Page 1

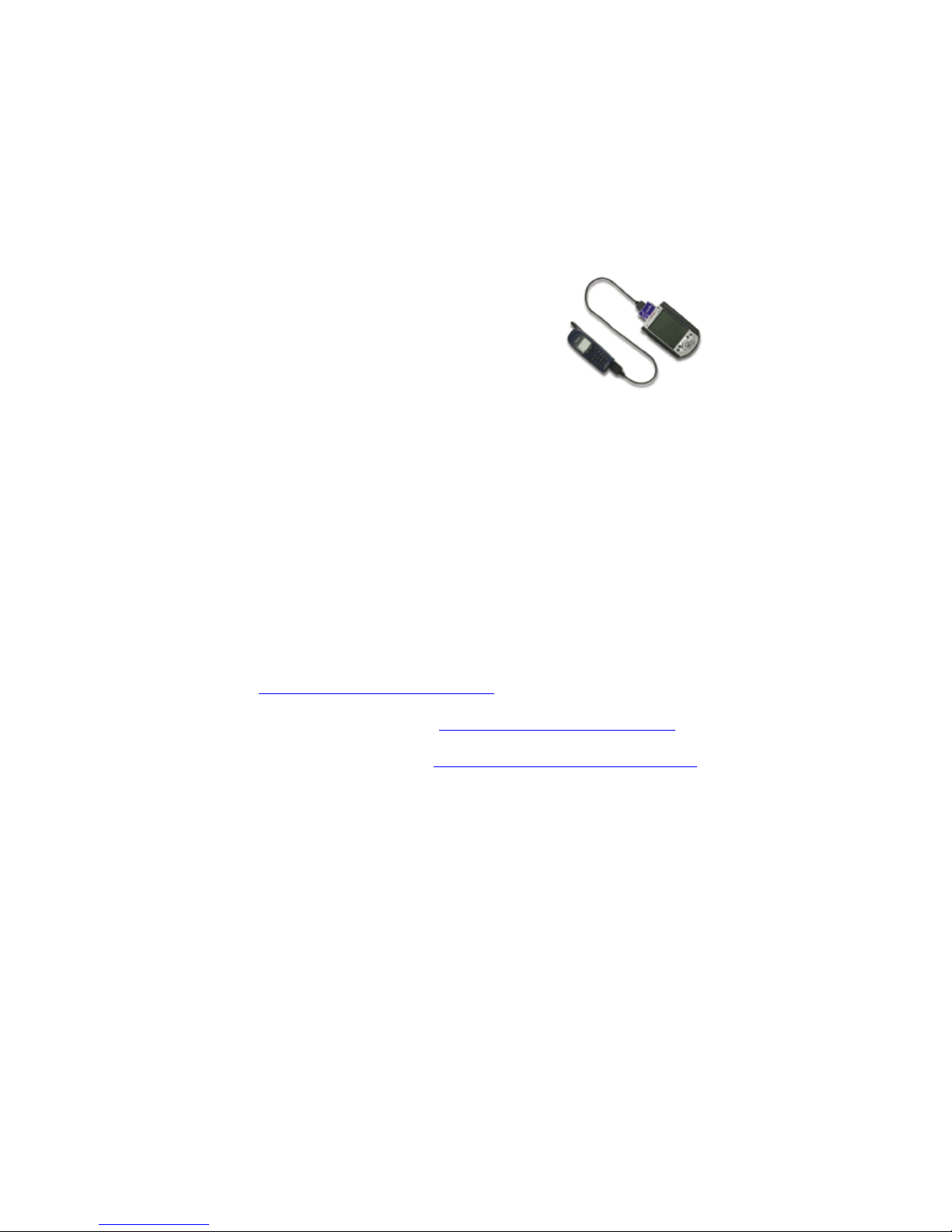
Digital Phone Card™
with GSM Software Modem
CompactFlash Card with attached cable for
connecting GSM phones to:
• Windows Powered Pocket PCs
• Windows CE-based Palm-size PCs, Handheld
PCs, and pen tablets
• Windows 9x/Me/2000/XP notebooks
User’s Guide
Page 2

How this Manual is Organized
This manual is designed to help you install and the operate the Socket
Digital Phone Card.
Chapter 1, Introduction, describes key features of the DPC and identifies
package contents.
Chapter 2, Preliminary Setup, explains the first several setup steps, which
are done the same for all Windows versions.
Chapter 3, Windows CE Setup, shows the later part of DPC setup for a
Windows Powered Pocket PC or Windows CE-based Palm-size PC,
Handheld PC Pro or pen tablet.
Chapter 4, SMS Messaging for Windows CE, explains how to send and
receive SMS messages for Windows CE.
Chapter 5, Windows 9x/Me Setup, shows the latter part of DPC setup for a
Windows 9x/Me notebook.
Chapter 6, Windows 2000/XP Setup, shows the latter part of DPC setup for a
Windows 2000/XP notebook.
Chapter 7, SMS Messaging for Windows 9x/Me/2000/XP, explains how
to send and receive SMS messages for Windows 9x/Me/2000/XP
notebooks.
Appendix A, Specifications, provides technical specifications for the DPC.
Appendix B, Hints and Tips, gives tips for using the system efficiently.
Appendix C, Troubleshooting, gives advice for fixing the most common
problems you may encounter using the DPC.
Appendix D, ISP Resources, lists some Internet Service Providers that you
may want to choose from to use with your Digital Phone Card.
Appendix E, Technical Support, tells you how to reach Socket’s technical
support department.
Page 3

Table of Contents
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 3
Overview 3
Working Wirelessly with the DPC 3
Package Contents 4
How to Use This User’s Guide 5
Installation Steps Summary 5
CHAPTER 2 PRELIMINARY SETUP 6
STEP 1: Register Your Card 6
STEP 2: Activate Data Service for Your Phone 6
STEP 3: Uninstall Old Socket DPC Software 6
STEP 4: Network Information Form 7
CHAPTER 3 WINDOWS CE SETUP 8
STEP 5: Install the Software 9
STEP 6: Insert the Card and Attach the Phone 11
STEP 7: Set up Remote Networking 12
STEP 8: Make a Data Call 15
CHAPTER 4 SMS MESSAGING FOR WINDOWS CE 17
CHAPTER 5 WINDOWS 9X/ME SETUP 21
STEP 5: Insert the Installation CD 21
STEP 6: Insert the Card and Attach the Phone 21
STEP 7: Install the Software 22
STEP 8: Set up Remote Networking 23
STEP 9: Make a Data Call 24
CHAPTER 6 WINDOWS 2000/XP SETUP 26
STEP 5: Insert the Installation CD 26
STEP 6: Insert the Card and Attach the Phone 26
STEP 7: Install the Software 27
STEP 8: Set up Remote Networking 28
STEP 9: Make a Data Call 30
CHAPTER 7 SMS MESSAGING FOR WINDOWS
9X/ME/2000/XP 31
APPENDIX A SPECIFICATIONS 37
APPENDIX B HINTS AND TIPS 39
Optimizing Signals and Connections 39
Choosing the Right Applications 39
Using Multiple Modems 39
TABLE OF CONTENTS | 1
Page 4

APPENDIX C TROUBLESHOOTING 40
APPENDIX D ISP RESOURCES 45
APPENDIX E TECHNICAL SUPPORT 48
LIMITED WARRANTY 49
COPYRIGHT NOTICE 51
REGULATORY COMPLIANCE 52
2 | TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page 5
Chapter 1 Introduction
Overview
The Socket Digital Phone Card (DPC) allows you
to connect your data-capable mobile phone to a
Windows–based mobile computer. Now you can
check email, browse the web, connect to your
office network and synchronize files— all
wirelessly!
When you use the Digital Phone Card, you don’t need a modem, because
your data-capable GSM phone simulates one. You can use the Digital Phone
Card with any software program that you use with a regular modem.
The DPC fits directly into the CompactFlash I/O slot of a Windows
Powered Pocket PC or Windows CE-based Palm-size PC, Handheld PC Pro
or pen tablet.
With the included CompactFlash-to-PC Card adapter, you can also use the
DPC in the PC Card slot of a Windows CE-based Handheld PC Pro or pen
tablet or Windows 9x/Me/2000/XP notebook.
Your retail box may not completely list all the mobile phones compatible
with your version of the DPC. For a complete, up-to-date listing, please
visit: www.socketcom.com/product/dpc.htm
For software updates, please visit: www.socketcom.com/product/dpc.htm
To register the DPC online, visit: www.socketcom.com/product/prodreg.htm
Working Wirelessly with the DPC
You can use your mobile computer’s remote communications capabilities to
make your mobile phone work as a wireless modem.
Wireless Web Browsing
If you have a web browser on your mobile computer (e.g., Pocket Internet
Explorer, Netscape, etc.), you can use the DPC to browse the Internet
anytime anywhere within your mobile phone’s coverage area. Simply use
the DPC to wirelessly connect to your office network or Internet Service
Provider (ISP), open your web browser, then surf the Internet!
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION | 3
Page 6

