Page 1

9" x 12" HORIZONTAL VARIABLE SPEED
METAL-CUTTING BANDSAW
WITH SLIDING VISE
MODEL SB1020
OWNER'S MANUAL
Hundreds of Thousands of Lathes Sold With a Tradition of Quality Since 1906!
Copyright © May, 2010 For Machines Mfg. Since 8/09
Page 2

For your convenience, any updates to this manual will be available to download free of charge
through our website at:
www.southbendlathe.com
Scope of Manual
This manual helps the reader understand the machine, how to prepare it for operation, how to control
it during operation, and how to keep it in good working condition. We assume the reader has a basic
understanding of how to operate this type of machine, but that the reader is not familiar with the
controls and adjustments of this specific model. As with all machinery of this nature, learning the
nuances of operation is a process that happens through training and experience. If you are not an
experienced operator of this type of machinery, read through this entire manual, then learn more
from an experienced operator, schooling, or research before attempting operations. Following this
advice will help you avoid serious personal injury and get the best results from your work.
We've made every effort to be accurate when documenting this machine. However, errors sometimes
happen or the machine design changes after the documentation process—so the manual may not
exactly match your machine. If a difference between the manual and machine leaves you in doubt,
contact our customer service for clarification.
We highly value customer feedback on our manuals. If you have a moment, please share your
experience using this manual. What did you like about it? Is there anything you would change to
make it better? Did it meet your expectations for clarity, professionalism, and ease-of-use?
South Bend Lathe, Inc.
C
/O Technical Documentation Manager
P.O. Box 2027
Bellingham, WA 98227
Email: manuals@southbendlathe.com
Manual Feedback
Updates
Customer Service
We stand behind our machines. If you have any service questions, parts requests or general questions
about the machine, feel free to contact us.
South Bend Lathe Co.
P.O. Box 2027
Bellingham, WA 98227
Phone: (360) 734-1540
Parts Department: (417) 886-2954
Fax: (360) 676-1075 (International)
Fax: (360) 734-1639 (USA Only)
Email: cs@southbendlathe.com
Page 3

Table of Contents
INTRODUCTION ...............................................................2
About This Machine .............................................2
Capabilities .........................................................2
Features .............................................................. 2
Identification ........................................................3
Machine Specifications ........................................ 4
SAFETY ................................................................................6
Understanding Risks of Machinery .................... 6
Basic Machine Safety ..........................................6
Additional Metal Bandsaw Safety ...................... 8
PREPARATION .................................................................9
Preparation Overview ..........................................9
Things You'll Need ...............................................9
Power Supply Requirements ............................... 9
Availability ..........................................................9
Full-Load Current Rating .................................... 9
Circuit Information ............................................10
Circuit Requirements for 110V ...........................10
Circuit Requirements for 220V ...........................10
Grounding Requirements ................................... 10
Extension Cords ................................................11
Unpacking .......................................................... 11
Inventory ............................................................11
Cleaning & Protecting ....................................... 12
Location ..............................................................13
Physical Environment ........................................13
Electrical Installation ........................................13
Lighting ............................................................ 13
Weight Load ......................................................13
Space Allocation ................................................ 13
Lifting & Moving ................................................14
Leveling & Mounting ......................................... 14
Leveling ............................................................ 14
Bolting to Concrete Floors ..................................15
Machine Mounts ................................................ 15
Power Connection .............................................. 16
Machine Setup ................................................... 16
Test Run .............................................................17
Inspections & Adjustments ............................... 17
OPERATION ....................................................................18
Operation Overview ........................................... 18
Description of Controls & Components ............19
Blade Selection ...................................................20
Blade Terminology .............................................20
Blade Length ..................................................... 20
Blade Width ...................................................... 20
Tooth Set ...........................................................21
Tooth Type ........................................................ 21
Blade Pitch (TPI) ...............................................22
Blade Changes ...................................................23
Blade Tension .....................................................24
Blade Breakage .................................................. 24
Blade Care & Break-In ...................................... 25
Blade Care ........................................................25
Blade Break-In ..................................................25
Downfeed Rate ...................................................25
Downfeed Pressure ............................................ 25
Blade Speed Chart .............................................26
Chip Inspection Chart ....................................... 26
Angle Cuts .......................................................... 27
Cuts to the Right ............................................... 27
Cuts to the Left .................................................27
Work Stop ........................................................... 27
Blade Guide ........................................................ 28
Vise Quick Release.............................................28
Workpiece Holding .............................................28
Cutting Fluid ......................................................29
Cutting Fluid System ........................................ 29
Operation Tips ................................................... 30
ACCESSORIES ..............................................................31
Accessories .........................................................31
MAINTENANCE ............................................................. 32
Maintenance Schedule .......................................32
Cleaning .............................................................32
Lubrication ......................................................... 32
Gearbox .............................................................33
Machine Storage ................................................ 33
TROUBLESHOOTING .................................................34
SERVICE........................................................................... 37
Blade Brush........................................................37
Angle Stops.........................................................37
Limit Switches ................................................... 38
Downfeed Stop Bolt ...........................................39
Squaring Blade ..................................................40
ELECTRICAL ................................................................... 42
Electrical Safety Instructions ...........................42
220V Conversion ................................................43
Electrical Box Wiring Diagram ......................... 44
Components Wiring Diagram ...........................45
Wiring Component Locations ............................ 46
PARTS................................................................................ 47
Cabinet & Base .................................................. 47
Head ...................................................................49
Machine Labels ..................................................52
WARRANTY & RETURNS .......................................... 53
Page 4

Model SB1020
INTRODUCTION
INTRODUCTION
About This Machine
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
Capabilities
This metal cutting bandsaw uses a gravity-fed
blade to make straight cuts through workpieces
that are clamped in a vise. Since the workpiece is
secured and remains stationary while the blade
lowers automatically, accuracy and operator
safety are maximized.
The vise on the Model SB1020 is capable of
holding rectangular stock up to 9" x 12" and
round stock up to 10".
After a cut is complete, the OFF switch is
triggered and the motor automatically turns off.
Features
In addition to its capabilities, the Model SB1020
has several features to increase versatility and
efficiency.
The headstock can be rotated to make angled
cuts from -45°–60° while variable blade speeds
ensure that the proper cutting speed is available
for a variety of workpiece sizes and materials.
Both the downfeed rate and pressure are
adjustable for fine-tuning each cutting operation
and an adjustable auto-OFF power switch
maximizes safety and minimizes energy use by
turning the machine off at the end of every cut.
A flood coolant system, comprised of a coolant
tank and pump in the machine base and an
adjustable nozzle at the blade provide adequate
coolant for optimum cutting efficiency and blade
life.
A storage compartment in the cabinet base
provides a convenient location for keeping spare
blades or other accessories and the transport
handle makes moving the machine easy.
-2-
Page 5
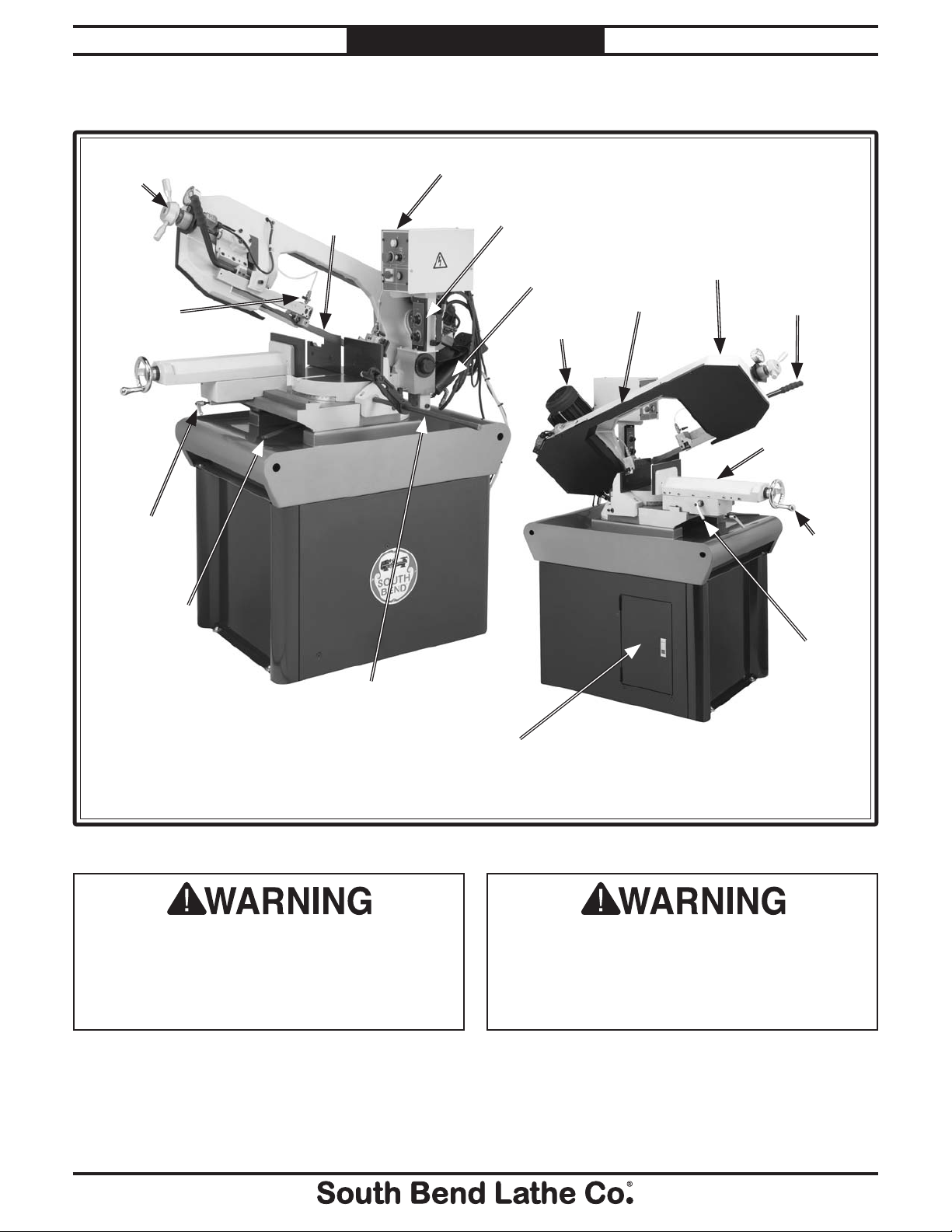
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1020
INTRODUCTION
Identification
Blade Tension
Knob
Coolant
Valve
Vise Slide
Lock
Blade
Control Panel
Downfeed
Controls
Downfeed
Ram
Motor
Blade
Cover
Headstock
Headstock
Vise
Vise
Handwheel
Swivel Lock
Handle
Front View
Work Stop
Figure 1. Identification.
Serious personal injury could occur if
you connect the machine to power before
completing the setup process. DO NOT
connect power until instructed to do so later
in this manual.
Vise Quick
Release
Rear View
Cabinet Access
Door
Untrained users have an increased risk
of seriously injuring themselves with this
machine. Do not operate this machine until
you have understood this entire manual and
received proper training.
-3-
Page 6
Model SB1020
Model SB1020
9" x 12" Horizontal Bandsaw
Product Dimensions:
Weight .......................................................................................................................................................................... 718 lbs.
Length/Width/Height ............................................................................................................................. 55
1
⁄8" x 271⁄2" x 605⁄8"
Foot Print (Length/Width) ...................................................................................................................................27
1
⁄2" x 605⁄8"
Space Required for Full Range of Movement (Length/Width/Height) .......................................................... 65" x 47" x 75"
Shipping Dimensions:
Type ................................................................................................................................................................ Wood Slat Crate
Weight ........................................................................................................................................................................... 838 lbs.
Length/Width/Height ....................................................................................................................................... 59" x 32" x 68"
Electrical:
Required Power Source .................................................................................................. 110V or 220V, Single-Phase, 60 Hz
Switch .................................................................................................................................................. Safety ON/OFF Switch
Switch Voltage .................................................................................................................................................................. 110V
Cord Length ................................................................................................................................................................... 11
1
⁄2 ft.
Cord Gauge .................................................................................................................................................................14 gauge
Full Load Amp Draw ........................................................................................................ 18 Amps @ 110V, 9 Amps @ 220V
Minimum Circuit Size .................................................................................................... 20 Amps @ 110V, 15 Amps @ 220V
Plug Included .......................................................................................................................................................................Yes
Included Plug Type .................................................................................................................................NEMA 5-15 for 110V
Recommended Plug Type for 220V ....................................................................................................................... NEMA 6-15
Motors:
Main
Type ........................................................................................................................................................................TEFC
Horsepower ........................................................................................................................................................... 1
1
⁄2 HP
Voltage ............................................................................................................................................................110V/220V
Phase .................................................................................................................................................................. 3-Phase
Amps ......................................................................................................................................................................... 5.1A
Speed ............................................................................................................................................................... 1725 RPM
Cycle .......................................................................................................................................................................60 Hz
Number Of Speeds .........................................................................................................................................................1
Pre-Wired ................................................................................................................................................................ 110V
Power Transfer ................................................................................................................................ Sealed Worm Gear
Bearings ................................................................................................................... Shielded and Permanently Sealed
Coolant Pump
Type ...................................................................................................................................................Sealed/Waterproof
Horsepower .............................................................................................................................................................
1
⁄8 HP
Voltage ............................................................................................................................................................110V/220V
Phase .......................................................................................................................................................... Single-Phase
Amps ................................................................................................................................................................. 0.9/0.45A
Speed ............................................................................................................................................................... 3450 RPM
Cycle .......................................................................................................................................................................60 Hz
Number Of Speeds .........................................................................................................................................................1
Pre-Wired ................................................................................................................................................................ 110V
P.O. Box 2027, Bellingham, WA 98227 U.S.A.
PHONE: (360) 734-1540 • © South Bend Lathe Co.
www.southbendlathe.com
Machine Specifications
INTRODUCTION
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
Machine Specifications
-4-
Page 7

