Page 1

1
Eddy DK
Programmer Guide
Ver 2.5.1.1
2011.11.09
Page 2
2
Revision Date
Document Version
Pages
Description
Feb-5-2009
2.1.0.1
All
Initial release by shlee
Sep-10-2009
2.1.0.2
All
Added WiFi
Oct-14-2009
2.1.0.3
11
J2 pin33 PC12 PC13
J2 pin35 PC13 PC12
Oct-22-2009
2.1.0.3
17,18,19
J2 pin33 PC12 PC13
J2 pin35 PC13 PC12
18,19
J2 pin33 J9_26 J9_33
J2 pin34 J9_25 J9_34
J2 pin33 J9_24 J9_35
Nov-23-2009
2.1.0.3
2,4,6
Added S4M
Jun-25-2010
2.1.1.1
All
Open Linux Version
Added Eddy-BT
Sep-15-2010
2.5.1.1
2,9
Added Eddy-CPU v2.5
Jan-20-2011
2.5.1.1
Added Eddy-S4M v2.5
Feb-15-2011
2.5.1.1
Added Eddy-CPU/mp v2.5
Aug-09-2011
2.5.1.1
Added Eddy-CPU/mp 32bit v2.5
Dec-09-2011
2.5.1.1.
Added Eddy-Wifi v3.0
Revision History
Page 3

3
Table of Contents
Chapter 1. Introduction ............................................................................................................... 5
1.1 About this document ........................................................................................................................ 5
1.2 Who should read this document? .................................................................................................... 5
1.3 Document organization .................................................................................................................... 6
1.4 Eddy-DK Related Documents .......................................................................................................... 7
1.5 Technical Support ............................................................................................................................ 8
Chapter 2. Getting Started .......................................................................................................... 9
2.1 What can you do with Eddy DK ? .................................................................................................... 9
2.2 Eddy-DK Package Contents ............................................................................................................ 9
2.3 Eddy-CPU v2.1 / v2.5..................................................................................................................... 10
2.4 Eddy-DK v2.1 ................................................................................................................................. 27
2.5 Eddy-S4M v2.1 / v2.5 ..................................................................................................................... 46
2.6 Eddy-S4M-DK v2.1 ........................................................................................................................ 58
2.7 Eddy-S4M-JiG v2.1 ........................................................................................................................ 68
2.8 Eddy-WiFi v3.0 ............................................................................................................................... 72
2.9 Eddy-BT v2.1 .................................................................................................................................. 74
2.10 Eddy-CPU/mp v2.5 ........................................................................................................................ 76
2.11 Eddy-CPU/mp 32bit v2.5 ............................................................................................................... 78
Chapter 3. Development Environment....................................................................................... 80
3.1 Source code folder structure ......................................................................................................... 80
3.2 Language ........................................................................................................................................ 81
3.3 Development Environment ............................................................................................................. 81
3.4 Installing on Windows OS .............................................................................................................. 81
3.5 Installation of Cygwin ..................................................................................................................... 82
3.6 Configuration of Windows Environment Variables ........................................................................ 84
3.7 Installation of Toolchain ................................................................................................................. 84
3.8 Installation of Eddy DK Source ...................................................................................................... 85
3.9 Installing on Linux ........................................................................................................................... 85
3.10 Installation of Toolchain ................................................................................................................. 86
3.11 Installation of Eddy DK Source ...................................................................................................... 86
3.12 Removing Development Environment ............................................................................................ 87
3.13 Removing Windows Development Environment ............................................................................ 87
3.14 Removing Linux Development Environment .................................................................................. 87
Chapter 4. Compiling of Application Program ........................................................................... 88
4.1 Program Type ................................................................................................................................. 88
4.2 Writing Application Program .......................................................................................................... 91
4.3 Writing Makefile .............................................................................................................................. 91
Page 4

4
4.4 Application Program Compile ........................................................................................................ 92
4.5 Compiling on Windows .................................................................................................................. 92
4.6 Compiling on Linux ......................................................................................................................... 92
4.7 Compiling with LemonIDE .............................................................................................................. 93
4.8 Running Application on Eddy ......................................................................................................... 93
4.9 Uploading and Executing on Eddy ................................................................................................ 93
4.10 Execute a file on Booting of Eddy ................................................................................................. 94
Chapter 5. Creating Firmware ................................................................................................... 95
5.1 How to Create a Firmware ............................................................................................................. 95
5.2 Firmware Upgrade .......................................................................................................................... 97
Chapter 6. Library Introduction ............................................................................................... 100
6.1 Introduction ................................................................................................................................... 100
6.2 Makefile ........................................................................................................................................ 100
6.3 System functions .......................................................................................................................... 100
6.4 Eddy Environment Function ......................................................................................................... 101
6.5 Serial functions ............................................................................................................................. 104
6.6 Ethernet functions ........................................................................................................................ 107
6.7 GPIO Functions ............................................................................................................................ 113
6.8 ADC Function ............................................................................................................................... 120
6.9 RTC Function ................................................................................................................................ 121
6.10 Debugging Function ..................................................................................................................... 122
Chapter 7. Eddy Software ...................................................................................................... 123
7.1 Software Structure Diagram ......................................................................................................... 123
7.2 Main Applications ......................................................................................................................... 124
7.3 eddy.c Application ........................................................................................................................ 124
7.4 Pinetd.c Application ..................................................................................................................... 124
7.5 Other Applications ........................................................................................................................ 124
Chapter 8. Handling HTML & CGI ........................................................................................... 125
8.1 WEB Configuration ....................................................................................................................... 125
8.2 Example of HTML Code ............................................................................................................... 125
8.3 Example CGI Code ....................................................................................................................... 127
Chapter 9. Appendix ............................................................................................................... 129
9.1 System recovery via Bootloader .................................................................................................. 129
9.2 System recovery via USB............................................................................................................. 134
9.3 Product Specification ................................................................................................................... 143
9.4 Ordering Infomation ...................................................................................................................... 150
Page 5

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
5
Chapter 1. Introduction
This chapter explains about this manual and introduces the related documents and support.
1.1 About this document
This manual explains about how a programmer can develop a customized application for Eddy module and how this
application can be uploaded and executed on the module. To help programmers with this work, information on
Eddy's operating system and API functions for convenient source writing is supplied.
After reading this document, a programmer can write his or her own application and execute it on the module.
1.2 Who should read this document?
This document is designed for programmers who wish to develop a new application using Eddy DK. It is strongly
recommended that the programmer read this document before starting any programming work. If you are an
administrator or an end user who just needs to apply the module into practical applications, you do not need to read
this document. User's Guide will be helpful in that case. This manual deals with the complete process of writing
source codes and making a firmware that can be uploaded and executed on Eddy module.
Page 6

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
6
1.3 Document organization
Chapter 1. Introduction is a preface with general information and introductory notices.
Chapter 2. Getting Started gives brief information needed before starting programming work.
Chapter 3. Writing Application explains about the process of writing a customized application and related work..
Chapter 4. Compiling Application deals with the process of compiling your application with Makefile.
Chapter 5. Creating Firmware helps you converting a compiled application into a firmware that can be accepted by
Eddy module.
Chapter 6. Library explains about the library and API functions you can use while programming and application.
Chapter 7. Eddy Software shows how to implement simple TCP/IP and serial routines using example source codes
that are included in the development kit.
Chapter 8. Handling HTML & CGI provides a guide for integrating your own applications with Eddy's web interface.
Chapter 9. Appendix provides programming notes and a list of default utilities.
Page 7

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
7
Document Name
Description
User Guide
Integration, configuration, and management of Eddy for the
administrator
Programmer’s Guide
Programmer’s application development guide, including in-depth
approach to compiling, linking, and creating firmware
API reference is also included with a list of available functions
for customized application programming
LemonIDE Manual
Guide for primary function of each tool contained in LemonIDE on
Windows and Linux.
Portview User Manual
Guide for SystemBase device server management application
Portview
COM Port Redirector User
Manual
Guide for SystemBase COM Port Redirector
TestView User Manual
Guide for TestView application for testing Eddy serial port and lan
port.
Document Name
Description
Eddy-CPU Spec Sheet
Specifications for Eddy CPU and DK board.
Eddy-S4M Spec Sheet
Eddy-S4M spec description
Eddy-WiFi Spec Sheet
Eddy-WiFi module spec description
Eddy-BT Spec Sheet
Eddy-BT module spec description
LemonIDE Spec Sheet
integrated development environment description
Eddy White Paper
An introductory reading for anyone new to embedded device server.
Deals with background, history, market environment, and technology
1.4 Eddy-DK Related Documents
The following table summarizes documents included in the Eddy-DK document set.
If you need brief information on Eddy or embedded device servers in general, please visit our corporate website at
http://www.sysbas.com/. You can view and/or download documents related to Eddy as well as latest software and
firmware updates. Available resources are as follows:
All documents are updated promptly, so check for the recent document update. The contents in these documents
are subject to change without any notice in advance.
Page 8

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
8
1.5 Technical Support
There are three ways you can get a technical support from SystemBase.
First, visit our website http://www.sysbas.com/ and go to ‘Technical Support’ menu. There you can read FAQ
and ask your own question as well.
Second, you can e-mail our technical support team. The mail address is tech@sysbas.com. Any kind of inquiries,
requests, and comments are welcome.
Finally, you can call us at the customer center for immediate support. Our technical support team will kindly help you
get over with the problem.
The number to call is 82-2-855-0501 (Extension number 225). Do not forget to dial the extension number after getting
a welcome message.
Copyright 2007 SystemBase Co., Ltd. All rights reserved.
Homepage: http://www.sysbas.com/
Tel: +82-2-855-0501
Fax: +82-2-855-0580
1601, DaeRyung Post Tower 1, 212-8, Guro-dong, Guro-gu, Seoul, Korea
Page 9

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
9
Chapter 2. Getting Started
This chapter explains about packaging and installation, and discusses key features of Eddy-DK.
2.1 What can you do with Eddy DK ?
Eddy DK is designed to help programmers to develop a customized application that can be applied to Eddy module
easier and faster. It has been a time-consuming and burdensome work to port an operating system and develop an
application on a new hardware. Eddy module and Software Development Kit makes this work easy.
Eddy DK is different with other device servers in which it can run customized applications. Users can upload most
existing socket/serial communication applications that are running on the Linux environment. This openness allows
users to apply wide variety of functions into the module with relatively less restrictions.
Eddy DK supports IDE (LemonIDE) and SDK environment to help programmers to execute their own applications on
the module. Programmers can easily write applications using the Linux environment, with the help of SDK and
example source codes. Cross-compiler running on the standard Linux environment helps your applications to run on
the Eddy module. Embedded Linux on Eddy can provide stable and rapid environment for your applications.
2.2 Eddy-DK Package Contents
Eddy-DK includes Eddy module.
Eddy-DK package contains as follows. Make sure following contents are included in the Eddy Serial DK Package.
- Case of Eddy-DK (Eddy-CPU v2.1/v2.5 1ea, Eddy-DK v2.1board 1ea)
- Case of Eddy-S4M-DK (Eddy-S4M v2.1 1ea, Eddy-S4M-DK board 1ea, (Option : Eddy-S4M-JIG))
- 1EA , Serial cable
- 1EA , LAN cable
- 1EA, USB A to B Cable
- 1EA , Power adaptor
- 1EA , CD (SystemBase SDK, LemonIDE, compile environment, utilities, manuals)
Page 10
Eddy DK Programmer Guide
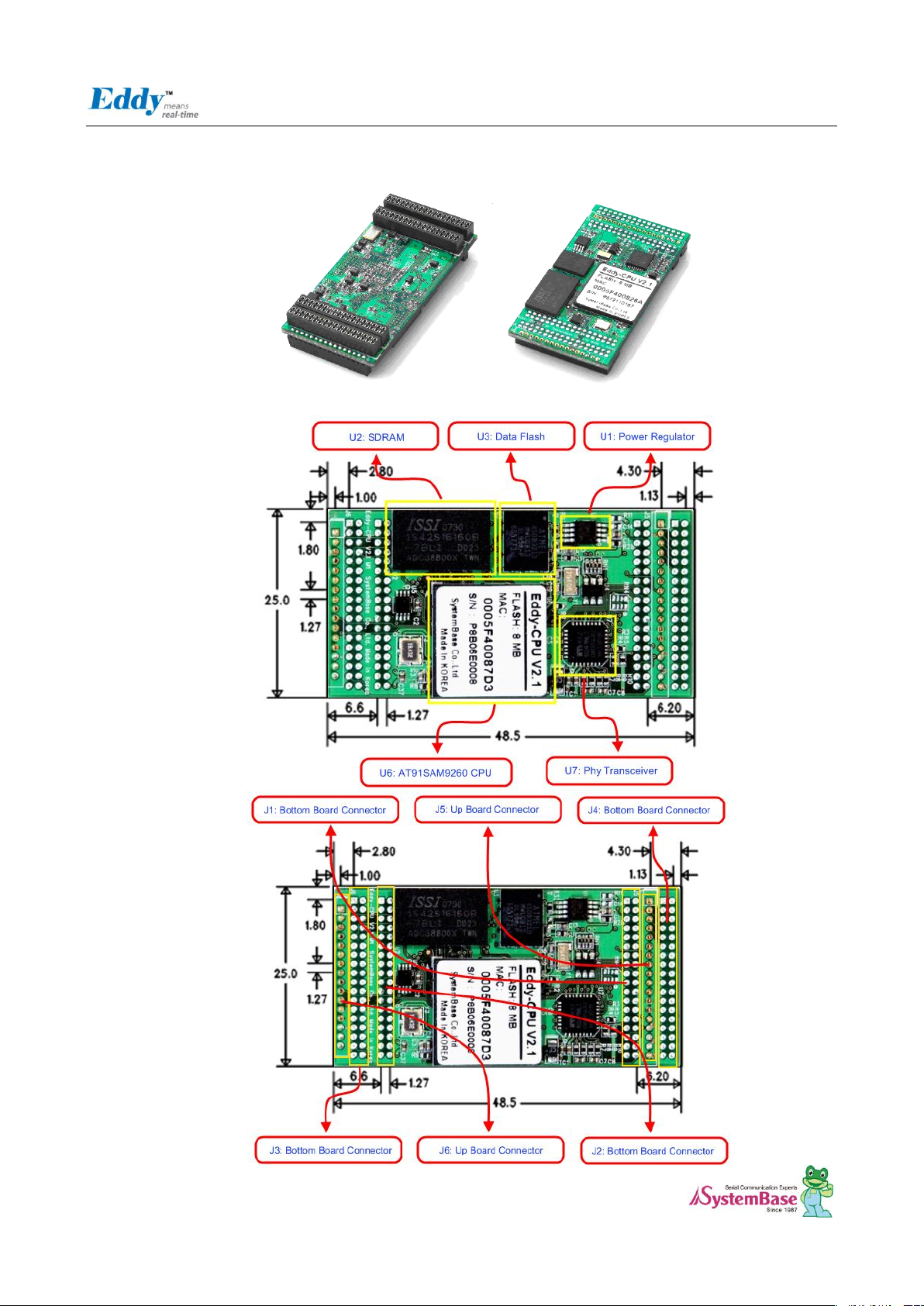
10
2.3 Eddy-CPU v2.1 / v2.5
Page 11
Eddy DK Programmer Guide
11
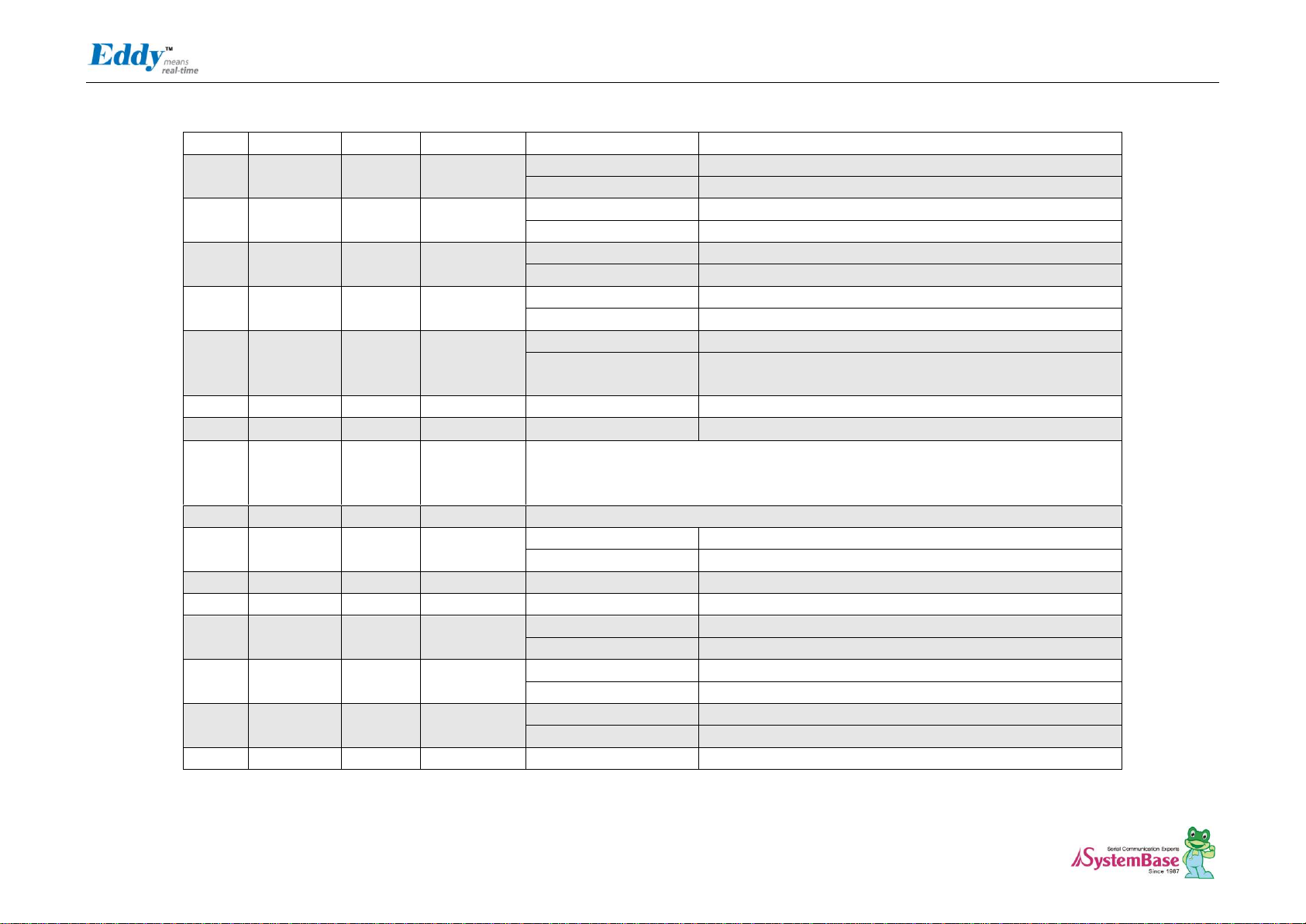
J1 J2
Pin
Signal Name
Pin
Signal Name
Pin
Signal Name
Pin
Signal Name
1
PA5
2
PA4
1 A15
2
A14 3 PC5
4 PC19
3 A13
4
A12 5 PC21
5 PC23
5 A11
5
A10
7
HDMA
8
NC
7 A9
8
A8 9 HDPA
10
DDM
9 A7
10
A6
11
PC26
12
DDP
11
A5
12
A4
13
PC4 (RDY#)
14
PC16
13
A3
14
A2
15
ICE_NTRST
16
RTCK
15
A1
16
A0
17
TDO
18
TMS
17
PC9
18
NWE
19
TDI
20
TCK
19
FPG
20
NRD
21
3.3V
22
GND
21
GND
22
3.3V
23
3.3V
24
GND
23
GND
24
3.3V
25
PB29 (CTS1)
26
PB28 (RTS1)
25
D7
26
D6
27
PB6 (TXD1)
28
PB7 (RXD1)
27
D5
28
D4
29
A20
30
A19
29
D3
30
D2
31
LAN_Speed
32
LAN_lLink
31
D1
32
D0
33
LAN_RX-
34
LAN_RX+
33
PC13
34
JTAGSEL
35
LAN_TX-
36
LAN_TX+
35
PC12
36
NC
Eddy-CPU v2.1/v2.5 Pin Assignment
Page 12

