Sony Ericsson K700 User Manual

K700
The next step in Imaging
February 2004
White Paper K700
Preface
Purpose of this document
This White Paper will be published in several revisions as the phone is developed. Therefore, some of the
headings and tables below contain limited information. Additional information and facts will be
forthcoming in later revisions.
The aim of this White Paper is to give the reader an understanding of technology and its main applications,
as well as the main functions and features of the phone.
Note: This document contains general descriptions for this specific Sony Ericsson mobile phone.
People who can benefit from this document include:
• Operators
• Service providers
• Software developers
• Support engineers
• Application developers
More information, useful for product, service and application developers, is published at
www.SonyEricsson.com/developer/, which contains up-to-date information about technologies, products
and tools.
This White Paper is published by:
Sony Ericsson Mobile Communications AB,
SE-221 88 Lund, Sweden
Phone: +46 46 19 40 00
Fax: +46 46 19 41 00
www.SonyEricsson.com
© Sony Ericsson Mobile Communications AB,
2004. All rights reserved. You are hereby
granted a license to download and/or print a
copy of this document.
Any rights not expressly granted herein are
reserved.
First edition (February 2004)
Publication number EN/LZT 108 6956 R1A
This document is published by Sony Ericsson
Mobile Communications AB, without any warranty*. Improvements and changes to this text
necessitated by typographical errors, inaccuracies of current information or improvements to
programs and/or equipment, may be made by
Sony Ericsson Mobile Communications AB at any
time and without notice. Such changes will, however, be incorporated into new editions of this
document. Printed versions are to be regarded as
temporary reference copies only.
*All implied warranties, including without limitation the implied warranties of merchantability or
fitness for a particular purpose, are excluded. In
no event shall Sony Ericsson or its licensors be
liable for incidental or consequential damages of
any nature, including but not limited to lost profits
or commercial loss, arising out of the use of the
information in this document.
2 February 2004

White Paper K700
Document conventions
The phone has a full graphic screen which supports 65,536 colours, referred to as 65k.
The screen images in this document are in JPG format and are thus of a lower resolution than the images
actually shown on the screen.
The Picture Messaging feature is referred to as MMS (Multimedia Messaging Service) throughout this
document.
Document history
Date Version Comment
2004-02-27 R1A First edition.
3 February 2004

Contents
Product overview ........................................................................................................5
Key functions and features .......................................................................................6
More in-phone functions ...........................................................................................8
Technologies in detail ...............................................................................................11
Entertainment ..........................................................................................................11
Media player ........................................................................................................11
Streaming ............................................................................................................13
Gaming ................................................................................................................14
SMIL ....................................................................................................................14
Imaging ....................................................................................................................15
VGA camera .........................................................................................................15
Messaging ...............................................................................................................16
My friends ............................................................................................................16
MMS ....................................................................................................................17
Connectivity ............................................................................................................20
Positioning ...........................................................................................................20
GPRS ...................................................................................................................20
Bluetooth™ wireless technology .........................................................................21
IrDA ......................................................................................................................23
Synchronization and data transfer ..........................................................................24
SyncML – an open standard for synchronization ................................................24
Remote synchronization ......................................................................................25
Local synchronization ..........................................................................................26
DRM .....................................................................................................................26
Object exchange – ‘Send as’ ...............................................................................29
Java .........................................................................................................................30
Java 2 Micro Edition ............................................................................................30
Java 3D ................................................................................................................31
White Paper K700
Facts and figures ......................................................................................................32
Technical specifications ..........................................................................................33
Terminology and abbreviations ...............................................................................55
Related information .................................................................................................58
Documents ..........................................................................................................58
Links ....................................................................................................................58
Trademarks and acknowledgements ..................................................................59
Index ...........................................................................................................................60
4 February 2004

White Paper K700
Product overview
This phone features the latest in imaging, advanced messaging and connectivity technology with a rich
offering of multimedia and entertainment functions. This includes for example, playing video clips with the
media player, taking pictures with the built-in camera and listening to the radio.
Easy-to-use imaging communication provides a dedicated camera button to minimize the number of
steps for taking and sending a picture or video clip.
Form follows function in this attractively designed phone with a compact body which cleverly includes
dual fronts, one for the phone and one for a real camera look and feel.
There is optimized memory for video communication with up to 32 MB of built-in memory for storage of
content such as pictures, music, ringtones, themes, games and video clips.
Easy access to music, images, video and games.
A powerful gaming solution for Java 3D with cutting edge graphics, multi-player games and a large 1.8
inch 65k TFT colour screen.
This phone supports GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) and GPRS (General Packet Radio
Service), triple band 900/1800/1900, GPRS 4+2. It also supports voice, circuit switched (cs) data and
packet switched (ps) data.
Note: To be able to give updated information about the implemented technology and functionality of this
product as soon as possible, this White Paper will be released in updated revisions.
5 February 2004

