Sony ICFCD-832 Service manual

ICF-CD832
SERVICE MANUAL
Ver 1.1 2004. 03
Section
SPECIFICATIONS
US Model
Canadian Model
Model Name Using Similar Mechanism ICF-CD831
CD
CD Mechanism Type KSM-213RDP
Optical Pick-up Name KSS-213R
AUDIO POWER SPECIFICATIONS
POWER OUTPUT AND TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION
With 8-ohm loads, both channels driven from 100 – 10,000 Hz; rated 1.0
W per channel minimum RMS power, with no more than 10% total
harmonic distortion in AC operation.
CD player section
System:
Compact disc digital audio system
Laser diode properties:
Material: GaAlAs
Wavelength: 780 nm
Emission duration: Continuous
Laser output: Less than 44.6 µW
(This output is the value measured at a distance of
about 200 mm from the objective lens surface on
the optical pick-up block with 7 mm aperture.)
Frequency response:
20 – 20,000 Hz dB
Wow and flutter:
Below measurable limit
Radio section
Frequency range:
FM: 87.5 – 108 MHz
AM: 530 – 1,710 kHz
+1
–1.5
General
Time display:
12-hour system
Speaker:
66 mm (2 5 ⁄8 inches) dia., 8 Ω
Power outputs:
1 W + 1 W (at 10% harmonic distortion)
Power requirements:
120 V AC, 60 Hz
Dimensions:
Approx. 229 × 104 × 218 mm (w/h/d)
(Approx. 9 1 ⁄8 × 4 1 ⁄8 × 8 5 ⁄8 inches) incl.
projecting parts and controls
Mass:
Approx. 1,650 g (3 lb. 10 oz.)
Design and specifications are subject to change without
notice.
9-877-554-02
2004C04-1
© 2004. 03
FM/AM CD CLOCK RADIO
Sony Corporation
Personal Audio Company
Published by Sony Engineering Corporation
1
ICF-CD832
Ver 1.1
CAUTION
Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures other than those specified herein may result in hazardous radiation exposure.
Flexible Circuit Board Repairing
• Keep the temperature of the soldering iron around 270˚C during
repairing.
• Do not touch the soldering iron on the same conductor of the
circuit board (within 3 times).
• Be careful not to apply force on the conductor when soldering
or unsoldering.
Notes on Chip Component Replacement
• Never reuse a disconnected chip component.
• Notice that the minus side of a tantalum capacitor may be dam-
aged by heat.
NOTES ON HANDLING THE OPTICAL PICK-UP BLOCK
OR BASE UNIT
The laser diode in the optical pick-up block may suffer electrostatic
breakdown because of the potential difference generated by the
charged electrostatic load, etc. on clothing and the human body.
During repair, pay attention to electrostatic breakdown and also use
the procedure in the printed matter which is included in the repair
parts.
The flexible board is easily damaged and should be handled with
care.
SAFETY CHECK-OUT
After correcting the original service problem, perform the following safety check before releasing the set to the customer:
Check the antenna terminals, metal trim, “metallized” knobs, screws,
and all other exposed metal parts for AC leakage.
Check leakage as described below.
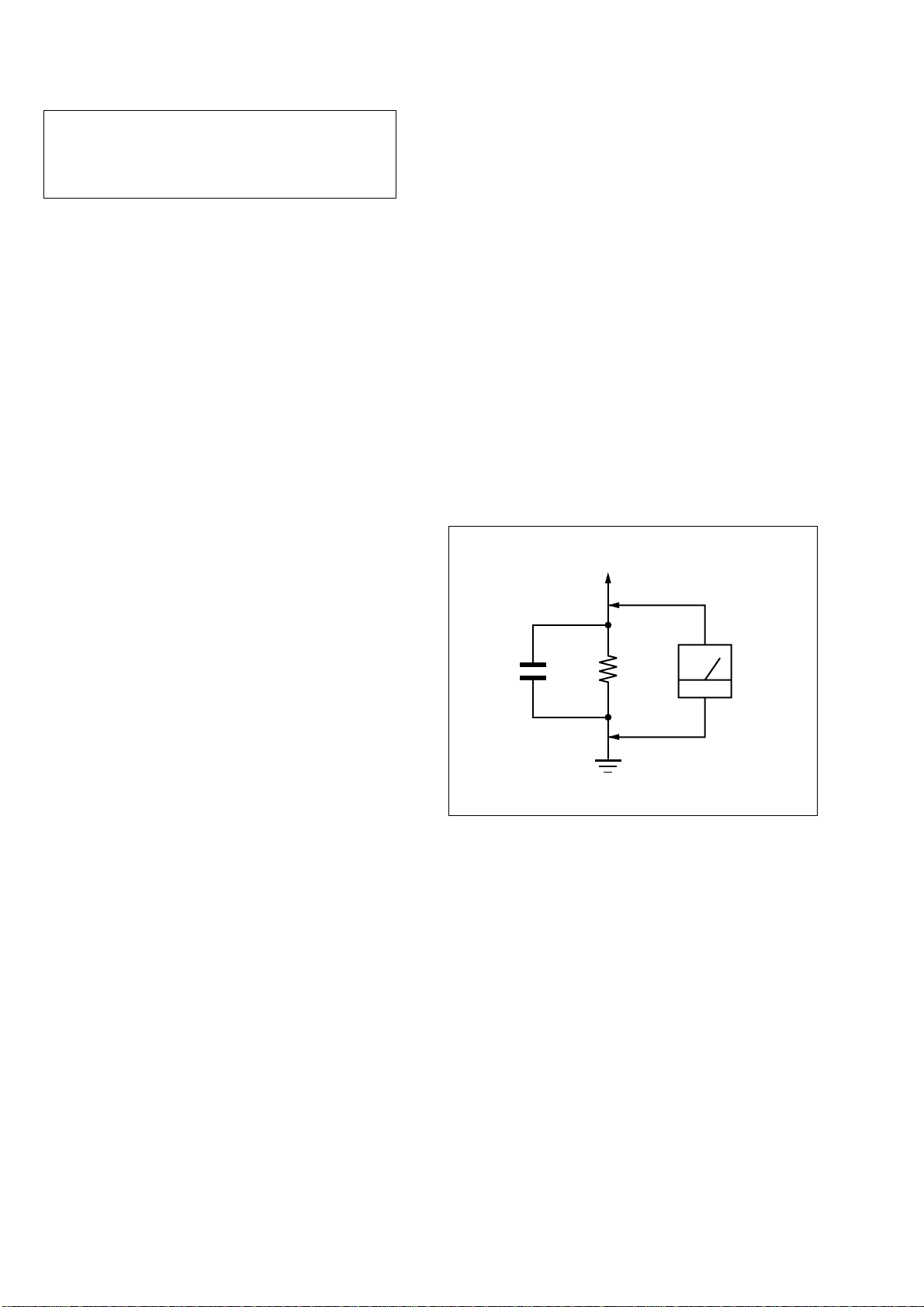
LEAKAGE TEST
The AC leakage from any exposed metal part to earth ground and
from all exposed metal parts to any exposed metal part having a
return to chassis, must not exceed 0.5 mA (500 microampers.).