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
12
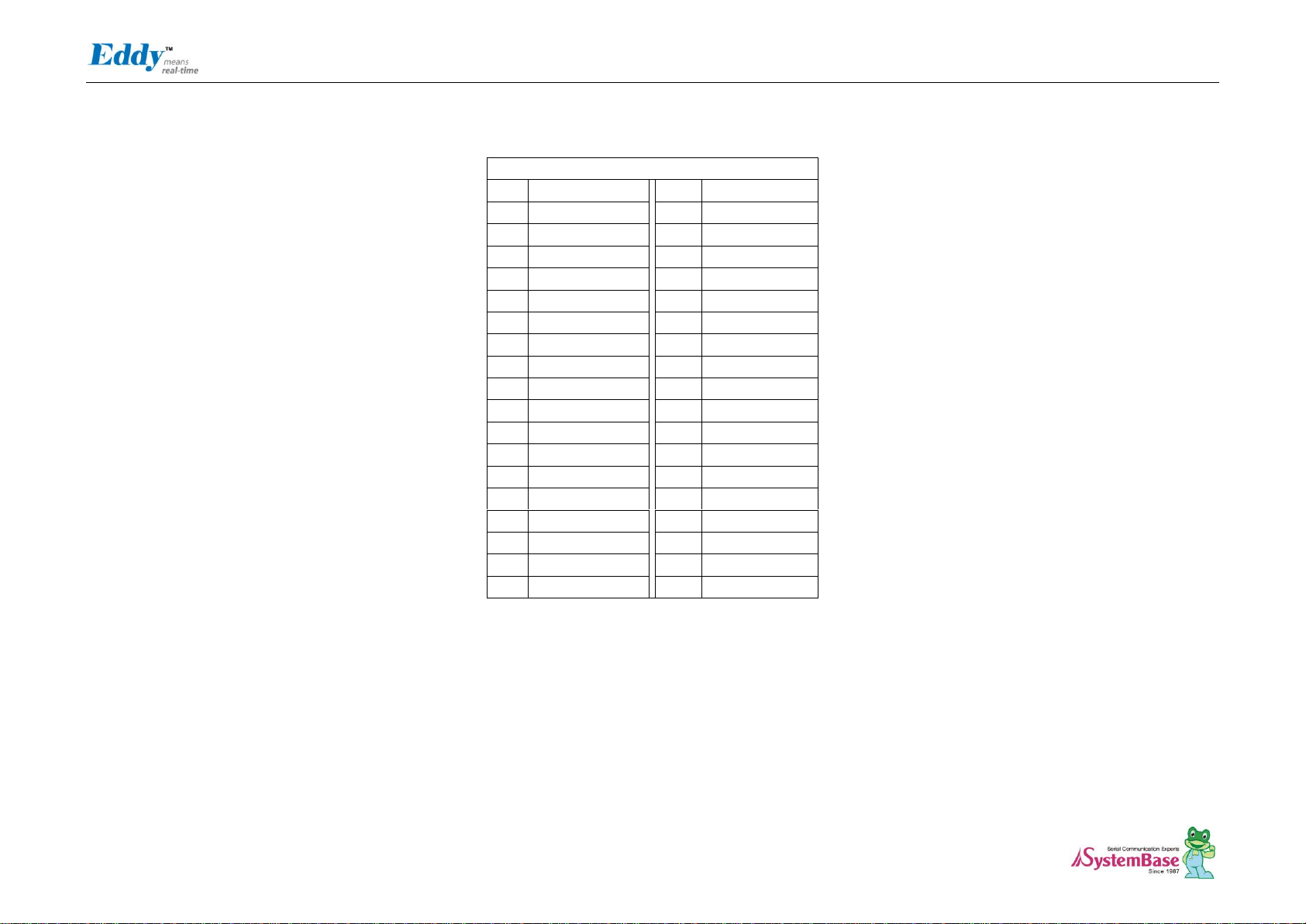
J3 J4
Pin
Signal Name
Pin
Signal Name
Pin
Signal Name
Pin
Signal Name
1
PID0
2 PID1
1 PB12
2 PB13
3
PID2
4 PID3
3 PB30
4 PB31
5
PID4
5 GND
5 PB0
5 PC22
7
PC14
8 PC17
7 PB1
8 PB16
9
PC18
10
PC8 (RTS3)
9 PB2
10
PB17
11
PC20
12
PC10 (CTS3)
11
PB3
12
PB18
13
PA22
14
PC15 (IRQ1)
13
BHDM
14
PB19
15
PB8
16
PB9 (RXD2)
15
BHDP
16
PB20
17
PB10
18
PB11(RXD3)
17
A16
18
PB21
19
PC0
20
PC1 (AD1)
19
A17
20
A18
21
PC2
22
PC3 (AD3)
21
D8
22
D9
23
PB14 (DRXD)
24
PB15 (DTXD)
23
D10
24
D11
25
GND
26
GND
25
D12
26
D13
27
BMS
28
NRST
27
D14
28
D15
29
PB23 / DCD0
30
PB5 / RXD0
29
TWD
30
TCK
31
PB4 / TXD0
32
PB24 / DTR0
31
NANDOE
32
NAND_CLE /
A22
33
PB22 / DSR0
34
PB26 / RTS0
33
NANDWE
34
NAND_ALE /
A21
35
PB27 / CTS0
36
PB25 / RI0
35
NC
36
NC
J5
J6
Pin
Signal Name
Pin
Signal Name
1
PB0
2
PB1
1
NC
3
PB2
2
NC
4
PB3
3
3.3V
5
3.3V
4
3.3V
6
3.3V
5 PC25 / BT_Factory
7
BHDM, USB Host Data(-)
6
PB10 / TXD3
8
BHDP, USB Host Data(+)
7
PB11 / RXD3
9
PA31 / TXD4
8
PC8 / RTS3
10
PA30 / RXD4
9
PC10 / CTS3
11
NRST
10
PC24 / BT_MODE
12
GND
11
NRST
13
GND
12
GND
14
PA9 / WPID0
13
GND
15
PC6 / WPID1
14
NC
16
PC7 / WPID2
15
NC
17
NC
16
NC
18
NC
Page 13
Eddy DK Programmer Guide
13
J1
Pin
Signal Name
Pin
Signal Name
1
PA5
2
PA4 3 PC5
4
PC19
5
PC21
5
PC23
7
HDMA
8
NC 9 HDPA
10
DDM
11
PC26
12
DDP
13
PC4 (RDY#)
14
PC16 (nRESET)
15
ICE_NTRST
16
RTCK
17
TDO
18
TMS
19
TDI
20
TCK
21
3.3V
22
GND
23
3.3V
24
GND
25
PB29 (CTS1)
26
PB28 (RTS1)
27
PB6 (TXD1)
28
PB7 (RXD1)
29
A20
30
A19
31
LAN_Speed
32
LAN_lLink
33
LAN_RX-
34
LAN_RX+
35
LAN_TX-
36
LAN_TX+
J1 Specifications
Page 14
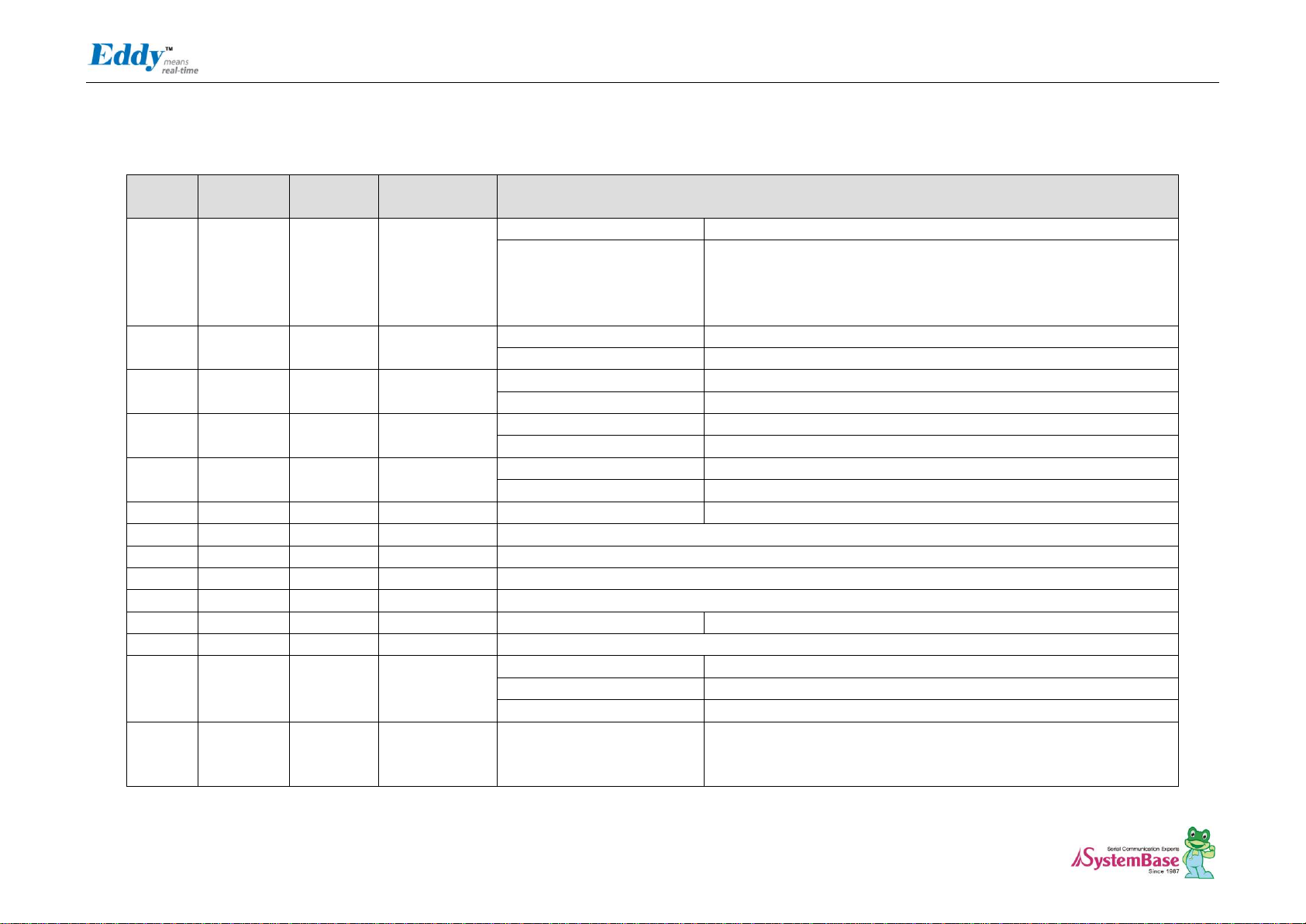
Eddy DK Programmer Guide
14
Pin No
Name
DK v2.1
Pin No
Expansion
Header Pin No
Description
1
PA5
J10_1
J4_2
Peripheral A : CTS2
UART #2 Clear to Send Signal
Peripheral B : MCBD1
Disabled.
Data Flash connected with SPI0 is used for Eddy-CPU v2.1/v2.5. For
this reason SPI0 and MCDB0, MCDB3, and MCCDB signals,
multiplexing, cannot be used, thus Multimedia Card Slot B is disabled.
2
PA4
J10_2
J4_1
Peripheral A : RTS2
UART #2 Request to Send Signal
Peripheral B : MCDB2
Disabled.
3
PC5
J10_3
J4_12
Peripheral A : A24
External Address Bus
Peripheral B : SPI1_NPCS1
SPI1(Serial Peripheral Interface) Peripheral Chip Select 1
4
PC19
J10_4
J4_24
Peripheral A : A24
Multimedia Card Slot B Data
Peripheral B : SPI1_NPCS2
SPI1(Serial Peripheral Interface) Peripheral Chip Select 2
5
PC21
J10_5
J4_26
Peripheral A : D21
External Data bus
Peripheral B : EF100
Ethernet(WAN) Force 100Mbit/sec.
6
PC23
J10_6
J4_28
Peripheral A : D23
External Data Bus
7
HDMA
J10_7
J1_27
USB Host Port A Data -
8
NC
J10_8
--
Not Connect
9
HDPA
J10_9
J1_29
USB Host Port A Data +
10
DDM
J10_10
-
USB Device Port Data -
11
PC26
J10_11 - D26
External Data Bus
12
DDP
J10_12
-
USB Device Port Data +
13
PC4
(RDY#)
J10_13
J4_11
Eddy-DK v2,1 : RDY#(OUT)
Ready signal. Output signal for CPU operation status
Peripheral A : A23
External Address Bus
Peripheral B : SPI1_NPCS2
SPI1(Serial Peripheral Interface) Peripheral Chip Select 2
14
PC16
(nRESET)
J10_14
J4_21
Eddy-DK v2,1 : nRESET#(IN)
Polling Input signal continually from External Reset key, implement as
below with checking the constant time of "Low."
Less than 5 seconds: General reset function.
J1 Pin Description
Page 15
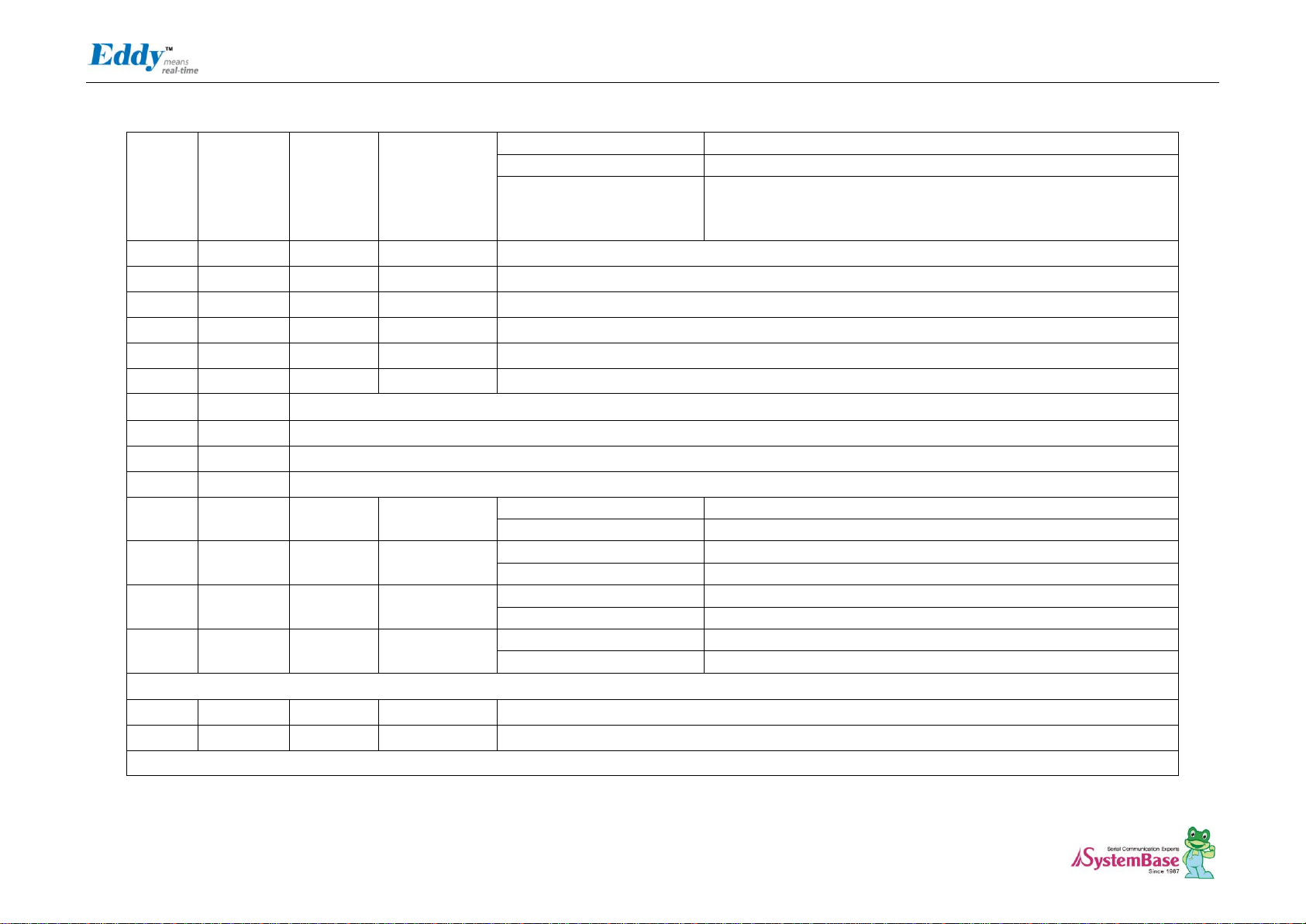
Eddy DK Programmer Guide
15
More than 5 seconds: Factory Default function.
Peripheral A : D16
External Data Bus
Peripheral B : SPI0_NPCS2
Disabled
SPI0_SPCK, SPI0_MISO, and SPI0_MOSI signals for SPI0 are disabled
as they are not connected externally.
15
ICE_NTRST
J10_15
J7_3
ICE Test Reset Signal
16
RTCK
J10_16
J7_11
Return Test Clock
17
TDO
J10_17
J7_13
Test Data Out
18
TMS
J10_18
J7_7
Test Mode Select
19
TDI
J10_19
J7_5
Test Data In
20
TCK
J10_20
J7_9
Test Clock
21
3.3V
3.0V to 3.6V power input
22
GND
Ground
23
3.3V
3.0V to 3.6V power input
24
GND
Ground
25
PB29
J10_25
J2_30
Peripheral A : CTS1
USART1 Clear To Send
Peripheral B : ISI_VSYNC
Image Sensor Vertical Synchronization
26
PB28
J10_26
J2_29
Peripheral A : RTS1
USART1 Request To Send
Peripheral B : ISI_PCK (IN)
Image Sensor Pixel Clock Provided by the Image Sensor
27
PB6
J10_27
J2_7
Peripheral A : TXD1
USART1 Transmit Data
Peripheral B : TCLK1
Timer Counter ch1 External CLK IN
28
PB7
J10_28
J2_8
Peripheral A : RXD11
USART1 Receive Data
Peripheral B : TCLK2
Timer Counter ch2 External CLK IN
Address Bus
29
A20
J10-29
J1_31
Address Bus
30
A19
J10_30
J1_32
Address Bus
Ethernet 10/100 (Auto MDI/MDIX)
Page 16
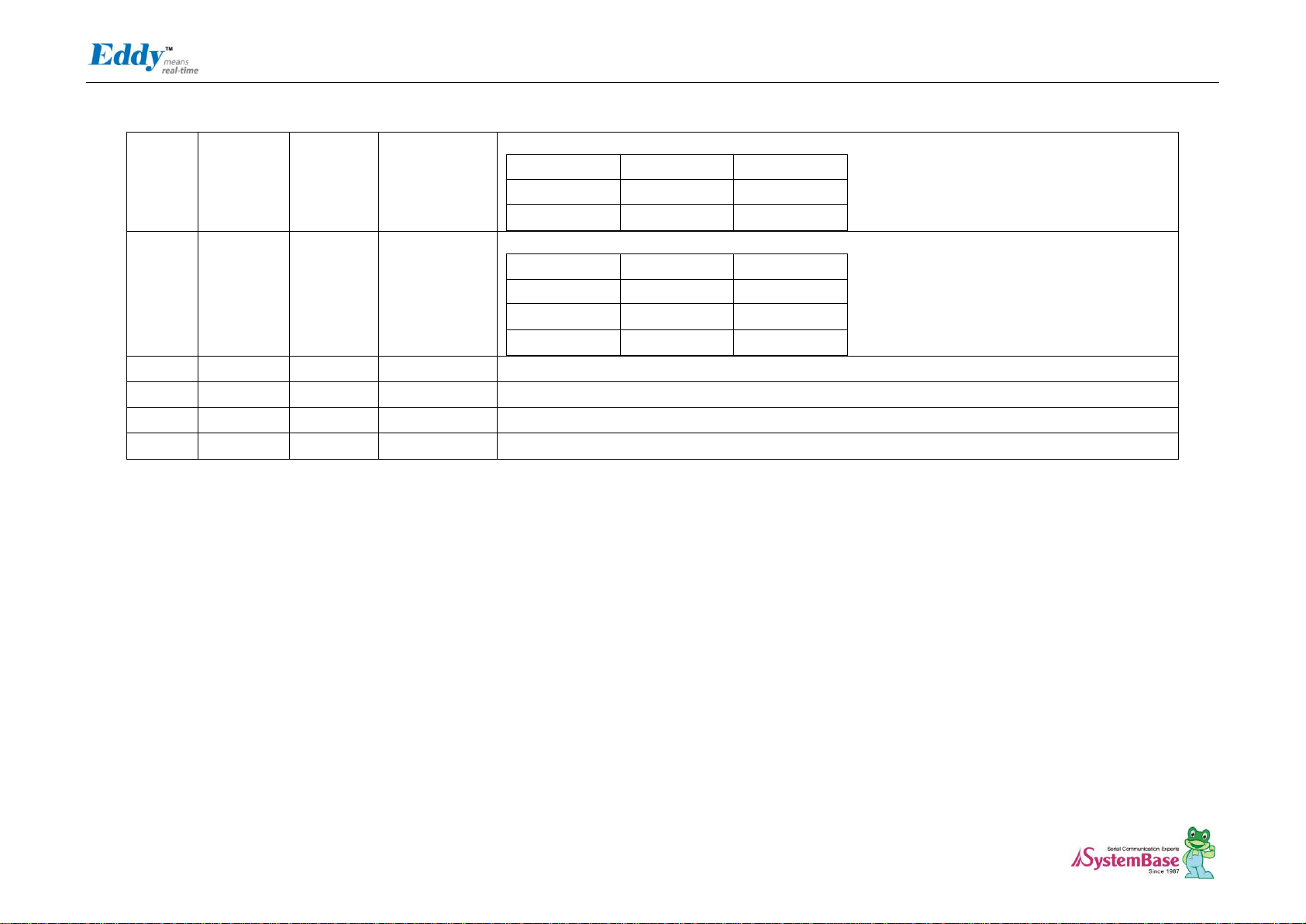
Eddy DK Programmer Guide
16
31
LED_Speed
J10_31
-
LAN connection speed
Speed
Pin State
LED Definition
10Base-T
H
OFF
100Base-TX
L
ON
32
LED_Link
J10_32
-
LAN connection status
Link/Activity
Pin State
LED Definition
No Link
H
OFF
Link L ON
Activity
Toggle
Blinking
33
LAN_RX-
J10_33 - CPU 내부 Ethernet PHY(WAN)의 Physical receive or transmit signal (- differential)
34
LAN_RX+
J10_34 - CPU 내부 Ethernet PHY(WAN)의 Physical receive or transmit signal (+ differential)
35
LAN_TX-
J10_35 - Physical transmit of CPU Internal Ethernet PHY(WAN) or receive signal (- differential)
36
LAN_TX+
J10_36 - Physical transmit of CPU Internal Ethernet PHY(WAN) or receive signal (+ differential)
Page 17
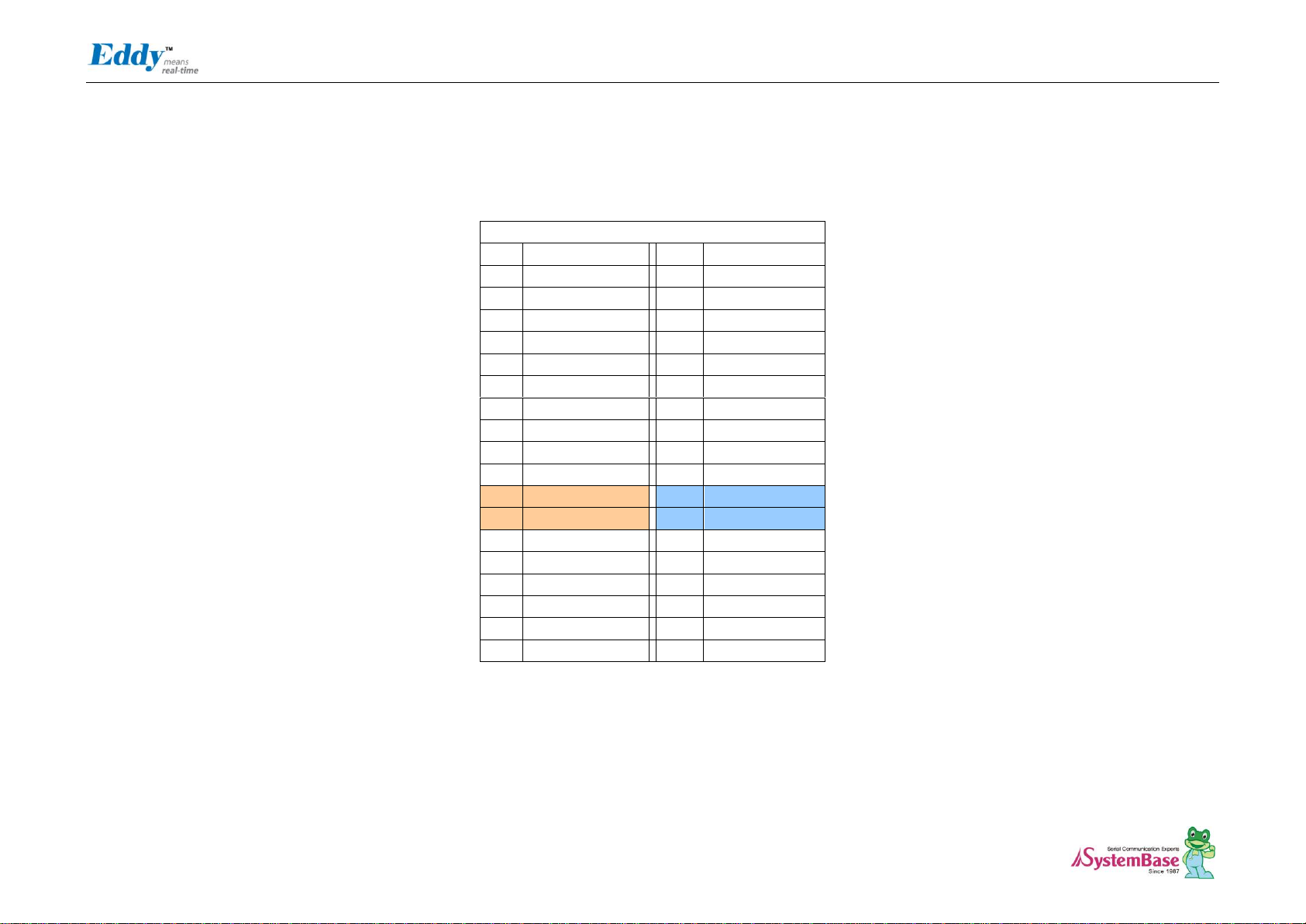
Eddy DK Programmer Guide
17
J2
Pin
Signal Name
Pin
Signal Name
1
A15
2
A14 3 A13
4
A12
5
A11
5
A10
7
A9
8
A8 9 A7
10
A6
11
A5
12
A4
13
A3
14
A2
15
A1
16
A0
17
PC9
18
NWE
19
FPG
20
NRD
21
GND
22
3.3V
23
GND
24
3.3V
