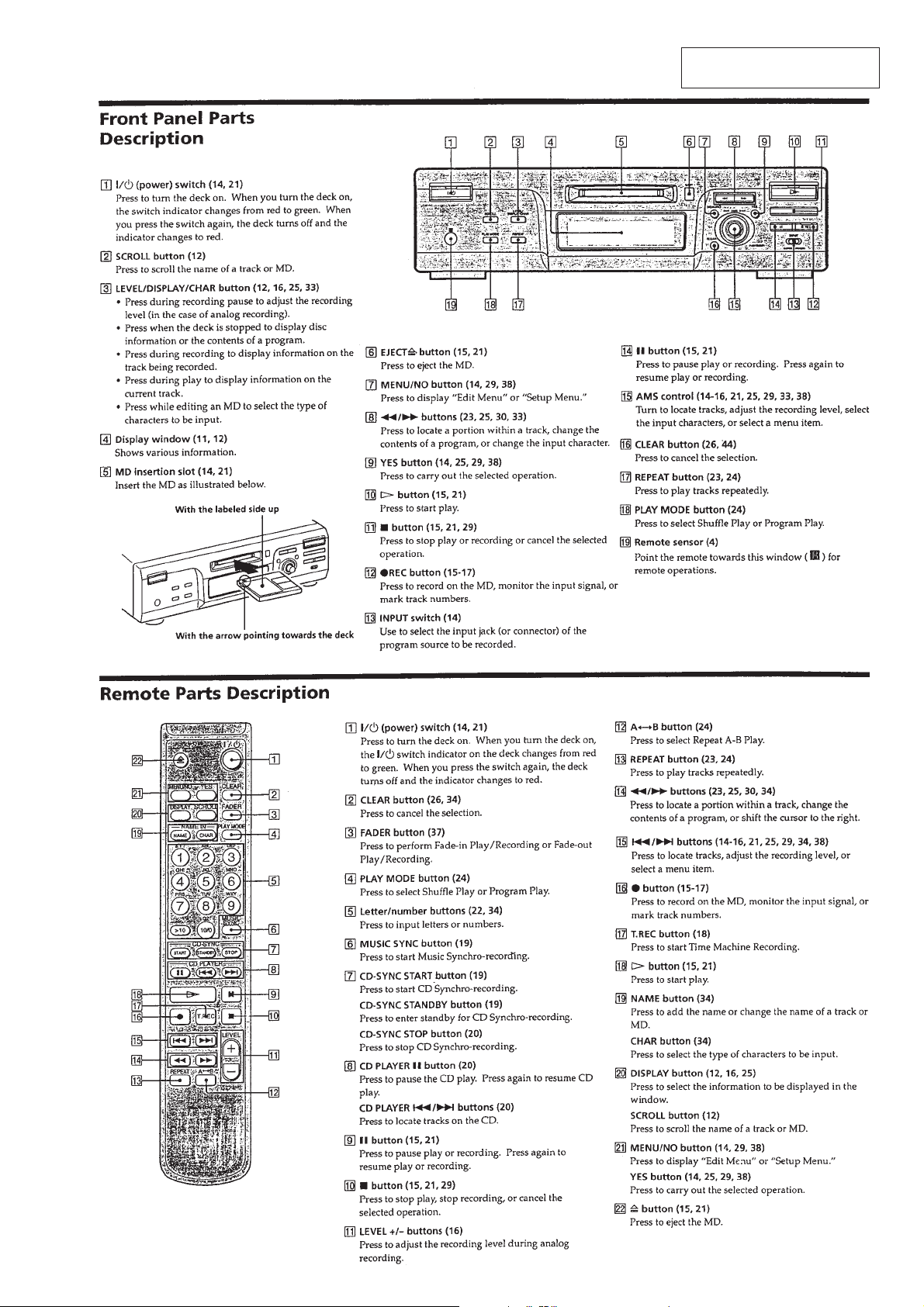
Page 1

MDS-M100
SERVICE MANUAL
U.S. and foreign patents licensed form Dolby Laboratories
Licensing Corporation.
SPECIFICATIONS
US Model
Canadian Model
AEP Model
UK Model
E Model
Model Name Using Similar Mechanism MDS-JE520
MD Mechanism Type MDM-5A
Optical Pick-up Type KMS-260A/J1N
MICROFILM
– Continued on next page –
MINIDISC DECK
Page 2

SELF-DIAGNOSIS FUNCTION
The self-diagnosis function consists of error codes for customers which are displayed automatically when errors occur, and error codes
which show the error history in the test mode during servicing. For details on how to view error codes for the customer, refer to the
following box in the instruction manual. For details on how to check error codes during servicing, refer to the following “Procedure for
using the Self-Diagnosis Function (Error History Display Mode)”.
PROCEDURE FOR USING THE SELF-DIAGNOSIS FUNCTION (ERROR HISTORY DISPLAY MODE)
Note: Perform the self-diagnosis function in the “error history display mode” in the test mode. The following describes the least required procedure. Be
careful not to enter other modes by mistake. If you set other modes accidentally, press the MENU/NO button to exit the mode.
1. While pressing the = AMS + knob and p button, connect the power plug to the outlet, and release the = AMS + knob
and p button.
2. Turn the = AMS + knob and when “[Service]” is displayed, press the [YES] button.
3. Turn the = AMS + knob to display “ERR DP MODE”.
4. Press the [YES] button to sets the error history mode and displays “total rec”.
5. Select the contents to be displayed or executed using the = AMS + knob.
6. Press the = AMS + knob to display or execute the contents selected.
7. Press the = AMS + knob another time returns to step 4.
8. Press the [MENU/NO] button to display “ERROR DP MODE” and exits the error history mode.
9. To exit the test mode, press the [REPEAT] button. The unit sets into the STANDBY state, the disc is ejected, and the test mode ends.
– 2 –
Page 3
Items of Error History Mode Items and Contents
Selecting the Test Mode
Display
total rec Displays the recording time.
Displayed as “rππππππh”.
The displayed time is the total time the laser is set to the high power state.
This is about 1/4 of the actual recording time.
The time is displayed in decimal digits from 0h to 65535h.
total play Displays the play time.
Displayed as “pππππππh”. The time displayed is the total actual play time. Pauses are not counted.
The time is displayed in decimal digits from 0h to 65535h.
retry err Displays the total number of retries during recording and number of retry errors during play.
Displayed as “rππ pππ”.
“r” indicates the retries during recording while “p” indicates the retry errors during play.
The number of retries and retry errors are displayed in hexadecimal digits from 00 to FF.
total err Displays the total number of errors.
Displayed as “total ππ”.
The number of errors is displayed in hexadecimal digits from 00 to FF.
err history Displays the 10 latest errors.
Displayed as “0π E@@”.
π indicates the history number. The smaller the number, the more recent is the error. (00 is the latest).
@@ indicates the error code.
Refer to the following table for the details. The error history can be switched by turning the =
knob.
er refresh Mode which erases the “retry err”, “total err”, and “err history” histories.
When returning the unit to the customer after completing repairs, perform this to erase the past error history.
After pressing the =
history.
“Complete!” will be displayed momentarily.
Be sure to check the following when this mode has been executed.
• The data has been erased.
• The mechanism operates normally when recording and play are performed.
tm refresh Mode which erases the “total rec” and “total play” histories.
These histories serve as approximate indications of when to replace the optical pickup.
If the optical pickup has been replaced, perform this operation and erase the history.
After pressing the =
history.
“Complete!” will be displayed momentarily.
Be sure to check the following when this mode has been executed.
• The data has been erased.
• The mechanism operates normally when recording and play are performed.
AMS + button and “er refresh?” is displayed, press the [YES] button to erase the
AMS + button and “tm refresh?” is displayed, press the [YES] button to erase the
Details of History
AMS +
Table of Error Codes
Error Code Error Code Details of Error
E00 No error
E01 Disc error. PTOC cannot be read
(DISC ejected)
E02 Disc error. UTOC error
(DISC not ejected)
E03 Loading error
E04 Address cannot be read (Servo has deviated)
Details of Error
E05 FOK has deviated
E06 Cannot focus (Servo has deviated)
E07 Recording retry
E08 Recording retry error
E09 Playback retry error
(Access error)
E0A Playback retry error (C2 error)
– 3 –
Page 4
SECTION 1
SERVICING NOTES
TABLE OF CONTENTS
SELF-DIAGNOSIS FUNCTION.................................... 2
1. SERVICING NOTES............................................... 4
2. GENERAL ................................................................... 11
3. DISASSEMBLY ......................................................... 12
4. TEST MODE.............................................................. 16
5. ELECTRICAL ADJUSTMENTS......................... 21
6. DIAGRAMS
6-1. IC Pin Function Description ........................................... 30
6-2. Block Diagram – SERVO Section – ............................... 37
6-3. Block Diagram – MAIN Section – ................................. 39
6-4. Note for Printed Wiring Boards and
Schematic Diagrams ....................................................... 42
6-5. Pr inted Wiring Board – BD Board – ............................. 43
6-6. Schematic Diagram – BD Board (1/2) – ........................ 45
6-7. Schematic Diagram – BD Board (2/2) – ........................ 47
6-8. Schematic Diagram – SW Board – ................................. 49
6-9. Pr inted Wiring Board – SW Board – .............................. 49
6-10. Printed Wiring Boards – TRANS Board – ..................... 53
6-11. Printed Wiring Board – MAIN Board – ......................... 55
6-12. Schematic Diagram – MAIN Board (1/2) – ................... 57
6-13. Schematic Diagram
– MAIN Board (2/2), TRANS Board – .......................... 59
6-14. Printed Wiring Boards – PANEL/PANEL 2 Boards – ... 61
6-15. Schematic Diagram – PANEL/PANEL 2 Boards –........ 63
7. EXPLODED VIEWS ................................................ 66
SAFETY CHECK-OUT
After correcting the original service problem, perform the following safety check before releasing the set to the customer:
Check the antenna terminals, metal trim, “metallized” knobs,
screws, and all other exposed metal parts for AC leakage.
Check leakage as described below.
LEAKAGE TEST
The AC leakage from any exposed metal part to earth ground and
from all exposed metal parts to any exposed metal part having a
return to chassis, must not exceed 0.5 mA (500 microampers).
Leakage current can be measured by any one of three methods.
1. A commercial leakage tester, such as the Simpson 229 or RCA
WT -540A. Follo w the manufacturers’ instructions to use these
instruments.
2. A battery-operated A C milliammeter. The Data Precision 245
digital multimeter is suitable for this job.
3. Measuring the voltage drop across a resistor by means of a
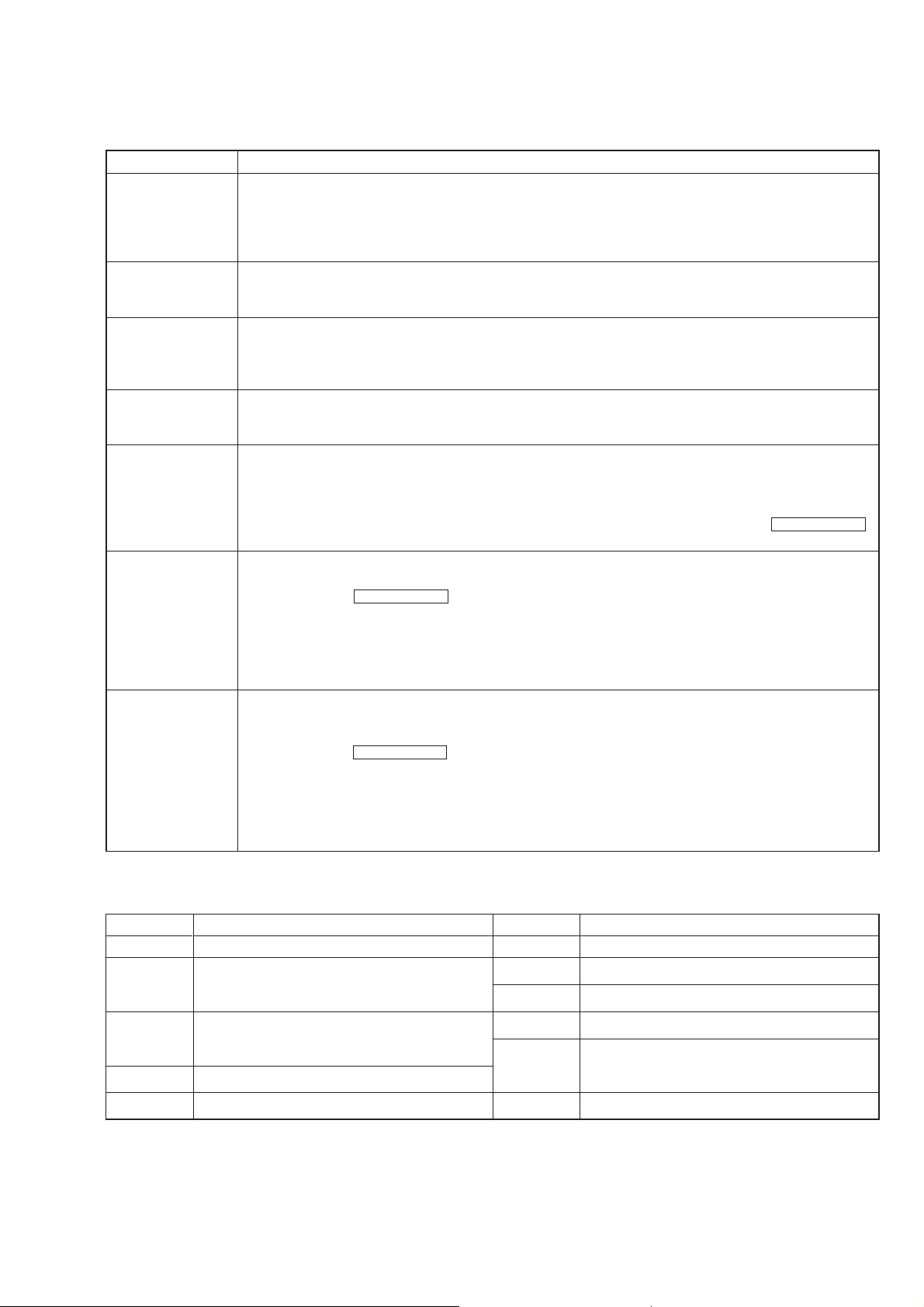
VOM or battery-operated AC voltmeter. The “limit” indication is 0.75 V, so analog meters must have an accurate lowvoltage scale. The Simpson 250 and Sanwa SH-63Trd are examples of a passive VOM that is suitable. Nearly all battery
operated digital multimeters that have a 2 V A C range are suitable. (See Fig. A)
To Exposed Metal
Parts on Set
0.15 µF
1.5 k
Ω
AC
voltmeter
(0.75 V)
8. ELECTRICAL PARTS LIST ............................... 70
Earth Ground
Fig. A. Using an AC voltmeter to check AC leakage.
MODEL IDENTIFICATION
— BACK PANEL —
Part No.
MODEL Part No.
US model 4-216-840-0π
Canadian model 4-216-840-1π
Singapore model 4-216-840-2π
AEP model 4-216-840-3π
UK model 4-216-840-4π
– 4 –
Page 5
CAUTION
Danger of explosion if battery is incorrectly replaced.
Replace only with the same or equivalent type recommended by
the manufacturer.
Discard used batteries according to the manufacturer’ s instructions.
ADVARSEL!
Lithiumbatteri-Eksplosionsfare ved fejlagtig håndtering.
Udskiftning må kun ske med batteri
af samme fabrikat og type.
Levér det brugte batteri tilbage til leverandøren.
ADVARSEL
Eksplosjonsfare ved feilaktig skifte av batteri.
Benytt samme batteritype eller en tilsvarende type
anbefalt av apparatfabrikanten.
Brukte batterier kasseres i henhold til fabrikantens
instruksjoner.
VARNING
Explosionsfara vid felaktigt batteribyte.
Använd samma batterityp eller en likvärdig typ som
rekommenderas av apparattillverkaren.
Kassera använt batteri enligt gällande föreskrifter.
Laser component in this product is capable of emitting radiation exceeding the limit for Class 1.
This appliance is classified as
a CLASS 1 LASER product.
The CLASS 1 LASER PRODUCT MARKING is located on
the rear exterior.
This caution
label is located
inside the unit.
CAUTION
Use of controls or adjustments or performance of procedures
other than those specified herein may result in hazardous radiation exposure.
VAROITUS
Paristo voi räjähtää, jos se on virheellisesti asennettu.
V aihda paristo ainoastaan laite valmistajan suosittelemaan tyyppiin.
Hävitä käytetty paristo valmistajan ohjeiden mukaisesti.
Flexible Circuit Board Repairing
• Keep the temperature of the soldering iron around 270 ˚C during repairing.
• Do not touch the soldering iron on the same conductor of the
circuit board (within 3 times).
• Be careful not to apply force on the conductor when soldering
or unsoldering.
Notes on chip component replacement
• Never reuse a disconnected chip component.
• Notice that the minus side of a tantalum capacitor may be damaged by heat.
SAFETY-RELATED COMPONENT WARNING!!
COMPONENTS IDENTIFIED BY MARK ! OR DOTTED
LINE WITH MARK ! ON THE SCHEMATIC DIA GRAMS
AND IN THE PARTS LIST ARE CRITICAL TO SAFE
OPERATION. REPLACE THESE COMPONENTS WITH
SONY PARTS WHOSE PART NUMBERS APPEAR AS
SHOWN IN THIS MANUAL OR IN SUPPLEMENTS PUBLISHED BY SONY.
ATTENTION AU COMPOSANT AYANT RAPPORT
À LA SÉCURITÉ!
LES COMPOSANTS IDENTIFIÉS P AR UNE MARQUE !
SUR LES DIAGRAMMES SCHÉMATIQUES ET LA LISTE
DES PIÈCES SONT CRITIQUES POUR LA SÉCURITÉ
DE FONCTIONNEMENT. NE REMPLACER CES COMPOSANTS QUE PAR DES PIÈCES SONY DONT LES
NUMÉROS SONT DONNÉS DANS CE MANUEL OU
DANS LES SUPPLÉMENTS PUBLIÉS PAR SONY.
– 5 –
Page 6
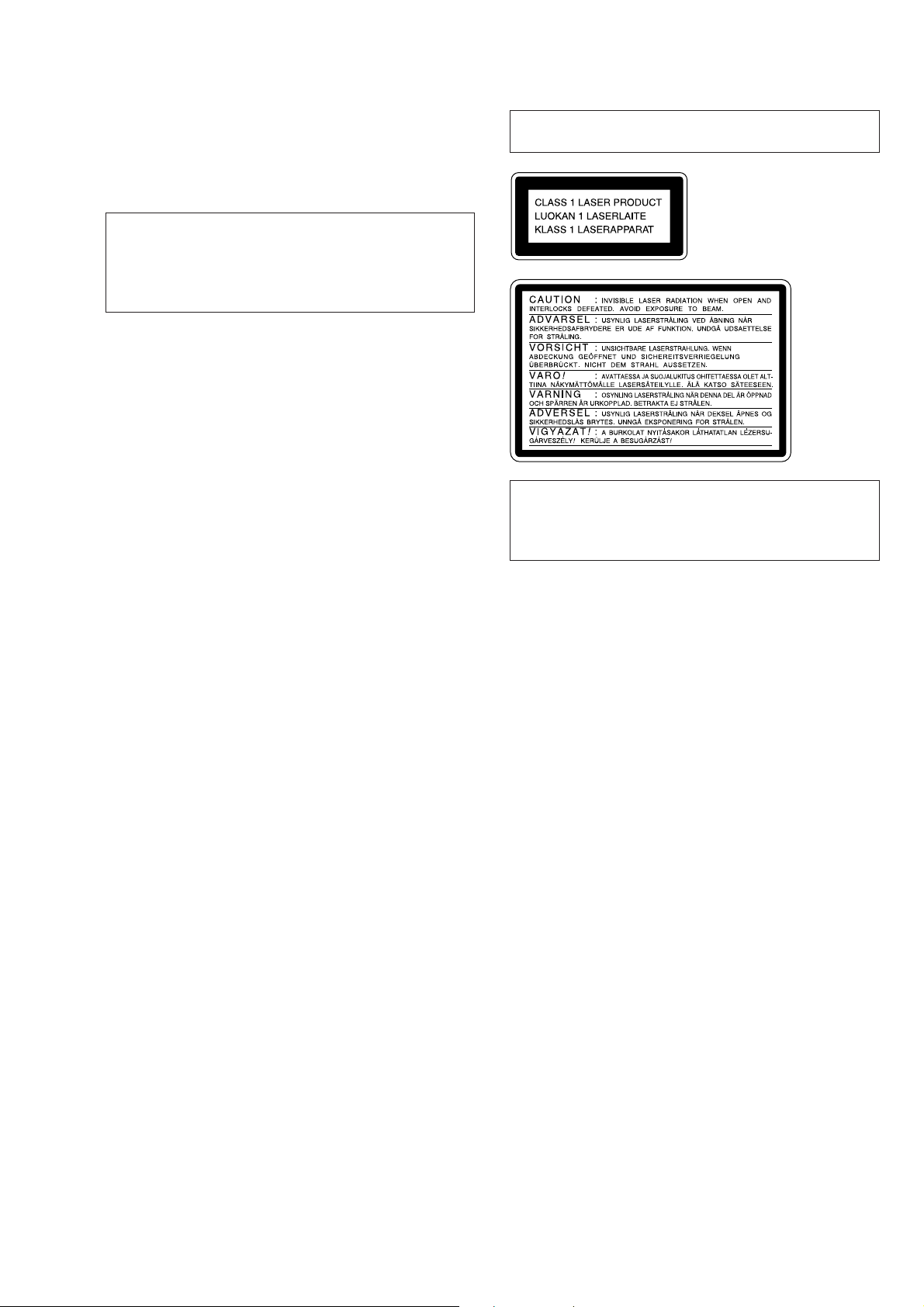
JIG FOR CHECKING BD BOARD WAVEFORM
r
The special jig (J-2501-149-A) is useful for checking the waveform of the BD board. The names of terminals and the checking items to be
performed are shown as follows.
GND: Ground
I+3V : For measuring IOP (Check the deterioration of the optical pick-up laser)
IOP : For measuring IOP (Check the deterioration of the optical pick-up laser)
TEO : TRK error signal (Traverse adjustment)
VC : Reference level for checking the signal
RF : RF signal (Check jitter)
Mechanism deck
RF
VC
TEO
IOP
I+3V
GND
5P Connector
RF
VC
TEO
IOP
I+3V
GND
CN110
6P connecto
for MDM-3
1
RF
VC
TEO
IOP
I+3V
5
for MDM-5
1
VC
RF
TEO
IOP
I+3V
6
GND
– 6 –
Page 7

