Page 1

A-DJ7-100-11(2)
Color Camera Module
Technical Manual
FCB-EX1020/EX1020P
2010 Sony Corporation
Page 2

Table of Contents
Features ..................................................................... 3
Precautions ................................................................ 4
Locations of Controls ............................................... 5
Basic Functions......................................................... 6
Overview of Functions ................................................ 6
Eclipse ...................................................................... 21
Spectral Sensitivity Characteristics .......................... 21
Vibration Specifications ............................................ 21
Key Switch Circuitry ................................................. 22
Key Function Specifications ..................................... 23
Initial Settings, Custom Preset and Backup ............. 26
Mode Condition ........................................................ 28
Command List ......................................................... 31
VISCA/RS-232C Commands ................................... 31
FCB Camera Commands ......................................... 37
Specifications .......................................................... 58
2
Page 3

Overview
Features
• The EX-view HADTM CCD features 380,000 (NTSC)
or 440,000 (PAL) effective picture elements and
high-sensitivity shooting. The minimum illumination
required is 1.4 lux (
OFF).
•A CCD for shooting a wide dynamic range is
employed to perform progressive or interlaced
scanning, and images with a wide dynamic range are
obtained by a newly developed image signal
processor (Wide Dynamic Range function).
Furthermore, it is possible to automatically switch to
this Wide Dynamic Range function, which enables
you to obtain optimal images ranging from the dark
areas of a subject to the light areas.
• Low-noise images can be obtained even in low light
environments using the 3D Noise Reduction (3D NR
+ 2D NR) function.
•A function to output interlaced or progressive images
by digital output (equivalent to ITU-R BT656) is
provided.
•36× optical zoom (432× with digital zoom)
•A Image Stabilizer function enables stable shooting.
• Supporting external synchronization (V-lock)
•Images with a high resolution (550 TV lines) can be
obtained using a newly developed Image Signal
Processor for improved picture quality.
•An infrared (IR) Cut-Filter can be disengaged from
the image path for increased sensitivity in low light
environments. The ICR will automatically engage
depending on the ambient light, allowing the camera
to be effective in day/night environment.
•VISCA is a communications protocol, which enables
the camera to be controlled remotely from a host
computer/controller.
• Six memory locations are provided to temporally
save and recall up to six sets of camera settings.
•A Privacy Zone Masking function (max. 24 blocks) is
available.
•A mosaic masking function has been added to the
privacy zone masking function.
1
/60 s (NTSC), 1/50 s (PAL), ICR
•A title composed of up to 11 lines can be set for
displaying on the screen. 20 characters can be used
on one line.
• E-FLIP and Mirror Image functions
•Alarm function with adjustable detection zones
•Adjustable AE response speed
With consideration given environmental protection,
this module is designed to operate with low power
consumption and also incorporates lead-free and
halogen-free circuit boards.
3
Page 4

Overview
Precautions
Software
Use of the demonstration software developed by Sony
Corporation or use of the software with customer
developed application software may damage hardware,
the application program or the camera. Sony
Corporation is not liable for any damages under these
conditions.
Operation
Start the camera control software on your computer
after you turn on the camera and the image is
displayed.
Operation and storage locations
Do not shoot images that are extremely bright (e.g.,
light sources, the sun, etc.) for long periods of time. Do
not use or store the camera in the following extreme
conditions:
• Extremely hot or cold places (operating temperature
–5 ˚C to +60 ˚C (41 ˚F to 140 ˚F))
•Close to generators of powerful electromagnetic
radiation such as radio or TV transmitters
•Where it is subject to fluorescent light reflections
•Where it is subject to unstable (flickering, etc.)
lighting conditions
•Where it is subject to strong vibration
•Where it is subject to radiation from laser beams
In case of abnormal operation, contact your authorized
Sony dealer or the store where you purchased the
product.
Phenomena specific to CCD image
sensors
The following phenomena that may appear in images
are specific to CCD (Charge Coupled Device) image
sensors. They do not indicate malfunctions.
White flecks
Although the CCD image sensors are produced with
high-precision technologies, fine white flecks may be
generated on the screen in rare cases, caused by cosmic
rays, etc.
This is related to the principle of CCD image sensors
and is not a malfunction.
The white flecks especially tend to be seen in the
following cases:
•when operating at a high environmental temperature
•when you have raised the master gain (sensitivity)
•when operating in Slow-Shutter mode
Vertical smear
When an extremely bright object, such as a strong
spotlight or flashlight, is being shot, vertical tails may
be produced on the screen, or the image may be
distorted.
Vertical tails shown on the
Monitor screen
image.
Care of the unit
Remove dust or dirt on the surface of the lens with a
blower (commercially available).
Other
Do not apply excessive voltage. (Use only the
specified voltage.) Otherwise, you may get an electric
shock or a fire may occur.
Bright object
(e.g. strong spotlight,
strong reflected light,
flashlight, the sun)
Aliasing
When fine patterns, stripes, or lines are shot, they may
appear jagged or flicker.
4
Page 5

Locations of Controls
Locations of Controls
Front
Back
Top
Bottom
1 Lens
2 CN500 jack
3 CN501 jack
4 CN702 jack (for key SW)
5 CN200 jack (for digital output)
6 TELE button
7 WIDE button
8 Tripod screw hole
When a tripod is used, please use
9
7 mm (
attach it to the camera. Also,
please be sure to attach the tripod
securely.
/32 in.) or less screw to
5
Page 6

Basic Functions
Basic Functions
Overview of Functions
VISCA commands are the basis of camera control.
Timing Chart
As VISCA Command processing can only be carried
out one time in a Vertical cycle, it takes the maximum
1V cycle time for an ACK/Completion to be returned.
If the Command ACK/Completion communication
time can be cut shorter than the 1V cycle time, then
every 1V cycle can receive a Command.
General Commands
Within
Query Commands
Within
In general
• Power On/Off
Powers the camera on and off. When the power is off,
the camera is able to accept only the lowest level of
VISCA Commands; the display and other features are
turned off.
• I/F Clear
Clears the Command buffer of the FCB camera.
Clearing the buffer can also be carried out from the
control application software when the power is on.
• Address Set
VISCA is a protocol, which normally supports a
daisy chain of up to seven connected cameras via RS232C interface. In such cases, the address set
command can be used to assign addresses from 1 to 7
to each of the seven cameras, allowing you to control
the seven cameras with the same personal computer.
Although the FCB camera does not support direct
connection of cameras in a daisy chain, be sure to use
the address set command to set the address whenever
a camera is connected for the first time.
• ID Write
Sets the camera ID.
• Mute
Blanks the screen and sends out a synchronizing
signal.
16 Byte
• Lens Initialize
Initializes the zoom and focus of the lens. Even when
power is already on, it initializes the zoom and the
focus.
• Comp Scan
A pixel blemish-masking feature, which can be made
to reevaluate overall CCD pixel blemishes and mask
severely flawed pixels automatically upon receiving
the COMP SCAN command. This feature helps to
mask the flaws found in CCD imagers, even after the
camera has been powered on for some time.
6
Page 7

Basic Functions
Zoom
The FCB camera employs a 36× optical zoom lens
combined with a digital zoom function; this camera
allows you to zoom up to 432×.
•Optical 36×, f = 3.4 to 122.4 mm (F 1.6 to F 4.5)
The horizontal angle of view is approximately 57.8
degrees (wide end) to 1.7 degrees (tele end).
Digital Zoom enlarges the center of the subject by
expanding each image in both the vertical and
horizontal directions. When 432× zoom is used, the
number of effective picture elements in each direction
reduces to
You can activate the zoom in the following three ways
•By pressing the TELE or WIDE buttons on the
camera itself
•Using a VISCA Command
• The Zoom Mode supports a Combined Mode and a
Separate Mode.
•Using an external key switch board connected to
the jack for the key SW.
1
/12 and the overall resolution deteriorates.
Using Standard Mode
Using Variable Mode
There are eight levels of zoom speed.
Direct Mode
Setting the zoom position enables quick
movement to the designated position.
Digital Zoom ON/OFF
In these standard and variable Speed Modes, it is necessary
to send Stop Command to stop the zoom operation.
Combined Mode
This is the previously existing zoom method.
After the optical zoom has reached its maximum
level, the camera switches to Digital Zoom Mode.
Separate Mode
In this mode, Optical Zoom and Digital Zoom can
be operated separately. You can use digital zoom
magnification at any time from within any level of
optical magnification.
About Continues Zoom position Reply
With ZoomDirect mode, or when zooming
according to a preset, the camera outputs zoom
position data when Continues Zoom position
Reply is set to ON via a command.
Continues Zoom position Reply: y0 07 04 69 0p
0p 0q 0q 0q 0q FF
pp: D-Zoom position
qqqq: Zoom position
Focus
Focus has the following modes, all of which can be set
using VISCA Commands.
• Auto Focus Mode
The minimum focus distance is 320 mm at the optical
wide end and 1500 mm at the optical tele end, and is
independent of the digital zoom.
The Auto Focus (AF) function automatically adjusts
the focus position to maximise the high frequency
content of the picture in a center measurement area,
taking into consideration the high luminance and
strong contrast components.
- Normal AF Mode
This is the normal mode for AF operations.
- Interval AF Mode
The mode used for AF movements carried out at
particular intervals. The time intervals for AF
movements and for the timing of the stops can be
set in one-second increments using the Set Time
Command. The initial value for both is set to five
seconds.
- Zoom Trigger Mode
When the zoom is changed with the TELE or the
WIDE buttons, the pre-set value (initially set at 5
seconds) becomes that for AF Mode. Then, it
stops.
AF sensitivity can be set to either Normal or LOW.
- Normal
Reaches the highest focus speed quickly. Use this
when shooting a subject that moves frequently.
Usually, this is the most appropriate mode.
- LOW
Improves the stability of the focus. When the
lighting level is low, the AF function does not take
effect, even though the brightness varies,
contributing to a stable image.
• Manual Focus Mode
Manual Focus has both a Standard Speed Mode and a
Variable Speed Mode. Standard Speed Mode focuses
at a fixed rate of speed. Variable Speed Mode has
eight speed levels that can be set using a VISCA
Command.
In these standard and variable Speed Modes, it is necessary to
send Stop Command to stop the zoom operation.
• One Push Trigger Mode
When a Trigger Command is sent, the lens moves to
adjust the focus for the subject. The focus lens then
holds that position until the next Trigger Command is
input.
• Infinity Mode
The lens is forcibly moved to a position suitable for
an unlimited distance.
• Near Limit Mode
Can be set in a range from 1000 (∞) to C000 (10 mm).
7
Page 8

Basic Functions
White Balance
White Balance has the following modes, all of which
can be set using VISCA Commands.
• Auto White Balance
This mode computes the white balance value output
using color information from the entire screen. It
outputs the proper value using the color temperature
radiating from a black subject based on a range of
values from 3000 to 7500K.
This mode is the factory setting.
• ATW
Auto Tracing White balance (2000 to 10000K)
• Indoor
3200K Base Mode
• Outdoor
5800K Base Mode
• One Push WB
The One Push White Balance mode is a fixed white
balance mode that may be automatically readjusted
only at the request of the user (One Push Trigger),
assuming that a white subject, in correct lighting
conditions, and occupying more than 1/2 of the
image, is submitted to the camera.
One Push White Balance data is lost when the power
is turned off. If the power is turned off, reset One
Push White Balance.
• Manual WB
Manual control of R and B gain, 256 steps each
• Outdoor Auto
This is an auto white balance mode specifically for
outdoors. It allows you to capture images with natural
white balance in the morning and evening.
• Sodium Vapor Lamp Auto
This is an auto white balance mode that is compatible
with sodium vapor lamps.
• Sodium Vapor Lamp
This is a fixed white balance mode specifically for
sodium vapor lamps.
Automatic Exposure Mode
A variety of AE functions are available for optimal
output of subjects in lighting conditions that range
from low to high.
• Full Auto
Auto Iris and Gain, Fixed Shutter Speed (NTSC: 1/60
sec., PAL: 1/50 sec.)
• Gain Limit Setting
The gain limit can be set in the AE mode. Use this
setting when image signal-to-noise ratio is
particularly important.
• Shutter Priority
1)
Variable Shutter Speed, Auto Iris and Gain
(1/1 to 1/10,000 sec., 16 high-speed shutter speeds
plus 6 low-speed shutter speeds)
1)Flicker can be eliminated by setting shutter to
t1/100s for NTSC models used in countries with a 50 Hz
power supply frequency
t1/120s for PAL models used in countries with a 60 Hz
power supply frequency
• Iris Priority
Variable Iris (F1.6 to Close, 18 steps), Auto Gain and
Shutter speed
• Manual
Variable Shutter, Iris and Gain
• Bright
Variable Iris and Gain (Close to F1.6, 17 steps at
0 dB: F1.6, 15 steps from 0 to 28 dB)
AE – Shutter priority
The shutter speed can be set freely by the user to a
total of 22 steps – 16 high speeds and 6 low speeds.
1
When the slow shutter is set, the speed can be
1
/15s, 1/8s, 1/4s, 1/2s, 1/1s. The picture output is read at a
/30s,
normal rate from the memory. The memory is updated
at a low rate from the CCD. AF capability is low.
In high speed mode, the shutter speed can be set up to
1/10,000s. The iris and gain are set automatically,
according to the brightness of the subject.
Data NTSC (s) PAL (s)
15 1/10000 1/10000
14 1/6000 1/6000
13 1/4000 1/3500
12 1/3000 1/2500
11 1/2000 1/1750
10 1/1500 1/1250
0F 1/1000 1/1000
0E 1/725 1/600
0D 1/500 1/425
0C 1/350 1/300
0B 1/250 1/215
0A 1/180 1/150
09 1/125 1/120
08 1/100 1/100
07 1/90 1/75
06 1/60 1/50
05 1/30 1/25
04 1/15 1/12
03 1/8 1/6
02 1/4 1/3
01 1/2 1/2
00 1/1 1/1
8
Page 9

Basic Functions
AE – Iris priority
The iris can be set freely by the user to 18 steps
between F1.6 and Close.
The gain and shutter speed are set automatically,
according to the brightness of the subject.
Data
11 F1.6 08 F8
10 F2 07 F9.6
0F F2.4 06 F11
0E F2.8 05 F14
0D F3.4 04 F16
0C F4 03 F19
0B F4.8 02 F22
0A F5.6 01 F28
09 F6.8 00 CLOSE
Setting value
Data
Setting value
AE – Manual
The shutter speed (22 steps), iris (18 steps) and gain
(16 steps) can be set freely by the user.
AE – Bright
The bright control function adjusts both gain and iris
using an internal algorithm, according to a brightness
level freely set by the user. Exposure is controlled by
gain when dark, and by iris when bright.
As both gain and iris are fixed, this mode is used when
exposing at a fixed camera sensitivity. When switching
from Full Auto or Shutter Priority Mode to Bright
Mode, the current status will be retained for a short
period of time.
Only when the AE mode is set to “Full Auto” or
“Shutter Priority,” can you switch it to “Bright.”
Gain
AGC
IRIS
MAX
OPEN
CLOSE
Gain curve
MIN
Dark Bright
Controlled
by gain
Bright limit which controllable
for this unit
IRIS curve
Controlled by IRIS
Data Iris Gain Data Iris Gain
1F F1.6 28 dB 0F F2.4 0 dB
1E F1.6 26 dB 0E F2.8 0 dB
1D F1.6 24 dB 0D F3.4 0 dB
1C F1.6 22 dB 0C F4 0 dB
1B F1.6 20 dB 0B F4.8 0 dB
1A F1.6 18 dB 0A F5.6 0 dB
19 F1.6 16 dB 09 F6.8 0 dB
18 F1.6 14 dB 08 F8 0 dB
17 F1.6 12 dB 07 F9.6 0 dB
16 F1.6 10 dB 06 F11 0 dB
15 F1.6 8 dB 05 F14 0 dB
14 F1.6 6 dB 04 F16 0 dB
13 F1.6 4 dB 03 F19 0 dB
12 F1.6 2 dB 02 F22 0 dB
11 F1.6 0 dB 01 F28 0 dB
10 F2 0 dB 00 CLOSE 0 dB
When switching from the Shutter Priority mode to the
Bright mode, the shutter speed set in the Shutter
Priority mode is maintained.
Spot Exposure Mode
In Full Auto AE, the level for the entire screen is
computed and the optimum Auto Iris and Gain levels
are determined. In Spot AE, a particular section of the
subject can be designated, and then that portion of the
image can be weighted and a value computed so that
Iris and Gain can be optimized to obtain an image.
For example, in an image with a lot of movement and
with varying levels of brightness, portions without
much change can be designated as such a “spot,” and
changes to the screen can be minimized in that area.
As shown in the diagram below, a range of 16 blocks
vertically and 16 blocks horizontally can be
designated.
In the case where the center is designated (shown in
black), the level is computed along with a weighted
value for the surrounding block (shaded), including the
specified portions; and then the Gain and Iris are set.
The value of the designated portions and the
surrounding areas should be calculated as 100%, the
rest should be set to 20%. The range of the Spot AE
frame is fixed to 5 blocks vertically and 4 blocks
horizontally.
Horizontal 16
0
123456789ABCDEF
0
1
2
Ver tical 16
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
A
B
C
D
E
F
(8,8)
9
Page 10

