................................697 lbs.
Length/Width/Height ................................................................................................................................... 22" x 36" x 67
Foot Print (Length/Width) ......................................................................................................................................16
Shipping Dimensions:
Type ...................................................................................................................................................................................Wood
Content ........................................................................................................................................................................ Machine
Weight ...........................................................................................................................................................................926 lbs.
Length/Width/Height ....................................................................................................................................... 77" x 42" x 29"
P.O. Box 2027, Bellingham, WA 98227 U.S.A.
0(/.%s
www.southbendlathe.com
For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09
© South Bend Lathe Co.
1
⁄4" x 31"
1
⁄2"
Electrical:
Required Power Source ..................................................................................................................... 110/220V, Single-Phase
Switch ..................................................................................................... Magnetic Contactor with Thermal Overload Relay
Switch Voltage ........................................................................................................................................................... 110/220V
Included Plug Type ................................................................................................................................................NEMA 5-15
Recommended Circuit Size ................................................................................................................................................ 15A
Motors:
Main
Type ............................................................................................................................TEFC Capacitor Start Induction
Horsepower .............................................................................................................................................................. 1 HP
Voltage .............................................................................................................................................................. 110/220V
Phase ..................................................................................................................................................................... Single
Amps ..........................................................................................................................................6A @ 220V/12A @ 110V
Speed ............................................................................................................................................................... 1725 RPM
Cycle .......................................................................................................................................................................60 Hz
Number Of Speeds .........................................................................................................................................................1
Power Transfer ............................................................................................................................................... Belt Drive
Bearings ............................................................................................................ Shielded and Permanently Lubricated
Grinder
Type ..................................................................................................................................... Open Drip Proof Induction
Horsepower .............................................................................................................................................................
Voltage ..................................................................................................................................................................... 110V
Phase ..................................................................................................................................................................... Single
Amps ......................................................................................................................................................................... 0.6A
Speed ............................................................................................................................................................... 3450 RPM
Cycle .......................................................................................................................................................................60 Hz
Number Of Speeds .........................................................................................................................................................1
Power Transfer ............................................................................................................................................ Direct Drive
Bearings ...................................................................................................................................... Sealed and Lubricated
1
⁄8 HP
-4-
Page 7

For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09 Model SB1021/SB1022
INTRODUCTION
Main Specifications:
Operation Information
Number of Blade Speeds .................................................................................................................................. Variable
Blade Speed Range .................................................................................................................................... 88–384 FPM
Blade Size Range ..................................................................................................................................................
Blade Length Range .................................................................................................................................118
1
⁄8"– 1⁄2"
1
⁄4"–119 1⁄2"
Cutting Capacity
Maximum Cutting Height ........................................................................................................................................ 7
Cutting Capacity Left of Blade .............................................................................................................................. 14
7
⁄8"
1
⁄8"
Table Information
Table Tilt .................................................................................................................. 15° Left/Right, 10° Forward/Back
Table Size ....................................................................................................................... 22
Floor to Table Height .............................................................................................................................................. 39
1
⁄8"W x 19 7⁄8" L x 1 5⁄8" Thick
1
⁄2"
Construction
Table ...................................................................................................................................Precision Ground Cast Iron
Wheels ............................................................................................................................................. Balanced Cast Iron
Tires ......................................................................................................................................................................Rubber
Blade Guide ........................................................................................................................... Hardened Steel/Tungsten
Body (Upper) .................................................................................................................................................... Cast Iron
Body (Lower) ........................................................................................................................................................... Steel
Base ..................................................................................................................................................................Cast Iron
Wheel Cover (Upper) ............................................................................................................................ Cast Aluminum
Wheel Cover (Lower) ......................................................................................................................... Pre-Formed Steel
Wheel Bearings ...................................................................... Japanese NSK Shielded and Permanently Lubricated
Paint .................................................................................................................................................................Urethane
Other Related Information
Wheel Diameter ...................................................................................................................................................... 14
Electric Blade Welder ............................................................................................................................. 220V, 2.0 KVA
Annealing Voltage ................................................................................................................................................... 220V
Other Specifications:
Country Of Origin ........................................................................................................................................................ Taiwan
Warranty .........................................................................................................................................................................1 Year
Serial Number Location ........................................................................................................ID Label on Upper Wheel Door
Assembly Time............................................................................................................................................................... 1 Hour
Features:
Allen Bradley Controls
Welding Station for Joining Blade Ends
Includes Blade Cutter, Electric Welder w/Clamp, Annealer, and Grinder
Infinitely Variable Cutting Speeds
Lower Wheel Cleaning Brush
Work Light
Chip Blower
Rubber Bonded Saw Wheels
1
⁄8"
-5-
Page 8
Model SB1021/SB1022
Machine Specifications
Model SB1022 14" Variable Speed
Vertical Metal Cutting Bandsaw
Product Dimensions:
Weight ..........................................................................................................................................................................697 lbs.
Length/Width/Height ................................................................................................................................... 22" x 36" x 67
Foot Print (Length/Width) ......................................................................................................................................16
Shipping Dimensions:
Type ...................................................................................................................................................................................Wood
Content ........................................................................................................................................................................ Machine
Weight ...........................................................................................................................................................................926 lbs.
Length/Width/Height ....................................................................................................................................... 77" x 42" x 29"
INTRODUCTION
P.O. Box 2027, Bellingham, WA 98227 U.S.A.
0(/.%s
© South Bend Lathe Co.
www.southbendlathe.com
For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09
1
⁄2"
1
⁄4" x 31"
Electrical:
Required Power Source .....................................................................................................................................220V, 3-Phase
Switch ..................................................................................................... Magnetic Contactor with Thermal Overload Relay
Switch Voltage .................................................................................................................................................................. 220V
Cord Included .......................................................................................................................................................................No
Recommended Cord Type .............................................................................................................16 Gauge, 4 Wire, 300VAC
Recommended Plug Type ..................................................................................................................................NEMA L15-15
Recommended Circuit Size .......................................................................................................................................... 15 amp
Motors:
Main
Type ............................................................................................................................TEFC Capacitor Start Induction
Horsepower .............................................................................................................................................................. 1 HP
Voltage ..................................................................................................................................................................... 220V
Phase ......................................................................................................................................................................Three
Amps ............................................................................................................................................................................ 3A
Speed ............................................................................................................................................................... 1725 RPM
Cycle .......................................................................................................................................................................60 Hz
Number Of Speeds .........................................................................................................................................................1
Power Transfer ............................................................................................................................................... Belt Drive
Bearings ............................................................................................................ Shielded and Permanently Lubricated
Grinder
Type ..................................................................................................................................... Open Drip Proof Induction
Horsepower .............................................................................................................................................................
Voltage ..................................................................................................................................................................... 110V
Phase ..................................................................................................................................................................... Single
Amps ......................................................................................................................................................................... 0.6A
Speed ............................................................................................................................................................... 3450 RPM
Cycle .......................................................................................................................................................................60 Hz
Number Of Speeds .........................................................................................................................................................1
Power Transfer ............................................................................................................................................ Direct Drive
Bearings ...................................................................................................................................... Sealed and Lubricated
1
⁄8 HP
-6-
Page 9

For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09 Model SB1021/SB1022
INTRODUCTION
Main Specifications:
Operation Information
Number of Blade Speeds .................................................................................................................................. Variable
Blade Speed Range .................................................................................................................................... 88–384 FPM
Blade Size Range ..................................................................................................................................................
Blade Length Range .................................................................................................................................118
1
⁄8"– 1⁄2"
1
⁄4"–119 1⁄2"
Cutting Capacity
Maximum Cutting Height ........................................................................................................................................ 7
Cutting Capacity Left of Blade .............................................................................................................................. 14
7
⁄8"
1
⁄8"
Table Information
Table Tilt .................................................................................................................. 15° Left/Right, 10° Forward/Back
Table Size ....................................................................................................................... 22
Floor to Table Height .............................................................................................................................................. 39
1
⁄8"W x 19 7⁄8" L x 1 5⁄8" Thick
1
⁄2"
Construction
Table ...................................................................................................................................Precision Ground Cast Iron
Wheels ............................................................................................................................................. Balanced Cast Iron
Tires ......................................................................................................................................................................Rubber
Blade Guide ........................................................................................................................... Hardened Steel/Tungsten
Body (Upper) .................................................................................................................................................... Cast Iron
Body (Lower) ........................................................................................................................................................... Steel
Base ..................................................................................................................................................................Cast Iron
Wheel Cover (Upper) ............................................................................................................................ Cast Aluminum
Wheel Cover (Lower) ......................................................................................................................... Pre-Formed Steel
Wheel Bearings ................................................................................................ Shielded and Permanently Lubricated
Paint .................................................................................................................................................................Urethane
Other Related Information
Wheel Diameter ...................................................................................................................................................... 14
Electric Blade Welder ............................................................................................................................. 220V, 2.0 KVA
Annealing Voltage ................................................................................................................................................... 220V
Other Specifications:
Country Of Origin ........................................................................................................................................................ Taiwan
Warranty .........................................................................................................................................................................1 Year
Serial Number Location ........................................................................................................ID Label on Upper Wheel Door
Assembly Time............................................................................................................................................................... 1 Hour
Features:
Allen Bradley Controls
Welding Station for Joining Blade Ends
Includes Blade Cutter, Electric Welder w/ Clamp, Annealer, and Grinder
Infinitely Variable Cutting Speeds
Lower Wheel Cleaning Brush
Work Light
Chip Blower
Rubber Bonded Saw Wheels
1
⁄8"
-7-
Page 10

Model SB1021/SB1022
SAFETY
SAFETY
For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09
Understanding Risks of Machinery
Operating all machinery and machining equipment can be dangerous or relatively safe depending
on how it is installed and maintained, and the operator's experience, common sense, risk awareness,
working conditions, and use of personal protective equipment (safety glasses, respirators, etc.).
The owner of this machinery or equipment is ultimately responsible for its safe use. This
responsibility includes proper installation in a safe environment, personnel training and usage
authorization, regular inspection and maintenance, manual availability and comprehension,
application of safety devices, integrity of cutting tools or accessories, and the usage of approved
personal protective equipment by all operators and bystanders.
The manufacturer of this machinery or equipment will not be held liable for injury or property
damage from negligence, improper training, machine modifications, or misuse. Failure to read,
understand, and follow the manual and safety labels may result in serious personal injury, including
amputation, broken bones, electrocution, or death.
The signals used in this manual to identify hazard levels are defined as follows:
Death or catastrophic
harm WILL occur.
Death or catastrophic
harm COULD occur.
Basic Machine Safety
1. Owner’s Manual: All machinery and
machining equipment presents serious
injury hazards to untrained users. To
reduce the risk of injury, anyone who uses
THIS item MUST read and understand
this entire manual before starting.
2. Personal Protective Equipment:
or servicing this item may expose the user
to flying debris, dust, smoke, dangerous
chemicals, or loud noises. These hazards
can result in eye injury, blindness, longterm respiratory damage, poisoning,
cancer, reproductive harm or hearing loss.
Reduce your risks from these hazards
by wearing approved eye protection,
respirator, gloves, or hearing protection.
Operating
Moderate injury or fire
MAY occur.
Machine or property
damage may occur.
3. Trained/Supervised Operators Only:
Untrained users can seriously injure
themselves or bystanders. Only allow
trained and properly supervised personnel
to operate this item. Make sure safe
operation instructions are clearly
understood. If electrically powered, use
padlocks and master switches, and remove
start switch keys to prevent unauthorized
use or accidental starting.
4. Guards/Covers:
moving parts during operation may cause
severe entanglement, impact, cutting,
or crushing injuries. Reduce this risk by
keeping any included guards/covers/doors
installed, fully functional, and positioned
for maximum protection.
Accidental contact with
-8-
Page 11

For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09 Model SB1021/SB1022
SAFETY
5. Entanglement: Loose clothing, gloves,
neckties, jewelry or long hair may
get caught in moving parts, causing
entanglement, amputation, crushing,
or strangulation. Reduce this risk by
removing/securing these items so they
cannot contact moving parts.
6. Mental Alertness: Operating this item
with reduced mental alertness increases
the risk of accidental injury. Do not let a
temporary influence or distraction lead to a
permanent disability! Never operate when
under the influence of drugs/alcohol, when
tired, or otherwise distracted.
7. Safe Environment:
powered equipment in a wet environment
may result in electrocution; operating near
highly flammable materials may result in a
fire or explosion. Only operate this item in
a dry location that is free from flammable
materials.
8. Electrical Connection: With electically
powered equipment, improper connections
to the power source may result in
electrocution or fire. Always adhere to all
electrical requirements and applicable
codes when connecting to the power source.
Have all work inspected by a qualified
electrician to minimize risk.
9. Disconnect Power: Adjusting or servicing
electrically powered equipment while it
is connected to the power source greatly
increases the risk of injury from accidental
startup. Always disconnect power
BEFORE any service or adjustments,
including changing blades or other tooling.
Operating electrically
11. Chuck Keys or Adjusting Tools:
to adjust spindles, chucks, or any moving/
rotating parts will become dangerous
projectiles if left in place when the machine
is started. Reduce this risk by developing
the habit of always removing these tools
immediately after using them.
12. Work Area:
increase the risks of accidental injury.
Only operate this item in a clean, nonglaring, and well-lighted work area.
13. Properly Functioning Equipment:
maintained, damaged, or malfunctioning
equipment has higher risks of causing
serious personal injury compared to
those that are properly maintained.
To reduce this risk, always maintain
this item to the highest standards and
promptly repair/service a damaged or
malfunctioning component. Always follow
the maintenance instructions included in
this documentation.
14. Unattended Operation:
powered equipment that is left unattended
while running cannot be controlled and is
dangerous to bystanders. Always turn the
power OFF before walking away.
15. Health Hazards: Certain cutting fluids
and lubricants, or dust/smoke created
when cutting, may contain chemicals
known to the State of California to cause
cancer, respiratory problems, birth defects,
or other reproductive harm. Minimize
exposure to these chemicals by wearing
approved personal protective equipment
and operating in a well ventilated area.
Clutter and dark shadows
Electrically
Tools used
Poorly
10. Secure Workpiece/Tooling:
workpieces, cutting tools, or rotating
spindles can become dangerous projectiles
if not secured or if they hit another object
during operation. Reduce the risk of this
hazard by verifying that all fastening
devices are properly secured and items
attached to spindles have enough clearance
to safely rotate.
Loose
16. Difficult Operations:
difficult operations with which you are
unfamiliar increases the risk of injury.
If you experience difficulties performing
the intended operation, STOP! Seek an
alternative method to accomplish the
same task, ask a qualified expert how the
operation should be performed, or contact
our Technical Support for assistance.
Attempting
-9-
Page 12