IOP DA T A RECORDING AND DISPLAY WHEN OPTICAL PICK-UP AND NON-V OLA TILE MEMOR Y (IC171
OF BD BOARD) ARE REPLACED
The IOP value labeled on the optical pick-up can be recorded in the non-volatile memory . By r ecording the value, it will eliminate the need
to look at the value on the label of the optical pick-up. When replacing the optical pick-up or non-v olatile memory (IC171 of BD board),
record the IOP value on the optical pick-up according to the following procedure.
Record Precedure:
1. While pressing the = AMS + knob and p button, connect the power plug to the outlet, and release the = AMS + knob
and p button.
2. Turn the = AMS + knob to display “[Service]”, and press the [YES] button.
3. Turn the = AMS + knob to display “lop Write” (C28), and press the [YES] button.
4. The display becomes “Ref=@@@.@” (@ is an arbitrary number) and the numbers which can be changed will blink.
5. Input the IOP value written on the optical pick-up.
To select the number : Turn the = AMS + knob.
To select the digit : Press the = AMS + knob.
6. When the [YES] button is pressed, the display becomes “Measu=@@@.@” (@ is an arbitrary number).
7. As the adjustment results are recorded for the 6 value. Leave it as it is and press the [YES] button.
8. “Complete!” will be displayed momentarily. The value will be recorded in the non-volatile memory and the display will become “Iop
Write”.
9. Press the [REPEAT] button to complete.
Display Precedure:
1. While pressing the = AMS + knob and p button, connect the power plug to the outlet, and release the = AMS + knob
and p button.
2. Turn th = AMS + knob to display “[Service]”, and press the [YES] button.
3. Turn the = AMS + knob to display “lop Read” (C27).
4. “@@.@/##.#” is displayed and the recorded contents are displayed.
@@.@: indicates the IOP value labeled on the optical pick-up.
##.# : indicates the IOP value after adjustment
5. To end, press the = AMS + knod or [MENU/NO] button to display “Iop Read”. Then press the [REPEAT] button.
– 7 –
Page 8
CHECKS PRIOR TO PARTS REPLACEMENT AND ADJUSTMENTS
Before performing repairs, perform the following checks to determine the faulty locations up to a certain extent.
Details of the procedures are described in “5 Electrical Adjustments”.
Laser power check
(6-2 : See page 23)
Traverse check
(6-3 : See page 23)
Focus bias check
(6-4 : See page 24)
C PLAY check
(6-5 : See page 24)
Self-recording/playback
check
(6-6 : See page 24)
Temperature
compensation
offset check
(6-1 : See page 23)
Criteria for Determination
(Unsatisfactory if specified value is not satisfied)
• 0.9 mW power
Specified value : 0.84 to 0.92 mW
• 7.0 mW power
Specified value : 6.8 to 7.2 mW
lop (at 7mW)
• Labeled on the optical pickup
Iop value ± 10mA
• Traverse waveform
Specified value : Below 10% offset
• Error rate check
Specified value : For points a, b, and c
C1 error : About 200
AD error : Above 00
• Error rate check
Specified value:
a. When using test disc (MDW-74/AU-1)
C1 error : Below 80
AD error : Below 2
b. When using check disc (TDYS-1)
C1 error : Below 50
• CPLAY error rate check
Specified value:
C1 error : Below 80
AD error : Below 2
• Unsatisfactory if displayed as T=@@ (##) [NG”
NG
(@@, ## are both arbitrary numbers)
• Clean the optical pick-up
• Adjust again
• Replace the optical pick-up
• Replace the optical pick-up
• Replace the optical pick-up
• Replace the optical pick-up
• Replace the optical pick-up
If always unsatisfactory:
• Replace the overwrite head
• Check for disconnection of the circuits around the
overwrite head
If occasionally unsatisfactory:
• Check if the overwrite head is distorted
• Check the mechanism around the sled
• Check for disconnection of the circuits around
D101 (BD board)
• Check the signals around IC101, IC121, CN102,
CN103 (BD board)
Measure if unsatisfactory:
Note:
The criteria for determination above is intended merely to determine if satisfactory or not, and does not serve as the specified value for adjustments.
When performing adjustments, use the specified values for adjustments.
– 8 –
Page 9
RETRY CAUSE DISPLAY MODE
• In this test mode, the causes for retry of the unit during recording can be displayed on the fluorescent indicator tube. During playback,
the “track mode” for obtaining track information will be set.
This is useful for locating the faulty part of the unit.
• The following will be displayed :
During recording and stop: Retry cause, number of retries, and number of retry errors.
During playback : Information such as type of disc played, part played, copyright.
These are displayed in hexadecimal.
Precedure:
1. Load a recordable disc whose contents can be erased into the unit.
2. Press the [MENU/NO] button. When “Edit Menu” is displayed on the fluorescent indicator tube, turn the = AMS + knob to
display “All Erase?”.
3. Press the [YES] button. (Or press the = AMS + knob)
4. When “All Erase??” is displayed on the fluorescent indicator tube, the music calendar number blinks.
5. Press the [YES] button to display “Complete!!”, and press the p button immediately. Wait for about 15 seconds while pressing the
button. (The = AMS + knob can be pressed instead of the [YES] button for the same results.)
6. When the “TOC” displayed on the fluorescent display tube goes off, release the p button.
7. Press the [REC] button to start recording. Then press the P button and start recording.
8. To check the “track mode”, press the · button to start play.
9. To exit the test mode, press the 1/u button, and turn OFF the power. When “TOC” disappears, disconnect the power plug from the
outlet.
r
[]
Fig. 1 Reading the Test Mode Display
(During recording and stop)
RTs@@c##e
Fluorescent display tube display
@@ : Cause of retry
## : Number of retries
: Number of retry errors
**
Reading the Retry Cause Display
Higher Bits Lower Bits
Hexadecimal
Bit
Binary
84218421
b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
00000001
00000010
00000100
00001000
00010000
00100000
01000000
10000000
**
Hexa-
decimal
01
02
04
08
10
20
40
80
Cause of Retry
shock
ader5
Discontinuous address
DIN unlock
FCS incorrect
IVR rec error
CLV unlock
Access fault
Fig. 2 Reading the Test Mode Display
(During playback)
@@####**$$
Fluorescent display tube display
@@ : Parts No. (name of area named on TOC)
## : Cluster
: Sector
**
$$ : Track mode (Track information such as copy-
right information of each part)
When track jump (shock) is detected
When ADER was counted more than five times
continuously
When ADIP address is not continuous
When DIN unlock is detected
When not in focus
When ABCD signal level exceeds the specified range
When CLV is unloc ked
When access operation is not performed normally
Address
Occurring conditions
Reading the Display:
Convert the hexadecimal display into binary display. If more than two causes, they will be added.
Example
When 42 is displayed:
Higher bit: 4 = 0100 n b6
Lower bit : 2 = 0010 n b1
In this case, the retry cause is combined of “CLV unlock” and “ader5”.
When A2 is displayed:
Higher bit: A = 1010 n b7+b5
Lower bit : 2 = 0010 n b1
The retry cause in this case is combined of “access fault”, “IVR rec error”, and “ader5”.
– 9 –
Page 10
Reading the Retry Cause Display
Higher Bits
Hexadecimal
Bit
Binary
Reading the Display:
Convert the hexadecimal display into binary display. If more than two causes, they will be added.
Example When 84 is displayed:
Higher bit: 8 = 1000 n b7
Lower bit : 4 = 0100 n b2
In this case, as b2 and b7 are 1 and others are 0, it can be determined that the retry cause is combined of “emphasis OFF”, “monaural”,
“original”, “copyright exists”, and “write allowed”.
Example When 07 is displayed:
Higher bit: 0 = 1000 n All 0
Lower bit : 7 = 0111 n b0+b1+b2
In this case, as b0, b1, and b2 are 1 and others are 0, it can be determined that the retry cause is combined of “emphasis ON”, “stereo”,
“original”, “copyright exists”, and “write prohibited”.
84218421
b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
00000001
00000010
00000100
00001000
00010000
00100000
01000000
10000000
Lower Bits
Hexa-
decimal
01
02
04
08
10
20
40
80
When 0
Emphasis OFF
Monaural
This is 2-bit display. Normally 01.
01:Normal audio. Others:Invalid
Audio (Normal)
Original
Copyright
Write prohibited
Details
When 1
Emphasis ON
Stereo
Invalid
Digital copy
No copyright
Write allowed
Hexadecimal n Binary Conversion Table
Hexadecimal Binary Hexadecimal Binary
0 0000 8 1000
1 0001 9 1001
2 0010 A 1010
3 0011 B 1011
4 0100 C 1100
5 0101 D 1101
6 0110 E 1110
7 0111 F 1111
– 10 –
Page 11
SECTION 2
GENERAL
This section is extracted from
instruction manual.
– 11 –
Page 12
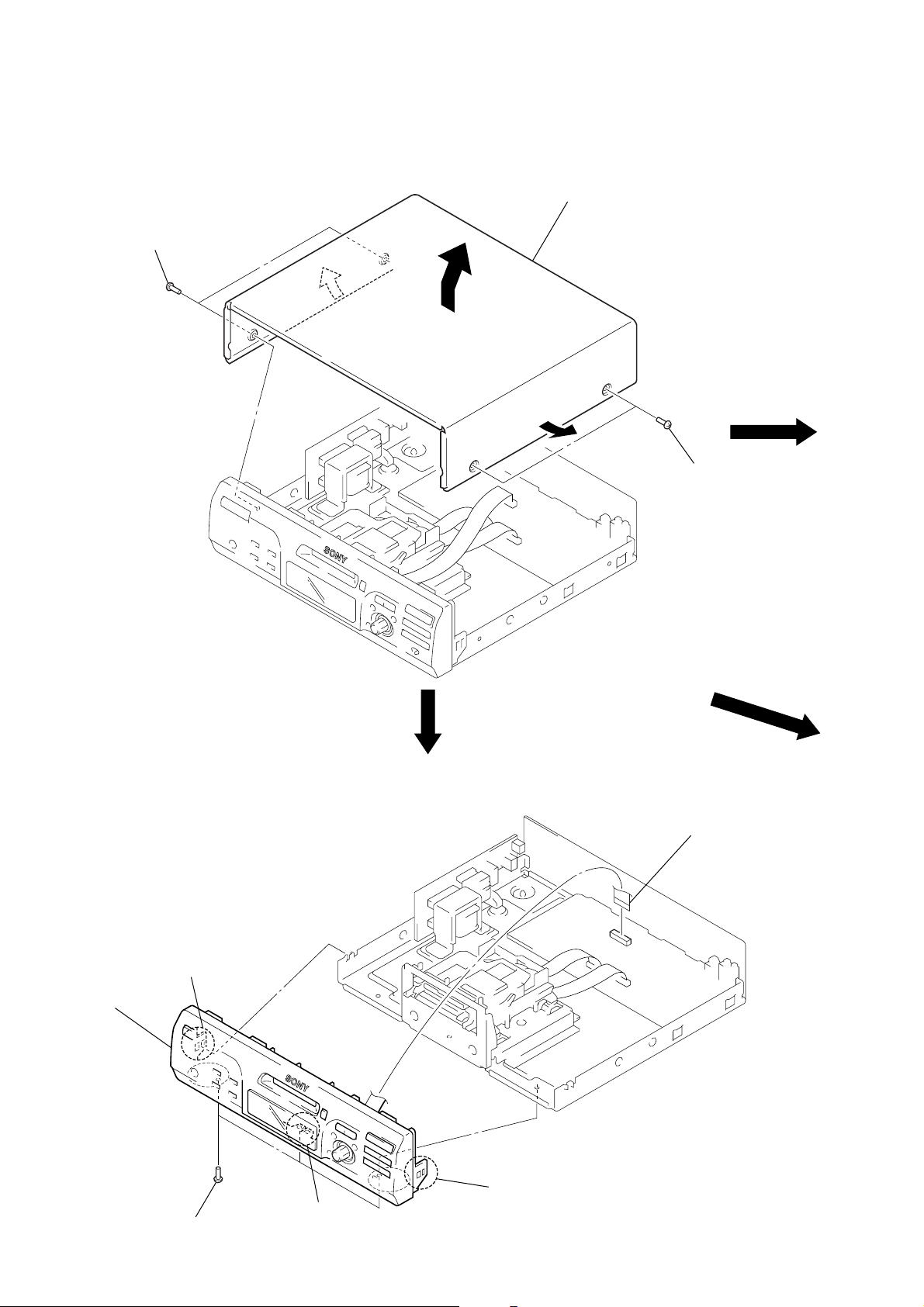
SECTION 3
)
DISASSEMBLY
Note: Follow the disassembly procedure in the numerical order given.
COVER
1
two screws
(CASE 3 TP2)
2
3
cover
2
1
two screws
(CASE 3 TP2)
FRONT PANEL SECTION
3
claw
4
front panel section
2
three screws
(BVTP3
×
8)
3
claw
3
claw
1
wire (flat type) (19 core
(CN421)
– 12 –
Page 13
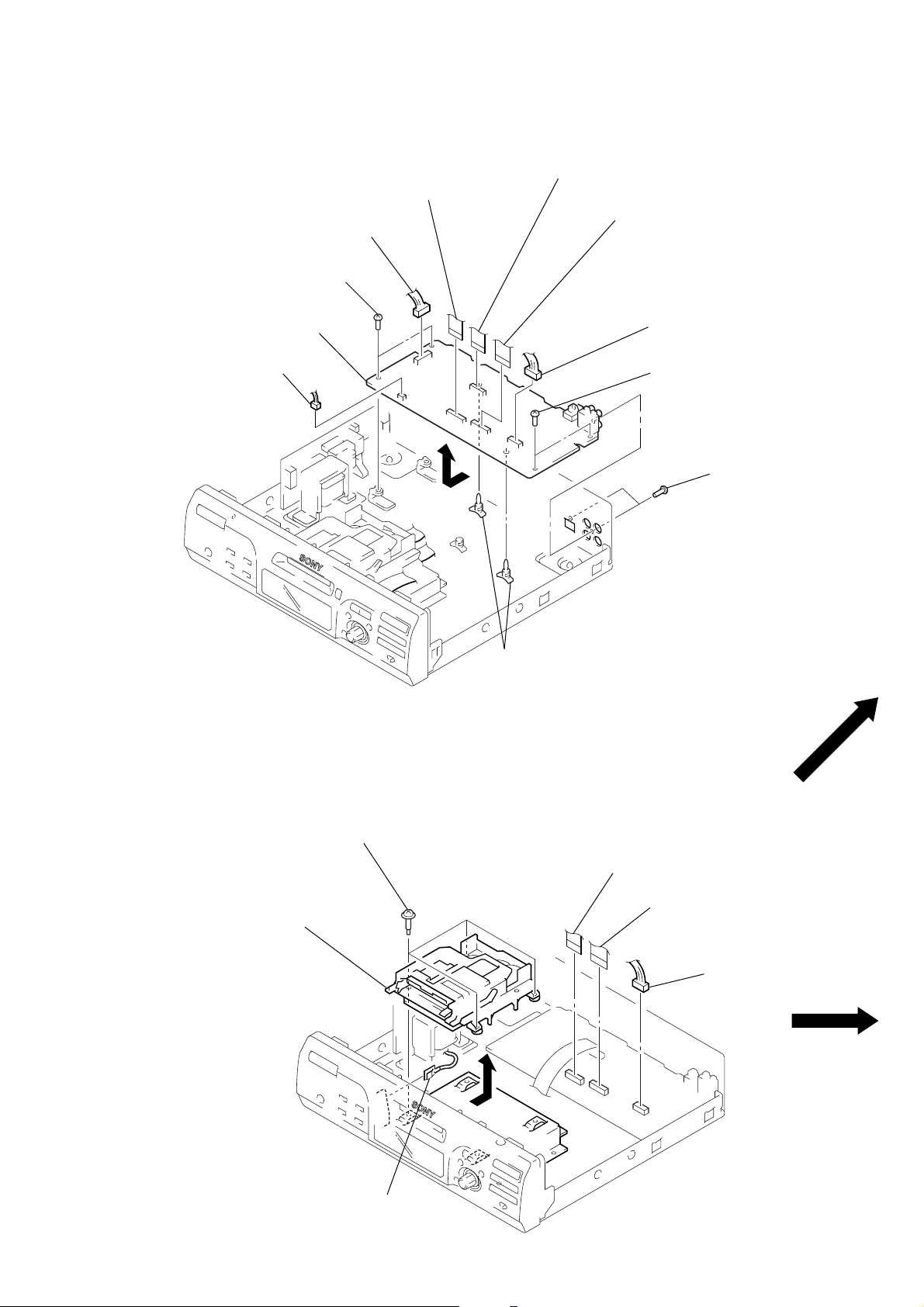
MAIN BOARD
)
2
connector
(CNP911)
5
MAIN board
2
3
two screws
(BVTP3
connector
(CNP920)
×
8)
1
wire (flat type) (21 core)
(CN411)
1
wire (flat type) (19 core)
(CN421)
1
wire (flat type) (23 core)
(CN501)
2
connector
(CN502)
3
two screws
(BVTP3
×
8)
3
two screws
(BVTP3
×
8
MECHANISM DECK SECTION (MDM-5A)
4
four step screws
(BVTTWH M3)
5
Remove the mechanism deck
(MDM-5A) to direction of
the arrow.
4
two PC board holders
1
wire (flat type) (21 core)
(CN411)
1
wire (flat type) (23 core)
(CN501)
2
connector
(CN502)
3
harnes
– 13 –
Page 14
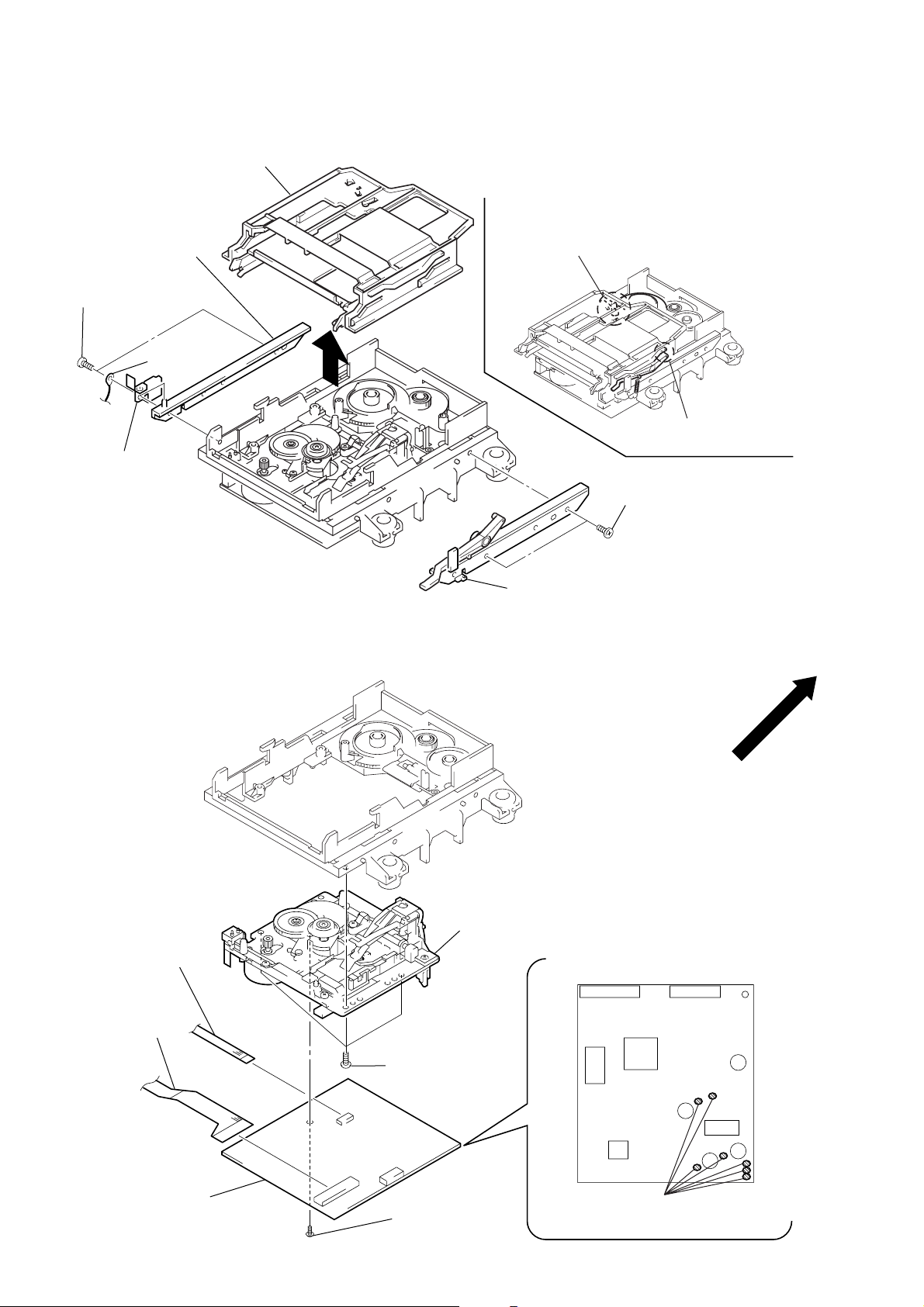
SLIDER (CAM)
7
slider (Cam)
• Note for Installation of Slider A (Cam)
4
bracket (Guide L)
1
two screws (P2.6 × 6)
2
harnes
3
leaf spring
BASE UNIT (MBU-5A), BD BOARD
Set the shaft of Cam gear to
be at the position in the figure.
Set the shaft of Lever (O/C) to
be at the position in the figure.
5
two screws (P2.6 × 6)
6
bracket (Guide R)
5
flexible board
(CN104)
6
flexible board
(CN101)
7
BD board
2
1
three screws
×
(P2.6
4
screw (M1.7 × 4)
– 14 –
base unit (MBU-5A)
6)
3
Remove the solder (Seven portion).
Page 15
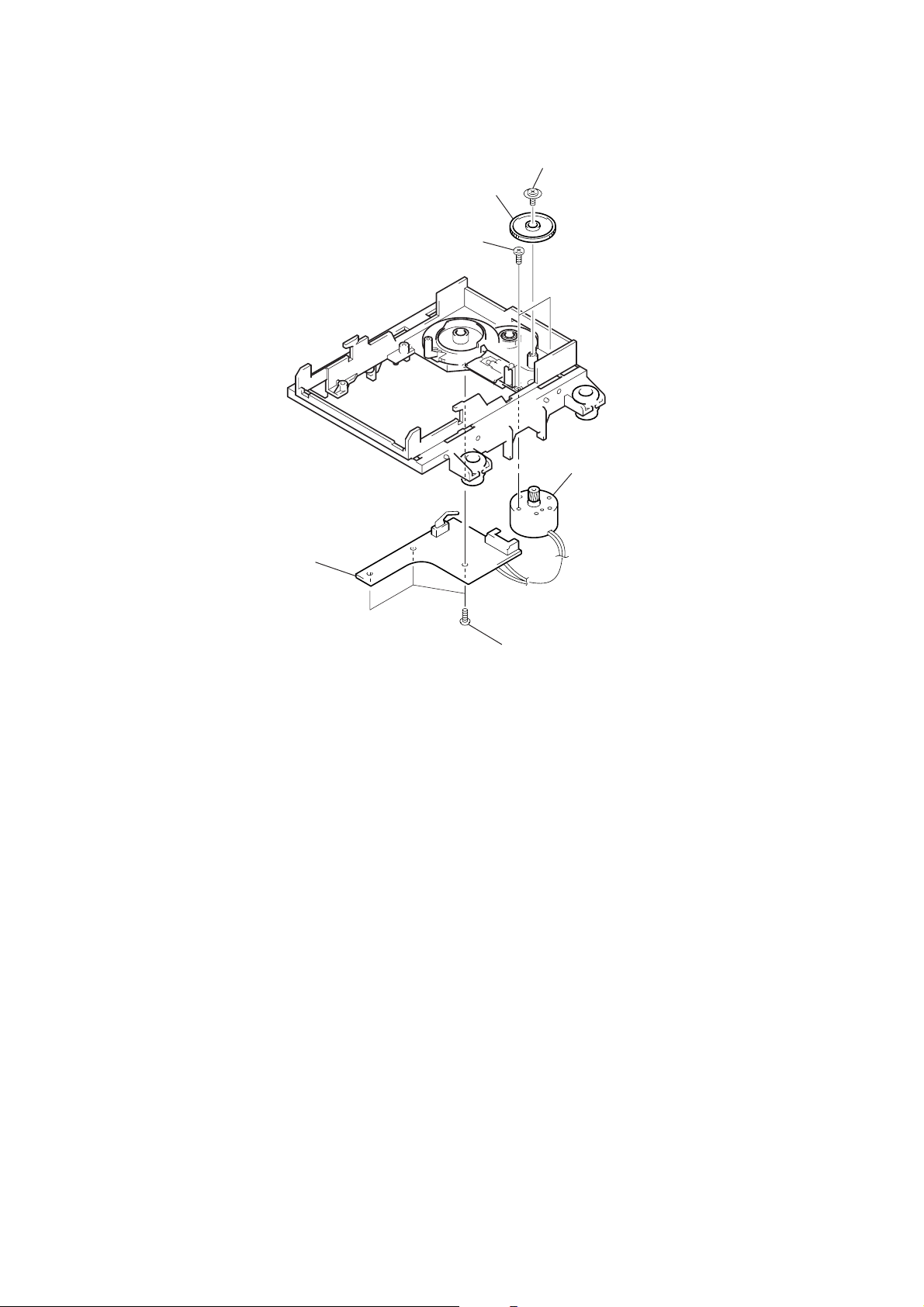
SW BOARD, LOADING MOTOR (M103)
)
3
6
SW board
2
two screws
(PWH1.7
gear (B)
×
4)
1
screw (PTPWH M2.6 × 6
4
loading motor (M103)
5
three screws (BTP2.6 × 6)
– 15 –
Page 16
SECTION 4
TEST MODE
1. PRECAUTIONS FOR USE OF TEST MODE
• As loading related operations will be performed regardless of the test mode operations being performed, be sure to check that the disc
is stopped before setting and removing it.
Even if the [EJECT] button is pressed while the disc is rotating during continuous playback, continuous recording, etc., the disc will
not stop rotating.
Therefore, it will be ejected while rotating.
Be sure to press the [EJECT] button after pressing the [MENU/NO] button and the rotation of disc is stopped.
1-1. Recording laser emission mode and operating buttons
• Continuous recording mode (CREC MODE)
• Laser power check mode (LDPWR CHECK)
• Laser power adjustment mode (LDPWR ADJUST)
• Traverse (MO) check (EF MO CHECK)
• Traverse (MO) adjustment (EF MO ADJUST)
• When pressing the [REC] button.
2. SETTING THE TEST MODE
The following are two methods of entering the test mode.
Procedure 1: While pressing the = AMS + knob and p button, connect the power plug to an outlet, and release the
Procedure 2: While pressing the = AMS + knob, connect the power plug to the outlet and release the = AMS + knob.
§
§
r
= AMS + knob and p button.
When the test mode is set, “[Check]” will be displayed. T urn the = AMS + knob switches between the following four
groups; ···Nn [Check] Nn [Adjust] Nn [Service] Nn [Develop] Nn ···.
When the test mode is set, “TEMP CHECK” will be displayed. By setting the test mode using this method, only the
“Check” group of method 1 can be executed.
3. EXITING THE TEST MODE
Press the [REPEAT] button. The disc is ejected when loaded, and “Standby” display blinks, and the STANDBY state is set.
4. BASIC OPERATIONS OF THE TEST MODE
All operations are performed using the = AMS + knob, [YES] button, and [MENU/NO] button.
The functions of these buttons are as follows.
Function name Function
= AMS + knob Changes parameters and modes
YES button Proceeds onto the next step. Finalizes input.
MENU/NO button Returns to previous step. Stops operations.
– 16 –
Page 17
5. SELECTING THE TEST MODE
There are 31 types of test modes as shown below. The groups can be switched by turn the = AMS + knob. After selecting the g roup
to be used, press the [YES] button. After setting a certain group, turn the = AMS + knob switches between these modes.
Refer to “Group” in the table for details selected.
All items used for servicing can be treated using group S. So be carefully not to enter other groups by mistake.
Display
TEMP CHECK
LDPWR CHECK
EF MO CHECK
EF CD CHECK
FBIAS CHECK
ScurveCHECK
VERIFYMODE
DETRK CHECK
TEMP ADJUST
LDPWR ADJUST
EF MO ADJUST
EF CD ADJUST
FBIAS ADJUST
EEP MODE
Impossible
Impossible
ERR DP MODE
Impossible
Impossible
Impossible
Impossible
Impossible
Impossible
ADJ CLEAR
AG Set (MO)
AG Set (CD)
Iop Read
Iop Write
S40 ******
CPLAY MODE
CREC MODE
No.
C01
C02
C03
C04
C05
C06
C07
C08
C09
C10
C11
C12
C13
C14
C15
C16
C17
C18
C19
C20
C21
C22
C23
C24
C25
C26
C27
C28
C29
C30
C31
Contents
Temperature compensation offset check
Laser power check
Traverse (MO) check
Traverse (CD) check
Focus bias check
S letter check
Non-volatile memory check
Detrack check
Temperature compensation offset adjustment
Laser power adjustment
Traverse (MO) adjustment
Traverse (CD) adjustment
Focus bias adjustment
Non-volatile memory control
Command transmission
Status display
Error history display, clear
Sled check
Access check
Outermost circumference check
Head position check
Same functions as CPLAY MODE
Same functions as CREC MODE
Initialization of non-volatile memory of adjustment value
Auto gain output level adjustment (MO)
Auto gain output level adjustment (CD)
IOP data display
IOP data write
Microprocessing version display
Continuous play mode
Continuous recording mode
Mark
(X)
(X)
(X)
(X) (!)
(X)
(X)
(X)
(X)
(X)
(X)
(X)
(X)
Group (*)
C: Check
S: Service
Group (*)
CS
CS
CS
CS
CS
C
C
C
AS
AS
AS
AS
AS
D
D
D
S
D
D
D
D
D
D
AS
AS
AS
CS
AS
CS
CASD
CASD
A: Adjust
D: Develop
• For details of each adjustment mode, refer to “5. Electrical Adjustments”.
For details of “ERR DP MODE”, refer to “Self-Diagnosis Function” on page 2.
• If a different mode has been selected by mistake, press the [MENU/NO] button to exit that mode.
• Modes with (X) in the Mark column are not used for servicing and therefore are not described in detail. If these modes are set accidentally, press the [MENU/NO] button to exit the mode immediately. Be especially careful not to set the modes with (!) as they will
overwrite the non-volatile memory and reset it, and as a result, the unit will not operate normally.
– 17 –
Page 18