25
D7
26
D6
27
D5
28
D4
29
D3
30
D2
31
D1
32
D0
33
PC13
34
JTAGSEL
35
PC12
36
NC
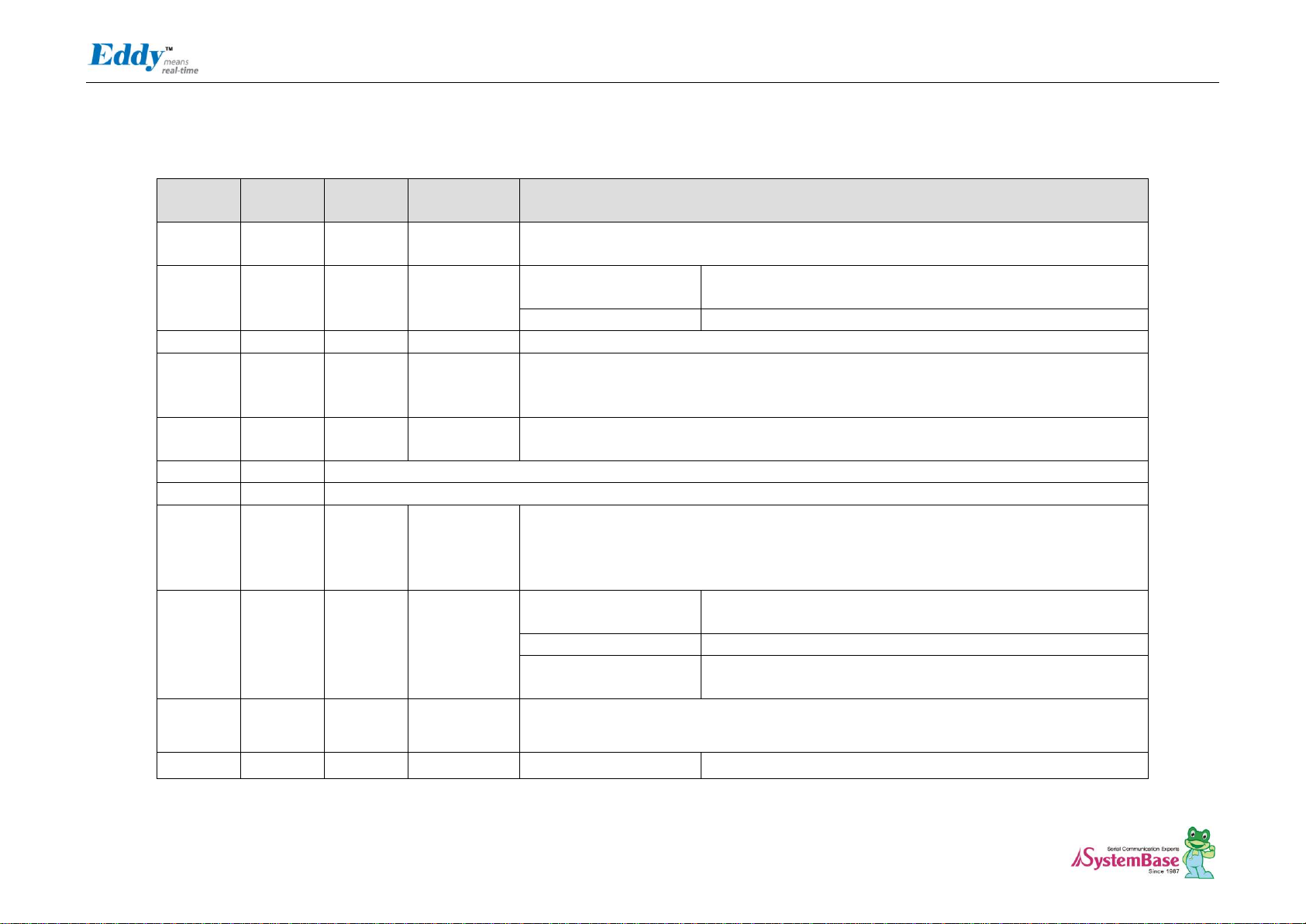
J2 Specifications
Connect USB cable to J1 while the jumper is connected to J2, so that applications can be compiled, linked, created, and uploaded to the Eddy-CPU module. (Please refer to
Programmer Guide for more information.)
Page 18
Eddy DK Programmer Guide
18
Pin No
Name
DK v2.1
Pin No
Expansion
Header Pin No
Description
1~16
A[15:0]
J9_1
-J9_16
J3_4-J3_20
External Address Bus 0-15 (0 at reset)
DK is directly connected with CPU and external connecter (J3) is connected by buffer.
17
PC9
J9_17
J4_14
Peripheral A : NCS5
External device Chip Select 5.
256MB memory area addressable, active low
Peripheral B : TIOB0
Timer Counter ch0 I/O Line B
18
NEW
J9_18
J1_21
External device Write Enable signal, active low
19
FPG
J9_19
-
For Flash Programming
You can program Data Flash in Eddy CPU v2.1/v2.5 via USB. Refer to 2.4.2.3 S6:NAND Flash &
Data Flash Chip Select for further information.
20
NRD
J9_20
J1_23
External device Read Enable signal, active low
21, 23
GND
Ground
22, 24
3.3V
3.0V to 3.6V power input
25~32
D[7:0]
J9_25
- J3_32
J3_29 - J3_36
External Data Bus 0-7
DK is directly connected with CPU and external connecter (J3) is connected by buffer. You
should enable PC13(NCS6 : Chip Select 6) for working buffer, if you reset, it becomes Pulled-up
input.
33
PC13
J9_33
J4_18
Edd-DK v2.1 : NCS6
Data Bus connected with external header can be used when NCS6
is enabled.
Peripheral A : FIQ
Fast Interrupt Input
Peripheral B : NCS6
External device Chip Select 6
256MB memory area addressable, active low
34
JTAGSEL
J9_34
-
JTAG boundary scan can be used by connecting pin34 and 36(J14 connection). This pin should
not be connected when using ICE (In-Circuit Emulator) or in normal operation status.
35
PC12
J9_35
J4_17
Peripheral A : IRQ0
External Interrupt Input 0
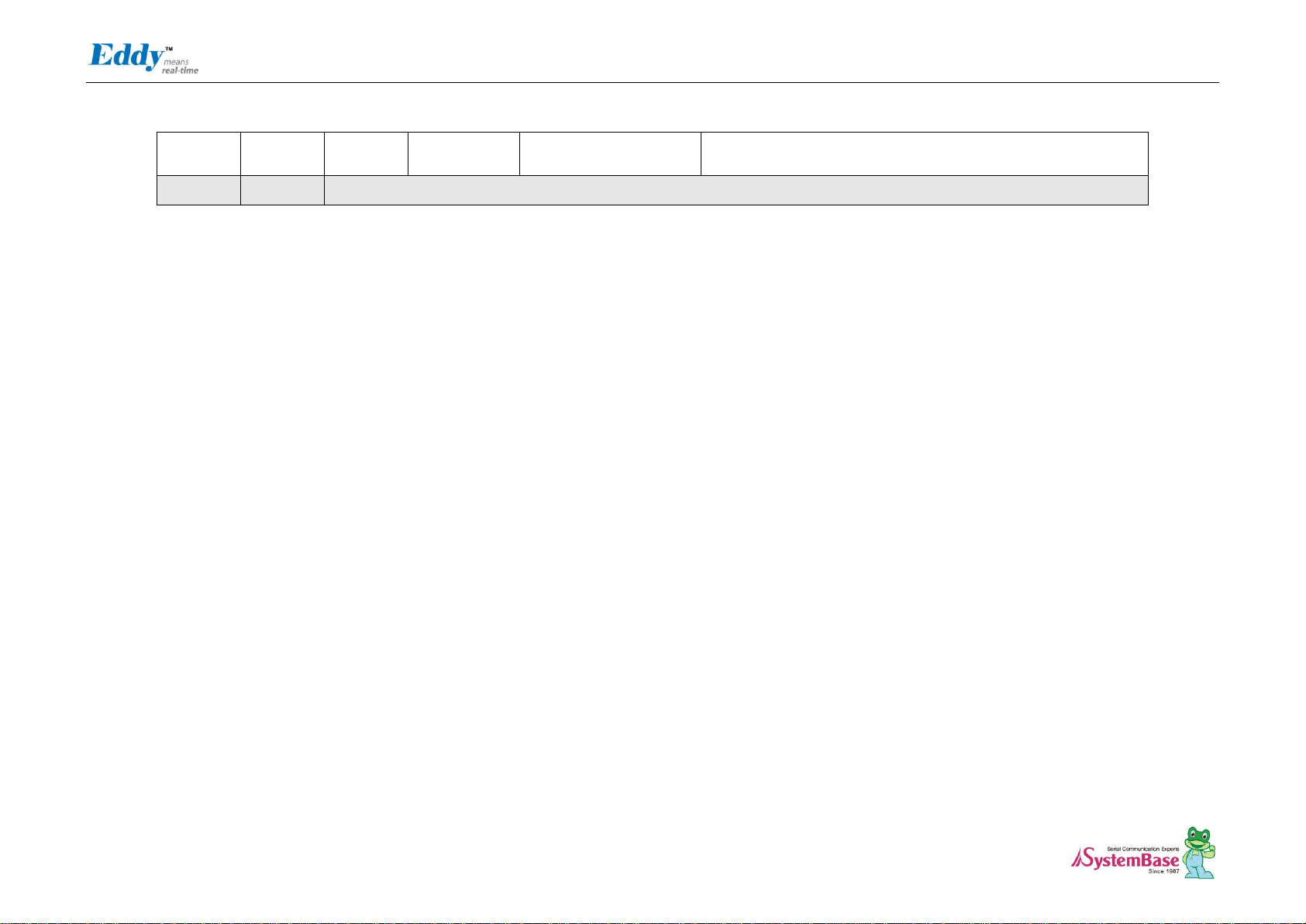
J2 Pin Description
Page 19
Eddy DK Programmer Guide
19
Peripheral B : NCS7
External device Chip Select 7.
256MB memory area addressable, active low
36
NC
Not Connect
Page 20
Eddy DK Programmer Guide
20
J3
Pin
Signal Name
Pin
Signal Name
1
PID0
2
PID1
3
PID2
4
PID3
5
PID4
5
GND
7
PC14
8
PC17
9
PC18
10
PC8 (RTS3)
11
PC20
12
PC10 (CTS3)
13
PA22
14
PC15 (IRQ1)
15
PB8
16
PB9 (RXD2)
17
PB10
18
PB11(RXD3)
19
PC0
20
PC1 (AD1)
21
PC2
22
PC3 (AD3)
23
PB14 (DRXD)
24
PB15 (DTXD)
25
GND
26
GND
27
BMS
28
NRST
29
PB23 / DCD0
30
PB5 / RXD0
31
PB4 / TXD0
32
PB24 / DTR0
33
PB22 / DSR0
34
PB26 / RTS0
35
PB27 / CTS0
36
PB25 / RI0
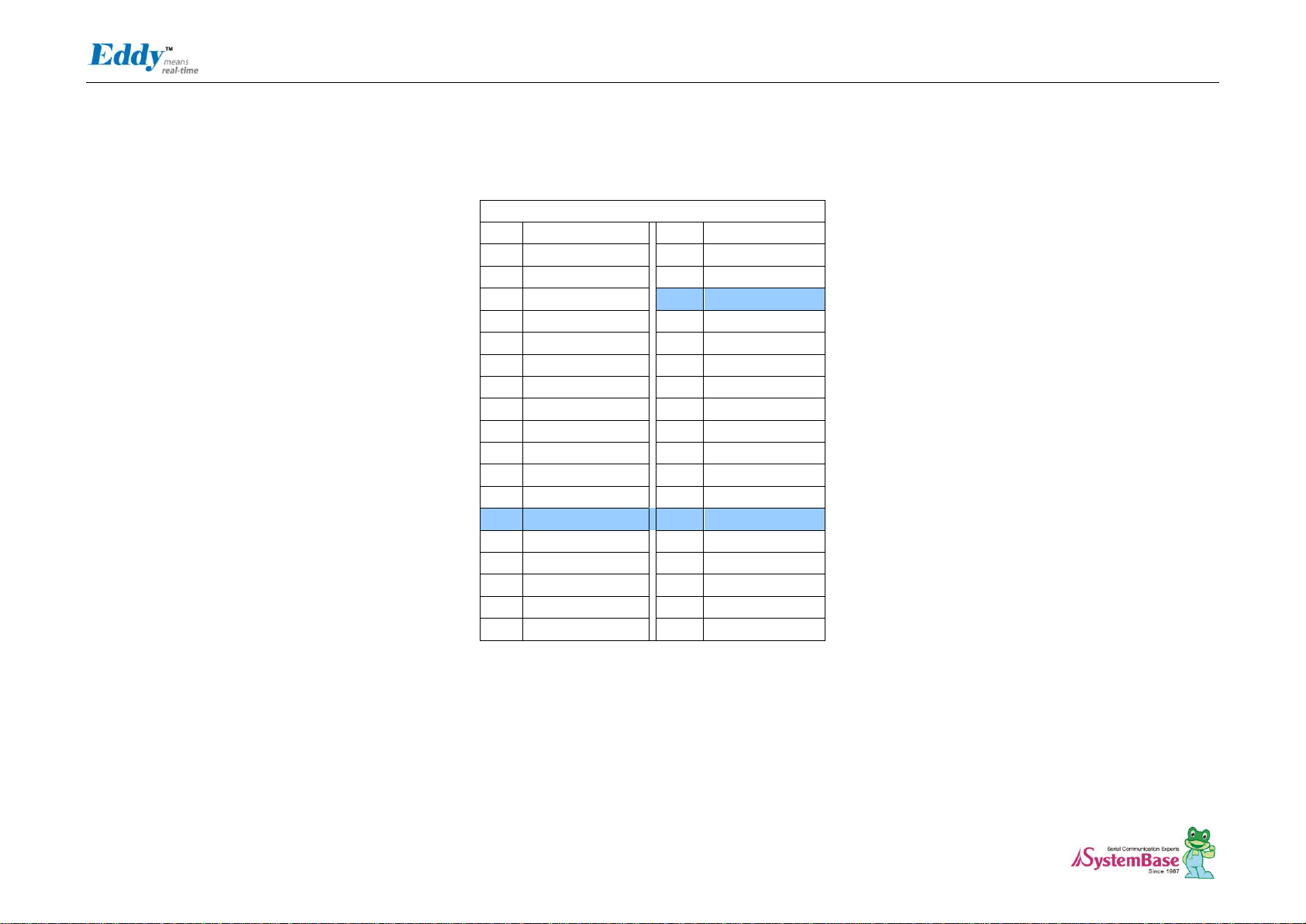
J3 Specifications
Page 21
Eddy DK Programmer Guide
21
Pin No
Name
DK v2.1
Pin No
Expansion
Header Pin
No
Description
1-5
PID[4:0]
J8_1
~J8_5
-
Product ID only used by the manufacturer.
Please do not work on these pins.
6,25,26
GND
Ground
7
PC14
J8_7
J4_19
Peripheral A : NCS3
External Device Chip Select 3
Peripheral B : IRQ2
External Interrupt Input 2
8
PC17
J8_8
J4_22
Peripheral A : D17
External Data Bus
Peripheral B :
SPI0_NPCS3
Disabled
9
PC18
J8_9
J4_23
Peripheral A : D18
External Data Bus
Peripheral B :
SPI1_NPCS1
SPI1(Serial Peripheral Interface) Peripheral Chip Select 1
10
PC8
J8_10
J4_13
Peripheral A : NCS4
External Device Chip Select 4
Peripheral B : RTS3
USART3 Request to Send
11
PC20
J8_11
J4_25
Peripheral A : D20
External Data Bus
Peripheral B :
SPI1_NPCS3
SPI1(Serial Peripheral Interface) Peripheral Chip Select 3
12
PC10
J8_12
J4_15
Peripheral A : A25
External Address Bus
Peripheral B : CTS3
USART3 Clear to Send
13
PA22
J8_13
-
Digital I/O Input 4
14
PC15
J8_14
J4_20
Peripheral A : NWAIT
External Wait Signal Input
Peripheral B : IRQ1
External Interrupt Input 2
15
PB8
J8_15
J2_9
Peripheral A : TXD2
UART2 Transmit Data
16
PB9
J8_16
J2_10
Peripheral A : RXD2
UART2 Receive Data
17
PB10
J8_17
J2_11
Peripheral A : TXD3
UART3 Transmit Data
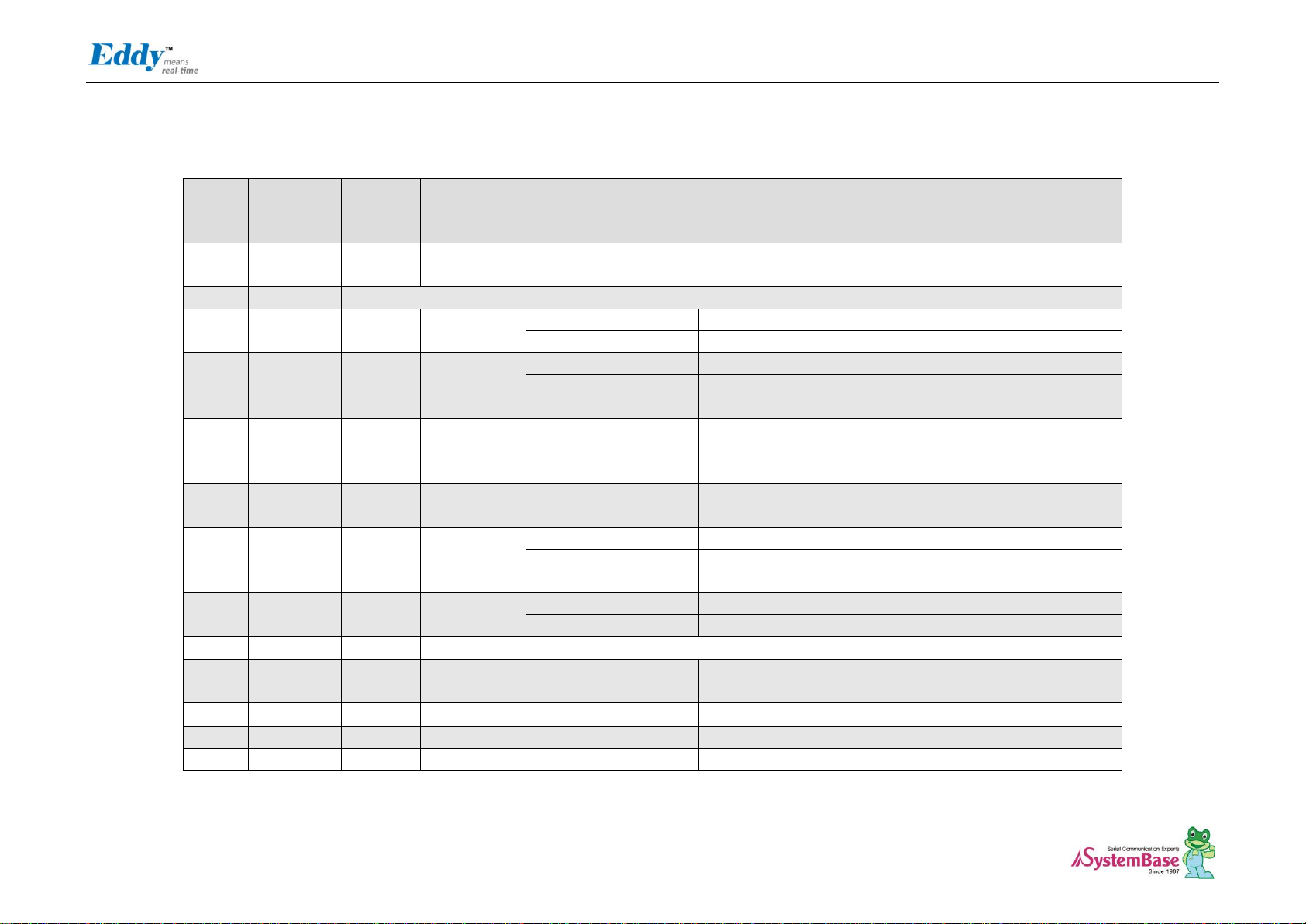
J3 Pin Description
Page 22
Eddy DK Programmer Guide
22
Peripheral B : ISI_D8
Image Sensor Data 8
18
PB11
J8_18
J2_12
Peripheral A : RXD3
UART3 Receive Data
Peripheral B : ISI_D9
Image Sensor Data 9
19
PC0
J8_19
J4_7
Peripheral A : AD0
Analog to Digital Converter Input Ch0
Peripheral B : SCK3
USART3 Serial Clock
20
PC1
J8_20
J4_8
Peripheral A : AD1
Analog to Digital Converter Input Ch1
Peripheral B : PCK0
Programmable Clock Output 0
21
PC2
J8_21
J4_9
Peripheral A : AD2
Analog to Digital Converter Input Ch2
Peripheral B : PCK1
Programmable Clock Output 1
22
PC3
J8_22
J4_10
Peripheral A : AD3
Analog to Digital Converter Input Ch3
Peripheral B :
SPI1_NPCS3
SPI1(Serial Peripheral Interface) Peripheral Chip Select 3
23
PB14
J8_23
J2_15
Peripheral A : DRXD
Debug Receive Data
24
PB15
J8_24
J2_16
Peripheral A : DTXD
Debug Transmit Data
27
BMS
J8_27
-
Boot Mode Select signal
BMS = 1, Boot on Embedded ROM
BMS = 0, Boot on External Memory
28
NRST
J8_28
J1_20
External device Reset signal, active low signal
29
PB23
J8_29
J4_28
Peripheral A : DCD0
USART0 Data Carrier Detection
Peripheral B : ISI_D3
Image Sensor Data 3
30
PB5
J8_30
J2_6
Peripheral A : RXD0
USART0 Receive Data
31
PB4
J8_31
J2_5
Peripheral A : TXD0
USART0 Transmit Data
32
PB24
J8_32
J2_25
Peripheral A : DTR0
USART0 Data Terminal Ready
Peripheral B : ISI_D4
Image Sensor Data 4
33
PB22
J8_33
J2_23
Peripheral A : DSR0
USART0 Data Set Ready
Peripheral B : ISI_D2
Image Sensor Data 2
34
PB26
J8_34
J2_27
Peripheral A : RTS0
USART0 Request To Send
Peripheral B : ISI_D6
Image Sensor Data 6
35
PB27
J8_35
J2_28
Peripheral A : CTS0
USART0 Clear To Send
Page 23

