Page 1

Date
Description
4/29/2011
First release supporting Windows (big and WinMo), Android and
BlackBerry
6/16/2011
Added iOS details
9/16/2011
ScanApiHelper support for iOS, new Error code
ESKT_OUTDATEDVERSION
10/19/2011
Added more information about xCode integration
11/04/2011
Added Recommendations chapter
12/02/2011
Adding more information regarding Android permissions in
Recommendations for Android.
01/06/2012
Re-ordered the paragraph, reworded the Concept paragraph, and
modified the IDE integration for Xcode.
06/19/2012
Adding the properties, and the description of the SoftScan feature.
09/19/2012
Adding the missing symbology ids (USPS Intel. and DPM).
12/06/2012
Adding the Android permission
android.permission.BLUETOOTH_ADMIN that is required.
01/15/2013
Added new statistical counter names
01/18/2013
Added 2 new error codes for determining why a COM port can’t be
opened
02/25/2013
Minor editorial updates based on feedback
05/29/2013
Update kSktScanPropIdTimersDevice
ScanAPI Reference
History
Page 2

Socket ScanAPI Reference
06/03/2013
Update the framework requirements for iOS ScanAPI RedLaser
06/3/2013
Correct all endian references to ‘big-endian’
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 2/152
Page 3

Socket ScanAPI Reference
6/2012 Document# 6410-00319 A
COPYRIGHT NOTICE
Copyright © 2012 Socket Mobile, Inc. All rights reserved.
Socket, the Socket logo, Battery Friendly, Socket Bluetooth Cordless Hand Scanner, and SocketScan are trademarks or
registered trademarks of Socket Mobile, Inc. Bluetooth and the Bluetooth logos are registered trademarks owned by Bluetooth
SIG, Inc., U.S.A. and licensed to Socket Mobile, Inc. All other brand and product names are trademarks of their respective
holders.
The Socket Bluetooth Cordless Hand Scanner includes technology licensed under United States Patent Numbers 5,902,991,
7,429,000 B1 and D526,320 S.
Reproduction of the contents of this manual without the permission of Socket Mobile is expressly prohibited. Please be aware
that the products described in this manual may change without notice. Feel free to contact Socket Mobile at:
Other than the above, Socket Mobile can assume no responsibility for anything resulting from the application of information
contained in this manual.
Please refrain from any applications of the Socket Bluetooth Cordless Hand Scanner that are not described in this manual.
Please refrain from disassembling the Bluetooth Cordless Hand Scanner. Disassembly of this device will void the product
warranty.
You can track new product releases, software updates and technical bulletins by visiting the Socket Mobile website at:
http://www.socketmobile.com.
Socket Mobile, Inc.
39700 Eureka Drive, Newark, CA 94560-4808, USA
+1-510-933-3000
USA/Canada Toll-free: 1-800-552-3300
http://www.socketmobile.com/contact
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 3/152
Page 4

Socket ScanAPI Reference
Table of contents
COPYRIGHT NOTICE ................................................................................................................ 3
1 Scanner connection overview .................................................................................. 7
1.1 Scanner connection information ........................................................................... 7
2 ScanAPI Introduction .............................................................................................. 10
3 SoftScan Feature ....................................................................................................... 11
3.1 Licensing requirements ...................................................................................... 11
3.2 iOS requirements ................................................................................................ 11
3.3 Android requirements ......................................................................................... 12
4 Concept ..................................................................................................................... 12
4.1 ScanAPI object ................................................................................................... 12
4.2 Device object ...................................................................................................... 13
4.3 ScanObject ......................................................................................................... 13
4.4 Using ScanAPI ................................................................................................... 14
4.5 ScanAPI configuration ....................................................................................... 14
4.6 Get or Set a property ........................................................................................ 15
4.7 Example of sending a command ...................................................................... 16
4.8 Handling asynchronous events or completion events .................................. 25
4.9 Termination ...................................................................................................... 25
5 ScanAPI Helper (available for Java, C# and Objective C) ..................................... 26
5.1 Handling the ScanAPI Helper notifications .................................................... 26
5.2 Set ScanAPI Helper notification ....................................................................... 32
5.3 Open ScanAPI Helper ....................................................................................... 32
5.4 Close ScanAPI Helper ....................................................................................... 32
5.5 Scanner arrival .................................................................................................. 32
5.6 Decoded data notification ................................................................................ 33
5.7 Scanner removal ............................................................................................... 33
5.8 Is there a connected Scanner ........................................................................... 34
5.9 Get the list of scanners ..................................................................................... 34
5.10 No Device Connected item ........................................................................... 34
6 IDE Integration ........................................................................................................ 34
6.1 C/C++ Version ................................................................................................... 34
6.2 Java Version ....................................................................................................... 34
6.3 C# Version ......................................................................................................... 36
6.4 Objective C Xcode integration .......................................................................... 36
7 Recommendations ..................................................................................................... 37
7.1 General ............................................................................................................... 37
7.2 Android ............................................................................................................... 37
7.3 iOS ...................................................................................................................... 38
8 Device Connection and Disconnection process .................................................... 38
8.1 Initial Connection ............................................................................................. 38
8.2 Subsequent Connection .................................................................................... 39
8.3 Reconnection ..................................................................................................... 39
8.4 Disconnection.................................................................................................... 39
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 4/152
Page 5

Socket ScanAPI Reference
8.5 Roaming ............................................................................................................. 40
8.6 Socket EZ Pair feature ...................................................................................... 40
9 API Functions ........................................................................................................... 41
9.1 Open Function ................................................................................................... 41
9.2 Close Function ................................................................................................... 46
9.3 Set Function....................................................................................................... 48
9.4 Get Function ...................................................................................................... 53
9.5 Wait Function .................................................................................................... 57
9.6 Release Function ............................................................................................... 60
10 ScanObject ............................................................................................................. 62
11 Asynchronous messages and events .................................................................. 63
11.1 Device Arrival ................................................................................................ 63
11.2 Device Removal ............................................................................................. 63
11.3 Terminate ...................................................................................................... 63
11.4 Set Complete .................................................................................................. 63
11.5 Get Complete ................................................................................................. 64
11.6 Events ............................................................................................................. 64
12 Introduction to Properties ................................................................................... 69
13 ScanAPI object properties ................................................................................... 70
13.1 Property kSktScanPropIdAbort ................................................................... 70
13.2 Property kSktScanPropIdVersion ................................................................ 71
13.3 Property kSktScanPropIdInterfaceVersion ................................................ 73
13.4 Property kSktScanPropIdConfiguration ..................................................... 74
13.5 Property kSktScanPropIdDataConfirmationMode ..................................... 76
13.6 Property kSktScanPropIdDataConfirmationAction ................................... 78
13.7 Property kSktScanPropIdMonitorMode ..................................................... 79
13.8 Property kSktScanPropIdSoftScanStatus ....................................................... 81
14 Device object properties ...................................................................................... 82
14.1 Property kSktScanPropIdVersionDevice .................................................... 82
14.2 Property kSktScanPropIdDeviceType ......................................................... 82
14.3 Property kSktScanPropIdDeviceSpecific .................................................... 84
14.4 Property kSktScanPropIdSymbologyDevice ............................................... 85
14.5 Property kSktScanPropIdTriggerDevice ..................................................... 87
14.6 Property kSktScanPropIdApplyConfigDevice ............................................ 88
14.7 Property kSktScanPropIdPreambleDevice ................................................. 89
14.8 Property kSktScanPropIdPostambleDevice ............................................... 89
14.9 Property kSktScanPropIdCapabilitiesDevice ............................................. 90
14.10 Property kSktScanPropIdChangeIdDevice ................................................. 92
14.11 Property kSktScanPropIdFriendlyNameDevice ......................................... 93
14.12 Property kSktScanPropIdSecurityModeDevice .......................................... 95
14.13 Property kSktScanPropIdPinCodeDevice ................................................... 96
14.14 Property kSktScanPropIdDeletePairingBondingDevice ............................ 97
14.15 Property kSktScanPropIdRestoreFactoryDefaultsDevice ......................... 98
14.16 Property kSktScanPropIdSetPowerOffDevice ............................................ 98
14.17 Property kSktScanPropIdButtonStatusDevice ........................................... 98
14.18 Property kSktScanPropIdSoundConfigDevice ............................................ 99
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 5/152
Page 6

Socket ScanAPI Reference
14.19 Property kSktScanPropIdTimersDevice ................................................... 102
14.20 Property kSktScanPropIdLocalAcknowledgmentDevice ........................ 104
14.21 Property kSktScanPropIdDataConfirmationDevice ................................. 105
14.22 Property kSktScanPropIdBatteryLevelDevice.......................................... 106
14.23 Property kSktScanPropIdLocalDecodeActionDevice ............................... 107
14.24 Property kSktScanPropIdBluetoothAddress ............................................ 108
14.25 Property kSktScanPropIdStatisticCountersDevice .................................. 108
14.26 Property kSktScanPropIdRumbleConfigDevice ....................................... 111
14.27 Property kSktScanPropIdProfileConfigDevice ......................................... 113
14.28 Property kSktScanPropIdDisconnectDevice............................................. 114
14.29 Property kSktScanPropIdDataStoreDevice .............................................. 115
14.30 Property kSktScanPropIdNotificationsDevice.......................................... 116
14.31 Property kSktScanPropIdConnectReasonDevice ..................................... 117
14.32 Property kSktScanPropIdPowerStateDevice ............................................ 118
14.33 Property kSktScanPropIdStartUpRoleSPPDevice .................................... 119
14.34 Property kSktScanPropIdConnectionBeepConfigDevice ......................... 120
14.35 Property kSktScanPropIdFlashDevice ......................................................... 121
14.36 Property kSktScanPropIdOverlayViewDevice ............................................. 122
15 ScanAPI Error handling and definitions ........................................................... 124
15.1 Error codes .................................................................................................. 127
16 Symbologies Enumeration ................................................................................. 129
17 Data confirmation feature ................................................................................. 130
18 Sample handling asynchronous events of ScanAPI ......................................... 131
19 SktScanAPIOwnership (available for Java platforms) ..................................... 138
19.1 Constructor .................................................................................................. 139
19.2 register ......................................................................................................... 140
19.3 unregister .................................................................................................... 142
19.4 askForOwnership ........................................................................................ 143
19.5 claimOwnership .......................................................................................... 144
19.6 releaseOwnership ....................................................................................... 146
19.7 Notification onScanApiOwnershipChange ................................................ 147
20 SoftScan feature ...................................................................................................... 150
20.1 Usage ............................................................................................................ 150
20.2 iOS integration. ............................................................................................. 151
20.3 Android integration ....................................................................................... 152
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 6/152
Page 7

Socket ScanAPI Reference
1 Scanner connection overview
This SDK is designed for use with the Socket CHS 7 series scanners on several
OS platforms including Apple iOS, Android, RIM, Windows Desktop and
Windows Mobile 6.x. The intended usage is to develop a native application that
includes built in support for the Socket 7 series scanners. This SDK gives the full
programmatic access to a connected 7 series scanner to customize the scanner
Symbology and data support, manages scanner feedback messages and
functions or modifies default scanner behavior.
Before beginning the process of implementing the ScanAPI into an application it
is first recommended reading through this intro regarding the connection process
of the scanner as this might answer many questions in regards to how an
application communicates with the scanner.
1.1 Scanner connection information
The connection information below applies mainly to the Android, RIM and
Windows operating systems.
For the iOS platform the connection is simplified based on the host iOS handling
the connection. It is recommended to refer to the readme.rtf file from the ScanAPI
SDK DMG install that is part of the ScanAPI iOS SDK..
1.1.1 Scanner HID mode
The CHS 7 series scanners are shipped by default in HID profile mode and will
display the following friendly name:
For the 7Xi series:
Socket 7Xi [xxxxxx] (where x’s are the last 6 digits of the BD address of the
scanner)
Or for the 7Ci/M/P series:
Socket CHS [xxxxxx]
In this mode the scanner functions as a standard HID keyboard device and can
be tested in this mode as if it is a keyboard.
It will NOT work with an application using ScanAPI.
NOTE: if the scanner in HID mode is discovered and tested it may cause conflicts
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 7/152
Page 8

Socket ScanAPI Reference
with discovering and using the scanner in SPP mode due to the fact that some
devices will cache the name and service information of the device.
Socket recommends that the pairing information is removed by deleting or
unpairing the device using the host device Bluetooth manager before connecting
the scanner in a different mode.
1.1.2 SPP Mode for the SDK
The SPP Mode is the required mode for the Scanner to be able to communicate
with an application using ScanAPI.
The SPP Mode has 2 configurations. One configuration called Acceptor, and
another called Initiator.
In Acceptor configuration, the scanner is discoverable and connectable and
basically waits for a host to connect. The scanner indicates that it is in this mode
by a slow blue LED flashing.
In Initiator configuration, the scanner knows the Bluetooth address of the host to
connect to.
Each time the scanner is powered on in this configuration, it will try to connect to
the host corresponding to the Bluetooth address it has in memory.
The scanner indicates that it is in this mode by a fast blue LED flashing. The
scanner stays in this mode until it successfully connects to the host or after a
2minutes timeout occurs, which it will signal by doing a long beep.
At this point the scanner can be powered off and on to retry to connect to the
host.
1.1.3 Initial connection to iOS host or to any host for a 7Ci,M and P
series
The process of connecting a scanner to an iOS host device or a 7Ci, M and P
scanner to any host device is the same and can be summarized to these simple
steps.
Step 1: The scanner must be in Acceptor mode.
For an iOS device, the scanner can be in configured in Acceptor mode by
scanning a barcode that has the value of “#FNC IOS ACCEPTOR
000000000000#” for a 7Xi or “#FNB00F40002#” for a 7Ci.
For any other host Device (not iOS) the scanner can be configured in Acceptor
mode by scanning a barcode that has the value of “#FNB00F40000#” for a 7 P,M
or Ci series, or “#FNC SPP ACCEPTOR 0000000000#” for a 7Xi series scanner.
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 8/152
Page 9

Socket ScanAPI Reference
The barcode can be a 2D barcode for a 7Xi scanner only.
Step 2: Discover and pair the scanner from the host.
By using the Bluetooth settings of your host device, discover and pair the
scanner. If a PIN code is request use “0000” (4 zeros) and the pairing should
complete.
For iOS host device this is the final step. The scanner can now be used by the
application using ScanAPI.
Step 3: (For all hosts but iOS devices) Instruct the scanner to connect back to the
host by using Socket EZ Pair application.
Once the scanner is configured correctly, it will always try to reconnect back to
the host each time it is powered on or back in range.
1.1.4 Simplified connection process to any host but iOS devices
There is a simplified process that can be used when the host Bluetooth device
address is known either by printing out barcode or by using 7xi with Socket
EzPair.
This process isn’t possible for iOS device as there is no API to retrieve the iOS
Bluetooth address and the iOS devices won’t authorize a scanner to connect
and pair unless the Bluetooth Settings page is displayed on the screen.
The following steps for 7Xi series is as simple as scanning a 2D barcode that has
the value: “#FNC SPP INITIATOR xxxxxxxxxxxx#” with xxxxxxxxxxxx replaced by
the host Bluetooth address, or by scanning out of the Socket EZ Pair screen the
2D barcode.
The same principle for 7 P, M and Ci series scanner, by scanning a Code 128
barcode that has the value: “#FNIxxxxxxxxxxxx#” with xxxxxxxxxxxx replaced by
the host Bluetooth address. NOTE the 7 P, M and Ci series scanner shoud be
first and only once set to SPP mode by scanning the “#FNB00F40000#” Code
128 barcode.
1.1.5 Connection Process integration
For the 7P, M and Ci series scanners there are two methods that canbe used to
configure the scanner to be an initiator to the host device:
Method 1:
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 9/152
Page 10

Socket ScanAPI Reference
Implement the 1D EZ Pair process in your app to select a pre discovered scanner
and configure it to be an initiator to the host device. This process is explained in
paragraph 8.6 Socket EZ Pair feature.
Method 2:
-Manually create an EZ Pair barcode with each host system Bluetooth address
so that the 1D scanner simply needs to scan the barcode to configure it as an
initiator to the host device
For the 7Xi series scanners you can just present the EZ pair barcode as part of
your application setup process.
Either way once that part is done your app just needs to have ScanAPI initialized
and waiting to receive the incoming connection of the scanner.
2 ScanAPI Introduction
ScanAPI delivers an application programming interface (API) to control and
configure Socket Bluetooth Cordless Handled Scanners (CHS) connected to a host
computer.
A ScanApi Helper component is provided for Objective C, C# and Java platforms to
integrate more easily ScanAPI into an application. ScanAPI Helper handles the
asynchronous events through callbacks, and gives an easy way to manipulate the
asynchronous commands an application can send to a CHS by providing a callback
mechanism that is invoked when the command response is received.
A CHS has severall properties that can be retrieved, modified or actioned.
CHS properties can be by example a symbology state, its friendly name, or triggering
a scan.
This API is asynchronous. The property operation is therefore a 2-step process. The
application sends a property get or set command and if this is successful, a property
get or set complete event is received with the CHS result of that property command.
At any time a CHS can send events to the host that are retrieved using the same
mechanism as the completion of the property operation.
ScanAPI has only one entry point to receive these asynchronous events making it
very easy to manage.
The other benefit of this asynchronous API is to be able to drive a scanner from a
graphical user interface (GUI) application without danger of blocking the user
interface while waiting for a lengthy operation to complete.
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 10/152
Page 11

Socket ScanAPI Reference
3 SoftScan Feature
The SoftScan is a feature that makes the host device built-in camera acting as a
barcode scanner. This feature is implemented using third-party technology and
therefore the developer should comply to the third-party license agreement.
Currently the SoftScan feature is available on for iOS and Android based devices.
This feature is not activated by default. In order to activate it, the application should
set the ScanAPI kSktScanPropIdSoftScanStatus to kSktScanEnableSoftScan. As soon
as ScanAPI is initialized and SoftScan is enabled, a SoftScanner device arrival event
is generated.
A device removal event is generated when the SoftScan feature is disabled by using
the same ScanAPI property with its value sets to kSktScanDisableSoftScan.
The SoftScanner doesn’t support all the properties described in this document and
returns a ESKT_NOTSUPPORTED error for them.
3.1 Licensing requirements
The third-party used for implementing the SoftScan feature is RedLaser from eBay
corporation. The RedLaser requires a license to be purchased in order to offer
unlimited scan. Without the license the SoftScanner is limited to 25 scans on a
particular host.
The License should be purchase on RedLaser portal, and the license file should be
part of the application package.
3.2 iOS requirements
The ScanAPI library for iOS is split in to 2 versions; one that supports the SoftScan
feature and one that doesn’t.
In the version that doesn’t support the SoftScan feature the required frameworks
are:
- externalAccessory.framework
- audioToolbox.framework
In the version that does support the SoftScan feature the extra frameworks required
are:
- QuartzCore.framework,
- CoreVideo.framework,
- CoreMedia.framework,
- CoreGraphics.framework,
- AVFoundation.framework,
- OpenGLES.framework,
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 11/152
Page 12

Socket ScanAPI Reference
- Security.framework,
- libiconv.dylib,
- libstdc++.dylib or libstd++6.0.9.dylib if you’re using OS6.x SDK.
3.3 Android requirements
The overlay view is a requirement for the SoftScanner in order to display the video
output in the application. This is implemented through an Activity that must be
added to the application manifest. This activity is defined as
com.SocketMobile.ScanAPI.SoftScanActivity.
The manifest should also have the following permissions:
- android.permission.CAMERA,
- android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE
- android.permission.INTERNET
A specific layout should be created that will be displayed as the overlay view of the
SoftScan. This layout can have a white rectangle that is called a “View Finder” that is
used as a scanning guide but also is use by the softscan scanner to improve the
barcode recognition in this region. The “View Finder” ID can be passed in the hash
table of the kSktScanPropIdOverlayViewDevice property. A flash button can be
added as well and its ID should be also specified in the same hash table of the same
property. If the flash feature is not available the SoftScan scanner will disable it
automatically.
The RedLaser libraries must be added to the Android application. The simplest way
for doing this is to copy the redlasersdk.jar and the armeabi/libredlaser.so in the
“libs” directory of the Android application. That “libs” subdirectory is automatically
taking in consideration by Android Development tools (ADT 18 or higher).
4 Concept
This API defines 3 main objects: ScanAPI object, Device object and ScanObject.
4.1 ScanAPI object
This object controls the API.
In order to use ScanAPI, this object must be opened first and this first open
initializes ScanAPI. The handle returned from this open must be used for any
subsequent ScanAPI operations.
All asynchronous events are received through this ScanAPI object.
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 12/152
Page 13