Leakage current can be measured by any one of three methods.
1. A commercial leakage tester, such as the Simpson 229 or RCA
WT-540A. Follow the manufacturers’ instructions to use these
instruments.
2. A battery-operated AC milliammeter. The Data Precision 245
digital multimeter is suitable for this job.
3. Measuring the voltage drop across a resistor by means of a
VOM or battery-operated AC voltmeter. The “limit” indication is 0.75 V, so analog meters must have an accurate lowvoltage scale. The Simpson 250 and Sanwa SH-63Trd are examples of a passive VOM that is suitable. Nearly all battery
operated digital multimeters that have a 2 V AC range are suitable. (See Fig. A)
To Exposed Metal
Parts on Set
NOTES ON LASER DIODE EMISSION CHECK
The laser beam on this model is concentrated so as to be focused on
the disc reflective surface by the objective lens in the optical pickup block. Therefore, when checking the laser diode emission,
observe from more than 30 cm away from the objective lens.
0.15 µF
1.5 k
Ω
Earth Ground
AC
voltmeter
(0.75 V)
Fig. A. Using an AC voltmeter to check AC leakage.
(Fig. A)
SAFETY-RELATED COMPONENT WARNING!!
COMPONENTS IDENTIFIED BY MARK 0 OR DOTTED LINE
WITH MARK 0 ON THE SCHEMATIC DIAGRAMS AND IN
THE PARTS LIST ARE CRITICAL TO SAFE OPERATION.
REPLACE THESE COMPONENTS WITH SONY P ARTS WHOSE
PART NUMBERS APPEAR AS SHOWN IN THIS MANUAL OR
IN SUPPLEMENTS PUBLISHED BY SONY.
2
ATTENTION AU COMPOSANT AYANT RAPPORT
À LA SÉCURITÉ!!
LES COMPOSANTS IDENTIFIÉS P AR UNE MARQUE 0 SUR LES
DIAGRAMMES SCHÉMATIQUES ET LA LISTE DES PIÈCES
SONT CRITIQUES POUR LA SÉCURITÉ DE FONCTIONNEMENT.
NE REMPLACER CES COMPOSANTS QUE PAR DES PIÈCES
SONY DONT LES NUMÉROS SONT DONNÉS DANS CE MANUEL
OU DANS LES SUPPLÉMENTS PUBLIÉS PAR SONY.

TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. SERVICING NOTES
1-1. Cord Dressing (Power Cord)............................................... 5
1-2. Pointer Alignment ............................................................... 5
2. GENERAL............................................................................ 6
3. DISASSEMBL Y
3-1. Cabinet (Upper) Assy.......................................................... 7
3-2. Lid (CD) .............................................................................. 8
3-3. Chassis Assy........................................................................ 8
3-4. Main Board, Drive Board.................................................... 9
3-5. Key (A) Board, Key (B) Board ...........................................9
3-6. CD Mechanism Deck ........................................................ 10
3-7. Optical Pick-up ................................................................. 10
4. ELECTRICAL ADJUSTMENTS
Tuner Section......................................................................... 11
CD Section ............................................................................ 13
5. DIAGRAMS
5-1. Circuit Boards Location .................................................... 14
5-2. Block Diagram – CD Section –......................................... 15
5-3. Block Diagram – Tuner Section –..................................... 16
5-4. Block Diagram – Main Section –...................................... 17
5-5. Printed Wiring Board – CD Section – ...............................18
5-6. Schematic Diagram – CD Section –.................................. 19
5-7. Schematic Diagram – Main Section –............................... 20
5-8. Printed Wiring Board – Main Section – ............................ 21
5-9. Schematic Diagram – Control, Display Section – ............ 22
5-10. Printed Wiring Boards – Key Section – ............................ 23
5-11. Printed Wiring Board – Drive Section – ........................... 24
5-12. Printed Wiring Board – Transformer Section –................. 25
5-13. IC Pin Description............................................................. 26
5-14. IC Block Diagrams............................................................ 26
ICF-CD832
6. EXPLODED VIEWS
6-1. Cabinet (Upper) Section.................................................... 28
6-2. Cabinet (Lower) Section ................................................... 29
6-3. Chassis Section ................................................................. 30
6-4. CD Mechanism Section..................................................... 31
7. ELECTRICAL PARTS LIST ........................................ 32
3
ICF-CD832
SECTION 1
SERVICING NOTES
CHUCK PLATE JIG ON REP AIRING
On repairing CD section, playing a disc without the lid (CD), use
Chuck Plate Jig.