Model SB1021/SB1022
SAFETY
For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09
Additional Metal Cutting Bandsaw Safety
Blade Condition: Do not operate with a
1.
dull, cracked or badly worn blade—they can
break during use or greatly decrease cutting
performance. Inspect blades for cracks and
missing teeth before each use.
Blade Replacement: Wear gloves to protect
2.
hands and safety glasses to protect eyes
when replacing the blade. When replacing
blades, make sure teeth face forward and
down toward the table in the direction of
blade travel.
Workpiece Handling: Your hands can be cut
3.
or drawn into the blade during operation if
the workpiece moves unexpectedly. Always
keep your hands a safe distance away from
the moving blade.
Welding And Grinding Safety: The welding
4.
station can be hazardous if used incorrectly
and without proper personal protection.
Always wear welding-approved gloves,
eye protection, and clothing when welding
blades. Touching any metal parts of the
blade, welder, or machine when activating
the welder could lead to electrocution.
Welding near flammables could cause a fire.
Hot Surfaces: Be aware that touching hot
5.
workpieces or chips after welding, grinding,
or cutting can cause burns.
7. Magnesium Fire Hazard: Use EXTREME
CAUTION if cutting magnesium. Using
the wrong cutting fluid or overheating the
material could lead to an extremely hot fire
that is difficult to extinguish. Additionally,
do not allow magnesium swarf or dust to pile
up around the machine and only dispose of
the waste using approved methods.
Entanglement Hazards: Always keep the
8.
blade guard correctly positioned and wheel
doors closed and secured when bandsaw is in
operation. Loose clothing, jewelry, long hair
and work gloves can be drawn into working
parts.
Maintenance/Service: All inspections,
9.
adjustments, and maintenance are to be
done with the power OFF and the plug
pulled from the outlet. Wait for all moving
parts to come to a complete stop.
Unstable Workpieces: Workpieces that
10.
cannot be supported or stabilized without
a vise or jig should not be cut on a vertical
metal-cutting bandsaw, because they can
unexpectedly move while cutting and
draw the operator's hands into the blade
causing serious personal injury. Examples
are chains, cables, round or oblong-shaped
workpieces, workpieces with internal or
built-in moving or rotations parts, etc.
Cutting Fluid Safety: This machine is
6.
designed for dry cutting operations. Floodtype cutting fluid setups should not be used
because the machine is not waterproof.
-10-
Clearing Chips: Metal chips can easily cut
11.
skin—even through a piece of cloth. Avoid
clearing chips by hand or with a rag. Use a
brush or vacuum to clear metal chips.
Page 13

For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09 Model SB1021/SB1022
prop
PREPARATION
Preparation Overview
PREPARATION
Things You'll Need
The purpose of the preparation section is to help
you prepare your machine for operation.
The typical preparation process is as follows:
1. Unpack the machine and inventory the
contents of the box/crate.
2. Clean the machine and its components.
3. Identify an acceptable location for the
machine and move it to that location.
4. Level the machine and either bolt it to the
floor or place it on mounts.
5. Assemble the loose components and make
any necessary adjustments or inspections to
ensure the machine is ready for operation.
6. Connect the machine to the power source.
7. Test run the machine to make sure it
functions
erly and is ready for operation.
During the setup process, operation, and
maintenance of your machine, you'll need the
following items:
For Lifting
s !FORKLIFTOROTHERPOWERLIFTINGDEVICE
rated for the weight of the machine.
s ,IFTING3TRAP or Chain (rated for at least
1000 lbs.)
For Power Connection
s !QUALIFIEDELECTRICIANTOENSUREASAFE
and code-compliant connection to the
power source. (Refer to Page 16 for
details.)
For Assembly
s Cotton Rags
s Mineral Spirits
s 3AFETY'LASSES
s Oil Can with any General Machine Oil
s Blade Tension Tool
s Grease Gun with any API GL 2 Grease
s Stiff Grease Brush
s Phillips Screwdriver #2
s &LOOR-OUNTING(ARDWARE!S.EEDED
s Hex Wrench 5mm
s Hex Wrench 6mm
s Combo Wrench
Socket
1
⁄2" or Ratchet and 1⁄2"
Unpacking
This item was carefully packaged to prevent
damage during transport. If you discover any
damage, please immediately call Customer
Service at (360) 734-1540 for advice. You may
need to file a freight claim, so save the containers
and all packing materials for possible inspection
by the carrier or its agent.
-11-
Page 14
Model SB1021/SB1022
A
PREPARATION
Cleaning & Protecting
For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09
The unpainted surfaces are coated at the factory
with a heavy-duty rust preventative that
prevents corrosion during shipment and storage.
The benefit of this rust preventative is that it
works very well. The downside is that it can be
time-consuming to thoroughly remove.
Be patient and do a careful job when cleaning
and removing the rust preventative. The time
you spend doing this will reward you with
smooth-sliding parts and a better appreciation
for the proper care of the unpainted surfaces.
lthough there are many ways to successfully
remove the rust preventative, we have cleaned
thousands of machines and found the following
process to be the best balance between efficiency
and minimized exposure to toxic fumes or
chemicals.
Before cleaning, gather the following:
s $ISPOSABLErags
s #LEANERDEGREASER (certain citrus-based
degreasers work extremely well and they
have non-toxic fumes)
s 3AFETYGLASSESDISPOSABLEGLOVES
Avoid chlorine-based solvents, such as
acetone or brake parts cleaner that may
damage painted surfaces. Always follow the
manufacturer’s instructions when using any
type of cleaning product.
Basic steps for removing rust preventative:
1. Put on safety glasses and disposable gloves.
2. #OATALLSURFACESTHATHAVERUSTPREVENTATIVE
with a liberal amount of your cleaner or
degreaser and let them soak for a few
minutes.
3. Wipe off the surfaces. If your cleaner or
degreaser is effective, the rust preventative
will wipe off easily.
Many cleaning solvents are
toxic if inhaled. Minimize
your risk by only using
these products in a well
ventilated area.
Note: Automotive degreasers, mineral spirits, or
7$sCANBEUSEDTOREMOVERUSTPREVENTATIVE
Before using these products, though, test them
on an inconspicuous area of a painted area to
make sure they will not damage it.
Gasoline and petroleum
products have low flash
GAS
points and can explode
or cause fire if used for
cleaning. Avoid using these
products to remove rust
preventative.
Note: To clean off thick coats of rust preventative
on flat surfaces, such as beds or tables, use
A0,!34)#PAINTSCRAPERTOSCRAPEOFFTHE
majority of the coating before wiping it off
WITHYOURRAG$ONOTUSEAMETALSCRAPEROR
it may scratch the surface.)
4. Repeat Steps 2–3 as necessary until clean,
then coat all unpainted surfaces with a
quality metal protectant or light oil to
prevent rust.
-12-
Page 15
For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09 Model SB1021/SB1022
PREPARATION
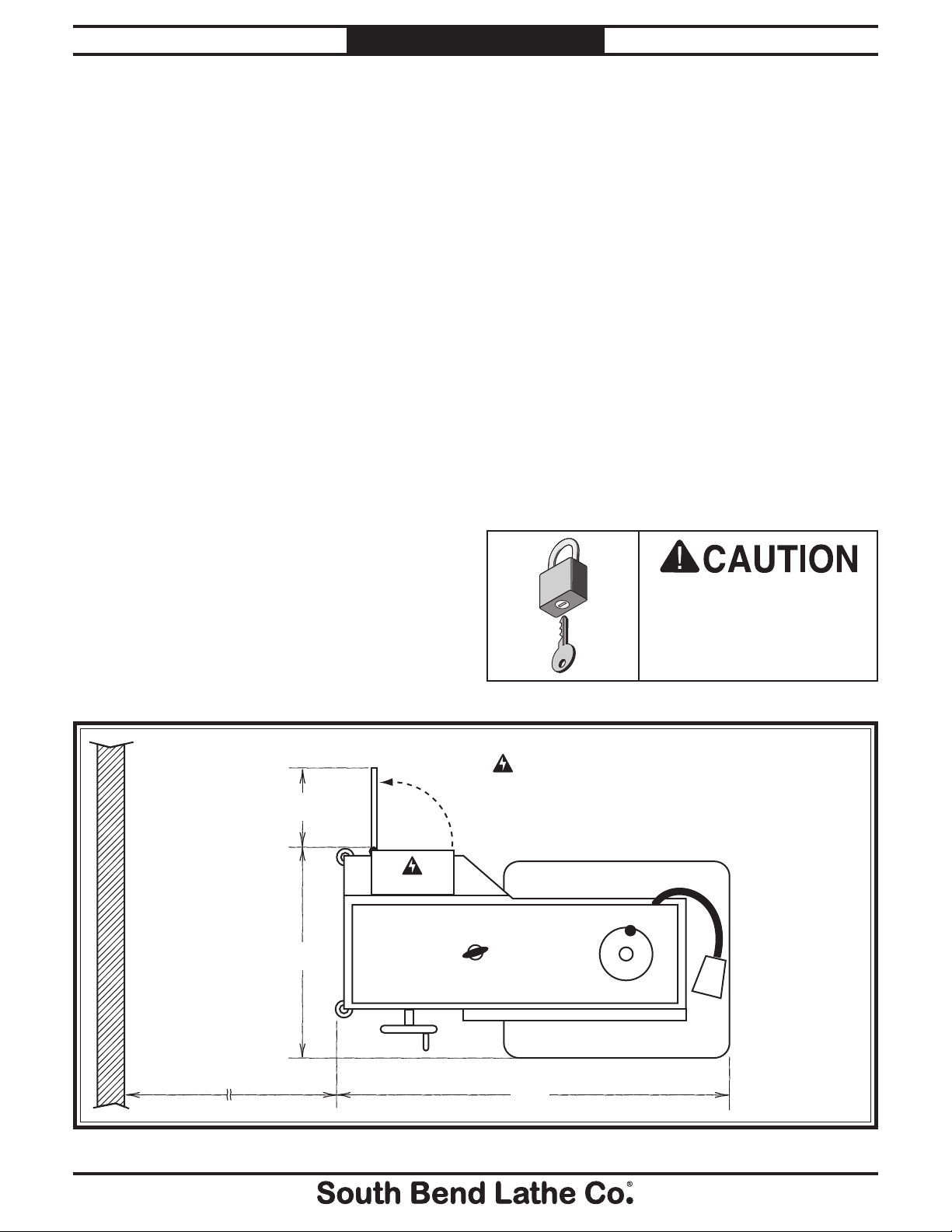
Location
Physical Environment
The physical environment where your machine
is operated is important for safe operation and
longevity of parts. For best results, operate this
machine in a dry environment that is free from
excessive moisture, hazardous or flammable
chemicals, airborne abrasives, or extreme
conditions. Extreme conditions for this type
of machinery are generally those where the
ambient temperature is outside the range of 41°–
104°F; the relative humidity is outside the range
of 20–95% (non-condensing); or the environment
is subject to vibration, shocks, or bumps.
Electrical Installation
Place this machine near an existing power
source. Make sure all power cords are protected
from traffic, material handling, moisture,
chemicals, or other hazards. Make sure to leave
access to a means of disconnecting the power
source or engaging a lockout/tagout device.
Weight Load
Refer to the Machine Specifications for the
weight of your machine. Make sure that the
surface upon which the machine is placed will
bear the weight of the machine, additional
equipment that may be installed on the machine,
and the heaviest workpiece that will be used.
Additionally, consider the weight of the operator
and any dynamic loading that may occur when
operating the machine.
Space Allocation
Consider the largest size of workpiece that will
be processed through this machine and provide
enough space around the machine for adequate
operator material handling or the installation
of auxiliary equipment. With permanent
installations, leave enough space around
the machine to open or remove doors/covers
as required by the maintenance and service
described in this manual.
Lighting
Lighting around the machine must be adequate
enough that operations can be performed
safely. Shadows, glare, or strobe effects that
may distract or impede the operator must be
eliminated.
8"
Wall
22"
Children or untrained
people may be seriously
injured by this machine.
Only install in an access
restricted location.
= Power connection
30"
37"
Figure 1. Clearances.
-13 -
Page 16
Model SB1021/SB1022
A
PREPARATION
For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09
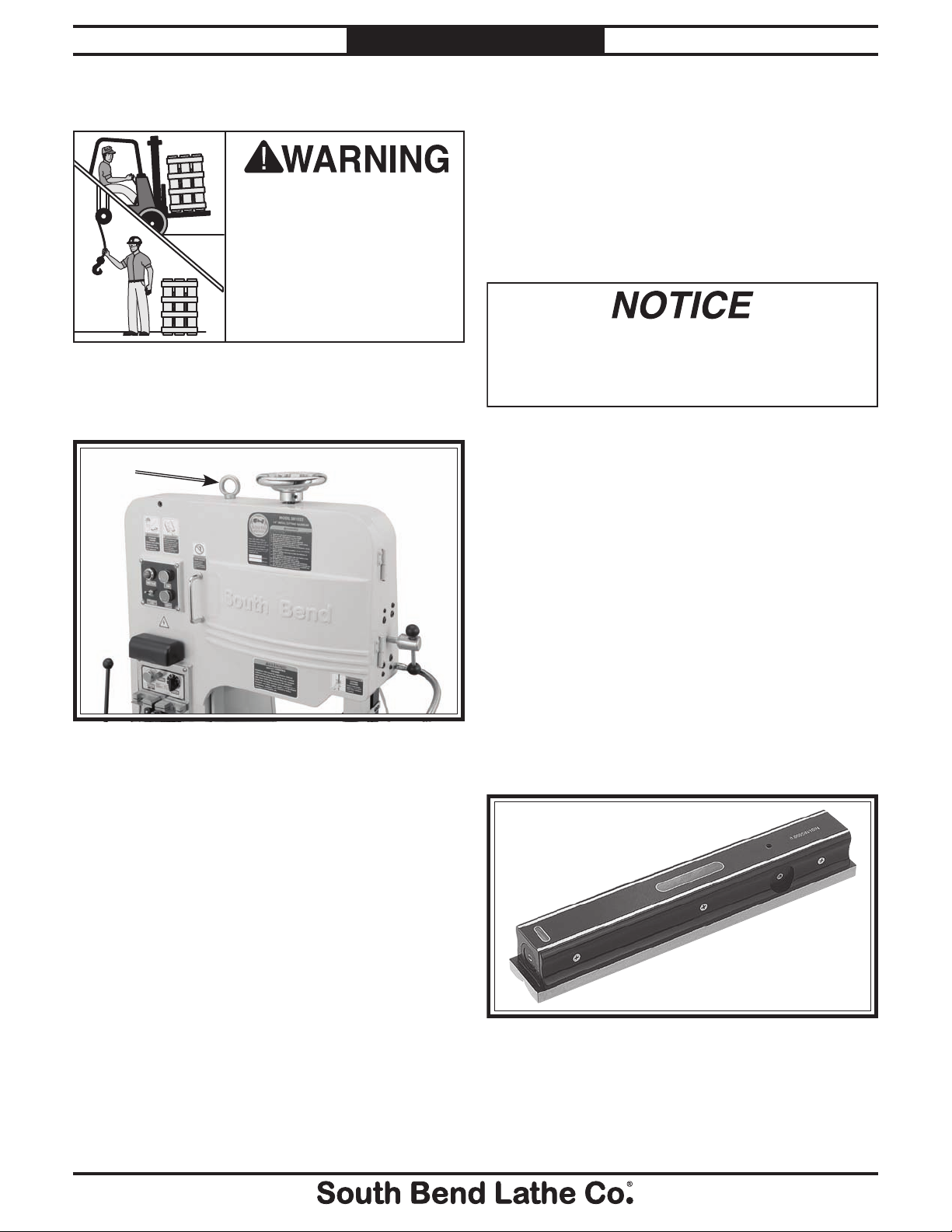
Lifting & Moving
This machine and its
parts are heavy! Serious
personal injury may occur
if safe moving methods are
not used. To reduce the
risk of a lifting or dropping
injury, ask others for help
and use power equipment.
Use a forklift to lift the machine off the pallet
and onto a suitable location using the lifting eye
shown in Figure 2.
Leveling & Mounting
Generally, you can either bolt your machine
to the floor or mount it on machine mounts.
lthough not required, we recommend that you
secure the machine to the floor and level it while
doing so. Because this is an optional step and
floor materials may vary, hardware for securing
the machine to the floor is not included.
We strongly recommend securing your
machine to the floor if it is hardwired to the
power source. Consult with your electrician to
ensure compliance with local codes.
Leveling
Leveling machinery helps precision components,
such as bed ways, remain straight and flat
during the lifespan of the machine. Components
on an unleveled machine may slowly twist due to
the dynamic loads placed on the machine during
operation.
For best results, use a precision level that
is at least 12" long and sensitive enough to
show a distinct movement when a 0.003" shim
(approximately the thickness of one sheet of
standard newspaper) is placed under one end of
the level.
Figure 2. Lifting location.
See the figure below for an example of a high
precision level.
Figure 3. Example of a precision level.
-14-
Page 17
For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09 Model SB1021/SB1022
A
PREPARATION
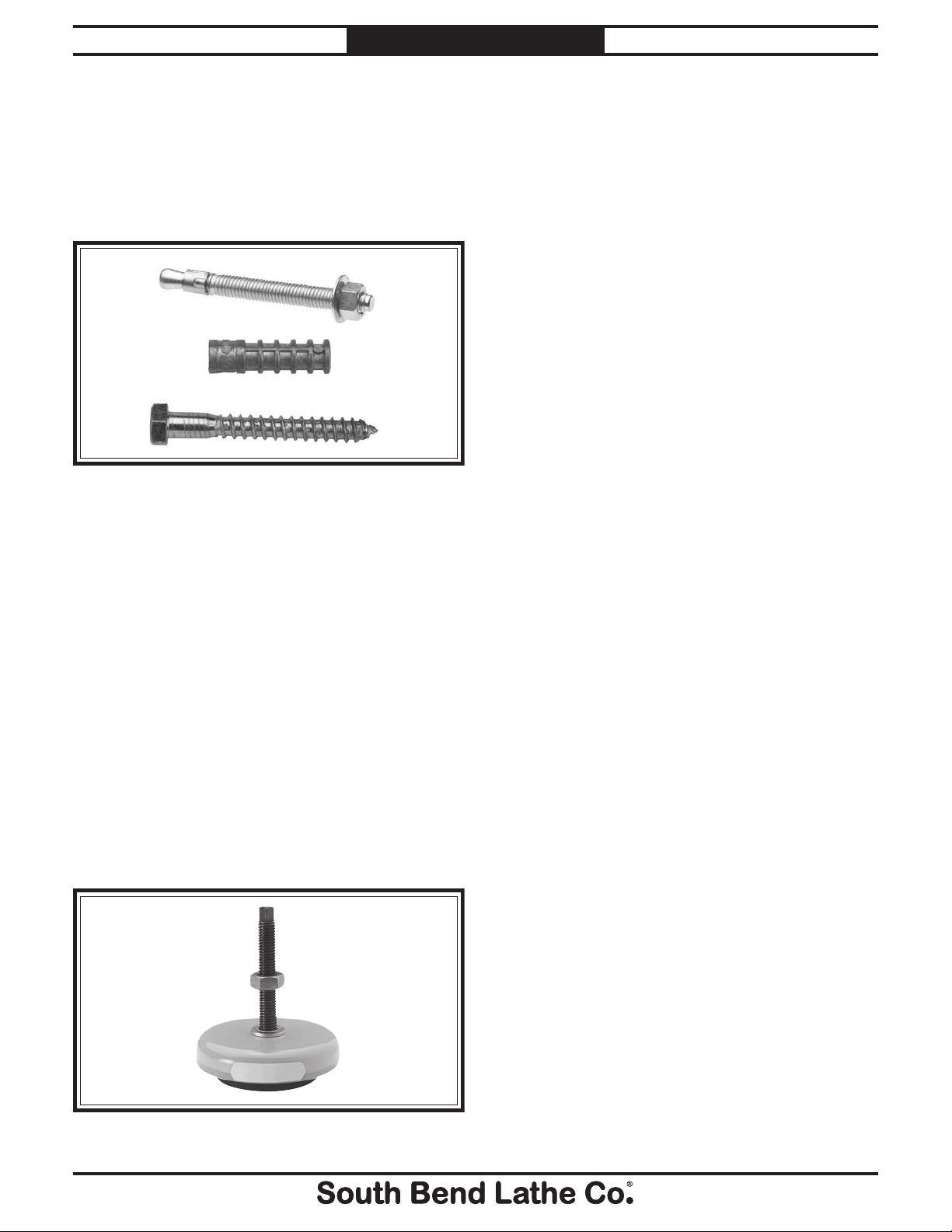
Bolting to Concrete Floors
Lag screws and anchors, or anchor studs
(below), are two popular methods for securing
machinery to a concrete floor. We suggest you
research the many options and methods for
securing your machine and choose the best one
for your specific application.
Anchor
Stud
Lag Screw
and Anchor
Figure 4. Common types of fasteners for bolting
machinery to concrete floors.
Machine Mounts
Machine mounts are rubber pads mounted to
a threaded stud, which can be fastened to the
bottom of the machine.
Assembly
This machine comes pre-assembled from the
factory. However, tension has been removed from
the blade for shipping purposes. Before operating
the machine for the first time, you MUST make
sure the blade is properly tensioned. Refer to the
Blade Tensioning procedure on Page 23 for
instructions about how to do this.
Initial Lubrication
Your machine was lubricated at the factory,
but we strongly recommend that you inspect all
lubrication points yourself and provide additional
lubrication if necessary. Refer to Lubrication on
Page 33 for specific details.
Inspections &
Adjustments
The following list of adjustments were performed
at the factory before your machine was shipped:
Machine mounts offer certain advantages such
as ease of installation, vibration dampening, and
easy leveling. They also make it easier to relocate
the machine later on.
The disadvantage of machine mounts is that the
machine can shift or move over time. For this
reason, electrical codes may limit their use if
the machine is hardwired to the power source.
lso, mounts may reduce the total surface area
of machine-to-floor contact, depending on the
design of the machine.
s Blade Guide Adjustment ..............Page 26
s V-Belt Adjustment ..........................Page 34
s Table Calibration ...........................Page 35
s Blade Tracking ................................Page 35
s Guide Post Alignment ...................Page 36
Be aware that machine components can shift
during the shipping process. Pay careful
attention to these adjustments as you test run
your machine. If you find that the adjustments
are not set according to the procedures in this
manual or your personal preferences, re-adjust
them.
Figure 5. Typical machine mount.
-15 -
Page 18

