Page 1

SN8P2714X_2715
USER’S MANUAL
V1.4
SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
SN8P2714
SN8P27142
SN8P27143
SN8P2715
S
O
Nii
S
O
SONIX reserves the right to make change without further notice to any products herein to improve reliability, function or design. SONIX does not
assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any product or circuit described herein; neither does it convey any license under its patent
rights nor the rights of others. SONIX products are not designed, intended, or authorized for us as components in systems intended, for surgical
implant into the body, or other applications intended to support or sustain life, or for any other application in which the failure of the SONIX product
could create a situation where personal injury or death may occur. Should Buyer purchase or use SONIX products for any such unintended or
unauthorized application. Buyer shall indemnify and hold SONIX and its officers, employees, subsidiaries, affiliates and distributors harmless against
all claims, cost, damages, and expenses, and reasonable attorney fees arising out of, directly or indirectly, any claim of personal injury or death
associated with such unintended or unauthorized use even if such claim alleges that SONIX was negligent regarding the design or manufacture of
the part.
N
X 88--
X
Biitt
B
Miiccrroo--
M
Coonnttrroolllleerr
C
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 1 V1.4
Page 2
AMENDMENT HISTORY
Version Date Description
VER 0.1 Aug. 2004 Preliminary Version first issue
VER 0.2 Jan. 2005 1. Add SN8P27142/ SN8P27143 relative data.
2. Fix ADC clock and Timer clock description.
3. Add LVD36 relative information.
4. Correct the LVD24 bit location from bit 3 to bit 4 in PFLAG register description.
5. Modify LVD code option related description
6. Modify TC0RATE and TC1RATE table.
7. Add TC0X8 and TC1X8 notice.
8. Release the ROM address 0x04 ~ 0x07 as general-purpose area.
9. Remove the instruction limitation at interrupt vector address (0x08)
10. Change IDE support version to M2IDE V1.04
11. Modify pin circuit diagram.
12. There is no Schmitt trigger input in port 4.
13. Add description of P0.3 without wakeup function
VER 0.3 Mar. 2005 1. Modify Zero flag description.
2. In instruction set table, change “S = 0”, otherwise “S = 1” to “S = 1”, otherwise “S =
0”
3. Fix ADC conversion time formula.
4. Remove “Note:For 12-bit resolution the conversion time is 16 steps”.
5. Remove “Note: Please use "@RST_WDT" macro to clear the watchdog timer
successfully both in S8KD-2 ICE emulation and real chip.”
6. Modify watchdog reset section
7. Fixed the slow mode current of electrical characteristic table.
VER 1.0
VER 1.1 Nov.2005
VER 1.2 Dec.2005
VER 1.3 Sep.2006
VER 1.4 Feb 2007
Sept 2005 1. Modify Programming Pin Mapping.
2. Modify PROGRAM CHECK LIST.
3. Modify P13 AVREF pin description
4. Modify 27142/143 pin assignment.
5. Modify P57,P66 TC0RATE、TC1RATE.
6. Modify P57,P66:TC0X8=1 Fosc/2~Fosc/256 to Fosc/1~Fosc/128
7. Modify P107 SLOW Mode Current.
8. ADD P97 “Note”.
Nov.2005 1. ADD Brown-Out reset circuit.
2. Working Voltage vs. Frequency graphs.
1. ADD ADC current.
2. Modify Topr value.
1. Remove 32k mode.
2. Modify P108 SN8P271XAXD to SN8P271XXD.
3. Modify P52 wakeup trigger signal.
4. Remove CHARACTERISTIC GRAPHS.
5. Modify reset section.
6. Limit Fcpu=Fosc/4~./8 when Noise Filter enable
7. Remove Pc
1. Modify 15.2 STANDARD ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTIC.
2. Add 15.3 CHARACTERISTIC GRAPHS.
3. Add chapter17 Marking Definition.
1. Modify ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTIC.
2. Modify RST/P0.3/VPP PIN DISCRIPTION.
SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 2 V1.4
Page 3

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
Table of Contents
AMENDMENT HISTORY .............................................................................................................. 2
1 PRODUCT OVERVIEW................................................................................................................. 8
1.1 FEATURES OF SN8P2710 SERIES........................................................................................... 8
1.2 SYSTEM BLOCK DIAGRAM ................................................................................................. 10
1.3 PIN ASSIGNMENT................................................................................................................ 11
1.3.1 SN8P27142 Pin Assignment .......................................................................................... 11
1.3.2 SN8P27143 Pin Assignment .......................................................................................... 11
1.3.3 SN8P2714K Pin Assignment.......................................................................................... 12
1.3.4 SN8P2715P Pin Assignment.......................................................................................... 12
1.4 PIN DESCRIPTIONS............................................................................................................. 13
1.5 PIN CIRCUIT DIAGRAMS ..................................................................................................... 14
2 CODE OPTION TABLE............................................................................................................... 15
3 ADDRESS SPACES ................................................................................................................... 16
3.1 PROGRAM MEMORY (ROM) ............................................................................................... 16
3.1.1 OVERVIEW.................................................................................................................... 16
3.1.2 USER RESET VECTOR ADDRESS (0000H)................................................................. 17
3.1.3 INTERRUPT VECTOR ADDRESS (0008H)................................................................... 17
3.1.4 GENERAL PURPOSE PROGRAM MEMORY AREA..................................................... 19
3.1.5 LOOKUP TABLE DESCRIPTION................................................................................... 19
3.1.6 JUMP TABLE DESCRIPTION........................................................................................ 21
3.2 DATA MEMORY (RAM)......................................................................................................... 23
3.2.1 OVERVIEW.................................................................................................................... 23
3.3 WORKING REGISTERS ....................................................................................................... 24
3.3.1 Y, Z REGISTERS........................................................................................................... 24
3.3.2 R REGISTERS...............................................................................................................25
3.4 PROGRAM FLAG.................................................................................................................. 25
3.4.1 RESET FLAG................................................................................................................. 25
3.4.2 LVD 2.4V FLAG .............................................................................................................. 25
3.4.3 LVD 3.6V FLAG .............................................................................................................. 25
3.4.4 CARRY FLAG................................................................................................................. 26
3.4.5 DECIMAL CARRY FLAG................................................................................................ 26
3.4.6 ZERO FLAG................................................................................................................... 26
3.5 ACCUMULATOR................................................................................................................... 27
3.6 STACK OPERATIONS .......................................................................................................... 28
3.6.1 OVERVIEW.................................................................................................................... 28
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 3 V1.4
Page 4

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
3.6.2 STACK REGISTERS...................................................................................................... 29
3.6.3 STACK OPERATION EXAMPLE.................................................................................... 30
3.7 PROGRAM COUNTER ......................................................................................................... 31
3.7.1 ONE ADDRESS SKIPPING ........................................................................................... 32
3.7.2 MULTI-ADDRESS JUMPING......................................................................................... 33
4 ADDRESSING MODE................................................................................................................. 34
4.1 OVERVIEW........................................................................................................................... 34
4.1.1 IMMEDIATE ADDRESSING MODE............................................................................... 34
4.1.2 DIRECTLY ADDRESSING MODE ................................................................................. 34
4.1.3 INDIRECTLY ADDRESSING MODE.............................................................................. 34
4.1.4 TO ACCESS DATA in RAM BANK 0.............................................................................. 35
5 SYSTEM REGISTER................................................................................................................... 36
5.1 OVERVIEW........................................................................................................................... 36
5.2 SYSTEM REGISTER ARRANGEMENT (BANK 0) ................................................................ 36
5.2.1 BYTES of SYSTEM REGISTER..................................................................................... 36
5.2.2 BITS of SYSTEM REGISTER ........................................................................................ 37
6 RESET......................................................................................................................................... 39
6.1 OVERVIEW........................................................................................................................... 39
6.2 POWER ON RESET.............................................................................................................. 40
6.3 WATCHDOG RESET ............................................................................................................ 40
6.4 BROWN OUT RESET ........................................................................................................... 41
6.4.1 BROWN OUT DESCRIPTION........................................................................................ 41
6.4.2 THE SYSTEM OPERATING VOLTAGE DECSRIPTION............................................... 42
6.4.3 BROWN OUT RESET IMPROVEMENT......................................................................... 42
6.5 EXTERNAL RESET............................................................................................................... 44
6.6 EXTERNAL RESET CIRCUIT ............................................................................................... 44
6.6.1 Simply RC Reset Circuit................................................................................................. 44
6.6.2 Diode & RC Reset Circuit............................................................................................... 45
6.6.3 Zener Diode Reset Circuit.............................................................................................. 45
6.6.4 Voltage Bias Reset Circuit.............................................................................................. 46
6.6.5 External Reset IC ........................................................................................................... 47
7 OSCILLATORS........................................................................................................................... 48
7.1 OVERVIEW........................................................................................................................... 48
7.1.1 OSCM REGISTER DESCRIPTION................................................................................ 49
7.1.2 EXTERNAL HIGH-SPEED OSCILLATOR...................................................................... 49
7.1.3 HIGH CLOCK OSCILLATOR CODE OPTION ............................................................... 49
7.1.4 SYSTEM OSCILLATOR CIRCUITS............................................................................... 50
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 4 V1.4
Page 5

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
7.1.5 External RC Oscillator Frequency Measurement............................................................ 51
7.2 INTERNAL LOW-SPEED OSCILLATOR............................................................................... 52
7.3 SYSTEM MODE DESCRIPTION........................................................................................... 53
7.3.1 OVERVIEW.................................................................................................................... 53
7.3.2 NORMAL MODE ............................................................................................................ 53
7.3.3 SLOW MODE.................................................................................................................53
7.3.4 POWER DOWN (SLEEP) MODE................................................................................... 53
7.4 SYSTEM MODE CONTROL.................................................................................................. 54
7.4.1 SN8P2710 SYSTEM MODE BLOCK DIAGRAM............................................................ 54
7.4.2 SYSTEM MODE SWITCHING ....................................................................................... 55
7.5 WAKEUP TIME ..................................................................................................................... 56
7.5.1 OVERVIEW.................................................................................................................... 56
7.5.2 HARDWARE WAKEUP.................................................................................................. 56
8 TIMERS COUNTERS.................................................................................................................. 57
8.1 WATCHDOG TIMER (WDT).................................................................................................. 57
8.2 TIMER COUNTER 0 (TC0).................................................................................................... 58
8.2.1 OVERVIEW.................................................................................................................... 58
8.2.2 TC0M MODE REGISTER............................................................................................... 59
8.2.3 TC0C COUNTING REGISTER....................................................................................... 61
8.2.4 TC0R AUTO-LOAD REGISTER..................................................................................... 63
8.2.5 TC0 TIMER COUNTER OPERATION SEQUENCE....................................................... 64
8.2.6 TC0 CLOCK FREQUENCY OUTPUT (BUZZER)........................................................... 66
8.3 TIMER COUNTER 1 (TC1).................................................................................................... 67
8.3.1 OVERVIEW.................................................................................................................... 67
8.3.2 TC1M MODE REGISTER............................................................................................... 68
8.3.3 TC1C COUNTING REGISTER....................................................................................... 70
8.3.4 TC1R AUTO-LOAD REGISTER..................................................................................... 72
8.3.5 TC1 TIMER COUNTER OPERATION SEQUENCE....................................................... 73
8.3.6 TC1 CLOCK FREQUENCY OUTPUT (BUZZER)........................................................... 75
8.4 PWM FUNCTION DESCRIPTION......................................................................................... 76
8.4.1 OVERVIEW.................................................................................................................... 76
8.4.2 PWM PROGRAM DESCRIPTION.................................................................................. 77
8.4.3 PWM Duty with TCxR changing ..................................................................................... 78
8.4.4 TCxIRQ and PWM Duty ................................................................................................. 79
9 INTERRUPT ................................................................................................................................ 80
9.1 OVERVIEW........................................................................................................................... 80
9.2 INTEN INTERRUPT ENABLE REGISTER ............................................................................ 80
9.3 INTRQ INTERRUPT REQUEST REGISTER......................................................................... 81
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 5 V1.4
Page 6

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
9.4 P0.0 INTERRUPT TRIGGER EDGE CONTROL REGISTER ................................................ 81
9.5 INTERRUPT OPERATION DESCRIPTION........................................................................... 82
9.5.1 GIE GLOBAL INTERRUPT OPERATION ...................................................................... 82
9.5.2 INT0 (P0.0) INTERRUPT OPERATION ......................................................................... 83
9.5.3 INT1 (P0.1) INTERRUPT OPERATION ......................................................................... 83
9.5.4 TC0 INTERRUPT OPERATION..................................................................................... 85
9.5.5 TC1 INTERRUPT OPERATION..................................................................................... 86
9.5.6 MULTI-INTERRUPT OPERATION................................................................................. 87
10 I/O PORT................................................................................................................................... 89
10.1 OVERVIEW......................................................................................................................... 89
10.2 I/O PORT FUNCTION TABLE ............................................................................................. 90
10.3 PULL-UP RESISTERS ........................................................................................................ 91
10.4 I/O PORT DATA REGISTER ............................................................................................... 94
11 8-CHANNEL ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTER................................................................. 96
11.1 OVERVIEW......................................................................................................................... 96
11.2 ADM REGISTER ................................................................................................................. 97
11.3 ADR REGISTERS ............................................................................................................... 97
11.4 ADB REGISTERS ............................................................................................................... 97
11.5 P4CON REGISTERS .......................................................................................................... 98
11.6 ADC CONVERTING TIME................................................................................................... 99
11.7 ADC CIRCUIT ................................................................................................................... 100
12 7-BIT DIGITAL TO ANALOG CONVERTER .......................................................................... 101
12.1 OVERVIEW....................................................................................................................... 101
12.2 DAM REGISTER ............................................................................................................... 102
12.3 D/A CONVERTER OPERATION ....................................................................................... 102
13 CODING ISSUE ...................................................................................................................... 103
13.1 TEMPLATE CODE ............................................................................................................ 103
13.2 PROGRAM CHECK LIST .................................................................................................. 107
14 INSTRUCTION SET TABLE ................................................................................................... 108
15 ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTIC ......................................................................................... 109
15.1 ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATING....................................................................................... 109
15.2 STANDARD ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTIC................................................................ 109
15.3 CHARACTERISTIC GRAPHS........................................................................................... 110
16 DEVELOPMENT TOOLS ........................................................................................................ 114
16.1 DEVELOPMENT TOOL VERSION ............................................................................................. 114
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 6 V1.4
Page 7