• Code number of Chuck Plate Jig: X-4918-255-1
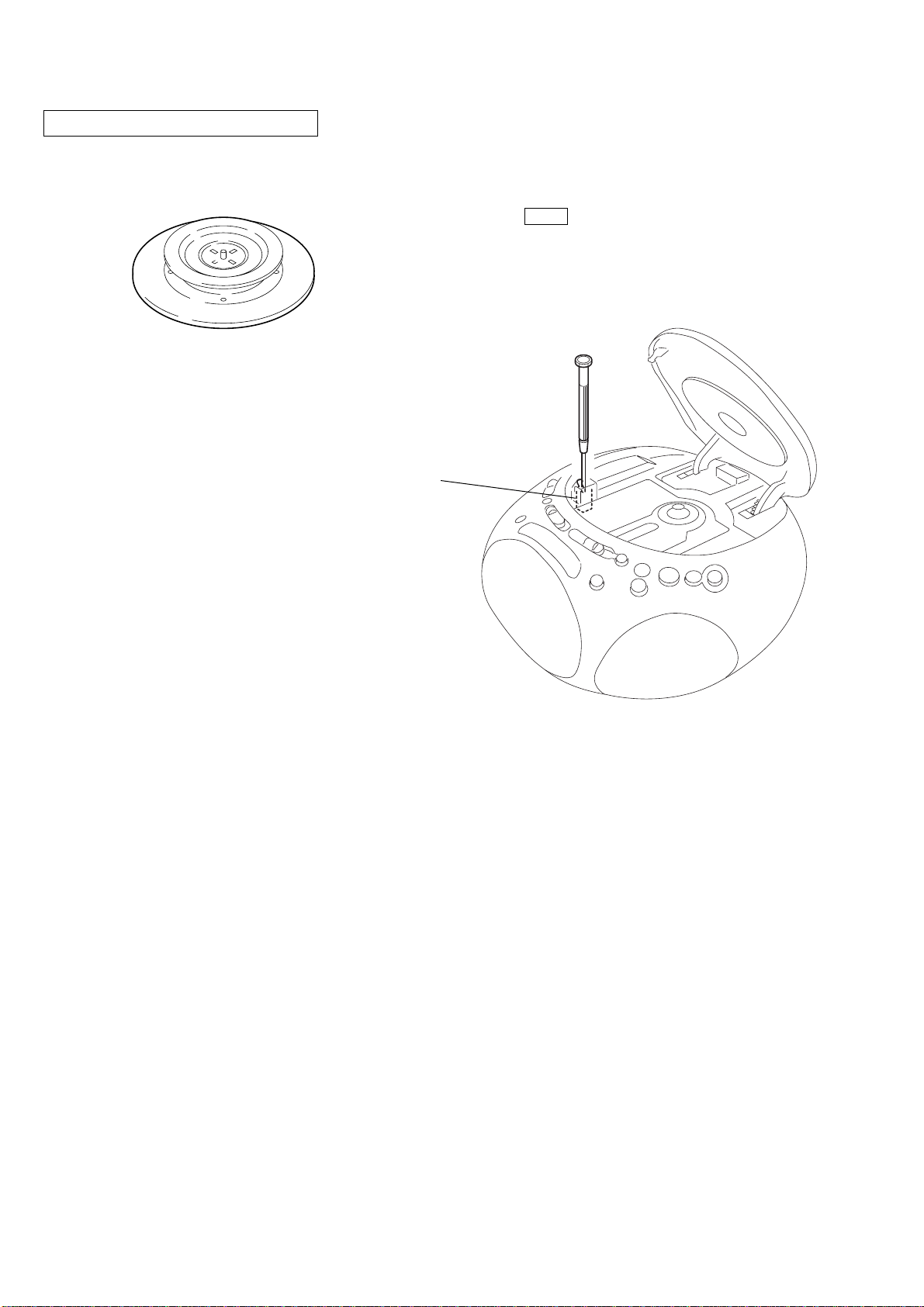
LASER DIODE AND FOCUS SEARCH OPERATION
CHECK
1. Turn ON the [POWER] button and press [CD] button to CD
position.
2. Open the CD lid.
3. Turn on S401 with screwdriver, etc. as following figure.
4. Press the N X (CD) button.
5. Confirm the laser diode emission while observing the objecting
lens. When there is no emission, Auto P ower Control circuit or
Optical Pick-up is broken.
Objective lens moves up and do wn three times for focus search.
S401
4
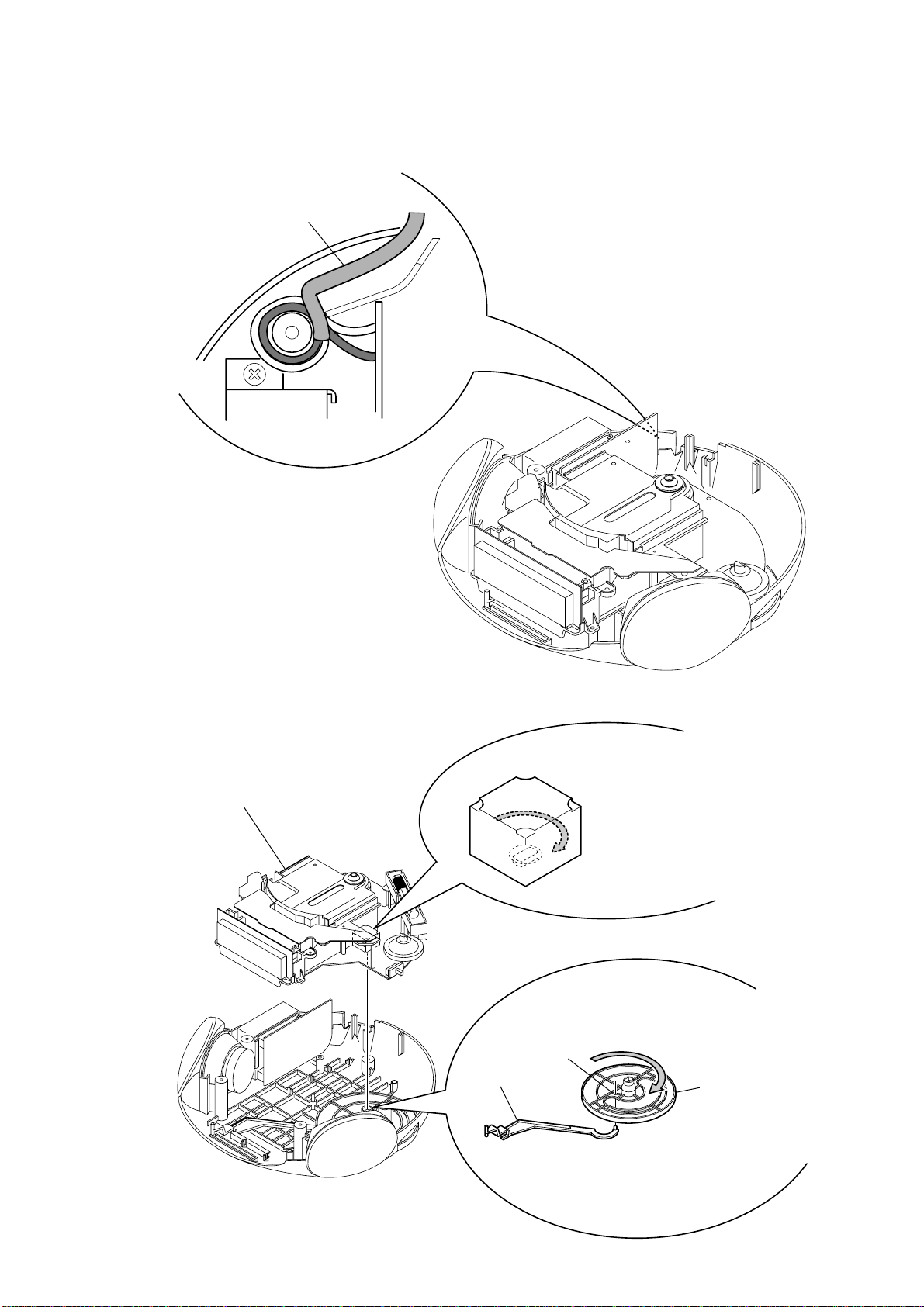