Wireless Email
You can set up your mobile computer’s Inbox to directly access your
IMAP4-enabled exchange server or ISP’s POP3 user accounts. Also, if you
have a web browser on your mobile computer, you can also use html-based
email services.
Wireless ActiveSync
While running ActiveSync wirelessly with the DPC, your mobile computer
works as if it were directly connected to a host computer. For information
about ActiveSync, refer to your mobile computer’s user manual.
Package Contents
The Socket Digital Phone Card for Pocket PCs package includes:
• A Socket Digital Phone Card (CompactFlash card Type I) with
permanently attached data cable, customized for specific GSM phones
• The Socket Digital Phone Card Installation CD
• The Quick Start Guide for Digital Phone Card for Pocket PCs
• A registration card
Digital Phone Card Installation CD
The Windows 9x/Me/2000 Upgrade Kit for the Digital Phone Card
includes these items:
• A CompactFlash-to-PC Card adapter
• The Socket DPC Upgrade Kit Installation CD
• The Quick Start Guide for Digital Phone Card for Windows
9x/Me/2000/XP
• A registration card
PC Card adapter Installation CD
Register the DPC online at: www.socketcom.com/product/prodreg.htm
4 | CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION
Page 7
How to Use This User’s Guide
Setting up the DPC begins the same for all Windows versions but ends
differently.
To set up the DPC, begin in Chapter 2, “Preliminary Setup,” which includes
instructions for Steps 1-5 for all Windows versions. After completing the
instructions in Chapter 2, proceed to the chapter for your specific Windows
version to complete Steps 6-9.
For instructions on SMS messaging, refer to Chapter 4, “SMS Messaging
for Windows CE,” or Chapter 7, “SMS Messaging for Windows
9x/Me/2000/XP.”
Installation Steps Summary
PRELIMINARY SETUP
STEP 1: Register your card.
STEP 2: Activate data service for your mobile phone.
STEP 3: Uninstall old Socket DPC software.
STEP 4: Complete the Network Information Form.
CHAPTERS 3-4: WINDOWS CE
STEP 5: Install the software.
STEP 6: Insert the card and attach the phone.
STEP 7: Set up remote networking.
STEP 8: Make a data call.
OPTIONAL: Use SMS messaging.
CHAPTERS 5-7: WINDOWS 9x/Me/2000/XP
STEP 5: Insert the installation CD.
STEP 6: Insert the card and attach the phone.
STEP 7: Install the software.
STEP 8: Set up remote networking.
STEP 9: Make a data call.
OPTIONAL: Use SMS messaging.
Please note that the sequence for inserting the card and installing the
software differs between Windows CE-based mobile computers and
Windows notebooks.
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION | 5
Page 8
Chapter 2 Preliminary Setup
This section explains the first three steps of DPC setup, which are done
similarly for all Windows versions. After performing the steps covered here,
complete DPC setup by proceeding to Part II. Find the section for your
specific Windows version.
The four steps covered in Part I include:
• Registering your card
• Activating data service for your mobile phone
• Network Information Form
STEP 1: Register Your Card
Register your DPC online at www.socketcom.com/product/prodreg.htm.
You can also use the product registration form included in your DPC
package.
STEP 2: Activate Data Service for Your Phone
Some mobile phone carriers activate data service only when requested and
may charge small fees. If necessary, ask your phone carrier for this feature.
Important! If data service is not activated for your mobile
phone, then you will not be able to use your phone for
any data connections!
STEP 3: Uninstall Old Socket DPC Software
Delete any DPC software you may have previously installed on your mobile
computer. See the README on the installation CD for uninstall procedures.
6 | CHAPTER 3: WINDOWS CE SETUP
Page 9
STEP 4: Network Information Form
Contact your office network administrator or Internet Service
Provider (ISP) for the information below. If you plan to use ISP
services offered by your mobile phone carrier, contact your carrier.
For a text-only form that you can email, go to the Docs folder on the
installation CD or visit: www.socketcom.com/pdf/dpcform.txt
1. Please provide the following dial-up information:
Dial-up number: ( ____ ) _______________
User name: _________________________
Password: _________________________
Domain: __________________________
2. Does the network support DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration
Protocol)? Most ISPs use DHCP.
YES. If Yes, then STOP. You do NOT need to answer Question 3.
NO. If No, then continue to Question 3. You may need only some
of the IP addresses listed below.
3. Please specify any applicable IP addresses:
(a) Mobile Computer IP address: _____ . _____ . _____ . _____
(b) Subnet Mask: _____ . _____ . _____ . _____
(c) Default Gateway: _____ . _____ . _____ . _____
(d) Primary DNS: _____ . _____ . _____ . _____
(e) Secondary DNS: _____ . _____ . _____ . _____
(f) Primary WINS: _____ . _____ . _____ . _____
(g) Secondary WINS: _____ . _____ . _____ . _____
For remote ActiveSync only: If your server does NOT have WINS
services enabled, you must use the IP address of your host computer
instead of a Primary WINS address.
(h) Host computer IP address: _____ . _____ . _____ . _____
INTRODUCTION | 7
Page 10
Chapter 3 Windows CE Setup
This chapter explains the latter part of DPC
setup for these Windows CE-based mobile
computers:
• Windows CE v3.0
Pocket PC and HPC 2000
• Windows CE v2.11
Handheld PC and Handheld PC Pro
Before you start the steps in this chapter, be sure to complete the
instructions in Chapter 2, “Preliminary Setup.”
Warning! Pocket PCs are not the same as Palm-size PCs!
For some steps, setup differs for the two mobile computers!
Pocket PCs are based on Windows CE v3.0, while Palm-size PCs are based
on Windows CE v2.11. If you are not sure whether you have a Pocket PC or
Palm-size PC, you can find out by identifying what Windows CE version
your mobile computer has. This is sometimes labeled as the Core System
Version.
To determine the Windows CE version of your mobile computer, go to
either:
• Start | Settings | System. On some mobile computers, you also need to
click on the About icon.
• Start | Settings | Control Panel | System. In the System Properties screen,
click on the System tab.
: Windows Powered
: Palm-size PC,
8 | CHAPTER 3: WINDOWS CE SETUP
Page 11
STEP 5: Install the Software
Follow these steps for software installation BEFORE inserting the DPC:
1. Make an active partnership between the mobile computer and a host PC.
An active partnership exists if data can be transferred between the
mobile computer and the host PC via the mobile computer’s serial or
USB connection cable or cradle.
2. Insert the Socket Digital Phone Card Installation CD into the host PC.
3. IF YOUR DEFAULT WEB BROWSER IS INTERNET EXPLORER,
you can install either the SETUP.HTM
or SETUP.EXE:
(a) Click Start then Run on the host PC.
(b) Type X:\SETUP.HTM or X:\SETUP.EXE
(Replace X with your CD drive letter.)
(c) In the File Download screen, select the option that lets you run
(or open) the file from its current location.
IMPORTANT! YOU MUST RUN THE FILE! DO NOT SAVE IT!
(d) A Security Warning screen will appear. Click Yes.
File Download screen from Internet Explorer 5.5
CHAPTER 3: WINDOWS CE SETUP | 9
Page 12