Key functions and features
White Paper K700
This phone is the next step in imaging for Sony
Ericsson products. The evolution of mobile
communications towards imaging will greatly
increase the scope for new applications and
services. In the area of multimedia in mobile
phones, Sony Ericsson can show its vast
experience in consumer electronics and
entertainment – music, pictures and games – as
well as its mobile technology leadership.
An eye-catching feature of this phone is the large
colour screen. It measures 176 pixels wide and 220
pixels high (176 x 220) in portrait mode and has
65,536 colours, allowing high-quality colour
imaging and video.
The phone has a loudspeaker mode and allows the
connection of a high-quality stereo headset. The
phone has an appealing design.
System
This phone supports GSM-GPRS and is a triple
band mobile phone.
Multimedia (streaming and download)
Media player
The Media player converts the
phone into a portable MP3/
MPEG4 player. Play music, watch
pictures and slide shows, as well
as streamed or downloaded video clips.
Radio
The radio is built-in and offers
instant and easy access to FM
radio channels.
The radio can be listened to with the portable
handsfree accessory or via the internal speaker.
With the radio, up to 20 favourite channels can be
stored with the preset function.
VGA camera
With the VGA camera, a camera is
always handy. Taking a picture or
recording a video clip and sending
it away as part of a picture
message or as an e-mail attachment is just a few
clicks away. The picture can also be sent via
bluetooth, infrared or cable.
By streaming media such as audio and video clips,
multimedia is available in realtime with minimal
downloading or waiting time. Media can also be
downloaded and saved in the phone memory and
then used with the Media player. Media such as
audio files, video clips or slide shows can be
played back at any time.
The camera also has 4X Digital zoom.
Photo light
The camera has a light to improve
taking pictures in darker
environments.
Sony Ericsson’s constant ambition of making
products easier to use, has had a great outcome:
QuickShare™.
QuickShare is the fastest, easiest and smartest
ever way to share images. With minimal hassle and
just a few clicks, moments can be captured with
the integrated camera and shared with friends!
But there is more to QuickShare than sending
images with a picture or e-mail message.
QuickShare is about ease of use of all the imaging
6 February 2004

White Paper K700
features of the product. Images can be shared
phone to phone, with Bluetooth, across the room
or between a phone and other paired devices such
as PDAs, PCs or printers. For example, it would be
possible to print a picture directly from the phone
using a Bluetooth enabled printer.
Full graphic 65k colour screen
The large 1.8 inch colour screen,
176 x 220 pixels, enhances
viewing, facilitating high-quality
multimedia and entertainment.
From standby, the phone features
a user interface built on the
“desktop” concept, which is
widely used in many computer
operating systems. From here,
navigation between different main
functions in the phone is done by selecting one of
the 3D icons representing these functions.
MMS
Reacting to the enormous
popularity of mobile phone
messaging, Sony Ericsson has
incorporated the latest messaging
standard, along with a colour display for an
enhanced imaging experience.
Say it in words, say it with pictures, animate it, add
sound. Have fun putting together multimedia
birthday and holiday greetings. On vacation, use
the mobile phone to send a digital postcard with
stylized text, digital pictures of the location, and
authentic sound clips, to friends and family back
home. When shopping, send a picture of a bargain
that a friend has been looking for.
With MMS, there are many interesting applications
to subscribe to, for example, stock information,
movie trailers and weather reports.
By pressing the Pre-play icon on the phone
desktop, you can, for example, go straight to a live
list of Top Music Hits. Choose a song, listen to it,
and if you like what you hear, you can buy it and
add it to Sounds. You can then listen to it or use it
as often as you want.
Content formats that are supported
All formats that are supported in the phone will be
possible to download. Music, video and images
may be previewed before purchase.The music
format is MIDI, MP3, WAV or AAC-LC (Polyphonic
24 voices or more).
How the service works
This service is owned by Sony Ericsson or hosted
by Sony Ericsson for a network operator. The preplay or other premium content is maintained and
managed, for example by Sony Music or Sony
Pictures. The content on offer can easily be suited
to a specific region or operator.
Implementation costs for network operators are
minimal and server communication is based on
existing, well-established standards. Sony Ericsson
offers first or second line support according to the
agreement on hosting a white label service or not.
High level co-operation is available for the design,
look and feel, of content management.
Operator benefits
This service is aimed at providing quality and
quantity revenue for network operators. This is truly
an APRU driver with low costs for operators. The
process involves:
• Downloading a list
• Previewing content
• Choosing content
•Buying content
Note: The availability of this unique application is
limited to specific markets, where relevant
infrastructure and agreements have been set up.
Pre-play
Content such as music, video and images may be
previewed before purchase.
User experience
A unique direct-link to download music, video,
games, themes and images, which is easy to use
and promises you best-selling content for mobile
download.
Other technical details
Security - Server communication is protected by
TLS.
Forward lock - Content cannot be exchanged with
other devices by the user, it is limited to use or
delete.
7 February 2004

