Page 1
DVP-S3000
RMT-D100E/D100U
SERVICE MANUAL
SPECIFICATIONS
US Model
Canadian Model
Chinese Model
Hong Kong Model
Singapore Model
• Audio/video/S-link connecting cord (1) (US, Canadian)
• Audio/Video connecting cord (1)
(Chinese, Hong Kong, Singapore)
• S video cable (1)
• Remote commander (remote) RMT -D100U (1) (US, Canadian)
• Remote commander (remote) RMT-D100E
(Chinese, Hong Kong, Singapore)
• sony R6 (size AA) batteries (2)
Design and specifications are subject to change without notice.
CD/DVD PLAYER
MICROFILM
Page 2
SAFETY CHECK-OUT
After correcting the original service problem, perform the following
safety checks before releasing the set to the customer:
1. Check the area of your repair for unsoldered or poorly-soldered connections. Check the entire board surface for solder
splashes and bridges.
2. Check the interboard wiring to ensure that no wires are
“pinched” or contact high-wattage resistors.
3. Look for unauthorized replacement parts, particularly transistors, that were installed during a previous repair. Point them
out to the customer and recommend their replacement.
4. Look for parts which, though functioning, show obvious signs
of deterioration. Point them out to the customer and recommend their replacement.
5. Check the line cord for cracks and abrasion. Recommend the
replacement of any such line cord to the customer.
6. Check the B+ voltage to see it is at the values specified.
7. Check the antenna terminals, metal trim, “metallized” knobs,
screws, and all other exposed metal parts for AC leakag e. Check
leakage as described below.
To Exposed Metal
Parts on Set
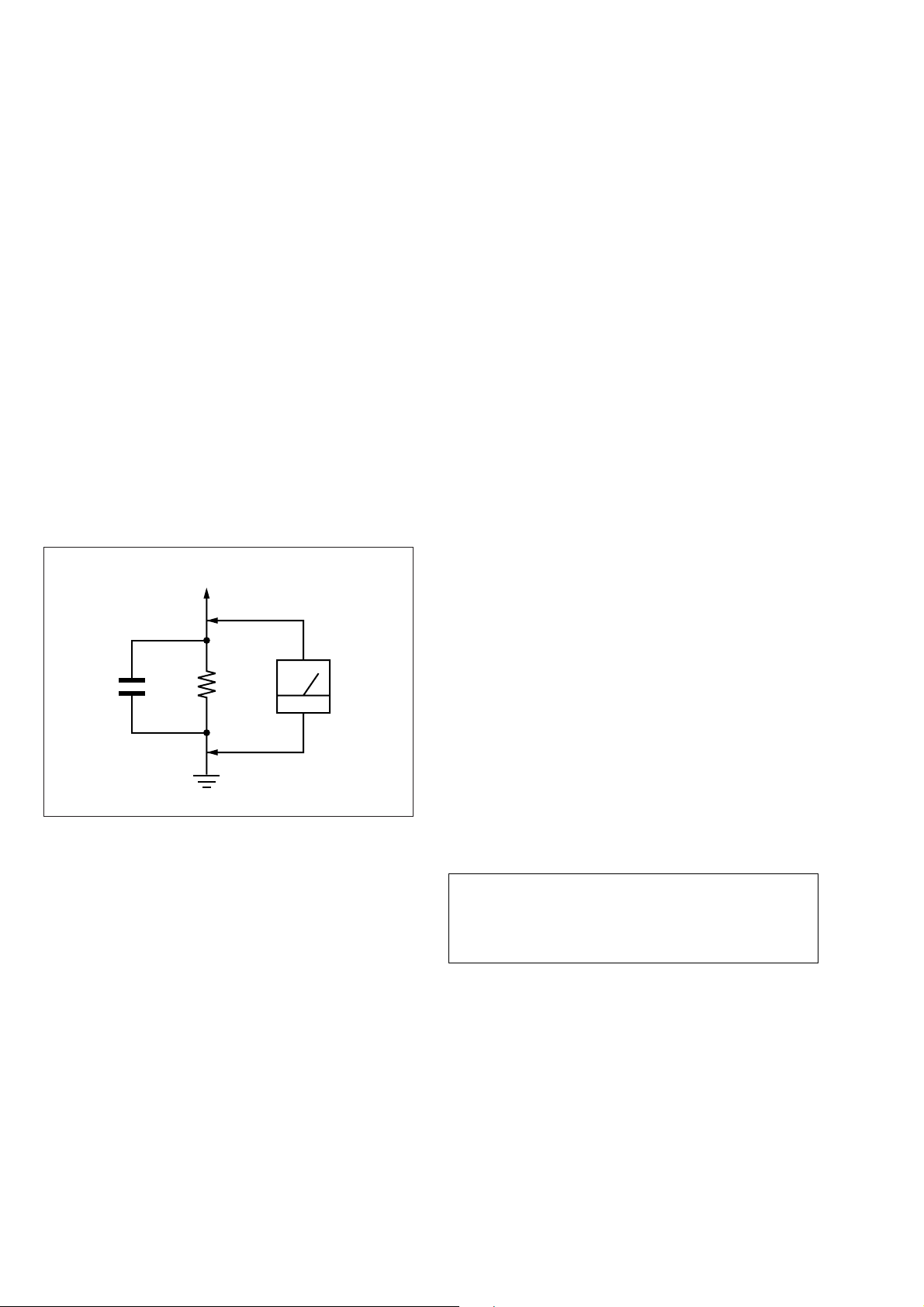
LEAKAGE TEST
The A C leakage from any exposed metal part to earth ground
and from all exposed metal parts to any exposed metal part having
a return to chassis, must not exceed 0.5 mA (500 microamperes).
Leakage current can be measured by any one of three methods.
1. A commercial leakage tester, such as the Simpson 229 or RCA
WT -540A. Follo w the manufacturers' instructions to use these
instruments.
2. A battery-operated A C milliammeter. The Data Precision 245
digital multimeter is suitable for this job.
3. Measuring the voltage drop across a resistor by means of a
VOM or battery-operated AC voltmeter. The “limit” indication is 0.75V, so analog meters must have an accurate lowvoltage scale. The Simpson 250 and Sanwa SH-63T rd are e xamples of a passive VOM that is suitable. Nearly all battery
operated digital multimeters that have a 2V AC range are suitable. (See Fig. A)
0.15 µF
1.5 k
Ω
Earth Ground
AC
Voltmeter
(0.75 V)
Fig. A Using AC voltmeter to check AC leakage
WARNING!!
WHEN SERVICING, DO NOT APPROACH THE LASER
EXIT WITH THE EYE TOO CLOSELY. IN CASE IT IS
NECESSARY TO CONFIRM LASER BEAM EMISSION,
BE SURE TO OBSER VE FROM A DISTANCE OF MORE
THAN 25 cm FROM THE SURFACE OF THE OBJECTIVE LENS ON THE OPTICAL PICK-UP BLOCK.
CAUTION:
The use of optical instrument with this product will increase eye
hazard.
CAUTION
Use of controls or adjustments or performance procedures other
than those specified herein may result in hazardous radiation
exposure.
SAFETY-RELATED COMPONENT WARNING!!
COMPONENTS IDENTIFIED BY MARK ! OR DOTTED LINE
WITH MARK ! ON THE SCHEMATIC DIAGRAMS AND IN
THE PARTS LIST ARE CRITICAL TO SAFE OPERATION.
REPLACE THESE COMPONENTS WITH SONY PAR TS WHOSE
P AR T NUMBERS APPEAR AS SHO WN IN THIS MANU AL OR
IN SUPPLEMENTS PUBLISHED BY SONY.
ATTENTION AU COMPOSANT AYANT RAPPORT
À LA SÉCURITÉ!
LES COMPOSANTS IDENTIFIÉS PAR UNE MARQUE ! SUR
LES DIAGRAMMES SCHÉMATIQUES ET LA LISTE DES
PIÈCES SONT CRITIQUES POUR LA SÉCURITÉ DE
FONCTIONNEMENT. NE REMPLACER CES COM- POSANTS
QUE PAR DES PIÈCES SONY DONT LES NUMÉROS SONT
DONNÉS DANS CE MANUEL OU D ANS LES SUPPLÉMENTS
PUBLIÉS PAR SONY.
– 2 –
Page 3

