Page 1

After you install ACID and start it for the first time, the registration wizard appears. This wizard offers easy
steps that enable you to register ACID online with Sonic Foundry. Alternately, you may register ACID
online at www.sonicfoundry.com at any time.
Registering your product provides you with exclusive access to a variety of technical support options,
notification of product updates, and special promotions exclusive to ACID registered users.
Registration assistance
If you do not have access to the Internet, registration assistance is available during normal weekday business
hours. Please contact our Customer Service Department by dialing one of the following numbers:
Telephone/Fax Country
1-800-577-6642 (toll-free) US, Canada, and Virgin Islands
+800-000-76642 (toll-free) Australia, Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, Sweden, UK,
+608-204-7703 All other countries
1-608-250-1745 (fax) All countries
Netherlands, and Japan
Customer service/sales
For a detailed list of customer service options, we encourage you to visit www.sonicfoundry.com. Use the
following numbers for telephone support during normal office hours:
Telephone/Fax/E-mail Country
1-800-577-6642 (toll-free) US, Canada, and Virgin Islands
+800-000-76642 (toll-free) Australia, Denmark, France, Germany, Italy, Sweden, UK,
Netherlands, and Japan
+608-204-7703 All other countries
1-608-250-1745 (fax) All countries
customerservice@sonicfoundr y.com
Technical support
For a detailed list of technical support options, we encourage you to visit www.sonicfoundry.com/support.
• To listen to your support options, please call 608-256-5555.
• Customers who have purchased ACID Pro receive 60 days of complimentary phone support. The
complimentary support begins the date of your first call. (Registration is required to receive this
complimentary support.) Please call (608) 204-7704 if you need assistance with your Pro version product.
User manual feedback
If you have comments or suggestions about this user manual, we would like to hear from you. Send us e-mail
at docfeedback@sonicfoundry.com.
Page 2

Sonic Foundry, Inc.
1617 Sherman Avenue
Madison, WI 53704
USA
The information contained in this manual is subject to change without notice and does not represent a
commitment on the part of Sonic Foundry. The software described in this manual is provided under the
terms of a license agreement or nondisclosure agreement. The software license agreement specifies the terms
and conditions for its lawful use.
Sonic Foundry and ACID are registered trademarks of Sonic Foundry, Inc. ASIO is a trademark and VST is
a registered trademark of Steinberg Media Technologies AG. AC-3 is a trademark of Dolby Laboratories.
Other brands and products named here are the trademarks or registered trademarks of Sonic Foundry, its
affiliates, or their respective holders.
Copyright © 2002-2003 Sonic Foundry, Inc. This user guide can be reproduced for noncommercial reference
or personal/private use only and may not be resold. Any reproduction in excess of fifteen copies or electronic
transmission requires the written permission of Sonic Foundry.
A special note concerning the use of the Dolby Digital trademark:
Dolby Laboratories encourages use of the Dolby Digital trademark to identify soundtracks that are encoded
in Dolby Digital. This is an effective way to inform listeners of the soundtrack format, and the use of a
standard logo promotes easy recognition in the marketplace. However, like any trademark, the Dolby Digital
logo may not be used without permission. Dolby Laboratories therefore provides a standard trademark license
agreement for companies who wish to use Dolby trademarks. This agreement should be signed by the
company that owns the program material being produced. Recording studios or production facilities which
provide audio production or encoding services for outside clients generally do not require a trademark
license.
If you would like more information on obtaining a Dolby trademark license, please contact Dolby
Laboratories Licensing Corporation. Information on trademark licensing plus instructions for using the
Dolby Digital trademark and marking audio formats can also be found on-line at http://www.dolby.com.
Dolby Laboratories Licensing Corporation
100 Potrero Ave.
San Francisco, CA 94520 USA
Phone: 415-558-0200
Fax: 415-863-1373
E-mail: tsa@dolby.com
http://www.dolby.com
Page 3

Table of Contents
Introducing ACID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Welcome to Sonic Foundry ACID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
System requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
Installing ACID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Using online help. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .12
Online help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
What’sThis? help . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Help on the Web . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Overview of ACID. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
1
Main interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Toolbar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Track list . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Track view . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Window docking area . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Keyboard command reference . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Audio signal flow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
MIDI signal flow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
What’s New?. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Mixing. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .29
Plug-in effects automation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
5.1 surround mixing and surround pan automation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Alternate time signatures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
ASIO driver support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Loop Cloning in the Chopper . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Bus tracks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Enhanced time stretching for Beatmapped tracks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
New audio panning types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
New envelope fade types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
ReWire support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page 4

2
MIDI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
MIDI piano roll editing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
MIDI step recording . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
MIDI event list editing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
VSTi support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Yamaha OPT support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Optimized DLS and VSTi soft synth controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Workspace . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Multiple media file previewing and Explorer enhancements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Hotkey commands for track muting and soloing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Optimized ACID playback . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Autosave crash recovery . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Customizable default track properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Video . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Windows Media Audio and Video import . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .32
Enhanced video handling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Getting Started . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Starting projects. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Setting project properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Opening existing projects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Getting media files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Previewing media from the Explorer window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Adding media to the project . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Understanding track types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Loops . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
One-shots . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Beatmapped . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
MIDI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Adding and editing events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Painting events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Changing the length of events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Erasing sections of events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Moving events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Using the cursor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Positioning the cursor with the mouse . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Positioning the cursor with the keyboard . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Positioning the cursor with the Go To command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page 5

Making selections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .42
Selecting an event . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Selecting multiple events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Creating time selections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 44
Creating event selections within time selections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
Working with tracks. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .44
Reordering tracks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Resizing tracks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Changing track colors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Renaming tracks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Duplicating tracks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 45
Deleting tracks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Copying, cutting, and pasting tracks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Adjusting the mix . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 46
Muting tracks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 47
Soloing tracks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Working with groups of tracks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Using undo and redo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
3
Using undo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
Undoing all edits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Using redo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Clearing the undo history . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Playing the project. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
Using the transport bar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
Using playback options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Using the Mixer window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 50
Viewing the Mixer window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Using the mixer toolbar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Renaming mixer controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Using the mixer’s faders . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
Saving, rendering, and delivering projects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Saving projects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Rendering projects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Publishing to the Internet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Writing to CD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Editing Events. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Copying events. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .59
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page 6

4
Pasting events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Using the Paste command . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Using Paste Repeat . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Using Paste Insert . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
Cutting events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Deleting events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Trimming events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
Splitting events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Splitting at the cursor position . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
Splitting an event . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Splitting multiple events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Splitting a time selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Splitting events within a time selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Joining events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Ripple editing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
Cutting events in ripple editing mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
Deleting events in ripple editing mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Pasting events in ripple editing mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Slipping and sliding events. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
Shifting the contents of (slipping) events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Slip-trimming events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Sliding events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Changing event properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Using event envelopes. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Setting an event’s volume envelope . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
Setting an event’s fade-in and -out envelope curve . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Creating crossfades between events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
Working in the Track View . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Using project markers and regions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Working with standard markers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
Working with time markers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Working with command markers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 73
Working with regions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Using snapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Choosing snapping options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 78
Changing tempo, time signature, and key. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Changing project tempo . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 79
Changing project time signature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
Changing project key . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 80
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page 7

Working with tempo/key/time signature change markers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 81
Changing a track’s key . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Changing an event’s key . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Adjusting time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Inserting time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 82
Fitting to time . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 83
Using the Chopper . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Working in the Chopper window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Viewing the Chopper . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Changing the Chopper grid . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Changing Chopper snapping options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Magnifying the Chopper . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Previewing in the Chopper . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Using Chopper toolbar and keyboard commands . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Inserting markers and regions in the Chopper . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .87
Creating selections in the Chopper . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
5
Placing files in the Chopper . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Creating selections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
Creating selections of a specific musical length . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Inserting increments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .88
Creating increments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Creating increments of a specific musical length . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .89
Creating increments of a custom musical length . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Inserting selections in the track view. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .90
Using the Insert Selection button . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Using copy and paste . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Dragging selections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Moving the insert position in the track view . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Saving Chopper selections as new files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Using the Chopper with one-shots . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
Working with Tracks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Using track effects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .93
Creating or adding to track plug-in chains . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Arranging plug-in chain order . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Bypassing plug-ins in a chain . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Removing plug-ins from chains . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
Saving plug-in chains as packages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Removing or bypassing all effects on tracks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page 8

6
Using track envelopes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Adding track envelopes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Adjusting envelopes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 99
Using the Envelope tool . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
Hiding track envelopes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
Removing track envelopes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Choosing stereo pan types . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Using the Beatmapper. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
Understanding stretching properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Configuring track properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Adjusting general track properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 105
Adjusting stretching properties for loop or Beatmapped tracks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 106
Adjusting track properties for MIDI tracks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Reloading files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 108
Replacing files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Saving file properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Mixing multiple tracks to a single track . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 109
Exporting loops . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 110
Using the Mixer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Using busses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Adding busses to the project . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Routing tracks to busses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 111
Routing busses to system hardware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Deleting busses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 112
Using assignable effects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Adding assignable effect controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 113
Working with assignable effects chains . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
Routing tracks to assignable effect controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 114
Routing assignable effect controls to busses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .114
Deleting assignable effect controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Using soft synth controls. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 115
Adding soft synth controls to projects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Modifying soft synth control properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 116
Using ACID with ReWire panel applications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .119
Deleting soft synth controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
Routing MIDI tracks to soft synth controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page 9

Using mixer controls. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .120
Working with mixer controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .120
Adding effects to mixer controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
Working with multiple mixer controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .125
Automating mixer controls in track view . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .125
Recording in ACID. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 127
Recording audio. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .127
Setting ACID’s recording properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .128
Setting recording levels . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
Recording multiple takes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .130
Reviewing and saving takes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
Working with MIDI. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Adding MIDI tracks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .131
Adding MIDI files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .131
Creating new MIDI files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
Recording MIDI tracks. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .131
7
Changing MIDI track properties . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .132
Pitch shifting MIDI tracks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
Setting root notes for MIDI tracks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
Working with tracks in a MIDI file . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Previewing MIDI files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
Using the piano roll editor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .134
Viewing the piano roll editor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .135
Previewing MIDI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .135
Selecting MIDI tracks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .136
Adding note events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Editing note events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .137
Quantizing note events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Deleting note events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Undoing and redoing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Saving MIDI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Using the list editor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .140
Viewing the list editor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
Previewing MIDI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .140
Filtering the list . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
Editing events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .141
Creating events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
Step recording events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page 10

8
Quantizing events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 146
Deleting events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
Undoing and redoing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
Saving MIDI . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
Loading third-party OPT plug-ins. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
Saving, reloading, or replacing MIDI files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 148
Routing MIDI tracks to MIDI devices or soft synth controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
Resetting MIDI ports. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
Rendering projects with MIDI tracks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Playing MIDI from external devices. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Adding external devices as MIDI inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .150
Assigning MIDI inputs to soft synth controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
Synchronizing using MIDI timecode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
Generating MIDI timecode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
Triggering from MIDI timecode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
Generating MIDI clock . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
Working with Video. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
Managing video. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
Adding or replacing video files . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
Removing the video track . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
Hiding and showing the video track . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
Synchronizing audio and video . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
Removing the video’s audio . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Changing frame numbering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Editing video events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Moving video events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Trimming video events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Slipping and sliding video events . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
Using the Video window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
Using toolbar buttons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
Using the shortcut menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
Viewing the status bar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
Previewing on external monitors. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
Scoring video with ACID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
Working with 5.1 Surround . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
What is 5.1 surround?. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
Setting up surround hardware. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 158
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page 11

Setting up surround projects. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .158
Routing to hardware in the mixer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
Assigning audio to the LFE channel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .160
Panning audio. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .160
Panning tracks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .161
Panning mixer controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .162
Using the Surround Panner window . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .163
Automating panning. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .165
Turning on panning keyframes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
Adding panning keyframes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
Working with keyframes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 166
Rendering surround projects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .168
Burning AC-3 files to DVD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169
Customizing ACID . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
Working with ACID windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .171
9
Docking and floating ACID windows . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .172
Changing the time ruler format . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .173
Using the ruler offset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 173
Using the project grid . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .174
Setting the grid type . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
Using the toolbar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .175
Hiding and displaying the toolbar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .175
Reordering toolbar buttons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .175
Adding buttons to the toolbar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .176
Removing buttons from the toolbar . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
Using the time display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .177
Changing cursor position . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177
Changing the time display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177
Monitoring MIDI timecode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 178
Setting default track properties. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .178
Setting ACID preferences. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .179
Using the General tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .179
Using the Audio tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
Using the MIDI tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .182
Using the VST Instruments tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 182
Using the ReWire Devices tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .183
Using the Video tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .183
Using the Editing tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .183
Using the Sync tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 184
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page 12

10
Using the Other tab . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 185
ACID Tips and Tricks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 187
Adding long media files quickly. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 187
Playing with duplicate tracks. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 187
Detuning paired tracks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 187
Duplicating with offset . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 188
Creating ping-pong pan effects . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 188
Adding depth with assignable effects. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 189
Playing double time/half time. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 189
Constructing the wall of sound. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 190
Adding through subtraction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 190
Tweaking the dynamics. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 190
Fading in and out of mixes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 190
Adding build ups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
Creating wah-wah effects with automated Track EQ . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
Making automated changes more stark. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
Abruptly changing volume or pan . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 191
Turning automated effects on and off . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 192
Making automated frequency changes more natural. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 192
Overriding compress/expand. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193
Slicing and dicing in the Chopper . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193
Chopping new loops for alternate time signatures . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193
Chopping multiple files into a new loop . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 193
Creating drum-roll build ups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
Creating drum fills . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
Creating one-track remixes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
Creating DJ-style crossfades . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 194
Creating pseudo-granular synthesis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
Building instrument solos . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
Building scales . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 195
Glossary . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 197
Index . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .i
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page 13
CHAPTER
Introducing ACID
1
1
Welcome to Sonic Foundry ACID
Congratulations on purchasing a revolutionary software application for Windows. Using Sonic Foundry
®
ACID
System requirements
In order to use ACID, your computer must satisfy the following minimum specifications:
• 300 MHz processor (400 MHz processor required for video scoring)
• Microsoft Windows 98SE, Me, 2000, or XP
• 64 MB RAM (128 MB recommended)
• 60 MB hard-disk space for program installation
• Windows-compatible sound card
• CD-ROM drive (required for installation from CD-ROM)
• Supported CD-recordable drive (required for CD burning)
• DirectX 8.0 (included on CD-ROM)
• Internet Explorer, version 4.0 or higher (version 5.0 included on CD-ROM)
you can create great music by simply picking, painting, and playing.
11
Installing ACID
Prior to installing ACID, we recommend that you exit all open applications and temporarily turn off any
virus protection.
Note:
If you’re installing ACID on a system running
Windows 2000, your user account must be a member of the
Administrators group to install ACID and a member of the
Power Users group (or higher) to register ACID.
1.
Insert the ACID CD-ROM. The ACID Installation screen appears if CD-ROM AutoPlay is enabled.
Note:
If CD-ROM AutoPlay is turned off, click and
choose
Run. In the Run dialog, enter the CD-ROM drive’s
letter and add :\setup.exe. Click OK to begin installation.
2.
Click Install Software to begin the installation process.
3.
Follow the on-screen prompts and enter the necessary information when required. At the final screen
prompt, click
Finish.
CHP. 1 INTRODUCING ACID
Page 14
12
Using online help
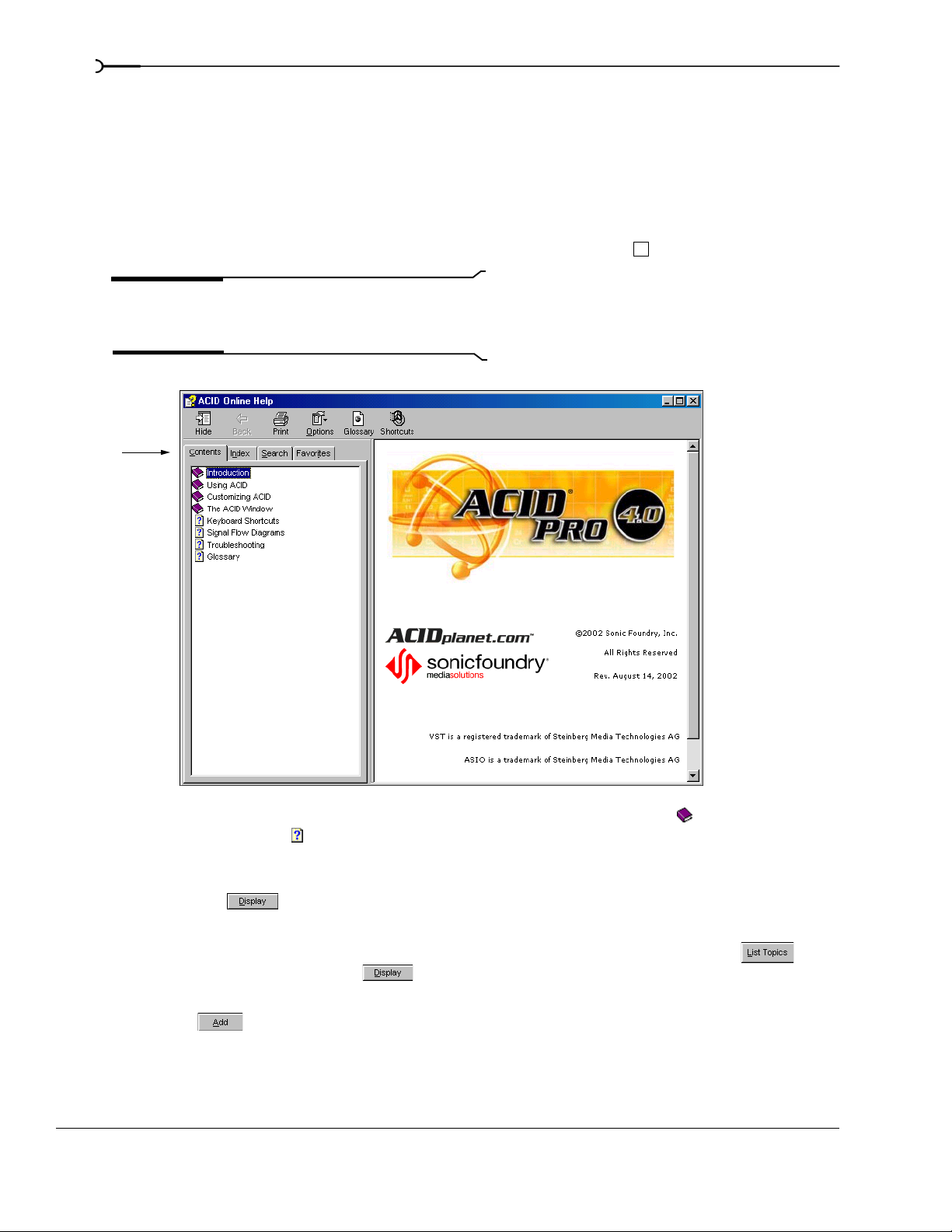
You can access two varieties of help within ACID:
• Online help
• What’sThis? help (also referred to as context-sensitive help)
Online help
To access online help, choose Contents and Index from the Help menu or press .
Note:
To view online help, Internet Explorer 4.0 or later
F1
must be installed on your system. Internet Explorer 5.0 is
included on the ACID CD-ROM for your convenience.
Tabs
The
Contents tab provides a list of available help topics. Double-click a closed book ( ) to open the pages
and then click a topic page ( ).
The
Index tab provides a complete listing of the help topics available. Scroll through the list of available
topics or type a word in the
Type in the keyword to find box to quickly locate topics related to that word. Select
the topic and click .
The
Search tab allows you to enter a keyword and display all of the topics in the online help that contain the
keyword you have entered. Type a keyword in the
Type in the word(s) to search for box and click .
Select the topic from the list and click .
The
Favorites tab allows you to keep topics that you revisit often in a separate folder. To add a topic to your
favorites, click on the
INTRODUCING ACID CHP. 1
Favorites tab.
Page 15
What’sThis? help
What’sThis? help allows you to view pop-up window descriptions for ACID menus, buttons, and dialog
boxes. Choose
What's This? from the Help menu, press , or click the What’sThis? help button ( ) on
Shift +F1
the toolbar and then click any ACID item. To use What’sThis? help in a dialog box, click the question mark
button ( ) in the upper-right corner of the dialog box and then click an item in the dialog box.
Help on the Web
Additional ACID help and information is available on the Sonic Foundry Web site. Choose Sonic Foundry
on the Web
from the Help menu to view a listing of Web pages pertaining to ACID and Sonic Foundry. If
your browser is not already open, ACID will automatically start it for you.
Overview of ACID
ACID is designed to be a powerful and flexible, but easy-to-use music creation application. Many of the
ACID operations, menu items, and shortcut keys are common to other Sonic Foundry applications.
The following sections provide a tour of the ACID work area.
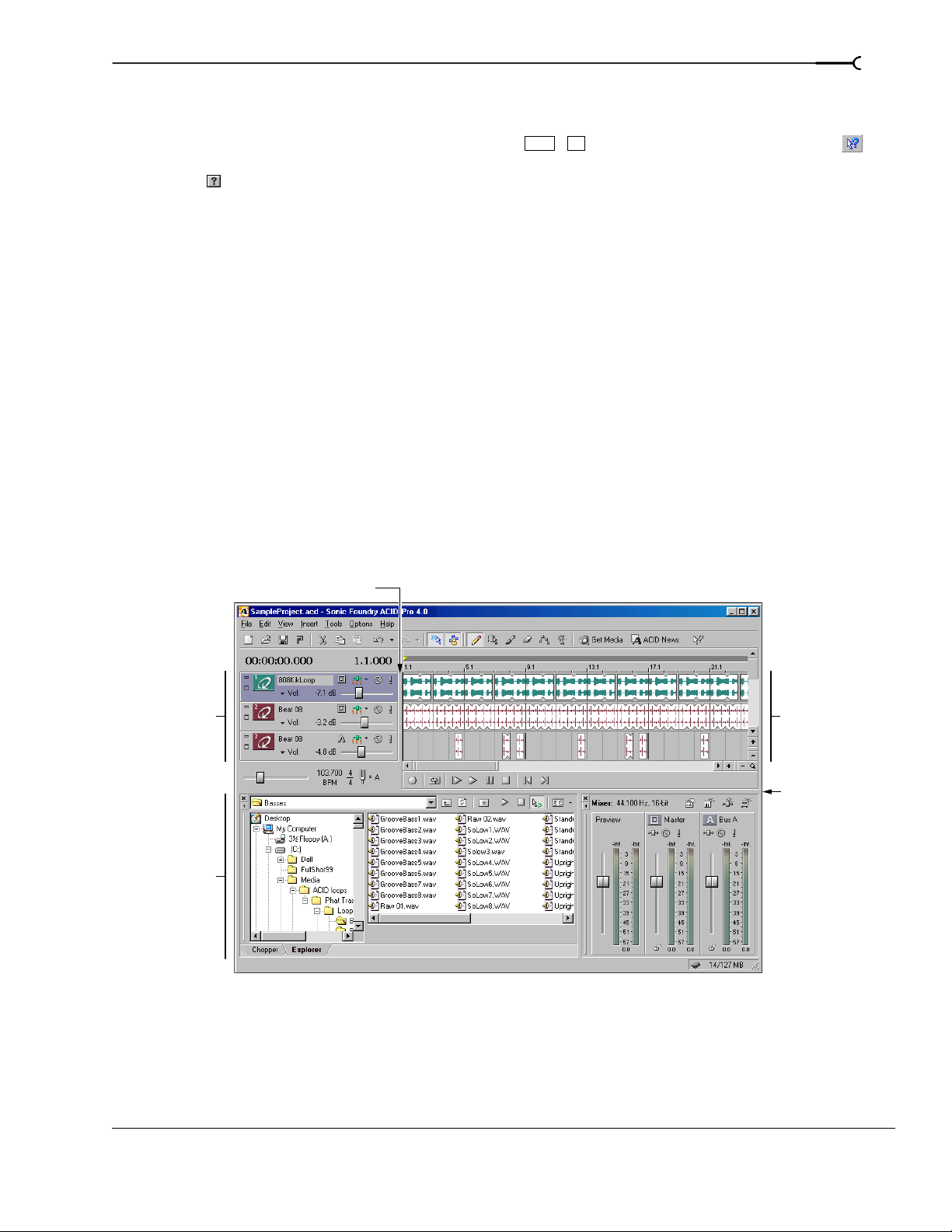
Main interface
The work area includes three main areas: the track list, the track view (or timeline), and the window
docking area. The other parts of the interface are tools and features used while creating and working with
your project. You can resize the track list, track view, and window docking area by dragging the dividers
between them.
13
Track list
Window
docking
area
Divider
Track view
Divider
CHP. 1 INTRODUCING ACID
Page 16