Basic Functions
Exposure Compensation
Exposure compensation is a function which offsets the
internal reference brightness level used in the AE
mode, by steps of 1.5 dB.
Data Step
0E 7 10.5 dB
0D 6 9 dB
0C 5 7.5 dB
0B 4 6 dB
0A 3 4.5 dB
09 2 3 dB
08 1 1.5 dB
07 0 0 dB
06 –1 –1.5 dB
05 –2 –3 dB
04 –3 –4.5 dB
03 –4 –6 dB
02 –5 –7.5 dB
01 –6 –9 dB
00 –7 –10.5 dB
Setting value
Slow AE (Automatic Exposure)
The slow AE Response (automatic exposure) function
allows you to reduce the exposure response speed.
Usually the camera is set up so that the optimum
exposure can be obtained automatically within about 1
second. However, using the slow AE response function
allows you to lengthen the automatic exposure
response speed from the factory setup speed (01 (hex)
up to approx. two minutes (30 (hex)).
For example, with the normal setting (about 1 second),
if the headlights of a car are caught by the camera, the
camera automatically adjusts the exposure so that it
can shoot a high-intensity subject (in this case, the
headlights). As a result, images around the headlights,
that is, the rest of the subject, except the headlights,
becomes relatively dark, and poorly distinguished.
However, using the slow AE function means the AE
response speed will be slower, and response time will
be longer. As a result, even if the camera catches a
high-intensity subject (e.g., the headlights) for a
moment, you can still easily distinguish the portions of
the image surrounding the headlights.
High Resolution Mode (Default)
A newly developed ISP function enables the filtering
of signals. This allows the camera to provide images
with a high resolution (550 TV lines).
Aperture Control
Aperture control is a function which adjusts the
enhancement of the edges of objects in the picture.
There are 16 levels of adjustment, starting from “no
enhancement.” When shooting text, this control may
help by making them sharper.
Back Light Compensation
When the background of the subject is too bright, or
when the subject is too dark due to shooting in the AE
mode, back light compensation will make the subject
appear clearer.
Wide Dynamic Range Mode (WD)
The Wide Dynamic Range mode is a function for
dividing an image into several blocks and correcting
blocked-up shadows and blown-out highlights in
accordance with the intensity difference. It enables you
to obtain images in which portions ranging from dark
to light can be recognized, even when capturing a
subject with a large intensity difference that is backlit
or includes extremely light portions.
A CCD for shooting a wide dynamic range is
employed, and a newly developed image signal
processor combines a long exposure signal (normal
shutter) and a signal of the high intensity portions
obtained by a short exposure (high-speed shutter) to
achieve images with a wide dynamic range.
Wide Dynamic Range Auto On/Off Mode
The wide dynamic range can be set to be automatically
switched ON/OFF in accordance with the intensity
difference obtained by dividing an image into several
blocks and then averaging the intensity of each block.
Wide Dynamic Range Auto On/Off Mode
Auto On/Off
When the intensity
difference between the
dark portions and light
portions of a subject
becomes large because
of back lighting or the
like, the wide dynamic
range mode is switched
ON.
When the subject
changes and the
intensity difference
between the dark
portions and light
portions becomes
small, the wide dynamic
range mode is switched
OFF.
10
Page 11

Basic Functions
The wide dynamic range mode includes the following
operation modes.
• WD Mode
This mode corrects blocked-up shadows and blownout highlights in accordance with the intensity
difference.
• WD Auto ON/OFF Mode
This mode switches WD ON/OFF automatically in
accordance with the intensity difference of the subject.
Configure the sensitivity for when WD is switched
from OFF to ON with the detection sensitivity
parameter.
• Exposure Ratio Mode
This mode fixes the shutter speed of a short exposure.
Configure the shutter speed of a long exposure by
setting the ratio with regards to a short exposure with
the exposure ratio parameter.
Blocked-up shadow correction is not performed in
this mode.
• Histogram Mode
This mode uses a histogram to correct blocked-up
shadows and blown-out highlights. (The operation is
similar to that of FCB-EX1010/P Dver.)
About WD Set Parameter
(Command: 8x 01 04 2D 0p 0q 0r 0s 0t 0u 00 00
FF)
p: Screen display (0: Combined image, 1: Long/short
division, 2: Long-time, 3: Short-time)
Set the screen display to a WD combination
image, long/short exposure division image,
long exposure image, or short exposure image.
q: Detection sensitivity (0: Low, 1: Mid, 2: Hi)
Select from three levels for detecting the
intensity within the image for when switching
Auto WD from OFF to ON.
r: Blocked-up shadow correction level can be
set to one of four levels. (0:L 1:M 2:H 3:S)
s: Blown-out highlight correction level can be
set to one of three levels. (0:L 1:M 2:H)
tu: Parameter to use in the exposure ratio mode.
Specify the short exposure time by setting
the magnification ratio (×1 to ×150) with
regards to a long exposure time.
Note
When the wide dynamic range mode is ON, solarization may be
observed in the images of some subjects. This phenomenon is
unique to wide dynamic range mode, and is not an indication of a
camera malfunction.
noise images can be obtained for the corresponding
image brightness of a moving subject.
This function has six steps: levels 1 to 5, plus off.
Level 1 applies to subject motion mainly using 2D
filter effects. With level 5, 2D and 3D filter effects are
maximized, providing the lowest-noise images,
although moving subjects may show trails.
At each level, two filters are set according to noise and
image motion characteristics, so the available level
selections depend on the situation. The default setting
is level 3.
StableZoom™
StableZoom is a function for performing correction
using the Image Stabilizer function in accordance with
the zoom ratio, and smoothly zooming up to
approximately ×40 using a combination of the optical
zoom and digital zoom. The digital zoom can be
further used to zoom up to ×432.
At the wide end, you can obtain images without any
reduction in the angle of view and resolution because
the digital zoom is not switched ON. On the other
hand, at the Tele end, the correction effect by the
Image Stabilizer function is at its maximum so blurring
is reduced.
The StableZoom function can be switched ON/OFF in
the register settings.
x432
approx.
x40
x36
Zoom
ratio
Blurring is corrected in this
digital zoom area.
Wide
Angle of view and resolution
Optical zoom position
StableZoom
Digital zoom
Optical zoom
The digital
zoom is not
switched ON
at the wide
end.
Tele
Color Enhancement
Noise Reduction
The NR (Noise Reduction) function removes noise
(both random and non-random) to provide clearer
images. By combining 2D filtering according to
brightness and image color, and 3D filtering according
to noise caused by motion and time difference, lower-
A captured color image is converted to 256 levels of
gray, and the binarization process is performed to
convert all gray levels brighter than the threshold value
to white, and all gray levels darker than the threshold
value to black. (Any value can be set for the threshold
level and hysteresis width.) Furthermore, any color can
be assigned to each of the negative and positive.
11
Page 12

Basic Functions
Note
Flickering in images during color enhancement is not an indication
of a camera malfunction. It can be reduced with the threshold level,
hysteresis width, and edge enhancement (aperture) settings.
Grayscale image
(256 levels)
Color image
Binarization
process
Assign any
color
Image Stabilizer
Switching ON the Image Stabilizer function reduces
image blurring caused by, for example, vibration,
which allows you to obtain images without much
blurring. A correction effect of approximately 90% is
possible for a vibration frequency of around 10 Hz.
The Image Stabilizer function employs the digital
zoom system, so the angle of view and resolution are
changed, but the sensitivity is maintained.
ICR (IR Cut-Removable) Mode
An infrared (IR) Cut-Filter can be disengaged from the
image path for increased sensitivity in low light
environments. The ICR will automatically engage
depending on the ambient light, allowing the camera to
be effective in day/night environments.
When the auto ICR mode is set to ON, the image
becomes black and white.
Auto ICR Mode
Auto ICR Mode automatically switches the settings
needed for attaching or removing the IR Cut Filter.
With a set level of darkness, the IR Cut Filter is
automatically disabled (ICR ON), and the infrared
sensitivity is increased. With a set level of brightness,
the IR Cut Filter is automatically enabled (ICR OFF).
Also, on systems equipped with an IR light, the
internal data of the camera is used to make the proper
decisions to avoid malfunctions.
Auto ICR Mode operates with the AE Full Auto
setting.
When Auto Slow Shutter is OFF (initial setting)
Hold Function of Image Stabilizer
With the Image Stabilizer function, suddenly stopping
high-speed movement (pan, tilt, etc.) of the camera
produces a blur sensor counteraction that may cause
image movement. In such a case, you can use a
command setting (hold) to maintain the correction of
the Image Stabilizer function. In this case the image
stabilizer is off, but there is no change in the angle of
view.
Temperature Reading Function
The conversion value (hex) of the temperature sensor
built into to the camera can be read by using a query
command. The conversion value has an error of ±3 C,
and because the temperature sensor is inside the
camera, this value is not the ambient temperature. Use
it as a reference value.
Slow shutter – Auto/Manual
When set to “Auto,” ensures that the slow shutter is set
automatically when the brightness drops. Effective
only when the AE mode is set to “Full Auto.”
Set to “Slow Shutter Manual” at shipment.
Note
The Slow Shutter Auto function is not available in WD mode.
ICR
ICR ON
Dark Bright
AGC
MAX
ICR OFF t ON
IRIS
OPEN
GAIN
SHUTTER
Shutter 1/60 sec
IRIS
When Auto Slow Shutter is ON
Note
When in Auto_ICR_OFF state and WB data is added (default), a
malfunction may occur when the subjects largely consisting of blue
and green colors are taken.
12
Page 13

Basic Functions
Camera ID
The ID can be set up to 65,536 (0000 to FFFF). As this
will be memorized in the nonvolatile memory inside,
data will be saved regardless of whether it has been
backed up.
Effect
It consists of the following functions.
• Neg. Art: Negative/Positive Reversal
• Black White: Monochrome Image
Others
E-FLIP
This function turns the video output from the camera
upside down.
Mirror Image
This function reverses the video output from the
camera horizontally.
Freeze
This function captures an image in the field memory of
the camera so that this image can be output
continuously.
Because communication inside the camera is based on V
cycle, the captured image is always the one 3V to 4Vs after
the sending of a Command. Thus, you can not specify a time
period after sending EVEN, ODD or a Command.
Memory (Position preset)
Using the position preset function, 6 sets of camera
shooting conditions can be stored and recalled.
This function allows you to achieve the desired status
instantly, even without adjusting the following items
each time.
• Zoom Position
• Digital Zoom On/Off
• Focus Auto/Manual
• Focus Position
• AE Mode
• Shutter control parameters
• Bright Control
• Iris control parameters
• Gain control parameters
• Exposure Compensation On/Off
• Exposure Level
• Backlight Compensation On/Off
• Slow Shutter Auto/Manual
• Slow AE Response speed
• White Balance Mode
• R/B Gain
• Aperture
• ICR Shoot On/Off
• WD On/Off
Custom Preset
As with the position preset function, the camera
shooting conditions can be stored and recalled. The
settings are recalled when the power is turned on.
For setting items, see the “Initial Settings, Custom
Preset and Backup” section on page 26.
User Memory Area
A user area of 16 bytes allows you to write data, such
as an ID for each customer, data for each system, and
so on, freely.
Note
Rewriting of memory is not unlimited. Be careful to avoid using
the memory area for such as unnecessary tasks as rewriting the
contents of the memory for every operation.
Register Setting
The camera’s default settings can be changed by the
register setting command.
Register Setting Command:
8x 01 04 24 mm 0p 0q FF
mm: Register No. (=00 to 7F)
pq: Register Value (=00 to FF)
Register Inquiry Command:
8x 09 04 24 mm FF
mm: Register No.
y0 50 0p 0p FF
pp: Register Value
(returned from the camera)
Example: To set communication speed to 38400 bps
8x 01 04 24 00 00 02 FF
After sending this command, turn power off and
back on (power reset) to resume communication
control at 38400 bps.
Example: Sending to confirm settings
8x 09 04 24 00 FF
y0 50 00 03 FF is returned from the camera
The register setting items and No. are as follows.
Baud Rate: 00
Communication speed can be changed.
OSD Language: 60
OSD Language can be changed.
CCD Scanning Mode: 72
CCD scanning mode can be changed.
Digital Output Mode: 73
The FCB camera supports various output modes.
This register “73” allows changing the output
mode.
For details, see “Register Setting” on page 57.
Zoom Limit: 50 (Wide end), 51 (Tele end)
The Wide and Tele zoom limits can be set.
E-Zoom Max: 52
The maximum digital zoom limit can be specified
(default is ×12).
StableZoom: 53
The StableZoom command can be enabled and
disabled with this command.
13
Page 14

Basic Functions
FocusTrace: 54
When zoom speed is given priority, using the
ZoomDirect command changes focus at high speed
(although the image may be blurred because focus
is not tracked). For example, the focus transition
time from Wide to Tele ends, which typically takes
2.8 seconds, can be reduced to 2 seconds.
FocusOffset: 55
Placing a dome cover in front of the camera may
cause the focal distance of the camera to change.
Especially at the Tele end, this effect exceeds the
AF range, so focus cannot track, although it
responds to changes in this value.
For details, see “Register Setting” on page 57.
Privacy Zone Settings
For details, see page 15.
Motion detection
For details, see page 19.
Title Display
•You can set a title composed of up to 11 lines. One
line can contain up to 20 characters.
•You can set display on/off, the horizontal position of
the first character, blinking state and color for each
line.
• The camera gives priority to lines of a title when the
camera status is displayed on the relevant line. On the
lines where a title is not set, the camera status is
displayed.
Line Number 00 to 0A
H-position 00 to 17
Blink
Color 03 Red
00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07
AB CDEF G H
08 09 0a 0b 0c 0d 0e 0f
IJKLMNOP
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
QR STUVWX
18 19 1a 1b 1c 1d 1e 1f
YZ& ? ! 1 2
20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27
00: Does not blink
01: Blinks
00 White
01 Yellow
02 Violet
04 Cyan
05 Green
06 Blue
34 5678 9 0
28 29 2a 2b 2c 2d 2e 2f
ÀÈ Ì ÒÙÁ É Í
30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37
ÓÚ ÂÊÔÆŒÃ
38 39 3a 3b 3c 3d 3e 3f
ÕÑ ÇßÄ Ï Ö Ü
40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47
Å$
48 49 4a 4b 4c 4d 4e 4f
ø“ : ‘ . , / -
F
¥DM£ ¿ ¡
Synchronization methods
Internal and external synchronization are available;
VISCA Commands allow you to switch between them.
• Internal synchronization
An internal vibrator inside the camera generates a
synchronizing signal as a basic oscillator.
NTSC=59.94 Hz
PAL=50 Hz
1)
• External synchronization (V-Lock Synchronization
When a TTL level V-Lock pulse is input, the camera
synchronizes to the input signal (V-lock
synchronization). The frequency of the input signal
synchronizes to within ±1Hz of the external
synchronization.
Also, 360 degree phase adjustment is possible due to
the phase adjustment of the V-lock signal.
When adjusting V-Phase, first make the phase
adjustment with the Line Lock mode, then switch to
Frequency Lock mode and enable external sync. If
not performing phase adjustment, switch to
Frequency Lock mode then enable external sync. See
“Command List” on page 31.
Note
Noise may occur when performing phase adjustment
with the Line Lock mode, although it should
disappear when switching to Frequency Lock mode
for external sync.
Because V-lock synchronization is a simple synchronization
method, color signals like a VBS “Genlock” signal cannot be
synchronized.
1)In V-lock synchronization, the camera makes a V-lock pulse
(VL-PULSE) which synchronizes to the commercial power
supply and uses it as the external synchronization input signal
of the camera, using the fact that the V cycle (59.97 Hz vertical
synchronization signal) and the frequency of the commercial
power supply (60 Hz). The synchronous signal of the camera
will automatically sychronizes to the VL-PULSE in the
camera.
)
14
Page 15

Basic Functions
Privacy Zone Masking Function
Privacy Zone masking protects private objects and
areas such as house windows, entrances, and exits
which are within the camera’s range of vision but not
subject to surveillance.
Privacy zone masking can be masked on the monitor to
protect privacy.
Timing chart
8x 01 .. .. FF
(Mask Setting Command)
Features
•Mask can be set on up to 24 places according to Pan/
Tilt positions.
•Mask can be displayed on 8 places per screen
simultaneously.
• Privacy Zones are displayed according to priority in
alphabetical order.
• Individual on/off zone masking settings.
•Two colors from among 29 colors including mosaic
can be individually set for each of 24 privacy zones.
• Interlocking control with zooming.
• Interlocking control with Pan/Tilt.
•Non-interlocking control with Pan/Tilt.
1V
Setting command is reflected
at this timing.
15
Page 16