White Paper K700
Java™ 2 Micro Edition
Download extra content with Java,
for example, new information- and
entertainment-based applications.
This gives users a chance to
personalize the functions and
features in their phones, and developers the
opportunity to create new applicatons.
Gaming
Gaming is already a very popular
feature in mobile phones, and with
Java, users can add new games
and skill levels to further enhance
the entertainment value of Sony Ericsson phones.
3D Games
Java 3D gaming software
introduces and supports cutting-
edge 3D graphics. Audio
developments such as 40 tones
polyphonic sound and force feedback provide a
much richer experience. With operator support,
there is the possibility for multi player games to
play against friends. The large 1.8” TFT screen
adds to a lasting gaming experience. Downloading
graphic intensive games requiring up to 32 MB
user memory is also possible with matching built-in
memory of up to 32 MB.
Bluetooth™ wireless technology
Using built-in Bluetooth wireless
technology, communication with
other Bluetooth devices is
supported via a radio link. Unlike
infrared, Bluetooth wireless technology is not
dependent on line-of-sight communication.
A device can be connected to the phone using
Bluetooth wireless technology up to 10 metres
away. For example, the phone can be answered at
a distance with a Bluetooth headset, when it rings.
The phone could be in a briefcase, a coat pocket or
even in another room. Two mobile phones, or a
phone and a computer, with Bluetooth wireless
technology can exchange data such as images,
video clips, business e-cards, music files and
calendar data.
Copyright protection – DRM
DRM (Digital Rights Management) features the
rights and copy protection of downloaded content
(audio, pictures, ringtones, video, entertainment
features such as games etc.).
Content-based services have great market
potential, and to encourage this, Sony Ericsson
plans to support DRM in all future multimedia
products. Sony Ericsson regards DRM as a key
enabler for content-based services, and is active in
supporting the ongoing standardization work of the
OMA (Open Mobile Alliance). Furthermore, any
additional market requirements for DRM will be
monitored.
More in-phone functions
Navigation key
The 4-directional + select key is
designed to easily navigate the
menu system. In a menu, it can be
gently pressed to select a feature.
It can also be used as a joystick with games.
Improved User Interface (UI)
Selection keys and the key assignment give a very
efficient interaction design with full flexibility to
handle all the new features and applications. Sony
Ericsson has focused on user-centred design and
extensive usability testing to solidify the new UI
paradigm. This ensures visibility in actions and
system status and consistency between
applications and similar actions. The large, highresolution colour screen is easily managed with the
navigational key.
8 February 2004

White Paper K700
Setup wizard
The setup wizard makes it possible for the user to
quickly and easily prepare the phone for use.
At the first start-up, the setup wizard starts and
helps the user with some core settings whilst giving
hints about the functionality of some important
keys: back and clear.
The setup wizard includes:
• setting the language
• setting time and time format
• setting date and date format
• the possibility to import contacts from a SIM
card
• hints about the Back and C keys.
Polyphonic sounds - 40 voices
Polyphonic sounds and the MIDI
format has revolutionized the
sound quality of ringtones in
mobile phones. With this format,
the user can play, compose, edit and send
melodies by using the Music DJ. The built-in sound
synthesizer uses wave tables, real instrument
sounds, with 40 voices polyphony. The new
composer has an improved graphical user interface
to simplify melody handling. All new and edited
melodies are stored in MIDI format.
File management
There is a file manager, similar to that, found on
many computers. In the file manager, the user has
an overview of the contents of the phone as well as
how much memory is allocated to each function
and feature.
supported by all major Web browsers. An XHTML
page can be viewed in both the WAP browser and
in any standard Web browser. All of the basic
XHTML features are supported, including text,
images, links, check boxes, radio buttons, text
areas, headings, horizontal rules and lists.
In addition to XHTML, the WAP browser supports
WML. The user can navigate between WML and
XHTML pages. WAP 2.0 also supports cookies,
often used by Web sites to store site-specific
information in the browser between visits to the
site. Cookies are often used by e-commerce sites
(in shopping carts and wish lists for example), and
to save the user from entering the same
information more than once.
Cascading style sheets (CSS)
Before style sheets were introduced on the Web,
developers had little control over the presentation
of their Web pages. An XHTML document specifies
the structure of the content, which part is a
paragraph, which part is a heading, and so on. It
does not specify how it shall be presented.
Browsers use a default presentation for documents
without style sheets. By adding a style sheet to the
document the developer can control the
presentation of the document, the colours, fonts,
and layout.
On the Web, the de facto standard style sheet
language is Cascading Style Sheets (CSS),
specified by the W3C and implemented in IE,
Netscape, and Opera. For mobile phones, the OMA
has identified a subset of CSS and extended it with
OMA specific style rules. The CSS subset and the
OMA extensions are called Wireless CSS (WCSS).
The WAP browser supports WCSS 1.1
GPRS (General Packet Radio Service)
GPRS uses Internet-style packet-based
technology. GPRS gives the benefits of a
permanently available connection to the mobile
Internet, but only uses the radio link for the length
of time it takes to transfer data. GPRS offers the
user the speed needed for satisfactory mobile
Internet usability. The phone supports GPRS 4+2.
WAP 2.0 supporting XHTML™
The WAP browser supports the markup languages
of WAP 2.0 – XHTML Mobile and XHTML Basic.
These two subsets of the Web standard XHTML are
My friends (Wireless Village)
To ensure inter operability of mobile instant
messaging and presence services, Sony Ericsson,
Ericsson, Motorola and Nokia have created the
Wireless Village Solution, an open standard. The
protocol is bearer-independent and can be
implemented in different networks. The Wireless
Village Instant Messaging and Presence Service
(IMPS) includes three primary features:
9 February 2004