14
Toolbar
The toolbar allows you to quickly access the most commonly used functions and features in ACID.
Opens a new project. You will be prompted to
save any changes to the current project.
Displays the Open File dialog. From this
window, you can browse all of the available
drives to select an ACID project or audio file
to open.
Saves any changes to the current project.
The first time you save a project, the Save As
dialog appears.
Opens the Publish wizard so you can share
your ACID creation on the Web.
Clears the selected items from the track view
and places them on the ACID clipboard. You
can then paste them to a new location.
Creates a copy of the selected items from the
track view on the ACID clipboard. You can
then paste them to a new location.
Inserts the contents of the ACID clipboard at
the current cursor position. The pasted items
cover any existing events. To make room for
pasted events, choose Paste Insert from the
Edit menu.
Reverses the last action performed. ACID
supports unlimited undos, allowing you to
restore the project to any state since the last
save.
Reverses an undo. Opens a frequently updated Web page containing
Turns the snapping feature on or off. With
snapping enabled, you can decide whether to
snap to the grid or to all elements (markers,
regions, etc.).
Locks envelope points so they move with an
event when it is moved along the timeline.
Activates the Draw tool to add and edit events.
Activates the Selection tool to select multiple
events.
Activates the Paint tool to insert events across
multiple tracks.
When used in conjunction with the Ctrl key, the
Paint tool can paint an entire one-shot, MIDI, or
Beatmapped media file to an event with one
click.
Activates the Erase tool to erase events or parts
of events.
When used in conjunction with the Ctrl key, the
Erase tool can erase an entire one-shot, MIDI
track, or Beatmapped track event with one click.
Activates the Envelope tool to select and modify
envelope points.
Activates the Time Selection tool to quickly select
all events within range of time.
Opens a dialog where you can download media
from the Internet.
special offers, tips, tricks, and other good stuff.
Activates What’sThis? help to obtain information
about a specific option, menu, or part of the
ACID window.
INTRODUCING ACID CHP. 1
Page 17

Track list
This list identifies the track order in your project and contains the track’s controls. The following sections
identify and briefly explain the controls located in the track list.
Bus assignment
Track number/type
Track name
View buttons
View buttons
These buttons control the track’s appearance (size) on the track list and the track view.
Track number and type
This area identifies the type of file (loop, one-shot, MIDI, Beatmapped) contained in the track as well as the
track’s number in the project. You can quickly change the track order by dragging selected tracks within the
track list.
Track FX
Mute
Solo
Surround panner (surround projects only)
Multipurpose slider
Multipurpose slider label
15
Track type icons
Loop
One-shot
Beatmapped
MIDI
Track n ame
When you add a file to a project, the track name is initially the same name as the file’s name. Right-click the
track name and choose
Bus assignment
Rename from the shortcut menu (or double-click) to change the track name.
Clicking the Bus Assignment button ( ) and selecting a letter from the menu allows you to assign the
corresponding track to the specified output bus. However, the button is only available in projects containing
multiple busses. For more information, see Adding busses to the project on page 111.
On a MIDI track, the
Device Selection button ( ) appears instead of the Bus Assignment button. This button
allows you to route a MIDI track to a soft synth or MIDI device. For more information, see Routing MIDI tracks
to MIDI devices or soft synth controls on page 149.
Track FX button
The Track FX button ( ) accesses the Audio Plug-In window from which you can add, edit, and apply effects
to the track. The button image changes ( ) to indicate when an automatable effect is present. For more
information, see Using track effects on page 93.
CHP. 1 INTRODUCING ACID
Page 18
16
Mute button
Clicking the Mute button ( ) temporarily suspends playback of the corresponding track, allowing you to
focus on the project’s remaining tracks. A muted track appears grayed out in the track view. For more
information, see Muting tracks on page 47.
Solo button
Clicking the Solo button ( ) isolates the track during playback by muting the project’s remaining tracks. For
more information, see Soloing tracks on page 48.
Surround panner
In 5.1 surround projects, the surround panner allows you to view and edit surround panning settings for a
track. Double-click a surround panner to view the Surround Panner window and make fine panning
adjustments. For more information, see Working with 5.1 Surround on page 157.
Multipurpose slider
This multipurpose slider allows you to control the following:
• A track’s volume relative to the project’s other tracks.
• A track’s placement in the stereo spectrum (panning).
• The level of the track’s signal being routed to each of the project’s busses.
• The level of the track’s signal being routed to an assignable effect control.
The multipurpose slider defaults to displaying a track’s volume control. ACID tracks are preset to -6.0
decibels (dB), but the volume range is -inf. to 12 dB. Each track’s slider position is independent from the
others; however, you can move sliders simultaneously by selecting multiple tracks before making your
adjustment. If you do not see this slider, expand the track.
You may choose what the slider controls by clicking the slider label. Changing the slider type for one track
changes it for all tracks so you can compare levels of the same control across the project. For more
information, see Adjusting the mix on page 46.
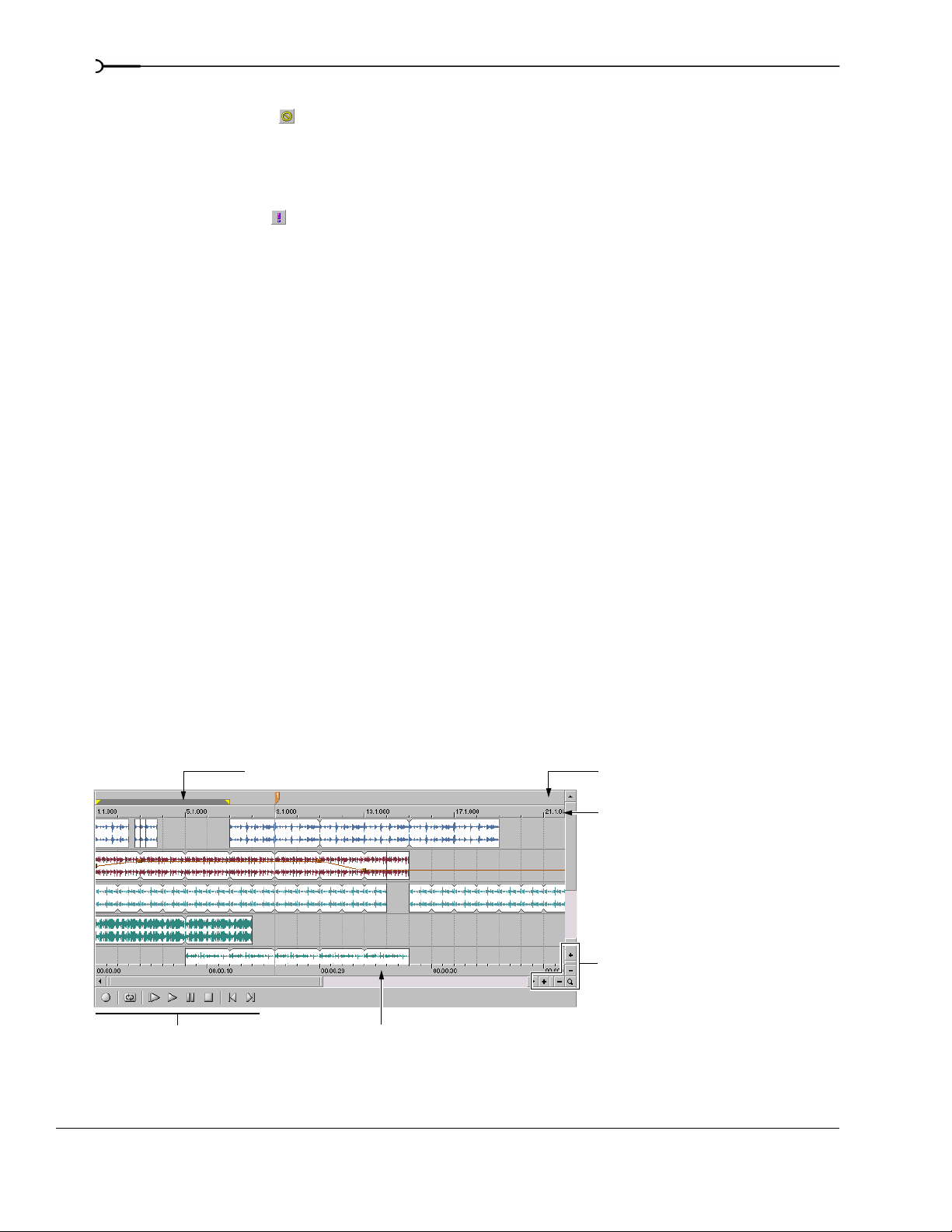
Track view
In the track view, you can view and edit the events in a track. The area in which events display is the
timeline. The track view contains other elements which are described in the following sections.
Loop bar
Marker bar
Beat ruler
Zoom controls
Transport Time ruler
INTRODUCING ACID CHP. 1
(if displayed)
Page 19
17
Marker bar
The marker bar runs the length of your project and contains the tags for markers and regions positioned
along the project’s timeline.
Beat ruler
The beat ruler allows you to place events in reference to the musical time of bars and beats. This ruler is
fixed and does not update when you change the tempo. This allows the events in the tracks to maintain
their size when you adjust the tempo.
Time ruler
The time ruler provides a timeline for your project. This ruler can show real time in many different formats.
For more information, see Changing the time ruler format on page 173. The ruler changes with tempo, since the
number of beats and beats per second of real time changes with tempo.
Tran sport bar
The transport bar contains the playback and cursor positioning buttons frequently used while working on
your project.
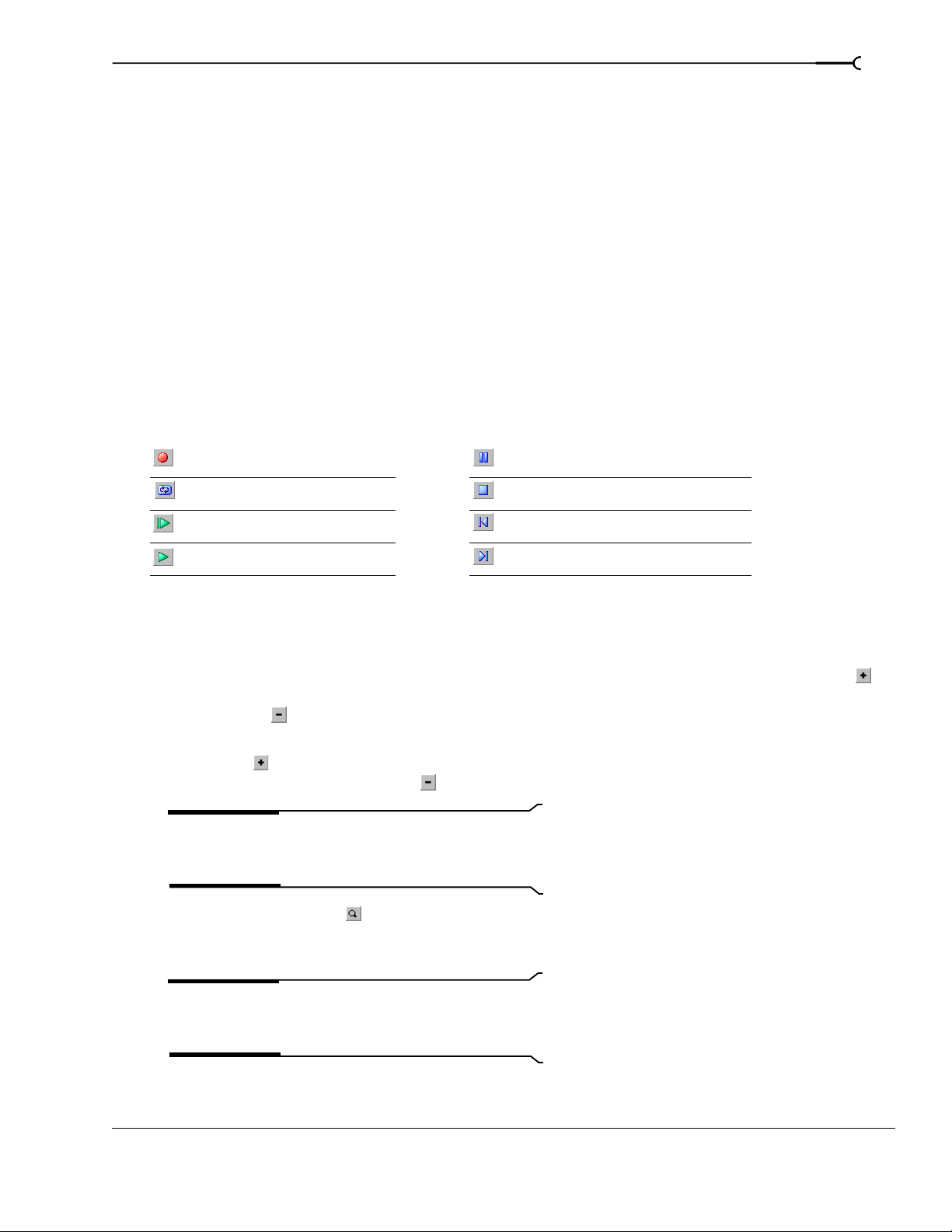
Record new track Pause/resume project playback
Loop playback Stop playback
Play from beginning of project Move cursor to start of project
Play project from cursor position Move cursor to end of project
ACID also includes keyboard shortcuts for these playback commands. For more information, see Playback
commands on page 19.
Zoom controls
To the right of the horizontal scroll bar are the time zoom controls. Clicking the Zoom In Time button ( )
increases the horizontal magnification of the project. To decrease the level of magnification, click the
Out Time button ( ).
Directly below the vertical scroll bar are the dedicated track height zoom controls. Clicking the
button ( ) increases the vertical magnification of the project. To decrease the level of magnification,
Height
click the
Zoom Out Track Height button ( ).
Note:
Double-clicking the horizontal or vertical scroll bars
Zoom In Track
Zoom
adjusts the magnification so that as much of the project (either
horizontally or vertically) is displayed as possible.
Click the
Zoom Tool button ( ) in the corner of the track view to temporarily change the cursor into the
Zoom tool. After you select an area of the track view to magnify, the cursor reverts to the previously active
tool.
Note:
Double-clicking the Zoom tool adjusts both the
horizontal and vertical magnification so that as much of the
project is displayed as possible.
CHP. 1 INTRODUCING ACID
Page 20
18
Window docking area
This area allows you to keep frequently-used windows available
while working on a project. Windows can be docked side by side
or in stacks in the windows docking area. For more information,
see Docking and floating ACID windows on page 172.
Two windows display in the window docking area when you
start ACID for the first time: the Explorer and the Mixer. The
Chopper™, Video, Audio Plug-In, Track Properties, Surround
Panner, and Soft Synth Properties windows can be docked or
undocked after they are displayed by choosing the desired
window from the
Tip:
You can quickly hide or show the window docking area
by pressing .
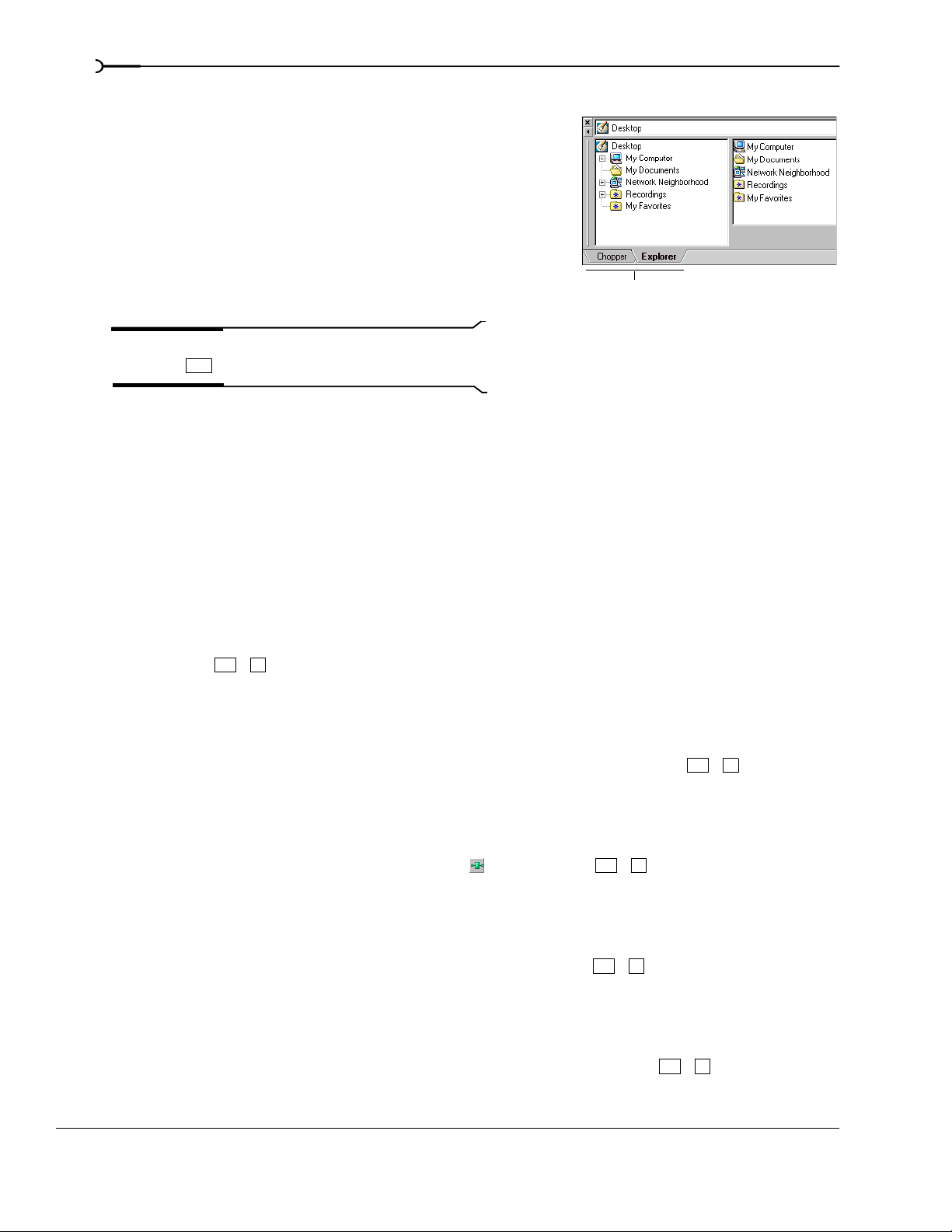
Explorer window
View menu.
F11
The Explorer window works similarly to the Windows Explorer. You can use the Explorer window to locate,
preview and select media files to be added to your project. You can also use the Explorer window to perform
common file management tasks, such as renaming files or creating folders.
Click a tab to
view a window
Mixer
The Mixer window provides access to output levels, as well as advanced features such as busses, assignable
effect chains, and soft synth controls. For more information, see Using the Mixer window on page 50.
Chopper
The Chopper isolates audio events so that you can dissect them and reinsert them into a project to produce
elaborate slice-n-dice effects with minimal effort. Display the Chopper by choosing
menu or pressing . For more information, see Using the Chopper on page 85.
Video
Alt +2
Chopper from the View
This window displays prerendered video files that can be imported and synchronized with an ACID project.
The video file displays during project playback and can be rendered with the project to an appropriate
Alt
format. Display the Video window by choosing
Video from the View menu or pressing . For more
+4
information, see Using the Video window on page 155.
Audio Plug-In
This window displays plug-ins and settings for track, assignable, bus, and soft synth effects chains. Display
the Audio Plug-In window by clicking any
FX button ( ) or by pressing . For more information, see
Alt +5
Using track effects on page 93 and Adding effects to mixer controls on page 121.
Track Properties
This window allows you to change track attributes and edit MIDI tracks using OPT plug-ins. Display the
Alt
Track Properties window by double-clicking a track’s icon or by pressing . For more information, see
+6
Configuring track properties on page 105 and Working with MIDI on page 131.
Surround Panner
This window allows you to control panning in a 5.1 surround project. Display the Surround Panner window
+7
by double-clicking the surround panner on a track or mixer control or by pressing . For more
Alt
information, see Working with 5.1 Surround on page 157.
INTRODUCING ACID CHP. 1
Page 21