Privacy Zone Setting Command List
Basic Functions
Command Set Command
CAM_PrivacyZone
SetMask
Display
SetMaskColor
SetPanTiltAngle
SetPTZMask
Non_InterlockMask
Grid On
Grid Off
CenterLineOn
Command Packet
8x 01 04 76 mm nn
0r 0r 0s 0s FF
8x 01 04 77 pp pp pp pp FF
8x 01 04 78 pp pp pp pp qq rr FF Setting Color of Mask
8x 01 04 79 0p 0p 0p 0q 0q 0q FF
8x 01 04 7B mm 0p 0p 0p
0q 0q 0q 0r 0r 0r 0r FF
8x 01 04 6F mm
0p 0p 0q 0q 0r 0r 0s 0s FF
8x 01 04 7C 02 FF
8x 01 04 7C 03 FF
8x 01 04 7C 04 FF
Comments
Setting Mask(Size)
See “mm: Mask setting list”, “nn: Setting”, and
“pp: x, qq:y, rr: w, ss: h” in “Parameters” on
page 17.
Setting Mask Display On/Off
See “pp pp pp pp: Mask bit” in “Parameters”
on page 17.
pp pp pp pp: Mask setting (0: OFF, 1: ON)
See “pp pp pp pp: Mask bit” and “qq, rr: Color
code” in “Parameters” on page 17.
qq: Color setting when setting the Mask bit
to 0
rr: Color setting when setting the Mask bit
to 1
Setting Pan/Tilt Angle
See “Setting pan/tilt angle” in “Parameters” on
page 17.
ppp: Pan angle, qqq: Tilt angle
Setting the direct position of PTZ
See “mm: Mask setting list” and “Setting pan/
tilt angle” in “Parameters” on page 17.
ppp: Pan , qqq: Tilt , rrrr: Zoom
Setting non-interlocking the mask to pan/tilt
See “mm: Mask setting list” and “pp:x, qq:y,
rr:w, ss:h” in “Parameters” on page 17.
Setting Grid Display On/Off
Setting the center line On
Privacy Zone Inquiry Command List
Inquiry Command Command Packet Inquiry Packet Comments
CAM_Privacy
DisplayInq
CAM_PrivacyPan
TiltInq
CAM_Privacy
PTZInq
CAM_Privacy
MonitorInq
8x 09 04 77 FF y0 50 pp pp pp pp FF
8x 09 04 79 FF y0 50 0p 0p 0p 0q 0q 0q FF
8x 09 04 7B mm FF y0 50 0p 0p 0p 0q 0q 0q 0r 0r
8x 09 04 6F FF
0r 0r FF
y0 50 pp pp pp pp FF
Inquiry about the status of Setting Mask
Display On/Off
See “pp pp pp pp: Mask bit” in “Parameters”
on page 17.
1:On, 0:Off
Inquiry about the pan/tilt position currently set
See “Setting pan/tilt angle” in “Parameters” on
page 17.
ppp: Pan, qqq: Tilt
Inquiry about pan/tilt/zoom position at the mm
Mask setting
See “mm: Mask setting list” and “Setting pan/
tilt angle” in “Parameters” on page 17.
ppp: Pan Position,
qqq: Tilt Position
rrrr: Zoom Position
Inquiry about the mask currently displayed
See “pp pp pp pp: Mask bit” in “Parameters”
on page 17.
16
Page 17

Parameters
Basic Functions
mm: Mask setting list
Mask Name mm (Hex)
Mask_A 00h
Mask_B 01h
Mask_C 02h
Mask_D 03h
Mask_E 04h
Mask_F 05h
Mask_G 06h
Mask_H 07h
Mask_I 08h
Mask_J 09h
Mask_K 0Ah
Mask_L 0Bh
Note
The priority order of the mask display is in the sequence from A
(highest) to X (lowest).
When you set the parameters of masks non-sequentially, it is
recommended that you set the mask whose priority order is higher,
first.
Mask Name mm (Hex)
Mask_M 0Ch
Mask_N 0Dh
Mask_O 0Eh
Mask_P 0Fh
Mask_Q 10h
Mask_R 11h
Mask_S 12h
Mask_T 13h
Mask_U 14h
Mask_V 15h
Mask_W 16h
Mask_X 17h
nn:Setting
nn Setting
00 Resetting the zone size (the value of w,h)
for the existing mask.
01 Setting newly the zone size (the value of
w,h).
pp: x, qq: y, rr: w, ss: h
160
3Ch
mask
h
120
B0h
C4h
Effective display area
0
w
(x,y)
50h
pp pp pp pp: Mask bit
pp pp pp pp
bit 7 6 5 43210765432107654321076543210
Mask - - X W V U T S - - R Q P O NM - - L K J I HG - - F E DCBA
The “-” must be “0”.
qq, rr: Color code
Mask (Color) Code (qq, rr) Semi-transparency (qq, rr)
Black 00h 10h
Gray1 01h 11h
Gray2 02h 12h
Gray3 03h 13h
Gray4 04h 14h
Gray5 05h 15h
Gray6 06h 16h
White 07h 17h
Red 08h 18h
Green 09h 19h
Blue 0Ah 1Ah
Cyan 0Bh 1Bh
Yellow 0Ch 1Ch
Magenta 0Dh 1Dh
Mosaic 7Fh –
Setting pan/tilt angle
Angle/Parameter of Angle (ppp, qqq)
090-180 -90 180
Set the angle resolution to 360 (degree)/4096 (1000h).
400h800h C00h
800h
17
Page 18

Basic Functions
Details of Setting Commands
Set Mask
Command: 8x 01 04 76 mm nn 0r 0r 0s 0s FF
Parameters:
mm Setting Mask
See “mm: Mask setting list” in “Parameters” on page 17.
nn Selects new setting or resetting for the zone. See “nn:
Setting” in “Parameters” on page 17.
rr Sets the half value “w” of the Mask Width.
ss Sets the half value “h” of the Mask Height.
See “pp: x, qq: y, rr: w, ss: h” in “Parameters” on page 17.
Comments: To set the mask, first display the object
at the center of the screen. When “nn” is set to 1,
the current Pan/Tilt/Zoom position is recorded in
internal memory.
When “nn” is set to 0, the Pan/Tilt/Zoom position
in memory is not changed.
Notes
• The tilt angle at which you can set the mask is between –70 to
+70 degrees.
• It is recommended that you set the size to at least twice the size
of the object (height and width).
Set Display
Command: 8x 01 04 77 pp pp pp pp FF
Parameter:
pp pp pp pp Each 24 Privacy Zones corresponds to 1 bit.
See “pp pp pp pp: Mask bit” in “Parameters” on
page 17.
Comments: Each of 24 Privacy zones can be
switched on and off individually by a single
VISCA command. If you want to display a
Privacy zone, you must set its bit to 1. If you do
not want to display a Privacy zone, you must set
its bit to 0.
Set Mask Color
Command: 8x 01 04 78 pp pp pp pp qq rr FF
Parameter:
pp pp pp pp Each 24 Privacy Zones correspond with the BIT.
See “pp pp pp pp: Mask bit” in “Parameters” on
page 17.
qq Set the color code include the semi-transparency
code.
rr Set the color code include the semi-transparency
code. See “qq, rr: Color code” in “Parameters” on
page 17.
Comments: Two different color masks can be
chosen.
The colors can be chosen from among 14 colors
including the possibility for semi-transparency of
each color. Therefore two colors from among the
total of 29 colors including mosaic can be
individually set for each of 24 privacy zones.
If the bit of parameter (pp pp pp pp) is set to “0”,
mask color will be “qq” color (Color code). If the
bit of parameter (pp pp pp pp) is set to “1”, the
mask color will be “rr” color (Color code).
Example: 8x 01 04 78 00 00 00 03 10 07 FF
The mask color of Mask_A and Mask_B is White
(color code 07h), and the mask color of the other
Mask (C to X) is semi-transparent Black (color
code 10h).
Set Pan Tilt Angle
Command: 8x 01 04 79 0p 0p 0p 0q 0q 0q FF
Parameter:
ppp Pan Angle
qqq Tilt Angle
See “Setting pan/tilt angle” in “Parameters” on page
17.
Comments: Pan/Tilt angle settings are hexadecimal
data.
The resolution of Pan/Tilt angle is 0.088 degrees.
Note
When you set the pan/tilt angle, locate the pan/tilt position at the
center point of the FCB camera’s position.
Set PTZ Mask
Command: 8x 01 04 7B mm 0p 0p 0p 0q 0q 0q 0r 0r
0r 0r FF
Parameter:
mm Setting Mask
See “mm: Mask setting list” in “Parameters” on page 17.
ppp Pan Angle (000 to FFF) See “Setting pan/tilt angle” on
page 17.
qqq Tilt Angle (000 to FFF) See “Setting pan/tilt angle” on
page 17.
rrrr Zoom Position (000 to 4000) See “Zoom Ratio and Zoom
Position (for reference)” on page 55.
Comments: Mask can be set at the desired position
by setting the pan tilt angle and zoom position
using this command. The set value can be input by
hexadecimal number.
18
Page 19

Basic Functions
Non Interlock Mask
Command: 8x 01 04 6F mm 0p 0p 0q 0q 0r 0r 0s 0s
FF
Parameters:
mm Setting Mask
See “mm: Mask setting list” in “Parameters” on page 17.
pp Sets the center position “x” of the Mask on screen.
qq Sets the center position “y” of the Mask on screen.
rr Sets the half value “w” of the Mask Width.
ss Sets the half value “h” of the Mask Height.
See “pp: x, qq: y, rr: w, ss: h” in “Parameters” on page 17.
Commands: Mask does not interlock with pan/tilt.
The limitations of parameters are as follows.
(hexadecimal representation)
x: ±50h
w: ±50h
y: ±3ch
h: ±3ch
Note
When the Set Mask command and the Non Interlock Mask
command are set to the same mask, the command set later
becomes effective.
Grid
Motion Detection Function
This function instructs the camera to detect movement
within the monitoring area and then send an alarm
signal automatically.
The Detect signal goes out through the serial command
(VISCA) communication line.
Features
•You can set a frame for the detection range of 12
(horizontally) × 8 (vertically) blocks.
•You can set up to four frames.
•When the motion is detected in the set frame, the
Alarm Replay VISCA command is sent.
• The threshold level for detection can be set (common
to four frames).
• The interval of alarm detection can be set up to 256
seconds in units of one second.
•You can set on/off for each frame.
•When the Block Mode is set to ON, the Alarm Reply
command is not sent. Use this mode for checking
when the camera is installed or for confirming the
camera operation.
• The frame number is also sent with Alarm Replay to
report in which frame the motion has been detected.
Use the grid displayed on the screen to set mask
positions (see the figure below).
By executing the Center Line On command, only the x
and y axes of the center are displayed. Grids lines
disappear.
14hex (20(10))
14hex (20(10))
Frames
Setting frames
You can set the frame by assigning the starting point
and terminating point vertically and horizontally. You
can set up to four frames.
When motion is detected within the rage
where frames overlap
The alarms are sent for both frames.
Frame 1
Frame 2
Frame 3
Frame 4
At this position, the
alarm for frame 3 is
sent.
Within this overlapped
range, alarms are sent for
both frame 3 and frame 4.
19
Page 20

Basic Functions
Sending Alarms
•When motion is detected, the Alarm Replay
command is issued via the serial command (VISCA)
communication line.
Alarm issue Alarm issue Alarm issue Alarm issue
Alarm interval
Motion is
detected
in frame 1.
Interval
Motion is
detected
in frame 1.
Motion is
detected
in frame 1.
Motion is
detected
in frame 1.
Setting Commands
• MD On/Off
The Display mode is selected by the Function Set
command and frames are set by the Frame Set
command. By sending an MD On command, the
frame is displayed when motion is detected in the set
frame. The Alarm Reply command is set via the
serial command (VISCA) communication line.
8x 01 04 1B 02 FF --- On
8x 01 04 1B 03 FF --- Off
• Function Set
Select the detected frame, and set the Threshold
Level and the Interval Time.
•When multiple motions are detected or motion is
detected in another frame within the set interval
following the original time the alarm was issued,
another alarm command is not issued.
•When motion is detected after the interval time
elapsed, the alarm is issued again.
Interval Interval
Motion is
detected
in frame 1.
Motion is
detected
in frame 2.
Motion is
detected
in frame 3.
Motion is
detected
in frame 3.
• Frame Set
You can set up to four frames by assigning the
starting and terminating points.
Note
Set a terminating point higher vertically and
horizontally than the starting point. If you set the
wrong value, the command yields an error.
8x 01 04 1D 0m 0p 0q 0r 0s FF
m: Select Detection Frame (0: Frame0, 1: Frame1, 2:
Frame2, 3: Frame3) -- (0, 1, 2, 3)
p: Frame set Start Horizontal Position -- (00 to 0B)
q: Frame set Start Vertical Position -- (00 to 07)
r: Frame set End Horizontal Position -- (01 to 0C)
s: Frame set End Vertical Position -- (01 to 08)
8x 01 04 1C 0m 0n 0p 0q 0r 0s FF
m: Display Mode on/off (bit0: Frame)
n: Detection Frame set on/off (bit0:Frame0,
bit1:Frame1, bit2:Frame2, bit3:Frame3)
-- (0 to F)
pq: Threshold -- (00 to FF)
rs: Interval time set -- (00 to FF)
(When pq and rs are 0, the command is received, but
the setting is disabled.)
•Alarm Reply
When motion is detected in the set frame, the camera
issues this command. This command includes the
information on the number of the detected frame.
y0 07 04 1B 0p FF
p: Frame Number (bit0: Frame0, bit1: Frame1, bit2:
Frame2, bit3: Frame3)
20
Page 21

Basic Functions
Eclipse
When designing the housing, refer to the dimensional
allowance as shown in the figure below.
Vibration
Specifications
Test Method (Random vibration)
• Fix the camera at the four fixation points of the base
using M2 screws.
• Perform the random vibration test under the
following conditions in the X, Y and Z directions for
20 minutes in each direction.
• The camera vibration specification is to have no
malfunction after this test.
2/s3
Power spectrum density
Effective overall value
Test time
5 to 50 Hz 4.14 m
50 to 100 Hz –36 dB/oct
2
14.3 m/s
20 minutes
{0.043 G2/Hz}
{1.46 G}
Spectral Sensitivity
Characteristics
Use the graph as a reference value. (We can not
guarantee these values.)
This data is measured when the IR cut filter is
removed and the characteristics of the lens and optical
source characteristics are ignored.
21
Page 22

Key Switch Circuitry
The circuitry shown below is an example. Note that all
switches in the figure do not function in all models.
For more information, refer to the command list, check
functions on the camera, or contact your Sony dealer.
Basic Functions
The CN101 is connected to the FCB camera main unit.
22
Page 23

Key Function Specifications
Basic Functions
Classification
ZOOM
FOCUS
AE
WD
Name
WIDE FAST
WIDE SLOW
TELE FAST
TELE SLOW
AF ON/OFF
NEAR
FAR
ONE PUSH
AF
INFINITY
AE AUTO
BRIGHT
SHUTTER
IRIS
BACK
LIGHT
EXP COMP
ON/OFF
EXP COMP
UP
EXP COMP
DOWN
WD ON/OFF
AUTO WD
ON/OFF
Function
Move ZOOM to WIDE side quickly.
Move ZOOM to WIDE side slowly.
Move ZOOM to TELE side quickly.
Move ZOOM to TELE side slowly.
Switch between Auto Focus and Manual Focus.
Move focus to NEAR side in Manual Focus
mode.
Move focus to FAR side in Manual Focus mode.
Perform AF operation once in Manual Focus
mode.
Move focus forcibly to Infinity resulting in
Manual Focus mode, regardless of the current
focus mode.
Switch to AE FULL Auto mode.
Switch to variable brightness mode (BRIGHT),
depending on the conditions for mode shifting.
Shutter priority AE mode
Iris priority AE mode
Switch backlight on/off in AE FULL Auto mode.
Switch the exposure compensation function ON/
OFF.
Increase the exposure compensation (UP).
(Used during exposure compensation mode. 1.5
dB increments.)
Decrease the exposure compensation (DOWN).
(Used during exposure compensation mode. 1.5
dB increments.)
Switch the Wide Dynamic Range mode ON/
OFF.
Switch the Auto Wide Dynamic Range mode
ON/OFF.
Button operation
Pressing repeatedly allowed.
Pressing repeatedly allowed.
Pressing repeatedly allowed.
Pressing repeatedly allowed.
Switch between Auto and
Manual.
Pressing repeatedly allowed.
Pressing repeatedly allowed.
Request One Push AF.
Request Infinity.
Request AE Full Auto.
Request Bright mode.
Pressing Up/Down key
repeatedly allowed.
Request shutter priority AE
mode.
Pressing Up/Down key
repeatedly allowed.
Request iris priority AE
mode.
Pressing Up/Down key
repeatedly allowed.
Switch on/off.
Switch on/off.
Request UP / pressing
repeatedly allowed.
Request DOWN / pressing
repeatedly allowed.
Switch on/off.
Switch on/off.
Mode display
ZOOM bar displayed
for 3 s.
ZOOM bar displayed
for 3 s.
ZOOM bar displayed
for 3 s.
ZOOM bar displayed
for 3 s.
Manual F indication
Near indication
Far indication
Manual F indication
flashes while request
is made.
Far indication
No display
Bright bar display
Shutter code display
Iris code display
Backlight indication
Exposure
compensation code
display
Exposure
compensation code
display
Exposure
compensation code
display
WDR character
display
WDR character
display when WD is
ON.
23
Page 24