Socket ScanAPI Reference
The ScanAPI object has few properties that can be retrieved or modified.
When an application is ready to use ScanAPI, it can open it by using the ScanAPI
Open API with no device name in the parameter.
4.2 Device object
The Device object represents a CHS. In order to use and receive events from a CHS,
its corresponding Device object must be opened.
The handle returned from opening a Device object is used by the application to
retrieve or modify a particular property of the CHS.
ScanAPI notifies the application each time a Device Object is available by sending a
Device Arrival event with a UUID identifying the Device Object. The application can
open this particular Device Object by specifying this UUID in the ScanAPI open API.
If a CHS disconnects from the host, a Device Removal is sent by ScanAPI to the
application to indicate that the matching Device Object is no longer valid and the
application should close it if it has it opened.
4.3 ScanObject
The ScanObject is a data placeholder used for exchanging information between the
application and the CHS or ScanAPI object.
A ScanObject holds 2 kinds of information: a property and a message.
When a ScanObject is sent from the application to ScanAPI, only the property
information in ScanObject is relevant.
When a ScanObject is received from ScanAPI by the application, the message
information is always relevant and depending on the message received the property
information might be relevant.
ScanAPI creates a ScanObject each time it receives an asynchronous event, and in
this case the application must release this ScanObject by calling a ScanAPI release
API.
The application can create a ScanObject to send specific information to either a
Device or ScanAPI. In this case the application is responsible for releasing the
ScanObject correctly.
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 13/152
Page 14

Socket ScanAPI Reference
4.4 Using ScanAPI
An application has two things to do in order to setup ScanAPI correctly. It needs first
to open ScanAPI by specifying no name in the open parameter API, and then starts
either a timer or a thread to consume the asynchronous events coming from
ScanAPI.
When a CHS connects to the host, ScanAPI sends a Device Arrival event to the
application through the application ScanAPI consumer logic.
The Device Arrival event contains an UUID identifying a Device Object that
represents a CHS. The application can open the Device Object by specifying this
UUID in the ScanAPI open function.
Once the Device Object is opened, the application can retrieve or modify the CHS
properties by using the get property or set property API.
The get property and set property APIs are asynchronous. These APIs return
success if the property has been sent correctly to the CHS. The property completion
event is received in the application consumer.
If the CHS doesn't respond to a get or set property within the timeout period (about
5 seconds), for whatever reason, a matching property get or set complete event is
generated with a timeout error.
Only one property can be sent at the time to the CHS. An error occurs if a property is
sent prior the completion of the previous property operation.
ScanAPI sends a Device Removal event when a CHS disconnects from the host. The
application should close the matching Device Object if it has it opened.
4.5 ScanAPI configuration
ScanAPI has one thread listening on a serial communication port. This configuration
can be retrieved or modified by creating a ScanObject and setting its property to
ScanAPI configuration property. The ScanObject can be sent to ScanAPI using the get
property or set property API to respectively retrieve or modify this property.
Modifying the ScanAPI configuration will prompt the listener thread to restart. An
error event is generated if the configuration is incorrect.
Each time the listener starts, a Listener Start event is generated.
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 14/152
Page 15

Socket ScanAPI Reference
ScanAPI drops the connection to a CHS if it was connected during the process of
changing the ScanAPI configuration.
Please refer to the ScanAPI object properties paragraph for more information.
4.6 Get or Set a property
The ScanAPI object and the Device object have both properties that can be retrieved
or altered by using the get property or set property API.
The process of getting or setting a property is simple. A ScanObject holds a Property
field. The application must create a ScanObject instance and fill its Property member
according to the property of the object it would like to modify.
A property has an ID, a data type,data value and a context. They must be specified
accordingly to the characteristics of the property that needs to be retrieved or
modified.
The context is a field an application can use for maintaining a context. This context is
returned when a property set or get operation completes.
Once the property member of the ScanObject has been filled correctly, the
application can call the get or set API with the reference of the object to which it
wishes to retrieve or modify the property.
If the API returns success, the application can wait for the completion to be received
through the wait API.
An application cannot send multiple properties to the same object before the
previous set or get property operation has been fully completed. An error is
generated during the Set or Get API call if the previous property of the same object
hasn’t been completed yet.
The application receives the complete event through its ScanAPI consumer logic that
uses the wait API with the ScanAPI object reference.
A ScanObject that is received from ScanAPI has always its message field filled out.
The property complete event is received in a ScanObject with a Message ID set to a
Get Complete ID or Set Complete ID.
The Message has a result field that indicates if the completion of the get or set
property has been successful or not. The Property member of the ScanObject
contains the Property ID matching to the one that has been set, and in case of
success, the data type and value are filled as expected.
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 15/152
Page 16

Socket ScanAPI Reference
An important point is the fact that a property set or get can fail for many reasons,
and some of them will require the application to retry the operation and some
should just be taken into consideration. For example, if a property returns a
REQUEST TIMEOUT error because the scanner is out of the range for a brief instant
or busy receiving decoded data, having retry logic can fix this issue.
4.7 Example of sending a command
This section describes the steps for sending a command to a device.
Let’s imagine an application using ScanAPI has a button on its UI to trigger a scan.
For clarity purposes we assume the application correctly handles the connection of
the scanner and has kept a handle to ScanAPI and to this scanner accessible.
The application has ScanAPI consumer logic that will receive the messages from
ScanAPI.
This consumer logic uses the wait API with the ScanAPI object reference that has
been previously opened with the open API with NULL as device name.
The button handler creates a ScanObject, and fills the Property part with a property
ID set to kSktScanPropIdTriggerDevice, a property type set to byte, and the property
byte value set to kSktScanTriggerStart as explained in the paragraph 14.5 Property
kSktScanPropIdTriggerDevice.
This button handler uses the set API to send this property to the device identified by
its reference. If the return code of this API is successful, the button handler can then
disable the trigger button indicating the trigger is in progress.
The application’s ScanAPI consumer logic that was waiting for ScanAPI messages by
using the wait API should receive the Set Complete message with the property ID set
to kSktScanPropIdTriggerDevice.
The result indicates if the trigger worked. At that point the device should have the
aim light turned on and should be ready to scan and decode data. The application
trigger button can then be enabled.
C++ Source code sample:
void CMyAppDlg::OnTriggerButton()
{
SKTRESULT Result=ESKT_NOERROR;
TSktScanObject ScanObj;
memset(&ScanObj,0,sizeof(ScanObj));
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 16/152
Page 17

Socket ScanAPI Reference
// initialize a ScanObject to
// trigger the device
ScanObj.Property.ID=kSktScanPropIdTriggerDevice;
ScanObj.Property.Type=kSktScanPropTypeByte;
ScanObj.Property.Byte=kSktScanTriggerStart;
// set the property with the
// device handle
Result=SktScanSet(m_hDevice,&ScanObj);
// check the Set result
if(SKTSUCCESS(Result))
m_TriggerBtn.Enable(FALSE);
else
{
// display an error message
DisplayError(_T("Unable to trigger: %d"),Result);
}
}
SKTRESULT CMyAppDlg::Consume(
IN SKTHANDLE hScanAPI,
IN unsigned long ulTimeoutInMilliseconds,
OUT BOOL* pbContinue)
{
SKTRESULT Result;
TSktScanObject* pSktObject=NULL;
Result=SktScanWait(hScanAPI,&pSktObject,ulTimeoutInMilliseconds);
if(SKTSUCCESS(Result))
{
if(Result!=ESKT_WAITTIMEOUT)
{
if(pSktObject)
{
switch(pSktObject->Msg.MsgID)
{
case kSktScanMsgIdDeviceArrival:
Result=HandleDeviceArrival(pSktObject);
break;
case kSktScanMsgIdDeviceRemoval:
Result=HandleDeviceRemoval(pSktObject);
break;
case kSktScanMsgIdTerminate:
// we are done with ScanAPI, somebody
// called SktSet with Abort MsgId
if(pbContinue)
*pbContinue=FALSE;// quit the for
TraceInfo(_T("Receive a Terminate Msg, \
then shutdown the App receiving \ thread"));
break;
case kSktScanMsgSetComplete:
case kSktScanMsgGetComplete:
Result=
HandleGetOrSetComplete(pSktObject);
break;
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 17/152
Page 18

Socket ScanAPI Reference
case kSktScanMsgEvent:
Result=
HandleAsynchronousEvent(pSktObject);
break;
default:
{
TraceInfo(_T("unknown Message ID \
received:0x%x"),
pSktObject->Msg.MsgID);
}
break;
}
// release the ScanObj we received in the wait
SktScanRelease(hScanAPI,pSktObject);
}
}
}
return Result;
}
// called from the ScanAPI consumer logic
// that is using SktScanWait API
void CMyAppDlg::HandleGetOrSetComplete(
IN TSktScanObject* pScanObj
)
{
switch(pScanObj->Property.ID)
{
case kSktScanPropIdTrigger:
// ungray out the trigger btn
m_TriggerBtn.Enable(TRUE);
if(!SKTSUCCESS(pScanObj->Msg.Result))
{
DisplayError(_T("Failed to trigger: %d"),
pScanObj->Msg.Result);
}
break;
}
}
C# source code:
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
private ISktScanApi _scanApi;
private ISktScanDevice _device;
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
InitializeScanAPI();
}
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 18/152
Page 19

Socket ScanAPI Reference
private void buttonTrigger_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// create a ScanObject instance
ISktScanObject scanObj =
SktClassFactory.createScanObject();
// Initialize a ScanObject to
// Trigger the device
scanObj.Property.ID =
ISktScanProperty.propId.kSktScanPropIdTriggerDevice;
scanObj.Property.Type =
ISktScanProperty.types.kSktScanPropTypeByte;
scanObj.Property.Byte =
ISktScanProperty.values.trigger.kSktScanTriggerStart;
// set the property with the device
// reference
long result = _device.SetProperty(scanObj);
if (SktScanErrors.SKTSUCCESS(result))
{
buttonTrigger.Enabled = false;
}
else
{
// display an error message
DisplayError("Unable to trigger: " + result);
}
}
// timer to checking and consuming ScanObject from ScanAPI
private void timerScanAPIConsumer_Tick(object sender,
{
ISktScanObject scanObj=null;
// wait for ScanAPI ScanObject
long result = _scanApi.WaitForScanObject(out scanObj, 10);
if (SktScanErrors.SKTSUCCESS(result))
{
if (result != SktScanErrors.ESKT_WAITTIMEOUT)
{
int propId = scanObj.Msg.ID;
switch (propId)
{
case ISktScanMsg.kSktScanMsgIdDeviceArrival:
result = HandleDeviceArrival(scanObj);
break;
case ISktScanMsg.kSktScanMsgIdDeviceRemoval:
result = HandleDeviceRemoval(scanObj);
break;
case ISktScanMsg.kSktScanMsgIdTerminate:
// we are done with ScanAPI, somebody
EventArgs e
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 19/152
Page 20

Socket ScanAPI Reference
// called Set with kSktScanPropIdAbort
// as Property ID
result = HandleTerminate(scanObj);
break;
case ISktScanMsg.kSktScanMsgGetComplete:
case ISktScanMsg.kSktScanMsgSetComplete:
result = HandleGetOrSetComplete(scanObj);
break;
case ISktScanMsg.kSktScanMsgEvent:
result = HandleEvent(scanObj);
break;
}
// release the ScanObject we received in the wait
_scanApi.ReleaseScanObject(scanObj);
}
}
}
private long HandleGetOrSetComplete(ISktScanObject scanObj)
{
long result = SktScanErrors.ESKT_NOERROR;
ISktScanProperty property = scanObj.Property;
switch (property.ID)
{
case ISktScanProperty.propId.kSktScanPropIdTriggerDevice:
// ungrey out the trigger button
buttonTrigger.Enabled = true;
result = scanObj.Msg.Result;
if (!SktScanErrors.SKTSUCCESS(result))
{
DisplayError("Failed to trigger: " + result);
}
break;
}
return result;
}
Java source code:
// handler for the Trigger button
class TriggerButtonHandler implements Runnable {
private ISktScanDevice _device=null;
private ButtonField _button;
// constructor
public TriggerButtonHandler(
ISktScanDevice device,
ButtonField button)
{
_device=device;
_button=button;
}
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 20/152
Page 21

Socket ScanAPI Reference
public void run() {
// create a ScanObject instance
ISktScanObject scanObj=
SktClassFactory.createScanObject();
// Initialize a ScanObject to
// Trigger the device
ISktScanProperty property=
scanObj.getProperty();
property.setID(
ISktScanProperty.propId.
kSktScanPropIdTriggerDevice);
property.setType(
ISktScanProperty.types.
kSktScanPropTypeByte);
property.setByte(
ISktScanProperty.values.trigger.
kSktScanTriggerStart);
// set the property with the device
// reference
long result=_device.SetProperty(scanObj);
// check the set result
if(SktScanErrors.SKTSUCCESS(result)){
_button.setVisualState(VISUAL_STATE_DISABLED);
}
else
{
// display an error message
DisplayError("Unable to trigger: "+result);
}
}
}
class ScanAPIConsumer extends TimerTask {
private ISktScanApi _scanApi;
private AppRef _appRef;
public ScanAPIConsumer(ISktScanApi scanApi,AppRef appRef)
{
_scanApi=scanApi;
_appRef=appRef;
}
public void run() {
ISktScanObject[]scanObj=new ISktScanObject[1];
// wait for scanAPI ScanObject
long result=_scanApi.WaitForScanObject(scanObj,10);
if(SktScanErrors.SKTSUCCESS(result))
{
if(result!=SktScanErrors.ESKT_WAITTIMEOUT)
{
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 21/152
Page 22

Socket ScanAPI Reference
int propId=
scanObj[0].getMessage().getID();
switch(propId){
case ISktScanMsg.kSktScanMsgIdDeviceArrival:
result=
HandleDeviceArrival(scanObj[0]);
break;
case ISktScanMsg.kSktScanMsgIdDeviceRemoval:
result=
HandleDeviceRemoval(scanObj[0]);
break;
case ISktScanMsg.kSktScanMsgIdTerminate:
// we are done with ScanAPI, somebody
// called Set with Abort as MsgID
result=
HandleTerminate(scanObj[0]);
break;
case ISktScanMsg.kSktScanMsgSetComplete:
case ISktScanMsg.kSktScanMsgGetComplete:
result=
HandleGetOrSetComplete(scanObj[0]);
break;
case ISktScanMsg.kSktScanMsgEvent:
break;
}
// release the ScanObj we received in the wait
_scanApi.ReleaseScanObject(scanObj[0]);
}
}
}
// called from the ScanAPI consumer logic
// that is using the wait API
private long HandleGetOrSetComplete(ISktScanObject scanObj) {
long result=SktScanErrors.ESKT_NOERROR;
ISktScanProperty property=scanObj.getProperty();
switch(property.getID()){
case ISktScanProperty.propId.
kSktScanPropIdTriggerDevice:
// ungray out the trigger btn
_appRef.getTriggerBtn().
setVisualState(VISUAL_STATE_NORMAL);
result=scanObj.getMessage().getResult();
if(!SktScanErrors.SKTSUCCESS(result)){
DisplayError("Failed to trigger: "+result);
}
break;
}
return result;
}
};
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 22/152
Page 23

Socket ScanAPI Reference
Objective C source code:
-(IBAction)btnClicked:(id)sender{
id<ISktScanObject> scanObj=[SktClassFactory createScanObject];
[[scanObj Property] setID:kSktScanPropIdTriggerDevice];
[[scanObj Property]setType:kSktScanPropTypeByte];
[[scanObj Property]setByte:kSktScanTriggerStart];
[_rootViewController AddPropertyToSet:scanObj];
[_rootViewController SendFirstPropertyToSet];
}
// timer handler for consuming ScanObject from ScanAPI
// if ScanAPI is not initialized this handler does nothing
-(void)onTimer{
if(_scanApiInitialized==true){
SKTRESULT result=[_scanapi WaitForScanObject:_scanObjectReceived TimeOut:0];
if (SKTSUCCESS(result)) {
if (result!=ESKT_WAITTIMEOUT) {
[self HandleScanObject:_scanObjectReceived];
[_scanapi ReleaseScanObject:_scanObjectReceived];
}
}
}
}
-(void) HandleScanObject:(id<ISktScanObject>)scanobject{
switch ([[scanobject Msg] MsgID]) {
case kSktScanMsgIdDeviceArrival:
[self HandleDeviceArrival:scanobject];
break;
case kSktScanMsgIdDeviceRemoval:
[self HandleDeviceRemoval:scanobject];
break;
case kSktScanMsgGetComplete:
[self DoGetComplete:scanobject];
break;
case kSktScanMsgSetComplete:
[self DoSetComplete:scanobject];
break;
case kSktScanMsgIdTerminate:
[_scanapi Close];
break;
case kSktScanMsgEvent:
[self HandleEvent:scanobject];
break;
default:
break;
}
}
-(void) DoGetComplete:(id<ISktScanObject>)scanObject{
SKTRESULT result=ESKT_NOERROR;
if (scanObject!=nil) {
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 23/152
Page 24

Socket ScanAPI Reference
result=[[scanObject Msg]Result];
id<ISktScanProperty> property=[scanObject Property];
int ID=[property getID];
switch (ID) {
case kSktScanPropIdFriendlyNameDevice:
result=[self OnFriendlyName:scanObject];
break;
case kSktScanPropIdBluetoothAddressDevice:
result=[self OnBtAddress:scanObject];
break;
case kSktScanPropIdDeviceType:
result=[self OnScannerType:scanObject];
break;
case kSktScanPropIdVersionDevice:
result=[self OnScannerFirmware:scanObject];
break;
case kSktScanPropIdBatteryLevelDevice:
result=[self OnBatteryLevel:scanObject];
break;
case kSktScanPropIdLocalDecodeActionDevice:
result=[self OnDecodeAction:scanObject];
break;
case kSktScanPropIdCapabilitiesDevice:
result=[self OnCapabilitiesDevice:scanObject];
break;
case kSktScanPropIdPostambleDevice:
result=[self OnPostambleDevice:scanObject];
break;
case kSktScanPropIdSymbologyDevice:
result=[self OnSymbologyInfo:scanObject];
break;
default:
break;
}
// send a notification to update the progress bar
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] postNotificationName:@"msg_name" object:nil
userInfo:nil];
// and send the next property if there is one
[self SendFirstPropertyFromList];
}
}
-(void) DoSetComplete:(id<ISktScanObject>)scanObject{
SKTRESULT result=ESKT_NOERROR;
if (scanObject!=nil) {
result=[[scanObject Msg]Result];
// send a notification to update the progress bar
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] postNotificationName:@"msg_name" object:nil
userInfo:nil];
_propertySetPending=NO;
// and send the next property if there is one
[self SendFirstPropertyToSet];
}
}
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 24/152
Page 25