Soft Synth Properties
This window allows you to change the attributes of soft synth controls in the Mixer window. Display the
Soft Synth Properties window by double-clicking a soft synth control’s icon or by pressing . For more
Alt +8
information, see Using soft synth controls on page 115.
Keyboard command reference
The ACID keyboard commands are shortcuts that you can use while working on your project.
Project file commands
Description Keys Description Keys
Create new project Ctrl+N Save project Ctrl+S
Create new project and bypass the
Project Properties dialog
Open existing project or media file Ctrl+O Close current project Ctrl+F4
Window view commands
Description Keys Description Keys
Set focus to track view Alt+0 Shift focus forward through open
View the Explorer window Alt+1 Shift focus backward through open
View the Chopper window Alt+2 Shift focus forward (clockwise)
View the Mixer window Alt+3 Shift focus backward
View the Video window Alt+4 Show/hide bus tracks U
View the Audio Plug-In window Alt+5 Show/hide window docking area F11
View the Track Properties window Alt+6 Show/hide track list Shift+F11
View the Surround Panner window Alt+7 Show/hide track list and window
View the Soft Synth Properties
window
Ctrl+Shift+N Open project’s properties Alt+Enter
F6
ACID windows
Shift+F6
ACID windows
Tab
through track list, track view, bus
track view, and bus track list
Shift+Tab
(counterclockwise) through track
list, bus track list, bus track view,
and track view
Ctrl+F11
docking area
Alt+8
19
Playback commands
Description Keys Description Keys
Start/stop playback Spacebar Record Ctrl+R
Stop playback Esc Go to start Ctrl+Home or W
Toggle looped playback on/off Q Go to end Ctrl+End
Play from start Shift+Spacebar (when working
in the track view)
Shift+F12 (from any window)
Play from cursor Ctrl+Spacebar (when working in
the track view)
F12 (from any window)
Pause/resume playback Enter (when working in the
track view)
Ctrl+F12 (from any window)
CHP. 1 INTRODUCING ACID
Skip backward Page Up
Skip forward Page Down
Reset all MIDI ports (panic button) Ctrl+Alt+F7
Page 22

20
Cursor placement commands
Description Keys Description Keys
Go to beginning of active loop
region or view (if no selection)
Go to end of active loop region or
view (if no selection)
Go to beginning of project Ctrl+Home or W Move left to marker(s) Ctrl+Left Arrow
Go to end of project Ctrl+End Move right to marker(s) Ctrl+Right Arrow
Move left by grid marks Page Up Move left to event edit points
Move right by grid marks Page Down Move right to event edit points
Go to
(using measures, beats, and ticks)
Go to
(using absolute time)
Move cursor to corresponding
marker or region
Home Center in view \
End Move cursor to opposite end of time
selection or loop bar
including fade edges
including fade edges
Ctrl+G Move by one pixel Left or Right Arrow
Shift+G Move through a video event one
frame at a time
Number keys (not on numeric
keypad)
Numeric keypad 5
Ctrl+Alt+Left Arrow
Ctrl+Alt+Right Arrow
Alt+Left or Right Arrow
Loop region commands
Description Keys Description Keys
Make a loop region Shift+Left or Right Arrow Double loop region length ‘ (apostrophe)
Extend loop region left by grid
marks
Extend loop region right by grid
marks
Expand loop region one pixel Shift+Left or Right Arrow Shift loop region right . (period)
Make a loop region during playback I (in) and O (out) Snap loop region to event edges Ctrl+Shift+Alt+Left or Right
Restore past loop regions
(up to last five)
Select loop region Shift+Q (when Time Selection
Shift+Page Up Halve loop region length ; (semicolon)
Shift+Page Down Shift loop region left , (comma)
Arrow
Backspace Expand loop region by one video
frame
tool is selected)
Shift+Alt+Left or Right Arrow
Selection commands
Description Keys Description Keys
Range selection (events) Shift+click range of events Select all Ctrl+A
Multiple selection (events) Ctrl+click individual events Unselect all Ctrl+Shift+A
Select loop region Shift+Q (when Time Selection
tool is selected)
Event commands
Description Keys Description Keys
Paint the entire media file as an
event for one-shot, Beatmapped,
and MIDI tracks
Erase entire event for one-shot,
Beatmapped, and MIDI tracks
Undo Ctrl+Z Slide: move the event while leaving
Redo Ctrl+Shift+Z Temporarily disable snapping while
Cut selection Ctrl+X Copy event Ctrl+drag event
Copy selection Ctrl+C Pitch down one semitone Numeric keypad Paste from clipboard Ctrl+V Pitch up one semitone Numeric keypad +
Paste repeat Ctrl+B Pitch down one octave Ctrl+Numeric keypad Paste insert Ctrl+Shift+V Pitch up one octave Ctrl+Numeric keypad +
Ctrl+click (on track with Paint
tool enabled)
Ctrl+click (on event with Erase
tool enabled)
Slip Trim: moves the media with the
edge as it is trimmed
Slip: move media within event
without moving the event
the relative position of the media in
place
moving event
Alt+drag edge of event
Alt+drag inside event
Ctrl+Alt+drag event
Shift+drag
INTRODUCING ACID CHP. 1
Page 23

Description Keys Description Keys
Delete selection Delete Pitch down 4 semitones
(Windows 2000 and XP only)
Move selected event(s) right one
pixel
Move selected event(s) left one pixel Numeric keypad 4 Reset pitch
Split event(s) S Change an event’s gain value Numeric keypad / or *
Join events J Change an event’s gain by 10% Shift+Numeric keypad / or *
Create fades F Change an event’s gain by 25% Ctrl+Numeric keypad / or *
Render to new track Ctrl+M Set an event’s gain to 0.0 dB Ctrl+Shift+Numeric keypad *
Trim/crop time-selected events only Ctrl+T Set an event’s gain to -inf (silence) Ctrl+Shift+Numeric keypad /
Numeric keypad 6 Pitch up 4 semitones
(Windows 2000 and XP only)
(Windows 2000 and XP only)
Shift+Numeric keypad -
Shift+Numeric keypad +
Ctrl+Shift+Numeric keypad - or
+
Track view commands
Description Keys Description Keys
Record Ctrl+R Show/hide bus tracks U
Turn on/off ripple edit mode Ctrl+L Turn on/off snapping F8
Select Draw tool Ctrl+D Toggle between snap to grid and
snap to all
Select next edit tool in list D Insert region R
Select previous edit tool in list Shift+D Insert marker M
Mark in point for selection I or [ Insert time marker H
Mark out point for selection O or ] Insert command marker C
Show/hide track panning envelope P Insert tempo change marker T
Insert/remove track panning
envelope
Show/hide track volume envelope V Insert tempo and key change
Insert/remove track volume
envelope
Toggle through display of track
effect automation envelopes
Adjust envelope point value in fine
increments without changing the
envelope point’s timeline position
Adjust envelope point value in
normal increments without changing
the envelope point’s timeline
position
Move envelope point’s timeline
position without changing its value
Shift+P Insert key change marker K
marker
Shift+V Insert time signature change marker Shift+K
E Change project tempo Alt+drag time marker
Ctrl+drag envelope point or
segment
Ctrl+Alt+drag envelope point
or segment
Alt+drag envelope point
Insert MIDI track Ctrl+Alt+Q
Render to new track Ctrl+M
Ctrl+F8
Shift+T
21
Track list commands
Description Keys Description Keys
Solo track X Decrease fader value Left Arrow
Mute track Z Increase fader value Right Arrow
Delete track Delete Move track selection up one track Up Arrow
Pitch down one semitone Numeric keypad - Move track selection down one track Down Arrow
Pitch up one semitone Numeric keypad + Multi-select tracks Shift+Up or Down Arrow
Pitch down four semitones
(Windows 2000 and XP only)
Pitch up four semitones
(Windows 2000 and XP only)
Pitch down one octave Ctrl+Numeric keypad - Select all tracks Ctrl+A
Pitch up one octave Ctrl+Numeric keypad + Unselect all tracks Ctrl+Shift+A
Reset pitch
(Windows 2000 and XP only)
CHP. 1 INTRODUCING ACID
Shift+Numeric keypad - Move track selection up one screen
of tracks
Shift+Numeric keypad + Move track selection down one
screen of tracks
Ctrl+Shift+Numeric keypad +/-
Page Up
Page Down
Page 24
22
View commands
Description Keys Description Keys
Zoom time in/out small increments
when track view has focus or zoom
to loop region (if one exists)
Zoom time in/out large increments
when track view has focus
Up or Down Arrow Zoom track height in/out small
increments when track view has
focus
Ctrl+Up or Down Arrow
Shift+Up or Down Arrow
Mixer commands
Description Keys Description Keys
Change selection of a mixer control Left/Right Arrow Move the left channel of the fader
Select multiple, adjacent mixer
controls
Select multiple nonadjacent mixer
controls
Move the fader of the selected mixer
control (for assignable effect
controls, moves the Out fader)
Shift+Left/Right Arrow Move the right channel of the fader
Ctrl+Left/Right Arrow Delete the selected bus or control Delete
Up/Down Arrow
for the selected mixer control
for the selected mixer control
Shift+Up/Down Arrow
Ctrl+Up/Down Arrow
MIDI commands
Description Keys Description Keys
Generate MIDI Timecode F7 Enable real-time MIDI Alt+F7
Trigger from MIDI Timecode Ctrl+F7 Reset all MIDI ports (panic button) Ctrl+Alt+F7
Generate MIDI Clock Shift+F7
Chopper commands
For more information, see Using Chopper toolbar and keyboard commands on page 86.
Surround Panner commands
For more information, see Moving the pan point on page 164.
Miscellaneous commands
Description Keys
Online help F1
What’sThis? help Shift+F1
Shortcut menu Shift+F10
Refresh screen F5
INTRODUCING ACID CHP. 1
Page 25

Mouse scroll-wheel shortcuts
Description Keys
Zoom in on timeline Default mouse wheel behavior
Horizontal scroll Shift+wheel
Vertical scroll Ctrl+wheel
Move by video frames Ctrl+Shift+Alt+wheel
Move the cursor in grid increments Ctrl+Shift+wheel
Auto-scrolling Press mouse wheel and move
Move fader Wheel over a fader
Make fine fader adjustments Ctrl+wheel over a fader
Move pan point front/back in
Surround Panner window
Move pan point left/right in
Surround Panner window
the mouse in the desired
direction
Default mouse wheel behavior
(when pan point is selected)
Shift+wheel
(when pan point is selected)
23
CHP. 1 INTRODUCING ACID
Page 26
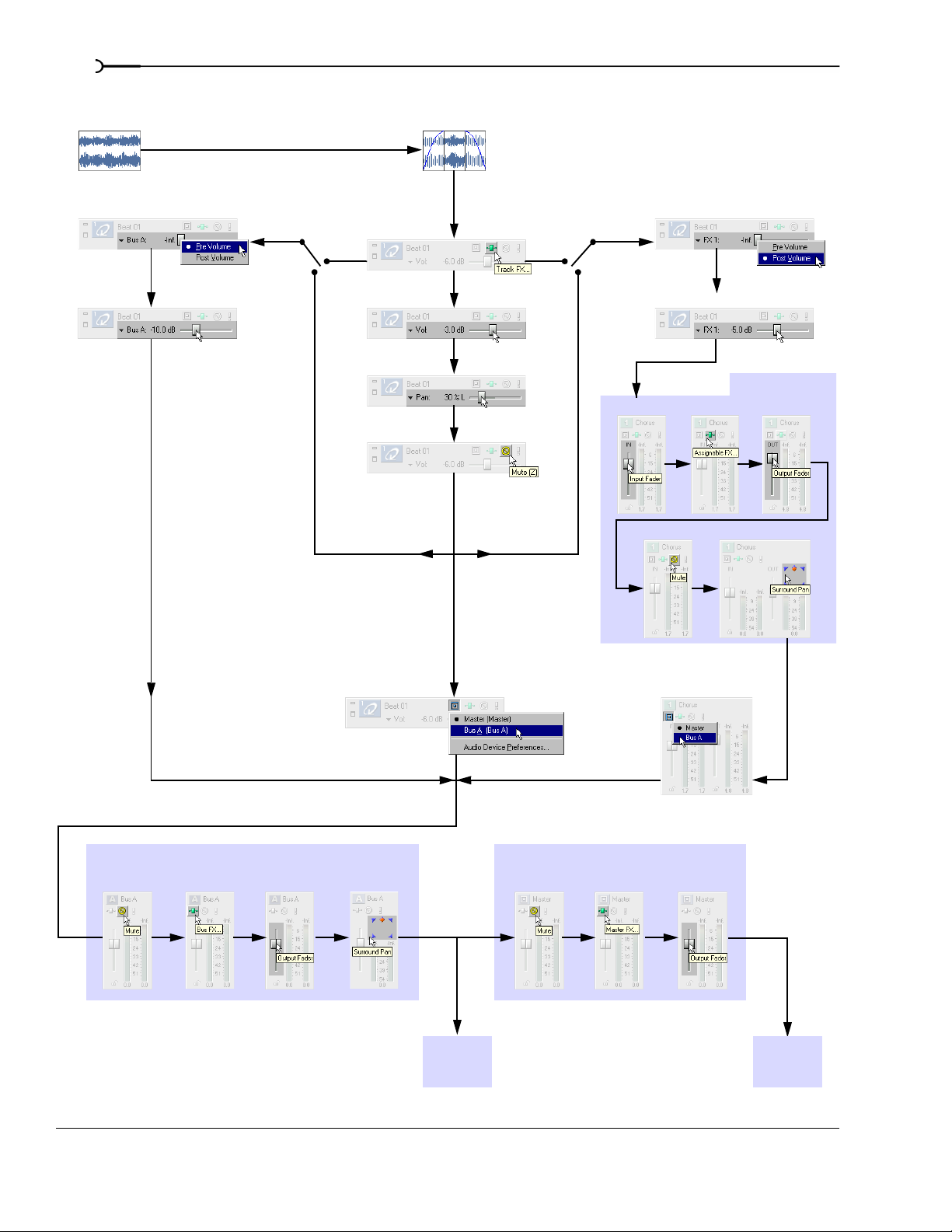
24
Audio signal flow
Audio event* Event envelope
Bus pre/post volume
Bus send
Post
Track FX
Pre
Track volume
Pan track
Mute track
Assignable FX
pre/post volume
Pre
Post
†
Assignable FX send
Assignable FX
Input Chain Output
‡
Mute
(Pan)
Bus Control
Bus assignment
Bus assignment
Master Bus Control
VolumeFX Mute
(Pan)
^
Hardware
output
VolumeFX Mute
Hardware
output
INTRODUCING ACID CHP. 1
Page 27

25
Notes on audio signal flow
* This diagram describes non-MIDI audio events. For MIDI events, see MIDI signal flow on page 26.
† In 5.1 surround projects, tracks routed to the Surround Master bus send surround panning (six-channel)
information. Tracks routed to busses (e.g., Bus A) send stereo panning (two-channel) information.
‡ Assignable effect chain panning is available only in 5.1 surround projects. In 5.1 surround projects,
assignable effect chains routed to the Surround Master bus send surround panning (six-channel)
information. Assignable effect chains routed to busses (e.g., Bus A) send stereo panning (two-channel)
information.
^ Bus panning is available only in 5.1 surround projects. In 5.1 surround projects, busses routed to the
Surround Master bus send surround panning (six-channel) information. Busses routed to hardware send
stereo panning (two-channel) information.
CHP. 1 INTRODUCING ACID
Page 28

26
MIDI signal flow
MIDI event Track volume
Mute track
Device or soft synth assignment
DLS or VSTi assignment
External
MIDI
device
Bus Control
Soft Synth Control
VolumeFX Mute
(Pan)
DLS
voice set
^
MIDI
Audio
VST
instrument
VolumeFX Mute
Master Bus Control
(Pan)*
VolumeFX Mute
Hardware
output
INTRODUCING ACID CHP. 1
Hardware
output
Page 29

27
Notes on MIDI signal flow
* Soft synth panning is available only in 5.1 surround projects. In 5.1 surround projects, soft synth controls
routed to the Surround Master bus send surround panning (six-channel) information. Soft synth controls
routed to busses (e.g., Bus A) send stereo panning (two-channel) information.
^ Bus panning is available only in 5.1 surround projects. In 5.1 surround projects, busses routed to the
Surround Master bus send surround panning (six-channel) information. Busses routed to hardware send
stereo panning (two-channel) information.
CHP. 1 INTRODUCING ACID
Page 30

28
INTRODUCING ACID CHP. 1
Page 31

CHAPTER
What’s New?
2
2
This chapter is intended for experienced ACID users. It simply addresses the question on everyone’s mind:
“What’s new in this version of ACID?”
Mixing
Plug-in effects automation
In ACID 4.0, you can automate the parameters of plug-ins, provided that the plug-ins support automation.
Effect automation relies on track envelopes, a tool you may already be familiar with from creating volume,
pan, bus send, or assignable effect send envelopes.
29
You can choose which parameters of a given effect to automate and then add points to a track envelope for
the different parameter settings. By viewing bus tracks, you can automate effects not only for tracks, but for
busses, assignable effects, and soft synth controls. For more information, see Bus tracks on page 30.
ACID 4.0 includes new Sonic Foundry automatable effects such as Flange/Wah-wah, Resonant Filter, and
Tr ac k E Q .
For more information, see Adding effect automation envelopes on page 98.
5.1 surround mixing and surround pan automation
ACID 4.0 introduces 5.1 surround mixing capability and surround panning automation. In a surround
project, you pan tracks or busses using the Surround Panner window. For even greater control, you can add
keyframes to automate panning changes over time.
Note:
ACID mixes 5.1-channel audio only. Authoring
software such as the Sonic Foundry 5.1 Surround Plug-In
Pack is required to encode final output in AC-3™ format.
For more information, see Working with 5.1 Surround on page 157.
Alternate time signatures
ACID 4.0 breaks free from the 4/4 model and allows you to see (and snap to) measures of any time signature
from 1/1 to 99/32. You can choose a custom time signature for the project, as well as change time signatures
along the timeline by adding time signature change markers. For more information, see Changing tempo, time
signature, and key on page 79.
CHP. 2 WHAT’S NEW?
Page 32

30
ASIO driver support
In addition to supporting Microsoft Mapper, Windows Classic Wave, and WDM drivers, ACID 4.0 now
supports ASIO™ drivers. With its more direct data delivery to the sound card, the ASIO driver model
provides professional users with faster audible responses. You can choose which driver model ACID uses on
the
Audio tab in the Preferences dialog. For more information, see Using the Audio tab on page 181.
Loop Cloning in the Chopper
ACID 4.0 provides the option to create new loops using the Chopper. Simply open a track in the Chopper,
make a selection for the new loop, and drag the selection to the track list. ACID saves the selection as a new
file and adds it to the project as a new track. For more information, see Saving Chopper selections as new files on
page 90.
Bus tracks
You can now view any mixer control (bus, assignable effect, or soft synth) on a track at the bottom of the
track view. This allows you to add envelopes to any of these controls. Want to pan several tracks as a group?
Route the tracks to a bus and pan the bus using a pan envelope on the bus track. Want your assignable effect
parameters to change over time? Add an effect automation envelope to the bus track for the assignable
effect. For more information, see Automating mixer controls in track view on page 125.
Enhanced time stretching for Beatmapped tracks
In ACID 4.0, you can time-stretch a Beatmapped track with less stuttering and improved playback.
New audio panning types
Whether you’re using standard stereo panning or 5.1 surround panning, you can choose from among five
types of panning for ACID tracks and busses. For more information, see Choosing stereo pan types on page 103.
New envelope fade types
ACID 4.0 provides three new fade types: smooth, sharp, and hold. Fade types determine the interpolation
between two envelope points. For more information, see Changing envelope fade curves on page 100.
ReWire support
ACID is now a ReWire mixer (host) application. For more information, see Using soft synth controls on page
115.
MIDI
MIDI piano roll editing
ACID 4.0 introduces a piano roll editor that you can use to create, edit, and quantize MIDI data. The piano
roll editor is one of two OPT (Open Plug-in Technology) plug-ins included in ACID 4.0. For more
information, see Using the piano roll editor on page 134.
MIDI step recording
The new list editor OPT plug-in allows you to step record MIDI from within ACID. For more information, see
Step recording events on page 145.
WHAT’S NEW? CHP. 2
Page 33