Basic Functions
Classification
WB
FEATURE
DISPLAY
UP/DOWN
PRESET
Name
AUTO WB
ONE PUSH
WB
ATW
INDOOR
OUTDOOR
MANUAL
WB
FREEZE
LR
REVERSE
E-FLIP
BLACK &
WHITE
NEGA ART
MUTE
DISPLAY
TITLE
EXEC
UP
DOWN
POS0
POS1
POS2
POS3
POS4
POS5
CUSTOM
POS PRESET
POS RESET
Function
Switch to AUTO WB mode.
Switch to One Push WB mode when pressed
once and capture data when pressed 2nd time.
Switch to ATW mode.
Enable WB at 3200K in INDOOR mode.
Enable WB at 5800K in OUTDOOR mode.
Switch to Manual WB mode.
Enable R control when pressed once and enable
B control when pressed 2nd time. Switchable
with UP/DOWN key.
Capture still image.
Horizontal reversal
Turn upside down
Black-and-white output
Negative art output
Muting video output
Display
Title setting
Confirm title setting.
Data UP key (priority for AE mode, Bright,
manual WB, title, and clock)
Data DOWN key (priority for AE mode, Bright,
manual WB, title, and clock)
Recall preset position 0.
Recall preset position 1.
Recall preset position 2.
Recall preset position 3.
Recall preset position 4.
Recall preset position 5.
Recall custom preset.
Write data.
Enabled when pressed together with POS button.
Delete data.
Enabled when pressed together with POS button.
Button operation
Request Auto WB mode.
Request One Push WB mode
and trigger.
Request ATW mode.
Request Indoor mode.
Request Outdoor mode.
Switch between R control
and B control in manual WB
mode. Pressing Up/Down
key repeatedly allowed.
Switch on/off.
Switch on/off.
Switch on/off.
Switch on/off.
Switch on/off.
Switch on/off.
Switch on/off.
Request setting. t Setting
is started with Exec.
Pressing Up/Down key
repeatedly allowed.
Select with Up/Down and
confirm with Exec.
Request UP.
Request DOWN.
Request recall.
Request recall.
Request recall.
Request recall.
Request recall.
Request recall.
Request recall.
Request setting. Enabled
when pressed together with
POS key.
Request deletion. Enabled
when pressed together with
POS key.
Mode display
No display
One Push indication
flashes at 0.8 Hz
before capturing data,
at 3.2 Hz during
capturing, and stays lit
after capturing.
ATW display
Indoor indication
Outdoor indication
“WB-MAN”
(character display)
CAPTURE indication
Horizontal reversal
indication
Turn upside down mark
B&W display
Neg Art display
No display
Display/no display
Title setting screen
display
Sets screen selection and
displays it in yellow.
Selection highlighted.
Selection highlighted.
RECALL POS0
RECALL POS1
RECALL POS2
RECALL POS3
RECALL POS4
RECALL POS5
RECALL
PRESET display
RESET display
24
Page 25

Basic Functions
Classification
Others
FUNCTION
Name
APERTURE
UP
APERTURE
DOWN
BRIGHT UP
BRIGHT
DOWN
AUTO SLOW
SHUTTER
ICR ON/OFF
STABILIZER
ON/OFF
POWER ON/
OFF
FUNCTION1
FUNCTION2
FUNCTION3
Function
Increase aperture (Aperture UP)
Decrease aperture (Aperture DOWN)
Raise brightness setting (Bright UP)
(When not in Bright mode, switching to Bright mode
is made automatically depending on the conditions.)
Lower brightness setting (Bright DOWN)
(When not in Bright mode, switching to Bright mode
is made automatically depending on the conditions.)
Switch Auto Slow Shutter on/off.
Switch ICR mode on/off
Switch the Image Stabilizer function ON/OFF.
Switch the POWER (Standby) ON/OFF.
–
–
–
Button operation
Request UP.
Request DOWN.
Request UP./Pressing
repeatedly allowed.
Request DOWN./Pressing
repeatedly allowed.
Switch on/off.
Switch on/off.
Switch on/off.
Switch on/off.
–
–
–
Mode display
Aperture bar displayed
for 3 s.
Aperture bar displayed
for 3 s.
Bright bar display
Bright bar display
“ASS” (character
display)
ICR indication
Image Stabilizer
“OFF” mark
–
–
–
–
25
Page 26

Basic Functions
Initial Settings, Custom Preset and Backup
Initial settings for the various functions of the FCB
camera are indicated in the “Initial settings” column.
The “Custom preset” column indicates whether the
custom preset function can be used to store the
settings. The function enables the stored settings to be
recalled automatically when the camera is turned on.
The “Back up at standby” column indicates whether
the data is preserved even when the camera is powered
OFF.
Mode/Position setting Initial settings
Zoom Position Wide end aa
D-Zoom On/Off On aa
D-Zoom Separate/Combine Combine aa
D-Zoom Position 00h aa
Focus Position — aa
Focus Auto/Manual Auto aa
Near Limit Setting 8000h (32 cm) aa
AF Sensitivity Normal aa
AF Mode Normal aa
AF Run Time 5 sec aa
AF Interval 5 sec aa
WB Mode Auto aa
WB Data (Rgain, Bgain) — aa
One Push WB Data — aa
AE Mode Full Auto aa
AE Response 01 aa
WD On/Off/Auto Off aa
Slow Shutter Mode Manual aa
Shutter Position 1/60sec (NTSC), 1/50sec (PAL) aa
Iris Position — aa
Gain Position — aa
Bright Position — aa
Exposure Compensation On/Off Off aa
Exposure Compensation Amount ±0 aa
BackLight On/Off Off aa
Spot AE On/Off Off aa
Spot AE Position Setting X=8, Y=8 aa
Aperture Level 6 aa
High Resolution Mode On/Off On aa
LR Reverse On/Off Off aa
Freeze On/Off Off ××
Picture Effect Off aa
ICR On/Off Off aa
Auto ICR On/Off Off aa
Auto ICR Threshold Level 0Ah aa
Custom Back up
preset at standby
A circle “a” in this column signifies that the data is preserved.
A cross “×” signifies that the data IS NOT preserved.
26
Page 27

Basic Functions
Mode/Position setting Initial settings
Camera Memory Same as the initial value setting aa
Display On/Off Off aa
Mute On/Off Off ××
WD Alarm On/Off Off × a
Auto ICR Alarm On/Off Off aa
Image Stabilizer On/Off/Hold Off aa
NR Level 3 aa
Gain Limit — aa
Color Enhancement On/Off Off aa
Title Display On/Off Off aa
Title Setting — aa
Mask Setting — aa
Mask Display On/Off Off aa
Mask Color Setting — aa
Grid/Center Line Display On/Off Off aa
Alarm On/Off Off aa
Alarm Mode — aa
Alarm Detect Level — aa
E-Flip On/Off Off aa
Privacy Zone On/Off Off aa
Privacy Zone Setting — aa
Key Lock On/Off Off aa
Camera ID 0000h aa
External Lock Mode Internal aa
V-Phase Vsync edge position aa
Alarm DayLight Threshold Level — aa
MD On/Off Off aa
MD Display Setting Off aa
MD Threshold Level 10h aa
MD Interval 1 sec aa
MD Window Setting — aa
ZoomPos Continuous Output On/Off Off × a
ZoomPos Continuous Output Interval 3Ch × a
A circle “a” in this column signifies that the data is preserved.
A cross “×” signifies that the data IS NOT preserved.
Custom Back up
preset at standby
Note
The number of times written to EEPROM (when Custom Preset is executed) is limited.
27
Page 28

Basic Functions
Mode Power Off Initializing Power On Freeze On MemRecall
Address Set aaaaa
IF_Clear aaaaa
Command Cancel aaaaa
Mode Condition
Condition
Power On/Off aaaaa
Lens
Mode Power Off Initializing Power On Freeze On MemRecall Zoom Direct Focus Direct ZmFo Direct Focus Auto
Zoom Tele/Wide/Stop ××a ×××a × a
Zoom Direct ××a ××aa × a
Zoom Focus Direct ××a ××××a ×
D-Zoom On/Off ××a ×××a × a
D-Zoom Separate/Combine ××a ×××a × a
D-Zoom Tele/Wide/Stop ××a ××aaaa
D-Zoom ×1/Max ××a ××aaaa
D-Zoom Direct ××a ××aaaa
Focus Far/Near/Stop ××a ××a ×××
Focus Direct ××a ××aa ××
Focus Auto/Manual ××a ××a ××a
One Push AF ××a ××a ×××
Focus Infinity ××a ××a ××a
Focus Near Limit ××a ××a ××a
AF Sensitivity Normal/Low ××a ××aaaa
AF Mode Norm/Interval/Zoom ××a ××aaaa
AF Activation Time/Interval Setting ××a ××aaaa
Camera Memory Set/Reset ××aa××××a
Camera Memory Recall ××aaa* ×××a
Lens Initialize ××aa ××××a
Comp Scan ××aa ××××a
* × during recalling from key
28
Page 29

OnePush ATW Manual
Sodium
Lamp AUTO
AUTO Lamp
Outdoor Sodium
Basic Functions
Mode Power Off Initializing Power On Freeze On MemRecall WB AUTO Indoor Outdoor
WB Mode Switchover ××a ××aaaaaaaaa
One Push WB ×× a ЧЧЧЧЧЧЧЧa ××
RGain Setting ×× a ЧЧЧЧЧЧЧЧЧЧa
White Balance
BGain Setting ×× a ЧЧЧЧЧЧЧЧЧЧa
Mode Power Off Initializing Power On Freeze On MemRecall AE Full Auto AE Manual ShutterPri Iris Priority Bright WD
AE Full Auto ××a ××a aaaaa
AE Manual ××a ××a aaaaa
Exposure
Shutter Priority ××a ××a aaaaa
Iris Priority ××a ××a aaaaa
Bright ××a ××a × a × aa
Shutter Setting ××a ×××aa ××a
Iris Setting ××a ×××a × a × a
Gain Setting ××a ×××a ×××a
Bright Setting ××a ЧЧЧЧЧЧaa
Slow Shutter Auto/Manual ××a ××a aaaa ×
Exposure Compensation On/Off ××a ××a aaaa ×
Exposure Compensation Setting ××a ××a aaaa ×
BackLight On/Off ××a ××a ЧЧЧЧЧ
SpotAE On/Off ××a ××a aaaa ×
SpotAE Setting ××a ××a aaaa ×
WD On/Off ××aaaaaaaaa
29
Page 30

Basic Functions
Others
Mode Power Off Initializing Power On Freeze On MemRecall
WD Alarm On/Off ××a ××
Aperture Setting ××a ××
High Resolution Mode On/Off ××aaa
LR_Reverse On/Off ××a ××
Freeze On/Off ××aa ×
Picture Effect Setting ××a ××
ICR On/Off ××a ××
Auto ICR On/Off ××a ××
Auto ICR Threshold Level Setting ××aaa
Auto ICR Alarm On/Off ××a ××
Image Stabilizer On/Off/Hold ××a ××
Display On/Off ××aaa
Mute On/Off ××aaa
Title Setting ××aaa
Mask On/Off ××aaa
Mask Setting ××aaa
Key Lock On/Off ××aaa
Alarm On/Off ××aaa
Alarm Mode ××aaa
MD On/Off ××aaa
MD Function Setting ××aaa
MD Window Setting ××aaa
ID Write ××aaa
Memory Save ××aaa
Register Value Setting ××aaa
Color Enhancement On/Off ××aaa
NR Level Setting ××aaa
External Synchronization
Mode Power Off Initializing Power On Freeze On MemRecall
External Lock Mode ××aaa
V-Phase Up/Down/Stop/Reset ××aaa
30
V-Phase Direct ××aaa
Page 31

Command List
Command List
VISCA1)/RS-232C
Commands
This Manual outlines an RS-232 control protocol and
command list for certain Sony cameras from which
control software can be developed.
THIS CONTROL PROTOCOL AND COMMAND
LIST IS PROVIDED BY SONY ON AN “AS-IS
BASIS” WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND.
SONY DOES NOT WARRANT ANY PARTICULAR
RESULT FROM THE USE OF THIS CONTROL
PROTOCOL AND COMMAND LIST AND
DISCLAIMS AND EXCLUDES ALL
WARRANTIES. EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, WITH
RESPECT TO THAT CONTROL PROTOCOL AND
COMMAND LIST, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
LIMITED TO, ANY OR ALL IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. IN
FACT, SONY SPECIFICALLY ACKNOWLEDGES
THAT SOFTWARE DEVELOPED BASED ON THIS
CONTROL PROTOCOL AND COMMAND LIST
MAY CAUSE MALFUNCTION OR DAMAGE TO
HARDWARE AND SOFTWARE USED WITH IT
(INCLUDING SONY HARDWARE AND
SOFTWARE) AND SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMS
ANY LIABILITY FOR ANY SUCH
MALFUNCTION OR DAMAGE. THIS CONTROL
PROTOCOL AND COMMAND LIST SHOULD BE
USED WITH CAUTION.
Overview of VISCA
In VISCA, the device outputting commands, for
example, a computer, is called the controller. The
device receiving the commands, an FCB camera is
called the peripheral device. In VISCA, up to seven
peripheral devices like the FCB camera can be
connected to one controller using communication
conforming to the RS-232C standard. The parameters
of RS-232C are as follows.
• Communication speed: 9.6 kbps/19.2 kbps/
38.4 kbps
• Data bits : 8
• Start bit : 1
• Stop bit : 1/2
• Non parity
Flow control using XON/XOFF and RTS/CTS, etc., is
not supported.
................................................................................................................................................................................................................................
1)VISCA is a protocol which controls consumer camcorders developed by Sony. “VISCA” is a trademark of Sony Corporation.
31
Page 32

Command List
VISCA Communication
Specifications
VISCA packet structure
The basic unit of VISCA communication is called a
packet. The first byte of the packet is called the header
and comprises the sender’s and receiver’s addresses.
For example, the header of the packet sent to the FCB
camera assigned address 1 from the controller (address
0) is hexadecimal 81H. The packet sent to the camera
Packet (3 to 16 bytes)
Header
Byte 1 Byte 2 Byte 3
Message (1 to 14 bytes)
assigned address 2 is 82H. In the command list, as the
header is 8X, input the address of the camera at X. The
header of the reply packet from the camera assigned
address 1 is 90H. The packet from the camera assigned
address 2 is A0H.
Some of the commands for setting cameras can be sent
to all devices at one time (broadcast). In the case of
broadcast, the header should be hexadecimal 88H.
When the terminator is FFH, it signifies the end of the
packet.
Terminator
FF
Sender’s
10
address
Bit 7
Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
(MSB)
Receiver’s address
(LSB)
Command and inquiry
● Command
Sends operational commands to the FCB camera.
● Inquiry
Used for inquiring about the current state of the
FCB camera.
Command Packet Note
Inquiry 8X QQ RR ... FF QQ
1)
QQ = 01 (Command), 09 (Inquiry)
2)
RR = 00 (Interface), 04 (camera 1), 06 (Pan/Tilter), 07 (camera 2)
X = 1 to 7: FCB camera address
1)
= Command/Inquiry,
2)
RR
= category code
11111111
Bit 7
Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
(MSB)
(LSB)
32
Page 33

Command List
Responses for commands and inquiries
● ACK message
Returned by the FCB camera when it receives a
command. No ACK message is returned for
inquiries.
● Completion message
Returned by the FCB camera when execution of
commands or inquiries is completed. In the case of
inquiry commands, it will contain reply data for the
inquiry after the 3rd byte of the packet. If the ACK
message is omitted, the socket number will contain
0.
Reply Packet Note
Ack X0 4Y FF Y = socket number
Completion (commands) X0 5Y FF Y = socket number
Completion (Inquiries) X0 5Y ... FF Y = socket number
X = 9 to F: FCB camera address + 8
● Error message
When a command or inquiry command could not be
executed or failed, an error message is returned
instead of the completion message.
Command execution cancel
To cancel a command which has already been sent,
send the Cancel command as the next command. To
cancel one of any two commands which have been
sent, use the cancel message.
Cancel Packet Note
Cancel 8X 2Y FF Y = socket number
X = 1 to 7: FCB camera address, Y = socket number
An error message will be returned for this command,
but this is not a fault. It indicates that the command has
been canceled.
Error Packet Description
X0 6Y 01 FF Message length error (>14 bytes)
X0 6Y 02 FF Syntax Error
X0 6Y 03 FF Command buffer full
X0 6Y 04 FF Command cancelled
X0 6Y 05 FF No socket (to be cancelled)
X0 6Y 41 FF Command not executable
X = 9 to F: FCB camera address + 8, Y = socket number
Socket number
When command messages are sent to the FCB camera,
it is normal to send the next command message after
waiting for the completion message or error message
to return. However to deal with advanced uses, the
FCB camera has two buffers (memories) for
commands, so that up to two commands including the
commands currently being executed can be received.
When the FCB camera receives commands, it notifies
the sender which command buffer was used using the
socket number of the ACK message. As the
completion message or error message also has a socket
number, it indicates which command has ended. Even
when two command buffers are being used at any one
time, an FCB camera management command and some
inquiry messages can be executed.
The ACK message is not returned for these commands
and inquiries, and only the completion message of
socket number 0 is returned.
33
Page 34

VISCA Device Setting
Command
Before starting control of the FCB camera, be sure to
send the Address command and the IF_Clear
command using the broadcast function.
For VISCA network administration
● Address
Sets an address of a peripheral device. Use when
initializing the network, and receiving the following
network change message.
● Network Change
Sent from the peripheral device to the controller
when a device is removed from or added to the
network. The address must be re-set when this
message is received.
Command List
Packet Note
Address 88 30 01 FF Always broadcasted.
Network Change X0 38 FF
X = 9 to F: FCB camera address + 8
VISCA interface command
● IF_Clear
Clears the command buffers in the FCB camera and
cancels the command currently being executed.
Command Packet Reply Packet Note
IF_Clear 8X 01 00 01FF X0 50 FF
IF_Clear (broadcast) 88 01 00 01 FF 88 01 00 01 FF
X = 1 to 7: FCB camera address (For inquiry packet)
X = 9 to F: FCB camera address +8 (For reply packet)
VISCA interface and inquiry
● CAM_VersionInq
Returns information on the VISCA interface.
Inquiry Inquiry Packet Reply Packet Description
CAM_VersionInq 8X 09 00 02 FF Y0 50 GG GG HH HH JJ JJ KK FF GGGG = Vender ID
(0020: Sony)
HHHH = Model ID
0450: FCB-EX1020
0451: FCB-EX1020P
JJJJ = ROM revision
KK = Maximum socket #(02)
X = 1 to 7: FCB camera address (For inquiry packet)
X = 9 to F: FCB camera address +8 (For reply packet)
34
Page 35