Socket ScanAPI Reference
4.8 Handling asynchronous events or completion events
The ScanAPI object maintains a queue to receive asynchronous events and property
operation complete events waitting for the application to consume them.
An application can retrieve these events by using the wait API.
This API returns a ScanObject that will need to get released once the application is
done with it by calling the release API.
The wait API returns immediately if there is an event in the queue, or it will wait the
specified input parameter time if the queue is empty.
Completion events or asynchronous events can arrive at any time and in any order.
The recommended way for handling these events is to create a switch statement on
the message ID received in the ScanObject.
There are only 6 possible message types: kSktScanMsgIdDeviceArrival,
kSktScanMsgIdDeviceRemoval, kSktScanMsgIdTerminate,
kSktScanMsgSetComplete, kSktScanMsgGetComplete and kSktScanMsgEvent.
For each of these message types a handler function can be called. Inside the handler
function, the Result member of the Message received should be checked to be sure
the process can continue.
The handler functions for the Set Property Complete or Get Property Complete
event can also have a switch statement on the property ID. If the application used
the context member of a property, the same context is then returned in the complete
property.
The decoded data or the CHS button’s press status is received in the handler
functions for the messages that have kSktScanMsgEvent as message ID.
4.9 Termination
When ScanAPI is no longer needed it can be terminated by setting an Abort property
to the ScanAPI object.
At that point, if there are any devices open, ScanAPI sends a Removal event for each
of the Device objects open, upon which the Device object should be closed by the
application using the close API.
Once all the Device objects have been closed, ScanAPI sends a Terminate event and
at that point it is safe to close ScanAPI.
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 25/152
Page 26

Socket ScanAPI Reference
5 ScanAPI Helper (available for Java, C# and Objective C)
ScanAPI Helper has been created to facilitate the integration of ScanAPI into an
application.
It is released as source code and therefore can be highly customizable for the need
of your application. Some basic and common features are provided as sample on
how to use ScanAPI.
NOTE: ScanAPI Helper is available for Java, C# and Objective C base code.
ScanAPI Helper maintains a list of commands to send to ScanAPI. Since properties
cannot be sent before the completion of the previous one, it offers an easy way to
queue the commands and provides a callback for each command completion.
A command in this context is either a “Set Property” or a “Get Property”.
By example, if an application wants to retrieve the friendly name and the version of
the connected device, it uses ScanAPIHelper to do a “PostGetFriendlyName” and a
“PostGetDeviceVersion” in a row, and for each of these functions, a callback is
passed, so when the Get Friendly Name completes, the callback is called and the
application can refresh the UI with the new friendly name, and it follows the same
logic when Get Device Version completes.
It retries sending the command up to 3 times if the command completion failed in
time out error.
The Java version of ScanAPI Helper creates a timer task to consume asynchronous
ScanObject coming from ScanAPI.
The C# and Objective C version of ScanAPI Helper does not create a timer, but
instead provides a method, DoScanAPIReceive, that has to be called from a timer
function or a thread.
The following paragraph describes the steps required for using ScanAPI Helper.
5.1 Handling the ScanAPI Helper notifications
Since most of the ScanAPI operations are asynchronous, it is very important to setup
a way for handling notifications. ScanAPI Helper provides a
ScanAPIHelperNotification interface or a ScanApiHelperDelegate protocol for
Objective C environment that must be implemented in order to handle the various
notifications correctly.
Here is how Scanner Settings for Android is using this interface:
private ScanApiHelperNotification _scanApiHelperNotification=new ScanApiHelperNotification() {
/**
* receive a notification indicating ScanAPI has terminated,
* then send an intent to finish the activity if it is still
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 26/152
Page 27

Socket ScanAPI Reference
* running
*/
public void onScanApiTerminated() {
_consumerTerminatedEvent.set();
if(_forceCloseUI){
Intent intent=new Intent(NOTIFY_CLOSE_ACTIVITY);
sendBroadcast(intent);
}
}
/**
* ScanAPI is now initialized, if there is an error
* then ask the activity to display it
*/
public void onScanApiInitializeComplete(long result) {
// if ScanAPI couldn't be initialized
// then display an error
if(!SktScanErrors.SKTSUCCESS(result)){
_scanApiOwnership.releaseOwnership();
String text=getString(R.string.failed_to_initialize_scanapi_error_)+result;
Intent intent=new Intent(NOTIFY_ERROR_MESSAGE);
intent.putExtra(EXTRA_ERROR_MESSAGE,text);
}
}
/**
* ask the activity to display any asynchronous error
* received from ScanAPI
*/
public void onError(long result) {
String text=getString(R.string.scanapi_is_reporting_an_error_)+result;
Intent intent=new Intent(NOTIFY_ERROR_MESSAGE);
intent.putExtra(EXTRA_ERROR_MESSAGE,text);
}
/**
* a device has disconnected. Update the UI accordingly
*/
public void onDeviceRemoval(DeviceInfo deviceRemoved) {
_currentSelectedDevice=null;
Intent intent=new Intent(NOTIFY_SCANNER_REMOVAL);
intent.putExtra(EXTRA_DEVICENAME,deviceRemoved.getName());
sendBroadcast(intent);
}
/**
* a device is connecting, update the UI accordingly
*/
public void onDeviceArrival(long result, DeviceInfo newDevice) {
Intent intent=null;
if(SktScanErrors.SKTSUCCESS(result)){
_currentSelectedDevice=newDevice;
intent=new Intent(NOTIFY_SCANNER_ARRIVAL);
intent.putExtra(EXTRA_DEVICENAME,newDevice.getName());
}
else
{
String text=getString(R.string.error_)+result+
getString(R.string._during_device_arrival_notification);
intent=new Intent(NOTIFY_ERROR_MESSAGE);
intent.putExtra(EXTRA_ERROR_MESSAGE,text);
}
sendBroadcast(intent);
}
/**
* ScanAPI is delivering some decoded data
* ask the activity to display them
*/
public void onDecodedData(DeviceInfo deviceInfo,
ISktScanDecodedData decodedData) {
Intent intent=new Intent(NOTIFY_DATA_ARRIVAL);
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 27/152
Page 28

Socket ScanAPI Reference
intent.putExtra(EXTRA_SYMBOLOGY_NAME,decodedData.getSymbologyName());
intent.putExtra(EXTRA_DECODEDDATA,decodedData.getData());
sendBroadcast(intent);
}
/**
* an error occurs during the retrieval of ScanObject
* from ScanAPI, this is critical error and only a restart
* can fix this.
*/
public void onErrorRetrievingScanObject(long result) {
Intent intent=new Intent(NOTIFY_ERROR_MESSAGE);
String text="Error unable to retrieve ScanAPI message: ";
text+="("+result+")";
text+="Please close this application and restart it";
intent.putExtra(EXTRA_ERROR_MESSAGE,text);
sendBroadcast(intent);
}
};
The same notification handler but this time for the BlackBerry version of Scanner
Settings:
private ScanApiHelperNotification _scanApiHelperNotification=new ScanApiHelperNotification() {
public void onScanApiTerminated() {
System.exit(0);
}
public void onScanApiInitializeComplete(long result) {
// Display an error message indicating that ScanAPI failed
// to initialize correctly
_scanAPIInitError=result;
if(SktScanErrors.SKTSUCCESS(result)){
synchronized(UiApplication.getEventLock()){
delete(_pleaseWaitWhileInitializingScanAPI);
add(_displayDeviceslist);
}
}
else{
UiApplication.getUiApplication().invokeLater(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
synchronized(UiApplication.getEventLock()){
Status.show("Unable to initialize ScanAPI
("+_scanAPIInitError+")");
_ScanApi=null;
delete(_pleaseWaitWhileInitializingScanAPI);
add(new LabelField("Please restart this
application",Field.FIELD_HCENTER));
}
}
});
}
}
public void onErrorRetrievingScanObject(long result) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
public void onError(long result) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
public void onDeviceRemoval(DeviceInfo deviceRemoved) {
synchronized(UiApplication.getEventLock()){
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 28/152
Page 29

Socket ScanAPI Reference
deviceRemoved.CloseScreenButThis(_this);
int size=_scanApiHelper.getDevicesList().size();
_displayDeviceslist.setSize(size);
}
_deviceconnected=false;
}
public void onDeviceArrival(long result, DeviceInfo newDevice) {
synchronized(UiApplication.getEventLock()){
int size=_scanApiHelper.getDevicesList().size();
_displayDeviceslist.setSize(size);
}
_deviceconnected=true;
}
public void onDecodedData(DeviceInfo deviceInfo,
ISktScanDecodedData decodedData) {
if(_scanwindow!=null)
_scanwindow.DoScannedData(decodedData.getData(),decodedData.getSymbologyName());
}
};
Same notification handler but this time from Objective C version of Scanner Settings:
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 29/152
Page 30

Socket ScanAPI Reference
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 30/152
Page 31

Socket ScanAPI Reference
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 31/152
Page 32

Socket ScanAPI Reference
5.2 Set ScanAPI Helper notification
ScanAPI Helper must be instructed to use your notification handler object and this
can be accomplished by calling the setNotification method (or setDelegate in
Objective C) with the reference to the notification interface implementation.
_scanApiHelper.setNotification(_scanApiHelperNotification);
This is important to use this function prior calling the open function to be sure to
trap all the notifications.
5.3 Open ScanAPI Helper
Once the ScanAPI Helper object has been instantiate by using the new function, it
can then be open using the open() method. The open() method doesn’t return
anything but instead the onScanApiInitializeComplete notification will be called
once the ScanAPI initialization process has been completed. A result code indicates
how successful the initialization was.
Example:
_scanApiHelper.open();
5.4 Close ScanAPI Helper
Once the application is done with ScanAPI, it can close it by calling the close method
of the ScanAPIHelper object as shown below:
_scanApiHelper.close();
The close method doesn’t return any value, but the notification
onScanApiTerminated will be called when ScanAPI has effectively shutdown.
5.5 Scanner arrival
When a scanner connects to the host, ScanAPI Helper notifies the application using
the onDeviceArrival notification and specifies a result code, and in case of success it
also specifies the device information (friendly name, device type). ScanAPI Helper
keeps the device information object into its devices list. The application can retrieve
this list at any time. In our Scanner Settings SDK sample application for Android
platform, this notification asks the activity to refresh with the new scanner
information or in case of an error, it displays an error message as described below:
/**
* a device is connecting, update the UI accordingly
*/
public void onDeviceArrival(long result, DeviceInfo newDevice) {
Intent intent=null;
if(SktScanErrors.SKTSUCCESS(result)){
_currentSelectedDevice=newDevice;
intent=new Intent(NOTIFY_SCANNER_ARRIVAL);
intent.putExtra(EXTRA_DEVICENAME,newDevice.getName());
}
else
{
String text=getString(R.string.error_)+result+
getString(R.string._during_device_arrival_notification);
intent=new Intent(NOTIFY_ERROR_MESSAGE);
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 32/152
Page 33

Socket ScanAPI Reference
intent.putExtra(EXTRA_ERROR_MESSAGE,text);
}
sendBroadcast(intent);
}
5.6 Decoded data notification
Each time a scanner decodes correctly a barcode, ScanAPI Helper calls the
onDecodedData notification with the device information object and the decoded
data. In the Scanner Settings for Android case the activity that has registered for the
NOTIFY_DATA_ARRIVAL intent will receive and display the decoded data. This
activity is the ScanWindowActivity.
Here is the code extract from Android Scanner Settings for this notification:
/**
* ScanAPI is delivering some decoded data
* as the activity to display them
*/
public void onDecodedData(DeviceInfo deviceInfo,
ISktScanDecodedData decodedData) {
Intent intent=new Intent(NOTIFY_DATA_ARRIVAL);
intent.putExtra(EXTRA_SYMBOLOGY_NAME,decodedData.getSymbologyName());
intent.putExtra(EXTRA_DECODEDDATA,decodedData.getData());
sendBroadcast(intent);
}
The BlackBerry version of Scanner Settings onDecodedData looks like this:
public void onDecodedData(DeviceInfo deviceInfo,
ISktScanDecodedData decodedData) {
if(_scanwindow!=null)
_scanwindow.DoScannedData(decodedData.getData(),decodedData.getSymbologyName());
}
5.7 Scanner removal
When a scanner disconnects from the host, the ScanAPI Helper notifies the
application by calling the notification onDeviceRemoval. Usually the application
updates its UI to reflect that change. The Scanner Settings for Android sends an
Intent to the Activity that has registered for it, as shown in the following lines:
/**
* a device has disconnected. Update the UI accordingly
*/
public void onDeviceRemoval(DeviceInfo deviceRemoved) {
_currentSelectedDevice=null;
Intent intent=new Intent(NOTIFY_SCANNER_REMOVAL);
intent.putExtra(EXTRA_DEVICENAME,deviceRemoved.getName());
sendBroadcast(intent);
}
The BlackBerry Scanner Settings version does something similar:
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 33/152
Page 34

Socket ScanAPI Reference
public void onDeviceRemoval(DeviceInfo deviceRemoved) {
synchronized(UiApplication.getEventLock()){
deviceRemoved.CloseScreenButThis(_this);
int size=_scanApiHelper.getDevicesList().size();
_displayDeviceslist.setSize(size);
}
_deviceconnected=false;
}
5.8 Is there a connected Scanner
At any point of time, the application can interrogate ScanApi Helper to know if there
is at least one device connected by using the following method:
_scanApiHelper.isDeviceConnected();
This might be useful to know what application menu should be displayed by
example, which could change in function of the connection status.
5.9 Get the list of scanners
The list of connected scanner reference can be retrieved by using the getDevicesList
method.
5.10 No Device Connected item
In some occasion the application might want to display a specific text when no
device is connected. The ScanAPI Helper method setNoDeviceText() allows the
application to specify a text that will be used to display the only item of the devices
list when no scanner is connected.
6 IDE Integration
6.1 C/C++ Version
ScanAPI has been compiled with Microsoft Visual Studio 2008. The inclusion of
ScanAPI in this environment in your C/C++ project can be done in 2 ways; by adding
the following lines in your source file directly:
#include “<SDK Install Path>\include\ScanAPI.h”
#pragma comment(“lib”,”<SDK Install Path>\\lib\ScanAPI.lib”
Or by adding only the include line in your source file and by adding the lib file in
your Project Link input settings.
6.2 Java Version
ScanAPI has been compiled using Eclipse Galileo (version 3.5).
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 34/152
Page 35

Socket ScanAPI Reference
ScanAPI is composed of two JAR files located under the lib directory of the SDK Java
portion.
Following are the steps required in order to include ScanAPI into your project and
workspace.
6.2.1 Setting up the Eclipse workspace
From Eclipse select the menu Window / Preferences.
For a BlackBerry target, select from the left tree control the path Java\Build
Path\User Libraries
Choose the “Import…” button and browse to where ScanAPI_SDK is installed to
select the ScanAPI_SDK.user libraries file. Check the ScanAPIBlackBerry option and
click OK.
For an Android target, select on the left tree control the path Java\Build
Path\Classpath Variables. Click on the “New…” button and type in the Name field:”
ScanAPI_Libs” and click the Folder… button to browse to where your ScanAPI_SDK
is installed to select the Lib folder underneath it. Click OK to validate your choice,
and Click OK again to add the New Variable Entry in your workspace.
6.2.2 Setting up the application project for using ScanAPI
For a BlackBerry target, go to your Java application project properties; select Java
Build Path in the tree on the left panel of your application properties dialog. On the
right panel, select the Libraries tab and click on the “Add Library…” button. In the
Add Library dialog window select “User Library” and click next. In the next screen
select the ScanAPI library corresponding to your targeted device platform and click
the Finish button.
For an Android target, go to your Java application project properties; select Java
Build Path in the tree on the left panel of your application properties dialog. Click on
the “Add Variable…” button, select the ScanAPI_Libs variables and click on Extend.
Select ScanAPIAndroid.jar and click OK. Repeat this operation but this time select
the ScanAPIFactoryAndroid.jar file. Both jar files are required in order to use
ScanAPI in your application.
At this point your Java application is ready to use ScanAPI.
6.2.3 Tools provided with ScanAPI SDK
There are 2 tools provides in the SDK and that are launched automatically during
the installation of ScanAPI SDK but they will not be launched if you have installed
ScanAPI SDK using the compressed SDK file.
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 35/152
Page 36

Socket ScanAPI Reference
UpdateWorkspace.jar tool creates a series of Path Variables that are used mostly for
compiling the SDK Sample application. The sample application is sharing source files
across BlackBerry and Android by using the Path Variable mechanism available in
Eclipse. Since the Path Variable contains a complete path, and not a relative path,
this tool updates these variables with the path of where the ScanAPI SDK installed
on the host machine. The Path Variables are stored in the Eclispe workspace. The
tool asks the user for the path of the workspace to update with these new Path
Variables.
SetupScanAPI_SDK.jar. tool modifies the project settings of the sample application
for Android platform and setup the ScanAPI SDK path in the user library file that is
used for the BlackBerry platform.
If only one platform is targeted, it is entirely safe to run both of these tools.
6.3 C# Version
ScanAPI has been compiled with Visual Studio 2008 and using the Compact
Framework 2.0 and the .NET framework 3.5.
The C# version uses a wrapper. ScanAPI has been compiled as a native (unmanaged)
DLL. This DLL is ScanAPIDLL.dll for Windows platforms and ScanAPIDLLWM.dll for
Windows Mobile platform. The managed API is assembled in ScanAPIManaged.dll
for Windows platforms and in ScanAPIManagedWM.dll for the Windows Mobile
platforms.
Both sets of DLLs are therefore required on the host device and should be located at
the same place. So for a Windows host, the application using ScanAPI should have in
its directory ScanAPIDLL.dll and ScanAPIManaged.dll. Same for a Windows Mobile
host, the application using ScanAPI should have in its directory ScanAPIDLLWM.dll
and ScanAPIManagedWM.dll.
In order to build your ScanAPI application, add the ScanAPI Managed reference in
the References folder of your application by browsing to where ScanAPI SDK is
installed on your developer machine, and pointing to the right dll. Depending on
where the ScanAPI SDK has been installed, the path may look like this:
C:\Program Files\Socket Mobile\SocketScan 10\ScanAPI_SDK\Windows\lib.
6.4 Objective C Xcode integration
ScanAPI is released in a static library form, a serie of header files and the source files
for ScanApiHelper, DeviceInfo and Debug.
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 36/152
Page 37

Socket ScanAPI Reference
The recommended way to integrate ScanAPI in your Xcode project is to drag and
drop the ScanAPI folder located at the root of the ScanAPI SDK into your Xcode
project.
The application must add the External accessory framework, and in the info plist the
“Supported External Accessory Protocol” should contains the string
“com.socketmobile.chs”.
Most of the time, ScanApiHelper should be integrated into one of the controller of
the iOS application. The header of this controller should contains the following line:
#import “ScanApiHelper.h”
The controller must derive from ScanApiHelperDelegate protocol.
7 Recommendations
7.1 General
The recommended approach of managing a scanner connection to the host is to
detect if a scanner is connected when needed in the application. It is not
recommended to control the connection and disconnection of the scanner as the
scanner can be disconnected or connected independently of the application state.
If an application has multiple views, but only one view requires a scanner to be
connected, the best approach for this view is to check if a scanner is connected. If a
scanner is not connected, then the application should direct the user on how to
connect the scanner to the host. This can be done by scanning a barcode, or simply
by turning on a scanner that is already paired to the host. The scanner can be left
connected through the life cycle of the application knowing that the power
consumption for both, the host and the scanner, is minimal in that operational
mode.
If the scanner doesn’t have any activity, it will shut itself down after a 2 hours
timeout. If for some reason, the host and the scanner are out of range, the scanner
will automatically try to reconnect to the host during a period of 45 seconds for a
CHS 7x series or up to 30 connection attempts for a CHS 7(E,M,P) series.
At any time the user can turn off or on the scanner. Upon turning the scanner back
one, it will reconnect automatically to the last paired host device.
7.2 Android
It is not recommended to attach ScanAPI or ScanApiHelper to the Activity class, as
this object will get destroy and re-created upon screen rotation causing a connection
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 37/152
Page 38