Model SB1021/SB1022
Power Connection
PREPARATION
3. Locate the power transformer in the
electrical panel (see Page 48, Figure 50)
and remove the wire attached to the 110V
terminal and connect it to the 220V terminal.
For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09
Electrocution or fire
may occur if machine is
ungrounded, incorrectly
connected to power, or
connected to an undersized
circuit. Use a qualified
electrician to ensure a safe
power connection.
Once your machine is set up and assembled as
previously described in this manual, it is ready to
be connected to the power source.
Use the information in this section to determine
the power source requirements needed to operate
this machine. If your existing power source does
not meet the stated requirements, consult with a
qualified electrician about running a new circuit.
Note About Extension Cords: Using an
incorrectly sized extension cord may decrease the
life of electrical components on your machine.
Note About 3-Phase Power (SB1022 Only):
DO NOT use a static phase converter to create
3-phase power—it can quickly decrease the life
of electrical components on your machine. If you
must use a phase converter, only use a rotary
phase converter and connect the wild wire to the
correct power connection terminal, shown in the
wiring diagram on Page 47.
220V Conversion for SB1021
Wiring diagrams are provided on Pages 44 and
46 in this manual, showing the Model SB1021
wired for both 110V and 220V. Refer to these
diagrams when following this procedure.
4. Turn the dial on the overload relay (see
Page 48, Figure 50) from 14A for 110V to
7A for 220V.
5. Locate the welding transformer in the
control panel (see Page 48, Figure 49).
Remove the wire connected to the #2
terminal and move it to the #5 terminal;
remove the wire connected to the #4 terminal
and move it to the #7 terminal.
6. The machine is now wired for 220V.
SB1021 110V (Prewired) Power
Source
Full Load Amp Draw ............................ 13.6 Amps
Permissible Voltage Range ....................99V–121V
Phase ................................................. Single-Phase
Frequency ...................................................... 60 Hz
Minimum Circuit Size ............................. 20 Amps
Included Plug ...................................... NEMA 5-15
Minimum Extension Cord Size ................14 AWG
Maximum Extension Cord Length ................ 50 ft.
SB1021 (220V) Power Source
Full Load Amp Draw .............................. 6.8 Amps
Permissible Voltage Range ..................198V–242V
Phase ................................................. Single-Phase
Frequency ...................................................... 60 Hz
Minimum Circuit Size ............................. 15 Amps
Recommended Plug/Receptacle .......... NEMA 6-15
Minimum Extension Cord Size ................14 AWG
Maximum Extension Cord Length ................ 50 ft.
SB1022 (220V 3-Phase) Power
To convert the Model SB1021 to operate on
220V:
1. DISCONNECT BANDSAW FROM POWER!
2. Rewire the motor for 220V, as shown in the
diagram on the inside of the motor junction
box. If there is not a diagram in the junction
box, use the motor wiring diagram in this
manual (see Page 46).
-16 -
Source
Full Load Amp Draw .............................. 3.6 Amps
Permissible Voltage Range ..................198V–242V
Phase ..........................................................3-Phase
Frequency ...................................................... 60 Hz
Minimum Circuit Size ............................. 15 Amps
Recommended Plug/Receptacle ......NEMA L15-15
Minimum Extension Cord Size ................16 AWG
Maximum Extension Cord Length ................ 50 ft.
Page 19

For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09 Model SB1021/SB1022
PREPARATION
4. Connect the machine to the power source.
Test Run
After all preparation steps have been completed,
the machine and its safety features must be
tested to ensure correct operation. If you discover
a problem with the operation of the machine or
its safety components, do not operate it further
until you have resolved the problem.
Note: Refer to Troubleshooting on Page 38 for
solutions to common problems that occur with
all metal bandsaws. If you need additional help,
contact our Tech Support at (360) 734-1540.
To reduce the risk of
serious injury when using
this machine, read and
understand this entire
manual before beginning
any operations.
5. Push the ON button. The green motor light
will illuminate and the motor will start.
6. Verify that the machine is operating
correctly. When operating correctly, the
machine runs smoothly with little or no
vibration or rubbing noises.
Note: For three phase-models, verify that the
blade is moving downward toward the table.
If so, the motor is running in the correct
direction. Proceed to Step 7.
s If the blade is moving in the upward
direction out of the table, stop the
machine immediately. It is likely wired
"out of phase." To correct this problem,
disconnect the machine from the power
source, and switch any two incoming
power wires at the main terminal block
(refer to Figure 50 on Page 48).
To test run your machine:
1. Read and follow the safety instructions at
the beginning of the manual, take required
safety precautions, and make sure the
machine is set up and adjusted properly
2. Clear away all tools and objects used during
assembly and preparation.
3. Make sure the blade is properly tensioned
and the blade guides are positioned correctly
(for detailed instructions, refer to Blade
Tensioning on Page 23, and Adjusting
Blade Guides on Page 26).
7. Adjust the blade speed through the full
range of operation. The speed should change
as you make the adjustments.
8. Press the STOP button, the green motor
light will go out, and the bandsaw will stop.
9. Turn the work lamp and the welding lamp
ON and OFF.
10. Turn the grinder ON and OFF.
-17-
Page 20
Model SB1021/SB1022
OPERATION
For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09
OPERATION
Operation Overview
The purpose of the operation section is to
familiarize you with the basic controls,
terminology, capabilities, and adjustments that
are necessary to use this machine.
To better understand the remaining parts of
this section, please take a moment to read this
overview.
To reduce the risk of
serious injury when using
this machine, read and
understand this entire
manual before beginning
any operations.
To complete a typical operation, the operator
does the following:
1. Examines the workpiece to make sure it is
suitable for cutting.
4. Adjusts the upper blade guide height to
approximately
for maximum blade support.
5. Puts on safety glasses, and rolls up sleeves
or secures any clothing or hair that could get
entangled with moving parts.
1
⁄8"–1⁄4" above the workpiece
Loose hair, clothing, or
jewelry could get caught
in machinery and cause
serious personal injury.
Keep these items away
from moving parts at all
times to reduce this risk.
During operation, small
metal chips may become
airborne, leading to serious
eye injury. Wear safety
glasses to reduce this risk.
2. Checks to make sure blade tension is correct,
and the blade guides are positioned correctly.
3. Marks the cut line on the workpiece.
Workpieces that cannot be stabilized from
unexpected movement should not be cut with
a vertical metal bandsaw due to the increased
risk of the operator's hands slipping into the
blade. Examples are chains, cables, balls, or
workpieces with built-in moving parts.
6. Turns the bandsaw ON, and adjusts blade
speed for the type of material being cut.
7. Presses the workpiece against the blade,
using light and even pressure and following
the cut line with the blade.
Depending on the workpiece material, the
operator may squirt a small amount of
cutting fluid at the cutting area to keep it
from overheating and smoking.
8. Turns the bandsaw OFF.
-18 -
Page 21

For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09 Model SB1021/SB1022
OPERATION
Controls
Refer to Figures 6–8 and the following
descriptions to become familiar with the basic
controls of this machine.
Motor Light: Lights when the ON button is
A.
pressed and there is power to the machine.
On Button: Turns the bandsaw motor ON.
B.
Off Button: Turns the bandsaw motor OFF.
C.
Clamping Pressure Dial: Sets the correct
D.
amount of pressure for pressing the ends of
the blades against each other.
Welding Clamp: Holds a segment of the
E.
bandsaw blade to be welded.
Lock Lever: Secures bandsaw blade for
F.
welding operations when rotated up.
Grinder Switch: Turns grinding wheel ON
G.
and OFF.
Shear Lever: Cuts the bandsaw blade.
H.
Welding Button: Activates the process of
I.
fusing the two blades together.
L. Variable Speed Handwheel: Adjusts blade
speed from 88 to 384 FPM.
L
Figure 7. Variable speed handwheel.
M. Blade Tensioning Handwheel: Increases or
decreases blade tension when rotated.
Guide Post Elevation Knob: Raises or
N.
lowers the guide post and upper blade guide
assembly.
Guide Post Lock Knob: Secures the guide
O.
post and upper blade guide assembly in
position.
M
J. Annealing Button: Heats up the blade joint,
then allows it to cool in a gradual manner to
establish weld strength.
Welder's Lamp Switch: Illuminates
K.
welding station when turned ON.
A
K
J
I
H
G
Figure 6. Front controls.
B
C
D
E
F
O
N
Figure 8. Blade controls.
-19 -
Page 22