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
23
Peripheral B : ISI_D7
Image Sensor Data 7
36
PB25
J8_36
J2_26
Peripheral A : RI0
USART0 Ring Indicator
Peripheral B : ISI_D5
Image Sensor Data 5
Page 24
Eddy DK Programmer Guide
24
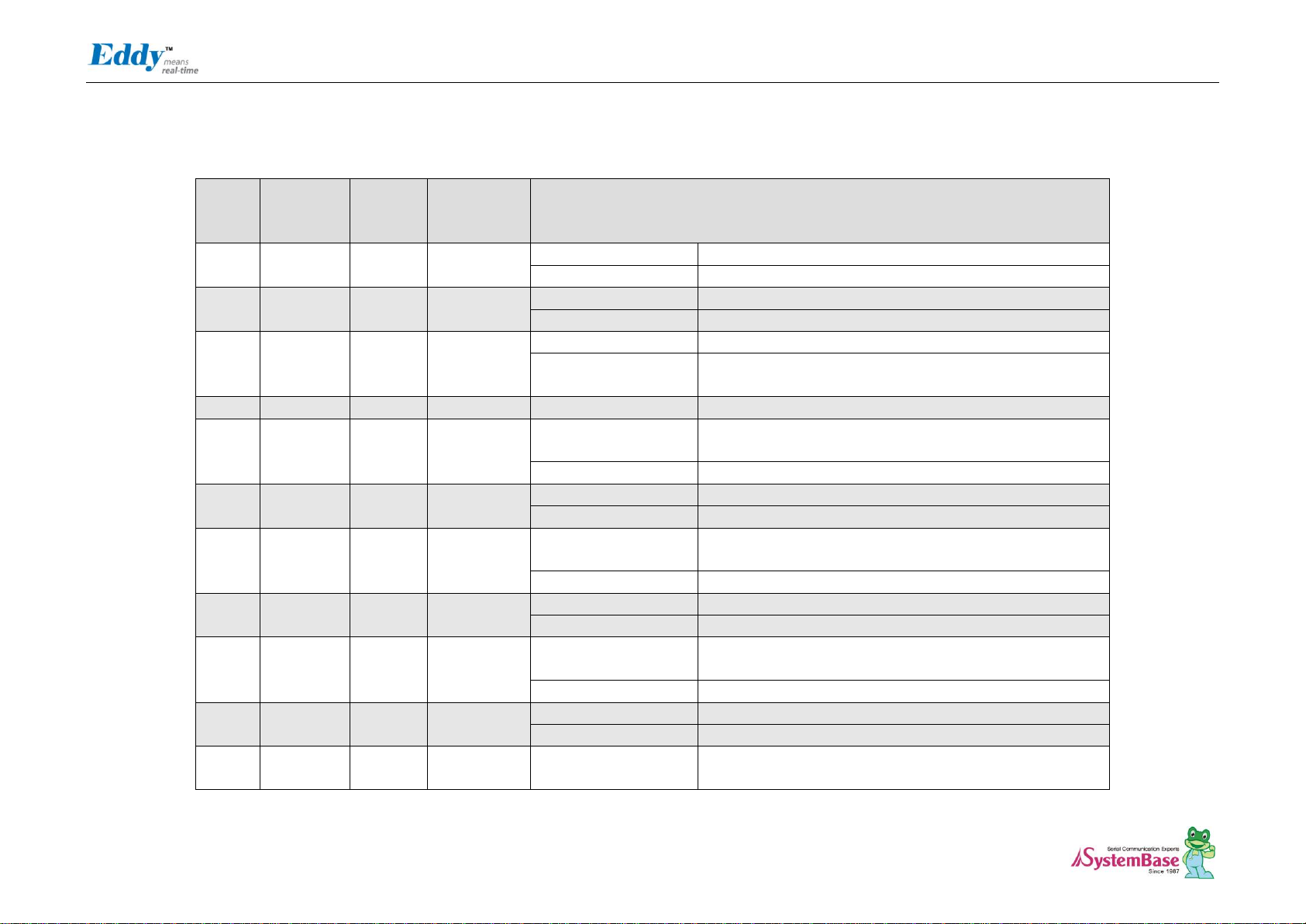
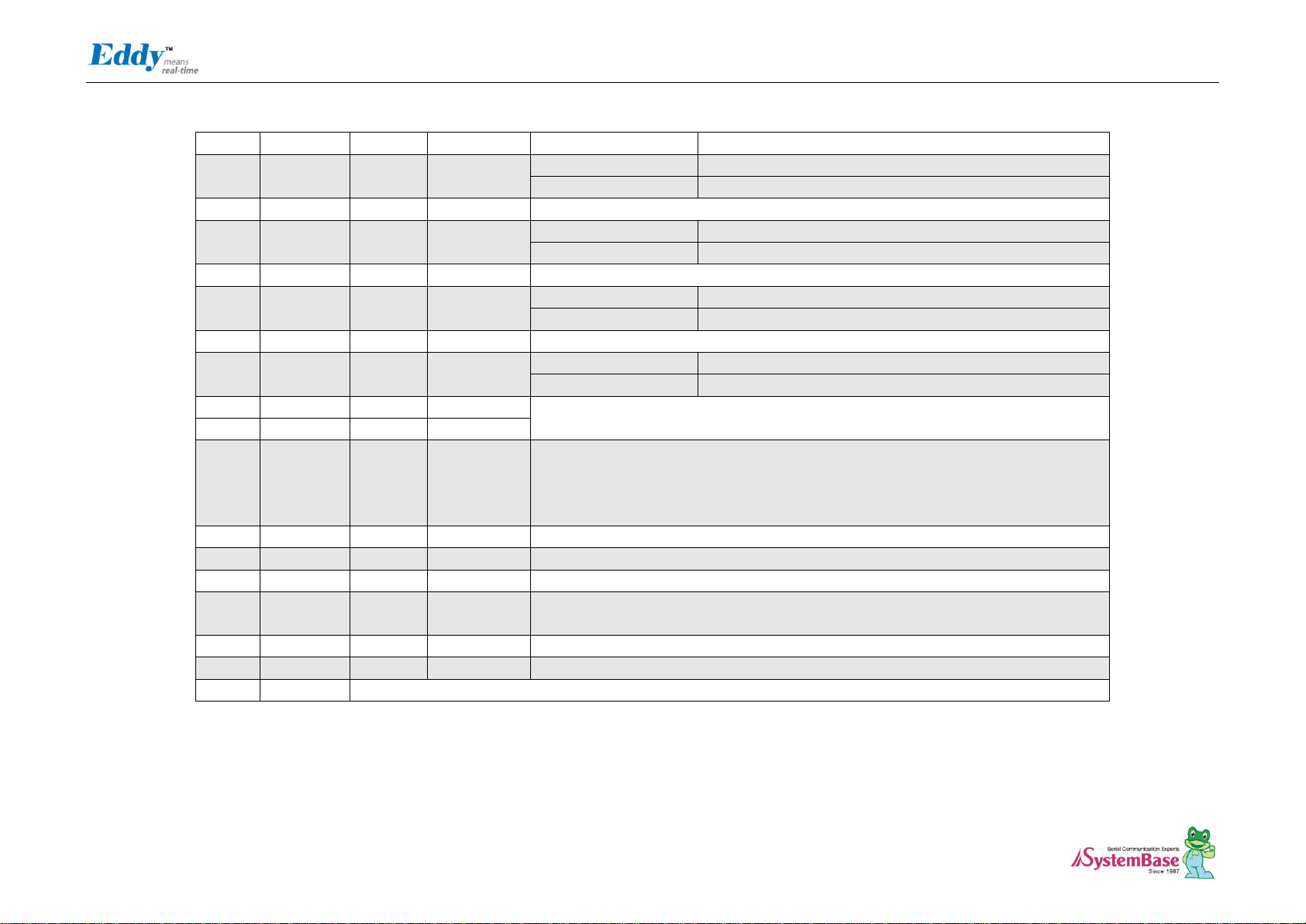
J4
Pin
Signal Name
Pin
Signal Name
1
PB12
2
PB13
3
PB30
4
PB31
5
PB0
5
PC22
7
PB1
8
PB16
9
PB2
10
PB17
11
PB3
12
PB18
13
BHDM
14
PB19
15
BHDP
16
PB20
17
A16
18
PB21
19
A17
20
A18
21
D8
22
D9
23
D10
24
D11
25
D12
26
D13
27
D14
28
D15
29
TWD
30
TCK
31
NANDOE
32
NAND_CLE / A22
33
NANDWE
34
NAND_ALE / A21
35
NC
36
NC
J4 Specifications
Page 25
Eddy DK Programmer Guide
25
Pin No
Name
DK v2.1
Pin No
Expansion
Header Pin
No
Description
1
PB12
J11_1
J2_17
Peripheral A : TXD5
USART5 Transmit Data
Peripheral B : ISI_D10
Image Sensor Data 10
2
PB13
J11_2
J2_18
Peripheral A : RXD5
USART5 Receive Data
Peripheral B : ISI_D11
Image Sensor Data 11
3
PB30
J11_3
J2_31
Peripheral A : PCK0
Programmable Clock Output 0
Peripheral B :
ISI_HSYNC
Image Sensor Horizontal Synchronization
4
PB31
J11_4
J2_32
Peripheral A : PCK1
Programmable Clock Output 1
5
PB0
J11_5
J2_2
Peripheral A :
SPI1_MISO
SPI1(Serial Peripheral Interface) Master In Slave Out
Peripheral B : TIOA3
Timer Counter ch3 I/O Line A
6
PC22
J11_6
J4_27
Peripheral A : D22
Peripheral B : TCLK5
Timer Counter ch5 External CLK IN
7
PB1
J11_7
J2_3
Peripheral A :
SPI1_MOSI
Peripheral B : TIOB3
Timer Counter ch3 I/O Line B
8
PB16
J11_8
J2_17
Peripheral A : TK0
SSC Transmit Clock
Peripheral B : TCLK3
Timer Counter ch3 External CLK IN
9
PB2
J11_9
J2_4
Peripheral A :
SPI1_SPCK
SPI1(Serial Peripheral Interface) Serial Clock
Peripheral B : ISI_D3
Image Sensor Data 3
10
PB17
J11_10
J2_18
Peripheral A : TF0
SSC Transmit Frame Sync
Peripheral B : TCLK4
Timer Counter ch4 External CLK IN
11
PB3
J11_11
J2_5
Peripheral A :
SPI1_NPCS0
SPI1(Serial Peripheral Interface) Peripheral Chip Select 0
J4 Pin Description
Page 26
Eddy DK Programmer Guide
26
Peripheral B : TIOA5
Timer Counter ch5 I/O Line A
12
PB18
J11_12
J2_19
Peripheral A : TD0
SSC Transmit Data
Peripheral B : TIOB4
Timer Counter ch4 I/O Line B
13
HDMB
J11_13
J1_28
USB Device Port Data -
14
PB19
J11_14
J2_20
Peripheral A : RD0
SSC Receive Data
Peripheral B : TIOB5
Timer Counter ch5 I/O Line B
15
HDPB
J11_15
J1_30
USB Device Port Data +
16
PB20
J11_16
J2_21
Peripheral A : RK0
SSC Receive Clock
Peripheral B : ISI_D0
Image Sensor Data 0
17
A16
J11_17
J3_3
External Address Bus
18
PB21
J11_18
J2_22
Peripheral A : RF0
SSC Receive Frame Sync
Peripheral B : ISI_D1
Image Sensor Data 1
19
A17
J11_19
J3_2
External Address Bus
20
A18
J11_20
J3_1
21-28
D[8:15]
J11_21
~J11_28
J3_28
~J3_21
External Data Bus 8-15
DK is directly connected with CPU and external connecter (J3) is connected by buffer.
PC13(NCS6 : Chip Select 6) should be enabled for working buffer, if it is reset, it work
as Pulled-up input.
29
TWD
J11_29
J4_3
Two-wire Serial Data. This pin cannot be used for GPIO.
30
TWCK
J11_30
J4_4
Two-wire Serial Data. This pin cannot be used for GPIO.
31
NANDOE
J11_31
-
NAND Flash Output Enable
32
A22
J11_32
J1_29
Address Bus
DK is directly connected with CPU and external connecter (J3) is connected by buffer.
33
NANDWE
J11_33
-
NAND Flash Write Enable
34
A21
J11_34
J1_30
Address Bus
35,36
NC
Not Connect
Page 27
Eddy DK Programmer Guide
27
NOTE:
Ensure that the input power supply for Eddy Serial DK is from 9V to 48V with 500 mA (or higher).
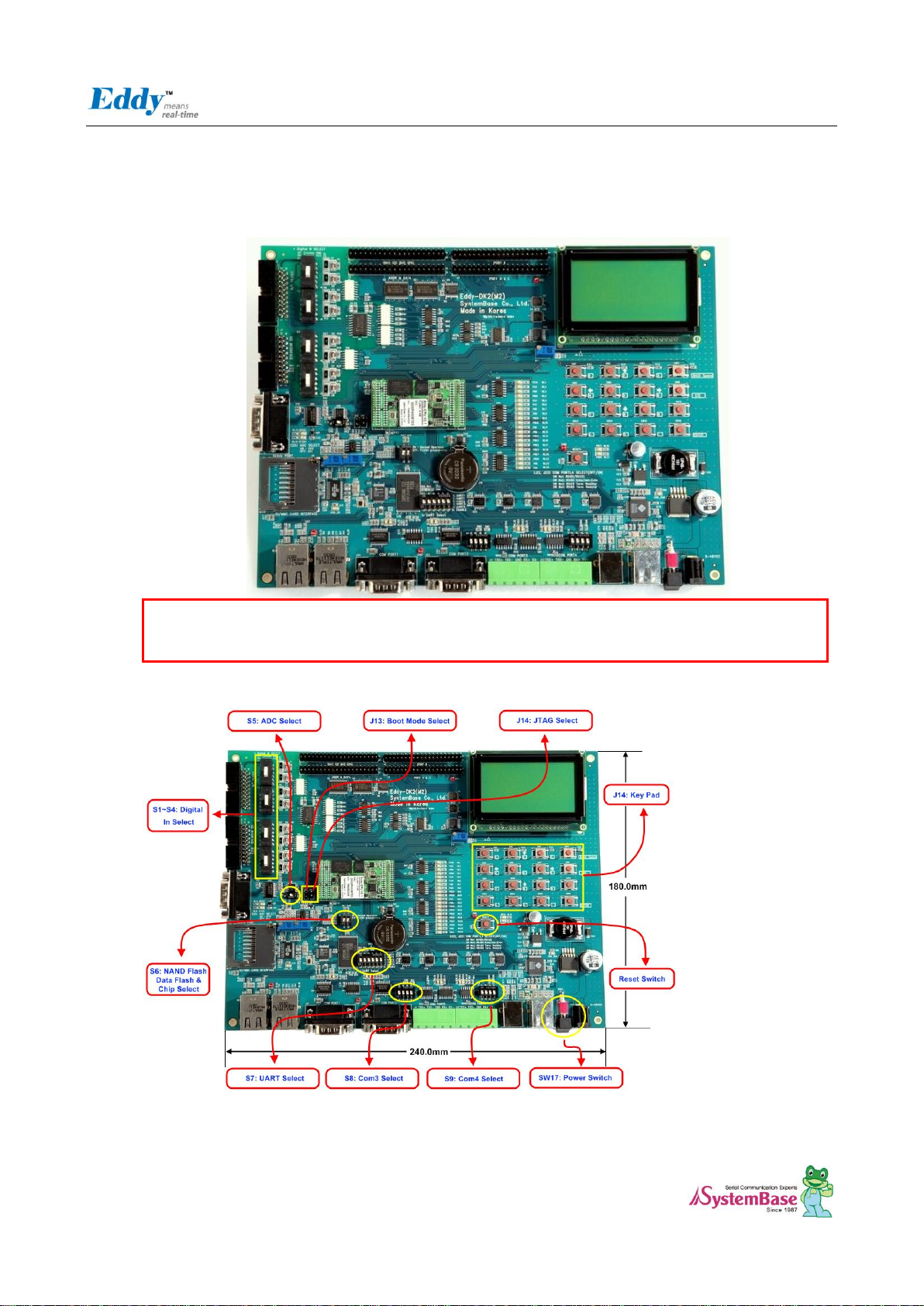
2.4 Eddy-DK v2.1
2.4.1 Modules’Locations
2.4.2 Switch Description
Page 28
Eddy DK Programmer Guide
28
MODE
Switch
설명
GND
Common
UP
Common GND
COM
(GND)
Isolated Input
Signal(Source)
Eddy DK v2.1
1.1K
4.7K
VCC
Common
Down
Common VCC
EXTERNAL POWER
Isolated Input
Signal(SINK)
Eddy DK v2.1
1.1K
4.7K
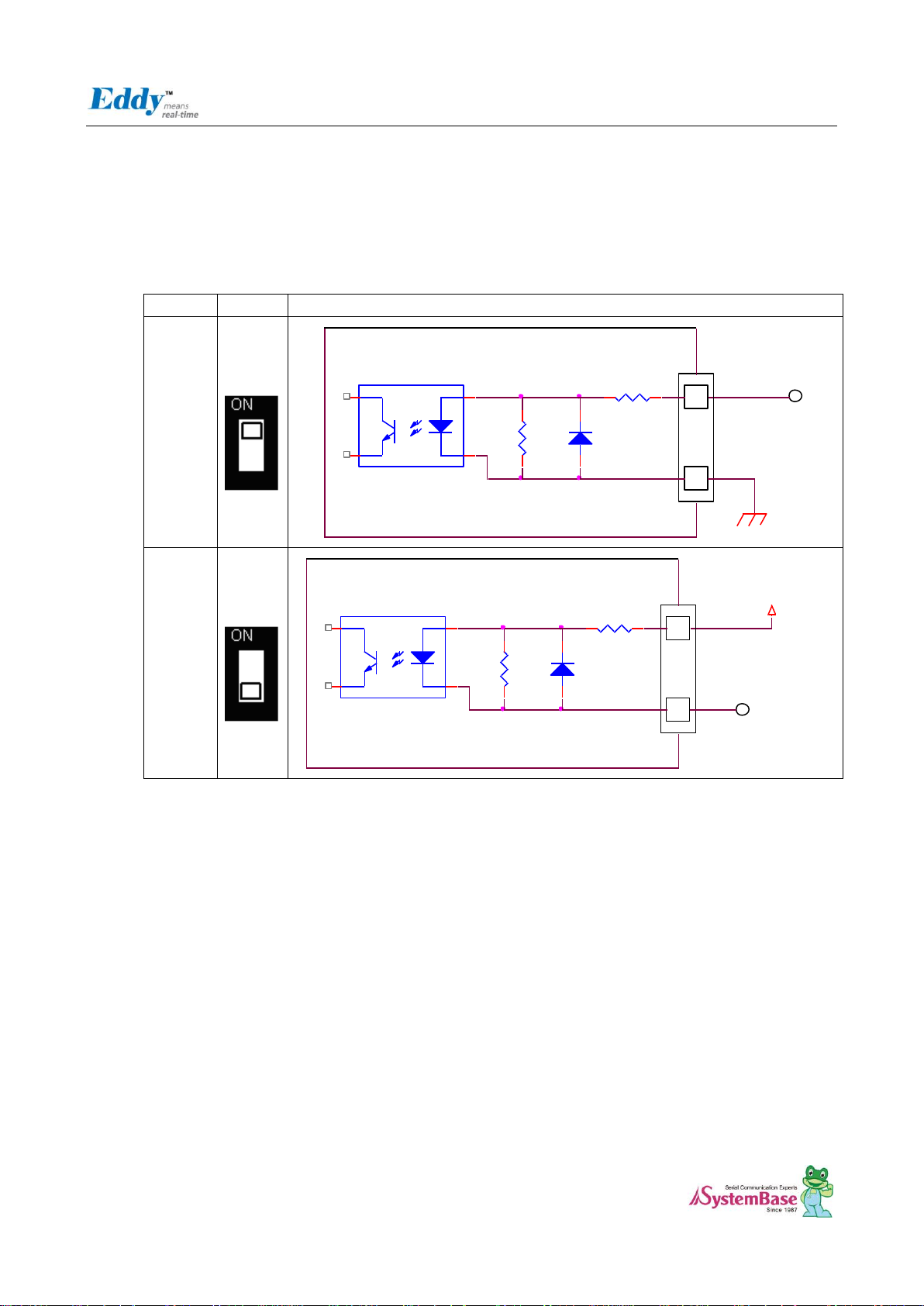
2.4.2.1. S1~S4: Digital In Select
It is possible to select the Distal Input mode with this switch (S1 ~ S4). In order to use VCC Common Mode, switch
down, and to use GNC Common Mode switch up refer to below feature.
This below schematic is just for reference, So you should make you own schematic with the current and voltage
that you want.
Common Input Setting (Switch S1~S4)
Page 29
Eddy DK Programmer Guide
29
ON
1
ON
PIN name
Fuction
Discription
I/O
PC0
ADC0
Temp. Sensor Input(LM50), RN: U22
IN
PC1
ADC1
Lux. Sensor Input(BH1600), RN: U26
IN
PC2
ADC2
Temp. Sensor Input(TMP300), RN: U24
IN
PC3
ADC3
N/A
IN
ON
ON
1 2
Flash Programming & Booting device Selection
Switch
No 1
Switch
No 2
Operation descriotion
OFF
OFF
For Flash Programming
This setting is needed in firmware Programming. refer to 9.2 System
recovery via USB
OFF
ON
Boot from Data Flash.
ON
OFF
Boot from Nand Flash
ON
ON
Boot from Data Flash or Nand Flash which have bootloader. if Both
devices have the bootloader, algorithm in CPU select the bootloader
of Data Flash.
(Reference : CPU Datasheet 13 장 AT91SAM9260 Boot Program)
SW Off : ADC mode
SW ON : GPIO mode
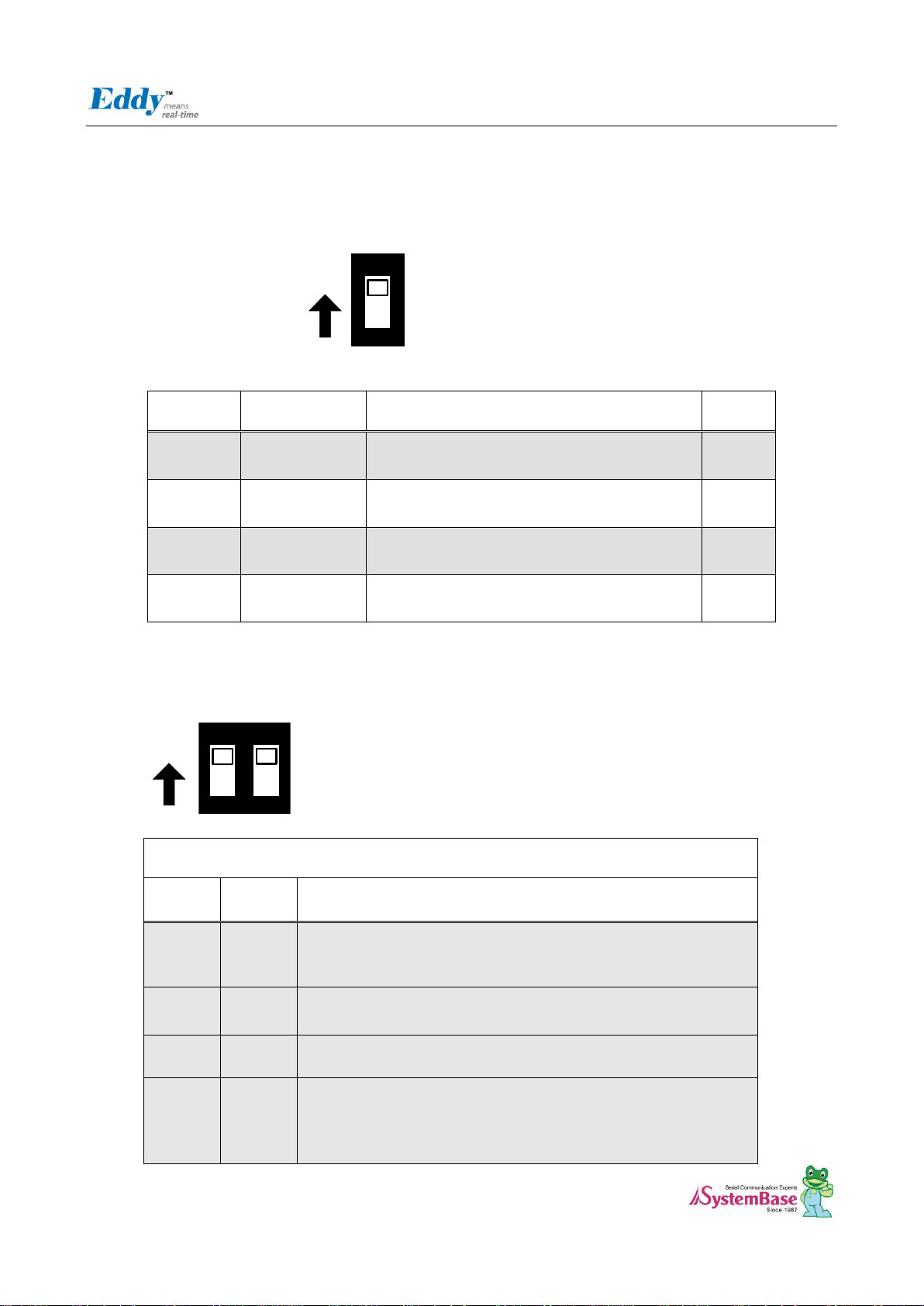
2.4.2.2. S5: ADC Select
You can choice the GPIO and ADC function with this switch. In order to use the ADC device, you should switch off.
And In order to use the GPIO function, you should switch on.
* RN = Reference Number
2.4.2.3. S6: NAND Flash & Data Flash Chip Select
This switch is Nand Flash & Data Flash Chip select switch. This switch is needed in firmware Programming.
Page 30
Eddy DK Programmer Guide
30
ON
ON
1 2 3 4 5 6
Serial Port & LED
Switch
Bank
Switch
No
Down Position(OFF)
Serial Port Test
UP Position(ON)
GPIO TEST (High : LED On)
S7
1
UART#0 TEST
UART#0 의 TXD, RXD, RTS, CTS
signals are connected with UART#0
RS232 driver IC.
GPIO (PB4, PB5, PB26, PB27) ports are
connected with the GPIO LED of DK
board and disconnected with the
UART#0 RS232 driver IC.
2
UART#0 TEST
UART#0 의 DTR, DSR, DCD, RI signals
are connected with UART#0 RS232
driver IC.
GPIO (PB24, PB22, PB23, PB25) ports
are connected with the GPIO LED of DK
board and disconnected with the
UART#0 RS232 driver IC.
3
UART#1 TEST
UART#1 의 TXD, RXD, RTS, CTS
signals are connected with UART#1
RS232 driver IC.
GPIO (PB6, PB7, PB28, PB29) ports are
connected with the GPIO LED of DK
board and disconnected with the
UART#1 RS232 driver IC.
4
UART#2 TEST
UART#2 의 TXD, RXD, RTS, CTS
signals are connected with UART#2
RS422/485 driver IC.
GPIO (PB8, PB9, PA4, PA5) ports are
connected with the GPIO LED of DK
board and disconnected with the
UART#2 RS422/485 driver IC.
5
UART#3 TEST
UART#3 의 TXD, RXD, RTS, CTS
signals are connected with UART#3
RS422/485 driver IC.
GPIO (PB10, PB11, PC8, PC10) ports
are connected with the GPIO LED of DK
board and disconnected with the
UART#3 RS422/485 driver IC.
6
For Serial Port & GPIO Test
Serial Port and GPIO LED of DK board
are enabled.
Connect to Expansion Header
UART#0~#3 and GPIO LEDs are
disconnected with the Eddy-CPU board
and directly connected with the
Expansion Header(J2, J4)
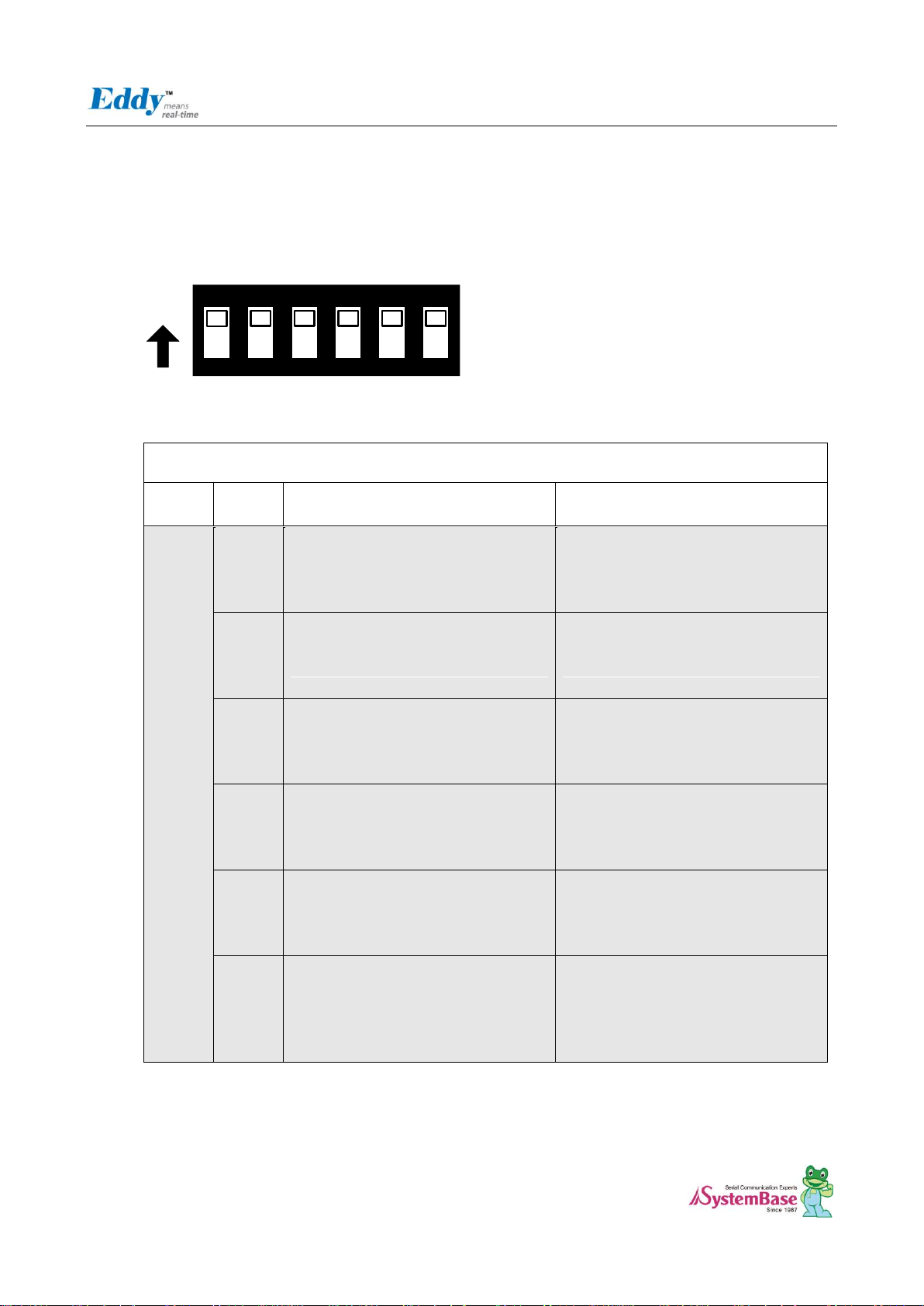
2.4.2.4. S7:UART Select
In order to test Serial Port, UART Select Switches are pulled down. It means that UARTs in CPU are connected to
Serial Port. If switches are pulled up, GPIO Ports are enabled and LEDs are controlled by GPIO Ports. And if Switch
No.6 is pulled up, GPIO ports are connected with the Expansion Headers.
Page 31