1-1. CORD DRESSING
(POWER CORD)
1) Set the power cord as shown in the figure.
power cord
ICF-CD832
1-2. POINTER ALIGNMENT
chassis assy
pointer
1
Turn this in the arrow direction
until stopped.
A
2
Fit the protrusion on the
pointer in the hole A.
3
Align the notch on the
boss of the knob (tune)
with the direction of CV1.
knob (tune)
5
ICF-CD832
SECTION 2
GENERAL
This section is extracted
from instruction manual.
6
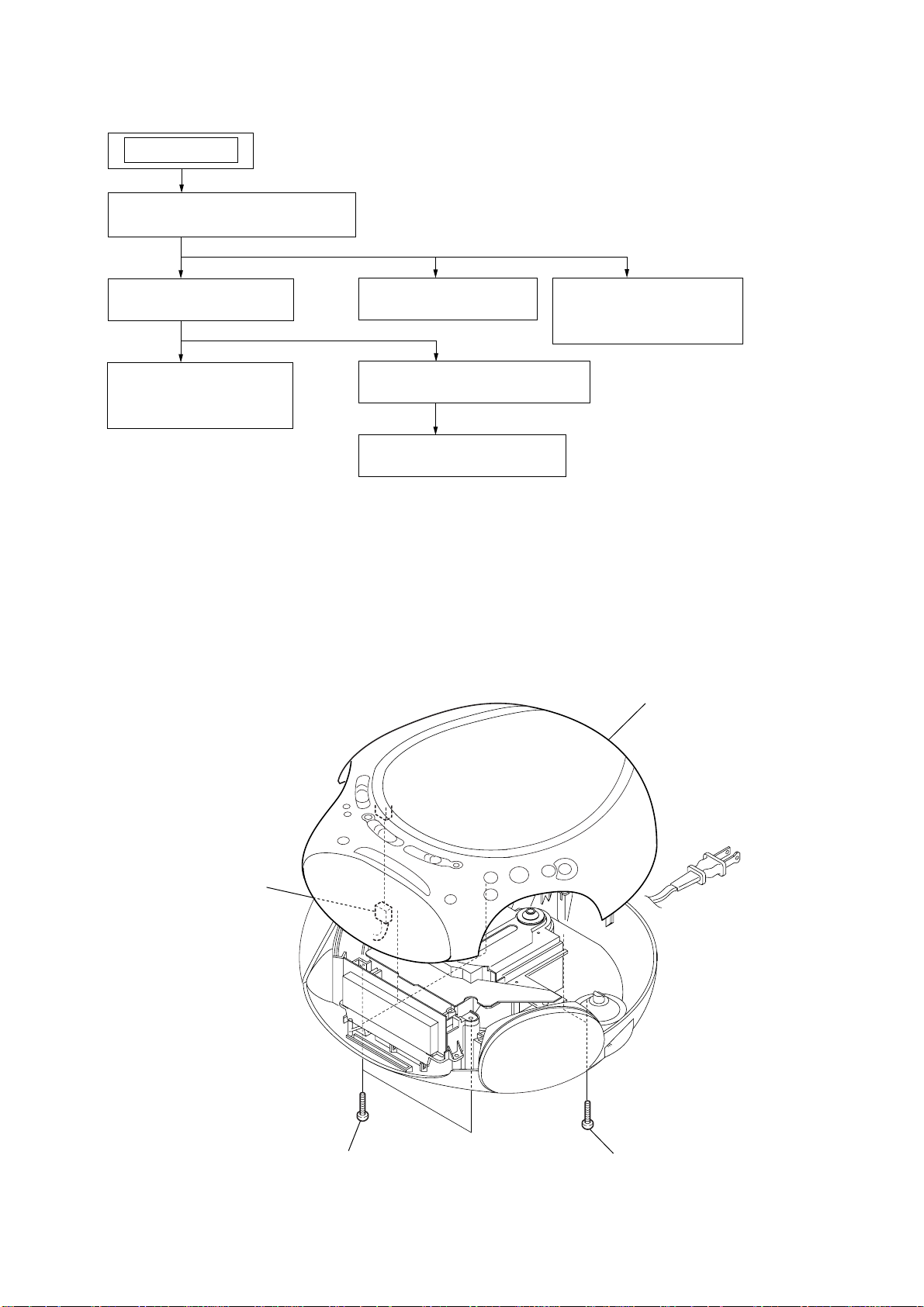
SECTION 3
y
DISASSEMBLY
• The equipment can be removed using the following procedure.