Model SB1021/SB1022
OPERATION
For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09
Blade Selection
Selecting the right blade for the cut requires a
knowledge of various blade characteristics.
Blade Terminology
Wavy
Alternate
Figure 9. Bandsaw blade terminology.
Raker
Blade Length
Measured by the blade circumference, blade
lengths are usually unique to the brand of your
bandsaw and the distance between the wheels.
Model Blade Length Range
SB1021/SB1022 ................................ 118
1
⁄4"–1191⁄2"
Blade Width
Measured from the back of the blade to the tip
of the blade tooth (the widest point), blade width
is often the first consideration given to blade
selection. Blade width dictates the largest and
smallest curve that can be cut, as well as how
accurately it can cut a straight line—generally
the wider the blade, the straighter it will cut.
Model Blade Width Range
SB1021/SB1022 ............................................
Always pick the blade width that best suits your
operation.
1
⁄8"–1⁄2"
A. Kerf: The amount of material removed by
the blade during cutting.
Tooth Set: The amount each tooth is bent
B.
left or right from the blade.
Gauge: The thickness of the blade.
C.
Blade Width: The widest point of the blade
D.
measured from the tip of the tooth to the
back edge of the blade.
Tooth Rake: The angle of the tooth face
E.
from a line perpendicular to the length of the
blade.
Gullet Depth: The distance from the tooth
F.
tip to the bottom of the curved area (gullet).
Tooth Pitch: The distance between tooth
G.
tips.
Curve Cutting: Use the chart in Figure 10
to choose the correct blade for curve cutting.
Determine the smallest radius curve that will be
cut on your workpiece and use the corresponding
blade width.
The list below shows the minimum
radius that can be cut by each blade
width.
Width Radius
1
⁄8" ....................................1⁄8"
3
⁄16" ...................................3⁄8"
1
⁄4'' ....................................5⁄8''
3
⁄8'' .................................... 11⁄4''
1
⁄2'' .................................... 21⁄2''
Figure 10. Blade width radii.
Blade Back: The distance between the
H.
bottom of the gullet and the back edge of the
blade.
Blade Pitch or TPI: The number of teeth per
I.
inch measured from gullet to gullet.
-20-
Page 23

For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09 Model SB1021/SB1022
OPERATION
Tooth Set
Three common tooth sets are alternate, wavy,
and raker (see Figure 11). Each removes
material in a different manner to make the kerf
in the workpiece.
Wavy
Alternate
Raker
Standard (or Raker)
Variable Pitch (VP)
Variable Pitch Positive Rake
Hook (or Claw)
Figure 11. Bandsaw blade tooth sets.
Alternate: An all-purpose arrangement of
bending the teeth evenly left and right of the
blade. Generally used for milder metals.
Wavy: Generally three or more teeth in a group
that are bent one way, followed by a non-set
tooth, and then a group bent the other way.
Recommended for straight cuts in thin metals or
thin-wall tubing.
Raker: Three teeth in a recurring group—one
bent left, next one bent right, and then a nonset tooth. The raker set is ideal for most contour
cuts.
Tooth Type
The most common tooth types are described
below and illustrated in Figure 12.
Standard or Raker: Equally spaced teeth set at
a "0" rake angle. Recommended for all purpose
use.
Skip (or Skip Tooth)
Figure 12. Bandsaw blade tooth types.
Variable Pitch (VP): Varying gullet depth and
tooth spacing, a "0" rake angle, excellent chip
removing capacity, and smooth cutting.
Variable Pitch with Positive Rake: Varying
gullet depth and tooth spacing, a positive rake
angle, better chip formation, and aggressive
cutting.
Hook or Claw: Wide gullets (round or flat),
equally spaced teeth, positive rake angle, and
fast cut with good surface finish.
Skip or Skip Tooth: Wide, flat gullets, a "0" rake
angle, equally spaced teeth, and recommended
for non-ferrous materials.
-21-
Page 24

Model SB1021/SB1022
OPERATION
For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09
Blade Pitch (TPI)
The chart below is a basic starting point for
choosing teeth per inch (TPI) for variable pitch
blades and standard raker set bi-metal blades/
HSS blades. However, for exact specifications
of bandsaw blades that are correct for your
operation, contact the blade manufacturer.
To select the correct blade pitch:
1. Measure the material thickness. This
measurement is the length of cut taken
from where the tooth enters the workpiece,
sweeps through, and exits the workpiece.
2. Refer to the "Material Width/Diameter"
row of the blade selection chart in Figure
13, and read across to find the workpiece
thickness you need to cut.
Material Width/Diameter
Material Shapes
Teeth Per Inch (TPI) for Variable Pitch Blades
3. Refer to the "Material Shapes" row and find
the shape of the material to be cut.
4. In the applicable row, read across to the
right and find the box where the row and
column intersect. Listed in the box is the
minimum TPI recommended for the variable
tooth pitch blades.
5. The "Cutting Speed Rate Recommendation"
section of the chart offers guidelines for
various metals, given in feet per minute
(FPM). Choose the speed closest to the
number shown in the chart.
TOOTH SELECTION
mm
inch
50
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 192
75 100 150 200 250 300 350 400
4/65/8
3/4
1
/
2
31/
2
2/3 1.4/2.5
3/4
2/3
CUTTING SPEED RATE RECOMMENDATION
Material Material Material Material
Carbon
Steel
Angle
Steel
Thin
Tube
Aluminum
Alloy
Copper
Alloy
Speed FPM
(M/Min)
196~354
(60) (108)
180~220
(54) (67)
180~220
(54) (67)
220~534
(67) (163)
229~482
(70) (147)
Tool Steel
High-Speed
Tool Steel
Cold-Work
Tool Steel
Hot-Work
Tool Steel
Oil~Hardened
Tool Steel
Speed FPM
(M/Min)
203
(62)
75~118
(25) (36)
95~213
(29) (65)
203
(62)
203~213
(62) (65)
Alloy
Steel
Mold Steel
Water
Hardened
Tool Steel
Stainless
Steel
CR Stainless
Steel
Figure 13. General guidelines for blade selection and speed chart.
Speed FPM
(M/Min)
111~321
(34) (98)
246
(75)
242
(75)
85
(26)
85~203
(26) (62)
Free Machining
Stainless Steel
Gray
Cast Iron
Ductile
Austenitic
Cast Iron
Malleable
Cast Iron
Plastics
450
1.5/.8
Speed FPM
(M/Min)
150~203
(46) (62)
108~225
(33) (75)
65~85
(20) (26)
321
(98)
220
(67)
-22-
Page 25

For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09 Model SB1021/SB1022
!
OPERATION
Blade Changes
!
To replace the blade:
1. DISCONNECT BANDSAW FROM POWER!
2. Open the upper and lower wheel doors,
release tension on the blade, and move the
blade guides away from the blade.
3. Put on heavy gloves, then slide the blade
off the upper and lower wheels, around the
blade post, and through the table slit.
4. Install a new blade in reverse order.
Always disconnect power
to the machine when
changing blades. Failure
to do this may result in
serious personal injury.
All saw blades are
dangerous and may cause
personal injury. To reduce
the risk of being injured,
wear leather gloves when
handling saw blades.
Note: Excessive blade contact with the wheel
flange during operation could lead to blade
and wheel damage.
6. Re-tension the blade (refer to the following
Blade Tensioning section).
7. Rotate the top wheel clockwise by hand
several times to make sure the blade tracks
evenly without wandering across the wheel
surface.
Note: If the blade wanders across the wheel
and away from the flange, the wheel
alignment may need to be adjusted. Refer
to Blade Tracking on Page 35 for detailed
instructions.
8. Adjust the upper and lower blade guides
(refer to Adjusting Blade Guides on
Page 26).
9. Close and secure the upper and lower wheel
doors.
Blade Tensioning
To prolong blade life, release the tension
on the blade if the machine will be idle
for an extended period of time.
5. Position the back edge of the blade so that it
is next to, but not against, the flange of the
top wheel (see Figure 14).
Wheel
Flange
Blade
Figure 14. Back edge of blade next to wheel flange.
Proper blade tension reduces the risk of blade
breakage and improves cutting performance.
To correctly tension the blade:
1. DISCONNECT BANDSAW FROM POWER!
2. Turn the blade tension handwheel until you
feel an average amount of resistance and
the handwheel wants to stop. Then turn the
handwheel an additional
1
⁄2 turn.
-23-
Page 26

Model SB1021/SB1022
OPERATION
For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09
Blade Breakage Blade Care & Break-In
Many conditions may cause a bandsaw blade to
break. Blade breakage is unavoidable, in some
cases, since it is the natural result of the peculiar
stresses that bandsaw blades must endure. Blade
breakage is also due to avoidable circumstances.
Avoidable blade breakage is most often the
result of poor care or judgment on the part of the
operator when mounting or adjusting the blade
or support guides.
The most common causes of blade breakage
are:
s Faulty alignment or adjustment of the blade
guides.
s Forcing or twisting a wide blade around a
tight radius.
s Feeding the workpiece too fast.
s Dull or damaged teeth.
s Over-tensioned blade.
s Top blade guide assembly set too high above
the workpiece. Adjust the top blade guide
assembly so that there is approximately
1
⁄8"–1⁄4" between the bottom of the assembly
and the workpiece.
Note: The blade guide assembly can be lowered
to within 2
s Using a blade with a lumpy or improperly
finished braze or weld.
s Continuously running the bandsaw when not
in use.
1
⁄2" of the table surface.
Blade Care
A bandsaw blade is a delicate piece of steel that
is subjected to tremendous strain. A bandsaw
blade will last longer if you give it fair treatment
and always use the appropriate feed rate for your
operation.
Be sure to select blades with the proper width,
set, type, and pitch for each application. The
wrong blade will produce unnecessary heat and
have a shortened life.
A clean blade will perform much better than
a dirty blade. Dirty or gummed up blades
pass through the cutting material with much
more resistance than clean blades. This extra
resistance also causes unnecessary heat.
Blade Break-In
The tips and edges of a new blade are extremely
sharp. Cutting at too fast of a feed rate can
fracture these tips and edges, causing the blade
to quickly become dull. Properly breaking-in a
blade allows these sharp edges to wear properly
without fracturing, thus keeping the blade sharp
longer.
To properly break-in a new blade:
1. Choose the correct speed for the blade and
material of the operation.
2. Reduce the feed pressure by half for the first
50–100 in
3. To avoid twisting the blade when cutting,
adjust the feed pressure when the total
width of the blade is in the cut.
2
of material cut.
s Leaving the blade tensioned when not in use.
s Using the wrong blade pitch (TPI) for the
workpiece thickness. The general rule of
thumb is to have no fewer than two teeth
in contact with the workpiece at all times
during cutting.
-24-
4. Use the Chip Inspection Chart on Page
25 to ensure that the optimal blade speed
and feed rate are being used.
Page 27

For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09 Model SB1021/SB1022
OPERATION
Blade Speed Chart
Use the blade speed chart in Figure 15 to
determine an appropriate speed to start with,
then examine the chips once you start cutting to
determine which way to adjust the speed or your
feed rate.
Material
Thickness
Alloy Steel 90 125 160
Aluminum 185 250 315
Brass (Soft) 375 500 625
Brass (Hard) 150 200 250
Bronze 150 200 250
Copper 185 250 315
Cast Iron 90 125 160
High Speed Steel 35 50 65
Low Carbon Steel 90 125 160
Medium Carbon Steel 75 100 125
Figure 15. Dry cutting blade speed chart.
Dry Cutting Speed (FPM)
0 - 1/2" 1/2" - 1" 1" +
Chip Inspection Chart
The best method for evaluating the cutting speed and feed rate for an operation is to inspect the chips
created by the cut. Refer to the chip inspection chart below for chip inspection guidelines.
Chip
Appearance
Chip
Description
Chip
Color
Blade
Speed
Feed
Pressure
Other
Actions
Thin & Curled Silver Good Good
Hard, Thick &
Short
Hard, Strong &
Thick
Hard, Strong &
Thick
Hard & Thin Silver Increase Decrease
Straight & Thin Silver Good Increase
Powdery Silver Decrease Increase
Brown or Blue Increase Decrease
Brown or Blue Increase Decrease
Silver or Light
Brown
Good
Decrease
Slightly
Check Blade
Pitch
Check Blade
Pitch
Curled Tight & Thin Silver Good Decrease
Figure 16. Chip inspection chart.
Check Blade
Pitch
-25-
Page 28

Model SB1021/SB1022
!
!
OPERATION
For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09
Positioning Guide Post
The guide post assembly is used for two
purposes: 1) To properly position the blade guard
to protect the operator from the exposed blade
between the workpiece and the upper wheel
housing, and 2) to position the upper blade
guides close to the workpiece for maximum blade
support.
To properly position the guide post:
1. DISCONNECT BANDSAW FROM POWER!
2. Hold the guide post knob with one hand and
loosen the guide post lock knob with the
other (Figure 17).
Guide Post Lock Knob
Adjusting Blade
Guides
The blade guides provide side-to-side and
rear support to keep the blade straight while
cutting. The blade guides and the rear support
have tungsten steel facing to reduce wear on
the guides. Properly adjusted blade guides are
essential to making accurate cuts.
If the blade guides rub the blade at either the
top or bottom of the blade, follow the guide post
alignment procedure on Page 36 for adjusting
the guide post parallel with the blade.
To properly adjust the upper and lower blade
guides:
1. DISCONNECT BANDSAW FROM POWER!
2. Make sure the bandsaw blade is properly
tensioned (Page 23) and the guide post is
locked.
Guide Post
Knob
Guide Post
Figure 17. Guide post assembly.
3. Position the bottom of the upper blade guides
approximately
then re-tighten the lock knob to secure the
setting.
1
⁄4" above the workpiece,
All saw blades are
dangerous and may cause
personal injury. To reduce
the risk of being injured,
wear leather gloves when
handling saw blades.
3. Use a Phillips head screwdriver to remove
the flange screws that secure the lower blade
guide cover, then remove the cover to access
the cap screws in the next step.
4. Use a 5mm hex wrench to loosen the cap
screws that secure the blade guide bracket
and blade support (see Figures 18–19).
Blade Guide Bracket
Cap Screw
Blade Support
Cap Screw
Figure 18. Upper blade guides and bracket.
-26-
Page 29

For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09 Model SB1021/SB1022
!
!
!
OPERATION
Blade Support
Cap Screw
Blade Guide
Bracket Cap
Screw
Figure 19. Lower blade guides and bracket.
5. Position the blade guides so that they are
approximately
(see Figure 20), then re-tighten the blade
guide bracket cap screw.
1
⁄16" behind the tooth gullets
Note: The blade guides must be adjusted far
enough back so that they are behind the
tooth gullets when the blade is deflected
back against the blade support.
7. Use a 3mm hex wrench to loosen the button
head cap screws that secure the upper blade
guard, to allow access to the blade support
cap screw in the next step.
8. Use a 5mm hex wrench to loosen the blade
guide cap screws (see Figure 21).
9. Fold a crisp dollar bill in half and place it
over the blade (between the blade guides and
the blade), as shown in Figure 22.
Blade Guide
1
⁄16"
Figure 20. Blade guides positioned approximately 1⁄16"
behind tooth gullets.
6. Slide the blade support (see Figure 21) up
to, but not touching, the back of the blade,
then re-tighten the blade support cap screw.
Blade Guide Cap
Screws
Dollar on Both
Sides of Blade
Figure 22. Using a dollar bill to set blade guide
spacing (blade guide cover removed for clarity).
10. Lightly pinch the dollar bill against the
blade with the blade guides, re-position the
air nozzle if necessary, then re-tighten the
blade guide cap screws.
Note: The goal is to position the blade guides
as close as possible to the blade without
touching it.
11. Secure the upper blade guide, then re-install
the lower blade guard cover.
Blade
Support
Figure 21. Blade guide assembly (upper assembly
shown without blade for clarity).
-27-
Page 30