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
31
ON
ON
1 2 3 4
COM PORT#3, #4 settings
Switch
Bank
Switch
No
Down Position(OFF)
UP Position(ON)
S8
Port#3
1
RS485 Half-Duplex mode
RS422 Full-Duplex mode
2
RS422(RX enabled)
RS485 echo-mode
RS485 non echo-mode
3
RS422 Termination Resistor
not connected
RS422 Termination Resistor
Connected
4
RS485 Termination Resistor
not connected
RS422 Termination Resistor
Connected
S9
Port#4
1
RS485 Half-Duplex mode
RS422 Full-Duplex mode
2
RS422(RX enabled)
RS485 echo-mode
RS485 non echo-mode
3
RS422 Termination Resistor
not connected
RS422 Termination Resistor
Connected
4
RS485 Termination Resistor
not connected
RS422 Termination Resistor
Connected
2.4.2.5. S8:COM3 & S9: COM4 Select
COM Port #3 and COM Port #4 set the RS422/RS485 mode.
Page 32

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
32
P10-P17
4x4 Key matrix
I/O
PB20
First Row line
IN
PB21
Second Row line
IN
PB30
Third Row line
IN
PB31
Forth Row line
IN
PC20
First Column line from left
IN
PC21
Second Column line from left
IN
PC22
Third Column line from left
IN
PC23
Fourth Column line from left
IN
Pin name
Function
Discription
I/O
PC16
nRESET
Polling Input signal continually from External Reset
key, implement as below with checking the constant
time of "Low."
Less than 5 seconds: General reset function.
More than 5 seconds: Factory Default function.
IN
2.4.2.6. SW1~SW16: Key Pad
Key Pad of DK board are consisted with the 4x4 matrix. GPIOs are set to Input mode to read the Key value. and Key
2, 4, 6, 8 also have the ▲(UP), ▼(DN), ◀(LEFT), ▶(RIGHT) direction function for LCD menu.
2.4.2.7. SW17: Power
In order to power up, pull up this switch.
2.4.2.8. Reset1: Reset
Page 33

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
33
PIN name
Function
Discription
I/O
PC10
CTS3
UART #3 Clear to Send
I
PC8
RTS3
UART #3 Request to Send
O
PB11
RXD3
UART #3 Receive Data
I
PB10
TXD3
UART #3 Transmit Data
O
PA5
CTS2
UART #2 Cleat to Send
I
PA4
RTS2
UART #2 Request to Send
O
PB9
RXD2
UART #2 Receive Data
I
PB8
TXD2
UART #2 Transmit Data
O
PB29
CTS1
UART #1 Cleat to Send
I
PB28
RTS1
UART #1 Request to Send
O
2.4.3 LED Description
2.4.3.1. GPIO LED
Eddy-CPU v2.1/v2.5 supports Max 56 GPIO ports. DK board has 20 GPIO LEDs of all GPIO to test. This GPIO LEDs
are controlled by UART select switches.(refer to 2.4.2.4 UART Select )
Page 34

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
34
PB7
RXD1
UART #1 Receive Data
I
PB6
TXD1
UART #1 Transmit Data
O
PB25
RI0
UART #0 Ring Indicator
I
PB23
DCD0
UART #0 Data Carrier Detection
I
PB22
DSR
UART #0 Data Set Ready
O
PB24
DTR0
UART #0 Data Terminal Ready
I
PB27
CTS0
UART #0 Clear to Send
I
PB26
RTS0
UART #0 Request to Send
O
PB5
RXD0
UART #0 Receive Data
I
PB4
TXD0
UART #0 Transmit Data
O
Symbol
Parameter
Conditions
Min
Typ
Max
Units
Io
Output Current
PA0-PA31 PB0-PB31 PC0-
PC3
16
PC4 - PC31 in 3.3V range
2*
mA
PC4 - PC31 in 1.8V range
4
41.2 DC Characteristics
* Eddy DK v2.1 has 3.3V range, so PC4-PC31 PIO is set to 2mA.
(Refer to CPU Datasheet의 41.2 DC characteristics )
2.4.3.2. Power, Ready LED
System Ready (RDY): Indicates that the system is operating normally. (Normal: LED blinks)
Power (PWR): Indicates that the 5 V power is being supplied. (Supplying power: Red LED ON)
2.4.3.3. Debug Port LED
DTXD (Debug Port Transmit Dta LED) : Shows transmission status of the Debug Port.
DRXD (Debug Port Receive Data LED) : Shows reception status of the Debug Port.
2.4.3.4. COM Port 1 LED
COM Port 1 Transmit LED : Shows transmission status of COM1 Port.
COM Port 1 Receive LED : Shows reception status of COM1 Port.
2.4.3.5. COM Port 2 LED
COM Port 2 Transmit LED : Shows transmission status of COM2 Port.
COM Port 2 Receive LED : Shows reception status of COM2 Port.
2.4.3.6. COM Port 3 LED
COM Port 3 Transmit LED : Shows transmission status of COM3 Port.
Page 35

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
35
COM Port 3 Receive LED : Shows reception status of COM3 Port.
2.4.3.7. COM Port 4 LED
COM Port 4 Transmit LED : Shows transmission status of COM4 Port.
COM Port 4 Receive LED : Shows reception status of COM4 Port.
Page 36

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
36
2.4.4 External Device Interface Description
Page 37

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
37
Pin
Signal
Description
1
TXD+
Transmit Data +
2
TXD-
Transmit Data -
3
RXD+
Receive Data +
6
RXD-
Receive Data -
LED
Description
Left Green
Upon 100BaseT link, it lights
Upon 10BaseT link, it off
Right Yellow
Default Lights, When the data is sent or
received, it blinks.
Pin
Signal
Description
1
DCD
Data Carrier Detection (Input) (COM Port 1 only)
2
RXD
Receive Data (Input)
3
TXD
Transmit Data (Output)
4
DTR
Data Terminal Ready (Output) (COM Port 1 only)
5
GND
Ground
6
DSR
Data Set Ready (input) (COM Port 1 only)
7
RTS
Request to Send (Output)
8
CTS
Clear to Send (Input)
9
RI
Ring Indicator (Input)
2.4.4.1. WAN & LAN Interface
WAN & LAN Port automatically recognizes Cross/ Direct.(auto MDIX)
2.4.4.2. COM Port 1 & COM Port 2
RS232
Page 38

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
38
Pin
Signal
Description
1
TXD+
Transmit differential data positive (Output)
2
TXD-
Transmit differential data negative (Output)
3
GND
Ground 4 RXD+
Receive differential data positive (Input)
5
RXD-
Receive differential data negative (input)
Pin
Signal
Description
1
TRX+
Transmit/Receive differential data positive
2
TRX-
Transmit/Receive differential data negative
2.4.4.3. COM Port 3 & COM Port 4
RS422 Full Duplex
RS485 Half Duplex
2.4.4.4. Debug Port
You can check debug message or status information with debug port.
Page 39

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
39
Contact
Polarity
Center (D : 2mm)
9-48VDC
Outer (D: 6.5mm)
Ground
Environment Setting
Debug port is configured as follows so user has to set his or her PC serial port connected to debug port as follows.
Speed: 115200 bps
Data bit: 8 bit
Parity bit: Non Parity
Stop bit: 1 bit
2.4.4.5. Power Jack
Page 40

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
40
2.4.5 Internal Device Description
2.4.5.1. EEPROM
Eddy-DK v2.1 has the AT25160, 2Kx8bit SPI EEPROM.
Page 41

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
41
Signal Name
Function
Description
I/O
P[00:07]
Data bits
Used for data transfer between the CPU and the LCD
module.
I/O
P10
/CS1
Chip enable for D2 (Segment 1 to 64)
IN
P11
/CS2
Chip enable for D3 (Segment 65 to 128)
IN
P12
R/W
R/W signal input is used to select the read /write
mode
High = Read mode, Low = Write mode
IN
P13
D/ I
Register selection input
High = Data register
Low = Instruction register (for write)
Busy flag address counter (for read)
IN
P14 E Start enable signal to read or write the data.
IN
Function
Description
I/O
P00-P07
DIO Output, Connected with DO[0:7]
OUT
P00
DIO output, DO0
P01
DIO output, DO1
P02
DIO output, DO2
P03
DIO output, DO3
P04
DIO output, DO4
P05
DIO output, DO5
P06
DIO output, DO6
P07
DIO output, DO7
P10-P17
DIO Intput, Connected with DI[0:7]
IN
P10
DIO Input, DI0
2.4.5.2. LCD Module
Graphic LCD Module (PowerTIP PG12864LRU-JCNH11Q and I2C-Bus I/O Expander IC PCA9539)
2.4.5.3. 16bit I2C Bus GPIO
This 16-bit I2C Bus GPIO (PCA9539) provides general-purpose remote I/O expansion.
Slave address of this chip is set to 0x74 in DK board. and Address can be changed with A1,A0 address input from
0x74 to 0x77.
16-bit I/O is used to Digital Input/Output as below, and this is connected with the Expansion Header also. If you use
for GPIO, it is possible to configure individually.
Page 42

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
42
P11
DIO Input, DI1
P12
DIO Input, DI2
P13
DIO Input, DI3
P14
DIO Input, DI4
P15
DIO Input, DI5
P16
DIO Input, DI6
P17
DIO Input, DI7
/INT
Connected with PB16 of Eddy-CPU
OUT
Page 43

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
43
Parameter
Symbol
MIN
TYP
MAX
Units
Normal Frequency
fo
32.768
KHz
Series Resistance
ESR
45,60
KΩ
Load Capacitance
CL 12.5
pF
2.4.5.4. RTC
- DS1340 (Dallas, I2C interface)
- 12.5pF load capacitance crystal must be used. (Refer to Crystal Spec below)
- Do not use another RTC Chip.
- Backup Battery: CR2032 (235mAh) Lithium Battery.
DS1340 Crystal Specifications
2.4.5.5. Temp Sensor
AD0(PC0)에 National LM50
2.4.5.6. Light Sensor
BH1600FVC (Rohm)
Viout = 0.6 x10-6 x Ev x R1
Where, Viout = IOUT output voltage [V]
Ev = lilluminance of the ALS(Ambient Light Sensor) surface [lx]
R1 = IOUT output resistor [Ω]
The Output voltage is caculated as below
Page 44

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
44
Eddy-CPU
v2.1 /v2.5
Signal Name
Function
Discription
I/O
A22
CLE
COMMAND LATCH ENABLE
The CLE input controls the activating path for
commands sent to the command register.
OUT
A21
ALE
ADDRESS LATCH ENABLE
The ALE input controls the activating path for
address to the internal address registers.
OUT
NANDOE
NANDOE
data-out control
OUT
NANDWE
NANDWE
controls writes to the I/O port
OUT
PC14(NCS3)
NANDCS
device selection control
OUT
PC17
RDYBSY
(R/B)
READY/BUSY OUTPUT
The R/B output indicates the status of the device
operation. When low, it indicates that a program,
erase or random read operation is in process and
returns to high state upon completion. It is an
open drain output and
does not float to high-z condition when the chip
is deselected or when outputs are disabled.
IN
D[0:7]
DATA
bits
DATA INPUTS/OUTPUTS
The I/O pins are used to input command,
address and data, and to output data during read
operations. The I/O pins float to high-z when the
chip is deselected or when the outputs are
disabled.
I/O
2.4.5.7. NAND Flash
- 256MB, 8bit Flash (Samsung K9F2G08U0A-PCB0)
- Chip Select #3 used, Address range : 0x4000_0000~0x4FFF_FFFF.
Page 45

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
45
Eddy-CPU
v2.1 /v2.5
Signal Name
DM9000B
Signal Name
Description
I/O
PC12/NCS7
CSN
Chip Select #7
Address : 0x8000 0000-0x8FFF FFFF
OUT
PC15/IRQ1
INTRN
Interrupt depend on EECK(pin20) setting.
1 : INT pin low active
0 : INT pin high active
EECK is not connected in DK board, so Interrupt is
acted with active high.
IN
A2
CMD
Command Type
When high, Data port
When low, INDEX port
OUT
D[0:15]
Data Bus
16-bit mode
I/O
2.4.5.8. Ethernet Controller (WAN Port)
- Davicom DM9000B Ethernet Controller
- 16 bit mode set.
- EECS pin should be connected with pull-up resistor to use link/speed LED.
- RJ45 Transformer Center Tap is powered by DM9000B AVDD18.
Page 46

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
46
[ Eddy-S4M V2.5 Block Diagram]
ON
1
ON
SDRAM
(32MB)
Data Flash
(8MB)
BUS
1.0V
USB SD
Controller
EMAC
3.3V
RTC
(I2C)
Serial
Driver IC
RS232 ; 2
Combo : 2
USB I/F
USB Hub
miniPCI TypeIII
PWR
Size : 59.75 x 61.8mm
AT91SAM9G20
Ethernet PHY
2.5 Eddy-S4M v2.1 / v2.5
Eddy-S4M is a high-performance mini PCI type embedded module which include ARM9 processor 32MB SDRAM,
8MB DataFlash, 10/100Base-T Ethernet port, Serial 4 Channel, RTC with Battery, minroSD, 4ch ADC, temperature
sensor, max 34 programmable GPIO pins. Eddy-S4M is 59.75 x 61.8mm size. If using Eddy-S4M-JIG board, user
could develop their customized device without other H/W development, which minimizing time and cost to develop.
Referring Example code and Evaluation Kit circuit allow developer to design device they want.
Eddy-S4M v2.5 is compatible with Eddy-S4M v2.1.
Page 47