TABLE OF CONTENTS
Section Title Page
Service Note .............................................................................4
1. GENERAL
This Player Can Play the Following Discs.......................1-1
Getting Started ...............................................................1-1
Basic Operations ............................................................1-2
Playing Discs in Various Modes ......................................1-8
Setting and Adjustments .................................................1-10
Additional Information .....................................................1-12
2. DISASSEMBLY
2-1. Top Case Removal..........................................................2-1
2-2. Front Panel Removal ......................................................2-1
2-3. AU-201, 203 Board Removal ..........................................2-1
2-4. MB-80 Board Removal....................................................2-1
2-5. MD Block Ass’y Removal................................................2-2
2-6. Try Removal....................................................................2-2
2-7. Optical Pick-up Removal.................................................2-2
2-8. TT-40 Board Removal .....................................................2-2
2-9. Internal Views .................................................................2-3
2-10. Circuit Boards .................................................................2-4
3. BLOCK DIAGRAMS
3-1. Overall Block Diagram 1 (RF, Servo, Audio Power) ........ 3-1
3-2. Overall Block Diagram 2 (Signal Process)......................3-6
3-3. RF/Servo Block Diagram ................................................3-11
3-4. Data Process Block Diagram ..........................................3-14
3-5. Video Block Diagram ......................................................3-16
3-6. System Control Block Diagram .......................................3-21
3-7. Audio Block Diagram ......................................................3-24
3-8. Mode Control Block Diagram ..........................................3-27
3-9. Power Supply Block Diagram..........................................3-30
4. PRINTED WIRING BOARDS AND SCHEMATIC
DIAGRAMS
4-1. Frame Schematic Diagram .............................................4-1
4-2. Printed Wiring Boards and Schematic Diagrams............4-5
TT-40, LM-56 Printed Wiring Boards...............................4-5
TT-40, LM-56 Schematic Diagram ..................................4-7
MB-80 Printed Wiring Board ...........................................4-12
MB-80 (Interface) Schematic Diagram............................4-17
MB-80 (CPU) Schematic Diagram ..................................4-21
MB-80 (Drive Control) Schematic Diagram.....................4-25
MB-80 (DVD Data Process) Schematic Diagram............4-28
MB-80 (CD ROM Decode) Schematic Diagram..............4-31
MB-80 (MPEG Video Decode) Schematic Diagram........4-35
MB-80 (Video EQ, Letter Box, Sub Picture)
Schematic Diagram ........................................................4-39
MB-80 (Audio Decode) Schematic Diagram ...................4-42
MB-80 (Video) Schematic Diagram ................................4-45
MB-80 (Digital Servo) Schematic Diagram .....................4-51
MB-80 (RF Block) Schematic Diagram ...........................4-55
MB-80 (Drive) Schematic Diagram .................................4-59
FP-611/619, PW-116/117 Printed Wiring Boards............4-63
FP-611/619, PW-116/117 Schematic Diagram................4-65
AU-201/203, PS-408/413 Schematic Diagram ...............4-67
AU-201/203, PS-408/413 Printed Wiring Boards............4-71
SR-740, SUB Printed Wiring Boards and
Schematic Diagram.........................................................4-74
SR-745, SUB Printed Wiring Boards and
Schematic Diagram.........................................................4-77
Section Title Page
5. IC PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTION
5-1. Interface Control Pin Function (MB-75 Board IC021) .....5-1
5-2. Drive Control Pin Function (MB-75 Board IC136)...........5-2
5-3. Extended Output Port 0 (MB-75 Board IC147) ...............5-3
5-4. Extended Output Port 1 (MB-75 Board IC148) ...............5-3
5-5. Extended Output Port 2 (MB-75 Board IC149) ...............5-3
5-6. Extended Output Port 3 (MB-75 Board IC150) ...............5-3
5-7 D/A Converter (MB-75 Board IC722)..............................5-3
5-8 System Control Pin Function (MB-75 Board IC090) .......5-4
6. TEST MODE
6-1. Starting up Test Mode .....................................................6-1
6-2. Syscon Diagnosis ...........................................................6-1
6-3. Drive Auto Adjustment ....................................................6-10
6-4. Drive Manual Operation ..................................................6-13
6-4-1. Drive Manual Operation wnu creen ...........................6-13
6-4-2. Disc Type ...................................................................6-13
6-4-3. Manual Control 1 .......................................................6-13
6-4-4. Manual Control 2 .......................................................6-14
6-4-5. Manual Control 3 .......................................................6-14
6-4-6. Manual Adjust 1 .........................................................6-15
6-4-7. Manual Adjust 2 .........................................................6-15
6-4-8. Auto Adjust ................................................................6-15
6-4-9. Check.........................................................................6-16
6-5. Emergency History .........................................................6-18
6-6. Other Checks ..................................................................6-18
7. ELECTRICAL ADJUSTMENT
7-1. Power Supply Check.......................................................7-1
1. PS-408/413 Board ..........................................................7-1
2. MB-80 Board...................................................................7-1
7-2. +5.2 V Adjustment...........................................................7-1
7-3. Adjustment of System Control ........................................7-2
1. 27 MHz Free Run............................................................7-2
2. 22 MHz Adjustment ........................................................7-2
3. 33 MHz Check ................................................................7-2
4. 33 MHz Lock Check........................................................7-2
5. 24 MHz Adjustment ........................................................7-3
6. 36 MHz Check ................................................................7-3
7. 36 MHz Lock Check........................................................7-3
8. 16 MHz Check ................................................................7-3
7-4. Adjustment of Video System
1. Video Level Adjustment ..................................................7-4
2. S-Terminal Output Check................................................7-4
3. Checking Composite Video Output B-Y..........................7-4
4. Checking Composite Video Output R-Y..........................7-5
5. Checking Composite Video Output Y ..............................7-5
6. Checking S Video Output S-C ........................................7-5
7. Checking S Video Output DC Level ................................7-5
7-5. Adjustment Related Parts Arrangement .........................7-6
8. REPAIR PARTS LIST
8-1. Exploded Views ..............................................................8-1
8-1-1. Case Assembly ..........................................................8-1
8-1-2. Front Panel Assembly ................................................8-2
8-1-3. Chassis Assembly .....................................................8-3
8-1-4. DVD Mechanism Chassis Assembly (1) ....................8-4
8-1-5. DVD Mechanism Chassis Assembly (2) ....................8-5
8-2. Electrical Parts List .........................................................8-6
– 3 –
Page 4
SER VICE NOTE
1. DISK REMOVAL PROCEDURE
(at POWER OFF)
1) Insert a cross-tip screwdriver into a hole at the bottom, and
rotate the cam gear 1 in direction A. (See Fig. 1)
Note: To prevent a damege of cam gear, rotate it in direction
A by 1/4 turn.
2) Draw out the tray 2 in direction B by hand, and remove a
disk. (See Fig. 1)
1
Cam gear
B
2 Tr a y
Hole
A
Fig. 1
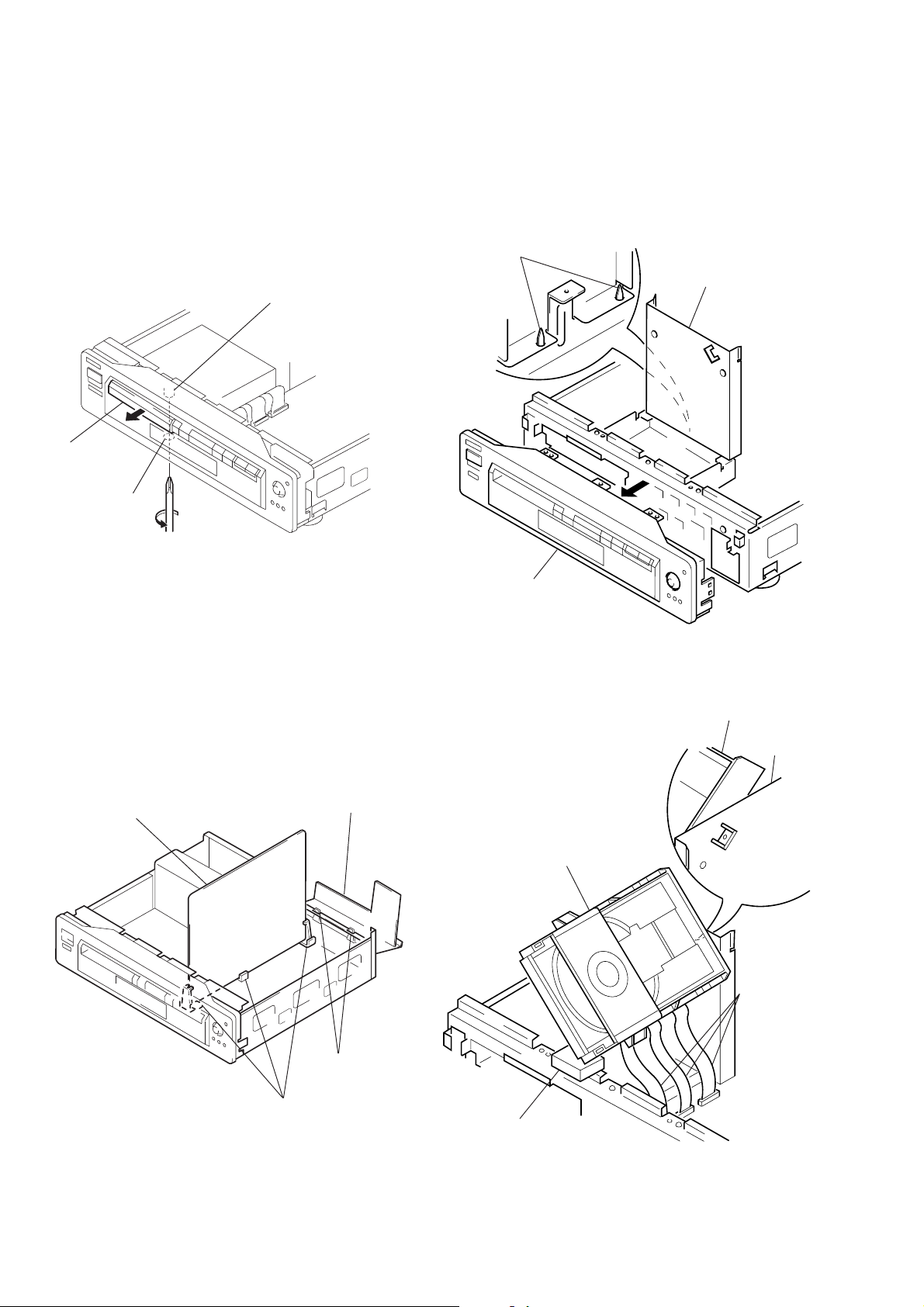
2. HOW T O SER VICE AU-201, 203 AND MB80 BOARDS
1) Remove the top case from the set. (Refer to 2-1)
2) Remove the AU-201, 203 board. (Refer to 2-3)
Note: Do not disconnect wiring.
3) Remove the MB-80 board. (Refer to 2-4)
Note: Do not disconnect wiring.
4) Erect MB-80 board on three circuit board holders. (See. Fig. 2)
5) Erect AU-201, 203 board on two claws. (See Fig. 2)
AU-201 board
(US, Canadian model)
AU-203 board
MB-80 board
(Chinese, Hong Kong, Singapore model)
3. HOW T O SERVICE THE MD BLOCK ASS’Y
1) Remove the top case from the main unit. (Refer to 2-1)
2) Remove the front panel. (Refer to 2-2)
Note: Do not disconnect wiring.
3) Remove the MD block ass’y. (Refer to 2-5)
4) Remove the MD upper cover, and mount as shown in Fig. 3.
Claws
MD upper cover
Front panel
Fig. 3
5) Install the MD block ass’y as shown in Fig. 4.
Note: Place a cushion at the position A.
6) Connect three flexible flat cables.
MD block ass’y
MD upper
cover
Three circuit board
holders
Fig. 2
MD block ass’y
Three flexible
flat cable
Two claws
A
Fig. 4
– 4 –
Page 5
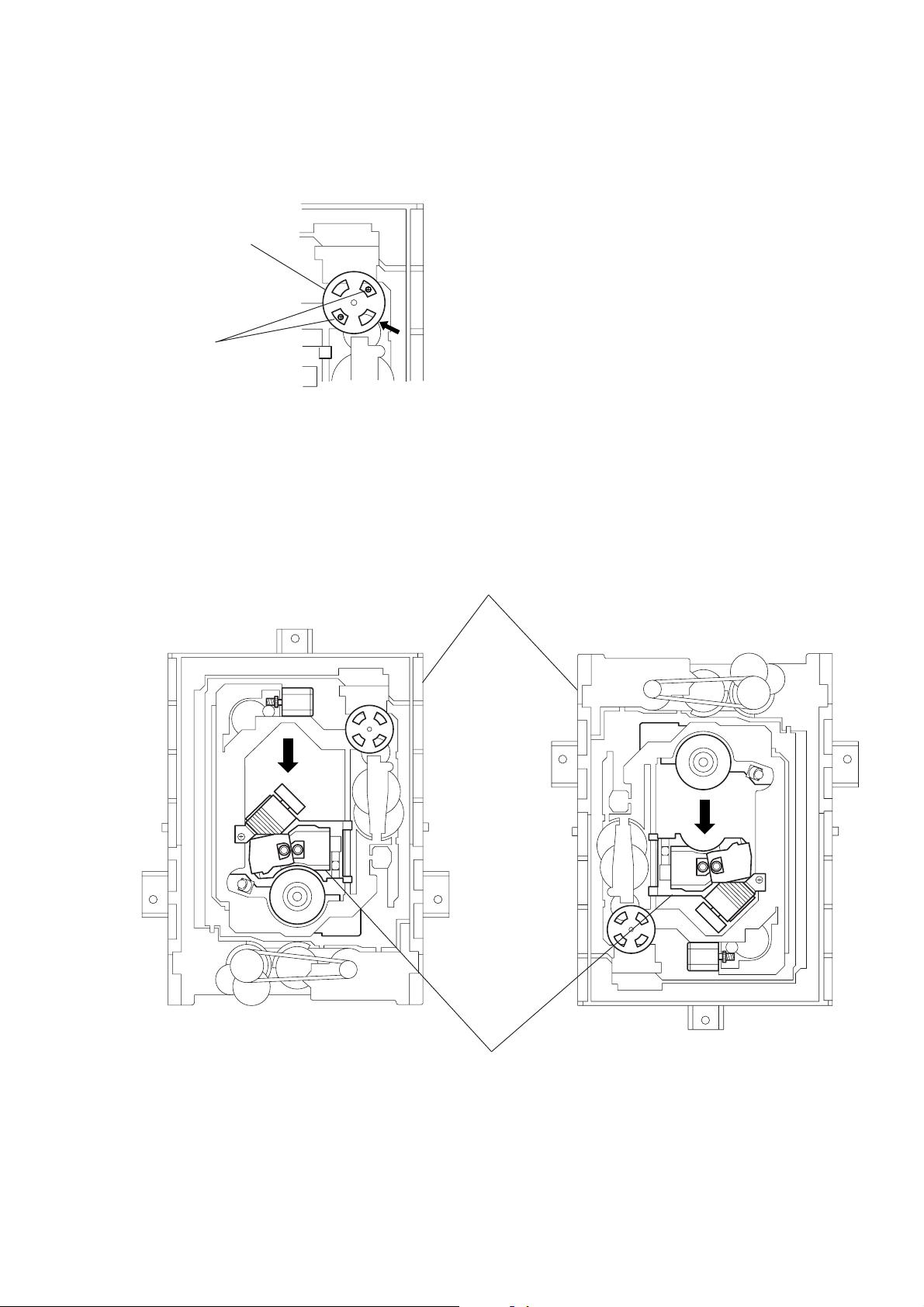
4. NOTE ON MOUNTEING SLED MOTOR
1) Push the sled motor assy 1 toward direction A. (See Fig.5)
2) Tighten two screws 2 (M1.7 × 2.5).
1 Sled motor ass’y
A
2 Two screws (M1.7 × 2.5)
Fig. 5
3) Raising the MD block assy 3 90 º with the side down.
confirm that the optical pick-up 4 falls by self weight.
(See Fig. 6)
4) Further, with the front side of MD block assy 3 up, confirm
that the optical pick-up falls by self weight.
Lower
Upper
Front side
3 MD block ass’y
4 Optical pick-up
Upper
Lower
Front side
Fig. 6
– 5 –
Page 6
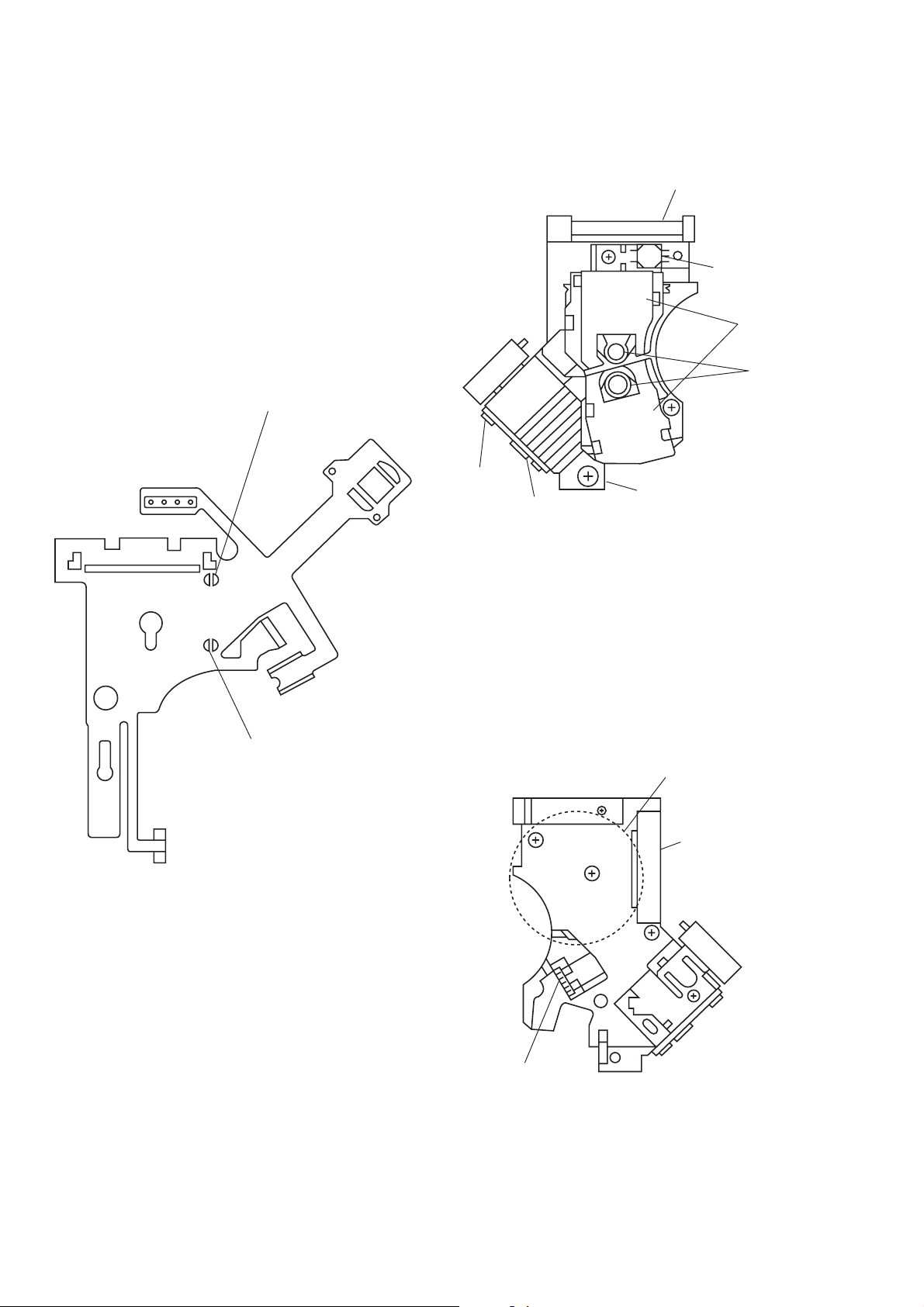
5. REPLACING OPTICAL PICK-UP
5-1. Handling
1) A red laser diode for DVD requires more attention to static
electricity than general infrared laser diodes for CD.
Because its durability to static electricity is far weaker than
that of infrared laser diodes, always use an earth band when
handling the optical pick-up block as service parts.
2) As for the flexible board KHS-180A (RP) packed as service
parts, the short lands have been soldered to protect from static
electricity. Accordingly, remove solders when replacing optical pick-up. (See Fig. 7)
DVD short land
3) In handling the KHS-180A (RP), do not touch inhibited parts
shown in Fig. 8, but grip the slide base bearing and U-shaped
guide.
Slide base bearing
Skew sensor
Lens actuator
covers
Objective lenses
Laser holder
U-shaped guide
OEIC
CD short land
Fig. 7 Flexible board
Touch inhibited parts
• Objective lens
• Skew sensor
• Laser holder
• Laser coupler
• Flexible board
• OEIC
• Lens actuator covers
Flexible board
Connector
– 6 –
Laser coupler
Fig. 8 KHS-180A (RP)
Page 7
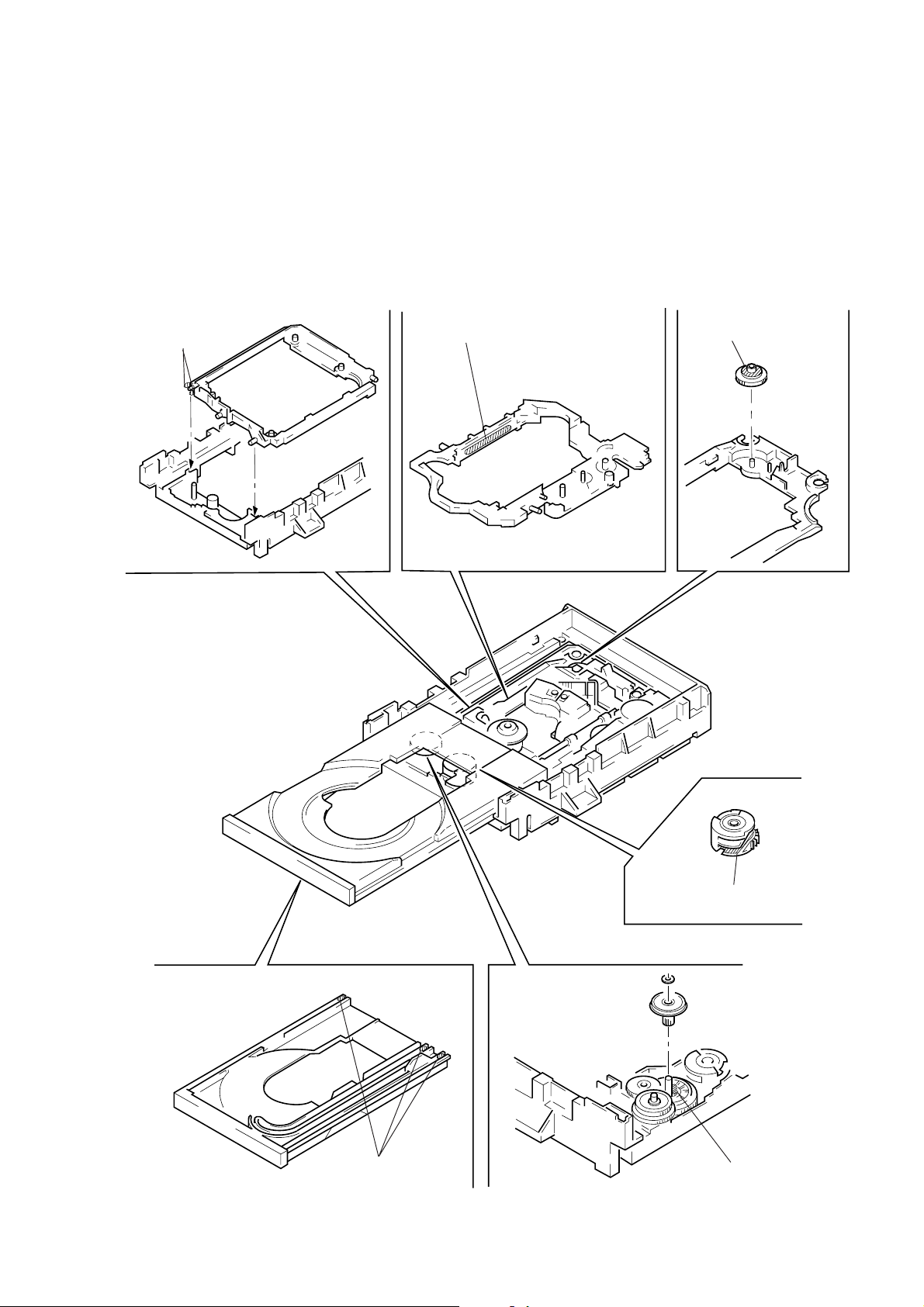
6. NOTE ON ASSEMBLING MECHANICAL DECK
6-1. Application of Grease
1) Grease must be applied if the following parts were replaced.
(See Fig. 9)
NOTE 1: Recommended grease is Foil KG-70MP.
NOTE 2: In applying grease, take care not to allow grease to
stick to other parts (particularly, r ubber belt, spindle
motor, and optical pick-up)
Base unit holder
2 bosses
Slide base
Skew cam
Tray 3 grooves
NOTE: Add grease if tray
moves slowly.
Cam gear
Loading pulley shaft
NOTE: Add grease if tray
generates noise
periodically.
Fig. 9
– 7 –
Page 8
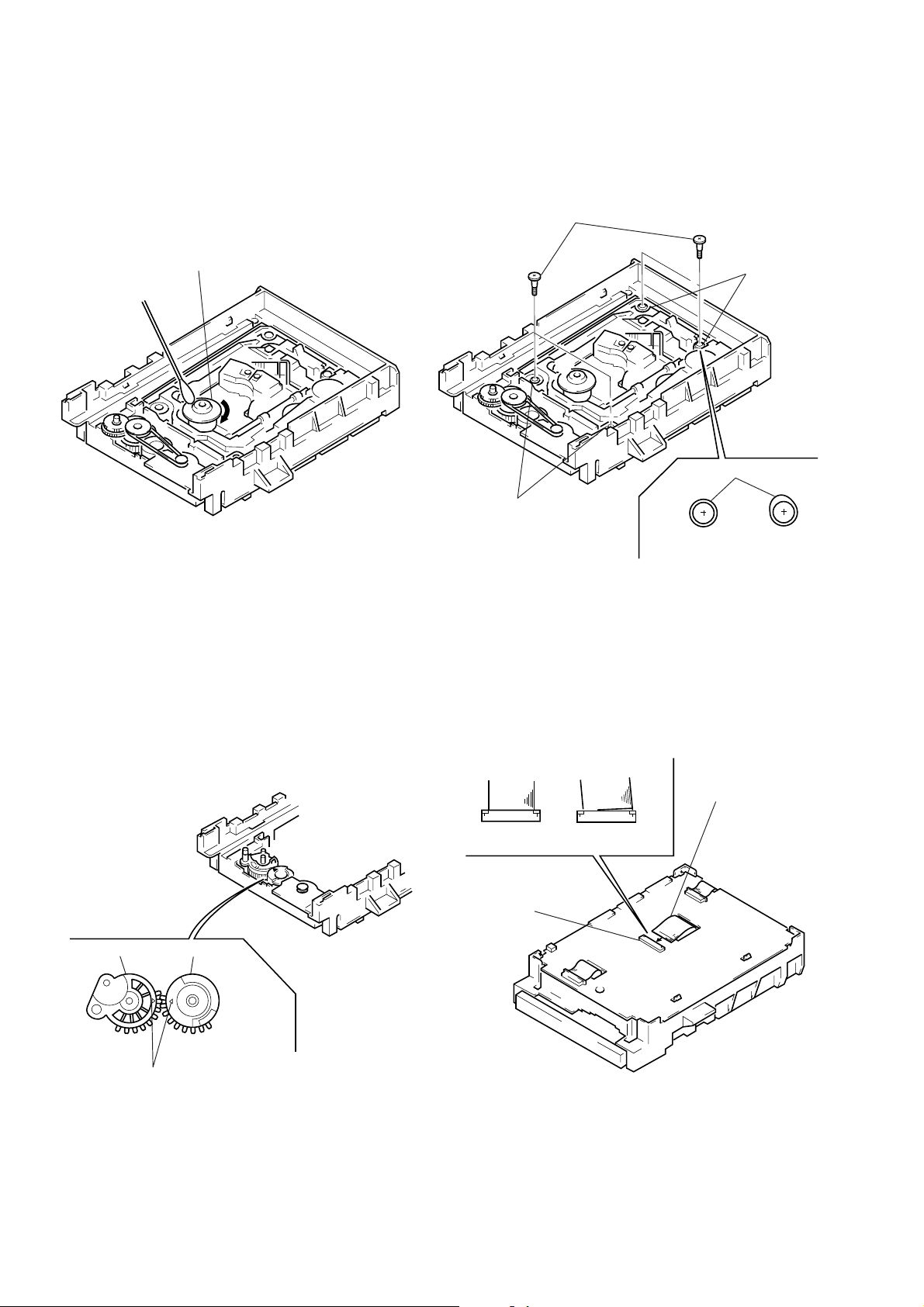
6-2. Cleaning Spindle Motor Turntable
1) Remove the tray. (Refer to 2-6)
2) Clean the spindle motor turntable if disc antiskid rubber
(black) is dirty. (See Fig.10)
Spindle motor
Turntable
6-4. Deformation of Insulator
1) Assemble the spindle base into the base unit.
2) Lock with 4 shoulder screws. (See Fig.12)
3) Check if 4 insulators deformed. (See Fig.12)
Four step screws
Two insulators
Insulator
Two insulators
Good NG
Fig. 10
6-3. Aligning Phase of Cam Gear and
Drive Gear
1) Align triangle marks when assembling the cam gear and
drive gear. (See Fig.11)
Drive gear Cam gear
Fig. 12
6-5. Note on connecting OPT Harness
1) The optical pick-up could be destroyed unless the OPT
harness is connected normally to the connector. (See Fig.13)
OPT harness
Good
Connector
NG
Align triangle marks.
Fig. 11 Fig. 13
– 8 –
Page 9
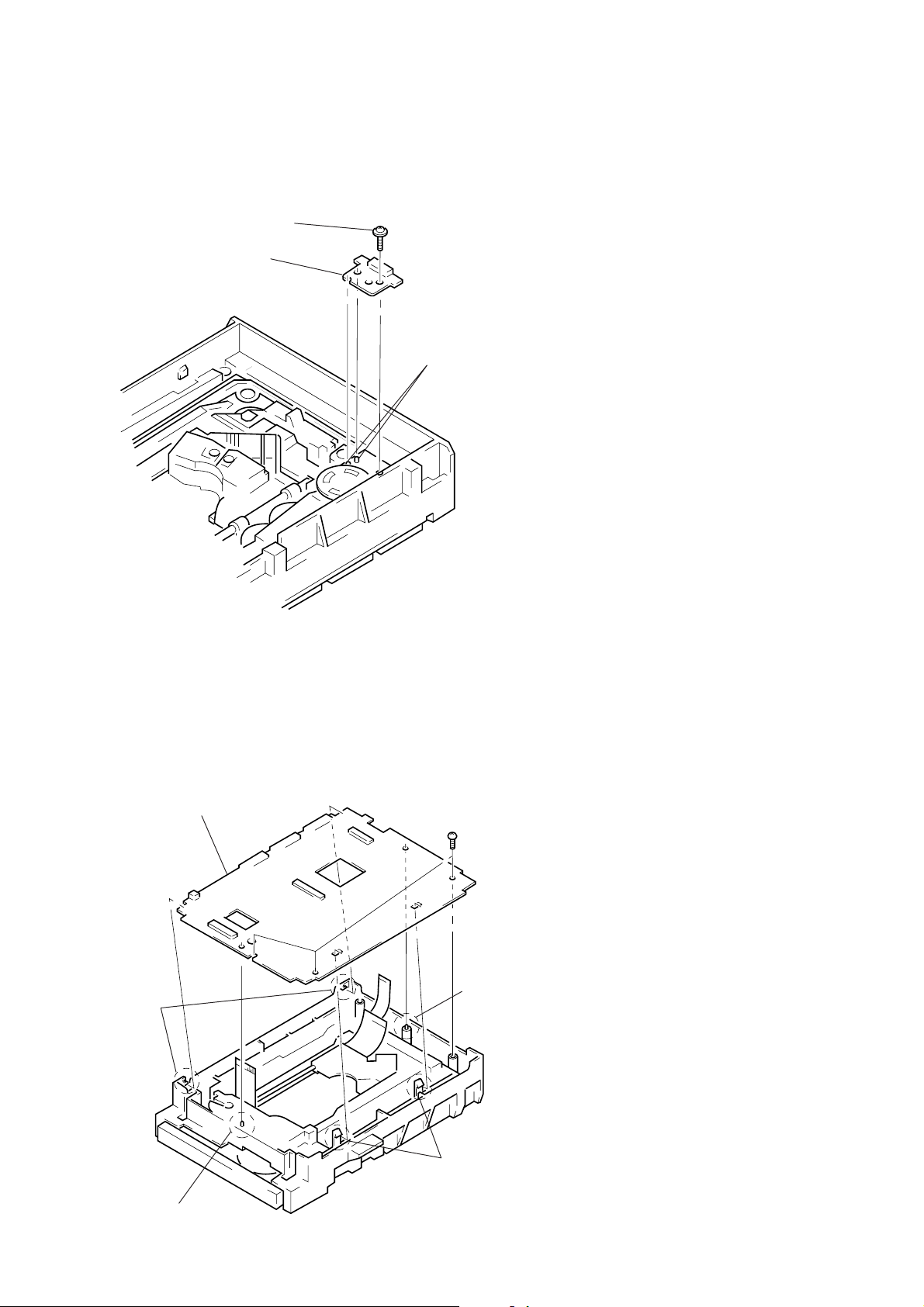
6-6. Note on Mounting LM-51 Board
1) Align two bosses. (See Fig.14)
2) Fix the board securely with screws (PTPWH 2 × 5). (The
sensor will not function normally if the board floats up.)
Screw
(PTPWH2 × 5)
LM-56 board
Two bosses
Fig.14
6-7. Note on Mounting TT-701 Board
1) Align two bosses. (See Fig.15)
2) Align four tabs. (See Fig.15)
3) Fix the board securely with 3 screws (BV 3 × 10). (The
sensor will not function normally if the board floats up.)
TT-40 board
Two claws
Three screws
(BV3 × 10)
Boss
Boss
Two claws
Fig.15
– 9 –
Page 10
DVP-S3000
SECTION 1
GENERAL
This section is extracted from
US model instruction manual.
1-1
Page 11
1-2
Page 12
1-3
Page 13
1-4
Page 14
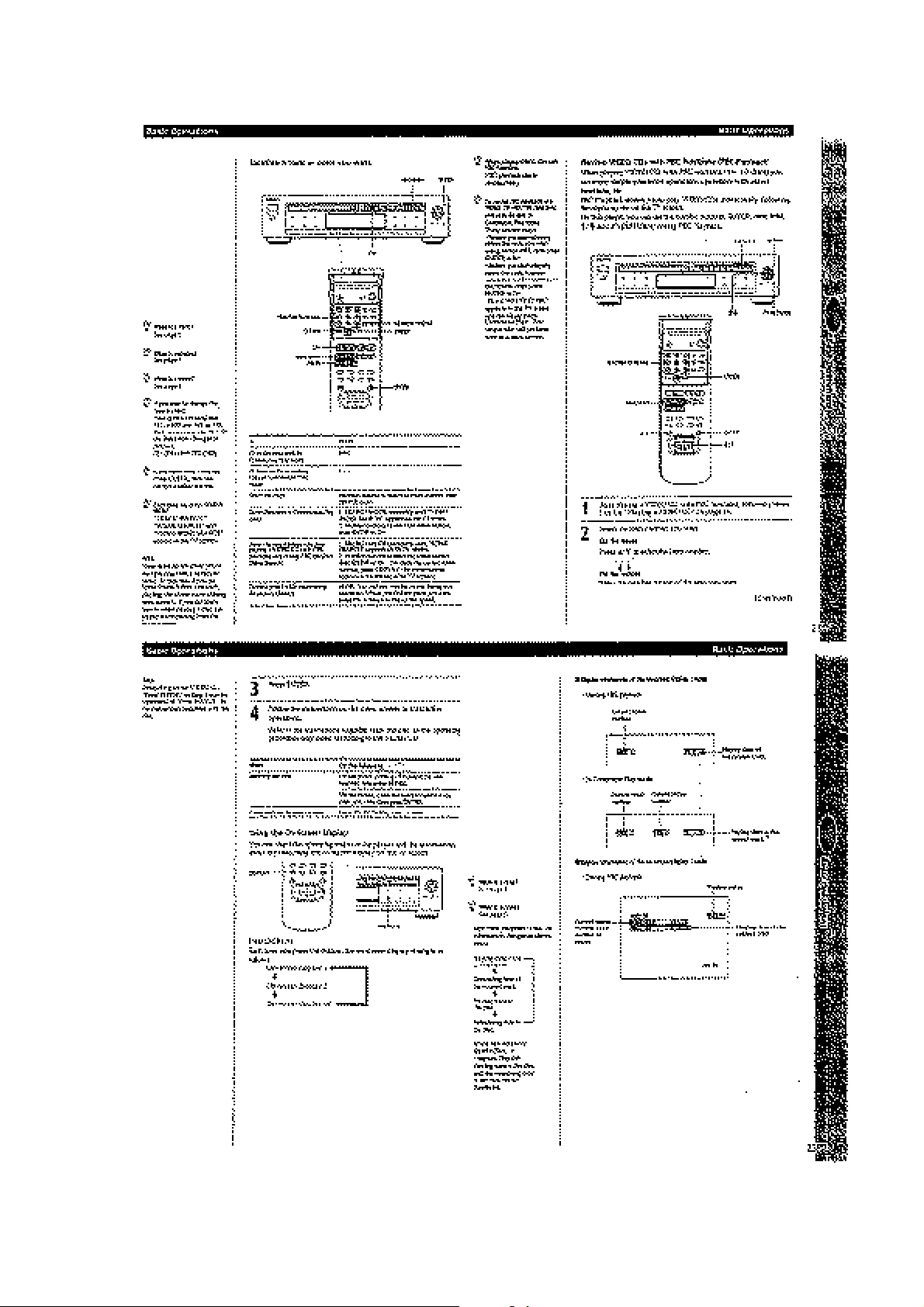
1-5
Page 15
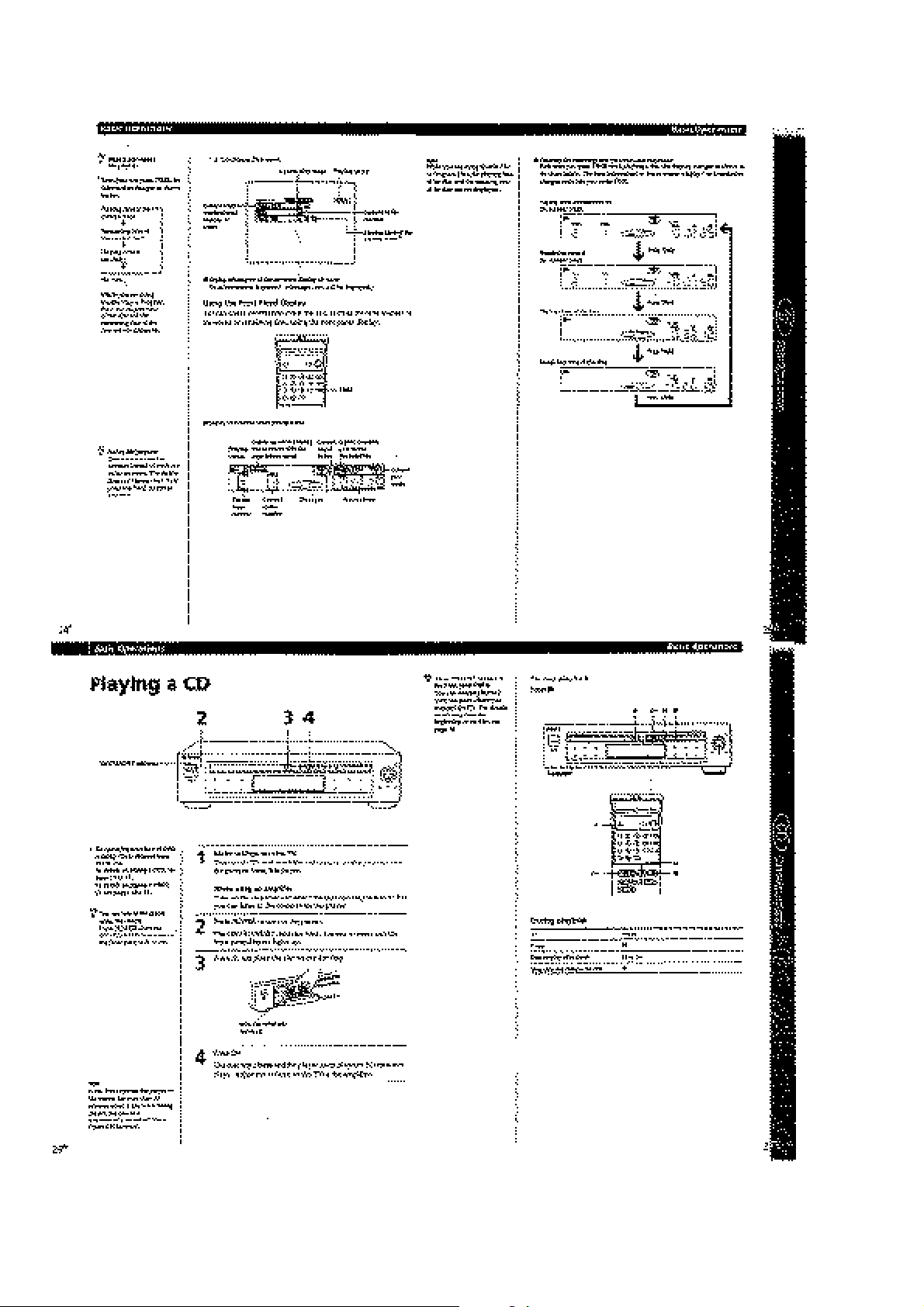
1-6
Page 16
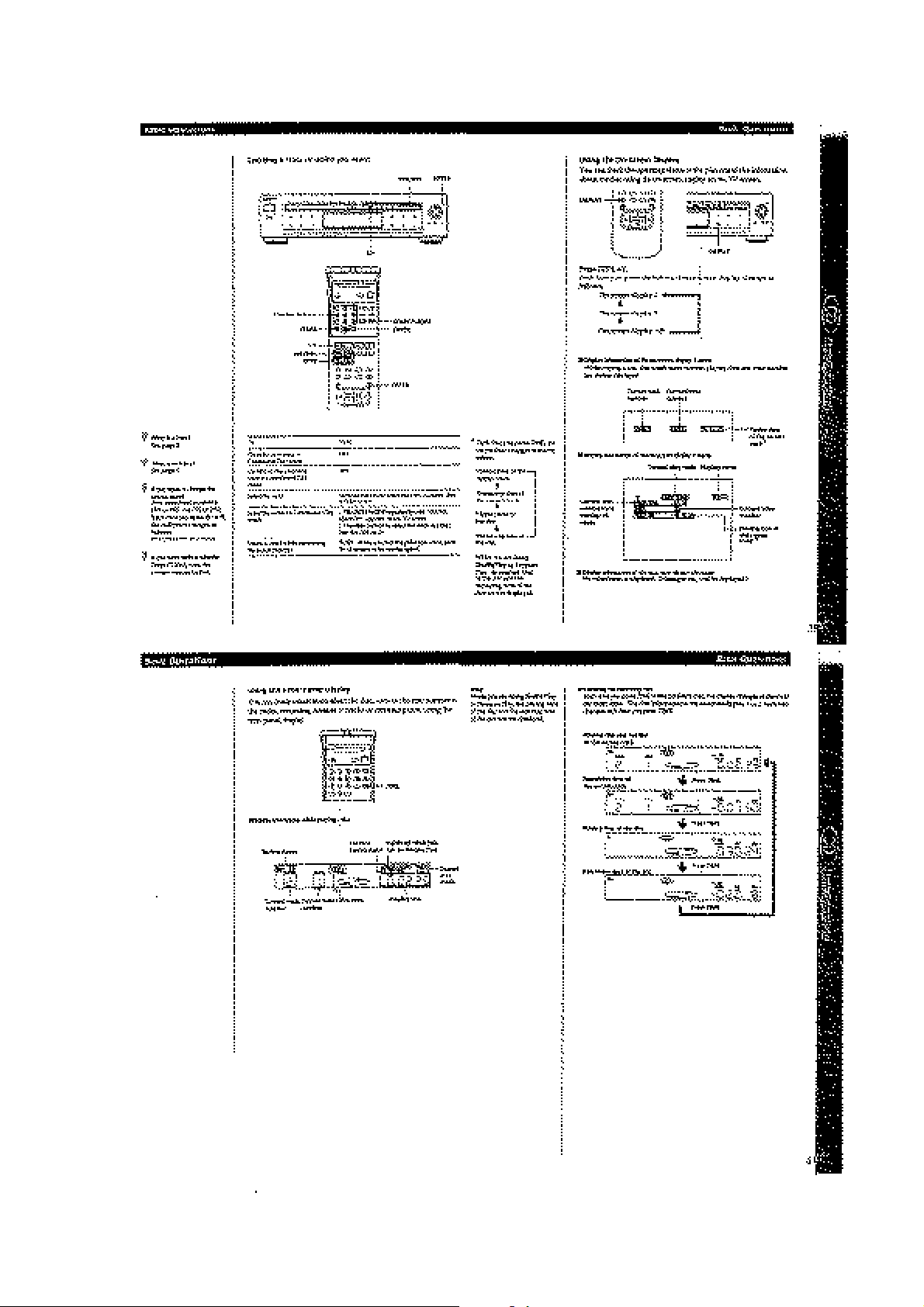
1-7
Page 17
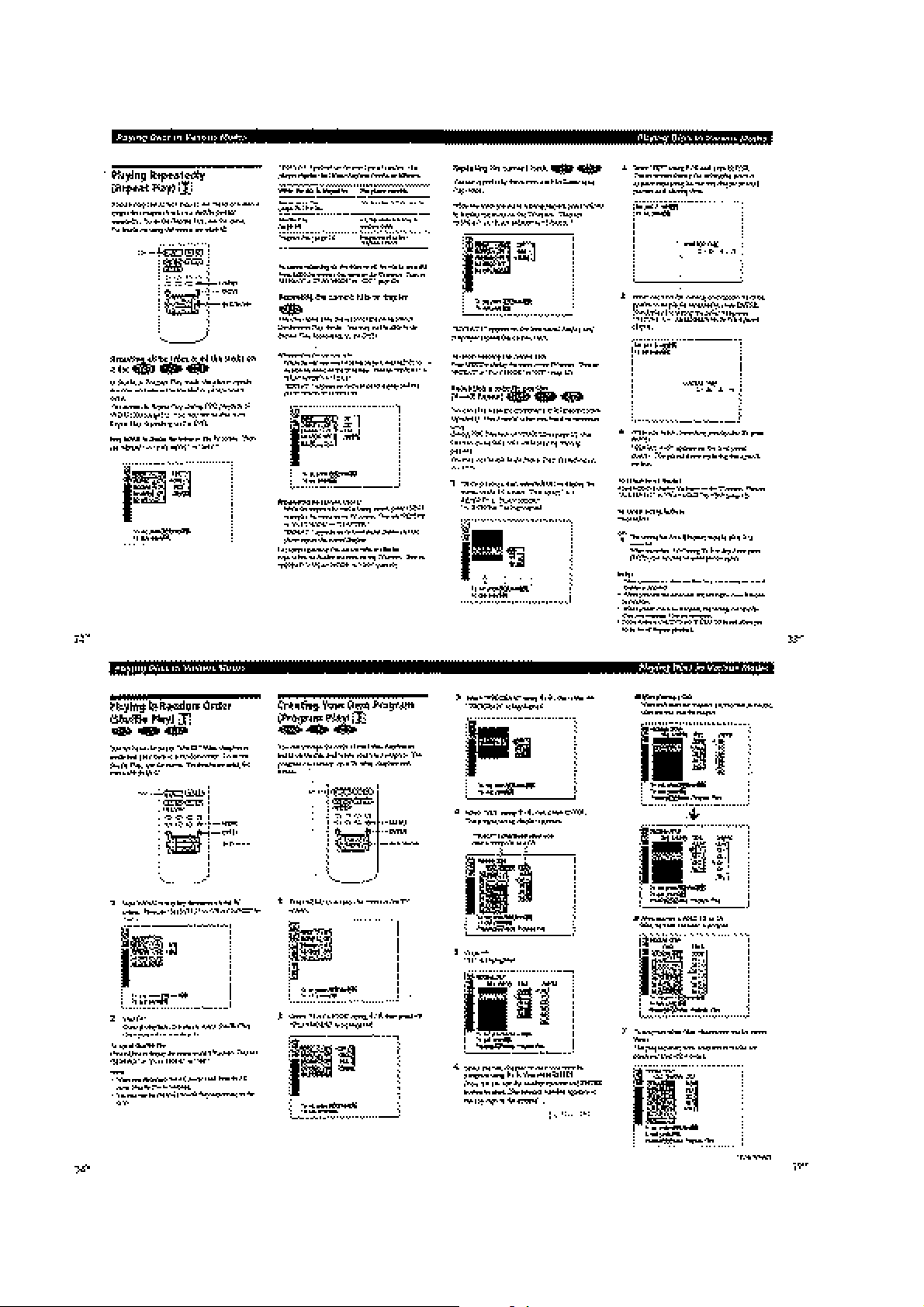
1-8
Page 18
1-9
Page 19
1-10
Page 20
1-11
Page 21
1-12
1-12 E
Page 22
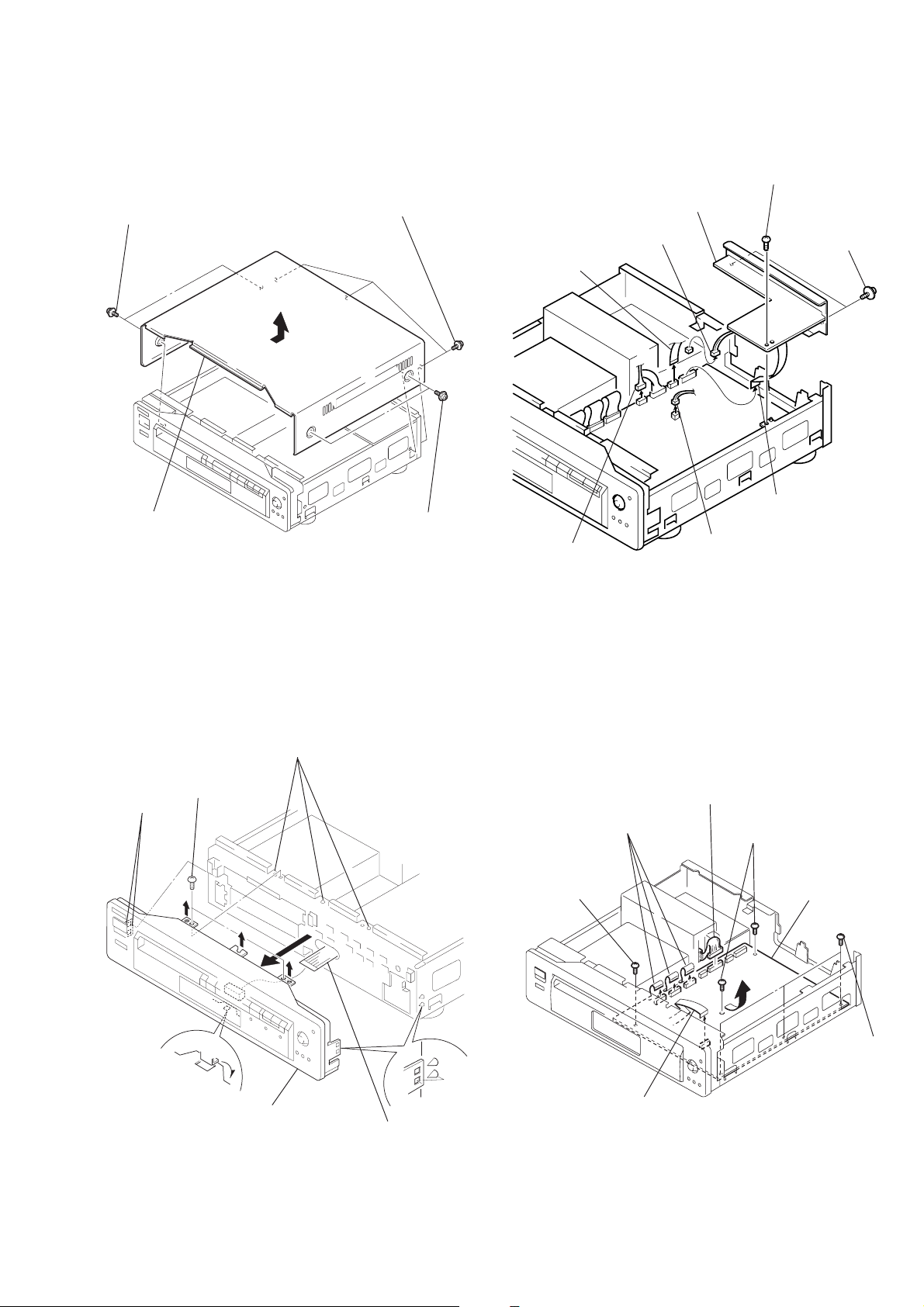
DVP-S3000
SECTION 2
DISASSEMBLY
Note: Follow the disassembly procedure in the numerical order given.
2-1. TOP CASE REMOVAL 2-3. AU-201, 203 BOARD REMOVAL
8 AU-201 board
1 Two tapping screws
2 Three tapping screws
(US, Canadian model)
AU-203 board
(Chinese, Hong Kong, Singapore
model)
2 Connector (CN954)
1 Flexible flat
cable (FAM-5)
(CN381)
7 Screw (BV3 × 10)
6 Two tapping screws
4 Top case
2-2. FRONT PANEL REMOVAL
2 Three bosses
1 Two screws
(BV3 × 10)
3 Two claws
3 Two tapping screws
3 Connector
(CN011)
5 Connector
(CN382)
2-4. MB-80 BOARD REMOVAL
1 Three flexible flat
cables (FTM-3)
(CN885/886/980)
4 Screw
(BV3 × 10)
2 Connector
(CN001)
5 Two screws
4 Flexible flat
cable (FAM-6)
(CN005)
(BV3 × 10)
7 MB-80 board
5 claw
6 Front panel
4 Two claws
7 Flexible flat
cable (FTT-4)
(CN101)
6 Three screws
(BV3 × 10)
3 Flexible flat
cable (FTT-4)
(CN009)
2-1
Page 23
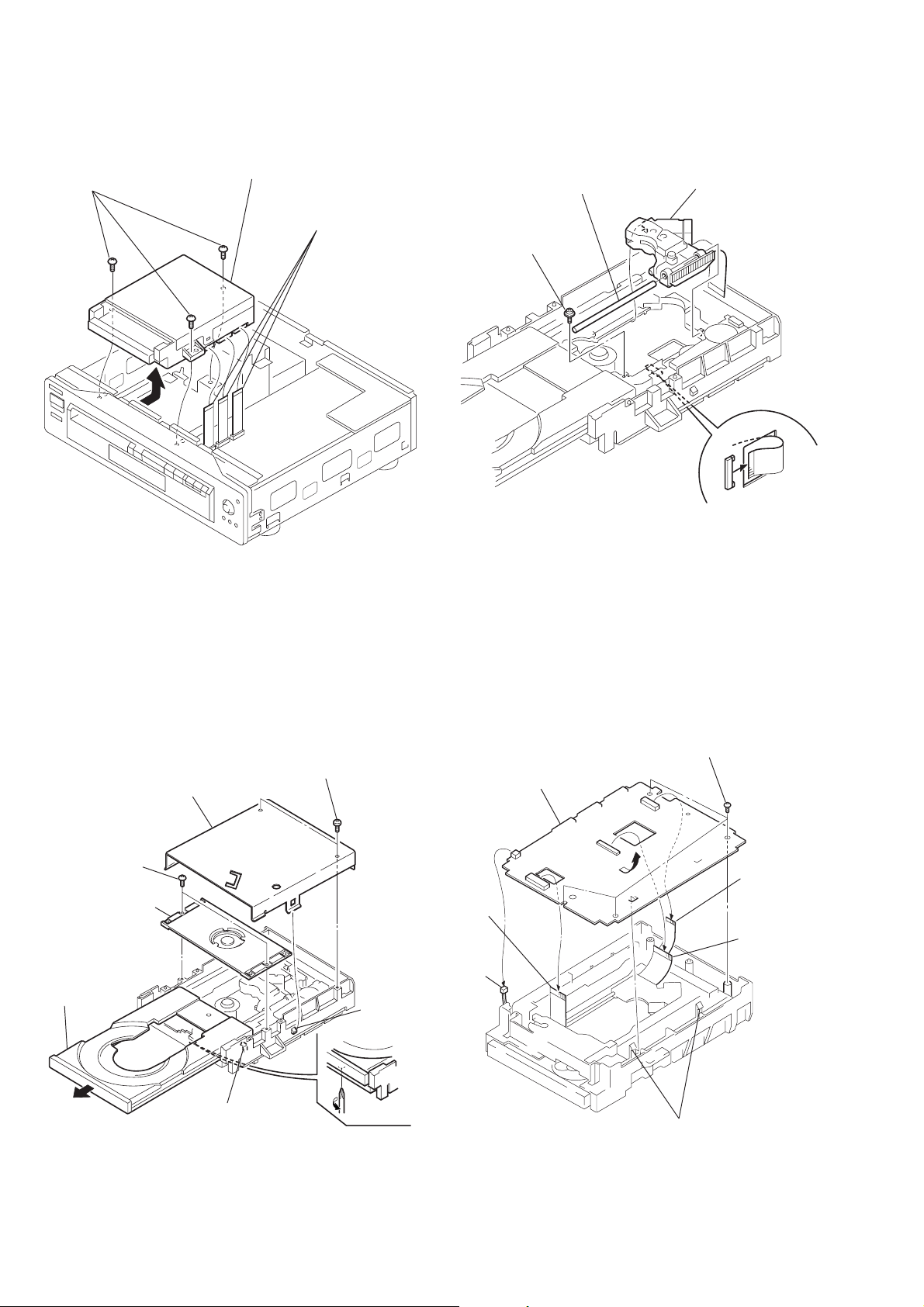
2-5. MD BLOCK ASS’Y REMOVAL 2-7. OPTICAL PICK-UP REMOVAL
2 Three screws
(BV3 × 10)
3 MD block ass’y
1 Three flexible flat
cables (FTM-3)
(CN005/006/007)
3 Main shaft
2 screw (PTTWH2 × 5)
4 Optical pick-up
1 OP-15 flexible board
(CN001)
2-6. TRAY REMOVAL
3 MD upper cover
4 Two screws
(BV3 × 10)
5 Press pully bracket
7 Pull the tray to direction
of the arrow B.
9 Remove
the tray
B
8 claw
1 Two screws (BV3 × 10)
2 claw
A
6 Rotate the cam gear to
direction of the arrow A .
2-8. TT-40 BOARD REMOVAL
2 Flat cable
(spindle motor)
(CN002)
1 Connector
(CN004)
5 Four screws
(BV3 × 10)
7 TT-40 board
3 LT-31 flexible
board
(CN003)
4 OP-15 flexible
board
(CN001)
6 Two claws
2-2
Page 24
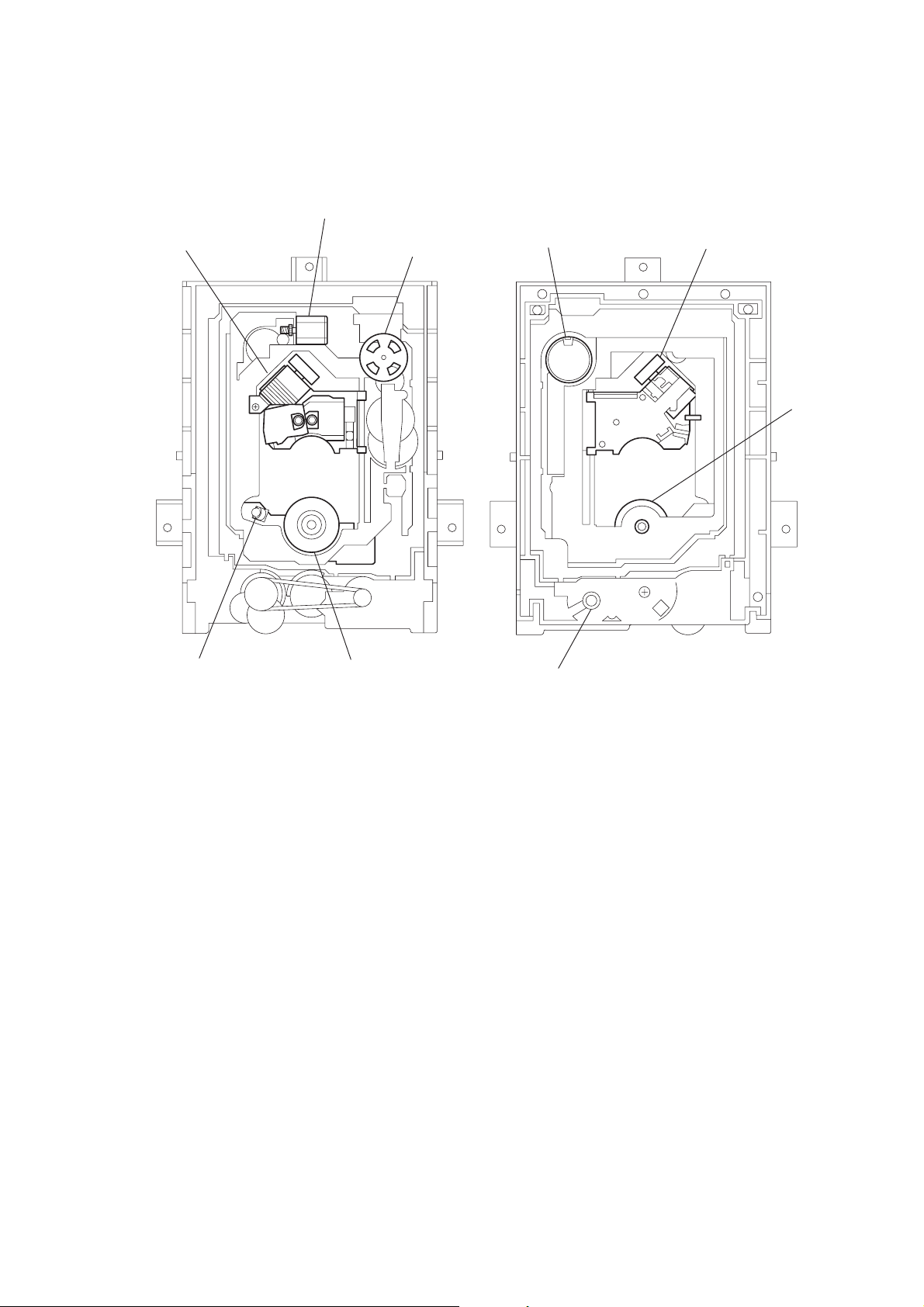
2-9. INTERNAL VIEWS
Optical pick-up (KHS-180A/J1N)
8-820-005-02
Skew motor ass’y
X-3947-138-1
Sled motor ass’y
X-3947-137-1
Sled motor ass’y
X-3947-137-1
Optical pick-up (KHS-180A/J1N)
8-820-005-02
DC motor (spindle)
1-698-944-11
KU160 (CD sensor)
8-749-013-33
DC motor (spindle)
1-698-944-11
Motor (loading)
1-698-942-21
2-3
Page 25
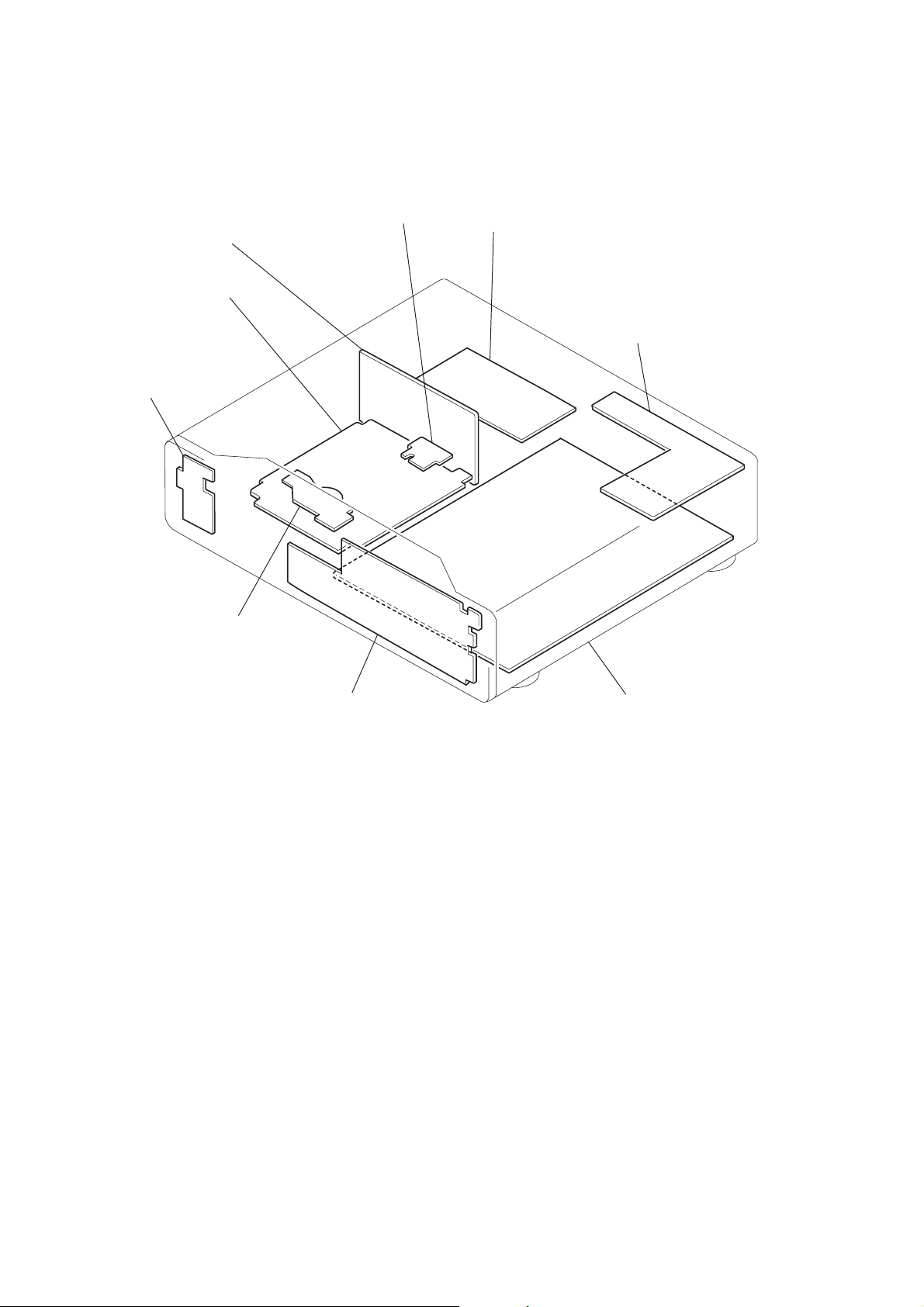
2-10. CIRCUIT BOARD LOCATION
SR-740
(US, Canadian model)
SR-745
(Chinese, Hong Kong, Singapore model)
SWITCHING
REGULATOR
TT-40
(RF/SERVO)
PW-116
(US, Canadian model)
PW-117
(Chinese, Hong Kong, Singapore model)
(IR/POWER SWITCH)
LM-56
(SLED)
PS-408
(US, Canadian model)
PS-413
(Chinese, Hong Kong, Singapore model)
(POWER)
AU-201
(US, Canadian model)
AU-203
(Chinese, Hong Kong, Singapore model)
(AUDIO)
DC MOTOR
(SPINDLE)
FP-611
(US, Canadian model)
FP-619
(Chinese, Hong Kong, Singapore model)
(FL DRIVER/FUNCTION SWITCH)
MB-80
(SIGNAL PROCESS/SERVO)
2-4
2-4 E
Page 26