Model SB1021/SB1022
OPERATION
For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09
Tilting Table
The bandsaw table tilts 15° to the left and 15° to
the right for basic cut angles, and 10° to the front
and 10° to the back for feed angles. When used
together, compound angled cuts can be made.
To tilt the table left or right:
1. DISCONNECT BANDSAW FROM POWER!
2. Use an 8mm wrench to loosen the two cap
screws on the cut angle trunnion underneath
the rear of the table (see Figure 23).
Cap Screws
Cap Screws
Blade Welding
Being able to quickly and safely weld a bandsaw
blade comes in handy for the following situations:
s 4OREJOINABLADETHATHASBEENPURPOSELY
cut for making an internal contour cut.
s 4OREPAIRABROKENBLADETHATISSTILLSHARP
and useful.
s 4OMAKEANEWBLADEFROMAROLLOFBULK
blade banding.
Your metal cutting bandsaw is equipped with a
blade welder that uses electrical current to heat
and fuse the blade ends together. This process
will leave the joint brittle, so an annealer is
also included to give the blade strength and
flexibility.
Feed Angle Tilt
Scale (One Shown)
Figure 23. Table tilt adjustment controls.
3. Using the cut angle tilt scale, adjust the
angle of the table for your operation, then retighten the cap screws.
Cut Angle Tilt
Scale
To tilt the table forward or backward:
1. DISCONNECT BANDSAW FROM POWER!
2. Use a 6mm hex wrench to loosen both sets
of cap screws on the two feed angle tilt scale
brackets (see Figure 23).
3. Using the two scales, adjust the angle of the
table for cutting a compound angle, then retighten the cap screws.
The electric current that flows through the
blade welder during operation could cause
serious personal injury or death. To reduce
the risk of electrocution or burns, never touch
any metal part of the welding station or blade
during welding or annealing.
To weld the ends of blade together:
1. Turn the bandsaw motor OFF.
2. Place the blade evenly against the back of
the blade shear and firmly pull the handle
down to square off the blade end (see Figure
24).
-28-
Figure 24. Using the blade shear to cut the blade.
Page 31

For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09 Model SB1021/SB1022
OPERATION
Note: To make a proper blade weld, the ends of
the blade must be evenly butted together
during the welding process. If necessary, use
the grinder to square up the ends or remove
any teeth that are in the welding zone (see
Figs. 25–26).
Figure 25. Using the grinder to square up the blade
end.
5. Loosen the welding clamps by pulling the
lock levers down.
6. Position the back of one blade end evenly
against the back of the welding clamp so
that the end is midway between the two
clamps, then rotate the lock lever as far up
as possible to hold the blade end in place (see
Figure 27).
Blade
End
Welding
Clamp
Lock Lever
Welding Zone
Grind Off
Figure 26. Blade ends and welding zone.
For good metal-to-metal contact between the
welding clamps and the blade, make sure the
blade material and the clamps are free from
any debris or flash before each use.
3. To ensure correct electrical continuity while
welding, use mineral spirits to clean off all
oil and debris from the first 6" of each end of
the blade.
4. Set the clamping pressure to 0" with the
clamping pressure dial (Figure 29).
Figure 27. Blade end properly position in welding
clamp and locked in place.
7. Use the illustration in Figure 28 and set the
correct clamping pressure setting for width
of the blade.
Note: The clamping pressure presses the blade
ends together to help form a strong weld.
The pressure scale is an approximation only.
If you have difficulty getting satisfactory
welds, experiment by increasing or
decreasing this pressure.
3
Above
⁄8" Blade
1
⁄4"-3⁄8" Blade
Clamping
Pressure
Dial
Figure 28. Blade clamping settings.
Up to
1
⁄4" Blade
-29-
Page 32

Model SB1021/SB1022
OPERATION
For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09
8. Place the other blade end in the opposite
welding clamp and position it so that it
evenly butts up against the opposing blade
end, then lock it in place by rotating the lock
lever all the way up, as shown in Figure 29.
Note: For a good blade weld, it is critical that the
blade ends evenly butt up against each other
without overlap, gaps, or misalignment.
Annealing
Button
Welding
Button
Clamping
Pressure
Dial
11. Inspect the weld. The welded joint should be
even across the width of the blade with no
gaps (see Figure 30).
Correct
Not Correct
Not Correct
Figure 30. Blade welded joint examples.
— If the weld is satisfactory, continue to
Step 12.
Figure 29. Blade ends in correct position for welding.
Light generated during the welding process
could cause serious eye damage. To reduce
your risk, always use eye protection approved
for welding when using the blade welder.
Burning sparks may be thrown in all
directions while welding. Protect yourself from
injury by not welding near flammables and
wearing spark-resistant clothing/gloves. Keep
fire extinguishing equipment readily available.
9. Press and release the welding button. The
blade ends will be welded together.
10. Rotate the lock levers down to release the
welding clamps, then rotate the clamping
pressure dial to "0".
— If the weld is NOT satisfactory, begin
again at Step 2.
12. Place the blade in the welding clamps with
the weld centered between the clamps and
re-tighten the lock levers.
Note: The welding operation leaves the blade
joint brittle. Annealing allows the material
to cool in gradual manner, giving the weld
strength and flexibility. When annealing, the
blade is heated until it turns a specific color
that is determined by the blade material.
The annealing process is unsuccessful (blade
breaks easily) if the weld is not heated
enough or if it is heated too much. For best
results, contact the blade manufacturer for
the proper annealing color.
-30-
Page 33

For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09 Model SB1021/SB1022
OPERATION
13. Press and hold the annealing button until
the weld zone turns the appropriate color,
then release the button.
Note: If you cannot get the proper annealing
color from the blade manufacturer, use the
recommendations below as a baseline and
experiment from there.
—Carbon Steel ..................... Dull Cherry Red
—Carbon Steel Hard Back ...................... Blue
—Bi-Metal ........................................... Orange
—High Speed Steel .............. Dull Cherry Red
14. Repeat Step 13 three to four more times,
allowing the weld to cool for about 30
seconds between each repetition. Each time
reduce the amount of time you press the
anneal button, to reduce the amount of heat
successively.
15. Allow the blade to cool, then re-inspect the
weld.
17. Re-clamp the blade in the welding clamps
with the joint centered, then repeat the
annealing process twice more. Each time
gradually reduce the amount of time you
anneal the weld.
18. Test the strength and flexibility of the weld
by bending the blade in an arc similar to that
of the bandsaw wheels. The blade should
bend in a smooth circular, rounded shape—
rather than a pointed fold (see Figure 31).
Correct
Not Correct
(Cut and reweld)
16. Grind away the weld bead on the top and
bottom of the joint so that the blade is flat
and will run smoothly on the wheels and
between the blade guides.
Note: Make sure not to grind the teeth or
blade body, or overheat the blade during
grinding—this will weaken the blade. A
small amount of ticking is acceptable during
cutting operations.
Figure 31. Correct blade weld bend for strength and
flexibility.
-31-
Page 34

Model SB1021/SB1022
!
MAINTENANCE
MAINTENANCE
Maintenance Schedule
For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09
Chip Brush
!
For optimum performance from your machine,
follow this maintenance schedule and refer to
any specific instructions given in this section.
Daily:
s #HECKCORRECTLOOSEMOUNTINGBOLTS
s Check/correct damaged or dull saw blade.
s Check/correct worn or damaged wires.
s Clean/protect table.
s #LEANMETALCHIPSFROMUPPERANDLOWER
wheel areas, and empty the chip chute.
s Correct any other unsafe condition.
Monthly:
s #HECKFOR6BELTTENSIONDAMAGEORWEAR
s ,UBRICATETENSIONLEADSCREWSANDGUIDEPOST
rack.
s 2EMOVETHEBLADEANDCLEANTHEWHEELS
Yearly:
s Open rear lower cover, inspect belts, and
tighten all fasteners (see Page 34).
Always disconnect
machine from power before
performing maintenance or
serious personal injury may
result.
Chip Chute
Figure 32. Lower wheel and chip chute.
Dressing Grinding
Wheel
Periodically dress the grinding wheel to square
it up and renew the abrasive surface. Dressing
is done in the same manner as a typical grinding
operation but using a diamond-tipped dressing
tool (see Figure 33).
Cleaning
Use a brush and a shop vacuum to remove chips
and other debris from the machine. Keep the
table rust-free with regular applications of a high
quality anti-rust product.
Once a month, remove the blade and thoroughly
clean all metal chips or oil from the wheel
surfaces. Redress the rubber tires if the become
glazed.
When cleaning the wheel areas, empty and clean
the chip chute and brush (Figure 32).
-32-
Figure 33. Example of diamond dressing tools.
Page 35

For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09 Model SB1021/SB1022
!
!
!
!
Lubrication
The bearings on your bandsaw are factory
lubricated and sealed. Leave them alone unless
they need to be replaced.
When needed, brush a light coat of multi-purpose
grease on the blade tension leadscrew (Figure
34).
MAINTENANCE
If the table becomes difficult to tilt, position
it so that you can brush a thin coat of multipurpose grease on the trunnion sliding surfaces
(see Figure 36), then move back-and-forth to
distribute.
Trunnion Sliding
Surfaces
Grease
Figure 34. Upper wheel leadscrew lubrication.
Use multi-purpose grease and a light machine oil
where in Figure 35.
Oil
Grease
Figure 36. Trunnion lubrication.
The sliding surfaces on the guide post may
occasionally need to be lubricated with a light
machine oil if the movement becomes stiff.
Oil
Grease
Fitting
Behind
Plate
Grease
Fitting
Figure 35. System lubrication points.
Oil
Figure 37. Guide post lubrication.
-33-
Page 36

Model SB1021/SB1022
!
MAINTENANCE
V-Belts
To ensure optimum power transfer from the
motor to the blade, the V-belts must be in good
condition and operate under proper tension.
Check V-belt tension at least every three
months—more often if the bandsaw is used daily.
V-belts stretch with use and must be periodically
re-tensioned. Replace the V-belts if they are
cracked, frayed, or badly worn. Refer to Figure
38 to identify V-belt locations.
Sprocket Drive
Pulley
Sprocket
Drive Belt
Air Pump
For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09
Note: When the machine is started, the belts will
automatically adjust to the correct tension.
Sprocket Drive Belt
Use a 17mm wrench and loosen the tensioner hex
bolt. Next use a 6mm hex wrench to loosen the
three intermediate pulley retaining cap screws so
the belt is loose. Replace the sprocket drive belt.
Re-tighten the intermediate hub and adjust the
tensioner hub to tension the new belt.
Air Pump Belt
Use a 10mm wrench to loosen the pump
mounting bolts, replace the belt and tension it
by positioning the air pump, then tighten the
mounting bolts.
Note: Make sure that when tightened, the pump
pulley is aligned with the motor drive pulley.
Tensioner
Intermediate
Pulley
Figure 38. System belt and pulley layout.
Left/Right Speed
Pulley Belts
To check/tension/replace the V-belts:
1. DISCONNECT BANDSAW FROM POWER!
2. Remove the rear motor access panel.
3. Push the center of each V-belt with moderate
force. When tensioned correctly, there should
be approximately
overtighten the belts or the bearings will
wear prematurely.
3
⁄16" of deflection. DO NOT
Speed Hub Belts
Rotate the speed handle left or right until the
belts are loose. Roll the belts off the pulleys to
replace them. (If you get them mixed up when
replacing, the belt on the left is the larger of the
two.)
Dressing Rubber Tires
As the bandsaw ages, the rubber tires on the
wheel may need to be redressed if they become
hardened or glazed over. Dressing the rubber
tires improves blade tracking and reduces
vibration/blade lead.
If the rubber tires become too worn, then blade
tracking will become extremely difficult. At that
point, redressing will no longer be effective, and
the rubber tires must be replaced.
To redress the rubber tires:
1. DISCONNECT BANDSAW FROM POWER!
2. Put on heavy gloves and remove the blade.
3. Use a brush and shop vacuum to clean any
chips from the rubber tires.
4. Hold a piece of 100-grit sandpaper against
the rubber tire and rotate the wheel by hand.
Only redress the rubber enough to expose a
fresh rubber surface.
a. Check surface area of tire to ensure a
uniformly sanded surface.
-34-
Page 37

For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09 Model SB1021/SB1022
!
SERVICE
Blade Tracking
SERVICE
Table Calibration
A blade that is tracking correctly runs cooler,
reduces wear-and-tear on the machine, and
increases cutting performance. When tracking
correctly, the blade rides next to, but not against,
the wheel flange. The tracking is controlled by
adjusting the upper wheel.
To adjust the upper wheel for blade tracking:
1. DISCONNECT BANDSAW FROM POWER!
2. Make sure the blade guides are adjusted
away from the blade so they will not
interfere with the change of blade position.
3. Ensure that the blade is correctly tensioned.
4. Using a 6mm hex wrench, loosen the four
locking cap screws (Figure 39).
Adjustment Set
Screw
To ensure the accuracy of angle cuts and
compound angle cuts, the scale pointers must
point to zero when the table is perpendicular or
90° to the blade.
To calibrate the table to zero:
1. DISCONNECT BANDSAW FROM POWER!
2. Make sure the blade tracking and tension
are set correctly.
3. Using a 6mm hex wrench, loosen the
trunnion cap screws (Figure 40).
Trunnion Cap
Screws
Feed Angle
Cap Screw
Upper
Wheel
Housing
Locking
Cap Screw
Figure 39. Wheel alignment.
5. Use a 5mm hex wrench to adjust the four set
screws (Figure 39) to tilt the upper wheel
in or out and bring blade tracking back to
normal. Only adjust each screw in small
increments.
6. Rotate the upper wheel by hand a couple
times in the normal direction of rotation.
Verify that the blade tracks next to, but not
against, the wheel flange. Repeat Steps 5-6
if necessary until the blade tracks correctly.
7. Tighten the locking cap screws and recheck
the tracking to make sure it did not change.
If it did, repeat Steps 4-7.
8. Adjust the blade guides back to their correct
position.
Feed Angle
Scale
Figure 40. Location of table scales.
4. Place a machinist's square on the table and
against the side of the blade, as shown in
Figure 41.
9O
MachinIst's
Blade
Square
Table
Figure 41. Checking that table is perpendicular to
blade.
Cut Angle
Scale
-35-
Page 38

Model SB1021/SB1022
!
!
5. Tilt the table until the blade and table top
are perpendicular, then tighten the trunnion
cap screws.
6. Loosen the scale pointer for the cut angle
scale (on the trunnion) and point it to zero.
SERVICE
For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09
7. Loosen the feed angle cap screw and place
the machinist's square against the back of
the blade.
8. Position the table perpendicular to the blade.
9. Tighten the feed angle cap screws.
10. Loosen the pointer for the feed angle scale,
and point it to zero. The table and blade are
now calibrated.
Guide Post Alignment
If the blade guide post does not raise and lower
exactly parallel with the blade, the clearances
between the blade guides and blade will change
as the guide post is moved, causing rubbing,
wear, and blade deflection. Blade guide clearance
must stay the same when the guide post is raised
and lowered along its full length of travel.
To align the guide post:
Guide Post
Receiver
Figure 42. Guide post system.
6. Using a 6mm hex wrench, loosen the four
guide post receiver cap screws (Figure 43).
Set Screws
Receiver Cap
Screws
1. DISCONNECT BANDSAW FROM POWER!
2. Make sure the blade tracking and tension
are set correctly.
3. Lower the blade guide post to the bottom of
its travel and lock it in place.
4. Adjust the blade guides as described on
Page 26.
5. Unlock the post just enough to allow it to
slide, move it all the way up, then examine
the clearances between the blade and blade
guides to see if they changed.
If these clearances changed beyond your
acceptable tolerances, the blade guide
receiver (Figure 42) can be adjusted to fix
this condition.
-36-
Figure 43. Guide post alignment controls.
7. Using a 5mm hex wrench, adjust the four set
screws to tilt the blade guide receiver in the
required direction.
8. Tighten the cap screws and recheck blade
guide clearance along the guide post path of
travel.
9. Repeat this procedure if necessary to finetune the guide post travel to acceptable
tolerances.
Page 39