IF YOUR DEFAULT WEB BROWSER IS NETSCAPE, DO NOT run
the SETUP.HTM
Instead, choose either of two options:
file on Netscape, because it will not work properly.
OPTION ONE: RUN SETUP.HTM ON INTERNET EXPLORER
(a) In the Internet Explorer screen, click File | Open.
(b) In the Open screen, type X:\SETUP.HTM
(Replace X with your CD drive letter.)
Open screen from Internet Explorer 5.5
(c) Proceed with the instructions described on the previous page for
Internet Explorer.
OPTION TWO: RUN THE SETUP.EXE FILE FROM THE PROPER
WINDOWS FOLDER
Click on My Computer or use Windows Explorer to manually browse
the CD to the WinCE (or other appropriate directory) and manually
launch the SETUP.EXE file found there.
Important! Be sure to choose the SETUP.EXE file, NOT the
SETUP.HTM file. The two file types have different icons:
EXE icon HTM icon for Netscape
4. Follow the instructions on the host PC screen until setup is done.
Note: After completing setup, your host PC may display a screen
reporting Application Downloading Complete. Click ok.
5. On your mobile computer, a screen may appear asking you to select your
GSM phone manufacturer. Make the appropriate selection, then tap ok.
6. Disconnect the mobile computer from the host computer.
7. Soft reset the mobile computer. Push the reset button, which may be on
the back of your mobile computer.
10 | CHAPTER 3: WINDOWS CE SETUP
Page 13

STEP 6: Insert the Card and Attach the Phone
y
With the mobile computer turned ON, insert the DPC into your mobile
computer’s card slot. If using a PC Card slot, insert the card into a
CompactFlash-to-PC Card adapter first. Then attach the free end of the
cable to your mobile phone.
Plug the card
into your mobile
computer’s card
slot…
…Then
attach
cable to
our mobile
phone.
CHAPTER 3: WINDOWS CE SETUP | 11
Page 14