VISCA Command/ACK Protocol
Command List
Command Command Message Reply Message
General Command 81 01 04 38 02 FF 90 41 FF (ACK)+90 51 FF
(Example) (Completion)
90 42 FF 90 52 FF
81 01 04 38 FF 90 60 02 FF (Syntax Error)
(Example)
81 01 04 38 02 FF 90 60 03 FF
(Example) (Command Buffer Full)
81 01 04 08 02 FF 90 61 41 FF
(Example) (Command Not Executable)
90 62 41FF
Inquiry Command 81 09 04 38 FF 90 50 02 FF (Completion)
(Example)
81 09 05 38 FF 90 60 02 FF (Syntax Error)
(Example)
Address Set 88 30 01 FF 88 30 02 FF
IF_Clear(Broadcast) 88 01 00 01 FF 88 01 00 01 FF
IF_Clear (For x) 8x 01 00 01 FF z0 50 FF (Completion)
Command Cancel 8x 2y FF z0 6y 04 FF
(Command Canceled)
z0 6y 05 FF (No Socket)
Comments
Returns ACK when a command has been accepted, and
Completion when a command has been executed.
Accepted a command which is not supported or a command
lacking parameters.
There are two commands currently being executed, and the
command could not be accepted.
Could not execute the command in the current mode.
ACK is not returned for the inquiry command.
Accepted an incompatible command.
Returned the device address to +1.
Returned the same command.
ACK is not returned for this command.
Returned when the command of the socket specified is canceled.
Completion for the command canceled is not returned.
Returned when the command of the specified socket has already
been completed or when the socket number specified is wrong.
35
Page 36

VISCA Camera-Issued Messages
ACK/Completion Messages
Command List
Command Messages
ACK z0 4y FF
(y:Socket No.)
Completion z0 5y FF
(y:Socket No.)
z = Device address + 8
Error Messages
Command Messages
Syntax Error z0 60 02 FF
Command Buffer Full z0 60 03 FF
Command Canceled z0 6y 04 FF
(y:Socket No.)
No Socket z0 6y 05 FF
(y:Socket No.)
Command Not Executable z0 6y 41 FF
(y:Socket No.)
Comments
Returned when the command is accepted.
Returned when the command has been executed.
Comments
Returned when the command format is different or when a command with illegal
command parameters is accepted.
Indicates that two sockets are already being used (executing two commands) and the
command could not be accepted when received.
Returned when a command which is being executed in a socket specified by the
cancel command is canceled. The completion message for the command is not
returned.
Returned when no command is executed in a socket specified by the cancel
command, or when an invalid socket number is specified.
Returned when a command cannot be executed due to current conditions. For
example, when commands controlling the focus manually are received during auto
focus.
Network Change Message
Command Message Comments
Network Change z0 38 FF Issued when power is being routed.
36
Page 37

FCB Camera Commands
New Command List (1/1)
Command Set Command Command Packet Comments
CAM_IRCorrection Standard 8x 01 04 11 00 FF FOCUS IR compensation data switching
IR Light 8x 01 04 11 01 FF
CAM_WB Outdoor Auto 8x 01 04 35 06 FF Outdoor auto
Sodium Lamp Auto 8x 01 04 35 07 FF Auto including sodium lamp source
Sodium Lamp 8x 01 04 35 08 FF Sodium lamp source fixed mode
CAM_Gain Gain Limit 8x 01 04 2C 0p FF p: Gain Positionf 4 (6 dB) to F (28 dB)
CAM_WD AutoOnOff 8x 01 04 3D 00 FF WideD ON/OFF auto switching
On (RatioFix) 8x 01 04 3D 01 FF WideD ON (fixed exposure ratio mode)
On (Dver Compati) 8x 01 04 3D 04 FF Wide ON (Dver operation)
Refresh 8x 01 04 10 0D FF WideD restart
Set Parameter 8x 01 04 2D 0p 0q 0r 0s 0t 0u p: Screen display
00 00 FF 0: Combined image, 1: Long/short division, 2: Long-time,
3: Short-time
q: Detection sensitivity (0: L 1: M 2: H)
r: Blocked-up shadow correction level (0: L 1: M 2: H 3: S)
s: Blown-out highlight correction level (0: L 1: M 2: H)
tu: Exposure ratio of short exposure (x1 to x150)
CAM_WDAlarmReply On 8x 01 04 3B 02 FF WideD auto switching alarm ON/OFF
Off 8x 01 04 3B 03 FF
(Reply) y0 07 04 3B 02 FF WideD OFF t ON
y0 07 04 3B 03 FF WideD ON t OFF
CAM_NR – 8x 01 04 53 0p FF p: NR Setting (0: OFF, level 1 to 5)
CAM On 8x 01 04 31 02 FF Auto ICR switching alarm ON/OFF
_AutoICRAlarmReply Off 8x 01 04 31 03 FF
(Reply) y0 07 04 31 02 FF ICR OFF t ON
y0 07 04 31 03 FF ICR ON t OFF
CAM_Stabilizer On 8x 01 04 34 02 FF Hand shake correction ON/OFF
Off 8x 01 04 34 03 FF
Hold 8x 01 04 34 00 FF Hand shake correction hold
CAM_ExtLock Internal Mode 8x 01 04 55 00 FF Internal Sync
Line Lock Mode 8x 01 04 55 01 FF V-Phase Adjustment
Frequency Lock Mode 8x 01 04 55 02 FF External Sync
CAM_ColorEnhance Parameter Set 8x 01 04 20 mm nn pp qq rr ss mm: Threshold level
tt uu FF nn: Hysteresis width
pp: Fixed color Y of high-intensity side
qq: Fixed color Cr of high-intensity side
rr: Fixed color Cb of high-intensity side
ss: Fixed color Y of low-intensity side
tt: Fixed color Cr of low-intensity side
uu: Fixed color Cb of low-intensity side
* Set 00h to 7Fh for each parameter.
On 8x 01 04 50 02 FF Color Enhancement ON/OFF
Off 8x 01 04 50 03 FF
Command List
37
Page 38

Command List (1/6)
Command Set Command Command Packet Comments
AddressSet Broadcast 88 30 01 FF Address setting
IF_Clear Broadcast 88 01 00 01 FF I/F Clesr
CommandCancel – 8x 2p FF p: Socket No. (=1 or 2)
CAM_Power On 8x 01 04 00 02 FF Power ON/OFF
Off 8x 01 04 00 03 FF
CAM_Zoom Stop 8x 01 04 07 00 FF
Tele(Standard) 8x 01 04 07 02 FF
Wide(Standard) 8x 01 04 07 03 FF
Tele(Variable) 8x 01 04 07 2p FF p=0 (Low) to 7 (High)
Wide(Variable) 8x 01 04 07 3p FF
Direct 8x 01 04 47 0p 0q 0r 0s FF pqrs: Zoom Position
CAM_DZoom On 8x 01 04 06 02 FF Digital zoom ON/OFF
Off 8x 01 04 06 03 FF
Combine Mode 8x 01 04 36 00 FF Optical/Digital Zoom Combined
Separate Mode 8x 01 04 36 01 FF Optical/Digital Zoom Separate
Stop 8x 01 04 06 00 FF
Tele(Variable) 8x 01 04 06 2p FF p=0 (Low) to 7 (High)
Wide(Variable) 8x 01 04 06 3p FF
x1/Max 8x 01 04 06 10 FF x1/MAX Magnification Switchover
Direct 8x 01 04 46 00 00 0p 0q FF pq: D-Zoom Position
CAM_Focus Stop 8x 01 04 08 00 FF
Far(Standard) 8x 01 04 08 02 FF
Near(Standard) 8x 01 04 08 03 FF
Far(Variable) 8x 01 04 08 2p FF p=0 (Low) to 7 (High)
Near(Variable) 8x 01 04 08 3p FF
Direct 8x 01 04 48 0p 0q 0r 0s FF pqrs: Focus Position
Auto Focus 8x 01 04 38 02 FF AF ON/OFF
Manual Focus 8x 01 04 38 03 FF
Auto/Manual 8x 01 04 38 10 FF
One Push Trigger 8x 01 04 18 01 FF One Push AF Trigger
Infinity 8x 01 04 18 02 FF Forced infinity
Near Limit 8x 01 04 28 0p 0q 0r 0s FF pqrs: Focus Near Limit Position
AF Sensitivity Normal 8x 01 04 58 02 FF AF Sensitivity High/Low
Low 8x 01 04 58 03 FF
CAM_AFMode Normal AF 8x 01 04 57 00 FF AF Movement Mode
Interval AF 8x 01 04 57 01 FF
Zoom Trigger AF 8x 01 04 57 02 FF
Active/Interval Time 8x 01 04 27 0p 0q 0r 0s FF pq: Movement Time, rs: Interval
CAM_IRCorrection Standard 8x 01 04 11 00 FF FOCUS IR compensation data switching
IR Light 8x 01 04 11 01 FF
CAM_ZoomFocus Direct 8x 01 04 47 0p 0q 0r 0s pqrs: Zoom Position
0t 0u 0v 0w FF tuvw: Focus Position
CAM_Initialize Lens 8x 01 04 19 01 FF Lens Initialization Start
Comp Scan 8x 01 04 19 02 FF Correction of CCD pixel blemishes
Command List
38
Page 39

Command List (2/6)
Command Set Command Command Packet Comments
CAM_WB Auto 8x 01 04 35 00 FF Normal Auto
Indoor 8x 01 04 35 01 FF Indoor mode
Outdoor 8x 01 04 35 02 FF Outdoor mode
One Push WB 8x 01 04 35 03 FF One Push WB mode
ATW 8x 01 04 35 04 FF Auto Tracing White Balance
Manual 8x 01 04 35 05 FF Manual Control mode
One Push Trigger 8x 01 04 10 05 FF One Push WB Trigger
Outdoor Auto 8x 01 04 35 06 FF Outdoor auto
Sodium Lamp Auto 8x 01 04 35 07 FF Auto including sodium lamp source
Sodium Lamp 8x 01 04 35 08 FF Sodium lamp source fixed mode
CAM_RGain Reset 8x 01 04 03 00 FF Manual Control of R Gain
Up 8x 01 04 03 02 FF
Down 8x 01 04 03 03 FF
Direct 8x 01 04 43 00 00 0p 0q FF pq: R Gain
CAM_BGain Reset 8x 01 04 04 00 FF Manual Control of B Gain
Up 8x 01 04 04 02 FF
Down 8x 01 04 04 03 FF
Direct 8x 01 04 44 00 00 0p 0q FF pq: B Gain
CAM_AE Full Auto 8x 01 04 39 00 FF Automatic Exposure mode
Manual 8x 01 04 39 03 FF Manual Control mode
Shutter Priority 8x 01 04 39 0A FF Shutter Priority Automatic Exposure mode
Iris Priority 8x 01 04 39 0B FF Iris Priority Automatic Exposure mode
Bright 8x 01 04 39 0D FF Bright Mode (Manual control)
CAM_SlowShutter Auto 8x 01 04 5A 02 FF Auto Slow Shutter ON/OFF
Manual 8x 01 04 5A 03 FF
CAM_Shutter Reset 8x 01 04 0A 00 FF Shutter Setting
Up 8x 01 04 0A 02 FF
Down 8x 01 04 0A 03 FF
Direct 8x 01 04 4A 00 00 0p 0q FF pq: Shutter Position
CAM_Iris Reset 8x 01 04 0B 00 FF Iris Setting
Up 8x 01 04 0B 02 FF
Down 8x 01 04 0B 03 FF
Direct 8x 01 04 4B 00 00 0p 0q FF pq: Iris Position
CAM_Gain Reset 8x 01 04 0C 00 FF Gain Setting
Up 8x 01 04 0C 02 FF
Down 8x 01 04 0C 03 FF
Direct 8x 01 04 4C 00 00 0p 0q FF pq: Gain Position
Gain Limit 8x 01 04 2C 0p FF p: Gain Position
CAM_Bright Reset 8x 01 04 0D 00 FF Bright Setting
Up 8x 01 04 0D 02 FF
Down 8x 01 04 0D 03 FF
Direct 8x 01 04 4D 00 00 0p 0q FF pq: Bright Position
CAM_ExpComp On 8x 01 04 3E 02 FF Exposure Compensation ON/OFF
Off 8x 01 04 3E 03 FF
Reset 8x 01 04 0E 00 FF Exposure Compensation Amount Setting
Up 8x 01 04 0E 02 FF
Down 8x 01 04 0E 03 FF
Direct 8x 01 04 4E 00 00 0p 0q FF pq: ExpComp Position
Command List
39
Page 40

Command List
Command List (3/6)
Command Set Command Command Packet Comments
CAM_Backlight On 8x 01 04 33 02 FF Back Light Compensation ON/OFF
Off 8x 01 04 33 03 FF
CAM_SpotAE On 8x 01 04 59 02 FF Spot Automatic Exposure Setting
Off 8x 01 04 59 03 FF
Position 8x 01 04 29 0p 0q 0r 0s FF pq: X (0 to F), rs: Y (0 to F)
CAM_AE_Response DIRECT 8x 01 04 5D pp FF Automatic Exposure Response Setting (01 to 30)
CAM_WD On 8x 01 04 3D 02 FF Wide-D ON/OFF
Off 8x 01 04 3D 03 FF
AutoOnOff 8x 01 04 3D 00 FF Wide dynamic ON/OF auto switching
On(RatioFix) 8x 01 04 3D 01 FF Wide dynamic ON (Fixed exposure ratio mode)
On(Dver Compati) 8x 01 04 3D 04 FF Wide dynamic ON (Dver operation)
Refresh 8x 01 04 10 0D FF Wide dynamic restart
Set Parameter 8x 01 04 2D 0p 0q 0r 0s 0t 0u p: Screen display
00 00 FF 0: Combined image, 1: Long/short division, 2: Long-time,
3: Short-time
q: Detection sensitivity (0: L 1: M 2: H)
r: Blocked-up shadow correction level (0: L 1: M 2: H 3: S)
s: Blown-out highlight correction level (0: L 1: M 2: H)
tu: Exposure ratio of short exposure (x1 to x150)
CAM_WDAlarmReply On 8x 01 04 3B 02 FF Wide dynamic auto switching alarm ON/OFF
Off 8x 01 04 3B 03 FF
(Reply) y0 07 04 3B 02 FF Wide dynamic OFF t ON
y0 07 04 3B 03 FF Wide dynamic ON t OFF
CAM_Aperture Reset 8x 01 04 02 00 FF Aperture Control
Up 8x 01 04 02 02 FF
Down 8x 01 04 02 03 FF
Direct 8x 01 04 42 00 00 0p 0q FF pq: Aperture Gain
CAM_HR On 8x 01 04 52 02 FF High-Resolusion Mode ON/OFF
Off 8x 01 04 52 03 FF
CAM_NR – 8x 01 04 53 0p FF p: NR Setting (0: OFF, level 1 to 5)
CAM_LR_Reverse On 8x 01 04 61 02 FF Mirror Image ON/OFF
Off 8x 01 04 61 03 FF
CAM_Freeze On 8x 01 04 62 02 FF Still Image ON/OFF
Off 8x 01 04 62 03 FF
CAM_PictureEffect Off 8x 01 04 63 00 FF Picture Effect Setting
Neg.Art 8x 01 04 63 02 FF
B&W 8x 01 04 63 04 FF
CAM_PictureFlip On 8x 01 04 66 02 FF Picture flip ON/OFF
Off 8x 01 04 66 03 FF
CAM_ICR On 8x 01 04 01 02 FF Infrared Mode ON/OFF
Off 8x 01 04 01 03 FF
CAM_AutoICR On 8x 01 04 51 02 FF Auto dark-field mode On/Off
Off 8x 01 04 51 03 FF
Threshold 8x 01 04 21 00 00 0p 0q FF pq: ICR ON t OFF threshold level
40
Page 41
Command List (4/6)
Command Set Command Command Packet Comments
CAM On 8x 01 04 31 02 FF Auto ICR switching Alarm ON/OFF
_AutoICRAlarmReply Off 8x 01 04 31 03 FF
(Reply) y0 07 04 31 02 FF ICR OFF t ON
y0 07 04 31 03 FF ICR ON t OFF
CAM_Stabilizer On 8x 01 04 34 02 FF Hand shake correction ON/OFF
Off 8x 01 04 34 03 FF
Hold 8x 01 04 34 00 FF Hand shake correction hold
CAM_Memory Reset 8x 01 04 3F 00 0p FF p: Memory Number (=0 to 5)
Set 8x 01 04 3F 01 0p FF
Recall 8x 01 04 3F 02 0p FF
CAM_Display On 8x 01 04 15 02 FF Display ON/OFF
(8x 01 06 06 02 FF)
Off 8x 01 04 15 03 FF
(8x 01 06 06 03 FF)
On/Off 8x 01 04 15 10 FF
(8x 01 06 06 10 FF)
CAM_Title Title Set1 8x 01 04 73 00 mm nn pp qq 00 00 L: Line Number, nn: H-Position
00 00 00 00 FF pp: Color, qq: Blink
Title Set2 8x 01 04 73 01 mm nn pp qq rr ss mnpqrstuvw: Display character setting
tt uu vv ww FF (1st to 10th character)
Title Set3 8x 01 04 73 02 mm nn pp qq rr ss mnpqrstuvw: Display character setting
tt uu vv ww FF (11th to 20th character)
Title Clear 8x 01 04 74 00 FF Clear title setting
On 8x 01 04 74 02 FF Title display ON/OFF
Off 8x 01 04 74 03 FF
CAM_MultiLineTitle Title Set1 8x 01 04 73 1L 00 nn pp L: Line Number, nn: H-position
qq rr 00 00 00 00 00 FF pp: Color, qq: Blink rr: Opening Title
Title Set2 8x 01 04 73 2L mm nn pp L: Line Number,
qq rr ss tt uu vv ww FF mnpqrstuvw: Setting of characters (1 to 10)
Title Set3 8x 01 04 73 3L mm nn pp L: Line Number,
qq rr ss tt uu vv ww FF mnpqrstuvw: Setting of characters (11 to 20)
Title Clear 8x 01 04 74 1p FF Title Setting clear (p: 0 to a, f= all lines)
On 8x 01 04 74 2p FF Title display On/Off (0 to a, f= all lines)
Off 8x 01 04 74 3p FF
CAM_Mute On 8x 01 04 75 02 FF Muting ON/OFF
Off 8x 01 04 75 03 FF
On/Off 8x 01 04 75 10 FF
Command List
41
Page 42