SET
3-1. CABINET (UPPER) ASSY
(Page 7)
ICF-CD832
3-3. CHASSIS ASSY
(Page 8)
3-4. MAIN BOARD,
DRIVE BOARD
3-2. LID (CD)
(Page 8)
3-6. CD MECHANISM DECK
(Page 10)
(Page 9)
3-7. OPTICAL PICK-UP
(Page 10)
Note : Follow the disassembly procedure in the numerical order given.
3-1. CABINET (UPPER) ASSY
3-5. KEY (A) BOARD,
KEY (B) BOARD
(Page 9)
3
cabinet (upper) sub ass
4
connector
2
four screws
(BV tapping (B3))
1
two screws
(BV tapping (B3))
7
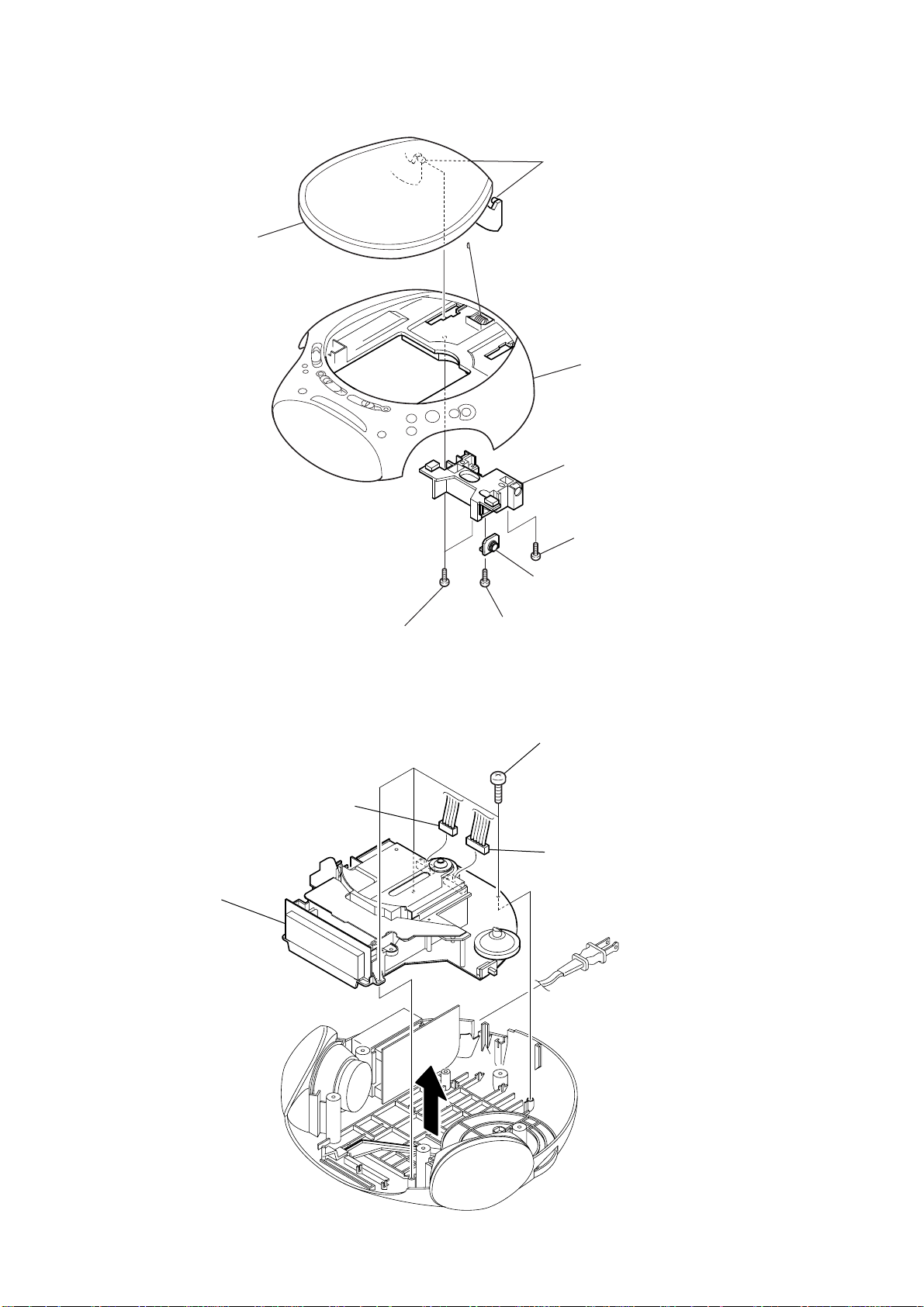
ICF-CD832
3-2. LID (CD)
7
CD lid sub assy
5
claws
cabinet (upper) sub assy
6
holder (CD)
3-3. CHASSIS ASSY
4
chassis assy