STEP 7: Set up Remote Networking
You will need your completed Network Information Form for this step.
Remote Networking Setup for Pocket PCs
1. Go to Start | Settings | Connections | Modem.
2. The Modem Connections screen will appear. Tap New Connection…
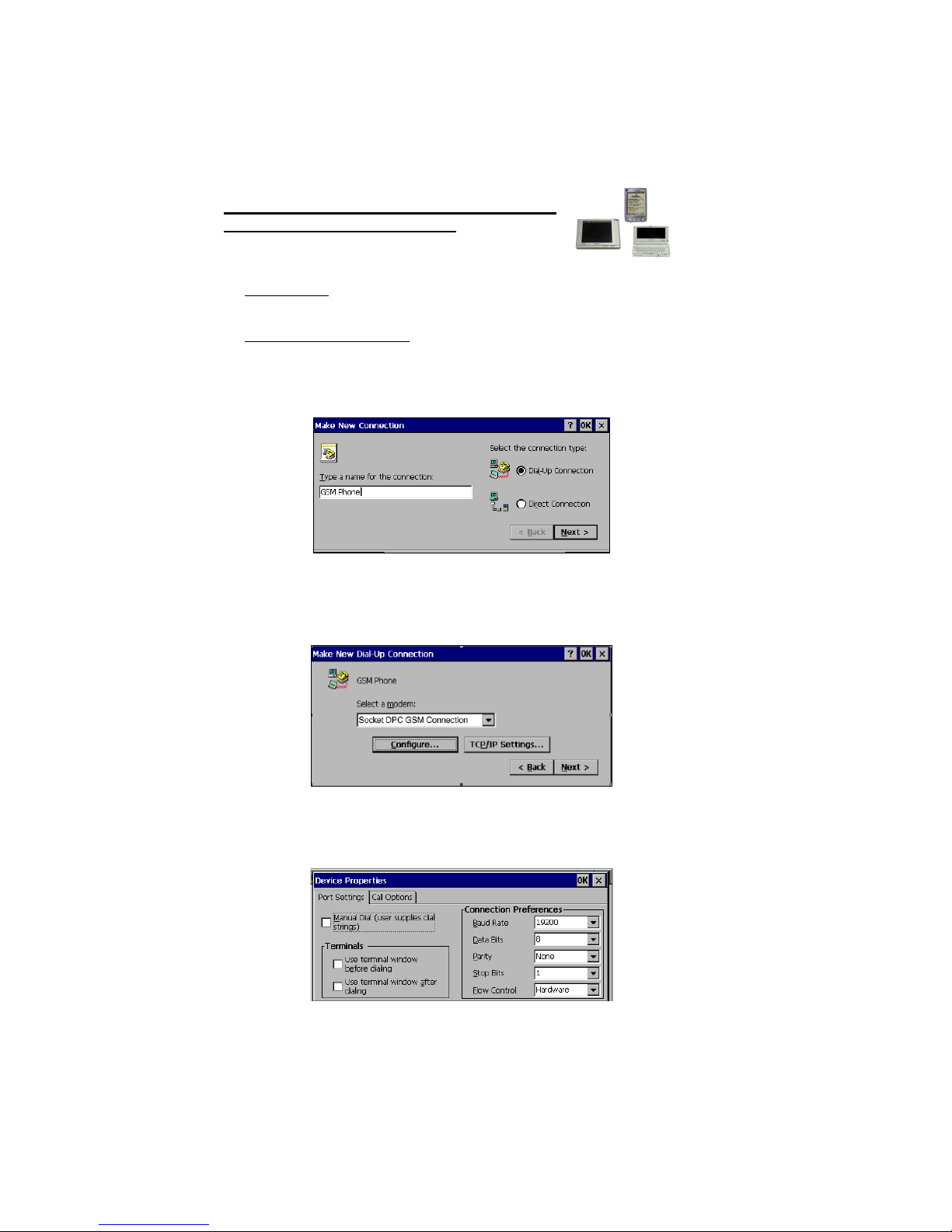
3. In the Make New Connection screen, enter a name for the connection,
such as “GSM Phone.”
In the Select a modem field, select the Socket DPC GSM Connection.
Make sure the Baud Rate is set to 19200 bps.
4. Tap on Advanced… Do NOT change the default settings in Port Settings.
Make New Connection screen
• If using DHCP, you can probably keep the default settings in the
TCP/IP and Name Servers screens. Tap ok.
• If NOT using DHCP, click on the TCP/IP and/or Name Servers tabs
and follow your Network Information Form to enter any necessary IP
addresses. When done, tap ok.
5. When you return to the Make New Connection screen, tap Next.
6. In the next screen, enter the dial-up number and tap Next. Spaces or
dashes are not required within the phone number.
7. In the next screen, uncheck Wait for dial tone before dialing. Tap Finish.
12 | CHAPTER 3: WINDOWS CE SETUP
Page 15
Remote Networking Setup for Palm-size PCs,
Handheld PCs, and Pen Tablets
1. Palm-size PC: Go to Start | Programs | Communications | Connections |
Make New Connection.
Handheld PC or pen tablet: Go to Start | Programs | Communication |
Remote Networking | Make New Connection.
2. In the Make New Connection screen, enter a name for the connection,
such as “GSM Phone.” Select Dial-Up Connection, then tap Next>.
Make New Connection screen from a Handheld PC
3. The Make New Dial-Up Connection screen will appear. In the Select a
modem menu, select the Socket DPC GSM Connection for your GSM
phone. (For example, Ericsson is listed below.) Tap on Configure…
Make New Dial-Up Connection screen from a Handheld PC
4. In the Port Settings screen, make sure the Baud Rate is set to 19200.
Tap on the Call Options tab.
Port Settings screen from a Handheld PC
CHAPTER 3: WINDOWS CE SETUP | 13
Page 16
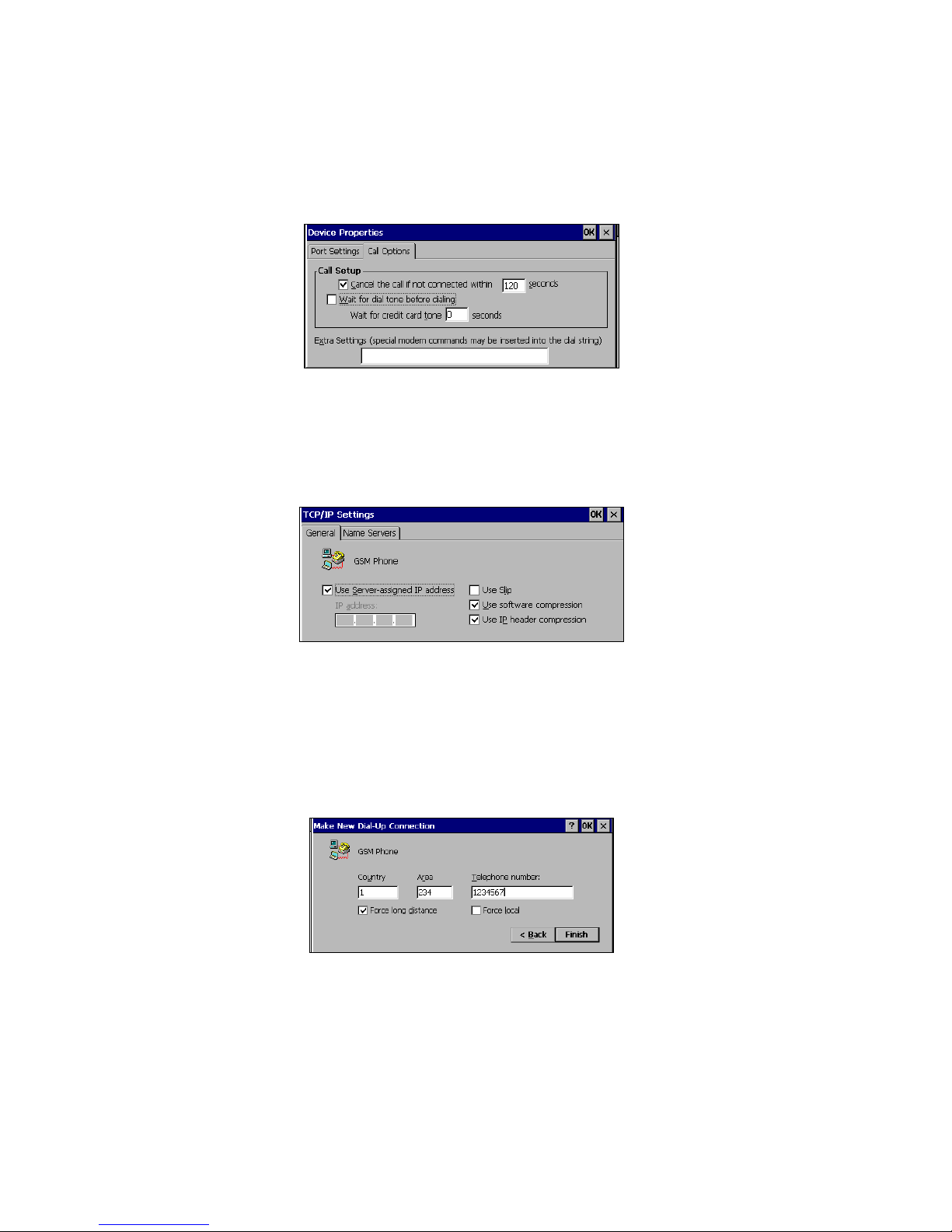
5. In Call Options, uncheck Wait for dial tone before dialing. Tap OK.
Call Options screen from a Handheld PC
6. In Make New Dial-Up Connection, tap on TCP/IP Settings…
7. In the TCP/IP Settings screen, follow your Network Information Form to
enter settings appropriate to your office network or ISP.
• If using DHCP, check Use server-assigned IP address. Tap OK.
General TCP/IP screen from a Handheld PC
• If NOT using DHCP, uncheck Use server-assigned IP address. Enter
your mobile computer IP address in the IP address field, and tap on
the Name Servers tab to enter DNS and/or WINS addresses. Tap OK.
8. In the Make New Dial-Up Connection screen, tap Next>.
9. In the next screen, enter the phone number of your office network or ISP.
Check Force long distance, then tap on the Finish button.
Dial-Up Connection settings screen from a Handheld PC
14 | CHAPTER 3: WINDOWS CE SETUP
Page 17
STEP 8: Make a Data Call
Preliminary Checklist
!
Are the cable and connectors fastened securely to the mobile computer
and phone?
!
Is the phone receiving a digital signal? A or equivalent will appear on
the display of some phones.
!
Is the mobile phone’s signal strength sufficient? A minimum strength of
two bars is recommended, but some phones can send data with one. For
a better signal, raise the antenna, hold the phone upright, and/or relocate.
!
Does your phone have enough battery power for your data call?
!
Is the Socket GSM program closed? The Socket GSM program uses the
same port needed for remote networking (e.g., making a data call).
Placing a Data Call
1. Windows CE v3.0: Go to Start | Programs | Connections.
Windows CE v2.11: Go to Start | Programs | Communication.
On some mobile computers, you also need to tap Remote Networking.
2. Tap on the icon for the wireless connection you created in Step 6.
Pocket PC icon Handheld PC icon
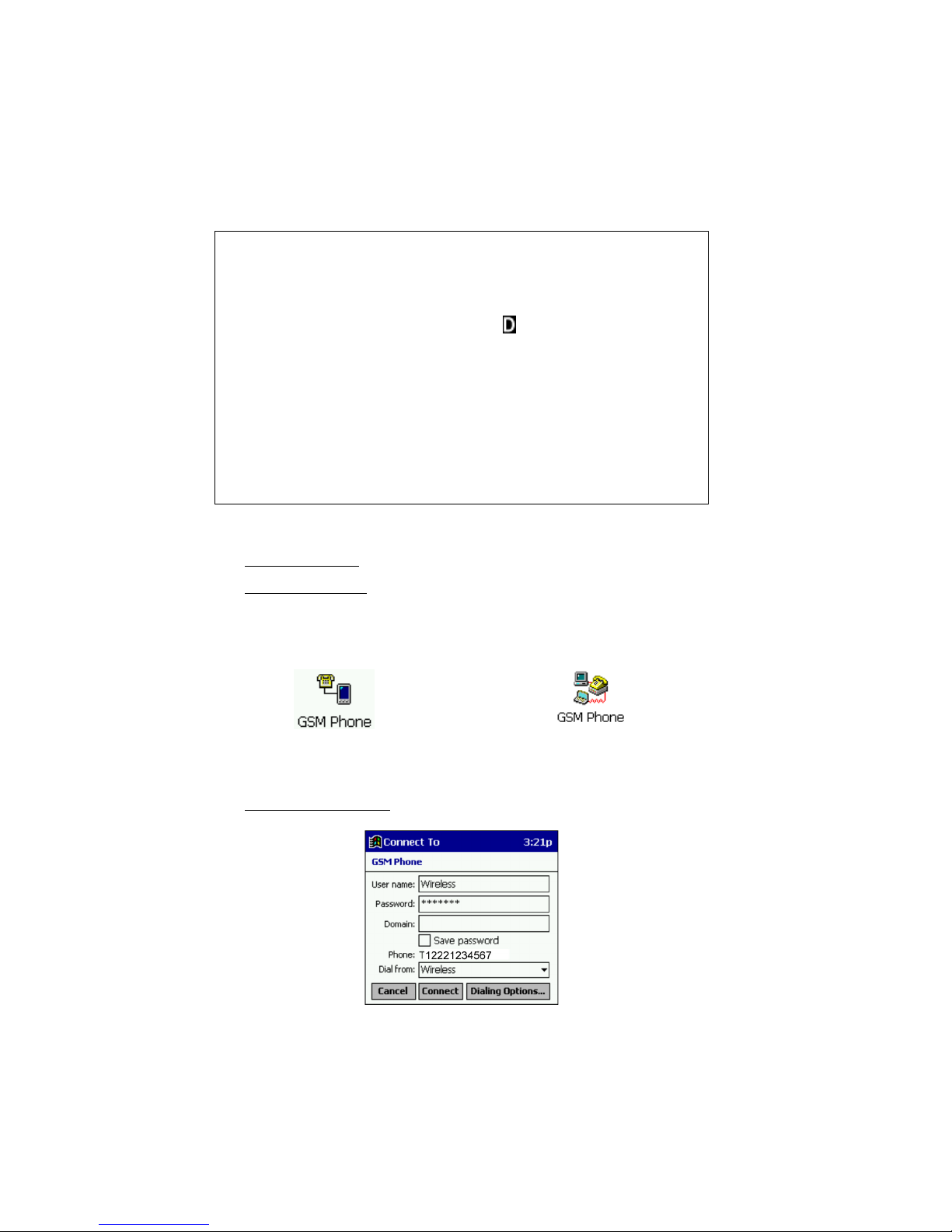
3. The Connect To screen will appear. Enter your User name and Password.
Windows CE v3.0 only: In the Dial from field, select Home.
Connect To screen from a Pocket PC
CHAPTER 3: WINDOWS CE SETUP | 15
Page 18