Socket ScanAPI Reference
drop of the eventual connected scanner. The scanner will automatically reconnect to
the host in this case, but the user experience won’t be ideal.
We recommend attaching ScanAPI or ScanApiHelper to the application class as
shown in our sample application ScannerSettings for the optimal user experience.
It is important to note that your application must request the permission to use
Bluetooth and to write in the external storage. This last permission is required
because the ScanAPI settings are stored into a file on the external storage.
These permissions are identified respectively as follow:
android.permission.BLUETOOTH,
android.permission.BLUETOOTH_ADMIN and
android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE.
If these permissions aren’t requested, the external storage will make ScanAPI
returning error ESKT_TESTFAILED (-1), and the Bluetooth one will make ScanAPI
returning error ESKT_UNABLEOPENDEVICE (-27) and then
ESKT_NOTHINGTOLISTEN (-47).
7.3 iOS
On an iOS device, the scanner will always stay connected to the host. If the
application goes to the background, the application is paused. The External
Accessory framework will then simulate a device disconnection to the application,
but the Bluetooth link remains active. When the application is brought back to the
foreground, the External Accessory framework simulates a device connection. Only
certain application types are authorized to run while in background. For these types
of applications, the connection to the scanner will stay alive and running. The
application types are multi-media (music applications playing music while moved to
the background), VOIP applications and location based applications. This restriction
is dictated by iOS and is out of the control of ScanAPI.
8 Device Connection and Disconnection process
With this Version 3 of CHS, in order to have the best user experience possible, the
CHS is always the initiator of the connection process. That is, the CHS will always be
the device to start the connection process, after an initial setup connection has been
made.
8.1 Initial Connection
The process of the initial connection starts by having the CHS scan a connect
barcode. Once the Bluetooth pairing process is completed, the ScanAPI object
generates a Device Arrival notification that contains the device information.
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 38/152
Page 39

Socket ScanAPI Reference
If the scanner is a 2D Imager scanner, 7X series, the connect barcode can be scanned
directly from the device screen. This can be accomplished through the use of Socket
EZ Pair which is a separate application released with the SDK.
If the scanner is a 1D Laser scanner, 7 series, the connect barcode must be printed
out on paper. Socket EZ Pair can configure the scanner to have it connect back to the
host without the need to scan a connect barcode. In this case, the 1D scanner must
be paired with the host first using the Bluetooth functionality present on the host.
The connect barcode contains the Bluetooth Device Address of the host. It could be a
Data Matrix 2D barcode for the 2D Imager scanner 7x series, or it could be a Code
128 1D barcode for the 1D Laser scanner 7 series. The 1D connect barcode can also
be used by the 2D Imager scanner 7x series. Refer to the scanner documentation for
more information about the connect barcode.
Some hosts require having their Bluetooth mode set to discoverable in order to
accept the first initial connection.
If the host is an iOS device, the connect barcode doesn’t contain the host Bluetooth
address, as iOS does not provide an API to retrieve the Bluetooth address, but
instead contains a command to switch the CHS into ‘iOS mode’. The initial
connection can be then started from the iOS Bluetooth manager by tapping on the
desired CHS listed in the Bluetooth discovered devices list. This will initiate the
pairing process and the CHS will connect back to the iOS device as soon as it is
powered on and do this until its connection information is cleared.
8.2 Subsequent Connection
Once the initial connection is made between the scanner and the host, the scanner
will automatically reconnect to the host each time it powers on. If the host doesn’t
have a ScanAPI application running at the time the scanner connects, the scanner
will try a certain number of times before aborting the connection process.
ScanAPI sends a device arrival notification to the application each time a scanner
connects to the host.
8.3 Reconnection
If the connection between the scanner and host is lost for any reason, such as the
scanner moving out of range of the host, the host suspending or going to sleep, the
scanner will try to reconnect to the host for a period of time (45 seconds for a 7X
CHS) or a fixed number of times (30 times for a 7(E,M,P)CHS) before going to idle
mode.
8.4 Disconnection
The disconnection process usually only happens when the scanner powers off. This
occurs when the user presses the scanner power button to shut it down, or if the
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 39/152
Page 40

Socket ScanAPI Reference
scanner is connected for a long period of time without activity and automatically
powers itself off.
There is also a property (kSktScanPropIdDisconnectDevice) that can be set to the
scanner to make it disconnect.
Each time a scanner disconnects, a device removal notification from ScanAPI is sent
to the application containing the scanner information.
8.5 Roaming
The scanner can connect from one host to another by simply scanning the connect
barcode of another host if available. Note this effectively pairs it to the new host.
8.6 Socket EZ Pair feature
This feature is not available for iOS devices. The Scanner reconnects automatically
as soon as the iOS device has successfully paired with the Scanner from its General
Bluetooth settings.
The Socket EZ Pair application configures a scanner to connect back to the host
either by scanning a barcode displayed on the screen or by using a set of properties
sent to the scanner. The latter case is described here.
In order to have ScanAPI connecting to a particular scanner, the ScanAPI
communication port configuration must be changed.
Usually, when a host discovers a scanner, it either assigns a communication port to
this particular scanner (Windows based platforms), or its friendly name is used to
initiate a Bluetooth connection (BlackBerry and Android platforms). If the ScanAPI
serial port configuration is modified to use an outbound port, ScanAPI will then
connect to the remote device that is assigned to this outbound port.
For the scanner to connect back to the host, ScanAPI needs to be re-configured to
use a generic inbound communications port that the scanner will connect back on.
Once ScanAPI has connected to the scanner using either its assigned communication
port or friendly name, the device arrival notification is received by the application.
At that time the application should send the following properties to configure the
scanner to reconnect back to the host:
- Property kSktScanPropIdProfileConfigDevice : to transmit the host Bluetooth
address to the scanner and to specify that the scanner should initiate the
connection in Serial Port Profile (SPP) mode.
- Property kSktScanPropIdDisconnectDevice: to disconnect the scanner and
make the new configuration active. At that point the scanner will try to
reconnect back to the host.
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 40/152
Page 41

Socket ScanAPI Reference
Once the last property has been set, the configuration of ScanAPI must be reverted
back to its original configuration so that it is waiting for an incoming connection.
The ScanAPI property kSktScanPropIdConfiguration “SerialPorts” is used in order to
read and modify the ScanAPI communication port.
NOTE: It is not recommended to use ScanAPI as the initiator of the connection. It
doesn’t have reconnection logic, and it will need to get restarted each time a
connection has to be made.
9 API Functions
The ScanAPI has 6 entry points: Open, Close, Get, Set, Wait and Release.
They all use a reference to either a ScanAPI object or a Device object. These
references are represented differently depending on the programming language
used.
For C/C++ language this reference is represented as SKTHANDLE. This handle is
initialized during the open function and invalidated after calling the close function.
For Java and C#, this reference is an interface. There are 2 interfaces, one for each
object it represents; ISktScanApi for representing a ScanAPI object and
ISktScanDevice for representing a Device object. The ISktScanApi interface is a
superset of the ISktScanDevice.
Objective C uses the same concept and same name except it is called protocol
instead of interface.
A request to get these interfaces instantiated can be made by using the
SktClassFactory, ie: ISktScanApi scanApi=SktClassFactory.createScanApiInstance();
Or in Objective C:
Id<ISktScanApi> scanApi=[SktClassFactory createScanApiInstance];
Having an interface or protocol instance is not enough to use the object it
represents. The open must be invoked to initialize the object, and the close will
invalidate the object.
9.1 Open Function
The Open function opens either ScanAPI object or a Device object.
ScanAPI object
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 41/152
Page 42

Socket ScanAPI Reference
In order to open a ScanAPI object, the device name should be set to NULL.
The first open of a ScanAPI object initializes the ScanAPI layer and starts the process
of listening for device connections.
Once this open is successful the application can use this ScanAPI object reference to
call the wait API in its consumer logic.
If, for some reason, ScanAPI layer cannot open the Bluetooth serial ports indicated
in its configuration, an error will be sent to the application through a ScanObject
with the Message ID set to Event Message ID.
Device object
In order to open a device object, the device GUID should be specified as the device
name parameter of the open API. The device GUID is retrieved from the device
arrival notification event.
The application will start to receive device asynchronous events as soon as it opens
the device object.
9.1.1 Syntax
C/C++ :
SKTRESULT SktScanOpen(
const char* pszDeviceName,
SKTHANDLE* phDevice
);
pszDeviceName
[in] the scanner device GUID in a string format to open a device or NULL to
open ScanAPI object. If the GUID “{11D47F36-BE62-4D28-9177-
89F1BF3DDD4B}” is specified, this API will return a handle to a ScanAPI
object that won’t have a listener thread and that can be used for editing the
ScanAPI configuration.
phDevice
[out] pointer to receive the reference of the Device object or ScanAPI object.
C#:
long ISktScanApi.Open(
String deviceName
);
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 42/152
Page 43

Socket ScanAPI Reference
deviceName:
[in] usually set to NULL in order to open ScanAPI object or it could be set to
“{11D47F36-BE62-4D28-9177-89F1BF3DDD4B}” to open ScanAPI object without a
listener thread. This last case is mostly used to edit a ScanAPI configuration without
conflicting with another application using ScanAPI.
long ISktScanDevice.Open(
String deviceName
);
deviceName
[in] the scanner device GUID in a string to open a device.
Java:
long ISktScanApi.Open(
String deviceName
);
deviceName:
[in] usually set to NULL in order to open ScanAPI object or it could be set to
“{11D47F36-BE62-4D28-9177-89F1BF3DDD4B}” to open ScanAPI object without a
listener thread. This last case is mostly used to edit a ScanAPI configuration without
conflicting with another application using ScanAPI.
long ISktScanDevice.Open(
String deviceName
);
deviceName
[in] the scanner device GUID as a string to open a particular device. This
device GUID can be retrieved from the Device Arrival message event.
Objective C:
-(SKTRESULT) open: (NSString*)deviceName;
of the protocol ISktScanApi.
deviceName:
[in] usually set to NULL in order to open ScanAPI object or it could be set to
“{11D47f36-BE62-4D28-9177-89F1BF3DDD4B}” to open ScanAPI object without a
listener thread. This latter case is used to edit a ScanAPI configuration without
conflicting with another application using ScanAPI.
Same message prototype for a device but this time from the protocol
ISktScanDevice.
-(SKTRESULT) open: (NNString*) deviceName;
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 43/152
Page 44

Socket ScanAPI Reference
deviceName:
[in] the scanner device GUID as a string to open a particular device. This
device GUID can be retrieved from the Device Arrival message event.
9.1.2 Return value
If the function succeeds the return value is ESKT_NOERROR.
9.1.3 Remarks
A close call should be done for each object that has been previously opened
If the open function is called more than once, it increases the reference count of the
object it opens. The same number of closes should be made in order to completely
close the object.
9.1.4 Example
C/C++:
SKTHANDLE hScanAPI=NULL;
SKTRESULT result=SktScanOpen(NULL,&hScanAPI);
if(SKTSUCCESS(result))
{
// do whatever needs to be done
...
}
Java or C#:
ISktScanApi _ScanApi=null;
_ScanApi=SktClassFactory.createScanApiInstance();
long result=_scanApi.Open(null);
if(SktScanErrors.SKTSUCCESS(result))
{
// do whatever needs to be done
}
Objective C:
SKTRESULT Result=ESKT_NOERROR;
id<ISktScanApi> scanApi=nil;
scanApi=[SktClassFactory createScanApiInstance];
Result=[scanApi open:nil];
if(SKTSUCCESS(Result)){
// do whatever needs to be done
}
See also:
Sample handling asynchronous events of ScanAPI
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 44/152
Page 45

Socket ScanAPI Reference
C/C++
Header
SktScanAPI.h, include SktScanErrors.h,
SktScanTypes.h
Import library
ScanAPI.lib
Minimum operating systems
Windows XP, Windows Mobile 5.0
C#
Reference
ScanAPIManaged.dll for Windows or
ScanAPIManagedWM.dll for Windows
Mobile
Minimum operating systems
Windows XP, Windows Mobile 5.0
Java
Import
com.SocketMobile.ScanAPI.ISktScanApi
com.SocketMobile.ScanAPI.SktClassFactory
Jar File
ScanAPIFactory.jar
ScanAPI.jar
Minimum operating system
RIM 5.0.0, Android 2.1
Objective C
Import
SktScanApi.h
ScanApi.h
Framework
libScanAPI.a
ExternalAccessory.framework
Minimum operating system
iOS 4.1
9.1.5 Function Information
9.1.6 See Also
Close Function
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 45/152
Page 46

Socket ScanAPI Reference
C/C++
Header
SktScanAPI.h, include SktScanErrors.h,
SktScanTypes.h
Import library
ScanAPI.lib
Minimum operating systems
Windows XP, Windows Mobile 5.0
C#
9.2 Close Function
This function closes ether a ScanAPI object or a Device object.
9.2.1 Syntax
C/C++:
SKTRESULT SktScanClose(
SKTHANDLE hDevice
);
hDevice
[in] Handle to the scanner device or ScanAPI to close.
Java or C#:
long ISktScanDevice.Close(); or
long ISktScanApi.Close();
Objective C:
-(SKTRESULT) close;
From the protocol ISktScanApi or ISktScanDevice.
9.2.2 Return Value
If the function succeeds it returns ESKT_NOERROR.
9.2.3 Remarks
Any pending operation attached to this device will be aborted.
Once the object is closed, any subsequent operation using this handle will return an
error of invalid handle.
9.2.4 Example
See Sample handling asynchronous events of ScanAPI
9.2.5 Function Information
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 46/152
Page 47

Socket ScanAPI Reference
Reference
ScanAPIManaged.dll for Windows or
ScanAPIManagedWM.dll for Windows
Mobile
Minimum operating systems
Windows XP, Windows Mobile 5.0
Java
Import
com.SocketMobile.ScanAPI.ISktScanApi
com.SocketMobile.ScanAPI.SktClassFactory
Jar File
ScanAPIFactory.jar
ScanAPI.jar
Minimum operating system
RIM 5.0.0, Android 2.1
Objective C
Import
SktScanApi.h
ScanApi.h
Framework
libScanAPI.a
ExternalAccessory.framework
Minimum operating system
iOS 4.1
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 47/152
Page 48

Socket ScanAPI Reference
9.3 Set Function
The Set function sets a property of an object identified by its reference. This function
returns immediately before the property set is actually done. The final status should
be checked using the Wait function.
9.3.1 Syntax
C/C++:
SKTRESULT SktScanSet(
SKTHANDLE hDevice,
TSktScanObject * pSktObj
);
hDevice
[in] handle of the device.
pSktObj
[in] pointer to an allocated TSktScanObject that contains the property and its
value to set.
Java or C#:
long ISktScanDevice.SetProperty(
ISktScanObject scanObj
);
Or
Long ISktScanApi.SetProperty(
ISktScanObject scanObj
);
scanObj
[in] reference to a ScanObject that contains the property and its value to set.
The ScanObject should be created using the
SktClassFactory.createScanObject().
Objective C:
-(SKTRESULT) setProperty: (id<ISktScanObject>) scanObj;
From the ISktScanApi or ISktScanDevice protocol.
scanObj
[in] reference to a ScanObject that contains the property and its value to set.
The ScanObject should be created using the [SktClassFactory
createScanObject] message. Once this object is no longer useful it should be
freed by using the message releaseScanObject of the same class,
[SktClassFactory releaseScanObject:scanObject];
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 48/152
Page 49

Socket ScanAPI Reference
9.3.2 Return Value
If the function succeeds it returns ESKT_NOERROR.
The return value is ESKT_INVALIDHANDLE if the object reference is invalid.
If the function is called before the completion of an outstanding set or get operation,
it returns ESKT_PENDINGOPERATIONNOTCOMPLETED.
9.3.3 Remarks
The Set function allows an application to set a property of a scanner or ScanAPI, or
to send a command such as triggering a scan.
The ScanObject contains a property structure that defines the property to set. This
structure has a property ID field, a property type field and a value field. These fields
must be set accordingly to the property otherwise an error code will be returned.
In the success case, it will always return the completion code in the ScanObject that
must be retrieved with Wait function.
The Set function will fail if it is called before the completion of a previous Set
function or Get function.
9.3.4 Example
C/C++:
void CMyAppDlg:OnTriggerButton()
{
SKTRESULT Result=ESKT_NOERROR;
TSktScanObject ScanObj;
memset(&ScanObj,0,sizeof(ScanObj));
// initialize a ScanObject to
// trigger the device
ScanObj.Property.ID=kSktScanPropIdTriggerDevice;
ScanObj.Property.Type=kSktScanPropTypeByte;
ScanObj.Property.Byte=kSktScanTriggerStart;
// set the property with the
// device handle
Result=SktScanSet(m_hDevice,&ScanObj);
// check the Set result
if(SKTSUCCESS(Result))
m_TriggerBtn.Enable(FALSE);
else
{
// display an error message
DisplayError(_T("Unable to trigger: %d"),Result);
}
}
Java:
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 49/152
Page 50

Socket ScanAPI Reference
// handler for the Trigger button
class TriggerButtonHandler implements Runnable {
private ISktScanDevice _device=null;
private ButtonField _button;
// constructor
public TriggerButtonHandler(
ISktScanDevice device,
ButtonField button)
{
_device=device;
_button=button;
}
public void run() {
// create a ScanObject instance
ISktScanObject scanObj=
SktClassFactory.createScanObject();
// Initialize a ScanObject to
// Trigger the device
ISktScanProperty property=
scanObj.getProperty();
property.setID(
ISktScanProperty.propId.
kSktScanPropIdTriggerDevice);
property.setType(
ISktScanProperty.types.
kSktScanPropTypeByte);
property.setByte(
ISktScanProperty.values.trigger.
kSktScanTriggerStart);
// set the property with the device
// reference
long result=_device.SetProperty(scanObj);
// check the set result
if(SktScanErrors.SKTSUCCESS(result)){
_button.setVisualState(VISUAL_STATE_DISABLED);
}
else
{
// display an error message
DisplayError("Unable to trigger: "+result);
}
}
}
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 50/152
Page 51