1
CN301
4
two screws
(BV tapping (B3))
3
screw
(BV tapping (B3))
2
damper
1
screw
(BV tapping (B3))
3
three screws
(BV tapping (B3))
2
CN901
8
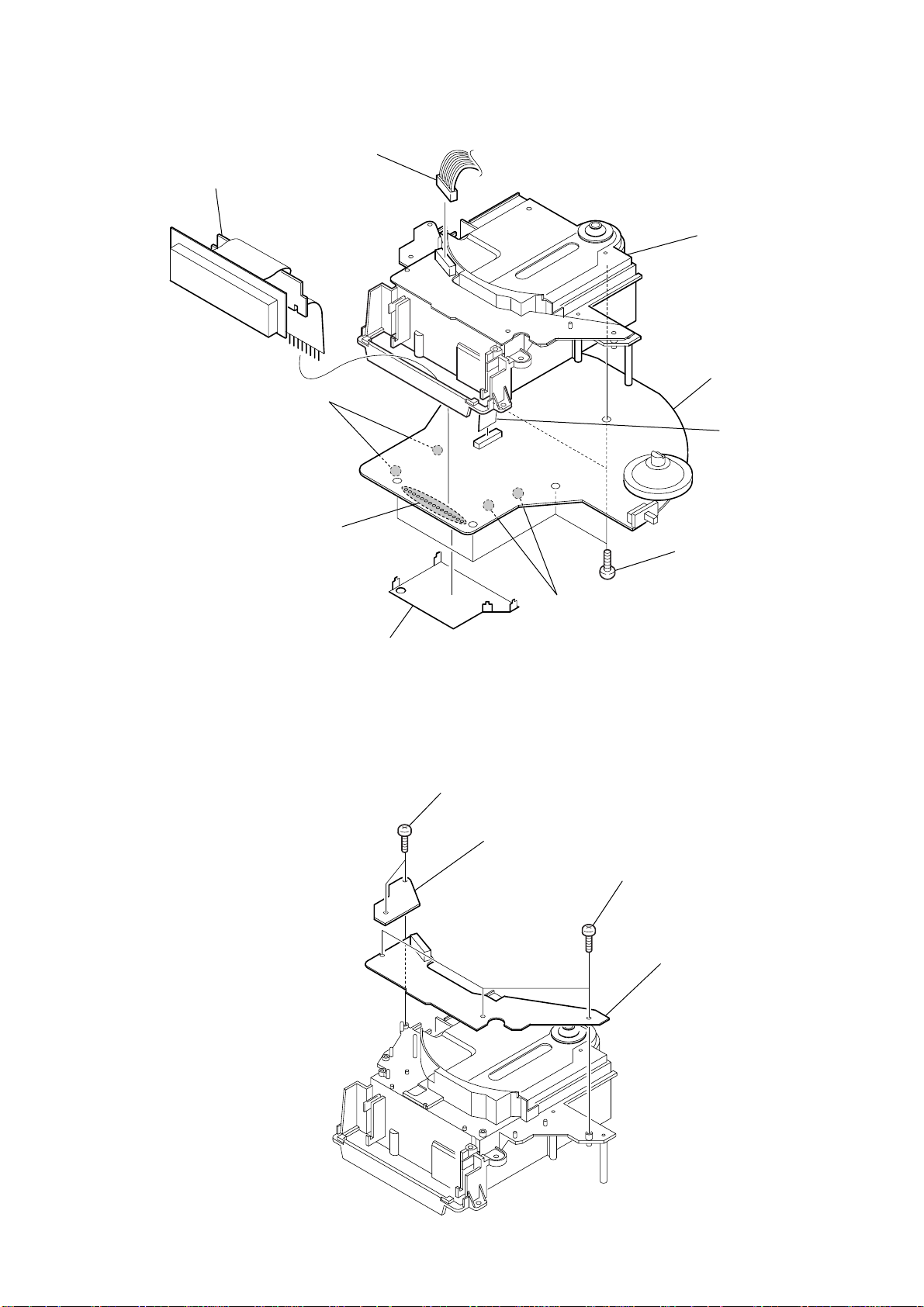
3-4. MAIN BOARD, DRIVE BOARD
d
d
1
CN601
6
DRIVE board
3
Removal the solders.
chassis assy
9
MAIN boar
8
CN501
ICF-CD832
5
Removal the solders.
3-5. KEY (A) BOARD, KEY (B) BOARD
4
shield plate (main)
1
two screws
(B 2x8)
2
KEY (A) board
2
Removal the solders.
3
three screws
(B 2x8)
7
five screws
(P 3x10)
4
KEY (B) boar
9
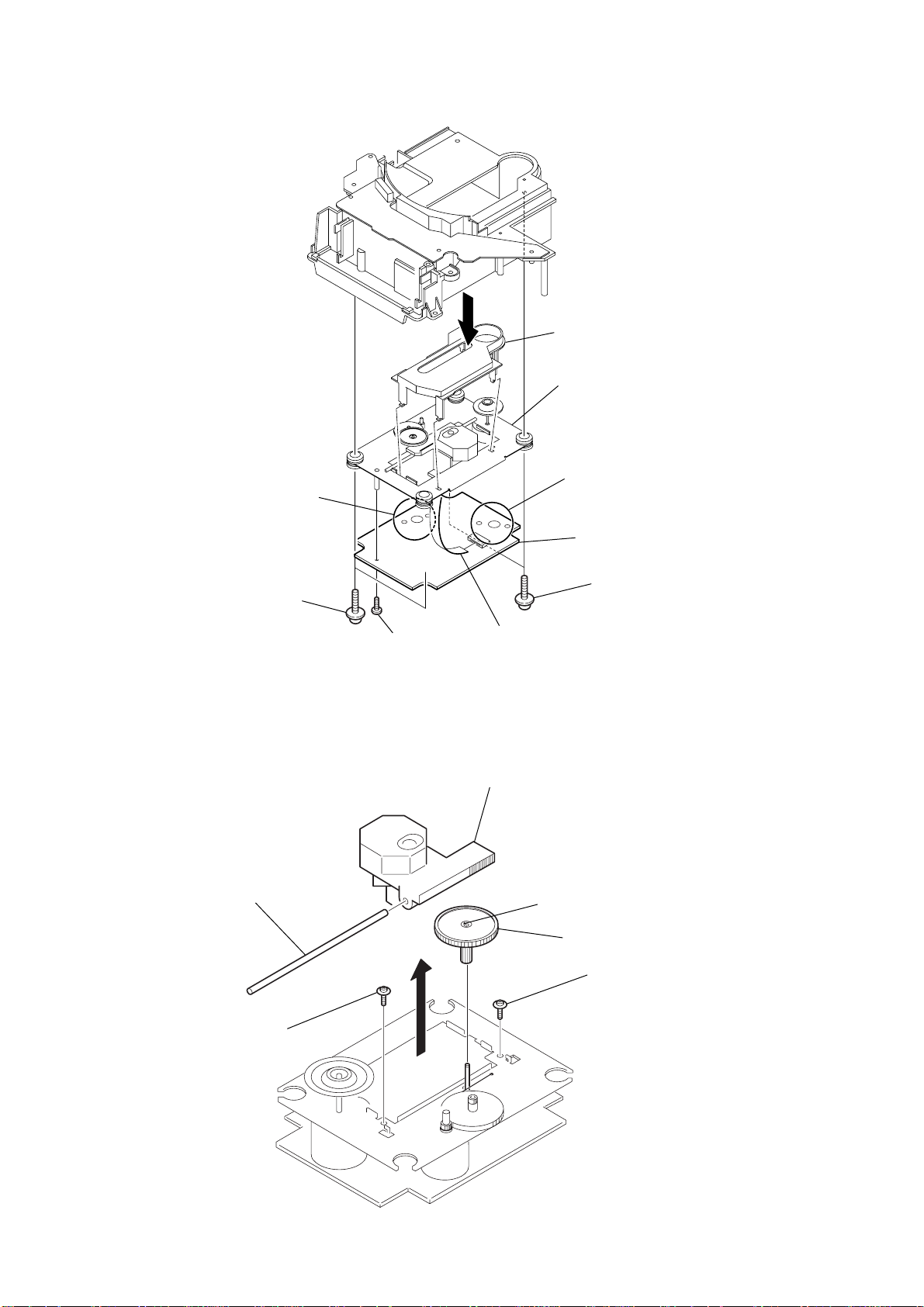
ICF-CD832
)
3-6. CD MECHANISM DECK
7
Removal the solders.