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
16.1.1 ICE (In circuit emulation)............................................................................................ 114
16.1.2 OTP Writer ................................................................................................................. 114
16.1.3 IDE (Integrated Development Environment)............................................................... 114
16.2 SN8P2715/SN8P2714 EV-KIT .......................................................................................... 115
16.2.1 PCB DESCRIPTION................................................................................................... 115
16.3 SN8P2715/14 EV-KIT CONNNECT TO SN8ICE 2K .......................................................... 116
16.4 TRANSITION BOARD FOR OTP PROGTRAMMING........................................................ 117
16.4.1 SN8P2715/2715 Rev. B TRANSITION BOARD......................................................... 117
16.4.2 CONNNECT Rev. B TRANSITION BOARD TO EASY WRITER................................ 117
16.5 OTP PROGRAMMING PIN TO TRANSITION BOARD MAPPING..................................................... 118
16.5.1 The pin assignment of Easy and MP EZ Writer transition board socket:.................... 118
16.5.2 The pin assignment of Writer V3.0 transition board socket: ....................................... 118
16.5.3 SN8P2710 Series Programming Pin Mapping:........................................................... 119
17 MARKING DEFINITION .......................................................................................................... 120
17.1 INTRODUCTION............................................................................................................... 120
17.2 MARKING INDETIFICATION SYSTEM............................................................................. 120
17.3 MARKING EXAMPLE........................................................................................................ 121
17.4 DATECODE SYSTEM....................................................................................................... 121
18 PACKAGE INFORMATION .................................................................................................... 122
18.1 P-DIP18 PIN...................................................................................................................... 122
18.2 SOP18 PIN........................................................................................................................ 123
18.3 P-DIP 20 PIN ..................................................................................................................... 124
18.4 SOP 20 PIN ....................................................................................................................... 125
18.5 SSOP20 PIN ..................................................................................................................... 126
18.6 SK-DIP28 PIN ................................................................................................................... 127
18.7 SOP28 PIN........................................................................................................................ 128
18.8 P-DIP 32 PIN ..................................................................................................................... 129
18.9 SOP 32 PIN ....................................................................................................................... 129
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 7 V1.4
Page 8
SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
1 PRODUCT OVERVIEW
1.1 FEATURES of SN8P2710 Series
Memory configuration
♦
OTP ROM size: 2K * 16 bits. Two internal interrupts: TC0, TC1
RAM size: 128 * 8 bits Two external interrupts: INT0, INT1
Eight levels stack buffer
I/O pin configuration
♦
Input only pin: P0
Bi-directional: P2, P4, P5
Wakeup: P0.0, P0.1, P0.2
External interrupt: P0.0, P0.1
Pull-up resisters: P0, P2, P4, P5 External high clock: RC type up to 10 MHz
P4 pins shared with ADC inputs. External high clock: Crystal type up to 16 MHz
Max 8-channel 12-bit ADC.
♦
One channel 7-bit DAC.
♦
Powerful instructions
♦
One clocks per instruction cycle (1T)
Most of instructions are one cycle only
All ROM area lookup table function (MOVC) SN8P27142: P-DIP 18 pins, SOP 18pins
SN8P27143:P-DIP 20 pins, SOP 20 pins, SSOP 20 pins
SN8P2714: SK-DIP 28 pins, SOP 28pins
SN8P2715: P-DIP 32 pins, SOP 32 pins
Four interrupt sources
♦
Two 8-bit Timer/Counter
♦
TC0: Auto-reload timer/Counter/PWM0/Buzzer output
TC1: Auto-reload timer/Counter/PWM1/Buzzer output
On chip watchdog timer.
♦
System clocks and Operating modes
♦
Internal low clock: RC type 16KHz(3V), 32KHz(5V)
Normal mode: Both high and low clock active
Slow mode: Low clock only
Sleep mode: Both high and low clock stop
Package (Chip form support)
♦
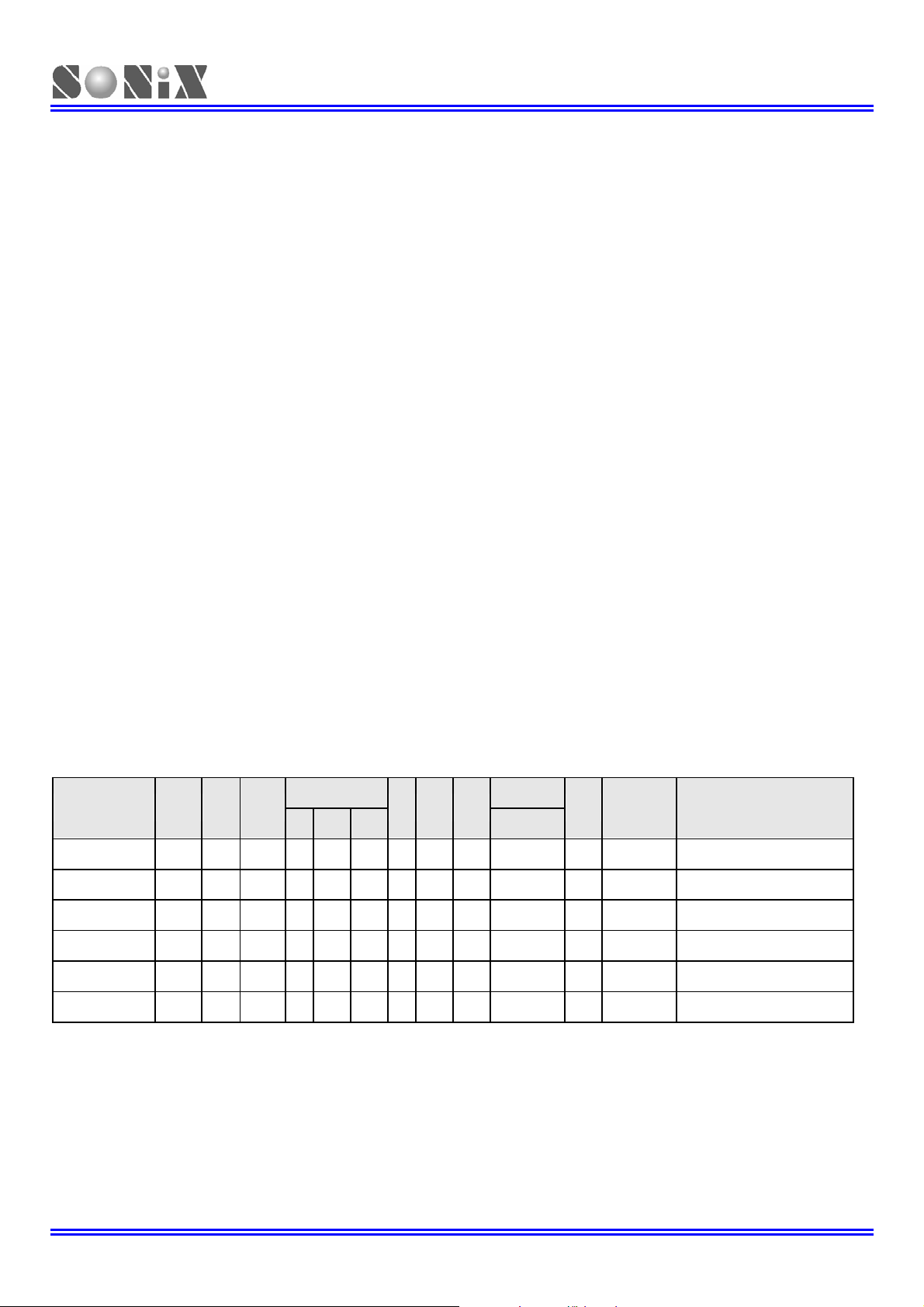
FEATURES SELECTION TABLE
CHIP ROM RAM Stack
SN8P27142 2K*16 128 8 - V V 15 5ch - 2 - 2 DIP18/SOP18
SN8P27143 2K*16 128 8 - V V 16 6ch - 2 - 2 DIP20/SOP20/SSOP20
SN8P2714 2K*16 128 8 - V V 23 8ch 1ch 2 - 3 SKDIP28/SOP28
SN8P2715 2K*16 128 8 - V V 27 8ch 1ch 2 - 3 DIP32/SOP32
SN8P2704A 4K*16 256 8 V V V 18 5ch 1ch 2 1 8 SKDIP28/SOP28
SN8P2705A 4K*16 256 8 V V V 23 8ch 1ch 2 1 9 DIP32/SOP32
Note: For SN8P27143 and SN8P27142 must configure P02R (bit 2 of P0UR) as “1” to avoid sleep mode fail.
Timer PWM
I/O ADC DAC
T0 TC0 TC1
Buzzer
SIO
Wakeup
Pin no.
Package
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 8 V1.4
Page 9
SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
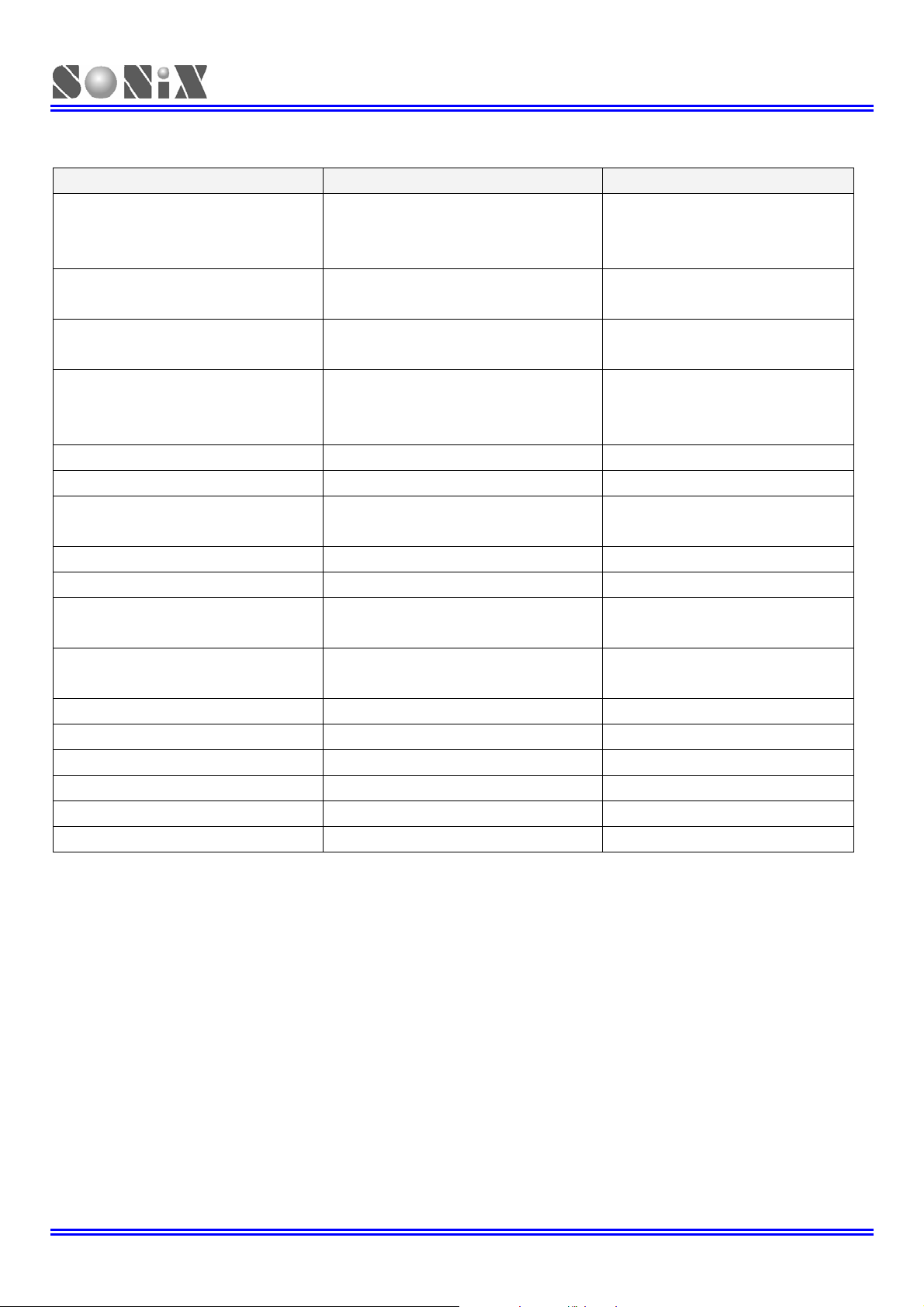
Compare SN8P2714/15 to SN8P2704A/05A
Item SN8P2714/15 SN8P2704A/05A
Excellent
AC Noise Immunity Capability
Memory
Maximum I/O pins
High Speed PWM
Programmable Open-Drain Output N/A P1.0 / P1.1 / P5.2 (SO)
B0MOV M, I No Limitation “I” can’t be 0E6h or 0E7h
B0XCH A, M No Limitation
Valid instruction in ROM address 8 No Limitation JMP or NOP
ADC Interrupt No Yes
ADC Clock Frequency
Valid Range of
TC0C/TC1C/TC0R/TC1R
Green mode No Yes
SIO Function No Yes
LVD Level: 2.0V always ON 1.8V always ON
Port 0 Input only port Bi-direction port
Interrupt Vector Instruction No Limitation NOP/JMP only
PUSH/POP Instruction No Yes
(Add an 47uF bypass Capacitor
between VDD and GND)
ROM: 2K x 16
RAM: 128 x 8
23 I/O in 28 pins package
27 I/O in 32 pins package
PWM Resolution: 8bit/6bit/5bit/4bit
8bit PWM up to 62.5K at 16Mhz
4bit PWM up to 1000K at 16Mhz
Four kinds of setting
(Configuration by ADCKS [1:0])
0x00 ~ 0xFF 0x00 ~ 0xFE
(Add an 47uF bypass Capacitor
between VDD and GND)
18 I/O in 28 pins package
23 I/O in 32 pins package
PWM Resolution: 8bit/6bit/5bit/4bit
8bit PWM up to 7.8125K at 16Mhz
4bit PWM up to 125K at 16Mhz
(Configuration by ADCKS [2:0])
Excellent
ROM: 4K x 16
RAM: 256 x 8
The address of M
can’t be 80h ~ FFh
Seven kinds of setting
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 9 V1.4
Page 10
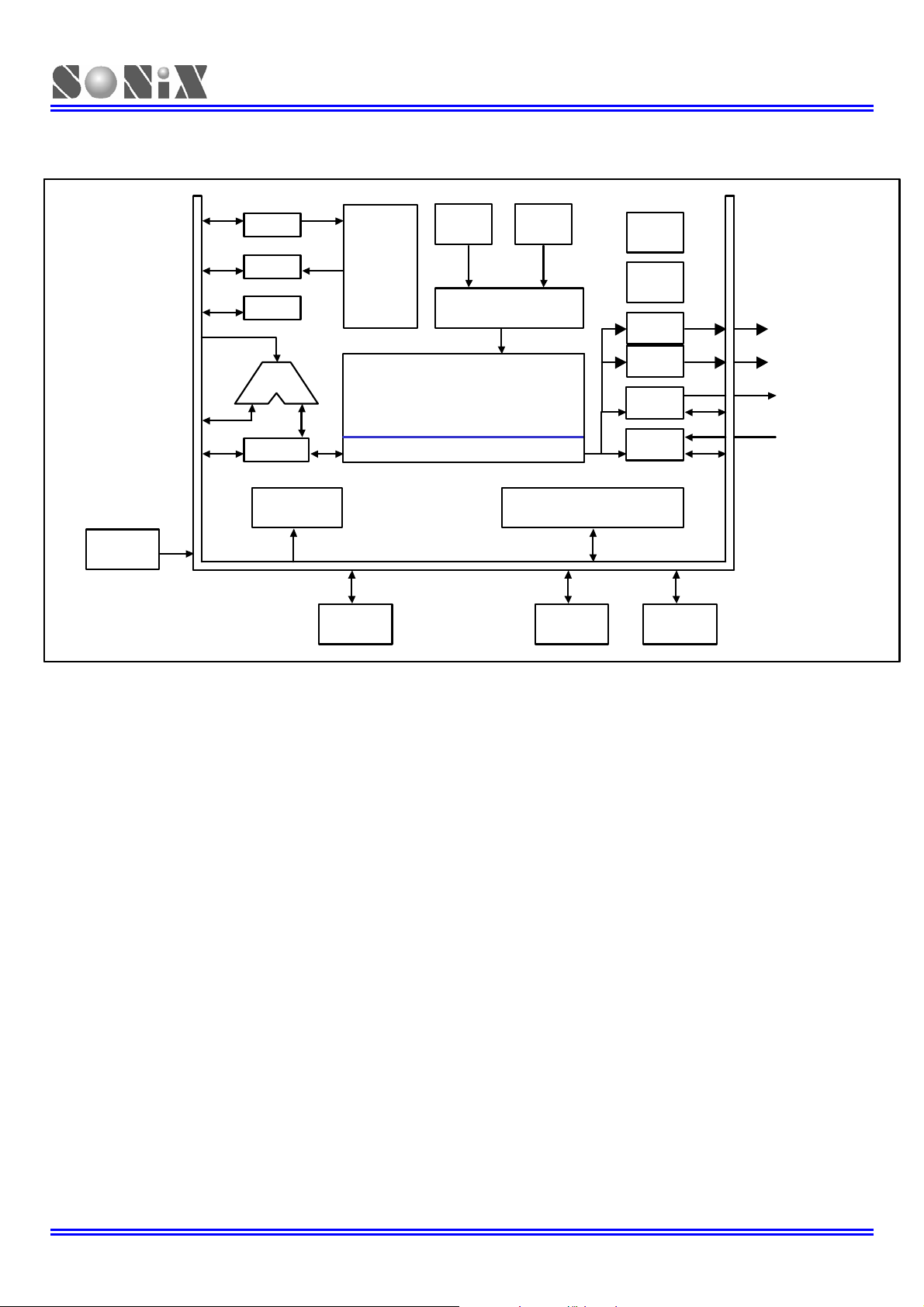
1.2 SYSTEM BLOCK DIAGRAM
H-OSC
PC
PC
IR
IR
FLAGS
FLAGS
ALU
ALU
ACC
ACC
INT ERRUPT
INT ERRUPT
CONTROL
CONTROL
OTP
OTP
ROM
ROM
SYSTEM REGISTER
SYSTEM REGISTER
H-OSC
TIMING GENERATOR
TIMING GENERATOR
RAM
RAM
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
Internal
Internal
CLK
CLK
TIMER & COUNTER
TIMER & COUNTER
Lo w Vo l t
Lo w Vo l t
Detector
Detector
Watch-Dog
Watch-Dog
Timer
Timer
PWM0
PWM0
PWM1
PWM1
DAC
DAC
ADC
ADC
SN8P2714X_2715
PWM0/Buzz er0
PWM0/Buzz er0
PWM1/Buzz er1
PWM1/Buzz er1
DAO
DAO
AIN0~AIN7
AIN0~AIN7
PORT 0
PORT 0
PORT 2 PORT 4 PORT 5
PORT 2 PORT 4 PORT 5
Figure 1-1.Simplified System Block Diagram
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 10 V1.4
Page 11
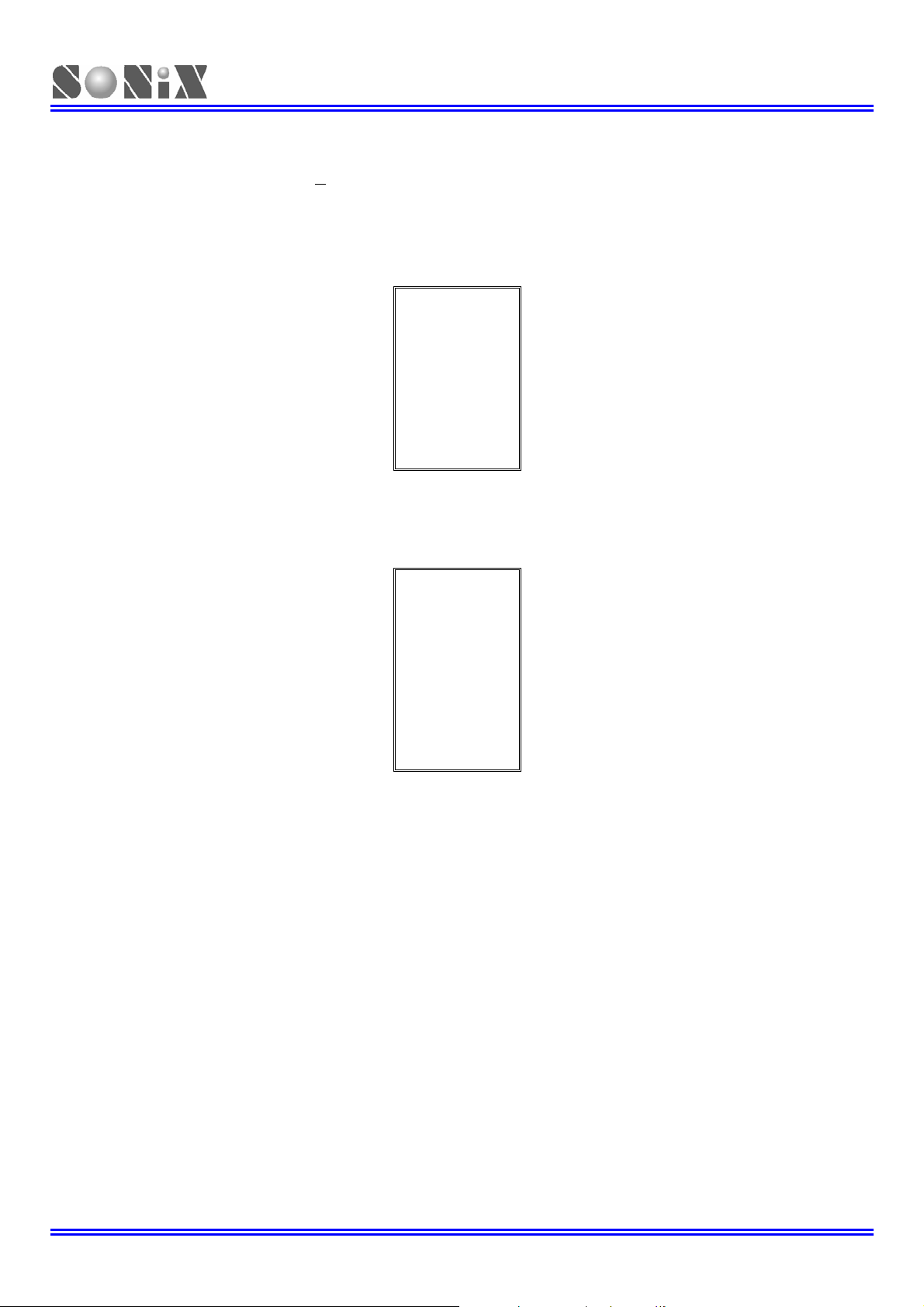
1.3 PIN ASSIGNMENT
Format Description:SN8P271xY Y = K > SK-DIP,P > P-DIP, S> SOP
1.3.1 SN8P27142 Pin Assignment
P0.1 1 U 18 P0.0
P5.6/XOUT
SN8P27142P
SN8P27142S
P2.0
P2.1
XIN
VSS
P4.4/AIN4
P4.3/AIN3
P4.2/AIN2
1.3.2 SN8P27143 Pin Assignment
P2.0 1 U 20 P0.1
P5.6/XOUT
SN8P27143P
SN8P27143S
SN8P27143X
P2.1
XIN
VSS
P4.5/AIN5
P4.4/AIN4
P4.3/AIN3
P4.2/AIN2
P4.1/AIN1
2 17
3 16
4 15
5 14
6 13
7 12
8 11
9 10
2 19
3 18
4 17
5 16
6 15
7 14
8 13
9 12
10 11
P5.0
P5.1
P5.3/BZ1/PWM1
P5.4/BZ0/PWM0
P0.3/RST/VPP
VDD
P4.0/AIN0
P4.1/AIN1
P0.0
P5.0
P5.1
P5.3/BZ1/PWM1
P5.4/BZ0/PWM0
P0.3/RST/VPP
VDD
AVREFH
P4.0/AIN0
SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
¾ Note: For SN8P27143 and SN8P27142 must configure P02R (bit 2 of P0UR) as “1” to avoid sleep mode
fail.
¾ Note: The ADC reference voltage (AVREFH) of SN8P27142/SN8P27143 is VDD.
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 11 V1.4
Page 12
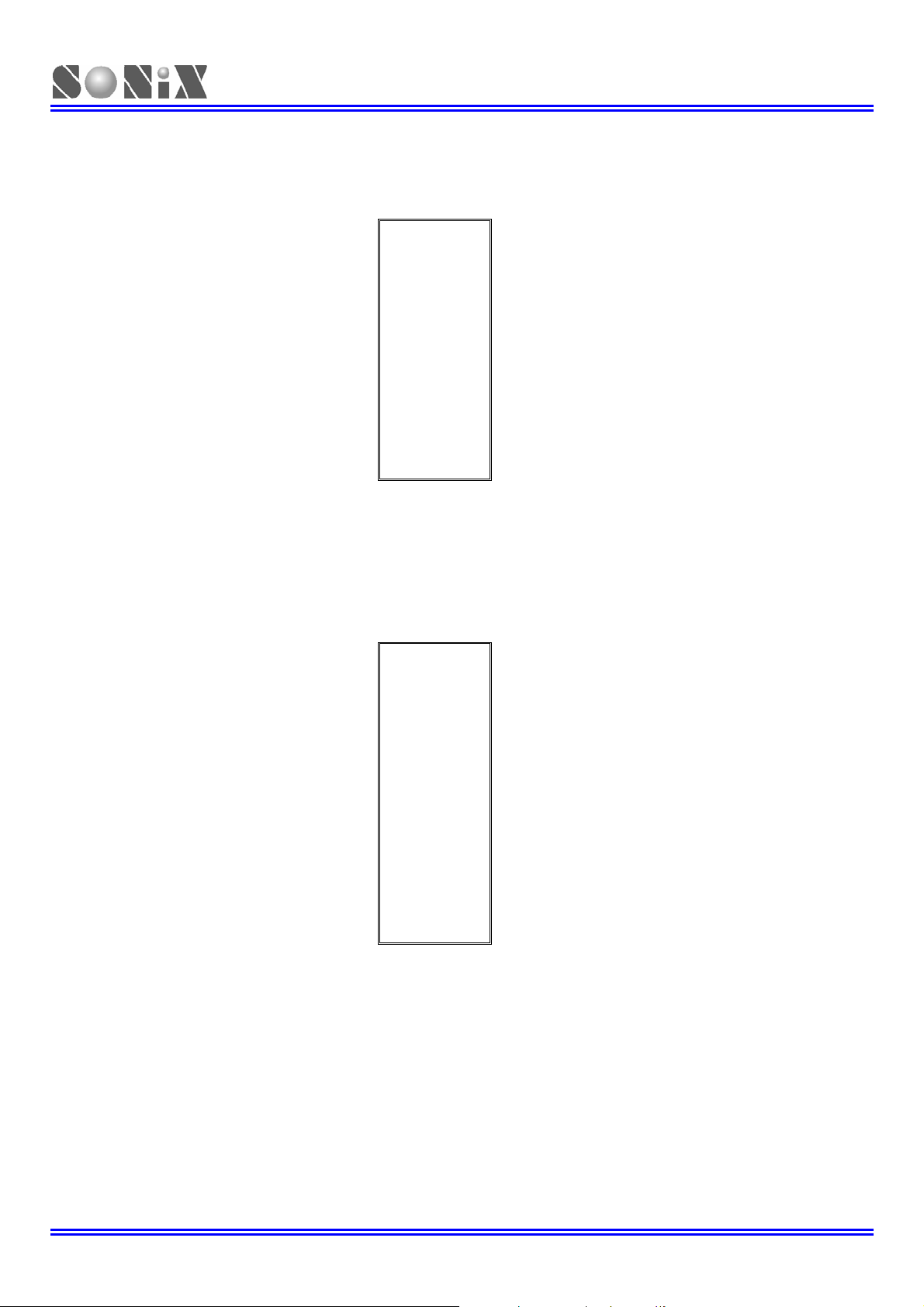
1.3.3 SN8P2714K Pin Assignment
P5.3/BZ1/PWM1 1 U 28
P5.2 2 27 DAC
P5.1 3 26 P0.3/RST/VPP
P5.0 4 25 VDD
P0.0/INT0 5 24 AVREFH
P0.1/INT1 6 23
P0.2 7 22
P2.0 8 21
P2.1 9 20
P2.2 10 19
P2.3 11 18
P2.4 12 17
P5.6/XOUT 13 16
XIN 14 15
SN8P2714K
SN8P2714S
1.3.4 SN8P2715P Pin Assignment
SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
P5.4/BZ0/PWM0
P4.0/AIN0
P4.1/AIN1
P4.2/AIN2
P4.3/AIN3
P4.4/AIN4
P4.5/AIN5
P4.6/AIN6
P4.7/AIN7
VSS
P5.5 1 U 32 DAO
P5.4/BZ0/PWM0 2 31 P0.3/RST/VPP
P5.3/BZ1/PWM1
P0.0/INT0
P0.1/INT1
3 30 VDD
P5.2
4 29 AVREFH
P5.1
5 28 P4.0/AIN0
P5.0
6 27 P4.1/AIN1
7 26 P4.2/AIN2
8 25 P4.3/AIN3
P0.2 9 24 P4.4/AIN4
P2.0
10 23 P4.5/AIN5
P2.1
11 22 P4.6/AIN6
P2.2
12 21 P4.7/AIN7
P2.3
13 20 VSS
P2.4
14 19 XIN
P2.5
15 18 P5.6/XOUT
P2.6 16 17 P2.7
SN8P2715P
SN8P2715S
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 12 V1.4
Page 13
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
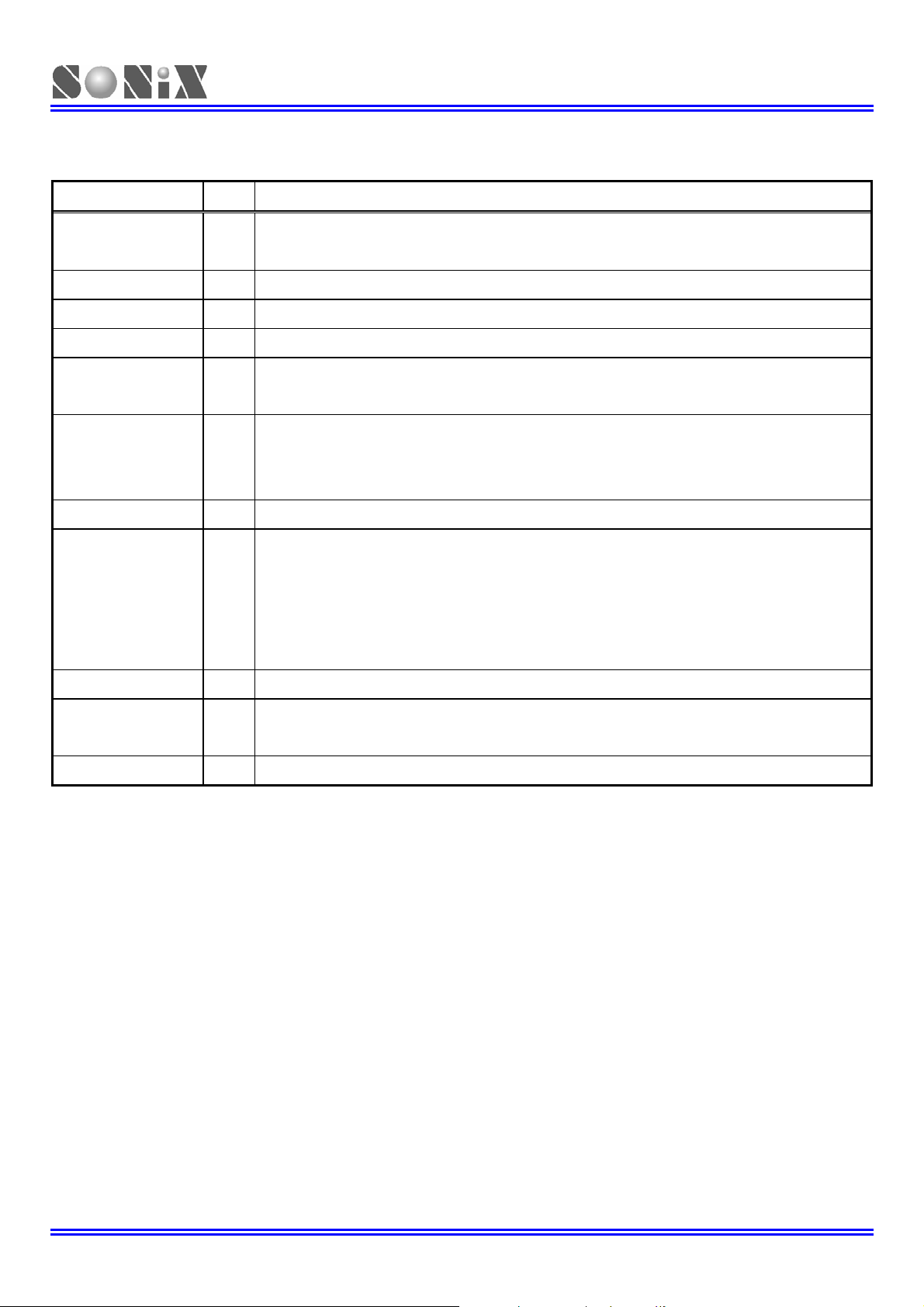
1.4 PIN DESCRIPTIONS
PIN NAME TYPE DESCRIPTION
P0 [1:0] / INT [1:0] I P0 [1:0]: Input only pin/ wakeup/pull-up/Schmitt trigger input
INT [1:0]: External interrupt
P0 .2 I P0.2: Input only pin/wake up/pull-up/Schmitt trigger input
P2 [7:0] I/O P2 [7:0] bi-direction pins/pull-up/Schmitt trigger input
P4 [7:0] / AIN [7:0] I/O Bi-direction pins/pull-up /ADC input/ without Schmitt trigger input
P5 [5:0] I/O Bi-direction pins/pull-up/Schmitt trigger input
P5.4: PWM0/BZ0, P5.3: PWM1/BZ1
AVREFH I ADC highest reference voltage input
(NOTE :The ADC reference voltage (AVREFH) of SN8P27142 and SN8P27143 are
VDD.)
DAO O Current type DAC output
SN8P2714X_2715
P0.3/RST/VPP I/P P0.3: Schmitt trigger input pin / NO pull-up, NO wakeup/ in RC mode
P0.3 is input only pin without pull-up resistor under P0.3 mode. Add the 100 ohm
external resistor on P0.3, when it is set to be input pin.
RST: External reset, active “low”
VPP: OTP programming pin
XIN I External oscillator input pin. / External RC oscillator input
XOUT/P5.6 I/O XOUT: External oscillator output pin.
P5.6: Bi-direction pin/pull-up/Schmitt trigger input in RC mode
VDD, VSS P Power supply pins.
Table 1-1. SN8P2714/15 Pin Description
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 13 V1.4
Page 14
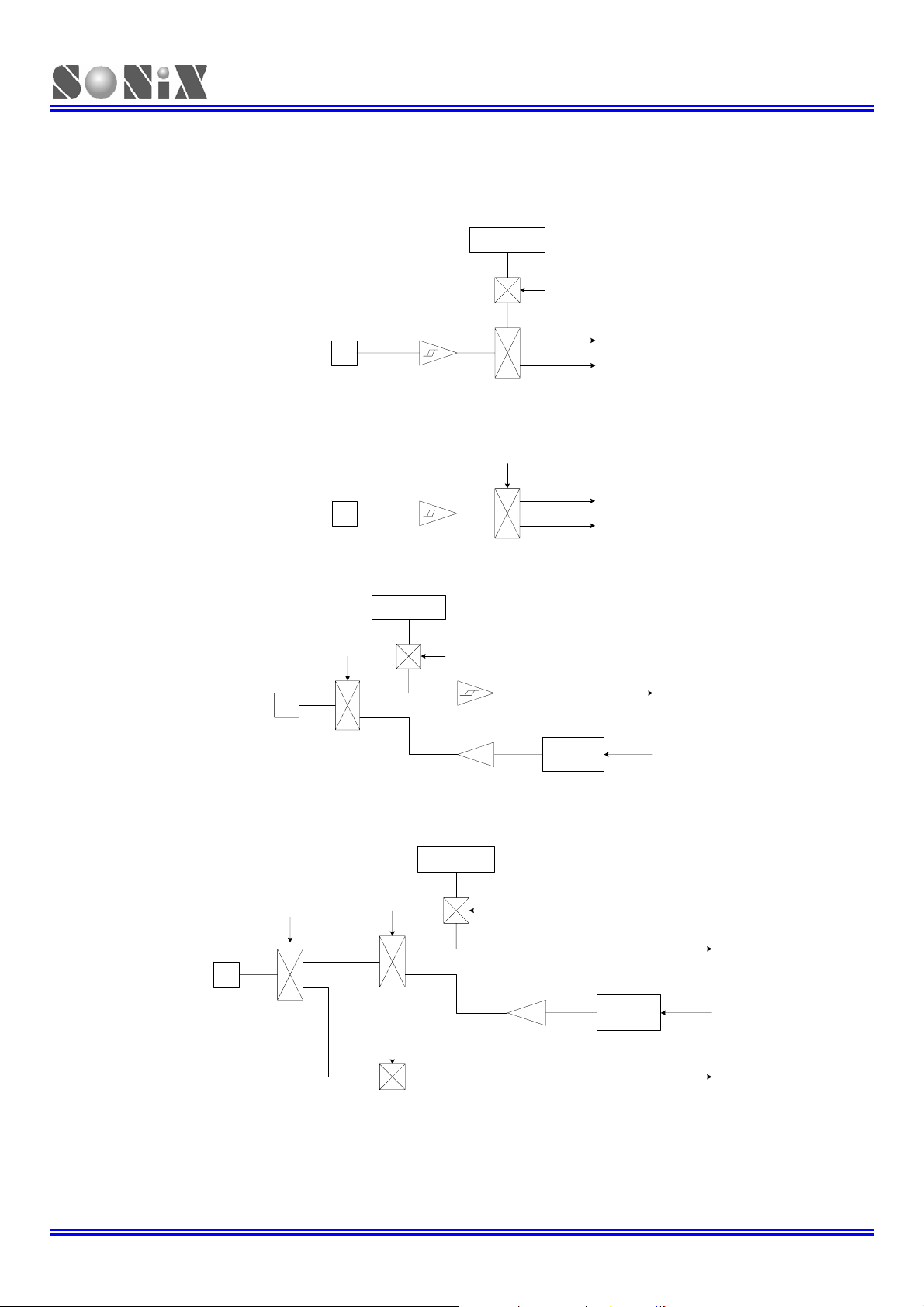
1.5 PIN CIRCUIT DIAGRAMS
Port 0.1 and P0.2 structure:
SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
Pull-Up
PnUR
Port 0.3 structure:
Port 2, 5 structure:
Port 4 structure:
Pin
Pin
Pin
PnM
Pull-Up
Code Option
PnM, PnUR
Pull-Up
Ext. Reset
Output
Latch
Int. Bus
Int. Rst
Int. Bus
Int. Rst
Input Bus
Output Bus
P4CON
Pin
PnM
GCHS
PnM, PnUR
Output
Latch
Input Bus
Output Bus
Int. ADC
Figure 1-2. Pin Circuit Diagram
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 14 V1.4
Page 15
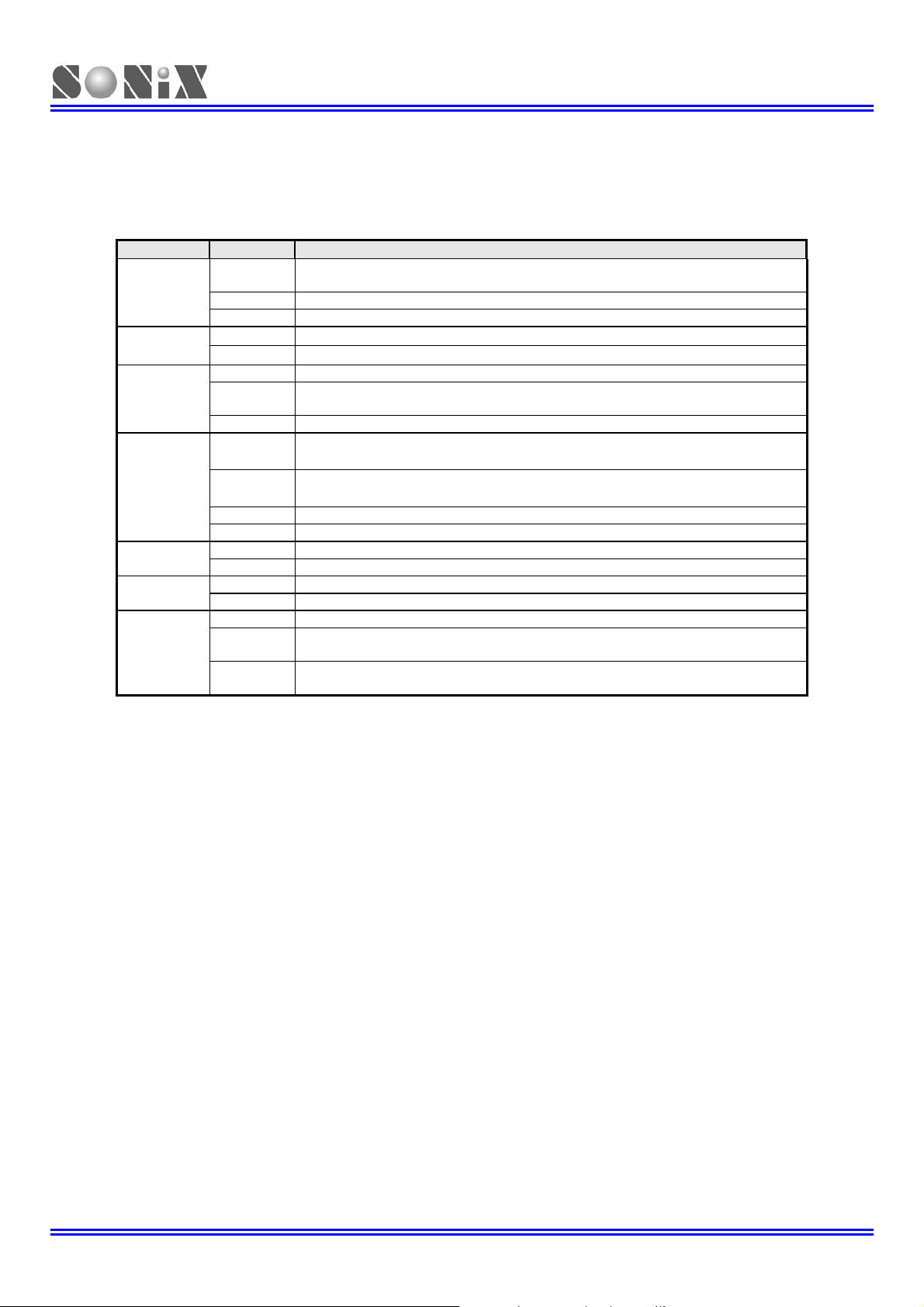
2 CODE OPTION TABLE
Code Option Content Function Description
Low cost external RC oscillator for high clock oscillator.
Output the Fcpu clock from Xout pin.
Enable Noise Filter and the Fcpu is Fosc/4~Fosc/8.
Disable Noise Filter and the Fcpu is Fosc/1~Fosc/8.
Normal mode: Enable Watchdog timer
Sleep mode: Stop Watchdog timer Stop
Instruction cycle is oscillator clock.
Notice: In Fosc/1, Noise Filter must be disabled.
Instruction cycle is 2 oscillator clocks.
Notice: In Fosc/2, Noise Filter must be disabled.
LVD will reset chip if VDD is below 2.0V
Enable LVD24 bit of PFLAG register for 2.4V low voltage indicator.
LVD will reset chip if VDD is below 2.4V
Enable LVD36 bit of PFLAG register for 3.6V low voltage indicator.
High_Clk
Noise_Filter
Watch_Dog
Fcpu
Security
RST_P0.3
LVD
Ext_RC
12M_X’tal High speed crystal /resonator (e.g. 12MHz ~ 16MHz) for high clock oscillator.
4M_X’tal Middle speed crystal /resonator (e.g. 4MHz ~ 10Mhz) for high clock oscillator.
Enable
Disable
Always_On Watchdog timer always on even in sleep (power down) mode.
Enable
Disable Disable Watchdog function.
Fosc/1
Fosc/2
Fosc/4 Instruction cycle is 4 oscillator clocks.
Fosc/8 Instruction cycle is 8 oscillator clocks.
Enable Enable ROM code Security function.
Disable Disable ROM code Security function.
Reset Enable external reset pin
P0.3 Enable P0.3 input only pin without pull-up register
LVD_L LVD will reset chip if VDD is below 2.0V
LVD_M
LVD_H
SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
Table 2-1. Code Option Table of SN8P2714x/2715
Notice:
¾ In high noisy environment, enable “Noise Filter” and set Watch_Dog as “Always_On” is
strongly recommended.
¾ Enable “Noise Filter” will limit the Fcpu = Fosc/4 or Fosc/8
¾ Fcpu code option is only available for High Clock
¾ Fosc = Fhosc (External high clock) in normal mode.
¾ Fosc = Flosc (Internal low RC clock) in slow mode.
¾ In slow mode, Fcpu = Fosc / 4.
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 15 V1.4
Page 16
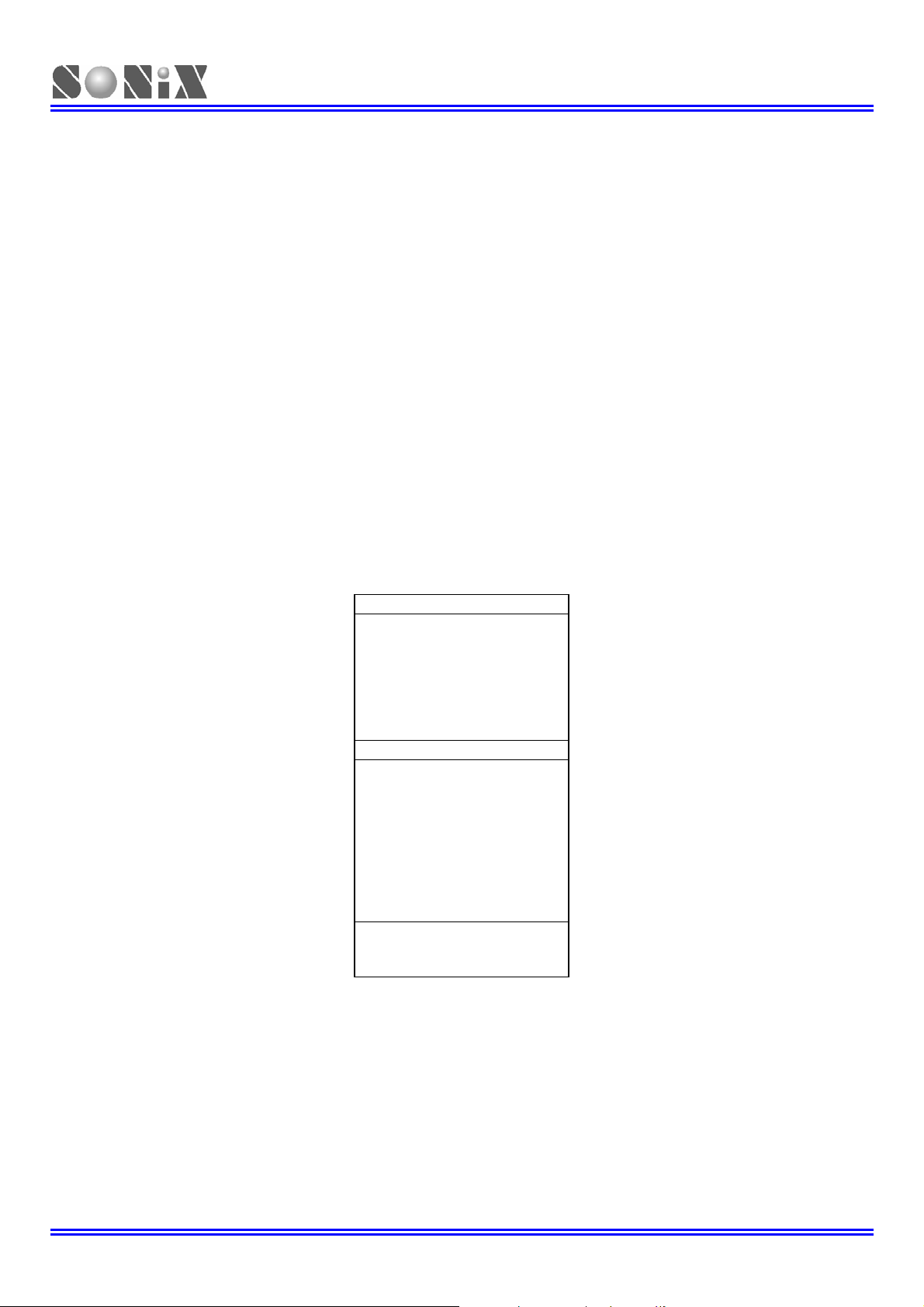
SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
3 ADDRESS SPACES
3.1 PROGRAM MEMORY (ROM)
3.1.1 OVERVIEW
ROM Maps for SN8P2710 devices provide 2K X 16-bit OTP programmable memory. The SN8P2710 program memory
is able to fetch instructions through 12-bit wide PC (Program Counter) and can look up ROM data by using ROM code
registers (R, X, Y, Z). In standard configuration, the device’s 2,048 x 16-bit program memory has four areas:
¾ 1-word reset vector addresses
¾ 1-word Interrupt vector addresses
¾ 4-words reserved area
¾ 2K words
All of the program memory is partitioned into three coding areas. The 1
vector area), the 2
nd
area is for the interrupt vector (0008H) and the 3ed area is user code area from 0009H to 07FBH.
st
area is located from 00H to 07H(The Reset
0000H
0001H Jump to user start address
0002H Jump to user start address
0003H Jump to user start address
0004H Jump to user start address
0005H Jump to user start address
0006H Jump to user start address
0007H
0008H
0009H User program
000FH
0010H
0011H
07FBH
07FCH
07FFH
Figure 3-1 ROM Address Structure
General purpose area
.
.
General purpose area
.
.
.
ROM
Reset vector
Interrupt vector
Code Option
User reset vector
Jump to user start address
User interrupt vector
End of user program
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 16 V1.4
Page 17