Socket ScanAPI Reference
C#:
private void buttonTrigger_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// create a ScanObject instance
ISktScanObject scanObj =
SktClassFactory.createScanObject();
// Initialize a ScanObject to
// Trigger the device
scanObj.Property.ID =
ISktScanProperty.propId.kSktScanPropIdTriggerDevice;
scanObj.Property.Type =
ISktScanProperty.types.kSktScanPropTypeByte;
scanObj.Property.Byte =
ISktScanProperty.values.trigger.kSktScanTriggerStart;
// set the property with the device
// reference
long result = _device.SetProperty(scanObj);
if (SktScanErrors.SKTSUCCESS(result))
{
buttonTrigger.Enabled = false;
}
else
{
// display an error message
DisplayError("Unable to trigger: " + result);
}
}
Objective C:
// handler for the Trigger button
-(void) triggerAction:(id)sender{
SKTRESULT Result=ESKT_NOERROR;
id<ISktScanObject>scanObj=nil;
scanObj=[SktClassFactory createScanObject];
// fill out the Scan Object property to trigger the
// device
[[scanObj Property]setID:kSktScanPropIdTriggerDevice];
[[scanObj Property]setType:kSktScanPropTypeByte];
[[scanObj Property]setByte:kSktScanTriggerStart];
// send the Set property message
Result=[_scanapi setProperty:scanObj];
// release the scanObj as it is not needed anymore
[SktClassFactory releaseScanObject:scanObj];
if(!SKTSUCCESS(Result)){
[self DisplayErrorMessage:@"Unable to trigger the device"];
}
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 51/152
Page 52
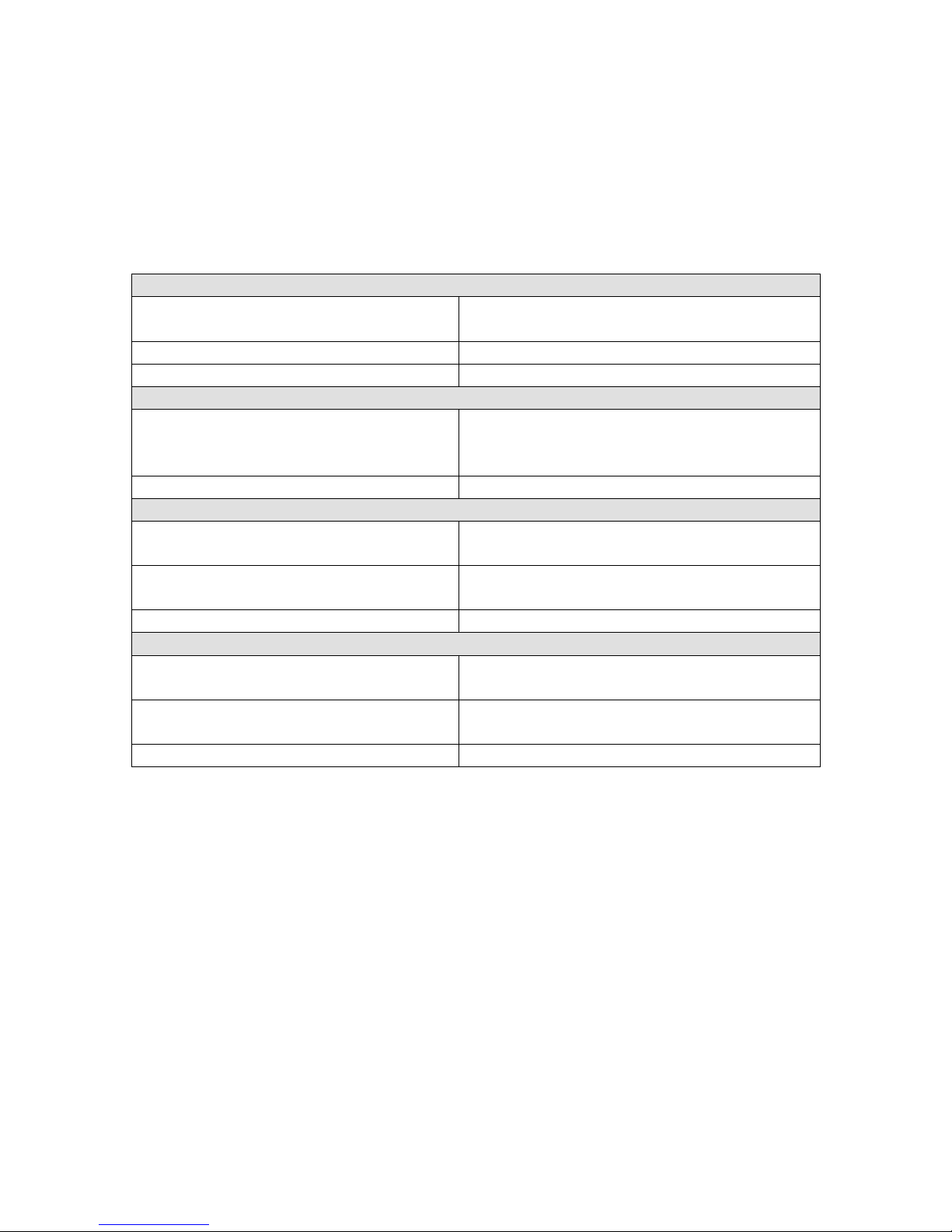
Socket ScanAPI Reference
C/C++
Header
SktScanAPI.h, include SktScanErrors.h,
SktScanTypes.h
Import library
ScanAPI.lib
Minimum operating systems
Windows XP, Windows Mobile 5.0
C#
Reference
ScanAPIManaged.dll for Windows or
ScanAPIManagedWM.dll for Windows
Mobile
Minimum operating systems
Windows XP, Windows Mobile 5.0
Java
Import
com.SocketMobile.ScanAPI.ISktScanApi
com.SocketMobile.ScanAPI.SktClassFactory
Jar File
ScanAPIFactory.jar
ScanAPI.jar
Minimum operating system
RIM 5.0.0, Android 2.1
Objective C
Import
SktScanApi.h
ScanApi.h
Framework
libScanAPI.a
ExternalAccessory.framework
Minimum operating system
iOS 4.1
}
9.3.5 Function Information
9.3.6 See Also
Get Function, Wait Function
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 52/152
Page 53

Socket ScanAPI Reference
9.4 Get Function
The Get function retrieves a property from ScanAPI object or from a device object
identified by its reference. This function returns immediately, and its final result
should be checked by using Wait function.
9.4.1 Syntax
C/C++:
SKTRESULT SktScanGet(
SKTHANDLE hDevice,
TSktScanObject* pSktObj
);
hDevice
[in] Handle to the device the property must be retrieved from.
pSktObj
[in] Pointer to a TSktScanObject that contains the property ID that needs to
be retrieved.
Java or C#:
long ISktScanDevice.GetProperty(
ISktScanObject scanObj
);
scanObj
[in] reference to a ScanObject that contains the property ID that needs to be
retrieved. The ScanObject should be created using the
SktClassFactory.createScanObject().
Objective C:
-(SKTRESULT) getProperty: (id<ISktScanObject>) scanObj;
From the ISktScanApi or ISktScanDevice protocol.
scanObj
[in] reference to a ScanObject that contains the property to get. The
ScanObject should be created using the [SktClassFactory createScanObject]
message. Once this object is no longer useful it should be freed using the
message releaseScanObject of the same class, [SktClassFactory
releaseScanObject:scanObject];
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 53/152
Page 54

Socket ScanAPI Reference
9.4.2 Return Value
If the function succeeds it returns ESKT_NOERROR.
The return value is ESKT_INVALIDHANDLE if the object reference is invalid.
If the function is called before the completion of an outstanding set or get operation,
it returns ESKT_PENDINGOPERATIONNOTCOMPLETED.
9.4.3 Remarks
This function returns immediately. In the success case, it will always return the
completion code in the ScanObject that must be retrieved with Wait function. The
Wait function returns the ScanObject structure with the Property field filled with the
result of the operation if it has been successful. The success code can be retrieve
from that same structure in the Result field.
9.4.4 Example
C/C++:
// Get device friendly name
SKTRESULT GetFriendlyName(
IN SKTHANDLE hDevice,
)
{
SKTRESULT Result=ESKT_NOERROR;
TSktScanObject ScanObj;
memset(&ScanObj,0,sizeof(ScanObj);
ScanObj.Property.ID=kSktScanPropIdFriendlyNameDevice;
ScanObj.Property.Type=kSktScanPropTypeNone;
// get the friendly name here
// the final result should be fetched
// in the Get Complete handler
Result=SktScanGet(hDevice,&ScanObj);
return Result;
}
Java or C#:
// get device friendly name
long GetFriendlyName(ISktScanDevice device)
{
long result=SktScanErrors.ESKT_NOERROR;
ISktScanObject scanObj;
scanObj=SktClassFactory.createScanObject();
ISktScanProperty property;
property=scanObj.getProperty();
property.setID(ISktScanProperty.propId.
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 54/152
Page 55
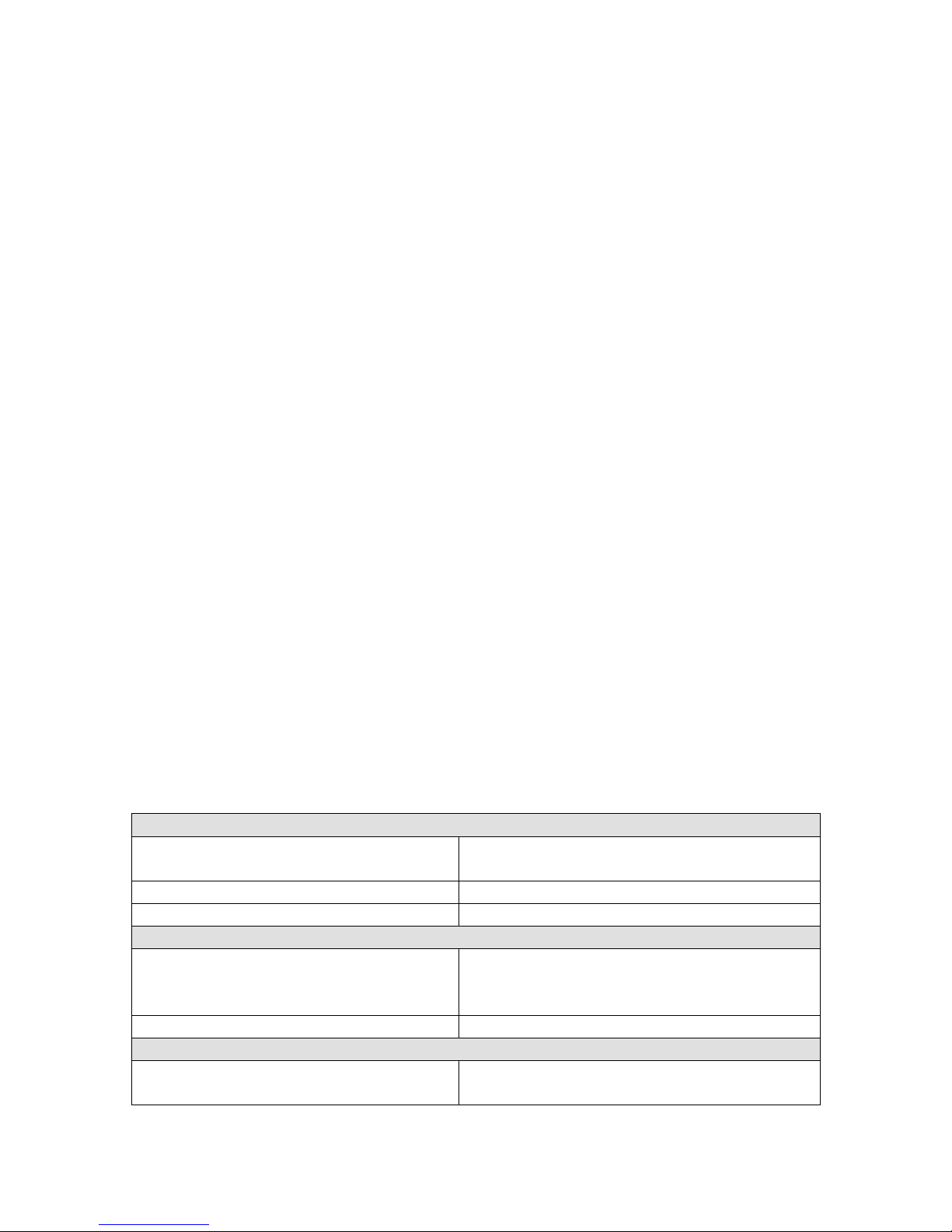
Socket ScanAPI Reference
C/C++
Header
SktScanAPI.h, include SktScanErrors.h,
SktScanTypes.h
Import library
ScanAPI.lib
Minimum operating systems
Windows XP, Windows Mobile 5.0
C#
Reference
ScanAPIManaged.dll for Windows or
ScanAPIManagedWM.dll for Windows
Mobile
Minimum operating systems
Windows XP, Windows Mobile 5.0
Java
Import
com.SocketMobile.ScanAPI.ISktScanApi
com.SocketMobile.ScanAPI.SktClassFactory
kSktScanPropIdFriendlyNameDevice);
property.setType(ISktScanProperty.types.
kSktScanPropTypeNone);
// get the friendly name here
// the final result should be fetched
// in the get complete handler
result=device.GetProperty(scanObj);
return result;
}
Objective C:
// Get the device friendly name
-(SKTRESULT)GetFriendlyName{
SKTRESULT Result=ESKT_NOERROR;
id<ISktScanObject>scanObj=nil;
// create a Scan Object
scanObj=[SktClassFactory createScanObject];
// fill out the Scan Object property to query the
// device friendly name
[[scanObj Property]setID:kSktScanPropIdFriendlyNameDevice];
[[scanObj Property]setType:kSktScanPropTypeNone];
// send the Get property message
Result=[_scanapi getProperty:scanObj];
// release the scanObj as it is not needed anymore
[SktClassFactory releaseScanObject:scanObj];
return Result;
}
9.4.5 Function Information
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 55/152
Page 56

Socket ScanAPI Reference
Jar File
ScanAPIFactory.jar
ScanAPI.jar
Minimum operating system
RIM 5.0.0, Android 2.1
Objective C
Import
SktScanApi.h
ScanApi.h
Framework
libScanAPI.a
ExternalAccessory.framework
Minimum operating system
iOS 4.1
9.4.6 See Also
Set Function, Wait Function
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 56/152
Page 57

Socket ScanAPI Reference
9.5 Wait Function
The Wait function waits for any asynchronous events. Only a ScanAPI object can be
used as reference for the wait function.
Most of the time, applications using ScanAPI, use a timer to consume the ScanAPI
asynchronous events. In this case, the wait function can be called with 0 as timeout
so that it returns immediately with timeout result if there is no ScanObject or with
no error result if it has retrieved a ScanObject.
9.5.1 Syntax
C/C++:
SKTRESULT SktScanWait(
SKTHANDLE hScanAPI,
TSktScanObject** ppSktObj,
DWORD dwTimeout
);
hScanAPI
[in] handle to ScanAPI object. This handle cannot be a handle of a scanner
device. If this handle is not a ScanAPI object, this function will return an
invalid handle error.
ppSktObj
[out] pointer to a TSktScanObject pointer. TSktScanObject is allocated by
ScanAPI. This object must be released when it is no longer needed.
dwTimeout
[in] a timeout value expressed in milliseconds. The timeout cannot be bigger
than 10000ms otherwise an error will be returned.
Java:
long ISktScanApi.WaitForScanObject(
ISktScanObject[] scanObj,
long ulTimeout
);
scanObj
[out] reference to a ScanObject that is allocated by ScanAPI. This object must
be released when it is no longer needed.
ulTimeout
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 57/152
Page 58

Socket ScanAPI Reference
[in] a timeout value expressed in milliseconds. The timeout cannot be bigger
than 10000ms otherwise an error will be returned.
C#:
long ISktScanApi.WaitForScanObject(
ISktScanObject out scanObj,
long ulTimeout
);
scanObj
[out] reference to a ScanObject that is allocated by ScanAPI. This object must
be released when it is no longer needed.
ulTimeout
[in] a timeout value expressed in milliseconds. The timeout cannot be bigger
than 10000ms otherwise an error will be returned.
Objective C:
-(SKTRESULT) waitForScanObject: (id<ISktScanObject>) scanObj TimeOut:
(unsigned long) ulTimeout;
Only from the ISktScanApi protocol.
scanObj
[in] reference to a ScanObject that will contain the asynchronous message
coming from ScanAPI. The ScanObject should be created using the
[SktClassFactory createScanObject] message. Once this object is no longer
useful it should first be released from ScanAPI using the ReleaseScanObject
API and then it should be freed by using the message releaseScanObject of
the same class, [SktClassFactory releaseScanObject:scanObject];
To avoid unnecessary calls to SktClassFactory, a good approach is at startup
of the application to create one ScanObject instance dedicated to be used for
any subsequent calls to this WaitForScanObject. Once the application is done
using ScanAPI, it can release this dedicated ScanObject.
ulTimeout
[in] timeout to wait for a ScanObject expresses in milliseconds. The timeout
cannot be bigger than 10000ms otherwise an error will be returned.
9.5.2 Return Value
If the function succeeds it returns ESKT_NOERROR.
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 58/152
Page 59

Socket ScanAPI Reference
C/C++
Header
SktScanAPI.h, include SktScanErrors.h,
SktScanTypes.h
Import library
ScanAPI.lib
Minimum operating systems
Windows XP, Windows Mobile 5.0
C#
Reference
ScanAPIManaged.dll for Windows or
ScanAPIManagedWM.dll for Windows
Mobile
Minimum operating systems
Windows XP, Windows Mobile 5.0
Java
Import
com.SocketMobile.ScanAPI.ISktScanApi
com.SocketMobile.ScanAPI.SktClassFactory
Jar File
ScanAPIFactory.jar
ScanAPI.jar
Minimum operating system
RIM 5.0.0, Android 2.1
Objective C
Import
SktScanApi.h
ScanApi.h
Framework
libScanAPI.a
ExternalAccessory.framework
Minimum operating system
iOS 4.1
If the object reference specified is not a ScanAPI object, the function returns
ESKT_INVALIDHANDLE.
If the timeout value is bigger than 10000 the function returns
ESKT_INVALIDTIMEOUT.
If the timeout occurs, the function returns ESKT_WAITTIMEOUT.
9.5.3 Remarks
The ScanObject retrieved using this API should be released by using the Release API.
Example
See Sample handling asynchronous events of ScanAPI
9.5.4 Function Information
9.5.5 See Also
Set Function
Get Function
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 59/152
Page 60

Socket ScanAPI Reference
Release Function.
9.6 Release Function
The Release function releases the ScanObject the Wait function has allocated. This
function must be called each time the Wait function returns success. Only a ScanAPI
object can be used as referenced when calling this Release function.
9.6.1 Syntax
C/C++:
SKTRESULT SktScanRelease(
SKTHANDLE hScanAPI,
TSktScanObject* pSktObj
);
hScanAPI
[in] handle to ScanAPI object. This handle cannot be a handle of a scanner
device. If this handle is not a ScanAPI object, this function will return an
invalid handle error.
pSktObj
[in] pointer to a TSktScanObject to release when it is no longer needed.
Java or C#:
long ISktScanApi.ReleaseScanObject(
ISktScanObject scanObj
);
scanObj
[in] reference to a ScanObject to release when it is no longer needed.
Objective C:
-(SKTRESULT) releaseScanObject: (id<ISktScanObject>) scanObj;
Only from the ISktScanApi protocol.
scanObj
[in] reference to a ScanObject that was received in WaitForScanObject API.
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 60/152
Page 61

Socket ScanAPI Reference
C/C++
Header
SktScanAPI.h, include SktScanErrors.h,
SktScanTypes.h
Import library
ScanAPI.lib
Minimum operating systems
Windows XP, Windows Mobile 5.0
C#
Reference
ScanAPIManaged.dll for Windows or
ScanAPIManagedWM.dll for Windows
Mobile
Minimum operating systems
Windows XP, Windows Mobile 5.0
Java
Import
com.SocketMobile.ScanAPI.ISktScanApi
com.SocketMobile.ScanAPI.SktClassFactory
Jar File
ScanAPIFactory.jar
ScanAPI.jar
Minimum operating system
RIM 5.0.0, Android 2.1
Objective C
Import
SktScanApi.h
ScanApi.h
Framework
libScanAPI.a
ExternalAccessory.framework
Minimum operating system
iOS 4.1
9.6.2 Return Value
If the function succeeds it returns ESKT_NOERROR.
If the object reference specified is not to a ScanAPI object, the function returns
ESKT_INVALIDHANDLE.
9.6.3 Remarks
9.6.4 Example
See the Sample handling asynchronous events of ScanAPI.
9.6.5 Function Information
9.6.6 See Also
Wait Function
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 61/152
Page 62

Socket ScanAPI Reference
Name
Description
kSktScanMsgIdDeviceArrival
Indicates a new device has arrived and is ready to
be used. The Device field contains the
information about that device.
kSktScanMsgIdDeviceRemoval
Indicates a device is no longer available through
ScanAPI. The only possible operation is the Close
API with the device reference. The Device field
contains the information about that device
including the GUID and the device reference if the
device is still open by the application.
kSktScanMsgIdTerminate
Indicates ScanAPI is ready for shutdown. All the
devices have been removed and closed by the
application. It is safe for the application to close
ScanAPI object after releasing the last ScanObject.
kSktScanMsgSetComplete
Indicates when a Set API operation is completed.
The result of this operation can be retrieved in
the Result field of the Message. The ScanObject
property field contains the property information.
kSktScanMsgGetComplete
Indicates when a Get API operation is completed.
The result of this operation can be retrieved in
the Result field of the message. The ScanObject
property field contains the property information.
kSktScanMsgEvent
An asynchronous event has been received.
10 ScanObject
The ScanObject is the main object that is exchanged between the application and
ScanAPI.
This object has two main members: Message and Property.
Only the Property is relevant when the application is sending a property to a
ScanAPI object or a Device object.
The Message member is relevant only when the application is receiving a ScanObject
from ScanAPI. The Property member is only relevant if the Message ID received is a
Get Complete or a Set Complete.
A Message has a message identifier field, a result field, a device field, and an event
field.
The identifier field indicates the type of message received. It can be one of the
following:
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 62/152
Page 63