White Paper K700
Presence
Presence information of other Wireless Village
users is received and displayed to indicate their
willingness to communicate. The user’s own
presence information is also sent for others to view.
If the user is interested in another person’s
presence status, he or she can search for this
person. If the person is found, the user may
subscribe to his/her presence information. The
presence information is displayed in a contact list.
Instant messaging
Instant messaging means “point-to-point
messaging” between Wireless Village users.
Messages can be sent to an entire contact list or to
a single user. Short message histories of the
communication are logged in a file, which can be
read off line. This is a sub-set file of the whole
communication and is limited by memory.
Groups
The user may join a chatroom and chat with the
other participants/members.
Connector cover
The connector cover is designed with three major
improvement areas:
1. User friendliness - gives the user a comfortable
grip, both when using the phone (in portrait mode)
and the camera (in landscape mode), by continuing
the smooth, curved frame.
2. Product quality - offers added protection
against dust, moisture and impact force.
3. Product appearance - improves the overall
appearance by hiding the connector when not in
use and continuing the smooth, curved frame.
E-mail
With inbox, outbox, save draft and reply options,
there are all the functions needed for effective email communication in a powerful mobile phone.
Constantly connected to a POP3, SMTP or IMAP4
e-mail server anywhere on the Internet, the phone
stores messages dynamically, depending on
available memory, and updates the inbox
automatically and over the air. Check e-mail
anywhere. Reply to e-mail on the move. Friends,
family and business contacts know that when they
send e-mail, it can be received, read and acted on
immediately. Pictures can be included in outgoing
e-mails and attachments that are received.
Hyperlinks in e-mails are supported.
Personalization
With themes, the user can change many settings in
the phone, for example colours, images and
ringtones, making it more personal. The phone
comes with a number of preloaded themes and
pictures, and more can be downloaded and
exchanged – sports, movie, seasonal and other
themes will be available on Sony Ericsson or
operator sites. Other personalizable features are
the start-up screen and the screen saver. Specific
pictures and ringtones can also be set for each
separate name in the phonebook.
10 February 2004
White Paper K700
Technologies in detail
Entertainment
Media player
The media player supports different audio and
video formats, streaming as well as download and
playback.
Music
The media player is a multi-format digital audio
player which enables the user to carry and play a
selection of favourite songs. A range of audio
formats are supported:
• AAC
Advanced Audio Coding. AAC is the latest
audio coding standard, defined in the MPEG-2
standard and is used for high-quality audio
compression. AAC provides higher quality than
MP3 at the same bit rate, or for the same audio
quality it uses a 30 percent lower bit rate. It sup
ports the coding of multichannel audio, with up
to 48 main channels and 16 low-frequency
-
channels. The AAC offers three different profiles
to facilitate trade off between quality, memory
and processing power requirements. They
include: Main Profile (MP), Low Complexity (LC)
and Scalable Sampling Rate (SSR).
•AMR
Adaptive Multi Rate. A medium quality compressed sound format.
• MIDI
Musical Instrument Digital Interface.
Unlike the other formats, MIDI is not a recording
of music, but a description which enables a
local synthesizer to play the music from the
instructions included in the MIDI file. Since a
MIDI file only represents player information, it is
far more concise than formats that store the
sound directly. An advantage is very small file
11 February 2004

White Paper K700
sizes. A disadvantage is the lack of specific
sound control. MIDI is ideal for polyphonic ring
tones.
•MP3
MP3 is the file extension for MPEG audio layer
3. Layer 3 is one of three coding schemes (layer
1, layer 2 and layer 3) for the compression of
audio signals. Layer 3 uses a very efficient com
pression method, removing all irrelevant parts of
a sound signal that the human ear cannot per
ceive. The result is, for example, CD digital
audio (CDDA) converted to MP3 with almost
untouched quality, compressed by a factor of
around 12. The high compression of audio in
MP3 files makes them relatively small, though
MP3 files can be created with different size and
quality compromises. The small file size,
together with the excellent sound quality, are
the main reasons for the MP3-format’s massive
popularity when sharing music over the Internet.
•WAV
Windows media audio video. A wave file is an
audio file format created by Microsoft, that has
become a standard PC audio file format for
everything from system and game sounds to
CD-quality audio. A wave file is identified by a
file name extension of WAV (.wav). Used prima
rily in PCs, the wave file format has been
accepted as a viable interchange medium for
other computer platforms, such as Macintosh.
This allows content developers to freely move
audio files between platforms for processing, for
example.
In addition to the uncompressed raw audio
data, the wave file format stores information
about the file's number of tracks (mono or ste
reo), sample rate, and bit depth.
Songs may be stored in the File manager. The
folder system enables the user to organize songs
into groups and create simple playlists of MP3
songs.
Songs may be collected in numerous ways,
including Internet download and file transfer from a
PC.
The media player is intelligently aware of other
applications in the phone:
• Playback is paused when a telephone call is
made or received.
-
-
• Playback is paused if the user starts another
-
-
application which requires the audio channels to
be dedicated to it.
• Playback of MP3 files continues if the user
switches to another application, providing
music whilst using other applications such as
the phonebook or calendar, or playing games.
Polyphonic ringtones
Background
The word “polyphony” means producing several
tones at the same time. Almost all music that we
listen to consists of polyphonic melodies.
Early Ericsson mobile phones supported a
proprietary non-polyphonic format called eMelody.
Due to the musical limitations of eMelody, and the
popularity of creating, sending and downloading
ring melodies, Ericsson and Sony Ericsson,
together with other manufacturers, created the
more advanced but non-polyphonic sound format –
iMelody.
The introduction of the MIDI format revolutionized
sound quality. MIDI files are small, and perfect for
mobile devices, which have limited storage
capacity.
MIDI is a specification for a communications
protocol principally used to control electronic
musical instruments. MIDI is today a well known
standard used by many musicians, composers and
arrangers.
A MIDI signal or file does not contain any music. It
contains binary data (information) of how a melody
is played and when this data reaches a synthesizer,
the synthesizer will translate the binary data to
music, when connected to an amplifier with
speakers so that the sound becomes audible.
Please visit www.midi.org for more information.
SP-MIDI
SP-MIDI stands for Scalable Polyphony MIDI. SPMIDI is based on the MIDI format and adapted for
mobile phones and other portable products. The
objective is to secure inter operability between
products with different sound capabilities.
12 February 2004