5-1. Operating the Continuous Playback Mode
1. Entering the continuous playback mode
(1) Set the disc in the unit. (Whichever recordable discs or discs for playback only are available.)
(2) Turn the =
AMS + knob and display “CPLAY MODE” (C30).
(3) Press the [YES] button to change the display to “CPLAY MID”.
(4) When access completes, the display changes to “C1 = AD = ”.
Note: The numbers “ ” displayed show you error rates and ADER.
2. Changing the parts to be played back
(1) Press the [YES] button during continuous playback to change the display as below.
“CPLAY MID” n “CPLAY OUT” n “CPLAY IN”
When pressed another time, the parts to be played back can be moved.
(2) When access completes, the display changes to “C1 = AD = ”.
Note: The numbers “ ” displayed show you error rates and ADER.
3. Ending the continuous playback mode
(1) Press the [MENU/NO] button. The display will change to “CPLAY MODE”.
(2) Press the [EJECT] button to remove the disc.
Note: The playback start addresses for IN, MID, and OUT are as follows.
§
IN 40h cluster
MID 300h cluster
OUT 700h cluster
5-2. Operating the Continuous Recording Mode (Use only when performing self-recording/palyback check.)
1. Entering the continuous recording mode
(1) Set a recordable disc in the unit.
(2) Turn the = AMS + knob and display “CREC MODE”.
(3) Press the [YES] button to change the display to “CREC MID” (C31).
(4) When access completes, the display changes to “CREC ( ” and REC lights up.
Note: The numbers “ ” displayed shows you the recording position addresses.
2. Changing the parts to be recorded
(1) When the [YES] button is pressed during continuous recording, the display changes as below.
“CREC MID” n “CREC OUT” n “CREC IN”
When pressed another time, the parts to be recorded can be changed. REC goes off.
(2) When access completes, the display changes to “CREC (
Note: The numbers “ ” displayed shows you the recording position addresses.
” and REC lights up.
3. Ending the continuous recording mode
(1) Press the [MENU/NO] button. The display changes to “CREC MODE” and REC goes off.
(2) Press the [EJECT] button to remove the disc.
Note 1: The recording start addresses for IN, MID, and OUT are as follows.
§
IN 40h cluster
MID 300h cluster
OUT 700h cluster
Note 2: The [MENU/NO] button can be used to stop recording anytime.
Note 3: Do not perform continuous recording for long periods of time above 5 minutes.
Note 4: During continuous recording, be careful not to apply vibration.
5-3. Non-Volatile Memory Mode (EEP MODE)
This mode reads and writes the contents of the non-volatile memory.
It is not used in servicing. If set accidentally, press the [MENU/NO] button immediately to exit it.
– 18 –
Page 19

6. FUNCTIONS OF OTHER BUTTONS
Function
·
p
)
0
SCROLL
PLAY MODE
LEVEL/DISPLAY/CHAR
EJECT §
REPEAT
Sets continuous playback when pressed in the STOP state. When pressed during continuous playback, the tracking servo
turns ON/OFF.
Stops continuous playback and continuous recording.
The sled moves to the outer circumference only when this is pressed.
The sled moves to the inner circumference only when this is pressed.
Switches between the pit and groove modes when pressed.
Switches the spindle servo mode (CLVS ˜ CLV A).
Switches the displayed contents each time the button is pressed
Ejects the disc
Exits the test mode
Contents
7. TEST MODE DISPLAYS
Each time the [DISPLAY/CHAR] button is pressed, the display changes in the following order.
1. Mode display
Displays “TEMP ADJUST”, “CPLAYMODE”, etc.
2. Error rate display
Displays the error rate in the following way.
C1 = ππππ AD = ππ
C1 = Indicates the C1 error.
AD = Indicates ADER.
3. Address display
The address is displayed as follows. (MO: recordable disc, CD: playback only disc)
Pressing the [SCROLL/CLOCKSET] button switches between the group display and bit display.
h = ππππ s = ππππ (MO pit and CD)
h = ππππ a = ππππ (MO groove)
h = Indicates the header address.
s = Indicates the SUBQ address.
a = Indicates the ADIP address.
Mode display
Error rate display
Address display
Auto gain display
(Not used in servicing)
Detrack check display
(Not used in servicing)
IVR display
(Not used in servicing)
Note: “–” is displayed when servo is not imposed.
4. Auto gain display (Not used in servicing)
The auto gain is displayed as follows.
AG = ππ/ππ[ππ]
5. Detrack check display (Not used in servicing)
The detrack is displayed as follows.
ADR = πππππππ
6. IVR display (Not used in servicing)
The IVR is displayed as follows.
[ππ][ππ][ππ
– 19 –
Page 20

MEANINGS OF OTHER DISPLAYS
Display
(
P
REC
SYNC
L.SYNC
OVER
B
ATRACK
DISC
SLEEP
MONO
When Lit
During continuous playback (CLV: ON)
Tracking servo OFF
Recording mode ON
CLV low speed mode
ABCD adjustment completed
Tracking offset cancel ON
Tracking auto gain OK
Focus auto gain OK
Pit
High reflection
CLV-S
CLV LOCK
Contents
When Off
STOP (CLV: OFF)
Tracking servo ON
Recording mode OFF
CLV normal mode
Tracking offset cancel OFF
Groove
Low reflection
CLV-A
CLV UNLOCK
– 20 –
Page 21

SECTION 5
ELECTRICAL ADJUSTMENTS
1. PARTS REPLACEMENT AND ADJUSTMENT
• Check and adjust the MDM and MBU as follows.
The procedure changes according to the part replaced
• Temperature compensation offset check
• Laser power check
• Traverse check
• Focus bias check
• C PLAY check
• Self-recording/playback check
• Abbreviation
OP :Optical pick-up
OWH : Overwrite head
OK
NG
Parts Replacement and Repair
Has the OWH been replaced?
NO
Has OP, IC171, IC101, or
IC121 been replaced?
YES
Initial setting of the adjustment value
Has OP or IC171 been replaced?
Check the sled and spindle
mechanisms.
Other causes can be suspected.
YES
NO
NO
YES
IOP information recording
(IOP value labeled on OP)
Has IC171 or D101
been replaced?
YES
Temperature compensation offset adjustment
• Laser power adjustment
• Traverse adjustment
• Focus bias adjustment
• Error rate adjustment
• Focus bias check
• Auto gain adjustment
– 21 –
NO
Page 22

2. PRECAUTIONS FOR CHECKING LASER DIODE
EMISSION
T o check the emission of the laser diode during adjustments, nev er
view directly from the top as this may lose your eye-sight.
3. PRECAUTIONS FOR USE OF OPTICAL
PICK-UP (KMS-260A)
As the laser diode in the optical pick-up is easily damaged by static
electricity, solder the laser tap of the fle xible board when using it.
Before disconnecting the connector, desolder first. Before connecting the connector, be careful not to remove the solder. Also
take adequate measures to prevent damage by static electricity.
Handle the flexible board with care as it breaks easily.
pick-up
laser tap
flexible board
Optical pick-up flexible board
4. PRECAUTIONS FOR ADJUSTMENTS
1. When replacing the following parts, perform the adjustments
and checks with ¬ in the order shown in the following table.
D101
BD Board
IC101, IC121
IC192
G
1. Initial setting of
adjustment value
2.Recording of IOP
information
(Value written in
the pick-up)
3.Temperature
compensation
offset adjustment
4.Laser power
adjustment
Optical
Pick-up
IC171
¬G¬¬
¬G¬GG
¬¬GGG
¬G¬¬¬
4. Use the following tools and measuring devices.
• Check Disc (MD) TDYS-1
(Parts No. 4-963-646-01)
• TEST DISK (MDW-74/AU-1) (Parts No. 8-892-341-41)
• Laser power meter LPM-8001 (Parts No. J-2501-046-A)
or MD Laser power meter 8010S (Parts No. J-2501-145-A)
• Oscilloscope (Measure after performing CAL of prove)
• Digital voltmeter
• Thermometer
• Jig for checking BD board waveform
(Parts No. : J-2501-149-A)
5. When observing several signals on the oscilloscope, etc.,
make sure that VC and ground do not connect inside the oscilloscope.
(VC and ground will become short-circuited)
6. Using the above jig enables the waveform to be check ed without the need to solder.
(Refer to Servicing Notes on page 6)
7. As the disc used will affect the adjustment results, make sure
that no dusts nor fingerprints are attached to it.
Laser power meter
When performing laser power checks and adjustment (electrical
adjustment), use of the new MD laser power meter 8010S (J-2501145-A) instead of the conventional laser power meter is convenient.
It sharply reduces the time and trouble to set the laser power meter
sensor onto the objective lens of the pick-up.
5. CREATING CONTINUOUSLY-RECORDED DISC
* This disc is used in focus bias adjustment and error rate check.
The following describes how to create a continuous recording
disc.
1. Insert a disc (blank disc) commercially available.
2. Turn the =
(C31)
3. Press the [YES] button again to display “CREC MID”.
Display “CREC (0300)” and start to recording.
4. Complete recording within 5 minutes.
5. Press the [MENU/NO] button and stop recording .
6. Press the [EJECT] button and remove the disc.
The above has been how to create a continuous recorded data for
the focus bias adjustment and error rate check.
Note :
• Be careful not to apply vibration during continuous-recording.
AMS + knob and display “CREC MODE”.
§
5.Traverse
adjustment
6.Focus bias
adjustment
7.Error rate check
8. Auto gain output
level adjustment
¬G¬¬G
¬G¬¬G
¬G¬¬G
¬G¬¬G
2. Set the test mode when performing adjustments.
After completing the adjustments, exit the test mode.
Perform the adjustments and checks in “group S” of the test
mode.
3. Perform the adjustments to be needed in the order shown.
– 22 –
Page 23