Socket ScanAPI Reference
11 Asynchronous messages and events
11.1 Device Arrival
The Wait API returns a ScanObject with its MsgID field set to
kSktScanMsgDeviceArrival and the Device structure field set to the device friendly
name, the device GUID that can be used in the Open API and the device type.
The device arrival can be received as soon as a scanner connects to the host
computer or if a scanner is connected before ScanAPI is initialized.
The device GUID is generated each time a scanner connects to the host. If the same
scanner connects and disconnects several times, its GUID will be different each time.
11.2 Device Removal
The device removal is received by the Wait API as soon as a scanner disconnects
from the host computer or during the termination process of ScanAPI.
The Wait API returns a ScanObject with its MsgID field set to
kSktScanMsgDeviceRemoval and the Device structure field set to the device friendly
name, the device GUID and the device object reference if this device was successfully
opened.
This device object reference can be directly used to close the device by using the
Close API.
If the device wasn’t opened, this reference is set to NULL and the GUID is an empty
string.
11.3 Terminate
The terminate message is received once a Set API has been invoked with the Abort
property, and once every device removal has been responded to by a close device.
When this message is received it is safe to stop the consumer logic that was waiting
on the asynchronous events, to release this last ScanObject and the ScanAPI object
reference can be safely close using the Close API.
11.4 Set Complete
When a Set API operation is completed, the Wait API returns with a ScanObject that
has its MsgID field set to kSktScanSetComplete. The Result field contains the result
of the Set operation, and the Property of the ScanObject contains the property ID for
which the operation has been completed. There is usually no property value on a Set
Complete event. As an example, if an application is changing a device friendly name
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 63/152
Page 64
Socket ScanAPI Reference
Byte 3
Byte 2
Byte 1
Byte 0
-reserved-
-reserved-
-reserved-
State
Macro name
Description
SKTPOWER_GETSTATE(powerStatus)
Returns the least significant byte
Byte 0 of the double word
powerStatus which represents the
power state.
using the Set API, the Set Complete will return the property ID of the friendly name,
but it won’t return the new friendly name.
11.5 Get Complete
When a Get API operation is completed, the Wait API returns with a ScanObject that
has its MsgID field set to kSktScanGetComplete. The Result field contains the result
of the Get operation. If the result is successful the data can be retrieved according to
the data type that is set in the Type field of the ScanObject Property member.
11.6 Events
Asynchronous events such as decoded data or low battery can be received in the
Wait API. The Msg field of the ScanObject has an event member that is defined by
ScanEvent.
The ScanEvent contains the event identifier and the event data. The event data
defines data that is associated to the event received. Event Data has a type
descriptor and a value that depends on the type descriptor, which could be None,
Byte, Ulong, Array, String or Decoded Data.
11.6.1 Power Event
The Power Event is received when the device has a change regarding its power. This
allows the application UI to display clearly the power state of the device by example
when the device is charging.
The Power Event is not activated by default. The device notification must be
modified in order to turn on this notification. This is accomplished by using the
property kSktScanPropIdNotificationDevice.
The power information is coded in a double word that can be decomposed in 4 fields
from the most significant byte to the least significant:
A helper macro can be used for retrieving the value.
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 64/152
Page 65

Socket ScanAPI Reference
C/C++:
The helper macro can be found in the SktScanPropIds.h file.
Java:
The helper macro can be found in com.SocketMobile.ScanAPI.SktScan.helper.
C#:
The helper macro can be found in ScanAPI.SktScan.helper.
Objective C:
The helper macro can be found in the SktScanPropIds.h file.
Event Data Type: kSktScanEventDataTypeUlong.
See also:
Property kSktScanPropIdBatteryLevelDevice
11.6.2 Decoded Data Event
The decoded data event occurs each time successful data has been decoded by the
scanner.
The event data contains a decoded data structure that has 3 fields; a string field to
hold the decoded data as received from the scanner, a string field to hold the
symbology name and a SymbologyID field that indicates the symbology ID the
decoded data has been extracted from.
The decoded data arrives in the application only if the application has previously
opened the device.
The decoded data is usually in 7-bit ASCII, however, if the scanner is a 2D Imager
scanner, the data may be in a binary format, such as UNICODE, Shift_JIS or raw
binary data, depending on the barcode scanned. The decoded data will always be
NULL terminated with a byte, and the null byte does not count in the length.
Event Data Type: kSktScanEventDataTypeDecodedData.
11.6.3 Buttons Event
The buttons event occurs each time a user presses a button on the device.
The event will be received only if the device has been previously opened and the
device has been configured to send those events.
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 65/152
Page 66
Socket ScanAPI Reference
7 6 5 4 3 2 1
0
Reserved
Reserved
Reserved
Ring
Detached
Power
button
Middle
button
Right
button
Left
button
Name
Description
SKTBUTTON_ISLEFTPRESSED(buttons)
Returns true if the left button is
pressed, false otherwise.
SKTBUTTON_ISRIGHTPRESSED(buttons)
Returns true if the right button is
pressed, false otherwise.
SKTBUTTON_ISMIDDLEPRESSED(buttons)
Returns true if the middle button is
pressed, false otherwise.
SKTBUTTON_ISPOWERPRESSED(buttons)
Returns true if the power button is
pressed, false otherwise.
SKTBUTTON_ISRINGDETACHED(buttons)
Returns true if the Ring unit is
detached from the wrist unit, false
otherwise.
The Buttons Event is not activated by default. The device notification must be
modified in order to turn on this notification. This is accomplished by using the
property kSktScanPropIdNotificationDevice.
The same property can be used to configure which button event the device will
send. See the Property kSktScanPropIdNotificationsDevice for more information.
The buttons code is a byte value with a bit field value and is defined as follows:
If the bit is set it means the button has been pressed.
A set of macros are defined to retrieve the status.
Several buttons can be pressed at the same time and the button code will reflect that
condition with multiple bits set to 1.
The button status can also be retrieved at any time by doing a get operation with the
Property kSktScanPropIdButtonStatusDevice.
NOTE:
On a scanner that has only one trigger button such as 7 series scanners, the Middle
button is the trigger button.
The power button will generate one event when it is pressed and another event
when it is released whereas the left and right buttons generate an event only when
they are pressed.
C/C++:
The helper macro can be found in the SktScanPropIds.h file
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 66/152
Page 67

Socket ScanAPI Reference
Byte 3
Byte 2
Byte 1
Byte 0
Battery Level Max
Battery Level Min
Battery Level
-reserved-
Java:
The helper macro can be found in com.SocketMobile.ScanAPI.SktScan.helper.
C#:
The helper macro can be found in ScanAPI.SktScan.helper.
Objective C:
The helper macro can be found in the SktScanPropIds.h file.
Event Data Type: kSktScanEventDataTypeByte.
See also:
Property kSktScanPropIdButtonStatusDevice
11.6.4 Error Event
This event occurs each time there is an error, usually during communication with
the device. The error code can be retrieve in the Result field of the message
structure.
Event Data Type: kSktScanEventDataTypeNone or kSktScanEventDataTypeString.
In the case of a String data type, the Event String data contains more information
about the error. For example, it might contain the communication port name that is
reporting an error.
11.6.5 Battery Level Event
The Battery Level Event is received when the device has a change regarding its
battery level. This allows the application UI to display an alert if the battery level
gets low.
The Battery Level Event is not activated by default. The device notification must be
modified in order to turn on this notification. This is accomplished by using the
property kSktScanPropIdNotificationDevice.
The device must be opened in order to receive this event.
The power information is coded in a Ulong that can be decomposed into three fields
from the most significant byte to the less significant:
A set of macros is defined in order to retrieve these values.
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 67/152
Page 68

Socket ScanAPI Reference
Macro name
Description
SKTBATTERY_GETCURLEVEL(batteryLevel)
Returns the Byte 1 of the double
word batteryLevel that contains
the current battery level within the
Min Level and the Max Level
values.
SKTBATTERY_GETMINLEVEL(batteryLevel)
Returns the Byte 2 of the double
word batteryLevel that contains
the level minimum.
SKTBATTERY_GETMAXLEVEL(batteryLevel)
Returns the Byte 3 of the double
word batteryLevel that contains
the level maximum.
C/C++:
The helper macro can be found in the SktScanPropIds.h file
Java:
The helper macro can be found in com.SocketMobile.ScanAPI.SktScan.helper.
C#:
The helper macro can be found in ScanAPI.SktScan.helper.
Objective C:
The helper macro can be found in the SktScanPropIds.h file.
Event Data Type: kSktScanEventDataTypeUlong.
See also:
Property kSktScanPropIdBatteryLevelDevice
11.6.6 Listener Started Event
When ScanAPI starts and is initialized, a listener started event is sent indicating the
listener is running and listening on the communication ports.
If the ScanAPI communication port configuration is modified, the listener will
restart in order to retrieve and apply the new configuration. During this process, the
listener sends a Listener Started event.
If for some reason the configuration is incorrect, or none of the communication
ports can be used, the listener will then wait for a new configuration after reporting
this error condition.
The application UI can then report a configuration issue that needs to be addressed.
As soon as a new configuration is applied, the application can refresh its UI status
when it receives the Listener Started event.
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 68/152
Page 69
Socket ScanAPI Reference
Get
Get Complete
Set
Set Complete
<data type>:
defines the
expected type for a
get operation.
<data type>:
defines the type
received in the get
complete
operation.
<data type>:
defines the
expected type for a
set operation
<data type>:
defines the type
received in the set
complete
operation.
Event Data Type: kSktScanEventDataTypeNone.
12 Introduction to Properties
The Property is a member of a ScanObject. There are used by an application to
retrieve or modify a scanner property by using the Get or Set API respectively.
Each of these operations is completed only upon reception of the Get Complete or
Set Complete events, which also contains the resulting property.
Properties are defined with a property identifier, a value type and a value.
A property contains a Context that is a user parameter field that can be associated to
the property. If an application is using this Context field during a Get or a Set
property operation, the matching Get Complete or Set Complete property received
will return the same Context value.
Once a Set or Get operation is successful the result will always be delivered in the
corresponding Set Complete or Get Complete event. The Msg structure of the
ScanObject received by the application contains the identifier for a Set Complete
message or a Get Complete message and the Result field indicates the success of the
Set or Get operation.
If for some reason the device cannot respond to a Set or Get property operation, that
operation will eventually time out (about 5s), and a Set or a Get complete with a
timeout error in the Msg Result field will be received by the application.
Each property defined in the next chapter accepts different data type for a Get
Operation or a Set Operation.
The data type has to be set accordingly prior performing the operation.
Here is the how this table is defined for each property:
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 69/152
Page 70
Socket ScanAPI Reference
Type
Definition
Not applicable
The current property does not support this operation.
None
The current property does not have any data attached for this
operation.
Byte
The current property has a byte as data. A byte is an 8-bit
value.
Ulong
The current property has an unsigned long as data. An
unsigned long is a 32 bit value.
Array
The current property has an array of bytes as data. The array
has a size field denoting the number of bytes in the array.
String
The current property has a UTF8 character string as data. The
string has a length field and is terminated with a NULL
character. The length does not include the NULL character.
Version
The current property has a Version structure as data.
Symbology
The current property has a Symbology structure as data.
Object
The current property holds a reference to an object. The
object definition depends on the Property.
The following table summarizes what the data type could be and what its definition
is.
There are two sets of properties; the first set applies to a ScanAPI object and the
second set applies to a Device object.
An error (ESKT_INVALIDHANDLE) is returned if a property is applied to a wrong
object. A wrong object would be a ScanAPI object when the property works only for
a Device object or vice versa.
An error (ESKT_INVALIDOPERATION) is returned if a property operation is not
applicable.
An error (ESKT_INVALIDPARAMETER) is returned if a property operation is used
with an incorrect property data type.
13 ScanAPI object properties
13.1 Property kSktScanPropIdAbort
This property is used to start the shutdown process of ScanAPI. This property must
be used in order to proceed to a clean shutdown. Once this property is set, a set
complete message should be received followed by a series of Device Removals if
there are any devices connected to the host. If their matching Device objects have
been opened by the application, they should be closed using the Close API. Once all
the Device objects have been close or if no device handle has been previously
opened, a Terminate message is received. Upon reception of this last message, it is
safe to stop the ScanAPI consumer logic that uses the Wait API, release this last
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 70/152
Page 71

Socket ScanAPI Reference
Get
Get Complete
Set
Set Complete
Not applicable
Not applicable
None
None
ScanAPI Interface Version
1.0.0 or higher
Get
Get Complete
Set
Set Complete
None
Version
Not applicable
Not applicable
message by using Release API and close ScanAPI by using the Close API with the
ScanAPI object reference.
This property can only be set. A get operation on this property will return an error.
Parameter type
Version
13.2 Property kSktScanPropIdVersion
This property is used to retrieve the version of ScanAPI. This property can only be
used with the Get function.
The value returned in a Get Complete Response is a Version structure. The
ScanObject Property has its type set to kSktScanPropTypeVersion indicating that its
SktScanVersion structure is valid and contains the retrieved information. If the
result code is successful, the version can be read from that structure.
The Version structure has 9 fields; Major, Middle, Minor, Build, Month, Day, Year,
Hour and Minute.
Each field of the Version structure is a 2-byte quantity. The Build is a 4-byte
quantity.
All the fields are normally displayed in Hexadecimal format; however the Build
number is usually displayed in a decimal format.
Parameter type
Example:
C/C++:
if(pScanObject->Property.Type==kSktScanPropTypeVersion)
{
printf("version: %x.%x.%x %d\nDate: %x/%02x/%02x %02x:%02x\n",
pScanObject->Property.Version.wMajor,
pScanObject->Property.Version.wMiddle,
pScanObject->Property.Version.wMinor,
pScanObject->Property.Version.dwBuild,
pScanObject->Property.Version.wYear,
pScanObject->Property.Version.wMonth,
pScanObject->Property.Version.wDay,
pScanObject->Property.Version.wHour,
pScanObject->Property.Version.wMinute);
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 71/152
Page 72

Socket ScanAPI Reference
}
Java
if(scanObject.getProperty().getType()==
ISktScanProperty.types.kSktScanPropTypeVersion){
OutputString("version: "+
Integer.toHexString(scanObject.getProperty().
getVersion().getMajor())+"."+
Integer.toHexString(scanObject.getProperty().
getVersion().getMiddle())+"."+
Integer.toHexString(scanObject.getProperty().
getVersion().getMinor())+" "+
scanObject.getProperty().
getVersion().getBuild()+"\nDate: "+
Integer.toHexString(scanObject.getProperty().
getVersion().getYear())+"/"+
Integer.toHexString(scanObject.getProperty().
getVersion().getMonth())+"/"+
Integer.toHexString(scanObject.getProperty().
getVersion().getDay())+" "+
Integer.toHexString(scanObject.getProperty().
getVersion().getHour())+":"+
Integer.toHexString(scanObject.getProperty().
getVersion().getMinute()));
}
C#:
switch(scanObject.Property.Type)
{
case ISktScanProperty.types.kSktScanPropTypeNone:
break;
/………………/
case ISktScanProperty.types.kSktScanPropTypeVersion:
OutputString("version: "+
Convert.ToString(data._scanObject.Property.Version.wMajor,16)+"."+
Convert.ToString(data._scanObject.Property.Version.wMiddle,16)+"."+
Convert.ToString(data._scanObject.Property.Version.wMinor,16)+
" "+
data._scanObject.Property.Version.dwBuild+CARRIAGE_RETURN+
"Date: "+
Convert.ToString(data._scanObject.Property.Version.wYear,16)+"/"+
Convert.ToString(data._scanObject.Property.Version.wMonth,16)+"/"+
Convert.ToString(data._scanObject.Property.Version.wDay,16)+" "+
Convert.ToString(data._scanObject.Property.Version.wHour,16)+":"+
Convert.ToString(data._scanObject.Property.Version.wMinute,16));
break;
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 72/152
Page 73

Socket ScanAPI Reference
ScanAPI Interface Version
1.0.0 or higher
default:
OutputString("Value: Type unknown or not implemented:" +
data._scanObject.Property.Type + CARRIAGE_RETURN);
break;
}
Objective C:
switch([[scanObj Property]getType]){
case kSktScanPropTypeNone:
break;
case kSktScanPropTypeVersion:
OutputString("version: %x.%x.%x %d\nDate: %x/%02x/%02x %02x:%02x\n",
[[[scanObj Property] Version ]getMajor],
[[[scanObj Property] Version ]getMiddle],
[[[scanObj Property] Version ]getMinor],
[[[scanObj Property] Version ]getBuild],
[[[scanObj Property] Version ]getYear],
[[[scanObj Property] Version ]getMonth],
[[[scanObj Property] Version ]getDay],
[[[scanObj Property] Version ]getHour],
[[[scanObj Property] Version ]getMinute]);
break;
/.../
default:
OutputString("Value: Type unknown or not implemented:%d\n",[[scanObj
Property]getType]);
break;
Version
13.3 Property kSktScanPropIdInterfaceVersion
This property is used to retrieve the ScanAPI interface version. If the interface
contract has been modified, this version will be changed to reflect that modification.
This is important for an application that uses ScanAPI as a separate component such
as a DLL, where ScanAPI can be updated without the need of the application code to
be recompiled. Therefore the ScanAPI DLL installed on the host might be different
from the ScanAPI used during the development of an application. An application can
check if the ScanAPI installed on the system has the expected interface.
ScanAPI will always try to provide a backward compatible interface. Therefore if the
interface version is higher than what the application expected, the application
should not have any problem using this version of ScanAPI. However, if the interface
version returned is lower, the application may not be able to run correctly if it uses
some property not available in the current version of the installed ScanAPI.
This property can only be used with the SktScanGet API. Using it with the SktScanSet
API will fail.
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 73/152
Page 74

Socket ScanAPI Reference
Get
Get Complete
Set
Set Complete
None
Version
Not applicable
Not applicable
ScanAPI Interface Version
1.0.0 or higher
Name
Description
Values
kSktScanConfigSerialComPort
Contains the list of
Serial Ports separated
by semi colon ScanAPI
will listen on.
COM3:;COM4:…
kSktScanConfigPath
Allows to retrieve the
configuration path
where ScanAPI save its
configuration on the
host.
This value can
only be read.
The Get
complete
returns the
path.
kSktScanConfigMonitorDbgLevel
Contains the actual
Debug Level for the
traces. This settings
works only if the
ScanAPI is compiled
with the Traces
capability turned on.
(Java platforms can use
this option).
This value is
expressed in
hexadecimal. A
value of 0x04
will trace only
the error. A
value of
0xfffff9f7 will
turn on all the
traces. The
ScanAPI will
need to be
closed and
restarted in
order for the
changes to take
Return Value
The value is returned in the Version structure of the Property. The Property type is
set to kSktScanPropTypeVersion. The version structure has 9 fields; Major, Middle,
Minor, Build, Month, Day, Year, Hour and Minute.
Parameter type
Version
13.4 Property kSktScanPropIdConfiguration
This property is used to set or get a ScanAPI property.
The following property values can be used:
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 74/152
Page 75