Command List (5/6)
Command Set Command Command Packet Comments
CAM_PrivacyZone SetMask 8x 01 04 76 mm nn mm: Mask Settings
0r 0r 0s 0s FF nn 00: Modify, 01: New
rr: W, ss:H
Display 8x 01 04 77 pp pp pp pp FF Mask Display ON/OFF
pp pp pp pp: Mask Settings (0:OFF, 1:ON)
SetMaskColor 8x 01 04 78 pp pp pp pp pp pp pp pp: Mask Color Settings
qq rr FF qq: Color Setting when 0 is selected
rr: Color Setting when 1 is selected
SetPanTiltAngle 8x 01 04 79 0p 0p 0p Pan/Tilt Angle Settings
0q 0q 0q FF ppp: Pan
qqq: Tilt
SetPTZMask 8x 01 04 7B mm 0p 0p 0p Pan/Tilt/Zoom Settings for Mask
0q 0q 0q 0r 0r 0r 0r FF ppp: Pan, qqq: Tilt, rrrr: Zoom
Non_InterlockMask 8x 01 04 6F mm mm: Non_Interlock Mask Settings
0p 0p 0q 0q 0r 0r 0s 0s FF pp: X, q: Y, rr: W, ss: H
GridOn 8x 01 04 7C 02 FF Grid Display ON/OFF
GridOff 8x 01 04 7C 03 FF Grid/Center Line Display Off
CenterLineOn 8x 01 04 7C 04 FF Center Line Display On
CAM_KeyLock Off 8x 01 04 17 00 FF Camera Control Enable/Disable
On 8x 01 04 17 02 FF
CAM_IDWrite – 8x 01 04 22 0p 0q 0r 0s FF pqrs: Camera ID (=0000 to FFFF)
CAM_MemSave Write 8x 01 04 23 0m 0p 0q 0r 0s FF m: Address (=0 to 7)
pqrs: Data (0000 to FFFF)
CAM_ExtLock Internal Mode 8x 01 04 55 00 FF Internal Sync
Line Lock Mode 8x 01 04 55 01 FF V-Phase Adjustment
Frequency Lock Mode 8x 01 04 55 02 FF External Sync
CAM_VPhase Stop 8x 01 04 05 00 FF –
Up 8x 01 04 05 02 FF
Down 8x 01 04 05 03 FF
Up (Step) 8x 01 04 05 2p FF p=step (1-7)
Down (Step) 8x 01 04 05 3p FF
Reset 8x 01 04 05 40 FF Restore Factory Settings
Direct 8x 01 04 45 0p 0q 0r 0s FF pqrs: V-Phase (0000 to)
(NTSC: 0000 to 20Chex, PAL: 0000 to 270hex)
CAM_Alarm On 8x 01 04 6B 02 FF Alarm ON/OFF
Off 8x 01 04 6B 03 FF
SetMode 8x 01 04 6C pp FF pp: Mode setting
00 Focus change detection
(reference value is not updated)
01 Focus change detection (reference value is updated)
02 AE change detection (reference value is not updated)
03 AE change detection (reference value is updated)
:
0C Day/Night judgement
SetDayNighLevel 8x 01 04 6D 0p 0p 0p 0q 0q 0q FF ppp: Day judgement level setting
qqq: Night judgement level setting
Alarm(Reply) y0 07 04 6B 01 FF Detection level “ Low” t “High”
y0 07 04 6B 00 FF Detection level “ High” t “Low”
Command List
42
Page 43

Command List
Command List (6/6)
Command Set Command Command Packet Comments
CAM_MD On 8x 01 04 1B 02 FF Motion Detection On/Off
Off 8x 01 04 1B 03 FF
Function Set 8x 01 04 1C 0m 0n 0p 0q 0r 0s FF m: Display mode
n: Detection Frame Set (0 to F)
pq: Threshold Level (00 to FF)
rs: Interval Time set (00 to FF)
Window Set 8x 01 04 1D 0m 0p 0q 0r 0s FF m: Select Detection Frame (0, 1, 2, 3)
p: Start Horizontal Position (00 to 0B)
q: Start Vertical Position (00 to 07)
r: Stop Horizontal Position (01 to 0C)
s: Stop Vertical Position (01 to 08)
Alarm (Reply) y0 07 04 1B 0p FF p: Detection Frame Number
CAM_Continuous On 8x 01 04 69 02 FF ZoomPosition data Continuous Output On/Off
ZoomPosReply Off 8x 01 04 69 03 FF
(Reply) y0 07 04 69 0p 0p 0q 0q 0q 0q FF pp: D-Zoom Position
* 00: When Zoom Mode is Combine
qqqq: Zoom Position
CAM_ – 8x 01 04 6A 00 00 0p 0p FF pp: Interval Time [Vertical timing]
ReplyIntervalTimeSet
CAM_RegisterValue – 8x 01 04 24 mm 0p 0p FF mm: Register No. (=00-7F)
pp: Register Value (=00-7F)
CAM_ColorEnhance Parameter Set 8x 01 04 20 mm nn mm: Threshold level
pp qq rr ss tt uu FF nn: Hysteresis width
pp: Fixed color Y of high-intensity side
qq: Fixed color Cr of high-intensity side
rr: Fixed color Cb of high-intensity side
ss: Fixed color Y of low-intensity side
tt: Fixed color Cr of low-intensity side
uu: Fixed color Cb of low-intensity side
* Set 00h to 7Fh for each parameter.
On 8x 01 04 50 02 FF Color Enhancement ON/OFF
Off 8x 01 04 50 03 FF
43
Page 44
Command List
New Query Command List (1/1)
Inquiry Command Command Packet Inquiry Packet Comments
CAM_IRCorrectionInq 8x 09 04 11 FF y0 50 00 FF Standard
y0 50 01 FF IR Light
CAM_WBModeInq 8x 09 04 35 FF y0 50 06 FF Outdoor Auto
y0 50 07 FF Sodium Lamp Auto
y0 50 08 FF Sodium Lamp
CAM_GainLimitInq 8x 09 04 2C FF y0 50 0q FF p: Gain Limit
CAM_WDModeInq 8x 09 04 3D FF y0 50 01 FF On (RatioFix)
y0 50 04 FF On (Dver operation)
CAM_WDParameterInq 8x 09 04 2D FF y0 50 00 0p 0q 0r 0s 0t 0u 00 00 FF p: Screen display
q: Detection sensitivity
r: Blocked-up shadow correction level
s: Blown-out highlight correction level
tu: Exposure ratio of short exposure
CAM_WDAlarmReplyInq 8x 09 04 3B FF y0 50 02 FF On
y0 50 03 FF Off
CAM_NRInq 8x 09 04 53 FF y0 50 0p FF p: NR level
CAM_StabilizerModeInq 8x 09 04 34 FF y0 50 02 FF On
y0 50 03 FF Off
y0 50 00 FF Hold
CAM_ExtLockInq 8x 09 04 55 FF y0 50 00 FF Internal Sync
y0 50 01 FF V-Phase Adjustment
y0 50 02 FF External Sync
CAM_ColorEnhanceInq 8x 09 04 20 FF y0 50 mm nn pp qq rr ss tt uu FF mm: Threshold level
nn: Hysteresis width
pp: Fixed color Y of high-intensity side
qq: Fixed color Cr of high-intensity side
rr: Fixed color Cb of high-intensity side
ss: Fixed color Y of low-intensity side
tt: Fixed color Cr of low-intensity side
uu: Fixed color Cb of low-intensity side
8x 09 04 50 FF y0 50 02 FF On
y0 50 03 FF Off
CAM_TempInq 8x 09 04 68 FF y0 50 00 00 0p 0p FF pq: Temperature * Lens temperature
44
Page 45
Command List
Inquiry Command List (1/4)
Inquiry Command Command Packet Inquiry Packet Comments
CAM_PowerInq 8x 09 04 00 FF y0 50 02 FF On
y0 50 03 FF Off
CAM_ZoomPosInq 8x 09 04 47 FF y0 50 0p 0q 0r 0s FF pqrs: Zoom Position
CAM_DZoomModeInq 8x 09 04 06 FF y0 50 02 FF D-Zoom On
y0 50 03 FF D-Zoom Off
CAM_DZoomC/SModeInq 8x 09 04 36 FF y0 50 00 FF Combine Mode
y0 50 01 FF Separate Mode
CAM_DZoomPosInq 8x 09 04 46 FF y0 50 00 00 0p 0q FF pq: D-Zoom Position
CAM_FocusModeInq 8x 09 04 38 FF y0 50 02 FF Auto Focus
y0 50 03 FF Manual Focus
CAM_FocusPosInq 8x 09 04 48 FF y0 50 0p 0q 0r 0s FF pqrs: Focus Position
CAM_FocusNearLimitInq 8x 09 04 28 FF y0 50 0p 0q 0r 0s FF pqrs: Focus Near Limit Position
CAM_AFSensitivityInq 8x 09 04 58 FF y0 50 02 FF AF Sensitivity Normal
y0 50 03 FF AF Sensitivity Low
CAM_AFModeInq 8x 09 04 57 FF y0 50 00 FF Normal AF
y0 50 01 FF Interval AF
y0 50 02 FF Zoom Trigger AF
CAM_AFTimeSettingInq 8x 09 04 27 FF y0 50 0p 0q 0r 0s FF pq: Movement Time, rs: Interval
CAM_IRCorrectionInq 8x 09 04 11 FF y0 50 00 FF Standard
y0 50 01 FF IR Light
CAM_WBModeInq 8x 09 04 35 FF y0 50 00 FF Auto
y0 50 01 FF In Door
y0 50 02 FF Out Door
y0 50 03 FF One Push WB
y0 50 04 FF ATW
y0 50 05 FF Manual
y0 50 06 FF Outdoor Auto
y0 50 07 FF Sodium Lamp Auto
y0 50 08 FF Sodium Lamp
CAM_RGainInq 8x 09 04 43 FF y0 50 00 00 0p 0q FF pq: R Gain
CAM_BGainInq 8x 09 04 44 FF y0 50 00 00 0p 0q FF pq: B Gain
CAM_AEModeInq 8x 09 04 39 FF y0 50 00 FF Full Auto
y0 50 03 FF Manual
y0 50 0A FF Shutter Priority
y0 50 0B FF Iris Priority
y0 50 0D FF Bright
CAM_SlowShutterModeInq 8x 09 04 5A FF y0 50 02 FF Auto
y0 50 03 FF Manual
CAM_ShutterPosInq 8x 09 04 4A FF y0 50 00 00 0p 0q FF pq: Shutter Position
CAM_IrisPosInq 8x 09 04 4B FF y0 50 00 00 0p 0q FF pq: Iris Position
CAM_GainPosInq 8x 09 04 4C FF y0 50 00 00 0p 0q FF pq: Gain Position
CAM_GainLimitInq 8x 09 04 2C FF y0 50 0q FF p: Gain Limit
CAM_BrightPosInq 8x 09 04 4D FF y0 50 00 00 0p 0q FF pq: Bright Position
CAM_ExpCompModeInq 8x 09 04 3E FF y0 50 02 FF On
y0 50 03 FF Off
CAM_ExpCompPosInq 8x 09 04 4E FF y0 50 00 00 0p 0q FF pq: ExpComp Position
CAM_BacklightModeInq 8x 09 04 33 FF y0 50 02 FF On
y0 50 03 FF Off
45
Page 46
Command List
Inquiry Command List (2/4)
Inquiry Command Command Packet Inquiry Packet Comments
CAM_SpotAEModeInq 8x 09 04 59 FF y0 50 02 FF On
y0 50 03 FF Off
CAM_SpotAEPosInq 8x 09 04 29 FF y0 50 0p 0q 0r 0s FF pq: X position, rs: Y position
CAM_AE_ResponseInq 8x 09 04 5D FF y0 50 pp FF pp: 01 to 20 (hex)
CAM_WDModeInq 8x 09 04 3D FF y0 50 02 FF On Wide-D
y0 50 03 FF Off
y0 50 00 FF AutoOnOff
y0 50 01 FF On (RatioFix)
y0 50 04 FF On (Dver operation)
CAM_WDParameterInq 8x 09 04 2D FF
CAM_WDAlarmReplyInq 8x 09 04 3B FF y0 50 02 FF On
CAM_ApertureInq 8x 09 04 42 FF y0 50 00 00 0p 0q FF pq: Aperture Gain
CAM_HRModeInq 8x 09 04 52 FF y0 50 02 FF On Hi-Resolution
CAM_LR_ReverseModeInq 8x 09 04 61 FF y0 50 02 FF On
CAM_FreezeModeInq 8x 09 04 62 FF y0 50 02 FF On
CAM_PictureEffectModeInq 8x 09 04 63 FF y0 50 00 FF Off
CAM_PictureFlipModeInq 8x 09 04 66 FF y0 50 02 FF On
CAM_ICRModeInq 8x 09 04 01 FF y0 50 02 FF On
CAM_AutoICRModeInq 8x 09 04 51 FF y0 50 02 FF On
CAM_AutoICRThresholdInq 8x 09 04 21 FF y0 50 00 00 0p 0q FF pq: ICR ON t OFF Threshold Level
CAM_AutoICRAlarmReplyInq 8x 09 04 31 FF y0 50 02 FF On
CAM_StabilizerModeInq 8x 09 04 34 FF y0 50 02 FF On
CAM_DisplayModeInq 8x 09 04 15 FF y0 50 02 FF On
(8x 09 06 06 FF) y0 50 03 FF Off
CAM_MuteModeInq 8x 09 04 75 FF y0 50 02 FF On
CAM_PrivacyDisplayInq 8x 09 04 77 FF y0 50 pp pp pp pp FF pp pp pp pp: Mask Display (0:OFF, 1:ON)
y0 50 0p 0q 0r 0s 0t 0u 00 00 FF
y0 50 03 FF Off
y0 50 03 FF Off
y0 50 03 FF Off
y0 50 03 FF Off
y0 50 02 FF Neg.Art
y0 50 04 FF B&W
y0 50 03 FF Off
y0 50 03 FF Off
y0 50 03 FF Off
y0 50 03 FF Off
y0 50 03 FF Off
y0 50 00 FF Hold
y0 50 03 FF Off
p: Screen display
q: Detection sensitivity
r: Blocked-up shadow correction level
s: Blown-out highlight correction level
tu: Exposure ratio of short exposure
46
Page 47

Command List
Inquiry Command List (3/4)
Inquiry Command Command Packet Inquiry Packet Comments
CAM_PrivacyPanTiltInq 8x 09 04 79 FF y0 50 0p 0p 0p 0q 0q 0q FF ppp: Pan
qqq: Tilt
CAM_PrivacyPTZInq 8x 09 04 7B mm FF y0 50 0p 0p 0p 0q 0q 0q 0r 0r mm: Mask Settings
0r 0r FF ppp: Pan
qqq: Tilt
rrr: Zoom
CAM_PrivacyMonitorInq 8x 09 04 6F FF y0 50 pp pp pp pp FF pp pp pp pp: Mask is displayed now.
CAM_KeyLockInq 8x 09 04 17 FF y0 50 00 FF Off
y0 50 02 FF On
CAM_IDInq 8x 09 04 22 FF y0 50 0p 0q 0r 0s FF pqrs: Camera ID
CAM_MemSaveInq 8x 09 04 23 0X FF y0 50 0p 0p 0q 0q FF X: 00 to 07 (Address)
ppqq: 0x0000 to 0xFFFF (Data)
CAM_ExtLockInq 8x 09 04 55 FF y0 50 00 FF Internal Sync
y0 50 01 FF V-Phase Adjustment
y0 50 02 FF External Sync
CAM_VPhasePosInq 8x 09 04 45 FF y0 50 0p 0q 0r 0s FF pqrs: V-Phase Position
CAM_VersionInq 8x 09 00 02 FF y0 50 00 20 mnpq: Model Code (04xx)
mn pq rs tu vw FF rstu: ROM version
vw: Socket Number (=02)
CAM_AlarmInq 8x 09 04 6B FF y0 50 02 FF On
y0 50 03 FF Off
CAM_AlarmModeInq 8x 09 04 6C FF y0 50 pp FF pp: Alarm Mode
CAM_AlarmDayNightLevelInq 8x 09 04 6D FF y0 50 0p 0p 0p
0q 0q 0q 0r 0r 0r FF
CAM_AlarmDetectLevelInq 8x 09 04 6E FF y0 50 01 FF Detection level “High”
y0 50 00 FF Detection level “Low”
CAM_MDModeInq 8x 09 04 1B FF y0 50 02 FF On
y0 50 03 FF Off
CAM_MDFunctionInq 8x 09 04 1C FF y0 50 0m 0n 0p 0q FF m: Display mode
CAM_MDWindowInq 8x 09 04 1D 0m FF y0 50 0p 0q 0r 0s FF m: Select Detection Frame (0, 1, 2, 3)
CAM_ContinuousZoomPos 8x 09 04 69 FF y0 50 02 FF On
ReplyModeInq y0 50 03 FF Off
CAM_ReplyIntervalTimeInq 8x 09 04 6A FF y0 50 00 00 0p 0p FF pp: Interval Time
CAM_RegisterValueInq 8x 09 04 24 mm FF y0 50 0p 0p ff mm: Register No. (00 to 7F)
ppp: Day judgement level setting
qqq: Night judgement level setting
rrr: Current Automatic Exposure level setting
n: Detection Frame Set (0 to F)
pq: Threshold Level (0 to FF)
rs: Interval Time set (0 to FF)
p: Start Horizontal Position (00 to 0B)
q: Start Vertical Position (00 to 07)
r: Stop Horizontal Position (01 to 0C)
s: Stop Vertical Position (01 to 08)
pp: Register Value (00 to FF)
47
Page 48