3
4
CD cover
0
CD mechanism deck
6
Removal the solders.
3-7. OPTICAL PICK-UP
2
two screws
(PWH 2.6x10)
5
sled shaft
5
screw
(BVTT 2x6)
4
9
CNP701
6
optical pick-up
claw
8
CD board
1
two screws
(PWH 2.6x10)
1
gear (A)
2
screw
(PWB tapping (M2)
10
3
screw
(PWB tapping (M2))
SECTION 4
l
ELECTRICAL ADJUSTMENTS
ICF-CD832
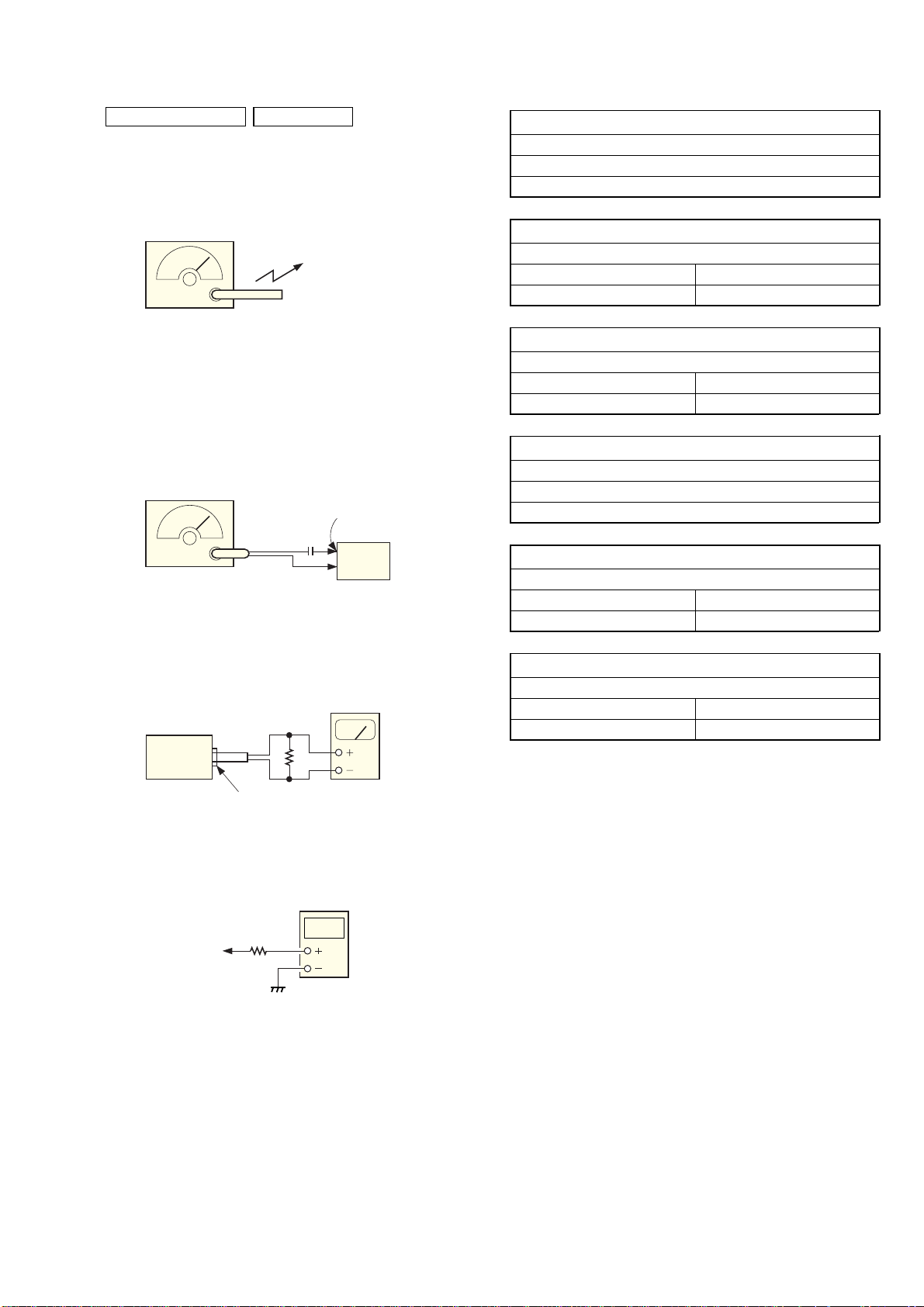
TUNER SECTION 0 dB = 1 µV
• AM Section
Setting:
BAND switch: AM
VOLUME control: MIN
AM RF signal
generator
Put the lead-wire
antenna close to
the set.