5-1
5-1. INTERFACE CONTROL PIN FUNCTION (IC021 on MB-80 Board (1/12))
Pin No. Pin Name I/O Function Pin No. Pin Name I/O Function
1,2 CL1, 0 I Input of sub clock (32kHz)
3,4 GND – Ground
5,6 X0–1 I Input of main clock (8MHz)
7 GND – Ground
8 RST I Input of RESET signal
9 RESET O SRESET (SYSCON)
10 INTMS O XINTM S (SYSCON)
11 AUDIO MUTE O SAUDIO MUTE (L)
12 IFDIAG I DIAG (H)
13 NITSC O NTSC (H) /PAL (L)
14,15 N.C. – Not used
16 FLCS O XFLCS (FL)
17 REF V I XREF-V (VSYNC)
18 INTSM I XINTSM (SYSCON)
19-24 N.C. – Not used
25 POWER CONT O POWER-CONT (H)
26 DA TA BOUND O DATA-BOUND
27 N.C. – Not used
28 CMOD I CMOD
29 P.FAIL O Power fail
30 CGSO O CGSO (FL & OSDC)
31 CGCLK O CGCLK (FL & OSDC)
32 WSIRCS I WSIRCS
33 CGCS O CGCS (OSDC)
34 V MUTE O Video mute
35 STATUS O STATUS (H)
36 N.C. – TSEL (OSDC) Not used
37 STATUS O FSEL (OSDC)
38 N.C. – TRE (OSDC) Not used
39-48 N.C. – Not used
49 VCC – Power supply
50-57 N.C. – Not used
58 GND – Ground
59-66 N.C. – Not used
67 VCC – Power supply
68-75 N.C. – Not used
76 CS I CS (SYSCON)
77 SI I SI (SYSCON)
78 SO O SO (SYSCON)
79 CLK I CLK (SYSCON)
80-82 N.C. – Not used
83 GND – Ground
84-87 AD0–3 I Analog input
88 TEST 1 I Input of TEST 1 signal
89 TEST 2 I Input of TEST 2 signal
90 N.C. – Not used
91 N.C. – Not used
92 VCC – Power supply
93 POWER-FAIL I Input of POWER-FAIL (AD INPUT)
94 N.C. – Not used
95 CGRA 16 I CGRA16 Character generator font ROM address 16
96 CGRA 17 I CGRA17 Character generator font ROM address 17
97 CGRA 18 I CGRA18 Character generator font ROM address 18
98 N.C. – Not used
99 N.C. – Not used
100 VCC – Power supply
5. IC PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTION
DVP-S3000
Page 27
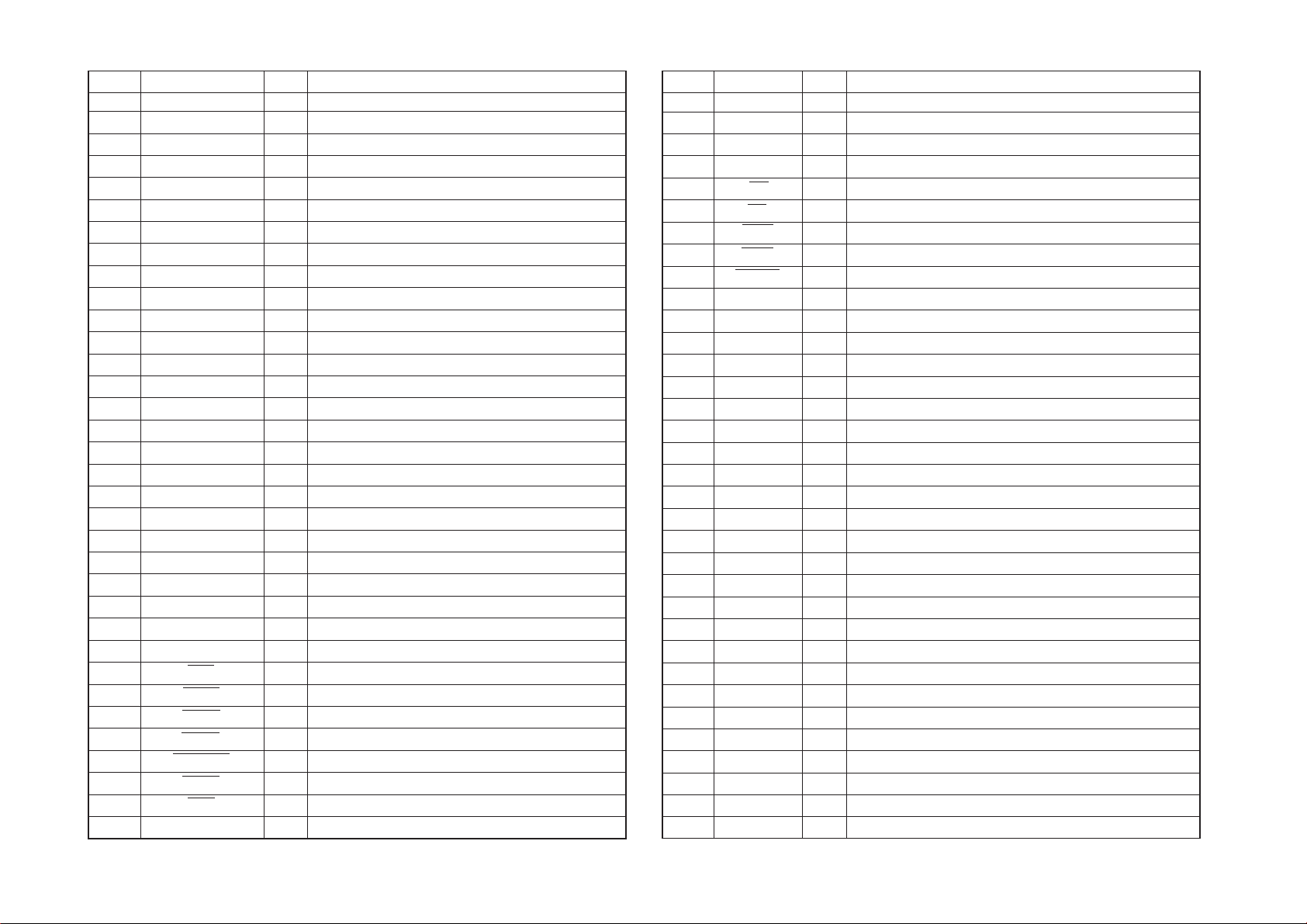
5-2
5-2. DRIVE CONTROL PIN FUNCTION (IC136 on MB-80 Board (3/12))
Pin No. Pin Name I/O Function Pin No. Pin Name I/O Function
1 VCC – Power supply
2 MRST O Peripheral circuits reset signal (L: Reset)
3 12 RST O 12V system power control signal
4 CD DET I Input of DVD/CD discriminate sensor
5 TRAY OUT I Tray out end (H: End)
6 CHUCK I Chucking down end (H: End)
7 LOCK I Good Frame Sync dat (H: OK, L: NG)
8 XPNM I RF Pro PLL Mode (L: Normal)
9 FOK I Focus OK (H: OK, L: NG)
10 N.C. – Not used
11 VSS – Ground
12 CPDTO O Serial data output to each IC
13 SDCS (SO) O Serial data output to jig
14 CPDTI I Serial data input from each IC
15 SDSC (SI) I Serial data input from jig
16 CPCK O Serial clock to each IC
17 SCKCS O Serial clock to jig
18–21 D0–3 I/O Data bus 0–3
22 VSS – Ground
23–25 D4–6 I/O Data bus 4–6
26–34 D7–15 I/O Data bus 7–15
35 VCC – Power supply
36–43 A0–7 O Address bus 0–7
44 VSS – Ground
45–50 A8–13 O Address bus 8–13
51–56 A14–19 O Address bus 14–19
57 VSS – Ground
58 WAIT I WAIT signal (fixed to “H”)
59 BREQ I Input of bus request
60 BACK O Output of bus ACK
61 SYS CLK O Output of system clock (for check)
62 STBY I Fixed to “H”
63 RES I Input of Reset by SH (L: Reset)
64 NMI I Fixed to “L”
65 VSS – Ground
66 EXTAL I Input of 16.9MHz
67 XTAL I Input of 16.9MHz
68 VCC – Power supply
69 AS O Address strobe
70 RD O Read
71 HWR O H_Write
72 LWR O L_Write
73–75 MD0–2 I Operation mode setting (Mode 2)
76 A VCC – Power supply
77 VREF – Reference voltage
78 N.C. – Not used
79 HYDET1 I Input of sled FG2
80 P FAIL I Power down pre signal
81 PI I Input of pull–in signal
82 SLD2– I Input of sled offset
83 SLD2+ I Input of sled offset
84 VCOM I Input of VCO adjustment
85 JIG BUSY I Serial busy signal from Jig
86 A VSS – Ground
87 SCOR I CXD2545 address storing request signal
88 INT-SC I Serial data
89 SOINT I Jitter storing request signal
90 SYS_INT I Interrupt request signal from Syscon
91 ROM BUSY I EEPROM Ready/Busy signal
92 VSS I Ground
93 TKC I Input of sled FG count
94 FCMPL I FEZC Low det
95 FCMPH O FEZC High det
96 SENS I Input of SENS signal
97 HFG I Input of spindle FG
98 DVDLDON O LD ON/OFF control for DVD
99 CDLCON O LD ON/OFF control for CD
100 LT MUTE O
Page 28

5-3. EXTENDED OUTPUT PORT0 (IC147 on MB-80 Board (3/12))
5-6. EXTENDED OUTPUT PORT3 (IC150 on MB-80 Board (3/12))
5-3
Pin No. Pin Name I/O Function
2 SQCK MSK O SubQ Read Clock Mask
5 ROM CS O Chip Select for EEPROM
6 DA XLD O Load Signal for D/A
9 SUBQ XOE O SubQ Output Enable
12 XLAT O Latch Signal for CXD2545
15 SDEN O Serial Output Enable For SSI3720
16 SLD MODE O Sled Control change
19 INT CS O Serial data forward request
5-4. EXTENDED OUTPUT PORT1 (IC148 on MB-80 Board (3/12))
Pin No. Pin Name I/O Function
2 XLT O Latch Signal for RF Pro
5 SOEN O Serial Output Enable for RF Pro
6 SCK MSK O Serial command transfer clock master
9 SCLK O SENS reading clock
12 FJUMP- O Focus Jump Pulse
15 FJUMP+ O Focus Jump Pulse
16 DRV BUSY O Communication inhibit request from system controller
19 LOCK MON O Spindle LOCK Monitor Out
5-5. EXTENDED OUTPUT PORT2 (IC149 on MB-80 Board (3/12))
Pin No. Pin Name I/O Function
2 DRV INT O Interrupt request to system controller
5 NST O Spindle forced stop (L: Stop) Active only at out of control
6 FHOLD O Focus Hold
9 FDWN O Focus Gain Down (L: Normal)
12 LOAD ON O Loading/Unloading Moter ON/OFF
15 DET ON O CD Det Sensor LED ON/OFF
16 LP ON O VCO Control
19 MUTE O Date output (CXD2545) control
Pin No. Pin Name I/O Function
2 TILT/H O Tilt Filter change
5 SPGC1 O Selection of low band boost (H: 12 cm, L: 8 cm)
6 CD/DVD O DVD/CD (H: DVD, L: CD)
9 Q4 – Not used
12 SPCTL0 O Spindle Control [SPCTL0: SPCTL1]
15 SPCTL1 O
16 CLVH O Spindle CLVH Control
19 Q8 – Not used
[0: 0] = control, [0: 1] = not control, [1: 0] = acceleration,
[1: 1] = deceleration
5-7. D/A CONVERTER (IC722 on MB-75 Board (10/12))
Pin No. Pin Name I/O Function
1 VSS – Ground
2 HYCNTR O Adjustment of hall element output
3 SDCNTR O Target sled speed
4 TI OFFSET O Tilt sensor offset output
5 LOAD/UNLOAD O Loading/Unloading Control
6 TI DRIVE O For tilt forced movement
7 SDINIT O Offset adjusting signal of sled motor drive
8 VDD – Power supply
9 VCC – Power supply
10 A08 – Not used
11 DO O Serial Data Output
12 LD I Serial Data Load
13 CLK I Serial Clock Input
14 DI I Serial Data Input
15 AVCO O For VCO adjustment
16 GND – Ground
Page 29
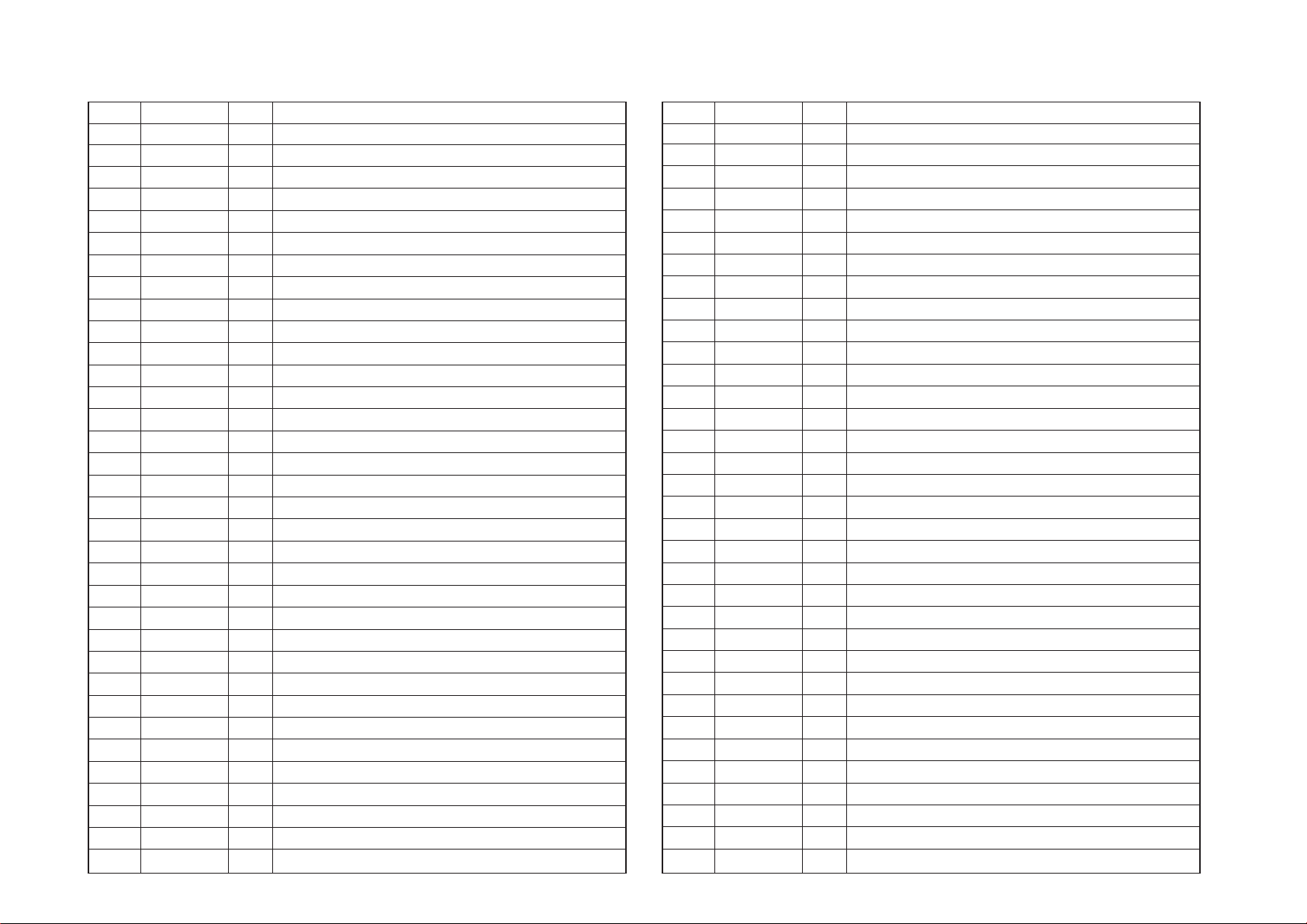
5-4
5-8. SYSTEM CONTROL PIN FUNCTION (IC090 on MB-80 Board (2/12))
Pin No. Pin Name I/O Function Pin No. Pin Name I/O Function
1 IRQ6 I Input of interrupt from CXD1186, CXD8663Q, CXD8669Q
2 IRQ7 I Input of interrupt from CXD1900
3 VSS – Digital ground
4–11 AD0–7 I/O Data bus AD0-AD7
12 VSS – Digital ground
13,14 AD8–9 I/O Data bus AD8, AD9
15 VCC – Digital power supply
16–21 AD10–15 I/O Data bus AD10-AD15
22 VSS – Digital ground
23–30 A0–7 O Address bus A0-A7
31 VSS – Digital ground
32–39 A8–15 O Address bus A8-A15
40 VSS – Digital ground
41,42 A16–17 O Address bus A16, A17
43 VCC – Digital power supply
44–47 A18–21 O Address bus A18-A21
48 CS0 O Chip select signal for external ROM
49 CS1 O Chip select signal for external RAM
50 CS2 – Not used
51 CS3 O Chip select signal for RAM common to drive controller
52 VSS – Digital ground
53 PA0 O Not used
54 PA1 O Output of squeeze mode
55 CS6 O Output of chip select signal to external device
56 WAIT I Input of wait signal
57 WR O Output of write signal
58 PA5 O Output of IF controller serial data control
59 RD O Output of read signal
60 PA7 O Not used
61 VSS – Digital ground
62 PA8 O Output of serial select signal to L chip
63 PA9 O Output of serial select signal to CXD1914
64 PA10 O Output of serial select signal to audio DAC
65 PA11 O Output of error free signal
66 IRQ0 I Input of interrupt signal from SP, BFD, drive controller
67 DREQ0 I Input of DMA request from CK
68 IRQ2 I Input of VSYNC (FID) interrupt signal
69 IRQ3 I Input of interrupt signal from CK, DSP5600
70 VCC – Digital power supply
71 CK O Output of internal clock
72 VSS – Digital ground
73 EXTAL – 20MHz crystal connection pin
74 XTAL – 20MHz crystal connection pin
75 VCC – Digital power supply
76 NMI – Not used
77 VCC – Digital power supply
78 WDTOVF – Not used
79 RES I Input of reset signal
80 MD0 I Input of mode select 0 (fixed to “1”)
81 MD1 I Input of mode select 1 (fixed to “0”)
82 MD2 I Input of mode select 2 (fixed to “0”)
83,84 VCC – Digital power supply
85 AVCC – Analog power supply
86 AVREF – Reference power supply
87 PC0 I Input of DIAG mode select signal
88 PC1 I Input of EMPH signal from CXD2545
89 PC2 I Input of request from drive controller
90 PC3 I Input of request from DSP56000
91 AVSS – Analog ground
92 PC4 I Input of FID signal from CXD1914
93 PC5 I Input of request from I/F controller
94 PC6 I Input of control 1
95 PC7 I Input of control 2
96 VSS – Digital ground
97 PB0 O Output of request to I/F controller
98 PB1 O Output of request to drive controller
99 VCC – Digital power supply
100 PB2 O Output of clock system switching (DVD/CD)
Page 30

5-5
5-5 E
Pin No. Pin Name I/O Function
101 PB3 O Output of reset signal to audio DAC
102 PB4 O Output of reset signal to peripheral device
103 PB5 O Output of serial select signal to DSP56000
104 PB6 O Output of HREQ signal latch reset to DSP56000
105 PB7 O Output of serial select signal to video equalizer
106 VSS – Digital ground
107 RxD0 I Input of serial data from other than CXD1914
108 TxDO1 O Output of serial data to other than CXD1914
109 RxD1 I Input of serial data from CXD1914
110 TxD1 O Output of serial data to CXD1914
111 SCK0 O Output of serial clock to other than CXD1914
112 SCK1 O Output of serial clock to CXD1914
Page 31
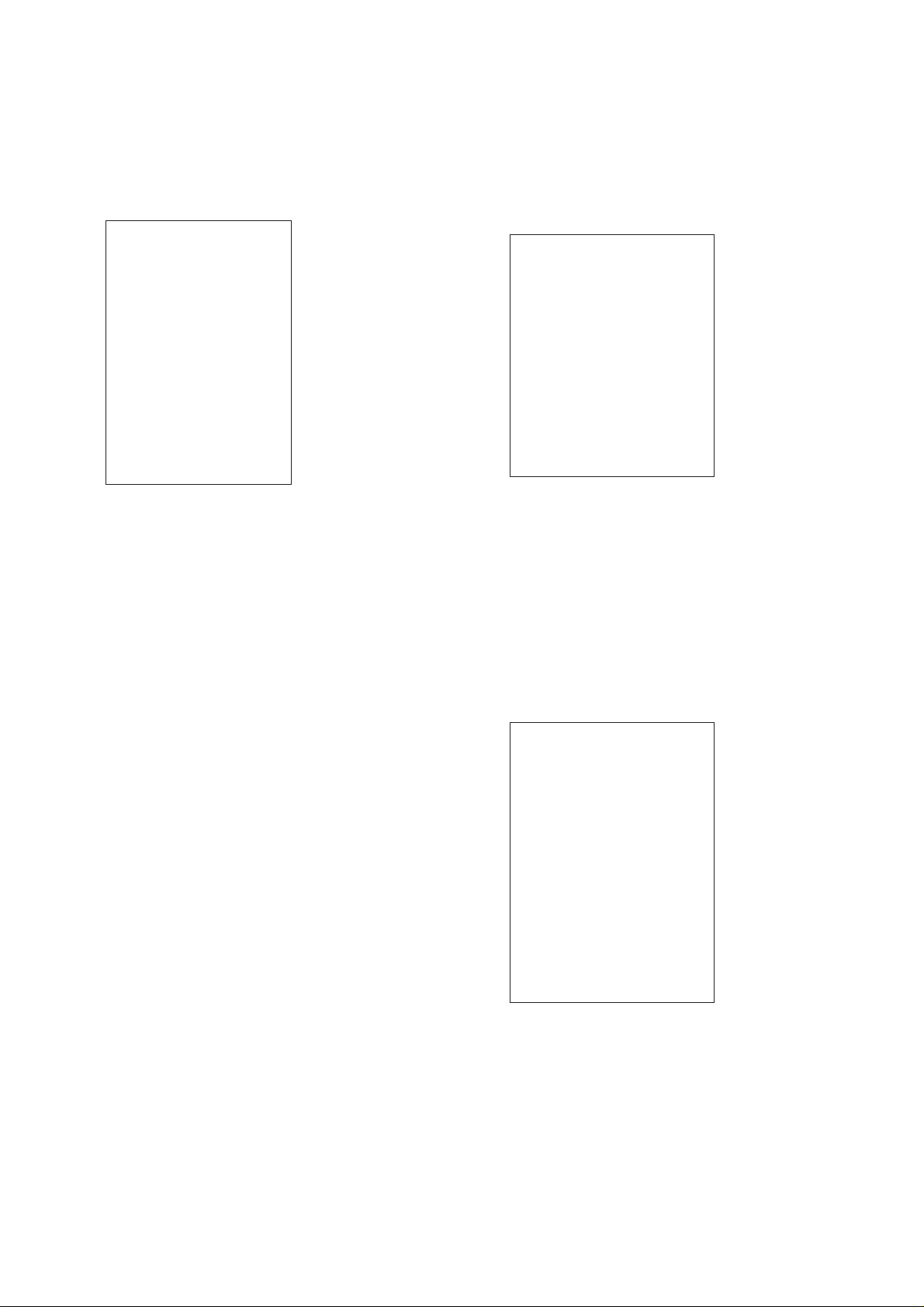
SECTION 6
TEST MODE
DVP-S3000
6-1. Starting up Test Mode
With the DVP-S3000 in standby status, press [TIME], [CLEAR],
and [POWER] keys on the standard commander in this order. And,
the Test mode starts up and the initial menu shown in Figure 1 appears on the video display.
Test Mode Menu
0. Syscon Diagnosis
1. Drive Auto Adjustment
2. Drive Manual Operation
3. Emergency History
4.OtherChecks
Exit: POWER Key
Figure 1 Initial menu
In the Test mode, necessary operations are all done with the keys
on standard commander or operation panel.
The test mode can be finished and the set returns to the power off
status when the [POWER] key is pressed whichever mode, except
during checking of Syscon Diagnosis, you are working in now.
6-2. Syscon Diagnosis
In the Syscon Diagnosis, intermittent blocks such as 0-ff, 500-5ff,
a00-aff, f00-fff, 1400-14ff, etc. (address) are checked. All of the
operation are done with standard commander keys, and a menu cannot be selected but all items are checked. After result display, you
can only select either “continue to next item” or “cancel”, and continue and retry in case of written data error are not available.
If [0] key on standard commander is pressed during initial menu
display, the Diagnosis screen as sho wn in Figure 2 is displayed, and
a checking starts from the top of diagnosis check items list sequentially. After a checking started, standard commander keys are accepted while a message or title is blinking, so that you can go to the
next job.
Syscon Diagnosis
IF con Ver.x.xx (xxxx)
SYScon Ver.x.xx (0000)
DRVcon Ver.0.00 (0000)
ROM Check
SIRCS:ff KEY:ff RATE: 29
Figure 2
In this mode, ROM revision number (Ver. No.) of each control IC
(MPU) and its checksum are displayed. However , Syscon checksum
and Drvcon value are obtained in the process of diagnosis check,
and therefore they are initially 0.
On the fifth line, an item is displayed, and IF control information is
displayed at the bottom though it is not related to a checking of
each item.
If Syscon Diagnosis is selected, a checking starts immediately, and
the result of initial ROM check and Syscon ROM checksum are
displayed as shown in Figure 3.
Syscon Diagnosis
IF con Ver.x.xx (xxxx)
SYScon Ver.x.xx (xxxx)
DRVcon Ver.0.00 (0000)
N Data in ( ) indicates
Syscon checksum
ROM Check
★★ Press Remocon Key★★
SIRCS:ff KEY:ff RATE: 29
Figure 3
6-1
Page 32
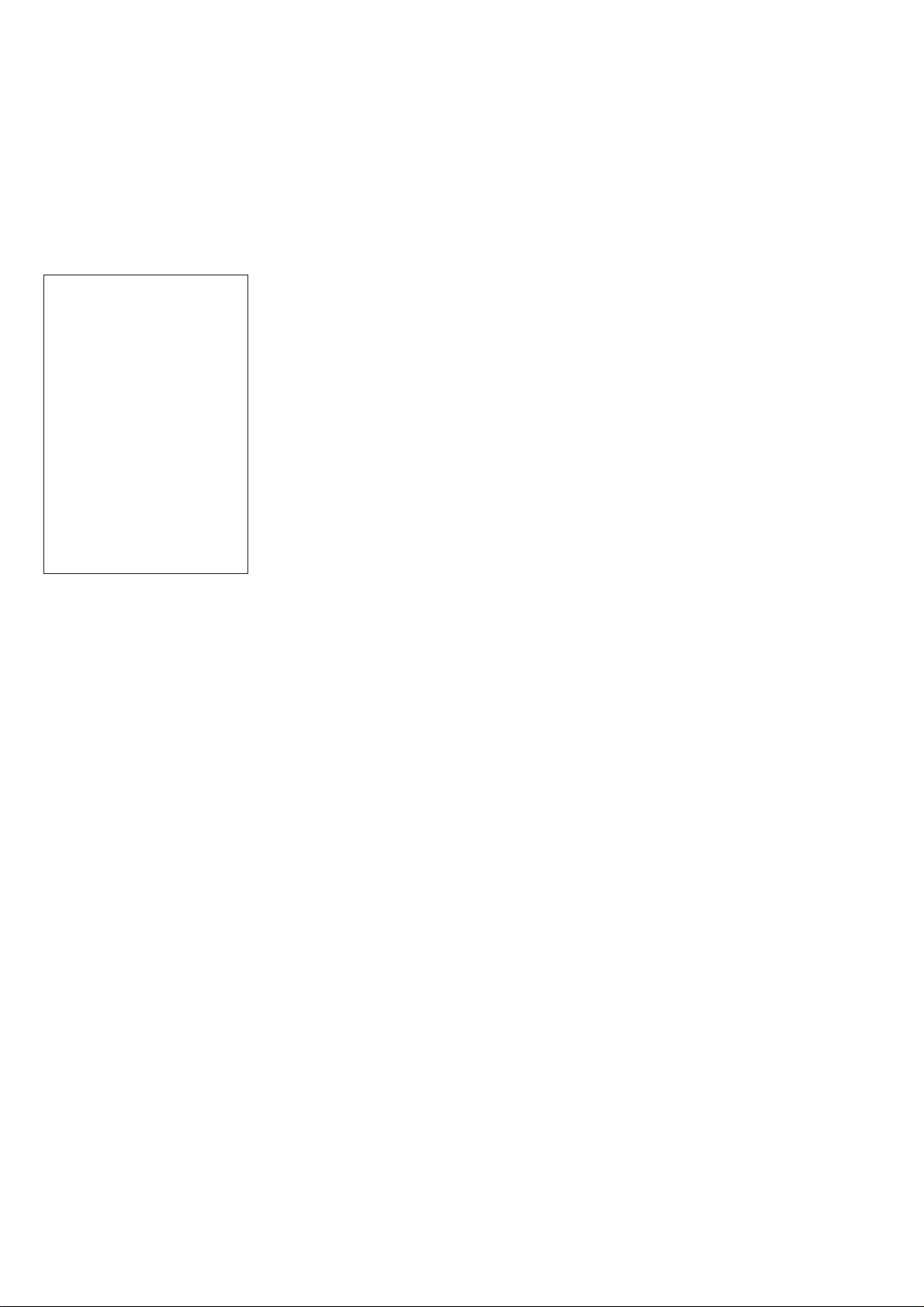
Confirm the result, and to cancel checking, press [RETURN],
[MENU], or [POWER]. Or, to continue next checking, press other
than these keys.
The ROM revision and checksum of Drvcon are displayed when
executing “DrvCon Data Exchange” and “DrvCon EPROM” respectively.
Also, in case of an error, the error code and information are displayed as shown in Figure 4.
Syscon Diagnosis
IF con Ver.x.xx (xxxx)
SYScon Ver.x.xx (xxxx)
DRVcon Ver.x.xx (xxxx)
CXD 1900BQ DRAM
Error Code: 05
Address: 000abcde
Write Data: fb
Read Data: ff
SIRCS:ff KEY:ff RATE: 29
Figure 4
N Name of item checked
N Error code
N Error address
N Written data (2/4 digits)
N Read data (2/4 digits)
(2-3) Syscon RAM (IC094) check
IC093 (Syscon ROM) n IC094 (Syscon RAM) collating check
Checking range: 0x01000000 - 0x0101ffff
IC093 (Syscon ROM) data (program codes) are transferred in DMA
mode in the unit of 64 bytes to the IC094 (Syscon RAM), then they
are read every 1 byte and compared with data in IC093. As the
Syscon RAM check is made by saving the data into internal RAM
(DMA transfer), the data are written and read every 64 bytes, and
interruption during that time is completely masked.
If compared data are not same, a checking is suspended, and error
code 05, its address, written data, and read data are displayed. Select the subsequent processing by pressing a key. As this check is
made through DMA transfer, if Repeat is selected, the data are transferred in DMA mode again to the block where this error occurred
and a checking is continued from the error address.
(3) Clock
(3-2) Audio clock system output switching (CD side)
I/O output
The audio clock system is switched to the CD side. In this check,
the Syscon itself does not detect an error. Observe output signals
with an instrument.
(3-3) Audio clock system output switching (DVD side)
Except error code “05” (write/read data mismatch error), the address and data fields show “0”. When a checking is over or cancelled, “Diag OK” or “Diag Error End” message blinks. If a key is
pressed here, the test mode initial menu is resumed. The “Diag
Error End” is displayed only when the Syscon detects an error, and
visual inspection result is out of the display.
6-2-1. General description of checking method
This section describes briefly a checking method for each item in
the order of menus.
Numbers in ( ) for respective items are diagnosis item numbers.
(2) Memory
(2-2) Syscon ROM (IC093) check
Calculation of checksum
Calculation range: 0x00000000 - 0x000fffff (at commercial products, 8Mbit ROM)
All 8bit data from address 0 to ROM size are added (checksum),
and output as 4-digit hexadecimal number.
In this check, the IC090 (Syscon) itself does not detect an error.
The result is displayed on the screen. Compare it with original ROM
checksum.
I/O output
The audio clock system is switched to the DVD side. In this check,
the Syscon itself does not detect an error. Observe output signals
with an instrument.
(4) Drvcon
(4-2) Drvcon (IC136) reset check
Hard Reset n DR V B USY response input
The Hard Reset signal is output, and after cancelling the reset,
whether DRV BUSY signal changes from “low” to “high” is
checked. The detection timing of DRV BUSY “low” is about 250
msec after the reset is cancelled. Also, whether the signal becomes
“high” later is checked.
After confirming “high” or “low” of DRV BUSY signal 250 msec
after reset was cancelled, if the signal does not go “high” though
about 300 msec elapsed, the reset error 02 is output.
6-2
Page 33