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1020
Main Specifications:
Operation Information
Head Swivel........................................................................................................................................ -45 deg to 60 deg.
Blade Speeds (Electrical Variable Speed) ................................................................................................ 92–360 FPM
Std. Blade Length ................................................................................................................................................. 108
1
⁄4"
Blade Size Range .................................................................................................................................................. 1-1
1
⁄16"
Cutting Capacities
Angle Cuts ................................................................................................................................................. -45 to 60 deg.
Vise Jaw Depth ....................................................................................................................................................... 12
5
⁄8"
Vise Jaw Height ........................................................................................................................................................ 5
1
⁄2"
Max. Capacity Rect. Height At 90D ........................................................................................................................... 9"
Max. Capacity Rect. Width At 90D .......................................................................................................................... 12"
Max. Capacity Rnd. At 90D ...................................................................................................................................... 10"
Max. Capacity Rect. Height At -45D ....................................................................................................................... 4
3
⁄4"
Max. Capacity Rect. Width At -45D ........................................................................................................................... 7"
Max. Capacity Rnd. At -45D .................................................................................................................................... 6
3
⁄4"
Max. Capacity Rect. Height At 45D ........................................................................................................................ 4
3
⁄4"
Max. Capacity Rect. Width At 45D ............................................................................................................................ 7"
Max. Capacity Rnd. At 45D ..................................................................................................................................... 7
7
⁄8"
Max. Capacity Rect. Height At 60D ........................................................................................................................ 4
1
⁄2"
Max. Capacity Rect. Width At 60D ......................................................................................................................... 6
1
⁄8"
Max. Capacity Rnd. At 60D ..................................................................................................................................... 4
1
⁄2"
Construction
Wheel Construction Upper ..............................................................................................................................Cast Iron
Wheel Construction Lower .............................................................................................................................. Cast Iron
Body Construction ...........................................................................................................................................Cast Iron
Base Construction ............................................................................................................................................Cast Iron
Stand Construction ................................................................................................................................................. Steel
Other
Wheel Size ................................................................................................................................................................12
5
⁄8"
Blade Guides Upper ...................................................................................................................................................Yes
Blade Guides Lower ...................................................................................................................................................Yes
Coolant Capacity ..................................................................................................................................................2
1
⁄2 Gal
Table Info
Floor to Cutting Area Height ..................................................................................................................................35
5
⁄8"
Other Specifications:
ISO Factory ................................................................................................................................................................ ISO 9001
Country Of Origin ........................................................................................................................................................ Taiwan
Warranty .........................................................................................................................................................................1 Year
Serial Number Location .................................................................................................................. ID Label on Body Frame
Customer Setup and Cleaning Time .................................................................................................. Approximately 1 Hour
Sound Rating (No Load) ...................................................................................................................................................80 db
Features:
Heavy-duty one-piece steel stand
Adjustable hydraulic down feed
Swivel mast with angle stops
Built-in coolant system
Storage cabinet
Dual position quick release vise with work stop
Double ball bearings on each side of blade
Quick change variable speed blade control
INTRODUCTION
1
108
⁄4"
1
1–1
⁄16"
-5-
Page 8

Model SB1020
Operating all machinery and machining equipment can be dangerous or relatively safe depending
on how it is installed and maintained, and the operator's experience, common sense, risk awareness,
working conditions, and use of personal protective equipment (safety glasses, respirators, etc.).
The owner of this machinery or equipment is ultimately responsible for its safe use. This
responsibility includes proper installation in a safe environment, personnel training and usage
authorization, regular inspection and maintenance, manual availability and comprehension,
application of safety devices, integrity of cutting tools or accessories, and the usage of approved
personal protective equipment by all operators and bystanders.
The manufacturer of this machinery or equipment will not be held liable for injury or property
damage from negligence, improper training, machine modifications, or misuse. Failure to read,
understand, and follow the manual and safety labels may result in serious personal injury, including
amputation, broken bones, electrocution, or death.
The signals used in this manual to identify hazard levels are defined as follows:
Death or catastrophic
harm WILL occur.
Moderate injury or fire
MAY occur.
Death or catastrophic
harm COULD occur.
Machine or property
damage may occur.
1. Owner’s Manual: All machinery and
machining equipment presents serious
injury hazards to untrained users. To
reduce the risk of injury, anyone who uses
THIS item MUST read and understand
this entire manual before starting.
2. Personal Protective Equipment:
Operating
or servicing this item may expose the user
to flying debris, dust, smoke, dangerous
chemicals, or loud noises. These hazards
can result in eye injury, blindness, longterm respiratory damage, poisoning,
cancer, reproductive harm or hearing loss.
Reduce your risks from these hazards
by wearing approved eye protection,
respirator, gloves, or hearing protection.
3. Trained/Supervised Operators Only:
Untrained users can seriously injure
themselves or bystanders. Only allow
trained and properly supervised personnel
to operate this item. Make sure safe
operation instructions are clearly
understood. If electrically powered, use
padlocks and master switches, and remove
start switch keys to prevent unauthorized
use or accidental starting.
4. Guards/Covers:
Accidental contact with
moving parts during operation may cause
severe entanglement, impact, cutting,
or crushing injuries. Reduce this risk by
keeping any included guards/covers/doors
installed, fully functional, and positioned
for maximum protection.
SAFETY
SAFETY
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
Understanding Risks of Machinery
Basic Machine Safety
-6-
Page 9

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1020
5. Entanglement: Loose clothing, gloves,
neckties, jewelry or long hair may
get caught in moving parts, causing
entanglement, amputation, crushing,
or strangulation. Reduce this risk by
removing/securing these items so they
cannot contact moving parts.
6. Mental Alertness: Operating this item
with reduced mental alertness increases
the risk of accidental injury. Do not let a
temporary influence or distraction lead to a
permanent disability! Never operate when
under the influence of drugs/alcohol, when
tired, or otherwise distracted.
7. Safe Environment:
Operating electrically
powered equipment in a wet environment
may result in electrocution; operating near
highly flammable materials may result in a
fire or explosion. Only operate this item in
a dry location that is free from flammable
materials.
8. Electrical Connection: With electically
powered equipment, improper connections
to the power source may result in
electrocution or fire. Always adhere to all
electrical requirements and applicable
codes when connecting to the power source.
Have all work inspected by a qualified
electrician to minimize risk.
9. Disconnect Power: Adjusting or servicing
electrically powered equipment while it
is connected to the power source greatly
increases the risk of injury from accidental
startup. Always disconnect power
BEFORE any service or adjustments,
including changing blades or other tooling.
10. Secure Workpiece/Tooling:
Loose
workpieces, cutting tools, or rotating
spindles can become dangerous projectiles
if not secured or if they hit another object
during operation. Reduce the risk of this
hazard by verifying that all fastening
devices are properly secured and items
attached to spindles have enough clearance
to safely rotate.
11. Chuck Keys or Adjusting Tools:
Tools used
to adjust spindles, chucks, or any moving/
rotating parts will become dangerous
projectiles if left in place when the machine
is started. Reduce this risk by developing
the habit of always removing these tools
immediately after using them.
12. Work Area:
Clutter and dark shadows
increase the risks of accidental injury.
Only operate this item in a clean, nonglaring, and well-lighted work area.
13. Properly Functioning Equipment:
Poorly
maintained, damaged, or malfunctioning
equipment has higher risks of causing
serious personal injury compared to
those that are properly maintained.
To reduce this risk, always maintain
this item to the highest standards and
promptly repair/service a damaged or
malfunctioning component. Always follow
the maintenance instructions included in
this documentation.
14. Unattended Operation:
Electrically
powered equipment that is left unattended
while running cannot be controlled and is
dangerous to bystanders. Always turn the
power OFF before walking away.
15. Health Hazards: Certain cutting fluids
and lubricants, or dust/smoke created
when cutting, may contain chemicals
known to the State of California to cause
cancer, respiratory problems, birth defects,
or other reproductive harm. Minimize
exposure to these chemicals by wearing
approved personal protective equipment
and operating in a well ventilated area.
16. Difficult Operations:
Attempting
difficult operations with which you are
unfamiliar increases the risk of injury.
If you experience difficulties performing
the intended operation, STOP! Seek an
alternative method to accomplish the
same task, ask a qualified expert how the
operation should be performed, or contact
our Technical Support for assistance.
SAFETY
-7-
Page 10

Model SB1020
SAFETY
Additional Metal Bandsaw Safety
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
1. Blade Condition. A dull or damaged
blade can break apart during operation,
increasing the risk of operator injury. Do
not operate with a dull, cracked or badly
worn blade. Inspect the blade for cracks or
missing teeth before each use.
2. Hand Placement. Hands could be cut
by the blade or crushed when lowering
the headstock. Never position fingers or
thumbs in line with the cut or under the
headstock while it is moving.
3. Blade Guard. Hands and fingers can easily
be cut by the bandsaw blade. To reduce the
risk of laceration injuries, do not operate
this bandsaw without the blade guard in
place.
4. Starting Position. To reduce the
likelihood of blade breakage and possible
entanglement, never turn the saw ON
with the blade resting on the workpiece.
6. Workpiece Handling. A shifting workpiece
can result in impact or laceration injuries.
To reduce the risk of injury, always securely
clamp the workpiece in the vise and use
additional support fixtures if needed. Never
hold the workpiece with your hands during
a cut. Flag long pieces to reduce the risk of
tripping over them.
7. Power Interruption. Unplug the machine
and turn the power switch OFF after a
power interruption. If left plugged in and
turned ON, this machine will start up when
power is restored, resulting in possible
entanglement, laceration, or amputation
hazards.
8. Hot Surfaces/Sharp Edges. Due to the
cutting process, a freshly cut workpiece,
chips, and some machine components can be
hot enough to burn you and sharp enough to
cut you. Allow components to cool and use
safe handling methods to reduce the risk of
these injuries.
5. Blade Replacement. The blade can only
make a safe and efficient cut if the teeth
are facing the workpiece. When replacing
blades, make sure the teeth face toward
the workpiece. Wear gloves to protect
hands and safety glasses to protect eyes.
9. Moving Blade. A moving bandsaw blade
presents a serious risk for laceration or
amputation injuries. Always allow the blade
to come to a complete stop before mounting
or repositioning a workpiece in the vise.
Never touch a moving blade.
-8-
Page 11