White Paper K700
Sound Recorder
The sound recorder can record both voice memos
and call conversations. Sound recorder saves
recordings directly to memory. The size and length
of recordings are limited by available storage
space.
Sounds are recorded in AMR format and saved in
Sounds.
Video clips
Moments can easily be shared with friends and
family in other geographical sites by capturing the
moment with the video recorder and then sending
the video clip in a picture message. The video
recorder supports QCIF.
Streaming
The media player supports download and playback
of MPEG-4 and H.263 formats for viewing video
clips in the phone.
Video clips may be downloaded from the Internet
or copied from a connected PC.
Files must be of types MP4 or 3GP, having video
encoded in MPEG-4 Simple Visual Profile and
audio in AAC or AMR format. Video may also be
encoded in H.263. The phone encodes video in
H.263 Profile 0 Level 10 format.
Streaming Support
The media player can be launched from hyperlinks
in the WAP browser, SDP files in the file manager or
in messages through hyperlinks. Content is
streamed using RTSP (Real Time Streaming
Protocol) session control.
Streaming media is a method of making audio,
video clips and other multimedia available in realtime.
The term streaming refers to the technique it is
based on. Previously an entire file had to be
downloaded before it could be played, whereas the
use of streaming means the end user can almost
immediately begin to watch or listen to the content
of a requested file. The data in the file is broken
down into small packets that are sent in a
continuous flow, a stream, to the end user. It is then
possible to begin viewing the file while the rest of
the packets are transferred.
Applications
The applications which can be built on top of the
streaming services can be classified into on
demand, and live information delivery applications.
Examples of the first category are music and video
clips, news on demand as well as on demand
instruction material. Live delivery of radio and
television are examples of live information delivery.
The following video and music codec is supported:
• MPEG-4 Simple Visual Profile Level 0
• H.263 Profile 0 Level 10
• H.263 Profile 3 Level 10 (decode only)
• AAC
•AMR
•MP4
•3GP
Examples of usage
Streaming of music (on demand)
Anna browses to a Web page and decides to check
out the latest top ten list of pop music. She wants
to know if there are any new cool songs. She picks
out a few, streams the music to her mobile phone
and listens to the songs through the stereo headset
or via the built-in loudspeaker.
Streaming of news (on demand)
Bob browses to a morning paper’s Web page and
decides to check the news. He wants to see the
five-minute version of the latest financial news. The
news is streamed to his terminal, and he can watch
it on the bus on his way to work.
Streaming/download of music video (on
demand)
Mike browses to a Web page and decides to check
out the latest rock videos. He finds a video he
wants to watch, so he clicks the link and then
streams a one-minute version of the video. He then
13 February 2004