Command List
Inquiry Command List (4/4)
Inquiry Command Command Packet Inquiry Packet Comments
CAM_ColorEnhanceInq 8x 09 04 20 FF y0 50 mm nn pp qq rr ss tt uu FF mm: Threshold level
nn: Hysteresis width
pp: Fixed color Y of high-intensity side
qq: Fixed color Cr of high-intensity side
rr: Fixed color Cb of high-intensity side
ss: Fixed color Y of low-intensity side
tt: Fixed color Cr of low-intensity side
uu: Fixed color Cb of low-intensity side
8x 09 04 50 FF y0 50 02 FF On
y0 50 03 FF Off
CAM_TempInq 8x 09 04 68 FF y0 50 00 00 0p 0p FF pq: Temperature * Lens temperature
48
Page 49

Command List
Block Inquiry Command List
Lens Control System Inquiry Commands.............. Command Packet 8x 09 7E 7E 00 FF
Byte Bit Comments
7
6
5
4
0
3
2
1
0
70 Completion Message (50h)
61
50
41
1
30
20
10
00
70
60
50
40
2
3
2
1
0
70
60
50
40
3
3
2
1
0
70
60
50
40
4
3
2
1
0
70
60
50
40
5
3
2
1
0
Destination Address
Source Address
Zoom Position (HH)
Zoom Position (HL)
Zoom Position (LH)
Zoom Position (LL)
Byte Bit Comments
70
60
50
40
6
3
2
1
0
70
60
50
40
7
3
2
1
0
70
60
50
40
8
3
2
1
0
70
60
50
40
9
3
2
1
0
70
60
50
10
11
40
3
2
1
0
70
60
50
40
3
2
1
0
Focus Near Limit (H)
Focus Near Limit (L)
Focus Position (HH)
Focus Position (HL)
Focus Position (LH)
Focus Position (LL)
Byte Bit Comments
70
60
50
12
13
14
15
40
30
20
10
00
70
60
5 DZoomMode 0: Combine
1: Separate
4 0: Normal 1: Interval
3 2: Zoom Trigger
2 AF Sensitivity 0: Slow
1: Normal
1 Digital Zoom 1:On 0:Off
0 Focus Mode 0:Manual 1:Auto
70
60
50
40
3 Low Contrast Detection 1: Yes
0: No
2 Camera Memory Recall
1: Executing 0: Stopped
1 Focus Command 1: Executing
0: Stopped
0 Zoom Command 1: Executing
0: Stopped
71 Terminator (FFh)
61
51
41
31
21
11
01
49
Page 50

Command List
Camera Control System Inquiry Commands ......... Command Packet 8x 09 7E 7E 01 FF
Byte Bit Comments
7
6
5
4
0
3
2
1
0
70 Completion Message (50h)
61
50
41
1
30
20
10
00
70
60
50
40
2
3
2
1
0
70
60
50
40
3
3
2
1
0
70
60
50
40
4
3
2
1
0
70
60
50
40
5
3
2
1
0
Destination Address
Source Address
R Gain (H)
R Gain (L)
B Gain (H)
B Gain (L)
Byte Bit Comments
70
60
50
40
6
3
2
1
0
70
60
50
40
7
3
2
1
0
70
60
50
4
8
3
2 Exposure Mode
1
0
70
60
5 High-Resolution 1: On 0: Off
4
9
10
11
Wide-D (1: Other than Off,
0: Off)
3 Spot AE 1: On 0: Off
2 Back Light 1:On 0:Off
1 Exposure Comp. 1:On 0:Off
0 Slow Shutter 1:Auto 0:Manual
70
60
50
4
3
2 Shutter Position
1
0
70
60
50
4
3
2 Iris Position
1
0
WB Mode
Aperture Gain
Byte Bit Comments
70
60
50
12
13
14
15
40
3
2
1
0
70
60
50
4
3
2 Bright Position
1
0
70
60
50
40
3
2
1
0
71 Terminator (FFh)
61
51
41
31
21
11
01
Gain Position
Exposure Comp. Position
50
Page 51

Command List
Other Inquiry Commands ........................................ Command Packet 8x 09 7E 7E 02 FF
Byte Bit Comments
7
6
5
4
0
3
2
1
0
70 Completion Message (50h)
61
50
41
1
30
20
10
00
70
60
50
40
2
3 Auto ICR Alarm (1: On, 0: Off)
2 Auto ICR 1: On 0: Off
1 Key Lock 1: On 0: Off
0 Power 1:On 0:Off
70
6 Stabilizer (1: On, 0: Off)
50
4 ICR 1: On 0: Off
3
3 Freeze 1:On 0:Off
2 LR Reverse 1:On 0:Off
10
00
70
60
5 Privacy Zone 1: On 0: Off
4 Mute 1: On 0: Off
4
3 Title Display 1: On 0: Off
2 Display 1: On 0: Off
10
00
70
60
50
40
5
30
2
1 Picture Effect Mode
0
Destination Address
Source Address
Byte Bit Comments
70
60
50
40
6
30
20
10
00
70
60
50
40
7
30
20
10
00
70
60
50
40
8
3
2
1
0
70
60
50
40
9
3
2
1
0
70
60
50
10
11
40
3
2
1
0
70
60
50
40
3
2
1
0
Camera ID (HH)
Camera ID (HL)
Camera ID (LH)
Camera ID (LL)
Byte Bit Comments
70
60
5 External Lock 1: Provided
0: Not provided
12
13
14
15
4 Memory 1: Provided 0: Not
provided
3 Clock 1: Provided 0: Not
provided
2 ICR 1: Provided 0: Not
provided
1 Stabilizer (1: Provided, 0: Not
provided)
0 System 1:PAL 0:NTSC
70
60
5 External Lock status (1: Lock,
0: Unlock)
4 External Lock Mode 1: Line
Lock 0: Internal
3
2
1
0
70
60
5
4
3
2
1
0
71 Terminator (FFh)
61
51
41
31
21
11
01
V-Phase (H)
V-Phase (L)
51
Page 52

Command List
Enlargement Function1 Query Command ............. Command Packet 8x 09 7E 7E 03 FF
Byte Bit Comments
7
6
5
4
0
3
2
1
0
70 Completion Message (50h)
61
50
41
1
30
20
10
00
70
60
50
24 0
3
2
1
0
70
60
50
34 0
3
2
1
0
70
60
50
44 0
3
2
1
0
70
60
50
54 0
3
2
1
0
Destination Address
Source Address
Digital Zoom Position (H)
Digital Zoom Position (L)
AF Activation Time (H)
AF Activation Time (L)
Byte Bit Comments
70
60
50
40
6
3
2
1
0
70
60
50
40
7
3
2
1
0
70
60
50
40
8
3
2
1
0
70
60
50
40
9
3
2
1
0
70
60
50
10
40
30
2 MD (1: On, 0: Off)
1 Alarm (1: On, 0: Off)
0 Picture flip (1: On, 0: Off)
AF Interval Time (H)
AF Interval Time (L)
SpotAE Position (X)
SpotAE Position (Y)
Byte Bit Comments
70
60
50
11
12
13
14
15
40
30
2 Advanced Privacy
(1: Provided, 0: Not provided)
1 Alarm (1: Provided, 0: Not
provided)
0 Picture flip (1: Provided,
0: Not provided)
70
60
50
4
3
2 AE Response
1
0
70
60
50
40
30
2
1 NR Level
0
70
60
50
40
3
2
1
0
71 Terminator (FFh)
61
51
41
31
21
11
01
Gain Limit
52
Page 53

Command List
Enlargement Function2 Query Command ............. Command Packet 8x 09 7E 7E 04 FF
Byte Bit Comments
7
6
5
4
0
3
2
1
0
70 Completion Message (50h)
61
50
41
1
30
20
10
00
70
60
50
24 0
30
2 WideD mode (0: OFF, 1: ON,
1 2: Auto ON/OFF, 3: ON
0 (RatioFIx), 4: ON (Dver))
70
60
50
34 0
3 WideD screen display
2 0: Combined image
1 WideD detection sensitivity
0 0: L 1: M 2: H
70
60
50
44 0
3
2
1
0
70
60
50
54 0
3
2 WideD short exposure
1 Exposure ratio (H)
0
Destination Address
Source Address
1: Long/short division
2: Long-time 3: Short-time
WideD blocked-up shadow
correction level 0: L 1: M 2: H
3: S
WideD blown-out highlight
correction level 0: L 1: M 2: H
Byte Bit Comments
70
60
50
40
6
3
2 WideD short exposure
1 Exposure ratio (L)
0
70
60
50
40
7
30
20
10
00
70
60
50
40
8
30
20
10
00
70
60
50
40
9
30
20
10
00
70
60
50
10
40
30
20
10
00
Byte Bit Comments
70
60
50
11
12
13
14
15
40
30
20
10
00
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
00
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
00
70
60
50
40
30
20
10
00
71 Terminator (FFh)
61
51
41
31
21
11
01
53
Page 54

VISCA Command Setting Values
Command List
Exposure control (1/2)
NTSC (s) PAL (s)
Shutter Speed 15 1/10000 1/10000
14 1/6000 1/6000
13 1/4000 1/3500
12 1/3000 1/2500
11 1/2000 1/1750
10 1/1500 1/1250
0F 1/1000 1/1000
0E 1/725 1/600
0D 1/500 1/425
0C 1/350 1/300
0B 1/250 1/215
0A 1/180 1/150
09 1/125 1/120
08 1/100 1/100
07 1/90 1/75
06 1/60 1/50
05 1/30 1/25
04 1/15 1/12
03 1/8 1/6
02 1/4 1/3
01 1/2 1/2
00 1/1 1/1
Iris 11 F1.6
10 F2
0F F2.4
0E F2.8
0D F3.4
0C F4
0B F4.8
0A F5.6
09 F6.8
08 F8
07 F9.6
06 F11
05 F14
04 F16
03 F19
02 F22
01 F28
00 CLOSE
Gain 0F 28 dB
0E 26 dB
0D 24 dB
0C 22 dB
0B 20 dB
0A 18 dB
09 16 dB
08 14 dB
07 12 dB
06 10 dB
05 8 dB
04 6 dB
03 4 dB
02 +2 dB
01 0
00 –3 dB
Gain Limit 0F +28 dB
0E +26 dB
0D +24 dB
0C +22 dB
0B +20 dB
0A +18 dB
09 +16 dB
08 +14 dB
07 +12 dB
06 +10 dB
05 +8 dB
04 +6 dB
54
Page 55

Command List
Exposure control (2/2)
IRIS GAIN
Bright 1F F1.6 28 dB
1E F1.6 26 dB
1D F1.6 24 dB
1C F1.6 22 dB
1B F1.6 20 dB
1A F1.6 18 dB
19 F1.6 16 dB
18 F1.6 14 dB
17 F1.6 12 dB
16 F1.6 10 dB
15 F1.6 8 dB
14 F1.6 6 dB
13 F1.6 4 dB
12 F1.6 2 dB
11 F1.6 0
10 F2 0
0F F2.4 0
0E F2.8 0
0D F3.4 0
0C F4 0
0B F4.8 0
0A F5.6 0
09 F6.8 0
08 F8 0
07 F9.6 0
06 F11 0
05 F14 0
04 F16 0
03 F19 0
02 F22 0
01 F28 0
00 CLOSE 0
Exposure Comp. 0E 7 10.5 dB
0D 6 9 dB
0C 5 7.5 dB
0B 4 6 dB
0A 3 4.5 dB
09 2 3 dB
08 1 1.5 dB
07 0 0 dB
06 –1 –1.5 dB
05 –2 –3 dB
04 –3 –4.5 dB
03 –4 –6 dB
02 –5 –7.5 dB
01 –6 –9 dB
00 –7 –10.5 dB
Zoom Ratio and Zoom Position
(for reference)
Zoom Ratio Optical Zoom
×36 Lens Positon Data
×1 0000
×2 166F
×3 1FF0
×4 257D
×5 2940
×6 2C02
×7 2E2B
×8 2FEE
×9 316A
×10 32B2
×11 33D4
×12 34D9
×13 35C8
×14 36A4
×15 3773
×16 3836
×17 38F0
×18 39A0
×19 3A49
×20 3AE8
×21 3B7F
×22 3C0C
×23 3C8E
×24 3D06
×25 3D73
×26 3DD4
×27 3E2C
×28 3E7C
×29 3EC2
×30 3F00
×31 3F38
×32 3F68
×33 3F94
×34 3FBD
×35 3FDF
×36 4000
55
Page 56

Command List
Digital Zoom Combine mode
X12-NTSC/PAL
Digital Zoom Digital Zoom
Ratio Position Data
×1 4000
×2 6000
×3 6A80
×4 7000
×5 7300
×6 7540
×7 76C0
×8 7800
×9 78C0
×10 7980
×11 7A00
×12 7AC0
Digital Zoom Separate mode
X12-NTSC/PAL
Digital Zoom Digital Zoom
Ratio Position Data
×100
×280
×3AA
×4C0
×5CC
×6D5
×7DB
×8E0
×9E3
×10 E6
×11 E8
×12 EB
Title setting
Line number 00 to 0A
H-position 00 to 17
Blink
Color 03 Red
00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07
AB CDE F G H
08 09 0a 0b 0c 0d 0e 0f
IJKLMNOP
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
QR S TUVWX
18 19 1a 1b 1c 1d 1e 1f
YZ & ? ! 1 2
20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27
34 5678 9 0
28 29 2a 2b 2c 2d 2e 2f
ÀÈ Ì ÒÙÁ É Í
30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37
ÓÚ ÂÊÔÆŒÃ
38 39 3a 3b 3c 3d 3e 3f
ÕÑ Ç ßÄ Ï ÖÜ
40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47
Å$
48 49 4a 4b 4c 4d 4e 4f
ø“ : ‘. , / -
F
¥DM£ ¿ ¡
00: Dose not blink
01: Blinks
00 White
01 Yellow
02 Violet
04 Cyan
05 Green
06 Blue
Lens control
Zoom Position
Focus Position
Focus Near
Limit
0000 to 4000 to 7AC0
Wide end Optical Digital
Tele end Tele end
1000 to C000
Far end Near end
1000: Over Inf
2000: 20 m
3000: 10 m
4000: 5 m As the distance on the left
5000: 3 m will differ due to temperature
6000: 2 m characteristics, etc., use as
7000: 1.5 m approximate values.
8000: 32 cm * The lower 1 byte is fixed at
9000: 9.5 cm 00.
A000: 4.5 cm
B000: 2 cm
C000: 1 cm
Temperature Reading Conversion Value
(Reference Value)
Reading Value Temperature
pq (hex) Conversion
Value (ºC)
00 –3 to 3
0A 7 to 13
14 17 to 23
1E 27 to 33
28 37 to 43
32 47 to 53
3C 57 to 63
56
Page 57

Command List
Register Setting
Register No. Value
VISCA 00 9600 bps
Baud Rate
OSD
Language
CCD Scanning 72 00 Interlaced
Mode
Digital Output 73 00 60p/50p
Mode
* Enabled when Clock rate:
the CCD 56 MHz
Zoom Limit
E-Zoom Max
StableZoom 53 00 OFF
FocusTrace 54 00 OFF
@ZoomDirect
FocusOffset 55 00-FF 00: None to
@DomeCover FF: Max.
1)
1)
1)
Scanning Mode
is Progressive.
1)
1)
1)
00 01 19200 bps
02 38400 bps
60
00 English
03 Chinese
01 Progressive
(30p/25p × 2)
01 60p/50p
Clock rate:
56 MHz
04 30p/25p
Clock rate:
28 MHz
(Stop analog
output)
50 00-FF Wide Limit
(0: Disabled)
51 00-FF Tele Limit
(0: Disabled)
52 00-FF Max. digital
zoom ratio =
256 ÷
(256-Value)
01 ON
01 ON
Others
AF Active Time
AF Interval Time
Spot AE X position 00 to 0F
Spot AE Y position 00 to 0F
R Gain 00 to FF
B Gain 00 to FF
Aperture Level 00 to 0F
NR Level 00 to 05
V-Phase 00 to
AE Response 01 to 30
AutoICR ON t
OFF Threshold Level
MD Threshold Level 00 to FF
MD Interval Time
MD Set Horizontal Position 00 to 0C
MD Set Vertical Position 00 to 08
Color Enhancement
Threshold Level
Color Enhancement
Hysteresis Width
Color Enhancement
Fixed Color Y
Color Enhancement
Fixed Color Cr
Color Enhancement
Fixed Color Cb
1)
Unit: One second
2)
40 center
1)
1)
00 to FF
00 to FF
020C (NTSC)
0270 (PAL)
00 to 1C
1)
00 to FF
00 to 7F
00 to 7F
00 to 7F
2)
2)
00 to 7F
00 to 7F
1)
The register settings are enabled when the power is turned off and then
back on again. After turning the power back on again, verify that the
mode settings have been changed.
57
Page 58