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
3.1.2 USER RESET VECTOR ADDRESS (0000H)
A 1-word vector address area is used to execute system reset. After power on reset or watchdog timer overflow reset,
then the chip will restart the program from address 0000h and all system registers will be set as default values. The
following example shows the way to define the reset vector in the program memory.
 Example: After power on reset, external reset active or reset by watchdog timer overflow.
ORG 0 ; 0000H
JMP START ; Jump to user program address.
. ;
ORG 10H
START: ; 0010H, The head of user program.
. ; User program
.
.
.
ENDP
; End of program
3.1.3 INTERRUPT VECTOR ADDRESS (0008H)
A 1-word vector address area is used to execute interrupt request. If any interrupt service is executed, the program
counter (PC) value is stored in stack buffer and points to 0008h of program memory to execute the vectored interrupt.
Users have to define the interrupt vector and the following example shows the way to define the interrupt vector in the
program memory.
 Example 1: This demo program includes interrupt service routine and the user program is behind the
interrupt service routine.
ORG 0 ; 0000H
JMP START ; Jump to user program address.
.
START: ; The head of user program.
ORG 8
B0XCH A, ACCBUF
B0MOV A, PFLAG
B0MOV PFLAGBUF, A
.
.
B0MOV A, PFLAGBUF
B0MOV PFLAG, A
B0XCH A, ACCBUF
RETI
.
.
.
JMP START
ENDP
; Interrupt service routine
; B0XCH doesn’t change C, Z flag
; Save PFLAG register in a buffer
; User code
; User code
; Restore PFLAG register from buffer
; End of interrupt service routine
; User program
; End of user program
; End of program
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 17 V1.4
Page 18

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
 Example 2: The demo program includes interrupt service routine and the address of interrupt service
routine is in a special address of general-purpose area.
ORG 0 ; 0000H
JMP START ; Jump to user program address.
. ; 0001H ~ 0007H are reserved
ORG 08
JMP MY_IRQ ; 0008H, Jump to interrupt service routine address
ORG 10H
START: ; 0010H, The head of user program.
. ; User program
.
.
.
MY_IRQ: ;The head of interrupt service routine
¾ Note: It is easy to get the rules of SONIX program from demo programs given above. These points are as
following.
1.The address 0000H is a “JMP” instruction to make the program go to general-purpose ROM area.
2. The interrupt service starts from 0008H. Users can put the whole interrupt service routine from 0008H
(Example1) or to put a “JMP” instruction in 0008H then place the interrupt service routine in other
general-purpose ROM area (Example2) to get more modularized coding style.
JMP START
B0XCH A, ACCBUF
B0MOV A, PFLAG
B0MOV PFLAGBUF, A
.
.
B0MOV A, PFLAGBUF
B0MOV PFLAG, A
RETI
ENDP
; End of user program
; B0XCH doesn’t change C, Z flag
; Save PFLAG register in a buffer
; User code
; User code
; Restore PFLAG register from buffer
; End of interrupt service routine
; End of program
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 18 V1.4
Page 19

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
3.1.4 GENERAL PURPOSE PROGRAM MEMORY AREA
The ROM locations 0001H~0007H and 0009H~07FBH are used as general-purpose memory. The area is stored
instruction’s op-code and look-up table data. The SN8P2710 includes jump table function by using program counter
(PC) and look-up table function by using ROM code registers (R, Y, Z).
The boundary of program memory is separated by the high-byte program counter (PCH) every 100H. In jump table
function and look-up table function, the program counter can’t leap over the boundary by program counter
automatically. Users need to modify the PCH value to “PCH+1” as the PCL overflow (from 0FFH to 000H).
3.1.5 LOOKUP TABLE DESCRIPTION
In the ROM’s data lookup function, Y register to the highest 8-bit and Z register to the lowest 8-bit data of ROM
address. After MOVC instruction is executed, the low-byte data of ROM then will be stored in ACC and high-byte data
stored in R register.
 Example: To look up the ROM data located “TABLE1”.
B0MOV Y, #TABLE1$M ; To set lookup table1’s middle address
B0MOV Z, #TABLE1$L ; To set lookup table1’s low address.
MOVC ; To lookup data, R = 00H, ACC = 35H
;
;
@@:
. . ;
TABLE1: DW 0035H ; To define a word (16 bits) data.
DW 5105H ; “
DW 2012H ; “
¾ CAUSION: The Y register can’t increase automatically if Z register cross boundary from 0xFF to 0x00.
Therefore, user must take care such situation to avoid loop-up table errors. If Z register overflow, Y
register must be added one. The following INC_YZ macro shows a simple method to process Y and Z
registers automatically.
¾ Note: Because the program counter (PC) is only 12-bit, the X register is useless in the application. Users
can omit “B0MOV X, #TABLE1$H”. SONiX ICE support more larger program memory addressing
capability. So make sure X register is “0” to avoid unpredicted error in loop-up table operation.
INCMS Z ; Z+1
JMP @F ; Not overflow
INCMS Y ; Z overflow (FFH Æ 00), Æ Y=Y+1
NOP ; Not overflow
MOVC ; To lookup data, R = 51H, ACC = 05H.
; Increment the index address for next address
 Example: INC_YZ Macro
INC_YZ MACRO
INCMS Z ; Z+1
JMP @F ; Not overflow
INCMS Y ; Y+1
NOP ; Not overflow
@@:
ENDM
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 19 V1.4
Page 20

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
The other coding style of loop-up table is to add Y or Z index register by accumulator. Be careful if carry happen. Refer
following example for detailed information:
 Example: Increase Y and Z register by B0ADD/ADD instruction
B0MOV Y, #TABLE1$M ; To set lookup table’s middle address.
B0MOV Z, #TABLE1$L ; To set lookup table’s low address.
GETDATA: ;
MOVC ; To lookup data. If BUF = 0, data is 0x0035
; If BUF = 1, data is 0x5105
; If BUF = 2, data is 0x2012
.
.
. . ;
TABLE1: DW 0035H ; To define a word (16 bits) data.
DW 5105H ; “
DW 2012H ; “
B0MOV A, BUF ; Z = Z + BUF.
B0ADD Z, A
B0BTS1 FC ; Check the carry flag.
JMP GETDATA ; FC = 0
INCMS Y ; FC = 1. Y+1.
NOP
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 20 V1.4
Page 21

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
3.1.6 JUMP TABLE DESCRIPTION
The jump table operation is one of multi-address jumping function. Add low-byte program counter (PCL) and ACC
value to get one new PCL. The new program counter (PC) points to a series jump instructions as a listing table. The
way is easy to make a multi-stage program.
When carry flag occurs after executing of “ADD PCL, A”, it will not affect PCH register. Users have to check if the jump
table leaps over the ROM page boundary or the listing file generated by SONIX assembly software. If the jump table
leaps over the ROM page boundary (e.g. from xxFFH to xx00H), move the jump table to the top of next program
memory page (xx00H). Here one page mean 256 words.
 Example : If PC = 0323H (PCH = 03H、PCL = 23H)
ORG 0X0100 ; The jump table is from the head of the ROM boundary
B0ADD PCL, A ; PCL = PCL + ACC, the PCH can’t be changed.
JMP A0POINT ; ACC = 0, jump to A0POINT
JMP A1POINT ; ACC = 1, jump to A1POINT
JMP A2POINT ; ACC = 2, jump to A2POINT
JMP A3POINT ; ACC = 3, jump to A3POINT
In following example, the jump table starts at 0x00FD. When execute B0ADD PCL, A. If ACC = 0 or 1, the jump
table points to the right address. If the ACC is larger then 1 will cause error because PCH doesn’t increase one
automatically. We can see the PCL = 0 when ACC = 2 but the PCH still keep in 0. The program counter (PC) will
point to a wrong address 0x0000 and crash system operation. It is important to check whether the jump table
crosses over the boundary (xxFFH to xx00H). A good coding style is to put the jump table at the start of ROM
boundary (e.g. 0100H).
 Example: If “jump table” crosses over ROM boundary will cause errors.
ROM Address
. .
. .
. .
0X00FD
0X00FE
0X00FF
0X0100
0X0101
. .
. .
SONIX provides a macro for safe jump table function. This macro will check the ROM boundary and move the jump
table to the right position automatically. The side effect of this macro is maybe wasting some ROM size. Notice the
maximum jmp table number for this macro is limited under 254.
@JMP_A MACRO VAL
IF (($+1) !& 0XFF00) !!= (($+(VAL)) !& 0XFF00)
JMP ($ | 0XFF)
ORG ($ | 0XFF)
ENDIF
ADD PCL, A
ENDM
¾ Note: “VAL” is the number of the jump table listing number.
B0ADD PCL, A ; PCL = PCL + ACC, the PCH can’t be changed.
JMP A0POINT ; ACC = 0
JMP A1POINT ; ACC = 1
JMP A2POINT
JMP A3POINT ; ACC = 3
; ACC = 2 Å jump table cross boundary here
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 21 V1.4
Page 22

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
 Example: “@JMP_A” application in SONIX macro file called “MACRO3.H”.
B0MOV A, BUF0 ; “BUF0” is from 0 to 4.
@JMP_A 5 ; The number of the jump table listing is five.
JMP A0POINT ; If ACC = 0, jump to A0POINT
JMP A1POINT ; ACC = 1, jump to A1POINT
JMP A2POINT ; ACC = 2, jump to A2POINT
JMP A3POINT ; ACC = 3, jump to A3POINT
JMP A4POINT ; ACC = 4, jump to A4POINT
If the jump table position is from 00FDH to 0101H, the “@JMP_A” macro will make the jump table to start from 0100h.
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 22 V1.4
Page 23

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
3.2 DATA MEMORY (RAM)
3.2.1 OVERVIEW
The SN8P2710 has internally built-in the data memory up to 128 bytes for storing the general-purpose data.
For SN8P2710
¾ 128 * 8-bit general purpose area in bank 0
¾ 128 * 8-bit system special register area
The memory is located in bank 0. The bank 0, using the first 128-byte location assigned as general-purpose area, and
the remaining 128-byte in bank 0 as system register.
BANK 0
000h 000h~07Fh of Bank 0 = To store general-
“ purpose data (128 bytes).
“
“
“
“
07Fh
080h 080h~0FFh of Bank 0 = To store system
“ registers (128 bytes).
“
“
“
“
0FFh
RAM location
General purpose area
System register
End of bank 0 area
Figure 3-2 RAM Location of SN8P2710
¾ Note: The undefined locations of system register area are logic “high” after executing read instruction
“MOV A, M”.
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 23 V1.4
Page 24
SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
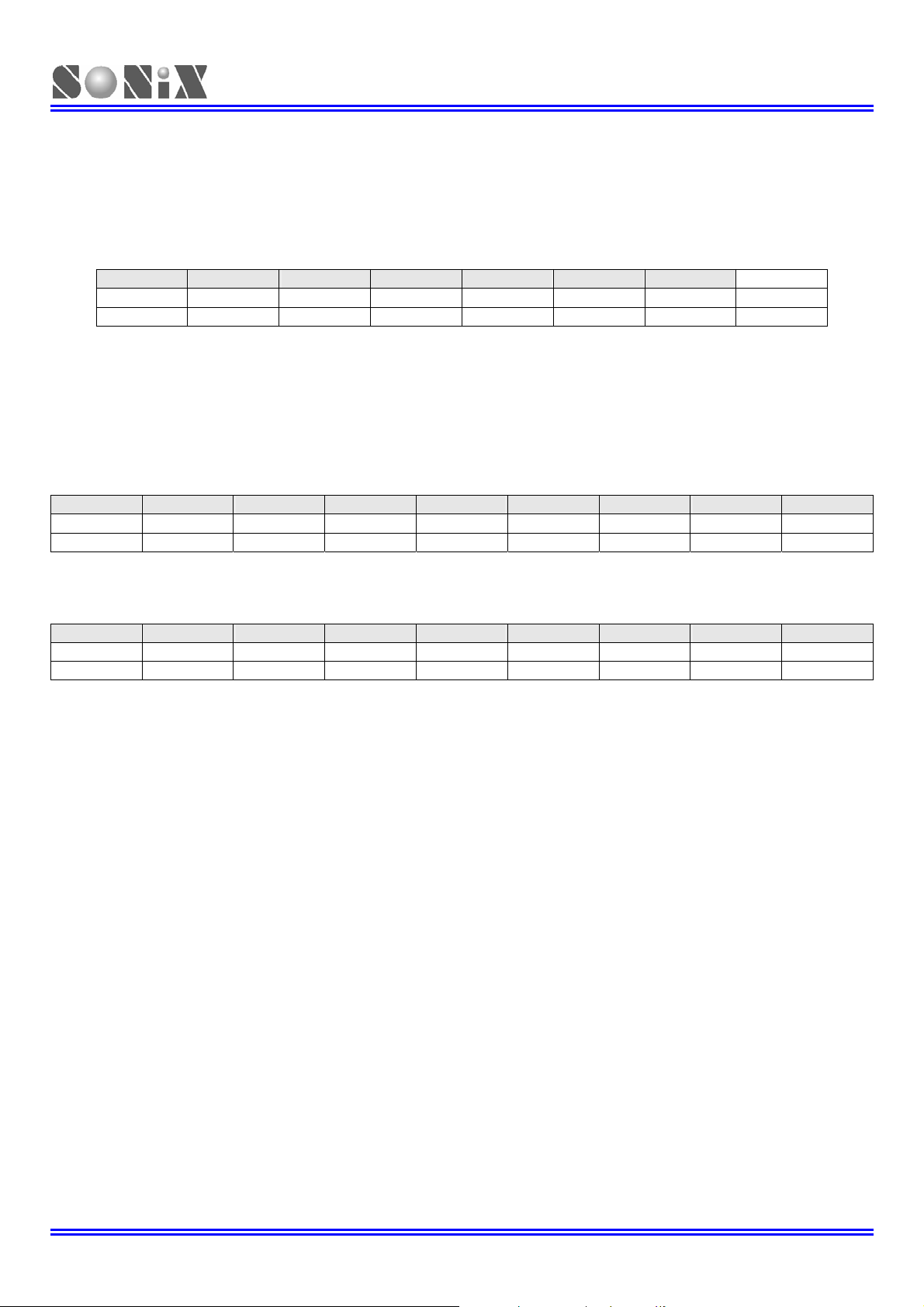
3.3 WORKING REGISTERS
The locations 82H to 84H of RAM bank 0 in data memory stores the specially defined registers such as register R, Y, Z,
respectively shown in the following table. These registers can use as the general purpose of working buffer and be
used to access ROM’s and RAM’s data. For instance, all of the ROM’s table can be looked-up with R, Y and Z
registers. The data of RAM memory can be indirectly accessed with Y and Z registers.
80H 81H 82H 83H 84H 85H
RAM
- - R/W R/W R/W -
3.3.1 Y, Z REGISTERS
The Y and Z registers are the 8-bit buffers. There are three major functions of these registers. First, Y and Z registers
can be used as working registers. Second, these two registers can be used as data pointers for @YZ register. Third,
the registers can be address ROM location in order to look-up ROM data.
Y initial value = XXXX XXXX
084H Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Y
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Z initial value = XXXX XXXX
083H Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
Z
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
The @YZ that is data point_1 index buffer located at address E7H in RAM bank 0. It employs Y and Z registers to
addressing RAM location in order to read/write data through ACC. The Lower 4-bit of Y register is pointed to RAM
bank number and Z register is pointed to RAM address number, respectively. The higher 4-bit data of Y register is
truncated in RAM indirectly access mode.
 Example: If want to read a data from RAM address 25H of bank 0, it can use indirectly addressing mode to
B0MOV Y, #00H ; To set RAM bank 0 for Y register
B0MOV Z, #25H ; To set location 25H for Z register
B0MOV A, @YZ ; To read a data into ACC
 Example: Clear general-purpose data memory area of bank 0 using @YZ register.
MOV A, #0
B0MOV Y, A ; Y = 0, bank 0
MOV A, #07FH
B0MOV Z, A ; Z = 7FH, the last address of the data memory area
CLR_YZ_BUF:
CLR @YZ ; Clear @YZ to be zero
DECMS Z ; Z – 1, if Z= 0, finish the routine
JMP CLR_YZ_BUF ; Not zero
CLR @YZ
END_CLR: ; End of clear general purpose data memory area of bank 0
.
Note: Please consult the “LOOK-UP TABLE DESCRIPTION” about Y, Z register look-up table application.
YBIT7 YBIT6 YBIT5 YBIT4 YBIT3 YBIT2 YBIT1 YBIT0
ZBIT7 ZBIT6 ZBIT5 ZBIT4 ZBIT3 ZBIT2 ZBIT1 ZBIT0
access data as following.
- - R Z Y -
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 24 V1.4
Page 25
SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
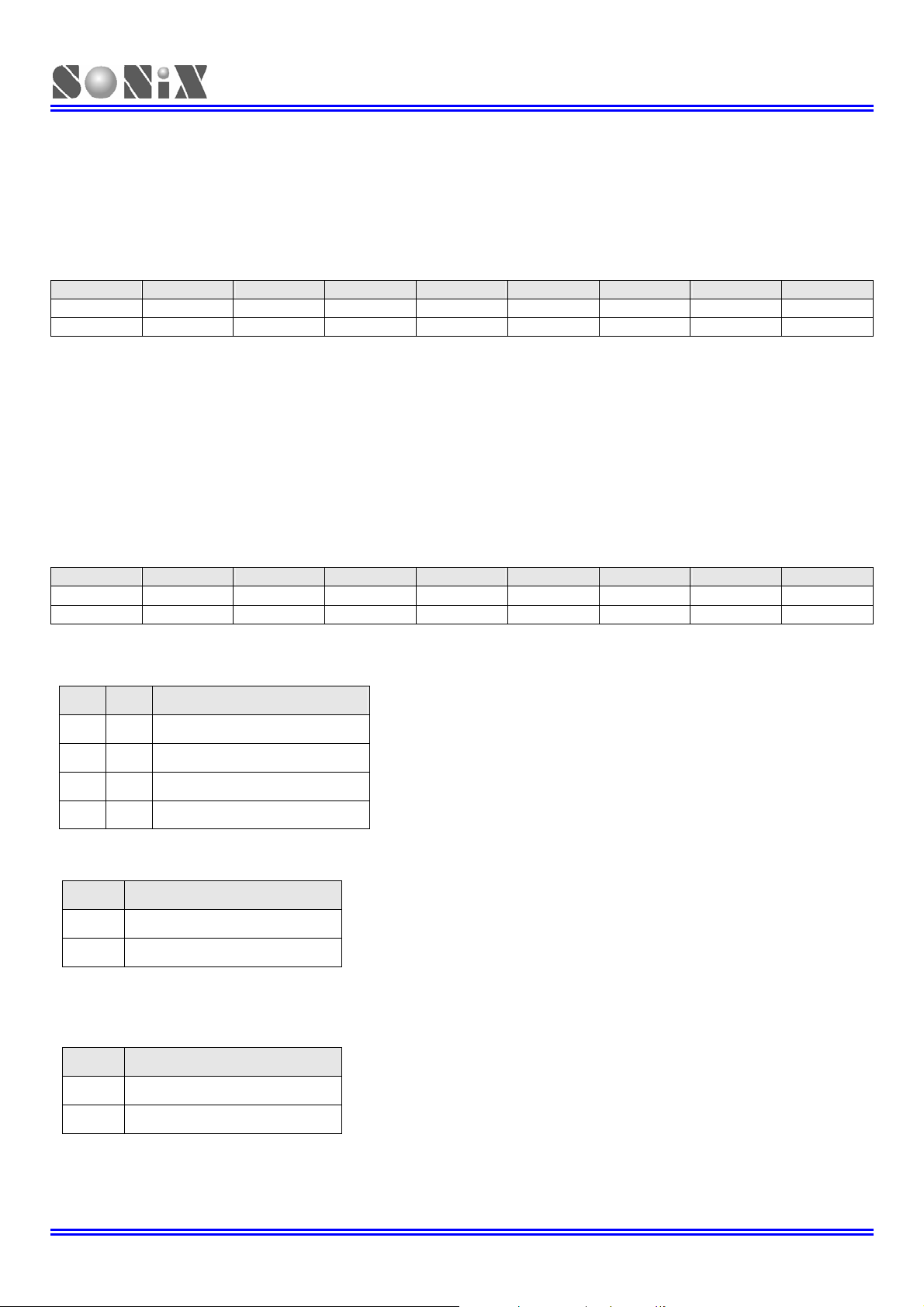
3.3.2 R REGISTERS
There are two major functions of the R register. First, R register can be used as working registers. Second, the R
registers can be store high-byte data of look-up ROM data. After MOVC instruction executed, the high-byte data of a
ROM address will be stored in R register and the low-byte data stored in ACC.
R initial value = XXXX XXXX
082H Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
R
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
¾ Note: Please consult the “LOOK-UP TABLE DESCRIPTION” about R register look-up table application.
RBIT7 RBIT6 RBIT5 RBIT4 RBIT3 RBIT2 RBIT1 RBIT0
3.4 PROGRAM FLAG
The PFLAG includes reset flag, low voltage detect flag, carry flag, decimal carry flag (DC) and zero flag (Z). If the result
of operating is zero or there is carry, borrow occurrence, then these flags will be set to PFLAG register.
PFLAG initial value = 00xx,x000
086H Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
PFLAG
R/W R/W R/W R/W - R/W R/W R/W
NT0 NPD LVD36 LVD24 - C DC Z
3.4.1 RESET FLAG
NT0 NPD Reset Status
0 0 Watch-dog time out
0 1 Reserved
1 0 Reset by LVD
1 1 Reset by external Reset Pin
3.4.2 LVD 2.4V FLAG
LVD24 VDD Status
1 VDD <= 2.4V
0 VDD > 2.4V
Note: This bit is only valid when code option LVD=LVD_M
3.4.3 LVD 3.6V FLAG
LVD36 VDD Status
1 VDD <= 3.6V
0 VDD > 3.6V
Note: This bit is only valid when code option LVD=LVD_H
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 25 V1.4
Page 26