For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09 Model SB1021/SB1022
!
!
SERVICE
Pinion Gear Backlash
During the life of the machine, the variable
speed handwheel may develop extra backlash
due to normal wear of the pinion gears. If this
lash becomes unacceptable, use this procedure to
reduce the backlash.
To reduce the pinion gear backlash:
1. DISCONNECT BANDSAW FROM POWER!
2. Remove the rear lower access panel, and use
a 4mm hex wrench to loosen both pinion gear
locking set screws (Figure 44) just enough
to adjust the pinion gears.
Pinion Gears
Leadscrew End Play
If you notice that the leadscrew has end play
and the variable speed handwheel has excess
backlash after the pinion gear lash has been
set, you can adjust the lead screw collars as an
additional measure to reduce the backlash.
To adjust the lead screw collars to reduce
backlash:
1. DISCONNECT BANDSAW FROM POWER!
2. Remove the rear lower access panel, and
use a 4mm hex wrench to loosen both collar
locking set screws just enough to adjust the
collars (Figure 45).
Leadscrew
Support Boss
Figure 44. Location of pinion gears.
3. Slide the pinions closer together, and tighten
the set screws. If excess backlash still exists,
refer to the Leadscrew End Play section,
then proceed to Step 4.
Note: Make sure that the set screws remain
aligned with the flats on the shaft. If one or
both setscrews do not return to their original
depth in the pinion gear after tightening, the
alignment has probably been lost and needs
to be corrected.
4. Clean and grease the pinion gears and the
leadscrew, then reinstall the access panel.
Leadscrew Collars w/
Locking Set Screws
Figure 45. Leadscrew adjustment locations.
3. Slide the right-hand leadscrew collar
against the support boss and tighten the set
screws. If excess backlash still exists at the
handwheel, you may have to readjust the
pinion gear lash, replace the leadscrew half
nut, or replace worn bolts or linkage (Figure
45).
Linkage
Leadscrew
Halfnut
Bolts
Figure 46. Linkage location and parts.
4. Reinstall the access panel.
-37-
Page 40

Model SB1021/SB1022
TROUBLESHOOTING
TROUBLESHOOTING
For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09
Troubleshooting
If you need replacement parts, or if you are unsure how to do any of the solutions given here, feel free
to call us at (360) 734-1540.
Symptom Possible Cause Possible Solution
Machine does not
start.
Main motor
chatters during
startup or during
operation.
Power supply switched off/has
1.
incorrect voltage.
Blown fuse/tripped circuit breaker
2.
at main panel.
Plug or receptacle is corroded or
3.
mis-wired.
Thermal overload relay has tripped.
4.
Break or short in wiring; or loose
5.
connections.
Motor ON/OFF switch at fault.
6.
Motor connection wired incorrectly.
7.
Start capacitor blown or at fault.
8.
Contactor not energized/has poor
9.
contacts.
Centrifugal switch at fault.
10.
Motor at fault.
11.
Extension cord (if used) is causing
1.
voltage drop.
Phase converter (if used) wild wire
2.
connected wrong.
Power supply has incorrect voltage
3.
on one or more legs.
Switch power supply on/verify voltage.
1.
Correct the cause of overload, then reset/replace
2.
fuse or breaker.
Clean/retighten contacts; correct the wiring.
3.
Allow relay/motor to cool. If necessary, press reset
4.
button inside switch.
Trace/replace broken or corroded wires; fix loose
5.
connections.
Replace switch.
6.
Wire motor correctly (refer to inside junction box
7.
cover or manual).
Replace start capacitor.
8.
Test all legs for power, test field coil and replace if
9.
at fault.
Adjust/replace centrifugal switch.
10.
Test for shorted windings, bad bearings and repair
11.
or replace.
Move machine closer to the power source or use a
1.
larger gauge or shorter extension cord.
Connect wild wire to the machine power supply
2.
terminal that is not part of the contactor field coil
power supply circuit.
Contact your power company to fix the power
3.
supply.
Machine operates
in reverse.
Machine has
excessive vibration
or noise.
-38-
Power connections wired out of
1.
phase (SB1022 only).
Motor fan rubbing on fan cover.
1.
Motor or table is loose.
2.
V-belt(s) loose.
3.
Guide post lock lever is loose.
4.
Machine incorrectly mounted on
5.
floor.
V-belt(s) worn or damaged.
6.
Pulley loose or not in alignment;
7.
shaft bent.
Centrifugal switch out of
8.
adjustment; at fault (SB1021 only)
Motor bearings worn or damaged.
9.
Phase converter (if used) wild wire
10.
incorrectly connected (SB1022
only).
1. Swap two power incoming power leads (see Page
47).
Fix/replace fan cover; replace loose or damaged fan.
1.
Tighten any loose fasteners.
2.
Tighten V-belt(s).
3.
Tighten the lock lever.
4.
Level/shim base; tighten/adjust mounting hardware
5.
or feet.
Replace V-belt(s). Use link belts if possible.
6.
Replace worn pulley, key, and shaft, and realign.
7.
Adjust/replace centrifugal switch.
8.
Replace motor bearings or replace motor.
9.
Connect wild wire to correct leg (must avoid
10.
transformer or sensitive electronics).
Page 41

For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09 Model SB1021/SB1022
TROUBLESHOOTING
Symptom Possible Cause Possible Solution
Machine stalls
or slows when
operating.
Too much pressure when feeding
1.
workpiece.
Motor is wired out of phase
2.
(SB1022 only).
Workpiece is warped and binding
3.
blade.
Blade is not correct for material
4.
being cut.
Belt(s) slipping.
5.
Motor overheated.
6.
Run capacitor at fault (SB1021
7.
only).
Pulley or sprocket slipping on shaft.
8.
Motor connection wired incorrectly.
9.
Contactor has poor contacts.
10.
Centrifugal switch at fault (SB1021
11.
only).
Motor at fault.
12.
Reduce pressure when feeding workpiece.
1.
2. Swap two power incoming power leads (see Page
47).
Fabricate a jig for better workpiece control.
3.
Use the correct blade for the operation. Refer to
4.
Blade Selection section beginning on Page 20.
Tension/replace belt(s); ensure pulleys are aligned.
5.
Let cool, clean motor, and reduce workload.
6.
Test/repair/replace.
7.
Replace pulley and key or set screw. Replace shaft
8.
if worn.
Review wiring diagram on motor cover; correct wire
9.
connections.
Test all legs for power, test field coil and replace if
10.
at fault.
Adjust/replace centrifugal switch if available.
11.
Test for shorted windings, bad bearings and repair
12.
or replace.
Handwheel has
excessive backlash,
endplay, binds, or
is difficult to move.
Cuts are not square
or the intended
angle is incorrect.
Grinder does not
work.
Work lamp or
welding lamp does
not work
Welder is
inoperative or
welds poorly.
Leadscrew is dirty or lacks proper
1.
lubrication.
Pinion gears out of adjustment.
2.
Bearing or leadscrew collar is worn
3.
or loose.
Linkage bolts, pins, and holes are
4.
loose or worn.
Leadscrew or leadscrew nut worn.
5.
Pointer or scale not calibrated or
1.
loose table.
Table guide post is loose or out of
2.
alignment.
Wiring or ON/OFF switch at fault
1.
Motor at fault.
2.
Bulb, wiring, or switch at fault.
1.
Transformer is at fault.
2.
Operator error.
1.
Wiring or welding switch at fault.
2.
Welder transformer at fault.
3.
1. Clean and lubricate the leadscrew (see Page 33).
Re-adjust pinion gears to reduce backlash (see
2.
Page 37).
Replace bearing or readjust leadscrew collar (see
3.
Page 37).
Replace linkage bolts, pins, and re-bush any worn
4.
pin holes.
Replace leadscrew or leadscrew nut.
5.
Zero table to blade and realign scale pointers (see
1.
Page 35). Tighten any loose fasteners.
Tighten any loose hardware or lock levers. Align the
2.
guide post (see Page 36).
Repair wiring or replace grinder switch.
1.
Replace motor.
2.
Replace bulb, repair wiring, replace switch.
1.
Replace transformer.
2.
Use welder as outlined in operations section and
1.
practice on scrap blades (see Page 28).
Repair wiring or replace welding switch.
2.
Replace welder transformer.
3.
-39-
Page 42

Model SB1021/SB1022
TROUBLESHOOTING
For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09
Symptom Possible Cause Possible Solution
Machine or blade
bogs down in the
cut.
Blade tracks
incorrectly, or
comes off wheels.
Excessive load on the blade.
1.
V-belts loose; belt squeals at times.
2.
V-belts worn and slips.
3.
Blade is loading up.
4.
Blade is dull, wanders, and gets
5.
pinched in the cut.
Blade is dull.
6.
The blade TPI is too coarse for the
7.
thin workpiece.
Blade is loose.
8.
Material requires cutting fluid.
9.
The run capacitor is at fault
10.
(SB1021 only).
Feed rate is too fast.
1.
Blade is not tracking correctly.
2.
Blade is bell-mouthed.
3.
Blade is dull, wanders, and gets
4.
pinched in the cut.
Rubber tire on wheel is damaged,
5.
glazed, or worn.
Wheels are not coplanar.
6.
Blade tension is too loose.
7.
Blade guides need adjustment.
8.
Incorrect blade for bandsaw.
9.
The blade has insufficient support.
10.
Wheel tires are loaded with metal
11.
shavings.
Reduce feed rate or increase blade speed
1.
Tighten V-belts.
2.
Replace V-belts.
3.
Install a blade with more suitable TPI or different
4.
style of teeth.
Replace blade, adjust guides and tracking.
5.
Replace blade.
6.
Use a blade with at least 2 teeth contacting the
7.
material at all times.
Clean wheels and increase blade tension.
8.
Use applicable cutting fluid.
9.
Replace the run capacitor.
10.
Reduce feed rate, or decrease blade TPI.
1.
Adjust blade tracking.
2.
Install new blade, and regularly remove tension
3.
from blade when not in use.
Replace blade, re-secure the workpiece from
4.
shifting.
Replace or dress rubber tires.
5.
Adjust wheels so they are parallel and aligned.
6.
Increase blade tension.
7.
Adjust blade guides.
8.
Install correct blade for machine.
9.
Tighten the blade guide as close to the workpiece as
10.
possible.
Clean wheel tires.
11.
The cut is crooked,
the blade wanders,
slow cuts, or shows
overheating on one
side of the cut or
the blade.
-40-
Blade spinning backwards due to
1.
machine being wired out of phase
(SB1022 only).
The feed pressure is too high.
2.
Too much side pressure when
3.
feeding workpiece.
Blade is loading up.
4.
Blade installed backwards.
5.
Dull blade; missing teeth.
6.
Blade too wide for size of radius
7.
being cut.
The blade speed is wrong.
8.
The blade tracking is wrong.
9.
1. Swap two power incoming power leads (see Page
47).
Decrease the feed rate.
2.
Feed workpiece straight into the blade.
3.
Install a blade with more suitable TPI or different
4.
style of teeth.
Check blade rotation as described in “test run” and
5.
reverse blade if necessary.
Replace blade.
6.
Install a smaller width blade, or increase blade
7.
tension.
Adjust feed rate and cutting speed as required.
8.
Adjust the blade tracking back to normal.
9.
Page 43

For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09 Model SB1021/SB1022
TROUBLESHOOTING
Symptom Possible Cause Possible Solution
Blade dulls
prematurely, or
metal sticking to
the blade.
Loud, repetitious
noise coming from
machine.
Ticking sound
when the saw is
running.
Blade wears on
one side or shows
overheating.
Blade is improperly broken in.
1.
The blade gullets are loading up
2.
with chips.
The blade TPI is too fine for the
3.
thick workpiece, and the teeth load
up and overheat.
The workpiece has hard spots,
4.
welds, or scale.
Pulley set screws or keys are
1.
missing or loose.
Motor fan is hitting the cover.
2.
V-belts are defective.
3.
Blade weld contacting blade guides.
1.
Blade weld may be failing.
2.
The blade guides are worn or mis-
1.
adjusted.
The blade support is inadequate.
2.
Wheels are not coplanar.
3.
Dull or incorrect blade.
4.
Blade is bell-mouthed.
5.
Replace blade, and complete blade break in
1.
procedure.
Use a blade that has larger gullets to carry out
2.
material.
Use a coarser-tooth blade, adjust feed rate, adjust
3.
blade speed, make sure the brush is working.
Replace the blade with a special blade for cutting
4.
hardened materials.
Inspect keys and set screws. Replace or tighten if
1.
necessary.
Adjust fan cover mounting position, tighten fan, or
2.
shim fan cover.
Replace V-belts.
3.
Grind blade weld down smaller.
1.
Cut and reweld the blade, or replace the blade.
2.
Re-adjust or replace the blade guides.
1.
Tighten the blade guide as close to the workpiece as
2.
possible.
Adjust wheels so they are parallel and aligned.
3.
Replace blade.
4.
Install new blade.
5.
Vibration when
operating or
cutting.
Loose or damaged blade.
1.
Worn wheel bearing.
2.
Wheels are not coplanar.
3.
Wheel tires worn or incorrectly
4.
installed.
Bent or dull blade.
5.
Wheels out of balance.
6.
Loose machine component.
7.
Belt has a high spot.
8.
Bandsaw blade wheel is bent or out
9.
of balance.
Tighten or replace blade.
1.
Check/replace wheel bearing.
2.
Adjust wheels so they are parallel and aligned.
3.
Replace or dress rubber tires.
4.
Replace blade.
5.
Replace wheels.
6.
Tighten loose component.
7.
Replace/adjust the V-belt.
8.
Check and replace for bad wheel or bearing.
9.
-41-
Page 44

Model SB1021/SB1022
ELECTRICAL
ELECTRICAL
For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09
Electrical Safety Instructions
These pages are accurate at the time of printing. In the constant effort to improve, however, we may
make changes to the electrical systems of future machines. Study this section carefully. If you see
differences between your machine and what is shown in this section, call Technical Support at (360)
734-1540 for assistance BEFORE making any changes to the wiring on your machine.
1.
Shock Hazard: It is extremely dangerous to
perform electrical or wiring tasks while the
machine is connected to the power source.
Touching electrified parts will result in
personal injury including but not limited to
severe burns, electrocution, or death. For
your own safety, disconnect machine from
the power source before servicing electrical
components or performing any wiring tasks!
Wire Connections: All connections must be
2.
tight to prevent wires from loosening during
machine operation. Double-check all wires
disconnected or connected during any wiring
task to ensure tight connections.
Modifications: Using aftermarket parts or
3.
modifying the wiring beyond what is shown
in the diagram may lead to unpredictable
results, including serious injury or fire.
Motor Wiring: The motor wiring shown
4.
in these diagrams is current at the time of
printing, but it may not match your machine.
Always use the wiring diagram inside the
Circuit Requirements: Connecting the
5.
machine to an improperly sized circuit will
greatly increase the risk of fire. To minimize
this risk, only connect the machine to a
power circuit that meets the minimum
requirements given in this manual.
Capacitors/Inverters: Some capacitors and
6.
power inverters store an electrical charge for
up to 10 minutes after being disconnected
from the power source. To reduce the risk of
being shocked, wait at least this long before
working on capacitors.
Wire/Component Damage: Damaged wires
7.
or components increase the risk of serious
personal injury, fire, or machine damage. If
you notice that any wires or components are
damaged while performing a wiring task,
replace those wires or components before
completing the task.
Experiencing Difficulties: If you are
8.
experiencing difficulties understanding the
information included in this section, contact
-42-
Page 45