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1020
Before installing the machine, consider the
availability and proximity of the required power
supply circuit. If an existing circuit does not meet
the requirements for this machine, a new circuit
must be installed.
To minimize the risk of electrocution, fire,
or equipment damage, installation work and
electrical wiring must be done by a qualified
electrician in accordance with all applicable
codes and standards.
The full-load current rating is the amperage
a machine draws at 100% of the rated output
power. On machines with multiple motors, this is
the amperage drawn by the largest motor or sum
of all motors and electrical devices that might
operate at one time during normal operations.
The full-load current is not the maximum
amount of amps that the machine will draw. If
the machine is overloaded, it will draw additional
amps beyond the full-load rating.
If the machine is overloaded for a sufficient
length of time, damage, overheating, or fire may
result—especially if connected to an undersized
circuit. To reduce the risk of these hazards,
avoid overloading the machine during operation
and make sure it is connected to a power supply
circuit that meets the requirements in the
following section.
PREPARATION
Preparation Overview
PREPARATION
Power Supply
The purpose of the preparation section is to help
you prepare your machine for operation. The
list below outlines the basic process to follow
to prepare your machine for operation. Specific
steps for each of these points will be covered in
detail later in this section.
The typical preparation process is as follows:
1. Unpack the machine and inventory the
contents of the carton.
2. Clean the machine and its components.
3. Make any necessary adjustments or
inspections to ensure the machine is ready
for operation.
4. Connect the machine to the power source.
5. Test run the machine to make sure it
functions properly and is ready for operation.
Things You'll Need
The items listed below are required to
successfully set up and prepare this machine for
operation.
Requirements
Availability
Electrocution or fire may
occur if machine is not
correctly grounded and
attached to the power
supply. Use a qualified
electrician to ensure a safe
power connection.
Full-Load Current Rating
For Lifting
• Aforkliftorotherpowerliftingdevicerated
for the weight of the machine.
• LiftingStraps or Chains (rated for at least
1000 lbs. each)
For Machine Setup
• Wrench12mm
• Wrench14mm
For Power Connection
• Apowersourcethatmeetstheminimum
circuit requirements for this machine. (Refer
to the Power Supply Requirements
section for details.)
• Aqualifiedelectriciantoensureasafeand
code-compliant connection to the power
source.
Full-Load Rating at 110V ................... 18 Amps
Full-Load Rating at 220V ..................... 9 Amps
-9-
Page 12
Model SB1020
This machine is prewired to operate on a 110V
power supply circuit that has a verified ground
and meets the following requirements:
For your own safety and protection of property,
consult a qualified electrician if you are unsure
about wiring practices or electrical codes in
your area.
Note: The circuit requirements listed in this
manual apply to a dedicated circuit—where only
one machine will be running at a time. If this
machine will be connected to a shared circuit
where multiple machines will be running at
the same time, consult a qualified electrician to
ensure that the circuit is properly sized for safe
operation.
A power supply circuit includes all electrical
equipment between the main breaker box or fuse
panel in your building and the incoming power
connections inside the machine. This circuit must
be safely sized to handle the full-load current
that may be drawn from the machine for an
extended period of time.
This machine can be converted to operate on
a 220V power supply. To do this, follow the
Voltage Conversion instructions included in
this manual. The intended 220V circuit must
have a verified ground and meet the following
requirements:
In the event of certain types of malfunctions or
breakdowns, grounding provides a path of least
resistance for electric current—in order to reduce
the risk of electric shock.
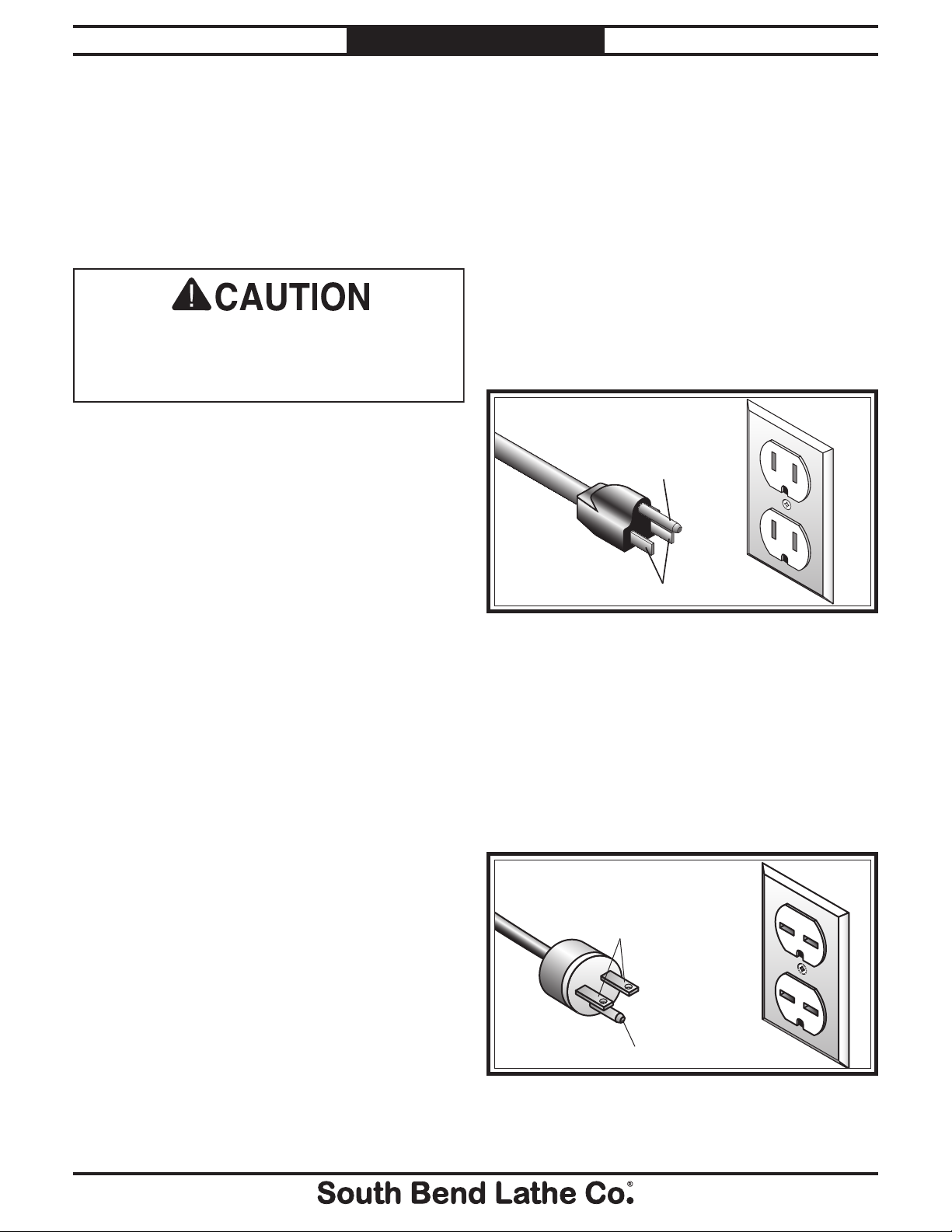
Grounding Prong
Current Carrying Prongs
5-15 PLUG
GROUNDED
5-15 RECEPTACLE
This machine is equipped with a power cord
that has an equipment-grounding wire and a
grounding plug (similar to the figure below).
The plug must only be inserted into a matching
receptacle (outlet) that is properly installed and
grounded in accordance with all local codes and
ordinances.
Use the plug type listed in the Circuit
Requirements for this voltage. The listed plug
(similar to the figure below) has an equipmentgrounding wire to safely ground the machine.
The plug must only be inserted into a matching
receptacle (outlet) that is properly installed and
grounded in accordance with all local codes and
ordinances.
Grounding Prong
Current Carrying Prongs
6-15 PLUG
GROUNDED
6-15 RECEPTACLE
PREPARATION
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
Circuit Information
Grounding Requirements
For 110V Connection (Prewired)
Circuit Requirements for 110V
Nominal Voltage ...............................110V/120V
Cycle .............................................................60 Hz
Phase ..............................................Single-Phase
Circuit Rating....................................... 20 Amps
Plug/Receptacle (included) ...........NEMA 5-15
Circuit Requirements for 220V
Nominal Voltage ...............................220V/240V
Cycle .............................................................60 Hz
Phase ..............................................Single-Phase
Circuit Rating....................................... 15 Amps
Plug/Receptacle ...............................NEMA 6-15
-10-
Figure 2. NEMA 5-15 plug and receptacle.
For 220V Connection
Figure 3. NEMA 6-15 plug and receptacle.
Page 13
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1020
This item was carefully packaged to prevent
damage during transport. If you discover any
damage, please immediately call Customer
Service at (360) 734-1540 for advice. You may
need to file a freight claim, so save the containers
and all packing materials for possible inspection
by the carrier or its agent.
Serious injury could occur if you connect
the machine to power before completing the
setup process. DO NOT connect to power until
instructed later in this manual.
Improper connection of the equipment-grounding
wire can result in a risk of electric shock. The
wire with green insulation (with or without
yellow stripes) is the equipment-grounding wire.
If repair or replacement of the power cord or
plug is necessary, do not connect the equipmentgrounding wire to a live (current carrying)
terminal.
Check with a qualified electrician or service
personnel if you do not understand these
grounding requirements, or if you are in doubt
about whether the tool is properly grounded.
If you ever notice that a cord or plug is
damaged or worn, disconnect it from power, and
immediately replace it with a new one.
We do not recommend using an extension cord
with this machine. If you must use one, only
use it if absolutely necessary and only on a
temporary basis.
Extension cords cause voltage drop, which may
damage electrical components and shorten motor
life. Voltage drop increases as the extension cord
size gets longer and the gauge size gets smaller
(higher gauge numbers indicate smaller sizes).
Any extension cord used with this machine
must contain a ground wire, match the required
plug and receptacle listed in the Circuit
Requirements for the applicable voltage, and
meet the following requirements:
PREPARATION
Unpacking
Inventory
The items listed below are optional components
and are not required for bandsaw operations.
Description Qty
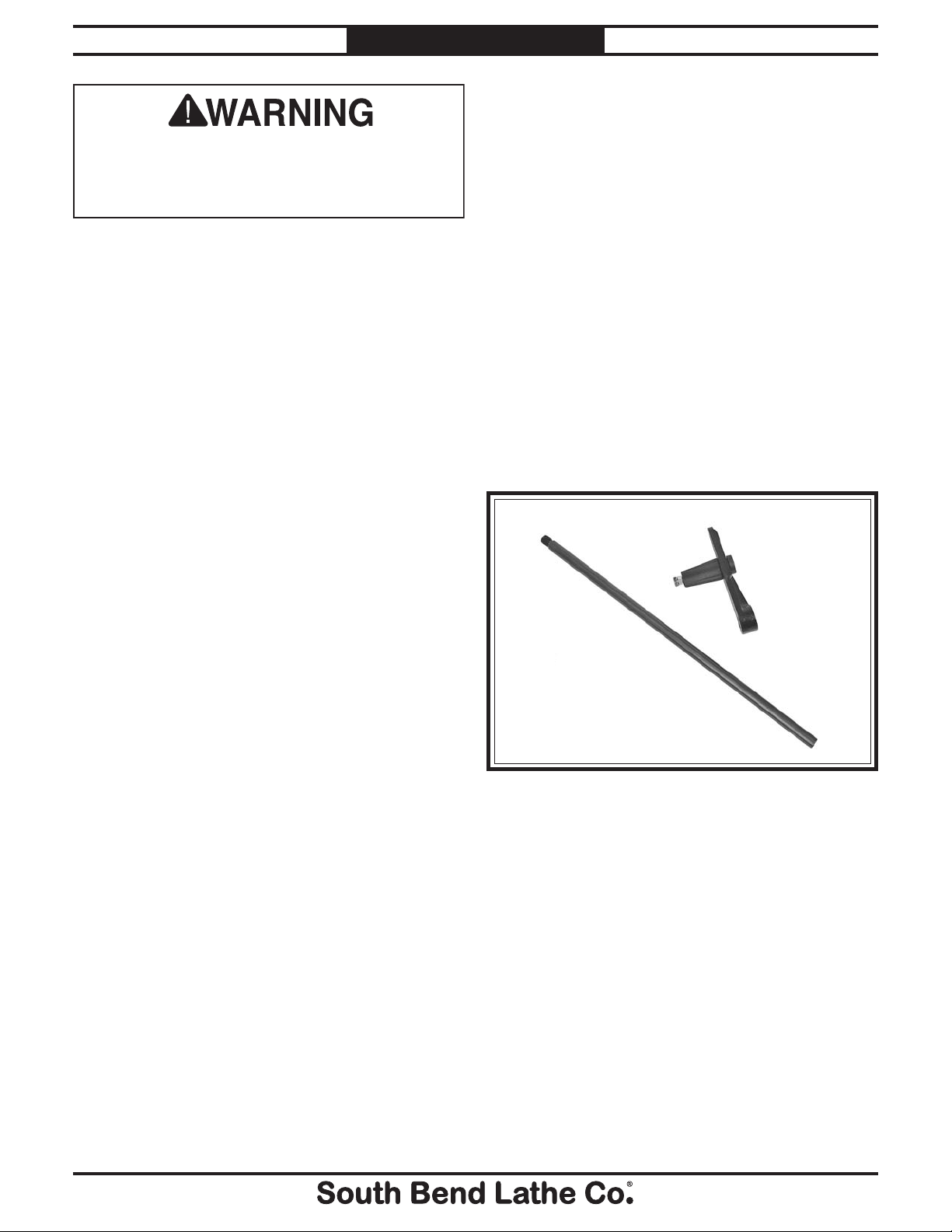
A. Work Stop .......................................................1
B. Work Stop Rod
Extension Cords
Minimum Gauge Size ............................12 AWG
Maximum Length (Shorter is Better) ....50 ft.
A
B
Figure 4. Inventory.
-11-
Page 14
Model SB1020
The unpainted surfaces are coated at the factory
with a heavy-duty rust preventative that
prevents corrosion during shipment and storage.
The benefit of this rust preventative is that it
works very well. The downside is that it can be
time-consuming to thoroughly remove.
Be patient and do a careful job when cleaning
and removing the rust preventative. The time
you spend doing this will reward you with
smooth-sliding parts and a better appreciation
for the proper care of the unpainted surfaces.
Although there are many ways to successfully
remove the rust preventative, we have cleaned
thousands of machines and found the following
process to be the best balance between efficiency
and minimized exposure to toxic fumes or
chemicals.
Before cleaning, gather the following:
• Disposablerags
• Cleaner/degreaser (certain citrus-based
degreasers work extremely well and they
have non-toxic fumes)
• Safetyglasses&disposablegloves
Note: Automotive degreasers, mineral spirits, or
WD•40canbeusedtoremoverustpreventative.
Before using these products, though, test them
on an inconspicuous area of a painted area to
make sure they will not damage it.
Basic steps for removing rust preventative:
1. Put on safety glasses and disposable gloves.
2. Coatallsurfacesthathaverustpreventative
with a liberal amount of your cleaner or
degreaser and let them soak for a few
minutes.
3. Wipe off the surfaces. If your cleaner or
degreaser is effective, the rust preventative
will wipe off easily.
Note: To clean off thick coats of rust preventative
on flat surfaces, such as beds or tables, use
aPLASTICpaintscrapertoscrapeoffthe
majority of the coating before wiping it off
withyourrag.(Donotuseametalscraperor
it may scratch the surface.)
4. Repeat Steps 2–3 as necessary until clean,
then coat all unpainted surfaces with a
quality metal protectant or light oil to
prevent rust.
GAS
Gasoline and petroleum
products have low flash
points and can explode
or cause fire if used for
cleaning. Avoid using these
products to remove rust
preventative.
Many cleaning solvents are
toxic if inhaled. Minimize
your risk by only using
these products in a well
ventilated area.
Avoid chlorine-based solvents, such as
acetone or brake parts cleaner that may
damage painted surfaces. Always follow the
manufacturer’s instructions when using any
type of cleaning product.
PREPARATION
Cleaning & Protecting
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
-12-
Page 15
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1020
Power
Connection
(Drawing Not to Scale)
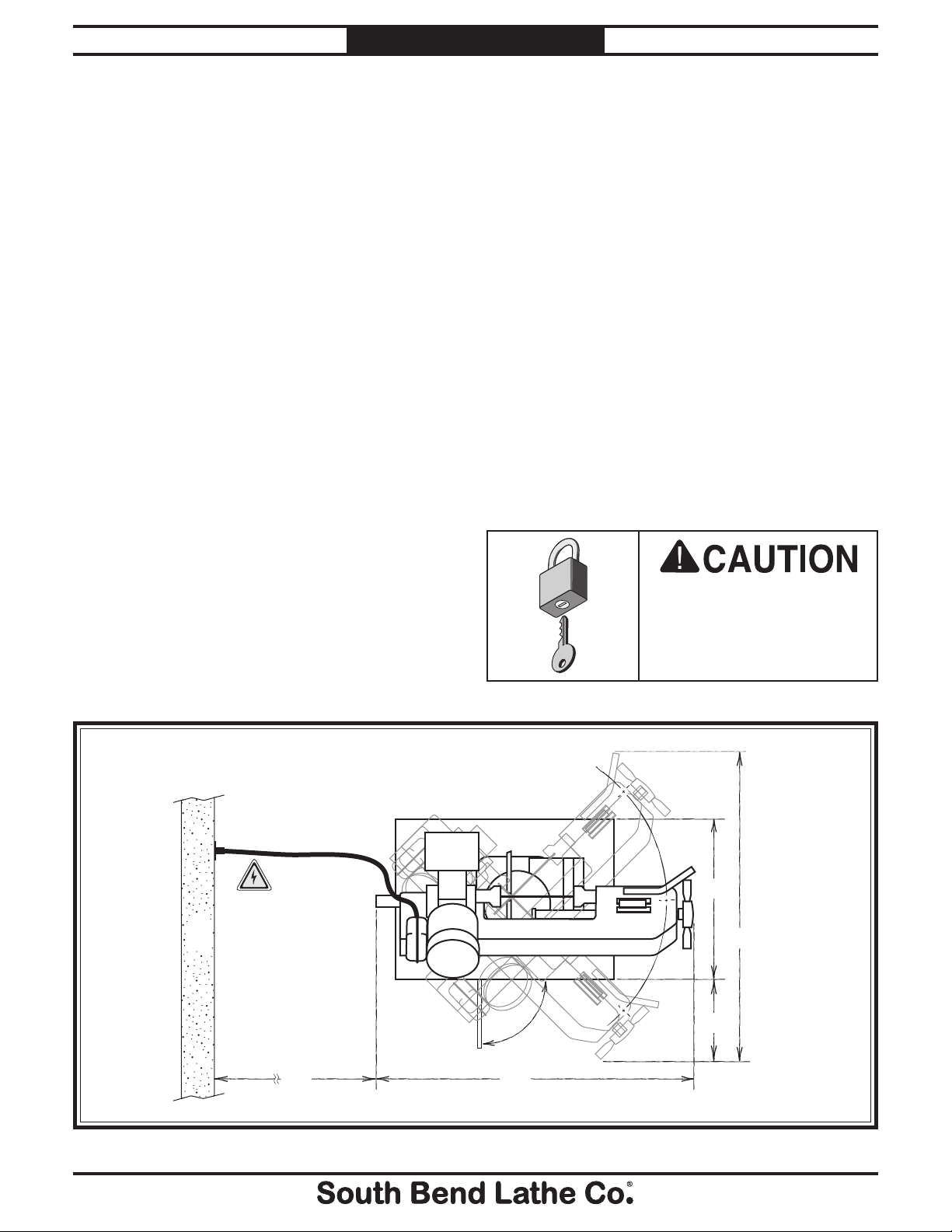
55"
Minimum
30"
27¾"
15"
60¾"
Wall
Weight Load
Refer to the Machine Specifications for the
weight of your machine. Make sure that the
surface upon which the machine is placed will
bear the weight of the machine, additional
equipment that may be installed on the machine,
and the heaviest workpiece that will be used.
Additionally, consider the weight of the operator
and any dynamic loading that may occur when
operating the machine.
Space Allocation
Consider the largest size of workpiece that will
be processed through this machine and provide
enough space around the machine for adequate
operator material handling or the installation
of auxiliary equipment. With permanent
installations, leave enough space around
the machine to open or remove doors/covers
as required by the maintenance and service
described in this manual.
Physical Environment
The physical environment where your machine
is operated is important for safe operation and
longevity of parts. For best results, operate this
machine in a dry environment that is free from
excessive moisture, hazardous or flammable
chemicals, airborne abrasives, or extreme
conditions. Extreme conditions for this type
of machinery are generally those where the
ambient temperature is outside the range of 41°–
104°F; the relative humidity is outside the range
of 20–95% (non-condensing); or the environment
is subject to vibration, shocks, or bumps.
Electrical Installation
Place this machine near an existing power
source. Make sure all power cords are protected
from traffic, material handling, moisture,
chemicals, or other hazards. Make sure to leave
access to a means of disconnecting the power
source or engaging a lockout/tagout device.
Lighting
Lighting around the machine must be adequate
enough that operations can be performed
safely. Shadows, glare, or strobe effects that
may distract or impede the operator must be
eliminated.
Children or untrained
people may be seriously
injured by this machine.
Only install in an access
restricted location.
PREPARATION
Location
Physical Environment
Electrical Installation
Lighting
Weight Load
Space Allocation
Figure 5. Clearances.
-13 -
Page 16
Model SB1020
Leveling machinery helps precision components,
such as bed ways, remain straight and flat
during the lifespan of the machine. Components
on an unleveled machine may slowly twist due to
the dynamic loads placed on the machine during
operation.
For best results, use a precision level that
is at least 12" long and sensitive enough to
show a distinct movement when a 0.003" shim
(approximately the thickness of one sheet of
standard newspaper) is placed under one end of
the level.
See the figure below for an example of a high
precision level.
We strongly recommend securing your
machine to the floor if it is hardwired to the
power source. Consult with your electrician to
ensure compliance with local codes.
Generally, you can either bolt your machine
to the floor or mount it on machine mounts.
Although not required, we recommend that you
secure the machine to the floor and level it while
doing so. Because this is an optional step and
floor materials may vary, hardware for securing
the machine to the floor is not included.
PREPARATION
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
Lifting & Moving
This machine and its
parts are heavy! Serious
personal injury may occur
if safe moving methods are
not used. To reduce the
risk of a lifting or dropping
injury, ask others for help
and use power equipment.
Unbolt the machine from its pallet, then insert
two round steel bars through the lifting holes
in the machine base. Attach lifting straps and
hooks to the bars as shown in Figure 6. Lift
the machine just high enough to clear the
pallet, then move it to its final location. Have an
assistant stabilize the machine while moving.
Leveling & Mounting
Leveling
Figure 6. Lifting location.
Figure 7. Example of a precision level.
-14-
Page 17
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1020
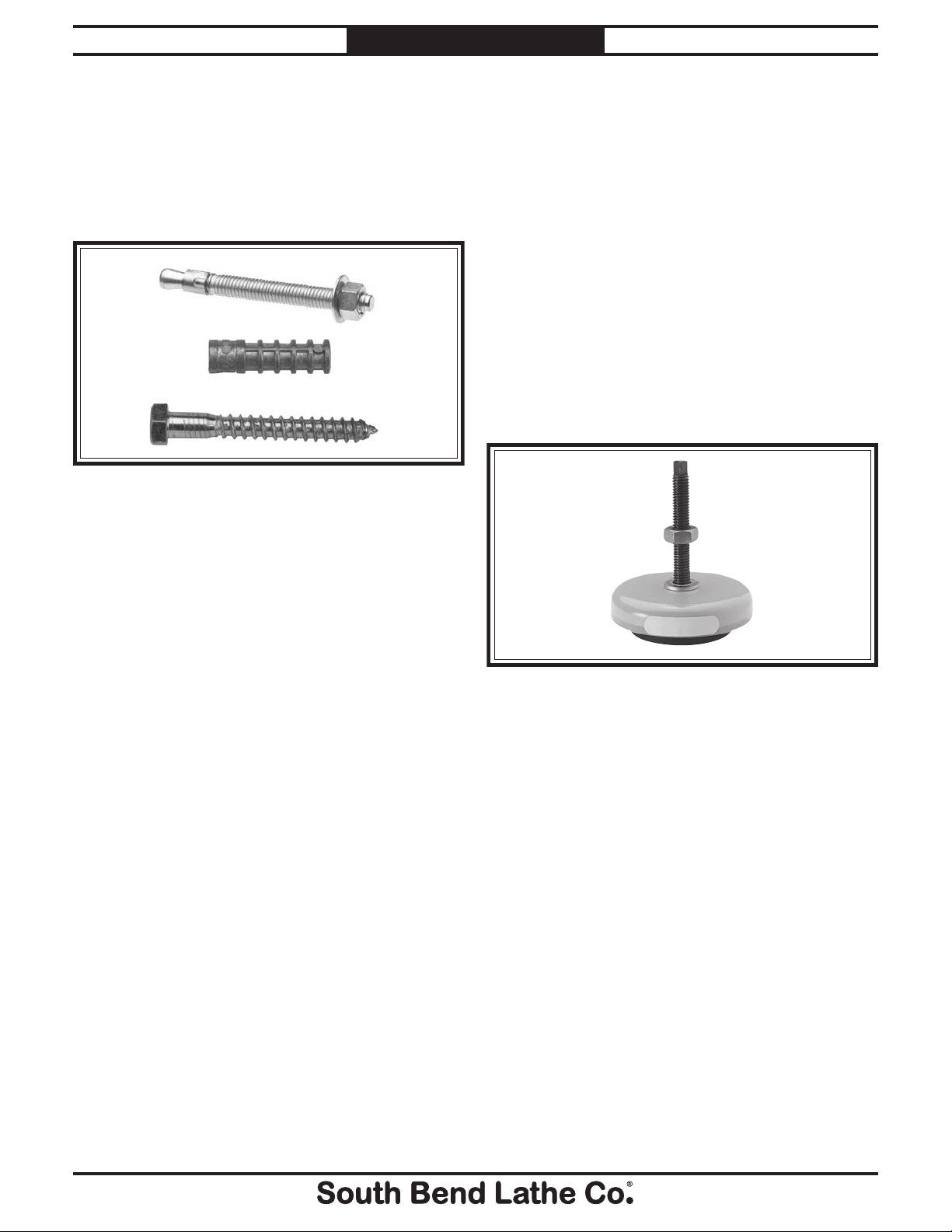
Lag Screw
and Anchor
Anchor
Stud
Lag screws and anchors, or anchor studs
(below), are two popular methods for securing
machinery to a concrete floor. We suggest you
research the many options and methods for
securing your machine and choose the best one
for your specific application.
Machine mounts are rubber pads mounted to
a threaded stud, which can be fastened to the
bottom of the machine.
Machine mounts offer certain advantages such
as ease of installation, vibration dampening, and
easy leveling. They also make it easier to relocate
the machine later on.
The disadvantage of machine mounts is that the
machine can shift or move over time. For this
reason, electrical codes may limit their use if
the machine is hardwired to the power source.
Also, mounts may reduce the total surface area
of machine-to-floor contact, depending on the
design of the machine.
PREPARATION
Bolting to Concrete Floors
Figure 8. Common types of fasteners for bolting
machinery to concrete floors.
Machine Mounts
Figure 9. Typical machine mount.
-15 -
Page 18