MIDI event list editing
ACID 4.0 includes a list editor OPT plug-in that gives you direct access to all MIDI data for a track. You can
use the list editor to add, edit, quantize, and delete MIDI events or to step record new MIDI material. For
more information, see Using the list editor on page 140.
VSTi support
You can route MIDI tracks in an ACID 4.0 project to a VST® instrument (VSTi) using the new soft synth
controls in the Mixer window. For more information, see Using soft synth controls on page 115.
Yamaha OPT support
ACID 4.0 is an early adopter for Yamaha's new Open Plug-in Technology (OPT) specification. You can
choose any OPT plug-in (including a piano roll editor and a list editor included with ACID) to edit a MIDI
track. This expands ACID's MIDI capabilities to allow plug-ins for MIDI edit views, MIDI effect processors
and filters, arpeggiators, and real-time panel automation. For more information, see Working with MIDI on page
131.
Optimized DLS and VSTi soft synth controls
With this release, you can route MIDI tracks to a soft synth control in the Mixer window. The soft synth
control acts as a sound module, allowing you to choose a DLS set or VST instrument to which you can route
MIDI tracks or external MIDI input devices. For more information, see Using soft synth controls on page 115.
31
Workspace
Multiple media file previewing and Explorer enhancements
The Explorer allows you to select multiple files and preview them in sequence. For more information, see
Previewing multiple media files on page 35.
You can also rename media files from within the Explorer window. Simply right-click a file, choose
from the shortcut menu, and enter a new name for the file.
Hotkey commands for track muting and soloing
X Z
Press to solo or to mute selected tracks or busses in your ACID 4.0 project.
Optimized ACID playback
The new ACID audio engine is designed to take advantage of the latest processing power, allowing you to
enjoy significant performance increases during playback.
Autosave crash recovery
ACID automatically saves your work for you so that you can recover your work if your system crashes. For
more information, see Using the General tab on page 179.
Customizable default track properties
Rename
You can choose the default volume, pan type, height, track effects, and MIDI editors for all new tracks you
create in ACID. For more information, see Setting default track properties on page 178.
CHP. 2 WHAT’S NEW?
Page 34

32
Video
Windows Media Audio and Video import
You can now add Windows Media Audio (WMA) and Windows Media Video (WMV) files to an ACID
project.
Enhanced video handling
ACID 4.0 provides two new options for rendering projects containing video: Stretch video to fill output frame
(do not letterbox)
In addition, the Video window now provides an option to display square pixels to compensate for any spatial
distortions due to non-square pixel aspect ratios. For more information, see Using the Video window on page
155.
and Fast video resizing. For more information, see Rendering projects on page 54.
WHAT’S NEW? CHP. 2
Page 35

CHAPTER
Getting Started
3
3
Now that you have an understanding of ACID’s interface and controls, you are ready to begin learning the
techniques needed to pick, paint, and play ACID projects. In this chapter you will learn the skills that will
allow you to create music in ACID, from locating media files to writing the finished project to CD.
Starting projects
Double-clicking the ACID icon on the desktop starts ACID. You can immediately begin building your
ACID project using the application’s default project properties. However, you may prefer to customize the
project properties prior to beginning the project.
Setting project properties
33
ACID allows you to configure project properties and add summary information prior to beginning a project.
Choosing
and
parameters and information in both tabs as defaults when starting all subsequent projects.
Note:
information at any time. Choose
menu to display the Project Properties dialog, which contains
the identical tabs and parameters as the New Project dialog.
Using the Summary tab
This tab allows you to enter information about the project. These boxes may be left blank or if information
exists, you may change it at any time.
Item Description
Title Enter the name or title of the project.
Artist Enter the name of the narrator, band, or artist(s) being recorded into the project.
Engineer Enter the name(s) of the people who mixed and edited the project.
Copyright Enter the date and ownership rights of the project.
Comments Enter information that identifies and describes the project.
Start all new projects with these
settings
New from the File menu displays the New Project dialog. This dialog contains two tabs: Summary
Audio. Selecting the Start all new projects with these settings check box configures ACID to use the
You can edit project audio properties and summary
Properties from the File
Select this check box if your projects’ requirements do not change or you want consistent
settings for future projects.
CHP. 3 GETTING STARTED
Page 36

34
Using the Audio tab
This tab allows you to set different characteristics the project uses to handle the audio.
Item Description
Master bus mode Choose either Stereo for a standard audio project or 5.1 Surround for a surround
project.
Number of additional stereo busses Enter the number of stereo busses that you want in your project. You may add up to 26
busses. The busses appear in the Mixer window.
on page 111
Sample rate Choose a sample rate from the drop-down list or enter your own rate. The sample rate
Bit depth Choose a bit depth from the drop-down list. A higher bit depth results in better quality
Enable low-pass filter on LFE Select this check box to limit the audio sent to the LFE channel in a 5.1 surround project.
Cutoff frequency for low-pass filter Enter a low-pass cutoff frequency value for 5.1 surround projects. ACID limits audio sent
Low-pass filter quality Choose a setting from the drop-down list to determine the sharpness of the low-pass
Start all new projects with these
settings
range is 2,000 Hz to 192,000 Hz. Higher sample rates result in better quality sound,
but also mean larger audio files.
sound, but also means larger audio files.
For more information, see Working with 5.1 Surround on page 157
to the LFE channel to frequencies lower than the value you enter. Applying a low-pass
filter approximates the bass-management system in a 5.1 decoder and ensures that
you’re sending only low-frequency audio to the LFE channel.
filter’s rolloff curve. Best produces the sharpest curve.
Select this check box if your project requirements do not change or you want consistent
settings for future projects.
.
For more information, see Using busses
.
Opening existing projects
1.
From the File menu, choose Open. The Open dialog appears.
2.
Choose a drive and folder from the Look in drop-down list.
3.
Select a file in the browse window or type a name in the File name box. Detailed information about the
selected file appears at the bottom of the dialog box.
4.
Choose a file type from the Files of type drop-down list to limit the files displayed in the dialog box.
5.
Click Open.
Note:
If ACID is unable to locate one of the media files
when you open an ACID project, you can choose to leave the
media offline and continue to edit events on the track. The
events point to the location of the source media file. If you
restore the source media file at a later time, the project opens
normally.
Opening ACID projects with embedded media
When you open an .acd-zip project, the project file and all media files are copied to the temporary files
folder.
Note:
You can customize the location of the temporary files
folder. For more information, see Using the General tab on
page 179.
Any changes you make to the project are saved to the files in this temporary folder until you save the .acd-zip
file again. For more information, see Saving projects on page 53.
GETTING STARTED CHP. 3
Page 37

Getting media files
Now that you’ve created a new project or opened an existing project, the next step is to add media to the
project. You can use the Explorer window to locate, preview and add media to your project. You can also
extract audio from a CD or download media from the Web.
Previewing media from the Explorer window
The Explorer window allows you to preview files in looped playback at the current project tempo before
adding them to your project. You can also preview files in the Explorer in conjunction with playing your
project, thereby allowing you to preview how a file will sound in the project.
35
To preview files, use the
Start Preview ( ), Stop Preview ( ), and Auto Preview ( ) buttons at the top of
the Explorer window.
Previewing a media file
Select the media file in the Explorer window that you want to preview.
1.
2.
Click the Start Preview button ( ). The media file begins looped playback. You can monitor its levels on
the preview bus.
3.
Click the Stop Preview button ( ) to end playback.
Previewing multiple media files
You can use the Explorer’s multiple-selection preview feature to preview a group of files in the order that you
select them.
1.
From the Options menu, choose Preferences, and on the Other tab of the Preferences dialog, select the
Enable multiple-selection preview in Explorer window check box.
If you want, you can enter values in the
play
box, and Number of Beatmapped measures to play box to specify how ACID previews different file types.
2.
Click OK to close the Preferences dialog.
3.
In the Explorer, select the media you want to preview. Hold while clicking to select multiple,
adjacent files or hold while clicking to select multiple, nonadjacent files.
4.
Click the Start Preview button ( ). ACID previews the first selected file in the list and continues through
Ctrl
the list of selected files. ACID changes a file’s icon to a
Number of times to repeat each Loop box, Seconds of each One-Shot to
Shift
Play icon ( ) to indicate which file is currently
previewing.
Note:
press +. Press to add all selected files to your
To add the currently previewing file to your project,
Ctrl Enter Enter
project.
Using Auto Preview
The Auto Preview button ( ) sets ACID to automatically play back media files when you select them in the
Explorer. If your project is currently playing when you select a new file, the new file plays back along with
your project. This feature allows you to listen to the media file in the context of your project.
Click the
CHP. 3 GETTING STARTED
Auto Preview button ( ) to toggle auto preview on or off.
Page 38

36
Adding media to the project
You must add media files to a project before you can paint, arrange, and process them. When you add a file to
a project, ACID creates a new track to accommodate it. ACID adds new tracks at the current volume of the
Preview fader in the Mixer window, unless you have set a default track volume level. For more information,
see Setting default track properties on page 178.
There are several methods of adding media files to a project.
Note:
ACID may create proxy files for media whose
compression scheme may cause working with them to be
inefficient and slow. For more information, see Proxy File on
page 201.
Note:
Before using long Beatmapped or long one-shot files
from CDs or shared network folders, copy the media to your
local drive for the best possible performance.
ACID temporary files
When you add a media file to a project from a removable device, ACID stores a copy of the media file in the
temporary files folder. This keeps the media file available for use even if the source of the media is no longer
accessible.
Note:
You can customize the location of the temporary files
folder. For more information, see Using the General tab on
page 179.
Be aware that the temporary files folder is cleared when you close ACID. However, files are not cleared from
the folder if ACID closes inappropriately.
Adding media files from the Explorer window
The Explorer window will likely be your primary means of locating media files used in projects. Display the
Explorer, if needed, by choosing
Explorer from the View menu, or by pressing .
Alt + 1
There are three ways to add media files from the Explorer window:
• Double-click the desired file.
• Drag the file from the Explorer to the track view or track list. Dragging a file from the Explorer to the
track name of an existing track allows you to replace the original file with the new file, while all events
remain in place.
• Right-click and drag a file to the track view or track list to specify the type of track to be created. When
you drop the file, a shortcut menu appears that allows you to choose whether to treat the file as a loop,
one-shot, Beatmapped track, or as an autodetected type.
Adding media files from the Open dialog
There are three ways to add media files from the Open dialog:
• Select the desired file and click
• Right-click the selected file and choose
Open.
Select from the shortcut menu.
• Double-click the selected file.
GETTING STARTED CHP. 3
Page 39

Adding media files from outside the application
You can also add a media file to a project by dragging it from Windows Explorer to the track view.
Adding multiple media files simultaneously
37
To add multiple media files to the project, +click (or +click) to select the files and drag them to the
Ctrl Shift
track view or the track list.
Extracting media files from CD
ACID allows you to extract 44,100 Hz, 16-bit, stereo data from CDs. ACID adds extracted CD tracks to new
tracks in your ACID project.
1.
Insert a CD in the CD-ROM drive.
2.
From the File menu, choose Extract Audio from CD. The Extract Audio from CD dialog appears.
3.
If you have more than one CD drive, choose the CD drive that contains the audio you want to extract
from the
4.
From the Action drop-down list, choose how you
Drive drop-down list.
want to extract audio:
• Choose
Read by track and select each track you
want to extract. ACID extracts each track to a
new track in your project.
• Choose
Read entire disc to extract the current CD
to a single file.
• Choose
Read by range and enter a starting time
and ending time (or a starting time and length).
ACID extracts the time range to a new track in
your project.
Click
Play to preview your selection. In order to
preview, your CD drive’s audio output must be
connected to your sound card, or you can connect
headphones to the front of the CD drive.
5.
From the Speed drop-down list, choose the speed at which you want to extract audio.
6.
Click OK. The Save As dialog appears.
7.
Enter a file name and choose a location for the new file(s).
Note:
ACID can automatically name extracted tracks for
you. From the
the
General tab, select the Autoname extracted CD tracks
Options menu, choose Preferences, and on
check box. For more information, see Using the General tab
on page 179.
8.
Click Save to start extracting audio.
ACID begins extracting data from the CD and displays a progress meter. If the file is longer than 30
seconds, the Beatmapper™ Wizard appears.
9.
Use the Beatmapper Wizard or choose to open the file as a one-shot. ACID adds the extracted file to a
track. For more information, see Using the Beatmapper on page 103.
CHP. 3 GETTING STARTED
Page 40

38
You can also double-click a CDA file in the Explorer window (or drag it to the track view) to extract a CD
track without opening the Extract Audio from CD dialog.
Note:
need to press to refresh the Explorer window to view the
When adding media from multiple CDs, you may
F5
new CD’s contents.
Downloading media files from the Web
The Get Media from the Web command allows you to view and download various audio and video files
available on the Internet.
1.
From the File menu, choose Get Media from the Web.
2.
Choose an icon from the left frame to specify the media provider from which you want to download files.
3.
Preview the file, select the file you want to open and click Download. The Browse for Folder dialog appears.
4.
Select a folder for the download. The selected file is downloaded to the folder specified in the Destination
box.
5.
When you are done downloading, close the Get Media from the Web dialog. ACID adds the file(s) to
your project.
Click
Show Details to display additional information about your download. In this mode, you can add files to
a download queue, specify where the downloaded files should be stored, and monitor the progress of your
downloads. Click
Start to begin downloading queued files, or click Hide Details to return to basic mode.
Understanding track types
When you add media to a project, ACID creates a new track for the file. Depending on the type of media you
add, ACID creates one of four track types to accommodate it: loop, one-shot, Beatmapped, or MIDI. You can
identify a track’s type by looking at the track number/type icon in the track header.
Loops
Loops are small chunks of audio that are designed to create a continuous beat or pattern when played
repeatedly. They are usually one to four measures long. Loops are the type of file that you will use most
frequently.
One-shots
One-shots are chunks of audio that are not designed to loop, and they are streamed from the hard disk rather
than stored in RAM if they are longer than three seconds. Things such as cymbal crashes and sound bites
could be considered one-shots.
Unlike loops, one-shots do not change pitch or tempo with the rest of a project.
Beatmapped
When you add a file that is longer than thirty seconds to a project, the Beatmapper Wizard starts, allowing
you to add tempo information to the file. As a result, these tracks respond to tempo and key changes just like
loops. For more information, see Using the Beatmapper on page 103.
GETTING STARTED CHP. 3
Page 41

Tip:
You can change the length of the file that starts the
Beatmapper in the
Audio tab of the Preferences dialog. For
more information, see Using the Audio tab on page 181.
MIDI
ACID creates a MIDI track when you open a MID, SMF, or RMI file. You can use MIDI tracks to record
data from and play back through synthesizers and other MIDI-compliant equipment. For more information,
see Working with MIDI on page 131.
Adding and editing events
You have added media to the project, and ACID has created tracks for the media files. Now you can add
events to the track view. The following sections describe three basic techniques used when working with
audio events: painting, deleting, and moving.
Painting events
After you add a media file to your project, you must paint it on the timeline in order to hear it. When you
paint on the media file’s track, you create an event that displays the file’s waveform. You can paint events on
the timeline using either the Draw tool or the Paint tool.
39
Note:
Media files must be added to the project before either
of these tools can be used to paint events.
Placing events with the Draw tool
The Draw tool is the most common method of placing events on the timeline. This tool allows you to add
track-specific events, one at a time. In addition, you can use the Draw tool to select, edit, and move events.
For more information, see Adding and editing events on page 39.
1.
Click the Draw Tool button ( ) or choose Editing Tool from the Edit menu and choose Draw from the
submenu. The pointer displays as a pencil icon.
2.
Place the Draw tool at the left edge of any track containing a media file.
3.
Click and hold the mouse button while dragging the Draw tool to the right. A waveform representing the
event appears on the timeline as you drag the mouse.
Notice that if you are placing a loop file on the timeline, small indentations appear along the top and
bottom edges of the event indicating the start and end points of each individual loop.
Tip:
Events can be also be drawn from right (end) to left
(beginning).
4.
Release the mouse button to end the event.
5.
Click the Play from Start button ( ) on the transport bar. The event plays back.
CHP. 3 GETTING STARTED
Page 42

40
Painting events with the Paint tool
Unlike the Draw tool, the Paint tool allows you to quickly paint multiple events across several tracks. This
can be useful when you need to quickly add several seemingly random events to a project. The Paint tool is
also best used for painting multiple one-shot events that will be evenly spaced on the grid lines.
1.
Click the Paint Tool button ( ) or choose Editing Tool from the Edit menu and choose Paint from the
submenu. The mouse pointer displays as a brush icon.
2.
Click and hold the mouse button while dragging the Paint tool randomly across the several tracks. Notice
that events are painted in every grid space the Paint tool contacts.
3.
Release the mouse button to stop adding events.
4.
Click the Play from Start button ( ) on the transport bar. All new events play back.
Tip:
With the Paint tool selected, you can use +click to
Ctrl
paint an entire event for one-shot, Beatmapped, and MIDI
tracks.
Changing the length of events
After an event is painted on the track view, you may discover that it is too long or not long enough;
however, ACID makes it easy to change the length of an event. You may find it helpful to turn snapping
options on by choosing
To alter an event’s length, click the
Snapping from the Options menu and choosing Enable from the submenu.
Draw Tool button ( ) and drag either end of the event. When you drag
the event past the end of the file, looped files repeat, but one-shot and Beatmapped tracks draw silence.
Original event
Drag the end
of the event...
...to increase its length.
Erasing sections of events
Occasionally you may need to delete only specific sections of an event and leave the rest of it intact. The
easiest method of deleting a section of an event is to use the Erase tool.
1.
Click the Erase Tool button ( ) or choose Editing Tool from the Edit menu and choose Erase from the
submenu. The pointer displays as an eraser icon.
2.
Drag in the track view to delete event data.
Tip:
With the Erase tool, you can delete an entire one-shot,
Beatmapped, or MIDI event. Just hold while you click
Ctrl
the event.
GETTING STARTED CHP. 3
Page 43

Moving events
The position of the left edge of an event indicates when the event becomes audible during playback. You can
move events along the timeline either individually or as a group.
In addition, you can stack events on top of one another. A longer event placed over a smaller event conceals
the smaller event and makes it inaudible. A smaller event placed over a larger event is audible and renders
the section of the longer event it covers inaudible.
1.
Click the Draw Tool button ( ).
2.
Click the event to be moved. The event is highlighted to indicate that it is selected.
41
Tip:
You can hold or to select multiple events.
3.
Drag the event to a new location on the track.
Note:
Multiple selected events move in relation to the event
Ctrl Shift
being dragged.
Using the cursor
ACID’s cursor is a flashing vertical line that spans the track view of the entire project. The cursor position
determines where events split, where playback/recording starts, and where clipboard contents are pasted. In
addition, the positioning of the cursor is essential to the creation of time selections.
Positioning the cursor with the mouse
1.
Click the Draw Tool button ( ).
2.
Click in the track view to position the cursor.
Positioning the cursor with the keyboard
While using the mouse to position the cursor in the timeline is quick and intuitive, it is not always precise.
For example, you may want the beginning of a guitar solo to coincide with a snare drum hit, or background
vocals to enter exactly 3 minutes and 24 seconds into a song. For these reasons, ACID also allows you to
position the cursor using your keyboard. For more information, see Cursor placement commands on page 20.
CHP. 3 GETTING STARTED
Page 44

42
Positioning the cursor with the Go To command
The Go To command is used to place the cursor at a specific location in the ACID project.
• Press to position the cursor based on the position displayed on the beat ruler. Specify a position
• Press to position the cursor based on the time displayed on the time ruler. Specify a time in the
Ctrl +G
(in measures.beats.ticks format) in the box that appears in the time display and press .
Shift +G
box that appears in the time display and press .
Tip:
You can also open the boxes in the time display by
Enter
Enter
double-clicking the desired value.
Making selections
You must select events before you can move or edit them.
Selecting an event
1.
Click the Draw Tool button ( ).
2.
Click an event. The event is highlighted.
Selected event
Selecting multiple events
ACID provides you with several methods of selecting multiple events:
• Press or while clicking events.
Ctrl
• Use the
• Use the
• Use the
• Use the Selection tool.
Note:
Unless stated otherwise, selections can only be made
using the Draw tool.
Shift
Select All on Track command.
Select Events to End command.
Select All command.
GETTING STARTED CHP. 3
Page 45

Selecting multiple events using the keyboard and mouse
43
Holding while clicking events allows you to select multiple, nonadjacent events that reside on any
Ctrl
track. This method is useful when you need to move several scattered events by an equal amount within the
project.
Holding allows you to select multiple, adjacent events. Selecting any two events while holding
Shift Shift
automatically selects all events located between the selected events. Events may be selected from the same
track or across tracks. This method is useful when you want to move several adjacent events by an equal
amount within the project.
Selecting multiple events using the Select All on Track command
Right-clicking any track in the track view and choosing Select All on Track from the shortcut menu selects
every event on the track.
Selecting multiple events using the Select Events to End command
Right-clicking an event in the track view and choosing Select Events to End from the shortcut menu selects
every event on the track after the selected event.
You use this command across multiple tracks by holding to click events on several tracks and then
right-clicking and choosing
Selecting events using the Select All command
Select Events to End from the shortcut menu.
Ctrl
Choosing Select All from the Edit menu selects all events in a project.
Selecting multiple events using the Selection tool
You can drag the Selection tool across the track view to select events across multiple tracks. This tool allows
you to select events using three methods: vertical, horizontal, and free selection.
Method Description Displays as...
Vertical Allows you to select all events on all
tracks within an interval of time.
Horizontal Allows you to select all events on a track
or several adjacent tracks.
Free selection Allows you to select a group of adjacent
events on adjacent tracks. This is ACID’s
default selection method.
1.
Click the Selection Tool button ( ) or choose Editing Tool from the Edit menu and choose Selection from
Parallel dashed line spanning the vertical
length of the project.
Parallel dashed line spanning the
horizontal length of the project.
Dashed line box.
the submenu.
2.
Place the pointer on the track view. The pointer displays as an arrow with an adjacent dotted box ( ).
3.
Drag the mouse on the track view. A dashed rectangular box appears on the track view and all events
within and adjacent to it are selected.
4.
While holding the left mouse button, click and release the right mouse button (referred to as toggleclicking). The selection method changes to vertical and again, all events within and adjacent to the
selection area are selected.
5.
Toggle-click the mouse once more. The selection method changes to horizontal and all events within and
adjacent to the selection area are selected.
CHP. 3 GETTING STARTED
Page 46