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
3.4.4 CARRY FLAG
C = 1: If executed arithmetic addition with occurring carry signal or executed arithmetic subtraction without borrowing
signal or executed rotation instruction with shifting out logic “1”.
C = 0: If executed arithmetic addition without occurring carry signal or executed arithmetic subtraction with borrowing
signal or executed rotation instruction with shifting out logic “0”.
3.4.5 DECIMAL CARRY FLAG
DC = 1: If executed arithmetic addition with occurring carry signal from low nibble or executed arithmetic subtraction
without borrow signal from high nibble.
DC = 0: If executed arithmetic addition without occurring carry signal from low nibble or executed arithmetic subtraction
with borrow signal from high nibble.
3.4.6 ZERO FLAG
Z = 1: ACC or arithmetic operation result is zero after executing a instruction. Refer instruction set table for
detailed information.
Z = 0: ACC or arithmetic operation result is not zero after executing a instruction. Refer instruction set table
for detailed information.
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 26 V1.4
Page 27

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
3.5 ACCUMULATOR
The ACC is an 8-bits data register responsible for transferring or manipulating data between ALU and data memory. If
the result of operating is zero (Z) or there is carry (C or DC) occurrence, then these flags will be set to PFLAG register.
ACC is not in data memory (RAM), so ACC can’t be access by “B0MOV” instruction during the instant addressing
mode.
 Example: Read and write ACC value.
; Read ACC data and store in BUF data memory
MOV BUF, A
. .
; Write a immediate data into ACC
MOV A, #0FH
. .
; Write ACC data from BUF data memory
MOV A, BUF
. .
The ACC value don’t store in any interrupt service executed. ACC must be exchanged to another data memory defined
by users. Thus, once interrupt occurs, these data must be stored in the data memory based on the user’s program as
follows.
 Example: ACC and working registers protection.
ACCBUF EQU 00H ; ACCBUF is ACC data buffer in bank 0.
INT_SERVICE:
B0XCH A, ACCBUF
B0XCH A, ACCBUF ; Re-load ACC
RETI ; Exit interrupt service vector
¾ Notice: To save and re-load ACC data must be used “B0XCH” instruction, or the PLAGE value maybe
modified by ACC.
B0MOV A, PFLAG
B0MOV PFLAGBUF, A
.
.
B0MOV A, PFLAGBUF
B0MOV PFLAG, A
; B0XCH doesn’t change C, Z flag
; Save PFLAG register in a buffer
; Restore PFLAG register from buffer
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 27 V1.4
Page 28
SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
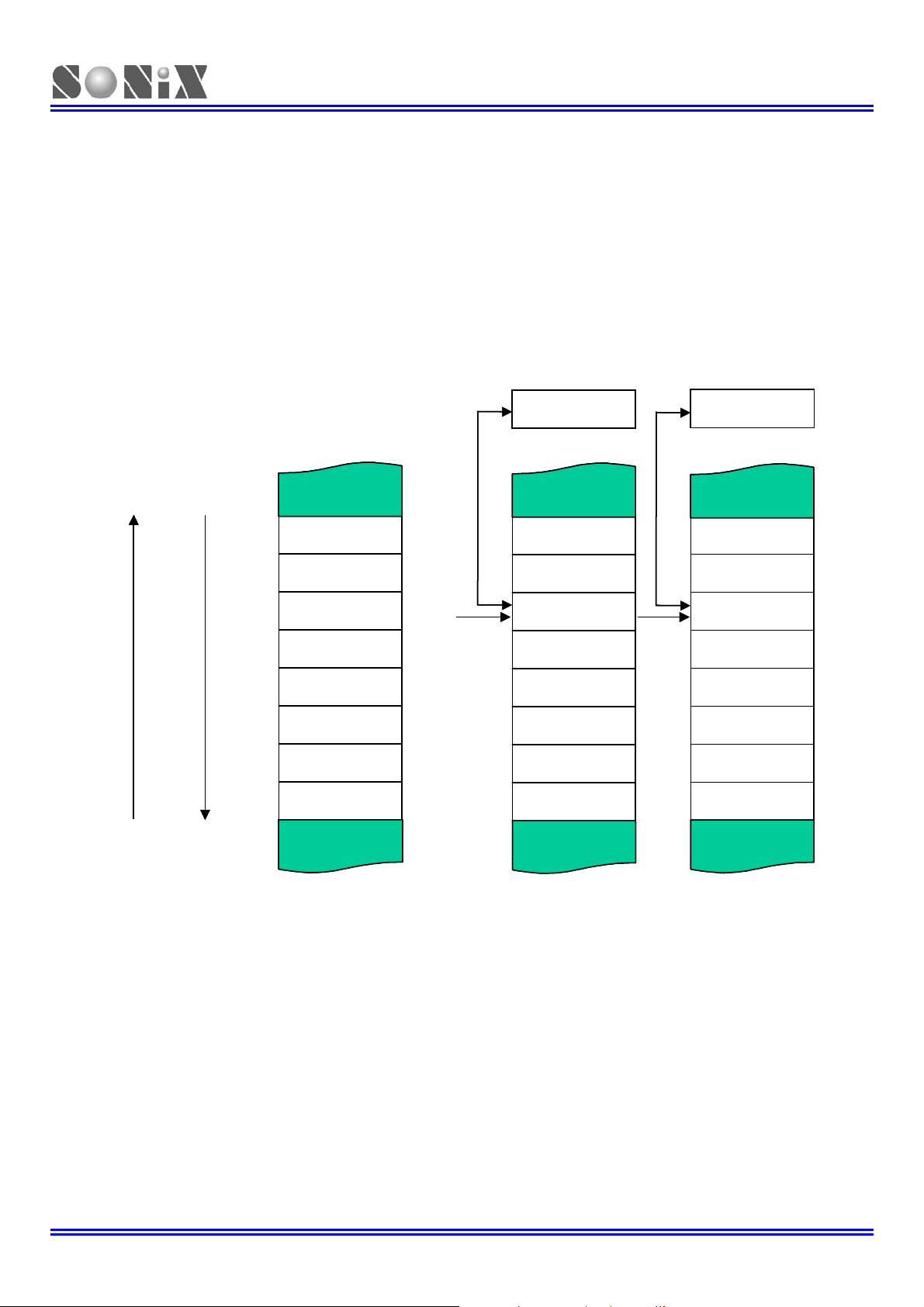
3.6 STACK OPERATIONS
3.6.1 OVERVIEW
The stack buffer of SN8P2710 has 8-level high area and each level is 11-bits length. This buffer is designed to save
and restore program counter’s (PC) data when interrupt service is executed. The STKP register is a pointer designed
to point active level in order to save or restore data from stack buffer for kernel circuit. The STKnH and STKnL are the
12-bit stack buffers to store program counter (PC) data.
STACK BUFFER
STACK BUFFER
PCL
PCL
PCLPCL
STK0L
STK0L
STK0L
RET /
RET /
RETI
RETI
CALL /
CALL /
interrupt
interrupt
STKP = 7
STKP = 7
STKP = 7
PCH
PCH
PCHPCH
STK0H
STK0H
STK0H
STKP + 1
STKP + 1
STKP + 1
STKP - 1
STKP - 1
STKP - 1STKP - 1
STKP = 6
STKP = 6
STKP = 6
STKP = 5
STKP = 5
STKP = 5
STKP = 4
STKP = 4
STKP = 4
STKP = 3
STKP = 3
STKP = 3
STKP = 2
STKP = 2
STKP = 2
STKP = 1
STKP = 1
STKP = 1
STKP = 0
STKP = 0
STKP = 0
STKP
STKPSTKP
Figure 3-3 Stack Operation
STK1H
STK1H
STK1H
STK2H
STK2H
STK2H
STK3H
STK3H
STK3H
STK4H
STK4H
STK4H
STK5H
STK5H
STK5H
STK6H
STK6H
STK6H
STK7H
STK7H
STK7H
STKP
STKPSTKP
STK1L
STK1L
STK1L
STK2L
STK2L
STK2L
STK3L
STK3L
STK3L
STK4L
STK4L
STK4L
STK5L
STK5L
STK5L
STK6L
STK6L
STK6L
STK7L
STK7L
STK7L
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 28 V1.4
Page 29
SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
3.6.2 STACK REGISTERS
The stack pointer (STKP) is a 4-bit register to store the address used to access the stack buffer, 11-bits data memory
(STKnH and STKnL) set aside for temporary storage of stack addresses.
The two stack operations are writing to the top of the stack (Stack-Save) and reading (Stack-Restore) from the top of
stack. Stack-Save operation decrements the STKP and the Stack-Resotre operation increments one time. That makes
the STKP always points to the top address of stack buffer and writes the last program counter value (PC) into the stack
buffer.
The program counter (PC) value is stored in the stack buffer before a CALL instruction executed or during interrupt
service routine. Stack operation is a LIFO type (Last in and first out). The stack pointer (STKP) and stack buffer
(STKnH and STKnL) are located in the system register area bank 0.
STKP (stack pointer) initial value = 0xxx x111
0DFH Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
STKP
R/W - - - - R/W R/W R/W
STKPBn: Stack pointer. (n = 0 ~ 3)
GIE: Global interrupt control bit. 0 = disable, 1 = enable. More detail information is in interrupt chapter.
 Example: Stack pointer (STKP) reset routine.
MOV A, #00000111B
B0MOV STKP, A
STKn (stack buffer) initial value = xxxx xxxx xxxx xxxx, STKn = STKnH + STKnL (n = 7 ~ 0)
0F0H~0FFH Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
STKnH
- - - - - R/W R/W R/W
0F0H~0FFH Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
STKnL
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
STKnH: Store PCH data as interrupt or call executing. The n expressed 0 ~7.
STKnL: Store PCL data as interrupt or call executing. The n expressed 0 ~7.
GIE - - - - STKPB2 STKPB1 STKPB0
- - - - - SnPC10 SnPC9 SnPC8
SnPC7 SnPC6 SnPC5 SnPC4 SnPC3 SnPC2 SnPC1 SnPC0
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 29 V1.4
Page 30
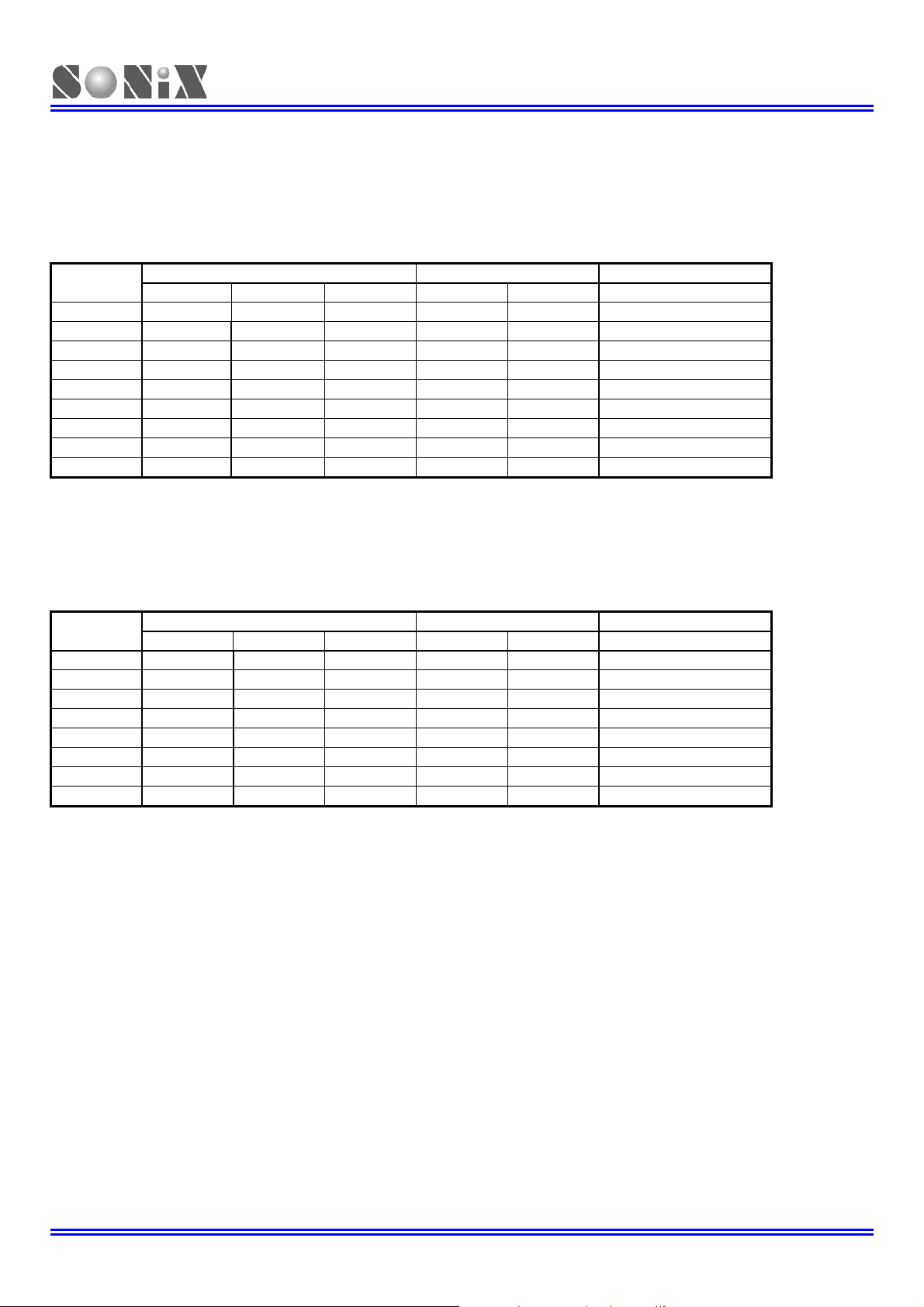
SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
3.6.3 STACK OPERATION EXAMPLE
The two kinds of Stack-Save operations to reference the stack pointer (STKP) and write the program counter contents
(PC) into the stack buffer are CALL instruction and interrupt service. Under each condition, the STKP is decremented
and points to the next available stack location. The stack buffer stores the program counter about the op-code address.
The Stack-Save operation is as following table.
Stack Level
STKPB2 STKPB1 STKPB0 High Byte Low Byte
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
>8
Table 3-1. STKP, STKnH and STKnL relative of Stack-Save Operation
STKP Register Stack Buffer Description
1 1 1 STK0H STK0L
1 1 0 STK1H STK1L
1 0 1 STK2H STK2L
1 0 0 STK3H STK3L
0 1 1 STK4H STK4L
0 1 0 STK5H STK5L
0 0 1 STK6H STK6L
0 0 0 STK7H STK7L
- - - - -
Stack Overflow
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
The RETI instruction is for interrupt service routine. The RET instruction is for CALL instruction. When a Stack-Restore
operation occurs, the STKP is incremented and points to the next free stack location. The stack buffer restores the last
program counter (PC) to the program counter registers. The Stack-Restore operation is as following table.
Stack Level
STKPB2 STKPB1 STKPB0 High Byte Low Byte
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
Table 3-2. STKP, STKnH and STKnL relative of Stack-Restore Operation
STKP Register Stack Buffer Description
0 0 0 STK7H STK7L
0 0 1 STK6H STK6L
0 1 0 STK5H STK5L
0 1 1 STK4H STK4L
1 0 0 STK3H STK3L
1 0 1 STK2H STK2L
1 1 0 STK1H STK1L
1 1 1 STK0H STK0L
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 30 V1.4
Page 31

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
3.7 PROGRAM COUNTER
The program counter (PC) is a 11-bit binary counter separated into the high-byte 3 bits and the low-byte 8 bits. This
counter is responsible for pointing a location in order to fetch an instruction for kernel circuit. Normally, the program
counter is automatically incremented with each instruction during program execution.
Besides, it can be replaced with specific address by executing CALL or JMP instruction. When JMP or CALL
instruction is executed, the destination address will be inserted to bit 0 ~ bit 10.
PC Initial value = xxxx 0000 0000 0000
Bit 15 Bit 14 Bit 13 Bit 12 Bit 11 Bit 10 Bit 9 Bit 8 Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
PC
PCH Initial value = xxxx x000
PCL Initial value = 0000 0000
- - - - - 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0CFH Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
PCH
- - - - - R/W R/W R/W
0CEH Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
PCL
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
- - - - - PC10 PC9 PC8
PC7 PC6 PC5 PC4 PC3 PC2 PC1 PC0
PCH PCL
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 31 V1.4
Page 32

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
3.7.1 ONE ADDRESS SKIPPING
There are 7 instructions (CMPRS, INCS, INCMS, DECS, DECMS, B0BTS0, B0BTS1) with one address skipping
function. If the result of these instructions is matched, the PC will add 2 steps to skip next instruction.
If the condition of bit test instruction is matched, the PC will add 2 steps to skip next instruction.
JMP C0STEP ; Else jump to C0STEP.
.
C0STEP: NOP
B0MOV A, BUF0 ; Move BUF0 value to ACC.
JMP C1STEP ; Else jump to C1STEP.
.
C1STEP: NOP
If the ACC is equal to the immediate data or memory, the PC will add 2 steps to skip next instruction.
JMP C0STEP ; Else jump to C0STEP.
.
C0STEP: NOP
If the result after increasing 1 or decreasing 1 is 0xffh (for DECS and DECMS) or 0x00h (for INCS and INCMS) ,
the PC will add 2 steps to skip next instruction.
INCS instruction:
JMP C0STEP ; Else jump to C0STEP.
.
C0STEP: NOP
INCMS instruction:
JMP C0STEP ; Else jump to C0STEP.
.
C0STEP: NOP
DECS instruction:
JMP C0STEP ; Else jump to C0STEP.
.
C0STEP: NOP
DECMS instruction:
JMP C0STEP ; Else jump to C0STEP.
.
C0STEP: NOP
B0BTS1
B0BTS0
CMPRS
INCS
INCMS
DECS
DECMS
FC ; Skip next instruction, if Carry_flag = 1
FZ ; Skip next instruction, if Zero flag = 0.
A, #12H ; Skip next instruction, if ACC = 12H.
BUF0 ; Skip next instruction, if BUF0 = 0X00H.
BUF0 ; Skip next instruction, if BUF0 = 0X00H.
BUF0 ; Skip next instruction, if BUF0 = 0XFFH.
BUF0 ; Skip next instruction, if BUF0 = 0XFFH.
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 32 V1.4
Page 33

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
3.7.2 MULTI-ADDRESS JUMPING
Users can jump round multi-address by either JMP instruction or ADD M, A instruction (M = PCL) to activate
multi-address jumping function. If carry signal occurs after execution of ADD PCL, A, the carry signal will not affect
PCH register.
 Example: If PC = 0323H (PCH = 03H、PCL = 23H)
; PC = 0323H
MOV A, #28H
B0MOV PCL, A ; Jump to address 0328H
. .
. .
; PC = 0328H . .
MOV A, #00H
B0MOV PCL, A ; Jump to address 0300H
 Example: If PC = 0323H (PCH = 03H、PCL = 23H)
; PC = 0323H
B0ADD PCL, A ; PCL = PCL + ACC, the PCH cannot be changed.
JMP A0POINT ; If ACC = 0, jump to A0POINT
JMP A1POINT ; ACC = 1, jump to A1POINT
JMP A2POINT ; ACC = 2, jump to A2POINT
JMP A3POINT ; ACC = 3, jump to A3POINT
. . ;
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 33 V1.4
Page 34

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
4 ADDRESSING MODE
4.1 OVERVIEW
The SN8P2710 provides three addressing modes to access RAM data, including immediate addressing mode, directly
addressing mode and indirectly address mode. The main purpose of the three different modes is described in the
following:
4.1.1 IMMEDIATE ADDRESSING MODE
The immediate addressing mode uses an immediate data to set up the location (MOV A, #I, B0MOV M,#I) in ACC or
specific RAM.
Immediate addressing mode
MOV A, #12H ; To set an immediate data 12H into ACC
4.1.2 DIRECTLY ADDRESSING MODE
The directly addressing mode uses address number to access memory location (MOV A,12H, MOV 12H,A).
Directly addressing mode
B0MOV A, 12H ; To get a content of location 12H of bank 0 and save in ACC
4.1.3 INDIRECTLY ADDRESSING MODE
The indirectly addressing mode is to set up an address in data pointer registers (Y/Z) and uses MOV instruction to
read/write data between ACC and @YZ register (MOV A,@YZ, MOV @YZ,A).
 Example: Indirectly addressing mode with @YZ register
CLR Y ; To clear Y register to access RAM bank 0.
B0MOV Z, #12H ; To set an immediate data 12H into Z register.
B0MOV A, @YZ ; Use data pointer @YZ reads a data from RAM location
; 012H into ACC.
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 34 V1.4
Page 35

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
4.1.4 TO ACCESS DATA in RAM BANK 0
In the RAM bank 0, this area memory can be read/written by these twoaccess methods.
 Example 1: To use RAM bank0 dedicate instruction (Such as B0xxx instruction).
B0MOV A, 12H ; To move content from location 12H of RAM bank 0 to ACC
 Example 2: To use indirectly addressing mode with @YZ register.
CLR Y ; To clear Y register for accessing RAM bank 0.
B0MOV Z, #12H ; To set an immediate data 12H into Z register.
B0MOV A, @YZ ; Use data pointer @YZ reads a data from RAM location
; 012H into ACC.
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 35 V1.4
Page 36