Model SB1020
PREPARATION
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
Power Connection
Electrocution or fire
may occur if machine is
ungrounded, incorrectly
connected to power, or
connected to an undersized
circuit. Use a qualified
electrician to ensure a safe
power connection.
Once your machine is set up and assembled as
previously described in this manual, it is ready to
be connected to the power source.
• Ifyouplantousethemachineat110V,
simply plug it into a receptacle on a 110V
circuit that meets the requirements listed on
Page 10.
Machine Setup
To ensure that your bandsaw arrives without
damage to the hinge system, a shipping strap
was installed. After removing the shipping strap,
you may choose to install the work stop.
To set up the machine:
1. Remove the shipping strap hex bolt and
strap as shown in Figure 10. Keep this
shipping strap in case you transport or ship
the bandsaw in the future.
Shipping Strap
• Ifyouplantousethemachineat220V,you
will have to convert the machine for 220V.
Refer to Electrical, beginning on Page 42.
Figure 10. Removing a shipping strap.
2. Thread the work stop rod into the vise base.
3. Slide the work stop onto the work stop rod,
position it as necessary, then tighten the set
screw shown in Figure 11.
Work Stop
-16 -
Set Screw
Figure 11. Installing work stop.
Page 19

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1020
Test Run
After all preparation steps have been completed,
the machine and its safety features must be
tested to ensure correct operation. If you discover
a problem with the operation of the machine or
its safety components, do not operate it further
until you have resolved the problem.
Note: Refer to Troubleshooting on Page 34
for solutions to common problems that may
occur with metal-cutting bandsaws. If you need
additional help, contact our Tech Support at
(360) 734-1540.
To test run your machine:
1. Read and follow the safety instructions at
the beginning of the manual, take the required safety precautions, and make sure the
machine is set up properly.
2. Clear away all tools and objects used during
assembly and preparation.
PREPARATION
4. Put on safety glasses and secure loose
clothing or long hair.
5. Lift the headstock to the raised position,
then close the downfeed knob to prevent it
from lowering.
6. Start the bandsaw, but keeping your finger
near the emergency stop button at all times
during the test run. The bandsaw should run
smoothly with little or no vibration.
— If you suspect any problems, immediately
turn the bandsaw OFF, disconnect it from
power, and correct the problem before
continuing.
— If you need any help with your bandsaw
call our Tech Support at (360) 734-1540.
7. Open the downfeed knob to lower the saw
through its full range of motion. When it
reaches the bottom of its travel, it should
turn OFF.
3. Open the downfeed knob (see Figure 12)
and allow the headstock to travel all the
way down. If the blade contacts the machine
base, adjust the downfeed stop bolt as
described in Downfeed Stop Bolt, on Page
39.
Downfeed
Knob
Figure 12. Downfeed valve location.
— If it does, Congratulations! The test run is
complete.
— If it does not, turn it OFF, disconnect it
from power, then proceed immediately to
Limit Switches, on Page 38.
Inspections &
Adjustments
The following list of adjustments were performed
at the factory before your machine was shipped.
If you find that the adjustments are not set
according to the procedures in this manual or
your personal preferences, re-adjust them.
• Squaring Blade ..................................Page 40
• BladeGuides .....................................Page 28
-17-
Page 20

Model SB1020
To reduce the risk of
serious injury when using
this machine, read and
understand this entire
manual before beginning
any operations.
The purpose of this overview is to provide
the novice machine operator with a basic
understanding of how the machine is used during
operation, so they can more easily understand
the controls discussed later in this manual.
Note: Due to the generic nature of this overview,
it is not intended to be an instructional guide
for performing actual machine operations.
To learn more about specific operations and
machining techniques, seek training from people
experienced with this type of machine, and do
additional research outside of this manual by
reading "how-to" books, trade magazines, or
websites.
OPERATION
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
OPERATION
Operation Overview
To complete a typical cutting operation, the
operator does the following:
1. Examines the workpiece to make sure it is
suitable for cutting.
2. Raises the headstock, then closes the
downfeed valve.
3. Adjusts the headstock angle for the type of
cut, then securely clamps the workpiece in
the vise.
4. Adjusts the guide post to within 1" of the
workpiece, and verifies that the blade is
properly tensioned.
5. Adjusts the downfeed rate adjust knob for
the correct feed rate.
6. Makes sure the workpiece and bandsaw are
stable and that there are no obstructions in
the way of the cut.
Loose hair, clothing, or
jewelry could get caught
in machinery and cause
serious personal injury.
Keep these items away
from moving parts at all
times to reduce this risk.
During operation, small
metal chips may become
airborne, leading to serious
eye injury. Wear safety
glasses to reduce this risk.
7. Puts on safety glasses.
8. Starts the bandsaw and waits for the blade
to reach full speed.
9. Opens the downfeed valve to lower the head
and blade into the workpiece, then allows
the bandsaw to complete the cut.
10. Once the bandsaw has stopped, raises the
head, and removes the workpieces.
-18 -
Page 21

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1020
OPERATION
P. Main Power Switch: Turns the saw ON/OFF.
Description of Controls
Q. Emergency Stop Button: Cuts power to the
& Components
motor.
Refer to Figures 13–15 and the following
descriptions to become familiar with the basic
controls and components used to operate this
machine.
A. Blade Tension Knob: Applies or releases
blade tension.
B. Blade Tension Gauge: Displays blade
tension.
C. Guide Post Lock Screw: Locks the guide post
in the position set by the operator.
D. Control Panel: Controls the electrical
components of the machine.
E. Downfeed Rate Adjust Knob: Controls the
speed at which the blade lowers into the cut.
F. Downfeed Valve: Controls the starting and
stopping of the headstock downfeed.
B
C
A
J
G
I
Figure 13. Controls and components (front).
H
D
E
F
G. Work Stop: An adjustable stop for cutting
multiple workpieces at the same length.
H. Vise Slide Lock Lever: Locks the vise in the
position set by the operator.
I. Swivel Lock Handle: Locks the headstock in
the position set by the operator.
J. Vise Handwheel: Controls the vise jaw
movement.
K. Headstock Handle: Serves as a lift-point for
the headstock.
L. Vise Jaw Quick Release Lever: Releases the
vise leadscrew so the vise can quickly open
or close without the use of the handwheel.
M. Indicator Lamp: Lights when the saw is ON.
N. Variable Blade Speed Knob: Adjusts the
blade speed.
L
Figure 14. Controls and components (rear).
M
Q
P
K
N
O
O. ON Button: Starts the saw and coolant pump.
Figure 15. Control panel.
-19 -
Page 22

Model SB1020
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
OPERATION
Blade Selection
Selecting the right blade for the cut requires a
knowledge of various blade characteristics. This
section breaks down blade characteristics to help
the reader make an informed decision about
what blade to use for a given operation.
Blade Terminology
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
Tooth Rake: The angle of the tooth face
E.
from a line perpendicular to the length of the
blade.
Gullet Depth: The distance from the tooth
F.
tip to the bottom of the curved area (gullet).
Tooth Pitch: The distance between tooth
G.
tips.
Blade Back: The distance between the bot-
H.
tom of the gullet and the back edge of the
blade.
Blade Pitch or TPI: The number of teeth per
I.
inch measured from gullet to gullet.
Blade Length
Measured by the blade circumference, blade
lengths are usually unique to the brand of your
bandsaw and the distance between the wheels.
Figure 16. Bandsaw blade terminology.
A. Kerf: The width of the cut made during op-
eration.
Tooth Set: The distance each tooth is bent
B.
left or right from the blade.
Gauge: The thickness of the blade.
C.
Blade Width: The widest point of the blade
D.
measured from the tip of the tooth to the
back edge of the blade.
Model Blade Length
SB1020 .......................................................... 108
1
⁄4"
Blade Width
Measured from the back of the blade to the tip
of the blade tooth (the widest point), blade width
is often the first consideration given to blade
selection. Blade width dictates the largest and
smallest curve that can be cut, as well as how
accurately it can cut a straight line—generally
the wider the blade, the straighter it will cut.
Model Blade Width
SB1020 ............................................................. 1
1
⁄16"
-20-
Page 23

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1020
Standard (or Raker)
Variable Pitch (VP)
Variable Pitch Positive Rake
Hook (or Claw)
Skip (or Skip Tooth)
Alternate
Wavy
Raker
OPERATION
Tooth Set
Three common tooth sets are alternate, wavy,
and raker (see Figure 17). Each removes
material in a different manner to make the kerf
in the workpiece.
Figure 17. Bandsaw blade tooth sets.
Alternate: An all-purpose arrangement with
teeth bent evenly left and right of the blade.
Generally used for milder metals.
Wavy: Generally three or more teeth in a group
that are bent one way, followed by a non-set
tooth, and then a group bent the other way.
Recommended for straight cuts in thin metals or
thin-wall tubing.
Raker: Three teeth in a recurring group—one
bent left, next one bent right, and then a nonset tooth. The raker set is ideal for most contour
cuts.
Tooth Type
The most common tooth types are described
below and illustrated in Figure 18. Each
removes, gathers, and expels material
differently.
Figure 18. Bandsaw blade tooth types.
Variable Pitch (VP): Varying gullet depth and
tooth spacing, a "0" rake angle, excellent chip
removing capacity, and smooth cutting.
Variable Pitch with Positive Rake: Varying
gullet depth and tooth spacing, a positive rake
angle, better chip formation, and aggressive
cutting.
Hook or Claw: Wide gullets (round or flat),
equally spaced teeth, positive rake angle, and
fast cut with good surface finish.
Skip or Skip Tooth: Wide, flat gullets, a "0" rake
angle, equally spaced teeth, and recommended
for non-ferrous materials.
Standard or Raker: Equally spaced teeth set at
a "0" rake angle. Recommended for all purpose
use.
-21-
Page 24