44
Creating time selections
ACID does not limit you to selecting events. Frequently, you may want to select only audio events occurring
within a time selection. You can do this using the Time Selection tool.
1.
Click the Time Selection Tool button ( ) or choose Editing Tool from the Edit menu and choose Time
Selection
2.
Drag the mouse in the track view. The selection area is highlighted on the track view.
3.
Release the mouse button. A time selection is created and all events within it are selected.
from the submenu. The pointer displays with an adjacent cursor ( ).
Note:
If the selection area is automatically snapping to the
track view’s grid lines, ACID’s snapping feature is turned on.
You can turn snapping off by pressing .
F8
Creating event selections within time selections
ACID also allows you to select specific events within a general time selection. This technique is useful for
selecting individual instruments from a particular section of a song. For example, you may want to copy all
percussion events from a song’s bridge and re-use them in the coda.
1.
Click the Time Selection Tool button ( ) or choose Editing Tool from the Edit menu and choose Time
Selection
2.
Drag the mouse in the track view. The selection area is highlighted on the track view.
3.
Release the mouse button. A selection is created and all events within it are selected.
4.
Hold and click any event that extends beyond the time selection. The entire event appears
highlighted; however, only the section of the event contained within the time selection is actually
selected.
Tip:
by continuing to hold while clicking events. In addition,
holding allows you to select the events of multiple
adjacent tracks within a selection.
from the submenu. The pointer displays with an adjacent cursor ( ).
Ctrl
You can select additional events within the time selection
Ctrl
Shift
Working with tracks
ACID automatically creates a new track for each media file added to a project, and all events placed on the
track derive from that file. Because of this, you can use track-level functions to affect every event on the
track. The following sections explain several basic track functions and features.
GETTING STARTED CHP. 3
Page 47

Reordering tracks
When building an ACID project, you may want to reorder the tracks to place similar instruments in
proximity to one another. For example, placing all drum loops together in the track view makes it easier for
you to fine-tune the mix of the song’s overall drum sound.
1.
Drag the track header to a new location in the track list. A heavy black horizontal line appears on the
track list to indicate where the track will be placed.
2.
Release the mouse button. The track is dropped in the new location and the entire track list/track view
adjusts accordingly.
45
Tip:
You can reorder multiple tracks by holding or
Ctrl Shift
while selecting tracks and dragging the tracks as a group.
Resizing tracks
ACID allows you to change the height of a track, thereby affecting how many tracks display in the track
view. This is especially useful when building a project with a large number of tracks. In addition, you can
decrease the track’s height until only the multipurpose slider,
Track FX button, Mute button, and Solo button
are visible.
1.
Drag the bottom edge of a track up or down in the track list. The pointer displays as a vertical stretch
icon ( ).
2.
Release the mouse button to establish the track’s new height.
Tip:
You can set the default height for all new tracks by right-
clicking the newly resized track in the track list and choosing
Set Default Track Properties from the shortcut menu. For
more information, see Setting default track properties on page
178.
Changing track colors
As mentioned previously, ACID automatically creates tracks to accommodate new media files. ACID also
supplies these tracks with a default color. However, you can change track colors to organize the tracks in
your project. To change the color, right-click the track in the track list, choose
Color from the shortcut
menu, and choose the desired color from the submenu.
Renaming tracks
To rename a track, right-click the track name and choose Rename from the shortcut menu, or double-click
the track name. Renaming a track applies to the project only and does not change the file associated with
the track.
Duplicating tracks
To duplicate a track, right-click it and choose Duplicate Track from the shortcut menu. ACID creates an
exact copy of the track and its events and adds it below the original track in the project. The words “Copy
of” appear before the name of the duplicate track to identify it in the track list.
For creative ways to use duplicate tracks, see Playing with duplicate tracks on page 187.
CHP. 3 GETTING STARTED
Page 48

46
Deleting tracks
You can delete unnecessary tracks from a project by selecting the track and using any of the following
methods:
• Choose
• Right-click a track and choose
• Press .
Delete from the Edit menu.
Delete Track from the shortcut menu.
Delete
Copying, cutting, and pasting tracks
Copying a track places an exact copy of the selected track on the clipboard, but leaves the track view
unchanged. To copy a track, select the track and do one of the following:
• Click the
• Choose
• Right-click the track header and choose
• Press .
Cutting a track removes it from the track view and places it on the clipboard. To cut a track, select it and do
one of the following:
• Click the
• Choose
• Right-click the track header and choose
• Press .
Tracks that are copied or cut to the clipboard can be pasted back into the current project or into a different
project an unlimited number of times. This is a useful way to share tracks between different compositions.
You can paste a track in one of the following ways:
Copy button ( ) on the toolbar.
Copy from the Edit menu.
Copy Track from the shortcut menu.
Ctrl +C
Cut button ( ) on the toolbar.
Cut from the Edit menu.
Cut Track from the shortcut menu.
Ctrl +X
• Click the
• Choose
• Right-click the track view and choose
• Press .
Paste button ( ) on the toolbar.
Paste from the Edit menu.
Paste Track from the shortcut menu.
Ctrl +V
Adjusting the mix
Use the multipurpose slider to adjust the mix of a specific track.
GETTING STARTED CHP. 3
Page 49

Click the slider label to choose what you want to adjust.
Function Description
Volume Controls how loud a track is in the mix. A value of 0 dB means that the track plays with no boost or cut from
Pan Controls the position of a track in the stereo field. Dragging the slider to the left places the track in the left
FX Controls the level of the track sent to each of the assignable effect chains that you have created. Dragging the
Bus Controls the level of the track sent to each of the additional busses that you have created for your project.
ACID. Dragging the fader to the left cuts the volume; dragging to the right boosts the volume.
speaker more than the right, while dragging the slider to the right places the track in the right speaker.
Because ACID uses true stereo panning, you can introduce clipping when panning a track to the left or right.
Unlike a left/right balance control—which simply decreases the volume of one channel—ACID’s default panning
mode actually adds the audio from one channel to the other. When panning a track, adjust the track volume
accordingly.
You can choose among five panning types to determine how ACID pans a track.
Choosing stereo pan types on page 103
fader to the left cuts the volume; dragging to the right boosts the volume.
Dragging the fader to the left cuts the volume; dragging the fader to the right boosts the volume.
.
For more information, see
47
Once you have chosen what you want to adjust, drag the slider to adjust the level. You can hold or
Ctrl Shift
to select multiple tracks and move the sliders together as a group.
Note:
When adjusting the mix of your tracks, remember to
look at the meters on the mixer. Because you are adding the
volumes of all the tracks together, it is easy to clip the audio
output. Make sure that the meters never display the red clip
indicator during playback.
Muting tracks
Each track has a Mute button (). Clicking this button shades the corresponding track (to indicate that it is
muted) and renders it inaudible during playback. Clicking the
its original level in the mix. Toggle-muting a track is an effective way of determining whether a track
contributes to the overall sound of a project.
You can also press to mute a track or group of tracks.
Tip:
Press and click the Mute button to mute only the
Z
Ctrl
selected track (and restore any other muted tracks). If the
selected track is already muted, press and click the
Ctrl
Mute
button to restore all tracks.
Mute button a second time returns the track to
CHP. 3 GETTING STARTED
Page 50

48
Soloing tracks
Located next to the Mute button, the Solo button ( ) allows you isolate tracks in a project during playback.
When you click this button during playback, the corresponding track remains audible and all other tracks are
muted. Clicking the
soloing a track is an effective method of configuring and previewing isolated track effects against how they
sound in the project.
Solo button a second time returns all tracks to their original levels in the mix. Toggle-
You can also press to solo a track or group of tracks.
Tip:
Press and click the Solo button to solo only the
X
Ctrl
selected track (and restore any other soloed tracks). If the
selected track is already soloed, press and click the
Ctrl
Solo
button to restore all tracks.
Working with groups of tracks
Select a group of tracks by holding the key while you click the track header of the desired tracks. Now
you can adjust the volume, panning, track color, and other track attributes simultaneously.
Ctrl
Using undo and redo
ACID provides unlimited undo and redo capabilities. ACID adds each edit you perform in the project to an
undo history, which allows you to quickly restore the project to any of its previous states. In addition,
undoing an edit automatically places it in the project’s redo history where it can be quickly re-performed.
However, any new edit performed on the project overwrites the redo history.
Note:
The undo and redo histories are cleared when you
close the project or exit ACID.
Using undo
To undo an edit, click the Undo button ( ) on the toolbar or press . Edits are undone in the reverse
order they were performed.
Tip:
You can also undo the most recent edit by choosing
Undo from the Edit menu.
Undoing a series of edits
Clicking the down arrow next to the Undo button ( ) displays the project’s undo history. The history
displays as a drop-down list with the most recent edit located at the top. Undoing an edit in the list requires
all subsequent edits to be undone as well.
1.
Click the arrow to the right of the Undo button ( ). The undo history appears.
2.
Locate the edit to be undone. Notice that all subsequent edits are automatically selected and the total
number of edits to be undone is indicated at the bottom of the drop-down list.
3.
Click the edit to be undone. The project is restored to the state it was in prior to the selected edit.
GETTING STARTED CHP. 3
Ctrl +Z
Page 51

Undoing all edits
Choosing Undo All from the Edit menu undoes all project edits and automatically adds them to the redo
history.
Using redo
49
To redo an edit, click the Redo button ( ) on the toolbar or press . Edits are re-performed in
Ctrl +Shift+Z
the reverse order they were undone.
Tip:
You can also redo the most recent undone edit by
choosing Redo from the Edit menu.
Redoing a series of edits
Clicking the down arrow next to the Redo button ( ) displays the project’s redo history. The history
displays as a drop-down list with the most recently undone edit located at the top. Redoing an edit in the list
requires all subsequently undone edits to be re-performed as well.
1.
Click the arrow to the right of the Redo button ( ). The redo history appears.
2.
Locate the edit to be redone. Notice that all subsequently undone edits are automatically selected and the
total number of edits to be redone is indicated at the bottom of the drop-down list.
3.
Click the edit to be redone. The project is restored to the state it was in prior to the selected undone edit.
Tip:
Clicking the desktop outside the drop-down list cancels
the redo operation.
Clearing the undo history
ACID allows you to clear the undo and redo histories without closing the project or exiting the application.
After the histories are cleared, ACID creates new ones as you continue building the project.
1.
From the Edit menu, choose Clear Undo History. A confirmation dialog appears, alerting you that this
action permanently deletes the current edit histories.
2.
Click Ye s to clear the edit histories or No to retain the current edit histories.
Playing the project
ACID provides several methods of playing your projects.
Using the transport bar
All buttons required to play your project are located on ACID’s transport bar. The transport bar should look
somewhat familiar to you, as it contains buttons found on most home CD and cassette players. For more
information, see Transport bar on page 17.
CHP. 3 GETTING STARTED
Page 52

50
Using playback options
As you build a project, you will likely have different playback needs. For example, you may want to hear the
project in its entirety when checking the final mix, but not when you are working on the ending. Because of
this, ACID offers three playback options:
• Playing the entire project.
• Playing from the cursor position.
• Playing in looped playback.
Playing the entire project
To begin playback from the beginning of the project, click the transport bar’s Play From Start button ( ) or
Shift +Space Space
press . To stop playback, click the transport bar’s
Playing from the cursor position
Stop button ( ) or press .
To begin playback from the current cursor position, click the transport bar’s Play button( ) or press .
To stop playback, click the transport bar’s
Playing in looped playback
Stop button ( ) or press .
Space
You can also limit playback to a specific loop region on the track view. This playback method uses the
transport bar’s
Loop Playback button ( ) and allows you to fine-tune mixes and effects while continually
listening to the selected area. For more information, see Transport bar on page 17.
1.
Drag the handles of the loop bar to create the desired loop region.
Handle Loop bar
2.
Click the Loop Playback button ( ) to turn on looped playback.
3.
Click the transport bar’s Play button ( ) or press . ACID begins playback of the selected area. To
stop playback, click the transport bar’s
Stop button ( ) or press .
Space
Space
Using the Mixer window
Space
The Mixer window is a dockable window with a default location in the lower-right corner of the ACID
workspace. The Mixer window contains the following controls:
•
A Preview fader, which allows you to adjust the loudness of media files previewed from the Explorer
window, Track Properties window, Beatmapper, or the Chopper. Also, the Preview fader’s volume
determines the volume of new tracks added to the project, unless you have set a default track volume
level. For more information, see Setting default track properties on page 178. This allows you to set up a quick
mix while you are adding media to your project.
• A Master bus fader, which controls the overall volume.
• Faders for up to 26 project busses when added to the project.
• Faders for up to 32 assignable effect chains when added to the project.
• Faders for up to 32 soft synth controls when added to the project.
The function of the bus, assignable effect, and soft synth controls are beyond the scope of this chapter. For
more information, see Using the Mixer on page 111.
GETTING STARTED CHP. 3
Page 53

Viewing the Mixer window
The Mixer window appears by default when you start ACID, but you can hide it if necessary. To view or hide
the Mixer window, choose
Mixer from the View menu or press . A check mark appears adjacent to
Alt +3
the command to indicate when the window is displayed.
Using the mixer toolbar
The Mixer window toolbar contains four buttons: Project Audio Properties, Insert FX, Insert Bus, and Insert Soft
Synth
.
Button Description
Displays the Project Properties dialog.
51
Adds an assignable effect chain to your project. The Plug-In Chooser
dialog appears so that you can create a plug-in chain.
information, see Using assignable effects on page 113
Adds another bus to your project. The Audio tab in the Project
Properties dialog updates to reflect the new number of busses.
information, see Using busses on page 111
Adds a soft synth control to your project. You can assign MIDI tracks or
external MIDI input devices to the soft synth control and assign the soft
synth control to a DLS set or VSTi plug-in.
Using soft synth controls on page 115
.
For more information, see
.
For more
.
For more
Renaming mixer controls
Double-clicking a mixer control name allows you to rename the control. Press to save the change.
Enter a new
name for the
mixer control
Enter
Using the mixer’s faders
Adjusting the Preview fader
Drag the fader up or down to adjust the preview volume.
Hiding the Preview fader
Once you have added all desired media files to a project, you may want to hide the Preview fader to make
room for additional busses, assignable effects, and soft synth controls. To hide the Preview fader, right-click
within the Mixer window and choose
hidden until you choose
CHP. 3 GETTING STARTED
Show Preview Fader from the shortcut menu again.
Show Preview Fader from the shortcut menu. The fader remains
Page 54

52
Adjusting split faders in the mixer
Split faders allow you to adjust the levels of the left and right channels independently. To move the faders
individually, drag the fader for the desired channel and release the mouse when it is in the correct position.
However, you can adjust both channels simultaneously by doing either of the following:
• Drag in the middle of the fader while making your adjustment.
• Click the
Lock Fader Channels button( ) before adjusting the fader.
You can also change the fader level by double-clicking:
• Double-click the fader to reset it to 0.0 dB.
• If you have set each channel differently, double-click either channel to match the remaining channel to
its level.
Changing meter resolution
ACID allows you select the meter resolution. This is useful when building a project from several media
source pools that have varying volume levels. To change the resolution, right-click a meter and choose the
desired resolution from the shortcut menu.
Note:
Changing the meter resolution of one fader
automatically changes all other meters in the mixer to match
the selected resolution.
Adjusting for clipping
The volume of certain media files may cause a meter to clip. Clipping results in a distorted audio signal and
displays in a red indicator at the top of the meter. If the meter clips, lower the volume and click the red clip
indicator to reset the meter. Continue adjusting the fader and resetting the meter until you eliminate the
clipping.
Tip:
You can also reset a meter by right-clicking it and
choosing Reset Clip from the shortcut menu.
Saving, rendering, and delivering projects
Though ACID provides you with the tools to quickly build impressive musical projects, you may find yourself
building elaborate projects over a period of weeks or even months. While you are working on a project, you
should save it in ACID’s native format, the ACID project file (.acd).
Important:
version of ACID in ACID 4.0, it will be unusable in earlier
versions of ACID. Use the Save As dialog to save the project
with a new name after editing it in ACID 4.0.
If you save a project created in an earlier
GETTING STARTED CHP. 3
Page 55

When you are finished building a project, ACID allows you to render projects in a variety of formats. You
should determine the project’s final format (or formats) based on how you will deliver the media. For
example, you would render your project to a streaming media format if you plan to publish it to the Internet.
Note:
Be aware that projects containing MIDI files that are
routed to external MIDI ports must be rerouted to internal
DLS sets or VST instruments (VSTi) to be included in the
rendered mix. For more information, see Rendering projects
with MIDI tracks on page 150.
Saving projects
An ACID project file (.acd) is the default file format for saving a new project and should be used for saving
unfinished projects. There are two ACID project file types.
Format Extension Description
ACID Project File .acd Contains all information regarding the project including
ACID Project with
Embedded Media
.acd-zip Contains all information regarding the project including
track layout, envelope settings, and effects parameters.
However, this type of file does not contain actual audio,
only references to the audio files.
track layout, envelope settings, and effects parameters. In
addition, all audio files used in the project are embedded
into the project file.
If you save a project in .acd-zip format, the project file and
all media files are copied to a temporary files folder. If you
continue to work on your project after saving the .acd-zip
file, your changes are saved to the files in this temporary
folder.
You can customize the location of the temporary files
For more information, see Using the General tab
folder.
on page 179
.
53
1.
To save a file, display the Save As dialog using any of the following options:
• Click the
• From the
• Press .
2.
From the Save in drop-down list, choose the drive and directory where the file will be saved.
3.
Enter a name for the project in the File name box.
4.
From the Save as type drop-down list, choose the desired ACID project file type.
5.
If you want ACID to save a copy of each of the project’s media files to the same location as your project
file, select the
6.
Click Save. ACID saves the project.
Save button ( ) on the toolbar.
Edit menu, choose Save.
Ctrl +S
Copy all media with project check box. This is available when saving as an ACID project file.
Once the project is saved, you can use the Save As command
from the
File menu to create a copy of the project with a new
name or save to a different ACID project file format.
CHP. 3 GETTING STARTED
Page 56

54
Rendering projects
Rendering refers to the process of converting the ACID project into a file that is formatted for a specific
playback method. Possible playback methods include media player applications, Internet streaming media,
CD-ROM, and CD audio. When an ACID project is rendered, it is not overwritten, deleted, or altered and
you are able to return to the original project to make changes and re-render.
1.
From the File menu, choose Render As. The Render
As dialog appears.
2.
From the Save in drop-down list, choose the drive and
folder where the file will be saved.
3.
Enter a new name for the project in the File name box.
4.
From the Save as type drop-down list, choose the
desired file format.
5.
If the selected file type supports it, you can choose an
encoding template from the
or click
Custom to create a new template. For more
information, see Creating custom rendering settings on
page 55.
6.
Select or clear the following check boxes as needed:
Te mp l a te drop-down list,
• Select the
Render loop region only check box if you
want to save only the portion of the project that is
contained within the loop region. The loop region
does not need to be active for this option to work.
• If the selected file type supports it, you can select the
Save project markers with media file check box to
include markers and regions in the rendered media file.
• Select the
own file. The
Stretch video to fill output frame (do not letterbox): Selecting this check box stretches the source video frame
•
Save each track as a separate file check box if you want to render each track in the project to its
File name box changes to Folder, which displays the name of the folder in the Save in box.
if the destination frame size differs. When this check box is cleared, ACID uses letterboxing or
pillarboxing to keep the frame aspect correct.
•
Fast video resizing: Selecting this check box speeds the process of saving video. When this check box is
cleared, the time required to save the file can increase dramatically. Clear this check box only when you
have critical material where nothing but the highest quality video rendering will do.
7.
Click Save. A progress dialog appears.
When rendering is complete, you can choose one of the following options:
• Click
• Click
• Click
Open to start the associated media player and play the newly rendered file.
Open Folder to open Windows Explorer and display the location of the newly rendered file.
Close to close the progress dialog and return to the ACID window.
GETTING STARTED CHP. 3
Page 57