6. CHECK PRIOR TO REPAIRS
r
r
These checks are performed before replacing parts according to
“approximate specifications” to determine the faulty locations. For
details, refer to “Checks Prior to Parts Replacement and Adjustments” (See page 8).
6-1. Temperature Compensation Offset Check
When performing adjustments, set the internal temperature and
room temperature of 22 °C to 28 °C.
Checking Procedure:
1. Turn the = AMS + knob to display “TEMP CHECK”
(C01).
2. Press the [YES] button.
3. “T=@@(##) [OK” should be displayed. If “T=@@ (##) [NG”
is displayed, it means that the results are bad.
(@@ indicates the current value set, and ## indicates the value
written in the non-volatile memory)
6-2. Laser Power Check
Before checking, check the IOP value of the optical pick-up.
(Refer to 5-8. Recording and Displaying IOP Information)
Connection :
Optical pick-up
objective lens
BD board
CN110 pin 5 (I +3V)
CN110 pin
4
(IOP)
Checking Procedure:
1. Set the laser power meter on the objective lens of the optical
pick-up. (When it cannot be set properly, press the 0 but-
[]
ton or ) button to move the optical pick-up)
Connect the digital volt meter to CN110 pin 5 (I+3V) and
CN110 pin 4 (IOP).
2. Then, turn the =
AMS + knob and display “LDPWR
CHECK” (C02).
3. Press the [YES] button once and display “LD 0.9 mW $ ”.
Check that the reading of the laser power meter become 0.84
to 0.92 mW.
4. Press the [YES] button once more and display “LD 7.0 mW $
”. Check that the reading the laser power meter and digital
volt meter satisfy the specified value.
Specification:
Laser power meter reading : 7.0 ± 0.2 mW
Digital voltmeter reading : Optical pick-up displayed value
(Optical pick-up label)
±10%
laser
power mete
digital voltmete
+
–
[]
Note 1: After step 4, each time the [YES] button is pressed, the display
will be switched between “LD 0.7 mW $ ”, “LD 6.2 mW $
”, and “LD Wp $ ”. Nothing needs to be performed
here.
6-3. Traverse Check
Note 1: Data will be erased during MO reading if a recorded disc is
used in this adjustment.
Note 2: If the traverse waveform is not clear, connect the oscilloscope
as shown in the following figure so that it can be seen more
clearly.
BD board
CN110 pin 3 (TEO)
1
CN110 pin
(VC)
330 k
Ω
10 pF
oscilloscope
(DC range)
+
–
Connection :
oscilloscope
(DC range)
BD board
CN110 pin 3 (TEO)
CN110 pin
1
(VC)
+
–
V: 0.1 V/div
H: 10 ms/div
Checking Procedure:
1. Connect an oscilloscope to CN110 pin 3 (TEO) and CN110
pin 1 (VC) of the BD board.
2. Load a disc (any available on the market). (Refer to Note 1)
3. Press the ) button and move the optical pick-up outside
[]
the pit.
4. Turn the = AMS + knob and display “EF MO
CHECK”(C03).
5. Press the [YES] button and display “EFB = MO-R”.
(Laser power READ power/Focus servo ON/tracking servo
OFF/spindle (S) servo ON)
6. Observe the waveform of the oscilloscope, and check that the
specified value is satisfied. Do not turn the = AMS +
knob.
(Read power traverse checking)
(Traverse Wavef orm)
A
VC
B
Specified value : Below 10% offset value
I
A – B
Offset value (%) = X 100
I
2 (A + B)
7. Press the [YES] button and display “EFB = MO-W”.
8. Observe the waveform of the oscilloscope, and check that the
specified value is satisfied. Do not turn the = AMS +
knob.
(Write power traverse checking)
KMS260A
27X40
B0825
lOP=82.5 mA in this case
lOP (mA) = Digital voltmeter reading (mV)/1 (Ω)
5. Press the [MENU/NO] button and display “LDPWR CHECK”
and stop the laser emission.
(The [MENU/NO] button is effective at all times to stop the
laser emission)
– 23 –
(Traverse Wavef orm)
VC
Specified value : Below 10% offset value
I
Offset value (%) = X 100
A – B
2 (A + B)
A
B
I
Page 24

9. Press the [YES] button display “EFB = MO-P”.
Then, the optical pick-up moves to the pit area automatically
and servo is imposed.
10. Observe the waveform of the oscilloscope, and c heck that the
specified value is satisfied. Do not turn the = AMS +
knob.
(Traverse Wavef orm)
A
VC
B
Specified value : Below 10% offset value
I
A – B
Offset value (%) = X 100
I
2 (A + B)
11. Press the [YES] button display “EF MO CHECK”
The disc stops rotating automatically.
12. Press the [EJECT] button and remove the disc.
§
13. Load the c heck disc (MD) TDYS-1.
14. Turn the = AMS + knob and display “EF CD CHECK”
(C04).
15. Press the [YES] button and display “EFB = CD”. Servo is
imposed automatically.
16. Observe the waveform of the oscilloscope, and c heck that the
specified value is satisfied. Do not turn the = AMS +
knob.
(Traverse Wavef orm)
A
VC
B
Specified value : Below 10% offset value
I
A – B
Offset value (%) = X 100
I
2 (A + B)
17. Press the [YES] button and display “EF CD CHECK”.
18. Press the [EJECT] button and take out the check disc.
§
6-4. Focus Bias Check
Change the focus bias and check the focus tolerance amount.
Checking Procedure :
1. Load the test disk (MDW-74/AU-1).
2. Turn the = AMS + knob and display “CPLAY MODE”
(C30).
3. Press the [YES] button twice and display “CPLAY MID”.
4. Press the [MENU/NO] button when “C = AD = ” is
displayed.
5. Turn the = AMS + knob and display “FBIAS CHECK”
(C05).
6. Press the [YES] button and display “ / c = ”.
The first four digits indicate the C1 error rate, the two digits
after [/] indicate ADER, and the 2 digits after [c =] indicate
the focus bias value.
Check that the C1 error is below 50 and ADER is below 2.
7. Press the [YES] button and display “ / b = ”.
Check that the C1 error is about 200 and ADER is below 2.
8. Press the [YES] button and display “ / a = ”.
Check that the C1 error is about 200 and ADER is below 2.
9. Press the [MENU/NO] button, next press the [EJECT] but-
§
ton and take out the test disc.
6-5. C PLAY Checking
MO Error Rate Check
Checking Procedure :
1. Load the test disk (MDW-74/AU-1).
2. Turn the = AMS + knob and display “CPLAY MODE”
(C30).
3. Press the [YES] button and display “CPLAY MID”.
4. The display changes to “C = AD = ”.
5. If the C1 error rate is below 80, check that ADER is below 2.
6. Press the
[EJECT] button and take out the test disc.
§
[MENU/NO] button, stop playback, press the
CD Error Rate Check
Checking Procedure :
1. Load the check disc (MD) TDYS-1.
2. Turn the = AMS + knob and display “CPLAY MODE”
(C30).
3. Press the [YES] button twice and display “CPLAY MID”.
4. The display changes to “C = AD = ”.
5. Check that the C1 error rate is below 50.
6. Press the [MENU/NO] button, stop playback, press the
[EJECT] button and take out the check disc.
§
6-6. Self-Recording/playback Check
Prepare a continuous recording disc using the unit to be repaired
and check the error rate.
Checking Procedure :
1. Insert a recordable disc (blank disc) into the unit.
2. Turn the = AMS + knob to display “CREC MODE”
(C31).
3. Press the [YES] button to display the “CREC MID”.
4. When recording starts, “ REC ” is displayed, this becomes
“CREC @@@@” (@@@@ is the address), and recording starts.
5. About 1 minute later, press the [MENU/NO] button to stop
continuous recording.
6. Turn the = AMS + knob to display “CPLAY MODE”
(C30).
7. Press the [YES] button to display “CPLAY MID”.
8. “C = AD = ” will be displayed.
9. Check that the C1 error becomes below 80 and the AD error
below 2.
10. Press the [MENU/NO] button to stop playback, and press the
[EJECT] button and take out the disc.
§
– 24 –
Page 25

7. INITIAL SETTING OF ADJUSTMENT VALUE
Optical pick-up
objective lens
laser
power meter
+
–
BD board
digital voltmeter
CN110 pin 5 (I +3V)
CN110 pin
4
(IOP)
Note:
Mode which sets the adjustment results recorded in the non-volatile
memory to the initial setting value. However the results of the temperature compensation offset adjustment will not change to the initial setting
value.
If initial setting is performed, perform all adjustments again excluding the
temperature compensation offset adjustment.
For details of the initial setting, refer to “4. Precautions on Adjustments”
and execute the initial setting before the adjustment as required.
Setting Procedure :
1. Turn the = AMS + knob to display “ADJ CLEAR (C24)”.
2. Press the [YES] button. “Complete!” will be displayed momentarily and initial setting will be executed, after which “ ADJ
CLEAR” will be displayed.
8. RECORDING AND DISPLAYING THE IOP
INFORMATION
The IOP data can be recorded in the non-volatile memory. The
IOP value on the label of the optical pickup and the IOP value
after the adjustment will be recorded. Recording these data eliminates the need to read the label on the optical pick-up.
Recording Procedure :
1. Turn the = AMS + knob to display “Iop Write” (C28),
and press the [YES] button.
2. The display becomes Ref=@@@.@ (@ is an arbitrary number) and the numbers which can be changed will blink.
3. Input the IOP value written on the optical pick-up.
To select the number : Turn the = AMS + knob.
To select the digit : Press the = AMS + knob
4. When the
“Measu=@@@.@” (@ is an arbitrary number).
5. As the adjustment results are recorded for the 6 value. Leave it
as it is and press the [YES] button.
6. “Complete!” will be displayed momentarily. The value will be
recorded in the non-volatile memory and the display will become “Iop Write”.
[YES] button is pressed, the display becomes
9. TEMPERATURE COMPENSATION OFFSET
ADJUSTMENT
Save the temperature data at that time in the non-volatile memory
as 25 ˚C reference data.
Note :
1. Usually, do not perform this adjustment.
2. Perform this adjustment in an ambient temperature of 22 ˚C to 28 ˚C.
Perform it immediately after the power is turned on when the internal
temperature of the unit is the same as the ambient temperature of 22 ˚C
to 28 ˚C.
3. When D101 has been replaced, perform this adjustment after the tem-
perature of this part has become the ambient temperature.
Adjusting Procedure :
1. Turn the = AMS + knob and display “TEMP ADJUST”
(C09).
2. Press the [YES] button and select the “TEMP ADJUST” mode.
3. “TEMP = [OK” and the current temperature data will be
displayed.
4. To save the data, press the [YES] button.
When not saving the data, press the [MENU/NO] button.
5. When the [YES] button is pressed, “TEMP = SAVE” will
be displayed and turned back to “TEMP ADJUST” display
then. When the [MENU/NO] button is pressed, “TEMP ADJUST” will be displayed immediately.
Specified Value :
The “TEMP = ” should be within “E0 - EF”, “F0 - FF”, “00 0F”, “10 - 1F” and “20 - 2F”.
10. LASER POWER ADJUSTMENT
Check the IOP value of the optical pick-up before adjustments.
(Refer to 8. Recording and Displaying IOP Information)
Connection :
Display Procedure :
1. Turn the = AMS + knob to display “Iop Read”(C27).
2. “@@.@/##.#” is displayed and the recorded contents are displayed.
@@.@ indicates the IOP value labeled on the pick-up.
##.# indicates the IOP value after adjustment
3. To end, press the = AMS + button or [MENU/NO] but-
ton to display “Iop Read”.
Adjusting Procedure :
1. Set the laser power meter on the objective lens of the optical
pick-up. (When it cannot be set properly , press the 0 button
[]
or ) button to move the optical pick-up.)
Connect the digital volt meter to CN110 pin 5 (I+3V) and
CN110 pin 4 (IOP).
2. Turn the =
AMS + knob and display “LDPWR AD-
JUST” (C10).
(Laser power : For adjustment)
3. Press the [YES] button once and display “LD 0.9 mW $ ”.
4. Turn the = AMS + knob so that the reading of the laser
power meter becomes 0.85 to 0.91 mW. Press the [YES] button after setting the range knob of the laser power meter, and
save the adjustment results. (“LD SAVE $ ” will be displayed for a moment.)
5. Then “LD 7.0 mW $ ” will be displayed.
6. Turn the = AMS + knob so that the reading of the laser
power meter becomes 6.9 to 7.1 mW, press the [YES] button
and save it.
Note: Do not perform the emission with 7.0 mW more than 15 seconds
continuously.
– 25 –
[]
Page 26

7. Then, turn the = AMS + knob and display “LDPWR
CHECK” (C02).
8. Press the [YES] button once and display “LD 0.9 mW $ ”.
Check that the reading of the laser power meter become 0.85
to 0.91 mW.
9. Press the [YES] button once more and display “LD 7.0 mW $
”. Check that the reading the laser power meter and digital
volt meter satisfy the specified value.
Note down the digital voltmeter reading value.
Specification:
Laser power meter reading: 7.0 ± 0.2 mW
Digital voltmeter reading : Optical pick-up displayed value
±10%
(Optical pick-up label)
KMS260A
27X40
B0825
lOP=82.5 mA in this case
lOP (mA) = Digital voltmeter reading (mV)/1 (
10. Press the
[MENU/NO] button and display “LDPWR CHECK”
Ω
)
and stop the laser emission.
(The [MENU/NO] button is effective at all times to stop the
laser emission.)
11. Turn the = AMS + knob to display “Iop Write”(C28).
12. Press the [YES] button. When the display becomes
Ref=@@@.@ (@ is an arbitrary number), press the [YES]
button to display “Measu=@@@.@” (@ is an arbitrary number).
13. The numbers which can be changed will blink. Input the Iop
value noted down at step 9.
To select the number : Turn the =
AMS + knob.
To select the digit : Press the = AMS + knob.
14. W hen the [YES] button is pressed, “Complete!” will be displayed momentarily. The value will be recorded in the nonvolatile memory and the display will become “Iop Write”.
Note 1: After step 4, each time the [YES] button is pressed, the display
will be switched between “LD 0.7 mW $ ”, “LD 6.2 mW $
”, and “LD Wp $ ”. Nothing needs to be performed
here.
11. TRAVERSE ADJUSTMENT
Note 1:Data will be erased during MO reading if a recorded disc is
used in this adjustment.
Note 2:If the traverse waveform is not clear, connect the oscilloscope
as shown in the following figure so that it can be seen more
clearly.
BD board
CN110 pin 3 (TEO)
1
CN110 pin
(VC)
330 k
Connection :
oscilloscope
(DC range)
BD board
CN110 pin 3 (TEO)
CN110 pin
1
(VC)
Adjusting Procedure :
1. Connect an oscilloscope to CN110 pin 3 (TEO) and CN110
pin 1 (VC) of the BD board.
2. Load a disc (any available on the market). (Refer to Note 1)
3. Press the ) button and move the optical pick-up outside
[]
the pit.
4. Turn the = AMS + knob and display “EF MO ADJUST”
(C10).
5. Press the [YES] button and display “EFB = MO-R”.
(Laser power READ power/Focus servo ON/tracking servo
OFF/spindle (S) servo ON)
6. Turn the =
AMS + knob so that the waveform of the
oscilloscope becomes the specified value.
(When the = AMS + knob is turned, the of “EFB=
” changes and the waveform changes.) In this adjustment,
waveform varies at intervals of approx. 2%. Adjust the waveform so that the specified value is satisfied as much as possible.
(Read power traverse adjustment)
(T r a v erse W a v ef orm)
VC
Ω
10 pF
+
–
oscilloscope
(DC range)
+
–
V: 0.1 V/div
H: 10 ms/div
A
B
Specification A = B
7. Press the [YES] button and save the result of adjustment to
the non-volatile memory (“EFB = SAV” will be displayed
for a moment. Then “EFB = MO-W” will be displayed).
– 26 –
Page 27

8. Turn the = AMS + knob so that the waveform of the
C1 error
about
200
B
C A Focus bias value
(F. BIAS)
oscilloscope becomes the specified value.
(When the = AMS + knob is turned, the of “EFB-
” changes and the waveform changes.) In this adjustment,
waveform varies at intervals of approx. 2%. Adjust the waveform so that the specified value is satisfied as much as possible.
(Write power traverse adjustment)
(T r av erse Wa v eform)
A
VC
B
Specification A = B
9. Press the [YES] button, and save the adjustment results in the
non-volatile memory. (“EFB = SAV” will be displayed for
a moment.)
10. “EFB = MO-P”. will be displayed.
The optical pick-up moves to the pit area automatically and
servo is imposed.
11. Turn the = AMS + knob until the waveform of the oscilloscope moves closer to the specified value.
In this adjustment, waveform varies at interv als of approx. 2%.
Adjust the waveform so that the specified value is satisfied as
much as possible.
(T r av erse Wa v eform)
A
VC
B
Specification A = B
12. Press the [YES] b utton, and save the adjustment results in the
non-volatile memory. (“EFB = SAV” will be displayed for
a moment.)
Next “EF MO ADJUST” is displa yed. The disc stops rotating
automatically.
13. Press the [EJECT] button and take out the disc.
§
14. Load the check disc (MD) TDYS-1.
15. T urn th e = AMS + knob and display “EF CD ADJUST”
(C12).
16. Press the [YES] button and display “EFB = CD”. Servo is
imposed automatically.
17. Turn the = AMS + knob so that the waveform of the
oscilloscope moves closer to the specified value.
In this adjustment, waveform varies at interv als of approx. 2%.
Adjust the waveform so that the specified value is satisfied as
much as possible.
18. Press the
[YES] button, display “EFB = SAV” for a mo-
ment and save the adjustment results in the non-volatile
memory.
Next “EF CD ADJUST” will be displayed.
19. Press the [EJECT] button and take out the disc.
§
12. FOCUS BIAS ADJUSTMENT
Adjusting Procedure :
1. Load the continuously-recorded disc. (Refer to “5. CREATING CONTINUOUSLY-RECORDED DISC”)
2. Turn the = AMS + knob and display “CPLAY MODE”
(C29).
3. Press the [YES] button and display “CPLAY MID”.
4. Press the [MENU/NO] button when “C1 = AD = ” is
displayed.
5. Turn the = AMS + knob and display “FBIAS ADJUST”
(C13).
6. Press the [YES] button and display “ / a = ”.
The first four digits indicate the C1 error rate, the two digits
after [/] indicate ADER, and the 2 digits after [a =] indicate
the focus bias value.
7. Turn the = AMS + knob in the clockwise direction and
find the focus bias value at which the C1 error rate becomes
about 200 (Refer to Note 2).
8. Press the [YES] button and display “ / b = ”.
9. Turn the = AMS + knob in the counterclockwise direction and find the focus bias value at which the C1 error rate
becomes about 200.
10. Press the [YES] button and display “ / c = ”.
11. Check that the C1 error rate is below 50 and ADER is 00.
Then press the [YES] button.
12. If the “( )” in “ - - ( )” is above 20, press the [YES]
button.
If below 20, press the [MENU/NO] button and repeat the adjustment from step 2.
13. Press the [EJECT] button and take out the disc.
Note 1: The relation between the C1 error and focus bias is as shown in
Note 2: As the C1 error rate changes, perform the adjustment using the
§
the following figure. Find points A and B in the follo wing figure
using the above adjustment. The focal point position C is automatically calculated from points A and B.
average vale.
(T r av erse Wa v eform)
A
VC
B
Specification A = B
– 27 –
Page 28

13. ERROR RATE CHECK
13-1. CD Error Rate Check
15. AUTO GAIN CONTROL OUTPUT LEVEL
ADJUSTMENT
Checking Procedure :
1. Load the check disc (MD) TDYS-1.
2. Turn the = AMS + knob and display “CPLAY MODE”
(C30).
3. Press the [YES] button twice and display “CPLAY MID”.
4. The display changes to “C1 = AD = ”.
5. Check that the C1 error rate is below 20.
6. Press the [MENU/NO] button, stop playback, press the
[EJECT] button and take out the check disc.
§
13-2. MO Error Rate Check
Checking Procedure :
1. Load the test disc (MDW-74/AU-1).
2. Turn the = AMS + knob and display “CPLAY MODE”
(C30).
3. Press the [YES] button and display “CPLAY MID”.
4. The display changes to “C1 = AD = ”.
5. If the C1 error rate is below 50, check that ADER is 00.
6. Press the [MENU/NO] button, stop playback, press the
[EJECT] button and take out the test disc.
§
14. FOCUS BIAS CHECK
Change the focus bias and check the focus tolerance amount.
Checking Procedure :
1. Load the continuously-recorded disc. (Refer to “5. CREATING CONTINUOUSLY-RECORDED DISC”)
2. Turn the = AMS + knob and display “CPLAY MODE”
(C30).
3. Press the
4. Press the [MENU/NO] button when “C1 = AD = ” is
displayed.
5. Turn the = AMS + knob and display “FBIAS CHECK”
(C05).
6. Press the [YES] button and display “ / c = ”.
The first four digits indicate the C1 error rate, the two digits
after [/] indicate ADER, and the 2 digits after [c =] indicate
the focus bias value.
Check that the C1 error is below 50 and ADER is below 2.
7. Press the [YES] button and display “ / b = ”.
Check that the C1 error is about 200 and ADER is below 2.
8. Press the [YES] button and display “ / a = ”.
Check that the C1 error is about 200 and ADER is below 2
9. Press the [MENU/NO] button, next press the [EJECT] button and take out the disc.
[YES] button twice and display “CPLAY MID”.
§
Be sure to perform this adjustment when the pickup is replaced.
If the adjustment results becomes “Adjust NG!”, the pickup may
be faulty or the servo system circuits may be abnormal.
15-1. CD Auto Gain Control Output Level Adjustment
Adjusting Procedure :
1. Insert the check disc (MD) TDYS-1.
2. Turn the = AMS + knob to display “AG Set (CD)” (C26).
3. When the [YES] button is pressed, the adjustment will be performed automatically.
“Complete!!” will then be displayed momentarily when the
value is recorded in the non-volatile memory, after which the
display changes to “AG Set (CD)”.
4. Press the [EJECT] button and take out the check disc.
15-2. MO Auto Gain Control Output Level Adjustment
Adjusting Procedure :
1. Insert the test disc (MDW-74/AU-1) for recording.
2. Turn the = AMS + knob to display “A G Set (MO)” (C25).
3. When the [YES] button is pressed, the adjustment will be performed automatically.
“Complete!!” will then be displayed momentarily when the
value is recorded in the non-volatile memory, after which the
display changes to “AG Set (MO)”.
4. Press the [EJECT] button and take out the test disc.
§
§
Note 1: If the C1 error and ADER are above other than the specified
value at points a (step 8. in the above) or b (step 7. in the abov e),
the focus bias adjustment may not have been carried out properly. Adjust perform the beginning again.
– 28 –
Page 29