(4-3) Drvcon common RAM (IC138) check
(4-6) Drvcon SRAM check
IC093 (Syscon ROM) n IC138 (common RAM) collating check
Checking range: 0x03000001 - 0x03000fff
After confirming that the RAM areas common to Drvcon are not
occupied by Drvcon (namely, the contents of common RAM addresses are true), the IC093 (Syscon RAM) codes are copied to the
IC138 (common RAM) areas from address 1, then the data are read
for checking. If all are same, the IC093 code bits are inverted and
checked again. If compared data are not same, a checking is suspended, and error code 05, its address, written data, and read data
are displayed.
After checking, reset the Drvcon because irregular values are written to the IC138.
If common RAM areas are occupied by Drvcon and they are not
opened even after about 2 seconds, the write error 03 is output.
(4-4) Drvcon data exchange check
IC090 (Syscon) n IC136 (Drvcon), IC136 (Drvcon) n IC090
(Syscon) command path check
The path check command is sent from IC090 (Syscon) to IC136
(Drvcon), and as a result, whether the data same as sent data is
returned to the IC138 (common RAM) is checked. In the Syscon
Diagnosis, only the ROM revision is displayed. If no response is
returned from Drvcon or the data are not same, the error code 73 is
output.
(4-5) Drvcon interrupt line check
IC136 (Drvcon) n IC090 (Syscon), IC090 (Syscon) n IC136
(Drvcon) interrupt line check
If CXD8663Q check command is sent from IC090 to IC136, the
IC136 returns IC181 (CXD8663Q) register read/write command.
Receiving this command, the IC090 outputs a response signal implying that the interrupt signal was received, then the IC136 confirms this signal input and writes the Command Done to the IC138
(common RAM).
When the Command Done is not returned even after 1 second, the
error code 70 (DRV INT is not detected) is output if the interrupt
signal has not been received, or the error code 71 (Drvcon does not
recognize SYS INT) is output if the interrupt signal has been received.
Also, upon detection of an error in IC181 (CXD8663Q) by this
command, the error code 30 is output.
If DRV INT signal is kept “low”, the Syscon repeats an interrupt
processing continuously, thus making error displa y impossible. For
this reason, only for this command, the Drvcon returns the DRV
INT signal to “high” even if SYS INT is not detected. (The Syscon
makes judgment whether Command Done is returned or not.)
Here, if the Syscon makes no response, the DRV INT signal itself
will be faulty.
IC090 (Syscon) n IC136 (Drvcon) check request command
The SRAM check command is sent from IC090 to IC136, and its
response result is displayed.
In case of an error, the error information of Drvcon is read, then the
error code 05, error address, written data, and read data are displayed.
(4-7) EEPROM check
IC090 (Syscon) n IC136 (Drvcon) check request command
The EEPROM check command is sent from IC090 to IC136, and
its response result is displayed.
The error code 74 when IC139 (EEPROM) write signal is not ready ,
or error code 05 when written data and read data are not same, error
address, written data, and read data are displayed.
(4-8) RF Processor check
IC090 (Syscon) n IC136 (Drvcon) check request command
The RF processor check command is sent from IC090 to IC136,
and its response result is displayed.
In case of an error in IC770 (RF processor), the error code 76 is
output.
(4-9) CXD2545 RAM check
The CXD2545 check command is sent from IC090 to IC136, and
its response result is displayed.
In case of an error in IC717 (CXD2545), the error code 75 is output.
(4-10) Drvcon ROM check
IC090 n IC136 check request command
The EPROM check command is sent from IC090 to IC136.
The Drvcon calculates checksum of IC140 (EPROM), and returns
its result and the checksum value is displayed, if there is no error.
Compare the result displayed on the screen with the checksum of
original EPROM.
(4-11) VCO offset automatic adjustment
IC090 n IC136 check request command
The VCO offset automatic adjust command is sent from IC090 to
IC136.
If automatic adjustment failed, the error code 77 is output.
(5) Data supply system
(5-2) IC217 (CXD8598R) reset check
Write to register n Hard reset n Read from register
Registers to be checked: TSC2 (0x06200011)
TSC1 (0x06200012)
TSC0 (0x06200013)
Data other than 0 are written to readable and writable registers in
IC217 (CXD8598R), and they are read after hard reset, then the
error code 02 is output if they are not cleared to 0.
6-3
Page 34

(5-3) IC217 (CXD8598R) register check
Register write n Register read collating check
As SERR signal from IC181 (CXD8663Q) to IC217 (CXD8598R)
is not initialized, this signal line is shut off and fixed to “high” before checking.
Registers to be checked: TSC2 (0x06200011)
TSC1 (0x06200012)
TSC0 (0x06200013)
Incrementing 1 each starting from 0, data are written to readable
and writable registers, then they are read for checking. Incrementing
initial value by 1 each, a check is repeated 256 times.
If compared data are not same, a checking is suspended, and error
code 05, its address, written data, and read data are displayed.
(5-4) IC181 (CXD8663Q) reset check
Write to register n Hard reset n Read from register
Register to be checked: INTRMASK (0x22)
Data other than 0 are written to readable and writable register in
IC181 (CXD8663Q), and they are read after hard reset, then the
error code 02 is output if they are not cleared to 0.
(5-5) IC181 (CXD863Q) register check
Register write n Register read collating check
Register mask data to be checked
0x20 0xbf
0x22 0xff
0x25 0xff
0x26 0xff
0x27 0xff
Incrementing 1 each starting from 0, data are written to readable
and writable registers, then they are read for checking. Incrementing
initial value by 1 each, a check is repeated 256 times. However,
some bits that cannot be written are masked.
If compared data are not same, a checking is suspended, and error
code 05, its address, written data, and read data are displayed.
(5-6) IC181 (CXD8663Q) DRAM check
ROM n IC181 (CXD8663Q) n DRAM n IC181 (CXD8663Q)
read collating check
Checking range: 0x00000000 - 0x0007ffff
ROM pattern is copied to all areas to be checked. Each time 256
bytes are copied, 255 bytes of original (ROM) address are returned.
A reading check is made after data are written to all areas.
If compared data are not same, a checking is suspended, and error
code 05, its address, written data, and read data are displayed.
(5-7) IC181 (CXD8663Q) interrupt line check
(5-8) IC181 (CXD8663Q) to IC217 (CXD8598R) connection check
IC093 (Syscon ROM) n IC181 (CXD8663Q) n IC217
(CXD8598R)
DVD bit stream data stored in IC093 are transferred to the IC182
(external DRAM of IC181), and IC217 (CXD8598R) transfer end
interruption is checked, which occurs by flowing data to the IC217
(CXD8598R). If the transfer end interruption is not detected, the
error code 21 is output.
As SERR signal from IC181 (CXD8663Q) to IC217 (CXD8598R)
is not initialized, this signal line is shut off and fixed to “high” before checking.
(5-9) IC184 (CXD8669AQ) reset check
Write to register n Hard reset n Read from register
Register to be checked: SYSINI (0xe1)
Data other than 0 are written to readable and writable register in
IC184 (CXD8669AQ), and they are read after hard reset, then the
error code 02 is output if they are not cleared to 0.
(5-10) IC184 (CXD8669AQ) register check
Register write n Register read collating check
Register mask data to be checked
0xe0 0x80
0xe1 0xff
0xe4 0xc0
0xe5 0xc0
0xe6 0xf8
Incrementing 1 each starting from 0, data are written to readable
and writable registers, then they are read for checking. Incrementing
initial value by 1 each, a check is repeated 256 times. However,
some bits that cannot be written are masked.
If compared data are not same, a checking is suspended, and error
code 05, its address, written data, and read data are displayed.
(5-11) IC216 (CXD1186) reset check
Write to register n Hard reset n Read from register
Registers to be checked: DADRC_L (0x06380007)
DADRC_H (0x06380008)
HXFRC_L (0x06380009)
HXFRC_H (0x0638000A)
HADRC_L (0x0638000B)
HADRC_H (0x0638000C)
IC093 (Syscon ROM) n IC181 (CXD8663Q) n IC217
(CXD8598R)
DVD bit stream data stored in IC093 are transferred to the IC182
(external DRAM of IC181), and the SD bus sector header detect
interruption is checked, which occurs by flowing data to the IC217
(CXD8598R).
If the header of SD bus sector in IC181 (CXD8663Q) is not
detected, the error code 31 is output.
Data other than 0 are written to readable and writable register in
IC216 (CXD1186), and they are read after hard reset, then the error
code 02 is output if they are not cleared to 0.
6-4
Page 35

(5-12) IC216 (CXD1186) register check
Register write n Register read collating check
Registers to be checked: DADRC_L (0x06380007)
DADRC_H (0x06380008)
HXFRC_L (0x06380009)
HXFRC_H (0x0638000A)
HADRC_L (0x0638000B)
HADRC_H (0x0638000C)
Incrementing 1 each starting from 0, data are written to readable
and writable registers, then they are read for checking. Incrementing
initial value by 1 each, a check is repeated 256 times.
If compared data are not same, a checking is suspended, and error
code 05, its address, written data, and read data are displayed.
(5-13) IC216 (CXD1186) SRAM check
IC093 (Syscon ROM) n IC216 (CXD1186) n IC215 (SRAM)
n IC216 read collating check
Checking range: 0x00000000 - 0x00007fff
IC093 ROM pattern is copied to all areas to be checked. Each time
256 bytes are copied, 255 bytes of original (ROM) address are returned. A reading check is made after data are written to all areas.
After SRAM write addresses are set, error code 03 when writing is
not ready, or after read addresses are set, error code 04 when reading is not ready is output, then a check is finished.
Also, if compared data are not same, a check is suspended, and
error code 05, its address, written data, and read data are displayed.
(5-14) IC216 (CXD1186) to IC217 (CXD8598R) connection check
IC093 (ROM) n IC216 (CXD1186) n IC217 (CXD8598R)
VCD bit stream data stored in IC093 are transferred to the IC215
(external SRAM of IC216), and IC217 (CXD8598R) transfer end
interruption is checked, which occurs by flowing data to the IC217
(CXD8598R).
If the transfer end interruption is not detected, the error code 21 is
output.
Further, SCR is read to check its value. If the v alue is not the one in
sector transferred, the error code 22 is output.
Incrementing 1 each starting from 0, data are written to readable
and writable register, then the y are read for checking. Incrementing
initial value by 1 each, a check is repeated 256 times. However,
some bits that cannot be written are masked.
If compared data are not same, a checking is suspended, and error
code 05, its address, written data, and read data are displayed.
(6-4) IC281 (CXD1900BQ) DRAM check
IC093 (ROM) n IC281 n IC280, IC282 n NIC284 (DRAM)
n IC281 read collating check
Checking range: 0x00000000 - 0x0003fff f (data bus width = 64bits)
IC093 ROM pattern is copied to all areas to be checked. Because of
large DRAM capacity , each time 256 bytes are copied, 255 bytes of
original (IC093) address are returned. A reading check is made
after data are written to all areas.
The error code 03 when writing is not ready, or error code 04 when
reading is not ready is output, then a check is finished.
Also, if compared data are not same, a check is suspended, and
error code 05, its address, written data, and read data are displayed.
However, the data are displayed every 8 bits, though the b us width
of IC281 (CXD1900BQ) is 64 bits. Namely, actual address is the
displayed value shifted by 3 bits to the right where lower 3 bits
indicate the byte position.
For example, in the case of display shown below:
IC281 (CXD1900BQ) DRAM
Error Code: 05
Address: 000abcde
Write Data: fb
Read Data: ff
If displayed value 0 0 0 A B C D E is expressed with binary number, 0000 0000 0000 1010 1011 1100 1101 1110.
If it is shifted by 3 bits to the right, 0000 0000 0000 0001 0101 0111
1001 1011 110. That is, assuming that the top of address 0 0 0 1 5
7 9 B in hexadecimal notation is 0th byte, the 6th byte is erroneous
such as FB n FF (as for the bit position in the same manner, the
53rd bit is 0 n 1, assuming that MSB is 0th and LSB is 63rd).
(6-5) CXD1914 VSync check
IC475 (CXD1914Q) VSync interrupt cycle measurement
(6) Video Decoder
(6-2) IC281 (CXD1900BQ) reset check
Write to register n Hard reset n Read from register
Register to be checked: PLYMOD (0x06080002)
Data other than 0 are written to readable and writable register in
IC281 (CXD1900BQ), and they are read after hard reset, then the
error code 02 is output if they are not cleared to 0.
(6-3) IC281 (CXD1900BQ) register check
Register write n Register read collating check
Register to be checked: PLYMOD (0x06080002)
The VSync interruption is enabled for about 160msec, and the number of VSync interruption from NTSC encoder is counted. The operation is normal if the count is more than 9 times and less than 11
times. If out of this range, the error code 41 is output.
The SCI1 interruption is also enabled, as the NTSC encoder processing is required due to VSync interruption.
(6-6) IC281 (CXD1900BQ) VSync interrupt line check
IC281 (CXD1900BQ) VSync interrupt detection check
The VSync interruption of IC281 (CXD1900BQ) is enabled and
whether interruption is made is checked. If no interruption is made
though 2 seconds elapsed, the error code 41 is output.
(6-7) IC217 (CXD8598R) to IC281 (CXD1900BQ) connection
6-5
Page 36

check
IC093 n IC216 n IC215 n IC216 n IC217 n IC281 n
IC280,
IC282 ~ NIC284
IC093 (ROM) n IC312 (CXD8600R) n IC313, IC319 (SRAM)
n IC312 read collating check
Checking range: 0x00000001 - 0x0003ff000
VCD bit stream data stored in IC093 are transferred via IC216
(CXD1186) to the IC215 (SRAM), and the sequence header interruption and transfer end interruption from IC281 are checked, which
occur by flowing data to the IC281 (CXD1900BQ) via IC216
(CXD1186) and IC217 (CXD8598R).
The error code 21 when transfer end interruption for transferred
sectors is not detected, or error code 42 when sequence header interruption is not detected is output.
(7) Subpictures
(7-2) IC312 (CXD8600R) reset check
Write to register n Hard reset n Read from register
Register to be checked: WRITE_READ_TOP (0x06000050)
Data other than 0 are written to readable and writable register in
IC312 (CXD8600R), and they are read after hard reset, then the
error code 02 is output if they are not cleared to 0.
(7-3) IC312 (CXD8600R) register check
Register write n Register read collating check
Registers to be checked: VB_LUMINANCE (0x06000050)
VB_LUMINANCE+1
VB_LUMINANCE+2
VB_LUMINANCE+3
VB_LUMINANCE+4
VB_LUMINANCE+5
VB_LUMINANCE+6
VB_LUMINANCE+7
VB_LUMINANCE+8
VB_LUMINANCE+9
VB_LUMINANCE+A
VB_LUMINANCE+B
VB_LUMINANCE+C
VB_LUMINANCE+D
VB_LUMINANCE+E
VB_LUMINANCE+F
The IC312 (CXD8600R) cannot designate read/write address of
SRAM. Internal pointer manages the addresses automatically. Accordingly, the reading order is same as the writing order.
IC093 pattern is copied to all areas to be checked. Each time 256
bytes are copied, 255 bytes of original (IC093) address are returned.
A reading check is made after data are written to all areas. As the
Syscon Diagnosis is a simplified check, actual check range is 1/5 of
the above mentioned checking range.
Unlike other RAM checks, the addresses are not skipped. The address 0 in each area has specific meaning, and therefore arbitrary
data cannot be written.
After the fixed data is written to address 0, a check starts from address 1, and the last 255 bytes are not checked because of a complicated program.
If compared data are not same, a check is suspended, and error code
05, its address, written data, and read data are displayed.
However, IC312 (CXD8600R) cannot designate an address, and
the repeat check is ignored.
Also, in case of an error in VB, 0x10000000 is added to the address
for explicit discrimination.
(7-5) IC217 (CXD8598R) to IC312 (CXD8600R) connection check
IC093 (ROM) n IC181 (CXD8663Q) n IC217 (CXD8598R)
n IC312 (CXD8600R)
The bit stream data including subpictures stored in IC093 (ROM)
are transferred to the IC182 (external DRAM of IC181). Then, SP
Arrive signal from IC312 is checked, which is generated by flowing the data to the IC312 (CXD8600R) via IC217 (CXD8598R).
The error code 61 is output when data arrival cannot be confirmed
though 2 seconds elapsed after data transfer request was sent to the
IC181 (CXD8663Q).
As SERR signal from IC181 (CXD8663Q) to IC217 (CXD8598R)
is not initialized, this signal line is shut off and fixed to “high” before checking.
When an error occurred, confirm (5-8) IC181 (CXD8663Q) to IC217
(CXD8598R) connection check.
(7-6) IC312 (CXD8600R) interrupt line check
The values written to the registers in IC312 (CXD8600R) are read
from the same address WRITE_READ_TOP in an y registers. Therefore, the Diagnosis function cannot read data after data were written to all registers. A checking is made by reading every register.
If compared data are not same, a check is suspended, and error code
05, its address, written data, and read data are displayed.
(7-4) IC312 (CXD8600R) SRAM check
IC093 (ROM) n IC181 (CXD8663Q) n IC217 (CXD8598R)
n IC312 (CXD8600R)
The bit stream data including subpictures stored in IC093 (ROM)
are transferred to the IC182 (external DRAM of IC181). Then, the
PTS interrupt is checked, which occurs by flowing the data to the
IC312 (CXD8600R) via IC217 (CXD8598R).
The error code 62 is output when an interruption cannot be confirmed though 2 seconds elapsed after data transfer request was
sent to the IC181 (CXD8663Q).
As SERR signal from IC181 (CXD8663Q) to IC217 (CXD8598R)
is not initialized, this signal line is shut off and fixed to “high” before checking.
When an error occurred, confirm (5-8) IC181 (CXD8663Q) to IC217
(CXD8598R) connection check.
(8) Video Related
6-6
Page 37

(8-2) Video encoder check (color bar output)
I/O output
The color bar is turned on for the NTSC encoder color bar enable
command IC475 (NTSC encoder).
In this check, the Syscon itself does not detect an error.
Confirm the video display screen.
(8-3) Video output check
IC093 (ROM) n IC216 (CXD1186) n IC217 (CXD8598R) n
IC281 (CXD1900BQ) n Video signal output
The bit stream data of still picture stored in IC093 (ROM) are transferred to the IC215 (SRAM of IC216), then the picture is displayed
on the video screen by flowing data to the IC281 (CXD1900BQ)
via IC217 (CXD8598R). If an error is present in any path, that code
is output and a checking is finished.
If no error is found, the controller waits for key entry.
Check the video display screen.
(8-4) IC310 (CXD8602Q) check (letter box output)
IC093 (ROM) n IC216 (CXD1186) n IC217 (CXD8598R) n
IC281 (CXD1900BQ) n IC310 (CXD8602Q) n Video signal
output
The bit stream data of still picture stored in IC093 (ROM) are transferred to the IC215 (SRAM of IC216), then the picture is displayed
on the video screen by flowing data to the IC281 (CXD1900BQ)
via IC217 (CXD8598R). In such a case, the letter box on command
is output on the IC310 (CXD8602Q).
If no error is found, the controller waits for key entry.
Check the video display screen.
(8-5) Video equalizer check (brightness control)
IC093 (ROM) n IC216 (CXD1186) n IC217 (CXD8598R) n
IC281 (CXD1900BQ) n IC317 (CXD8664Q) n Video signal
output
The bit stream data of still picture stored in IC093 (ROM) are transferred to the IC215 (SRAM of IC216), then the picture is displayed
on the video screen by flowing data to the IC281 (CXD1900BQ)
via IC217 (CXD8598R).
If no error is found, the brightness change command is sent to the
IC317 (CXD8664Q). The controller waits for key entry after changing the brightness twice.
Confirm that the brightness of video display screen changes.
(8-6) Subpicture output check
IC093 (ROM) n IC181 (CXD8663Q) n IC217 (CXD8598R)
n IC312 (CXD8600R) n Video signal output
The bit stream data including subpicture stored in IC093 (ROM)
are transferred to the IC312 (CXD8600R) via IC181 (CXD8663Q)
and IC217 (CXD8598R), and the picture is displayed on the video
screen unless an error is found.
Check the video display screen.
Make S-terminal output potential 0V.
In this check, the Syscon itself does not detect an error.
Observe the potential at the S-terminal with an instrument.
(8-8) S-terminal output check (5V)
I/O output
Make S-terminal output potential 5V.
In this check, the Syscon itself does not detect an error.
Observe the potential at the S-terminal with an instrument.
(8-9) S-terminal output check (2.5V)
(9) Audio Related
(9-2) IC380 (CXD8603R) reset check
Write to register n Hard reset n Read from register
Register to be checked: RAADRS (0x06100004)
Data other than 0 are written to readable and writable register in
IC380 (CXD8603R), and they are read after hard reset, then the
error code 02 is output if they are not cleared to 0.
Though this register has 16-bit length, MSB is always 0.
(9-3) IC380 (CXD8603R) register check
Register write n Register read collating check
Register to be checked: RAADRS (0x06100004)
Incrementing 1 each starting from 0, data are written to readable
and writable register, then the y are read for checking. Incrementing
initial value by 1 each, a check is repeated 32768 times.
If compared data are not same, a checking is suspended, and error
code 05, its address, written data, and read data are displayed. Because of 16-bit length, 4-digit data is displayed (however, MSB is
always 0).
(9-4) IC380 (CXD8603R) SRAM check
IC093 (ROM) n IC380 (CXD8603R) n IC383 (SRAM) n
IC380 read collating check
Checking range: 0x00000000 - 0x00007fff
IC093 (ROM) pattern is copied to all areas to be checked. Each
time 256 bytes are copied, 255 bytes of original (IC093) address
are returned. A reading check is made after data are written to all
areas.
The data write/read to IC383 (SRAM) are executed every 256 bytes
using the direct access function of the IC380 (CXD8603R). If compared data are not same, a checking is
suspended, and error code 05, its address, written data, and read
data are displayed.
(8-7) S-terminal output check (0V)
(9-5) IC217 (CXD8598R) to IC380 (CXD8603R) connection check
6-7
Page 38

IC093 (ROM) n IC216 (CXD1186) n IC217 (CXD8598R) n
IC380 (CXD8603R) SRAM read collating check
(CXD8603R) is read for checking.
The error code 10 is output if the data are not same as original bit
stream data.
The bit stream data of MPEG-AUDIO stored in IC093 (ROM) are
transferred by only one sector to the IC215 (external SRAM of
IC216), then they are flown to the IC380 (CXD8603R) via IC217
(CXD8598R).
If no error is found, the data are transferred to the SRAM in IC380
(CXD8603R) and compared with original ROM data.
The first 512 bytes in code buff er are read from IC380 (CXD8603R)
SRAM into internal RAM of CPU, and whether 256 byte pattern
after 12th bytes in effectiv e area of MPEG-AUDIO bit stream data
stored in ROM is contained is searched. If not found, the pattern to
be searched is shifted one byte each, and a searching is repeated
maximum 256 times. The check passed if 256 bytes are same successively.
If same pattern is not found, the error code 10 is output.
(9-6) Audio decoder boot check
AC-3 codes are downloaded to the audio decoder.
The error code 50 if download is not terminated successfully, or
error code 51 if AC-3 codes downloading failed is output.
When an error occurred here, the subsequent audio related diagnosis may be rejected, resulting in unconditional output of error code
50.
(9-7) IC380 (CXD8603R) interrupt line check
IC093 (ROM) n IC181 (CXD8663Q) n IC217 (CXD8598R) n
IC380 (CXD8603R)
The bit stream data including Navi Pack stored in IC093 (ROM)
are transferred to the DRAM of IC181 (CXD8663Q). Then, the
Navi Ready interruption is checked, which occurs by flowing the
data to the IC380 (CXD8603R) via IC217 (CXD8598R).
The error code 55 is output when an interruption cannot be confirmed though 2 seconds elapsed after data transfer request was
sent to the IC181 (CXD8663Q).
As SERR signal from IC181 (CXD8663Q) to IC217 (CXD8598R)
is not initialized, this signal line is shut off and fixed to “high” before checking.
When an error occurred, confirm (5-8) IC181 (CXD8663Q) to IC217
(CXD8598R) connection check.
(9-8) DREQ/NCST check
(9-9) MPEG audio digital output check
IC093 (ROM) n IC216 (CXD1186) n IC217 (CXD8598R) n
IC380 (CXD8603R) n Digital Audio I/F audio signal output
The bit stream data of MPEG-Audio stored in IC093 (ROM) are
transferred to the IC216 (CXD1186). Then, the data are flown to
the Digital Audio Interface via IC217 (CXD8598R) and CK to regenerate audio signals.
For the data, audio frequencies are different between left and right
channels. Using left and right channels mixing function, the same
stream is checked three times in the order of left channel, right channel, and both channels on.
In this diagnosis, the kind of expected errors is many because of
complicated paths, but the diagnosis is finished upon detection of
an error.
Confirm the content of error from the error code list.
If no error is detected, a sound is generated three times, then a message is output and the controller waits for key entry.
(9-10) MPEG audio analog output check
IC093 (ROM) n IC216 (CXD1186) n IC217 (CXD8598R) n
CK n Analog Audio I/F audio signal output
The bit stream data of MPEG-Audio stored in IC093 (ROM) are
transferred to the IC216 (CXD1186). Then, the data are flown to
the Analog Audio Interface via IC217 (CXD8598R) and CK to regenerate audio signals.
For the data, audio frequencies are different between left and right
channels. Using left and right channels mixing function, the same
stream is checked three times in the order of left channel, right channel, and both channels on.
In this diagnosis, the kind of expected errors is many because of
complicated paths, but the diagnosis is finished upon detection of
an error.
Confirm the content of error from the error code list.
If no error is detected, a sound is generated three times, then a message is output and the controller waits for key entry.
(9-11) Audio attenuator check
IC093 (ROM) n IC216 (CXD1186) n IC217 (CXD8598R) n
IC380 (CXD8603R) n Analog Audio I/F audio signal output
IC093 (ROM) n IC181 (CXD8663Q) n IC217 (CXD8598R) n
IC380 (CXD8603R) read data pattern check
The bit stream data including Navi Pack stored in IC093 (ROM)
are transferred to the DRAM of IC181 (CXD8663Q). Then, the
data are flown to the IC380 (CXD8603R) via IC217 (CXD8598R).
The error code 55 is output when Navi Ready interruption cannot
be confirmed though 2 seconds elapsed after data transfer request
was sent to the IC181 (CXD8663Q).
As SERR signal from IC181 (CXD8663Q) to IC217 (CXD8598R)
is not initialized, this signal line is shut off and fixed to “high” before checking.
When an error occurred, confirm (5-8) IC181 (CXD8663Q) to IC217
(CXD8598R) connection check.
If no error is found, the Navi Pack transferred to the SRAM in IC380
The bit stream data of MPEG-Audio stored in IC093 (ROM) are
transferred to the IC216 (CXD1186). Then, the data are flown to
the Analog Audio Interface via IC217 (CXD8598R) and IC380
(CXD8603R) to regenerate audio signals.
In such a case, DAC attenuation value is set to 1/4 of normal value
to lower the volume.
For the data, audio frequencies are different between left and right
channels. Using left and right channels mixing function, the same
stream is checked three times in the order of left channel, right channel, and both channels on.
In this diagnosis, the kind of expected errors is many because of
complicated paths, but the diagnosis is finished upon detection of
an error.
Confirm the content of error from the error code list.
If no error is detected, a sound is generated three times, then a mes-
6-8
Page 39

sage is output and the controller waits for key entry.
Check if the volume level becomes lower (about half) than that in
(9-10).
(9-12) AC-3 audio output check
IC093 (ROM) n IC181 (CXD8663Q) n IC217 (CXD8598R) n
IC380 (CXD8603R) n Audio signal output
The bit stream data including AC-3 audio stored in IC093 (ROM)
are transferred to the DRAM of IC181 (CXD8663Q). Then, the
data are flown to the IC380 (CXD8603R) via IC217 (CXD8598R)
to regenerate audio signals.
As SERR signal from IC181 (CXD8663Q) to IC217 (CXD8598R)
is not initialized, this signal line is shut off and fixed to “high” before checking.
This diagnosis turns on all channels to turn on both analog and
digital outputs.
If no error is detected, a sound is generated, then a message is output and the controller waits for key entry.
g Diagnosis Error code list
01: A mode not supported was selected
02: Reset error
03: Data write error
04: Data read error
05: Written and read data are not same
91: Check of this item is cancelled by key entry
92: Check of all items is cancelled by key entry
99: Other errors
10: Data transfer error between chips
12: Stop by time out
21: IC217 (CXD8598R) transfer end interrupt is not detected
22: IC217 (CXD8598R) SCR not same
30: Drvcon detects an error in IC181 (CXD8663Q)
31: IC181 (CXD8663Q) SD bus sector header is not detected
41: Vsync interrupt is not detected
42: Sequence header is not detected
50: Audio related chips initialize error
51: Audio stream change error
52: Audio decoder is not in play mode
53: Audio decoder is not in stop mode
54: IC380 (CXD8603R) chip PTS is not detected
55: IC380 (CXD8603R) chip NAVI is not detected
56: No data arrives at IC380 (CXD8603R) chip code buffer
57: No data in IC380 (CXD8603R) chip code buffer is consumed
61: No sub-picture data arrives
62: Sub-picture PTS is not detected
70: DRV INT is not detected
71: Drvcon does not recognize SYS INT
72: Drvcon does not make a response
73: Drvcon communication data error
74: Drvcon EEPROM busy time out
75: Drvcon CXD2545 NG
76: Drvcon RF processor NG
77: Drvcon VCO preset NG
90: Error judged by inspector
6-9
Page 40
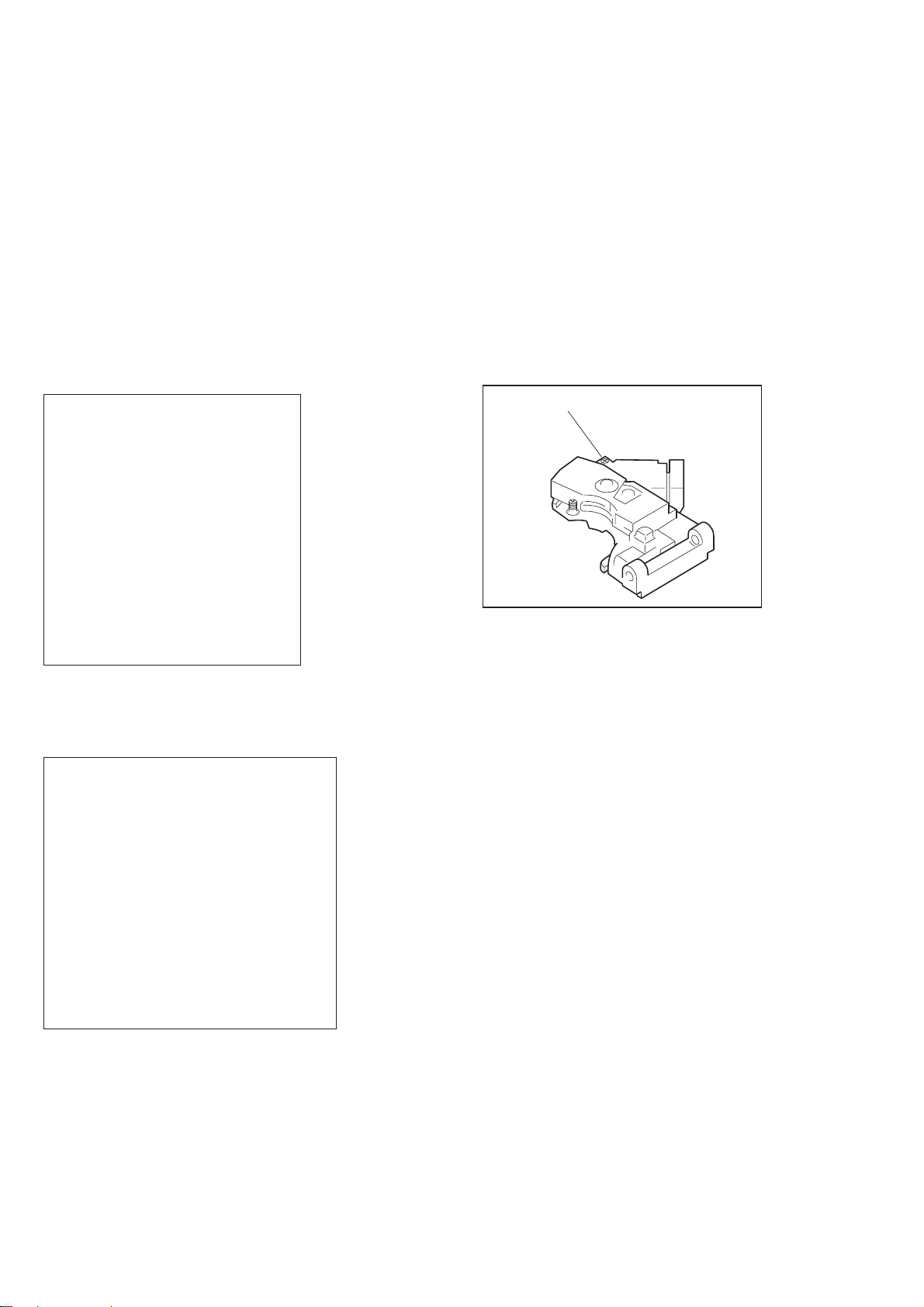
6-3. Drive Auto Adjustment
The drive can be automatically adjusted, except disc change and
tangential skew adjustment. For a disc, use the disc for adjustment.
In case of abnormality, press the [stop] key to stop adjustment.
If the drive does not stop, prevent secondary failure by taking proper
action such as disconnection of the power cable. This adjustment
should be made after repair is finished and no trouble is present in
the drive.
A trouble, if present, causes NG and the adjustment to be aborted.
As the secondary failure could occur, perform automatic adjustment after the drive is completely repaired.
With the initial menu displayed, press [1] on standard commander,
and the screen as shown in Figure 5 will appear.
The tray opens after the ENTER key is pressed and the initialization is finished. Then, place the D VD_SL disc for adjustment. Press
the ENTER key to start adjustment. During adjustment, the tangential skew adjustment screen is displayed. Make this adjustment only
when the pickup was replaced.
As for adjustment, rotate the T -SKEW adjusting screw on the pic kup
so that the displayed jitter becomes minimum (CCW makes jitter
smaller). Avoid extreme rotation or interference of screwdriver with
the disc. After adjustment, a message to apply a scre w locking agent
will be displayed if jitter value is within the specification. Then,
apply a drip of locking agent to the recess of screw . Hence, change
discs following the given messages on OSD, and the adjustment is
finished if there is no problem.
Note that if “All” is selected, the data of previous adjustment are
erased and initial values are set.
Drive Auto Adjustment
SA.00000 SI.00 EMG.OO
Select No.
0: All 3: CD
2: DVD SL 4: DVD-DL
STOP: Press STOP Key
Figure 5
If “All” is selected, the screen shown in Figure 6 is displayed.
Drive Auto Adjustment
SA.00000 SI.00 EMG.OO
N Blinking
T-SKEW adjusting screw
Figure 7
0: Adjustment ALL
0: All 2: CD
2: DVD SL 3: DVD-DL
START: Press ENTER Key
STOP: Press STOP Key
Figure 6
N Blinking
6-10
Page 41
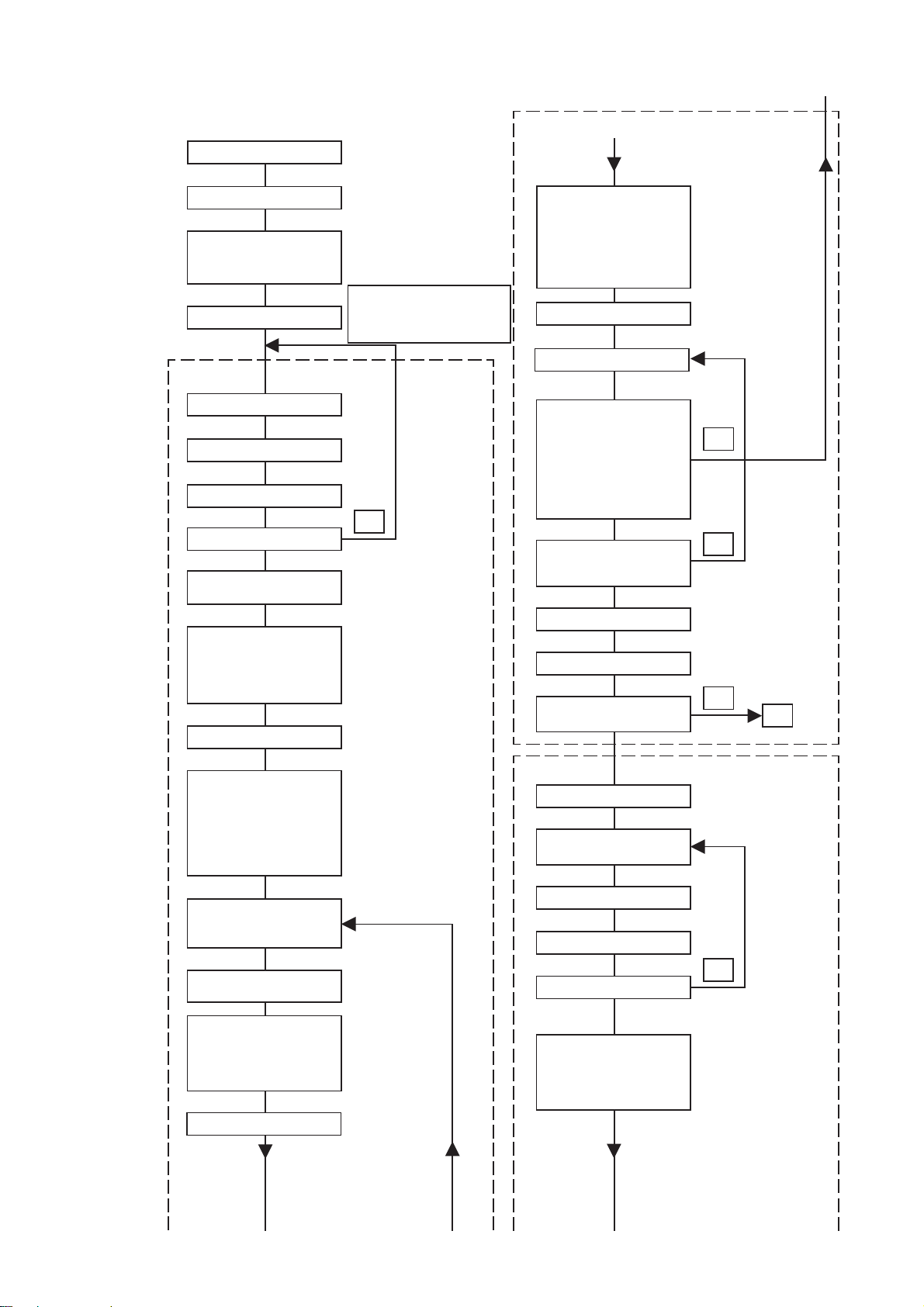
Drive Automatic Adjustment Flowchart
Service Mode ON
Loading
HYDET init
sled init
HOME Position
Adj. disc selection
DVD_SL
adjustment
Eject
Place DVD_SL disc for adj.
Loading
disc type check
EEPROM Default set
(Only if selecting ALL)
LDON
SP ON
Tilt ON
Focus ON
CLVS
Auto Tracking Offset
Note:If selecting other than ALL,
adjustment routine for
selected disc only is
executed
NG
Brake ON
FOK check
Tracking ON
Sled ON
Brake OFF
AGC ON
CLVA
JITTER ON
Tangential skew adjustment
Jitter OFF
Auto Focus Offset
Auto Tilt Offset
Auto Focus Offset
Auto Focus Gain
Auto Tracking Gain
Auto EQ
Pull in Memory
Jitter ON
Jitter Check
Jitter OFF
Servo Stop
Screw locking agent
search check
stop
NG
NG
NG
stop
Brake ON
FOK check
Tracking ON
Sled ON
Brake OFF
AGC ON
CLVA
Auto Focus Offset
Auto Tilt Offset
Auto Focus Offset
Servo Stop
Home Position
LDON
SP ON
Tilt ON
Focus ON
CLVS
Tan-Position
CD adjustment
Eject
Disc change
DVD_SLnCD
Loading
Go to Home Position
NG
disc type check
LDON
SP ON
Tilt ON
Focus ON
CLVS
(to next page)
6-11
Page 42