Supported formats for rendering
The following table briefly describes the file formats available for rendering a project.
Format Extension Description
AIFF File .aif The standard audio file format for audio used on Macintosh
MPEG-1 and MPEG-2 .mpg MPEG files are a format used when burning audio and video to a
MPEG-1 Layer 3 .mp3 A highly compressed format used for portable digital players and
Ogg Vorbis .ogg A patent-free audio encoding and streaming technology.
QuickTime .mov QuickTime for Microsoft Windows.
RealMedia .rm The RealNetworks standard for streaming media via the Web. This
Sonic Foundry Perfect
Clarity Audio
Sonic Foundry Wave64 .w64 A Sonic Foundry proprietary wave format that does not have a
Video for Windows .avi The standard video file format used on Windows-based
Wave .wav The standard audio file format used on Windows-based
Windows Media Audio .wma The Microsoft audio format used to create files for streaming or
Windows Media Video .wmv The Microsoft audio and video format used to create files for
.pca A Sonic Foundry proprietary lossless audio compression format.
computers.
Video CD, Super Video CD, or DVD. ACID supports MPEG-1 and
MPEG-2 file creation through the use of the MainConcept MPEG
plug-in.
Internet sharing of media. ACID provides 20 free MP3 encodes.
After you have used the free encodes, you must register the
plug-in to continue rendering MP3s.
option renders both audio and video into one file.
restricted file size (unlike Windows standard WAV format which is
limited to ~2GB).
computers.
computers.
downloading via the Web.
streaming or downloading via the Web.
55
Note:
Some plug-ins, such as MP3, may require
registration.
Creating custom rendering settings
The Custom Settings dialog appears when you click Custom in the Save As dialog. You can use the Custom
Settings dialog to create custom encoding templates for many of the file formats available in ACID.
1.
From the File menu, choose Render As. The Render As dialog appears.
2.
Choose your preferred file format from the Save as type drop-down list. If the format allows you to create
custom settings, the
3.
Click Custom. The Custom Settings dialog appears.
4.
Make the appropriate setting changes for the chosen file format. For help on individual settings, click the
What’sThis? Help button ( ) and click a setting.
Tip:
To save the custom settings for future use, enter a name
for the template in the
Te mp l a te button ( ).
5.
Click OK. The Custom Settings dialog closes.
Custom button becomes active.
Te mp l a te box and click the Save
CHP. 3 GETTING STARTED
Page 58

56
Publishing to the Internet
When your project is finished, you have the option of publishing it to the Internet. The most common place
to publish your project is ACIDplanet.com, a virtual community of ACID users. ACIDplanet.com allows
you to do the following:
• Share your music.
• Listen to projects built by other ACID enthusiasts.
• Download free loops.
• Enter remix contests co-sponsored by Sonic Foundry and major record labels.
Publishing your project to the Internet involves two distinct procedures: creating a personal account and
uploading the project.
Creating a personal account
ACID allows you to create accounts at Web sites where you can publish your song files. Each Web site that
offers publishing directly through ACID will guide you through its own account creation process. If you
haven’t created an account and you attempt to publish a song, you will be directed to complete the Publish
Setup utility.
1.
From the File menu, choose Publish Setup.
2.
Follow the on-screen instructions to set up your account.
At any time, you can go back and create another account at a different Web site. The Web site you are
currently logged into in the Publish Setup utility is where ACID publishes your song when you choose
Publish from the File menu.
Uploading a project
Publishing a project file copies your media to the Web so you can share it with other Web users. The
following procedure assumes you already have an account set up with a publish provider. If not, you will first
be redirected to set up an account. After successfully creating an account, you will be directed back to the
Publish feature.
1.
From the File menu, choose Publish. The Publish dialog appears.
2.
Select the appropriate radio button to specify whether the song to be published is the current ACID song
or a different song.
• To publish your current ACID song, choose a streaming format and bit rate.
• To publish a different song, enter the path to the song or click
Browse to locate the file. This song must
already be in a streaming format.
3.
Click Next. If you are publishing the current ACID song, ACID renders it in the format and bit rate you
specified. A window appears from the publish provider with directions for completing the publishing
process.
4.
Follow the instructions provided by the publish provider. ACID begins uploading the file to the provider.
A progress dialog informs you when the upload is finished.
5.
Click OK. The publish provider provides a link to the song on their Web site; however, this may vary
depending on provider.
GETTING STARTED CHP. 3
Page 59

Writing to CD
ACID allows you to burn your projects to CD using supported CD-R/CD-RW drives. ACID renders your
project so it can be played on consumer CD players; however, the disc must be closed before it can be played
in a CD player.
Note:
ACID writes the entire project length to a CD track.
If your project has events on muted tracks that extend beyond
the end of the audible material, the muted events burn as
silence at the end of your CD track. To burn just a portion of
a project, create a loop region and select the
only check box.
1.
Insert a blank CD in a supported CD-R/CD-RW drive.
2.
From the Tool s menu, choose Burn Track-at-Once Audio CD.
Notice that the Burn Track-at-Once Audio CD dialog indicates the amount of time that the current
project will fill on the CD as well as the total amount of time remaining on the CD. If the
audio
value exceeds the Time available on disc value, ACID does not allow you to write the track to the CD.
Note:
If there is no CD in the CD-R/CD-RW drive, only
the Cancel button is available in this dialog.
Burn loop region
Time needed for
57
3.
Choose a setting from the Action drop-down list:
• Choose
Burn audio to begin recording audio to your CD when you click Start. You must close the disc
before it can be played in an audio CD player.
• Choose
Test, then burn audio to test whether your files can be written to the CD without encountering
buffer underruns. Recording begins after the test if it is successful.
• Choose
Test only to test whether your files can be written to the CD without encountering buffer
underruns. No audio is recorded to the CD.
• Choose
Close disc to close your disc without adding any audio when you click Start. Closing a disc allows
your files to be played on an audio CD player. You cannot add tracks to a CD once it has been closed.
• Choose
4.
Select your burning options:
• Select the
• Select the
Erase RW disc to erase a rewritable CD when you click Start.
Erase RW disc before burning check box to erase a rewritable CD before you begin burning.
Close disc when done burning check box to close the CD after burning. Closing a disc allows
your files to be played on an audio CD player. You cannot add tracks to a CD once it has been closed.
• Select the
• Select the
Eject disc when done check box to eject the CD automatically when burning is complete.
Burn loop region only check box to burn only the selected loop region. Clear the check box to
burn the entire project.
5.
From the Drive drop-down list, choose the drive for burning CDs.
6.
From the Speed drop-down list, choose the speed at which you want to burn. Choosing Max uses your
drive’s fastest possible speed; decrease the setting if you have difficulty burning because of buffer
underruns.
7.
Click Start.
Important:
Once ACID begins writing to the CD,
cancelling the write operation renders the CD unusable.
CHP. 3 GETTING STARTED
Page 60

58
GETTING STARTED CHP. 3
Page 61

CHAPTER
Editing Events
4
4
In this chapter, you’ll learn about basic event editing techniques such as cutting, copying, pasting, trimming,
splitting, and joining events. You’ll also learn how to use ripple editing to expand the possibilities of timeline
editing. Finally, you’ll take a look at advanced editing techniques such as slipping and sliding events,
changing event properties, and adding event envelopes.
Note:
For the basic event editing topics in this chapter, make
sure that ripple editing is turned off. Verify that the
Edits
command in the Options menu is not selected. For
more information, see Ripple editing on page 64.
Ripple
59
Copying events
Copying an event, a time selection, or event within a time selection places an exact copy of the selected
event(s) on the clipboard, but leaves the track view unchanged. Events copied to the clipboard can be
pasted in the project an unlimited number of times. In addition, clipboard content remains on the clipboard
until replaced by new content.
1.
Select the event data you want to copy or make a time selection. For more information, see Making
selections on page 42.
2.
Copy the event data using any of the following methods:
• Click the
• Choose
• Right-click the selection and choose
• Press .
Copy button ( ) on the toolbar.
Copy from the Edit menu.
Copy from the shortcut menu.
Ctrl +C
Pasting events
The clipboard’s contents can be pasted in a project an unlimited number of times. However, an event is
always pasted in the track it was copied/cut from. In addition, pasting the contents of the clipboard over an
existing event results in the pasted event overlapping the existing event. To avoid pasting over existing
events, you have two options:
• Use the
• Turn on ripple editing. For more information, see Ripple editing on page 64.
Paste Insert command. For more information, see Using Paste Insert on page 60.
CHP. 4 EDITING EVENTS
Page 62

60
When events are cut/copied to the clipboard and subsequently pasted into a project, ACID maintains and
pastes the time data inherent in the cut/copied events. For example, if you select two events on the same
track that are separated by five seconds of silence, copying and pasting these events results in the five
seconds of silence also being pasted into the project.
Original events
Pasted events
Taking this concept a step further, if you select discontinuous events from several tracks, copying and pasting
these events results in any selected time data being pasted into the project as well. This maintains the
relative position of events in the project.
Original events Pasted events
Using the Paste command
1.
Place the cursor at the desired position on the timeline.
2.
Paste the clipboard contents using any of the following methods:
• Click the
• Choose
• Right-click the track view and choose
• Press .
Paste button ( ) on the toolbar.
Paste from the Edit menu.
Paste from the shortcut menu.
Ctrl +V
Using Paste Repeat
When building projects, you often need to paste the contents of the clipboard several times. Rather than
repeatedly pasting and moving the content, the
times and at what interval the clipboard’s contents are pasted on the track view. This is a useful way of
quickly building a project that uses a repetitive riff or structure. For example, you can build the backing
tracks for a twelve-bar blues, copy them, and use
Paste Repeat command allows you to specify the number of
Paste Repeat to paste several copies of it in the project.
1.
Click the Time Selection Tool button ( ).
2.
Drag the mouse in the track view to create a time selection spanning several events and copy it to the
clipboard.
3.
Click the Go To End button ( ) on the transport bar or press to send the cursor to the end of
Ctrl +End
the project.
Ctrl
4.
From the Edit menu, choose Paste Repeat or press . The Paste Repeat dialog appears.
5.
Enter a number in the Number of times to paste box.
6.
Select the End to end radio button and click OK. ACID pastes the events end to end the number of times
+B
specified in step five, starting at the cursor position.
Using Paste Insert
To insert the contents of the ACID clipboard at the current cursor position and force existing events to
move in time to accommodate the pasted events, choose
If the cursor is in the middle of an event, the event splits at the cursor position where the new events are
pasted. For more information, see Splitting events on page 62.
EDITING EVENTS CHP. 4
Paste Insert from the Edit menu.
Page 63

Cutting events
Cutting an event, a time selection, or an event within a time selection removes the audio data from the
track view and places it on the clipboard. Once data is placed on the clipboard, it can be pasted back into
the project an unlimited number of times. Clipboard content remains on the clipboard until it is replaced by
new data.
1.
Select the event data you want to cut or make a time selection. For more information, see Making selections
on page 42.
2.
Cut the event data using any of the following methods:
61
• Click the
• Choose
• Right-click the selection and choose
• Press .
Cut button ( ) on the toolbar.
Cut from the Edit menu.
Cut from the shortcut menu.
Ctrl +X
All selected events are removed from the track view and placed on the clipboard.
Deleting events
Deleting an event, a time selection, or an event within a time selection removes the data from the track
view and discards it. Deleted events are not placed on the clipboard and do not replace or interfere with
current clipboard content. In addition, deleted events cannot be pasted back into a project.
Note:
Deleted data can only be replaced in a project using
Undo command. For more information, see Using undo
the
on page 48.
1.
Select the event data you want to delete or make a time selection. For more information, see Making
selections on page 42.
2.
Delete the event data using any of the following methods:
• Choose
• Right-click the selected event and choose
• Press .
Delete from the Edit menu.
Delete from the shortcut menu.
Delete
All selected events are removed from the track view and discarded.
Trimming events
Whereas deleting allows you to select event data to be removed from the project, trimming allows you to
select the data that remains. Trimming is performed by creating a time selection or selecting an event within
a time selection and subsequently deleting all unselected data.
1.
Create a time selection or select specific events within a time selection. For more information, see Creating
time selections on page 44.
2.
CHP. 4 EDITING EVENTS
Ctrl +T
Press to trim the data within the selection. All unselected event data is removed from the track
view and discarded.
Page 64

62
Splitting events
Splitting is a quick way to create independently functioning events from a single one. You might consider
splitting an event if you want to adjust a small part of the track. For example, you may want to apply pitch
shift to a guitar track for a few measures and then return the track to its original setting.
Splitting occurs at the cursor position or at the in and out points of a time selection. When you split an
event, ACID creates a new ending point for the original event and creates a starting point for the newly
created event.
When you split an event, the newly created events abut each other. If
Quick fade edges to prevent clicks is
selected in the Event Properties dialog, ACID adds fades at the split point. For more information, see Changing
event properties on page 68.
Split position Two events
However, you may move either of the events, which creates a gap.
Split position
Two events
Splitting at the cursor position splits all selected events that the cursor crosses on all tracks.
1.
Select the event(s) that you want to split.
2.
Place the cursor where you want the split to occur or make a time selection.
3.
From the Edit menu, choose Split or press . The result of the split depends on how events were selected.
S
Splitting at the cursor position
Splitting at the cursor position splits all events that the cursor crosses on all tracks.
Events before splitting Events after splitting
Cursor position
and split point
EDITING EVENTS CHP. 4
After the split, the three events
become six events
Page 65

Splitting an event
Selecting a single event prior to splitting prevents other events from being split at the cursor’s position.
Events before splitting Events after splitting
63
Event to
be split
Cursor position
and split point
Only the selected
event splits
at the cursor
position
Splitting multiple events
Selecting multiple events splits only the selected events at the cursor’s position. Be sure to set your cursor
position before selecting events. Attempting to set your cursor after selecting events causes you to lose your
event selection.
Events before splitting Events after splitting
Events to
be split
Cursor position
and split point
Only the selected
events split
at the cursor
position
Splitting a time selection
Making a time selection allows you to split events at the time selection’s in and out points across all tracks.
Events before splitting Events after splitting
Loop bar
In point Out point
CHP. 4 EDITING EVENTS
Loop bar
Split point Split point
Page 66

64
Splitting events within a time selection
When selecting events within a time selection, only the selected events in the time range split at the in and
out points.
Events before splitting Events after splitting
Selection bar
Selection bar
Only the selected
event splits at
the in and out
points
In point Out point
Event to be
split at the time
selection’s in and
out points
Split point Split point
Joining events
You may join events on ACID tracks that have been segmented along the timeline. Joining events is an
efficient way to redraw an event and remove any splits or silent regions between events.
You would want to join events if you decided that the event should play uninterrupted over the specified
time range.
1.
Select the events or range of events that you want to join. For more information, see Selecting multiple events
on page 42.
2.
From the Edit menu, choose Join or press . The selected events are joined.
J
Select all the events that you want to join.
You can also select the first and last events
you want to join, creating an event selection range.
After you join the events, a single event appears.
Joining events is similar to dragging the
edge of an existing event
Ripple editing
ACID includes a ripple editing feature. This feature is a timeline-based procedure that allows you to cut,
delete, and paste events or portions of events within a time selection and simultaneously adjust the position
of all later events on a selected track. The existing events’ timeline position adjusts by the total amount of
the time selection that is being cut, deleted or pasted from the clipboard.
Ctrl
You may turn on ripple editing mode by choosing
Note:
Ripple editing is only available when a time selection is
Ripple Edits from the Options menu or pressing .
present.
EDITING EVENTS CHP. 4
+L
Page 67

Cutting events in ripple editing mode
Cutting events or portions of events removes them and their time information from their respective tracks.
This information is placed on the clipboard, from which you may paste the information back into your
project.
1.
From the Options menu, choose Ripple Edits to enter ripple editing mode.
2.
Click the event to be cut or make a time selection.
65
To cut multiple events, use the key, the key, or the
Ctrl Shift
Selection ( ) tool to select the events. For
more information, see Selecting multiple events on page 42.
3.
Click the Cut button ( ) on the toolbar to cut the event(s) to the clipboard.
The cut events and their time information are removed from the selected track(s) and placed on the
clipboard. Existing events in the selected track(s) move forward to occupy the space created by the cut.
Cutting time selections in ripple editing mode
Events within the time selection are reproduced and placed on the clipboard. Also, the time information is
placed on the clipboard. Existing events occurring after the time selection move forward in the project by
the length of the time selection.
Events before cut Clipboard contents Events after cut
Existing events
adjust to occur
sooner in the
project
Cutting time and event selections in ripple editing mode
Events and portions of events within the time selection are reproduced and placed on the clipboard. Also,
the time information is placed on the clipboard. Existing events occurring later than the time selection
move forward by the length of the time selection. Only tracks containing selected events are affected by the
ripple edit.
Events before cut Clipboard contents Events after cut
Existing events on
the top track adjust
to occur sooner in the
project
CHP. 4 EDITING EVENTS
Page 68

66
Deleting events in ripple editing mode
Deleting events or portions of events removes them and their time information from their respective tracks.
However, this information is not placed on the clipboard. Existing events move forward when you delete
material from a selected track.
1.
From the Options menu, choose Ripple Edits to enter ripple editing mode.
2.
Click the event to be deleted or make a time selection.
To cut multiple events, use the key, the key, or the
Ctrl Shift
Selection ( ) tool to select the events. For
more information, see Selecting multiple events on page 42.
3.
Deleting time selections in ripple editing mode
Delete
Press to delete the event(s).
Events within the time selection and their time information are removed from the project. Existing events
occurring after the time selection move forward in the project by the length of the time selection. When
information is deleted, it is not placed on the clipboard.
Events before delete Clipboard contents Events after delete
Deleted information is not
placed on the clipboard.
Existing events
adjust to occur
sooner in the
project
Deleting time and event selections in ripple editing mode
Events within the time selection and their time information are removed from the project. Existing events
occurring after the time selection move forward in the project by the length of the time selection. When
information is deleted, it is not placed on the clipboard.
Events before delete Clipboard contents Events after delete
Deleted information is not
placed on the clipboard.
Existing events on the
top track adjust to
occur sooner in the
project
Pasting events in ripple editing mode
Once information is copied to the clipboard, you may choose a variety of ways to paste the clipboard items
into tracks. For more information, see Pasting events on page 59. The following procedures explain pasting
information in ripple editing mode.
Note:
Events are always pasted into their own tracks at the
cursor position.
1.
From the Options menu, choose Ripple Edits to enter ripple editing mode.
2.
Move the cursor to the desired timeline location.
3.
Place the cursor within the track where you want to paste the event.
4.
Click the Paste button ( ) on the toolbar to paste the event into the track.
EDITING EVENTS CHP. 4
Page 69

67
Clipboard information is pasted at the cursor’s position on the track. Existing events or portions of events
after the cursor adjust to occur later in the project. The amount of adjustment is based on the total length of
the information being pasted.
Pasting single track information in ripple editing mode
The information on the clipboard determines how many tracks are affected when you paste. If you have
copied or cut information from one track, only the selected track is affected by the pasted event and time
information.
Clipboard contents Events before paste Events after paste
Existing event
adjusts to move
later in the project.
Paste
position
Newly pasted
event
Pasting multitrack information in ripple editing mode
ACID can paste multiple events as easily as single events.
Clipboard contents Events before paste Events after paste
These events will be
pasted
Note:
Pasting in ripple editing mode ripples only the events
Paste
position
Existing events on the tracks adjust
later in the project
on the tracks that receive the clipboard contents. If you want
to ripple all tracks at the paste position, use the
Paste Insert
command from the Edit menu.
Newly pasted events
Slipping and sliding events
To help you picture what happens when you slip and slide events, think of an event as a window to a media
file. The window can display the entire media file or a small section. When the window displays only a
portion of the media file, you can move either the window or the underlying media to adjust the media
played by an event:
• When you slip an event, your event maintains its place on the timeline, but the media file moves in the
direction you drag.
• When you slide an event, the media file maintains its place on the timeline, but the event moves in the
direction you drag.
CHP. 4 EDITING EVENTS
Page 70

68
Original loop event
Slipping the event two measures to the right
Slip-trimming the event two measures to the right
Sliding the event two measures to the right
Shifting the contents of (slipping) events
Alt
Hold while dragging an event. The slip cursor appears ( ).
As you drag the event, the contents of the event shift, but the event does not move. You can use this
technique when you want to maintain an event’s length and position but want the to event play a different
section of the source media file.
For creative ways to use event slipping, see Duplicating with offset on page 188.
Slip-trimming events
Alt
Hold while dragging the right or left edge of an event. The slip-trim cursor appears ( ).
As you drag the event edge, the media moves with the event edge.
Sliding events
Ctrl +Alt
Hold while dragging an event. The slide cursor appears ( ).
As you drag, the relative position of the media remains fixed on the track, and the event position changes.
You can use this technique when you want to maintain an event’s length but want the event to play a
different section of the source media file at a different point in your project.
Changing event properties
To access event properties, right-click the event and choose Properties
from the shortcut menu, or simply double-click the event.
These properties are saved in the project but are not saved into the file
when you save changes to a track in the Track Properties window
more information, see Saving file properties on page 109.
. For
EDITING EVENTS CHP. 4
Page 71

The following table describes each of the settings in the Event Properties dialog.
Item Description
Start offset The Start offset for an event specifies a playback starting position that is
Pitch shift The Pitch shift value specifies a pitch shift for the selected event. Event-based
Speed The Speed setting allows you to change the playback speed of an event on a
Quick fade edges to
prevent clicks
different than the beginning of the file. This is especially useful for loops; you
can change the feel of a loop by simply starting on beat two rather than beat
one.
pitch shift is calculated after the project key and any pitch shift assigned to a
track.
For more information, see Changing tempo, time signature, and key on
.
page 79
one-shot track. Changing the speed also changes the pitch.
When you add an offset to an event so that it does not end on a loop point, you
can introduce an audible click at the edges of the event. Select the Quick fade
edges to prevent clicks check box, and ACID performs a quick fade-in or
fade-out on the event edges.
To adjust a quick fade, zoom into the event and hover over the upper-left or
upper-right corner of an event until the cursor is displayed as . Drag the
edge of the fade to adjust its duration.
event’s fade-in and -out envelope curve on page 70
For more information, see Setting an
.
Using event envelopes
69
ACID enables you to use envelopes on individual events. Envelopes give you the ability to control each
event’s fade-in, fade-out, and overall volume. Envelopes are useful for transitional effects between events by
subtly fading out one event’s volume while another fades in.
These envelopes are different than track envelopes because they affect only the event whereas track
envelopes can affect multiple events on the track. For more information, see Using track envelopes on page 97.
The event’s volume level and fade curves are represented by a line on the event.
Setting an event’s volume envelope
You can control an event’s overall volume by setting an envelope at the desired decibel (dB) level.
1.
Place the mouse pointer at the top of the event. The envelope cursor ( ) appears.
2.
Drag the volume line to the desired level. As you drag the volume line, ACID displays the event’s decibel
level.
3.
Release the mouse to set the event’s dB level.
After you set the event volume level, you may change it later by dragging the envelope line.
CHP. 4 EDITING EVENTS
Page 72