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
5 SYSTEM REGISTER
5.1 OVERVIEW
The system special register is located at 80h~FFh. The main purpose of system registers is to control the peripheral
hardware of the chip. Using system registers can control I/O ports, ADC, PWM, timers and counters by programming.
The Memory map provides an easy and quick reference source for writing application program.
5.2 SYSTEM REGISTER ARRANGEMENT (BANK 0)
5.2.1 BYTES of SYSTEM REGISTER
SN8P2710
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F
- - R Z Y - PFLAG - - - - - - - - -
8
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
9
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - P4CON -
A
DAM ADM ADB ADR - - - - - - - - - - - PEDGE
B
- - P2M - P4M P5M - - INTRQ INTEN OSCM -
C
P0 - P2 - P4 P5 - - T0M - TC0M TC0C TC1M TC1C TC1R STKP
D
P0UR - P2UR - P4UR P5UR - @YZ - - - - - - - -
E
STK7L STK7H STK6L STK6H STK5L STK5H STK4L STK4H STK3L STK3H STK2L STK2H STK1L STK1H STK0L STK0H
F
WDTR
TC0R PCL PCH
Table 5-1. System Register Arrangement of SN8P2710
Description
PFLAG = ROM page and special flag register. R = Working register and ROM lookup data buffer.
DAM = DAC’s mode register. Y, Z = Working, @YZ and ROM addressing register.
ADB = ADC’s data buffer. ADM = ADC’s mode register.
PnM = Port n input/output mode register. ADR = ADC’s resolution selects register.
INTRQ = Interrupts’ request register. Pn = Port n data buffer.
OSCM = Oscillator mode register. INTEN = Interrupts’ enable register.
T0M = Timer/ Counter 0, Timer/ Counter 1 speed selection . PCH, PCL = Program counter.
TC1M = Timer/Counter 1 mode register. TC0M = Timer/Counter 0 mode register.
TC1C = Timer/Counter 1 counting register. TC0C = Timer/Counter 0 counting register.
STKP = Stack pointer buffer. TC0R = Timer/Counter 0 auto-reload data buffer.
@HL = RAM HL indirect addressing index pointer. TC1R = Timer/Counter 1 auto-reload data buffer.
P4CON= Port 4 configuration setting STK0~STK7 = Stack 0 ~ stack 7 buffer.
¾ Note:
@YZ = RAM YZ indirect addressing index pointer.
a). All of register names had been declared in SONiX 8-bit MCU assembler.
b). One-bit name had been declared in SONiX 8-bit MCU assembler with “F” prefix code.
c). It will get logic “H” data, when use instruction to check empty location.
d). The low nibble of ADR register is read only.
e). “b0bset”, “b0bclr”, ”bset”, ”bclr” instructions only support “R/W” registers.
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 36 V1.4
Page 37

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
5.2.2 BITS of SYSTEM REGISTER
SN8P2710 System register table
Address Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 R/W Remarks
080H
081H
082H RBIT7 RBIT6 RBIT5 RBIT4 RBIT3 RBIT2 RBIT1 RBIT0 R/W R
083H ZBIT7 ZBIT6 ZBIT5 ZBIT4 ZBIT3 ZBIT2 ZBIT1 ZBIT0 R/W Z
084H YBIT7 YBIT6 YBIT5 YBIT4 YBIT3 YBIT2 YBIT1 YBIT0 R/W Y
085H
086H NT0 NPD LVD36 LVD24 - C DC Z R/W PFLAG
087H - - - - - - - - - -
0AEH P4CON7 P4CON6 P4CON 5 P4CON4 P4CON3 P4CON2 P4CON1 P4CON0 W P4CON
0B0H DAENB DAB6 DAB5 DAB4 DAB3 DAB2 DAB1 DAB0 R/W DAM data register
0B1H ADENB ADS EOC GCHS - CHS2 CHS1 CHS0 R/W ADM mode register
0B2H ADB11 ADB10 ADB9 ADB8 ADB7 ADB6 ADB5 ADB4 R ADB data buffer
0B3H - ADCKS1 - ADCKS0 ADB3 ADB2 ADB1 ADB0 R/W ADR register
0B4H - - - - - - - - -
0B5H - - - - - - - - -
0B6H - - - - - - - - -
0B8H - - - - - - - - -
0BFH - - - P00G1 P00G0 - - - R/W PEDGE
0C0H - - - - - - - - -
0C1H - - - - - - - - -
0C2H P27M P26M P25M P24M P23M P22M P21M P20M R/W P2M I/O direction
0C3H - - - - - - - - -
0C4H P47M P46M P45M P44M P43M P42M P41M P40M R/W P4M I/O direction
0C5H - P56M P55M P54M P53M P52M P51M P50M R/W P5M I/O direction
0C8H - TC1IRQ TC0IRQ - - - P01IRQ P00IRQ R/W INTRQ
0C9H - TC1IEN TC0IEN - - - P01IEN P00IEN R/W INTEN
0CAH - - - - CPUM0 CLKMD STPHX - R/W OSCM
0CCH WDTR7 WDTR6 WDTR5 WDTR4 WDTR3 WDTR2 WDTR1 WDTR0 W WDTR
0CDH TC0R7 TC0R6 TC0R5 TC0R4 TC0R3 TC0R2 TC0R1 TC0R0 W TC0R
0CEH PC7 PC6 PC5 PC4 PC3 PC2 PC1 PC0 R/W PCL
0CFH - - - - - PC10 PC9 PC8 R/W PCH
0D0H - - - - P03 P02 P01 P00 R P0 data buffer
0D1H - - - - - - - - -
0D2H P27 P26 P25 P24 P23 P22 P21 P20 R/W P2 data buffer
0D3H - - - - - - - - -
0D4H P47 P46 P45 P44 P43 P42 P41 P40 R/W P4 data buffer
0D5H - P56 P55 P54 P53 P52 P51 P50 R/W P5 data buffer
0D8H - - - - TC1X8 TC0X8 - - R/W T0M
0D9H - - - - - - - - -
0DAH TC0ENB TC0rate2 TC0rate1 TC0rate0 TC0CKS ALOAD0 TC0OUT
0DBH TC0C7 TC0C6 TC0C5 TC0C4 TC0C3 TC0C2 TC0C1 TC0C0 R/W TC0C
0DCH TC1ENB TC1rate2 TC1rate1 TC1rate0 TC1CKS ALOAD1 TC1OUT
0DDH TC1C7 TC1C6 TC1C5 TC1C4 TC1C3 TC1C2 TC1C1 TC1C0 R/W TC1C
0DEH TC1R7 TC1R6 TC1R5 TC1R4 TC1R3 TC1R2 TC1R1 TC1R0 W TC1R
0DFH GIE - - - - STKPB2 STKPB1 STKPB0 R/W STKP stack pointer
0E0H - - - - - P02R P01R P00R W P0UR
0E1H - - - - - - - - -
0E2H P27R P26R P25R P24R P23R P22R P21R P20R W P2UR
0E3H - - - - - - - - -
0E4H P47R P46R P45R P44R P43R P42R P41R P40R W P4UR
0E5H - P56R P54R P54R P53R P52R P51R P50R W P5UR
0E6H - - - - - - - - -
0E7H @YZ7 @YZ6 @YZ5 @YZ4 @YZ3 @YZ2 @YZ1 @YZ0 R/W @YZ index pointer
0E9H - - - - - - - - -
0F0H S7PC7 S7PC6 S7PC5 S7PC4 S7PC3 S7PC2 S7PC1 S7PC0 R/W STK7L
0F1H - - - - - S7PC10 S7PC9 S7PC8 R/W STK7H
0F2H S6PC7 S6PC6 S6PC5 S6PC4 S6PC3 S6PC2 S6PC1 S6PC0 R/W STK6L
0F3H - - - - - S6PC10 S6PC9 S6PC8 R/W STK6H
PWM0OUT
PWM1OUT
R/W TC0M
R/W TC1M
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 37 V1.4
Page 38

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
Address Bit7 Bit6 Bit5 Bit4 Bit3 Bit2 Bit1 Bit0 R/W Remarks
0F4H S5PC7 S5PC6 S5PC5 S5PC4 S5PC3 S5PC2 S5PC1 S5PC0 R/W STK5L
0F5H - - - - - S5PC10 S5PC9 S5PC8 R/W STK5H
0F6H S4PC7 S4PC6 S4PC5 S4PC4 S4PC3 S4PC2 S4PC1 S4PC0 R/W STK4L
0F7H - - - - - S4PC10 S4PC9 S4PC8 R/W STK4H
0F8H S3PC7 S3PC6 S3PC5 S3PC4 S3PC3 S3PC2 S3PC1 S3PC0 R/W STK3L
0F9H - - - - - S3PC10 S3PC9 S3PC8 R/W STK3H
0FAH S2PC7 S2PC6 S2PC5 S2PC4 S2PC3 S2PC2 S2PC1 S2PC0 R/W STK2L
0FBH - - - - - S2PC10 S2PC9 S2PC8 R/W STK2H
0FCH S1PC7 S1PC6 S1PC5 S1PC4 S1PC3 S1PC2 S1PC1 S1PC0 R/W STK1L
0FDH - - - - - S1PC10 S1PC9 S1PC8 R/W STK1H
0FEH S0PC7 S0PC6 S0PC5 S0PC4 S0PC3 S0PC2 S0PC1 S0PC0 R/W STK0L
0FFH - - - - - S0PC10 S0PC9 S0PC8 R/W STK0H
Table. Bit System Register Table of SN8P2710
Note:
a). To avoid system error, please be sure to put all the “0” as it indicates in the above table
b). All of register name had been declared in SONiX 8-bit MCU assembler.
c). One-bit name had been declared in SONiX 8-bit MCU assembler with “F” prefix code.
d). “b0bset”, “b0bclr”, ”bset”, ”bclr” instructions only support “R/W” registers.
e). For detail description please refer file of “System Register Quick Reference Table”
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 38 V1.4
Page 39

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
6 RESET
6.1 OVERVIEW
The system would be reset in three conditions as following.
z Power on reset
z Watchdog reset
z Brown out reset
z External reset (only supports external reset pin enable situation)
When any reset condition occurs, all system registers keep initial status, program stops and program counter is
cleared. After reset status released, the system boots up and program starts to execute from ORG 0.
Finishing any reset sequence needs some time. The system provides complete procedures to make the power on
reset successful. For different oscillator types, the reset time is different. That causes the VDD rise rate and start-up
time of different oscillator is not fixed. RC type oscillator’s start-up time is very short, but the crystal type is longer.
Under client terminal application, users have to take care the power on reset time for the master terminal requirement.
The reset timing diagram is as following.
Power
External Reset
Watchdog Reset
System Status
VDD
VSS
VDD
VSS
Watchdog Normal Run
Watchdog Stop
System Normal Run
System Stop
LVD Detect Level
Power On
Delay Time
External Reset
Low Detect
External Reset
High Detect
External
Reset Delay
Time
Watchdog
Overflow
Watchdog
Reset Delay
Time
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 39 V1.4
Page 40

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
6.2 POWER ON RESET
The power on reset depend no LVD operation for most power-up situations. The power supplying to system is a rising
curve and needs some time to achieve the normal voltage. Power on reset sequence is as following.
z Power-up: System detects the power voltage up and waits for power stable.
z External reset (only external reset pin enable): System checks external reset pin status. If external reset pin is
not high level, the system keeps reset status and waits external reset pin released.
z System initialization: All system registers is set as initial conditions and system is ready.
z Oscillator warm up: Oscillator operation is successfully and supply to system clock.
z Program executing: Power on sequence is finished and program executes from ORG 0.
6.3 WATCHDOG RESET
Watchdog reset is a system protection. In normal condition, system works well and clears watchdog timer by program.
Under error condition, system is in unknown situation and watchdog can’t be clear by program before watchdog timer
overflow. Watchdog timer overflow occurs and the system is reset. After watchdog reset, the system restarts and
returns normal mode. Watchdog reset sequence is as following.
z Watchdog timer status: System checks watchdog timer overflow status. If watchdog timer overflow occurs, the
system is reset.
z System initialization: All system registers is set as initial conditions and system is ready.
z Oscillator warm up: Oscillator operation is successfully and supply to system clock.
z Program executing: Power on sequence is finished and program executes from ORG 0.
Watchdog timer application note is as following.
z Before clearing watchdog timer, check I/O status and check RAM contents can improve system error.
z Don’t clear watchdog timer in interrupt vector and interrupt service routine. That can improve main routine fail.
z Clearing watchdog timer program is only at one part of the program. This way is the best structure to enhance the
watchdog timer function.
Note: Please refer to the “WATCHDOG TIMER” about watchdog timer detail information.
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 40 V1.4
Page 41

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
6.4 BROWN OUT RESET
6.4.1 BROWN OUT DESCRIPTION
The brown out reset is a power dropping condition. The power drops from normal voltage to low voltage by external
factors (e.g. EFT interference or external loading changed). The brown out reset would make the system not work well
or executing program error.
VDD
System Work
Well Area
V1
V2
VSS
Brown Out Reset Diagram
The power dropping might through the voltage range that’s the system dead-band. The dead-band means the power
range can’t offer the system minimum operation power requirement. The above diagram is a typical brown out reset
diagram. There is a serious noise under the VDD, and VDD voltage drops very deep. There is a dotted line to separate
the system working area. The above area is the system work well area. The below area is the system work error area
called dead-band. V1 doesn’t touch the below area and not effect the system operation. But the V2 and V3 is under the
below area and may induce the system error occurrence. Let system under dead-band includes some conditions.
DC application:
The power source of DC application is usually using battery. When low battery condition and MCU drive any loading,
the power drops and keeps in dead-band. Under the situation, the power won’t drop deeper and not touch the system
reset voltage. That makes the system under dead-band.
AC application:
In AC power application, the DC power is regulated from AC power source. This kind of power usually couples with AC
noise that makes the DC power dirty. Or the external loading is very heavy, e.g. driving motor. The loading operating
induces noise and overlaps with the DC power. VDD drops by the noise, and the system works under unstable power
situation.
The power on duration and power down duration are longer in AC application. The system power on sequence
protects the power on successful, but the power down situation is like DC low battery condition. When turn off the AC
power, the VDD drops slowly and through the dead-band for a while.
V3
System Work
Error Area
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 41 V1.4
Page 42

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
6.4.2 THE SYSTEM OPERATING VOLTAGE DECSRIPTION
To improve the brown out reset needs to know the system minimum operating voltage which is depend on the system
executing rate and power level. Different system executing rates have different system minimum operating voltage.
The electrical characteristic section shows the system voltage to executing rate relationship.
System Mini.
Vdd (V)
Normal Operating
Area
Operating Voltage.
Dead-Band Area
Reset Area
System Rate (Fcpu)
System Reset
Voltage.
Normally the system operation voltage area is higher than the system reset voltage to VDD, and the reset voltage is
decided by LVD detect level. The system minimum operating voltage rises when the system executing rate upper even
higher than system reset voltage. The dead-band definition is the system minimum operating voltage above the system
reset voltage.
6.4.3 BROWN OUT RESET IMPROVEMENT
How to improve the brown reset condition? There are some methods to improve brown out reset as following.
z LVD reset
z Watchdog reset
z Reduce the system executing rate
z External reset circuit. (Zener diode reset circuit, Voltage bias reset circuit, External reset IC)
Note: 1. The “ Zener diode reset circuit”, “Voltage bias reset circuit” and “External reset IC” can
completely improve the brown out reset, DC low battery and AC slow power down conditions.
2. For AC power application and enhance EFT performance, the system clock is 4MHz/4 (1 mips)
and use external reset (“ Zener diode reset circuit”, “Voltage bias reset circuit”, “External reset
IC”). The structure can improve noise effective and get good EFT characteristic.
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 42 V1.4
Page 43

LVD reset:
SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
Power
System Status
VDD
VSS
System Normal Run
System Stop
LVD Detect Voltage
Power is below LVD Detect
Voltage and System Reset.
Power On
Delay Time
The LVD (low voltage detector) is built-in Sonix 8-bit MCU to be brown out reset protection. When the VDD drops and
is below LVD detect voltage, the LVD would be triggered, and the system is reset. The LVD detect level is different by
each MCU. The LVD voltage level is a point of voltage and not easy to cover all dead-band range. Using LVD to
improve brown out reset is depend on application requirement and environment. If the power variation is very deep,
violent and trigger the LVD, the LVD can be the protection. If the power variation can touch the LVD detect level and
make system work error, the LVD can’t be the protection and need to other reset methods. More detail LVD
information is in the electrical characteristic section.
Watchdog reset:
The watchdog timer is a protection to make sure the system executes well. Normally the watchdog timer would be
clear at one point of program. Don’t clear the watchdog timer in several addresses. The system executes normally and
the watchdog won’t reset system. When the system is under dead-band and the execution error, the watchdog timer
can’t be clear by program. The watchdog is continuously counting until overflow occurrence. The overflow signal of
watchdog timer triggers the system to reset, and the system return to normal mode after reset sequence. This method
also can improve brown out reset condition and make sure the system to return normal mode.
If the system reset by watchdog and the power is still in dead-band, the system reset sequence won’t be successful
and the system stays in reset status until the power return to normal range.
Reduce the system executing rate:
If the system rate is fast and the dead-band exists, to reduce the system executing rate can improve the dead-band.
The lower system rate is with lower minimum operating voltage. Select the power voltage that’s no dead-band issue
and find out the mapping system rate. Adjust the system rate to the value and the system exits the dead-band issue.
This way needs to modify whole program timing to fit the application requirement.
External reset circuit:
The external reset methods also can improve brown out reset and is the complete solution. There are three external
reset circuits to improve brown out reset including “Zener diode reset circuit”, “Voltage bias reset circuit” and “External
reset IC”. These three reset structures use external reset signal and control to make sure the MCU be reset under
power dropping and under dead-band. The external reset information is described in the next section.
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 43 V1.4
Page 44

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
6.5 EXTERNAL RESET
External reset function is controlled by “Reset_Pin” code option. Set the code option as “Reset” option to enable
external reset function. External reset pin is Schmitt Trigger structure and low level active. The system is running when
reset pin is high level voltage input. The reset pin receives the low voltage and the system is reset. The external reset
operation actives in power on and normal running mode. During system power-up, the external reset pin must be high
level input, or the system keeps in reset status. External reset sequence is as following.
z External reset (only external reset pin enable): System checks external reset pin status. If external reset pin is
not high level, the system keeps reset status and waits external reset pin released.
z System initialization: All system registers is set as initial conditions and system is ready.
z Oscillator warm up: Oscillator operation is successfully and supply to system clock.
z Program executing: Power on sequence is finished and program executes from ORG 0.
The external reset can reset the system during power on duration, and good external reset circuit can protect the
system to avoid working at unusual power condition, e.g. brown out reset in AC power application…
6.6 EXTERNAL RESET CIRCUIT
6.6.1 Simply RC Reset Circuit
VDD
R1
47K ohm
R2
100 ohm
C1
0.1uF
This is the basic reset circuit, and only includes R1 and C1. The RC circuit operation makes a slow rising signal into
reset pin as power up. The reset signal is slower than VDD power up timing, and system occurs a power on signal
from the timing difference.
R
VSS
T
S
MCU
VCC
GND
Note: The reset circuit is no any protection against unusual power or brown out reset.
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 44 V1.4
Page 45

6.6.2 Diode & RC Reset Circuit
SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
VDD
C1
R1
47K ohm
R2
100 ohm
R
VSS
T
S
MCU
VCC
GND
DIODE
0.1uF
This is the better reset circuit. The R1 and C1 circuit operation is like the simply reset circuit to make a power on signal.
The reset circuit has a simply protection against unusual power. The diode offers a power positive path to conduct
higher power to VDD. It is can make reset pin voltage level to synchronize with VDD voltage. The structure can
improve slight brown out reset condition.
Note: The R2 100 ohm resistor of “Simply reset circuit” and “Diode & RC reset circuit” is necessary to limit
any current flowing into reset pin from external capacitor C in the event of reset pin breakdown due
to Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) or Electrical Over-stress (EOS).
6.6.3 Zener Diode Reset Circuit
VDD
R1
33K ohm
Vz
R2
10K ohm
The zener diode reset circuit is a simple low voltage detector and can improve brown out reset condition
completely. Use zener voltage to be the active level. When VDD voltage level is above “Vz + 0.7V”, the C terminal of
the PNP transistor outputs high voltage and MCU operates normally. When VDD is below “Vz + 0.7V”, the C terminal
of the PNP transistor outputs low voltage and MCU is in reset mode. Decide the reset detect voltage by zener
specification. Select the right zener voltage to conform the application.
B
R3
40K ohm
E
Q1
S
R
T
C
MCU
VSS
VCC
GND
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 45 V1.4
Page 46

6.6.4 Voltage Bias Reset Circuit
R1
47K ohm
R2
10K ohm
B
R3
2K ohm
SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
VDD
E
Q1
S
R
T
C
MCU
VSS
VCC
GND
The voltage bias reset circuit is a low cost voltage detector and can improve brown out reset condition completely.
The operating voltage is not accurate as zener diode reset circuit. Use R1, R2 bias voltage to be the active level. When
VDD voltage level is above or equal to “0.7V x (R1 + R2) / R1”, the C terminal of the PNP transistor outputs high
voltage and MCU operates normally. When VDD is below “0.7V x (R1 + R2) / R1”, the C terminal of the PNP transistor
outputs low voltage and MCU is in reset mode.
Decide the reset detect voltage by R1, R2 resistances. Select the right R1, R2 value to conform the application. In the
circuit diagram condition, the MCU’s reset pin level varies with VDD voltage variation, and the differential voltage is
0.7V. If the VDD drops and the voltage lower than reset pin detect level, the system would be reset. If want to make the
reset active earlier, set the R2 > R1 and the cap between VDD and C terminal voltage is larger than 0.7V. The external
reset circuit is with a stable current through R1 and R2. For power consumption issue application, e.g. DC power
system, the current must be considered to whole system power consumption.
Note: Under unstable power condition as brown out reset, “Zener diode rest circuit” and “Voltage bias
reset circuit” can protects system no any error occurrence as power dropping. When power drops
below the reset detect voltage, the system reset would be triggered, and then system executes
reset sequence. That makes sure the system work well under unstable power situation.
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 46 V1.4
Page 47

6.6.5 External Reset IC
VDD
Reset
Capacitor
IC
Bypass
0.1uF
RST
VDD
R
S
T
SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
MCU
VSS
VSS
VCC
GND
The external reset circuit also use external reset IC to enhance MCU reset performance. This is a high cost and good
effect solution. By different application and system requirement to select suitable reset IC. The reset circuit can
improve all power variation.
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 47 V1.4
Page 48

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
7 OSCILLATORS
7.1 OVERVIEW
The SN8P2710 highly performs the dual clock micro-controller system. The dual clocks are high-speed clock and
low-speed clock. The high-speed clock frequency is supplied through the external oscillator circuit. The low-speed
clock frequency is supplied through on-chip RC oscillator circuit.
STPHX
High_Clk code option
Fcpu code option
CLKMD
XIN
XOUT
z Fosc = Fhosc (External high clock) in normal mode
z Fosc = Flosc (Internal low RC clock) in slow mode
z Fosc is system clock, Fcpu is instruction cycle clock
z Fcpu = Fosc/1 ~ Fosc/8 in normal mode
z Fcpu = Fosc/4 in slow mode
The system clock is required by the following peripheral modules:
9 Timer ( TC0 / TC1 / Watchdog timer)
9 PWM output (PWM0, PWM1)
9 Buzzer output (TC0OUT, TC1OUT)
9 ADC converter
HXOSC.
CPUM 0
LXOSC.
Fosc
÷4 or ÷ 8 (Noise Filter code option Enable)
÷1 ~ ÷ 8 (Noise Filter code option Disable)
Fosc
÷ 4
Figure 7-1 System Clock Block Diagram
Fcpu
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 48 V1.4
Page 49

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
7.1.1 OSCM REGISTER DESCRIPTION
The OSCM register is an oscillator control register. It can control oscillator select, system mode.
OSCM initial value = xxx0 000x
0CAH Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
OSCM
- - - - R/W R/W R/W -
Bit [4:3] CPUM 0: CPU operating mode control bit.
0 = normal mode
1 = sleep (power down) mode. Always enter normal mode after wakeup.
Bit 2 CLKMD: Select instruction cycle clock (Fcpu) source
0 Fcpu came form External high clock (Fhosc). Operation mode is normal mode.
1 Fcpu came from Internal low clock (Flosc). Operation mode is slow mode.
Bit1 STPHX: Stop High clock control bit.
0=High clock free running.
1=High clock stop.
- - - - CPUM0 CLKMD STPHX -
7.1.2 EXTERNAL HIGH-SPEED OSCILLATOR
The high clock oscillator of SN8P2710 can be configured as four different oscillator types. There are external RC
oscillator modes, high crystal/resonator mode (12M code option), standard crystal/resonator mode (4M code option).
For different application, the users can select one of suitable oscillator mode by programming “High_Clk” code option
to generate system high-speed clock source after reset.
 Example: Stop external high-speed oscillator.
B0BSET FSTPHX ; To stop external high-speed oscillator only.
B0BSET FCPUM0 ; To stop external high-speed oscillator and internal low-speed
; oscillator called power down mode (sleep mode).
7.1.3 HIGH CLOCK OSCILLATOR CODE OPTION
SN8P2710 provide four oscillator modes for different applications. These modes are 4M, 12M and RC. The main
purpose is to support different oscillator types and frequencies. High-speed crystal needs more current but the low one
doesn’t. For crystals, there are three steps to select. User can select oscillator mode from Code Option table before
compiling. The table is as follow.
Code Option Content Function Description
Ext_RC
High_Clk
12M_X’tal High speed crystal /resonator (e.g. 12MHz ~ 16MHz) for high clock oscillator.
4M_X’tal Middle speed crystal /resonator (e.g. 4MHz ~ 10Mhz) for high clock oscillator.
Low cost external RC oscillator for high clock oscillator.
Output the Fcpu clock from Xout pin.
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 49 V1.4
Page 50

7.1.4 SYSTEM OSCILLATOR CIRCUITS
SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
20PF
CRYSTAL
20PF
Figure 7-2. Crystal/Ceramic Oscillator
R
C
Figure 7-3. RC Oscillator
VDD
XIN
XOUT
VSS
VDD
XIN
XOUT
VSS
MCU
MCU
External Clock Input
Figure 7-4. External clock input
¾ Note1: The VDD and VSS of external oscillator circuit must be from the micro-controller. Don’t connect
them from the neighbor power terminal.
¾ Note2: The external clock input mode can select RC type oscillator or crystal type oscillator of the code
option and input the external clock into XIN pin.
¾ Note3: The power and ground of external oscillator circuit must be connected from the micro-controller’s
VDD and VSS. It is necessary to step up the performance of the whole system.
VDD
XIN
XOUT
VSS
MCU
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 50 V1.4
Page 51