4. (Optional) For convenience, you can check the Save password box, but
your password will be saved only after
you start the connection.
5. For some mobile computers, you need to modify the dial properties so
the mobile computer can dial properly. For instructions, refer to the
mobile computer’s user manual.
6. Tap Connect. When your mobile computer starts calling, you should see
the call status on both the mobile computer screen and phone display.
Connect To screen from a Pocket PC
7. When the mobile computer status screen reports that you have
Connected, a connection icon will also appear in the task tray:
Pocket PC icon Handheld PC icon
Ending a Data Call
1. Windows CE v3.0 only
2. Tap on the connection icon in the task tray, shown above.
: Go to Start | Today.
3. In the status screen that appears, tap Disconnect. The task tray icon will
disappear, and your mobile phone will hang up.
Connection status screen from a Pocket PC
16 | CHAPTER 3: WINDOWS CE SETUP
Page 19

Chapter 4 SMS Messaging for
Windows CE
The GSM version of the Digital Phone Card includes software for SMS
messaging.
Socket’s SMS program includes two folders: the SMS folder and the
Phonebook folder. The SMS folder is for creating, modifying, and storing
messages, while the Phonebook folder is for creating, modifying, and
storing contact information, including information on your phone’s SIM
card.
This section primarily shows Pocket PC screens. Except where noted,
screens from other device types are functionally equivalent.
Preliminary Checklist
!
Is your mobile phone turned ON?
!
Is SMS service activated for your phone? Most carriers charge an extra
fee for SMS service.
!
Has all remote networking connections on the mobile computer ended?
Remote networking uses the same port needed for Socket GSM software.
Launch the program
2. Go to Start | Programs | Socket GSM.
Any Handheld device
icon on the desktop.
: For a shortcut, you can tap on the Socket GSM
3. When the program launches, a title screen will appear, reporting your
mobile phone’s status on the bottom. Your phone display may also
display a message such as “Accessory Connected.”
If your phone is not ready, you will not be able to send any SMS
messages. Refer to Appendix D, “Troubleshooting” section.
CHAPTER 4: SMS MESSAGING FOR WINDOWS CE | 17
Page 20

Create a SMS message from the SMS folder
1. Make sure the SMS folder is open. The Phonebook button will be below
the icons. If you would like to send a message to someone in your SIM,
Phone or other folder, tap on the icon for that folder.
Pocket PC Handheld PC
2. Tap on File. In the pop-up menu, select New SMS.
You can also start a New SMS by using these shortcuts:
• Pocket PC/Palm-size PC
: Tap and hold your stylus in the large white
area below the Number and Message bar. In the pop-up menu that
appears below your stylus, select New SMS.
• Any Handheld
: Tap on the New SMS icon:
3. In the next screen, in the To field, enter the recipient’s SMS number
(mobile phone number). The plus sign “+” must precede each number.
Or, if you would like to send a message to recipient(s) listed in the
currently open SMS folder, (e.g., SIM), tap on Multiple Recipients.
In the list that appears below, select a recipient. Make sure the SMS
number begins with the plus sign “+”, then tap Add Numbers. The
recipient will appear in the To field. Repeat to add other recipients.
IMPORTANT! EACH SMS NUMBER MUST BEGIN WITH “+”
18 | CHAPTER 4: SMS MESSAGING FOR WINDOWS CE
Page 21

4. Select the Coding system compatible for your keyboard (e.g., 7 Bit for
normal text, 8 Bit for special characters or UCS2 for Chinese characters).
Note: The maximum possible length of your message depends on what
coding system you use. Normal text messages with 7 Bit coding can hold
up to 160 characters (a space counts as a character).
In the large field, enter a message, noting the character Count. Tap Send.
Make a Phonebook Entry
7. Make sure the Phonebook is open. Tap on the Phonebook button. The
Phonebook button should move above the icons.
Pocket PC Handheld PC
8. Tap on the SIM or Phone icon, wherever you want to store the new
Phonebook entry. If you create a new Phonebook archive (explained
later), you can also store the entry there.
SIM contains contact information stored on your mobile phone’s SIM
card, while Phone contains contact information stored directly on your
mobile phone (only certain phones can do this). Using the Phonebook is
an easy way to enter contacts into your SIM card or phone (rather than
using phone buttons).
Contacts contains contact information stored on the mobile computer.
You cannot use the Phonebook to add information to Contacts.
9. Tap File | New Phonebook Entry.
You can also start a New SMS by using these shortcuts:
• Pocket PC/Palm-size PC
: Tap and hold your stylus. In the pop-up
menu, select New Phonebook Entry.
• Any Handheld
10. In the next screen, enter a Name and Number. Tap ok.
IMPORTANT! THE NUMBER MUST BEGIN WITH “+”
: Tap on the New Phonebook Entry icon:
CHAPTER 4: SMS MESSAGING FOR WINDOWS CE | 19
Page 22

Create a SMS Message from the Phonebook
1. Make sure the Phonebook is open. Tap on the Phonebook button.
2. Tap on SIM, Phone, or Contacts, wherever you stored the entry you wish
to access.
3. In the next screen, select the entry, then tap File | New SMS.
You can also use these shortcuts:
• Pocket PC/Palm-size PC
: Tap the entry to select it, then hold your
stylus there. In the pop-up menu, select New SMS.
• Any Handheld device
icon.
: Select the entry, then tap on the New SMS
4. Complete the remaining steps as described in Creating an SMS Message
from the SMS Folder. However, the SMS number should automatically
appear in the To field. Make sure the SMS number begins with the “+”
symbol.
Archive a Message
1. Make sure the SMS folder is open. Tap on the SMS button. The
Phonebook button should move below the icons.
2. Tap on SIM, Phone or Sent Items, wherever the message you wish to
archive is currently located.
3. Select the message.
4. Tap Edit. In the pop-up menu, select Cut or Copy.
You can also use these shortcuts:
• Pocket PC/Palm-size PC
: Tap and hold your stylus. In the pop-up
menu, select Cut or Copy.
• Any Handheld
: Tap on the Cut or Copy icon:
5. Tap on the icon for the archive you wish to store the message in.
6. Tap Edit | Paste.
You can also use these shortcuts:
• Pocket PC/Palm-size PC
: Tap and hold your stylus. In the pop-up
menu, select Paste.
• Any Handheld
: Tap on the Paste icon:
20 | CHAPTER 4: SMS MESSAGING FOR WINDOWS CE
Page 23

Chapter 5 Windows 9x/Me Setup
This section covers the latter part of the setup for Windows 9x/Me. For
Steps 1-4, refer to Chapter 2, “Preliminary Setup.”
STEP 5: Insert the Installation CD
Insert the installation CD into the CD drive of your notebook computer.
STEP 6: Insert the Card and Attach the Phone
1. Plug the DPC into the PC Card adapter, with the purple label on top.
Do NOT insert the DPC upside down, or damage may occur.
Insert the DPC
into the adapter
with the card’s
colorful label
on top.
2. With the notebook computer turned ON, insert the combined unit into
the PC Card slot. Windows notebooks in most cases will signal that the
DPC has been properly inserted via a beep, task tray icon and/or
message screen.
3. Connect the free end of the data cable to the data part of the mobile
phone. The data port is typically on the bottom or side of the mobile
phone and usually is the same port used to charge the phone.
CHAPTER 5: WINDOWS 9x/Me SETUP | 21
Page 24

STEP 7: Install the Software
After inserting the DPC, complete these steps for software installation:
1. The first time you insert the DPC, a new hardware or device driver
wizard will appear.
Add New Hardware Wizard from Windows 98
2. Follow the wizard to install the DPC drivers, inserting the installation
CD and making the appropriate selection below as prompted:
a. Windows 95
b. Windows 98
the next screen, select CD-ROM drive.
— Select Other locations and specify your CD drive.
— Select Search for the best driver for your device. In
Add New Hardware Wizard from Windows 98
c. Windows Me — Select Specify the location of the driver. In the next
screen, select Search for a suitable driver for my device, and check
Removable Media.
Important! For Windows Me, DO NOT select Automatic search for
a new driver!
3. Follow the remaining instructions until installation is complete.
22 | CHAPTER 5: WINDOW S 9x/Me SETUP
Page 25