Adjustment Location:
– BD BOARD (Side A) –
CN101
D101
NOTE
IC171
GND
I+3V
IOP
TEO
RF
VC
CN110
– BD BOARD (Side B) –
IC101
IC121
IC192
Note: It is useful to use the jig. for checking the waveform. (Refer to
Servicing Notes on page 6)
– 29 –
Page 30

SECTION 6
DIAGRAMS
6-1. IC PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTION
• BD BOARD IC101 CXA2523AR (RF AMP, FOCUS/TRACKING ERROR AMP)
Pin No. Pin Name I/O Description
1II
2JI
3VCO
4 to 9 A to F I
10 PD I
11 APC O
12 APCREF I
13 GND —
14 TEMPI I
15
16 SWDT I
17 SCLK I
18 XLAT I
19 XSTBY I
20 F0CNT I
21 VREF O
22 EQADJ I
23 3TADJ I
24 VCC —
25 WBLADJ I
26 TE O
27 CSLED I
28 SE O
29 ADFM O
30 ADIN I
31 ADAGC I
32 ADFG O
33 AUX O
34 FE O
35 ABCD O
36 BOTM O
37 PEAK O
38 RF O
39 RFAGC I
40 AGCI I
41 COMPO O
42 COMPP I
43 ADDC I
44 OPO O
45 OPN I
46 RFO O
47 MORFI I
48 MORFO O
TEMPR O
I-V converted RF signal I input from the optical pick-up block detector
I-V converted RF signal J input from the optical pick-up block detector
Middle point voltage (+1.65V) generation output terminal
Signal input from the optical pick-up detector
Light amount monitor input from the optical pick-up block laser diode
Laser amplifier output terminal to the automatic power control circuit
Reference voltage input terminal for setting laser power
Ground terminal
Connected to the temperature sensor
Output terminal for a temperature sensor reference voltage
Writing serial data input from the CXD2654R (IC121)
Serial data transfer clock signal input from the CXD2654R (IC121)
Serial data latch pulse signal input from the CXD2654R (IC121)
Standby signal input terminal “L”: standby (fixed at “H” in this set)
Center frequency control voltage input terminal of internal circuit (BPF22, BPF3T, EQ) input
from the CXD2654R (IC121)
Reference voltage output terminal Not used (open)
Center frequency setting terminal for the internal circuit (EQ)
Center frequency setting terminal for the internal circuit (BPF3T)
Power supply terminal (+3.3V)
Center frequency setting terminal for the internal circuit (BPF22)
Tracking error signal output to the CXD2654R (IC121)
Connected to the external capacitor for low-pass filter of the sled error signal
Sled error signal output to the CXD2654R (IC121)
FM signal output of the ADIP
Receives a ADIP FM signal in AC coupling
Connected to the external capacitor for ADIP AGC
ADIP duplex signal (22.05 kHz ± 1 kHz) output to the CXD2654R (IC121)
Auxiliary signal (I
Focus error signal output to the CXD2654R (IC121)
Light amount signal (ABCD) output to the CXD2654R (IC121)
Light amount signal (RF/ABCD) bottom hold output to the CXD2654R (IC121)
Light amount signal (RF/ABCD) peak hold output to the CXD2654R (IC121)
Playback EFM RF signal output to the CXD2654R (IC121)
Connected to the external capacitor for RF auto gain control circuit
Receives a RF signal in AC coupling
User comparator output terminal Not used (open)
User comparator input terminal Not used (fixed at “L”)
Connected to the external capacitor for cutting the low band of the ADIP amplifier
User operational amplifier output terminal Not used (open)
User operational amplifier inversion input terminal Not used (fixed at “L”)
RF signal output terminal
Receives a MO RF signal in AC coupling
MO RF signal output terminal
3
signal/temperature signal) output to the CXD2654R (IC121)
– 30 –
Page 31

• BD BOARD IC121 CXD2654R
(DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSOR, DIGITAL SERVO PROCESSOR, EFM/ACIRC ENCODER/DECODER,
SHOCK PROOF MEMORY CONTROLLER, ATRAC ENCODER/DECODER)
Pin No. Pin Name I/O Description
1 MNT0 (FOK) O
2 MNT1 (SHOCK) O
3 MNT2 (XBUSY) O
4 MNT3 (SLOCK) O
5 SWDT I
6 SCLK I (S)
7 XLAT I (S)
8 SRDT O (3)
9 SENS O (3)
10 XRST
11
SQSY O
Focus OK signal output to the system controller (IC501)
“H” is output when focus is on (“L”: NG)
Track jump detection signal output to the system controller (IC501)
Busy monitor signal output to the system controller (IC501)
Spindle servo lock status monitor signal output to the system controller (IC501)
Writing serial data signal input from the system controller (IC501)
Serial data transfer clock signal input from the system controller (IC501)
Serial data latch pulse signal input from the system controller (IC501)
Reading serial data signal output to the system controller (IC501)
Internal status (SENSE) output to the system controller (IC501)
I (S)
Reset signal input from the system controller (IC501) “L”: reset
Subcode Q sync (SCOR) output to the system controller (IC501)
“L” is output every 13.3 msec Almost all, “H” is output
12
13 RECP I
14 XINT O Interrupt status output to the system controller (IC501)
15 TX I
16 OSCI I System clock signal (512Fs=22.5792 MHz) input terminal
17 OSCO O System clock signal (512Fs=22.5792 MHz) output terminal Not used (open)
18 XTSL I
19 DIN0 I
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29 FS256 O
30 DVDD — Power supply terminal (+3.3V) (digital system)
31 to 34
35
36 to 40
41 A11 O
42 DVSS — Ground terminal (digital system)
43 XOE O Output enable signal output to the D-RAM (IC124) “L” active
44 XCAS O Column address strobe signal output to the D-RAM (IC124) “L” active
* I (S) stands for schmitt input, I (A) for analog input, O (3) for 3-state output, and O (A) for analog output in the column I/O.
DQSY O
DIN1 I Digital audio signal input terminal when recording mode (for digital optical input)
DOUT O
DATAI I Serial data input terminal Not used (fixed at “L”)
LRCKI I L/R sampling clock signal (44.1 kHz) input terminal Not used (fixed at “L”)
XBCKI I Bit clock signal (2.8224 MHz) input terminal Not used (fixed at “L”)
ADDT I Recording data input from the A/D, D/A converter (IC301)
DADT O Playback data output to the A/D, D/A converter (IC301)
LRCK O L/R sampling clock signal (44.1 kHz) output to the A/D, D/A converter (IC301)
XBCK O Bit clock signal (2.8224 MHz) output to the A/D, D/A converter (IC301)
A03 to A00 O Address signal output to the D-RAM (IC124)
A10 O
A04 to A08 O Address signal output to the D-RAM (IC124)
Digital In U-bit CD format subcode Q sync (SCOR) output to the system controller (IC501)
“L” is output every 13.3 msec Almost all, “H” is output
Laser power selection signal input from the system controller (IC501)
“L”: playback mode, “H”: recording mode
Recording data output enable signal input from the system controller (IC501)
Writing data transmission timing input (Also serves as the magnetic head on/off output)
Input terminal for the system clock frequency setting
“L”: 45.1584 MHz, “H”: 22.5792 MHz (fixed at “H” in this set)
Digital audio signal input terminal when recording mode (for digital optical input) Not used
Digital audio signal output terminal when playback mode (for digital optical output)
Not used
Clock signal (11.2896 MHz) output terminal Not used (open)
Address signal output to the external D-RAM Not used (open)
Address signal output to the external D-RAM Not used (open)
– 31 –
Page 32

Pin No. Pin Name I/O Description
45 A09 O Address signal output to the D-RAM (IC124)
46 XRAS O Row address strobe signal output to the D-RAM (IC124) “L” active
47 XWE O Write enable signal output to the D-RAM (IC124) “L” active
48 D1 I/O
49 D0 I/O
50 D2 I/O
Two-way data bus with the D-RAM (IC124)
51 D3 I/O
52 MVCI
I (S)
Digital in PLL oscillation input from the external VCO Not used (fixed at “L”)
53 ASYO O Playback EFM full-swing output terminal
54 ASYI I (A) Playback EFM asymmetry comparator voltage input terminal
55 AVDD — Power supply terminal (+3.3V) (analog system)
56 BIAS I (A) Playback EFM asymmetry circuit constant current input terminal
57 RFI I (A) Playback EFM RF signal input from the CXA2523AR (IC101)
58 AVSS — Ground terminal (analog system)
59 PCO O (3) Phase comparison output for master clock of the recording/playback EFM master PLL
60 FILI I (A) Filter input for master clock of the recording/playback master PLL
61 FILO O (A) Filter output for master clock of the recording/playback master PLL
62 CLTV I (A) Internal VCO control voltage input of the recording/playback master PLL
63 PEAK I (A) Light amount signal (RF/ABCD) peak hold input from the CXA2523AR (IC101)
64 BOTM I (A) Light amount signal (RF/ABCD) bottom hold input from the CXA2523AR (IC101)
65 ABCD I (A) Light amount signal (ABCD) input from the CXA2523AR (IC101)
66 FE I (A) Focus error signal input from the CXA2523AR (IC101)
67 AUX1 I (A) Auxiliary signal (I
3
signal/temperature signal) input from the CXA2523AR (IC101)
68 VC I (A) Middle point voltage (+1.65V) input from the CXA2523AR (IC101)
69 ADIO O (A) Monitor output of the A/D converter input signal Not used (open)
70 AVDD — Power supply terminal (+3.3V) (analog system)
71 ADRT I (A) A/D converter operational range upper limit voltage input terminal (fixed at “H” in this set)
72 ADRB I (A) A/D converter operational range lower limit voltage input terminal (fixed at “L” in this set)
73 AVSS — Ground terminal (analog system)
74 SE I (A) Sled error signal input from the CXA2523AR (IC101)
75 TE I (A) Tracking error signal input from the CXA2523AR (IC101)
76 DCHG I (A) Connected to the +3.3V power supply
77 APC I (A) Error signal input for the laser automatic power control Not used (fixed at “H”)
78 ADFG
I (S)
ADIP duplex FM signal (22.05 kHz ± 1 kHz) input from the CXA2523AR (IC101)
79 F0CNT O Filter f0 control signal output to the CXA2523AR (IC101)
80 XLRF O Serial data latch pulse signal output to the CXA2523AR (IC101)
81 CKRF O Serial data transfer clock signal output to the CXA2523AR (IC101)
82 DTRF O Writing serial data output to the CXA2523AR (IC101)
83 APCREF O
Control signal output to the reference voltage generator circuit for the laser automatic power
control
84 LDDR O PWM signal output for the laser automatic power control Not used (open)
85 TRDR O Tracking servo drive PWM signal (–) output to the BH6511FS (IC152)
86 TFDR O Tracking servo drive PWM signal (+) output to the BH6511FS (IC152)
87 DVDD — Power supply terminal (+3.3V) (digital system)
88 FFDR O Focus servo drive PWM signal (+) output to the BH6511FS (IC152)
89 FRDR O Focus servo drive PWM signal (–) output to the BH6511FS (IC152)
* I (S) stands for schmitt input, I (A) for analog input, O (3) for 3-state output, and O (A) for analog output in the column I/O.
– 32 –
Page 33

Pin No. Pin Name I/O Description
90 FS4 O Clock signal (176.4 kHz) output terminal (X’tal system) Not used (open)
91 SRDR O Sled servo drive PWM signal (–) output to the BH6511FS (IC152)
92 SFDR O Sled servo drive PWM signal (+) output to the BH6511FS (IC152)
93 SPRD O Spindle servo drive PWM signal (–) output to the BH6511FS (IC152)
94 SPFD O Spindle servo drive PWM signal (+) output to the BH6511FS (IC152)
95
96
97
98
99 DVSS — Ground terminal (digital system)
100 EFMO O EFM signal output terminal when recording mode
* I (S) stands for schmitt input, I (A) for analog input, O (3) for 3-state output, and O (A) for analog output in the column I/O.
FGIN
TEST1 I
TEST2 I
TEST3 I
I (S)
Input terminal for the test (fixed at “L”)
– 33 –
Page 34

• MAIN BOARD IC501 M30620MC-400FP (SYSTEM CONTROLLER)
A
Pin No. Pin Name I/O Description
1, 2 NC
3C1O
4
ADER
5 SQSY
6 RMC
7 A1 IN
8 BYTE
9 CNVSS
10 XT-IN
11 XT-OUT
12 S.RST I
13 XOUT
14 GND
15 XIN
16 +3.3V
17
NMI I Non-maskable interrupt input terminal (fixed at “H” in this set)
18 DQSY
19 P.DOWN
KEYBOARD CLK
20
KEYBOARD DAT
21
22 BEEP OUT
23 XINT
24 to 27 NC
28 L3-CLOCK O
29 NC
30 L3-DATA
31 SWDT O
32 SRDT I
33 SCLK O
34 FLCS
35
FLDATA O Serial data output to the FL/LED driver (IC761)
36 NC
37 FLCLK
38 to 40 NC
41 NC
42 JOG1
43 JOG0 I
44 NC
45
A1 OUT O Sircs remote control signal output of the CONTROL A1 Not used
46 NC
47 L3-MODE
48 DA RST O
49 MUTE O
O Not used (open)
Monitor output terminal for the test C1 error rate is output when test mode
O
Monitor output terminal for the test ADER is output when test mode
Subcode Q sync (SCOR) input from the CXD2654R (IC121)
I
“L” is input every 13.3 msec Almost all, “H” is input
I Remote control signal input from the remote control receiver (IC781)
I Sircs remote control signal input of the CONTROL A1 Not used
I External data bus line byte selection signal input “L”: 16 bit, “H”: 8 bit (fixed at “L”)
— Ground terminal
I Sub system clock input terminal (32.768 kHz) Not used (fixed at “L”)
O Sub system clock output terminal (32.768 kHz) Not used (open)
System reset signal input from the reset signal generator (IC406) “L”: reset
For several hundreds msec. after the power supply rises, “L” is input, then it changes to “H”
O Main system clock output terminal (10 MHz)
— Ground terminal
I Main system clock input terminal (10 MHz)
— Power supply terminal (+3.3V)
Digital In U-bit CD format subcode Q sync (SCOR) input from the CXD2654R (IC121)
I
“L” is input every 13.3 msec Almost all, “H” is input
I Power down detection signal input terminal “L”: power down, normally: “H”
I
Not used (open)
I
Not used (open)
O Beep sound drive signal output terminal Not used (open)
I Interrupt status input from the CXD2654R (IC121)
O Not used (open)
Serial data transfer clock signal output to the A/D, D/A converter (IC301)
O Not used (open)
O Serial data output to the A/D, D/A converter (IC301)
Writing data output to the CXD2654R (IC121)
Reading data input from the CXD2654R (IC121)
Serial clock signal output to the CXD2654R (IC121)
O Chip select signal output to the FL/LED driver (IC761)
O Not used (open)
O Serial data transfer clock signal output to the FL/LED driver (IC761)
O Not used (open)
I Not used (fixed at “L”)
I
JOG dial pulse input from the rotary encoder (S713 = AMS +) (B phase input)
JOG dial pulse input from the rotary encoder (S713 = AMS +) (A phase input)
O Not used (open)
I Not used (fixed at “L”)
O L3 mode control signal output to the A/D, D/A converter (IC301)
Reset signal output for the A/D, D/A converter “L”: reset Not used (open)
Audio line muting on/off control signal output terminal “L”: line muting on
– 34 –
Page 35

Pin No. Pin Name I/O Description
e
50 STB O
51 CHACK IN I
52 NC
53 PACK-OUT I
54 LDIN O
55 LDOUT
56 LD-LOW
57, 58 NC
59 REC-P I
60 PB-P I
61 REC/PB
62 +3.3V
63
64 GND
65 SDA I/O
66 MNT3 (SLOCK) I
67 WR-PWR
68 PROTECT I
69 REFLECT I
70 LDON O
71 SENS
72 MNT1 (SHOCK) I
73 DIG-RST O
74 MNT2 (XBUSY) I
75 XLATCH
NC O Not used (open)
Relay drive signal output for the power on/off “L”: standby mode, “H”: relay on
Detection input from the disc chucking-in detect switch “L”: chucking
Not used (fixed at “H”)
O Not used (open)
Detection input from the loading-out detect switch (S602)
“L” at a load-out position, others: “H”
Motor control signal output to the loading motor driver (IC441) “L” active *1
O Motor control signal output to the loading motor driver (IC441) “L” active *1
Loading motor drive voltage control signal output for the loading motor driver (IC441)
O
“H” active
O Not used (open)
Detection input from the recording position detect switch (S601) “L” active
Detection input from the playback position detect switch (S604) “L” active
O Not used (open)
— Power supply terminal (+3.3V)
— Ground terminal
Two-way data bus with the EEPROM (IC171)
Spindle servo lock status monitor signal input from the CXD2654R (IC121)
Laser power select signal output to the CXD2654R (IC121) and HF module switch circuit
O
“L”: playback mode, “H”: recording mode
Rec-proof claw detect input from the protect detect switch (S102) “H”: write protect
Detection input from the disc reflection rate detect switch (S102)
“L”: high reflection rate disc, “H”: low reflection rate disc
Laser diode on/off control signal output to the automatic power control circuit “H”: laser on
I Internal status (SENSE) input from the CXD2654R (IC121)
Track jump detection signal input from the CXD2654R (IC121)
Reset signal output to the CXD2654R (IC121) and BH6511FS (IC152) “L”: reset
Busy signal input from the CXD2654R (IC121)
O Serial data latch pulse signal output to the CXD2654R (IC121)
Laser modulation select signal output to the HF module switch circuit
Playback power: “H”, Stop: “L”,
Recording power:
0.5 sec
Pin No. Pin Name I/O Description
79 SCL O
80 SCTX O
81 CLOCK SET0
82 CLOCK SET1
83
84 LED1 O
85 OPT SEL0
86 OPT SEL1
87 MODEL SEL0 I
88 MODEL SEL1 I
89 REC
90 BEEP SW
91
92
93
94
95
96 AVSS
97
98 VREF I Reference voltage (+3.3V) input terminal (for A/D converter)
99 +3.3V
100
LED0 O
NC O Not used (open)
SOURCE I INPUT switch (S731) input terminal (A/D input) “L”: digital input, “H”: analog input
KEY3 I Key input terminal (A/D input) Not used (fixed at “H”)
KEY2 I
KEY1 I
KEY0 I
MONO/ST
Clock signal output to the EEPROM (IC171)
Recording data output enable signal output to the CXD2654R (IC121) and overwrite head
driver (IC181) Writing data transmission timing output (Also serves as the magnetic head on/off
output)
Destination setting terminal
I
(US and Canadian models: fixed at “L”, AEP, UK and E models: fixed at “H”)
Destination setting terminal
I
(US and Canadian models: fixed at “H”, AEP, UK and E models: fixed at “L”)
LED drive signal output of the r REC indicator (D741) “L”: LED on
LED drive signal output of the · indicator (D742) “L”: LED on
O Not used (open)
O Not used (open)
Setting terminal for the model (fixed at “H” in this set)
Setting terminal for the model (Not used (open))
O Not used (open)
I BEEP switch input terminal “L”: beep off, “H”: beep on Not used
Key input terminal (A/D input) S721 to S726 (EJECT §, PLAY MODE, REPEAT, SCROLL,
LEVEL/DISPLAY/CHAR, I/u keys input)
Key input terminal (A/D input)
S711 to S714 (MENU/NO, YES, PUSH ENTER, CLEAR keys input)
— Ground terminal
Key input terminal (A/D input) S701 to S706 (r REC, p, ), 0, P, · keys input)
— Power supply terminal (+3.3V) (for analog system )
I
Recording mode switch input terminal “L”: mono, “H”: stereo Not used (open)
76 MOD
77 LIMIT-IN
78
*1 Loading motor (M103) control
Terminal
MNT0 (FOK)
LDIN (pin %¢)
LDOUT (pin %∞)
Mod
O
2 sec
Detection input from the sled limit-in detect switch (S101)
I
The optical pick-up is inner position when “L”
Focus OK signal input from the CXD2654R (IC121)
I
“H” is input when focus is on (“L”: NG)
LOADING EJECT BRAKE RUN IDLE
“L” “H” “L” “H”
“H” “L” “L” “H”
– 35 – – 36 –
Page 36