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
7.1.5 External RC Oscillator Frequency Measurement
There is one way to get the Fosc frequency of external RC oscillator by instruction cycle (Fcpu). We can get the Fosc
frequency of external RC from the Fcpu frequency. The sub-routine to get Fcpu frequency of external oscillator is as
the following.
Example: Fcpu instruction cycle of external oscillator
B0BSET P2M.0 ; Set P2.0 to be output mode for outputting Fcpu toggle
signal.
@@:
B0BSET P2.0 ; Output Fcpu toggle signal in low-speed clock mode.
B0BCLR P2.0 ; Measure the Fcpu frequency by oscilloscope.
JMP @B
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 51 V1.4
Page 52

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
7.2 INTERNAL LOW-SPEED OSCILLATOR
The internal low-speed oscillator is built in the micro-controller. The low-speed clock’s source is a RC type oscillator
circuit. The low-speed clock can supplies clock for system clock, timer counter, watchdog timer, and so on.
 Example: Stop internal low-speed oscillator.
B0BSET FCPUM0 ; To stop external high-speed oscillator and internal low-speed
; oscillator called power down mode (sleep mode).
¾ Note: The internal low-speed clock can’t be turned off individually. It is controlled by CPUM0 bit of OSCM
register.
The low-speed oscillator uses RC type oscillator circuit. The frequency is affected by the voltage and temperature of
the system. In common condition, the frequency of the RC oscillator is about 16KHz at 3V and 32KHz at 5V. The
relative between the RC frequency and voltage is as following.
Internal RC vs. VDD
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
Fintrc (KHz)
5
0
1.80 2.00 2.50 3.00 3.50 4.00 4.50 5.00 5.50 6.00 6.50
7.329
25.338
22.003
18.668
15.333
11.998
8.663
32.008
28.673
VDD (Volts)
Figure 7-5. Internal RC vs. VDD Diagram
 Example: To measure the internal RC frequency is by instruction cycle (Fcpu). The internal RC frequency is
the Fcpu multiplied by 4. So we can get the Fosc frequency of internal RC from the Fcpu
frequency.
B0BSET P2M.0 ; Set P2.0 to be output mode for outputting Fcpu toggle signal.
B0BSET FCLKMD ; Switch the system clock to internal low-speed clock mode.
@@:
B0BSET P2.0 ; Output Fcpu toggle signal in low-speed clock mode.
B0BCLR P2.0 ; Measure the Fcpu frequency by oscilloscope.
JMP @B
38.678
35.343
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 52 V1.4
Page 53

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
7.3 SYSTEM MODE DESCRIPTION
7.3.1 OVERVIEW
The chip is featured with low power consumption by switching around three different modes as following.
In actual application, the user can adjust the chip’s controller to work in these three modes by using OSCM register.
7.3.2 NORMAL MODE
In normal mode, the system clock source is external high-speed clock. After power on, the system works under normal
mode. All software and hardware are executed and working. In normal mode, system can get into power down mode
and slow mode.
7.3.3 SLOW MODE
In slow mode, the system clock source is internal low-speed RC clock. To set CLKMD = 1, the system switch to slow
mode. In slow mode, the system works as normal mode but the slower clock. The system in slow mode can get into
normal mode and power down mode. To set STPHX = 1 to stop the external high-speed oscillator, and then the
system consumes less power.
7.3.4 POWER DOWN (SLEEP) MODE
The power down mode is also called sleep mode. The chip stops working as sleeping status. The power consumption
is very less almost to zero. The power down mode is usually applied to low power consuming system as battery power
productions. To set CUPM0 = 1, the system gets into power down mode. The external high-speed and low-speed
oscillators are turned off. The system can be waked up by P0 (P0.0, P0.1, P0.2) wakeup trigger signal(P0.0, P0.1, P0.2
level change).
Note:
¾ Watch_Dog code option = “Enable”
Stop in power down (sleep) mode.
Enable in normal mode mode.
¾ Watch_Dog code option = “Always_ON”.
Enable in normal mode and power down (sleep) mode.
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 53 V1.4
Page 54

7.4 SYSTEM MODE CONTROL
7.4.1 SN8P2710 SYSTEM MODE BLOCK DIAGRAM
Power Down Mode
Power Down Mode
(Sleep Mode)
(Sleep Mode)
P0 wake-up function active.
P0 wake-up function active.
External reset circuit active.
External reset circuit active.
CPUM0 = 1
CPUM0 = 1
CLKMD = 1
CLKMD = 1
Normal Mode Slow Mode
Normal Mode Slow Mode
Figure 7-6. SN8P2710 System Mode Block Diagram
CLKMD = 0
CLKMD = 0
SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
POWER
MODE NORMAL SLOW
HX osc. Running By STPHX Stop
LX osc. Running Running Stop
CPU instruction Executing Executing Stop
TC0/TC1 *Active *Active Inactive
Watchdog timer Active Active
Internal
interrupt
External
interrupt
Wakeup source - -
All active All active All inactive
All active All active All inactive
Table 7-1. Operating Mode Description
DOWN
(SLEEP)
By Watchdog
code option
P0, Reset by
RST, LVD,
*Watchdog
REMARK
* Active by
program
* Watchdog
code option
must be
“Always_ON”
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 54 V1.4
Page 55

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
7.4.2 SYSTEM MODE SWITCHING
Switch normal/slow mode to power down (sleep) mode.
CPUM0 = 1
B0BSET FCPUM0 ; Set CPUM0 = 1.
During the sleep, only the wakeup pin and reset can wakeup the system back to the normal mode.
Switch normal mode to slow mode.
B0BSET FCLKMD ;To set CLKMD = 1, Change the system into slow mode
B0BSET FSTPHX ;To stop external high-speed oscillator for power saving.
¾ Note: To stop high-speed oscillator is not necessary and user can omit it.
Switch slow mode to normal mode (The external high-speed oscillator is still running)
B0BCLR FCLKMD ;To set CLKMD = 0
Switch slow mode to normal mode (The external high-speed oscillator stops)
If external high clock stop and program want to switch back normal mode. It is necessary to delay at least 10mS for
external clock stable.
B0BCLR FSTPHX ; Turn on the external high-speed oscillator.
B0MOV Z, #27 ; If VDD = 5V, internal RC=32KHz (typical) will delay
@@: DECMS Z ; 0.125ms X 81 = 10.125ms for external clock stable
JMP @B
;
B0BCLR FCLKMD ; Change the system back to the normal mode
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 55 V1.4
Page 56

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
7.5 WAKEUP TIME
7.5.1 OVERVIEW
The external high-speed oscillator needs a delay time from stopping to operating. The delay is very necessary and
makes the oscillator to work stably. Some conditions during system operating, the external high-speed oscillator often
runs and stops. Under these conditions, the delay time for external high-speed oscillator restart is called wakeup time.
There are two conditions need wakeup time. One is power down mode to normal mode. The other one is slow mode to
normal mode. For the first case, SN8P2710 provides 4096 oscillator clocks to be the wakeup time. However, in the last
case, users need to make the wakeup time by themselves.
7.5.2 HARDWARE WAKEUP
When the system is in power down mode (sleep mode), the external high-speed oscillator stops. For wakeup into
normal, SN8P2710 provides 4096 external high-speed oscillator clocks to be the wakeup time for warming up the
oscillator circuit. After the wakeup time, the system goes into the normal mode. The value of the wakeup time is as
following.
The Wakeup time = 1/Fosc * 3584 (sec) + X’tal settling time
The x’tal settling time is depended on the x’tal type. Typically, it is about 2~4mS.
 Example: In power down mode (sleep mode), the system is waked up by P0 trigger signal. After the wakeup
time, the system goes into normal mode. The wakeup time of P0 wakeup function is as following.
The wakeup time = 1/Fosc * 3584 = 1.001 ms (Fosc = 3.58MHz)
The total wakeup time = 1.001 ms + x’tal settling time
Under power down mode (sleep mode), there are only I/O ports with wakeup function making the system to return
normal mode. Port 0.0 and Port 0.1 wakeup function always enables.
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 56 V1.4
Page 57

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
8 TIMERS COUNTERS
8.1 WATCHDOG TIMER (WDT)
This built-in WDT watchdog 4-bit binary up counter designed for monitoring program execution. If the program is
operated into the unknown status by noise interference or program dead lock, WDT’s overflow signal will reset this chip
to restart operation. In normal operation flow, the user must clear watchdog timer before overflow occurs to prevent the
program from unexpected system reset. The clock source of watchdog timer (WDT) always comes from internal low
speed RC oscillator. The overflow time of WDT is about:
1 / ( 16K ÷ 512 ÷ 16 ) ~ 0.5s @ 3V
1 / ( 32K ÷ 512 ÷ 16 ) ~ 0.25s @ 5V
0CCH Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
WDTR
Read/Write R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
After reset - - - - - - - -
Write WDTR with “0x5A” to clear the Watchdog Timer.
Note:
¾ The watchdog timer can be set “Always_ON”,”Enable” and “Disabled” at the code option.
¾ Watch_Dog code option = “Enable”
Stop in power down (sleep) mode.
Enable in normal mode.
¾ Watch_Dog code option = “Always_ON”.
Enable in normal mode and power down (sleep) mode.
 Example: An operation of watchdog timer is as following. To clear the watchdog timer counter in the top
Main:
MOV A,#0x5A
MOV WDTR,A ; Clear the watchdog timer counter.
. .
CALL SUB1
CALL SUB2
. .
. .
. .
JMP MAIN
WDTR7 WDTR6 WDTR5 WDTR4 WDTR3 WDTR2 WDTR1 WDTR0
of the main routine of the program.
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 57 V1.4
Page 58

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
8.2 TIMER COUNTER 0 (TC0)
8.2.1 OVERVIEW
The TC0 is an 8-bit binary up timer and event counter for general-purpose timer, buzzer and PWM output. TC0 has a
auto re-loadable counter that consists of two parts: an 8-bit reload register (TC0R) into which you write the counter
reference value, and an 8-bit counter register (TC0C) whose value is automatically incremented by counter logic.
TC0 out
PWM0OUT
TC0 Ti me ou t
Fosc
Fcpu
(8-TC0RATE)
÷ 2
P0.0
(Schmitter trigger)
TC0 X8
TC0 CK S
TC0 ENB
CPUM 0
TC0 R r eload
data buffer
load
TC0 C
8-bit binary counter
Aload0
Com pare
Internal P5.4 I/O circuit
Auto. reload P5.4
Buzzer
÷2
R
S
PWM
Figure 8-1. Timer Count TC0 Block Diagram
The main purposes of the TC0 timer counter is as following.
¾ 8-bit programmable timer: Generates interrupts at specific time intervals based on the selected clock
frequency.
¾ Arbitrary frequency output (Buzzer output): Outputs selectable clock frequencies to the BZ0 pin (P5.4).
¾ PWM function: PWM output can be generated by the PWM1OUT bit and output to PWM0OUT pin (P5.4).
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 58 V1.4
Page 59

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
8.2.2 TC0M MODE REGISTER
The TC0M is the timer counter mode register, which is an 8-bit read/write register. By loading different value into the
TC0M register, users can modify the timer counter clock frequency dynamically when program executing.
Eight rates for TC0 timer can be selected by TC0RATE0 ~ TC0RATE2 and TC0X8 bits. If TC0X8=1 the TC0 clock will
come from Fosc and the range is from Fosc/1 to Fosc/128, if TC0X8=0 (Initial), the range is from Fcpu/2 to Fcpu/256.
The TC0M initial value is zero and the rate is Fcpu/256. The bit7 of TC0M named TC0ENB is the control bit to start
TC0 timer. The combination of these bits is to determine the TC0 timer frequency.
T0M initial value = xxxx 00xx
0D8H Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
T0M - - - - TC1X8 TC0X8 -
- - - - R/W R/W Bit3 TC1X8: Multiple TC1 timer speed eight times. Refer TC1M register for detailed information.
0 = TC1 clock came from Fcpu
1 = TC1 clock came from Fosc
Bit2 TC0X8: Multiple TC0 timer speed eight times. Refer TC0M register for detailed information.
0 = TC0 clock came from Fcpu
1 = TC0 clock came from Fosc
Note: Under TC0 event counter mode (TC0CKS=1), TC0X8 bit and TC0RATE are useless.
TC0M initial value = 0000 0000
0DAH Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
TC0M
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Bit 7 TC0ENB: TC0 counter enable bit.
Bit [6:4] TC0RATE [2:0]: TC0 internal clock rate select bits. Only for TC0CKS = 0
Bit 3 TC0CKS: TC0 clock source select bit.
Bit 2 ALOAD0: Auto-reload control bit.
Bit 1 TC0OUT: TC0 time-out toggle signal output control bit. Only valid when PWM0OUT = 0
TC0ENB TC0RATE2 TC0RATE1 TC0RATE0 TC0CKS ALOAD0 TC0OUT PWM0OUT
0 = disable
1 = enable
TC0Rate TC0X8=0 TC0X8=1
000 Fcpu/256 Fosc/128
001 Fcpu/128 Fosc/64
010 Fcpu/64 Fosc/32
011 Fcpu/32 Fosc/16
100 Fcpu/16 Fosc/8
101 Fcpu/8 Fosc/4
110 Fcpu/4 Fosc/2
111 Fcpu/2 Fosc/1
0 = Internal clock source (Fcpu or Fosc)
1 = External clock source input from P0.0 (INT0) pin.
0 = None auto-reload
1 = Auto-reload.
0 = Disable TC0OUT signal output and enable P5.4’s I/O function,
1 = Enable TC0OUT signal output and disable P5.4’s I/O function.
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 59 V1.4
Page 60

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
Bit 0 PWM0OUT: PWM output control bit. Refer “PWM Function Description” section for detailed information.
0 = Disable the PWM output
1 = Enable the PWM output (Auto-disable the TC0OUT function.)
PWM0OUT = 1, TC0X8=0
Max PWM
ALOAD0 TC0OUT TC0 Overflow boundary PWM duty range
0 0 FFh to 00h 0/256 ~ 255/256 7.8125K Overflow per 256 count
0 1 3Fh to 40h 0/64 ~ 63/64 31.25K Overflow per 64 count
1 0 1Fh to 20h 0/32 ~ 31/32 62.5K Overflow per 32 count
1 1 0Fh to 10h 0/16 ~ 15/16 125K Overflow per 16 count
PWM0OUT = 1, TC0X8=1
ALOAD0 TC0OUT TC0 Overflow boundary PWM duty range
0 0 FFh to 00h 0/256 ~ 255/256 62.5K Overflow per 256 count
0 1 3Fh to 40h 0/64 ~ 63/64 250K Overflow per 64 count
1 0 1Fh to 20h 0/32 ~ 31/32 500K Overflow per 32 count
1 1 0Fh to 10h 0/16 ~ 15/16 1000K Overflow per 16 count
Note: When TC0CKS=1, TC0 became an external event counter and TC0RATE is useless. No more P0.0
interrupt request will be raised. (P0.0IRQ will be always 0).
Frequency
(Fosc = 16M)
(Fcpu = 4M)
Max PWM
Frequency
(Fosc = 16M)
(Fcpu = 4M)
Note
Note
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 60 V1.4
Page 61

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
8.2.3 TC0C COUNTING REGISTER
TC0C is an 8-bit counter register for the timer counter (TC0). TC0C must be reset whenever the TC0ENB is set “1” to
start the timer counter. TC0C is incremented by one with a clock pulse which the frequency is determined by
TC0RATE0 ~ TC0RATE2. When TC0C has incremented to “0FFH”, it is will be cleared to “00H” in next clock and an
overflow is generated. Under TC0 interrupt service request (TC0IEN) enable condition, the TC0 interrupt request flag
will be set “1” and the system executes the interrupt service routine.
TC0C initial value = xxxx xxxx
0DBH Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
TC0C
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
The equation of TC0C initial value is as following.
 Example: To set 10ms interval time for TC0 interrupt at 3.58MHz high-speed mode. TC0C value (74H) = 256 -
TC0C7 TC0C6 TC0C5 TC0C4 TC0C3 TC0C2 TC0C1 TC0C0
TC0C initial value = 256 - (TC0 interrupt interval time * input clock)
(10ms * fcpu/256)
TC0C initial value = 256 - (TC0 interrupt interval time * input clock)
= 256 - (10ms * 3.58 * 10
= 256 - (10
= 116
= 74H
-2
* 3.58 * 106 / 256)
6
/ 256)
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 61 V1.4
Page 62

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
TC0_Counter=8-bit, TC0X8=0
TC0RATE TC0CLOCK
000 fcpu/256 73.2 ms 286us 8000 ms 31.25 ms
001 fcpu/128 36.6 ms 143us 4000 ms 15.63 ms
010 fcpu/64 18.3 ms 71.5us 2000 ms 7.8 ms
011 fcpu/32 9.15 ms 35.8us 1000 ms 3.9 ms
100 fcpu/16 4.57 ms 17.9us 500 ms 1.95 ms
101 fcpu/8 2.28 ms 8.94us 250 ms 0.98 ms
110 fcpu/4 1.14 ms 4.47us 125 ms 0.49 ms
111 fcpu/2 0.57 ms 2.23us 62.5 ms 0.24 ms
TC0_Counter=6-bit , TC0X8=0
TC0RATE TC0CLOCK
000 fcpu/256 18.3 ms 71.5us 2000 ms 7.8 ms
001 fcpu/128 9.15 ms 35.8us 1000 ms 3.9 ms
010 fcpu/64 4.57 ms 17.9us 500 ms 1.95 ms
011 fcpu/32 2.28 ms 8.94us 250 ms 0.98 ms
100 fcpu/16 1.14 ms 4.47us 125 ms 0.49 ms
101 fcpu/8 0.57 ms 2.23us 62.5 ms 0.24 ms
110 fcpu/4 0.285 ms 1.11us 31.25 ms 0.12 ms
111 fcpu/2 0.143 ms 0.56 us 15.63 ms 0.06 ms
High speed mode (fcpu = 3.58MHz / 4) Low speed mode (fcpu = 32768Hz / 4)
Max overflow interval One step = max/256 Max overflow interval One step = max/256
High speed mode (fcpu = 3.58MHz / 4) Low speed mode (fcpu = 32768Hz / 4)
Max overflow interval One step = max/256 Max overflow interval One step = max/256
TC0_Counter=5-bit, TC0X8=0
TC0RATE TC0CLOCK
000 fcpu/256 9.15 ms 35.8us 1000 ms 3.9 ms
001 fcpu/128 4.57 ms 17.9us 500 ms 1.95 ms
010 fcpu/64 2.28 ms 8.94us 250 ms 0.98 ms
011 fcpu/32 1.14 ms 4.47us 125 ms 0.49 ms
100 fcpu/16 0.57 ms 2.23us 62.5 ms 0.24 ms
101 fcpu/8 0.285 ms 1.11us 31.25 ms 0.12 ms
110 fcpu/4 0.143 ms 0.56 us 15.63 ms 0.06 ms
111 fcpu/2 71.25 us 0.278 us 7.81 ms 0.03 ms
High speed mode (fcpu = 3.58MHz / 4) Low speed mode (fcpu = 32768Hz / 4)
Max overflow interval One step = max/256 Max overflow interval One step = max/256
TC0_Counter=4-bit, TC0X8=0
TC0RATE TC0CLOCK
000 fcpu/256 4.57 ms 17.9us 500 ms 1.95 ms
001 fcpu/128 2.28 ms 8.94us 250 ms 0.98 ms
010 fcpu/64 1.14 ms 4.47us 125 ms 0.49 ms
011 fcpu/32 0.57 ms 2.23us 62.5 ms 0.24 ms
100 fcpu/16 0.285 ms 1.11us 31.25 ms 0.12 ms
101 fcpu/8 0.143 ms 0.56 us 15.63 ms 0.06 ms
110 fcpu/4 71.25 us 0.278 us 7.81 ms 0.03 ms
111 fcpu/2 35.63 us 0.139 us 3.91 ms 0.015 ms
High speed mode (fcpu = 3.58MHz / 4) Low speed mode (fcpu = 32768Hz / 4)
Max overflow interval One step = max/256 Max overflow interval One step = max/256
Table 8-1. The Timing Table of Timer Count TC0
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 62 V1.4
Page 63

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
8.2.4 TC0R AUTO-LOAD REGISTER
TC0R is an 8-bit register for the TC0 auto-reload function. TC0R’s value applies to TC0OUT and PWM0OUT functions..
Under TC0OUT application, users must enable and set the TC0R register. The main purpose of TC0R is as following.
¾ Store the auto-reload value and set into TC0C when the TC0C overflow. (ALOAD0 = 1).
¾ Store the duty value of PWM0OUT function.
TC0R initial value = xxxx xxxx
0CDH Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
TC0R
W W W W W W W W
The equation of TC0R initial value is like TC0C as following.
Note: The TC0R is write-only register can’t be process by INCMS, DECMS instructions.
TC0R7 TC0R6 TC0R5 TC0R4 TC0R3 TC0R2 TC0R1 TC0R0
TC0R initial value = 256 - (TC0 interrupt interval time * input clock)
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 63 V1.4
Page 64

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
8.2.5 TC0 TIMER COUNTER OPERATION SEQUENCE
The TC0 timer counter’s sequence of operation can be following.
¾ Set the TC0C initial value to setup the interval time.
¾ Set the TC0ENB to be “1” to enable TC0 timer counter.
¾ TC0C is incremented by one with each clock pulse which frequency is corresponding to T0M selection.
¾ TC0C overflow when TC0C from FFH to 00H.
¾ When TC0C overflow occur, the TC0IRQ flag is set to be “1” by hardware.
¾ Execute the interrupt service routine.
¾ Users reset the TC0C value and resume the TC0 timer operation.
 Example: Setup the TC0M and TC0C without auto-reload function.
B0BCLR FTC0IEN ; To disable TC0 interrupt service
B0BCLR FTC0ENB ; To disable TC0 timer
MOV A,#00H ;
B0MOV TC0M,A ; To set TC0 clock = fcpu / 256
MOV A,#74H ; To set TC0C initial value = 74H
B0MOV TC0C,A ;(To set TC0 interval = 10 ms)
B0BSET FTC0IEN ; To enable TC0 interrupt service
B0BCLR FTC0IRQ ; To clear TC0 interrupt request
B0BSET FTC0ENB ; To enable TC0 timer
 Example: Setup the TC0M and TC0C with auto-reload function.
B0BCLR FTC0IEN ; To disable TC0 interrupt service
B0BCLR FTC0ENB ; To disable TC0 timer
MOV A,#00H ;
B0MOV TC0M,A ; To set TC0 clock = fcpu / 256
MOV A,#74H ; To set TC0C initial value = 74H
B0MOV TC0C,A ; (To set TC0 interval = 10 ms)
B0MOV TC0R,A ; To set TC0R auto-reload register
B0BSET FTC0IEN ; To enable TC0 interrupt service
B0BCLR FTC0IRQ ; To clear TC0 interrupt request
B0BSET FTC0ENB ; To enable TC0 timer
B0BSET ALOAD0 ; To enable TC0 auto-reload function.
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 64 V1.4
Page 65

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
 Example: TC0 interrupt service routine without auto-reload function.
ORG 8 ; Interrupt vector
JMP INT_SERVICE
INT_SERVICE:
B0XCH A, ACCBUF ; B0XCH doesn’t change C, Z flag
B0MOV A, PFLAG ;
B0MOV PFLAGBUF, A ; Save PFLAG register in a buffer ; Save
B0BTS1 FTC0IRQ ; Check TC0IRQ
JMP EXIT_INT ; TC0IRQ = 0, exit interrupt vector
B0BCLR FTC0IRQ ; Reset TC0IRQ
MOV A,#74H ; Reload TC0C
B0MOV TC0C,A
. . ; TC0 interrupt service routine
. .
JMP EXIT_INT ; End of TC0 interrupt service routine and exit interrupt
vector
. .
. .
EXIT_INT:
;
B0MOV A, PFLAGBUF
B0MOV PFLAG, A ; Restore PFLAG register from buffer
B0XCH A, ACCBUF ; Restore ACC value.
RETI ; Exit interrupt vector
 Example: TC0 interrupt service routine with auto-reload.
ORG 8 ; Interrupt vector
JMP INT_SERVICE
INT_SERVICE:
B0XCH A, ACCBUF ; B0XCH doesn’t change C, Z flag
B0MOV A, PFLAG ;
B0MOV PFLAGBUF, A ; Save PFLAG register in a buffer
B0BTS1 FTC0IRQ ; Check TC0IRQ
JMP EXIT_INT ; TC0IRQ = 0, exit interrupt vector
B0BCLR FTC0IRQ ; Reset TC0IRQ
. . ; TC0 interrupt service routine
. .
JMP EXIT_INT ; End of TC0 interrupt service routine and exit interrupt
vector
. .
. .
EXIT_INT:
B0MOV A, PFLAG ;
B0MOV PFLAGBUF, A ; Save PFLAG register in a buffer
B0XCH A, ACCBUF ; Restore ACC value.
RETI ; Exit interrupt vector
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 65 V1.4
Page 66

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
8.2.6 TC0 CLOCK FREQUENCY OUTPUT (BUZZER)
TC0 timer counter provides a frequency output function. By setting the TC0 clock frequency, the clock signal is output
to P5.4 and the P5.4 general purpose I/O function is auto-disable. The TC0 output signal divides by 2. The TC0 clock
has many combinations and easily to make difference frequency. This function applies as buzzer output to output
multi-frequency.
Figure 8-2. The TC0OUT Pulse Frequency
 Example: Setup TC0OUT output from TC0 to TC0OUT (P5.4). The Fcpu is 4MHz. The TC0OUT frequency is
1KHz. Because the TC0OUT signal is divided by 2, set the TC0 clock to 2KHz. The TC0 clock
source is from external oscillator clock. T0C rate is Fcpu/4. The TC0RATE2~TC0RATE1 = 110.
TC0C = TC0R = 131, TC0X8=1.
MOV A,#01100000B
B0MOV TC0M,A ; Set the TC0 rate to Fcpu/4
MOV A,#131 ; Set the auto-reload reference value
B0MOV TC0C,A
B0MOV TC0R,A
B0BCLR FTC0X8
B0BSET FTC0OUT ; Enable TC0 output to P5.4 and disable P5.4 I/O function
B0BSET FALOAD0 ; Enable TC0 auto-reload function
B0BSET FTC0ENB ; Enable TC0 timer
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 66 V1.4
Page 67

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
8.3 TIMER COUNTER 1 (TC1)
8.3.1 OVERVIEW
The timer counter 1 (TC1) is used to generate an interrupt request when a specified time interval has elapsed. TC1
has a auto re-loadable counter that consists of two parts: an 8-bit reload register (TC1R) into which you write the
counter reference value, and an 8-bit counter register (TC1C) whose value is automatically incremented by counter
logic.
TC1 out
PWM1OUT
TC1 Ti me ou t
Fosc
Fcpu
(8-TC0RATE)
÷ 2
P0.1
(Schmitter trigger)
TC1 X8
TC1 CK S
TC1 ENB
CPUM0
TC1 R reload
data buffer
load
TC1 C
8-bit binary counter
Aload1
Com pare
Internal P5.3 I/O circuit
Auto. reload P5.3
Buzzer
÷2
R
S
PWM
Figure 8-3. Timer Count TC1 Block Diagram
The main purposes of the TC1 timer is as following.
¾ 8-bit programmable timer: Generates interrupts at specific time intervals based on the selected clock
frequency.
¾ Arbitrary frequency output (Buzzer output): Outputs selectable clock frequencies to the BZ1 pin (P5.3).
¾ PWM function: PWM output can be generated by the PWM1OUT bit and output to PWM1OUT pin (P5.3).
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 67 V1.4
Page 68