STEP 8: Set up Remote Networking
You will need your completed Network Information Form for this step.
1. Windows 9x: Go to My Computer | Dial-Up Networking | Make New
Connection.
Note: For some Windows 98 versions, a Welcome to Dial-Up Networking
screen will appear instead of Make New Connection. Click Next>.
Windows Me: Go to My Computer | Control Panel | Dial-Up Networking |
Make New Connection.
2. In the top field, enter a name for your wireless connection, such as
“GSM Phone.” Select Socket GSM Modem from the modem list. Click
Next>.
3. In the next screen, enter your network’s dial-up number. Click Next>.
Make New Connection screen from Windows 98
4. The next screen will report that you have successfully created the
connection. Click Finish.
• If using DHCP, you are ready to use your connection. Restart your
machine, then go ahead and make a data call.
• If NOT using DHCP, then you must modify your connection’s
properties to enter any necessary IP addresses.
5. To modify the connection’s properties, in the Dial-Up Networking screen,
right-click on the icon for your wireless connection. Select Properties.
6. Windows 9x: Click on Server Types.
Windows Me
: Click on the Networking tab.
7. Using your Network Information Form, enter any necessary settings. To
modify IP, DNS, and/or WINS addresses, click on TCP/IP Settings...
8. In the TCP/IP Settings screen, enter any necessary settings. Click OK.
9. You should return to the main connection properties screen. Click OK.
10. Restart your machine to make sure the changes take effect.
CHAPTER 5: WINDOWS 9x/Me SETUP | 23
Page 26

STEP 9: Make a Data Call
Preliminary Checklist
!
Are the cable and connectors fastened securely to the mobile computer
and phone?
!
Is the phone receiving a digital signal? A or equivalent will appear on
the display of some phones.
!
Is the mobile phone’s signal strength sufficient? A minimum strength of
two bars is recommended, but some phones can send data with one. For
a better signal, raise the antenna, hold the phone upright, and/or relocate.
!
Does your phone have enough battery power for your data call?
!
Is the Socket GSM program closed? The Socket GSM program uses the
same port needed for remote networking, (e.g., making a data call).
Placing a Data Call
1. Windows 9x
Windows Me
2. Double-click on your wireless connection.
: Go to My Computer | Dial-Up Networking.
: Go to My Computer | Control Panel | Dial-Up Networking.
3. Enter the User Name and Password. Verify the number and location and
click Connect.
Note: If you select the Save password option, the information will be
saved only after you click Connect.
4. When the computer starts calling, you should see the call status on both
the computer screen and phone display.
5. When connected, the status screen will report that you are successfully
connected, and a connection icon will appear in the task tray.
24 | CHAPTER 5: WINDOW S 9x/Me SETUP
Connect To screen from Windows 98
Connection icon
Page 27

Ending a Data Call
1. Double-click on the connection icon in the task tray, shown above.
2. In the connection status screen, click Disconnect. The icon will disappear
from the task tray, and the mobile phone will hang up.
CHAPTER 5: WINDOWS 9x/Me SETUP | 25
Page 28

Chapter 6 Windows 2000/XP Setup
This section covers the latter part of the setup for Windows 2000/XP. For
Steps 1-4, refer Chapter 2, “Preliminary Setup.”
STEP 5: Insert the Installation CD
Insert the installation CD into the CD drive of your notebook computer.
STEP 6: Insert the Card and Attach the Phone
1. Plug the DPC into the PC Card adapter, with the purple label on top.
Do NOT insert the DPC upside down, or damage may occur.
Insert the DPC
into the adapter
with the card’s
colorful label
on top.
2. With the notebook computer turned ON, insert the combined unit into
the PC Card slot. Windows notebooks in most cases will signal that the
DPC has been properly inserted via a beep, task tray icon and/or
message screen.
3. Connect the free end of the data cable to the data part of the mobile
phone. The data port is typically on the bottom or side of the mobile
phone and usually is the same port used to charge the phone.
26 | CHAPTER 6: WINDOW S 2000 SETUP
Page 29

STEP 7: Install the Software
After inserting the installation CD and the DPC, complete these steps for
software installation:
1. The first time you insert the DPC, a device driver or new hardware
wizard will appear. Click Next>.
2. Follow the wizard to install the DPC drivers, making the appropriate
selection below as prompted:
a. Windows 2000
the next screen, select Specify a location. Browse your CD drive for
the Windows2KXP folder.
— Select Search for a suitable driver for my device. In
Upgrade Device Driver Wizard from Windows 2000
b. Windows XP — Select Install from a list or specific location and
browse your CD drive for the Windows2KXP folder.
Found New Hardware Wizard from Windows XP
Note: Windows may report that the product has not passed Windows
logo testing to verify compatibility with Windows XP.
Ignore and click Continue Anyway.
3. Follow the remaining instructions until installation is complete.
CHAPTER 6: WINDOWS 2000/XP NOTEBOOKS | 27
Page 30

STEP 8: Set up Remote Networking
1. Windows 2000 — Go to My Computer | Control Panel |
Network and Dial-up Connections | Make New Connection.
Windows XP — Go to Start | Control Panel | Network Connections |
Create a new connection.
2. A connection wizard will appear. Click Next>.
New Connection Wizard from Windows XP
3. Follow the wizard to set up a new network connection, making the
following selections as prompted:
(a) Windows 2000 —
• Network Connection Type: Select Dial-up to the Internet
• Select a Device: Select Socket GSM Modem.
(b) Windows XP —
• Network Connection Type: Select Connect to the Internet
• Getting Ready: Select Set up my connection manually
• Internet Connection: Select Connect using a dial-up modem
• Select a Device: Select Socket GSM Modem.
4. After completing the wizard, in most cases, your connection is now
ready, and you are ready to dial. However, if you have special TCP/IP
settings to enter, you still need to configure your connection for these
settings.
5. To configure your connection for TCP/IP settings, complete the
following:
28 | CHAPTER 6: WINDOW S 2000/XP NOTEBOOKS
Page 31

Entering TCP/IP Settings
1. Windows 2000 — After completing the wizard, you will return to the
Network and Dial-up Connections screen. Right-click on the icon for your
new connection. In the pop-up menu, select Properties.
Windows XP — After completing the wizard, the Connect screen will
appear for your new connection. Click on Properties.
2. In the connection properties screen, click on the Networking tab.
To enter TCP/IP settings, check Internet Protocol and click on Properties.
Networking screen from Windows XP
3. In the Internet Protocol Properties screen, enter any necessary IP
addresses. If needed, click on the Advanced button to enter DNS, WINS
or other settings.
Internet Protocol Properties screen from Windows XP
4. When done entering your settings, click OK. Restart your computer to
make sure the changes take effect.
CHAPTER 6: WINDOWS 2000/XP NOTEBOOKS | 29
Page 32

STEP 9: Make a Data Call
Preliminary Checklist
!
Is the DPC properly inserted into the mobile computer and connected
securely to the phone?
!
Is the phone receiving a digital signal? A or equivalent will appear on
the display of some phones.
!
Is the mobile phone’s signal strength sufficient? A minimum strength of
two bars is recommended, but some phones can send data with one. For
a better signal, raise the antenna, hold the phone upright, and/or relocate.
!
Does your phone have enough battery power for your data call?
Placing a Data Call
1. Windows 2000
up Connections. Double-click on the connection you just configured.
— Go to My Computer | Control Panel | Network and Dial-
Windows XP — Go to Start | Control Panel | Network Connections.
Double-click on the connection you just configured.
2. Make sure the correct User Name and Password are entered. Verify the
other dialing information, and click Dial.
Note: If you select the Save password option, the information will be
saved only after you click Dial.
Connect screen (Windows XP) Dialing status screen (Windows XP)
3. When the computer starts calling, you should see the call status on both
the computer screen and phone display.
4. When connected, the status screen will report that you are successfully
connected, and a connection icon will appear in the task tray.
Ending a Data Call
Double-click on the connection icon in the task tray. In the status screen,
click Disconnect. The icon will disappear, and your phone will hang up.
30 | CHAPTER 6: WINDOW S 2000/XP NOTEBOOKS
Page 33

Chapter 7 SMS Messaging for
Windows 9x/Me/2000/XP
The GSM version of the Digital Phone Card includes software for SMS
messaging.
Socket’s SMS program includes two folders: the SMS folder and the
Phonebook folder. The SMS folder is for creating, modifying, and storing
messages, while the Phonebook is for creating, modifying, and storing
contact information, including information on your phone’s SIM card.
This section primarily shows Windows 98 screens. Except where noted,
screens from Windows 95/Me/2000/XP are functionally equivalent.
Preliminary Checklist
!
Is your mobile phone turned ON?
!
Is SMS service activated for your phone? Most carriers charge an extra
fee for SMS service.
!
Have all remote networking connections on the mobile computer ended?
Remote networking uses the same port needed by Socket GSM software.
Launch the program
1. Go to Start | Programs | Socket GSM.
Program icon
2. When the program launches, a title screen will appear, reporting your
mobile phone’s status on the bottom.
Title screen
If your phone is not ready, you will not be able to send any SMS
messages. Refer to the “Troubleshooting” section in the User’s Guide on
the installation CD for help.
CHAPTER 7: SMS FOR WINDOWS 9x/Me/2000/XP | 31
Page 34