Specifications
Specifications
Picture elements FCB-EX1020: Approx. 380K pixels
FCB-EX1020P: Approx. 440K pixels
Horizontal resolution
550 TV lines (WIDE end)
Lens 36× zoom
F= 3.4 mm (WIDE) to 122.4 mm
(TELE), F1.6 to F4.5
Zoom movement speed
(NTSC)
Optical WIDE/Optical TELE
4.0 sec (Focus Tracking ON)
2.7 sec (Focus Tracking OFF)
Optical WIDE/Digital TELE 6.0 sec
Digital WIDE/Digital TELE 2.1 sec
(PAL)
Optical WIDE/Optical TELE
4.0 sec (Focus Tracking ON)
2.7 sec (Focus Tracking OFF)
Optical WIDE/Digital TELE 6.2 sec
Digital WIDE/Digital TELE 2.3 sec
Focus Movement time
∞ to Near 1.0 sec
Digital zoom 12× (432× with optical zoom)
Angle of view (H)
Approx. 57.8 degree (WIDE end) to
Approx. 1.7 degree (TELE end)
Min. working distance
320 mm (WIDE end), 1500 mm
(TELE end)
Sync system Internal/External (V-Lock)
Min. illumination
(Interlace mode) 1.4 lux/1/60 sec (NTSC), 1/50 sec
(PAL) (Typical value)
0.1 lux/1/4 sec (NTSC), 1/3 sec
(PAL) (Typical value)
ICR-ON Mode
0.01 lux/1/4 sec (NTSC), 1/3 sec
(PAL)
Recommended illumination
100 to 100,000 lux
S/N ratio 50 dB (Weight ON)
Back light compensation
ON/OFF
Electronic shutter speed
FCB-EX1020: 1/4 to
1/10000 sec. (20 steps)
FCB-EX1020P: 1/3 to
1/10000 sec. (20 steps)
White balance AUTO, ATW, Indoor, Outdoor,
One Push WB, Manual WB,
Outdoor Auto, Sodium Vapor
Lamp (Fix/Auto)
Gain Auto/Manual (–3 dB to +28 dB,
16 steps)
Max. Gain Limit (6 dB to 28 dB,
12 steps)
Wide dynamic range
ON/OFF/AUTO
3D noise reduction
ON/OFF (level 5 to 1 / OFF,
6 steps)
Image Stabilizer ON/OFF/HOLD
Color Enhancement
ON/OFF
Aperture control 16 steps
Preset 6-POSITIONS
Serial interface VISCA protocol (TTL/CMOS)
9.6 Kbps, 19.2 Kbps, 38.4 Kbps,
Stop bit, 1/2 bit
Video Output VBS: 1.0 Vp-p (Sync negative),
Y/C Output
Digital (ITU-R BT656 equiv.)
Progressive/Interlace
Storage temperature/Humidity
–20 °C to +60 °C (–4 °F to +140 °F)/
20% to 95%
Operating temperature/Humidity
–5 °C to +60 °C (32 °F to +122 °F)/
20% to 80%
Power requirements/Power consumption
6 to 12 V DC/2.4 W (5.1 W)
Weight Approx. 230 g (8.1 oz.)
Dimensions 50.0 × 57.5 × 87.9 mm
Design and specifications are subject to change
without notice.
(2 × 2
3
/8 × 3 1/2 in.) (w/h/d)
58
Page 59

Specifications
Digital Output Function
Operation Mode Digital Output (ITU-R BT656 equiv.)
Interlace FCB-EX1020/P: 60i/50i, clock rate: 28 MHz
Interlace WD
Progressive FCB-EX1020/P: 60p/50p, clock rate: 56 MHz
FCB-EX1020/P: 60p/50p (30p/25p × 2), clock rate: 56 MHz
FCB-EX1020/P: 30p/25p, clock rate: 28 MHz
Progressive WD FCB-EX1020/P: 60p/50p (30p/25p × 2), clock rate: 56 MHz
FCB-EX1020/P: 30p/25p, clock rate: 28 MHz
Slow shutter is not available in the Interlace WD or Progressive WD mode.
Digital Output Characteristics
DC characteristics
ITEM SIGN Rating Value UNIT
MIN MAX
Output voltage Digtal Signal out [7] - [0] VOH1 2.58 V
Digital Clock
VOL1 0.4 V
AC characteristics
MODEL MODE ITEM SIGN Typ
FCB-EX1020 (NTSC) Interlace Clock cycle period tcyc (ns) 35.2
Data output setup time tsu (ns) 13.5
Data output hold time thd (ns) 18.5
Progressive Clock cycle period tcyc (ns) 17.6
Data output setup time tsu (ns) 12.5
Data output hold time thd (ns) 2.5
FCB-EX1020P (PAL) Interlace Clock cycle period tcyc (ns) 35.2
Data output setup time tsu (ns) 14.6
Data output hold time thd (ns) 18.5
Progressive Clock cycle period tcyc (ns) 17.4
Data output setup time tsu (ns) 5.5
Data output hold time thd (ns) 9.5
59
Page 60
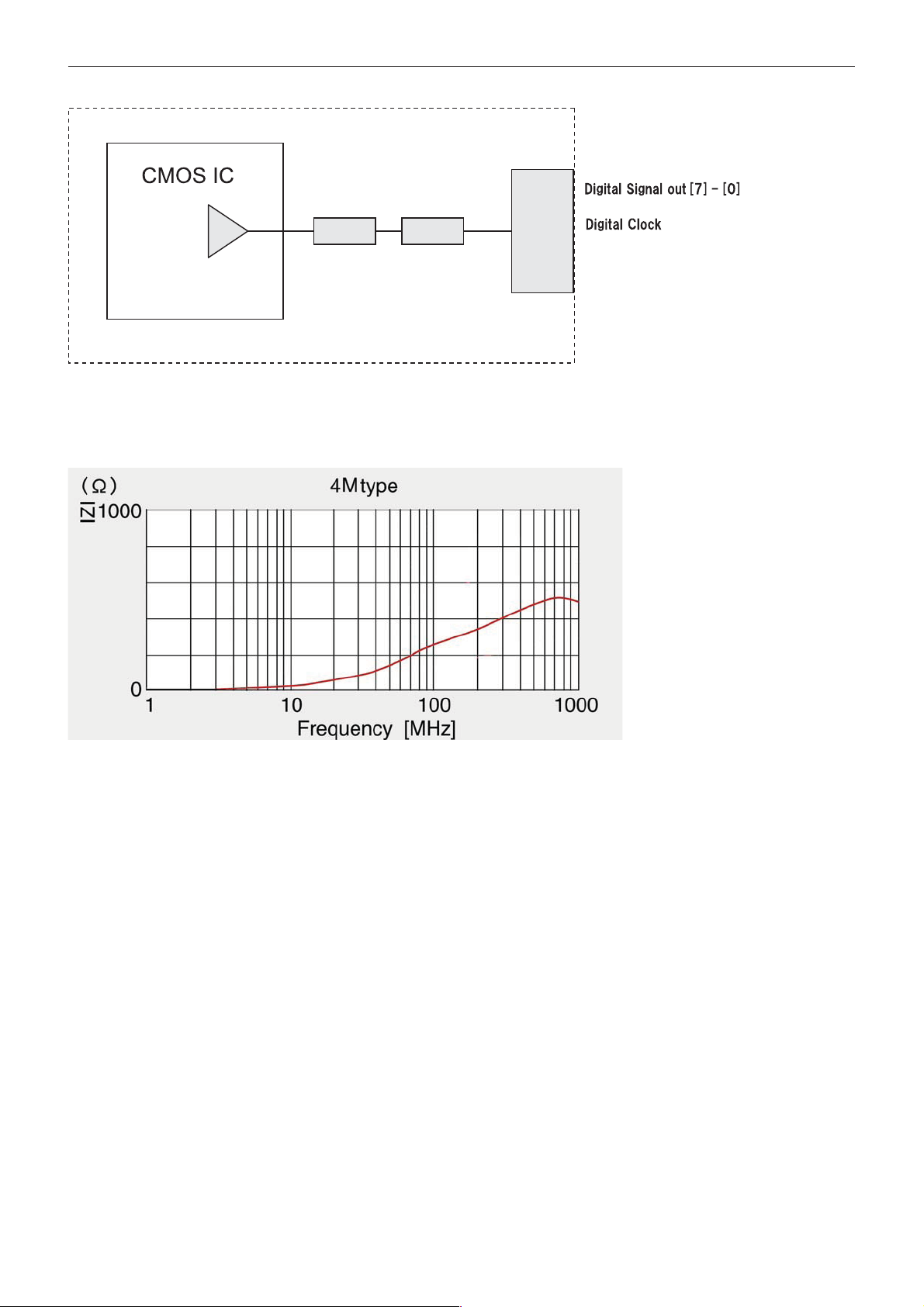
FCB Interior – Digital Output
Specifications
Resistance
Ferrite
Beads
Ferrite Beads
Product number: BK20104M241-T (Taiyo Yuden)
Impedance Frequency Characteristics (Reference)
Connector
60
Page 61
FCB-EX1020P
Digital Output Timing [50p mode]
Specifications
Horizontal
CLK [56.75 MHz]
Data out [0-7]
Vertical
Data out [0-7]
4CLK
SAV
24H
BLK
Cb0
4CLK
BLK
Y0
1504CLK Effective pixel
Cr0
Y1
Y2
Cb1
1H = 1816CLK
Cr1
Y3
Cb
582H Effective line
Y
625H
4CLK
BLK
Y
Cb
Cr
Y
4CLK
EAV
Cr
Y
BLK : Black data (Y 10, Cb/Cr 80)
BLK
304CLK
BLK
19H2H
BLK
FCB-EX1020P
Digital Output Timing [25p mode]
Horizontal
4CLK
SAV
CLK [28.375 MHz]
Data out [0-7]
Vertical
24H
BLK
Data out [0-7]
1H = 1816CLK
4CLK 4CLK
1504CLK Effective pixel
BLK BLK
Cr0
Y1
Cb0
Y0
Cb1
Cr1
Y3
Y2
Cb
Y
Y
Cb
Cr
625H
582H Effective line
4CLK
EAV
Cr
Y
Y
2H
BLK
304CLK
BLK
19H
BLK
BLK : Black data (Y 10, Cb/Cr 80)
61
Page 62

FCB-EX1020
Digital Output Timing [60p mode]
Specifications
Horizontal
CLK [57.2727 MHz]
Data out [0-7]
Vertical
Data out [0-7]
4CLK
SAV
20H
BLK
Cb0
4CLK
BLK
Y0
1536CLK Effective pixel
Cr0
Y1
Y2
Cb1
1H = 1820CLK
Cr1
Y3
Cb
494H Effective line
Y
Cr
525H
4CLK
BLK
Y
Cb
Y
4CLK
EAV
Cr
Y
BLK : Black data (Y 10, Cb/Cr 80)
2H
BLK
276CLK
BLK
11H
BLK
FCB-EX1020
Digital Output Timing [30p mode]
Horizontal
4CLK
SAV
CLK [28.6363 MHz]
Data out [0-7]
Vertical
20H
BLK
Data out [0-7]
Cb0
4CLK
BLK
Y0
1536CLK Effective pixel
Cr0
Y1
Y2
Cb1
1H = 1820CLK
Cr1
Y3
494H Effective line
4CLK
BLK
Cb
Y
Y
Cb
Cr
Y
4CLK 276CLK
EAV
Cr
Y
BLK
525H
2H
BLK
11H
BLK
BLK : Black data (Y 10, Cb/Cr 80)
62
Page 63

FCB-EX1020
Digital Output Timing [60i mode]
Specifications
Horizontal
CLK [28.6363 MHz]
Data out [0-7]
Vertical
Data out [0-7]
FLD2
2H
1H = 1820CLK
4CLK
SAV
Cb0
4CLK
BLK
Y0
Cr0
1536CLK Effective pixel
Y1
Cb1
Cr1
Y3
Y2
4CLK
BLK
Cb
Y
Y
Cb
Cr
Y
4CLK
EAV
Cr
Y
276CLK
BLK
FLD1 ODD LINE FLD2 EVEN LINE
13H
BLKBLK BLK
247H Effective line
3H
3H 13H
BLK BLK
247H Effective line
BLK : Black data (Y 10, Cb/Cr 80)
3H
2H
BLKBLK
FCB-EX1020P
Digital Output Timing [50i mode]
Horizontal
4CLK
SAV
CLK [28.375 MHz]
Data out [0-7]
Vertical
Data out [0-7]
FLD2
2H
BLK
19H
BLK
1H = 1816CLK
1504CLK Effective pixel
Y1
Cb1
Cr1
Y3
Y2
4CLK
BLK
Cb
Y
Y
Cb
Cr
Y
4CLK
EAV
Cr
Y
Cb0
4CLK
BLK
Y0
Cr0
FLD1 ODD LINE FLD2 EVEN LINE
291H Effective line
1H
BLK3HBLK
19H
BLK
291H Effective line
304CLK
BLK
2H1H
BLKBLK
BLK : Black data (Y 10, Cb/Cr 80)
63
Page 64

DIGITAL Image Output Y, Cr, Cb 4:2:2 FORMAT
Specifications
64
Page 65

Dimensions
Front Left side
Specifications
50
25
CN702
ø38.6
5
(27.5)30
57.5
±0.1
20 ±0.1
20
Top Right side
87.9
10
2.5
48.3
±0.1
2-M2
10
4.5
36.5
22.5
15
20 ±0.1 28 ±0.1
Within a depth of 3 mm (
CN200
"D"Mark
9-M2
Within a depth of 3 mm
1
(
/8 in.) or less form the
side
1
/8 in.) or less form the side
85.2
SW
ø34.016
21 ±0.1
(57.5)
25.4 ±0.1
14 ±0.1
73 ±0.1
4-M2
1
Within a depth of 3 mm (
or less form the top surface
/8 in.)
Bottom Back
1/4-20UNC
Within a depth of 7 mm (
less form the bottom surface
20
27 ±0.1
16 ±0.1
(Tripod screw for camera)
9
/32 in.) or
1453
8-M2
1
Within a depth of 3 mm (
or less form the bottom surface
/8 in.)
CN501
CN500
9.5
7.5
36 29
±0.1
40.2 33 ±0.1
Unit: mm (inches)
65
Page 66

Specifications
Pin assignment
Frequency: 60 Hz ±1 Hz (FCB-EX1020)
50 Hz ±1 Hz (FCB-EX1020P)
Amplitude: 3 V ±0.5 V square wave (50% duty)
CMOS level
V Phase Adjustment Range: 0° to 360° from V SYNC
falling edge
Recommended Input Waveform
CN500
J.S.T. Mfg Co. S4B-ZR-SM4A-TF(LF)
Pin No. Name Level
1 Y_Out
2 GND (for Y signal)
3 C_Out
4 GND (for C signal)
CN501
KYOCERA ELCO Co. 00 6200 509 130 000+
Pin No. Name Level
1 RxD CMOS 5 V (low: max 0.8 V,
high: min 2.0 V) Read Data
2 TxD CMOS 5 V (low: max 0.1 V,
high: min 4.4 V) Send Data
3 GND (for RxD&TxD)
4 DC IN 9.0 V±3 V
5 GND (for DC IN)
6 VBS OUT 1.0 V±0.2 V
7 GND (for VBS OUT)
8V LOCK PULSE External VD-Lock Pulse
(EX.FV: Negative, 3 Vp-p
50% duty)
9 GND (VL PULSE)
CN702
KYOCERA ELCO Co. 086222012101848+
Pin No. Name Level
1 GND
2 GND
3 KEY AD0
4 KEY AD1
5 KEY AD2
6 KEY AD3
7 KEY AD4
8 KEY AD5
9 KEY AD6
10 KEY AD7
11 NC
12 Strobe
66
Page 67

CN200
KYOCERA ELCO Co. 086222012101848+
Pin No. Name Level
1 GND
2 Digital Out 0 0 - 3.3 Vp-p
3 Digital Out 1 0 - 3.3 Vp-p
4 Digital Out 2 0 - 3.3 Vp-p
5 Digital Out 3 0 - 3.3 Vp-p
6 Digital Out 4 0 - 3.3 Vp-p
7 Digital Out 5 0 - 3.3 Vp-p
8 Digital Out 6 0 - 3.3 Vp-p
9 Digital Out 7 0 - 3.3 Vp-p
10 GND
11 CLOCK 0 - 3.3 Vp-p
12 GND
Note
Image noise may occur when using digital output. Take measures
such as attaching a ferrite core to the FFC as needed. The
recommended maximum FFC length is 150 mm.
Specifications
Strobe signal specifications
67
 Loading...
Loading...