Auto Tracking Offset
Layer0 check
NG
Brake ON
FOK check
Tracking ON
Sled ON
Brake OFF
Auto Focus Offset
Auto Focus Gain
Auto Tracking Gain
Pull in Memory
Jitter ON
Jitter check
Jitter OFF
search check
DVD_DL
adjustment
Disc change
CD n DVD_DL
Loading
disc type check
Focus ON
Auto Focus Offset
CLVA
stop
Eject
LDON
SP ON
Tilt ON
CLVS
NG
NG
NG
stop
stop
Servo stop
Jitter ON
Jitter check
Jitter OFF
CLVS
F_Jump(0 n 1)
Auto Tracking Offset
Brake ON
FOK check
Tracking ON
Sled ON
Brake OFF
CLVA
Layer1 check
Auto Focus Offset
Auto Focus Gain
Auto Tracking Gain
Auto EQ
Pull in Memory
Jitter ON
Jitter check
Jitter OFF
search check
(incl. layer Jump)
stop
Auto VCO
NG
stop
NG
stop
NG
stop
NG
stop
NG
stop
Brake ON
FOK check
Tracking ON
Sled ON
Brake OFF
ACG ON
CLVA
Auto Focus Offset
Auto Tilt Offset
Auto Focus Offset
Auto Focus Gain
Auto Tracking Gain
Auto EQ
Pull in Memory
Eject
Remove disc
loading
End
NG
stop
6-12
Page 43

6-4. Drive Manual Operation
6-4-2. Disc T ype
In performing manual operation, observe the following points:
Select correct disc type on the Disc Type screen.
First, select “7. Check” and execute “4. Hydet init” and “5. Sled
init”. (See Figure 9)
With the initial menu displayed, if [2] on standard commander is
pressed, the screen shown in Figure 11 is displayed.
In case of abnormality, press [stop] immediately to stop operation
and turn off the power.
Do not execute Auto Adjust while executing FG Pause.
Also, as these commands are not protected, take care not to press
wrong key.
6-4-1. Drive Manual Operation Menu Screen
Drive Manual Operation
SA.000000 SI.00 EMG.00
0. Disc Type
1. Manual Control 1
2. Manual Control 2
3. Manual Control 3
4. Manual Adjust 1
5. Manual Adjust 2
6. Auto Adjust
7. Check
Figure 8
Disk type
SA.000000 SI.00 EMG.00
0. DVD SL 12cm
1. CD 12cm
2. DVD DL 12cm
3. DVD SL 8cm
4. CD 8cm
5. DVD DL 8cm
6. Disc type check
DVD SL 12cm
Figure 10
On this screen, select the type of disc used.
“6. Disc type check” judges the disc loaded. Confirm that judgment
result meets the loaded disc type.
Judgment may fail if adjustment is not made yet immediately after
EEPROM Default Set. The CD which is not cut up to the CD/VDV
detection sensor position is judged as DVD. The optical system
will be damaged if other disc is loaded after selecting DVD DL.
6-4-3. Manual Control 1
Manual Control 1
This screen provides a menu for manual operation, and you can go
directly to each screen from here. T o return to this screen from each
screen, press the RETURN key.
For switching between respective screens, use the CLEAR key.
check
SA.000000 SI.00 EMG.00
0. SRAM Check
1. EEPRM Check
2. CDDET Check
3. EPROM Default
4. Hydet Init
5. Sled Init
6. EEPROM Data
Figure 9
SA.000000 SI.00 EMG.00
0. LD off 7. CLVS
1. SP off 8. CLVA
2. Tilt off 9. FG
3. Focus off n. Sled FWD
4. Brake off N. Sled RVS
5. Track off . Tilt Up
6. Sled off . Tilt Down
DVD SL 12cm
Figure 11
On this screen, turn on/off servo operation items necessary for playing.
Normally, turn on the items from 1 sequentiall y , and normal trace is
executed at CLVA. For the Brake, turn it off after turning on the
Sled. During normal operation, AGC is turned on.
n
n
6-13
Page 44

0. LD : Turn on/off the laser diode.
1. SP : Turn on/off the spindle.
At SP ON, the spindle runs in constant velocity mode.
2. TILT : Turn on/off the tilt servo.
3. Focus : Focus searching is executed and focus is turned on.
Operation is terminated if focus is not turned on after
focus search is retried about 3 times.
4. Brake : Turn on/off the tracking brake.
If turning on the tracking, turn on the brake.
Also, turn off the brake during tracing.
5. Track : Turn on/off the tracking servo.
6. Sled : Turn on/off the sled servo.
7. CLVS : Spindle rough servo.
8. CLVA : Spindle normal servo.
9. FG : Spindle in constant velocity mode
n. : Move the sled system outside.
Perform this with the tracking turned off.
N. : Move the sled system inside.
Perform this with the tracking turned off.
. : Move the tilt system up.
n
n
. : Move the tilt system down.
This screen will be used mainly for layer jump control.
Confirm the sector information (SI) so as not to mistake layer jump
direction of DVD_DL.
The layer is 0 when SI is even number, or layer is 1 when odd
number.
Wrong jump direction causes OPT failure.
0. AGC : Turn on/off focus error auto gain control on pull-in
level.
1. Pause : Pause is made by executing track jump once per
revolution.
2. FCS.Srch : The focus drive system is checked by applying
same voltage to the focus drive as that in focus
search.
3. Defect : Turn on/off defect.
4. Tilt H : Increase tilt gain.
5. FJ0 n 1 : After layer jump L0 n L1, tracking loop is not
turned on.
6. FJ1 n 0 : After layer jump L1 n L0, tracking loop is not
turned on.
7. LJ0 n 1 : After layer jump L0 n L1, tracking loop is turned
on.
8. LJ1 n 0 : After layer jump L1 n L0, tracking loop is turned
on.
6-4-5. Manual Control 3
Manual Control 3
SA.000000 SI.00 EMG.00
6-4-4. Manual Control 2
Manual Control 2
SA.000000 SI.00 EMG.00
0. AGC off 5. FJ0 n 1
1. Pause off 6. FJ1 n 0
2. FCS. Srch off 7. LJ0 n 1
3. Defect off 8. LJ1 n 0
4. Tilt_H off
DVDDL 12cm
Figure 12
0. FWD ITJ 5. Eject
1. RVS ITJ 6. Load
2. FWD 500TJ 7. Door Open
3. RDS 500TJ 8. Door Close
4. Home
DVD SL 12cm
Figure 13
On this screen, track jump, etc. are executed.
6-14
Page 45

0. FWD 1TJ : Jump one track forward.
1. RVS 1TJ : Jump one track reversely.
2. FWD 500TJ : Jump 500 tracks forward (fine search).
3. RVS 500TJ : Jump 500 tracks reversely (fine search).
4. HOME : Move to home position.
5. Eject : Eject disc (not including door open). Execute this
with the door left open.
6. Load : Load disc (not including door close)
7. Door Open : Open the front panel door.
8. Door Close : Close the front panel door. Execute this in the
loading completed status.
6-4-6. Manual Adjust 1
Manual Adjust 1
6-4-7. Manual Adjust 2
Manual Adjust 2
SA.000000 SI.00 EMG.00
0. Jitter on
1. 4 Focus Offset xx
2. Tilt Offset
SA.000000 SI.00 EMG.00
0. 4 TRK. Off set xx
1. Focus Gain
2. TRK. Gain
3. Tilt Gain
4. Sled Gain
5. VCO Offset
DVDSL 12cm
Figure 14
On this screen, manual adjustment can be made where jitter measurement is not executed.
0. TRK Offset: Adjust tracking offset.
1. Focus Gain : Adjust focus gain.
2. TRK Gain : Adjust tracking gain.
3. Tilt Gain : The tilt gain is fixed, and no adjustment is made.
4. Sled Gain : Do not adjust this.
5. VCO Offset: Set VCO control voltage.
$
28
DVD_SL 12cm
Figure 15
On this screen, manual adjustment can be made where jitter measurement is executed.
0. Jitter : Turn on/off jitter measurement. Jitter will not be
measured unless the drive runs at CLVS or CL V A.
1. Focus Offset: Adjust focus offset.
2. Tilt offset : Adjust tilt offset.
6-4-8. Auto Adjust
Auto Adjust
SA.000000 SI.00 EMG.00
0. Auto Tilt Gain
1.4 Auto TRK. Offset
2. Auto Tilt Offset
3. Auto Focus Offset
4. Auto EQ
5. Auto Focus Gain
6. Auto TRK. Gain
7.auto VCO
DVDSL 12cm
Figure 16
On this screen, each item can be automatically adjusted individually.
Note, however, that there are some restrictions.
6-15
Page 46

0. Auto Tilt Gain : Adjust tilt gain. Adjusted result is not reflected on the ROM. Executed this at least
with LD and Tilt turned on. (Not used at
present)
1. Auto TRK Offset : Adjust tracking offset automatically. Adjusted result is reflected on the ROM. Turn
off tracking with the Focus turned on. Do
not execute this at outside track because
pickup moves outside. It is recommended to
turn on CLVS.
2. Auto Tilt Offset : Adjust tilt offset automatically . Adjusted result is reflected on the ROM. Execute this
with CLVA turned on. If NG, retry this after
focus offset and tangential skew are adjusted.
3. Auto Focus Offset: Adjust focus offset automatically. Adjusted
result is reflected on the ROM. Execute this
with CLVA turned on. If NG, retry this after
tilt offset and tangential skew are adjusted.
4. Auto EQ : Adjust RF equalizer properly. Adjusted result is not reflected on the ROM. Execute
this with CLVA turned on.
5. Auto Focus Gain : Adjust focus gain automatically. Adjusted
result is reflected on the ROM. Execute this
with CL VA turned on if possible. If NG, the
system will be defective, and repair it.
6. Auto TRK gain :Adjust tracking gain automatically. Adjusted
result is reflected on the ROM. Execute this
with CL VA turned on if possible. If NG, the
system will be defective, and repair it.
7. Auto VCO : Adjust VCO voltage. Adjusted result is reflected on the ROM. Execute this with all
items turned OFF.
6-4-9. Check
check
SA.000000 SI.00 EMG.00
0. SRAM Check ok
1. EEPRM Check (ok)
2. CDDET Check (CD)
3. EEPROM Default set (set)
4. Hydet Init (OK)
5. Sled Init (OK)
6. EEPROM Data
DVDSL 12cm
Figure 17
On this screen, various checking can be made. Note, however, that
some items such as EEPROM Default set are not recoverable.
0. SRAM check : Check communication between H8 and
SRAM (CXK58257).
1. EEPROM check : Check communication between H8 and
EEPROM (AK6420).
2. CDDET check : Check CD detection sensor. Result is
shown on the right side.
3. EEPROM Default set : Use this to set EEPROM set values to
default values. Before executing this, it
is recommended to record current values.
4. Hydet init : Initialize for direct searching.
5. Sled init : Cancel the sled stop position offset.
6. EEPROM data : Display EEPROM set values list.
Display is made with HEX numbers
“00”~”FF”.
If the check on this screen is NG EMG turns to the number that is
not “00..”
6-16
Page 47

EEPROM data screen display (at default setting)
EEPROM data
CD DVD
Set No. 00 SL L0 L1
Focus Offset 80 80 80 80
Focus Gain 30 18 30 30
TRK Offset 80 80 80 80
TRK Gain 30 30 30 30
Tilt Offset 80 80 80 80
Pullin Level 9e 9f ab ab
Sled Gain 10 18 18 18
EQ Init 3a 35 30
VCO Offset 76 76 76
Figure 18
This screen displays various set values including adjusted results
stored in the EEPROM.
Set No. : Nothing is displayed (00 is displayed)
Focus Offset : 00~FF 80 center (DVD_SL)
Focus Gain : 00~7F 20 center (DVD_SL)
TRK. Offset : 00~FF 80 center (DVD_SL)
TRK. Gain : 00~7F 30 center (DVD_SL)
Tilt Offset : 00~FF 80 center (DVD_SL)
Pullin Level : 80~B0 approx. (DVD_SL)
EQ Init : Fixed value
VCO Offset : 70~80 approx. (DVD_SL)
6-17
Page 48
6-5. Emergency History
With the initial menu displayed, press [3] ke y on the standard commander, and the information on emergency history of Drvcon and
Syscon will be displayed. This information is giv en over two pages,
which can be changed over with [1] and [2] keys. To return to the
initial menu, press [0] key.
EMG. Hist Page.01
N Page
The following hidden commands are available. Data clear can be
confirmed from the fact that the screen display changes.
Clearing laser ON hours
Press [DISPLAY] and [CLEAR] keys on the standard commander
in this order.
Clearing emergency history
Press [TITLE] and [CLEAR] keys on the standard commander in
this order.
After repair is finished, always clear emergency history data.
CD000000 Hour
EMGMech Disc TimeH T imeM T imeL
00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00
Page 1: 1Key
Page 2: 2Key
Exit : 0key
Figure 19
EMG. Hist Page.02
DVD000000 Hour
00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00
00 00 00 00 00 00
Page 1: 1Key
Page 2: 2Key
Exit : 0key
Figure 20
N CD laser ON hours
Emergency history
N
of Drvcon (latest)
Emergency history (2)
N
of Drvcon
Emergency history (3)
N
of Drvcon
Emergency history (4)
N
of Drvcon
N DVD laser ON hours
Emergency history (5)
N
of Drvcon
Emergency history (6)
N
of Drvcon
Emergency history (7)
N
of Drvcon
Emergency history (6)
of Syscon
Emergency history (5)
of Syscon
Emergency history (4)
of Syscon
Emergency history (3)
of Syscon
Emergency history (2)
of Syscon
Emergency history
(latest) of Syscon
Clearing Syscon preset
Press [DVD MENU] and [CLEAR] keys on the standard commander
in this order.
For EMG code, Mech mode, and Disc information of history display, see “Drvcon emer gency code list”, “Drvcon Mech mode list”,
and “Drvcon disc status list”.
6-6. Other Checks
With the initial menu displayed, press [4] ke y on the standard commander, and the information such as destination and R OM re vision
will be displayed. At this time, LED and display tube lighting chec k
is also executed.
Rom Revision
IF con Ver.x.xx (xxxx)
SYScon Ver.x.xx (xxxx)
DRVcon Ver.x.xx (xxxx)
Area Type (xx)
Region (xx)
SW1 OFF
SW2 OFF
SIRCS:ff KEY:ff RATE: 29
Figure 21
After mode is selected, checksum calculation and information reading are executed, thus requiring time before display.
Also, during this display, LEDs and display tube are all turned on.
The status of keys on standard commander and operation panel is
displayed in real time. However, if [POWER] key is pressed, the
power is turned off after display. Also, this mode is terminated if
pressing [RETURN] key.
The door is opened/closed by pressing [PANEL] key on operation
panel.
When [RETURN] key is pressed, LED and display tube are turned
off and the initial screen is resumed.
Note: A number of two decimal places of Rom Revision is a
design management code and therefore ignore it.
N IFcon rev., checksum
N Syscon rev., checksum
N Drvcon rev., checksum
N Destination of set
N Set region number
N Status of S001
N Status of S002
N IFcon internal information
6-18
Page 49

How to see Emergency History
Communication system
80: Communication NG
(b) Syscon emergency codes list
13
1 EMG CODE
2 MECH MODE
3 DISC
4 TIME (MSB)
5 TIME
6 TIME (LSB)
1 EMG CODE
a) Drvcon emergency code list
Initial
00: No Emergency
01: RAM check NG (IC138)
02: ROM check NG (ICS140)
03: EEPROM RW NG (IC139)
04: EEPROM BUSY Time Out (IC139)
05: CXD2545 (IC717) check NG
06: CXD8599 (IC710) check NG
07: CXD8663 (IC181) check NG
08: HYDET NG
09: SDCNTL NG
0A: VCO NG
0B: Focus Gain Adj NG
0C: Trk Gain Adj NG
0D: Jitter NG
Door & Tray system
10: Door Time Out
11: Tray T ime Out
Spindle system
20: Spindle Lock Time Out
21: Spindle Out of Control
Sled system
30: Home Position Time Out
31: Sled FG NG
32: Sled Drv NG
Tilt system start up/down
50: Focus Search Time Out
Trace system
60: CL VLOCK NG
61: PLL NG
62: Address Continuity NG
63: PLL Lock Time Out
64: CLV Lock Time Out
65: Layer slip NG
Seek system
70: Address Read NG
71: Seek NG
72: Focus Jump NG
73: TOC Read Time Out
74: FOK NG
75: Req Address NG
76: Req Time NG
77: Req Track No NG
2
4
DVD : Selector address
CD : minute & second frame
5
6
Stop system
10: Stop request from drive controller was received
11: At the mode change command, the mode could not be
changed within specified time and the drive stopped.
12: Retry due to supply error failed and the drive stopped.
13: Disc directory configuration and information file are ille-
gal and the drive stopped.
14: The drive stopped as a DVD-R disc was used.
15: Coded data could not be decoded and the drive stopped.
16: At slow R, the destination of reverse search is illegal and
the drive stopped.
17: Information file reading failed and the drive stopped.
Retry system
20: Disc data reading failed and retry was made.
21: Video decoder operation failed and retry was made.
22: Retry was made due to DMX error.
23: At slow R, retry was made due to data supply time out.
24: At slow R, retry was made due to wrong Navi Pack address.
25: At slow R, video decoder operation failed and retry was made.
26: At slow R, retry was made due to failure of display pic-
ture preparation.
27: At FF/FR, retry was made due to data supply time out.
28: At FF/FR, video decoder operation failed and retry was made.
Power system
80: The power turned off because of power off request from
drive controller
81: The mode change to Stop mode failed and the power
turned off.
2 MECH MODE (Drvcon Mech mode list)
00: Power ON Ready (immediately after power on)
10: Eject
20: Stop
30: Trace (data supply mode)
40: Pause
50: Scan
60: Mecha Initialize
70: Load
80: Unload
90: Spin Up (disc startup operation)
A0: Spin Down (disc stop operation)
B0: Seek (search mode)
C0: Error Recovery
D0: Service
3 DISC (Drvcon status list)
bit Value:0 Value:1
0:DVD/CD DVD CD
1:12cm/8cm 12cm 8cm
2:Layer Single Dual
3:Reflectivity High Low
4:Judge/No judge Judge No judge
5:Disc/No disc Disc No disc
6:CDROM Not True
7:Track Density (DVD) 0.74 mm 0.80 mm
Note: If judge/no judge is not “judge”, correct data have not been
written.
6-19
6-19 E
Page 50

SECTION 7
ELECTRICAL ADJUSTMENT
DVP-S3000
In making adjustment, refer to 7-5. Adjustment
Related Parts Arrangement.
This section describes procedures and instructions necessary for
adjusting electrical circuits in this set.
Instruments required:
1) Color monitor TV
2) Oscilloscope 1 or 2 phenomena, band width over 100 MHz,
with delay mode
3) Frequency counter (over 8 digits)
4) Digital voltmeter
5) Standard commander
6) DVD reference disc
HLX-502 (J-6090-068-A) (dual layer)
HLX-503 (J-6090-069-A) (single layer)
7-1. Power Supply Check
1. PS-408/413 Board
Mode E-E
Instrument Digital voltmeter
EVER +5V check
Test point CN954 1 pin
Specification 5 ±0.5V
POWER FAIL check
Test point CN954 2 pin
Specification 4V ~ 5V (POWER ON)
Checking method:
1) Confirm that each voltage satisfies the specification.
2. MB-80 Board
Mode E-E
Instrument Digital voltmeter
–7V check
Test point W001 9 pin
Specification –7 ±0.5V
+12V check
Test point W001 7 pin
Specification +12 ±0.5V
+5.2V check
Test point W001 1, 2 pins
Specification +5.2 ±0.2V
Checking method:
1) Confirm that each voltage satisfies the specification.
7-2. +5.2 V Adjustment
(SR-740/745 board)
Mode E-E
Measuring Insrument Digital voltmerter
Measurement Point Pin !™ of CN201
Adjusting Element VR 201
Specified Value +5.2 ± 0.2 V
7-1
Page 51

7-3. Adjustment of System Control
1. 27MHz Free Run (MB-80 board)
<Purpose>
27MHz is the reference clock for the MPEG system, and if it is not
adjusted correctly, checking of 22 MHz and 33 MHz lock in the
following steps will result in NG.
Mode E-E
Test point TP018 (27MHz FREE RUN)
Instrument Oscilloscope, Frequency counter
Adjusting element RV001
Specification 27000000 ±100Hz
Adjusting method:
1) Connect TP025 (XULK) to the GND.
2) Confirm that the waveform at TP018 is normal.
3) Adjust RV001 to attain 27000000 ± 100 Hz.
4) After adjustment, disconnect TP025 from GND.
3. 33 MHz Check (MB-80 board)
<Purpose>
33 MHz is the reference clock for audio system to play CD (including video CD), and if it is not adjusted correctly, no sound will be
generated or sounds will be distorted.
Mode E-E
Test point TP019 (33 MHz)
Instrument Oscilloscope, Frequency counter
Specification 33868800 ±150Hz
Checking method:
1) In the “0” Syscon Diagnosis of the test mode initial menu,
select the CD mode.
2) Confirm that the waveform at TP019 is normal.
3) Confirm that the frequency is 33868800 ±150Hz.
Figure 7-3
Figure 7-1
2. 22MHz Adjustment (MB-80 board)
<Purpose>
22MHz is the reference clock to generate 33 MHz clock, and if it is
not adjusted correctly, checking of 33 MHz will result in NG.
Mode E-E
Test point TP022 (512fs)
Instrument Oscilloscope, Frequency counter
Adjusting element CT001
Specification 22579200 ±100Hz
Adjusting method:
1) In the “0” Syscon Diagnosis of the test mode initial menu,
select the CD mode.
2) Confirm that the waveform at TP022 is normal.
3) Adjust CT001 to attain 22579200 ±100Hz.
4. 33 MHz Lock Check (MB-80 board)
<Purpose>
This checks whether 33 MHz is synchronized with reference clock
27MHz for MPEG system. If it is not locked, the sounds and pictures are not synchronous during MPEG playing or playing is suspended.
Mode E-E
Test point TP021 (PH-COMP)
Instrument Oscilloscope, Frequency counter
Specification 21.6 ±0.01kHz
Checking method:
1) In the “0” Syscon Diagnosis of the test mode initial menu,
select the CD mode.
2) Confirm that a rectangular wave at TP021 is locked.
3) Confirm that the frequency is 21.6 ±0.01kHz.
Figure 7-4
Figure 7-2
7-2
Page 52
5. 24 MHz Adjustment (MB-80 board)
<Purpose>
24 MHz is the reference clock to generate 36 MHz clock, and if it is
not adjusted correctly, checking of 36 MHz will result in NG.
Mode E-E
Test point TP022 (512fs)
Instrument Oscilloscope, Frequency counter
Adjusting element CT002
Specification 24576000 ±100Hz
7. 36 MHz Lock Check (MB-80 board)
<Purpose>
This checks whether 36 MHz is synchronized with reference clock
27 MHz for MPEG system. If it is not locked, the sounds and pictures are not synchronous during MPEG playing or playing is suspended.
Mode E-E
Test point TP021 (PH-COMP)
Instrument Oscilloscope, Frequency counter
Specification 24.0 ±0.01 kHz
Adjusting method:
1) In the “0” Syscon Diagnosis of the test mode initial menu,
select the DVD mode.
2) Confirm that the waveform at TP022 is normal.
3) Adjust CT002 to attain 24576000 ±100Hz.
Figure 7-5
6. 36 MHz Check (MB-80 board)
<Purpose>
36 MHz is the reference clock for audio system to play DVD, and if
it is not adjusted correctly, no sound will be generated or sounds
will be distorted.
Mode E-E
Test point TP020 (36 MHz)
Instrument Oscilloscope, Frequency counter
Specification 36864000 ±150 Hz
Checking method:
1) In the “0” Syscon Diagnosis of the test mode initial menu,
select the DVD mode.
2) Confirm that the waveform at TP020 is normal.
3) Confirm that the frequency is 36864000 ±150 Hz.
Checking method:
1) In the “0” Syscon Diagnosis of the test mode initial menu,
select the DVD mode.
2) Confirm that a rectangular wave at TP021 is locked.
3) Confirm that the frequency is 24.0 ±0.01 kHz.
Figure 7-7
8. 16 MHz Check (MB-80 board)
<Purpose>
16 MHz is the reference clock for audio system to play CD (including video CD), and if it is not adjusted correctly, no sound will be
generated or sounds will be distorted.
Mode E-E
Test point IC770 20 pin
Instrument Oscilloscope, Frequency counter
Specification 16934400 ±75 Hz.
Checking method:
1) Confirm that the waveform at IC770 @º pin is normal.
2) Confirm that the frequency is 16934400 ±75 Hz.
Figure 7-6
Figure 7-8
7-3
Page 53

7-4. Adjustment of Video System
1. Video Level Adjustment (MB-80 board)
<Purpose>
This adjustment is made to satisfy the NTSC Standard, and if not
adjusted correctly, the brightness will be too large or small.
Mode
Signal Color bars
Test point CN005 !¡ pin (terminating 75 )
Instrument Oscilloscope
Adjusting element RV479
Specification 1 ±0.02 Vp-p
Adjusting method:
1) In the test mode initial menu “0” Syscon Diagnosis, set so that
CXD1914 color bars are generated.
2) Adjust the RV479 to attain 1 ±0.02 Vp-p.
CXD1914 (ENC) check in test mode
menu “0” Syscon Diagnosis
3. Checking Composite Video Output B-Y(MB-80 board)
<Purpose>
This checks composite video output B-Y. If it is incorrect, correct
colors will not be displayed when connected to, for instance, projector.
Mode
CXD1914 (ENC) check in test mode menu “0”
Syscon Diagnosis
Signal Color bars
Test point CN005 1 pin (terminating 75 )
Instrument Oscilloscope
Specification 700 ±30 mVp-p
Checking method:
1) Confirm that the B-Y level is 700 ±30 mVp-p.
700 ±30 mVp-p
1 ±0.05 Vp-p
Figure 7-9
2. S-terminal Output Check (MB-80 board)
<Purpose>
Check S-terminal video output. If it is incorrect, pictures will not
be displayed correctly in spite of connection to the TV with an Sterminal cable.
Mode
CXD1914 (ENC) check in test mode menu “0”
Syscon Diagnosis
Signal Color bars
Test point CN005 7 pin (terminating 75 )
Instrument Oscilloscope
Specification 1 ±0.05 Vp-p
Checking method:
1) In the test mode initial menu “0” Syscon Diagnosis, set so that
CXD1914 color bars are generated.
2) Confirm that the S-Y level is 1 ± 0.05 Vp-p.
Figure 7-11
4. Checking Composite Video Output R-Y(MB-80 board)
<Purpose>
This checks composite video output R-Y. If it is incorrect, correct
colors will not be displayed when connected to, for instance, projector.
Mode
CXD1914 (ENC) check in test mode menu “0”
Syscon Diagnosis
Signal Color bars
Test point CN005 3 pin (terminating 75 )
Instrument Oscilloscope
Specification 700 ±30 mVp-p
Checking method:
1) Confirm that the R-Y level is 700 ± 30 mVp-p.
700 ±30 mVp-p
Figure 7-10
1 ±0.05 Vp-p
Figure 7-12
7-4
Page 54

5. Checking Composite Video Output Y (MB-80 board)
<Purpose>
This checks composite video output Y. If it is incorrect, correct
brightness will not be attained when connected to, for instance, projector.
Mode
CXD1914 (ENC) check in test mode menu “0”
Syscon Diagnosis
Signal Color bars
Test point CN005 5 pin (terminating 75 )
Instrument Oscilloscope
Specification 1 ±0.05 Vp-p
Checking method:
1) Confirm that the Y level is 1 ±0.05 Vp-p.
1 ±0.05 Vp-p
Figure 7-13
6. Checking S Video Output S-C (MB-80 board)
<Purpose>
This checks whether the S-C satisfies the NTSC Standard. If it is
not correct, the colors will be too dark or light.
Mode
CXD1914 (ENC) check in test mode menu “0”
Syscon Diagnosis
Signal Color bars
Test point CN005 9 pin
Instrument Oscilloscope
Specification 286 ±20 mVp-p
7. Checking S Video Output DC Level (MB-80 board)
<Purpose>
This checks signals for S1 and S2 compatible TV. If they are not
correct, the TV will not switch automatically to letter box, etc.
Mode
CXD1914 (ENC) check in test mode menu “0”
Syscon Diagnosis
Signal Color bars
Test point CN005 9 pin
Instrument Digital voltmeter
Specification S-terminal 0V: 0V
S-terminal 5V: 5.0 V
+0
–1.5
Connection:
9
8
CN005
Digital voltmeter
100µF
+
75
Ω
±
1%
100k
±
1%
Checking method:
1) In the test mode initial menu “0” Syscon Diagnosis, select Sterminal 0V.
Confirm that the voltage at CN005 9 pin is 0V.
2) Press any key to select S-terminal 5V.
Confirm that the voltage at CN005 9 pin is 5.0 V.
+0
–1.5
7-5. Adjustment Related Parts Arrangement
MB-80 BOARD (Side A)
11
CN005
9
8
7
6
5
3
2
1
W001
1
12
RV001
27 MHz FREE-RUN
TP022
512 fs
CT001
22 MHz
TP021
PH-COMP
51
80
CN382
TP020
36 MHz
IC002
30
20
1
IC770
IC381
CT022
24 MHz
TP019
33 MHz
RV479
VIDEO
LEVEL
TP018
27 MHz FREE-RUN
TP025
XULK
Connection:
9
8
CN005
Oscilloscope
100µF
+
75
Ω
±
1%
100k
±
1%
Checking method:
1) Confirm that the S-C burst is 286 ±20 mVp-p.
Figure 7-14
286 ±20 mVp-p
SR-740/745 BOARD (Side A)
CN101
VR201
+5.2V
CN201
12
ICS140
PS-408/413 BOARD (Side A)
T901
1
F001
CN954
1
3
7-5
7-6 E
Page 55
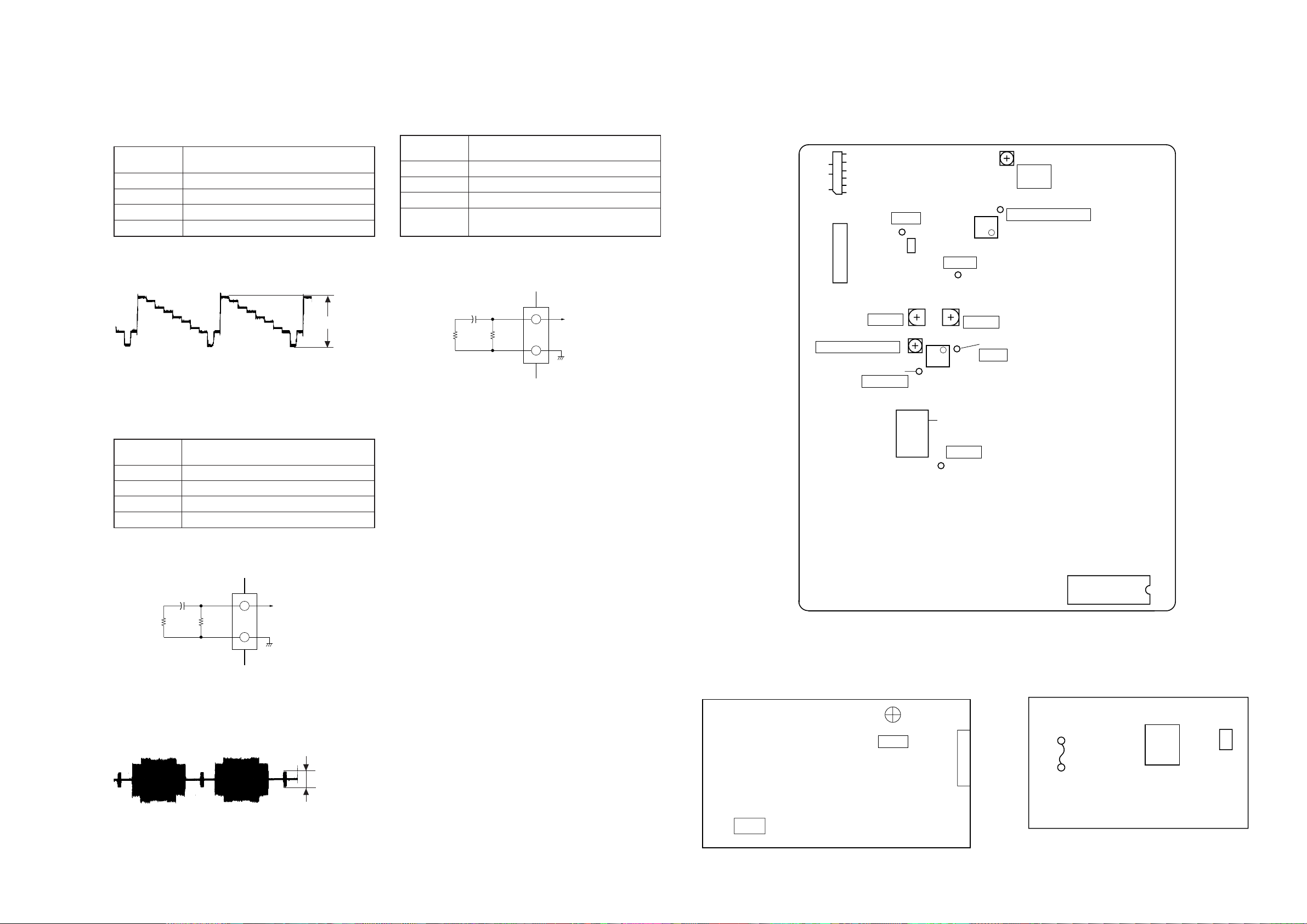
5. Checking Composite Video Output Y (MB-80 board)
<Purpose>
This checks composite video output Y. If it is incorrect, correct
brightness will not be attained when connected to, for instance, projector.
Mode
CXD1914 (ENC) check in test mode menu “0”
Syscon Diagnosis
Signal Color bars
Test point CN005 5 pin (terminating 75 )
Instrument Oscilloscope
Specification 1 ±0.05 Vp-p
Checking method:
1) Confirm that the Y level is 1 ±0.05 Vp-p.
1 ±0.05 Vp-p
Figure 7-13
6. Checking S Video Output S-C (MB-80 board)
<Purpose>
This checks whether the S-C satisfies the NTSC Standard. If it is
not correct, the colors will be too dark or light.
Mode
CXD1914 (ENC) check in test mode menu “0”
Syscon Diagnosis
Signal Color bars
Test point CN005 9 pin
Instrument Oscilloscope
Specification 286 ±20 mVp-p
7. Checking S Video Output DC Level (MB-80 board)
<Purpose>
This checks signals for S1 and S2 compatible TV. If they are not
correct, the TV will not switch automatically to letter box, etc.
Mode
CXD1914 (ENC) check in test mode menu “0”
Syscon Diagnosis
Signal Color bars
Test point CN005 9 pin
Instrument Digital voltmeter
Specification S-terminal 0V: 0V
S-terminal 5V: 5.0 V
+0
–1.5
Connection:
9
8
CN005
Digital voltmeter
100µF
+
75
Ω
±
1%
100k
±
1%
Checking method:
1) In the test mode initial menu “0” Syscon Diagnosis, select Sterminal 0V.
Confirm that the voltage at CN005 9 pin is 0V.
2) Press any key to select S-terminal 5V.
Confirm that the voltage at CN005 9 pin is 5.0 V.
+0
–1.5
7-5. Adjustment Related Parts Arrangement
MB-80 BOARD (Side A)
11
CN005
9
8
7
6
5
3
2
1
W001
1
12
RV001
27 MHz FREE-RUN
TP022
512 fs
CT001
22 MHz
TP021
PH-COMP
51
80
CN382
TP020
36 MHz
IC002
30
20
1
IC770
IC381
CT022
24 MHz
TP019
33 MHz
RV479
VIDEO
LEVEL
TP018
27 MHz FREE-RUN
TP025
XULK
Connection:
9
8
CN005
Oscilloscope
100µF
+
75
Ω
±
1%
100k
±
1%
Checking method:
1) Confirm that the S-C burst is 286 ±20 mVp-p.
Figure 7-14
286 ±20 mVp-p
SR-740/745 BOARD (Side A)
CN101
VR201
+5.2V
CN201
12
ICS140
PS-408/413 BOARD (Side A)
T901
1
F001
CN954
1
3
7-5
7-6 E
Page 56