30% amplitude
modulation by
400 Hz signal
• FM Section
Setting:
BAND switch: FM
VOLUME control: MIN
FM RF signal
generator
0.01 F
75 kHz frequency
deviation by 1 kHz signal
output level : as low as possible
FM lead wire
antenna termina
set
AM IF ADJUSTMENT
Adjust for a maximum reading on level meter.
T1
450 kHz
AM FREQUENCY COVERAGE ADJUSTMENT
Adjust for a maximum reading on level meter.
L4 CT4
520 kHz 1,750 kHz
AM TRACKING ADJUSTMENT
Adjust for a maximum reading on level meter.
L1 CT1
600 kHz 1,400 kHz
FM IF ADJUSTMENT
Adjust for a maximum reading on level meter.
T2
10.7 MHz
FM FREQUENCY COVERAGE ADJUSTMENT
Adjust for a maximum reading on level meter.
L5 CT3
86.5 MHz 109.5 MHz
• Connecting Level Meter (FM and AM)
level meter
(range: 0.5–5 V ac)
16 Ω
set
speaker terminal
• Connecting Digital Voltmeter (FM and AM)
digital
voltmeter
100 kΩ
TP (VT)
•Repeat the procedures in each adjustment several times, and the
frequency coverage and tracking adjustments should be finally
done by the trimmer capacitors.
FM TRACKING ADJUSTMENT
Adjust for a maximum reading on level meter.
L2 CT2
86.5 MHz 109.5 MHz
Adjustment Location: See page 12.
11
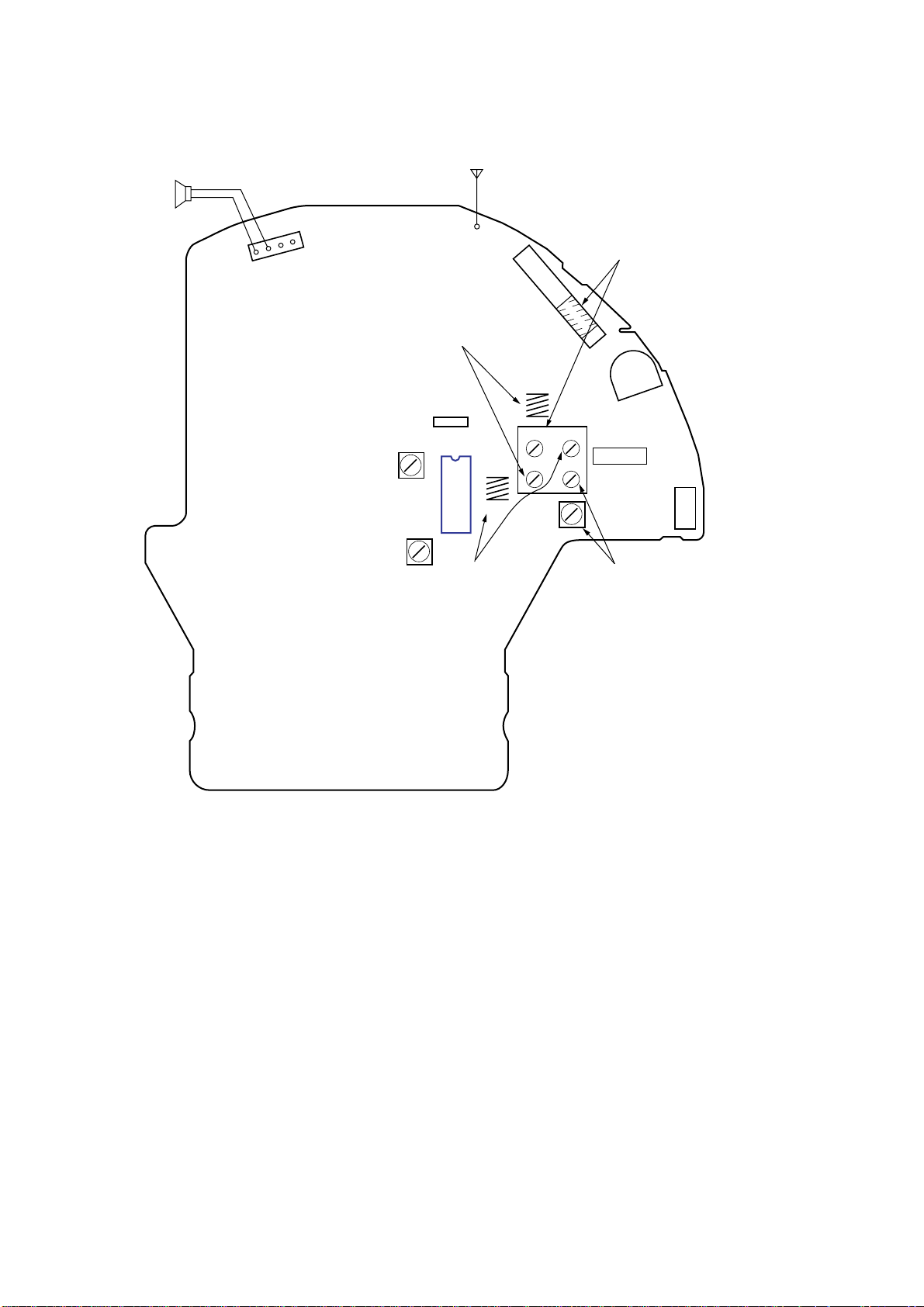
ICF-CD832
Y
Adjustment Location:
SP101
(SPEAKER)
4
CN301
FM LEAD WIRE
ANTENNA
1
CT2,L2
FM TRACKING
ADJUSTMENT
ANT1
L1
CT1,L1
AM TRACKING
ADJUSTMENT
T1
AM IF
ADJUSTMENT
T2
FM IF
ADJUSTMENT
— MAIN BOARD (component side) —
BPF1
IC1
L5
CT3,L5
FM FREQUENCY
COVERAGE
ADJUSTMENT
L2
CT1
CT2
CT3
CT4
L4
TUNING
RV301
CV1
S1
CT4,L4
AM FREQUENC
COVERAGE
ADJUSTMENT
12
 Loading...
Loading...