Create a SMS message without accessing the Phonebook
1. Make sure the SMS folder is open. To open it, click on the SMS button.
When the SMS folder is open, the Phonebook button will be at the
bottom of the screen, and the title bar will say Socket DPC – SMS.
SMS
button
SMS folder
2. Click on the New SMS icon: . Or go to File | New SMS.
3. In the next screen, in the To field, enter the recipient’s SMS number
(mobile phone number).
IMPORTANT! THE SMS NUMBER MUST BEGIN WITH “+”
SMS Message screen
Select the Coding system compatible for your keyboard (e.g., 7 Bit for
normal text, 8 Bit for special characters or UCS2 for Chinese characters).
Note: 7Bit messages can hold 160 characters, 8Bit messages can hold
140, and UCS2 messages can hold 70. A space counts as a character.
In the main field, enter a message. Note the character Count. Click Send.
32 | CHAPTER 7: SMS FOR WINDOWS 9x/Me/2000/XP
Page 35

Make a Phonebook Entry
1. Make sure the Phonebook is open. To open it, click on the Phonebook
button. The Phonebook button should move right below the SMS button,
and the title bar will say Socket DPC - Phonebook.
Phonebook
button
Phonebook folder
2. Select SIM or Phone, wherever you want to store the new Phonebook
entry. If you create a new Phonebook archive (explained later), you can
also store the entry there.
SIM contains contact information stored on your mobile phone’s SIM
card, while Phone contains contact information stored directly on your
mobile phone (only certain phones can do this). Using the Phonebook is
an easy way to enter contacts into your SIM card or phone (rather than
using phone buttons).
3. Click on the New Phonebook Entry icon:
Or go to File | New Phonebook Entry.
4. In the next screen, enter a Name and Number. Click OK.
IMPORTANT! THE NUMBER MUST BEGIN WITH “+”
CHAPTER 7: SMS FOR WINDOWS 9x/Me/2000/XP | 33
Phonebook Entry screen
Page 36

Create a SMS Message by Accessing a Phonebook Entry
1. Make sure the Phonebook is open. Click on the Phonebook button.
2. Select SIM, Phone, Contacts, or wherever else you stored the entry you
wish to access.
3. In the next screen, select the entry. Click once on the recipient’s name.
IMPORTANT! Make sure the SMS number begins with “+”!!!
Phonebook SIM folder
4. Click on the New SMS icon:
Or go to File | New SMS.
5. In the next screen, in the To field, the recipient’s name should
automatically be entered.
SMS Message screen
34 | CHAPTER 7: SMS FOR WINDOWS 9x/Me/2000/XP
Page 37

6. To send the message to other recipients in your phonebook, click on
Multiple Recipients. From the contact list, click on the name(s) of each
additional recipient, then click on Add numbers. The name of each new
recipient will be added to the To field.
SMS Message screen for multiple recipients
7. Select the coding, and enter a message. Click Send.
SMS Message screen for multiple recipients
CHAPTER 7: SMS FOR WINDOWS 9x/Me/2000/XP | 35
Page 38

Archive a Message
1. Make sure the SMS folder is open. To open it, click on the SMS button.
The Phonebook button will move to the bottom of the screen.
SMS
button
SMS folder
2. Select SIM, Phone or Sent Items, wherever the message you wish to
archive is currently located.
3. Select the message. Click once on the SMS number.
SMS SIM folder
4. Click on the Cut or Copy button:
Or go to Edit | Cut or Copy.
5. Double-click on the archive you wish to store the message in:
6. Click on the Paste button:
36 | CHAPTER 7: SMS FOR WINDOWS 9x/Me/2000/XP
Or go to Edit | Paste.
Page 39

Appendix A Specifications
Physical Characteristics:
CF Card Size: 1.43 x 1.69 x 0.13 in (36.4 x 42.8 x 3.3 mm)
Interconnect Cable Length: 22 in (559 mm)
Power Consumption:
Standby: 0 mA (0 mW)
Typical: 3 mA (10 mW)
Interface Standards:
CompactFlash Interface: CompactFlash CF, Type I
With PC Card Adapter: PCMCIA, Type II
Serial Communications: TTL
Baud rate: Up to 115.2 Kbps
GSM Network:
Typical Data Rate Throughput: 9600 kbps
Operating System Support:
Windows CE (v2.11 or greater)
Windows 9x/Me/2000/XP (with Upgrade Kit)
GSM Handsets Supported:
For a complete, up-to-date list of GSM handsets supported, please visit:
www.socketcom.com/product/dpc.htm
Software Compatibility: Windows COM port
Hardware Compatibility:
Standard Card (without PC Card adapter):
All Windows Powered Pocket PCs. All Windows CE-based Palm-size
PCs including devices from Casio, Compaq, and HP. All Windows
CE-based Handheld PC Pro devices with CompactFlash I/O slot.
With PC Card adapter:
All Windows CE Handheld PC Pros. All Windows 9x/Me/2000/XP
notebooks.
Software Included:
GSM software modem, SMS messaging, and Phonebook management.
APPENDIX A: SPECIFICIATIONS | 37
Page 40

Compatible Applications:
Windows Remote Dialup, ActiveSync, Pocket Outlook, Acrobat Reader,
AOL Mail Client, EZOS WAP Browser, MSN Mail Client, PacketVideo
Player, movianVPN, FTP, Telnet, AvantGO, Citrix, pcANYWHERE,
streaming video, etc.
Warranty:
CompactFlash Card and Non-removable Cable: Lifetime (Three years
if not registered)
To register your product online, visit: www.socketcom.com/prodreg.html
Certification:
FCC: Part 15, Class B, CE: EN55024:1998, C-TICK s.182
38 | APPENDIX A: SPECIFICATIONS
Page 41

Appendix B Hints and Tips
Optimizing Signals and Connections
For best results, follow these guidelines before connecting for a data call:
1. Make sure the cable and connectors are fastened securely to your
mobile computer and your phone.
2. Make sure the phone is receiving a digital signal. A
will appear on the display of some phones.
3. Make sure the signal strength is sufficient. A minimum signal strength
of two bars is recommended, although some phones may successfully
transfer data with only one. To optimize the signal, extend the antenna,
position the phone upright and, if necessary, move to a different location.
4. Make sure your phone has enough battery power for your data call.
Choosing the Right Applications
Not all applications are ideal for wireless networking. For example, it takes
longer to download a large file wirelessly than it does over a landline phone
line with a regular modem. Experiment with your applications to find out
which work best wirelessly.
Using Multiple Modems
Pocket PCs and other Windows CE-based devices can support multiple
modems, but each modem needs a separate dial-up connection. When
making a data call, be sure to choose the connection for the modem in use.
To make multiple dial-up connections, follow the steps outlined in the
“Setting up Remote Networking” section for your device, but include the
following modifications:
1. In the Make New Connection screen, when naming connections, select
names that clearly distinguish the modem in use, such as "Internet
Service Provider-Wireless" and "Internet Service Provider-Landline."
2. In the Select a modem box, choose Socket DPC Connection for a wireless
connection. Choose your existing modem for a landline connection.
For other applications, such as faxing, refer to your fax program’s user
documentation on using multiple modems or changing between modems.
or equivalent
APPENDIX B: HINTS AND TIPS | 39
Page 42