White Paper K700
decides to download and pay for the complete
video. A memory check is automatically performed
to make sure that his mobile phone has enough
free memory.
Streaming of live radio (broadcast)
Linda wants to check out and listen to her favourite
radio station. She browses to the home page and
starts to stream the content. The content is audio
or audio with pictures of the artist.
Streaming of live traffic information (broadcast)
Nick wants to know if there is a traffic jam on the
highway before he heads for home. He browses the
page for local traffic information. There is a traffic
jam, so he takes an alternative route home.
Gaming
Gaming is now seen as a standard feature in
mobile phones, where Sony Ericsson promises to
be a step ahead in this regard. This is not only due
to faster download capability on the network. There
are some other reasons why the actual gaming
experience is better – the way Java has been
implemented, the fact that more processing power
has been dedicated to the games, the large 65k
colour screen and more sophisticated graphics
with Java 3D and the Mascot API. The result is
User-created content (Web album)
Sheila and Tom are on vacation. They want to show
their friends how fantastic the beach is. They
record a video clip and upload it to a Web album.
Their friends can then stream or download the clip
to their PC or mobile phone.
Market and revenue possibilities
As streaming means “seeing the product without
having it”, it can be extensively used in the music
and film industry. There are also great revenue
possibilities for subscription-based content; for
example, the user can subscribe to several on
demand services such as news and traffic
information.
games with improved graphics that react faster to
user commands when using the navigational key
as a joystick or game controller. The phone takes
mobile gaming to new heights.
Supporting J2ME (Java 2 Micro Edition), the phone
lets users download and run new games and
applications. This is a great way to upgrade the
game gallery, install work-supportive programs and
personalize the phone.
SMIL
SMIL stands for Synchronized Multimedia
Integration Language and is pronounced “smile”.
SMIL is an advanced XML-based protocol, and
Sony Ericsson’s MMS implementation supports a
subset of the SMIL 2.0 protocol according to OMA
MMS IOP document version 1.2.
The use of SMIL in a product allows the user to
create and transmit PowerPoint-style presentations
on the mobile device. Using a media editor, users
can incorporate text, audio, images, video clips
and animations to assemble full multimedia
presentations. The user can decide in which order
the image and text will be displayed, as well as for
how long the images and text lines are to be shown
on the display.
Media types
There are certain media formats that support
continuous media (speech, audio and video). The
following media types are supported for SMIL:
• AMR narrow band speech codec MIME media
type
• MPEG-4 AAC audio codec MIME media type
• MPEG-4 video codec MIME media type
• H.263 video codec MIME media type
The media types for JPEG and GIF can be used
both in the 'content-type' field in http and in the
“type” attribute in SMIL 2.0. The following media
types are to be used:
• JPEG MIME media type
14 February 2004

White Paper K700
• GIF MIME media type All these media are pointed out by MIME
(Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) types.
Imaging
VGA camera
VGA camera
With the integrated VGA camera, the user can take
pictures and video clips and store them in the
phone memory. The user can send them as an
attachment in an e-mail or a picture message. The
picture can also be sent via bluetooth, infrared or
cable.
Using the camera or video
When the dedicated camera button is pressed,
camera or video is started, depending on what was
last used.
A large viewfinder is presented in the display and
QuickShare offers a minimal number of steps that
take you to the send options as follows:
• 3 steps for camera: start, capture and send.
• 4 steps for video: start, capture, stop and send.
The camera or video can also be started in the
menu.
Panorama pictures
The camera can create panorama pictures by
stitching together several different pictures into one
large picture. This is done with the help of a unique
image processing technique.
• QQVGA (160 x 120 pixels)
• QVGA (320 x 240 pixels)
• VGA (640 x 480 pixels
Video format
Video clips can be recorded, played and sent using
the following codec:
• H.263
More VGA camera features
The camera has full automatic exposure control
that selects the optimal exposure time needed to
get an excellent picture. When operating the
viewfinder, the camera adjusts the exposure time.
The lighting conditions found indoors and outdoors
may differ significantly. This may give rise to false
colours in photographs. To compensate for this,
the VGA camera is equipped with automatic white
balance. This feature automatically adjusts for
different lighting environments in order to produce
images with correct colours under most conditions.
The camera also has a photo light to improve
taking pictures in darker environments.
Using this feature is very user friendly. The user
simply takes a picture and then moves the camera
slightly sideways and then takes a new picture.
This can be repeated several times until the user
selects to save the panorama where all the different
pictures are stitched together.
Image formats
The camera is able to send pictures in the following
resolutions:
15 February 2004