MDS-M100
6-2. BLOCK DIAGRAM – MD SERVO Section –
HR901
OVER WRITE HEAD
48 47
APC
PD
I
J
A
B
C
D
E
F
IN4R
IN4F
IN2F
IN2R
IN1F
IN1R
IN3F
IN3R
RF AMP
I-V
AMP
I-V
AMP
LD/PD
AMP
16PSB
3
4
29
30
19
18
14
15
MORFO
SPFD
SPRD
F
C B
I J
D A
E
LASER DIODE
OPTICAL PICK-UP
(KMS-260A/J1NP)
2-AXIS
DEVICE
(TRACKING)
HF MODULE
DETECTOR
LDPD
(SPINDLE)
FCS+
(FOCUS)
05
ILCC
M101
M102
(SLED)
FCS–
TRK+
TRK–
MOD
I
J
B
A
C
D
E
F
AUTOMATIC
POWER
CONTROL
Q162, 163
LASER ON
PD
SWITCH
Q101
FOCUS/TRACKING COIL DRIVE,
SPINDLE/SLED MOTOR DRIVE
6
M
8
27
M
25
21
23
12
10
1
2
4
5
6
7
8
9
11
10
IC152
OUT4F
OUT4R
OUT2F
OUT2R
OUT1F
OUT1R
OUT3F
OUT3R
– 37 –
MORFI
OVER WRITE
HEAD DRIVE
IC181, Q181, 182
RFO
46
B.P.F.
3T
AT
AMP
CONVERTER
APCREF
12
APCREF
83
SFDR
92
SRDR
91
FFDR
88
FRDR
89
TFDR
86
TRDR
85
SCTX
WBL
B.P.F.
ABCD
AMP
WBL3TEQ
V-I
F0CNT
20
FOCUS/TRACKING ERROR AMP
40
TEMP
ADFM
29 30
FOCUS
ERROR AMP
TRACKING
ERROR AMP
13
RECP
AUTOMATIC
POWER
CONTROL
DIGITAL
SERVO
SIGNAL
PROCESS
PWM GENERATOR
DIGITAL SERVO
SIGNAL PROCESSOR
DIGITAL SIGNAL PROCESSOR,
EFM/ACIRC ENCODER/DECODER,
SHOCK PROOF MEMORY CONTROLLER,
ATRAC ENCODER/DECODER
IC121 (1/2)
RF AMP,
IC101
& EQ
EQ
SCLK
1716 18
AUX
WBL
PEAK
BOTM
ADFG
ABCD
XLAT
67
AUX1
RF
38
33
37
36
32
35
FE
34
TE
26
SE
28
65
66
FE
ABCD
ANALOG MUX
A/D CONVERTER
FROM CPU
INTERFACE
AUTO
SEQUENCER
AGCI
PEAK &
BOTTOM
ADIN
COMMAND
SERIAL/
PARALLEL
CONVERTER,
DECODER
SWDT
IC121 (2/2)
RF AGC
LDON
15
TX
SHOCK PROOF
MEMORY CONTROLLER
SENS
9 8 5 6 7
5
18
237132
XINT
SQSY
DQSY
ATRAC
ENCODER/DECODER
CPU
INTERFACE
SRDT
SWDT
SCLK
XLAT
31 33 75 78 72 74 66
SRDT
SWDT
SCLK
XLATCH
SENS
SAMPLING
RATE
CONVERTER
DIGITAL
AUDIO
INTERFACE
INTERNAL BUS
MONITOR
CONTROL
MNT0
MNT1
1 2 3 4
FOK
SHOCK
MNT0 (FOK)
MNT1 (SHOCK)
ADDT
25
DATAI
22
XBCKI
24
LRCKI
23
DIN0
19
DIN1
20
DOUT
21
DADT
26
MNT2
MNT3
SLOCK
XBUSY
MNT3 (SLOCK)
MNT2 (XBUSY)
WAVE SHAPER
28
2927
XBCK
LRCK
FS256
CLOCK
GENERATOR
SYSTEM CONTROLLER
IC501 (1/2)
IC601 (1/2)
OSCI
OSCO
XOE
XWE
XRAS
XCAS
16
17
D0 – D3A00 – A09
49, 48, 50, 51
34 – 31, 36 – 40, 45
43 16
47 3
46 4
44 17
SCTX
DIVIDER
IC123
1, 2, 18, 19
6 – 9, 11 – 15, 5
80
DQ1 – DQ4
D-RAM
IC124
A0 – A9
XOE
XWE
XRAS
XCAS
ADDT
DIGITAL IN
OPTICAL
RECEIVER
IC611
DADT, BCK, LRCK
512FS
• SIGNAL PATH
(Page 39)
A
(Page 39)
B
(Page 39)
C
: PLAY (ANALOG OUT)
FILTER
100
60
59
62
61
53
54
57
78
79
IC121 (1/2)
EFMO
FILI
PCO
CLTV
FILO
ASYO
ASYI
RFI
ADFG
F0CNT
PLL
COMPA-
RATOR
ADIP
DEMODULATOR/
DECODER
SPINDLE
SERVO
SPFD
94 93
SPRD
PROCESSOR
XRST
10
EFM/ACIRC
ENCODER/DECODER
SUBCODE
DQSY11SQSY14XINT
12
70
: REC (ANALOG IN)
DIG-RST
73
67
WR-PWR
MOD
76
75
64
74
63
TE
SE
PEAK
BOTM
LOADING
MOTOR DRIVE
IC441
XLRF
CKRF
DTRF
XLAT
80
SCLK
81
SWDT
82
HF MODULE
SWITCH
IC103, Q102 – 104
LDIN
54
55
5
IN1 IN2
OUT1 OUT2
2
10
M
M103
(LOADING)
LDOUT
6
UNREG
+12V
4
REFERENCE
VOLTAGE SWITCH
Q441, 442
56
LD-LOW
VZ
LIMIT-IN
REC-P
PACK-OUT
PB-P
REFLECT
PROTECT
77
59
53
60
69
68
S102
(REFLECT/PROTECT DETECT)
HIGH REFELECT RATE/
WRITE PROTECT
LOW REFELECT RATE/
UN-PROTECT
(LIMIT IN)
(REC POSITION)
(PACK OUT)
(PLAY POSITION)
: REC (DIGITAL IN)
S101
S601
S602
S604
– 38 –
Page 37

6-3. BLOCK DIAGRAM – MAIN Section –
A
(Page 38)
ADDT
DATAO
18
A/D, D/A CONVERTER
IC301
DIGITAL MIXER,
DECIMATION
FILTER
A/D
CONVERTER
BLOCK
0dB/6dB
SWITCH
VINL1
VINR1
MDS-M100
• SIGNAL PATH
J101
2
4
L
R
LINE
(ANALOG) IN
: PLAY (ANALOG OUT)
: REC (ANALOG IN)
B
(Page 38)
C
(Page 38)
C769, R769
X513
10MHz
OSC
DADT, BCK,
LRCK
512FS
DIGITAL
INTERFACE
L3DATA
L3CLK
15 14 13
30
28
L3-DATA
L3-CLOCK
RST
60521
DSP FEATURE,
INTERPOLATION
FILTER
PEAK DET
L3MODE
47
L3-MODE
NOISE
SHAPER
LED0
LED1
83
84
LED DRIVE
Q742
LED DRIVE
Q741
CONVERTER
CLOCK
GENERATOR
SYSTEM CONTROLLER
IC501 (2/2)
D742
·
D741
r REC
DADT
BCK
LRCK
XIN
15
XOUT
13
59
OSCI
OSCO
58
P1
DATAI
19
BCK
16
WS
17
L3-BUS INTERFACE
EEPROM
IC171
SDA
SCL
5 6
7965
SCL
SDA
FLDATA
FLCLK
FLCS
35 37 34 19 12 50
6162
63
CS
CLK
DAT
FL/LED DRIVER
IC761
5 – 39
G1 – G12S1 – S35
40 – 51
G13
D/A
BLOCK
VOUTL
VOUTR
SYSCLK
26
24
12
ROTARY
ENCODER
GND
= AMS +
PUSH ENTER
JOG0
1 3
A
S713
4243
B
JOG1
SW
LINE AMP
IC381 (1/2)
LINE AMP
IC381 (2/2)
OSC
IC351
KEY0 – KEY2
54
LOW-PASS
IC386 (1/2)
LOW-PASS
IC386 (2/2)
22.5792MHz
REMOTE CONTROL
RECEIVER
97, 95, 94
FILTER
FILTER
X351
IC781
RMC
92
SOURCE
S731
INPUT
ANALOG
DIGITAL
MUTING
Q191, 291
MUTING
CONTROL SWITCH
Q390
D391
496
MUTE
P.DOWN
STB
S.RST
D390
L
LINE
(ANALOG) OUT
R
+5V
MD MECHANISM
DECK SECTION B+
+3.3V
MD MECHANISM
DECK SECTION,
DIGITAL IN CIRCUIT B+
+3.3V
REGULATOR
IC192
ANALOG
LINE OUT
CIRCUIT
–32V
(FL DRIVER (IC761) B–)
LOADING MOTOR
DRIVER (IC441) B+
+5V
REGULATOR
IC411
UNREG +6V
UNREG –6V
–32V
REGULATOR
IC421
UNREG +12V
AC
(TO FL771)
RECT
D411, 412
RECT
D461, 462,
D466, 467
RECT
D421
AC F-1
AC F-2
T901
POWER
TRANSFORMER
RELAY DRIVE
D408
Q911
LITHIUM
BATTERY
+3.3V
REGULATOR
IC401
BT406
– 40 –
G1 – G12
FL771
FL DRIVE
Q767
G13
S701 – 706, 711, 712,
S714, 721 – 726
RESET SIGNAL
GENERATOR
IC406
SYS +3.3V
D409 D406
BACK UP +3.3V
LED DRIVE
Q751
SEG1 – SEG35
D751
I/u
05
FLUORESCENT INDICATOR TUBE
– 39 –
RY901
RECT
D401 – 404
POWER DOWN
DETECT
IC601 (2/2)
D431
T910
POWER
TRANSFORMER
D432
D433
VOLTAGE
SELECTOR
S951
(Singapore)
(EXCEPT Singapore)
AC IN
Page 38

• Circuit Boards Location
B
These are omitted.
CE
Q
d
6-4. NOTE FOR PRINTED WIRING BOARDS AND SCHEMATIC DIAGRAMS
BD board
PANEL 2 board
TRANS board
PANEL board
AC SELECT board (Singapore)
SW board
MAIN boar
Note on Printed Wiring Board:
• X : parts extracted from the component side.
• Y : parts extracted from the conductor side.
• p : parts mounted on the conductor side.
®
•
• b : Pattern from the side which enables seeing.
Caution:
Pattern face side: Parts on the pattern face side seen from
(Side B) the pattern face are indicated.
Parts face side: Parts on the par ts face side seen from
(Side A) the parts face are indicated.
• Indication of transistor.
• Abbreviation
: Through hole.
CND : Canadian model
SP : Singapore model
Note on Schematic Diagram:
• All capacitors are in µF unless otherwise noted. pF: µµF
50 WV or less are not indicated except for electrolytics
and tantalums.
• All resistors are in Ω and 1/
specified.
• % : indicates tolerance.
¢
•
• C : panel designation.
• U : B+ Line.
• V : B– Line.
• V oltages and wav eforms are dc with respect to ground in
• Voltages are tak en with a V OM (Input impedance 10 MΩ).
• Waveforms are taken with a oscilloscope.
• Circled numbers refer to wavefor ms.
• Signal path.
• Abbreviation
: internal component.
Note:
The components identified by mark ! or dotted
line with mark ! are critical for safety.
Replace only with part
number specified.
playback mode.
Voltage variations may be noted due to normal produc-
tion tolerances.
Voltage variations may be noted due to normal produc-
tion tolerances.
E : PLAY (ANALOG OUT)
j : REC (ANALOG IN)
l : REC (DIGITAL IN)
CND : Canadian model
SP : Singapore model
4
W or less unless otherwise
Note:
Les composants identifiés par
une marque ! sont critiques
pour la sécurité.
Ne les remplacer que par une
piéce portant le numéro
spécifié.
– 41 –
– 42 –
Page 39

6-5. PRINTED WIRING BOARD – BD Board – • See page 41 for Circuit Boards Location.
HIGH REFLECT RATE/
S102
REFLECT DET,
PROTECT DET
LOW REFLECT RATE/
UNPROTECT
WRITE PROTECT
MDS-M100
(SLIDE)
(SPINDLE)
BLK
RED
• Semiconductor
Location
Ref. No. Location
D101 A-1
D181 D-3
D183 D-3
IC103 B-1
IC123 D-2
IC171 D-1
Q102 B-1
Q103 C-1
Q104 B-1
– 43 –
• Semiconductor
Location
Ref. No. Location
IC101 A-3
IC121 C-3
IC124 C-3
IC152 B-1
IC181 C-1
IC192 D-1
Q101 B-3
Q162 B-3
Q163 B-3
Q181 C-1
Q182 C-2
(Page 55)
(Page 56)
– 44 –
Page 40

MDS-M100
6-6. SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM – BD Board (1/2) – • See page 65 for Waveforms. • See page 70 for IC Block Diagrams.
(Page 47)
– 45 –
(Page 47)
(Page 47)
(Page 48)
(Page 48)
– 46 –
(Page 48)
(Page 48)
Page 41

6-7. SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM – BD Board (2/2) – • See page 65 for Waveforms. • See page 51 for IC Block Diagram.
MDS-M100
(Page 58)
(Page 45)
(Page 45) (Page 45)
(Page 46)
(Page 46)
(Page 46) (Page 46)
(Page 57)
The components identified by mark ! or dotted
line with mark ! are critical for safety.
Replace only with part number specified.
Les composants identifiés par une marque ! sont
critiques pour la sécurité. Ne les remplacer que
par une piéce portant le numéro spécifié.
– 47 –
• Voltages and waveforms are dc with respect to ground
under no-signal conditions.
no mark : STOP
( ) : PLAY
< > : REC
: Impossible to measure
∗
– 48 –
Page 42

MDS-M100
6-8. SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM – SW Board –
6-9. PRINTED WIRING BOARD – SW Board –
• See page 41 for Circuit Boards Location.
(REC POSITION)
(LOADING)
(PACK OUT)
(Page 56)
(Page 57)
• IC Block Diagrams
– BD Board –
IC101 CXA2523AR
RFA1
1I
2J
CVB
3VC
4A
IVR
5B
IVR
6C
IVR
7D
IVR
8E
IVR
9F
IVR
GSW
10PD
11APC
12APCREF
+
–
MORFO47MORFI46RFO45OPN
48
+
–
+
–
+
–
+
–
+
–
+
–
+
–
+
–
IV
OPO43ADDC42COMPP41COMPO40AGCI39RF AGC38RF37PEAK
44
USROP
–
+
RFA2
–
–
–
–
–
–
–
AA
BB
CC
DD
EE
FF
+
1
2
1
2
GRVA
EBAL
–
HLPT
OFST
GRV
+
–
+
–
FBAL
–1
–2
–2
–1
PBSW
–
–
–
–
+
+
–
–
–
–
+
+
EE'
EFB TESW
ESW
FF'
AUXSW
RFA3
PTGR
ABCDA
FEA
ATA
COMMAND
SCRI - PARA
DECODE
–
+
–
+
+
–
BPF3T
BPF22
WBL
WBL
RF AGC EQ
USRC
PEAK
BOTTOM
WBL
ADIP
PTGR
PEAK3T
P-P
PBH
AGC
WBL
3T
EQ
BGR
VREF
3T
3T WBL
DET
–1
–2
–1
–2
DET
TEMP
EQ
AUX
SW
BPFC
SEA
TEA
VI CONV
TG
TG
36
BOTM
35
ABCD
34
FE
33
AUX
32 ADFG
31 ADAGC
30 ADIN
29 ADFM
28 SE
27 CSLED
26 TE
25 WBLADJ
14
13
GND
TEMPI
05
– 49 –
15
TEMPR
SWDT
SCLK
XLAT
XSTBY
– 50 –
F0CNT
VREF
EQADJ
3TADJ
VCC
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
Page 43

IC121 CXD2654R
EFMO
DVSS
TEST3
100
99 98 97 96 95 94 93
1
MNT0
2
MNT1
MNT2
MNT3
SWDT
SCLK
XLAT
SRDT
SENS
XRST
SQSY
DQSY
RECP
XINT
TX
OSCI
OSCO
XTSL
DIN0
DIN1
DOUT
MONITOR
CONTROL
3
4
5
6
CPU I/F
7
8
9
10
11
SUBCODE
PROCESSOR
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
CLOCK
GENERATOR
TEST2
EACH
BLOCK
EACH
BLOCK
TEST1
FGIN
SPINDLE
SERVO
DECODER
EACH
BLOCK
SPFD
ADIP
SPRD
DIGITAL
AUDIO
I/F
SFDR91SRDR90FS489FRDR88FFDR87DVDD86TFDR85TRDR84LDDR83APCREF82DTRF81CKRF80XLRF79F0CNT78ADFG77APC76DCHG
92
PWM
GENERATOR
SERVO
DSP
SHOCK RESISTANT
MEMORY CONTROLLER
SAMPLING
RATE
CONVERTER
CONVERTER
A/D
AUTO
SEQUENCER
ENCODER/
EFM/ACIRC
ANALOG
MUX
DECODER
COMP
PLL
– MAIN Board –
IC301 µDA1341TS/N2
VSS(AD) 1
VINL1
VDD(AD)
75
TE
74
SE
73
AVSS
72
ADRB
71
ADRT
70
AVDD
69
ADIO
68
VC
67
AUX1
66
FE
65
ABCD
64
BOTM
63
PEAK
62
CLTV
61
FILO
60
FILI
59
PCO
58
AVSS
57
RFI
56
BIAS
55
AVDD
54
ASYI
53
ASYO
VINR1
VADCN
VINL2
VADCP
VINR2
OVERFL
VDDD
VSSD
SYSCLK
L3MODE 13
L3CLOCK
IC406 M62016L
1
GND INT RESET CD VCC
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
14
+
–
+
–
2 3
0dB/6dB
SWITCH
0dB/6dB
SWITCH
COM
COM
PGA
PGA
ADC1L
ADC1R
ADC2L
ADC2R
INTERRUPT SIGNAL
GENERATING BLOCK
RESET SIGNAL
GENERATING BLOCK
4
DIGITAL
AGC
L3-BUS
INTERFACE
5
DIGTAL MIXER
DECIMATION FILTER
DIGITAL
INTERFACE
DSP FEATURES
REAK
DETECTOR
DAC
DAC
NOISE SHAPER
INTERPOLATION FILTER
IC421 M5293L
GND
2
ON/OFF
REFERENCE
4
VOLTAGE
IN
1
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
VREF
VSS(DAC)
VOUTL
VDD(DAC)
VOUTR
QMUTE
AGCSTAT
TEST2
TEST1
DATAI
DATAO
WS
BCK
L3DATA
OVERHEAT
PROTECTION
5k
REFERENCE
5
3
VOLTAGE
OUT
27k
+
–
OVERCURRENT
LIMITTER
22
DATAI
LRCKI
XBCKI
ADDT
23
24
25
30
28
29
26
27
LRCK
XBCK
DADT
FS256
DVDD
ATRAC
ENCODER/DECODER
ADDRESS/DATA BUS A00 - A11, D0 - D3
42
41
A1140A0839A0738A0637A0536A0435A1034A0033A0132A0231A03
43
DVSS
XOE
44
45
XCAS
A09
IC152 BH6511FS-E2
CAPA–
CAPA+
IN2R
IN2F
VM2
OUT2F
PGND2
OUT2R
VM12
OUT1R
PGND1
OUT1F
VM1
32 31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17
CHARGE
PUMP.
OSC
INTERFACE
INTERFACE
AMP
AMP
AMP
AMP
AMP
PREDRIVEPREDRIVE
PREDRIVEPREDRIVE
AMPAMPAMP
46
XWE
XRAS
IN1F
INTERFACE
INTERFACE
IN1R
V
PSB
52
MVCI
51
D3
50D249D048D147
DD
V
DD
IC441 LB1641
T.S.D O.C.P
MOTOR
DRIVE
FWD/REV/STOP
CONTROL LOGIC
2 3
1
GND
DRIVE
MOTOR
NOISE
FILTER
5 6 7 8 9 10
4
VCC 1
FWD.IN
REV.IN
CLAMP
VCC 2
NOISE
FILTER
MOTOR
DRIVE
DRIVE
MOTOR
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
VG
GND
IN4R
IN4F
VM4
OUT4F
PGND4
OUT4R
VM34
OUT3R
PGND3
OUT3F
VM3
IN3F
IN3R
– 51 – – 52 –
PSB
Page 44

MDS-M100
6-10. PRINTED WIRING BOARDS – TRANS Board – • See page 41 for Circuit Boards Location.
(Page 55)
(Page 55)
(Page 54)
(Page 53)
– 53 –
– 54 –
Page 45

6-11. PRINTED WIRING BOARD – MAIN Board – • See page 41 for Circuit Boards Location.
MDS-M100
(Page 53)
(Page 44) (Page 44)
(Page 49)
(Page 54)
• Semiconductor Location
Ref. No. LocationRef. No. Location
D390 C-4
D391 C-4
D401 A-1
D402 B-1
D403 B-1
D404 B-1
D406 C-2
D408 C-2
D409 C-2
D411 D-2
D412 D-2
D421 D-2
D422 D-3
D431 D-1
D432 D-2
D433 D-2
D461 D-2
D462 D-2
D466 D-2
D467 D-2
D911 A-2
IC301 B-10
IC351 A-10
IC381 C-10
IC386 D-10
IC401 A-2
IC406 B-2
IC411 B-4
IC421 D-3
IC441 B-9
IC501 C-7
IC601 D-9
IC611 D-9
Q191 D-9
Q291 D-9
Q390 D-4
Q441 B-9
Q442 B-9
Q911 A-1
(Page 61)
– 55 –
– 56 –
Page 46

MDS-M100
6-12. SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM – MAIN Board (1/2) – • See page 65 for Waveform.
(Page 47)
(Page 47)
(Page 49)
(Page 59)
(Page 64)
– 57 –
(Page 59)
• Voltages and waveforms are dc with respect to ground
under no-signal conditions.
no mark : PLAY
– 58 –
Page 47