Model SB1020
TOOTH SELECTION
50
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 192½ 3½
75 100 150 200 250 300 350 400
2/3
2/3
2/3 1.4/2.5
1.4/2.5
1.5/.8
1.5/.8
3/4
3/4
3/4
4/6
4/6
5/8
450
mm
inch
OPERATION
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
Blade Pitch (TPI)
The chart below is a basic starting point for
choosing teeth per inch (TPI) for variable pitch
blades and standard raker set bi-metal blades/
HSS blades. However, for exact specifications
of bandsaw blades that are correct for your
operation, contact the blade manufacturer.
To select the correct blade pitch:
1. Measure the material thickness. This
measurement is the distance from where
each tooth enters the workpiece to where it
exits the workpiece.
2. Refer to the "Material Width/Diameter"
row of the blade selection chart in Figure
19, and read across to find the workpiece
thickness you need to cut.
Material Width/Diameter
Material Shapes
3. Refer to the "Material Shapes" row and find
the shape of the material to be cut.
4. In the applicable row, read across to the
right and find the box where the row and
column intersect. Listed in the box is the
minimum TPI recommended for the variable
tooth pitch blades.
5. The "Cutting Speed Rate Recommendation"
section of the chart offers guidelines for
various metals, given in feet per minute
(FPM). Choose the speed closest to the
number shown in the chart.
Teeth Per Inch (TPI) for Bandsaw Blades
-22-
Figure 19. General guidelines for blade selection and speed chart.
Page 25

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1020
!
Blade Travel
!
OPERATION
Blade Changes
Change blades when they become dull, damaged,
or if the operation requires a different type of
blade.
To change the blade on the bandsaw:
1. DISCONNECT BANDSAW FROM POWER!
2. Raise the head of the bandsaw, then remove
the blade cover.
3. Loosen the tension knob and slip the blade
off of the wheels.
Figure 21. Blade cutting direction.
4. Install the new blade through both blade
guides, as shown in Figure 20, and around
the bottom wheel.
Figure 20. Typical blade installation.
5. Hold the blade around the bottom wheel
with one hand and slip it around the top
wheel with the other hand, keeping the blade
between the blade guides.
Note: It is sometimes possible to flip the
blade inside out, in which case the blade will
be installed in the wrong direction. Check to
make sure the blade teeth are facing toward
the workpiece, as shown in Figure 21, after
installing it on the bandsaw. Some blades
will have a directional arrow you can use as
a guide.
6. When the blade is around both wheels,
adjust the position so the back of the blade
is against the wheel shoulder, as shown in
Figure 22.
Wheel Shoulder
Blade
Guides
Figure 22. Typical blade/wheel position.
7. Tighten the tension knob so the blade will
not slip on the wheels upon startup.
8. Connect the bandsaw to the power source.
9. Briefly turn the bandsaw ON then OFF to
position the blade and resume the previous
tracking. Proceed to Blade Tension on
Page 24.
-23-
Page 26

Model SB1020
!
OPERATION
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
blade selection
Blade Tension
Proper blade tension is essential to avoid blade
vibration, twist, or`slippage on the wheels. A
correctly tensioned blade provides long life,
straight cuts, and efficient cutting times.
The three major signs of incorrect blade tension
are: 1) The blade stalls in the cut and slips on the
wheels, 2) the blade frequently breaks, and 3) the
bandsaw does not make straight cuts.
To tension the blade on the bandsaw:
1. Make sure the blade is tracking properly.
2. DISCONNECT BANDSAW FROM POWER!
3. Loosen and slide the blade guide as far out
as it will go, then tighten it down again.
4. Turn the tension knob in Figure 23
clockwise to tighten the blade or clockwise to
loosen the blade.
Tension
Gauge
Blade Breakage
Many conditions may cause a bandsaw blade to
break. Some of these conditions are unavoidable
and are the natural result of the stresses placed
on the bandsaw; other causes of blade breakage
are avoidable.
The most common causes of avoidable blade
breakage are:
• Faulty alignment or adjustment of the blade
guides.
• Forcing or twisting a wide blade around a
tight radius.
• Feeding the workpiece too fast.
• Dull or damaged teeth.
• Over-tensioned blade.
• Top blade guide assembly set too high above
the workpiece. Adjust the top blade guide
assembly so that there is approximately
1
⁄8"–1⁄4" between the bottom of the assembly
and the workpiece. Understand that with
smaller workpieces, this may not be possible.
In these cases, simply adjust the blade guide
as far down as possible.
Blade
Tension
Knob
Figure 23. Adjusting blade tension.
5. Tighten the blade until the tension gauge
moves into the green section.
-24-
• Using a blade with a lumpy or improperly
finished braze or weld.
• Continuously running the bandsaw when not
in use.
• Leaving the blade tensioned when not in use.
• Using the wrong blade pitch (TPI) for the
workpiece thickness. The general rule of
thumb is to have no fewer than three teeth
in contact with the workpiece when starting
a cut and at all times during cutting.
Page 27

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1020
OPERATION
Blade Care & Break-In
Blade Care
To prolong blade life, always use a blade with
the proper width, set, type, and pitch for each
application. Maintain the appropriate feed rate,
feed pressure, and blade speed and pay attention
to the chip characteristics (Refer to the Chip
Inspection Chart on Page 26). Keep your
blades clean, since dirty or gummed up blades
pass through the cutting material with much
more resistance than clean blades, causing
unnecessary heat.
Blade Break-In
The tips and edges of a new blade are extremely
sharp. Cutting at too fast of a feed rate or too
slow of a blade speed can fracture these tips
and edges, quickly dulling the blade. Properly
breaking-in a blade allows these sharp edges
to wear without fracturing, thus keeping the
blade sharp longer. Below is a typical break-in
procedure. For aftermarket blades, refer to the
manufacturer's break-in procedure to keep from
voiding the warranty.
Use the Chip Inspection Chart on Page 26 as
a guide to evaluate the chips and ensure that the
optimal blade speed and feed rate are being used.
To properly break-in a new blade:
1. Choose the correct speed for the blade and
material of the operation.
2. Reduce the feed pressure by half for the first
50–100 in
2
of material cut.
Downfeed Rate
Start and stop downfeed with the downfeed knob.
The downfeed rate is adjusted by turning the
downfeed rate adjust knob (Figure 24). Turning
the knob clockwise decreases the downfeed rate
and turning the knob counterclockwise increases
the downfeed rate.
Downfeed Rate
Adjust Knob
Downfeed
Knob
Figure 24. Downfeed pressure adjustment.
Downfeed Pressure
The downfeed pressure is controlled by the
spring shown in Figure 25.
To decrease downfeed pressure, turn the cap
screw clockwise to increase spring tension.
To increase downfeed pressure, turn the cap
screw counterclockwise to release spring tension.
3. To avoid twisting the blade when cutting,
adjust the feed pressure when the total
width of the blade is in the cut.
Cap
Screw
Spring
Figure 25. Downfeed rate adjustment.
-25-
Page 28

Model SB1020
Copper
Alloy
229~482
(70) (147)
203~213
(62) (65)
85-203
(26) (62)
220
(67)
220~534
(67) (163)
203
(62)
85
(26)
321
(98)
180~220
(54) (67)
95~213
(29) (65)
242
(75)
65~85
(20) (26)
180~220
(54) (67)
75~118
(25) (36)
246
(75)
108~225
(33) (75)
196~354
(60) (108)
203
(62)
111~321
(34) (98)
150~203
(46) (62)
Aluminum
Alloy
Thin
Tube
Angle
Steel
Carbon
Steel
Speed FPM
(M/Min)
Speed FPM
(M/Min)
Speed FPM
(M/Min)
Speed FPM
(M/Min)
Material Material Material Material
Tool Steel
Mold Steel
High-Speed
Tool Steel
Alloy
Steel
Water
Hardened
Tool Steel
Stainless
Steel
CR Stainless
Steel
Free Machining
Stainless Steel
Gray
Cast Iron
Ductile
Austenitic
Cast Iron
Malleable
Cast Iron
Plastics
Cold-Work
Tool Steel
Hot-Work
Tool Steel
Oil-Hardened
Tool Steel
CUTTING SPEED RATE RECOMMENDATION
thin & curled
thin & curled
short, hard & thick
thin & curled
short, hard & thick
thick, hard & strong
thin & curled
short, hard & thick
thick, hard & strong
thick, hard & strong
thin & curled
short, hard & thick
thick, hard & strong
thick, hard & strong
hard & thin
thin & curled
short, hard & thick
thick, hard & strong
thick, hard & strong
thin & straight
hard & thin
thin & curled
short, hard & thick
thick, hard & strong
thick, hard & strong
thin & straight
powdery
hard & thin
thin & curled
short, hard & thick
thick, hard & strong
thick, hard & strong
thin & straight
powdery
thin & curled tightly
hard & thin
OPERATION
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
Blade Speed Chart
The chart in Figure 26 offers blade speed guidelines for various metals, given in feet per minute
(FPM) and meters per minute (M/Min). Choose the closest available speed on the machine, then
adjust the feed rate as necessary, using the appearance of the chips produced as a guide. Refer to
the Chip Inspection Chart that follows for recommendations on adjusting feed rate or blade speed
based on the appearance of the chips produced.
Figure 26. Dry cutting blade speed chart.
Chip Inspection Chart
The best method for choosing the cutting speed and feed rate for a cutting operation is to inspect the
chips created by the cut. These chips are indicators of what is commonly referred to as the "chip load."
Refer to the chip inspection chart below to evaluate chip characteristics and determine whether to
adjust feed rate/pressure, blade speed, or both.
Chip
Appearance
Hard, Thick & Short Brown or Blue Increase Decrease
Hard, Coiled & Thin Silver Increase Decrease
-26-
Coiled, Tight & Thin Silver Good Decrease
Chip
Description
Chip
Color
Blade
Speed
Feed Rate/
Pressure
Thin & Curled Silver Good Good
Hard, Strong &
Thick
Hard, Strong,
Curled & Thick
Brown or Blue Increase Decrease
Silver or Light
Brown
Good
Decrease
Slightly
Straight & Thin Silver Good Increase
Powdery Silver Decrease Increase
Figure 27. Chip inspection chart.
Check Blade
Check Blade
Check Blade
Other
Actions
Pitch
Pitch
Pitch
Page 29

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1020
!
OPERATION
3. Loosen the vise slide lock (see Figure 28).
Angle Cuts
The headstock can be swiveled to cut angles
from 0–60° to the left and 0–45° to the right for
a total swing of 105°. When making cuts to the
right, the vise should remain in the left-most
position. If you need to make a cut to the left, you
will have to move the vise to the right side of the
machine.
Cuts to the Right
1. DISCONNECT BANDSAW FROM POWER!
2. Loosen the lock handle shown in Figure
28, then swivel the headstock to the desired
angle, using the angle scale as a guide.
Swivel Lock
Handle
4. Slide the vise to the right until it stops.
Figure 29. Moving vise.
5. Move the saw through its full range of
motion to make sure the blade will not
contact the vise during operation, then
tighten the swivel lock handle.
Vise Slide
Lock
Figure 28. Swivel base.
3. Move the saw through its full range of
motion to make sure the blade will not
contact the vise during operation, then
tighten the swivel lock handle.
Angle Scale
Cuts to the Left
1. DISCONNECT BANDSAW FROM POWER!
2. Lift the headstock to the upmost position,
then close the downfeed valve to prevent it
from lowering.
Work Stop
The Model SB1020 is equipped with a work
stop that can be used to quickly position the
workpiece during a repetitive cutting operation.
Adjust the work stop as needed, then tighten the
set screw and knob to lock it in place, as shown
in Figure 30.
Knob
Set Screw
Figure 30. Work stop.
-27-
Page 30

Model SB1020
!
NOT
RECOMMENDED
RECOMMENDED
OPERATION
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
Blade Guide
The upper blade guide should adjusted to
approximately
The support provided by having the blade guide
close to the workpiece ensures straight cuts and
reduces blade tendency to twist or drift.
To adjust the blade guide:
1. DISCONNECT BANDSAW FROM POWER!
2. Loosen the cap screw in Figure 31 and slide
the blade guide to approximately
from the workpiece, then re-tighten the cap
screw.
1
⁄4" away from the workpiece.
1
⁄4" away
Blade Guide
Vise Quick Release
The Model SB1020 has a vise quick release
handle that allows the operator to quickly
adjust the opening of the jaws without the use
of the handwheel. Rotate the handle clockwise
to disengage the vise leadscrew, then slide the
vise open or closed as needed. To re-engage the
leadscrew, release the vise quick release handle.
Vise Quick Release
Handle
Cap Screw
Figure 31. Blade guides.
Figure 32. Vise quick release handle.
Workpiece Holding
Figure 33 shows the correct methods for holding
different workpiece shapes.
Figure 33. Workholding options by material shape.
-28-
Page 31

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1020
OPERATION
Cutting Fluid
While simple in concept and function, many
issues must be taken into account to find and use
the correct cutting fluid. Always follow all product
warnings and contact the f luid manufacturer for
unanswered questions.
Use the information below as a guideline to choose
the appropriate cutting fluid. Always refer to the
cutting fluid manufacturer for specific application
and safety information:
• Forcuttinglowalloy,lowcarbon,and
general-purpose category metals with a
bi-metal blade —use a water soluble cutting
fluid.
• Forcuttingstainlesssteels,highcarbon,and
high alloy metals, brass, copper and mild
steels—use "Neat Cutting Oil" (commonly
undiluted mineral oils) that have extreme
pressure additives (EP additives).
Cutting Fluid System
This bandsaw has a built-in cutting fluid system
that extends the life of your bandsaw blades
by lowering the temperature of the blade and
workpiece and washing away chips.
To use the cutting fluid system:
1. Thoroughly clean and remove any foreign
material that may have fallen inside the
reservoir during shipping.
2. Place the filter screen and drain tube in the
reservoir as shown in Figure 34.
Drain
Tube
• For cutting cast iron, cutting fluid is not
recommended.
Remember: Too much flow at the cutting fluid
nozzles will make a mess and can make the work
area unsafe; and not enough fluid at the cut will
heat the blade, causing the blade teeth to load up
and break.
Tip: Using a refractometer or hydrometer to
replenish water in water-based coolant can extend
the life of blades and coolant, and ensure consistent cutting results.
BIOLOGICAL AND POISON
HAZARD! Use proper personal
protection equipment when
handling cutting fluid and
follow federal, state, and fluid
manufacturer requirements
to properly dispose of cutting
fluid.
High
Low
Figure 34. Filter screen and hose.
3. Fill the reservoir to the "high" mark with
your chosen cutting fluid solution.
Magnesium fires are
extremely dangerous!
When cutting magnesium,
always use a cutting fluid
intended for this type of
metal and carefully follow
the fluid manufacturer's
recommendations.
-29-
Page 32