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
47
[Eddy-S4M v2.1]
[Eddy-S4M v2.5]
Page 48

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
48
Pin
Signal
Pin
Signal
Pin
Signal
Pin
Signal
1
JTAG_TDI
2
JTAG_TDO
63
3.3V
64
PB13
Key Key
65
PB16
66
PB17
2
JTAG_TMS
4
JTAG_RTCK
67
PB18
68
PB19
3
JTAG_TCK
6
ICE_NTRST
69
GND
70
3.3V
7
LAN_RX+
8
LAN_TX+
71
PB20
72
PB21
9
LAN_RX-
10
LAN_TX-
73
PB30
74
GND
11
LAN_Speed
12
LAN_LINK
75
PC0
76
PB31
13
P3_RX-
14
RDY#
77
GND
78
PC1
15
GND
16
NC
79
PC2
80
PC3
17
P3_RX+
18
NC
81
PC5
82
GND
19
3.3V
20
DCD0
83
GND
84
PC9
21
P3_TX+
22
DTR0
85
PC10
86
PC12
23
GND
24
3.3V
87
PC13
88
3.3V
25
P3_TX-
26
nRESET
89
3.3V
90
PC14
27
GND
28
3.3V
91
PC15
92
PC17
29
P4_RX+
30
RxD0#
93
PC18
94
PC19
31
3.3V
32
GND
95
PC24
96
PC20
33
P4_RX-
34
RTS0
97
NC
98
PC25
35
P4_TX+
36
TxD0#
99
I2C_TWCK
100
I2C_TWD
37
GND
38
CTS0
101
GND
102
GND
39
P4_TX-
40
3.3V
103
DDM
104
DDP
41
DEBUG_TxD
42
DSR0
105
DM2
106
DP2
43
DEBUG_RxD
44
RI0
107
DM3
108
DP3
45
PA5
46
RxD1#
109
DM4
110
DP4
47
PA22
48
RTS1
111
SDDATA0
112
SDDATA1
49
GND
50
GND
113
SDDATA2
114
GND
51
PA30
52
TxD1#
115
SDCMD
116
SDDATA3
53
NC
54
CTS1
117
SDCDN
118
SDCLK
55
GND
56
NRST
119
JTAG_SEL
120
SDWP
57
PB0
58
PB1
121
NC
122
BMS
59
PB2
60
PB3
123
NC
124
3.3V
61
PB12
62
GND
2.5.1 miniPCI Card Type III Connector Pinout (J5)
Page 49

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
49
S4M
Pin No
(124)
Name
S4M-JIG
Pin HDR
(46*2)
S4M-DK
Pin HDR
(46*2)
Description
1
TDI - -
Test Data IN
2
TDO - -
Test Data Out
3
TMS - -
Test Mode Select
4
RTCK - -
Return Test Clock
5
TCK - -
Test Clock
6
NTRST
-
-
Test Reset
119
JTAGSEL
-
-
JTAG boundary scan can be used by connecting J3.
This pin should not be connected when using ICE (In-Circuit
Emulator) or in normal operation status.
S4M
Pin No
(124)
Name
S4M-JIG
Pin HDR
(46*2)
S4M-
DK
Pin
HDR
(46*2)
Description
7
LAN_RX+
J5 pin2
J7 Pn2
Ethernet PHY Physical receive or transmit signal (+ differential) in CPU
8
LAN_TX+
J5 pin1
J7 Pin1
Ethernet PHY Physical receive or transmit signal (- differential) in CPU
9
LAN_RX-
J5 pin3
J7 pin3
Ethernet PHY Physical receive or transmit signal (+ differential) in CPU
10
LAN_TX-
J5 pin4
J7 pin4
Ethernet PHY Physical receive or transmit signal (- differential) in CPU
11
LAN_Speed
J5 pin6
J7 pin6
LAN connection status LED
Link/Activity
Pin State
LED Definition
No Link
H
OFF
Link L ON
Activity
Toggle
Blinking
12
LAN_Link
J5 pin5
J7 pin5
Link/Activity
Pin State
LED Definition
No Link
H
OFF
Link L ON
Activity
Toggle
Blinking
2.5.2 Connector Pinout of Boards
2.5.2.1. ICE and JTAG
2.5.2.2. Ethernet signal from or to PHYceiver
Page 50

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
50
S4M
Pin No
(124)
Name
S4M-JIG
Pin HDR
(46*2)
S4M-DK
Pin HDR
(46*2)
Description
13
P2_RX-
J4 pin20
J6 pin20
COM port #3 Receive differential data negative (Input)
RS422/485 inverting receiver input of Eddy-S4M module
14
RDY#
J4 pin45
J6 pin45
Indicate state of CPU ( normal : blinking)
17
P2_RX+
J4 pin19
J6 pin19
COM port #3 Receive differential data positive (Input)
RS422/485 Noninverting receiver input of Eddy-S4M module
20
DCD0
J4 pin9
J6 pin9
COM port #1 Data Carrier Detection signal
RS232 receiver input of Eddy-S4M module
21
P2_TX+
J4 pin17
J6 pin17
COM port #3 Transmit differential data positive (Output)
RS422/485 Noninverting driver ouput of Eddy-S4M module
22
DTR0
J4 pin7
J6 pin7
COM port #1 Data Terminal Ready signal
RS232 driver output of Eddy-S4M module
25
P2_TX-
J4 pin18
J6 pin18
COM port #3 Transmit differential data negative (Output)
RS422/485 inverting driver ouput of Eddy-S4M module
26
nRESET
J4 pin46
J6 pin46
Reset Input. In S/W, continuously check the interval of ‚LOW‛
when polling input signal from external Reset Key.
Under 5sec : Normal reset function
Over 5sec : Factory Default function
29
P3_RX+
J4 pin23
J6 pin23
COM port #4 Receive differential data negative (Input)
RS422/485 Noninverting receiver input in Eddy-S4M module
30
RxD0#
J4 pin4
J6 pin4
COM port #1 Receive Data signal
RS232 receiver input in Eddy-S4M module
33
P3_RX-
J4 pin24
J6 pin24
COM port #4 Receive differential data negative (Input)
RS422/485 inverting receiver input in Eddy-S4M module
34
RTS0
J4 pin5
J6 pin5
COM port #1 Request To Send signal
RS232 driver output in Eddy-S4M module
35
P3_TX+
J4 pin21
J6 pin21
COM port #4 Transmit differential data positive (Output)
RS422/485 Noninverting driver ouput in Eddy-S4M module
36
TxD0#
J4 pin3
J6 pin3
COM port #1 Transmit Data signal
RS232 driver output in Eddy-S4M module
38
CTS0
J4 pin6
J6 pin6
COM port #1 Request to Send signal
RS232 receiver input in Eddy-S4M module
39
P3_TX-
J4 pin22
J6 pin22
COM port #4 Transmit differential data negative(Output)
RS422/485 inverting driver ouput in Eddy-S4M module
41
DTxD#
J4 pin1
J6 pin1
Transmit Data signal of Debug Port
RS232 driver output in Eddy-S4M module
2.5.2.3. Serial (RS232 & COMBO) and PIOA (Peripheral I/O Controller A)
Page 51

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
51
42
DSR0
J4 pin8
J6 pin8
COM port #1 Data Set Ready signal
RS232 receiver input in Eddy-S4M module
43
DRxD
J4 pin2
J6 pin2
Receive Data signal of Debug Port
RS232 receiver input in Eddy-S4M module
44
RI0
J4 pin8
J6 pin8
COM port #1 Ring Indicator signal
RS232 receiver input in Eddy-S4M module
45
PA5
J5 pin7
J7 pin7
Only used for GPIO
46
RxD1#
J4 pin12
J6 pin12
COM port #1 Receive Data signal
RS232 receiver input in Eddy-S4M module
47
PA22
J5 pin8
J7 pin8
Only used for GPIO
48
RTS1
J4 pin13
J6 pin13
COM port #1 Request to Send signal
RS232 driver output in Eddy-S4M module
51
PA30
J5 pin9
J7 pin9
Only used for GPIO
52
TxD1#
J4 pin11
J6 pin11
COM port #1 Request to Send signal
RS232 driver output in Eddy-S4M module
54
CTS1
J4 pin14
J6 pin14
COM port #1 Request to Send signal
RS232 receiver input in Eddy-S4M module
56
NRST
J5 pin46
J7 pin46
External device Reset output signal (active low)
Page 52

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
52
S4M
Pin No
(124)
Name
S4M-JIG
Pin HDR
(46*2)
S4M-DK
Pin HDR
(46*2)
Description
57
PB0
J5 pin11
J7 pin11
Peripheral A : SPI1_MISO
SPI1(Serial Peripheral Interface)
Master In Slave Out
Peripheral B : TIOA3
Timer Counter ch3 I/O Line A
58
PB1
J5 pin12
J7 pin12
Peripheral A : SPI1_MOSI
SPI1(Serial Peripheral Interface)
Master Out Slave In
Peripheral B : TIOB3
Timer Counter ch3 I/O Line B
59
PB2
J5 pin13
J7 pin13
Peripheral A : SPI1_SPCK
SPI1(Serial Peripheral Interface) Serial
Clock
60
PB3
J5 pin14
J7 pin14
Peripheral A : SPI1_NPCS0
SPI1(Serial Peripheral Interface)
Peripheral Chip Select 0
Peripheral B : TIOA5
Timer Counter ch5 I/O Line A
61
PB12
J5 pin17
J7 pin17
Peripheral A : TXD5
USART5 Transmit Data
64
PB13
J5 pin18
J7 pin18
Peripheral A : RXD5
USART5 Receive Data
65
PB16
J5 pin119
J7 pin119
Peripheral A : TK0
SSC Transmit Clock
Peripheral B : TCLK3
Timer Counter ch3 External CLK IN
66
PB17
J5 pin20
J7 pin20
Peripheral A : TF0
SSC Transmit Frame Sync
Peripheral B : TCLK4
Timer Counter ch4 External CLK IN
67
PB18
J5 pin21
J7 pin21
Peripheral A : TD0
SSC Transmit Data
Peripheral B : TIOB4
Timer Counter ch4 I/O Line B
68
PB19
J5 pin22
J7 pin22
Peripheral A : RD0
SSC Receive Data
Peripheral B : TIOB5
Timer Counter ch5 I/O Line B
71
PB20
J5 pin23
J7 pin23
Peripheral A : RK0
SSC Receive Clock
72
PB21
J5 pin24
J7 pin24
Peripheral A : RF0
SSC Receive Frame Sync
73
PB30
J5 pin25
J7 pin25
Peripheral A : PCK0
Programmable Clock Output 0
75
PC0
J5 pin27
J7 pin27
Peripheral A : AD0
Analog to Digital Converter Input Ch0
76
PB31
J5 pin26
J7 pin26
Peripheral A : PCK1
Programmable Clock Output 1
2.5.2.4. PIOB and PIOC (Peripheral I/O Controller B/C)
Page 53

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
53
78
PC1
J5 pin28
J7 pin28
Peripheral A : AD1
Analog to Digital Converter Input Ch1
Peripheral B : PCK0
Programmable Clock Output 0
79
PC2
J5 pin29
J7 pin29
Peripheral A : AD2
Analog to Digital Converter Input Ch2
Peripheral B : PCK1
Programmable Clock Output 1
80
PC3
J5 pin30
J7 pin30
Peripheral A : AD3
Analog to Digital Converter Input Ch3
Peripheral B : SPI1_NPCS3
SPI1(Serial Peripheral Interface)
Peripheral Chip Select 3
81
PC5
J5 pin33
J7 pin33
Peripheral B : SPI1_NPCS1
SPI1(Serial Peripheral Interface)
Peripheral Chip Select 1
84
PC9
J5 pin34
J7 pin34
Only GPIO
85
PC10
J5 pin35
J7 pin35
Only GPIO
86
PC12
J5 pin36
J7 pin36
Only GPIO
87
PC13
J5 pin37
J7 pin37
Only GPIO
90
PC14
J5 pin38
J7 pin38
Only GPIO
91
PC15
J5 pin39
J7 pin39
Only GPIO
92
PC17
J5 pin40
J7 pin40
Only GPIO
93
PC18
J5 pin41
J7 pin41
Peripheral B : SPI1_NPCS1
SPI1(Serial Peripheral Interface)
Peripheral Chip Select 1
94
PC19
J5 pin42
J7 pin42
Peripheral B : SPI1_NPCS2
SPI1(Serial Peripheral Interface)
Peripheral Chip Select 2
95
PC24
J5 pin44
J7 pin44
Only GPIO
96
PC20
J5 pin43
J7 pin43
Peripheral B : SPI1_NPCS3
SPI1(Serial Peripheral Interface)
Peripheral Chip Select 3
98
PC25
J5 pin45
J7 pin45
Only GPIO
S4M
Pin No
(124)
Name
S4M-JIG
Pin HDR
(46*2)
S4M-DK
Pin HDR
(46*2)
Description
99
I2C_TWCK
J4 pin43
J6 pin43
Two-wire Serial Clock.
This can be used GPIO pin unless RTC function is used.
100
I2C_TWD
J4 pin44
J6 pin44
Two-wire Serial Data. This can be used GPIO pin unless
RTC function is used.
2.5.2.5. Two Wire Interface
Page 54

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
54
S4M
Pin No
(124)
Name
S4M-JIG
Pin HDR
(46*2)
S4M-DK
Pin HDR
(46*2)
Description
103
DDM
J4 pin25
J6 pin25
USB Device Port Data –
104
DDP
J4 pin26
J6 pin26
USB Device Port Data +
105
DM2
J4 pin27
J6 pin27
USB Port2 Data –. Connected to DSPORT2 of GL850A
USB 2.0 Hub Controller.
106
DP2
J4 pin27
J6 pin27
USB Port2 Data +. Connected to DSPORT2 of GL850A
USB 2.0 Hub Controller.
107
DM3
J4 pin29
J6 pin29
USB Port3 Data –. Connected to DSPORT2 of GL850A
USB 2.0 Hub Controller.
108
DP3
J4 pin30
J6 pin30
USB Port3 Data +. Connected to DSPORT2 of GL850A
USB 2.0 Hub Controller.
109
DM4
J4 pin33
J6 pin33
USB Port4 Data -. Connected to DSPORT2 of GL850A
USB 2.0 Hub Controller.
110
DP4
J4 pin34
J6 pin34
USB Port4 Data +. Connected to DSPORT2 of GL850A
USB 2.0 Hub Controller.
S4M
Pin No
(124)
Name
S4M-JIG
Pin HDR
(46*2)
S4M-DK
Pin HDR
(46*2)
Description
111
SDDATA0
J4 pin35
J6 pin35
SD Data0
112
SDDATA1
J4 pin36
J6 pin36
SD Data1
113
SDDATA2
J4 pin37
J6 pin37
SD Data2
115
SDCMD
J4 pin38
J6 pin38
SD command
116
SDDATA3
J4 pin39
J6 pin39
SD Data3
117
SDCDN
J4 pin40
J6 pin40
SD card detect
118
SDCLK
J4 pin41
J6 pin41
SD Clock
120
SDWP
J4 pin42
J6 pin42
SD Write Protect
122
BMS
-
-
Boot Mode Select signal
BMS = 1, Boot on Embedded ROM
BMS = 0, Boot on External Memory
2.5.2.6. Universal Serial Bus
2.5.2.7. Multimedia Card Interface
Page 55

55
S4M
Pin No
(124)
Name
S4M-JIG
Pin HDR
(46*2)
S4M-DK
Pin HDR
(46*2)
Description
16, 18, 53,
97,
121, 123
NC
J5 pin10
J5 pin10
No Connection
15, 23, 27,
32, 37, 49,
50, 55, 62,
69, 74, 77,
82, 83, 101,
102, 114
GND
J4: 31,32
J5: 31,32
J6: 31,32
J7: 31,32
Ground
19, 24, 28,
31, 40, 63,
70, 88, 89,
124
3.3V
J4: 15,16
J6: 15,16
3.0 to 3.6V power input
2.5.2.8. etc
Eddy DK Programmer Guide
Page 56

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
56
ON
1
ON
Switch No 1
Operation descriotion
OFF
For Flash Programming
Store firmware image to Flash memory through USB Device.
(Only via Window Host). For more information, please refer to
chapter 9, system recovery.
ON
Normal booting via Eddy-S4M v2.1 Data Flash
2.5.3 Switch Operation
2.5.4 LED Operation
System Ready (RDY): Indicate normal state of system (Normal: blinking)
2.5.5 Ethernet
Since there is KSZ8041NL PHY in Eddy-S4M module, when integrating Ethernet, just connect RJ45 in
which transformer located
WARNING : When you use RJ45 which has transformer in its internal circuit, it is possible to each product
doesn’t have equal PIN spec. Therefore, you must confirm PIN number
Bellow is KSZ8041NL functions
• Fully compliant to IEEE 802.3u Standard
• Supports MDI/MDI-X auto crossover (Auto-MDI)
• MII interface support
• RMII interface support with external 50MHz system clock
• ESD rating (6kV)
• Built-in 1.8V regulator for core
• Available in 32-pin (5mm x 5mm) MLF® package
Page 57

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
57
Parameter
Symbol
MIN
TYP
MAX
Units
Normal Frequency
fo 32.768
KHz
Series Resistance
ESR
45,60
KΩ
Load Capacitance
CL 12.5 pF
2.5.6 RTC
- We used D1340 which is connected I2C interface.
- In DS1340, you must use crystal of load capacitance = 12.5pF (Refer to bellow Crystal spec)
- You have to confirm Crystal spec because some RTC Chips have different spec
- We used CR2032 (235mAh) Lithium with Backup Battery
DS1340 Crystal Specifications
2.5.7 Temp Sensor
we used LM50(National) to AD0(PC0)
Page 58

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
58
2.6 Eddy-S4M-DK v2.1
Eddy-S4M DK is Development Kit supporting programmer can easily materialize and test their application.
2.6.1 Switch and Connector explanation
Page 59

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
59
Switch No
Down Position(OFF)
UP Position(ON)
1
PB0 Value
Low
High
2
PB0 input value
Low
High
3
PB0 input value
Low
High
4
PB0 input value
Low
High
ON
ON
1 2
Switch No
Down Position(OFF)
UP Position(ON)
1
RS422 Termination Resistor not connected
RS422 Termination Resistor Connected
2
RS485 Termination Resistor not connected
RS422 Termination Resistor Connected
1
RS422 Termination Resistor not connected
RS422 Termination Resistor Connected
2
RS485 Termination Resistor not connected
RS422 Termination Resistor Connected
J6 J7
Pin
Signal
Pin
Signal
Pin
Signal
Pin
Signal
1
DTxD
2
DRxD
1
LAN_RX+
2
LAN_TX+
3
TxD0#
4
RxD0#
3
LAN_RX-
4
LAN_TX-
5
RTS0
6
CTS0
5
LAN_Speed
6
LAN_LINK
7
DTR0
8
DSR0
7
PA5 8 PA22
9
DCD0
10
RI0 9 PA30
10
NC
11
TxD1#
12
RxD1#
11
PB0
12
PB1
13
RTS1
14
CTS1
13
PB2
14
PB3
15
3.3V
16
3.3V
15
5V
16
5V
2.6.1.1. S2 : GPIO Input Configuration
After configure PB0-PB4 to input, you can confirm whether the input value is changing with dip switch control.
2.6.1.2. S3,4 : Terminal Resistor selection
COM Port #3 and COM Port #4 is Combo port which support RS422/RS485 interface. Terminal resistors in each port
are configured by switch upon each Terminal Block.
2.6.1.3. J6,J7 : JIG Board connector(Socket)
Page 60

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
60
17
P3_TX+
18
P3_TX-
17
PB12
18
PB13
19
P3_RX+
20
P3_RX-
19
PB16
20
PB17
21
P4_TX+
22
P4_TX-
21
PB18
22
PB19
23
P4_RX+
24
P4_RX-
23
PB20
24
PB21
25
DDM
26
DDP
25
PB30
26
PB31
27
DM2
28
DP2
27
PC0
28
PC1
29
DM3
30
DP3
29
PC2
30
PC3
31
GND
32
GND
31
GND
32
GND
33
DM4
34
DP4
33
PC5
34
PC9
35
SDDATA0
36
SDDATA1
35
PC10
36
PC12
37
SDDATA2
38
SDDATA3
37
PC13
38
PC14
39
SDCMD
40
SDCLK
39
PC15
40
PC17
41
SDCDN
42
SDWP
41
PC18
42
PC19
43
TWCK
44
TWD
43
PC20
44
PC24
45
RDY#
46
nRESET(IN)
45
PC25
46
NRST(OUT)
2.6.1.4. U7 : Light Sensor
Bellow is comparison between luminance and out current. We used BH1600FVC (Rohm)
The Output voltage is caculated as below
Viout = 0.6 x10-6 x Ev x R1
Where, Viout = IOUT output voltage [V]
Ev = lilluminance of the ALS(Ambient Light Sensor) surface [lx]
R1 = IOUT output resistor [Ω]
Page 61

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
61
2.6.2 Interface Explanation
2.6.2.1. Power, Ready LED
System Ready (RDY): Indicate normal state of system (Normal: blinking)
Power (PWR): indicate Power is inserted (RED LED ON state)
Page 62

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
62
Pin Name
Signal Name
Descriotion
Debug Port
TxD
Debug Port Tx LED
RxD
Debug Port Rx LED
COM Port 1
(RS232)
TxD
COM Port1 Tx LED
RxD
COM Port1 Rx LED
COM Port 2
(RS232)
TxD
COM Port2 Tx LED
RxD
COM Port2 Rx LED
COM Port 3
(RS422/RS485)
TxD
If RS422 is COM Port3 Tx LED
If RS485 is Tx/Rx Common LED
RxD
If RS422 is COM Port3 Rx LED
If RS485 is LED Off (Not Used)
COM Port 4
(RS422/RS485)
TxD
If RS422 is COM Port4 Tx LED
If RS485 is Tx/Rx Common LED
RxD
If RS422 is COM Port4 Rx LED
If RS485 is LED Off (Not Used)
No
Pin Name
Descriotion
I/O 1 PC25
GPIO Only
I/O
2
PC24
GPIO Only
I/O
3
PC20
GPIO or SPI1_NPCS3
I/O 4 PC19
GPIO or SPI1_NPCS2
I/O 5 PC18
GPIO or SPI1_NPCS1
I/O 6 PC17
GPIO Only
I/O
7
PC15
GPIO Only
I/O
8
PC14
GPIO Only
I/O
9
PC13
GPIO Only
I/O
10
PC12
GPIO Only
I/O
11
PC10
GPIO Only
I/O
12
PC9
GPIO Only
I/O
13
PC5
GPIO or SPI1_NPCS1
I/O
14
PC3
GPIO or AD3 or SPI1_NPCS3
I/O
15
PC2
GPIO or AD2 or PCK0
I/O
16
PC1
GPIO or AD1 or PCK0
I/O
17
PC0
GPIO or AD0
I/O
18
PB31
GPIO or PCK1
I/O
19
PB30
GPIO or PCK0
I/O
20
PB21
GPIO or RF0
I/O
21
PB20
GPIO or RK0
I/O
2.6.2.2. Serial Port LED
Operation description
2.6.2.3. GPIO LED
Eddy-S4M Provide max 34ea GPIO port.
Page 63