70
Setting an event’s fade-in and -out envelope curve
You can control an event’s envelope fade-in and -out characteristics by adjusting the event’s envelope
handles. These handles allow you to control the length and dB level of fade-ins and fade-outs. Also, you can
change the type of curve that the event uses to control the volume’s fade characteristics.
1.
Place the mouse pointer on the upper corner of the event. The envelope cursor ( ) appears.
2.
Drag the envelope cursor and position the envelope curve. As you drag the cursor, ACID displays the
following information:
• The event decibel level.
• The length (in measures.beats.ticks) of the fade-in or fade-out.
3.
Release the mouse to set the fade-in or fade-out characteristics.
Changing the event’s fade curve type
You can set an event’s fade curves (fast, linear, slow, smooth, or sharp) that are used to raise or lower the
volume over time. Right-click the fade region, select
appropriate fade curve from the submenu.
Fade Type from the shortcut menu, and choose the
Creating crossfades between events
ACID allows you to quickly create crossfades between overlapping events painted on different tracks.
1.
Select two events. The events must overlap, but do not need to be on adjacent tracks.
2.
For creative ways to use crossfades, see Creating DJ-style crossfades on page 194.
F
Press . The end of the first event fades out, and the second event fades in.
EDITING EVENTS CHP. 4
Page 73

CHAPTER
Working in the
Track View
5
5
This chapter introduces you to several ACID features that increase your productivity, such as markers,
regions, and snapping options. You’ll also learn about the different ways to change a project’s tempo, key and
time signature. Finally, you’ll learn several options for adjusting the project timeline.
Using project markers and regions
ACID markers and regions identify areas of your project and provide navigational cues for quickly finding
those areas. After you insert markers and regions, you may adjust their position along the project’s timeline
and label them with meaningful names for your reference.
Marker type Description
Marker (standard) Markers identify specific reference points in your project. Points that you may
Time marker Time markers are fixed to the time ruler and mark absolute time in your
want to identify are introductions, bridges, refrains, choruses, or whatever
you choose.
project. They are very useful when scoring video.
71
Command marker Command markers indicate when an instruction or function occurs in a
streaming media file.
Regions Regions subdivide your project into time segments. Regions have in and out
points, which allow them to function as permanent time selections.
Working with standard markers
Markers are tools that can make creating music easier by identifying specific points along the project’s
timeline. They can be named, moved, and serve as snap and navigational points for the cursor and events.
When you place markers, ACID automatically numbers them in the order that you place them.
Placing markers
Markers are placed at the cursor position. You may place a marker in one of the following ways:
• From the
• Right-click the marker bar, choose
from the submenu.
• Press . You may use this method to place a marker while the project is playing.
Insert menu, choose Marker.
Markers/Regions from the shortcut menu, and choose Insert Marker
M
Marker barMarker
CHP. 5 WORKING IN THE TRACK VIEW
Page 74

72
Moving markers
Place the mouse pointer on the marker to be moved. The hand cursor ( ) appears.
1.
2.
Drag the marker to the desired position.
Naming markers
ACID allows you to name markers in your project. You may want to name markers based on parts of the
project. For example, you may want to identify choruses, refrains, bridges, or instrument solos as reference
points along the timeline.
1.
Place the mouse pointer on the marker to be named. The hand cursor ( ) appears.
2.
Right-click the marker and choose Rename from the shortcut menu. A box appears next to the marker.
3.
Type a marker name in the box and press to save the name.
Tip:
You can use the same steps to rename a marker.
Enter
Alternately, you can double-click the marker and enter a new
name.
Navigating to markers
While you are working on your project, you may have scrolled to a portion of the project where the cursor is
not visible. There are two ways to move the cursor directly to the selected marker:
• Right-click the marker and choose
Go To from the shortcut menu.
• Click the marker once.
• Press the number key (not on the numeric keypad) corresponding to the marker number.
Tip:
You may also navigate from one marker to the next by
pressing +left/right arrow key.
Adjusting tempo to match cursor to marker
Ctrl
Position the cursor, right-click the marker tab, and choose Adjust tempo to match cursor to marker from the
shortcut menu. The project tempo changes so that the cursor position matches the selected marker.
Deleting markers
You may remove markers from the project at any time. Because markers are automatically numbered when
they are placed, ACID does not renumber the remaining markers when one is deleted. Rather, the remaining
markers retain their numbers. However, if you add markers later, ACID begins numbering to fill the
sequence gap.
For example, if you have five markers in your project and delete markers three and four, the remaining
markers are listed as one, two and five. When you add markers again, ACID begins numbering the markers as
three and four.
1.
Place the mouse pointer on the marker to be deleted. The hand cursor ( ) appears.
2.
Right-click the marker and choose Delete from the shortcut menu. The marker is removed from the
project.
WORKING IN THE TRACK VIEW CHP. 5
Page 75

Working with time markers
Unlike standard markers, time markers are tied to absolute time within your project. They are added
differently than standard markers and appear on the time ruler at the bottom of the track view. Otherwise,
time markers can be manipulated just like other markers.
Placing time markers
Time markers are placed at the cursor position. You may place a time marker in one of the following ways:
73
• From the
• Press . You may use this method to place a time marker while the project is playing back.
Insert menu, choose Time Marker.
H
Time marker
Note:
ACID does not number time markers.
Adjusting tempo to match marker to cursor
Using this function with time markers is particularly useful when scoring video. For more information, see
Scoring video with ACID on page 156.
Position the cursor, right-click the marker tab, and choose
Adjust tempo to match marker to cursor from the
shortcut menu. The project tempo changes so the time marker matches the cursor position.
You can also align the marker and cursor by holding while dragging the marker. For example, hold
Alt Alt
while dragging a time marker to a location on the beat ruler. The project tempo adjusts so the time at the
marker occurs on a specific beat. For example, if you place a time marker at 10 seconds on the time ruler and
Alt
hold while dragging the marker to 5.1 on the beat ruler, ACID adjusts the project’s tempo so the first
beat of measure five occurs at ten seconds.
Working with command markers
Command markers add interactivity to a multimedia presentation streamed over the Internet. As your media
plays, any number of other actions can be programmed to execute. These commands are a part of the
Windows Media and RealMedia streaming formats. Most frequently, these actions add text or open a related
Web site. The specific commands available vary depending on the final format of your project.
Note:
drive or CD-ROM, but in order to stream properly across the
Internet, the file must be on a streaming media server. Check
with your internet service provider for details and availability
of this service.
CHP. 5 WORKING IN THE TRACK VIEW
Streaming media files can be played back from a hard
Page 76

74
Placing command markers
Command markers appear on the command ruler, which is above the marker bar.
URL command marker
Command ruler
Marker bar
1.
Position the cursor where you want to place the command marker.
2.
From the Insert menu, choose Command, or press .
3.
Complete the Command Properties dialog:
• From the
Te mp la t e drop-down list, choose a custom
C
template. For more information, see Saving command
properties as a custom template on page 74.
• From the
Command drop-down list, choose the type of
command. For more information, see Defining streaming
media commands on page 75.
• Enter parameters in the
Parameter box to define the
behavior of the command.
• Enter your own notes or comments in the
Comment
box.
• Specify the timing of the command in the
Position box. Command markers are automatically set to the
current cursor position unless you change this value.
4.
Click OK. The new command marker appears on the command bar.
After you create a command marker, you can move the marker by dragging it to a new location.
Editing command marker properties
Double-click any command marker to open the Command Properties dialog and edit its contents. You can
also right-click a command marker and choose
Saving command properties as a custom template
Edit from the shortcut menu.
If you plan to use a command more than once, you can save command properties as a template. You can then
reuse the command properties by selecting the template from the
Te mp l a te drop-down list.
1.
Create a command and complete the Command Properties dialog.
2.
Click in the Te mp l at e box and enter a name for the template.
3.
Click the Save Template button ( ).
Tip:
ACID saves your metadata command templates in the
cmdtemp.xml file in the ACID program folder. You can edit
this file directly to modify your templates.
WORKING IN THE TRACK VIEW CHP. 5
Page 77

75
Defining streaming media commands
In a streaming media file, command markers can be used to display headlines, show captions, link to Web
sites, or any other function you define.
ACID includes several command types that you may add to a streaming media file. Some command types are
exclusive to either the Windows Media (WMA or WMV) or the RealMedia (RM) file types.
Command Player Type Description
URL Windows Media
and RealMedia
TEXT Windows Media Displays text in the captioning area of the Windows Media Player located
WMClosedCaption Windows Media Displays the entered text in the captioning window defined by an HTML
WMTextBodyText Windows Media Displays the entered text in the text window defined by an HTML layout page.
WMTextHeadline Windows Media Displays the entered text in the headline window defined by an HTML layout
Title Windows Media
and RealMedia
Author Windows Media
and RealMedia
Copyright Windows Media
and RealMedia
HotSpotPlay RealMedia Allows you to define an area in the RealPlayer video display that users can
HotSpotBrowse RealMedia Allows you to define an area in the RealPlayer video display that users can
HotSpotSeek RealMedia Allows you to define an area in the RealPlayer video display that users can
Indicates when an instruction is sent to the user’s Internet browser to change
the content being displayed. With this command, you enter the URL that
displays at a specific time during the rendered project’s playback.
below the video display area. You enter the text that displays during playback.
layout file.
file.
Displays the entered text on the player’s title bar.
Displays the entered text (author’s name) when a user selects About this
Presentation from the RealPlayer’s shortcut menu or Properties from the
Windows Media shortcut menu.
Displays the entered copyright information when a user selects About this
Presentation from the RealPlayer’s shortcut menu or Properties from the
Windows Media shortcut menu.
click to jump to another RealMedia file.
click to jump to a Web page that you specify.
click to jump to a point in the current RealMedia file.
Defining HotSpot commands
Hotspots are defined using the following parameter syntax:
HotSpotPlay MM:SS (LEFT, TOP, RIGHT, BOTTOM) "LABEL" FILENAME
HotSpotBrowse MM:SS (LEFT, TOP, RIGHT, BOTTOM) "LABEL" URL
HotSpotSeek MM:SS (LEFT, TOP, RIGHT, BOTTOM) "LABEL" MM:SS
The
Parameter box for a typical HotSpotBrowse command for a hotspot rectangle that is 50 pixels wide by 20
pixels tall and lasts for 10 seconds would look like this:
HotSpotBrowse 00:10 (0, 0, 50, 20) "Sonic Foundry" http:\\www.sonicfoundry.com
All parameters are optional except the last. The hotspot defaults to the entire duration of the file and the
entire video frame if the duration and dimensions are not specified.
Adjusting tempo to match cursor to marker
Position the cursor, right-click the marker tab, and choose Adjust tempo to match cursor to marker from the
shortcut menu. The project tempo changes so that the cursor position matches the selected command
marker.
Deleting command markers
To delete a command marker, right-click the marker and choose Delete from the shortcut menu.
CHP. 5 WORKING IN THE TRACK VIEW
Page 78

76
Working with regions
Regions are useful tools that allow you to subdivide your project into time sections by designating in and out
points along the timeline. Regions can function as permanent time selections for playback and editing
purposes. Like markers, regions can serve as reference points and may be moved, named, and provide snap
points for the cursor and events.
When you place regions, ACID automatically numbers them in the order that you place them.
Placing and moving regions
Regions are placed at the start and end points of a loop region (time selection). You may place a region in
one of the following ways:
• From the
• Right-click the marker bar, choose
Insert menu, choose Region.
Markers/Regions from the shortcut menu, and choose Insert Region
from the submenu.
• Press .
R
Region start
Region end
Loop region
After you place a region, you may change its position by dragging the region tag to the desired position.
Tip:
You can move a region without changing its size by
holding while dragging either region tag.
Naming regions
Alt
ACID allows you to name the placed regions in your project. You may want to name regions based on parts
of the project or to define the amount of time that the regions encompass. For example, you may want to
identify introductions, solos, or special time-related features in your project as reference points.
1.
Right-click the region’s start tag and choose Rename from the shortcut menu. A box appears next to the
tag.
2.
Type a region name and press to save the name.
WORKING IN THE TRACK VIEW CHP. 5
Enter
Page 79

77
Navigating to regions
While you are working on your project, you may have scrolled to a portion of the project where the cursor is
not visible. You may click in the track view to move and view the cursor or you may use region tags to bring
the cursor into view.
To move the cursor to the selected region tag, right-click the region tag and choose
Go To from the shortcut
menu.
Tip:
You may also navigate between regions in your project
by pressing +left/right arrow key or the number key (not
Ctrl
on the numeric keypad) corresponding to the region number.
Selecting regions
You may use the region’s start and end tags to make a time selection across all tracks in your project. The
information within the time selection can then be used for playback or editing.
To select a region, right-click a region tag and choose
Select Region from the shortcut menu. The loop bar
appears between the region tags and the tracks are highlighted.
Loop bar
Deleting regions
You may remove regions from the project at any time. Because regions are automatically numbered when
they are placed, ACID does not renumber the existing regions when one is removed. Rather, the existing
regions retain their numbers. However, if you add regions later, ACID begins numbering to fill the sequence
gap that exists.
For example, if you have six regions in your project and delete regions four and five, the remaining regions
are listed as one, two, three and six. When you add regions again, ACID begins numbering the regions as
four and five.
To remove a region from a project, right-click the region tag marker and choose
Delete from the shortcut
menu.
CHP. 5 WORKING IN THE TRACK VIEW
Page 80

78
Using snapping
Snapping helps you to align events in your project with other items. ACID is preset to snap event edges to
the project’s grid lines as you drag an event along the track. If snapping is enabled and the
turned off, the event’s edges automatically align to these designated snap points:
• Cursor position
• Grid lines
• Markers
• Regions start and end points
• Loop region (time selection) in and out points
You may turn on snapping for these elements in the project or limit snapping to grid lines.
Snap point examples
Grid Only option is
Choosing snapping options
If the snap function is preventing you from placing an event precisely where you want it, you may turn
snapping off. Turning off snapping prevents events from automatically aligning to the cursor, grid lines,
markers, regions, and time selections.
The
Options menu allows you to toggle snap functions. The button image next to the Enable command
indicates when snapping is turned on. The button image next to the
of snapping in use.
Select to turn all snapping on/off
Select to toggle between snapping
to grid lines only and snapping to all
elements.
Tip:
You can temporarily suspend snapping while dragging by
holding down the key.
Turning snapping on and off
Shift
You may turn snapping on and off in one of the following ways:
• Click the
• From the
• Press .
Enable Snapping button ( ) on the Toolbar.
Options menu, choose Snapping, and choose Enable from the submenu.
F8
Grid Only command indicates the type
Snapping to grid lines
With snapping turned on, you may choose to snap only to grid lines. From the Options menu, choose
Snapping, and choose Grid Only from the submenu. The button image next to the command indicates that it
is active.
WORKING IN THE TRACK VIEW CHP. 5
Page 81

Snapping to all elements
With snapping turned on, you may choose to snap to all elements. From the Options menu, choose
Snapping, and choose Grid Only from the submenu. The button image next to the Grid Only command
appears deselected when snapping to all elements.
79
Tip:
Ctrl +F8
Press to toggle between grid only and all
elements.
Changing tempo, time signature, and key
You can set a tempo, time signature, and key for your ACID project. You can also make adjustments during
playback.
ACID allows you to add specific tempo, time signature, and key changes within a project using tempo/key/
time signature change markers. These markers appear on the marker bar above the track view. When the
cursor passes over one of these markers, the master project tempo, key, and/or time signature changes in real
time.
Set the tempo, time signature, and key for the whole project... ...or change these elements dynamically in the timeline.
Project Tempo
slider
Project Key
Project Time Signature
Project Tempo
Changing project tempo
With ACID, you can change the tempo of a project without affecting the project’s key.
Changing tempo using the Project Tempo slider
Drag the Project Tempo slider at the bottom of the track list. Dragging the slider to the left slows the tempo,
while dragging it to the right speeds the tempo.
Tip:
Double-click the tempo value
next to the
enter an exact value. Press
when you are finished.
As you drag the
a track is being stretched to match the project tempo. The mark in the center of the bar represents the
original tempo of a file. When the bar appears to the right of the mark, the project tempo is faster than the
original file; when the bar appears to the left of the mark, the project tempo is slower than the original file.
The amount of change also displays as a percentage at the right end of the bar.
Project Tempo slider to
Enter
Project Te mp o slider, a colored bar appears under each track’s name to represent the amount
CHP. 5 WORKING IN THE TRACK VIEW
Page 82

80
As you drag the slider, a colored bar appears for each track.
Project tempo is slower
than file tempo.
Project tempo is faster
than file tempo.
Project Tempo slider
Changing project tempo to match file tempo
Each track’s shortcut menu contains the option Use Original Tempo. The original tempo of the file used on
the track appears to the right of this option in the shortcut menu. To change the project’s tempo to match
the original file tempo, simply choose
Use Original Tempo from the shortcut menu.
Changing project time signature
Click the Project Time Signature control and select a time signature from the menu to adjust a project’s time
signature. Select
Other from the menu to enter a custom time signature.
Changing project key
Click the Project Key control and select a key from the menu to adjust a project’s key.
Project Key control
This feature makes it possible to use media that are in different keys in the same project: each loop that has a
specified root note is transposed to the key indicated by the
For example, if three loops have root notes of A, B, and C, and your
pitch-shifts the loops by five, three, and two semitones, respectively.
Note:
If the root note for a track is set to Don’t Transpose in
the Track Properties window, the track does not pitch shift
with the rest of the project.
Project Key control.
Project Key control is set to D, ACID
WORKING IN THE TRACK VIEW CHP. 5
Page 83

Working with tempo/key/time signature change markers
Tempo/key/time signature change markers allow you to make changes to the tempo, key, and/or time
signature at specified points in your project.
Note:
Time signature changes must occur on the first beat of
a measure.
Adding tempo/key/time signature change markers
Position the cursor where you want the change to occur.
1.
2.
From the Insert menu, choose Tempo/Key/Time Signature Change. The Tempo/Key/Time Signature
Change dialog appears.
3.
Select the check boxes for the types of changes you want to
occur at the cursor position.
•
Key Change changes the key of all tracks until ACID
encounters another tempo/key/time signature change marker.
Tempo Change changes the tempo of all tracks until ACID
•
encounters another tempo/key/time signature change marker.
•
Time Signature Change changes the time signature of all tracks
until ACID encounters another tempo/key/time signature
change marker.
81
4.
Specify the desired change information and click OK to close the dialog. A marker appears in the marker
bar at the cursor position that displays the change information.
Editing tempo/key/time signature change markers
There are several ways to edit the tempo/key/time signature change marker:
• Position the cursor on or after the marker and adjust the
Project Tempo, Project Time Signature, or Project Key
controls. The marker’s text reflects the change.
• Right-click the marker, choose
Edit from the shortcut menu, and enter the appropriate change in the
Tempo/Key/Time Signature Change dialog.
• Double-click the marker and enter the appropriate change in the Tempo/Key/Time Signature Change
dialog.
Adjusting tempo to match cursor to marker
Position the cursor, right-click the marker tab, and choose Adjust Tempo to Match Cursor to Marker from the
shortcut menu. The project tempo changes so that the cursor position matches the selected marker.
Deleting tempo/key/time signature change markers
To delete a marker, right-click the marker and choose Delete from the shortcut menu.
CHP. 5 WORKING IN THE TRACK VIEW
Page 84

82
Changing a track’s key
You can change the key of an entire track without affecting the project’s key. For creative ways to use track key
changes, see Detuning paired tracks on page 187.
1.
Right-click the track and choose Properties from the shortcut menu. The Track Properties window
appears.
2.
On the General tab, enter the number of semitones by which to adjust the key in the Pitch Shift box or use
the spinner control. Use the minus (-) key for negative values.
3.
Close the Track Properties window. The pitch shift displays in the track’s icon.
Tip:
Another way to change the key of the track is to select
+
the track in the track list and press or on the numeric
-
keypad.
Changing an event’s key
You can change the key of an individual event without affecting the pitch of the track or project.
Right-click the event in the track view, choose
and choose
Up Semitone or Down Semitone from the submenu. The pitch shifts one
Pitch Shift from the shortcut menu,
semitone in the direction specified, and the amount of shift displays on the event
itself.
You can also change an event’s key using keyboard shortcuts. For more information, see Event commands on
page 20.
Adjusting time
ACID provides two commands for adjusting your project’s timeline: Insert Time and Fit to Time.
Inserting time
Use the Insert Time command to insert a specified amount of blank space into the project at the current
cursor position. This feature can be used to create space in the project for new events.
1.
Position the cursor where you want to insert time.
2.
From the Insert menu, choose Time. The Insert Time dialog appears.
3.
Enter the amount of time you want to insert and click
Note:
The Insert Time dialog uses the measures.beats.ticks
OK.
format used by the beat ruler.
WORKING IN THE TRACK VIEW CHP. 5
Page 85

Fitting to time
The Fit to Time command allows you to adjust the project’s overall length to a specified amount of time.
83
Note:
The maximum and minimum length is limited to
reduce the possibility of creating audible artifacts through the
compression/expansion process.
1.
From the Edit menu, choose Fit to Time. The Fit to Time dialog appears with the current project length
displayed in the
2.
Enter the new project length in the New length box. The length is always entered in time format,
New length box.
regardless of the format used on the time ruler.
3.
Click
OK. The dialog closes and ACID adjusts the tempo to alter the project’s length.
CHP. 5 WORKING IN THE TRACK VIEW
Page 86