Messaging
My friends
Sony Ericsson’s application - My friends - is an
enhanced messaging facility that offers a user
friendly and versatile way to quickly get in touch
with contacts.
The My friends application merges the Phonebook
and messaging functionalities that we commonly
find in phones. At a click you can access your list of
contacts, and with another click you can choose
how you want to communicate with them - via
SMS, MMS, e-mail or chat.
White Paper K700
The application also enables you to view the
‘presence’, or availability of the contacts in My
friends. You can easily and quickly find out whether
they are in a meeting or free to speak to you. You
can then choose how you wish to contact them.
My friends contains all the information you need
about your contacts.
You can have:
• a select list of up to 20 people
• their contact information such as phone
number, e-mail, chat and mail addresses
• call information - calls to and from them
• presence information - their availability, online
status (on or off), text or image they choose to
show you.
You can present similar information about your own
availability and status.
You have access to chatrooms, and can form
wireless communities of business associates or
contacts.
The main view
You can access the My friends sub-menu by
clicking the Messaging desktop icon.
The icon in the status bar indicates the online
status of the chosen friend in the list, and indicates
new, unread messages if any.
The most likely action (which is context dependent)
is available on the left softkey.
Additional actions become available to you when
you press the More key.
Adding contacts to My friends
You can add a contact from the Phonebook to the
My friends list, and you can change the position of
the friend in the list. This enables you to have your
list of immediate business or social contacts at
hand, so you can establish easy communication
with them almost instantly.
Note: To realise this application’s complete
potential, access to a Wireless Village server is
required.
Managing My friends
Your list of immediate contacts may change to suit
business demands. You may need to interact with
new sets of people depending on your current
project or work at hand. Or you may simply want to
alter your list of personal friends whom you want to
keep in constant touch with.
You can manage the My friends list to quickly alter
the list of contacts that you want displayed. You
can sort the names, edit nicknames, block or
delete friend, or link a friend to Phonebook.
16 February 2004
Viewing the status of contacts in My
friends
You can view your contact’s status and decide how
you want to communicate with him or her. You may
want to call or send an SMS, MMS, or e-mail, or
join your friend in a chatroom.
Access to the chatroom
The My friends application supports creating
chatrooms and inviting your friends (on your My
friends list) to the chatroom. You can bookmark
associates you would like to chat with. The
application can establish connectivity between
different service offerings that enable chat between
terminals.
White Paper K700
MMS
There are virtually no limits to the content of a
Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS)
transmission. An MMS message can contain text,
graphics, animations, images, audio clips and ring
melodies. For third party developers’ information,
please visit
and look for the MMS developers guidelines.
MMS completes the potential of messaging.
Sending digital postcards and PowerPoint-style
presentations is expected to be among the most
popular user applications of MMS. Eagerly awaited
by young users in particular, MMS is projected to
fuel the growth of related market segments by as
much as 40%.
Multimedia Messaging uses WAP (Wireless
Application Protocol) or http as bearer technology
which also can be powered by the transmission
technology GPRS. This allows users to send and
receive messages that look like PowerPoint
presentations. The messages may include any
www.SonyEricsson.com/developer/
combination of text, graphics, photographic
images, speech, music clips and video. MMS will
serve as the default mode of messaging on all
terminals, making total content exchange second
nature. From utility to sheer fun, it offers benefits at
every level and to every kind of user.
Over the air (OTA) configuration
Users can easily get MMS into their phone. MMS
supports OTA, meaning that the user does not have
to configure the settings manually. The
configuration is done by the operator via OTA.
Note: The specification is in accordance with
Ericsson Nokia OTA configuration v7.1.
MMS objects
Although MMS is a direct descendant of SMS, the
difference in content is dramatic. The size of an
average SMS message is about 140 bytes, while
the maximum size of an MMS message is 100 kb.
17 February 2004