Model SB1020
4. Adjust the valves on the coolant hoses to
control the flow of coolant (see Figure 35).
Make sure that the pressure is not so high
that coolant spills on the floor and creates a
slipping hazard.
OPERATION
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
Operation Tips
Review the following tips to help you safely and
effectively operate your bandsaw and get the
maximum life out of your saw blades.
Coolant Control Valves
Figure 35. Coolant control valve.
NOTICE
Keep the tray chip screen clear so coolant can
recycle to the pump reservoir. NEVER operate
the pump with the reservoir below the low
mark or you may over-heat the pump and void
your warranty!
• Usetheworkstoptoquicklyandaccurately
cut multiple pieces of stock to the same
length.
• Letthebladereachfullspeedbefore
engaging the workpiece. Never start a cut
with the blade in contact with the workpiece.
• Payattentiontothechipsproducedbythe
cutting operation and use their appearance
to fine-tune the blade speed, feed speed,
and pressure (refer to the Chip Inspection
Chart on Page 26).
• Waituntilthebladehascompletelystopped
before removing the workpiece from the vise,
and avoid touching the cut end—it could be
very hot!
Release blade tension at the end of each use
to prolong blade life.
-30-
Page 33

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1020
ACCESSORIES
Accessories
This South Bend merchandise may be available
through your local South Bend Lathe Co. dealer.
If you do not have a dealer in your area, please
call us at (360) 734-1540 or email us at
cs@southbendlathe.com.
SB1298—SBL Bench Lathe Shop Clock
SB1299—SBL Toolroom Lathe Shop Clock
SB1300—SBL Lathe with Man
These fine traditional shop clocks are constructed
with a metal antique-finished frame. They are
easy to read from a distance and measure 14"
in diameter. Pictures just don't do them justice.
They are very nice quality clocks and perfect for
the South Bend Lathe aficionado.
ACCESSORIES
SBL Gearhead T-Shirt
SBL One Good Turn T-Shirt
100% Cotton, preshrunk T-shirts, available in
sizes S, M, L, XL, 2XL, 3XL.
SB1298 SB1299
SB1300
Figure 36. Antique-finished South Bend shop clocks.
Figure 37. Official South Bend Lathe T-Shirts.
-31-
Page 34

Model SB1020
!
MAINTENANCE
MAINTENANCE
Maintenance Schedule
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
Lubrication
Before applying lubricant to any area, wipe the
area clean to avoid contamination.
Always disconnect
machine from power before
performing maintenance or
serious personal injury may
result.
For optimum performance from your machine,
follow this maintenance schedule and refer to
any specific instructions given in this section.
Daily
• Check/correctloosemountingbolts.
• Check/correct damaged or dull saw blade.
• Check/correct worn or damaged wires.
• Clean/protect table.
• Cleanmetalchipsfromupperandlower
wheel areas, and empty the chip chute.
• Correct any other unsafe condition.
Monthly
• Lubricateall components outlined in this
section, with the exception of the gearbox.
• Monitorgearboxoillevelbyremovingthefill
plug and checking that the oil level is even
with the fill hole (with headstock lowered)
Lubricate the following areas:
A. Blade Tension Mechanism: Open the main
blade guard, then drop a few drops of oil on
the tension knob lead screw.
B. Blade and Guides: Drop a few drops of light
machine oil on the blade and the blade
guides daily.
C. Gear Box: Change the gear oil annually.
D. Table and Machined Surfaces: Keep bare
metal surfaces rust-free with regular
applications of a quality way oil.
E. Vise Leadscrew: Clean the leadscrew, then
brush on a thin layer oft grease as needed.
A
B
E
C
Yearly
• Lubricategearbox.
Cleaning
Use a brush and a shop vacuum to remove chips
and other debris from the machine. Keep the
non-painted surfaces rust-free with regular
applications of a high quality rust preventative.
Periodically remove the blade and thoroughly
clean all metal chips or built-up grease from the
wheel surfaces and blade housing.
D
Figure 38. Lubrication points.
-32-
Page 35

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1020
MAINTENANCE
Gearbox
Items Needed Qty
Wrench 4mm ......................................................... 1
Mobilgear 600 XP 680 or ISO 680 Equivalent
Gear Oil ........................ Approximately 1 Pint
Drain Pan .............................................................. 1
Shop Rags ...............................................As needed
Wooden Blocks .......................................As needed
To change the gearbox oil:
1. DISCONNECT BANDSAW FROM POWER!
2. Loosen the gearbox fill plug (see Figure 39).
Machine Storage
All machinery will develop serious rust problems
and corrosion damage if it is not properly
prepared for storage. If decommissioning this
machine, use the steps in this section to ensure
that it remains in good condition.
To prepare your machine for storage or
decommission it from service:
1. DISCONNECT BANDSAW FROM POWER!
2. Thoroughly clean all unpainted, bare metal
surfaces, then coat them with a light weight
grease or rust preventative. Take care to
ensure these surfaces are completely covered
but that the grease or rust preventative is
kept off of painted surfaces.
If the machine will be out of service for only
a short period of time, use a quality mediumweight machine oil (not auto engine oil) in
place of the grease or rust preventative.
Fill Plug
Figure 39. Gearbox fill plug.
3. Place the drain pan under the drain plug,
then remove the drain plug (see Figure 40)
to drain the oil.
Drain Plug
Figure 40. Gear box lubrication.
4. Replace the drain plug, lower the headstock,
then add oil through the fill plug hole until
the oil level reaches the fill hole.
3. Loosen or remove the blade so it does not
stretch or rust while the machine is stored.
4. If the machine will be out of service for only
a short period of time, start the machine
once a week and run all gear-driven
components for a few minutes. This will
put a fresh coat of gear oil on the gearing
components inside the gearbox.
If it will be out of service for a long period
of time, drain, then completely fill the
gearbox with the recommended gear oil so
components above the normal oil level do
not develop rust. (Make sure to put a tag
on the controls as a reminder for the recommissioning process to adjust the gear oil
level before starting the machine.)
5. Completely cover the machine with a tarp
or plastic sheet that will keep out dust and
resist liquid or moisture. If machine will be
stored in/near direct sunlight, use a cover
that will block the sun's rays.
5. Replace the fill plug.
-33-
Page 36

Model SB1020
!
TROUBLESHOOTING
TROUBLESHOOTING
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
If you need replacement parts, or if you are unsure how to do any of the solutions given here, feel free
to call us at (360) 734-1540.
Symptom Possible Cause Possible Solution
Machine does not
start.
Main motor
chatters during
startup or during
operation.
Machine has
excessive vibration
or noise.
1.
Power supply switched off/has
incorrect voltage.
2.
Blown fuse/tripped circuit breaker
at main panel.
3.
Plug or receptacle is corroded or
mis-wired.
4.
Break or short in wiring; or loose
connections.
5.
Motor wired incorrectly.
6.
Motor ON/OFF switch at fault.
7.
Start capacitor blown or at fault.
8.
Centrifugal switch at fault.
9.
Motor at fault.
1.
Extension cord (if used) is causing
voltage drop.
2.
Power supply has incorrect voltage
on one or more legs.
1.
Blade is missing teeth.
2.
Guide post is loose.
3.
Motor or table is loose.
4.
Machine incorrectly mounted on
floor.
5.
Centrifugal switch out of
adjustment; at fault.
6.
Air is in the hydraulic system,
causing the headstock to "hop".
7.
Motor bearings worn or damaged.
8.
Wheel bearings are worn.
1.
Switch power supply on/verify voltage.
2.
Correct the cause of overload, then reset/replace
fuse or breaker.
3.
Clean/retighten contacts; correct the wiring.
4.
Trace/replace broken or corroded wires; fix loose
connections.
5.
Wire motor correctly (refer to inside junction box
cover or manual).
6.
Replace switch.
7.
Replace start capacitor.
8.
Adjust/replace centrifugal switch.
9.
Test for shorted windings, bad bearings and repair
or replace.
1.
Move machine closer to the power source or use a
larger gauge or shorter extension cord.
2.
Contact your power company to fix the power
supply.
1.
Replace blade.
2.
Tighten the guide post.
3.
Tighten any loose fasteners.
4.
Level/shim base; tighten/adjust mounting hardware
or feet.
5.
Adjust/replace centrifugal switch.
6.
Bleed hydraulic system.
7.
Replace motor bearings or replace motor.
8.
Replace wheel bearings.
-34-
Page 37

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1020
!
TROUBLESHOOTING
Symptom Possible Cause Possible Solution
Motor stalls
or slows when
operating.
Workpiece angle
incorrect or out of
square.
Blade tracks
incorrectly, slips on
wheels, or comes
off wheels.
1.
Too much pressure when feeding
workpiece.
2.
Workpiece is warped and binding
blade.
3.
Blade is dull, wanders, and gets
pinched in the cut.
4.
Blade is loose.
5.
Blade is loading up.
6.
Blade is not correct for material
being cut.
7.
Motor overheated.
8.
Motor wired incorrectly.
9.
Motor at fault.
1.
Scale not calibrated or loose vise.
2.
Blade guides are loose or out of
alignment.
1.
Blade tension is too loose.
2.
Incorrect blade for bandsaw.
3.
Feed rate is too fast.
4.
Blade guides need adjustment.
5.
Blade is bell-mouthed.
6.
Blade is dull, wanders, and gets
pinched in the cut.
7.
Wheels are loaded with metal
shavings.
8.
The blade has insufficient support.
1.
Reduce pressure when feeding workpiece.
2.
Fabricate a jig for better workpiece control.
3.
Replace blade, adjust guides and tracking.
4.
Clean wheels and increase blade tension.
5.
Install a blade with more suitable TPI or different
style of teeth.
6.
Use the correct blade for the operation. Refer to
Blade Selection section beginning on Page 24.
7.
Let cool, clean motor, and reduce workload.
8.
Review wiring diagram on motor cover; correct wire
connections.
9.
Test for shorted windings, bad bearings and repair
or replace.
1.
Zero fence to blade and realign scale. Tighten any
loose fasteners.
2.
Tighten any loose hardware or lock levers. Align the
blade guides (see Page 28).
1.
Increase blade tension (see Page 24).
2.
Install correct blade for machine (see Page 24).
3.
Reduce feed rate, or decrease blade TPI.
4.
Adjust blade guides (see Page 40).
5.
Install new blade, and regularly remove tension
from blade when not in use.
6.
Replace blade, re-secure the workpiece from
shifting.
7.
Clean wheels.
8.
Tighten the blade guide as close to the workpiece as
possible (not less than
1
⁄4").
-35-
Page 38

Model SB1020
!
TROUBLESHOOTING
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
Symptom Possible Cause Possible Solution
The cut is crooked,
the blade wanders,
cuts slow, or shows
overheating on one
side of the cut or
the blade.
Blade dulls
prematurely, or
metal sticking to
the blade.
1.
The feed rate/pressure is too high.
2.
Loose blade.
3.
Blade is loading up.
4.
Incorrect coolant mixture for
workpiece/cut.
5.
Blade installed backwards.
6.
Dull blade; missing teeth.
7.
The blade speed is wrong.
1.
Blade is improperly broken in.
2.
The blade gullets are loading up
with chips.
3.
The blade TPI is too fine for the
workpiece, so the teeth load up and
overheat.
4.
Incorrect coolant mixture for
workpiece/cut.
5.
The workpiece has hard spots,
welds, or scale.
1.
Decrease the feed rate/pressure (see Page 25).
2.
Keep blade properly tensioned (see Page 24).
3.
Install a blade with more suitable TPI or different
style of teeth.
4.
Use correct coolant mixture (refer to coolant
manufacturer's recommended mixture).
5.
Check blade rotation as described in “test run” and
reverse blade if necessary.
6.
Replace blade 23.
7.
Adjust feed rate and cutting speed as required (see
Page 25).
1.
Replace blade, and complete blade break in
procedure (see Pages 23 & 24).
2.
Use a blade that has larger gullets to carry out
material.
3.
Use a coarser-tooth blade, adjust feed rate, adjust
blade speed, make sure the brush is working.
4.
Use correct coolant mixture (refer to coolant
manufacturer's recommended mixture).
5.
Replace the blade with a special blade for cutting
hardened materials.
Repetitive ticking
noise coming from
machine.
Blade wears on
one side or shows
overheating.
Vibration when
operating or
cutting.
1.
Blade is missing teeth.
2.
Blade weld contacting blade guides.
3.
Blade weld may be failing.
1.
The blade guides are worn or misadjusted.
2.
The blade support is inadequate.
3.
Dull or incorrect blade.
4.
Incorrect coolant mixture for
workpiece/cut.
5.
Blade is bell-mouthed.
1.
Loose or damaged blade.
2.
Worn wheel bearing.
3.
Bent or dull blade.
4.
Loose machine component.
5.
Wheels worn or incorrectly
installed.
6.
Bandsaw blade wheel appears bent.
1.
Replace blade 23.
2.
Grind blade weld down smaller.
3.
Cut and reweld the blade, or replace the blade.
1.
Re-adjust or replace the blade guides.
2.
Tighten the blade guide as close to the workpiece as
possible.
3.
Replace blade (see Page 23).
4.
Use correct coolant mixture (refer to coolant
manufacturer's recommended mixture).
5.
Install new blade (see Page 23).
1.
Tighten or replace blade (see Pages 24 & 23).
2.
Check/replace wheel bearing.
3.
Replace blade (see Page 23).
4.
Tighten loose component.
5.
Replace wheels.
6.
Check and replace for bad wheel or bearing.
-36-
Page 39

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1020
Stationary Jaw
Movable
Jaw
Square
Blade
Vise
SERVICE
SERVICE
Blade Brush Angle Stops
The Model SB1020 has a blade brush to help
keep metal chips off the blade wheels. It will
wear over time and require re-adjustment when
it no longer contacts the blade.
Tools Needed Qty
Hex Wrench 4mm .................................................1
To adjust the blade brush:
1. DISCONNECT BANDSAW FROM POWER!
2. Loosen the button head cap screws shown in
Figure 41.
Blade Brush
The swivel base is equipped with three angle
stops to provide quick adjustments to 60° to the
left, 0°, and 45 to the right°. If cuts made using
these stops are not sufficiently accurate, the
stops will need to be adjusted.
Tools Needed Qty
Wrench 12mm ....................................................... 1
To adjust the angle stops:
1. DISCONNECT BANDSAW FROM POWER!
2. Rotate the headstock to the right
approximately 10°, engage the 0° angle stop
(Figure 42) by flipping it up, then rotate the
headstock to the left until it stops against
the 0° stop. Tighten the headstock lock lever.
0° Stop Bolt
Button
Head Cap
Screws
Figure 41. Blade brush adjustments.
3. Slide the blade brush bracket as needed so
1
the blade extends approximately
⁄8" into the
bristles of the brush. Hold the bracket in
position, then re-tighten the button head cap
screws.
Figure 42. 0° Angle stop.
3. Lower the headstock, then place a square
flat on the table and against both the
stationary jaw and the blade, as shown in
Figure 43.
Figure 43. Testing vise/blade squareness.
-37-
Page 40