8-1. EXPLODED VIEWS
DVP-S3000
SECTION 8
REPAIR PARTS LIST
NOTE:
• -XX and -X mean standardized parts, so they
may have some difference from the original
one.
• Items marked “∗” are not stocked since they
are seldom required for routine service. Some
delay should be anticipated when ordering
these items.
• Color Indication of Appearance Parts
Example:
KNOB, BALANCE (WHITE) . . . (RED)
↑↑
Parts Color Cabinet’s Color
• Abbreviation
CND: Canadian HK: Hong Kong
CH : Chinese SP : Singapore
8-1-1. CASE ASSEMBLY
5
6
#3
• The mechanical parts with no reference number in the exploded views are not supplied.
• Hardware (# mark) list and accessories and
packing materials are given in the last of the
electrical parts list.
3
The components identified by mark
! or dotted line with mark ! are critical for safety.
Replace only with part number specified.
Les composants identifie´s par une
marque ! sont critiques pour la
se´curite´.
Ne les remplacer que par une pie´ce
portant le neme´ro spe´cifie´.
4
3
2
7
#3
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
1 X-3602-115-1 FOOT ASSY (CH, HK, SP)
1 X-3947-227-1 FOOT ASSY (US, CND)
2 3-979-416-01 COVER, TRAY (US, CND)
2 3-979-416-11 COVER, TRAY (CH, HK)
2 3-979-416-21 COVER, TRAY (SP)
3 3-710-901-41 SCREW, TAPPING (US, CND, SP)
3 3-710-901-51 SCREW, TAPPING (CH, HK)
* 4 3-974-981-01 CASE, TOP (SP)
3
#3
1
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
* 4 3-974-981-11 CASE, TOP (US, CND)
* 4 3-974-981-21 CASE, TOP (CH, HK)
5 1-475-086-31 COMMANDER, STANDARD (RMT-D100E)
5 1-475-086-51 COMMANDER, STANDARD (RMT-D100U)
6 9-939-686-01 LID, BATTERY CASE (for RMT-D100E/D100U)
* 7 3-979-417-01 HOLDER, MD
#1
(CH, HK, SP)
(US, CND)
8-1
Page 57

8-1-2. FRONT PANEL ASSEMBLY
52
53
51
54
55
56
#2
59
58
63
57
61
60
63
62
63
63
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
51 A-6062-026-A PANEL BLOCK ASSY (1010UC) (US, CND)
51 A-6062-028-A PANEL BLOCK ASSY (1010SP) (SP)
51 A-6062-029-A PANEL BLOCK ASSY (1010CN) (CH, HK)
52 4-963-404-21 EMBLEM (5-A), SONY (US, CND, SP)
52 4-963-404-81 EMBLEM (5-A), SONY (CH, HK)
53 3-979-425-01 BUTTON, POWER (POWER) (US, CND)
53 3-979-425-11 BUTTON, POWER (POWER) (CH, HK)
53 3-979-425-21 BUTTON, POWER (POWER) (SP)
54 3-979-426-01 BUTTON, MENU (US, CND)
54 3-979-426-11 BUTTON, MENU (CH, HK)
54 3-979-426-21 BUTTON, MENU (SP)
55 3-979-430-01 BUTTON, PLAY (§. ·. P. p. =. +)
(US, CND)
55 3-979-430-11 BUTTON, PLAY (§. ·. P. p. =. +)
(CH, HK)
55 3-979-430-21 BUTTON, PLAY (§. ·. P. p. =. +)
(SP)
56 3-979-431-01 BUTTON, DISPLAY (US, CND)
56 3-979-431-21 BUTTON, DISPLAY (CH, HK, SP)
57 3-979-429-01 BUTTON, TITLE (US, CND)
57 3-979-429-11 BUTTON, TITLE (CH, HK)
57 3-979-429-21 BUTTON, TITLE (SP)
58 3-979-428-01 BUTTON, ENTER (US, CND)
58 3-979-428-11 BUTTON, ENTER (CH, HK)
58 3-979-428-21 BUTTON, ENTER (SP)
* 59 A-6065-046-A PW-117 BOARD, COMPLETE (CH, HK, SP)
* 59 A-6065-058-A PW-116 BOARD, COMPLETE (US, CND)
60 3-979-427-01 BUTTON, CURSOR (US, CND)
60 3-979-427-11 BUTTON, CURSOR (CH, HK)
60 3-979-427-21 BUTTON, CURSOR (SP)
* 61 A-6065-045-A FP-619 BOARD, COMPLETE (CH, HK, SP)
* 61 A-6065-057-A FP-611 BOARD, COMPLETE (US, CND)
62 3-979-555-01 SPRING, ELECTROSTATIC
63 3-979-433-01 SCREW (+P 2.6), TAPPING
8-2
Page 58
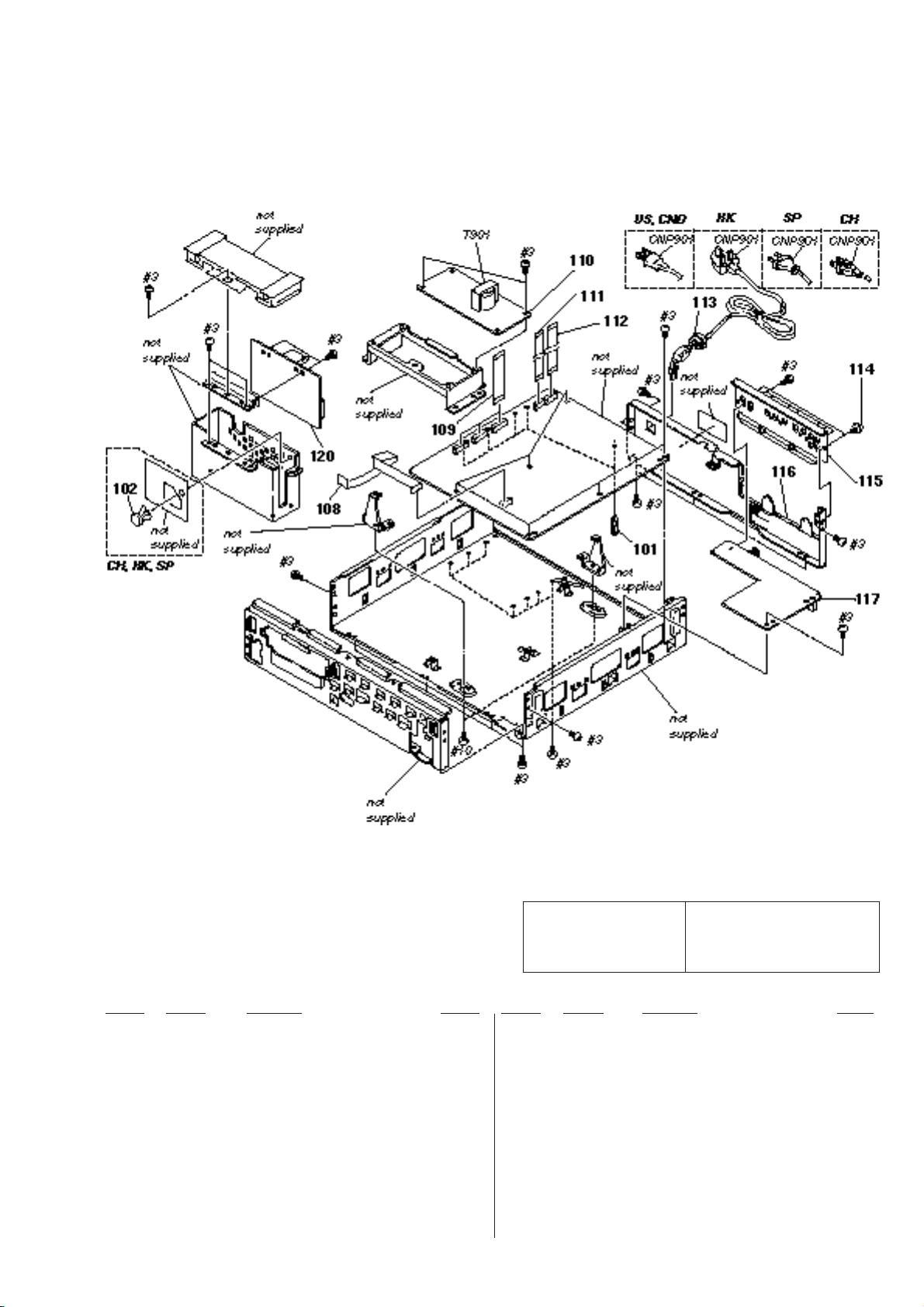
8-1-3. CHASSIS ASSEMBLY
The components identified by
mark ! or dotted line with
mark ! are critical for safety.
Replace only with part number
specified.
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
* 101 3-691-950-01 SPACER, P.C.BOARD
102 3-531-576-01 RIVET (CH, HK, SP)
108 1-782-867-11 CABLE, FLEXIBLE FLAT (FTT-4) 13P
109 1-782-191-11 CABLE, FLEXIBLE FLAT (FTM-3)
* 110 A-6065-044-A PS-413 BOARD, COMPLETE (CH, HK, SP)
* 110 A-6065-056-A PS-408 BOARD, COMPLETE (US, CND)
111 1-782-193-11 CABLE, FLEXIBLE FLAT (FAM-5)
112 1-782-865-11 CABLE, FLEXIBLE FLAT (FAM-6) 20P
113 3-703-571-12 BUSHING (2104), CORD
114 3-710-901-41 SCREW, TAPPING
* 115 3-979-418-01 PLATE, JACK (US, CND)
* 115 3-979-418-21 PLATE, JACK (CH, HK, SP)
* 116 3-974-969-31 PANEL, REAR (CH, HK, SP)
* 116 3-974-969-21 PANEL, REAR (US, CND)
* 117 A-6065-043-A AU-203 BOARD, COMPLETE (CH, HK, SP)
* 117 A-6065-055-A AU-201 BOARD, COMPLETE (US, CND)
! 120 1-468-199-11 SR-740 BOARD, COMPLETE (US, CND)
! 120 1-468-200-11 SR-745 BOARD, COMPLETE (CH, HK, SP)
! CNP901 1-690-609-81 CORD, POWER (US, CND)
! CNP901 1-751-673-31 CORD, AC POWER (HK)
! CNP901 1-782-510-11 CORD, POWER (CH)
! CNP901 1-782-960-11 CORD, POWER (SP)
! T901 1-429-784-11 TRANSFORMER, POWER (US, CND)
! T901 1-431-593-11 TRANSFORMER, POWER (CH, HK, SP)
Les composants identifiés par une
marque ! sont critiques pour la
sécurité.
Ne les remplacer que par une pièce
portant le neméro spécifié.
8-3
Page 59
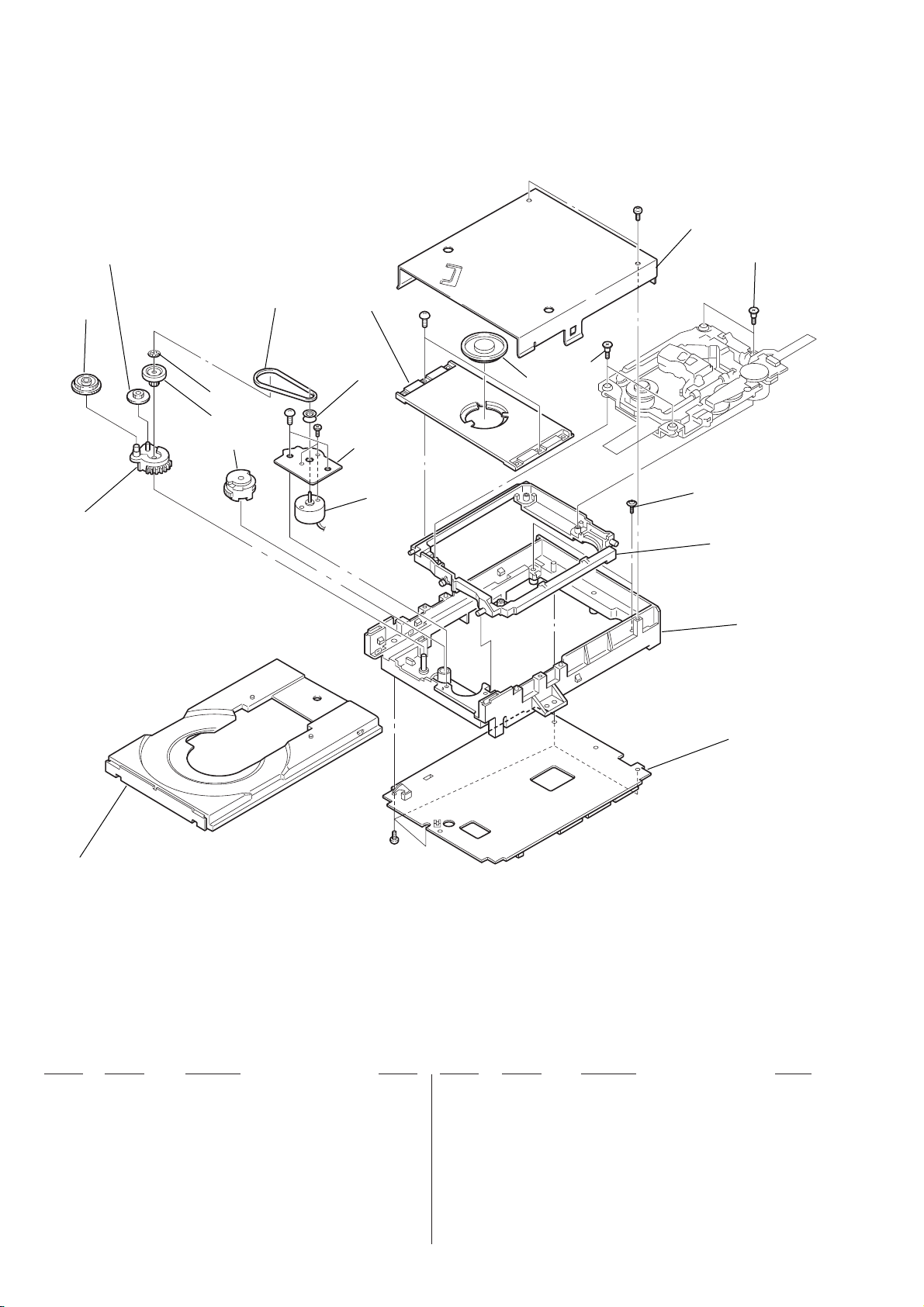
8-1-4. DVD MECHANISM CHASSIS ASSEMBLY (1)
#3
not supplied
154
153
155
157
156
152
158
#3
160
159
#7
not supplied
M903
166
#3
166
161
162
163
164
165
151
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
151 3-975-090-01 TRAY
152 3-975-073-01 GEAR, CAM
153 3-975-087-01 GEAR, DRIVE
154 3-975-086-01 GEAR, TRAY DRIVING
155 3-975-072-01 GEAR, LOADING (MIDWAY)
156 3-975-071-01 PULLEY, LOADING
157 3-669-596-00 WASHER (2.3), STOPPER
158 3-975-070-01 BELT
159 3-975-085-01 PULLEY, MOTOR
#3
160 3-975-089-01 BRACKET, PRESS PULLEY
* 161 3-975-074-01 PULLEY, PRESS
162 3-975-077-01 SCREW, BU STOPPER
* 163 3-975-088-01 HOLDER, BASE UNIT
* 164 X-3947-008-4 BASE ASSY, LO
* 165 A-6065-052-A TT-40 BOARD, COMPLETE
166 4-981-923-01 SCREW (M), STEP
M903 1-698-942-21 MOTOR (LOADING)
8-4
Page 60

8-1-5. DVD MECHANISM CHASSIS ASSEMBLY (2)
207
208
M901
217
215
215
206
205
202
#9
204
218
219
209
215
213
214
215
210
M501
216
211
220
215
M902
212
202
The components identified by mark
202
#8
201
203
202
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
* 201 3-975-066-01 STOPPER, SKEW SHAFT
* 202 3-975-061-01 INSULATOR
* 203 3-975-056-01 BASE, SPINDLE
204 3-975-058-01 CAM, SKEW
* 205 3-975-063-01 BASE, SLIDE
* 206 3-975-065-01 SHAFT, MAIN
! 207 8-820-005-02 OPTICAL PICK-UP KHS-180A/J1N
208 1-665-390-11 OP-15 FLEXIBLE BOARD
209 3-975-067-01 GEAR, RACK
* 210 3-975-064-01 RETAINER, SLED GEAR
* 213 3-975-059-01 RETAINER, SKEW GEAR
214 3-975-057-01 GEAR, SKEW
215 4-974-711-01 SCREW (2X5) (P TYIGHT), (+) PTTWH
216 4-974-725-01 SCREW (M1.7X2.5), P
217 8-749-013-33 IC KU160 (CD SENSOR)
218 A-4683-008-A GEAR ASSY, LIMITTER
219 4-974-720-01 GEAR (S-B)
220 4-974-726-01 GEAR (S-A)
M501 X-3947-137-1 MOTOR ASSY, SLED
M901 1-698-944-11 MOTOR, DC (SPINDLE)
! or dotted line with mark ! are critical for safety.
Replace only with part number specified.
Les composants identifie´s par une
marque ! sont critiques pour la
se´curite´.
Ne les remplacer que par une pie´ce
portant le neme´ro spe´cifie´.
* 211 A-6065-053-A LM-56 BOARD, COMPLETE
212 1-665-327-11 LT-31 FLEXIBLE BOARD
M902 X-3947-138-1 MOTOR ASSY, SKEW
8-5
Page 61

DVP-S3000
AU-201 AU-203
8-2. ELECTRICAL PARTS LIST
NOTE:
• Due to standardization, replacements in the
parts list may be different from the parts specified in the diagrams or the components used
on the set.
• -XX and -X mean standardized parts, so they
may have some difference from the original
one.
• RESISTORS
All resistors are in ohms.
METAL: Metal-film resistor.
METAL OXIDE: Metal oxide-film resistor.
F: nonflammable
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
* A-6065-055-A AU-201 BOARD, COMPLETE (US,Canadian)
* A-6065-043-A AU-203 BOARD, COMPLETE
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
**********************
(Ref.No. 2,000 Series)
< CAPACITOR >
C410 1-162-283-31 CERAMIC 120PF 10% 50V
C411 1-162-283-31 CERAMIC 120PF 10% 50V
C412 1-106-343-00 MYLAR 1000PF 5% 200V
C413 1-130-484-00 MYLAR 0.012uF 5% 50V
C414 1-130-495-00 MYLAR 0.1uF 5% 50V
C415 1-126-023-11 ELECT 100uF 20% 25V
C416 1-136-808-11 FILM 100PF 5% 100V
C417 1-128-489-11 ELECT 3300uF 20% 16V
C510 1-162-283-31 CERAMIC 120PF 10% 50V
C511 1-162-283-31 CERAMIC 120PF 10% 50V
• Items marked “*” are not stocked since they
are seldom required for routine service.
Some delay should be anticipated when ordering these items.
• SEMICONDUCTORS
In each case, u: µ, for example:
uA. . : µA. . uPA. . : µPA. .
uPB. . : µPB. . uPC. . : µPC. .
uPD. . : µPD. .
• CAPACITORS
uF: µF
• COILS
uH: µH
C814 1-136-850-11 FILM 0.1uF 5% 63V
C815 1-124-721-11 ELECT 10uF 20% 50V
C816 1-124-910-11 ELECT 47uF 20% 50V
C819 1-136-850-11 FILM 0.1uF 5% 63V
C820 1-136-850-11 FILM 0.1uF 5% 63V
C821 1-136-850-11 FILM 0.1uF 5% 63V
C822 1-124-721-11 ELECT 10uF 20% 50V
C823 1-124-721-11 ELECT 10uF 20% 50V
C824 1-124-689-11 ELECT 1000uF 20% 16V
C827 1-163-239-11 CERAMIC CHIP 33PF 5% 50V
C845 1-124-721-11 ELECT 10uF 20% 50V
CN701 1-770-648-11 CONNECTOR, FFC/FPC 20P
* CN801 1-770-642-11 CONNECTOR, FFC/FPC 11P
* CN802 1-564-704-11 PIN, CONNECTOR (SMALL TYPE) 2P
* CN803 1-564-705-11 PIN, CONNECTOR (SMALL TYPE) 3P
The components identified by mark
! or dotted line with mark ! are
critical for safety.
Replace only with part number
specified.
Les composants identifiés par une
marque ! sont critiquens pour la
sécurité.
Ne les remplacer que par une pièce
portant le neméro spécifié.
When indicating parts by reference
number, please include the board.
< CONNECTOR >
C512 1-106-343-00 MYLAR 1000PF 5% 200V
C513 1-130-484-00 MYLAR 0.012uF 5% 50V
C514 1-130-495-00 MYLAR 0.1uF 5% 50V
C515 1-126-023-11 ELECT 100uF 20% 25V
C516 1-136-808-11 FILM 100PF 5% 100V
C517 1-128-489-11 ELECT 3300uF 20% 16V
C709 1-163-009-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.001uF 10% 50V
(US,Canadian)
C710 1-126-023-11 ELECT 100uF 20% 25V
C711 1-137-399-11 FILM 0.1uF 5% 50V
C715 1-163-239-11 CERAMIC CHIP 33PF 5% 50V
C716 1-107-682-11 CERAMIC CHIP 1uF 10% 16V
C801 1-126-046-11 ELECT 3.3uF 20% 50V
C802 1-163-009-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.001uF 10% 50V
C803 1-163-251-11 CERAMIC CHIP 100PF 5% 50V
C804 1-163-251-11 CERAMIC CHIP 100PF 5% 50V
C805 1-124-721-11 ELECT 10uF 20% 50V
C806 1-124-721-11 ELECT 10uF 20% 50V
C807 1-161-494-00 CERAMIC 0.022uF 25V
C808 1-161-494-00 CERAMIC 0.022uF 25V
C809 1-161-494-00 CERAMIC 0.022uF 25V
C810 1-161-494-00 CERAMIC 0.022uF 25V
C811 1-124-910-11 ELECT 47uF 20% 50V
C812 1-124-721-11 ELECT 10uF 20% 50V
C813 1-136-850-11 FILM 0.1uF 5% 63V
< DIODE >
D501 8-719-404-49 DIODE MA111
D506 8-719-404-49 DIODE MA111
D727 8-719-056-89 DIODE MA8120-TX (US,Canadian)
D729 8-719-404-49 DIODE MA111
< FERRITE BEAD >
FB701 1-414-553-11 INDUCTOR 0UH
FB702 1-414-553-11 INDUCTOR 0UH
FB703 1-414-553-11 INDUCTOR 0UH
FB704 1-414-553-11 INDUCTOR 0UH
FB705 1-414-553-11 INDUCTOR 0UH
FB706 1-414-553-11 INDUCTOR 0UH
FB707 1-414-553-11 INDUCTOR 0UH
FB711 1-414-553-11 INDUCTOR 0UH
FB712 1-414-553-11 INDUCTOR 0UH (US,Canadian)
FB713 1-414-135-11 INDUCTOR CHIP 0UH
FB714 1-414-135-11 INDUCTOR CHIP 0UH
FB715 1-414-135-11 INDUCTOR CHIP 0UH
* FB720 1-500-449-21 BEAD, FERRITE (SMD)
< FILTER >
FL401 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL501 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
8-6
Page 62
AU-201 AU-203 FP-611 FP619
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
FL503 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL701 1-416-488-11 COIL, TRAP (US,Canadian)
FL702 1-416-488-11 COIL, TRAP (US,Canadian)
< IC >
IC401 8-759-712-02 IC NJM2114D
IC501 8-759-712-02 IC NJM2114D
IC701 8-749-921-12 IC GP1F32T (DIGITAL OPTICAL OUT)
IC702 8-759-242-70 IC TC7WU04F
IC801 8-759-370-62 IC CXD8505BQ
< JACK >
* J701 1-779-872-11 JACK, PIN 4P (LINE OUT AUDIO1,2)
J702 1-764-188-21 JACK (SMALL TYPE)(DIA. 3.5)(S LINK)
(US,Canadian)
J703 1-779-744-11 JACK, PIN 1P (LINE OUT VIDEO)
J704 1-764-591-11 CONNECTOR, ROUND TYPE (S VIDEO OUT)
J706 1-779-382-11 JACK, PIN 1P (DIGITAL COAXIAL OUT)
< COIL >
L401 1-408-947-00 INDUCTOR 2.2mH
L501 1-408-947-00 INDUCTOR 2.2mH
L503 1-410-119-11 INDUCTOR 1mH
< TRANSISTOR >
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
R513 1-259-422-11 CARBON 560 5% 1/6W
R514 1-259-380-11 CARBON 10 5% 1/6W
R515 1-259-422-11 CARBON 560 5% 1/6W
R517 1-216-065-00 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/10W
R519 1-216-065-00 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/10W
R520 1-259-423-11 CARBON 620 5% 1/6W
R706 1-216-049-91 METAL GLAZE 1K 5% 1/10W
(US,Canadian)
R711 1-216-009-00 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/10W
R713 1-216-022-00 METAL CHIP 75 5% 1/10W
R803 1-216-182-00 METAL GLAZE 220 5% 1/8W
R804 1-216-182-00 METAL GLAZE 220 5% 1/8W
R805 1-216-182-00 METAL GLAZE 220 5% 1/8W
R806 1-216-198-91 METAL GLAZE 1K 5% 1/8W
R807 1-216-198-91 METAL GLAZE 1K 5% 1/8W
R808 1-216-198-91 METAL GLAZE 1K 5% 1/8W
R809 1-216-198-91 METAL GLAZE 1K 5% 1/8W
R810 1-216-198-91 METAL GLAZE 1K 5% 1/8W
R819 1-259-464-11 CARBON 33K 5% 1/6W
R820 1-259-464-11 CARBON 33K 5% 1/6W
R821 1-259-464-11 CARBON 33K 5% 1/6W
R822 1-259-464-11 CARBON 33K 5% 1/6W
R823 1-259-464-11 CARBON 33K 5% 1/6W
R824 1-259-464-11 CARBON 33K 5% 1/6W
R825 1-259-464-11 CARBON 33K 5% 1/6W
Q203 8-729-424-18 TRANSISTOR UN2113
Q204 8-729-424-18 TRANSISTOR UN2113
Q303 8-729-424-18 TRANSISTOR UN2113
Q401 8-729-231-55 TRANSISTOR 2SC2878-AB
Q403 8-729-231-55 TRANSISTOR 2SC2878-AB
Q501 8-729-231-55 TRANSISTOR 2SC2878-AB
Q503 8-729-231-55 TRANSISTOR 2SC2878-AB
< RESISTOR >
R221 1-216-097-91 METAL GLAZE 100K 5% 1/10W
R222 1-216-097-91 METAL GLAZE 100K 5% 1/10W
R321 1-216-097-91 METAL GLAZE 100K 5% 1/10W
R405 1-259-458-11 CARBON 18K 5% 1/6W
R406 1-259-458-11 CARBON 18K 5% 1/6W
R407 1-259-460-11 CARBON 22K 5% 1/6W
R408 1-259-460-11 CARBON 22K 5% 1/6W
R409 1-259-427-11 CARBON 910 5% 1/6W
R410 1-259-434-11 CARBON 1.8K 5% 1/6W
R411 1-259-488-11 CARBON 330K 5% 1/6W
R412 1-259-422-11 CARBON 560 5% 1/6W
R413 1-259-422-11 CARBON 560 5% 1/6W
R414 1-259-380-11 CARBON 10 5% 1/6W
R415 1-259-422-11 CARBON 560 5% 1/6W
R417 1-216-065-00 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/10W
R419 1-216-065-00 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/10W
R420 1-259-423-11 CARBON 620 5% 1/6W
R505 1-259-458-11 CARBON 18K 5% 1/6W
R506 1-259-458-11 CARBON 18K 5% 1/6W
R507 1-259-460-11 CARBON 22K 5% 1/6W
R508 1-259-460-11 CARBON 22K 5% 1/6W
R509 1-259-427-11 CARBON 910 5% 1/6W
R510 1-259-434-11 CARBON 1.8K 5% 1/6W
R511 1-259-488-11 CARBON 330K 5% 1/6W
R512 1-259-422-11 CARBON 560 5% 1/6W
R826 1-259-464-11 CARBON 33K 5% 1/6W
R829 1-216-049-91 METAL GLAZE 1K 5% 1/10W
R830 1-216-121-91 METAL GLAZE 1M 5% 1/10W
< TRANSFORMER >
T701 1-459-795-11 COIL (WITH CORE)
* A-6065-057-A FP-611 BOARD, COMPLETE (US,Canadian)
* A-6065-045-A FP-619 BOARD, COMPLETE
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
***************************
(Ref.No. 2,000 Series)
3-884-241-01 SHEET (C), ADHESIVE
< CAPACITOR >
C001 1-163-031-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 50V
C002 1-126-163-11 ELECT 4.7uF 20% 50V
C003 1-163-251-11 CERAMIC CHIP 100PF 5% 50V
C004 1-124-589-11 ELECT 47uF 20% 16V
C005 1-165-319-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 50V
C006 1-124-589-11 ELECT 47uF 20% 16V
C007 1-124-589-11 ELECT 47uF 20% 16V
C008 1-124-248-00 ELECT 22uF 20% 35V
C009 1-126-163-11 ELECT 4.7uF 20% 50V
C010 1-126-154-11 ELECT 47uF 20% 6.3V
C011 1-163-031-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 50V
C012 1-165-319-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 50V
C104 1-165-319-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 50V
C105 1-165-319-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 50V
C106 1-163-031-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 50V
C107 1-163-031-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 50V
C108 1-163-031-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 50V
8-7
Page 63

FP-611 FP619 LM-56 MB-80
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
< CONNECTOR >
CN101 1-691-647-11 SOCKET, CONNECTOR 13P
CN151 1-506-486-11 PIN, CONNECTOR 7P
< DIODE >
D001 8-719-210-39 DIODE EC10QS-04
D003 8-719-210-39 DIODE EC10QS-04
D004 8-719-420-90 DIODE MA8051-M
D005 8-719-977-69 DIODE DTZ24B
D006 8-719-404-49 DIODE MA111 (US,Canadian)
D007 8-719-404-49 DIODE MA111 (US,Canadian)
D101 8-719-404-49 DIODE MA111
D102 8-719-404-49 DIODE MA111
D103 8-719-032-98 LED SEL5820A-TP15 (DNR)
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
< FERRITE BEAD >
FB101 1-414-135-11 INDUCTOR CHIP 0UH
FB102 1-414-135-11 INDUCTOR CHIP 0UH
* FB103 1-500-449-21 BEAD, FERRITE (SMD)
< FILTER >
FL001 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
< IC >
IC001 8-759-438-82 IC uPD16311GC-AB6
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
R108 1-216-059-00 METAL CHIP 2.7K 5% 1/10W
R109 1-216-063-91 METAL GLAZE 3.9K 5% 1/10W
R110 1-216-071-00 METAL CHIP 8.2K 5% 1/10W
R111 1-216-059-00 METAL CHIP 2.7K 5% 1/10W
R112 1-216-063-91 METAL GLAZE 3.9K 5% 1/10W
R113 1-216-071-00 METAL CHIP 8.2K 5% 1/10W
R114 1-216-063-91 METAL GLAZE 3.9K 5% 1/10W
R115 1-216-059-00 METAL CHIP 2.7K 5% 1/10W
R116 1-216-037-00 METAL CHIP 330 5% 1/10W
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
R117 1-216-071-00 METAL CHIP 8.2K 5% 1/10W
R118 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
< SWITCH >
S101 1-762-365-21 SWITCH, TACTILE (RETURN)
S102 1-762-365-21 SWITCH, TACTILE (ENTER)
S103 1-762-365-21 SWITCH, TACTILE (TITLE)
S104 1-762-365-21 SWITCH, TACTILE (DVD MENU)
S105 1-771-215-11 SWITCH, TACTILE (←/↑/↓/→)
S109 1-762-365-21 SWITCH, TACTILE (OPEN/CLOSE)
S110 1-762-365-21 SWITCH, TACTILE (PREV)
S111 1-762-365-21 SWITCH, TACTILE (NEXT)
S112 1-762-365-21 SWITCH, TACTILE (PAUSE)
S113 1-762-365-21 SWITCH, TACTILE (PLAY)
S114 1-762-365-21 SWITCH, TACTILE (STOP)
S115 1-762-365-21 SWITCH, TACTILE (DISPLAY/DNR)
< COIL >
L001 1-414-185-41 INDUCTOR 22uH
< FLUORECENT INDICATOR >
ND001 1-517-639-11 TUBE, FLUORESCENT INDICATOR
< TRANSISTOR >
Q001 8-729-105-29 TRANSISTOR 2SA1385
Q002 8-729-010-05 TRANSISTOR MSB709-RT1
< RESISTOR >
R001 1-216-009-00 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/10W
R002 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R003 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R004 1-216-081-00 METAL CHIP 22K 5% 1/10W
R005 1-216-063-91 METAL GLAZE 3.9K 5% 1/10W
R006 1-216-063-91 METAL GLAZE 3.9K 5% 1/10W
R007 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R013 1-216-091-00 METAL CHIP 56K 5% 1/10W
R014 1-216-049-91 METAL GLAZE 1K 5% 1/10W
R019 1-216-025-91 METAL GLAZE 100 5% 1/10W
R020 1-216-025-91 METAL GLAZE 100 5% 1/10W
R021 1-216-025-91 METAL GLAZE 100 5% 1/10W
R023 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R024 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R025 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R026 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R105 1-216-059-00 METAL CHIP 2.7K 5% 1/10W
R106 1-216-063-91 METAL GLAZE 3.9K 5% 1/10W
R107 1-216-071-00 METAL CHIP 8.2K 5% 1/10W
< TRANSFORMER >
T001 1-448-740-31 TRANSFORMER, DC-DC CONVERTER
* A-6065-053-A LM-56 BOARD, COMPLETE
**********************
(Ref.No. 3,000 Series)
< CONNECTOR >
CN501 1-691-799-11 SOCKET, CONNECTOR 8P
< IC >
IC501 8-719-052-42 IC ELEMENT, HOLE HW-108A-FT(D)
IC502 8-719-052-42 IC ELEMENT, HOLE HW-108A-FT(D)
MB-80 BOARD, COMPLETE
**********************
(Ref.No. 1,000 Series)
< CAPACITOR >
C005 1-126-206-11 ELECT CHIP 100uF 20% 6.3V
C009 1-126-204-11 ELECT CHIP 47uF 20% 16V
C010 1-126-204-11 ELECT CHIP 47uF 20% 16V
C012 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C013 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C014 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C015 1-162-913-11 CERAMIC CHIP 8PF 0.5PF 50V
C016 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C017 1-126-206-11 ELECT CHIP 100uF 20% 6.3V
C018 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
8-8
Page 64