84
WORKING IN THE TRACK VIEW CHP. 5
Page 87

CHAPTER
Using the Chopper
6
6
The Chopper allows you to quickly create slice-and-dice effects. For creative ways to use the Chopper, see
Slicing and dicing in the Chopper on page 193.
Working in the Chopper window
Selecting a track automatically places it in the Chopper where it can be immediately manipulated and
inserted into the track view.
Toolbar
Beat ruler
85
Time ruler
Transport bar
Viewing the Chopper
Alt
To display the Chopper, choose Chopper from the View menu or press .
Changing the Chopper grid
The Chopper’s grid uses the same increments available on the track view. To change the grid display, right-
click the waveform area of the Chopper, choose
desired display from the submenu.
Changing Chopper snapping options
The snapping behavior of the track view and Chopper are linked. To enable snapping in both components,
choose
When snapping is turned on, you can choose between snapping only to the grid or snapping to all elements.
For more information, see Using snapping on page 78.
Snapping from the Options menu and choose Enable from the submenu, or press .
Grid Spacing from the shortcut menu, and choose the
+2
F8
CHP. 6 USING THE CHOPPER
Page 88

86
Magnifying the Chopper
There are three ways of adjusting the magnification of the Chopper.
• Click the
Zoom In Time () and Zoom Out Time ( ) buttons located in the lower-right corner of the
window.
• Click within the Chopper and use the mouse wheel.
• Quickly magnify a selection by right-clicking and choosing
Zoom to Loop Region from the shortcut menu.
Previewing in the Chopper
The Chopper contains a dedicated transport bar that can be used to preview selections prior to inserting
them into the project.
Using Chopper toolbar and keyboard commands
In addition to the transport bar, the Chopper contains a toolbar that is designed to make creating selections
quick and easy. The following table briefly describes the toolbar buttons and the associated keyboard
commands.
Button Keyboard Function
/ A
or
Ctrl +,
Ctrl +.
N
;
(semicolon)
(comma)
(period)
Inserts the Chopper selection in the track view at the current cursor
position.
Shifts the track view’s cursor position to the left by the length of the
increment arrow.
Shifts the track view’s cursor position to the right by the length of the
increment arrow.
Links the length of the increment arrow with the length of the selection.
When toggled on, the length of the increment remains equal to the
length of the selection. When toggled off, you can configure the
increment independently of the Chopper selection.
Halves the length of the Chopper selection.
‘’
(apostrophe)
< ,
or (comma)
> .
or (period)
Ctrl +Shift+,
Ctrl
+Shift+.
Ctrl
+;
(semicolon)
Ctrl
+
(apostrophe)
‘’
R
M
I
O
(comma)
(period)
Doubles the length of the Chopper selection.
Shifts the Chopper selection to the left by the length of the selection.
Shifts the Chopper selection to the right by the length of the selection.
Shifts the selection left by the increment length.
Shifts the selection right by the increment length.
Doubles the length of the increment arrow.
Halves the length of the increment arrow.
Inserts a region.
Inserts a marker.
Marks the start point of a loop region.
Marks the end point of a loop region. Once the endpoint is established,
the loop region becomes highlighted.
USING THE CHOPPER CHP. 6
Page 89

Inserting markers and regions in the Chopper
When working with events in the Chopper, you can drop markers and create regions just like in the track
view. For more information, see Using project markers and regions on page 71.
These markers and regions are saved with the project when it is saved. They can also be saved back to the
original media file by clicking the
Save File button ( ) in the Track Properties window. For more
information, see Saving file properties on page 109.
Creating selections in the Chopper
After you place a file in the Chopper, you can use the toolbar, transport bar, and mouse (or their keyboard
equivalents) to create and preview selections within the file. When have made the selection you want, you
can insert the selection into the track view.
Placing files in the Chopper
To place a file in the Chopper, do any of the following:
• Select a track in the track list.
• Select an event.
• Right-click an event and choose
Select in Chopper from the shortcut menu.
87
Note:
If you choose Select in Chopper on an event that
contains only a portion of a file, ACID places the entire
contents of the file in the Chopper. The part of the waveform
selected, however, matches the contents of the selected event.
This allows you to see the event in the context of the entire
media file.
Creating selections
To create a selection, drag the mouse, or hold while pressing the arrow keys. A shaded region appears
in the Chopper to indicate the current selection, and its start point, end point, and length display at the
bottom-right corner of the window in measures.beats.ticks format. You can preview the selection at any time
by clicking the
Play button ( ) on the Chopper’s transport bar or pressing .
Increment
Shift
Space
Start End
CHP. 6 USING THE CHOPPER
Length
Page 90

88
Note:
In addition, an increment arrow appears on the track
view above the selected block. For more information, see
Inserting increments on page 88.
As you make a selection in the Chopper, a colored block appears in the track view. This block indicates
where the selection will be placed on the track view when you insert it from the Chopper.
Creating selections of a specific musical length
You may want to create a selection with a length corresponding to a musical value. You can easily do this in
ACID using the Chopper’s selection shortcut menu.
1.
Create a selection or place the cursor in the Chopper. For more information, see Creating selections on page
87.
2.
Right-click and choose the desired musical length from the shortcut menu. ACID creates a selection
equal to the specified musical length.
Inserting increments
In addition to creating selections, the Chopper allows you to configure the sections of silence between
selections painted on a track. When you click the
increment arrow length with the selection length. This forces the increment and selection lengths to remain
equal, thereby allowing you to insert selections seamlessly, end-to-end, in the project.
Link Arrow to Selection button ( ), ACID links the
Selection and increment length
When the
Link Arrow to Selection button is toggled off, the increment arrow is displayed in black and you are
Chopper selection inserted end-to-end three times
able to establish a increment length that is independent of the selection length. The increment arrow can be
set by dragging either end of the arrow or by using the increment shortcut menu.
When the increment length is greater than the length of the selection, ACID inserts an appropriate amount
of silence following the selection when you insert it in the track view. This affects the track’s insert position
and allows you to paint selections separated by the specified increment.
Increment greater than selection
USING THE CHOPPER CHP. 6
Selection inserted with specified increment three times
Page 91

When the increment length is less than the length of the selection, ACID overlaps the selections as you
insert them in the track view.
89
Increment less than selection
Selection overlaps when inserted three times
Creating increments
1.
Verify that the Link Arrow to Selection button ( ) is toggled off and the increment arrow is displayed in
black.
2.
Drag the point of the arrow to configure an increment of the desired length.
Tip:
While dragging the increment arrow, the Chopper’s
middle status value temporarily displays the length of the
increment.
Creating increments of a specific musical length
The increment shortcut menu, like the selection shortcut menu, allows you to create increments that
correspond to the specified musical length.
1.
Verify that the Link Arrow to Selection button ( ) is toggled off and the increment arrow is displayed in
black.
2.
Right-click the increment arrow and choose the desired musical value from the shortcut menu. The
increment length is automatically configured to the selected value in both the Chopper and the track
view.
Creating increments of a custom musical length
1.
Verify that the Link Arrow to Selection button ( ) is toggled off and the increment arrow is displayed in
black.
2.
Right-click the increment arrow and choose Custom from the shortcut menu. The Custom Length dialog
appears.
3.
Choose the desired increment format from the drop-down menu.
4.
Enter an appropriate value in the adjacent box and click OK. The increment length is automatically
configured to the selected value in both the Chopper and the track view.
Note:
It is possible to set an increment value that results in
the increment arrow extending beyond the scope of the
Chopper. If this occurs, an accurate depiction of the
increment still appears in the track view.
CHP. 6 USING THE CHOPPER
Page 92

90
Inserting selections in the track view
You can add selections from the Chopper to your project in several ways.
Using the Insert Selection button
After you create the desired selection and increment, you can insert the selection in the project at the track
view’s cursor position by clicking the
the cursor moves to the end of the increment.
• If the increment length is equal to the selection length, selections are painted end-to-end.
• If the increment length is greater than the selection length, an appropriate amount of silence is painted
prior to the next insert position.
• If the increment length is less than the selection length, selections overlap.
Using copy and paste
You can right-click the selection in the Chopper and choose Copy from the shortcut menu to copy the
current selection to the clipboard. You can then use the
view. After the event is pasted, the cursor advances to the end of the pasted event.
Note:
When you paste a selection from the Chopper to the
track view, ACID ignores the increment setting.
Insert Selection button ( ). After the Chopper inserts the audio,
Paste command to insert the selection in the track
Dragging selections
You can drag a Chopper selection from the Chopper to the track view. Release the mouse at the location
where you want to insert the selection.
Moving the insert position in the track view
Click the Move Track View Cursor Left button ( ) and the Move Track View Cursor Right button ( ) to move
the current insert position in the track view left/right by the increment length.
Saving Chopper selections as new files
You can quickly create a new loop by making a selection in the Chopper and saving the selection as a new
file. ACID adds the file to your project as a new track.
1.
Make a selection in the Chopper.
2.
Right-click the selection and choose Chop to New Track from the shortcut menu. Alternately, press
Ctrl +M
Tip:
track list.
3.
In the File name box, enter a name for the new file.
. The Chop to New Track dialog appears.
You can also drag a selection from the Chopper to the
4.
From the Save as type box, choose a file format for the new file.
USING THE CHOPPER CHP. 6
Page 93

5.
From the Te mp l at e drop-down list, choose a template for rendering the file, or click Custom to create
custom rendering settings. For more information, see Creating custom rendering settings on page 55.
6.
Click Save.
ACID saves the selection and adds the file as a loop to a new track in the project.
Using the Chopper with one-shots
Selections of loops and Beatmapped files transfer flawlessly between the Chopper and the track view because
the beats are clearly identified. However, one-shot files present more of a problem. You can use the following
method to create accurate single-hit selections in one-shot files.
1.
Verify that ACID’s snapping options are active. If snapping is not active, choose Snapping from the
Options menu and choose Enable from the submenu, or press .
2.
Verify that the Link Arrow to Selection button ( ) is selected.
3.
Create a selection of the desired musical length in the Chopper. For more information, see Creating
selections of a specific musical length on page 88.
F8
91
4.
From the Options menu, choose Snapping, and choose Enable from the submenu, or press to toggle all
F8
snapping options off.
5.
Click the Link Arrow to Selection button ( ) to toggle the linking option off. You can now adjust the
selection without changing the increment.
6.
Drag the middle of the increment arrow to reposition selection length in the Chopper.
7.
Use the mouse and/or keyboard to fine-tune the selection. The increment arrow does not change.
8.
Insert the desired selection data in the track view. For more information, see Inserting selections in the track
view on page 90.
9.
Repeat steps six through eight to insert all desired selections in the track view.
CHP. 6 USING THE CHOPPER
Page 94

92
USING THE CHOPPER CHP. 6
Page 95

CHAPTER
Working with Tracks
7
7
This chapter covers advanced track features including track effect chains, track envelopes, and stereo
panning modes. You’ll also learn more about track types, track properties, and rendering tracks to new files.
Using track effects
ACID enables you to create DirectX plug-in chains, adjust the order of plug-ins on a chain, bypass a plug-in,
remove plug-ins from the chain, and save frequently used chains as presets.
The EQ plug-in is assigned to all tracks by default; however, it does not use CPU power or affect the sound
until you adjust its settings. You can remove the EQ plug-in if desired. For more information, see Removing
plug-ins from chains on page 95.
93
Important:
altering effects (such as time stretch, gapper/snipper, pitchshift without preserving duration, and some vibrato settings)
with an ACID project. Time-altering effects cause a track to
play out of synchronization with the waveform display in the
track view and with other tracks.
In addition, you can use effect plug-ins in the Mixer window by applying effect chains to busses or soft
synths, or by creating assignable effect chains and routing tracks to them. For more information, see Using the
Mixer on page 111.
Creating or adding to track plug-in chains
A plug-in chain can contain one or more plug-ins. When you add multiple plug-ins, you may set the
processing sequence that the track’s events go through when the project is played back. Moreover, the plug-
ins that you add to the chain may be added more than once. For example, a plug-in chain could look
something like this: EQ, Compression, EQ, and Noise Gate.
After you create a plug-in chain, ACID processes the track’s events by each plug-in in its respective order on
the chain. The events’ effects processing is cumulative, so in some cases, you may want to rearrange the order
of plug-ins to achieve the desired sound. For more information, see Arranging plug-in chain order on page 95.
1.
Click the Tr a ck FX button ( ). The Audio Plug-In window appears.
Note:
plug-in chain includes automatable effects ( ) or does not
include automatable effects ( ). By default, an ACID Pro
track plug-in chain includes the Track EQ plug-in, which is
automatable. For more information, see Adding effect
automation envelopes on page 98.
We recommend that you do not use time-
The Track FX button indicates whether the current
CHP. 7 WORKING WITH TRACKS
Page 96

94
2.
Click the Edit Chain button ( ) to display the Plug-In Chooser dialog.
Chain area
3.
Select the plug-ins that you want to add. There are three ways to add a plug-in to the chain:
• Double-click the plug-in.
• Drag the plug-in to the chain area.
• Select the plug-in and click the
4.
Rearrange the order of plug-ins as needed by dragging plug-ins to different locations in the chain or by
selecting a plug-in and clicking the
5.
Click OK. The Plug-In Chooser dialog closes. The Audio Plug-In window displays the plug-in chain and
Add button.
Shift Plug-In Left () and Shift Plug-In Right ( ) buttons.
the settings for the plug-in last selected on the Plug-In Chooser dialog.
6.
Click a specific plug-in and adjust the effect’s parameters manually, or choose one of the presets from the
Preset drop-down list. For more information about effect parameters, click the Plug-In Help button ( ) in
the Audio Plug-In window.
Tip:
You can save an effect’s parameters as a preset to be
used in other projects. To save a preset, enter a name in the
Preset box and click the Save Preset ( ) button.
7.
Click the Close button ( ) to close the Audio Plug-In window.
You can use a track effect chain as a default for all new tracks you create. For more information, see Setting
default track properties on page 178.
Automating plug-in parameters
You can automate the parameters of certain plug-ins by adding envelopes to the track. For more information,
see Adding effect automation envelopes on page 98.
WORKING WITH TRACKS CHP. 7
Page 97

Arranging plug-in chain order
The plug-ins are cumulative during playback. For example, when the track’s signal passes through the EQ, it
carries the EQ’s settings as it passes through the compression plug-in, then the signal carries both those plug-
in settings to the next plug-in.
Because of this cumulative effect, you may need to arrange plug-ins in a certain order so that one plug-in’s
processing does not adversely affect the next plug-in on the chain. There is no right or wrong way to order
plug-ins, although some plug-ins work better when they follow another. However, the plug-in order in the
chain is strictly based on your preferences and desired output.
1.
Click the Tr a ck FX button ( ). The Audio Plug-In window appears.
2.
There are two ways to arrange plug-ins in your chain:
• Drag the plug-in to a new location in the chain.
• Right-click the plug-in and choose Move Left or Move Right from the shortcut menu.
3.
Click the Close button ( ) to close the Audio Plug-In window.
Bypassing plug-ins in a chain
You can bypass a plug-in without removing it from the chain by clearing the check box for the plug-in.
Alternately, right-click the plug-in and choose
Bypass from the shortcut menu.
95
Tip:
To bypass (or re-enable) all plug-ins in a chain, right-
click the
Enable All.
Bypassing effect automation
Track FX button ( ) and choose Bypass All or
For plug-in chains that include effect automation using envelopes, you can bypass automation by clicking
the
Bypass FX Automation button ( ). This does not remove any effect automation envelopes from the
track, but rather temporarily bypasses processing of the effect automation. You can toggle this button on and
off to hear the difference between the plug-in chain as a standard (non-automated) effect versus an
automated effect.
Removing plug-ins from chains
1.
Click the Tr a ck FX button ( ). The Audio Plug-In window appears.
2.
Right-click the plug-in and choose Remove from the shortcut menu, or click the Remove Selected Plug-In
button ( ).
3.
Click the Close button ( ) to close the Audio Plug-In window.
Tip:
To remove all plug-ins in a chain, right-click the Track
FX button ( ) and choose Delete All.
CHP. 7 WORKING WITH TRACKS
Page 98

96
Saving plug-in chains as packages
ACID allows you to save plug-in chains as packages so that you may use them again with other projects. If
you use a combination of plug-ins often, saving them as a package saves you time. Effect packages retain their
chain order and individual plug-in settings.
You may save plug-in chains as packages from existing chains on tracks or when you are creating a plug-in
chain. The plug-in chains that you save as packages appear in the Plug-In Chooser dialog in the
Chains
folder. You can apply an effect package to a track the same way you assign a plug-in to a track.
Once you have created custom presets for effects or effect chains, you can use the Preset Manager to back up,
transfer, or delete custom presets from any of the plug-ins you use in ACID. For more information, see Using
the Preset Manager on page 124.
1.
Click the Tr ack F X button ( ). The Audio Plug-In window appears.
Packaged
Note:
If the track has no plug-in chain, clicking the Track FX
button ( ) displays the Plug-In Chooser dialog.
2.
Click the Edit Chain button ( ) to display the Plug-In Chooser dialog.
3.
Add and arrange plug-ins to create a plug-in chain and click OK.
4.
Click a specific plug-in and adjust the effect’s parameters manually, or choose one of the presets from the
Preset drop-down list. For more information about effect parameters, click the Plug-In Help button ( ) in
the Audio Plug-In window.
5.
Click the Save Chain Preset button ( ). The Save Plug-In Package dialog appears.
6.
Enter a name for the package.
7.
Click OK to save the plug-in chain as an effect package.
Removing or bypassing all effects on tracks
You can clear a track of all effects by right-clicking the Track FX button ( ) and choosing Delete All from the
shortcut menu.
You can bypass all of a track’s effects without removing them by right-clicking the
choosing
choose
Bypass All from the shortcut menu. To apply them again, right-click the Tra c k F X button ( ) and
Enable All from the shortcut menu.
Track FX button ( ) and
WORKING WITH TRACKS CHP. 7
Page 99

Using track envelopes
Track envelopes allow you to control volume, panning, assignable effect send levels, bus send levels, and
effect parameters (for effects that support automation) for a specific track. You can distinguish the various
envelopes by their color.
Envelope type Envelope color
Volume Blue
Pan Red
Bus send Purple
Assignable effect send Green
Effect automation Wood tones (various)
Tip:
You can customize ACID envelope colors. For more
information, see Using the Other tab on page 185.
Adding track envelopes
This section describes how to add each type of track envelope. For creative ways to use track envelopes, see
ACID Tips and Tricks on page 187.
97
Adding volume or pan envelopes
Select the track to which you want to add the envelope. (You may select multiple tracks.)
1.
2.
Add the envelope to the selected track(s) in one of following ways:
• From the
• Right-click the track header in the track list, choose
and choose
• Press (volume envelope) or (pan envelope).
Insert menu, choose Envelopes, and choose Volume or Pan from the submenu.
Insert/Remove Envelope from the shortcut menu,
Vol ume or Pan from the submenu.
Shift + V Shift +P
A blue line appears across the track(s) for a volume envelope, and a red line appears across the track(s) for
a pan envelope.
Envelope line
Note:
Because the default panning mode is additive, you can
introduce clipping when panning a track to the left or right.
Choose an appropriate pan type and adjust the track volume
accordingly. For more information, see Choosing stereo pan
types on page 103.
CHP. 7 WORKING WITH TRACKS
Page 100

98
Adding bus envelopes
A bus envelope controls the level of a track sent to a particular bus. Before you can add a bus envelope, you
must add busses to the project. For more information, see Adding busses to the project on page 111.
1.
Select the track to which you want to add the bus envelope. (You may select multiple tracks.)
2.
Add the envelope to the selected track(s) in one of the following ways:
• From the
Insert menu, choose Envelopes, and choose the bus for which you want to add an envelope
from the submenu.
• Right-click the track header in the track list, choose
Insert/Remove Envelope from the shortcut menu,
and choose the appropriate bus from the submenu.
A purple line representing the envelope appears across the track(s).
Adding assignable effect envelopes
An assignable effect envelope controls the level of a track sent to a particular assignable effect chain. Before
you can add an assignable effect envelope, you must add an assignable effect chain to the project. For more
information, see Adding assignable effect controls on page 113.
1.
Select the track to which you want to add the assignable effect envelope. (You may select multiple
tracks.)
2.
Add the envelope to the selected track(s) in one of following ways:
• From the
Insert menu, choose Envelopes, and choose the assignable effect chain for which you want to
add an envelope from the submenu.
• Right-click the track header in the track list, choose
Insert/Remove Envelope from the shortcut menu,
and choose the appropriate assignable effect chain from the submenu.
A green line representing the envelope appears across the track(s).
Adding effect automation envelopes
If a plug-in supports automation, you can use envelopes to adjust effect parameters over time. The
appearance of the plug-in in the Plug-In Chooser window indicates whether the plug-in supports
automation. Plug-ins with this icon ( ) support automation, while plug-ins with this icon ( ) do not. In
addition, you can quickly locate plug-ins that support automation in the
Automatable subfolder.
For creative ways to use effect automation envelopes, see Creating wah-wah effects with automated Track EQ on
page 191 and Turning automated effects on and off on page 192.
1.
Click the Tr ack F X button ( ) on a track to open the Audio Plug-In window.
If no track effects exist, clicking the
Track FX button displays the Plug-In Chooser. Use the Plug-In
Chooser to create an effect chain including an automatable plug-in. For more information, see Creating or
adding to track plug-in chains on page 93.
2.
Click the FX Automation button ( ) to display the FX Automation Chooser.
3.
Click a plug-in at the top of the FX Automation Chooser. A list of the effect’s automatable parameters
appears.
WORKING WITH TRACKS CHP. 7
 Loading...
Loading...