For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09 Model SB1021/SB1022
ELECTRICAL
Wiring Overview
CONTROL
A
PANEL
See Page 44
and Figure 48.
WELDER’S
B
LAMP
D
WORK
LAMP
A
B
C
D
WELDING UNIT
C
See Page 44
and Figure 49
See Page 47
and Figure 47
F
MOTOR
E
ELECTRICAL
PANEL
See Page 47
and Figure 50
E
*
BLACK
BLUE
BROWN
May Represent Multiple Wires
NOTICE:
WIRING DIAGRAM COLOR KEY
BLUE
WHITE
GREEN
GRAY
The photos and diagrams included in this section are best viewed in color. You can
see them in color at www.southbendlathe.com.
RED
LIGHT
BLUE
ORANGE
PINK
PURPLE
TURQUIOSE
WHITE
YEL LOW
GREEN
YEL LOW
F
-43-
Page 46

Model SB1021/SB1022
ELECTRICAL
For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09
SB1021/2 Control Panel & Welding Unit
3
3
A
CONTROL PANEL
WELDER’S LAMP
WELDING UNIT
C
Right
Welding
Clamp
DC
D;;
B
4
7
Annealing Button
Left
Welding
Clamp
4
D;;
1
23
EdlZgAVbe
LZaYZg»h
AVbe
DC
('&
R
23
Sensor
Welding Button
1
7
6
2
1
6
1
UPPER DOOR
LIMIT SWITCH
WORK LAMP
D
w/ SWITCH
LOWER DOOR
LIMIT SWITCH
1234567
T
SB1022 220V Transformer Wiring
Indicates
area requiring
changes when
converting to
220V
Start Capacitor
6MFD 250VAC
220V Transformer
115/230V 2KVA
Ya Chang Electric
1234567
T
Grinder
Switch
6
Grinder
Motor
6
1
5
3
2
4
ON
1
OFF
2
2
4
6
3
4
1
R
T
2
6
2
6
1
1
To Electrical Panel
1
-44-
Page 47

For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09 Model SB1021/SB1022
ELECTRICAL
SB1021 110V Electrical Panel, Motor & Cord
E
ELECTRICAL PANEL
0V
110V
220V
T
R
1
2
TRANSFORMER
Model: S-034-005-1
Class: B
Capacity: 110VA 1-Ph 50/60Hz
Primary Voltage:
0V/110V/220V
GND
R
R
T
T
4
3
2
1
R
T
GND
3
4
1
R
T
2
6
2
6
1
1
To Welding Unit/
Control Panel
1 L1
3L2 5L3 13NO
A1
A2
4
4
4
3
3
3
2T1
C16
4T2 6T3 14NO
10
4
R T
4 R T
2
2T1 4T2 6T3
U
2
W
U
12345678910 11 12
U
95
96 97 98
11 15
7
5.4
1
W
W
1
Allen-Bradley
Test Reset
E1-Plus
19
23
27
2
1
2 6 6
1
Ground
Neutral
Hot
110 VAC
5-15 PLUG
(Prewired)
T3
T8
T1
T2
T4
T5
GND
F
MOTOR
110V
-45-
Page 48

Model SB1021/SB1022
ELECTRICAL
For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09
SB1021 220V Motor Rewire
SB1021 220V Electrical Panel, Motor & Cord
E
ELECTRICAL PANEL
0V
110V
220V
T
R
1
2
TRANSFORMER
Model: S-034-005-1
Class: B
Capacity: 110VA 1-Ph 50/60Hz
Primary Voltage:
0V/110V/220V
GND
R
R
T
T
4
3
2
1
R
T
GND
3
4
1
R
T
2
6
2
6
1
1
To Welding Unit/
Control Panel
Ground
T8
T3
T4
1 L1
3L2 5L3 7L4
T2
A1
A2
4
4
T5
3
3
3
2T1
C16
4T2 6T3 8T4
400
4
R T
4 R T
T1
2
2T1 4T2 6T3
U
2
W
U
12345678910 11 12
U
Neutral
Hot
95
96 97 98
11 15
7
5.4
1
W
W
1
Allen-Bradley
Test Reset
E1-Plus
19
23
27
2
1
2 6 6
1
4
Indicates
areas requiring
changes when
converting to
220V
-46-
220 VAC
6-15 PLUG
(Prewired)
GND
F
MOTOR
220V
Page 49

For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09 Model SB1021/SB1022
ELECTRICAL
SB1022 220V Electrical Panel, Motor & Cord
E
ELECTRICAL PANEL
T
1
2
2T1 4T2 6T3
U
2
V
W
U
V
TRANSFORMER
Model: S-034-005-1
Capacity: 110VA 1-Ph 50/60Hz
Class: B
Primary Voltage:
0V/110V/220V
95
96 97 98
3.2
1
W
Test Reset
16
Allen-Bradley
E1-Plus
2
0V
110V
R
220V
2T1
C09
4T2 6T3 14NO
10
3
3
4
R T
R
R
S
T
T
1 L1
3L2 5L3 13NO
4
3
2
1
A1
A2
4
4
R
S
T
E
4
<C9
3
4
R
T
6
2
6
1
To Welding Unit/
Control Panel
Ground
220 VAC
L15-15 PLUG
(as recommended)
12345678910 11 12
1
1
2
1
3
U5
4 R T
U2
V
U
6
6
W2
V2
W5
<C9
V5
W
Hot
U
V
W
Hot
Hot
F
MOTOR
220V
For Phase Coverter Wild Wire (If Used)
-47-
Page 50

Model SB1021/SB1022
ELECTRICAL
Electrical Component Pictures
For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09
Electrical Pictures
Terminal Strip
Welding Transformer
Figure 49. Welding Panel.
Power Transformer
Figure 47. Motor.
Figure 48. Control Panel & Welder's Lamp.
Main Terminal Block
Overload Relay
Figure 50. Electrical Box.
-48-
Page 51

For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09 Model SB1021/SB1022
PARTS
PARTS
Lower Frame
47
39
4
5
48
4
5
3
2
1
19
1
3
6
7
6
8
1
6
14
12
11
1
1
1
11
15
16
17
18
13
1
9
1
2
10
6
22
23
24
26
27
25
30
26
32
35
33
31
31
32
25
28
29
34
36
37
13
40
41
42
21
20
38
31
39
43
46
45
44
-49-
Page 52

Model SB1021/SB1022
PARTS
For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09
Lower Frame Parts List
REF PART # DESCRIPTION REF PART # DESCRIPTION
1 PSS20M SET SCREW M8-1.25 X 8 25 PW03M FLAT WASHER 6MM
2 PSB1021002 LOCK COLLAR 26 PLW03M LOCK WASHER 6MM
3 PW04M FLAT WASHER 10MM 27 PFN07M FLANGE NUT M4-.7
4 PLW06M LOCK WASHER 10MM 28 PSB1021028 BRACKET
5 PCAP72M CAP SCREW M10-1.5 X 30 29 PSB1021029 BRUSH
6 PSB1021006 LOCK COLLAR 30 PB08M HEX BOLT M6-1 X 20
7 PSB1021007 SHAFT 31 PLW04M LOCK WASHER 8MM
8 PSB1021008 BEVEL GEAR 32 PS16M PHLP HD SCR M8-1.25 X 16
9 PSB1021009 BEVEL GEAR 33 PCAP31M CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 25
10 PSB1021010 LEADSCREW 34 PW01M FLAT WASHER 8MM
11 PSB1021011 RUBBER RING 35 PCAP13M CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 30
12 PSB1021012 LEADSCREW NUT 36 PSB1021036 RIVET 5 X 20
13 PW01M FLAT WASHER 8MM 37 PSB1021037 CHIP DEFLECTOR
14 PCAP14M CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 20 38 PSB1021038 BASE
15 PSB1021015 FRONT VENT COVER 39 PCAP14M CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 20
16 PSB1021016 HANDWHEEL 40 PSB1021040 LOWER FRAME
17 PSB1021017 HANDWHEEL HANDLE 41 PSB1021041 LOWER DOOR
18 PSB1021018 DRIVE WHEEL 42 PN06M HEX NUT M5-.8
19 PSB1021019 RUBBER TIRE 43 PS03M PHLP HD SCR M6-1 X 8
20 PSB1021020 LOCK KNOB 44 PSB1021044 DOOR HANDLE
21 PCAP31M CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 25 45 PSB1021045 SOUTH BEND NAMEPLATE
22 PS48M PHLP HD SCR M4-.7 X 50 46 PS05M PHLP HD SCR M5-.8 X 8
23 PSB1021023 LOWER DOOR SAFETY SWITCH 47 PSB1021047 LOWER REAR COVER
24 PB08M HEX BOLT M6-1 X 20 48 PSB1021048 BRACKET
-50-
Page 53

For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09 Model SB1021/SB1022
PARTS
Drive System
115
117
119
136
134-1
114
118
109
113
116
104
135
108
112
134-2
134
107
110
105
121
125
106
111
127
132
133
105
122
131
104
128
129
130
137
109
123
126
103
108
138
124
139
102
126
140
141
101
124
143
142
100
153
103
187
152
157
144
156
120
105
151
154
145
158
146
131
161
155
159
150
167
160
169
166
122
131
161
148
149
162
163
105
164
SB1021 Only
134-4
134-5
134-3
174
175
179
173
150
172
155
180
176
171
161
181
131
170
162
182
168
186
166
183
184
120
155
185
177
131
155
170
165
168
148
131
178
-51-
Page 54

Model SB1021/SB1022
PARTS
For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09
Drive System Parts List
REF PART # DESCRIPTION REF PART # DESCRIPTION
100 PSB1021100 GREASE FITTING 139 PCAP84M CAP SCREW M10-1.5 X 35
101 PR03M EXT RETAINING RING 12MM 140 PCAP63M CAP SCREW M12-1.75 X 60
102 P6201Z-N BALL BEARING 6201 Z NSK 141 PSB1021141 SUPPORT ARM
103 PSB1021103 STATIONARY PULLEY 142 PSB1021142 SHAFT
104 PVM26 V-BELT M26 143 PFH05M FLAT HD SCR M5-.8 X 12
105 PSS20M SET SCREW M8-1.25 X 8 144 PSB1021144 SLEEVE
106 PSB1021106 AIR PUMP PULLEY 145 PSB1021145 MOVABLE PULLEY
107 PCAP02M CAP SCREW M6-1 X 20 146 PFH05M FLAT HD SCR M5-.8 X 12
108 PLW03M LOCK WASHER 6MM 148 PCAP11M CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 16
109 PW03M FLAT WASHER 6MM 149 PSB1021149 SPROCKET
110 PSB1021110 PUMP HOUSING 150 PSB1021150 CHAIN
111 P6201Z-N BALL BEARING 6201 Z NSK 151 PSB1021151 HUB
112 PSB1021112 PUMP ROTOR 152 PSB1021152 BEARING SEAT
113 PSB1021113 ROTOR BLADE 153 P6205-OPEN-N BALL BEARING 6205 OPEN NSK
114 PSB1021114 AIR NOZZLE 154 PCAP13M CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 30
115 PSB1021115 AIR HOSE 155 PW01M FLAT WASHER 8MM
116 PSB1021116 NOZZLE HOUSING 156 PK160M KEY 6 X 6 X 65
117 PSB1021117 END CAP 157 PK42M KEY 6 X 6 X 30
118 PLW03M LOCK WASHER 6MM 158 PSB1021158 SHAFT
119 PCAP01M CAP SCREW M6-1 X 16 159 PR11M EXT RETAINING RING 25MM
120 PVA40 V-BELT A40 160 PSB1021160 PILLOW BLOCK BEARING
121 PSB1021121 MOTOR PULLEY 161 PLW06M LOCK WASHER 10MM
122 PVA36 V-BELT A36 162 PCAP84M CAP SCREW M10-1.5 X 35
123 PCAP02M CAP SCREW M6-1 X 20 163 PSB1021163 PLATE
124 PN09M HEX NUT M12-1.75 164 PR08M EXT RETAINING RING 19MM
12
5 PCAP170M CAP SCREW M12-1.75 X 70165 PSB1021165 PULLEY
126 PW06M FLAT WASHER 12MM 166 PVA47 V-BELT A47
127 PSB1021127 CONNECTOR 167 PCAP84M CAP SCREW M10-1.5 X 35
128 PCAP119M CAP SCREW M12-1.75 X 55 168 PCAP40M CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 35
129 PK23M KEY 5 X 5 X 25 169 PSB1021169 BEARING SEAT
130 PN03M HEX NUT M8-1.25 170 P6204Z-N BALL BEARING 6204 Z NSK
131 PLW04M LOCK WASHER 8MM 171PK74M KEY 6 X 6 X 35
132 PW01M FLAT WASHER 8MM 172 PSB1021172 SPROCKET SHAFT
133 PCAP40M CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 35 173 PSB1021173 BRACKET
134 PSB1021134 MOTOR 1HP 110/220V 1PH (SB1021) 174 PCAP84M CAP SCREW M10-1.5 X 35
134 PSB1022134 MOTOR 1HP 220V 3PH (SB1022) 175 PLW06M LOCK WASHER 10MM
134-1 PSB1021134-1 MOTOR FAN COVER (SB1021) 176 PSB1021176 PIVOT SHAFT
134-1 PSB1022134-1 MOTOR FAN COVER (SB1022) 177 PSB1021177 PULLEY
134-2 PSB1021134-2 MOTOR FAN (SB1021) 178 PR25M INT RETAINING RING 47MM
134-2 PSB1022134-2 MOTOR FAN (SB1022) 179 PSB1021179 BLOCK
134-3 PSB1021134-3 MOTOR WIRING BOX (SB1021) 180 PSB1021180 SHAFT
134-3 PSB1021134-3 MOTOR WIRING BOX (SB1022) 181 PR05M EXT RETAINING RING 1
134-4 PSB1021134-4 CAPACITOR COVER(SB1021) 182 PR21M INT RETAINING RING 35MM
134-5 PSB1021134-5 S CAPACITOR 400M 125V (SB1021) 183 PSB1021183 PULLEY
135 PSB1021135 WIRING GROMMET 184 PR21M INT RETAINING RING 35MM
136 PSB1021136 MOTOR CORD 185 PR05M EXT RETAINING RING 15MM
137 PSB1021137 BRACKET 186 P6202ZZ-N BALL BEARING 6202 ZZ NSK
138 PLW06M LOCK WASHER 10MM 187 P6202Z-N BALL BEARING 6202 Z NSK
5MM
-52-
Page 55

For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09 Model SB1021/SB1022
PARTS
Upper Frame
283
282
281
204
203
202
201
206
202
201
207
208
209
210
280
279
278
277
276
217
214
215
223
219
222
214
218
213
220
224
221
212
211
225
226
227
232
240
228
229
230
234
231
238
261
233
235
239
236
237
242
240
259
238
243
264
260
204
244
247
265
257
258
255
263
262
256
250
245
266
267
248
246
249
268
251
269
254
204
269
270
253
275
270
271
252
272
274
204
273
-53-
Page 56