Model SB1020
Stationary Jaw
Movable
Jaw
Square
Blade
Vise
45° R
60° L
!
4. If the square does not fit snugly against both
the stationary jaw and the blade, loosen the
jam nut shown in Figure 44, then thread
the stop bolt inward.
Jam Nut
Figure 44. Stop adjustment.
5. Loosen the headstock lock lever, rotate the
headstock so that the blade is square to
the vise, then re-tighten the headstock lock
lever.
Stop Bolt
SERVICE
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
Limit Switches
The Model SB1020 is equipped with limit
switches that prevent the saw from operating
if the blade is not properly tensioned and stop
the saw motor when it reaches the end of a cut.
If either of these functions does not operate
correctly, you will need to adjust the appropriate
limit switch.
To adjust the blade tension switch:
1. DISCONNECT BANDSAW FROM POWER!
2. Tension the blade until the tension gauge
reads 20,000 PSI, which is the transition
from yellow to green.
3. Use a 3mm hex wrench to loosen the two
button head cap screws that secure the blade
tension switch bracket shown in Figure 46.
Button Head
Cap Screws
Blade
Tension
Switch
6. Adjust the stop bolt as needed until it just
touches the cast iron swivel base, as shown
in Figure 44, then snug the jam nut against
the stop block without turning the stop bolt.
7. Repeat this procedure for the 60° left and 45°
right stops using a 45° square and a 30°/60°
triangle (or an adjustable square), as shown
in Figure 45.
Switch Plate
Figure 46. Blade tension limit switch.
4. Slide the switch away from the switch plate
to make sure it releases, then slowly slide it
back towards the switch plate just until you
hear the switch click. Hold it in this position,
the re-tighten the button head cap screws.
5. Release tension from the blade. If the switch
does not immediately click again, signaling
that tension has been released, repeat Steps
3–4, slightly adjusting the switch away from
the switch plate.
Figure 45. 60° left and 45° right stop adjustment.
-38-
Page 41

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1020
SERVICE
To adjust the headstock travel switch:
1. DISCONNECT BANDSAW FROM POWER!
2. Fully lower the headstock by opening the
downfeed valve. Allow it to come to a stop on
its own (see Downfeed Stop Bolt on this
page for more details).
3. Loosen the Phillips head screws that secure
the blade travel limit switch shown in
Figure 46.
Phillip Head
Screws
Downfeed Stop Bolt
The Model SB1020 has an adjustable stop bolt to
prevent the blade from contacting the table when
the headstock reaches the bottom of its travel. If
the blade contacts the table, or if the blade does
not travel far enough to complete the cut, this
bolt will have to be adjusted.
To adjust the downfeed stop bolt:
1. DISCONNECT BANDSAW FROM POWER!
2. Adjust the downfeed stop bolt and jam nut
shown in Figure 48 with a 14mm wrench, so
the bandsaw blade teeth are just below the
table surface when the cut is complete.
3. Tighten the jam nut against the base to pre-
vent the stop bolt from loosening during use.
Limit
Switch
Figure 47. Blade stop limit switch
(viewed from above).
4. Slide the switch away from the control panel
column to make sure it releases, then slowly
slide it back towards the column just until
you hear the switch click. Hold it in this
position, then re-tighten the Phillips head
screws.
5. Lift the headstock, then allow it to lower
on its own, adjusting the feed rate knob if
necessary. Listen for a click from the switch
when the headstock reaches the bottom of
its travel. If the switch does not click, repeat
Steps 3–4, slightly adjusting the switch
slightly towards the control panel column.
Downfeed Stop Bolt
Figure 48. Adjusting downfeed stop bolt.
-39-
Page 42

Model SB1020
SERVICE
Squaring Blade
A blade that is perpendicular to the table surface
provides the best cutting results with minimal
side loading and blade wear. The blade is held
perpendicular to the table by the two blade
guides. Each guide is held in place by two cap
screws and aligned with the four set screws
shown in Figure 49.
Blade Guide
(1 of 2)
Set
Screws
Cap
Screws
Figure 49. Blade guide adjustments.
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
4. If the blade is not square to the table, loosen
the cap screws shown in Figure 49 one to
two turns. Remove the blade brush assembly
(refer to Page 37), then repeat for the second
blade guide.
— If the top of the blade tilts away from
the square, loosen the top two set screws
shown in Figure 49 and tighten the
bottom two set screws an equal amount
while keeping an eye on the blade
squareness (the amount you tighten and
loosen the screws depends on how far
from square the blade is). Repeat for the
second blade guide.
— If the bottom of the blade tilts away from
the square, tighten the top two set screws
shown in Figure 49 an equal amount and
loosen the bottom two set screws while
keeping an eye on the blade squareness
(the amount you tighten and loosen the
screws depends on how far from square
the blade is). Repeat for the second blade
guide.
To square the blade to the table:
1. DISCONNECT BANDSAW FROM POWER!
2. Separate the blade guides as far as possible,
then lower the bandsaw all the way until it
contacts the downfeed stop bolt.
3. Place a square on the table bed and against
the edge of the blade, as shown in Figure
50, then check different points along the
length of the table between the blade guides.
Square
Blade
Table
5. Tighten the cap screws loosened in Step 4.
6. Repeat Steps 3–5 as necessary until the
blade is perfectly square to the table.
-40-
Figure 50. Squaring the blade.
Page 43

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1020
NOTES
-41-
Page 44

Model SB1020
1. Shock Hazard: It is extremely dangerous to
perform electrical or wiring tasks while the
machine is connected to the power source.
Touching electrified parts will result in
personal injury including but not limited to
severe burns, electrocution, or death. For
your own safety, disconnect machine from
the power source before servicing electrical
components or performing any wiring tasks!
2.
Wire Connections: All connections must be
tight to prevent wires from loosening during
machine operation. Double-check all wires
disconnected or connected during any wiring
task to ensure tight connections.
3.
Modifications: Using aftermarket parts or
modifying the wiring beyond what is shown
in the diagram may lead to unpredictable
results, including serious injury or fire.
4.
Motor Wiring: The motor wiring shown
in these diagrams is current at the time of
printing, but it may not match your machine.
Always use the wiring diagram inside the
5.
Circuit Requirements: Connecting the
machine to an improperly sized circuit will
greatly increase the risk of fire. To minimize
this risk, only connect the machine to a
power circuit that meets the minimum
requirements given in this manual.
6.
Capacitors/Inverters: Some capacitors and
power inverters store an electrical charge for
up to 10 minutes after being disconnected
from the power source. To reduce the risk of
being shocked, wait at least this long before
working on capacitors.
7.
Wire/Component Damage: Damaged wires
or components increase the risk of serious
personal injury, fire, or machine damage. If
you notice that any wires or components are
damaged while performing a wiring task,
replace those wires or components before
completing the task.
8.
Experiencing Difficulties: If you are
experiencing difficulties understanding the
information included in this section, contact
The photos and diagrams included in this section are best viewed in color. You can
see them in color at www.southbendlathe.com.
BLACK
WHITE
GREEN
RED
BLUE
BROWN
G RAY
ORANGE
YELLOW
YELLOW
GREEN
PURPLE
PINK
LIGHT
BLUE
BLUE
WHITE
TURQUIOSE
NOTICE:
WIRING DIAGRAM COLOR KEY
ELECTRICAL
ELECTRICAL
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
Electrical Safety Instructions
These pages are accurate at the time of printing. In the constant effort to improve, however, we may
make changes to the electrical systems of future machines. Study this section carefully. If you see
differences between your machine and what is shown in this section, call Technical Support at (360)
734-1540 for assistance BEFORE making any changes to the wiring on your machine.
-42-
Page 45

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1020
5
2
3
6
1
4
Neutral
GND
OVERLOAD
RESET
12
34
GND
GND
ON/OFF
SWITCH
6
1
4
5
2
3
6
1
4
5
2
3
Neutral
Hot
GND
Ground
110 VAC
5-15 Plug
(As Recommended)
OVER LOAD
RESET
OVERLOAD
RESET
12
34
GND
GND
GND
ON/OFF
SWITCH
12
34
GND
GND
ON/OFF
SWITCH
SERVICE
3. Use a wire nut to connect wires #2, #3, and
220V Conversion
#5, then wrap them with electrical tape.
Wiring diagrams are provided in this section
showing the Model SB1020 wired for both 110V
and 220V. Refer to these diagrams if needed
when following this procedure. Additionally,
you must purchase a 220V switch in order to
4. Connect wires #1 and #6 to the upper right
terminal and wire #4 to the lower right
terminal shown in Figure 52. Tighten the
terminal screws to secure the wires.
complete the conversion.
Items Needed Qty.
220V Switch (Part No. PSB1020204) ................... 1
220V
Wiring
Phillips Screwdriver #2 ........................................1
Wrench 18mm ....................................................... 1
Wire Nut (sized for three 14 Ga. wires) ...............1
Electrical Tape ....................................... As needed
Wire Stripper .......................................... As needed
To convert the Model SB1020 to 220V:
1. DISCONNECT BANDSAW FROM POWER!
2. Open the motor junction box, then loosen the
wire terminal screws indicated in Figure 51.
Remove the wires connected to those terminals.
110V Wiring
Loosen These
Terminal Screws
Figure 51. Wiring terminal locations.
Tighten These
Terminal Screws
Figure 52. Rewired for 220V.
5. Close the motor junction box.
6. Remove the four hex bolts that secure the
machine to the cabinet, then with the help
of another person, remove the machine from
the cabinet. Carefully place the machine on
its side to gain access to the underside of the
base.
7. Remove the black plastic switch cover from
behind the switch. Disconnect the two wires
from the back of the switch, then remove the
switch.
8. Install the 220V switch into the machine
base, then replace the two wires removed in
Step 7 in the corresponding locations from
which they were removed.
9. Replace the switch cover, then with the help
of another person, place the machine back
onto the cabinet and secure it with the hex
bolts removed in Step 6.
-43-
Page 46

Model SB1020
1584
3
U
X1
X2
V W
L1 L2
230V
Jumper Moved
for 220V
115V
P1
P3
P2
762
COOLING
FAN
V1
6
0
3
3
7
2 4
4
9
1
2
2
W1
L1
L1
L2
L2
L1
L2
V2
V2
U2
U2
L1
L2
L2
U1
V1
W1
U1
0
6
6
6
P1
P2
P3
1
2
2
2
3
1
1
G | 0 | 110 | 220 | 0 | 24
Transformer
LCE TBSM 20VA
Variable Frequency AC Drive
RFVE 26D (4736F)
115/230VAC 50/60Hz
Max Current: 22.0/14.0 Amp
Output: 0-230VAC 0-50, 60, 100, 120Hz
Contactor
Telemechanique
LC1K09 10B7
Blade
Speed
Knob
Emergency
Stop Switch
Control Panel
(Viewed from behind)
Power Lamp
ON/OFF
Switch (Both Sides Shown)
Start
Button
ETI VLC10
3W Max.
P1
P2
P3
230V
115V
ELECTRICAL
Electrical Box Wiring Diagram
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
Wiring
1
To Page 45
READ PAGE 42 BEFORE
DOING ANY WIRING!
-44-
Page 47

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1020
1
7
2 8
V1
U1
W1
9
3
6
5
4
1
7
2 8
V1
U1
W1
9
3
6
5
4
V2
V2
U2
U2
41
3 2
S. Capacitor
3MFD 450VAC
GND
V2
V2
U2
U2
41
3 2
S. Capacitor
3MFD 450VAC
GND
REWIRED FOR 220V
(NOTE JUMPER LOCATIONS)
PUMP MOTOR
PRE-WIRED FOR 110V
PUMP MOTOR
REWIRED FOR 220V
SAW MOTOR
REWIRED FOR 220V
SAW MOTOR
PRE-WIRED FOR 110V
BLADE COVER
LIMIT SWITCH
SAW TRAVEL
LIMIT SWITCH
BLADE
TENSION
LIMIT SWITCH
REWIRED FOR 220V
REWIRED FOR 220V
12
11
2324
Neutral
Hot
Ground
110 VAC
220 VAC
5-15 Plug
(Included)
Hot
Hot
Ground
6-15 Plug
(As Recommended)
220
VAC
G
G
REWIRED FOR 220V
ELECTRICAL
Wiring
Components Wiring Diagram
2
To Page 44
READ PAGE 42 BEFORE
DOING ANY WIRING!
-45-
Page 48

Model SB1020
ELECTRICAL
Wiring Component Locations
Control Panel &
Electrical Box
Blade Tension
Limit Switch
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
Headstock
Travel Limit
Switch
Figure 53. Wiring component locations.
Coolant Pump
Blade Cover
Limit Switch
Figure 54. Coolant pump motor location. Figure 55. Blade cover limit switch location.
-46-
READ PAGE 42 BEFORE
DOING ANY WIRING!
Page 49

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1020
233
235
231
232
234
226
216-1
220
219
216
222
223
217
210-1
185
182
186-3
186-1
190
180-4
170
171
172
182
184-2
184-1
184-4
184-3
184-5
184-6
181
180
180-1
180-3
184
188
189
186-4
186
196
198
194
186-2
182
187
186-3
195
193
200
199
201
207
67
194-1
180-5
180-2
215-5
214
191
192
194-2
194-3
197
196-1
258
261
196-2
196-3
196-4
221
250-1
250-2
250-5
250-4
250-6
250-3
260
259
258
209-1
209-2
116
117
165-7
165-3
165-1
165-4
165-5
165-6
165-8
165-2
215-1
215-2
215-4
215-3
165
250
215
209
241
242
240
243
245
252
251
246
PARTS
PARTS
Cabinet & Base
-47-
Page 50