MB-80
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
C020 1-126-206-11 ELECT CHIP 100uF 20% 6.3V
C021 1-104-852-11 TANTAL. CHIP 22uF 20% 10V
C023 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C025 1-104-852-11 TANTAL. CHIP 22uF 20% 10V
C027 1-162-912-11 CERAMIC CHIP 7PF 0.5PF 50V
C029 1-162-907-11 CERAMIC CHIP 2PF 0.25PF 50V
C035 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C036 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C037 1-126-206-11 ELECT CHIP 100uF 20% 6.3V
C039 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C040 1-126-206-11 ELECT CHIP 100uF 20% 6.3V
C041 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C042 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C043 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C044 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C046 1-126-206-11 ELECT CHIP 100uF 20% 6.3V
C047 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C048 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C049 1-162-924-11 CERAMIC CHIP 56PF 5% 50V
C051 1-162-921-11 CERAMIC CHIP 33PF 5% 50V
C052 1-126-206-11 ELECT CHIP 100uF 20% 6.3V
C053 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C054 1-164-227-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.022uF 10% 25V
C055 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C057 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C058 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C070 1-162-905-11 CERAMIC CHIP 1PF 0.25PF 50V
C071 1-162-907-11 CERAMIC CHIP 2PF 0.25PF 50V
C074 1-162-915-11 CERAMIC CHIP 10PF 0.5PF 50V
C075 1-162-915-11 CERAMIC CHIP 10PF 0.5PF 50V
C076 1-162-918-11 CERAMIC CHIP 18PF 5% 50V
C077 1-162-915-11 CERAMIC CHIP 10PF 0.5PF 50V
C078 1-162-917-11 CERAMIC CHIP 15PF 5% 50V
C079 1-162-915-11 CERAMIC CHIP 10PF 0.5PF 50V
C080 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C081 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C082 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C083 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C084 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C086 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C087 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C088 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C089 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C091 1-162-919-11 CERAMIC CHIP 22PF 5% 50V
C092 1-162-919-11 CERAMIC CHIP 22PF 5% 50V
C096 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C097 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C098 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C099 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C100 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C101 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C102 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C105 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C106 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C107 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C108 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C109 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C110 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C116 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
C117 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C118 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C120 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C122 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C123 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C124 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C125 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C126 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C127 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C128 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C129 1-104-851-11 TANTAL. CHIP 10uF 20% 10V
C130 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C134 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C136 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C137 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C139 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C140 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C142 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C143 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C144 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C147 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C148 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C150 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C151 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C152 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C154 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C156 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C158 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C159 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C160 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C161 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C162 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C164 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C165 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C166 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C167 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C169 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C170 1-162-919-11 CERAMIC CHIP 22PF 5% 50V
C171 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C172 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C173 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C174 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C180 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C181 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C182 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C183 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C184 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C185 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C188 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C189 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C190 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C191 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C192 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C193 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C194 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C195 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C196 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C198 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
8-9
Page 65

MB-80
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
C199 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C205 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C206 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C207 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C208 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C209 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C210 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C211 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C212 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C213 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C214 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C215 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C216 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C217 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C218 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C219 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C220 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C221 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C222 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C223 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C224 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C225 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C226 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C230 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C231 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C232 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C234 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C235 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
C278 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C279 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C280 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C281 1-104-535-11 FILM CHIP 470PF 5% 50V
C282 1-104-537-11 FILM CHIP 680PF 5% 50V
C284 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C285 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C286 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C287 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C288 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C291 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C307 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C308 1-104-851-11 TANTAL. CHIP 10uF 20% 10V
C313 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C316 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C318 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C319 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C320 1-126-205-11 ELECT CHIP 47uF 20% 6.3V
C323 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C324 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C325 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C326 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C327 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
(US,Canadian)
C328 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
(US,Canadian)
C329 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
(US,Canadian)
C236 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C237 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C238 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C239 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C240 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C241 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C242 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C243 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C245 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C247 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C248 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C250 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C251 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C252 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C253 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C255 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C256 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C257 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C265 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C266 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C267 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C268 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C270 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C271 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C272 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C273 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C274 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C275 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C276 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C277 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C331 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
(US,Canadian)
C333 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C334 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C361 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C362 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C363 1-126-206-11 ELECT CHIP 100uF 20% 6.3V
C369 1-126-205-11 ELECT CHIP 47uF 20% 6.3V
C371 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C372 1-162-917-11 CERAMIC CHIP 15PF 5% 50V
C374 1-126-205-11 ELECT CHIP 47uF 20% 6.3V
C375 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C376 1-126-205-11 ELECT CHIP 47uF 20% 6.3V
C378 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C379 1-162-917-11 CERAMIC CHIP 15PF 5% 50V
C381 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C384 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C385 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C386 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C387 1-126-206-11 ELECT CHIP 100uF 20% 6.3V
C388 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C389 1-162-917-11 CERAMIC CHIP 15PF 5% 50V
C390 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C395 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C396 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C400 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C401 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C403 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C404 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C405 1-107-686-11 TANTAL. CHIP 4.7uF 20% 16V
8-10
Page 66

MB-80
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
C406 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C407 1-104-851-11 TANTAL. CHIP 10uF 20% 10V
C409 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C411 1-104-851-11 TANTAL. CHIP 10uF 20% 10V
C418 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C419 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C420 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C429 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C430 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C431 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C433 1-126-205-11 ELECT CHIP 47uF 20% 6.3V
C434 1-126-205-11 ELECT CHIP 47uF 20% 6.3V
C439 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C440 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C441 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C442 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C443 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C444 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C446 1-126-206-11 ELECT CHIP 100uF 20% 6.3V
C447 1-126-206-11 ELECT CHIP 100uF 20% 6.3V
C448 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C449 1-126-205-11 ELECT CHIP 47uF 20% 6.3V
C451 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C452 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C454 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C455 1-164-227-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.022uF 10% 25V
C456 1-109-982-11 CERAMIC CHIP 1uF 10% 10V
C457 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C458 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C459 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C460 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C461 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C462 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C463 1-126-206-11 ELECT CHIP 100uF 20% 6.3V
C466 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C469 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C475 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C476 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C477 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C480 1-162-962-11 CERAMIC CHIP 470PF 10% 50V
C481 1-162-962-11 CERAMIC CHIP 470PF 10% 50V
C483 1-164-004-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 25V
C484 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C486 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C487 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C490 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C492 1-104-851-11 TANTAL. CHIP 10uF 20% 10V
C493 1-162-927-11 CERAMIC CHIP 100PF 5% 50V
C494 1-165-176-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.047uF 10% 16V
C495 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C496 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C497 1-164-489-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.22uF 10% 16V
C498 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C499 1-162-965-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.0015uF 10% 50V
C500 1-104-851-11 TANTAL. CHIP 10uF 20% 10V
C501 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C502 1-162-968-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.0047uF 10% 50V
C515 1-126-206-11 ELECT CHIP 100uF 20% 6.3V
C518 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
C519 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C520 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C522 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C523 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C524 1-104-851-11 TANTAL. CHIP 10uF 20% 10V
C525 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C526 1-162-959-11 CERAMIC CHIP 330PF 5% 50V
C527 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C528 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C529 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C530 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C531 1-104-851-11 TANTAL. CHIP 10uF 20% 10V
C532 1-104-851-11 TANTAL. CHIP 10uF 20% 10V
C533 1-104-851-11 TANTAL. CHIP 10uF 20% 10V
C534 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C535 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C536 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C537 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C538 1-164-217-11 CERAMIC CHIP 150PF 5% 50V
C539 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C540 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C541 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C542 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C543 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C544 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C545 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C546 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C547 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C548 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C549 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C550 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C552 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C554 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C555 1-126-206-11 ELECT CHIP 100uF 20% 6.3V
C558 1-162-964-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.001uF 10% 50V
C574 1-164-489-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.22uF 10% 16V
C575 1-164-245-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.015uF 10% 25V
C577 1-104-851-11 TANTAL. CHIP 10uF 20% 10V
C580 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C581 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C583 1-162-969-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.0068uF 10% 25V
C585 1-164-489-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.22uF 10% 16V
C586 1-128-596-11 ELECT CHIP 3.3uF 20% 50V
C587 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C588 1-162-968-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.0047uF 10% 50V
C589 1-162-967-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.0033uF 10% 50V
C590 1-162-968-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.0047uF 10% 50V
C591 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C592 1-162-967-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.0033uF 10% 50V
C593 1-164-346-11 CERAMIC CHIP 1uF 16V
C594 1-164-346-11 CERAMIC CHIP 1uF 16V
C595 1-162-967-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.0033uF 10% 50V
C596 1-162-962-11 CERAMIC CHIP 470PF 10% 50V
C598 1-162-967-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.0033uF 10% 50V
C599 1-164-346-11 CERAMIC CHIP 1uF 16V
C600 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C601 1-162-967-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.0033uF 10% 50V
C602 1-162-962-11 CERAMIC CHIP 470PF 10% 50V
C603 1-165-176-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.047uF 10% 16V
8-11
Page 67
MB-80
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
C604 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C605 1-164-227-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.022uF 10% 25V
C606 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C607 1-164-346-11 CERAMIC CHIP 1uF 16V
C608 1-164-227-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.022uF 10% 25V
C609 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C610 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C611 1-164-156-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C612 1-164-156-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C613 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C614 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C615 1-164-156-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C616 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C617 1-164-156-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C618 1-164-156-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C619 1-164-346-11 CERAMIC CHIP 1uF 16V
C620 1-126-204-11 ELECT CHIP 47uF 20% 16V
C621 1-164-346-11 CERAMIC CHIP 1uF 16V
C622 1-126-204-11 ELECT CHIP 47uF 20% 16V
C623 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C624 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C625 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C626 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C627 1-164-346-11 CERAMIC CHIP 1uF 16V
C628 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C629 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C630 1-164-156-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C633 1-164-156-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C634 1-164-156-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C635 1-164-156-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C636 1-164-346-11 CERAMIC CHIP 1uF 16V
C637 1-126-204-11 ELECT CHIP 47uF 20% 16V
C638 1-164-156-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C639 1-164-156-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C640 1-164-156-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C641 1-164-156-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C642 1-164-156-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C643 1-164-346-11 CERAMIC CHIP 1uF 16V
C644 1-164-346-11 CERAMIC CHIP 1uF 16V
C645 1-126-204-11 ELECT CHIP 47uF 20% 16V
C646 1-164-346-11 CERAMIC CHIP 1uF 16V
C647 1-164-156-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C648 1-164-156-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C649 1-164-156-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C650 1-164-346-11 CERAMIC CHIP 1uF 16V
C651 1-165-176-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.047uF 10% 16V
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
C671 1-165-176-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.047uF 10% 16V
C672 1-165-176-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.047uF 10% 16V
C674 1-162-965-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.0015uF 10% 50V
C676 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C678 1-162-967-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.0033uF 10% 50V
C679 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C802 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
C803 1-104-852-11 TANTAL. CHIP 22uF 20% 10V
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
C804 1-104-852-11 TANTAL. CHIP 22uF 20% 10V
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
C805 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
C806 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
C807 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C808 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
C810 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
C811 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
C812 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
C813 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
C814 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
C815 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
C816 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
C817 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
C818 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
C819 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
C820 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
C821 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
C822 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
C652 1-164-217-11 CERAMIC CHIP 150PF 5% 50V
C653 1-165-176-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.047uF 10% 16V
C654 1-164-217-11 CERAMIC CHIP 150PF 5% 50V
C655 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C656 1-164-227-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.022uF 10% 25V
C657 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C658 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C659 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C660 1-164-346-11 CERAMIC CHIP 1uF 16V
C662 1-162-927-11 CERAMIC CHIP 100PF 5% 50V
C663 1-164-227-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.022uF 10% 25V
C664 1-162-927-11 CERAMIC CHIP 100PF 5% 50V
C901 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C902 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C903 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C904 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C905 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C906 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
< CONNECTOR >
CN005 1-779-344-11 CONNECTOR, FFC/FPC 20P
CN008 1-573-806-21 PIN, CONNECTOR (1.5MM) (SMD)6P
* CN009 1-784-023-21 CONNECTOR, FLEXIBLE 13P
* CN011 1-564-507-11 PLUG, CONNECTOR 4P
8-12
Page 68

MB-80
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
* CN135 1-573-304-11 CONNECTOR, BOARD TO BOARD 8P
CN381 1-774-766-11 CONNECTOR, FFC/FPC 11P
* CN382 1-770-469-21 PIN, CONNECTOR (PC BOARD) 2P
CN885 1-779-343-11 CONNECTOR, FFC/FPC 23P
CN886 1-779-343-11 CONNECTOR, FFC/FPC 23P
CN980 1-779-343-11 CONNECTOR, FFC/FPC 23P
CN981 1-573-768-21 PIN, CONNECTOR (1.5MM) (SMD)5P
< TRIMMER >
CT001 1-141-422-11 CAP, ADJ 10PF
CT002 1-141-422-11 CAP, ADJ 10PF
< DIODE >
D001 8-719-055-86 DIODE KV1470TL1-3
D037 8-719-420-14 DIODE MA8082-M (US,Canadian)
D601 8-719-404-49 DIODE MA111
D766 8-719-421-27 DIODE MA728
D886 8-719-404-49 DIODE MA111
< FUSE >
! F001 1-533-710-11 FUSE (SMD)(1.6A)
! F003 1-533-771-21 FUSE (SMD)(0.8A)
! F005 1-533-771-21 FUSE (SMD)(0.8A)
! F006 1-533-710-11 FUSE (SMD)(1.6A)
! F007 1-533-710-11 FUSE (SMD)(1.6A)
! F008 1-533-710-11 FUSE (SMD)(1.6A)
! F009 1-533-710-11 FUSE (SMD)(1.6A)
! F010 1-533-771-21 FUSE (SMD)(0.8A)
! F011 1-533-771-21 FUSE (SMD)(0.8A)
! F805 1-533-855-21 FUSE (SMD)(0.125A)
! F806 1-533-855-21 FUSE (SMD)(0.125A)
< FERRITE BEAD >
FB005 1-414-553-11 INDUCTOR 0UH
FB006 1-414-553-11 INDUCTOR 0UH
FB008 1-414-553-11 INDUCTOR 0UH
FB015 1-414-553-11 INDUCTOR 0UH
FB053 1-500-283-11 INDUCTOR, FERRITE BEAD
FB054 1-500-283-11 INDUCTOR, FERRITE BEAD
FB055 1-500-283-11 INDUCTOR, FERRITE BEAD
FB056 1-500-283-11 INDUCTOR, FERRITE BEAD
FB059 1-500-283-11 INDUCTOR, FERRITE BEAD
FB060 1-500-283-11 INDUCTOR, FERRITE BEAD
FB061 1-500-283-11 INDUCTOR, FERRITE BEAD
FB180 1-412-390-21 INDUCTOR CHIP 0uH
FB181 1-412-390-21 INDUCTOR CHIP 0uH
< FILTER >
FL001 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL002 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL003 1-239-400-11 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL004 1-239-400-11 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL005 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
FL006 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL007 1-239-400-11 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL008 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL009 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL010 1-239-400-11 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL011 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL012 1-239-400-11 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL013 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL014 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL015 1-239-400-11 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL016 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL033 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL034 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL035 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL036 1-239-400-11 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL037 1-239-400-11 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL038 1-239-400-11 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL039 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL040 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL041 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL042 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL043 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL044 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL045 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL090 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL091 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL092 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL093 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL135 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL136 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL137 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL138 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL139 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL180 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL181 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL182 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL183 1-239-400-11 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL184 1-239-400-11 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL185 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL186 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL215 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL216 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL217 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL280 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL281 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL282 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL283 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL284 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL285 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL310 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL311 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL312 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL313 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL314 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
8-13
The components identified by
mark ! or dotted line with
mark ! are critical for safety.
Replace only with part number
specified.
Les composants identifiés par une
marque ! sont critiques pour la
sécurité.
Ne les remplacer que par une pièce
portant le neméro spécifié.
Page 69

MB-80
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
FL315 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
FL316 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
FL380 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL381 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL382 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL383 1-239-400-11 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL384 1-239-400-11 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL475 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL476 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL477 1-239-400-11 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL479 1-233-894-21 FILTER, LOW PASS (14MHz)
FL480 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL481 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL482 1-239-400-11 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL483 1-239-400-11 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL484 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL716 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL717 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
< IC >
IC002 8-759-449-38 IC MSM10S0050-039GS-2K
IC003 8-759-431-14 IC PQ3TZ53U
IC004 8-759-510-71 IC BA10358F-E2
IC005 8-759-431-14 IC PQ3TZ53U
IC006 8-759-981-48 IC RC082M2G2
IC008 8-759-271-88 IC TC7SHU04FU-TE85R
IC009 8-759-271-88 IC TC7SHU04FU-TE85R
IC010 8-759-447-77 IC TC7WH74FU(TR12R)
IC011 8-759-447-77 IC TC7WH74FU(TR12R)
IC012 8-759-081-44 IC TC74VHC04F(EL)
IC015 8-759-434-20 IC PST572DML
IC016 8-759-423-49 IC MC74F125MEL
IC017 8-759-058-58 IC TC7S04FU(TE85R)
IC021 8-759-481-49 IC MB89099PF-G-DPX1010U-BND
(US,Canadian)
IC021 8-759-481-50 IC MB89099PF-G-DPX1010E-BND
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
IC022 8-759-356-27 IC NJM2129M-TE2 (US,Canadian)
IC024 8-759-196-97 IC TC7SH32FU-TE85R
IC025 8-759-196-93 IC TC7SH00FU-TE85R
IC026 8-759-196-93 IC TC7SH00FU-TE85R
IC027 8-759-271-86 IC TC7SH04FU-TE85R
IC028 8-759-271-86 IC TC7SH04FU-TE85R
IC090 8-759-489-89 IC HD6437034AD49F
IC092 8-759-058-62 IC TC7S08FU(TE85R)
IC093 8-759-481-47 IC MSM534002C-DPX1010GS-AKR1
IC094 8-759-449-34 IC HM628128ALFP-5
IC095 8-759-344-37 IC MC74AC138MEL
IC096 8-759-423-32 IC MC74AC32MEL
IC097 8-759-096-87 IC TC7WU04FU(TE12R)
IC098 8-759-423-49 IC MC74F125MEL
IC099 8-759-180-53 IC TC74AC244FS-EL
IC100 8-759-423-38 IC MC74ACT245MEL
IC101 8-759-423-38 IC MC74ACT245MEL
IC102 8-759-423-49 IC MC74F125MEL
IC103 8-759-423-33 IC MC74AC74MEL
IC104 8-759-180-53 IC TC74AC244FS-EL
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
IC105 8-759-180-53 IC TC74AC244FS-EL
IC106 8-759-423-38 IC MC74ACT245MEL
IC135 8-759-180-53 IC TC74AC244FS-EL
IC136 8-759-427-97 IC HD6413002F17
IC137 8-759-344-37 IC MC74AC138MEL
IC138 8-759-448-51 IC N341256SO-55TE2
IC139 8-759-468-72 IC AK6420HM-E2
IC140 8-759-481-51 IC MSM532000B-DPX1010RS
IC141 8-759-423-49 IC MC74F125MEL
IC142 8-759-180-53 IC TC74AC244FS-EL
IC144 8-759-196-97 IC TC7SH32FU-TE85R
IC145 8-759-423-49 IC MC74F125MEL
IC146 8-759-096-87 IC TC7WU04FU(TE12R)
IC147 8-759-270-56 IC SN74HC377ANS-E20
IC148 8-759-270-56 IC SN74HC377ANS-E20
IC149 8-759-270-56 IC SN74HC377ANS-E20
IC150 8-759-270-56 IC SN74HC377ANS-E20
IC154 8-759-058-62 IC TC7S08FU(TE85R)
IC180 8-759-423-33 IC MC74AC74MEL
IC181 8-759-460-93 IC CXD8663Q
IC182 8-759-490-27 IC HM514800CLJ7Z
IC183 8-759-196-97 IC TC7SH32FU-TE85R
IC184 8-759-460-94 IC CXD8669AQ
IC185 8-759-082-57 IC TC7W04FU(TE12R)
IC215 8-759-448-51 IC N341256SO-55TE2
IC216 8-752-363-62 IC CXD1186CQ
IC217 8-759-449-40 IC CXD8598R
IC219 8-759-423-49 IC MC74F125MEL
IC280 8-759-389-93 IC HM514260CTT-7Z
IC281 8-752-386-59 IC CXD1900BQ
IC282 8-759-389-93 IC HM514260CTT-7Z
IC283 8-759-389-93 IC HM514260CTT-7Z
IC284 8-759-389-93 IC HM514260CTT-7Z
IC310 8-759-449-39 IC CXD8602Q
IC311 8-759-350-08 IC MSM518222B-30GS-KR1
IC312 8-759-449-45 IC CXD8600R
IC313 8-759-449-34 IC HM628128ALFP-5
IC315 8-759-186-57 IC TC74VHC175F(EL)
IC316 8-759-442-77 IC MSM518126-50JSDR1
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
IC317 8-759-453-79 IC CXD8664Q
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
IC318 8-752-381-72 IC CXD1853Q
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
IC380 8-759-490-29 IC CXD8603BR
IC381 8-759-449-42 IC DSP56009
IC382 8-759-082-57 IC TC7W04FU(TE12R)
IC383 8-759-448-51 IC N341256SO-55TE2
IC385 8-759-058-62 IC TC7S08FU(TE85R)
IC474 8-759-711-58 IC NJM78L05UA
IC475 8-752-379-07 IC CXD1914Q
IC485 8-759-066-59 IC TC74HC4053AFS-EL
IC486 8-759-066-59 IC TC74HC4053AFS-EL
IC487 8-759-066-59 IC TC74HC4053AFS-EL
IC491 8-759-449-30 IC MB90091APF-G-001-BND
IC492 8-759-186-26 IC TC74VHC02F(EL)
IC493 8-759-079-46 IC TC74VHC00FS(EL)
IC494 8-759-490-77 IC MSM534001C-CPX1010GS-KR1
IC717 8-752-369-78 IC CXD2545Q
8-14
Page 70
MB-80
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
IC722 8-759-067-52 IC MB88347PFV-G-BND-ER
IC723 8-759-510-73 IC BA10393F-E2
IC768 8-759-448-71 IC BU4053BCFV-E2
IC769 8-759-331-71 IC NJM4558E(TE2)
IC770 8-759-449-41 IC CXD8599Q
IC771 8-759-701-36 IC NJM3403AM(TE2)
IC775 8-759-510-71 IC BA10358F-E2
IC777 8-759-510-73 IC BA10393F-E2
IC778 8-759-510-73 IC BA10393F-E2
IC886 8-759-701-36 IC NJM3403AM(TE2)
IC887 8-759-333-63 IC LB1896-TE-B
IC888 8-759-701-39 IC NJM3404AM
IC889 8-759-384-55 IC LA6527N-TE-B
IC890 8-759-449-55 IC BA5970FP-E2
IC891 8-759-452-00 IC BA6295AFP-E2
IC892 8-759-448-71 IC BU4053BCFV-E2
IC982 8-759-701-39 IC NJM3404AM
IC983 8-759-448-71 IC BU4053BCFV-E2
< COIL >
L003 1-409-529-41 COIL, CHOKE 10uH
L004 1-409-529-41 COIL, CHOKE 10uH
L005 1-409-529-41 COIL, CHOKE 10uH
L006 1-409-529-41 COIL, CHOKE 10uH
L013 1-412-939-11 INDUCTOR 1uH
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
Q520 8-729-230-63 TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-YG
Q521 8-729-230-63 TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-YG
Q522 8-729-230-63 TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-YG
Q526 8-729-420-24 TRANSISTOR 2SB1218A-QRS
Q527 8-729-420-24 TRANSISTOR 2SB1218A-QRS
Q528 8-729-420-24 TRANSISTOR 2SB1218A-QRS
Q532 8-729-230-63 TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-YG
Q533 8-729-230-63 TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-YG
Q534 8-729-230-63 TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-YG
Q538 8-729-143-13 TRANSISTOR 2SC4176-B34
Q539 8-729-143-13 TRANSISTOR 2SC4176-B34
Q540 8-729-143-07 TRANSISTOR 2SA1610-Y33
Q542 8-729-420-24 TRANSISTOR 2SB1218A-QRS
Q543 8-729-420-24 TRANSISTOR 2SB1218A-QRS
Q544 8-729-420-24 TRANSISTOR 2SB1218A-QRS
Q545 8-729-230-63 TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-YG
Q546 8-729-230-63 TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-YG
Q547 8-729-230-63 TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-YG
Q552 8-729-403-35 TRANSISTOR UN5113
Q563 8-729-230-63 TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-YG
Q564 8-729-420-24 TRANSISTOR 2SB1218A-QRS
Q565 8-729-230-63 TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-YG
Q566 8-729-420-24 TRANSISTOR 2SB1218A-QRS
Q567 8-729-230-63 TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-YG
Q568 8-729-420-24 TRANSISTOR 2SB1218A-QRS
L014 1-412-939-11 INDUCTOR 1uH
L020 1-414-755-11 INDUCTOR 22uH
L475 1-409-556-11 COIL, CHOKE 47uH
L476 1-414-755-11 INDUCTOR 22uH
L477 1-414-755-11 INDUCTOR 22uH
L483 1-414-755-11 INDUCTOR 22uH
L484 1-414-755-11 INDUCTOR 22uH
L485 1-216-295-11 CONDUCTOR, CHIP (2012)
L486 1-216-295-11 CONDUCTOR, CHIP (2012)
L488 1-414-755-11 INDUCTOR 22uH
L489 1-414-755-11 INDUCTOR 22uH
L492 1-409-556-11 COIL, CHOKE 47uH
L496 1-414-755-11 INDUCTOR 22uH
L769 1-409-556-11 COIL, CHOKE 47uH
L770 1-414-756-11 INDUCTOR 47uH
L771 1-409-556-11 COIL, CHOKE 47uH
L773 1-414-756-11 INDUCTOR 47uH
< TRANSISTOR >
Q003 8-729-230-63 TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-YG
Q004 8-729-922-65 TRANSISTOR 2SD1760F5-PQR
Q090 8-729-015-76 TRANSISTOR UN5211-TX
Q091 8-729-015-76 TRANSISTOR UN5211-TX
Q496 8-729-230-63 TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-YG
Q497 8-729-230-63 TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-YG
Q498 8-729-230-63 TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-YG
Q499 8-729-230-63 TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-YG
Q500 8-729-230-63 TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-YG
Q501 8-729-230-63 TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-YG
Q502 8-729-420-24 TRANSISTOR 2SB1218A-QRS
Q508 8-729-230-63 TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-YG
Q511 8-729-420-24 TRANSISTOR 2SB1218A-QRS
Q515 8-729-420-24 TRANSISTOR 2SB1218A-QRS
Q516 8-729-420-24 TRANSISTOR 2SB1218A-QRS
Q584 8-729-230-63 TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-YG
Q585 8-729-230-63 TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-YG
Q586 8-729-230-63 TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-YG
Q587 8-729-230-63 TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-YG
Q588 8-729-230-63 TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-YG
Q589 8-729-230-63 TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-YG
Q765 8-729-230-63 TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-YG
Q766 8-729-015-76 TRANSISTOR UN5211-TX
Q886 8-729-230-63 TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-YG
Q887 8-729-403-35 TRANSISTOR UN5113
Q888 8-729-230-63 TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-YG
Q889 8-729-822-84 TRANSISTOR 2SB1202FAST
Q890 8-729-403-35 TRANSISTOR UN5113
Q891 8-729-403-35 TRANSISTOR UN5113
< RESISTOR >
R002 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R003 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R004 1-216-857-11 METAL CHIP 1M 5% 1/16W
R005 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R006 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R007 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R008 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R009 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R010 1-216-857-11 METAL CHIP 1M 5% 1/16W
R011 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R012 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R013 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R014 1-216-793-11 METAL GLAZE 4.7 5% 1/16W
R015 1-216-793-11 METAL GLAZE 4.7 5% 1/16W
R016 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R017 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R020 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R021 1-216-817-11 METAL CHIP 470 5% 1/16W
8-15
Page 71

MB-80
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
R022 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R023 1-216-857-11 METAL CHIP 1M 5% 1/16W
R024 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R025 1-218-871-11 METAL GLAZE 10K 0.50% 1/16W
R026 1-218-871-11 METAL GLAZE 10K 0.50% 1/16W
R027 1-216-845-11 METAL CHIP 100K 5% 1/16W
R028 1-216-845-11 METAL CHIP 100K 5% 1/16W
R030 1-216-837-11 METAL CHIP 22K 5% 1/16W
R031 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R032 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R033 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R034 1-216-841-11 METAL CHIP 47K 5% 1/16W
R035 1-216-813-11 METAL CHIP 220 5% 1/16W
R036 1-216-842-11 METAL CHIP 56K 5% 1/16W
R037 1-216-839-11 METAL CHIP 33K 5% 1/16W
R038 1-216-837-11 METAL CHIP 22K 5% 1/16W
R039 1-216-837-11 METAL CHIP 22K 5% 1/16W
R041 1-216-198-91 METAL GLAZE 1K 5% 1/8W
R042 1-216-815-11 METAL CHIP 330 5% 1/16W
R043 1-216-198-91 METAL GLAZE 1K 5% 1/8W
R044 1-216-198-91 METAL GLAZE 1K 5% 1/8W
R045 1-216-827-11 METAL CHIP 3.3K 5% 1/16W
R047 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R052 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R057 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R058 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R062 1-216-797-11 METAL CHIP 10 5% 1/16W
R063 1-216-820-11 METAL CHIP 820 5% 1/16W
R067 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R068 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R074 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R075 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R076 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R077 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R078 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R079 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R080 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R081 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R082 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R083 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R084 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R085 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R086 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R087 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R088 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R089 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R090 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R091 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R092 1-216-837-11 METAL CHIP 22K 5% 1/16W
R093 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R094 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R095 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R096 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R097 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R098 1-216-857-11 METAL CHIP 1M 5% 1/16W
R100 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R101 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R102 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
R103 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R104 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R105 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R106 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R108 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R112 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R113 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R119 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R120 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R122 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R123 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R124 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R125 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R126 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R127 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R128 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R129 1-216-841-11 METAL CHIP 47K 5% 1/16W
R130 1-216-841-11 METAL CHIP 47K 5% 1/16W
R131 1-216-841-11 METAL CHIP 47K 5% 1/16W
R132 1-216-841-11 METAL CHIP 47K 5% 1/16W
R134 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R136 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R137 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R138 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R139 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R141 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R143 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R144 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R145 1-216-841-11 METAL CHIP 47K 5% 1/16W
R146 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R148 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R149 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R150 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R151 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R154 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R155 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R156 1-216-864-11 METAL CHIP 0 5% 1/16W
R158 1-216-864-11 METAL CHIP 0 5% 1/16W
R162 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R163 1-218-484-11 METAL GLAZE 750 5% 1/16W
R165 1-216-813-11 METAL CHIP 220 5% 1/16W
R166 1-216-813-11 METAL CHIP 220 5% 1/16W
R167 1-218-484-11 METAL GLAZE 750 5% 1/16W
R168 1-216-803-11 METAL CHIP 33 5% 1/16W
R169 1-216-803-11 METAL CHIP 33 5% 1/16W
R170 1-216-803-11 METAL CHIP 33 5% 1/16W
R171 1-216-803-11 METAL CHIP 33 5% 1/16W
R172 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R173 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R174 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R175 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R176 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R177 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R179 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R181 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R182 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R183 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R184 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R185 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
8-16
Page 72

MB-80
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
R186 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R195 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R196 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R197 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R198 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R199 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R200 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R201 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R202 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R204 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R206 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R209 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R212 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R213 1-216-813-11 METAL CHIP 220 5% 1/16W
R214 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R215 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R216 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R217 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R218 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R219 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R220 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R221 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R222 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R223 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R224 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R225 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R226 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R227 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R228 1-216-803-11 METAL CHIP 33 5% 1/16W
R229 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R230 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R231 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R232 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R233 1-216-837-11 METAL CHIP 22K 5% 1/16W
R235 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R241 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R250 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R251 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R260 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R269 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
R318 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R319 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R320 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R321 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R325 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R326 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R327 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R328 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R329 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R331 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R332 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R334 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
(US,Canadian)
R335 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R336 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R337 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R338 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R339 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R340 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R341 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R342 1-216-813-11 METAL CHIP 220 5% 1/16W
R361 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R362 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R363 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R364 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R365 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R366 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R367 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R368 1-216-845-11 METAL CHIP 100K 5% 1/16W
R369 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R370 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R371 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R372 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R373 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R374 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R375 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R376 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R377 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
(US,Canadian)
R270 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R271 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R272 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R273 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R299 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R300 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R302 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R303 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R305 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R307 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R308 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R309 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R310 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R311 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R312 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R313 1-216-841-11 METAL CHIP 47K 5% 1/16W
R315 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R316 1-216-841-11 METAL CHIP 47K 5% 1/16W
R317 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R378 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
(US,Canadian)
R379 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
(US,Canadian)
R380 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R382 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R386 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R387 1-216-841-11 METAL CHIP 47K 5% 1/16W
R388 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R389 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R390 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R391 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R421 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R422 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R426 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R433 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R434 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R435 1-216-803-11 METAL CHIP 33 5% 1/16W
R436 1-216-803-11 METAL CHIP 33 5% 1/16W
8-17
Page 73