63
22
PB19
GPIO or RTD0 or TIOB5
I/O
23
PB18
GPIO or TD0 or TIOB4
I/O
24
PB17
GPIO or TF0 or TCLK4
I/O
25
PB16
GPIO or RxD5 or TCLK3
I/O
26
PB13
GPIO or RxD5
I/O
27
PB12
GPIO or TxD5
I/O
28
PB3
GPIO or SPI1_NPCS0 or TIOA5
I/O
29
PB2
GPIO or SPI1_SPCK
I/O
30
PB1
GPIO or SPI1_MOSI or TIOB3
I/O
31
PB0
GPIO or SPI1_MISO or TIOA3
I/O
32
PA30
GPIO Only
I/O
33
PA22
GPIO Only
I/O
34
PA5
GPIO Only
I/O
Symbol
Parameter
Conditions
Min
Typ
Max
Units
Io
Output Current
PA0-PA31 PB0-PB31 PC0-
PC3
16
PC4 - PC31 in 3.3V range
2*
mA
PC4 - PC31 in 1.8V range
4
Eddy DK Programmer Guide
PIO line has high-drive current capable so that can drive about 16mA except PC4-PC31(2mA).
(41.2 DC characteristics of CPU Datasheet, Refer to bellow)
AT91SAM9260 DC Characteristics
* Since Eddy-S4M v2.1 is 3.3V range, PC4-PC31 PIO can drive 2mA.
Page 64

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
64
Pin
Signal
Description
1
TXD+
Physical transmit or receive signal (+ differential)
2
TXD-
Physical transmit or receive signal (- differential)
3
RXD+
Physical transmit or receive signal (+ differential)
6
RXD-
Physical transmit or receive signal (- differential)
LED
Description
Left Green
LAN Connection Speed
Speed
Pin
State
LED Definition
10Base-T
H
OFF
100Base-TX
L
ON
Right Yellow
LAN Connection Status
Speed
Pin
State
LED Definition
No Link
H
OFF
Link L ON
Activity
Toggle
Blinking
2.6.2.4. J10 : Ethernet
Since there is KSZ8041NL PHY in Eddy-S4M module, when integrating Ethernet, just connect RJ45 in
which transformer located
WARNING : When you use RJ45 which has transformer in its internal circuit, it is possible to each product
doesn’t have equal PIN spec. Therefore, you must confirm PIN number
Bellow is KSZ8041NL functions
• Fully compliant to IEEE 802.3u Standard
• Supports MDI/MDI-X auto crossover (Auto-MDI)
• MII interface support
• RMII interface support with external 50MHz system clock
• ESD rating (6kV)
• Built-in 1.8V regulator for core
• Available in 32-pin (5mm x 5mm) MLF® package
Page 65

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
65
Pin
Signal
Description
1
DCD
Data Carrier Detection (Input) (COM Port 1 only)
2
RXD
Receive Data (Input)
3
TXD
Transmit Data (Output)
4
DTR
Data Terminal Ready (Output) (COM Port 1 only)
5
GND
Ground 6 DSR
Data Set Ready (input) (COM Port 1 only)
7
RTS
Request to Send (Output)
8
CTS
Clear to Send (Input)
9
RI
Ring Indicator (Input)
Pin
Signal
Description
1
TXD+
Transmit differential data positive (Output)
2
TXD-
Transmit differential data negative (Output)
3
GND
Ground 4 RXD+
Receive differential data positive (Input)
5
RXD-
Receive differential data negative (input)
2.6.2.5. J17, 18 : COM Port 1 & Port 2
RS232
* COM Port 2 provide only TxD, RxD, RTS, CTS signal.
2.6.2.6. J13, 14 : COM Port 3 & Port 4
RS422 Full Duplex
Page 66

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
66
Pin
Signal
Description
1
TRX+
Transmit/Receive differential data positive
2
TRX-
Transmit/Receive differential data negative
RS485 Half Duplex
J15 : Debug Port
You can confirm debug massage and information of state through debug port.
Environment Configuration
Debug port is configured like below so that you must change serial port (connected with debug port) configuration
like bellow.
- Speed : 115200 bps
- Data bit : 8 bit
- Parity bit : Non Parity
- Stop bit : 1 bit
- Flow control : none
Page 67

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
67
Contact
Polarity
Center (D : 2mm)
5VDC
Outer (D: 6.5mm)
Ground
Pin
Signal
Pin
Signal
1
PA5 2 PA22
3
PA30
4
NC 5 PB0 6 PB1 7 PB2 8 PB3 9 PB12
10
PB13
11
PB16
12
PB17
13
PB18
14
PB19
15
3.3V
16
3.3V
17
PB20
18
PB21
19
PB30
20
PB31
21
PC0
22
PC1
23
PC2
24
PC3
25
PC5
26
PC9
27
PC10
28
PC12
29
PC13
30
PC14
31
GND
32
GND
33
PC15
34
PC17
35
PC18
36
PC19
37
PC20
38
PC24
39
PC25
40
nRESET(IN)
41
RDY#
42
NRST(OUT)
43
TWCK
44
TWD
2.6.2.7. S1 : Power Jack
GPIO Connector pinout
Page 68

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
68
Contact
Polarity
Center (D : 2mm)
5VDC
Outer (D: 6.5mm)
Ground
2.7 Eddy-S4M-JiG v2.1
Eddy-S4M JIG board is test board which enable of user to integrate and test their application with Eddy-S4M. JIG
board include mini connector for joining Eddy-S4M, Ethernet RJ45, USB Host, Power, Reset Switch, and providing
connectors to all Eddy-S4M functions.
2.7.1 J6 : Power Jack
Page 69

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
69
Pin
Signal
Description
1
TXD+
Physical transmit or receive signal (+ differential)
2
TXD-
Physical transmit or receive signal (- differential)
3
RXD+
Physical transmit or receive signal (+ differential)
6
RXD-
Physical transmit or receive signal (- differential)
LED
Description
Left Green
LAN Connection Speed
Speed
Pin
State
LED Definition
10Base-T
H
OFF
100Base-TX
L
ON
Right Yellow
LAN Connection Status
Speed
Pin
State
LED Definition
No Link
H
OFF
Link L ON
Activity
Toggle
Blinking
2.7.2 J1 : Ethernet
Since there is KSZ8041NL PHY in Eddy-S4M module, when integrating Ethernet, just connect RJ45 in
which transformer located
WARNING : When you use RJ45 which has transformer in its internal circuit, it is possible to each product
doesn’t have equal PIN spec. Therefore, you must confirm PIN number
Bellow is KSZ8041NL functions
• Fully compliant to IEEE 802.3u Standard
• Supports MDI/MDI-X auto crossover (Auto-MDI)
• MII interface support
• RMII interface support with external 50MHz system clock
• ESD rating (6kV)
• Built-in 1.8V regulator for core
• Available in 32-pin (5mm x 5mm) MLF® package
Page 70

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
70
Pin
Definition
Description
I/O
PC16
nRESET
Polling Input signal continually from External Reset
key, implement as below with checking the constant
time of "Low."
Less than 5 seconds: General reset function.
More than 5 second: Factory Default function.
IN
J4 J5
Pin
Signal
Pin
Signal
Pin
Signal
Pin
Signal
1
DTxD
2
DRxD
1
LAN_RX+
2
LAN_TX+
3
TxD0#
4
RxD0#
3
LAN_RX-
4
LAN_TX-
5
RTS0
6
CTS0
5
LAN_Speed
6
LAN_LINK
7
DTR0
8
DSR0
7
PA5 8 PA22
9
DCD0
10
RI0 9 PA30
10
NC
11
TxD1#
12
RxD1#
11
PB0
12
PB1
13
RTS1
14
CTS1
13
PB2
14
PB3
15
3.3V
16
3.3V
15
5V
16
5V
2.7.3 J2 : USB Host
J2 is connected to USB HUB ControllerEddy-S4M in Eddy-S4M. Bellow is its PIN spec
2.7.4 RESET switch
2.7.5 J4, 5 : Expansion Header
Provide most function of eddy-S4M with pin connector.
You can confirm the function with direct conjunction to Eddy-S4M-DK.
Page 71

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
71
17
P3_TX+
18
P3_TX-
17
PB12
18
PB13
19
P3_RX+
20
P3_RX-
19
PB16
20
PB17
21
P4_TX+
22
P4_TX-
21
PB18
22
PB19
23
P4_RX+
24
P4_RX-
23
PB20
24
PB21
25
DDM
26
DDP
25
PB30
26
PB31
27
DM2
28
DP2
27
PC0
28
PC1
29
DM3
30
DP3
29
PC2
30
PC3
31
GND
32
GND
31
GND
32
GND
33
DM4
34
DP4
33
PC5
34
PC9
35
SDDATA0
36
SDDATA1
35
PC10
36
PC12
37
SDDATA2
38
SDDATA3
37
PC13
38
PC14
39
SDCMD
40
SDCLK
39
PC15
40
PC17
41
SDCDN
42
SDWP
41
PC18
42
PC19
43
TWCK
44
TWD
43
PC20
44
PC24
45
RDY#
46
nRESET(IN)
45
PC25
46
NRST(OUT)
Page 72

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
72
2.8 Eddy-WiFi v3.0
(* Eddy-WiFi v2.1 is not compatible. please check previous manual.)
Linking to Eddy-CPU and Eddy-S4M, Eddy-WiFi module enables to use various types of serial device (Security
equipment, telecommunications device, modem, data output devices, industrial instruments etc.) through
wireless LAN. Eddy-WiFi module supports IEEE 802.11b/g/n.
For application development, please refer to WiFi.c, the source code for Eddy-WiFi module.
Page 73

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
73
LEFT
Description
RIGHT
Description
1
NA
1
NA
2
NA
2
NA
3
NA
4
NA
5 VCC(3.3V)
6 VCC(3.3V)
7 USB Host Data(-)
8 USB Host Data(+)
9
NA
10
NA
11
H/W Reset
12
Ground
13
Ground
14
NA
15
NA
3
NA
16
NA
4
NA
17
NA
18
NA
Page 74

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
74
2.9 Eddy-BT v2.1
Eddy-BT module is based on Bluetooth 2.0 and supports communication distance of up to 1,000m. Linking to Eddy-
CPU and Eddy-S4M, Eddy-BT module enables communication with various types of Bluetooth device in Bluetooth
method. Eddy-BT module‘s communication interface supports serial method. To connect to Eddy-CPU, Eddy-S4M,
it uses 4th serial port.
Since it is not considered to use Eddy-BT in Eddy‘s operating environment, it can lose data in case of using HW Flow
Control. (4th port is composed to support RS422 or RS 485. Since it uses RTS/CTS signal line in Auto Toggle method,
it can not be used for HW flow control of RS232.)
To use Eddy-BT right, please refer to test_bluetooth.c, the sample source code.
Page 75

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
75
LEFT
Description
RIGHT
Description
1
NA
1 NA 2 NA
2 NA
3
NA
3 NA
4
VCC(3.3V)
4 NA
5
Factory Reset
5 VCC(3.3V)
6
UART TXD
6 VCC(3.3V)
7
UART RXD
7 NA
8
UART RTS
8 NA
9
UART CTS
9 NA
10
Pairing Signal
10
NA
11
H/W Reset
11
H/W Reset
12
NA
12
Ground
13
NA
13
Ground
14
Ground
14
NA
15
Ground
15
NA
16
Ground
16
NA
17
NA
18
NA
Page 76

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
76
Pin
Signal
Pin
Signal
Pin
Signal
Pin
Signal
1
LAN_RX+
2
LAN_TX+
63
PB8
64
PB9
Key Key
65
PB10
66
PB11
3
LAN_RX-
4
LAN_TX-
67
PB12
68
PB13
5
LAN_Speed
6
LAN_LINK
69
DRXD
70
DTXD
7
FPG
8
RDY#
71
PB16
72
PB17
9
3.3V
10
GND
73
PB18
74
PB19
11
D0
12
D1
75
PB20
76
PB21
13
D2
14
D3
77
PB22
78
PB23
15
D4
16
D5
79
PB24
80
PB25
17
D6
18
D7
81
PB26
82
PB27
19
D8
20
D9
83
PB28
84
PB29
21
D10
22
D11
85
PB30
86
PB31
23
D12
24
D13
87
3.3V
88
GND
25
D14
26
D15
89
PC0
90
PC1
27
NRD
28
NWE
91
PC2
92
PC3
29
3.3V
30
GND
93
PC5
94
PC8
31
A0
32
A1
95
PC9
96
PC10
33
A2
34
A3
97
PC12
98
PC13
35
A4
36
A5
99
PC14
100
PC15
37
A6
38
A7
101
nRESET
102
PC17
39
A8
40
A9
103
PC18
104
PC19
2.10 Eddy-CPU/mp v2.5
Eddy-CPU/mp V2.5 Mini PCI Card Type III System Connector Pinout(J3)
Page 77

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
77
41
A10
42
A11
105
PC20
106
PC21
43
A12
44
A13
107
PC22
108
PC23
45
A14
46
A15
109
3.3V
110
GND
47
3.3V
48
GND
111
GND
112
PC26
49
PA4
50
PA22
113
TWCK
114
TWD
51
PA5
52
PA30
115
DDP
116
DDM
53
PA31
54
NRST
117
HDPA
118
HDPB
55
PB0
56
PB1
119
HDMA
120
HDMB
57
PB2
58
PB3
121
NAND_OE
122
A21
59
PB4
60
PB5
123
NAND_WE
124
A22
61
PB6
62
PB7
J2
J1
Pin
Signal Name
Pin
Signal Name
1
PB0
2
PB1
1
NC
3
PB2
2
NC 4 PB3
3
3.3V
5
3.3V
4
3.3V
6
3.3V
5
PC25 / BT_Factory
7
BHDM, USB Host Data(-)
6
PB10 / TXD3
8
BHDP, USB Host Data(+)
7
PB11 / RXD3
9
PA31 / TXD4
8
PC8 / RTS3
10
PA30 / RXD4
9
PC10 / CTS3
11
NRST
10
PC24 / BT_MODE
12
GND
11
NRST
13
GND
12
GND
14
PA9 / WPID0
13
GND
15
PC6 / WPID1
14
NC
16
PC7 / WPID2
15
NC
17
NC
16
NC
18
NC
Page 78

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
78
Pin
Signal
Pin
Signal
Pin
Signal
Pin
Signal
1
LAN_RX+
2
LAN_TX+
63
PB8
64
PB9
Key Key
65
PB10
66
PB11
3
LAN_RX-
4
LAN_TX-
67
PB12
68
PB13
5
LAN_Speed
6
LAN_LINK
69
DRXD
70
DTXD
7
FPG
8
RDY#
71
PB16
72
PB17
9
3.3V
10
GND
73
PB18
74
PB19
11
D0
12
D1
75
PB20
76
PB21
13
D2
14
D3
77
PB22
78
PB23
15
D4
16
D5
79
PB24
80
PB25
17
D6
18
D7
81
PB26
82
PB27
19
D8
20
D9
83
PB28
84
PB29
21
D10
22
D11
85
PB30
86
PB31
23
D12
24
D13
87
3.3V
88
GND
25
D14
26
D15
89
PC0
90
PC1
27
NRD
28
NWE
91
PC2
92
PC3
29
3.3V
30
GND
93
PC5
94
PC8
31
A0
32
A1
95
PC9
96
PC10
33
A2
34
A3
97
PC12
98
PC13
35
A4
36
A5
99
PC14
100
PC15
37
A6
38
A7
101
nRESET
102
PC17
39
A8
40
A9
103
PC18
104
PC19
41
A10
42
A11
105
PC20
106
PC21
U5 : SDRAM
U1 : AMR9
(400MHz)
U4 : Data Flash
J1,J2 : WiFi
Connector
J3 : mini PCI Slot
U7 : 1.0V Regulator
(Bottom)
U6 : 10/100 PHY
2.11 Eddy-CPU/mp 32bit v2.5
Eddy-CPU/mp V2.5 Mini PCI Card Type III System Connector Pinout(J3)
Page 79

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
79
43
A12
44
A13
107
PC22
108
PC23
45
A14
46
A15
109
3.3V
110
GND
47
3.3V
48
GND
111
GND
112
PC26
49
PA4
50
PA22
113
TWCK
114
TWD
51
PA5
52
PA30
115
DDP
116
DDM
53
PA31
54
NRST
117
HDPA
118
HDPB
55
PB0
56
PB1
119
HDMA
120
HDMB
57
PB2
58
PB3
121
NAND_OE
122
A21
59
PB4
60
PB5
123
NAND_WE
124
A22
61
PB6
62
PB7
J2
J1
Pin
Signal Name
Pin
Signal Name
1
PB0
2
PB1
1
NC 3 PB2
2
NC
4
PB3
3
3.3V
5
3.3V
4
3.3V
6
3.3V
5
PC25 / BT_Factory
7
BHDM, USB Host Data(-)
6
PB10 / TXD3
8
BHDP, USB Host Data(+)
7
PB11 / RXD3
9
PA31 / TXD4
8
PC8 / RTS3
10
PA30 / RXD4
9
PC10 / CTS3
11
NRST
10
PC24 / BT_MODE
12
GND
11
NRST
13
GND
12
GND
14
PA9 / WPID0
13
GND
15
PC6 / WPID1
14
NC
16
PC7 / WPID2
15
NC
17
NC
16
NC
18
NC
Page 80

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
80
Note
All material related to Eddy including documentation, reference sources and utilities are periodically
updated to www.embeddedmodule.com without prior notice. Please visit and download latest
updates from the site.
Filesystem_2.1.x,
firmware
ramdisk
src
tools
root
Eddy_APPs
Open Source
Busybox
Dropbear
snmp
.
.
vsftpd
include
SB_APIs
web
htdocs
cgi
Chapter 3. Development Environment
This chapter explains the process of application programming and other important notes.
SDK‘s folder structures are as follows.
3.1 Source code folder structure
Firmware Folder
Boot Loader, kernel, filesystem, image are stored.
Ramdisk Folder
Filesystem images are created here
root: Linux Filesystem for Eddy is stored.
Tools Folder
Tools used for creating image files is stored.
Src Folder
Source codes of applicatons in Eddy are stored.
Please refer Chapter4. Compiling Application for the detail description of src folder.
Eddy-APPs folder contains the source code of the basic application.
Page 81

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
81
Windows
Linux
Windows XP SP2
Windows 2000
Windows 2003
Red Hat 9.0
Fedora Core 4, 5, 6
SUSE Linux Enterprise Server 10.2
Ubuntu Linux 6.x, 7.x
Debian Linuv 4.0
CentOS 4.5
Asianux edition 3
Other folders contain open sources for Eddy applications.
3.2 Language
Eddy-DK application should be composed with C language. All example source codes provided are composed in C
language. You can use more than one source file if you are using C programming Language. If you are familiar with
programming with ANSI C, there will be no difficulties creating applications for Eddy.
3.3 Development Environment
Eddy DK requires Windows or Linux host system.
Officially supported Oss are as follows.
3.4 Installing on Windows OS
This chapter will describe how to install Eddy Development Environment on Windows host.
The explanation of this manual based on Windows XP.
To establish Eddy‘s integrated development environment, LemonIDE, please refer to ‚LemonIDE_User_Guide‛
for further instructions.
Page 82

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
82
Select ‚Install from Local Folder‛ and click
‚Next‛.
3.5 Installation of Cygwin
To execute LemonIDE on Windows hosts, some of libraries from Linux system are required.
Cygwin is a virtual Linux program for Windows. To install Cygwin, please refer to Cygwin-Setup.zip in SDK/Windows
folder of Eddy DK CD. After unzipping this file in Windows PC, run Setup.exe file.
Page 83

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
83
Select installation folder as ‚c:\cygwin‛.
Select a folder which Cygwin-Setup.zip is
unzipped. .
If it is unzipped in C:\cygwin-Setup folder,
select ‚c:\cygwin-setup‛ folder..
Select the package to install.
Only select ‚Devel‛ as left picture.
Make sure the option changed to ‚Install‛
from ‚Default:.
Page 84

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
84
3.6 Configuration of Windows Environment Variables
Path should be added in order to refer required Eddy libraries in Windows environment.
Select ‚Desktop‛ ‚My Computer‛ Right click ‚Properties‛ select ‚Advanced‛ tab click
‚Environment Variables‛.
Select Path from System Variable and add the following line on the very beginning.
C:\cygwin\bin;
3.7 Installation of Toolchain
Toolchain compiles source codes composed on Windows environment and make it executable on the target, Eddy.
Eddy. Toolchain installation file, ‚toolchain-windows-arm-411.tgz‛, can be found under SDK/Windows folder in
Eddy DK‘s CD. Copy the file to the root folder of ‚C:‛, and unzip the file from Windows command line as
below.
Toolchain should be installed to ‚c:\cygwin\opt\lemonix\cdt‛.
Note that the command is case-sensitive.
Page 85

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
85
3.8 Installation of Eddy DK Source
Install Eddy DK Source. DK Source file, ‚filesystem_2.x.x.x.tar.gz‛, can be found under SDK folder of Eddy DK
‘s CD. Copy the file to the root folder of ‚C:‛, and unzip the file from Windows command line as below.
DK Source should be installed to c:\eddy_DK_2xx‚.
Note that the command is case sensitive.
3.9 Installing on Linux
This chapter will describe how to install Eddy Development Environment on Linux host.
The explanation of this manual based on Fedora Core 5.
To establish Eddy‘s integrated development environment, LemonIDE, please refer to ‚LemonIDE_User_Guide‛
for further instructions.
Page 86