Socket ScanAPI Reference
effect.
kSktScanConfigMonitorDbgFileLineLevel
Add or remove the file
and line information in
the traces. This feature
works only on
Windows Platforms.
This value is
expressed in
hexadecimal.
kSktScanConfigMonitorDbgChannel
Modify the channel to
where the debug traces
are directed.
This value is
expressed in
hexadecimal.
0x01 for the
normal debug
window.
0x08 for using
the application
output if
correctly setup.
A value of 0x09
will display
traces on both,
debug window
and application
output.
The value of the serial port configuration contains a list of COM port names where
each item of the list is separated by semi colon: “COM3:;COM4:”
In order to set the property, the configuration name should be specified in the
property string field with an equal sign and the new value for this configuration.
Example
TSktScanObject ScanObj;
memset(&ScanObj,0,sizeof(ScanObj);
// allocate memory to receive the new config string
ScanObj.Property.String.pValue=new char[64];
if(ScanObj.Property.String.pValue)
{
ScanObj.Property.ID=kSktScanPropIdConfiguration;
ScanObj.Property.Type=kSktScanPropTypeString;
printf(ScanObj.Property.String.pValue,"%s=%s",
kSktScanConfigSerialComPort,"COM3:;COM4:");
ScanObj.Property.String.nLength=
strlen(ScanObj.Property.String.pValue);
// set the configuration here
Result=SktScanSet(hScanAPI,&ScanObj);
// done with this buffer
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 75/152
Page 76

Socket ScanAPI Reference
Get
Get Complete
Set
Set Complete
String
String
String
None
ScanAPI Interface Version
1.0.0 or higher
delete[]ScanObj.Property.String.pValue;
}
else
{
// ... handle the error
}
NOTE:
Changing the COM port ScanAPI is listening will cause ScanAPI to shutdown any
active connections and restart its listener thread on the newly specified COM port. If
the COM port doesn’t exist or cannot be opened an error
(ESKT_UNABLEOPENDEVICE) is generated and sent to the application as an
asynchronous message. ScanAPI generates an error (ESKT_NOTHINGTOLISTEN) if
no COM port can be successfully open.
C/C++:
The configuration define can be found in the SktScanPropIds.h file.
Java:
The configuration define can be found in
com.SocketMobile.ScanAPI.ISktScanProperty.values.configuration.
C#:
The configuration define can be found in
ScanAPI.ISktScanProperty.values.configuration
Objective C:
The configuration define can be found in the SktScanPropIds.h file.
Parameter type
Version
13.5 Property kSktScanPropIdDataConfirmationMode
This property is used to read or modify the Data Confirmation feature.
The Data Confirmation feature controls how decoded data should be acknowledged.
Decoded data can be acknowledged at three different locations; locally on the
scanner device, remotely on the host at the ScanAPI level or at the application level.
The advantage of acknowledging the data locally on the device is speed, but the
operator doesn’t know for sure the data has arrived at the application level. The
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 76/152
Page 77

Socket ScanAPI Reference
Name
Description
kSktScanDataConfirmationModeOff
ScanAPI layer doesn’t try to alter the
actual device configuration. It will be
whatever the device has its local
acknowledgment set.
kSktScanDataConfirmationModeDevice
The decoded data is confirmed locally on
the device.
kSktScanDataConfirmationModeScanAPI
The decoded data is confirmed at
ScanAPI level if an application has
previously opened the device handle.
kSktScanDataConfirmationModeApp
The decoded data is confirmed at the
application level. The application should
send a Set property with the identifier
set to
kSktScanPropIdDataConfirmationDevice.
Get
Get Complete
Set
Set Complete
None
Byte
Byte
None
advantage for the application acknowledging the decoded data is to confirm that it
corresponds to something expected by the application and if not then the
application can acknowledge negatively the decoded data letting the operator know
the barcode he or she just scanned is incorrect. The problem with this mode of
acknowledgment is the small time lag that it introduces between each scan
operation.
This property value is a type of byte and its value is summarized in the following
table:
C/C++:
The data confirmation defines can be found in the SktScanPropIds.h file.
Java:
The configuration define can be found in
com.SocketMobile.ScanAPI.ISktScanProperty.values.confirmationMode.
C#:
The configuration define can be found in
ScanAPI.ISktScanProperty.values.confirmationMode.
Objective C:
The data confirmation defines can be found in the SktScanPropIds.h file.
Parameter type
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 77/152
Page 78

Socket ScanAPI Reference
ScanAPI Interface Version
1.0.0 or higher
Name
Description
kSktScanDataConfirmationRumbleNone
No rumble
kSktScanDataConfirmationRumbleGood
Rumble indicating a good action
kSktScanDataConfirmationRumbleBad
Rumble indicating an incorrect action
kSktScanDataConfirmationBeepNone
No beep
kSktScanDataConfirmationBeepGood
Beep indicating a good action
kSktScanDataConfirmationBeepBad
Beep indicating an incorrect action
kSktScanDataConfirmationLedNone
No LED flashing
kSktScanDataConfirmationLedGreen
LED flashing in green
kSktScanDataConfirmationLedRed
LED flashing in red
Version
See also
Data confirmation feature
13.6 Property kSktScanPropIdDataConfirmationAction
This property reads or sets the ScanAPI Data Confirmation Action.
The Data Confirmation Action is used by ScanAPI only if the Data Confirmation
Mode is set to kSktScanDataConfirmationModeScanAPI.
In that mode, when ScanAPI receives decoded data, it will respond with the Action
defined by this property.
The Action is defined by a set of bits. There are 3 actions that can be configured;
Rumble, Beep and LED. The Rumble can be set on device that doesn’t have a Rumble
motor, but will have no effect.
Some helper macros have been defined to help to configure this setting.
The following table summarizes the possible values that can be used with the macro
SKTDATACONFIRMATION.
Example
ScanObj.Property.ID=kSktScanPropIdDataConfirmationAction;
ScanObj.Property.Type=kSktScanPropTypeUlong;
ScanObj.Property.Ulong=SKTDATACONFIRMATION(0,
kSktScanDataConfirmationRumbleNone, kSktScanDataConfirmationBeepNone,
kSktScanDataConfirmationLedNone);
C/C++:
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 78/152
Page 79

Socket ScanAPI Reference
Get
Get Complete
Set
Set Complete
None
Ulong
Ulong
None
ScanAPI Interface Version
1.0.0 or higher
Name
Description
kSktScanMonitorDbgLevel
This monitor mode changes the debug
level. The Debug level is described
below.
kSktScanMonitorDbgChannel
This monitor mode changes the channel
where the traces can be outputted.
kSktScanMonitorDbgFileLineLevel
This monitor mode changes the level
from which the traces will have the line
number and the file name in the traces.
The helper macro and the defines can be found in the SktScanPropIds.h file.
Java:
The helper macro can be found in com.SocketMobile.ScanAPI.SktScan.helper and the
values are defined in
com.SocketMobile.ScanAPI.ISktScanProperty.values.dataConfirmation
C#:
The helper macro can be found in ScanAPI.SktScan.helper and the values are defined
in ScanAPI.ISktScanProperty.values.dataConfirmation.
Objective C:
The helper macro and the defines can be found in the SktScanPropIds.h file.
Parameter type
Version
See also:
Data confirmation feature
13.7 Property kSktScanPropIdMonitorMode
This property is used to configure the debug option of ScanAPI.
NOTE:
C/C++ and C#:
This property works only if ScanAPI has been compiled in Debug mode. It will
have no effect on a release build. Only release builds are included with the SDK.
The monitor mode output traces in a remote debugger.
There are three monitor modes that can be changed and they are described in the
following table:
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 79/152
Page 80
Socket ScanAPI Reference
The default only outputs the line number
and the file name if a trace is at the
specified error level.
Name
Value
Description
DBGSKT_CORET
0x00000011
Traces from the Core
DBGSKT_COREW
0x00000012
Warning from the Core
DBGSKT_COREE
0x00000014
Errors from the Core
DBGSKT_LISTENERT
0x00000021
Traces from the listener
DBGSKT_LISTENERW
0x00000022
Warnings from the
listener
DBGSKT_LISTENERE
0x00000024
Errors from the listener
DBGSKT_PROTOCOLT
0x00000041
Traces from the protocol
DBGSKT_PROTOCOLW
0x00000042
Warnings from the
protocol
DGBSKT_PROTOCOLE
0x00000044
Errors from the protocol
DBGSKT_SERIALT
0x00000081
Traces from the serial
interface
DBGSKT_SERIALW
0x00000082
Warnings from the serial
interface
DBGSKT_SERIALE
0x00000084
Errors from the serial
interface
DBGSKT_DEVICEINTT
0x00000101
Traces from the device
interface
DGBSKT_DEVICEINTW
0x00000102
Warnings from the device
interface
DGBSKT_DEVICEINTE
0x00000104
Errors from the device
interface
DBGSKT_RXT
0x00000201
Traces from the receive
path
DBGSKT_RXW
0x00000202
Warning from the receive
path
DBGSKT_RXE
0x00000204
Errors from the receive
path
DBGSKT_TXT
0x00000401
Traces from the transmit
Debug Level Definition
The Debug Level is defined in a 32 bit variable and is defined as follows:
Bit 0: Level Trace
Bit 1: Level Warning
Bit 2: Level Error
Bit 3: Level Always.
Bit 4 to Bit 31: Modules.
The Modules are defined in this table:
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 80/152
Page 81
Socket ScanAPI Reference
path
DBGSKT_TXW
0x00000402
Warnings from the
transmit path
DBGSKT_TXE
0x00000404
Errors from the transmit
path
Get
Get Complete
Set
Set Complete
Byte
Ulong
Array
None
ScanAPI Interface Version
1.0.0 or higher
Name
Description
kSktScanEnableSoftScan
Enables the SoftScan feature when used
in the Set operation, or the SoftScan
feature is enabled when retrieved in the
Get Complete response.
kSktScanDisableSoftScan
Disables the SoftScan feature when used
in the Set operation or the SoftScan
feature is disabled when retrieved in the
Get Complete response.
The Get property can be used to retrieve a particular monitor mode. The property
must have its byte value set to one of the monitor modes. The Get complete contains
the actual level in its Ulong value.
The Set property can be used to change the monitor mode level. An array of 5 bytes
should be initialized with the first byte set to the particular monitor mode, and the 4
remaining bytes should contain the new 32 bit value in big-endian format.
Parameter type
Version
13.8 Property kSktScanPropIdSoftScanStatus
This property enables or disables the SoftScan feature. The SoftScan feature uses the
device camera to scan a barcode. Some devices might not meet all of the
requirements for such an operation. When the SoftScan is enabled and the
requirements are all met for scanning a barcode using the camera, then a new
device arrival will be generated with the necessary information for opening a
SoftScan scanner.
ScanAPI generates a device removal when the SoftScan scanner is disabled by using
this same property to turn this feature off.
The possible values for the byte data field are described in the following table:
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 81/152
Page 82

Socket ScanAPI Reference
Get
Get Complete
Set
Set Complete
None
Byte
Byte
None
ScanAPI Interface Version
1.0.1 or higher
Get
Get Complete
Set
Set Complete
None
Version
Not applicable
Not applicable
ScanAPI Interface Version
1.0.0 or higher
Value
Description
kSktScanDeviceTypeInterfaceNone
Unspecified interface type for this device
kSktScanDeviceTypeInterfaceSD
Secure Digital IO interface
kSktScanDeviceTypeInterfaceCF
Compact Flash interface
kSktScanDeviceTypeInterfaceBluetooth
Bluetooth interface
kSktScanDeviceTypeInterfaceSerial
Serial cable interface
Parameter type
Version
14 Device object properties
14.1 Property kSktScanPropIdVersionDevice
This property retrieves the version information of a connected device. The version
of the device can be read upon reception of the Get Complete event. The property
has its type set to kSktScanPropTypeVersion, and the version field of the property
contains the version information of the device identified by its handle. The version is
described by 9 fields: wMajor, wMiddle, wMinor, dwBuild, wYear, wMonth, wDay,
wHour and wMinute.
These fields are all expressed in hexadecimal except for the dwBuild field that is
expressed in decimal.
Parameter type
Version
14.2 Property kSktScanPropIdDeviceType
This property is used to retrieve the Device Type of a connected device.
A device type is defined in a 32-bit value composed of 2 types of information.
The first is the interface type that can be one of the following values:
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 82/152
Page 83
Socket ScanAPI Reference
Value
Description
kSktScanDeviceTypeProductIdNone
Unspecified product ID
kSktScanDeviceTypeProductId7
Product from the series 7 family
kSktScanDeviceTypeProductId7x
Product from the series 7x family
kSktScanDeviceTypeProductId9
Product from the series 9 family
kSktScanDeviceTypeProductId7xi
Product from the series 7x supporting
iOS host.
kSktScanDeviceTypeProductIdSoftScan
Device Camera used as barcode scanner.
Value
Description
kSktScanDeviceTypeNone
Unspecified device
kSktScanDeviceTypeScanner7
For the CHS family
kSktScanDeviceTypeScanner7x
For the CHS 7x family
kSktScanDeviceTypeScanner9
For the CRS family
kSktScanDeviceTypeScanner7xi
For the CHS 7x family supporting the iOS
host.
kSktScanDeviceTypeSoftScan
For the device camera used as barcode
scanner.
The second is the product identifier which can be one of the following values:
There are currently four device types identified in this SDK and there are defined as
follow:
NOTE:
The CRS family is supported by ScanAPI since version 10.0.4.
The SoftScan feature is supported by ScanAPI since version 10.0.9.
A set of predefined macros can be used in order to retrieve one of the two
information types contained in the device type.
SKTRETRIEVE_PRODUCTID(deviceType)
This macro retrieves the product identification from the device type.
SKTRETRIEVE_INTERFACETYPE(deviceType)
This macro retrieves the interface type from the device type.
C/C++:
The helper macro can be found in the SktScanPropIds.h file.
Java:
The helper macro can be found in com.SocketMobile.ScanAPI.SktScan.helper.
C#:
The helper macro can be found in ScanAPI.SktScan.helper.
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 83/152
Page 84
Socket ScanAPI Reference
Get
Get Complete
Set
Set Complete
None
Ulong
Not applicable
Not applicable
ScanAPI Interface Version
1.0.0 or higher
Byte
Size
Description
0 1 Operation
1 1 Group ID
2 1 Function ID
3
Variable
Function payload without
Checksum
Byte
Size
Description
0 1 Size including this byte
1 1 Operation
2 1 Status
3 1 Flags
4
Variable
Payload without
checksum
Objective C:
The helper macro can be found in the SktScanPropIds.h file.
This property cannot be used with the SktScanSet API.
Property Type
Version
14.3 Property kSktScanPropIdDeviceSpecific
This property can send a device specific command. The command depends on the
device type connected to the host. ScanAPI acts just as a pass-through without
interpreting any data in the command that is sent to the device using this property.
The command should be set in the Array member of the property, and the response
command is returned in the Array member of the property.
The command format depends on the device used. The command format for the 7x
series is different from the command format used in the 7 series.
The command format for the 7x series is decomposed as described in the following
table.
The command format for the 7 series is decomposed as described in the following
table.
Property type
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 84/152
Page 85

Socket ScanAPI Reference
Get
Get Complete
Set
Set Complete
Array
Array
Array
Array
ScanAPI Interface Version
1.0.0 or higher
Name
Description
ID
Contains the Symbology ID (e.g.
kSktScanSymbologyCode39)
Flags
Indicates if the Param field is used or
not.
Status
Indicates the status of the symbology,
This status can be one of the following:
kSktScanSymbologyStatusDisable,
kSktScanSymbologyStatusEnable,
kSktScanSymbologyStatusNotSupported
Param
Contains extra parameters about the
symbology. Not used in this version.
Name
Contains the symbology name. The name
field is ignored when the application is
doing a get or set operation. Only a get
complete returns the name of the
symbology.
Name
Definition
kSktScanSymbologyStatusEnable
The symbology is present and activated.
kSktScanSymbologyStatusDisable
The symbology is present but
deactivated.
kSktScanSymbologyStatusNotSupported
The symbology is not supported by the
device.
Name
Definition
kSktScanSymbologyNotSpecified
The symbology ID is unknown or not
specified.
kSktScanSymbologyAustraliaPost
Austrial Post
Version
14.4 Property kSktScanPropIdSymbologyDevice
This property is used to retrieve or set the status of a particular symbology. A
symbology is identified by a unique ID. A ScanAPI symbology structure is used in
order to manipulate the setting of a symbology.
This structure is TSktScanSymbology. It has the following fields:
A symbology that has a kSktScanSymbologyStatusNotSupported status means the
device doesn’t support this symbology.
The following table gives the possible Symbology Status.
The following table gives the list of Symbology ID.
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 85/152
Page 86
Socket ScanAPI Reference
kSktScanSymbologyAztec
AZTEC
kSktScanSymbologyBooklandEan
BOOKLAND EAN
kSktScanSymbologyBritishPost
British Post
kSktScanSymbologyCanadaPost
Canada Post
kSktScanSymbologyChinese2of5
Chinese 2 of 5
kSktScanSymbologyCodabar
CODABAR
kSktScanSymbologyCodablockA
CODABLOCK A
kSktScanSymbologyCodablockF
CODABLOCK F
kSktScanSymbologyCode11
Code 11
kSktScanSymbologyCode39
Code 39
kSktScanSymbologyCode39Extended
Code 39 Full ASCII
kSktScanSymbologyCode39Trioptic
Code 39 Trioptic
kSktScanSymbologyCode93
Code 93
kSktScanSymbologyCode128
Code 128
kSktScanSymbologyDataMatrix
Data Matrix
kSktScanSymbologyDutchPost
Dutch Post
kSktScanSymbologyEan8
EAN 8
kSktScanSymbologyEan13
EAN 13
kSktScanSymbologyEan128
EAN 128
kSktScanSymbologyEan128Irregular
EAN 128 Irregular
kSktScanSymbologyEanUccCompositeAB
EAN UCC Composite AB
kSktScanSymbologyEanUccCompositeC
EAN UCC Composite C
kSktScanSymbologyGs1Databar
GS1 DATABAR
kSktScanSymbologyGs1DatabarLimited
GSI DATABAR Limited
kSktScanSymbologyGs1DatabarExpanded
GS1 DATABAR Expanded
kSktScanSymbologyInterleaved2of5
Interleaved 2 of 5
kSktScanSymbologyIsbt128
ISBT 128
kSktScanSymbologyJapanPost
Japan Post
kSktScanSymbologyMatrix2of5
Matrix 2 of 5
kSktScanSymbologyMaxicode
Maxicode
kSktScanSymbologyMsi
MSI
kSktScanSymbologyPdf417
PDF 417
kSktScanSymbologyPdf417Micro
PDF 417 Micro
kSktScanSymbologyPlanet
Planet US Post
kSktScanSymbologyPlessey
PLESSEY
kSktScanSymbologyPostnet
POSTNET US Post
kSktScanSymbologyQRCode
QR Code
kSktScanSymbologyStandard2of5
Standard 2 of 5
kSktScanSymbologyTelepen
Telepen
kSktScanSymbologyTlc39
TLC 39
kSktScanSymbologyUpcA
UPC A
kSktScanSymbologyUpcE0
UPC E0
kSktScanSymbologyUpcE1
UPC E1
kSktScanSymbologyUspsIntelligentMail
USPS Intelligent Mail
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 86/152
Page 87