6-13. SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM – MAIN Board (2/2), TRANS Board – • See page 65 for Waveforms. • See page 52 for IC Block Diagrams.
(Page 58)
MDS-M100
(Page 58)
– 59 –
The components identified by mark ! or dotted
line with mark ! are critical for safety.
Replace only with part number specified.
Les composants identifiés par une marque ! sont
critiques pour la sécurité. Ne les remplacer que
par une piéce portant le numéro spécifié.
• Voltages and waveforms are dc with respect to ground
under no-signal conditions.
no mark : PLAY
– 60 –
Page 48

MDS-M100
6-14. PRINTED WIRING BOARDS – PANEL/PANEL 2 Boards – • See page 41 for Circuit Boards Location.
(Page 55)
• Semiconductor
Location
Ref. No. Location
D741 B-1
D742 A-1
IC761 B-7
Q741 B-1
Q742 B-1
Q767 C-5
– 61 –
– 62 –
Page 49

6-15. SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM – PANEL/PANEL 2 Boards – • See page 65 for Waveform.
MDS-M100
– 63 –
(Page 57)
• Voltages and waveforms are dc with respect to ground
under no-signal conditions.
no mark : STOP
– 64 –
Page 50

SECTION 7
EXPLODED VIEWS
• Wavef orms
– BD Board –
1 IC101 1, 2 (I, J) (Play mode)
2 IC101 4 (A) (Play mode)
0.46 Vp-p
0.1 Vp-p
6 IC121 @• (XBCK)
2.8224 MHz
7 IC121 @ª (FS256)
11.29 MHz
3.8 Vp-p
3.8 Vp-p
3 IC301 !§ (BCK)
2.8224 MHz
4 IC301 !¶ (WS)
44.1 kHz
4.3 Vp-p
4 Vp-p
NOTE:
• -XX and -X mean standardized parts, so they
may have some difference from the original
one.
• Color Indication of Appearance Parts
Example:
KNOB, BALANCE (WHITE) . . . (RED)
↑↑
Parts Color Cabinet's Color
• Abbreviation
CND: Canadian model
SP : Singapore model
(1) COVER SECTION
11
• Items marked “*” are not stocked since they
are seldom required for routine service. Some
delay should be anticipated when ordering
these items.
• The mechanical parts with no reference number in the exploded views are not supplied.
• Hardware (# mark) list and accessories and
packing materials are given in the last of the
electrical parts list.
The components identified by
mark ! or dotted line with mark
! are critical for safety.
Replace only with part number
specified.
Les composants identifiés par une
marque ! sont critiquens pour la
sécurité.
Ne les remplacer que par une pièce
portant le numéro spécifié.
12
11
3 IC101 8, 9 (E, F) (Play mode)
4 IC121 !§ (OSCI)
22.581 MHz
5 IC121 @¶ (LRCK)
0.06Vp-p
3.1 Vp-p
3.2 Vp-p
8 IC121 (º (FS4)
176.4 kHz
– MAIN Board –
1 IC501 !∞ (XIN)
10 MHz
2 IC301 !™ (SYSCLK)
3.2 Vp-p
2.6 Vp-p
3 Vp-p
5 IC351 1
22.5792 MHz
– PANEL Board –
1 IC761 %• (OSC0)
540 ns
1.5 Vp-p
1.6 Vp-p
10
8
2
9
3
4
5
6
#1
1
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
1 4-216-828-01 KNOB (AMS)
2 X-4951-046-1 FRONT PANEL ASSY
3 4-996-698-01 EMBLEM, SONY
4 4-996-690-12 LID (CARTRIDGE)
5 4-976-593-11 SPRING (LID), TORSION
8
7
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
* 7 A-4724-590-A PANEL BOARD, COMPLETE
8 4-951-620-01 SCREW (2.6X8), +BVTP
9 1-790-510-11 WIRE (FLAT TYPE) (19 CORE)
* 10 1-673-305-11 PANEL 2 BOARD
11 3-363-099-01 SCREW (CASE 3 TP2)
44.1 kHz
22.5792 MHz
– 65 –
6 4-989-517-21 KNOB (INPUT)
* 12 4-216-839-01 COVER
– 66 –
Page 51

(2) CHASSIS SECTION
54
53
#1
55
#1
65
56
57
58
#1
59
AEP, SP
63
UK
63
US, CND
63
not supplied
not
supplied
MDM-5A
T901
not
supplied
not supplied
#1
#1
#1
61
62
51
The components identified by
mark ! or dotted line with
mark ! are critical for safety.
Replace only with part number specified.
#1
64
SP
52
Les composants identifiés par une
marque ! sont critiques pour la
sécurité.
Ne les remplacer que par une pièce
portant le numéro spécifié.
SP
#1
60
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
* 51 X-4951-211-1 CHASSIS ASSY
52 4-965-822-01 FOOT
53 4-999-839-01 SCREW (+BVTTWH M3), STEP
* 54 1-673-306-11 TRANS BOARD
55 3-703-249-01 SCREW, S TIGHT, +PTTWH 3X6
* 56 A-4724-589-A MAIN BOARD, COMPLETE (US, CND)
* 56 A-4724-628-A MAIN BOARD, COMPLETE (SP)
* 56 A-4724-631-A MAIN BOARD, COMPLETE (AEP, UK)
57 1-790-512-11 WIRE (FLAT TYPE) (21 CORE)
58 1-790-513-11 WIRE (FLAT TYPE) (23 CORE)
* 59 3-703-244-00 BUSHING (2104), CORD
* 60 4-216-840-01 BACK PANEL (US)
* 60 4-216-840-11 BACK PANEL (CND)
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
* 60 4-216-840-21 BACK PANEL (SP)
* 60 4-216-840-31 BACK PANEL (AEP)
* 60 4-216-840-41 BACK PANEL (UK)
61 1-500-051-11 BEAD, FERRITE (WITH CASE)
62 4-943-687-01 HOLDER, PC BOARD
! 63 1-696-586-21 CORD, POWER (UK)
! 63 1-777-071-31 CORD, POWER (AEP, SP)
! 63 1-783-531-31 CORD, POWER (US, CND)
* 64 1-673-307-11 AC SELECT BOARD (SP)
65 1-569-972-21 SOCKET, SHORT 2P
! T901 1-433-697-11 TRANSFORMER, POWER (US, CND)
! T901 1-433-698-11 TRANSFORMER, POWER (AEP, UK)
! T901 1-433-699-11 TRANSFORMER, POWER (SP)
– 67 –
Page 52

(3) MECHANISM SECTION
(MDM-5A)
220
213
#7
203
209
207
202
201
208
210
213
211
214
212
215
203
M103
216
217
218
219
221
207
#7
206
#6
#7
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
* 201 1-668-111-11 SW BOARD
* 202 4-996-217-01 CHASSIS
203 4-996-223-11 INSULATOR (F) (BLACK)
* 204 4-996-218-01 BRACKET (GUIDE R)
205 4-996-277-01 SPRING (O/C), TENSION
206 4-996-226-01 LEVER (O/C)
207 4-999-347-01 INSULATOR (R) (GREEN)
* 208 4-996-225-01 BRACKET (GUIDE L)
209 4-988-466-11 SPRING (ELECTROSTATIC), LEAF
210 4-996-219-01 GEAR (CAM GEAR)
204
MBU-5A
212 4-996-221-01 GEAR (B)
213 4-933-134-01 SCREW (+PTPWH M2.6X6)
214 4-996-224-01 SCREW (1.7X3), +PWH
215 4-996-227-01 LEVER (HEAD)
216 4-996-229-01 SPRING (HEAD LEVER), TORSION
217 4-996-212-01 LEVER (LIMITTER)
218 4-996-213-01 SPRING (LIMITTER), TORSION
219 4-996-216-01 SPRING (HOLDER), TENSION
* 220 4-996-211-01 SLIDER (CAM)
221 A-4680-409-A HOLDER COMPLETE ASSY
205
211 4-996-220-01 GEAR (A)
M103 X-4949-670-1 MOTOR ASSY, LOADING
– 68 –
Page 53

(4) BASE UNIT SECTION
(MBU-5A)
#3
264
252
265
#4
266
HR901
271
#3
263
270
not supplied
272
not supplied
M101
S102
254
253
M102
#3
262
#4
#3
#5
not supplied
261
#3
#3
252
257
267
269
#3
268
255
256
259
260
258
251
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
251 A-4724-063-A BD BOARD, COMPLETE
252 3-372-761-01 SCREW (M1.7), TAPPING
* 253 4-996-267-01 BASE (BU-D)
* 254 4-996-255-01 BASE (BU-C)
255 4-900-590-01 SCREW, PRECISION SMALL
256 4-996-258-01 SPRING, COMPRESSION
257 4-996-262-01 GEAR (SL-C)
* 258 1-667-954-11 FLEXIBLE BOARD
* 259 4-210-664-11 BASE (BU-A)
! 260 8-583-028-02 OPTICAL PICK-UP KMS-260A/J1N
* 261 4-996-252-01 CHASSIS, BU
* 262 4-996-254-01 BASE (BU-B)
263 4-967-688-11 MAGNET, ABSORPTION
252
The components identified by
mark ! or dotted line with
mark ! are critical for safety.
Replace only with part number specified.
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
264 4-996-260-01 GEAR (SL-A)
265 4-996-261-01 GEAR (SL-B)
266 4-996-264-01 SPRING (SHAFT), LEAF
267 4-996-265-01 SHAFT, MAIN
268 4-996-256-11 SL (BASE)
269 4-996-257-01 RACK (SL)
270 4-996-263-01 SPRING (CLV), TORSION
271 4-988-560-01 SCREW (+P 1.7X6)
272 4-211-036-01 SCREW (1.7X2.5), +PWH
HR901 1-500-502-11 HEAD, OVER WRITE
M101 A-4672-516-A MOTOR ASSY, SPINDLE
M102 A-4672-515-A MOTOR ASSY, SLED
S102 1-762-148-21 SWITCH, PUSH (2 KEY)
Les composants identifiés par une
marque ! sont critiques pour la
sécurité.
Ne les remplacer que par une pièce
portant le numéro spécifié.
(REFLECT DET, PROTECT DET)
– 69 –
Page 54

AC SELECT BD
SECTION 8
ELECTRICAL PARTS LIST
NOTE:
• Due to standardization, replacements in the
parts list may be different from the parts specified in the diagrams or the components used
on the set.
• -XX and -X mean standardized parts, so they
may have some difference from the original
one.
• RESISTORS
All resistors are in ohms.
METAL: Metal-film resistor.
METAL OXIDE: Metal oxide-film resistor.
F: nonflammable
• Abbreviation
CND: Canadian model
SP : Singapore model
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
* 1-673-307-11 AC SELECT BOARD (SP)
***************
< SWITCH >
! S951 1-771-474-11 SWITCH, POWER (VOLTAGE SELECTOR)
**************************************************************
A-4724-063-A BD BOARD, COMPLETE
*******************
• Items marked “*” are not stocked since they
are seldom required for routine service.
Some delay should be anticipated when ordering these items.
• SEMICONDUCTORS
In each case, u: µ, for example:
uA. . : µA. . uPA. . : µPA. .
uPB. . : µPB. . uPC. . : µPC. .
uPD. . : µPD. .
• CAPACITORS
uF: µF
• COILS
uH: µH
C142 1-163-251-11 CERAMIC CHIP 100PF 5% 50V
C143 1-163-251-11 CERAMIC CHIP 100PF 5% 50V
C144 1-163-251-11 CERAMIC CHIP 100PF 5% 50V
C146 1-163-038-00 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C151 1-126-206-11 ELECT CHIP 100uF 20% 6.3V
C152 1-163-038-00 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C153 1-163-021-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 50V
C156 1-163-038-00 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C158 1-163-019-00 CERAMIC CHIP 0.0068uF 10% 50V
The components identified by
mark ! or dotted line with mark
! are critical for safety.
Replace only with part number
specified.
Les composants identifiés par une
marque ! sont critiquens pour la
sécurité.
Ne les remplacer que par une pièce
portant le numéro spécifié.
When indicating parts by reference
number, please include the board.
< CAPACITOR >
C101 1-125-822-11 TANTALUM 10uF 20% 10V
C102 1-163-038-00 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C103 1-125-822-11 TANTALUM 10uF 20% 10V
C104 1-125-822-11 TANTALUM 10uF 20% 10V
C105 1-163-021-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 50V
C106 1-163-275-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.001uF 5% 50V
C107 1-163-038-00 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C108 1-163-038-00 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C109 1-163-037-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.022uF 10% 25V
C111 1-164-344-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.068uF 10% 25V
C112 1-163-017-00 CERAMIC CHIP 0.0047uF 5% 50V
C113 1-109-982-11 CERAMIC CHIP 1uF 10% 10V
C115 1-164-489-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.22uF 10% 16V
C116 1-163-037-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.022uF 10% 25V
C117 1-163-809-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.047uF 10% 25V
C118 1-163-038-00 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C119 1-125-822-11 TANTALUM 10uF 20% 10V
C121 1-125-822-11 TANTALUM 10uF 20% 10V
C122 1-163-021-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 50V
C123 1-163-038-00 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C124 1-163-038-00 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C127 1-163-038-00 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C128 1-163-021-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 50V
C129 1-107-823-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.47uF 10% 16V
C130 1-163-251-11 CERAMIC CHIP 100PF 5% 50V
C131 1-163-023-00 CERAMIC CHIP 0.015uF 5% 50V
C132 1-107-823-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.47uF 10% 16V
C133 1-163-017-00 CERAMIC CHIP 0.0047uF 5% 50V
C134 1-163-038-00 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C135 1-163-038-00 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C160 1-104-601-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 10V
C161 1-104-601-11 ELECT CHIP 10uF 20% 10V
C163 1-163-021-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 50V
C164 1-163-021-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 50V
C167 1-163-038-00 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C168 1-163-038-00 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C169 1-125-822-11 TANTALUM 10uF 20% 10V
C171 1-163-038-00 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C181 1-104-913-11 TANTALUM CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C183 1-163-038-00 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C184 1-117-970-11 ELECT CHIP 22uF 20% 10V
C185 1-164-611-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.001uF 10% 500V
C187 1-104-913-11 TANTALUM CHIP 10uF 20% 16V
C188 1-163-021-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.01uF 10% 50V
C189 1-163-989-11 CERAMIC CHIP 0.033uF 10% 25V
C190 1-126-206-11 ELECT CHIP 100uF 20% 6.3V
C191 1-163-038-00 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C196 1-163-038-00 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
C197 1-163-038-00 CERAMIC CHIP 0.1uF 25V
< CONNECTOR >
CN101 1-569-479-51 CONNECTOR, FPC 21P
CN102 1-784-833-21 CONNECTOR,FFC (LIF (NON-ZIF)) 21P
CN103 1-784-834-21 CONNECTOR,FFC (LIF (NON-ZIF)) 23P
CN104 1-770-687-11 CONNECTOR, FFC/FPC 4P
CN110 1-695-440-21 PIN, CONNECTOR (PC BOARD) 6P
< DIODE >
D101 8-719-988-61 DIODE 1SS355TE-17
D181 8-719-046-86 DIODE F1J6TP
D183 8-719-046-86 DIODE F1J6TP
C136 1-126-206-11 ELECT CHIP 100uF 20% 6.3V
– 70 –
The components identified by
mark ! or dotted line with
mark ! are critical for safety.
Replace only with part number specified.
Les composants identifiés par une
marque ! sont critiques pour la
sécurité.
Ne les remplacer que par une pièce
portant le neméro spécifié.
Page 55

BD
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
< IC/TRANSISTOR >
IC101 8-752-080-95 IC CXA2523AR
IC103 8-729-903-10 TRANSISTOR FMW1
IC121 8-752-389-44 IC CXD2654R
IC123 8-759-096-87 IC TC7WU04FU (TE12R)
IC124 8-759-334-38 IC MSM51V4400-70TS-K
IC152 8-759-430-25 IC BH6511FS-E2
IC171 8-759-487-04 IC BR24C02F-E2
IC181 8-759-481-17 IC MC74ACT08DTR2
IC192 8-759-460-72 IC BA033FP-E2
< COIL/SHORT >
L101 1-414-813-11 FERRITE 0uH
L102 1-414-813-11 FERRITE 0uH
L103 1-414-813-11 FERRITE 0uH
L105 1-414-813-11 FERRITE 0uH
L106 1-414-813-11 FERRITE 0uH
L121 1-414-813-11 FERRITE 0uH
L122 1-414-813-11 FERRITE 0uH
L151 1-412-029-11 INDUCTOR CHIP 10uH
L152 1-412-029-11 INDUCTOR CHIP 10uH
L153 1-412-032-11 INDUCTOR CHIP 100uH
L154 1-412-032-11 INDUCTOR CHIP 100uH
L161 1-414-813-11 FERRITE 0uH
L162 1-414-813-11 FERRITE 0uH
L181 1-216-295-00 SHORT 0
< TRANSISTOR >
Q101 8-729-028-91 TRANSISTOR DTA144EUA-T106
Q102 8-729-026-53 TRANSISTOR 2SA1576A-T106-QR
Q103 8-729-028-99 TRANSISTOR RN1307-TE85L
Q104 8-729-028-99 TRANSISTOR RN1307-TE85L
Q162 8-729-101-07 TRANSISTOR 2SB798-DL
Q163 8-729-028-91 TRANSISTOR DTA144EUA-T106
Q181 8-729-018-75 FET 2SJ278MY
Q182 8-729-017-65 FET 2SK1764KY
< RESISTOR >
R103 1-216-049-11 RES, CHIP 1K 5% 1/10W
R104 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R105 1-216-065-00 RES, CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/10W
R106 1-216-133-00 METAL CHIP 3.3M 5% 1/10W
R107 1-216-113-00 METAL CHIP 470K 5% 1/10W
R109 1-216-295-00 SHORT 0
R110 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R111 1-216-295-00 SHORT 0
R112 1-216-089-00 RES, CHIP 47K 5% 1/10W
R113 1-216-049-11 RES, CHIP 1K 5% 1/10W
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
R132 1-216-097-91 RES, CHIP 100K 5% 1/10W
R133 1-216-117-00 METAL CHIP 680K 5% 1/10W
R134 1-216-049-11 RES, CHIP 1K 5% 1/10W
R135 1-216-061-00 METAL CHIP 3.3K 5% 1/10W
R136 1-216-049-11 RES, CHIP 1K 5% 1/10W
R137 1-216-295-00 SHORT 0
R140 1-216-029-00 METAL CHIP 150 5% 1/10W
R142 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R143 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R144 1-216-025-00 RES, CHIP 100 5% 1/10W
R145 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R146 1-216-037-00 METAL CHIP 330 5% 1/10W
R147 1-216-025-00 RES, CHIP 100 5% 1/10W
R148 1-216-045-00 METAL CHIP 680 5% 1/10W
R149 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R150 1-216-295-00 SHORT 0
R151 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R152 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R158 1-216-097-91 RES, CHIP 100K 5% 1/10W
R159 1-216-097-91 RES, CHIP 100K 5% 1/10W
R160 1-216-295-00 SHORT 0
R161 1-216-057-00 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/10W
R162 1-216-057-00 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/10W
R163 1-216-057-00 METAL CHIP 2.2K 5% 1/10W
R164 1-216-045-00 METAL CHIP 680 5% 1/10W
R165 1-216-097-91 RES, CHIP 100K 5% 1/10W
R166 1-220-149-11 RESISTER 2.2 10% 1/2W
R167 1-216-065-00 RES, CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/10W
R169 1-219-724-11 METAL CHIP 1 1% 1/4W
R170 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R171 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R173 1-216-121-00 RES, CHIP 1M 5% 1/10W
R175 1-216-065-00 RES, CHIP 4.7K 5% 1/10W
R177 1-216-061-00 METAL CHIP 3.3K 5% 1/10W
R179 1-216-085-00 METAL CHIP 33K 5% 1/10W
R180 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R182 1-216-089-00 RES, CHIP 47K 5% 1/10W
R183 1-216-089-00 RES, CHIP 47K 5% 1/10W
R184 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R185 1-216-081-00 METAL CHIP 22K 5% 1/10W
R186 1-216-089-00 RES, CHIP 47K 5% 1/10W
R188 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R189 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R190 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R195 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
R196 1-216-295-00 SHORT 0
R197 1-216-295-00 SHORT 0
R115 1-216-049-11 RES, CHIP 1K 5% 1/10W
R117 1-216-113-00 METAL CHIP 470K 5% 1/10W
R120 1-216-025-00 RES, CHIP 100 5% 1/10W
R121 1-216-097-91 RES, CHIP 100K 5% 1/10W
R123 1-216-295-00 SHORT 0
R124 1-216-025-00 RES, CHIP 100 5% 1/10W
R125 1-216-025-00 RES, CHIP 100 5% 1/10W
R127 1-216-025-00 RES, CHIP 100 5% 1/10W
R129 1-216-295-00 SHORT 0
R131 1-216-073-00 METAL CHIP 10K 5% 1/10W
< SWITCH >
S101 1-762-596-21 SWITCH, PUSH (1 KEY) (LIMIT IN)
S102 1-762-148-21 SWITCH, PUSH (2 KEY)
(REFLECT DET, PROTECT DET)
**************************************************************
– 71 –
Page 56