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
86
Note
Carry out all install procedures under the super user privileges.
Example below assumes that CDROM is mounted on /mnt/cdrom
# cd /
# tar -zxvf /mnt/cdrom/SDK/linux/lemonide*.tar.gz -C /
[root@localhost eddy-DK_2xx]# ls -al
Total 32
drwxr-xr-x 6 shlee work 4096 Nov 26 14:43 .
drwxrwxr-- 26 shlee work 4096 Nov 30 21:25 ..
drwxr-xr-x 4 shlee work 4096 Noc 26 14:46 src
-rwxr-xr-x 1 shlee work 2822 Nov 26 14:43 Env.sh
-rwxr-xr-x 1 shlee work 171 Nov 26 14:43 Make.check
drwxr-xr-x 2 shlee work 4096 Nov 29 17:50 firmware
drwxr-xr-x 5 shlee work 4096 Nov 29 17:50 ramdisk
drwxr-xr-x 4 shlee work 4096 Nov 26 14:47 tool
# pwd
/home/shlee
# tar -zxvf filesystem_2.1.x.x.tar.gz
3.10 Installation of Toolchain
Toolchain compiles source codes composed on Linux environment and make it executable on the target, Eddy.
Toolchain install file, ‚lemonide_linux_10x.tar.gz‛, can be found under SDK/linux folder in Eddy DK‘s CD.
Toolchain should be installed to /opt/lemonix.
Note that the command is case sensitive.
If CDROM is mounted on a different location, path displayed below will bear difference.
3.11 Installation of Eddy DK Source
Install the entire source of Eddy DK. Eddy DK Source file, ‚Filesystem_2.x.x.x.tar.gz‛, can be found under SDK
folder on Eddy DK‘s CD.
Install Eddy DK Source as shown below. The eddy_DK_2xx folder will be created after the installation.
Unzip the file. If Eddy_DK_2xx folder is created, the installation is completed. The below shows the contents of
Eddy_DK_2xx folder.
Page 87

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
87
# rm –rf filesystem_2.1.x.x ; Removal of Eddy DK Source
# rm -rf /opt/Lemonix ; Removal of Eddy ToolChain
3.12 Removing Development Environment
Development Environment can be removed by simply deleting the folder where installed files are located.
3.13 Removing Windows Development Environment
Delete the folders where DK Source and Cywin are installed.
3.14 Removing Linux Development Environment
Page 88

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
88
Folder Name
Description
busybox-1.5.0
Linux Utility containing basic commands for the shell
dropbear-0.50
SSH (Secure Shell) Server
gdbserver
Remote debugging program for LemonIDE
(Only executable file provided.)
mtd-util
Management program for Mtd
openssl-0.9.7c
OpenSSL Library (SSL type)
matrixssl-1-8-3
Matrixssl program (SSL type)
thttpd-2.25b
HTTP Server
vsftpd-2.0.5/
FTP Server
ddns-1.8
DDNS Server
ethtool-6
Ethernet based network testing program
netkit-ftp-0.18
ftp client
target-agent
Program helps to upload, download and execute user‘s programs,
linked with LemonIDE. The source code not provided.
Net-snmp-5.4.1
SNMP V1/V2/V3 program
Iptables-1.3.7
Bridge program for NAT function of LAN port
RT73
WiFi Device Driver
Wireless_tools.29
Wireless support Tool Applications
Wpa_supplicant-0.6.9
Wireless support Tool Applications
8712_linux_v2.6
RTL-8712 Device Driver
Chapter 4. Compiling of Application Program
4.1 Program Type
This chapter explains how to compose application program, load to Eddy to execute and store it to flash memory of
Eddy as a firmware.
Application programs running in Eddy are made of Device Server functions. SystemBase does not provide part of
application source running in Device server. Developers can refer to open source, socket and serial provided as
sample source. Since these are optimized to enable application, developers can use its advantage. The followings
are open sources in src folder.
Page 89

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
89
File Name
Description
Source
Availability
eddy.c
Program which runs first when boots up Eddy. It also operates
Eddy as configuration.
O
pinetd.c
Eddy’s most significant program which runs and monitors
subordinate programs.
In case of building new application, if it is registered in this file,
the registered application is running when booted.
O
com_redirect.c
Program which enables to recognize Eddy’s serial port as its
Com port on Windows PC in network.
X
tcp_client.c
Program which connects to server and exchanges data between
serial port and socket.
X
tcp_server.c
Program which waits for socket connection and exchanges data
between serial port and socket.
X
detect.c
Program that interworks with Portview’s detector.
X
Portview.c
Agent of NMS program for Windows, Portview, provided by
SystemBase
X
tcp_broadcast.c
As a multi TCP server function, it supports client connection up
to 5 and broadcasts serial data to the whole client.
X
tcp_multiplex.c
As a multi TCP server function, it supports client connection up
to 5 and transmits serial data to each client.
X
udp.c
UDP server and client program which exchanges data between
UDP socket and serial port.
X
wifi.c
WiFI Operating Source
This sample source reads Config file of Flash and runs WiFi as
the registered setting.
O
test_bluetooth.c
Bluetooth Application Sample Source
Sample source of Eddy-BT module connected to Eddy-CPU,
Eddy-S4M.
O
test_read_config.c
Flash Configuration Read/Write sample source
O
test_serial.c
Serial port application sample source
This sample source opens port number appointed to Argment
and retransmits the received data to the other socket.
O
test_serial_to_lan-1.c
serial to lan communication application sample source
This sample source reads Config file information of Flash and
waits for TCP socket connection. After connection, it exchanges
data between serial and socket port.
O
test_serial_to_lan-2.c
serial to lan communication application sample source
This sample source reads Config file information of Flash and
tries TCP connection.to the registered server. After connection,
it exchanges data between serial and socket port.
O
In case you make new application program, refer to sample source in Eddy_APPs folder. Among the programs in
Eddy_APPs folder, source for device server application is not provided. So, refer to source code for various
purposes provided as sample.
Page 90

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
90
test_tcp_server.c
TCP socket communication application sample source
This sample source waits for TCP connection to socket number
appointed to argment and retransmits the received data to the
other socket.
O
test_tcp_client.c
TCP socket communication application sample source
This sample source tries connection to IP address and socket
number of the server appointed to argment. After connection, it
retransmits the received data to the other socket.
O
test_udp_server.c
UDP socket communication application sample source
This sample source waits for UDP connection to socket number
appointed to argment and retransmits the received data to the
other socket.
O
test_udp_client.c
UDP socket communication application sample source
This sample source tries UDP connection to IP address and
socket number of the server appointed to argment. After
connection, it retransmits the received data to the other socket.
O
def.c
Eddy Configuration program
Program which links to telnet and enables configuration of Eddy
O
upgrade.c
Firmware update program
O
testdk.c
Eddy-DK, Eddy-S4M-DK Test Program
O
ddns_agent.c
Program that delivers Eddy IP information to DDNS server
O
test_gpio_led.c
GPIO LED Test Program (Only Eddy-DK)
O
test_gpio_pin.c
GPIO Pin Test Program (Only Eddy-DK)
O
test_adc.c
ADC (Analog Disgital Converter) Test Program
O
test_sio.c
Serial Port Test Program
O
test_rtc.c
RTC (Real Time Clock) Test Program
O
test_dio.c
DIO (Digital Input Output) Test Program
(Only Eddy-DK)
O
test_keypad.c
Key Pad Test Program (Only Eddy-DK)
O
test_mmc.c
SD Memory Test Program
O
test_lcd.c
LCD Test Program (Only Eddy-DK)
O
test_nand.c
NAND Flash Test Program (Only Eddy-DK)
O
test_spi_eeprom.c
EEPROM Test Program linked to SPI interface(Only Eddy-DK)
O
/include
Folder where there is a header file for application
O
/SB_APIs
Library folder in Eddy
X
/web
Html code of web and CGI source folder running in Eddy
O
Page 91

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
91
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
While (1)
{
printf("hello world !!!\n");
sleep (1);
}
}
TARGET = eddy pinetd def ddns_agent \
upgrade portview upgradetftp detect \
tcp_server tcp_client tcp_multiplex tcp_broadcast \
udp rt_test hello_world
udp : udp.o
rm -f $@
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) $(LDFLAGS) $(IFLAGS) -o $@ $ $@.o $(LIBS)
$(STRIP) $@
Hello_World : Hello_World.o
Rm -f $@
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) $(LDFLAGS) $(IFLAGS) -o $@ $ $@.o
$(STRIP) $@
4.2 Writing Application Program
This chapter shows how to write an application program for Eddy.
First, create a ‚hello_world.c‛ file under the ‚scr/Eddy_APPs‛ directody.
4.3 Writing Makefile
To compile an application program, compile information of the application program has to be registered on the
Eddyy_APPs/Makefile folder. The below is description of ‚Makefile‛ under folder of src/Eddy_APPs/.
The picture blow shows the environment setting area for an application program compile.
Add a name under the ‚TARGET‛ highlighted as red, and register to the compile environment.
Page 92

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
92
C:\eddy_DK_2xx[\src/Eddy_APPs> make hello_world
/opt/lemonix/cdt/bin/arm-linux-gcc -O2 -g -Wall -Wno-nonnull -c -o Hello_World.o Hello_World.c
/opt/lemonix/cdt/bin/arm-linux-gcc -L/opt/lemonix/cdt/lib -L/opt/lemonix/cdt/bin Hello_World.o -o
Hello_World
C:\eddy_DK_2xx[\src/Eddy_APPs>
C:\eddy_DK_2xx[\src/Eddy_APPs> ls
Hello_world SB_APIs def.c eddy kt.c pinetd portview.o
tcp_client.c tcp_client tcp_multiplex.o . . .
[shlee@localhost Eddy_APPs]$make hello_world
/opt/lemonix/cdt/bin/arm-linux-gcc -O2 -g -Wall -Wno-nonnull -c -o hello_world.o hello_world.c
/opt/lemonix/cdt/bin/arm-linux-gcc -L/opt/lemonix/cdt/lib -L/opt/lemonix/cdt/bin hello_world.o
…………
[shlee@localhost Eddy_APPs]$ ls
Hello_World* SB_APIs/ def.c* eddy* kt.c pinetd* portview.o
server* tcp_client* tcp_multiplex.o tcps* upgrade* . . .
4.4 Application Program Compile
Compile the application program to execute on Eddy after registering the compile environment to the ‚Makefile‛.
4.5 Compiling on Windows
Enter ‚make‛ command through cmd(command prompt) on the folder where ‚Makefile‛ is located. As shown
below, if a compile is successfully completed, execution file named ‚Hello_World‛ would be created. Of course,
as this file was cross-compiled, it can not run on Windows environment. Upload this file to Eddy using a FTP to
execute the file on Eddy, (Files uploaded with FTPs will not permanently saved on Eddy.).
This will be further explained on the next chapter, Chpater 5 Creating Firmware.
4.6 Compiling on Linux
To compile a source file on Linux environment, enter ‚make‛ command on the folder where ‚Makefile‛ is
located. As shown below, if a compile is successfully completed, execution file named Hello_World would be
created. Of course, as this file was cross-compiled, it can not run on Linux environment. Upload this file to Eddy
using a FTP to execute the file on Eddy, (Files uploaded with FTPs will not permanently saved on Eddy.).
This will be further explained on the next chapter, Chpater 5 Creating Firmware.
Page 93

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
93
[shlee@localhost Eddy_APPs]$ ftp 192.168.0.223
Name (192.168.0.223:shlee): eddy
331 Please specify the password.
Password:
230 Login successful.
ftp> cd /tmp
ftp> bin
ftp> put hello_world
8914 bytes sent in 0.00027 seconds (3.3e+04 Kbytes/s)
ftp> bye
[shlee@localhost Eddy_APPs]$
4.7 Compiling with LemonIDE
LemonIDE is an IDE(Integrated Development Environment) based on Eclipse platform and provides an intuitive GUI
interface. LemonIDE can be used in both Windows and Linux environments. Source coding, compile, remote
debugging and creating a firmware image can be all carried out with LemonIDE.
Refer to ‚LemonIDE_User_Guide‛ for detailed information.
4.8 Running Application on Eddy
To run an application on Eddy, there are several methods. First method is to convert an application as a firmware
and loads it into the flash memory area and execute. However, this method is not recommended for developing
phase of application, since it is time consuming task. Second method is to load and execution file of an application
to RAM type file system by using the FTP Server on Eddy DK, and execute it from there. This method is suitable for
developing phase of application; however the application loaded to Eddy will be deleted when the power is
disconnected.
The LemonIDE integrated developing environment provides advanced solution. LemonIDE debugging tool supports
the direct transmission of compiled applications to Eddy. By using this tool, the user can execute and check the
result instantly on site.
If you wish to use LemonIDE, please refer to ‚LemonIDE_User_Guide‛.
4.9 Uploading and Executing on Eddy
Connect to Eddy by using FTP.
ID and password for FTP server are same as the one using with telnet connection.
The example below shows how to upload an example file, ‚hello_world‛, to /tmp folder of Eddy on Linux using
FTP.
When uploading a file, ‚bin‛ command must be entered first for binary mode.
For uploading enter ‚put <file name> on the command line.
On Windows environment, use FTP program of Windows on the Command Prompt.
When the transmission is completed, a user can check the file using Telnet terminal connected Eddy.
The file is executable using ‚chmod‛ command; however the mode has to be switched to executable.
Page 94

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
94
# ls
hello_world login.id thttpd.log login.pw
thttpd.pid utmp . . .
#
# chmod 777 hello_world
#
# ./hello_world
Welcome to Eddy !
Welcome to Eddy !
Welcome to Eddy !
Welcome to Eddy !
//<=================================================================
// Here User Application Launching !!
// -----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//
// ex) Task_Launch ("/sbin/hello", argument);
// | |
// | +---- Integer argument
// +--------------- Application name with path
//
//=================================================================>
Task_Launch ("/sbin/hello_world", 0);
signal(SIGCHLD, sig_chld);
After switching to Executable Mode, execute the file by entering ‚/hello_world‛.
To terminate a program, press ‚Ctr‛ and ‚C‛ key simultaneously.
4.10 Execute a file on Booting of Eddy
If auto running is not necessary, you can skip this section.
If the application is successfully executed on Eddy, make a firmware image and load to Flash memory of Eddy to
execute on booting.
Register the application to ‚pinetd.c‛ on the folder of Eddy_APPS.
If ‚printed.c‛ is modified, a user must re-compile it by executing ‚make pinetd‛ as above example of section
4.4.
Page 95

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
95
(NOTE)
Provided DK Sources are Linux based. Some commands are not executable on Windows
environment. To prevent this problem, a suffix, ‚exe‛, has to be added for some utilities after
file name as shown below.
../tool/genext2fs ../tool/genext2fs.exe
../tool/mkimage ../tool/mkimage.exe
IMAGE=ramdisk
FW_NAME = eddy-fs-2.x.x.x.bin Name and Version Info of Firmware Image
FIRMWARE_DIR = ../firmware Folder to store created firmware
install:
#@echo "Making ramdisk image..."
#$(TOOL) -b 8192 -d root -D device_table.txt ramdisk
#../tool/genext2fs -U -b 5110 -d root -D device_table.txt ramdisk
#../tool/genext2fs -U -b 7158 -d root -D device_table.txt ramdisk
#../tool/mkcramfs -q -D device_table.txt root ramdisk
./tool/genext2fs.exe -U -b 10240 -N 1024 -d root -D device_table.txt ramdisk Make size of
Ramdisk to 10,240 K and register the device of Eddy/dev as indicated on Devide_table.txt.
gzip -vf9 ramdisk
est -f ramdisk.gz
./tool/mkimage.exe -A arm -O linux -T ramdisk -C gzip -a 0 -e 0 -n $(FW_NAME) -d ./ramdisk.gz
$(FW_NAME)
test -f $(FW_NAME)
mv $(FW_NAME) $(FIRMWARE_DIR)/
release: Register the desired application to the folder for copying to Eddy
cp -f ../src/Eddy_APPs/hello_world root/sbin
cp -f ../src/Eddy_APPs/eddy root/sbin
Chapter 5. Creating Firmware
On the previous chapter, we explained how to make and compile application program with sample program. This
chapter introduces methods to create a firmware which permanently saves the application into the Eddy module and
apply it to hardware of Eddy.
5.1 How to Create a Firmware
Firmware image can be created on filesystem_2.x.x.x/ramdisk folder.
Modify ‚Makefile‛ on filesystem_2.x.x.x/ramdisk folder to create a firmware image.
Version info, required Ramdisk amount and desired application to copy can be set up on the ‚Makefile‛.
Page 96

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
96
cp -f ../src/Eddy_APPs/com_redirect root/sbin
cp -f ../src/Eddy_APPs/tcp_server root/sbin
cp -f ../src/Eddy_APPs/tcp_client root/sbin
cp -f ../src/Eddy_APPs/tcp_broadcast root/sbin
cp -f ../src/busybox-1.5.0/busybox root/bin
cp -f ../src/dropbear-0.50/dropbear root/usr/local/sbin
cp -f ../src/dropbear-0.50/dropbearkey root/usr/local/sbin
cp -f ../src/ethtool-6/ethtool root/usr/local/sbin
cp -f ../src/net-snmp-5.4.1/agent/snmpd root/usr/local/sbin
[shlee@localhost ramdisk]$ make release
.
.
[shlee@localhost ramdisk]$ make install
.
.
[shlee@localhost ramdisk]$ ls ../firmware
-rwxr-xr-x -----------------------------------------eddy-bl-2.x.x.x.bin
-rwxr-xr-x -----------------------------------------eddy-bs-2.x.x.x.bin
-rwxr-xr-x -----------------------------------------eddy-os-2.x.x.x.bin
-rwxr-xr-x -----------------------------------------eddy-fs-2.x.x.x.bin
.
[shlee@localhost ramdisk]$ make release
.
.
[shlee@localhost ramdisk]$ make install
.
.
List of task on the ‚Makefile‛ options are as follows;
Make release ; Copy modules registered on the release to Ramdisk area.
Make install ; Create a Filesystem to a firmware image for using on Eddy.
If the modification of ‚Makefile‛ is completed, execute ‚make release and ‚make install‛ in turns and create a
Firmware image.
Created firmware is stored on the ‚FIRMWARE_DIR‛ folder stated on the ‚Makefile‛.
On Windows, use cmd(command prompt) to carry out procedures explained on Linux.
Makefile options are as follows.
Make release ; copy module in release to ramdisk area
Make cfg ; create firmware image of Eddy enviromental files in ramdisk/flash
Make install ; create a firmware image of Eddy’s Filesystem
If changes to Makefile are complete, use ‚make install‛ command to create firmware image.
Firmware will be created in ‚FIRMWARE_DIR‛ folder defined in Makefile.
On Windows, use cmd(command prompt) to carry out procedures explained on Linux.
Page 97

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
97
[shlee@localhost ramdisk]$ ls ../firmware
-rwxr-xr-x -----------------------------------------eddy-bl-2.x.x.x.bin
-rwxr-xr-x -----------------------------------------eddy-bs-2.x.x.x.bin
-rwxr-xr-x -----------------------------------------eddy-os-2.x.x.x.bin
-rwxr-xr-x -----------------------------------------eddy-fs-2.x.x.x.bin
.
FTP
Upload a firmware image using FTP program, and execute the upgrade
command to save it to the Flash memory using Telnet.
Web Browser
Connect to Web server of Eddy and save a firmware to the Flash memory.
Please refer Eddy_User_Guide for detail information.
Boot Loader
Use the boot loader which operates on booting to save a firmware through
the debugging port of Eddy DK board.
Please refer ‚the chapter 9: System Recovery‛ for detail.
USB
Use USB client port of Eddy DK board to upload a firmware.
Please refer ‚the chapter 9: System Recovery‛ for detail.
[shlee@localhost firmware]$ ftp 192.168.0.223
Connected to 192.168.0.223.
Name (192.168.0.223:shlee): eddy
331 Please specify the password.
Password:
230 Login successful.
ftp> cd /tmp
250 Folder successfully changed.
ftp> bin
200 Switching to Binary mode.
ftp> put eddy-fs-2.1.x.x.bin
local: eddy-fs-2.x.x.x.bin remote: eddy-fs-2.x.x.x.bin
227 Entering Passive Mode (192,168,0,223,195,50)
150 Ok to send data.
226 File receive OK.
2104287 bytes sent in 0.47 seconds (4.3e+03 Kbytes/s)
ftp> bye
As shown in the picture above, a new firmware file ‚eddy-fs-2.x.x.x.bin‛ has been created. Now you have to
upload the firmware image to Eddy via Web or FTP, save it to Eddy’s flash memory, and reset Eddy. Then Eddy
will run as the loaded firmware settings.
5.2 Firmware Upgrade
Upload created firmware file to Eddy and save on the Flash Memory.
Eddy provides four ways of upgrading method.
This section explains how to upload a firmware using a FTP.
On Windows, FTP can be used in cmd(command prompt) to carry out upload process.
Upload the created firmware, ‚eddy-fs-2.x.x.x.bin‛, to the /tmp folder of Eddy, using an FTP.
Page 98

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
98
221 Goodbye.
[shlee@localhost firmware]$
# pwd
/tmp
# ls eddy-fs-2.x.x.x.bin
eddy-fs-2.x.x.x.bin
#
# upgrade eddy-fs-2.x.x.x.bin
FileSystem Erase ... 2388341 Bytes
FileSystem Write ... eddy-fs-2.x.x.x.bin, 2388341 Bytes
2388341 (2388341 bytes)
Flash Write OK
Flash Verify OK
…
Eddy login: eddy
Password:
# cd /sbin
# ls
hello_world ifconfig nameif switch_root
com_redirect ifdown pinetd sysctl
…
# ps -ef
PID USER COMMAND
1 root init
2 root [posix_cpu_timer]
3 root [softirq-high/0]
.
.
xx root /sbin/hello_world 1
Use Telnet to check ‚eddy-fs-2.x.x.x.bin‛ file is in the /tmp folder.
Use ‚upgrade eddy-fs-2.x.x.x.bin‛ command to update the firmware.
In order for the updated firmware to take effect, you need to reboot the module.
After rebooting you can see the sample program running using Telnet program as shown below.
Execution result of application program only output to the console port of Eddy. The console is a debug port of
Eddy DK board and only execution result of application program is generated.
The result can be seen on a computer screen using a serial emulator program such as hyper-terminal on Windows
by connecting the debug port to PC and setting communication speed to 115K, None, 8, 1.
Page 99

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
99
Welcome to Eddy !
Welcome to Eddy !
Welcome to Eddy !
Welcome to Eddy !
Welcome to Eddy !
Welcome to Eddy !
Welcome to Eddy !
Page 100

Eddy DK Programmer Guide
100
SB_GetTick
Function
Returns time measured after Eddy has been booted in msec.
Format
Unsigned long SB_GetTick (Void);
Parameter
None
Returns
0 ~ 4,294,967,295
Notice
Returned value is system tick counter in msec unit.
After it reaches the maximum value 0xffffffff of unsigned long type, it
starts from zero again - which is about period of 50 days.
SB_msleep
Function
Delays in msec unit.
Format
void SB_msleep (int msec);
Parameter
msec
Configure delay time in msec unit.
Chapter 6. Library Introduction
This chapter introduces useful libraries and API functions that are applicable with Eddy-Serial DK.
6.1 Introduction
All the functions introduced in this chapter are all APIs included in SB_APIs.a of /src/Eddy_APPs/SB_APIs folder. You
also need to mention this library in the Makefile. All sample source codes accompanied with Eddy-DK use this library,
and you can see the source codes and Makefile for more information.
6.2 Makefile
Library is in /src/Eddy_APPs/SB_APIs/ folder, as a form of SB_API.a.
You need to specify in the Makefile in order to use this library, so please refer to the Makefile inside /src/Eddy_APPs/
folder.
6.3 System functions
Timer and delay functions needed for making application program.
 Loading...
Loading...