Model SB1021/SB1022
PARTS
For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09
Upper Frame Parts List
REF PART # DESCRIPTION REF PART # DESCRIPTION
201 PW03M FLAT WASHER 6MM 244 PSB1021244 HOSE CLAMP
202 PCAP06M CAP SCREW M6-1 X 25 245 PSB1021245 AIR NOZZLE
203 PSB1021203 LEVER 246 PSB1021246 AIR HOSE
204 PSB1021204 KNOB 247 PSB1021247 BLADE GUIDE
206 PSB1021206 LOCKING LINK 248 PSB1021248 BLADE GUIDE BRACKET
207 PSB1021207 UPPER SHEAR BLADE 249 PSB1021249 SPECIAL DOWEL PIN
208 PCAP13M CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 30 250 PSB1021250 THREADED PIN
209 PW01M FLAT WASHER 8MM 251 PCAP04M CAP SCREW M6-1 X 10
210 PSB1021210 SHEAR BRACKET 252 PS11M PHLP HD SCR M6-1 X 16
211 PN01M HEX NUT M6-1 253 PSB1021253 UPPER BLADE GUARD
212 PW03M FLAT WASHER 6MM 254 PSB1021254 BLADE GUIDE BAR
213 PSB1021213 LOWER SHEAR BLADE 255 PSB1021255 HANDLE
214 PCAP03M CAP SCREW M5-.8 X 8 256 PSB1021256 EXTENSION SPRING
215 PSB1021215 ALIGNMENT BRACKET 257 PW04M FLAT WASHER 10MM
217 PCAP40M CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 35 258 PLW06M LOCK WASHER 10MM
218 PSB1021218 WELDING STATION COVER 259 PN02M HEX NUT M10-1.5
219 PSB1021219 SPACER 260 PCAP70M CAP SCREW M10-1.5 X 45
220 PLW04M LOCK WASHER 8MM 261 PCAP71M CAP SCREW M10-1.5 X 60
221 PS04M PHLP HD SCR M8-1.25 X 20 262 PSS14M SET SCREW M8-1.25 X 12
222 PS40M PHLP HD SCR M5-.8 X 16 263 PCAP01M CAP SCREW M6-1 X 16
223 PSB1021223 HANDLE 264 PSB1021264 BLADE COVER
224 PSB1021224 UPPER DOOR 265 PLW03M LOCK WASHER 6MM
225 PSB102122
226 PSB1021226 DOOR LATCH 267 PN01M HEX NUT M6-1
227 PLW01M LOCK WASHER 5MM 268 PSB1021268 BLADE GUIDE BAR HOUSING
228 PN06M HEX NUT M5-.8 269 PSS94M SET SCREW M10-1.5 X 25
229 PSB1021229 SAFETY SWITCH BRACKET 270 PCAP40M CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 35
230 PS11M PHLP HD SCR M6-1 X 16 271 PSB1021271 THREADED STUD
231 PW04M FLAT WASHER 10MM 272 PSB1021272 LOCKING HUB
232 PS08M PHLP HD SCR M5-.8 X 12 273 PSB1021273 LOCKING HUB COVER
233 PLW06M LOCK WASHER 10MM 274 PSB1021274 WORK LAMP 110V
234 PN02M HEX NUT M10-1.5 275 PSS10M SET SCREW M10-1.5 X 20
235 PN06M HEX NUT M5-.8 276 PCAP13M CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 30
236 PLW01M LOCK WASHER 5MM 277 PCAP13M CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 30
237 PN06M HEX NUT M5-.8 278 PSS10M SET SCREW M10-1.5 X 20
238 PLW01M LOCK WASHER 5MM 279 PN04M HEX NUT M4-.7
239 PSB1021239 HINGE 280 PSB1021280 UPPER DOOR SAFETY SWITCH
240 PS40M PHLP HD SCR M5-.8 X 16 281 PS48M PHLP HD SCR M4-.7 X 50
242 PCAP06M CAP SCREW M6-1 X 25 282 PSB1021282 LIFTING EYE BOLT
243 PW03M FLAT WASHER 6MM 283 PSB1021283 UPPER FRAME
5 SPACER 266 PCAP01M CAP SCREW M6-1 X 16
-54-
Page 57

For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09 Model SB1021/SB1022
PARTS
Table & Tensioning System
300
316
310
315
309
313
301
308
314
318
324
302
311
320
303
304
307
319
312
303
302
305
306
317
325
321
322
323
348
346
345
321
303
302
334
349
305
335
347
334
331
350
345
344
303
339
336
332
302
302
330
338
337
342
343
341
301
329
302
333
327
326
328
330
302
329
-55-
Page 58

Model SB1021/SB1022
PARTS
For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09
Table & Tensioning System Parts List
REF PART # DESCRIPTION REF PART # DESCRIPTION
300 PSB1021300 TABLE 325 PR26M INT RETAINING RING 52MM
301 PCAP05M CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 50 326 PSB1021326 LOCK KNOB
302 PLW04M LOCK WASHER 8MM 327 PCAP13M CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 30
303 PW01M FLAT WASHER 8MM 328 PSB1021328 IDLER WHEEL
304 PSB1021304 LEFT TRUNNION BRACKET 329 PCAP14M CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 20
305 PCAP40M CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 35 330 PSB1021330 RETAINING PLATE
306 PSB1021306 TABLE SUPPORT 331 PB03M HEX BOLT M8-1.25 X 16
307 PSB1021307 BLADE GUIDE SUPPORT 332 PSB1021332 RETAINING PLATE
308 PW03M FLAT WASHER 6MM 333 PSB1021333 TRACKING BRACKET
309 PLW03M LOCK WASHER 6MM 334 P6205Z-N BALL BEARING 6205 Z NSK
310 PCAP07M CAP SCREW M6-1 X 30 335 PSB1021335 SPACER
311 PSB1021311 THREADED PIN 336 PR26M INT RETAINING RING 52MM
312 PSB1021312 SPECIAL DOWEL PIN 337 PSB1021337 IDLER SHAFT
313 PSB1021313 BLADE GUIDE BRACKET 338 PSB1021338 LOCK COLLAR
314 PSB1021314 BLADE GUIDE 339 PSS20M SET SCREW M8-1.25 X 8
315 PW03M FLAT WASHER 6MM 341 PSB1021341 TENSION LEADSCREW
316 PCAP06M CAP SCREW M6-1 X 25 342 PSB1021342 HANDWHEEL
317 PCAP04M CAP SCREW M6-1 X 10 343 PSS20M SET SCREW M8-1.25 X 8
318 PSB1021318 LOWER BLADE GUARD 344 PSB1021344 RIGHT TRUNNION BRACKET
319 PW02M FLAT WASHER 5MM 345 PS08M PHLP HD SCR M5-.8 X 12
320 PS40M PHLP HD SCR M5-.8 X 16 346 PSB1021346 POINTER
321 PW04M FLAT WASHER 10MM 347 PSB1021347 POINTER
322 PLW06M LOCK WASHER 10MM 348 PSB1021348 TABLE TRUNNION
323 PCAP72M CAP SCREW M10-1.5 X 30 349 PW04M FLAT WASHER 10MM
324 PSB1021324 RUBBER TIRE 350 PCAP90M CAP SCREW M10-1.5 X 55
-56-
Page 59

For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09 Model SB1021/SB1022
PARTS
Electrical Cabinet
410
411
405
404
406
400
403
402
401
407
412
408
409
413
415
420
419
418
REF PART # DESCRIPTION REF PART # DESCRIPTION
400 PSB1021400 CABINET DOOR 411 PSB1021411 HINGE PIN
401 PSB1021401 OL RELAY AB 193-EEEB 5.4-27A (SB1021) 412 PB47M HEX BOLT M6-1 X 40
401 PSB1022401 OL RELAY AB 193-EEDB 3.2-16A (SB1022) 413 PSB1021413 STRAIN RELIEF NUT
402 PSB1021402 WIRE LOOM 414 PSB1021414 STRAIN RELIEF
403 PSB1021403 TRANSFORMER YA CHANG 220V 1A 415 PSB1021415 WIRE LOOM
404 PSB1021404 ELECTRICAL PANEL 416 PSB1021416 TERMINAL BLOCK 24P
405 PS07M PHLP HD SCR M4-.7 X 8 417 PS07M PHLP HD SCR M4-.7 X 8
406 PS02M PHLP HD SCR M4-.7 X 12 418 PSB1021418 WIRE LOOM
407 PSB1021407 TERMINAL BLOCK 8P 419 PSB1021419 WIRE LOOM
408 PN01M HEX NUT M6-1 420 PSB1021420 CONT. AB 100-C16-400 110V (SB1021)
409 PS07M PHLP HD SCR M4-.7 X 8 420 PSB1022420 CONT. AB 100-C09-400 110V (SB1022)
410 PSB1021410 ELECTRICAL CABINET
417
416
414
-57-
Page 60

Model SB1021/SB1022
PARTS
Welder & Control Panel
For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09
536
534
537
532
534
533
535
533
532
543
535
519
544
545
544
555
547
557
549
548
560
571
556
519
564
558
553
562
559
554
561
547
570
572
563
569
565
564
547
581
566
563
547
566
562
561
567
576
576
577
531
572
573
574
575
531
501
502
500
504
505
503
550
506
512
514
513
515
507
519
516
508
509
511
510
516
508
520
517
513
518
521
515
516
522
523
525
526
521
524
531
530
529
528
527
-58-
Page 61

For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09 Model SB1021/SB1022
PARTS
Welder & Control Panel Breakdown
REF PART # DESCRIPTION REF PART # DESCRIPTION
500 PSB1021500 CAM 535 PSB1021535 TOGGLE SWITCH
501 PW03M FLAT WASHER 6MM 536 PSB1021536 CONTROL PANEL
502 PN01M HEX NUT M6-1 537 PS09M PHLP HD SCR M5-.8 X 10
503 PSB1021503 SPRING ARM 543 PSB1021543 LAMP COVER
504 PSB1021504 SPACER 544 PS09M PHLP HD SCR M5-.8 X 10
505 PCAP01M CAP SCREW M6-1 X 16 545 PSB1021545 WELDING PANEL
506 PCAP38M CAP SCREW M5-.8 X 25547 PSB1021547 RIVET M2 X 6
507 PSB1021507 LOWER EXTENSION SPRING 548 PSB1021548 WELDING CONTROL PANEL
508 PN06M HEX NUT M5-.8 549 PSB1021549 PRESSURE KNOB
509 PS48 PHLP HD SCR 5-40 x 3/4 550 PSB1021550 SPRING ARM BRACKET
510 PLW11 LOCK WASHER #5553 PFH01M FLAT HD SCR M5-.8 X 15
511 PSB1021511 SWITCH 554 PFH05M FLAT HD SCR M5-.8 X 12
512 PSB1021512 SLIDE SEAT 555 PSB1021555 JAW INSULATOR
513 PCAP38M CAP SCREW M5-.8 X 25556 PSB1021556 CAM PIVOT SHAFT
514 PSB1021514 UPPER EXTENSION SPRING 557 PSB1021557 RIGHT ELECTRODE
515 PCAP03M CAP SCREW M5-.8 X 8 558 PCAP33M CAP SCREW M5-.8 X 12
516 PW02M FLAT WASHER 5MM 559 PSB1021559 RIGHT LOWER JAW
517 PLW01M LOCK WASHER 5MM 560 PSB1021560 RIGHT CONNECTING PLATE
518 PSB1021518 SLIDE BLOCK 561 PCAP97M CAP SCREW M5-.8 X 6
519 PSB1021519 ANNEAL SWITCH 562 PLW01M LOCK WASHER 5MM
520 PSB1021520 ANNEAL SWITCH BRACKET 563 PSB1021563 SPECIAL SCREW M8-1.25 X 16
521 PSB1021521 WELD SWITCH 564 PR73M EXT RETAINING RING 5MM
5
22 PCAP24M CAP SCREW M5-.8 X 16 565 PSB1021565 RIGHT CLAMP LEVER
523 PW02M FLAT WASHER 5MM 566 PSB1021566 KNOB
524 PSB1021524 INSULATING WASHER 5MM 567 PSB1021567 LEFT CLAMP LEVER
525 PSB1021525 INSULATING SPACER 5MM 569 PSB1021569 LEFT LOWER JAW
526 PSB1021526 WELDING TRANSFORMER 570 PSB1021570 LEFT CONNECTING PLATE
527 PN06M HEX NUT M5-.8 571 PSB1021571 LEFT ELECTRODE
528 PFH30M FLAT HD SCR M5-.8 X 8 572 PFH07M FLAT HD SCR M5-.8 X 10
529 PSB1021529 GRINDER CAPACITOR 573 PSB1021573 GUARD RETAINING RING
530 PSB1021530 GRINDER MOTOR 574 PSB1021574 GRINDING WHEEL GUARD
531 PSB1021531 TOGGLE SWITCH 575 PN05 HEX NUT 1/4-20
532 PSB1021
533 PSB1021533 POWER LAMP 577 PSB1021577 GRINDING WHEEL 1/4 X 5/8 X 2-1/2
534 PSB1021534 ON SWITCH 581 PSB1021581 WELDING INSTRUCTION PLATE
532 OFF SWITCH 576 PW06 FLAT WASHER 1/4
-59-
Page 62

Model SB1021/SB1022
Machine Labels
600
PARTS
For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09
607
603
606
605
608
609
602
601
603
604
611
610
602
REF PART # DESCRIPTION REF PART # DESCRIPTION
600 PSB1021600 MACHINE ID LABEL (SB1021) 606 PSB1021606 SPEED CHANGE NOTICE LABEL
600 PSB1022600 MACHINE ID LABEL (SB1022) 607 PSBLABEL03VL EYE INJURY HAZARD LABEL
601 PSB1021601 UNSTABLE W/P HAZARD LABEL 608 PSBLABEL01VL READ MANUAL LABEL
602 PSBLABEL02VS DISCONNECT WARNING LABEL 609 PSBLABEL13VS DOOR INJURY HAZARD LABEL
603 PSBLABEL15M ELECTRICITY LABEL 610 PSB1021610 SOUTH BEND GRAY TOUCH-UP PAINT
604 PSB1021604 CUTTING HAZARD LABEL 611 PSB1021611 MODEL NUMBER LABEL (SB1021)
605 PSB1021605 SPEED LABEL 611 PSB1022611 MODEL NUMBER LABEL (SB1022)
The safety labels provided with your machine are used to make the operator aware of the
machine hazards and ways to prevent injury. The owner of this machine MUST maintain the
original location and readability of these safety labels. If any label is removed or becomes
unreadable, REPLACE that label before using the machine again. Contact South Bend Lathe Co. at
(360) 734-1540 or www.southbendlathe.com to order new labels.
-60-
Page 63

WARRANTY
WARRANTY & RETURNS
Warranty
This quality product is warranted by South Bend Lathe Company to the original buyer for one year
from the date of purchase. This warranty does not apply to consumable parts, or defects due to any
kind of misuse, abuse, negligence, accidents, repairs, alterations or lack of maintenance. We do not
reimburse for third party repairs. In no event shall we be liable for death, injuries to persons or
property, or for incidental, contingent, special or consequential damages arising from the use of our
products.
We do not warrant or represent that this machine complies with the provisions of any law, act, code,
regulation, or standard of any domestic or foreign government, industry, or authority. In no event
shall South Bend’s liability under this warranty exceed the original purchase price paid for this
machine. Any legal actions brought against South Bend Lathe Company shall be tried in the State of
Washington, County of Whatcom.
This is the sole written warranty for this machine. Any and all warranties that may be implied by
law, including any merchantability or fitness, for any purpose, are hereby limited to the duration of
this warranty. To take advantage of this warranty, contact us by mail or phone to give us the details
of the problem you are having.
Thank you for your business and continued support.
Page 64

Printed In Taiwan #TRCRBLTSJB12079
 Loading...
Loading...