Socket ScanAPI Reference
kSktScanSymbologyDirectPartMarking
Direct Part Marking optimization
kSktScanSymbologyLastSymbologyID
Last symbology ID, this is not an actual
symbology.
Get
Get Complete
Set
Set Complete
Symbology
Symbology
Symbology
None
ScanAPI Interface Version
1.0.0 or higher
Name
Description
kSktScanTriggerStart
Start a scan
kSktScanTriggerStop
Stop a scan
kSktScanTriggerEnable
Enable the trigger button
kSktScanTriggerDisable
Disable the trigger button
The enumeration of the available symbologiwa of a device can be done by doing get
operations with the symbology ID incremented one by one from
kSktScanSymbologyNotSpecified+1 to kSktScanSymbologyLastSymbolID-1. For
more information please see section 16.
C/C++:
The Symbology ID and Symbology status defines can be found in SktScanTypes.h
file.
Java:
The Symbology ID and Symbology status defines can be found in:
com.SocketMobile.ScanAPI.ISktScanSymbology.id and
com.SocketMobile.ScanAPI.ISktScanSymbology.status
C#:
The Symbology ID and Symbology status defines can be found in:
ScanAPI.ISktScanSymbology.id and ScanAPI.ISktScanSymbology.status.
Objective C:
The Symbology ID and Symbology status defines can be found in SktScanTypes.h
file.
Property type
Version
See also:
11.6.2 Decoded Data Event
14.5 Property kSktScanPropIdTriggerDevice
This property allows the application to start or stop a trigger operation of a device
remotely or to activate/deactivate the device trigger button. This property can only
be used in a Set operation. Its Byte value can have one of the following values:
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 87/152
Page 88

Socket ScanAPI Reference
Get
Get Complete
Set
Set Complete
Not applicable
Not applicable
Byte
None
ScanAPI Interface Version
1.0.0 or higher
Get
Get Complete
Set
Set Complete
Not applicable
Not applicable
None
None
ScanAPI Interface Version
1.0.0 or higher
NOTE: Enabling or Disabling the trigger will be not effective on CHS 7C
version:3.4.0.1869. It will return an error (ESKT_RECEIVEUNEXPECTEDCOMMAND)
for both of these commands. This version of the CHS 7C is a limited release and this
issue has been fixed in the next revision of the scanner.
C/C++:
The Trigger defines can be found in SktScanPropIds.h file.
Java:
The Trigger defines can be found in
com.SocketMobile.ScanAPI.ISktScanProperty.values.trigger
C#:
The Trigger defines can be found in ScanAPI.ISktScanProperty.values.trigger.
Objective C:
The helper macro can be found in the SktScanPropIds.h file.
Property type
Version
See also:
4.7 Example of sending a command
14.6 Property kSktScanPropIdApplyConfigDevice
This property applies the device configuration stored on the host to the device.
This property can only be set and doesn’t have any parameters.
Property type
Version
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 88/152
Page 89
Socket ScanAPI Reference
Get
Get Complete
Set
Set Complete
None
String
String
None
ScanAPI Interface Version
1.0.0 or higher
14.7 Property kSktScanPropIdPreambleDevice
This property can be used to set or get the device preamble. When a preamble is set,
it will be added in front of the decoded data. The preamble is defined as a string with
a length that can contain any value for each character from 0 (0x00) to 255 (0xff).
NOTE: The 7 series 3.1 scanners don’t support a true preamble. The preamble
is actually stored on the device as part as the friendly name and postamble.
The total amount of characters for the friendly name, preamble and postamble
cannot be bigger than 28 characters. If a preamble is too long, an error
ESKT_INVALIDPARAMETER would be generated in the return of the
SktScanSet API. If the device is used without ScanAPI, the preamble won’t
appear in front of the decoded data.
The 7 series 3.2 or higher scanners support a limited preamble. The preamble
can only be one character long. It can be used without ScanAPI once it is setup.
The 7 series version can be determined by the Version property Major and
Middle values.
These remarks do not apply for the 7x series.
Property type
Version
14.8 Property kSktScanPropIdPostambleDevice
This property can be used to set or get the device postamble. When a postamble is
set, it will be added at the tail of the decoded data. The postamble is defined as a
string with a length that can contains any value for each character from 0 (0x00) to
255 (0xff).
NOTE: The 7 series v3.1 don’t support a true postamble. The postamble is
actually stored on the device as part as the friendly name and preamble. The
total amount of characters for the friendly name, preamble and postamble
cannot be bigger than 28 characters. If a postamble is too long, an error
ESKT_INVALIDPARAMETER would be generated in the return of the
SktScanSet API. If the device is used without ScanAPI, the postamble won’t
appear at the tail of the decoded data.
The 7 series v3.2 or higher support a limited postamble. The postamble can
only be 2 characters long. It can be used without ScanAPI once it is setup.
These remarks don’t apply for the 7x series.
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 89/152
Page 90

Socket ScanAPI Reference
Get
Get Complete
Set
Set Complete
None
String
String
None
ScanAPI Interface Version
1.0.0 or higher
31 30 29 28 27 26 25 24 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
X
33222222222211111111119 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
0
Property type
Version
14.9 Property kSktScanPropIdCapabilitiesDevice
This property can be used to get the device capabilities.
The capabilities of a device have been divided in 2 groups: General and Local
Functions.
The General group contains the information about the device to determine if it has a
Local Function Group capability.
The Local Function Group regroups the features that are implemented locally on the
device, such as Friendly Name, Sound, Led flash, Rumble, etc.
The features that belong to the General Group are features implemented in any type
of device, such as Device Type, Symbology settings, Trigger etc… Most of the time,
these features are implemented in the scanner engine.
The Get Request has a one-byte parameter to interrogate the one of the capabilities
group.
The following table describes the capabilities of each group.
If the Get Property byte value is set to kSktScanCapabilityGeneral, the return value
of the Get Complete Property is a Ulong describing the general capability. In the
current version of ScanAPI only Bit 0 is set to 1 if the device supports Local
Functions.
The X is set to 1 when the device supports Local Functions.
If the Get Property byte value is set to kSktScanCapabilityLocalFunctions, the return
value of the Get Complete Property is an unsigned long (Ulong) describing the Local
Functions capability.
In the current version of ScanAPI, the Bit 0 is set to 1 if the device supports Rumble
mode and the Bit 1 is set to 1 if the Change ID feature is present.
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 90/152
Page 91

Socket ScanAPI Reference
1 0 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Y
X
Bit 0 is set to 1 when the device supports Rumble Mode.
Bit 1 is set to 1 when the device supports the Change ID feature.
These are the constants used for capability definition:
kSktScanCapabilityLocalFunctionRumble and
kSktScanCapabilityLocalFunctionChangeID.
Example:
switch (scanObj.Property.ID)
{
case ISktScanProperty.propId.kSktScanPropIdFriendlyNameDevice:
/………………/
break;
case ISktScanProperty.propId.kSktScanPropIdCapabilitiesDevice:
if (SktScanErrors.SKTSUCCESS(result))
{ selectedScanner.OriginalProperties.Configuration.DoesRumble =
((scanObj.Property.Ulong&
ISktScanProperty.values.capabilityLocalFunctions.kSktScanCapabilityLocalFunctionRumble)==
ISktScanProperty.values.capabilityLocalFunctions.kSktScanCapabilityLocalFunctionRumble);
}
else
{
// unable to get the capabilities even after multiple
// retries by ScanAPI Helper
StopRetrievingPropertiesAndDisplayError("Failed to retrieve the Capabilities: " +
result);
}
break;
case ISktScanProperty.propId.kSktScanPropIdPostambleDevice:
/………………/
break;
}
C/C++:
The constants definitions for the capabilities can be found in SktScanPropIds.h file.
Java:
The constants definition for the capabilities can be found in
com.SocketMobile.ScanAPI.ISktScanProperty.values.capabilityGroup
com.SocketMobile.ScanAPI.ISktScanProperty.values.capabilityGeneral
com.SocketMobile.ScanAPI.ISktScanProperty.values.capabilityLocalFunctions
C#:
The constants definition for the capabilities can be found in
ScanAPI.ISktScanProperty.values.capabilityGroup
ScanAPI.ISktScanProperty.values.capabilityGeneral
ScanAPI.ISktScanProperty.values.capabilityLocalFunctions
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 91/152
Page 92

Socket ScanAPI Reference
Get
Get Complete
Set
Set Complete
Byte
Ulong
Not applicable
Not applicable
ScanAPI Interface Version
1.0.0 or higher
Get
Get Complete
Set
Set Complete
None
Ulong
Not applicable
Not applicable
Objective C:
The constants definitions for the capabilities can be found in SktScanPropIds.h file.
Property type
Version
14.10 Property kSktScanPropIdChangeIdDevice
This property returns a Change ID of the device symbology configuration and the
device preamble and postamble. This Change ID will reflect any configuration
change in the scanner engine that could have been made outside ScanAPI by
scanning a scanner engine configuration barcode.
This feature is useful to figure out if the device has a different symbology
configuration or preamble/postamble than the host has stored for this device.
The enumeration of all the supported symbologies can be a lengthy operation that
can be greatly improved by implementing a symbology cache mechanism.
The first time a device is connected to the host, its symbology status gets
enumerated and stored into a cache. The change ID is also requested.
If the device disconnects and then reconnects at a later time to this host, the change
ID is requested and compared with the ChangeID stored in the host cache.
If the change ID is the same then the symbology can be displayed out of the cache
without requesting it from the device.
If the ChangeID is different, this means the symbology on the device has been
altered, and it will require a new enumeration of the symbology from the device.
The change ID is a Ulong value that is a checksum of all the scanner engine settings
(including symbology activation and preamble/postamble).
Other scanner properties aren’t cover by this Change ID such as beeps/LED/Rumble
configuration, friendly name, data store, and confirmation settings.
Parameter type
Version
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 92/152
Page 93

Socket ScanAPI Reference
ScanAPI Interface Version
1.0.0 or higher
14.11 Property kSktScanPropIdFriendlyNameDevice
This property is used to read or modify the friendly name of a device. The friendly
name is carried as a string in the property.
The friendly name of a device is what appears during a Bluetooth device discovery
process. The main purpose of changing the friendly name of a device is to have an
easy way to identify a particular device.
The changes are active immediately upon success of the Set Complete operation.
The friendly name size can be as long as 32 UTF8 characters including the null
terminator.
Example:
C/C++:
// Set a new friendly name
SKTRESULT SetNewFriendlyName(
IN SKTHANDLE hDevice,
IN const char* pszNewFriendlyName
)
{
SKTRESULT Result=ESKT_NOERROR;
TSktScanObject ScanObj;
memset(&ScanObj,0,sizeof(ScanObj);
ScanObj.Property.ID=kSktScanPropIdFriendlyNameDevice;
ScanObj.Property.Type=kSktScanPropTypeString;
ScanObj.Property.String.pValue=pszNewFriendlyName;
ScanObj.Property.String.nLength=
strlen(pszNewFriendlyName);
// set the friendly name here
// the final result should be fetched
// in the Set Complete handler
Result=SktScanSet(hDevice,&ScanObj);
return Result;
}
Java:
public long SetNewFriendlyName(ISktScanDevice device,String newFriendlyName){
long result=SktScanErrors.ESKT_NOERROR;
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 93/152
Page 94

Socket ScanAPI Reference
ISktScanObject scanObj=
SktClassFactory.createScanObject();
ISktScanProperty property=
scanObj.getProperty();
property.setID(ISktScanProperty.propId.
kSktScanPropIdFriendlyNameDevice);
property.setType(ISktScanProperty.types.
kSktScanPropTypeString);
property.getString().setValue(newFriendlyName);
// set the friendly name here
// the final result should be fetched
// in the Set Complete handler
result=device.SetProperty(scanObj);
return result;
}
C#:
private long SetNewFriendlyName(
ISktScanDevice device,
String newFriendlyName
)
{
long result = SktScanErrors.ESKT_NOERROR;
ISktScanObject scanObj =
SktClassFactory.createScanObject();
scanObj.Property.ID = ISktScanProperty.propId.kSktScanPropIdFriendlyNameDevice;
scanObj.Property.Type =
ISktScanProperty.types.kSktScanPropTypeString;
scanObj.Property.String.Value = newFriendlyName;
result = device.SetProperty(scanObj);
return result;
}
Objective C:
-(SKTRESULT) setFriendlyName:(id<ISktScanDevice>)device FriendlyName: (NSString*)friendlyName{
SKTRESULT Result=ESKT_NOERROR;
id<ISktScanObject>scanObj=nil;
scanObj=[SktClassFactory createScanObject];
[[scanObj Property]setID:kSktScanPropIdFriendlyNameDevice];
[[scanObj Property]setType:kSktScanPropTypeString];
[[scanObj Property]setString:friendlyName];
// set the friendly name here
// the final result should be fetched
// in the set Complete handler
Result=[device setProperty:scanObj];
return Result;
}
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 94/152
Page 95

Socket ScanAPI Reference
Get
Get Complete
Set
Set Complete
None
String
String
None
ScanAPI Interface Version
1.0.0 or higher
Value
Description
kSktScanSecurityModeNone
No security
mode on the
device.
kSktScanSecurityModeAuthentication
Mode
Authentication
on the device.
Any host
attempting to
connect to this
device will be
asked for a PIN
code
kSktScanSecurityModeAuthenticationEncryption
Same as above
but with data
encryption
enabled
between the
host and the
device.
kSktScanSecurityModeAuthenticationEncryptionSingleBDAddress
Same as above
but the device
only keeps the
security
NOTE: For the 7 series v3.1, ScanAPI uses the friendly name memory to store
the preamble and the postamble. The total amount of characters for the
friendly name, preamble and postamble cannot be bigger than 28 characters.
If a friendly name is too long to be stored along with the preamble and
postamble, an error ESKT_INVALIDPARAMETER would be generated in the
return of the SktScanSet API.
This remark doesn’t apply for the 7 series v3.2 or 7x series.
Property type
Version
14.12 Property kSktScanPropIdSecurityModeDevice
This property gets or set the security mode of a device.
The security mode can be one of the following values:
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 95/152
Page 96
Socket ScanAPI Reference
information for
one host.
Connecting to
another host
cause the
security
process to start
all over again.
Get
Get Complete
Set
Set Complete
None
Byte
Byte
None
ScanAPI Interface Version
1.0.0 or higher
Get
Get Complete
Set
Set Complete
Not applicable
Not applicable
String
None
ScanAPI Interface Version
1.0.0 or higher
C/C++:
These security constants are defined in SktScanPropIds.h file.
Java:
These security constants are defined in
com.SocketMobile.ScanAPI.ISktScanProperty.values.securityMode
C#:
These security constants are defined in
ScanAPI.ISktScanProperty.values.securityMode
Objective C:
These security constants are defined in SktScanPropIds.h file.
Parameter type
Version
14.13 Property kSktScanPropIdPinCodeDevice
This property sets a new pin code for a connected device. The new PIN code should
be a string and cannot be longer than 16 characters. The new PIN code will have
effect at the next connection of the device. Changing the PIN code of the connected
device won’t disconnect device. The new PIN code will be required by the host when
the device connects the next time.
Parameter type
Version
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 96/152
Page 97

Socket ScanAPI Reference
Name
Description
kSktScanDeletePairingCurrent
Delete the Pairing and Bonding
information only for the current host.
kSktScanDeletePairingAll
Delete the Pairing and Bonding
information for all the hosts the device
may know of.
Get
Get Complete
Set
Set Complete
Not applicable
Not applicable
Byte
None
ScanAPI Interface Version
1.0.0 or higher
14.14 Property kSktScanPropIdDeletePairingBondingDevice
This property deletes the Bluetooth pairing and bonding information from the
device identified by its reference. Once the pairing and bonding information have
been deleted from the device, the device stays connected. The new pairing and
bonding information will be created at the next connection of the device to the host.
This property can only be used in a Set operation and has one parameter indicating
if the pairing and bonding information should be deleted for all the hosts the
scanner might know or only for the current host.
A constant has been defined for each of these modes:
C/C++:
The delete and pairing constants are defined in SktScanPropIds.h file.
Java:
The delete and pairing constants are defined in
com.SocketMobile.ScanAPI.ISktScanProperty.values.deletePairing
C#:
The delete and pairing constants are defined in
ScanAPI.ISktScanProperty.values.deletePairing
Objective C:
The delete and pairing constants are defined in SktScanPropIds.h file.
Parameter type
Version
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 97/152
Page 98
Socket ScanAPI Reference
Get
Get Complete
Set
Set Complete
Not applicable
Not applicable
None
None
ScanAPI Interface Version
1.0.0 or higher
Get
Get Complete
Set
Set Complete
Not applicable
Not applicable
None
None
ScanAPI Interface Version
1.0.0 or higher
14.15 Property kSktScanPropIdRestoreFactoryDefaultsDevice
This property sets the connected device to its factory defaults. The device will
power down once the factory defaults have been applied and the Set Complete has
been sent.
Parameter type
Version
14.16 Property kSktScanPropIdSetPowerOffDevice
This property turns the power off from the device causing it to disconnect.
This property can only be used in a Set operation and doesn’t have any parameters.
This is one of the rare cases where a Set Complete might not be received before the
device drops the connection. From the application point of view, the device removal
might come before the Set Complete timeout error. If the application closes right
away the device upon reception of the device removal event, the Set Complete
timeout error will never be received by the application.
Parameter type
Version
14.17 Property kSktScanPropIdButtonStatusDevice
This property gets the button status of the connected device.
The button status is coded in one byte as a bit field indicating the status of each
button on the device.
A set of macros can be used in order to retrieve the status of a particular button. The
macro returns a Boolean to indicate if the button is pressed (true) or released (false)
or, in the case of the Series 9 Ring Scanner, it is detached (true) or attached (false).
The macro definitions can be found in paragraph 11.6.3 Buttons Event.
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 98/152
Page 99
Socket ScanAPI Reference
Get
Get Complete
Set
Set Complete
None
Byte
Not applicable
Not applicable
ScanAPI Interface Version
1.0.0 or higher
Name
Description
kSktScanSoundActionTypeGoodScan
Sound played when a good scan
occurs when the host is sending a
positive data confirmation
kSktScanSoundActionTypeGoodScanLocal
Sound played when the device
locally acknowledges a good scan.
kSktScanSoundActionTypeBadScan
Sound played when a bad scan
occurs when the host is sending a
negative data confirmation
kSktScanSoundActionTypeBadScanLocal
Sound played when the device
locally acknowledges a bad scan.
Name
Description
kSktScanSoundFrequencyNone
No sound
C/C++:
The helper macro can be found in the SktScanPropIds.h file.
Java:
The helper macro can be found in com.SocketMobile.ScanAPI.SktScan.helper.
C#:
The helper macro can be found in ScanAPI.SktScan.helper.
Objective C:
The helper macro can be found in the SktScanPropIds.h file.
Parameter type
Version
14.18 Property kSktScanPropIdSoundConfigDevice
This property gets or sets the sound configuration of the connected device.
Each action can have its own sound definition.
Here is the list of possible actions:
A sound configuration is composed of two parameters; the number of tones and the
tones. A tone is defined by its frequency, its duration and the pause before the next
tone.
These parameters are expressed as 16 bit words in big-endian format.
The frequency can be set to one of the following values:
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 99/152
Page 100
Socket ScanAPI Reference
kSktScanSoundFrequencyLow
Low frequency sound
kSktScanSoundFrequencyMedium
Medium frequency sound
kSktScanSoundFrequencyHigh
High frequency sound
Name
Size
Present
Description
Sound Action
2 bytes
Get Complete, Set
Configuration of a
particular sound
action.
Number of Tones
2 bytes
Get Complete, Set
Define the number
of tones present in
this configuration.
The maximum
number of tones is
five (5).
Frequency Tone 1
2 bytes
Get Complete, Set
Define the
frequency of the
first tone.
Duration Tone 1
2 bytes
Get Complete, Set
Define the duration
of the first tone.
The duration range
is 50 (0x32) to
32767 (0x7FFF)
Pause Tone 1
2 bytes
Get Complete, Set
Define the pause
length of the first
tone. The pause
range is from 50
(0x32) to 32767
(0x7FFF)
… same 3 last fields
for the subsequent
tones until Number
of Tone is reached
Word Values
Description
kSktScanSoundActionTypeGoodScanLocal
Configuration for the Good Scan Local
The duration and the pause are expressed in milliseconds. The minimum values are
160ms for duration and 100ms for pause.
The sound configuration is summarized in the following table:
The Get request property uses only a byte value to request the configuration of a
particular sound action.
The following is an example of an array that can be used for the Set request:
© 2013 Socket Mobile, Inc. 100/152
 Loading...
Loading...