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
8.3.2 TC1M MODE REGISTER
The TC1M is an 8-bit read/write timer mode register. By loading different value into the TC1M register, users can
modify the timer clock frequency dynamically as program executing.
Eight rates for TC1 timer can be selected by TC1RATE0 ~ TC1RATE2 bits. If TC1X8=1 the TC1 clock will come from
Fosc and the range is from Fosc/1 to Fosc/128. if TC1X8=0 (Initial), the range is from Fcpu(Fosc)/2 to Fcpu(Fosc)/256.
The TC1M initial value is zero and the rate is Fcpu/256. The bit7 of TC1M called TC1ENB is the control bit to start TC1
timer. The combination of these bits is to determine the TC1 timer clock frequency and the intervals.
T0M initial value = xxxx 00xx
0D8H Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
T0M - - - - TC1X8 TC0X8 -
- - - - R/W R/W Bit3 TC1X8: Multiple TC1 timer speed eight times. Refer TC1M register for detailed information.
0 = TC1 clock came from Fcpu
1 = TC1 clock came from Fosc
Bit2 TC0X8: Multiple TC0 timer speed eight times. Refer TC0M register for detailed information.
0 = TC0 clock came from Fcpu
1 = TC0 clock came from Fosc
Note: Under TC1 event counter mode (TC1CKS=1), TC1X8 bit and TC1RATE are useless.
TC1M initial value = 0000 0000
0DCH Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
TC1M
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Bit 7 TC1ENB: TC1 counter enable bit.
Bit [6:4] TC1RATE [2:0]: TC1 internal clock rate select bits. Only for TC1CKS = 0
Bit 3 TC1CKS: TC1 clock source select bit.
Bit 2 ALOAD1: Auto-reload control bit.
Bit 1 TC1OUT: TC1 time-out toggle signal output control bit. Only valid when PWM1OUT = 0
TC1ENB TC1RATE2 TC1RATE1 TC1RATE0 TC1CKS ALOAD1 TC1OUT PWM1OUT
0 = disable
1 = enable
TC1Rate TC1X8=0 TC1X8=1
000 Fcpu/256 Fosc/128
001 Fcpu/128 Fosc/64
010 Fcpu/64 Fosc/32
011 Fcpu/32 Fosc/16
100 Fcpu/16 Fosc/8
101 Fcpu/8 Fosc/4
110 Fcpu/4 Fosc/2
111 Fcpu/2 Fosc/1
0 = Internal clock source (Fcpu/Fosc)
1 = External clock source input from P0.1 (INT1) pin.
0 = none auto-reload
1 = auto-reload.
0 = Disable TC1OUT signal output and enable P5.3’s I/O function,
1 = Enable TC1OUT signal output and disable P5.3’s I/O function.
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 68 V1.4
Page 69

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
Bit 0 PWM1OUT: PWM output control bit. Refer “PWM Function Description” section for detailed information.
0 = Disable the PWM output
1 = Enable the PWM output (Auto-disable the TC1OUT function.)
PWM1OUT = 1, TC1X8=0
Max PWM
ALOAD1 TC1OUT TC1 Overflow boundary PWM duty range
0 0 FFh to 00h 0/256 ~ 255/256 7.8125K Overflow per 256 count
0 1 3Fh to 40h 0/64 ~ 63/64 31.25K Overflow per 64 count
1 0 1Fh to 20h 0/32 ~ 31/32 62.5K Overflow per 32 count
1 1 0Fh to 10h 0/16 ~ 15/16 125K Overflow per 16 count
PWM0OUT = 1, TC1X8=1
ALOAD0 TC0OUT TC0 Overflow boundary PWM duty range
0 0 FFh to 00h 0/256 ~ 255/256 62.5K Overflow per 256 count
0 1 3Fh to 40h 0/64 ~ 63/64 250K Overflow per 64 count
1 0 1Fh to 20h 0/32 ~ 31/32 500K Overflow per 32 count
1 1 0Fh to 10h 0/16 ~ 15/16 1000K Overflow per 16 count
Frequency
(Fosc = 16M)
(Fcpu = 4M)
Max PWM
Frequency
(Fosc = 16M)
(Fcpu = 4M)
Note: When TC1CKS=1, TC1 became an external event counter and TC1RATE is useless. No more P0.1
interrupt request will be raised. (P0.1IRQ will be always 0).
Note
Note
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 69 V1.4
Page 70

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
8.3.3 TC1C COUNTING REGISTER
TC1C is an 8-bit counter register for the timer counter (TC1). TC1C must be reset whenever the TC1ENB is set “1” to
start the timer. TC1C is incremented by one with a clock pulse which the frequency is determined by TC1RATE0 ~
TC1RATE2. When TC1C has incremented to “0FFH”, it is will be cleared to “00H” in next clock and an overflow is
generated. Under TC1 interrupt service request (TC1IEN) enable condition, the TC1 interrupt request flag will be set
“1” and the system executes the interrupt service routine.
TC1C initial value = xxxx xxxx
0DDH Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
TC1C
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
The interval time of TC1 basic timer table.
The equation of TC1C initial value is as following.
 Example: To set 10ms interval time for TC1 interrupt at 3.58MHz high-speed mode. TC1C value (74H) = 256 -
TC1C7 TC1C6 TC1C5 TC1C4 TC1C3 TC1C2 TC1C1 TC1C0
TC1C initial value = 256 - (TC1 interrupt interval time * input clock)
(10ms * fcpu/256)
TC1C initial value = 256 - (TC1 interrupt interval time * input clock)
= 256 - (10ms * 3.58 * 10
= 256 - (10
= 116
= 74H
-2
* 3.58 * 106 / 256)
6
/ 256)
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 70 V1.4
Page 71

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
TC1_Counter=8-bit, TC1X8=0
TC1RATE TC1CLOCK
000 fcpu/256 73.2 ms 286us 8000 ms 31.25 ms
001 fcpu/128 36.6 ms 143us 4000 ms 15.63 ms
010 fcpu/64 18.3 ms 71.5us 2000 ms 7.8 ms
011 fcpu/32 9.15 ms 35.8us 1000 ms 3.9 ms
100 fcpu/16 4.57 ms 17.9us 500 ms 1.95 ms
101 fcpu/8 2.28 ms 8.94us 250 ms 0.98 ms
110 fcpu/4 1.14 ms 4.47us 125 ms 0.49 ms
111 fcpu/2 0.57 ms 2.23us 62.5 ms 0.24 ms
TC1_Counter=6-bit, TC1X8=0
TC1RATE TC1CLOCK
000 fcpu/256 18.3 ms 71.5us 2000 ms 7.8 ms
001 fcpu/128 9.15 ms 35.8us 1000 ms 3.9 ms
010 fcpu/64 4.57 ms 17.9us 500 ms 1.95 ms
011 fcpu/32 2.28 ms 8.94us 250 ms 0.98 ms
100 fcpu/16 1.14 ms 4.47us 125 ms 0.49 ms
101 fcpu/8 0.57 ms 2.23us 62.5 ms 0.24 ms
110 fcpu/4 0.285 ms 1.11us 31.25 ms 0.12 ms
111 fcpu/2 0.143 ms 0.56 us 15.63 ms 0.06 ms
High speed mode (fcpu = 3.58MHz / 4) Low speed mode (fcpu = 32768Hz / 4)
Max overflow interval One step = max/256 Max overflow interval One step = max/256
High speed mode (fcpu = 3.58MHz / 4) Low speed mode (fcpu = 32768Hz / 4)
Max overflow interval One step = max/256 Max overflow interval One step = max/256
TC1_Counter=5-bit, TC1X8=0
TC1RATE TC1CLOCK
000 Fcpu/256 9.15 ms 35.8us 1000 ms 3.9 ms
001 Fcpu/128 4.57 ms 17.9us 500 ms 1.95 ms
010 fcpu/64 2.28 ms 8.94us 250 ms 0.98 ms
011 fcpu/32 1.14 ms 4.47us 125 ms 0.49 ms
100 fcpu/16 0.57 ms 2.23us 62.5 ms 0.24 ms
101 fcpu/8 0.285 ms 1.11us 31.25 ms 0.12 ms
110 fcpu/4 0.143 ms 0.56 us 15.63 ms 0.06 ms
111 fcpu/2 71.25 us 0.278 us 7.81 ms 0.03 ms
High speed mode (fcpu = 3.58MHz / 4) Low speed mode (fcpu = 32768Hz / 4)
Max overflow interval One step = max/256 Max overflow interval One step = max/256
TC1_Counter=4-bit, TC1X8=0
TC1RATE TC1CLOCK
000 Fcpu/256 4.57 ms 17.9us 500 ms 1.95 ms
001 Fcpu/128 2.28 ms 8.94us 250 ms 0.98 ms
010 fcpu/64 1.14 ms 4.47us 125 ms 0.49 ms
011 fcpu/32 0.57 ms 2.23us 62.5 ms 0.24 ms
100 fcpu/16 0.285 ms 1.11us 31.25 ms 0.12 ms
101 fcpu/8 0.143 ms 0.56 us 15.63 ms 0.06 ms
110 fcpu/4 71.25 us 0.278 us 7.81 ms 0.03 ms
111 fcpu/2 35.63 us 0.139 us 3.91 ms 0.015 ms
High speed mode (fcpu = 3.58MHz / 4) Low speed mode (fcpu = 32768Hz / 4)
Max overflow interval One step = max/256 Max overflow interval One step = max/256
Table 8-2. The Timing Table of Timer Count TC1
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 71 V1.4
Page 72

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
8.3.4 TC1R AUTO-LOAD REGISTER
TC1R is an 8-bit register for the TC1 auto-reload function. TC1R’s value applies to TC1OUT and PWM1OUT functions.
Under TC1OUT application, users must enable and set the TC1R register. The main purpose of TC1R is as following.
¾ Store the auto-reload value and set into TC1C when the TC1C overflow. (ALOAD1 = 1).
¾ Store the duty value of PWM1OUT function.
TC1R initial value = xxxx xxxx
0DEH Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
TC1R
W W W W W W W W
The equation of TC1R initial value is like TC1C as following.
Note: The TC1R is write-only register can’t be process by INCMS, DECMS instructions.
TC1R7 TC1R6 TC1R5 TC1R4 TC1R3 TC1R2 TC1R1 TC1R0
TC1R initial value = 256 - (TC1 interrupt interval time * input clock)
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 72 V1.4
Page 73

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
8.3.5 TC1 TIMER COUNTER OPERATION SEQUENCE
The TC1 timer’s sequence of operation can be following.
¾ Set the TC1C initial value to setup the interval time.
¾ Set the TC1ENB to be “1” to enable TC1 timer counter.
¾ TC1C is incremented by one with each clock pulse which frequency is corresponding to TC1M selection.
¾ TC1C overflow if TC1C from FFH to 00H.
¾ When TC1C overflow occur, the TC1IRQ flag is set to be “1” by hardware.
¾ Execute the interrupt service routine.
¾ Users reset the TC1C value and resume the TC1 timer operation.
 Example: Setup the TC1M and TC1C without auto-reload function.
B0BCLR FTC1IEN ; To disable TC1 interrupt service
B0BCLR FTC1ENB ; To disable TC1 timer
B0BCLR FTC1X8 ;
MOV A,#00H ;
B0MOV TC1M,A ; To set TC1 clock = fcpu / 256
MOV A,#74H ; To set TC1C initial value = 74H
B0MOV TC1C,A ;(To set TC1 interval = 10 ms)
B0BSET FTC1IEN ; To enable TC1 interrupt service
B0BCLR FTC1IRQ ; To clear TC1 interrupt request
B0BSET FTC1ENB ; To enable TC1 timer
 Example: Setup the TC1M and TC1C with auto-reload function.
B0BCLR FTC1IEN ; To disable TC1 interrupt service
B0BCLR FTC1ENB ; To disable TC1 timer
B0BCLR FTC1X8 ;
MOV A,#00H ;
B0MOV TC1M,A ; To set TC1 clock = fcpu / 256
MOV A,#74H ; To set TC1C initial value = 74H
B0MOV TC1C,A ; (To set TC1 interval = 10 ms)
B0MOV TC1R,A ; To set TC1R auto-reload register
B0BSET FTC1IEN ; To enable TC1 interrupt service
B0BCLR FTC1IRQ ; To clear TC1 interrupt request
B0BSET FTC1ENB ; To enable TC1 timer
B0BSET ALOAD1 ; To enable TC1 auto-reload function.
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 73 V1.4
Page 74

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
 Example: TC1 interrupt service routine without auto-reload function.
ORG 8 ; Interrupt vector
JMP INT_SERVICE
INT_SERVICE:
B0XCH A, ACCBUF ; B0XCH doesn’t change C, Z flag
B0MOV A, PFLAG
B0MOV PFLAGBUF, A ; Save PFLAG register in a buffer
B0BTS1 FTC1IRQ ; Check TC1IRQ
JMP EXIT_INT ; TC1IRQ = 0, exit interrupt vector
B0BCLR FTC1IRQ ; Reset TC1IRQ
MOV A,#74H ; Reload TC1C
B0MOV TC1C,A
. . ; TC1 interrupt service routine
. .
JMP EXIT_INT ; End of TC1 interrupt service routine and exit interrupt
vector
. .
. .
EXIT_INT:
B0MOV A, PFLAGBUF
B0MOV PFLAG, A ; Restore PFLAG register from buffer
B0XCH A, ACCBUF ; Restore ACC value.
RETI ; Exit interrupt vector
 Example: TC1 interrupt service routine with auto-reload.
ORG 8 ; Interrupt vector
JMP INT_SERVICE
INT_SERVICE:
B0XCH A, ACCBUF ; B0XCH doesn’t change C, Z flag
B0MOV A, PFLAG
B0MOV PFLAGBUF, A ; Save PFLAG register in a buffer
B0BTS1 FTC1IRQ ; Check TC1IRQ
JMP EXIT_INT ; TC1IRQ = 0, exit interrupt vector
B0BCLR FTC1IRQ ; Reset TC1IRQ
. . ; TC1 interrupt service routine
. .
JMP EXIT_INT ; End of TC1 interrupt service routine and exit interrupt
vector
. .
. .
EXIT_INT:
B0MOV A, PFLAGBUF
B0MOV PFLAG, A ; Restore PFLAG register from buffer
B0XCH A, ACCBUF ; Restore ACC value.
RETI ; Exit interrupt vector
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 74 V1.4
Page 75

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
8.3.6 TC1 CLOCK FREQUENCY OUTPUT (BUZZER)
TC1 timer counter provides a frequency output function. By setting the TC1 clock frequency, the clock signal is output
to P5.3 and the P5.3 general purpose I/O function is auto-disable. The TC1 output signal divides by 2. The TC1 clock
has many combinations and easily to make difference frequency. This function applies as buzzer output to output
multi-frequency.
Figure 8-4. The TC1OUT Pulse Frequency
 Example: Setup TC1OUT output from TC1 to TC1OUT (P5.3). The Fcpu is 4MHz. The TC1OUT frequency is
1KHz. Because the TC1OUT signal is divided by 2, set the TC1 clock to 2KHz. The TC1 clock
source is from external oscillator clock. TC1 rate is Fcpu/4. The TC1RATE2~TC1RATE1 = 110.
TC1X8=1, TC1C = TC1R = 131.
B0BCLR FTC1X8 ;
MOV A,#01100000B
B0MOV TC1M,A ; Set the TC1 rate to Fcpu/4
MOV A,#131 ; Set the auto-reload reference value
B0MOV TC1C,A
B0MOV TC1R,A
B0BSET FTC1OUT ; Enable TC1 output to P5.3 and disable P5.3 I/O function
B0BSET FALOAD1 ; Enable TC1 auto-reload function
B0BSET FTC1ENB ; Enable TC1 timer
¾ Note: The TC1OUT frequency table is as TC0OUT frequency table. Please consult TC0OUT frequency
table. (Table 7-2~7-5)
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 75 V1.4
Page 76

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
8.4 PWM FUNCTION DESCRIPTION
8.4.1 OVERVIEW
PWM function is generated by TC0/TC1 timer counter and output the PWM signal to PWM0OUT pin (P5.4)/
PWM1OUT pin (P5.3). The 8-bit counter counts modulus 256, from 0-255, inclusive. The value of the 8-bit counter is
compared to the contents of the reference register TC0R/TC1R. When the reference register value (TC0R/TC1R) is
equal to the counter value TC0C/TC1C, the PWM output goes low. When the counter reaches zero, the PWM output is
forced high.
Initial PWM output level is low until the counter value cross boundary (e.g. TC0C changes from FFH back to 00H), the
PWM outputs are forced to high level. The pulse width ratio (duty cycle) is defined by TC0R/TC1R registers and the
overflow boundary is defined by ALOAD0/ALOAD1 and TC0OUT/TC1OUT bits. PWM output can be held at low level
by continuously loading the TC0R/TC1R with 00H. By continuously loading the TC0R with boundary value (e.g. FFH),
you can hold the PWM output to high level, except for the last pulse of the clock source, which sends the output low.
PWM0OUT = 1, TC0X8=0
ALOAD0
ALOAD1
TC0OUT
TC1OUT
TC0 Overflow boundary
TC1 Overflow boundary
PWM duty range
0 0 FFh to 00h 0/256 ~ 255/256 7.8125K Overflow per 256 count
0 1 3Fh to 40h 0/64 ~ 63/64 31.25K Overflow per 64 count
1 0 1Fh to 20h 0/32 ~ 31/32 62.5K Overflow per 32 count
1 1 0Fh to 10h 0/16 ~ 15/16 125K Overflow per 16 count
ALOAD0
ALOAD1
TC0OUT
TC1OUT
TC0R
TC1R
0 0 00000000 to 11111111 0/256 to 255/256
0 1 XX000000 to XX111111 0/64 to 63/64
1 0 XXX00000 to XXX11111 0/32 to 31/32
1 1 XXXX0000 to XXXX1111 0/16 to 15/16
Table 8-2. The PWM Duty Cycle Table
Max PWM
Frequency
(Fcpu = 4M)
PWM Duty Range
Note
NOTE: If PWM0OUT or TC0OUT is enabled, P5.4 mode will be forced as output mode automatically.
When PWM0OUT or TC0OUT is disabled, P5.4 mode will be defined by P54M bit.
01 128 ..... 254 255.....
01 128 ..... 254 255.....
TC0/TC1 Clock
TC0/TC1 Clock
TC0R/TC1R = 00H
TC0R/TC1R = 00H
TC0R/TC1R = 01H
TC0R/TC1R = 01H
TC0R/TC1R = 80H
TC0R/TC1R = 80H
TC0R/TC1R = FFH
TC0R/TC1R = FFH
01 128 ..... 254 255..........
High
High
High
High
High
High
High
Low
Low
Low
Low
Low
Low
Low
Low
Low
01 128 ..... 254 255.....
01 128 ..... 254 255.....
01 128 ..... 254 255..........
Figure 8-5 The Output of PWM with different TC0R/TC1R.
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 76 V1.4
Page 77

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
8.4.2 PWM PROGRAM DESCRIPTION
 Example: Setup PWM0 output from TC0 to PWM0OUT (P5.4). The Fcpu is 4MHz. The duty of PWM is 30/256.
The PWM frequency is about 1KHz. The PWM clock source is from external oscillator clock. TC0
rate is Fcpu/4. The TC0RATE2~TC0RATE1 = 110. TC0C = TC0R = 30.
B0BCLR FTC0X8 ;
B0BCLR FTC1X8 ;
MOV A,#01100000B
B0MOV TC0M,A ; Set the TC0 rate to Fcpu/4
B0MOV TC0M,A ; Set the TC0 rate to Fcpu/4
MOV A,#0x00 ;First Time Initial TC0
MOV A,#30 ; Set the PWM duty to 30/256
B0MOV TC0R,A
B0BCLR FTC0OUT ; Disable TC0OUT function.
B0BSET FPWM0OUT ; Enable PWM0 output to P5.4 and disable P5.4 I/O function
B0BSET FTC0ENB ; Enable TC0 timer
¾ Note1: The TC0R and TC1R are write-only registers. Don’t process them using INCMS, DECMS
instructions.
¾ Note2: Set TC0C at initial is to make first duty-cycle correct.
 Example: Modify TC0R/TC1R registers’ value.
MOV A, #30H ; Input a number using B0MOV instruction.
B0MOV TC0R, A
INCMS BUF0 ; Get the new TC0R value from the BUF0 buffer defined by
B0MOV A, BUF0 ; programming.
B0MOV TC0R, A
¾ Note3: That is better to set the TC0C and TC0R value together when PWM0 duty modified. It protects the
PWM0 signal no glitch as PWM0 duty changing. That is better to set the TC1C and TC1R value together
when PWM1 duty modified. It protects the PWM1 signal no glitch as PWM1 duty changing.
¾ Note4: The TC0OUT function must be set “0” when PWM0 output enable. The TC1OUT function must be
set “0” when PWM1 output enable.
¾ Note5: The PWM can work with interrupt request.
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 77 V1.4
Page 78

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
8.4.3 PWM Duty with TCxR changing
In PWM mode, the system will compare TCxC and TCxR all the time. When TCxC<TCxR, the PWM will output logic
“High”, when TCxC≧TCxR, the PWM will output logic “Low”. If TCXC is changed in certain period, the PWM duty will
change in next PWM period.
When TCxR is fixed all the time, the PWM waveform is also the same
TC0C = TC0R
TC0C overflow and
Set TC0IRQ = 1
0xFF
TC0C Value
0x00
PWM0 Output
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Above diagram is shown the waveform with fixed TCxR. In every TCxC overflow PWM output “High, when
TCxC≧TCxR PWM output ”Low”.
When TCxR changing in the program processing, the PWM waveform will became:
TC0C < TC0R
PWM Low to High
TC0C > = TC0R
PWM High to Low
TC0C overflow and
Set TC0IRQ = 1
0xFF
TC0C Value
0x00
Update New TC0R!
Old TC0R < TC0C < New TC0R
Old TC0R Old TC0R
New TC0R
New TC0R
Updat e New TC0R!
New TC0R < TC0C < Old TC0R
New TC0R
New TC0R
PWM0 Output
Period
1
1st PWM
2
Update PWM Duty
3
2nd PWM
4
Update PWM Duty
5
3th PWM
In period 2 and period 4, new Duty (TCxR) is set. However, the PWM still keep the same duty in period 2 and period 4.
and the duty changed in next period. By this way, system can avoid the PWM not changing or H/L changing twice in
the same cycle and will prevent the unexpected or error operation.
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 78 V1.4
Page 79

8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
8.4.4 TCxIRQ and PWM Duty
In PWM mode, the frequency of TC0IRQ is depended on PWM duty range.
ALOADx TCxOUT TCx Overflow boundary PWM duty range TCxIRQ Frequency
0 0 FFh to 00h 0/256 ~ 255/256 TCx clock / 256
0 1 3Fh to 40h 0/64 ~ 63/64 TCx clock / 64
1 0 1Fh to 20h 0/32 ~ 31/32 TCx clock / 32
1 1 0Fh to 10h 0/16 ~ 15/16 TCx clock / 16
From following diagram, the TC0IRQ frequency is related with PWM duty.
SN8P2714X_2715
TC0 Overflow,
TC 0IRQ = 1
0xFF
TC0C Value
0x00
PWM 0 Output
(Duty Range 0~255)
TC0 Overflow,
TC 0IRQ = 1
0xFF
TC0C Value
0x00
PWM 0 Output
(Duty Range 0~63)
TC0 Overflow,
TC 0IRQ = 1
0xFF
TC0C Value
0x00
PWM 0 Output
(Duty Range 0~31)
TC0 Overflow,
TC 0IRQ = 1
0xFF
TC0C Value
0x00
PWM 0 Output
(Duty Range 0~15)
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 79 V1.4
Page 80

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
9 INTERRUPT
9.1 OVERVIEW
The SN8P2710 provides 4 interrupt sources, including two internal interrupts (TC0, TC1) and two external interrupts
(INT0, INT1). These external interrupts can wakeup the chip from power down mode to high-speed normal mode. The
external clock input pins of INT0/INT1 are shared with P0.0/P0.1 pins. Once interrupt service is executed, the GIE bit in
STKP register will clear to “0” for stopping other interrupt request. When interrupt service exits, the GIE bit will set to “1”
to accept the next interrupts’ request. All of the interrupt request signals are stored in INTRQ register. The user can
program the chip to check INTRQ’s content for setting executive priority.
¾ Note: 1.The GIE bit must enable at first and all interrupt operations work.
9.2 INTEN INTERRUPT ENABLE REGISTER
INTEN is the interrupt request control register including two internal interrupts, two external interrupts. One of the
register to be set “1” is to enable the interrupt request function. Once of the interrupt occur, the program jump to ORG
8 to execute interrupt service routines. The program exits the interrupt service routine when the returning interrupt
service routine instruction (RETI) is executed.
INTEN initial value = 0000 0000
0C9H Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
INTEN
- R/W R/W - - - R/W R/W
Bit 6 TC1IEN: Timer interrupt control bit.
0 = Disable TC1 Interrupt
1 = Enable TC1 Interrupt
Bit 5 TC0IEN: Timer interrupt control bit.
0 = Disable TC0 Interrupt
1 = Enable TC10Interrupt
Bit 1 P01IEN: External P0.1 interrupt control bit.
0 = Disable P01 Interrupt
1 = Enable P01 Interrupt
Bit 0 P00IEN: External P0.0 interrupt control bit.
0 = Disable P00 Interrupt
1 = Enable P00 Interrupt
- TC1IEN TC0IEN - - - P01IEN P00IEN
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 80 V1.4
Page 81

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
9.3 INTRQ INTERRUPT REQUEST REGISTER
INTRQ is the interrupt request flag register. The register includes all interrupt request indication flags. Each one of
these interrupt request occurs, the bit of the INTRQ register would be set “1”. The INTRQ value needs to be clear by
programming after detecting the flag. In the interrupt vector of program, users know the any interrupt requests
occurring by the register and do the routine corresponding of the interrupt request.
INTRQ initial value = x00x xx00
0C8H Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
INTRQ
- R/W R/W - - - R/W R/W
Bit 6 TC1IRQ: TC1 timer interrupt request controls bit.
0 = Non request from TC1
1 = Request from TC1
Bit 5 TC0IRQ: TC0 timer interrupt request controls bit.
0 = Non request from TC0
1 = Request from TC0
Bit 1 P01IRQ: External P0.1 interrupt request bit.
0 = Non-request from P01
1 = Request from P01
Bit 0 P00IRQ: External P0.0 interrupt request bit.
0 = Non-request from P00
1 = Request from P00
- TC1IRQ TC0IRQ - - - P01IRQ P00IRQ
9.4 P0.0 INTERRUPT TRIGGER EDGE CONTROL REGISTER
PEDGE initial value = xxx1 0xxx
0BFH Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
PEDGE
- - - R/W R/W - - -
Bit [4:3] P00G [1:0]: P0.0 interrupt trigger edge control register
00 = Reserved
01 = Rising edge
10 = Falling edge (Reset default setting)
11 = Falling and rising edge both (level change trigger)
- - -
P00G1 P00G0 - - -
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 81 V1.4
Page 82