White Paper K700
That is why the key word to describe MMS content
is rich. Complete with words, sounds and images,
MMS content is endowed with the user’s ideas,
feelings and personality. An MMS message can
contain one or more of the following:
Te xt
As with SMS and EMS (Enhanced Messaging
Service), an MMS message can consist of normal
text. The length of the text is unlimited. The main
difference between an EMS and MMS message is
that in an MMS message, text can be accompanied
not only by simple pixel images or melodies but by
photographic images, graphics, audio clips and
video clips.
Te mp l at e s
The phone comes with a number of MMS predefined templates, for example templates for
birthday cards, meeting requests etc.
Audio
MMS provides the ability to send and receive full
sound (MIDI, MP3, iMelody, AMR) messages. Not
only can users share a favourite song or ringtone
with a friend, they can also use the mobile phone to
record a sound and send it along with a message.
As sound includes speech as well as music, this
extra dimension to an MMS message allows for a
spontaneous and immediate personal expression
in communication messaging. Rather than sending
a downloaded birthday jingle in EMS, a user can,
for example, send a clip of his or her own personal
rendition of “Happy Birthday”. The phone supports
the MIDI format.
PIM communication with MMS
By using MMS, it is easy to handle PIM (Personal
Information Manager) information. The user can
send and receive business cards (vCard), calendar
entries such as appointments (vCal) and notes
(text/plain).
Streaming content in MMS
Streaming makes it possible to view files while they
are being downloaded to the phone. The MPEG-4
file format can be used for continuous media along
the entire delivery chain envisaged by the MMS,
independent of whether the final delivery is done by
streaming or download, thus enhancing
interoperability.
In particular, the following stages are considered:
• Upload from the originating terminal to the MMS
proxy.
• File exchange between MMS servers.
• Transfer of the media content to the receiving
terminal, either by file download or by stream
ing. In the first case, the self-contained file is
transferred, whereas in the second case the
content is extracted from the file and streamed
according to open payload formats. In this case,
no trace of the file format remains in the content
that is transmitted over the wire or over the air.
Additionally, the MPEG-4 file format can be used
for storage in servers and the “hint track”
mechanism can be used to prepare for streaming.
-
Pictures and themes
By using the integrated camera, users can take a
picture or video clip and immediately send it to a
recipient. The ability to send pictures is one of the
most exciting attributes of MMS, as it allows users
to share meaningful moments with friends, family
and colleagues.
Mobile picture transmission also offers inestimable
utility in business applications, from sending onsite pictures of a construction project to capturing
and storing an interesting design concept for later
review. Editing a picture by adding text allows
users to create their own electronic postcards, an
application that is expected to substantially cut into
the traditional postcard market.
Themes (downloaded or pre-defined) can be
exchanged via MMS.
MMS technical features
The MMS standard, just like that of SMS, offers
store-and-forward transmission (instant delivery) of
messages, rather than a mailbox-type model. MMS
is a person-to-person communications solution,
meaning that the user gets the message directly
into the mobile phone. He or she does not have to
call the server to get the message downloaded to
the mobile. Unlike SMS, the MMS standard uses
WAP as its bearer protocol. MMS will take
advantage of the high speed data transport
technology GPRS and support a variety of image,
video and audio formats to facilitate a complete
communications experience.
18 February 2004
White Paper K700
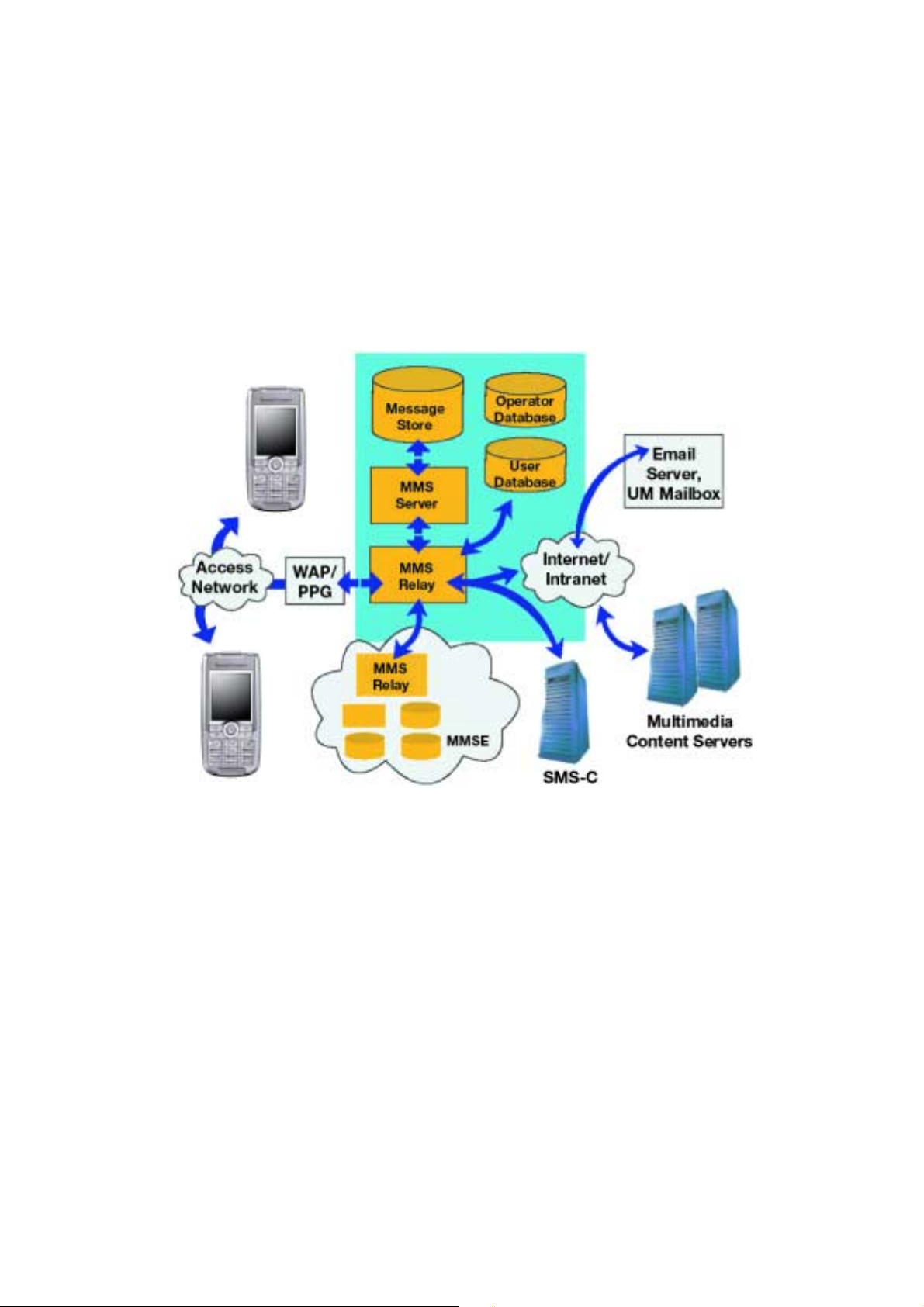
Architecture
The MMS Centre (MMS-C) is comprised of the
MMS Server, the MMS Proxy-Relay and the MMS
Store. The MMS Centre is the central element of
the MMS network architecture, providing storage
and operational support, enabling instant delivery
of multimedia messages from terminal-to-terminal
and terminal-to-e-mail, and supporting flexible
addressing. The centre’s MMS Proxy-Relay
interacts with the application being run on the
MMS-enabled terminal to provide various
messaging services. WAP or http is used as the
bearer of an MMS message between the MMS-C
and the MMS client (application). The WAP
Gateway is used for delivery and retrieval of
messages. Information is read in the WAP browser.
Figure 1. The architecture of MMS
Message conversion
The MMS-C is able to perform limited message
conversion - for example, from MMS to SMS - so
that processing and air time is not wasted in
sending messages to mobile terminals that do not
have adequate capability to receive them. It also
handles service aspects such as store and forward,
guaranteed delivery, subscriber preferences,
operator constraints, and billing information. The
MMS-C also vouches for high quality messaging,
for example by format conversion. This means that
the MMS-C recognizes which formats are
supported in the mobile phone, and adapts the
MMS messages to these formats.
19 February 2004
 Loading...
Loading...