MAIN
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
* A-4724-589-A MAIN BOARD, COMPLETE (US, CND)
* A-4724-628-A MAIN BOARD, COMPLETE (SP)
* A-4724-631-A MAIN BOARD, COMPLETE (AEP, UK)
*********************
7-685-872-09 SCREW +BVTT 3X8 (S)
< BATTERY >
BT406 1-528-887-11 BATTERY, LITHIUM SECONDARY
< CAPACITOR >
C101 1-162-290-31 CERAMIC 470PF 10% 50V
C102 1-126-964-11 ELECT 10uF 20% 50V
C181 1-128-551-11 ELECT 22uF 20% 25V
C182 1-162-600-11 CERAMIC 0.0047uF 30% 16V
C183 1-162-294-31 CERAMIC 0.001uF 10% 50V
C184 1-126-963-11 ELECT 4.7uF 20% 50V
C185 1-162-282-31 CERAMIC 100PF 10% 50V
C201 1-162-290-31 CERAMIC 470PF 10% 50V
C202 1-126-964-11 ELECT 10uF 20% 50V
C281 1-128-551-11 ELECT 22uF 20% 25V
C282 1-162-600-11 CERAMIC 0.0047uF 30% 16V
C283 1-162-294-31 CERAMIC 0.001uF 10% 50V
C284 1-126-963-11 ELECT 4.7uF 20% 50V
C285 1-162-282-31 CERAMIC 100PF 10% 50V
C300 1-126-934-11 ELECT 220uF 20% 10V
C301 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C302 1-126-934-11 ELECT 220uF 20% 10V
C303 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C304 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C305 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C306 1-126-934-11 ELECT 220uF 20% 10V
C307 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C308 1-126-934-11 ELECT 220uF 20% 10V
C350 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C351 1-162-205-31 CERAMIC 18PF 5% 50V
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
C431 1-126-966-11 ELECT 33uF 20% 50V
C432 1-128-551-11 ELECT 22uF 20% 25V
C441 1-126-933-11 ELECT 100uF 20% 16V
C442 1-162-306-11 CERAMIC 0.01uF 20% 16V
C443 1-162-306-11 CERAMIC 0.01uF 20% 16V
C461 1-126-964-11 ELECT 10uF 20% 50V
C466 1-126-964-11 ELECT 10uF 20% 50V
C500 1-131-347-00 TANTALUM 1uF 10% 35V
C512 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C516 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C519 1-162-294-31 CERAMIC 0.001uF 10% 50V
C531 1-162-282-31 CERAMIC 100PF 10% 50V
C533 1-162-282-31 CERAMIC 100PF 10% 50V
C562 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C571 1-162-282-31 CERAMIC 100PF 10% 50V
C572 1-162-282-31 CERAMIC 100PF 10% 50V
C573 1-162-282-31 CERAMIC 100PF 10% 50V
C575 1-162-282-31 CERAMIC 100PF 10% 50V
C594 1-162-294-31 CERAMIC 0.001uF 10% 50V
C595 1-162-294-31 CERAMIC 0.001uF 10% 50V
C597 1-162-294-31 CERAMIC 0.001uF 10% 50V
C598 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C599 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C601 1-162-306-11 CERAMIC 0.01uF 20% 16V
C611 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C612 1-126-963-11 ELECT 4.7uF 20% 50V
C613 1-162-306-11 CERAMIC 0.01uF 20% 16V
C912 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C913 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
< CONNECTOR >
CN406 1-568-683-11 PIN, CONNECTOR (PC BAORD) 2P
* CN502 1-568-934-11 PIN, CONNECTOR 7P
CNP920 1-691-770-11 PLUG (MICRO CONNECTOR) 8P
CNS411 1-784-418-11 CONNECTOR, FFC (LIF(NON-ZIF) 21P
C352 1-162-203-31 CERAMIC 15PF 5% 50V
C370 1-126-933-11 ELECT 100uF 20% 16V
C371 1-126-934-11 ELECT 220uF 20% 10V
C380 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C381 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C385 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C386 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C398 1-162-282-31 CERAMIC 100PF 10% 50V
C401 1-126-936-11 ELECT 3300uF 20% 16V
C402 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C404 1-126-933-11 ELECT 100uF 20% 16V
C406 1-124-252-00 ELECT 0.33uF 20% 50V
C407 1-162-294-31 CERAMIC 0.001uF 10% 50V
C411 1-126-939-11 ELECT 10000uF 20% 16V
C412 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C416 1-126-926-11 ELECT 1000uF 20% 10V
C421 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C422 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C423 1-128-576-11 ELECT 100uF 20% 63V
C424 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C425 1-126-967-11 ELECT 47uF 20% 50V
C426 1-128-551-11 ELECT 22uF 20% 63V
CNS421 1-779-287-11 CONNECTOR, FFC (LIF(NON-ZIF))19P
CNS501 1-784-417-11 CONNECTOR, FFC (LIF(NON-ZIF) 23P
< DIODE >
D390 8-719-911-19 DIODE 1SS119
D391 8-719-911-19 DIODE 1SS119
D401 8-719-210-21 DIODE 11EQS04
D402 8-719-210-21 DIODE 11EQS04
D403 8-719-210-21 DIODE 11EQS04
D404 8-719-210-21 DIODE 11EQS04
D406 8-719-911-19 DIODE 1SS119
D408 8-719-024-99 DIODE 11ES2-NTA2B
D409 8-719-210-21 DIODE 11EQS04
D411 8-719-024-99 DIODE 11ES2-NTA2B
D412 8-719-024-99 DIODE 11ES2-NTA2B
D421 8-719-024-99 DIODE 11ES2-NTA2B
D422 8-719-109-81 DIODE RD4.7ESB2
D431 8-719-911-19 DIODE 1SS119
D432 8-719-911-19 DIODE 1SS119
D433 8-719-911-19 DIODE 1SS119
D461 8-719-024-99 DIODE 11ES2-NTA2B
D462 8-719-024-99 DIODE 11ES2-NTA2B
– 72 –
Page 57

MAIN
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
D466 8-719-024-99 DIODE 11ES2-NTA2B
D467 8-719-024-99 DIODE 11ES2-NTA2B
D911 8-719-911-19 DIODE 1SS119
< INDUCTOR >
FB356 1-412-473-21 INDUCTOR (SMALL TYPE)
FB357 1-412-473-21 INDUCTOR (SMALL TYPE)
FB358 1-412-473-21 INDUCTOR (SMALL TYPE) (US, CND)
< IC >
IC301 8-759-553-65 IC UDA1341TS/N2
IC351 8-759-917-18 IC SN74HCU04AN
IC381 8-759-634-50 IC M5218AL
IC386 8-759-634-50 IC M5218AL
IC401 8-759-445-59 IC BA033T
IC406 8-759-481-02 IC M62016L
IC411 8-759-231-53 IC TA7805S
IC421 8-759-633-42 IC M5293L
IC441 8-759-822-09 IC LB1641
IC501 8-759-577-40 IC M30620MC-400FP
IC601 8-759-917-18 IC SN74HCU04AN
IC611 8-749-012-70 IC GP1F38R (DIGITAL OUT)
< JACK >
J101 1-784-429-11 JACK, PIN 4P (LINE (ANALOG) IN/OUT)
< COIL >
L450 1-410-509-11 INDUCTOR 10uH
L451 1-410-509-11 INDUCTOR 10uH
L611 1-410-509-11 INDUCTOR 10uH
< TRANSISTOR >
Q191 8-729-900-74 TRANSISTOR DTC143TS
Q291 8-729-900-74 TRANSISTOR DTC143TS
Q390 8-729-422-57 TRANSISTOR UN4111
Q441 8-729-900-80 TRANSISTOR DTC114ES
Q442 8-729-119-76 TRANSISTOR 2SA1175-HFE
Q911 8-729-119-78 TRANSISTOR 2SC403SP-51
< RESISTOR >
R81 1-249-441-11 CARBON 100K 5% 1/4W
(US, CND)
R82 1-249-441-11 CARBON 100K 5% 1/4W
(EXCEPT US, CND)
R87 1-249-441-11 CARBON 100K 5% 1/4W
R101 1-249-417-11 CARBON 1K 5% 1/4W
R102 1-249-441-11 CARBON 100K 5% 1/4W
R106 1-249-430-11 CARBON 12K 5% 1/4W
R181 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R182 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R183 1-249-433-11 CARBON 22K 5% 1/4W
R184 1-247-864-11 CARBON 24K 5% 1/4W
R185 1-249-417-11 CARBON 1K 5% 1/4W
R186 1-249-417-11 CARBON 1K 5% 1/4W
R187 1-249-437-11 CARBON 47K 5% 1/4W
R188 1-249-415-11 CARBON 680 5% 1/4W
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
R189 1-249-411-11 CARBON 330 5% 1/4W
R201 1-249-417-11 CARBON 1K 5% 1/4W
R202 1-249-441-11 CARBON 100K 5% 1/4W
R206 1-249-430-11 CARBON 12K 5% 1/4W
R281 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R282 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R283 1-249-433-11 CARBON 22K 5% 1/4W
R284 1-247-864-11 CARBON 24K 5% 1/4W
R285 1-249-417-11 CARBON 1K 5% 1/4W
R286 1-249-417-11 CARBON 1K 5% 1/4W
R287 1-249-437-11 CARBON 47K 5% 1/4W
R288 1-249-415-11 CARBON 680 5% 1/4W
R289 1-249-411-11 CARBON 330 5% 1/4W
R351 1-247-903-00 CARBON 1M 5% 1/4W
R352 1-249-413-11 CARBON 470 5% 1/4W
R355 1-249-407-11 CARBON 150 5% 1/4W
R356 1-249-409-11 CARBON 220 5% 1/4W
R391 1-249-441-11 CARBON 100K 5% 1/4W
R392 1-247-883-00 CARBON 150K 5% 1/4W
R406 1-249-409-11 CARBON 220 5% 1/4W
R407 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R420 1-247-881-00 CARBON 120K 5% 1/4W
R422 1-249-441-11 CARBON 100K 5% 1/4W
R423 1-249-409-11 CARBON 220 5% 1/4W
R424 1-249-409-11 CARBON 220 5% 1/4W
R431 1-247-807-31 CARBON 100 5% 1/4W
R432 1-249-826-11 CARBON 620 5% 1/4W
R433 1-247-822-11 CARBON 430 5% 1/4W
R434 1-249-433-11 CARBON 22K 5% 1/4W
R435 1-249-438-11 CARBON 56K 5% 1/4W
R436 1-247-891-00 CARBON 330K 5% 1/4W
R437 1-249-417-11 CARBON 1K 5% 1/4W
R441 1-249-431-11 CARBON 15K 5% 1/4W
R442 1-249-433-11 CARBON 22K 5% 1/4W
R443 1-249-434-11 CARBON 27K 5% 1/4W
R509 1-249-441-11 CARBON 100K 5% 1/4W
R513 1-247-903-00 CARBON 1M 5% 1/4W
R519 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R530 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R531 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R532 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R533 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R542 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R543 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R550 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R551 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R553 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R559 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R560 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R566 1-249-441-11 CARBON 100K 5% 1/4W
R568 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R569 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R571 1-249-441-11 CARBON 100K 5% 1/4W
R573 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R574 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R575 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R577 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
– 73 –
Page 58

MAIN PANEL PANEL 2
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
R581 1-249-441-11 CARBON 100K 5% 1/4W
(EXCEPT US, CND)
R582 1-249-441-11 CARBON 100K 5% 1/4W
(US, CND)
R592 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R593 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R594 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R595 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R597 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R613 1-247-895-00 CARBON 470K 5% 1/4W
R614 1-249-437-11 CARBON 47K 5% 1/4W
R623 1-247-895-00 CARBON 470K 5% 1/4W
R624 1-249-437-11 CARBON 47K 5% 1/4W
R801 1-249-426-11 CARBON 5.6K 5% 1/4W
R803 1-249-425-11 CARBON 4.7K 5% 1/4W
R804 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R911 1-249-425-11 CARBON 4.7K 5% 1/4W
R912 1-249-437-11 CARBON 47K 5% 1/4W
< VIBRATOR >
X351 1-579-314-11 VIBRATOR, CRYSTAL (22.5792MHz)
X513 1-781-174-21 VIBRATOR, CERAMIC (10MHz)
**************************************************************
* A-4724-590-A PANEL BOARD, COMPLETE
**********************
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
Q767 8-729-900-74 TRANSISTOR DTC143TS
< RESISTOR >
R702 1-249-421-11 CARBON 2.2K 5% 1/4W
R703 1-247-843-11 CARBON 3.3K 5% 1/4W
R704 1-249-425-11 CARBON 4.7K 5% 1/4W
R705 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R706 1-249-435-11 CARBON 33K 5% 1/4W
R712 1-249-421-11 CARBON 2.2K 5% 1/4W
R713 1-247-843-11 CARBON 3.3K 5% 1/4W
R714 1-249-425-11 CARBON 4.7K 5% 1/4W
R722 1-249-421-11 CARBON 2.2K 5% 1/4W
R723 1-247-843-11 CARBON 3.3K 5% 1/4W
R724 1-249-425-11 CARBON 4.7K 5% 1/4W
R725 1-249-429-11 CARBON 10K 5% 1/4W
R741 1-249-409-11 CARBON 220 5% 1/4W
R742 1-249-409-11 CARBON 220 5% 1/4W
R760 1-247-807-31 CARBON 100 5% 1/4W
R761 1-247-807-31 CARBON 100 5% 1/4W
R762 1-247-807-31 CARBON 100 5% 1/4W
R763 1-247-807-31 CARBON 100 5% 1/4W
R767 1-249-441-11 CARBON 100K 5% 1/4W
R769 1-247-843-11 CARBON 3.3K 5% 1/4W
< SWITCH >
* 4-216-341-01 HOLDER (FL)
* 4-921-941-01 CUSHION (FL)
< CAPACITOR >
C701 1-126-153-11 ELECT 22uF 20% 6.3V
C760 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C761 1-162-294-31 CERAMIC 0.001uF 10% 50V
C762 1-162-294-31 CERAMIC 0.001uF 10% 50V
C763 1-162-294-31 CERAMIC 0.001uF 10% 50V
C764 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C765 1-126-153-11 ELECT 22uF 20% 6.3V
C766 1-164-159-11 CERAMIC 0.1uF 50V
C769 1-162-215-31 CERAMIC 47PF 5% 50V
< CONNECTOR >
CNS701 1-778-449-11 CONNECTOR, FFC/FPC 19P
* CNS702 1-565-481-11 CONNECTOR, BOARD TO BOARD 5P
< LED >
D741 8-719-046-44 LED SEL5221S (r)
D742 8-719-046-43 LED SEL5421E-TP15 (·)
< FLUORESCENT INDICATOR TUBE >
FL771 1-517-804-11 INDICATOR TUBE, FLUORESCENT
S701 1-762-875-21 SWITCH, KEYBOARD (r REC)
S702 1-762-875-21 SWITCH, KEYBOARD (p)
S703 1-762-875-21 SWITCH, KEYBOARD ())
S704 1-762-875-21 SWITCH, KEYBOARD (0)
S705 1-762-875-21 SWITCH, KEYBOARD (P)
S706 1-762-875-21 SWITCH, KEYBOARD (·)
S711 1-762-875-21 SWITCH, KEYBOARD (MENU/NO)
S712 1-762-875-21 SWITCH, KEYBOARD (YES)
S713 1-475-139-11 ENCODER, ROTARY
(= AMS +, PUSH ENTER)
S714 1-762-875-21 SWITCH, KEYBOARD (CLEAR)
S721 1-762-875-21 SWITCH, KEYBOARD (EJECT §)
S722 1-762-875-21 SWITCH, KEYBOARD (PLAY MODE)
S723 1-762-875-21 SWITCH, KEYBOARD (REPEAT)
S724 1-762-875-21 SWITCH, KEYBOARD (SCROLL)
S725 1-762-875-21 SWITCH, KEYBOARD (LEVEL/DISPLAY/CHAR)
S731 1-571-427-11 SWITCH, SLIDE (INPUT)
**************************************************************
* 1-673-305-11 PANEL 2 BOARD
*************
< CAPACITOR >
C781 1-124-584-00 ELECT 100uF 20% 10V
C782 1-162-306-11 CERAMIC 0.01uF 20% 16V
< IC >
IC761 8-759-426-98 IC MSM9202-02GS-K
< TRANSISTOR >
Q741 8-729-422-57 TRANSISTOR UN4111
Q742 8-729-422-57 TRANSISTOR UN4111
< CONNECTOR >
* CNP702 1-569-799-11 PLUG, CONNECTOR 5P
< LED >
D751 8-719-046-44 LED SEL5221S (1/u)
– 74 –
Page 59

PANEL 2 SW TRANS
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
< IC >
IC781 8-749-013-92 IC GP1UC7X (g)
< TRANSISTOR >
Q751 8-729-422-57 TRANSISTOR UN4111
< RESISTOR >
R726 1-249-435-11 CARBON 33K 5% 1/4W
R751 1-249-409-11 CARBON 220 5% 1/4W
R781 1-249-401-11 CARBON 47 5% 1/4W
R782 1-247-807-31 CARBON 100 5% 1/4W
< SWITCH >
S726 1-762-875-21 SWITCH, KEYBOARD (1/u)
**************************************************************
* 1-668-111-11 SW BOARD
*********
< CONNECTOR >
CN601 1-506-486-11 PIN, CONNECTOR 7P
< SWITCH >
S601 1-572-126-21 SWITCH, PUSH (1 KEY) (REC POSITION)
S602 1-572-126-21 SWITCH, PUSH (1 KEY) (PACK OUT)
S604 1-771-264-11 SWITCH, PUSH (DETECTION)(1 KEY)
(PB POSITION)
**************************************************************
* 1-673-306-11 TRANS BOARD
************
< CAPACITOR >
! C901 1-113-920-11 CERAMIC 0.0022uF 20% 250V
! C902 1-113-920-11 CERAMIC 0.0022uF 20% 250V
< CONNECTOR >
* CN901 1-580-230-11 PIN, CONNECTOR (PC BOARD) 2P
< LINE FILTER >
Ref. No. Part No. Description Remark
MISCELLANEOUS
**************
9 1-790-510-11 WIRE (FLAT TYPE) (19 CORE)
57 1-790-512-11 WIRE (FLAT TYPE) (21 CORE)
58 1-790-513-11 WIRE (FLAT TYPE) (23 CORE)
61 1-500-051-11 BEAD, FERRITE (WITH CASE)
! 63 1-696-586-21 CORD, POWER (UK)
! 63 1-777-071-31 CORD, POWER (AEP, SP)
! 63 1-783-531-31 CORD, POWER (US, CND)
* 258 1-667-954-11 FLEXIBLE BOARD
! 260 8-583-028-02 OPTICAL PICK-UP KMS-260A/J1NP
HR901 1-500-502-11 HEAD, OVER WRITE
M101 A-4672-516-A MOTOR ASSY, SPINDLE
M102 A-4672-515-A MOTOR ASSY, SLED
M103 X-4949-670-1 MOTOR ASSY, LOADING
S102 1-762-148-21 SWITCH, PUSH (2 KEY)
(REFLECT DET, PROTECT DET)
! T901 1-433-697-11 TRANSFORMER, POWER (US, CND)
! T901 1-433-698-11 TRANSFORMER, POWER (AEP, UK)
! T901 1-433-699-11 TRANSFORMER, POWER (SP)
************************************************************
**************
HARDWARE LIST
**************
#1 7-685-646-79 SCREW +BVTP 3X8 TYPE2 N-S
#3 7-621-772-20 SCREW +B 2X5
#4 7-621-772-40 SCREW +B 2X8
#5 7-627-852-08 SCREW, PRECISION +P 1.7X2.5
#6 7-685-533-19 SCREW +BTP 2.6X6 TYPE2 N-S
#7 7-685-133-19 SCREW +P 2.6X6 TYPE2 NON-SLIT
************************************************************
ACCESSORIES & PACKING MATERIALS
********************************
1-418-270-11 REMOTE COMMANDER (RM-D30P)
1-574-264-11 CORD, OPTICAL PLUG
1-776-263-51 CORD, CONNECTION
3-866-678-11 MANUAL, INSTRUCTION (ENGLISH)
3-866-678-21 MANUAL, INSTRUCTION (FRENCH, SPANISH,
PORTUGUESE) (CND, AEP)
! LF901 1-411-547-11 FILTER, LINE
< RELAY >
! RY911 1-765-324-11 RELAY
< POWER TRANSFORMER >
! T901 1-433-702-11 TRANSFORMER, POWER (US, CND)
! T901 1-433-703-11 TRANSFORMER, POWER (AEP, UK)
! T901 1-433-704-11 TRANSFORMER, POWER (SP)
! T910 1-433-697-11 TRANSFORMER, POWER (US, CND)
! T910 1-433-698-11 TRANSFORMER, POWER (AEP, UK)
! T910 1-433-699-11 TRANSFORMER, POWER (SP)
**************************************************************
– 75 –
3-866-678-31 MANUAL, INSTRUCTION (GERMAN, DUTCH,
3-866-678-41 MANUAL, INSTRUCTION (CHINESE) (SP)
4-981-643-11 COVER, BATTERY (for RM-D30P)
The components identified by
mark ! or dotted line with
mark ! are critical for safety.
Replace only with part number specified.
Les composants identifiés par une
marque ! sont critiques pour la
sécurité.
Ne les remplacer que par une pièce
portant le neméro spécifié.
SWEDISH, ITALIAN) (AEP)
Page 60

MDS-M100
Sony Corporation
Home A&V Products Company9-928-837-11
– 76 –
Printed in Japan © 1999. 3
99C0586-1
Published by Quality Assurance Dept.
(Shinagawa)
 Loading...
Loading...