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
9.5 INTERRUPT OPERATION DESCRIPTION
SN8P2710 provides 4 interrupts. The operation of the 4 interrupts is as following.
9.5.1 GIE GLOBAL INTERRUPT OPERATION
GIE is the global interrupt control bit. All interrupts start work after the GIE = 1. It is necessary for interrupt service
request. One of the interrupt requests occurs, and the program counter (PC) points to the interrupt vector (ORG 8) and
the stack add 1 level.
STKP initial value = 0xxx 1111
0DFH Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
STKP
R/W - - - - R/W R/W R/W
Bit 7 GIE: Global interrupt control bit.
0 = Disable Interrupt function
1 = Enable Interrupt function
 Example: Set global interrupt control bit (GIE).
B0BSET FGIE ; Enable GIE
¾ Note: The GIE bit must enable and all interrupt operations work.
GIE - - - - STKPB2 STKPB1 STKPB0
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 82 V1.4
Page 83

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
9.5.2 INT0 (P0.0) INTERRUPT OPERATION
The INT0 is triggered by falling edge. When the INT0 trigger occurs, the P00IRQ will be set to “1” however the P00IEN
is enable or disable. If the P00IEN = 1, the trigger event will make the P00IRQ to be “1” and the system enter interrupt
vector. If the P00IEN = 0, the trigger event will make the P00IRQ to be “1” but the system will not enter interrupt vector.
Users need to care for the operation under multi-interrupt situation.
 Example: INT0 interrupt request setup.
B0BSET FP00IEN ; Enable INT0 interrupt service
B0BCLR FP00IRQ ; Clear INT0 interrupt request flag
B0BSET FGIE ; Enable GIE
 Example: INT0 interrupt service routine.
ORG 8 ; Interrupt vector
JMP INT_SERVICE
INT_SERVICE:
B0XCH A, ACCBUF ; B0XCH doesn’t change C, Z flag
B0MOV A, PFLAG
B0MOV PFLAGBUF, A ; Save PFLAG register in a buffer
B0BTS1 FP00IRQ ; Check P00IRQ
JMP EXIT_INT ; P00IRQ = 0, exit interrupt vector
B0BCLR FP00IRQ ; Reset P00IRQ
. . ; INT0 interrupt service routine
. .
EXIT_INT:
B0MOV A, PFLAGBUF
B0MOV PFLAG, A ; Restore PFLAG register from buffer
B0XCH A, ACCBUF ; Restore ACC value.
RETI ; Exit interrupt vector
9.5.3 INT1 (P0.1) INTERRUPT OPERATION
The INT1 is triggered by falling edge. When the INT1 trigger occurs, the P01IRQ will be set to “1” however the P01IEN
is enable or disable. If the P01IEN = 1, the trigger event will make the P01IRQ to be “1” and the system enter interrupt
vector. If the P01IEN = 0, the trigger event will make the P01IRQ to be “1” but the system will not enter interrupt vector.
Users need to care for the operation under multi-interrupt situation.
 Example: INT1 interrupt request setup.
B0BSET FP01IEN ; Enable INT1 interrupt service
B0BCLR FP01IRQ ; Clear INT1 interrupt request flag
B0BSET FGIE ; Enable GIE
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 83 V1.4
Page 84

8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
 Example: INT1 interrupt service routine.
ORG 8 ; Interrupt vector
JMP INT_SERVICE
INT_SERVICE:
B0XCH A, ACCBUF ; B0XCH doesn’t change C, Z flag
B0MOV A, PFLAG
B0MOV PFLAGBUF, A ; Save PFLAG register in a buffer
B0BTS1 FP01IRQ ; Check P01IRQ
JMP EXIT_INT ; P01IRQ = 0, exit interrupt vector
B0BCLR FP01IRQ ; Reset P01IRQ
. . ; INT1 interrupt service routine
. .
EXIT_INT:
B0MOV A, PFLAGBUF
B0MOV PFLAG, A ; Restore PFLAG register from buffer
B0XCH A, ACCBUF ; Restore ACC value.
RETI ; Exit interrupt vector
SN8P2714X_2715
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 84 V1.4
Page 85

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
9.5.4 TC0 INTERRUPT OPERATION
When the TC0C counter occurs overflow, the TC0IRQ will be set to “1” no matter the TC0IEN is enable or disable. If
the TC0IEN = 1, the trigger event will make the TC0IRQ to be “1” and the system enter interrupt vector. If the TC0IEN
= 0, the trigger event will make the TC0IRQ to be “1” but the system will not enter interrupt vector. Users need to care
for the operation under multi-interrupt situation.
 Example: TC0 interrupt request setup.
B0BCLR FTC0IEN ; Disable TC0 interrupt service
B0BCLR FTC0ENB ; Disable TC0 timer
MOV A, #20H ;
B0MOV TC0M, A ; Set TC0 clock = Fcpu / 64
MOV A, #74H ; Set TC0C initial value = 74H
B0MOV TC0C, A ; Set TC0 interval = 10 ms
B0BSET FTC0IEN ; Enable TC0 interrupt service
B0BCLR FTC0IRQ ; Clear TC0 interrupt request flag
B0BSET FTC0ENB ; Enable TC0 timer
B0BSET FGIE ; Enable GIE
 Example: TC0 interrupt service routine.
ORG 8 ; Interrupt vector
JMP INT_SERVICE
INT_SERVICE:
B0XCH A, ACCBUF ; B0XCH doesn’t change C, Z flag
B0MOV A, PFLAG
B0MOV PFLAGBUF, A ; Save PFLAG register in a buffer
B0BTS1 FTC0IRQ ; Check TC0IRQ
JMP EXIT_INT ; TC0IRQ = 0, exit interrupt vector
B0BCLR FTC0IRQ ; Reset TC0IRQ
MOV A, #74H
B0MOV TC0C, A ; Reset TC0C.
. . ; TC0 interrupt service routine
. .
EXIT_INT:
B0MOV A, PFLAGBUF
B0MOV PFLAG, A ; Restore PFLAG register from buffer
B0XCH A, ACCBUF ; Restore ACC value.
RETI ; Exit interrupt vector
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 85 V1.4
Page 86

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
9.5.5 TC1 INTERRUPT OPERATION
When the TC1C counter occurs overflow, the TC1IRQ will be set to “1” no matter the TC1IEN is enable or disable. If
the TC1IEN = 1, the trigger event will make the TC1IRQ to be “1” and the system enter interrupt vector. If the TC1IEN
= 0, the trigger event will make the TC1IRQ to be “1” but the system will not enter interrupt vector. Users need to care
for the operation under multi-interrupt situation.
 Example: TC1 interrupt request setup.
B0BCLR FTC1IEN ; Disable TC1 interrupt service
B0BCLR FT C1ENB ; Disable TC1 timer
MOV A, #20H ;
B0MOV TC1M, A ; Set TC1 clock = Fcpu / 64
MOV A, #74H ; Set TC1C initial value = 74H
B0MOV TC1C, A ; Set TC1 interval = 10 ms
B0BSET FTC1IEN ; Enable TC1 interrupt service
B0BCLR FTC1IRQ ; Clear TC1 interrupt request flag
B0BSET FTC1ENB ; Enable TC1 timer
B0BSET FGIE ; Enable GIE
 Example: TC1 interrupt service routine.
ORG 8 ; Interrupt vector
JMP INT_SERVICE
INT_SERVICE:
B0XCH A, ACCBUF ; B0XCH doesn’t change C, Z flag
B0MOV A, PFLAG
B0MOV PFLAGBUF, A ; Save PFLAG register in a buffer
B0BTS1 FTC1IRQ ; Check TC1IRQ
JMP EXIT_INT ; TC1IRQ = 0, exit interrupt vector
B0BCLR FTC1IRQ ; Reset TC1IRQ
MOV A, #74H
B0MOV TC1C, A ; Reset TC1C.
. . ; TC1 interrupt service routine
. .
EXIT_INT:
B0MOV A, PFLAGBUF
B0MOV PFLAG, A ; Restore PFLAG register from buffer
B0XCH A, ACCBUF ; Restore ACC value.
RETI ; Exit interrupt vector
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 86 V1.4
Page 87

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
9.5.6 MULTI-INTERRUPT OPERATION
In most conditions, the software designer uses more than one interrupt request. Processing multi-interrupt request
needs to set the priority of these interrupt requests. The IRQ flags of the 4 interrupt are controlled by the interrupt event
occurring. But the IRQ flag set doesn’t mean the system to execute the interrupt vector. The IRQ flags can be triggered
by the events without interrupt enable. Just only any the event occurs and the IRQ will be logic “1”. The IRQ and its
trigger event relationship is as the below table.
Interrupt Name Trigger Event Description
P00IRQ P0.0 trigger. Falling edge.
P01IRQ P0.1 trigger. Falling edge.
TC0IRQ TC0C overflow.
TC1IRQ TC1C overflow.
There are two things need to do for multi-interrupt. One is to make a good priority for these interrupt requests. Two is
using IEN and IRQ flags to decide executing interrupt service routine or not. Users have to check interrupt control bit
and interrupt request flag in interrupt vector. There is a simple routine as following.
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 87 V1.4
Page 88

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
 Example: How does users check the interrupt request in multi-interrupt situation?
ORG 8 ; Interrupt vector
NOP
B0XCH A, ACCBUF ; B0XCH doesn’t change C, Z flag
B0MOV A, PFLAG
B0MOV PFLAGBUF, A ; Save PFLAG register in a buffer
INTP00CHK: ; Check INT0 interrupt request
B0BTS1 FP00IEN ; Check P00IEN
JMP INTP01CHK ; Jump check to next interrupt
B0BTS0 FP00IRQ ; Check P00IRQ
JMP INTP00 ; Jump to INT0 interrupt service routine
INTP01CHK: ; Check INT1 interrupt request
B0BTS1 FP01IEN ; Check P01IEN
JMP INTTC0CHK ; Jump check to next interrupt
B0BTS0 FP01IRQ ; Check P01IRQ
JMP INTP01 ; Jump to INT1 interrupt service routine
INTTC0CHK: ; Check TC0 interrupt request
B0BTS1 FTC0IEN ; Check TC0IEN
JMP INTTC1CHK ; Jump check to next interrupt
B0BTS0 FTC0IRQ ; Check TC0IRQ
JMP INTTC0 ; Jump to TC0 interrupt service routine
INTTC1HK: ; Check TC1 interrupt request
B0BTS1 FTC1IEN ; Check TC1IEN
JMP INT_EXIT ; Jump check to next interrupt
B0BTS0 FTC1IRQ ; Check TC1IRQ
JMP INTTC1 ; Jump to TC1 interrupt service routine
INT_EXIT:
B0MOV A, PFLAGBUF
B0MOV PFLAG, A ; Restore PFLAG register from buffer
B0XCH A, ACCBUF ; Restore ACC value.
RETI ; Exit interrupt vector
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 88 V1.4
Page 89

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
10 I/O PORT
10.1 OVERVIEW
The SN8P2710 provides up to four ports for users’ application, consisting of one input only port (P0), three I/O ports
( P2, P4, P5). The direction of I/O port is selected by PnM register and register PnUR is defined for user setting pull-up
register. After the system resets, all ports work as input function without pull-up resistors.
Port 0.1 and P0.2 structure:
Pull-Up
PnUR
Port 0.3 structure:
Port 2, 5 structure:
Port 4 structure:
Pin
Pin
Pin
PnM
Pull-Up
Pull-Up
Ext. Reset
Code Option
PnM, PnUR
Output
Latch
Int. Bus
Int. Rst
Int. Bus
Int. Rst
Input Bus
Output Bus
P4CON
Pin
PnM
GCHS
PnM, PnUR
Output
Latch
Input Bus
Output Bus
Int. ADC
Figure 10-1. The I/O pin circuit Diagram
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 89 V1.4
Page 90

10.2 I/O PORT FUNCTION TABLE
Port/Pin I/O Function Description Remark
General-purpose input function
P0.0~P0.1 I
P0.2 I
P0.3 I
P2.0~P2.7 I/O General-purpose input/output function
P4.0~P4.7 I/O
P5.0~P5.6 I/O General-purpose input/output function
External interrupt (INT0~INT1)
Wakeup for power down mode
General-purpose input function
Wakeup for power down mode
General-purpose input function
Share with Reset pin
General-purpose input/output function
ADC analog signal input
Table 10-1. I/O Function Table
SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
P0.0: TC0 external clock input pin
P0.1: TC1 external clock input pin
No pull-up, No wakeup function
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 90 V1.4
Page 91

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
10.3 PULL-UP RESISTERS
Pull-up register can set Pull-up register by Port. The typical pull-up register value is 200K@3V and 100K@5V.
¾ Port0
0E0H Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
P0UR
Read/Write - - - - - W W W
After reset - - - - - 0 0 0
¾ Port2
0E2H Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
P2UR
Read/Write W W W W W W W W
After reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
¾ Port4
0E4H Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
P4UR
Read/Write W W W W W W W W
After reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
¾ Port5
0E5H Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
P5UR
Read/Write W W W W W W W
After reset 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
 Example: I/O Pull up Register
CLR P0UR ; Disable Port0 Pull-up register.
MOV A, #01H ; ,
B0MOV P0UR, A ; Enable Port0.0 Pull-up Register
- - - - - P02R P01R P00R
P27r P26R P25R P24R P23R P22R P21R P20R
P47R P46R P45R P44R P43R P42R P41R P40R
P56R P55R P54R P53R P52R P51R P50R
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 91 V1.4
Page 92

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
I/O PORT MODE
The port direction is programmed by PnM register. Port 0 is always input mode. Port 1,2,3,4 and 5 can select input or
output direction.
P2M initial value = 0000 0000
0C2H Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
P2M
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Bit [7:0] P2 [7:0] M: P2.0~P2.7 I/O direction control bit.
P4M initial value = 0000 0000
0C4H Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
P4M
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Bit [7:0] P4 [7:0] M: P4.0~P4.7 I/O direction control bit.
P5M initial value = x000 0000
0C5H Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
P5M
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
Bit [6:0] P5 [6:0] M: P5.0~P5.6 I/O direction control bit.
P27M P26M P25M P24M P23M P22M P21M P20M
0 = Set P2 as input mode
1 = Set P2 as output mode
P47M P46M P45M P44M P43M P42M P41M P40M
0 = Set P4 as input mode
1 = Set P4 as output mode
P56M P55M P54M P53M P52M P51M P50M
0 = Set P5 as input mode
1 = Set P5 as output mode
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 92 V1.4
Page 93

8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
 Example: I/O mode selecting.
CLR P2M
CLR P4M
CLR P5M
MOV A, #0FFH ; Set all ports to be output mode.
B0MOV P2M, A
B0MOV P4M, A
B0MOV P5M, A
B0BCLR P2M.5 ; Set P2.5 to be input mode.
B0BSET P2M.5 ; Set P2.5 to be output mode.
SN8P2714X_2715
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 93 V1.4
Page 94

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
10.4 I/O PORT DATA REGISTER
P0 initial value = xxxx xxxx
0D0H Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
P0
- - - - R R R R
P2 initial value = xxxx xxxx
0D2H Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
P2
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
P4 initial value = xxxx xxxx
0D4H Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
P4
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
P5 initial value = xxxx xxxx
0D5H Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
P5
R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W R/W
 Example: Read data from input port.
B0MOV A, P0 ; Read data from Port 0
B0MOV A, P2 ; Read data from Port 2
B0MOV A, P4 ; Read data from Port 4
B0MOV A, P5 ; Read data from Port 5
 Example: Write data to output port.
MOV A, #55H ; Write data 55H to Port 1, Port2, Port 4, Port 5
B0MOV P2, A
B0MOV P4, A
B0MOV P5, A
- - - - P03 P02 P01 P00
P27 P26 P25 P24 P23 P22 P21 P20
P47 P46 P45 P44 P43 P42 P41 P40
P56 P55 P54 P53 P52 P51 P50
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 94 V1.4
Page 95

8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
 Example: Write one bit data to output port.
B0BSET P2.3 ; Set P2.3 and P4.0 to be “1”.
B0BSET P4.0
B0BCLR P2.3 ; Set P2.3 and P5.5 to be “0”.
B0BCLR P5.5
 Example: Port bit test.
B0BTS1 P0.0 ; Bit test 1 for P0.0
.
B0BTS0 P2.5 ; Bit test 0 for P2.5
SN8P2714X_2715
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 95 V1.4
Page 96

SN8P2714X_2715
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
A
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
11 8-CHANNEL ANALOG TO DIGITAL
CONVERTER
11.1 OVERVIEW
This analog to digital converter of SN8P2710 has 8-input sources with up to 4096-step resolution to transfer analog
signal into 12-bits digital data. The sequence of ADC operation is to select input source (AIN0 ~ AIN7) at first, then set
GCHS and ADS bit to “1” to start conversion. When the conversion is complete, the ADC circuit will set EOC bit to “1”
and final value output in ADB register.
IN0/P4.0
IN0/P4.0
IN0/P4.0
IN1/P4.1
IN1/P4.1
IN1/P4.1
IN2/P4.2
IN2/P4.2
IN2/P4.2
IN3/P4.3
IN3/P4.3
IN3/P4.3
IN4/P4.4
IN4/P4.4
IN4/P4.4
IN5/P4.5
IN5/P4.5
IN5/P4.5
IN6/P4.6
IN6/P4.6
IN6/P4.6
IN7/P4.7
IN7/P4.7
IN7/P4.7
¾ Note: The analog input level must be between the AVREFH and AVREFL.
¾ Note: The AVREFH level must be between the AVDD and VSS + 2.0V.
¾ Note: ADC programming notice:
Set ADC input pin I/O direction as input mode
Disable pull-up resistor of ADC input pin
Disable ADC before enter power down (sleep) mode to save power consumption.
Set related bit of P4CON register to avoid extra power consumption in power down mode.
Delay 100uS after enable ADC (set ADENB = “1”) to wait ADC circuit ready for conversion.
Disable ADC (set ADENB = “0”) before enter sleep mode to save power consumption.
/D
CONVERTER
Figure 11-1. AD Converter Function Diagram
CONVERTER
/D
(ADC)
(ADC)
DB
U
TS
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 96 V1.4
Page 97

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
11.2 ADM REGISTER
ADM initial value = 0000 x000
0B1H Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
ADM
R/W R/W R/W R/W - R/W R/W R/W
Bit 7 ADENB: ADC control bit.
Bit 6 ADS: ADC start bit.
Bit 5 EOC: ADC status bit.
Bit 4 GCHS: Global channel select bit.
Bit [2:0] CHS [2:0]: ADC input channels select bit.
ADENB ADS EOC GCHS - CHS2 CHS1 CHS0
0 = Disable ADC function
1 = Enable ADC function
0 = ADC convert stop
1 = ADC convert starting
0 = Progressing
1 = End of converting and reset ADS bit
0 = Disable AIN channel
1 = Enable AIN channel
000 = AIN0, 001 = AIN1, 010 = AIN2, 011 = AIN3
100 = AIN4, 101 = AIN5, 110 = AIN6, 111 = AIN7
11.3 ADR REGISTERS
ADR initial value = x00x 0000
0B3H Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
ADR ADCKS1 ADCKS0 ADB3 ADB2 ADB1 ADB0
R/W R/W R R R R
Bit 6,4 ADCKS [1:0]: ADC’s clock source select bit.
ADCKS1 ADCKS0 ADC Clock Source
0 0 Fcpu/16
0 1 Fcpu/8
1 0 Fcpu
1 1 Fcpu/2
Bit [3:0] ADB [3:0]: ADC data buffer.
ADB11~ADB0 bits for 12-bit ADC
11.4 ADB REGISTERS
ADB initial value = xxxx xxxx
0B2H Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
ADB
R R R R R R R R
ADB is ADC data buffer to store AD converter result. The ADB is only 8-bit register including bit 4~bit11 ADC data. To
combine ADB register and the low-nibble of ADR will get full 12-bit ADC data buffer. The ADC buffer is a read-only
register. the ADC data is stored in ADB and ADR registers.
¾ Note: ADB [0:11] value is unknown when power on.
ADB11 ADB10 ADB9 ADB8 ADB7 ADB6 ADB5 ADB4
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 97 V1.4
Page 98

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
The AIN’s input voltage v.s. ADB’s output data
AIN n
0/4095*AVREFH 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1/4095*AVREFH 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
. . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . .
4094/4095*AVREFH 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0
4095/4095*AVREFH 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
For different applications, users maybe need more than 8-bit resolution but less than 12-bit ADC converter. To process
the ADB and ADR data can make the job well. First, the AD resolution must be set 12-bit mode and then to execute
ADC converter routine. Then delete the LSB of ADC data and get the new resolution result. The table is as following.
ADC
Resolution
8-bit O O O O O O O O x x x x
9-bit O O O O O O O O O x x x
10-bit O O O O O O O O O O x x
11-bit O O O O O O O O O O O x
12-bit O O O O O O O O O O O O
O = Selected, x = Delete
ADB1
ADB10 ADB9 ADB8 ADB7 ADB6 ADB5 ADB4 ADB3 ADB2 ADB1 ADB0
1
ADB ADR
ADB11 ADB10 ADB9 ADB8 ADB7 ADB6 ADB5 ADB4 ADB3 ADB2 ADB1 ADB0
11.5 P4CON REGISTERS
ADB initial value = 0000 0000
0AEH Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0
P4CON
W W W W W W W W
The Port 4 is shared with ADC input function. Only one pin of port 4 can be configured as ADC input in the same time
by ADM register. The other pins of port 4 are digital I/O pins. Connect an analog signal to COMS digital input pin,
especially the analog signal level is about 1/2 VDD will cause extra current leakage. In the power down mode, the
leakage current will be a big issue. Unfortunately, if users connect more than one analog input signal to port 4 will
encounter above current leakage situation. P4CON is Port4 Configuration register. Write “1” into P4CON [7:0] will
configure related port 4 pin as pure analog input pin to avoid current leakage.
Bit[7:0] P4CON [7:0] Port4 Configuration register.
0 = P4.X can be an analog input (ADC input) or digital I/O pins.
1 = P4.X is pure analog input, can’t be a digital I/O pin.
P4CON7 P4CON6 P4CON5 P4CON4 P4CON3 P4CON2 P4CON1 P4CON0
Note: When Port4 [7:0] is general I/O port not ADC channel, P4CON [7:0] must set to “0” or the Port4
input signal would be isolated
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 98 V1.4
Page 99

SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
11.6 ADC CONVERTING TIME
12-bit ADC conversion time = 1/(ADC clock / 4 )*16 sec
High Clock (Fosc) = 4MHz
Fcpu ADCKS1 ADCKS0 ADC Clock ADC Converting Time
0 0 Fcpu/16 1/( ( 4MHz / 1 ) / 16 /4 ) x16= 256 us
Fosc/ 1
Fosc/ 2
Fosc/ 4
Fosc/ 8
¾ Note: ADC function can work in slow mode also. In slow mode, the Fcpu = LXOSC / 4 (LXOSC is internal
low RC oscillator).
¾ Note: Because the frequency of LXOSC (internal low RC oscillator) will vary with different temperature
and VDD, so ADC converting time will be effected.
 Example : Configure AIN0 as 12-bit ADC input and start ADC conversion then enter power down mode.
ADC0:
B0BSET FADENB ; Enable ADC circuit
CALL Delay100uS ; Delay 100uS to wait ADC circuit ready for conversion
MOV A, #0FEh
B0MOV P4UR, A ; Disable P4.0 pull-up resistor
B0BCLR FP40M ; Set P4.0 as input pin
MOV A, #01h
B0MOV P4CON, A ; Set P4.0 as pure analog input
MOV A, #40H
B0MOV ADR, A ; To set 12-bit ADC and ADC clock = Fosc.
MOV A,#90H
B0MOV ADM,A ; To enable ADC and set AIN0 input
B0BSET FADS ; To start conversion
WADC0:
B0BTS1 FEOC ; To skip, if end of converting =1
JMP WADC0 ; else, jump to WADC0
B0MOV A,ADB ; To get AIN0 input data bit11 ~ bit4
B0MOV Adc_Buf_Hi, A
B0MOV A,ADR ; To get AIN0 input data bit3 ~ bit0
AND A, 0Fh
B0MOV Adc_Buf_Low, A
Power_Down . .
B0BCLR FADENB ; Disable ADC circuit
B0BSET FCPUM0 ; Enter sleep mode
0 1 Fcpu/8 1/( ( 4MHz / 1 ) / 8 /4 ) x16= 128 us
1 0 Fcpu 1/( ( 4MHz / 1 ) / 1 /4 ) x16= 16 us
1 1 Fcpu/2 1/( ( 4MHz / 1 ) / 2 /4 ) x16= 32 us
0 0 Fcpu/16 1/( ( 4MHz / 2 ) / 16 /4 ) x16= 512 us
0 1 Fcpu/8 1/( ( 4MHz / 2 ) / 8 /4 ) x16= 256 us
1 0 Fcpu 1/( ( 4MHz / 2 ) / 1 /4 ) x16= 32 us
1 1 Fcpu/2 1/( ( 4MHz / 2 ) / 2 /4 ) x16= 64 us
0 0 Fcpu/16 1/( ( 4MHz / 4 ) / 16 /4 ) x16= 1024 us
0 1 Fcpu/8 1/( ( 4MHz / 4 ) / 8 /4 ) x16= 512 us
1 0 Fcpu 1/( ( 4MHz / 4 ) / 1 /4 ) x16= 64 us
1 1 Fcpu/2 1/( ( 4MHz / 4 ) / 2 /4 ) x16= 128 us
0 0 Fcpu/16 1/( ( 4MHz / 8 ) / 16 /4 ) x16= 2048 us
0 1 Fcpu/8 1/( ( 4MHz / 8 ) / 8 /4 ) x16= 1024 us
1 0 Fcpu 1/( ( 4MHz / 8 ) / 1 /4 ) x16= 128 us
1 1 Fcpu/2 1/( ( 4MHz / 8 ) / 2 /4 ) x16= 256 us
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 99 V1.4
Page 100

11.7 ADC CIRCUIT
Analog Signal Input
Analog Signal Input
VDD
VDD
AVREF
AVREF
AIN0/P40
AIN0/P40
0.1uF
0.1uF
AVREFH is connected to VDD.
SN8P2714X_2715
8-bit micro-controller build-in 12-bit ADC
MCU
MCU
VDD
VDD
AVREF
Reference Voltage Input
Reference Voltage Input
Analog Signal Input
Analog Signal Input
0.1uF
47uF
47uF
AVREFH is connected to external AD reference voltage.
Figure 11-2. The AINx and AVREFH Circuit of AD Converter
¾ Note: The capacitor between AIN and GND is a bypass capacitor. It is helpful to stable the analog signal.
Users can omit it.
0.1uF
AVREF
AIN0/P40
AIN0/P40
MCU
MCU
SONiX TECHNOLOGY CO., LTD Page 100
V1.4
 Loading...
Loading...