MB-80
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
R437 1-216-807-11 METAL CHIP 68 5% 1/16W
R438 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R444 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R446 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R447 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R448 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R449 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R453 1-218-831-11 METAL GLAZE 220 0.50% 1/16W
R459 1-216-797-11 METAL CHIP 10 5% 1/16W
R463 1-218-831-11 METAL GLAZE 220 0.50% 1/16W
R464 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R466 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R467 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R471 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R472 1-216-815-11 METAL CHIP 330 5% 1/16W
R473 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R474 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R475 1-218-831-11 METAL GLAZE 220 0.50% 1/16W
R480 1-216-827-11 METAL CHIP 3.3K 5% 1/16W
R481 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R482 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R483 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R489 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R491 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
R492 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R493 1-216-823-11 METAL CHIP 1.5K 5% 1/16W
R495 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R498 1-216-827-11 METAL CHIP 3.3K 5% 1/16W
R499 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R501 1-216-827-11 METAL CHIP 3.3K 5% 1/16W
R506 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R507 1-216-831-11 METAL CHIP 6.8K 5% 1/16W
R511 1-216-827-11 METAL CHIP 3.3K 5% 1/16W
R514 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R518 1-216-845-11 METAL CHIP 100K 5% 1/16W
R519 1-216-849-11 METAL CHIP 220K 5% 1/16W
R521 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R525 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R526 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R531 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R532 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R533 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R540 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R541 1-216-827-11 METAL CHIP 3.3K 5% 1/16W
R542 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R543 1-216-827-11 METAL CHIP 3.3K 5% 1/16W
R544 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R545 1-216-827-11 METAL CHIP 3.3K 5% 1/16W
R549 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R550 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R551 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R555 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R556 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R557 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R561 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R562 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R563 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R565 1-216-817-11 METAL CHIP 470 5% 1/16W
R566 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
R567 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R568 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R569 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R570 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R571 1-216-807-11 METAL CHIP 68 5% 1/16W
R572 1-216-807-11 METAL CHIP 68 5% 1/16W
R573 1-216-807-11 METAL CHIP 68 5% 1/16W
R574 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R575 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R576 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R577 1-216-807-11 METAL CHIP 68 5% 1/16W
R578 1-216-807-11 METAL CHIP 68 5% 1/16W
R579 1-216-807-11 METAL CHIP 68 5% 1/16W
R580 1-216-807-11 METAL CHIP 68 5% 1/16W
R581 1-216-807-11 METAL CHIP 68 5% 1/16W
R582 1-216-807-11 METAL CHIP 68 5% 1/16W
R583 1-216-803-11 METAL CHIP 33 5% 1/16W
R584 1-216-803-11 METAL CHIP 33 5% 1/16W
R585 1-216-803-11 METAL CHIP 33 5% 1/16W
R586 1-216-803-11 METAL CHIP 33 5% 1/16W
R587 1-216-803-11 METAL CHIP 33 5% 1/16W
R588 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R590 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R591 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R597 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R601 1-216-803-11 METAL CHIP 33 5% 1/16W
R602 1-216-803-11 METAL CHIP 33 5% 1/16W
R603 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R616 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R617 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R618 1-218-839-11 METAL GLAZE 470 0.50% 1/16W
R619 1-216-823-11 METAL CHIP 1.5K 5% 1/16W
R620 1-218-851-11 METAL GLAZE 1.5K 0.50% 1/16W
R621 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R622 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R623 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R624 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R625 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R626 1-216-864-11 METAL CHIP 0 5% 1/16W
R628 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R629 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R633 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R634 1-216-807-11 METAL CHIP 68 5% 1/16W
R635 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R642 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R643 1-218-851-11 METAL GLAZE 1.5K 0.50% 1/16W
R645 1-216-845-11 METAL CHIP 100K 5% 1/16W
R650 1-216-841-11 METAL CHIP 47K 5% 1/16W
R651 1-216-841-11 METAL CHIP 47K 5% 1/16W
R653 1-216-845-11 METAL CHIP 100K 5% 1/16W
R654 1-216-827-11 METAL CHIP 3.3K 5% 1/16W
R655 1-216-827-11 METAL CHIP 3.3K 5% 1/16W
R666 1-216-807-11 METAL CHIP 68 5% 1/16W
R675 1-216-839-11 METAL CHIP 33K 5% 1/16W
R677 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R678 1-218-839-11 METAL GLAZE 470 0.50% 1/16W
R679 1-216-823-11 METAL CHIP 1.5K 5% 1/16W
R680 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
8-18
Page 74

MB-80
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
R681 1-218-851-11 METAL GLAZE 1.5K 0.50% 1/16W
R682 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R683 1-218-839-11 METAL GLAZE 470 0.50% 1/16W
R684 1-216-823-11 METAL CHIP 1.5K 5% 1/16W
R685 1-216-827-11 METAL CHIP 3.3K 5% 1/16W
R686 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R687 1-216-827-11 METAL CHIP 3.3K 5% 1/16W
R688 1-216-849-11 METAL CHIP 220K 5% 1/16W
R689 1-216-856-11 METAL CHIP 820K 5% 1/16W
R690 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R691 1-216-827-11 METAL CHIP 3.3K 5% 1/16W
R692 1-216-827-11 METAL CHIP 3.3K 5% 1/16W
R693 1-216-857-11 METAL CHIP 1M 5% 1/16W
R694 1-216-857-11 METAL CHIP 1M 5% 1/16W
R701 1-218-871-11 METAL GLAZE 10K 0.50% 1/16W
R702 1-218-877-11 METAL GLAZE 18K 0.50% 1/16W
R703 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R704 1-216-830-11 METAL CHIP 5.6K 5% 1/16W
R705 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R706 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R712 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R713 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R714 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R715 1-216-837-11 METAL CHIP 22K 5% 1/16W
R721 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R723 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R725 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R727 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R731 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R736 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R737 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R738 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R739 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R740 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R741 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
R742 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R743 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R744 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R745 1-216-849-11 METAL CHIP 220K 5% 1/16W
R746 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R747 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R748 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R749 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R750 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R751 1-216-823-11 METAL CHIP 1.5K 5% 1/16W
R752 1-216-824-11 METAL CHIP 1.8K 5% 1/16W
R753 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R754 1-216-851-11 METAL CHIP 330K 5% 1/16W
R755 1-216-827-11 METAL CHIP 3.3K 5% 1/16W
R757 1-216-837-11 METAL CHIP 22K 5% 1/16W
R758 1-218-827-11 METAL GLAZE 150 0.50% 1/16W
R759 1-218-864-11 METAL GLAZE 5.1K 0.50% 1/16W
R760 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R763 1-216-857-11 METAL CHIP 1M 5% 1/16W
R764 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R765 1-216-839-11 METAL CHIP 33K 5% 1/16W
R766 1-216-837-11 METAL CHIP 22K 5% 1/16W
R767 1-216-827-11 METAL CHIP 3.3K 5% 1/16W
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
R768 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R769 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R770 1-216-837-11 METAL CHIP 22K 5% 1/16W
R771 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R775 1-216-827-11 METAL CHIP 3.3K 5% 1/16W
R776 1-216-851-11 METAL CHIP 330K 5% 1/16W
R777 1-216-841-11 METAL CHIP 47K 5% 1/16W
R779 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R780 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R781 1-216-837-11 METAL CHIP 22K 5% 1/16W
R785 1-216-857-11 METAL CHIP 1M 5% 1/16W
R787 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R788 1-216-839-11 METAL CHIP 33K 5% 1/16W
R789 1-216-819-11 METAL CHIP 680 5% 1/16W
R790 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R791 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R793 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R794 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R795 1-216-857-11 METAL CHIP 1M 5% 1/16W
R796 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R797 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R798 1-216-839-11 METAL CHIP 33K 5% 1/16W
R799 1-216-819-11 METAL CHIP 680 5% 1/16W
R800 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R801 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R802 1-218-863-11 METAL GLAZE 4.7K 0.50% 1/16W
R803 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R804 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R805 1-216-837-11 METAL CHIP 22K 5% 1/16W
R806 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R807 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R808 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R809 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R812 1-216-835-11 METAL CHIP 15K 5% 1/16W
R815 1-218-446-11 METAL CHIP 1 5% 1/16W
R816 1-218-446-11 METAL CHIP 1 5% 1/16W
R817 1-216-134-00 METAL CHIP 2.2 5% 1/8W
R818 1-216-134-00 METAL CHIP 2.2 5% 1/8W
R819 1-218-446-11 METAL CHIP 1 5% 1/16W
R820 1-218-446-11 METAL CHIP 1 5% 1/16W
R821 1-216-134-00 METAL CHIP 2.2 5% 1/8W
R822 1-216-134-00 METAL CHIP 2.2 5% 1/8W
R823 1-218-859-11 METAL GLAZE 3.3K 0.50% 1/16W
R824 1-218-863-11 METAL GLAZE 4.7K 0.50% 1/16W
R825 1-218-863-11 METAL GLAZE 4.7K 0.50% 1/16W
R826 1-216-845-11 METAL CHIP 100K 5% 1/16W
R827 1-216-845-11 METAL CHIP 100K 5% 1/16W
R828 1-218-851-11 METAL GLAZE 1.5K 0.50% 1/16W
R829 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R830 1-216-845-11 METAL CHIP 100K 5% 1/16W
R831 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R833 1-216-855-11 METAL CHIP 680K 5% 1/16W
R834 1-218-875-11 METAL GLAZE 15K 0.50% 1/16W
R835 1-218-875-11 METAL GLAZE 15K 0.50% 1/16W
R837 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R838 1-216-839-11 METAL CHIP 33K 5% 1/16W
R839 1-218-871-11 METAL GLAZE 10K 0.50% 1/16W
R840 1-216-849-11 METAL CHIP 220K 5% 1/16W
R842 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
8-19
Page 75
MB-80
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
R843 1-216-849-11 METAL CHIP 220K 5% 1/16W
R845 1-216-845-11 METAL CHIP 100K 5% 1/16W
R846 1-218-861-11 METAL GLAZE 3.9K 0.50% 1/16W
R847 1-218-862-11 METAL GLAZE 4.3K 0.50% 1/16W
R848 1-218-871-11 METAL GLAZE 10K 0.50% 1/16W
R849 1-218-877-11 METAL GLAZE 18K 0.50% 1/16W
R850 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R852 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R853 1-218-871-11 METAL GLAZE 10K 0.50% 1/16W
R854 1-216-789-11 METAL CHIP 2.2 5% 1/16W
R855 1-218-871-11 METAL GLAZE 10K 0.50% 1/16W
R856 1-218-855-11 METAL GLAZE 2.2K 0.50% 1/16W
R857 1-216-789-11 METAL CHIP 2.2 5% 1/16W
R858 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R859 1-216-789-11 METAL CHIP 2.2 5% 1/16W
R860 1-216-789-11 METAL CHIP 2.2 5% 1/16W
R861 1-216-798-11 METAL GLAZE 12 5% 1/16W
R862 1-216-797-11 METAL CHIP 10 5% 1/16W
R865 1-216-840-11 METAL CHIP 39K 5% 1/16W
R866 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R867 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R868 1-216-798-11 METAL GLAZE 12 5% 1/16W
R869 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R870 1-216-798-11 METAL GLAZE 12 5% 1/16W
R871 1-216-797-11 METAL CHIP 10 5% 1/16W
R872 1-216-864-11 METAL CHIP 0 5% 1/16W
R873 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R874 1-216-797-11 METAL CHIP 10 5% 1/16W
R875 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R876 1-216-797-11 METAL CHIP 10 5% 1/16W
R877 1-216-797-11 METAL CHIP 10 5% 1/16W
R878 1-216-797-11 METAL CHIP 10 5% 1/16W
R879 1-216-797-11 METAL CHIP 10 5% 1/16W
R880 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R881 1-216-823-11 METAL CHIP 1.5K 5% 1/16W
R882 1-216-841-11 METAL CHIP 47K 5% 1/16W
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
R906 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R907 1-217-671-11 METAL CHIP 1 5% 1/10W
R909 1-218-901-11 METAL GLAZE 180K 0.50% 1/16W
R910 1-216-839-11 METAL CHIP 33K 5% 1/16W
R911 1-218-901-11 METAL GLAZE 180K 0.50% 1/16W
R912 1-218-901-11 METAL GLAZE 180K 0.50% 1/16W
R913 1-216-839-11 METAL CHIP 33K 5% 1/16W
R914 1-218-901-11 METAL GLAZE 180K 0.50% 1/16W
R918 1-216-827-11 METAL CHIP 3.3K 5% 1/16W
R919 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R920 1-218-859-11 METAL GLAZE 3.3K 0.50% 1/16W
R921 1-216-845-11 METAL CHIP 100K 5% 1/16W
R922 1-216-844-11 METAL CHIP 82K 5% 1/16W
R924 1-216-864-11 METAL CHIP 0 5% 1/16W
R925 1-216-845-11 METAL CHIP 100K 5% 1/16W
R926 1-216-864-11 METAL CHIP 0 5% 1/16W
R927 1-216-864-11 METAL CHIP 0 5% 1/16W
R928 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R929 1-218-272-11 METAL GLAZE 5.1K 5% 1/16W
R930 1-216-845-11 METAL CHIP 100K 5% 1/16W
R932 1-216-845-11 METAL CHIP 100K 5% 1/16W
R933 1-216-845-11 METAL CHIP 100K 5% 1/16W
R943 1-216-864-11 METAL CHIP 0 5% 1/16W
R944 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R947 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
R948 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
R949 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
R950 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
R967 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
R968 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
R883 1-216-797-11 METAL CHIP 10 5% 1/16W
R884 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R885 1-216-837-11 METAL CHIP 22K 5% 1/16W
R886 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R887 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R888 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R889 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R890 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R891 1-216-797-11 METAL CHIP 10 5% 1/16W
R892 1-216-797-11 METAL CHIP 10 5% 1/16W
R893 1-218-901-11 METAL GLAZE 180K 0.50% 1/16W
R894 1-217-671-11 METAL CHIP 1 5% 1/10W
R895 1-216-854-11 METAL CHIP 560K 5% 1/16W
R896 1-216-839-11 METAL CHIP 33K 5% 1/16W
R897 1-217-671-11 METAL CHIP 1 5% 1/10W
R898 1-218-901-11 METAL GLAZE 180K 0.50% 1/16W
R899 1-218-901-11 METAL GLAZE 180K 0.50% 1/16W
R900 1-216-839-11 METAL CHIP 33K 5% 1/16W
R901 1-217-671-11 METAL CHIP 1 5% 1/10W
R902 1-216-841-11 METAL CHIP 47K 5% 1/16W
R903 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R904 1-218-901-11 METAL GLAZE 180K 0.50% 1/16W
R969 1-218-873-11 METAL GLAZE 12K 0.50% 1/16W
R970 1-216-849-11 METAL CHIP 220K 5% 1/16W
R971 1-216-864-11 METAL CHIP 0 5% 1/16W
R972 1-216-845-11 METAL CHIP 100K 5% 1/16W
R973 1-216-864-11 METAL CHIP 0 5% 1/16W
R983 1-216-864-11 METAL CHIP 0 5% 1/16W
(US,Canadian)
R984 1-216-864-11 METAL CHIP 0 5% 1/16W
(US,Canadian)
R985 1-216-864-11 METAL CHIP 0 5% 1/16W
(US,Canadian)
R986 1-216-864-11 METAL CHIP 0 5% 1/16W
(US,Canadian)
R987 1-216-864-11 METAL CHIP 0 5% 1/16W
(US,Canadian)
R988 1-216-864-11 METAL CHIP 0 5% 1/16W
(US,Canadian)
R989 1-216-864-11 METAL CHIP 0 5% 1/16W
(US,Canadian)
R990 1-216-864-11 METAL CHIP 0 5% 1/16W
(US,Canadian)
8-20
Page 76

MB-80 PS-408 PS-413
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
R991 1-216-864-11 METAL CHIP 0 5% 1/16W
(US,Canadian)
R992 1-216-864-11 METAL CHIP 0 5% 1/16W
(US,Canadian)
R994 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
R995 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
R996 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
R997 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R998 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
R999 1-216-829-11 METAL CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/16W
< CONPOSITION CIRCUIT BLOCK >
* RB280 1-233-270-11 NETWORK, RES (8 GANG) 10K
* RB281 1-233-270-11 NETWORK, RES (8 GANG) 10K
* RB282 1-233-270-11 NETWORK, RES (8 GANG) 10K
* RB283 1-233-270-11 NETWORK, RES (8 GANG) 10K
* RB284 1-233-270-11 NETWORK, RES (8 GANG) 10K
* RB285 1-233-270-11 NETWORK, RES (8 GANG) 10K
* RB286 1-233-270-11 NETWORK, RES (8 GANG) 10K
* RB287 1-233-270-11 NETWORK, RES (8 GANG) 10K
* RB288 1-233-270-11 NETWORK, RES (8 GANG) 10K
* RB289 1-233-270-11 NETWORK, RES (8 GANG) 10K
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
RZ065 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
RZ066 1-216-841-11 METAL CHIP 47K 5% 1/16W
(Hong Kong)
< THERMISTOR >
TH001 1-810-814-21 THERMISTOR, NTC (1608)
TH002 1-810-814-21 THERMISTOR, NTC (1608)
< VIBRATOR >
X001 1-767-402-21 VIBRATOR, CRYSTAL (22.5792MHz)
X002 1-767-399-11 VIBRATOR, CRYSTAL (24.576MHz)
X003 1-767-401-11 VIBRATOR, CRYSTAL (27MHz)
X004 1-578-689-21 VIBRATOR (8MHz)
X090 1-760-655-41 VIBRATOR, CRYSTAL (20MHz)
X280 1-767-474-21 OSCILLATOR, CRYSTAL (66MHz)
* A-6065-056-A PS-408 BOARD, COMPLETE (US,Canadian)
* A-6065-044-A PS-413 BOARD, COMPLETE
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
**********************
(Ref.No. 2,000 Series)
1-533-223-11 HOLDER, FUSE
< CAPACITOR >
< VARIABLE RESISTOR >
RV001 1-238-663-11 RES, ADJ, CARBON 4.7K
RV479 1-238-663-11 RES, ADJ, CARBON 4.7K
< RESISTOR >
RZ005 1-216-801-11 METAL CHIP 22 5% 1/16W
RZ020 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
RZ021 1-216-836-11 METAL CHIP 18K 5% 1/16W
RZ021 1-216-827-11 METAL CHIP 3.3K 5% 1/16W
RZ021 1-216-832-11 METAL CHIP 8.2K 5% 1/16W
(Hong Kong,Singapore)
RZ031 1-216-817-11 METAL CHIP 470 5% 1/16W
RZ032 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
RZ033 1-216-817-11 METAL CHIP 470 5% 1/16W
RZ034 1-216-817-11 METAL CHIP 470 5% 1/16W
RZ035 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
RZ036 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
RZ038 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
RZ039 1-216-817-11 METAL CHIP 470 5% 1/16W
RZ040 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
RZ053 1-216-841-11 METAL CHIP 47K 5% 1/16W
RZ054 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
RZ055 1-216-831-11 METAL CHIP 6.8K 5% 1/16W
RZ061 1-216-843-11 METAL CHIP 68K 5% 1/16W
RZ062 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
RZ063 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
RZ064 1-216-805-11 METAL CHIP 47 5% 1/16W
(US,Canadian)
(Chinese)
C902 1-104-705-11 FILM 0.1uF 20% 250V
C952 1-126-942-61 ELECT 1000uF 20% 25V
C954 1-126-964-11 ELECT 10uF 20% 50V
C955 1-126-964-11 ELECT 10uF 20% 50V
C956 1-126-960-11 ELECT 1uF 20% 50V
< CONNECTOR >
CN901 1-580-230-11 PIN, CONNECTOR (PC BOARD) 2P
CN902 1-691-960-11 PIN, CONNECTOR (PC BOARD) 3P
* CN954 1-564-705-11 PIN, CONNECTOR (SMALL TYPE) 3P
< DIODE >
! D951 8-719-200-82 DIODE 11ES2
! D952 8-719-200-82 DIODE 11ES2
! D953 8-719-200-82 DIODE 11ES2
! D954 8-719-200-82 DIODE 11ES2
D956 8-719-911-19 DIODE 1SS119
D957 8-719-911-19 DIODE 1SS119
< FUSE >
! F901 1-532-743-11 FUSE, GLASS TUBE (2A/125V)(US,Canadian)
! F901 1-532-203-11 FUSE, TIME-LAG (T2AL/250V)
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
< TERMINAL >
* ET951 1-537-738-21 TERMINAL, EARTH
< FILTER >
FL951 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
FL952 1-233-893-21 FILTER, CHIP EMI
8-21
The components identified by
mark ! or dotted line with
mark ! are critical for safety.
Replace only with part number
specified.
Les composants identifiés par une
marque ! sont critiques pour la
sécurité.
Ne les remplacer que par une pièce
portant le neméro spécifié.
Page 77
PW-116 PW-117
TT-40PS-408 PS-413
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
< IC >
IC951 8-759-708-05 IC NJM78L05A
< LINE FILTER >
! LF901 1-416-446-11 FILTER, LINE
< TRANSISTOR >
Q951 8-729-421-19 TRANSISTOR UN2213
Q952 8-729-424-46 TRANSISTOR UN211E
< RESISTOR >
R951 1-216-089-91 METAL GLAZE 47K 5% 1/10W
R952 1-216-089-91 METAL GLAZE 47K 5% 1/10W
< TRANSFORMER >
! T901 1-429-784-11 TRANSFORMER, POWER (US,Canadian)
! T901 1-431-593-11 TRANSFORMER, POWER
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
* A-6065-058-A PW-116 BOARD, COMPLETE (US,Canadian)
* A-6065-046-A PW-117 BOARD, COMPLETE
(Chinese,Hong Kong,Singapore)
**********************
(Ref.No. 4,000 Series)
< CAPACITOR >
C151 1-126-154-11 ELECT 47uF 20% 6.3V
< DIODE >
D151 8-719-404-49 DIODE MA111
D152 8-719-404-49 DIODE MA111
D153 8-719-981-49 LED GL3ED8 (ON/STANDBY)
< IC >
IC151 8-749-011-22 IC GP1U27X
< COIL >
L151 1-412-031-11 INDUCTOR CHIP 47uH
< TRANSISTOR >
Q151 8-729-424-08 TRANSISTOR UN2111
< RESISTOR >
R151 1-247-815-91 CARBON 220 5% 1/4W
R152 1-249-415-11 CARBON 680 5% 1/4W
R154 1-216-081-00 METAL CHIP 22K 5% 1/10W
< SWITCH >
S151 1-762-365-21 SWITCH, TACTILE (POWER)
S153 1-762-365-21 SWITCH, TACTILE (SET UP MENU)
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
* A-6065-052-A TT-40 BOARD, COMPLETE
*********************
(Ref.No. 3,000 Series)
< CAPACITOR >
C001 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C002 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C014 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C015 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C020 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C025 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C026 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C027 1-162-964-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.001uF 10% 50V
C028 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C029 1-162-966-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.0022uF 10% 50V
C030 1-162-966-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.0022uF 10% 50V
C031 1-162-966-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.0022uF 10% 50V
C032 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C033 1-162-966-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.0022uF 10% 50V
C035 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C036 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C037 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C038 1-164-739-11 CERAMIC CHIP 560PF 5% 50V
C039 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C040 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C041 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C042 1-162-964-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.001uF 10% 50V
C043 1-164-172-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.0056uF 10% 25V
C044 1-164-172-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.0056uF 10% 25V
C045 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C046 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C047 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C048 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C049 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C050 1-165-176-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.047uF 10% 16V
C051 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C052 1-164-677-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.033uF 10% 16V
C053 1-164-677-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.033uF 10% 16V
C054 1-162-927-11 CERAMIC CHIP 100PF 5% 50V
C055 1-109-982-11 CERAMIC CHIP 1uF 10% 10V
C056 1-165-176-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.047uF 10% 16V
C057 1-164-217-11 CERAMIC CHIP 150PF 5% 50V
C058 1-162-962-11 CERAMIC CHIP 470PF 10% 50V
C059 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C060 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C061 1-128-004-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C062 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C063 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C068 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C073 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C074 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C075 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C076 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C077 1-107-826-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 10% 16V
C078 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
The components identified by
mark ! or dotted line with
mark ! are critical for safety.
Replace only with part number
specified.
Les composants identifiés par une
marque ! sont critiques pour la
sécurité.
Ne les remplacer que par une pièce
portant le neméro spécifié.
8-22
Page 78

TT-40
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
C079 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C080 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C085 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C086 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C087 1-162-964-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.001uF 10% 50V
C088 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C089 1-162-970-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 25V
C090 1-126-205-11 ELECT CHIP 47uF 20% 6.3V
< CONNECTOR >
CN001 1-779-342-21 CONNECTOR, FFC/FPC 42P
* CN002 1-695-154-11 SOCKET, CONNECTOR 18P
* CN003 1-764-895-21 SOCKET, CONNECTOR 10P
CN004 1-580-055-21 PIN, CONNECTOR 2P
CN005 1-779-341-11 CONNECTOR, FFC/FPC 23P
CN006 1-779-341-11 CONNECTOR, FFC/FPC 23P
CN007 1-779-341-11 CONNECTOR, FFC/FPC 23P
< DIODE >
D001 8-719-404-49 DIODE MA111
D002 8-719-404-49 DIODE MA111
D003 8-719-421-27 DIODE MA728
< IC >
IC001 8-759-449-56 IC SSI33P3720
IC002 8-752-069-93 IC CXA1791M-T6
IC003 8-759-701-39 IC NJM3404AM
IC004 8-759-062-66 IC TC7S66F(TE85R)
< COIL >
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
R028 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R029 1-216-797-11 METAL CHIP 10 5% 1/16W
R030 1-216-817-11 METAL CHIP 470 5% 1/16W
R034 1-218-348-11 METAL GLAZE 110K 5% 1/16W
R035 1-218-348-11 METAL GLAZE 110K 5% 1/16W
R036 1-216-154-00 METAL GLAZE 15 5% 1/8W
R037 1-216-856-11 METAL CHIP 820K 5% 1/16W
R038 1-216-856-11 METAL CHIP 820K 5% 1/16W
R039 1-216-820-11 METAL CHIP 820 5% 1/16W
R040 1-216-797-11 METAL CHIP 10 5% 1/16W
R041 1-216-837-11 METAL CHIP 22K 5% 1/16W
R042 1-216-837-11 METAL CHIP 22K 5% 1/16W
R044 1-216-845-11 METAL CHIP 100K 5% 1/16W
R045 1-216-864-11 METAL CHIP 0 5% 1/16W
R046 1-216-845-11 METAL CHIP 100K 5% 1/16W
R047 1-216-834-11 METAL CHIP 12K 5% 1/16W
R048 1-216-851-11 METAL CHIP 330K 5% 1/16W
R049 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R050 1-216-817-11 METAL CHIP 470 5% 1/16W
R051 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R052 1-218-872-11 METAL GLAZE 11K 0.50% 1/16W
R053 1-218-859-11 METAL GLAZE 3.3K 0.50% 1/16W
R054 1-216-837-11 METAL CHIP 22K 5% 1/16W
R055 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R056 1-216-857-11 METAL CHIP 1M 5% 1/16W
R057 1-216-864-11 METAL CHIP 0 5% 1/16W
R062 1-216-815-11 METAL CHIP 330 5% 1/16W
R063 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R064 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R065 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
L001 1-412-031-11 INDUCTOR CHIP 47uH
L002 1-412-031-11 INDUCTOR CHIP 47uH
L003 1-412-031-11 INDUCTOR CHIP 47uH
< PHOTO INTERRUPTER >
PH001 8-749-011-97 PHOTO INTERUPTER GP1S93
< TRANSISTOR >
Q001 8-729-420-24 TRANSISTOR 2SB1218A-QRS
Q002 8-729-230-63 TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-YG
Q003 8-729-903-46 TRANSISTOR 2SB1132-T100-QR
Q004 8-729-903-46 TRANSISTOR 2SB1132-T100-QR
Q005 8-729-903-46 TRANSISTOR 2SB1132-T100-QR
Q007 8-729-230-63 TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-YG
Q008 8-729-015-76 TRANSISTOR UN5211-TX
Q009 8-729-230-63 TRANSISTOR 2SC4116-YG
< RESISTOR >
R001 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R002 1-211-992-11 METAL GLAZE 91 0.50% 1/16W
R005 1-216-815-11 METAL CHIP 330 5% 1/16W
R006 1-216-841-11 METAL CHIP 47K 5% 1/16W
R007 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R008 1-216-810-11 METAL CHIP 120 5% 1/16W
R009 1-216-810-11 METAL CHIP 120 5% 1/16W
R010 1-216-827-11 METAL CHIP 3.3K 5% 1/16W
R017 1-216-827-11 METAL CHIP 3.3K 5% 1/16W
R027 1-216-154-00 METAL GLAZE 15 5% 1/8W
R068 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R070 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R071 1-216-841-11 METAL CHIP 47K 5% 1/16W
R075 1-216-814-11 METAL CHIP 270 5% 1/16W
R078 1-216-833-11 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/16W
R088 1-216-837-11 METAL CHIP 22K 5% 1/16W
R091 1-216-841-11 METAL CHIP 47K 5% 1/16W
R092 1-216-825-11 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/16W
R093 1-216-845-11 METAL CHIP 100K 5% 1/16W
R095 1-216-853-11 METAL CHIP 470K 5% 1/16W
R096 1-216-851-11 METAL CHIP 330K 5% 1/16W
R097 1-216-837-11 METAL CHIP 22K 5% 1/16W
R098 1-216-821-11 METAL CHIP 1K 5% 1/16W
R099 1-216-837-11 METAL CHIP 22K 5% 1/16W
R100 1-216-837-11 METAL CHIP 22K 5% 1/16W
R102 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R103 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R104 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R105 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R106 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R107 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R108 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R109 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R111 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R112 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R113 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R114 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R115 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R116 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
8-23
Page 79

TT-40
SR-740 SR-745
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
R117 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R118 1-216-809-11 METAL CHIP 100 5% 1/16W
R124 1-216-831-11 METAL CHIP 6.8K 5% 1/16W
R125 1-216-849-11 METAL CHIP 220K 5% 1/16W
R126 1-216-839-11 METAL CHIP 33K 5% 1/16W
R128 1-216-864-11 METAL CHIP 0 5% 1/16W
< SWITCH >
S001 1-771-046-11 SWITCH, PUSH LEVER (TRAY)
! 1-468-199-11 SR-740 BOARD (Ref.No. 5,000 Series)
(Include SUB BOARD) (US, Canadian)
******************
< CAPASITOR >
C105 9-939-926-01 ELECT 330uF 250V
C112 1-126-968-51 ELECT 100uF 50V
C201 1-126-798-11 ELECT 2200uF 10V
C202 1-126-960-51 ELECT 1uF 50V
C203 1-126-926-11 ELECT 1000uF 20% 10V
C204 1-126-798-11 ELECT 2200uF 10V
C206 9-933-770-01 ELECT 1000uF 16V
C207 1-126-935-11 ELECT 470uF 20% 16V
C209 9-933-770-01 ELECT 1000uF 16V
C210 1-126-935-11 ELECT 470uF 20% 16V
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
< VARIABLE RESISTOR >
VR201 9-939-928-01 RESISTOR,VARIABLE 500
! 1-468-200-11 SR-745 BOARD (Ref.No. 6,000 Series)
(Include SUB BOARD) (Chinese, Hong Kong, Singapore)
***************
< CAPASITOR >
C105 9-939-933-01 ELECT 100uF 400V
C112 1-126-968-51 ELECT 100uF 50V
C201 1-126-798-11 ELECT 2200uF 10V
C202 1-126-960-51 ELECT 1uF 50V
C203 1-126-926-11 ELECT 1000uF 20% 10V
C204 1-126-798-11 ELECT 2200uF 10V
C206 9-933-770-01 ELECT 1000uF 16V
C207 1-126-935-11 ELECT 470uF 20% 16V
C209 9-933-770-01 ELECT 1000uF 16V
C210 1-126-935-11 ELECT 470uF 20% 16V
< DIODE >
! D101 8-719-510-19 DIODE D2SBA60
D102 8-710-160-74 DIODE RD22FB
D104 9-900-534-01 DIODE ERA18-02
D106 9-900-514-01 DIODE MA165
D107 8-719-030-25 DIODE EG01C
< DIODE >
! D101 8-719-510-19 DIODE D2SBA60
D102 8-710-160-74 DIODE RD22FB
D104 9-900-534-01 DIODE ERA18-02
D106 9-900-514-01 DIODE MA165
D107 8-719-030-25 DIODE EG01C
D201 8-719-310-55 DIODE FMB24L
D202 8-719-035-04 DIODE MA4240
D203 9-909-291-01 DIODE S3L20U
D205 9-909-291-01 DIODE S3L20U
< IC >
! IC101 8-759-387-65 IC FA5317 (SUB)
! IC201 9-900-532-01 IC AN1431T
< PHOTO CUPPLER >
PC101 9-900-518-01 CUPPLER, PHOTO PC817
PC102 9-900-518-01 CUPPLER, PHOTO PC817
< TRANSISTOR >
! Q101 9-939-924-01 TRANSISTOR 2SK2662
! Q102 8-729-920-70 TRANSISTOR 2SC1740
< RESISTOR >
R106 1-216-031-11 METAL CHIP 180 1/10W
R204 9-936-251-01 CARBON 2.2K 1/4W
D201 8-719-310-55 DIODE FMB24L
D202 8-719-035-04 DIODE MA4240
D203 9-909-291-01 DIODE S3L20U
D205 9-909-291-01 DIODE S3L20U
< IC >
! IC101 8-759-387-65 IC FA5317 (SUB)
! IC201 9-900-532-01 IC AN1431T
< PHOTO CUPPLER >
PC101 9-904-180-01 CUPPLER, PHOTO PC120
PC102 9-904-180-01 CUPPLER, PHOTO PC120
< TRANSISTOR >
! Q101 9-936-231-01 TRANSISTOR 2SK1535
! Q102 8-729-920-70 TRANSISTOR 2SC1740
< RESISTOR >
R106 1-216-031-11 METAL CHIP 180 1/4W
R113 1-260-304-71 CARBON 10 1/2W
R203 9-936-251-01 CARBON 2.2K 1/4W
R204 9-936-251-01 CARBON 2.2K 1/4W
< VARIABLE RESISTOR >
VR201 9-939-936-01 RESISTOR,VARIABLE 500
The components identified by
mark ! or dotted line with
mark ! are critical for safety.
Replace only with part number
specified.
Les composants identifiés par une
marque ! sont critiques pour la
sécurité.
Ne les remplacer que par une pièce
portant le neméro spécifié.
8-24
Page 80

MISCELLANEOUS
***************
108 1-782-867-11 CABLE, FLEXIBLE FLAT (FTT-4) 13P
109 1-782-191-11 CABLE, FLEXIBLE FLAT (FTM-3)
111 1-782-193-11 CABLE, FLEXIBLE FLAT (FAM-5)
112 1-782-865-11 CABLE, FLEXIBLE FLAT (FAM-6) 20P
! 207 8-820-005-02 OPTICAL PICK-UP KHS-180A/J1N
217 8-749-013-33 IC KU160 (CD SENSOR)
! CNP901 1-690-609-81 CORD, POWER (US, Canadian)
! CNP901 1-751-673-31 CORD, AC POWER (Hong Kong)
! CNP901 1-782-510-11 CORD, POWER (Chinese)
! CNP901 1-782-960-11 CORD, POWER (Singapore)
! F901 1-532-743-11 FUSE, GLASS TUBE (2A/125V)(US, Canadian)
! F901 1-532-203-00 FUSE, TIME-LAG (T2AL/250V)
(Chinese, Hong Kong, Singapore)
M501 X-3947-137-1 MOTOR ASSY, SLED
M901 1-698-944-11 MOTOR, DC (SPINDLE)
M902 X-3947-138-1 MOTOR ASSY, SKEW
M903 1-698-942-21 MOTOR (LOADING)
**************
HARDWARE LIST
**************
* 3-977-720-01 CUSHION
* 3-979-420-01 INDIVIDUAL CARTON (US, Canadian)
* 3-979-420-11 INDIVIDUAL CARTON (Singapore)
* 3-979-420-21 INDIVIDUAL CARTON (Chinese)
* 3-979-420-31 INDIVIDUAL CARTON (Hong Kong)
9-939-686-01 LID, BATTERY CASE (for RMT-D100E/D100U)
#1 7-685-885-09 SCREW +BVTT 4X16 (S)
#2 7-685-534-19 SCREW +BTP 2.6X8 TYPE2 N-S
#3 7-685-647-79 SCREW +BVTP 3X10 TYPE2 IT-3
#4 7-685-659-79 SCREW +BVTP 4X8 TYPE2 IT-3
#7 7-627-852-08 SCREW, PRECISION +P 1.7X2.5
#8 7-685-105-19 TPG +P 2X8, TYPE 2, NON-SLIT
#9 7-627-852-17 +P 1.7X4
ACCESSORIES & PACKING MATERIALS
********************************
1-475-086-31 COMMANDER, STANDARD (RMT-D100E)
(Chinese, Hong Kong, Singapore)
1-475-086-51 COMMANDER, STANDARD (RMT-D100U)
1-575-334-11 CORD, CONNECTION (STEREO AV CABLE 1.5m)
(Chinese, Hong Kong, Singapore)
1-575-335-21 CORD, CONNECTION (S-VIDEO CABLE 1.5m)
1-782-997-11 CORD, CONNECTION
(STEREO AV S LINK CABLE 1.5m)
* 3-694-922-01 SHEET, PROTECTION
3-861-127-11 MANUAL, INSTRUCTION (ENGLISH,FRENCH)
3-861-127-21 MANUAL, INSTRUCTION (ENGLISH,CHINESE)
3-861-127-31 MANUAL, INSTRUCTION (ENGLISH,CHINESE)
3-861-127-41 MANUAL, INSTRUCTION (ENGLISH,CHINESE)
(US, Canadian)
(US, Canadian)
(US, Canadian)
(Singapore)
(Chinese)
(Hong Kong)
8-25
8-25 E
The components identified by
mark ! or dotted line with
mark ! are critical for safety.
Replace only with part number
specified.
Les composants identifiés par une
marque ! sont critiques pour la
sécurité.
Ne les remplacer que par une pièce
portant le neméro spécifié.
Page 81

DVP-S3000
9-921-656-11
Sony Corporation
Home A&V Products Company
– 200 –
Printed in Japan © 1997. 9
97J0503-2 (2)
Published by General Engineering Dept.
(Osaki East)
 Loading...
Loading...