Model SB1020
REF PART # DESCRIPTION REF PART # DESCRIPTION
67 P32007 TAPER ROLLER BEARING 32007 196-2 PSB1020196-2 SPACER
110 PCAP01M CAP SCREW M6-1 X 16 196-3 PSB1020196-3 SWIVEL BASE SHAFT FLAT WASHER
111 PN01M HEX NUT M6-1 196-4 PN32M HEX NUT M14-2
116 PSB1020116 LOWER CONTROL BOX PANEL 197 PFH05M FLAT HD SCR M5-.8 X 12
117 PS09M PHLP HD SCR M5-.8 X 10 198 PB116M HEX BOLT M10-1.5 X 45
165 PSB1020165 WORK STOP ASSEMBLY 199 P32007 TAPER ROLLER BEARING 32007
165-1 PSS01M SET SCREW M6-1 X 10 200 PSB1020200 BEARING CAP
165-2 PSB1020165-2 WORK STOP ROD 201 PSB1020201 SPANNER NUT
165-3 PSB1020165-3 KNOB BOLT 1/4-20 207 PS20M PHLP HD SCR M5-.8 X 15
165-4 PW06 FLAT WASHER 1/4 209 PSB1020209 LOWER CONTROL BOX
165-5 PSB1020165-5 WORK STOP BRACKET 209-1 PSB1020209-1 DOWNFEED RATE KNOB
165-6 PSB1020165-6 DISTANCE BRACKET 209-2 PSB1020209-2 START/STOP KNOB
165-7 PN02M HEX NUT M10-1.5 210-1 PORP016 O-RING 15.8 X 2.4 P16
165-8 PB32M HEX BOLT M10-1.5 X 25 214 PSB1020214 UPPER CONTROL BOX PLATE
170 PSB1020170 VISE HANDWHEEL 215 PSB1020215 UPPER CONTROL BOX ASSEMBLY
171 PRP91M ROLL PIN 5 X 35 215-1 PSB1020215-1 POWER LAMP
172 PSB1020172 BUSHING 215-2 PSB1020215-2 EMERGENCY STOP BUTTON
180 PSB1020180 SMALL VISE JAW 215-3 PSB1020215-3 BLADE SPEED SWITCH
180-1 PSS29M SET SCREW M6-1 X 35 215-4 PSB1020215-4 START/RESET BUTTON
180-2 PN01M HEX NUT M6-1 215-5 PSB1020215-5 UPPER CONTROL BOX
180-3 PRP93M ROLL PIN 6 X 25 216 PSB1020216 DRAIN PLUG 3/8PT
180-4 PSB1020180-4 VISE GIB 216-1 PORP015 O-RING 14.8 X 2.4 P15
180-5 PSS17M SET SCREW M8-1.25 X 6 217 PSB1020217 OIL SIGHT GLASS
181 PSB1020181 LARGE VISE JAW 219 PLW06M LOCK WASHER 10MM
182 PFH02M FLAT HD SCR M6-1 X 12 220 PB56M CAP SCREW M10-1.5 X 20
184 PSB1020184 VISE BASE 221 PSB1020221 COOLANT DRAIN PAN ASSEMBLY
184-1 PSB1020184-1 COMPRESSION SPRING 222 PSB1020222 COOLANT SCREEN
184-2 PSB1020184-2 PLUNGER 223 PS07M PHLP HD SCR M4-.7 X 8
184-3 PSB1020184-3 GEAR SHAFT 226 PSB1020226 BRACKET
184-4 PSB1020184-4 SHAFT BUSHING 231 PCAP72M CAP SCREW M10-1.5 X 30
184-5 PSB1020184-5 LOCK LEVER 232 PSB1020232 THREADED RETAINER
184-6 PSS06M SET SCREW M8-1.25 X 16 233 PSB1020233 ADJUSTMENT LEVER
185 PSB1020185 RIGHT VISE BRACKET 234 PW04M FLAT WASHER 10MM
186 PSB1020186 SWIVEL BASE 235 PB56M CAP SCREW M10-1.5 X 20
186-1 PSB1020186-1 LEFT VISE SUPPORT 240 PSB1020240 COOLANT PUMP 1/8HP 110/220V 1PH
186-2 PSB1020186-2 RIGHT VISE SUPPORT 241 PS11M PHLP HD SCR M6-1 X 16
186-3 PCAP77M CAP SCREW M12-1.75 X 30 242 PLW03M LOCK WASHER 6MM
186-4 PSS78M SET SCREW M12-1.75 X 25 243 PSB1020243 PIPE ELBOW 3/8 X 3/8"
187 PSB1020187 LEFT VISE BRACKET 245 PSB1020245 COOLANT HOSE 8 X 1300MM
188 PSB1020188 LOCK LEVER SHAFT 246 PSB1020246 COOLANT TANK
189 PSB1020189 LOCK LEVER 250 PSB1020250 CABINET ASSEMBLY
190 PSB1020190 VISE LEADSCREW 250-1 PSB1020250-1 LEFT CABINET PANEL
191 PW01M FLAT WASHER 8MM 250-2 PSB1020250-2 FRONT CABINET PANEL
192 PCAP31M CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 25 250-3 PSB1020250-3 REAR CABINET PANEL W/DOOR
193 PSS06M SET SCREW M8-1.25 X 16 250-4 PSB1020250-4 TOP RIGHT CABINET PANEL
194 PSB1020194 SWIVEL BASE CAP 250-5 PSB1020250-5 BOTTOM RIGHT CABINET PANEL
194-1 PSB1020194-1 BUSHING 250-6 PSB1020250-6 SHELF PANEL
194-2 PSB1020194-2 BRACKET 258 PFH23M FLAT HD SCR M8-1.25 X 16
194-3 PCAP31M CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 25 259 PW01M FLAT WASHER 8MM
195 PN02M HEX NUT M10-1.5 260 PN03M HEX NUT M8-1.25
196 PSB1020196 SWIVEL BASE SHAFT 261 PSB1020261 VISE TRAVEL STOP
196-1 PSB1020196-1 BUSHING
PARTS
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
Cabinet & Base Parts List
-48-
Page 51

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1020
72
39
52
45
44
43
45
42
41
44
43
32
105
45
22
27
40
100
46
44
104
42
41
60
99
5
106
32
45
40
39
44
46
294-7
10
82
48
12
47
35
11
10-1
13
51
25
38
23
101
5
6
103
58
59
35
6
96
102
20
26
21
30
15
9
16
8
14
53
56
294-4
294-1
294-2
294-5
294-3
2
4
7
2-2
2-1
3
79
78
17
18
80
1
83
84
81
63
64
88
74
87
90
19
89
108
107
55
82
54
65
73
109
71-1
85
86
77
71
76
75
28
29
202
320
202-1
321
322
323
94
92
298
298-1
301
300
91
93-1
93
92-1
298-2
294-6
50-2
50-1
50
71-2
71-3
71-4
298-1
49-1
49-3
49-4
49-2
49-5
322
294-4
294
300-1
49
294-5
PARTS
Head
-49-
Page 52

Model SB1020
REF PART # DESCRIPTION REF PART # DESCRIPTION
1 PSB1020001 BOW CASTING 49-5 PN01M HEX NUT M6-1
2 PSB1020002 ANCHOR BRACKET 50 PSB1020050 LIMIT SWITCH BRACKET
2-1 PSB1020002-1 ANCHOR PLATE 50-1 PSB1020050-1 LIMIT SWITCH
2-2 PS09M PHLP HD SCR M5-.8 X 10 50-2 PS51M PHLP HD SCR M4-.7 X 30
3 PSB1020003 MOUNT SHAFT 51 PSB1020051 SCALE
4 PCAP14M CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 20 52 PSS02M SET SCREW M6-1 X 6
5 PSB1020005 BEARING CHIP COVER 53 PRIV009M STEEL FLUTED RIVET 2 X 6MM
6 P32006 TAPER ROLLER BEARING 32006 54 PSB1020054 RIGHT BLADE ADJUSTMENT BRACKET
7 PLW04M LOCK WASHER 8MM 55 PSS02M SET SCREW M6-1 X 6
8 PB118M HEX BOLT M8-1.25 X 45 56 PBHS20M BUTTON HD CAP SCR M8-1.25 X 30
9 PN03M HEX NUT M8-1.25 58 PSB1020058 RIGHT BLADE GUARD
10 PSB1020010 POINTER 59 PW02M FLAT WASHER 5MM
10-1 PSB1020010-1 PRESSURE GAUGE 60 PS08M PHLP HD SCR M5-.8 X 12
11 P51203 THRUST BEARING 51203 63 PCAP47M CAP SCREW M10-1.5 X 40
12 PSB1020012 HANDWHEEL HANDLE 64 PCAP64M CAP SCREW M10-1.5 X 25
13 PSB1020013 BLADE TENSION HANDWHEEL 65 PSB1020065 HEAD PIVOT SHAFT
14 PSB1020014 LEADSCREW LOCK WASHER 16MM 71 PSB1020071 MOTOR 1-1/2HP 220/440V 3PH
15 PSB1020015 BLADE TENSION LEADSCREW 71-1 PK11M KEY 6 X 6 X 40
16 PN13M HEX NUT M16-2 71-2 PSB1020071-2 MOTOR FAN COVER
17 PCAP14M CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 20 71-3 PSB1020071-3 MOTOR FAN
18 PSB1020018 FIXED BLOCK 71-4 PSB1020071-4 MOTOR JUNCTION BOX
19 PRP28M ROLL PIN 5 X 40 72 PB08M HEX BOLT M6-1 X 20
20 PCAP71M CAP SCREW M10-1.5 X 60 73 PLW03M LOCK WASHER 6MM
21 PSB1020021 FIXED BLOCK 74 PSB1020074 GEAR BOX ASSEMBLY
22 PCAP14M CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 20 75 PLW06M LOCK WASHER 10MM
23 PSS11M SET SCREW M6-1 X 16 76 PCAP64M CAP SCREW M10-1.5 X 25
25 PSB1020025 LEFT BLADE GUIDE BRACKET 77 PSB1020077 GEARBOX COVER
26 PSS16M SET SCREW M8-1.25 X 10 78 PSB1020078 HOSE FITTING 8MM X 1/4PT
27 PSB1020027 KNOB BOLT M6-1 X 15 79 PCAP28M CAP SCREW M6-1 X 15
28 PSB1020028 CONNECTING TUBE 80 PSB1020080 3-WAY VALVE
29 PSB1020029 TUBE COVER 81 PSB1020081 COOLANT TUBE 6 X 240MM
30 PW04M FLAT WASHER 10MM 82 PSB1020082 COOLANT VALVE ASSEMBLY
32 PS62M PHLP HD SCR M6-1 X 30 83 PSB1020083 HOSE FITTING 6MM X 18PT
35 PB05M HEX BOLT M6-1 X 8 84 PSB1020084 COOLANT TUBE 6 X 800MM
38 PSB1020038 LEFT BLADE ADJUSTMENT BRACKET 85 PCAP64M CAP SCREW M10-1.5 X 25
39 PSS09M SET SCREW M8-1.25 X 20 86 PSB1020086 DRIVE SHAFT WASHER
40 PN03M HEX NUT M8-1.25 87 PK118M KEY 8 X 7 X 50
41 PSB1020041 FRONT BLADE GUIDE 88 PSB1020088 DRIVE SHAFT
42 PSB1020042 REAR BLADE GUIDE 89 PSB1020089 KEY 8 X 7 X 25
43 PSB1020043 REAR BLADE GUIDE SHAFT 90 P6208ZZ BALL BEARING 6208ZZ
44 P608ZZ BALL BEARING 608ZZ 91 PSB1020091 SPRING BRACKET
45 PR39M EXT RETAINING RING 8MM 92 PSB1020092 EXTENSION SPRING
46 PSB1020046 FRONT BLADE GUIDE SHAFT 92-1 PSB1020092-1 SPRING CONNECTOR
47 PS68M PHLP HD SCR M6-1 X 10 93 PN02M HEX NUT M10-1.5
48 PSB1020048 LEFT BLADE GUARD 93-1 PSB1020093-1 BOLT CUSHION
49 PSB1020049 POWER SWITCH ASSEMBLY 94 PCAP173M CAP SCREW M10-1.5 X 110
49-1 PSB1020049-1 LIMIT SWITCH BRACKET 96 PSB1020096 IDLER WHEEL
49-2 PS51M PHLP HD SCR M4-.7 X 30 99 PSB1020099 SPANNER NUT
49-3 PW03M FLAT WASHER 6MM 100 PSB1020100 BLADE 0.032 X 1 X 108-1/8 5-8TPI
49-4 PS68M PHLP HD SCR M6-1 X 10
PARTS
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
Head Parts List
-50-
Page 53

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1020
REF PART # DESCRIPTION REF PART # DESCRIPTION
101 PSB1020101 DRIVE WHEEL 294-4 PW03M FLAT WASHER 6MM
102 PSB1020102 DRIVE SHAFT FLAT WASHER 294-5 PN01M HEX NUT M6-1
103 PB49M HEX BOLT M12-1.75 X 20 294-6 PW03M FLAT WASHER 6MM
104 PSB1020104 BLADE COVER 294-7 PBHS11M BUTTON HD CAP SCR M6-1 X 10
105 PSB1020105 KNOB BOLT M6-1 X 14 298 PB73M HEX BOLT M10-1.5 X 50
106 PW03M FLAT WASHER 6MM 298-1 PW04M FLAT WASHER 10MM
107 PS09M PHLP HD SCR M5-.8 X 10 298-2 PN02M HEX NUT M10-1.5
108 PSB1020108 HOSE CLIP 8MM 300 PSB1020300 HYDRAULIC CYLINDER
109 PCAP11M CAP SCREW M8-1.25 X 16 300-1 PSB1020300-1 CYLINDER VALVE ASSEMBLY
202 PSB1020202 SPRING CLAMPING BOLT M10-1.5 301 PCAP173M CAP SCREW M10-1.5 X 110
202-1 PN02M HEX NUT M10-1.5 320 PSB1020320 HOSE CLAMP
294 PSB1020294 BLADE BRUSH ASSEMBLY 321 PSB1020321 LIMIT SWITCH BRACKET
294-1 PSB1020294-1 BRUSH BRACKET 322 PSB1020322 LIMIT SWITCH
294-2 PSB1020294-2 BRUSH 323 PCAP21M CAP SCREW M4-.7 X 30
294-3 PB29M HEX BOLT M6-1 X 30
PARTS
Head Parts List
-51-
Page 54

Model SB1020
401
402
403
404
405
406
407
408
409
410
411
412
413
414
The safety labels provided with your machine are used to make the operator aware of the
machine hazards and ways to prevent injury. The owner of this machine MUST maintain the
original location and readability of these safety labels. If any label is removed or becomes
unreadable, REPLACE that label before using the machine again. Contact South Bend Lathe Co. at
(360) 734-1540 or www.southbendlathe.com to order new labels.
REF PART # DESCRIPTION REF PART # DESCRIPTION
401 PSB1020401 MAIN CONTROL PANEL LABEL 408 PSB1020408 MACHINE NUMBER LABEL
402 PSBLABEL14HL CUTTING HAZARD LABEL 409 PSB1020409 BIOHAZARD WARNING LABEL
403 PSBLABEL02HL SHOCK WARNING LABEL 410 PSB1020410 DOWNFEED CONTROLS LABEL
404 PSB1020404 MACHINE ID LABEL 411 PSBPAINT01 SB GRAY TOUCH-UP PAINT
405 PSBLABEL15L ELECTRICITY LABEL 412 PSBPAINT03 SB DARK BLUE TOUCH-UP PAINT
406 PSBLABEL04HL EYE INJURY HAZARD LABEL 413 PSBPAINT02 SB LIGHT BLUE TOUCH-UP PAINT
407 PSBLABEL01HL READ MANUAL LABEL 414 SB1320 SOUTH BEND NAMEPLATE 125MM
Machine Labels
PARTS
For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09
-52-
Page 55

For Machines Mfg. Since 8 /09 Model SB1020
This quality product is warranted by South Bend Lathe Company to the original buyer for one year
from the date of purchase. This warranty does not apply to consumable parts, or defects due to any
kind of misuse, abuse, negligence, accidents, repairs, alterations or lack of maintenance. We do not
reimburse for third party repairs. In no event shall we be liable for death, injuries to persons or
property, or for incidental, contingent, special or consequential damages arising from the use of our
products.
We do not warrant or represent that this machine complies with the provisions of any law, act, code,
regulation, or standard of any domestic or foreign government, industry, or authority. In no event
shall South Bend’s liability under this warranty exceed the original purchase price paid for this
machine. Any legal actions brought against South Bend Lathe Company shall be tried in the State of
Washington, County of Whatcom.
This is the sole written warranty for this machine. Any and all warranties that may be implied by
law, including any merchantability or fitness, for any purpose, are hereby limited to the duration of
this warranty. To take advantage of this warranty, contact us by mail or phone to give us the details
of the problem you are having.
Thank you for your business and continued support.
WARRANTY & RETURNS
WARRANTY
-53-
Page 56

South Bend Lathe Co.
P.O. Box 2027
Bellingham, WA 98227
PHONE: (360) 734-1540 (Administrative Offi ces)
FAX: (360) 676-1075 (International)
FAX: (360) 734-1639 (USA only)
southbendlathe.com
Printed In Taiwan #JB12924
 Loading...
Loading...