Appendix C Troubleshooting
SYMPTOM:
My computer ...
… does not recognize my GSM phone [modem].
… does not respond to AT commands.
… cannot place a call.
POSSIBLE REASONS SOLUTION
Your GSM phone is turned off. Turn on your GSM phone.
Your phone is not communicating
properly with your computer.
The data cable is loose or
detached.
Other software is using the COM
port.
Your software is set up to use a
modem other than the GSM phone.
Your fax software is set to Auto
Answer and uses the COM port.
SYMPTOM:
My call fails immediately.
OR
I get a message like CALL FAILED on my phone.
POSSIBLE REASONS SOLUTION
The phone battery died. Recharge or replace the battery.
Temporary network anomaly. Call again. CALL FAILED usually
SYMPTOM:
I get a message like NO NETWORK on my phone.
POSSIBLE REASONS SOLUTION
You left the GSM coverage area
during the call.
Turn your GSM phone off, then
turn it on again.
Make sure you are using the right
data cable and securely fasten it.
Deactivate the software using the
COM port. ActiveSync and
HotSync usually use the COM port.
Configure your software for the
GSM phone as its modem.
Disable the Auto Answer feature
on your fax software.
disappears after a second try. If it
doesn’t, turn your phone off, then
on again. If the problem persists,
your GSM service may be down.
Raise the phone antenna. If you
still don’t get digital coverage,
return to the coverage area to call.
40 | APPENDIX C: TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 43

SYMPTOM:
My computer dials but cannot connect.
POSSIBLE REASONS SOLUTION
Your software is set up for a
modem other than the GSM phone.
You are dialing the wrong number. Check the number, including the
The number you are dialing is long
distance.
The modem you are calling is out
of service.
You have left the GSM coverage
area.
Your user name and/or password
are incorrect.
Configure your software for your
GSM phone as the modem.
area code. Verify the number with
your Internet Service Provider or
corporate network support.
Check the area code of the number
you are dialing. You may need to
add a 1 for long distance.
Contact your ISP or office network
support to verify the status of their
server and modems.
Raise the phone antenna and check
the display. If digital coverage is
still not accessible, return to the
coverage area to place your call..
Enter the correct information.
SYMPTOM:
My phone shows that the call connected, but my
communications software does not.
POSSIBLE REASONS SOLUTION
The call took so long to connect
that the software timed out.
Increase your software’s time-out
interval and try calling again.
SYMPTOM:
My communications software shows that the call is
connected, but my phone does not.
POSSIBLE REASONS SOLUTION
Your call was dropped, but your
software is still waiting to connect.
Cancel the call from your software
and try again.
APPENDIX C: TROUBLESHOOTING | 41
Page 44

SYMPTOM:
I get a message like NETWORK NOT RESPONDING
or CHECK OPERATOR SERVICES on my phone.
POSSIBLE REASON SOLUTION
The GSM account needs updating. Call your GSM service provider.
SYMPTOM:
I get disconnected in mid-session.
POSSIBLE REASONS SOLUTION
The GSM signal has faded, or you
have left the GSM coverage area.
Your phone battery died. Recharge or replace the battery.
The data cable is loose or
detached.
The modem you are calling is out
of service.
Your call was dropped. Try the call again.
You were automatically
disconnected due to inactivity.
Raise the phone antenna. If you
still don’t get digital coverage,
return to the coverage area to call
Securely fasten the data cable.
Contact your Internet Service
Provider or corporate network
support to verify the status of their
server and modems.
Some software will end a call after
some inactivity. Disable or change
the automatic disconnect feature.
SYMPTOM:
I cannot configure SMS Services.
POSSIBLE REASONS SOLUTION
You are in the middle of an active
data call.
End the data call and try
configuring again.
SYMPTOM:
When I try to send an SMS message, NO MATCHING
ENTRY WAS FOUND for the number.
POSSIBLE REASONS SOLUTION
Your SMS number is not in the
contact list.
In Inbox, go to Services, Options,
then tap on the Address tab. In the
In Contacts, get addresses from:
drop list, select None, then tap OK.
42 | APPENDIX C: TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 45

SYMPTOM:
The data is transmitting slowly.
POSSIBLE REASONS SOLUTION
The network has a maximum
connection speed of 9600 bps.
Due to heavy loads, dial-in or web
servers are responding slowly.
For advice on efficient usage, visit:
www.DigitalPhoneCard.com
Connect another time, when your
office network or ISP is less busy.
SYMPTOM:
I cannot receive voice calls.
POSSIBLE REASONS SOLUTION
Your GSM phone is set up to
receive data or fax calls only.
Follow the instructions that came
with your phone to set up for voice
calls. You can usually do this
through the phone menu.
SYMPTOM:
I cannot receive fax calls.
POSSIBLE REASONS SOLUTION
The phone is not set up to receive
fax calls.
Your fax software is not answering
in time.
Follow the instructions that came
with your phone to set up for fax
calls. You can usually do this
through the phone menu.
Set your software to answer after
fewer rings, preferably 0. Consult
the software user manual for help.
SYMPTOM:
I cannot receive data calls.
POSSIBLE REASONS SOLUTION
The phone is not set up to receive
data calls.
Your communications software is
not answering in time.
Follow the instructions that came
with your phone to set up for data
calls. You can usually do this
through the phone menu.
Set your software to answer after
fewer rings, preferably 0. Consult
the software's user manual for help.
APPENDIX C: TROUBLESHOOTING | 43
Page 46

SYMPTOM:
I cannot access my email.
OR
I cannot use my web browser.
POSSIBLE REASONS SOLUTION
You are not connected to your
corporate network or ISP.
Your dial-up networking settings
are incorrect.
Your user name(s) and/or
password(s) for your services are
incorrect.
Connect again.
Reconfigure the connection with
the correct settings for your office
network or ISP.
Enter the correct information for
all services, including email, NT
servers and proxy servers.
44 | APPENDIX C: TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 47

Appendix D ISP Resources
Here are a few Internet Service Providers (ISPs) that are known to work
with the Pocket PC and other Windows CE-based devices. The information
in this listing is subject to change without notice.
For the most accurate, up-to-date information on connecting to a specific
ISP with a Pocket PC, please contact the ISP directly or go visit:
http://www.pocketpc.com
Name of ISP
Advanced Systems Network DNS: 205.167.153.4
http://www.as.net/
POP3 server: pop3.as.net
SMTP mail host: smtp.as.net
Alternate Access DNS: Server
http://www.aa.net
POP3 server: mail.aa.net
SMTP mail host: mail.aa.net
AT&T WorldNet Service DNS: 204.127.160.2
http://www.att.com/worldnet/
POP3 server: postoffice.worldnet.att.net
SMTP mail host: mailhost.worldnet.att.net
Note: Login name and password are different from pop3 user
CompuServe DNS: 149.174.211.5
http://www.compuserve.com/
POP3 server: pop.site1.sci.com
SMTP mail host: smtp.site1.csi.com
Note: See http ://www.craigte ch.co .uk/hpc/cservefaq.htm l
Drizzle DNS: 216.162.192.2
http://www.drizzle.com
POP3 server: pop.drizzle.com
SMTP mail host: smtp.drizzle.com
Note: Logon using <username>-ppp
Earthlink DNS: 207.217.126.81
http://www.earthlink.net
POP3 server: mail.earthlink.net
SMTP mail host: mail.earthlink.net
Note: Requires ELN/ before the logon user name. For more help,
ISP Settings for Windows CE
Alt DNS: 205.167.153.2
Alt DNS: Server
Alt DNS: 204.127.129.2
name and password.
Alt DNS: 149.174.213.5
Alt DNS: 216.162.192.3
Alt DNS: 207.217.77.82
see: http://help.earthlink.net/techsupport/other/wince/menu.html
APPENDIX D: ISP RESOURCES | 45
Page 48

Erols Internet DNS: 205.252.116.10
http://www.erols.com/
Alt DNS: 205.252.116.19
POP3 server: pop.erols.com
SMTP mail host: smtp.erols.com
Note: Add 4-6 commas after dial string if not using K56Flex.
MCI WorldCom Internet DNS: 204.70.127.127
http://www.wcom.com
Alt DNS: 204.70.127.128
POP3 server: mail.internetmci.com
SMTP mail host: mail.internetmci.com
MindSpring DNS: 207.69.188.185
http://www.mindspring.com
Alt DNS: 207.69.188.186
POP3 server: pop.mindspring.com
SMTP mail host: mail.mindspring.com
MSN POP3 server: email not supported
http://www.msn.com STMP mail host: email not supported
Note: Requires MSN/ before user name. Great for browsing the
web. Email not supported for Pocket PCs at this time, but
Hotmail can be used.
(use Hotmail®)
(use Hotmail®)
Nocharge.com DNS: not needed
http://www.nocharge.com/
Note: Username: guest; Password: password; Can use Hotmail
Alt DNS: not needed
or Yahoo Mail for email.
Prodigy Internet DNS: 198.83.19.241
http://www.prodigy.com
Alt DNS: 198.83.19.244
POP3 server: pop.prodigy.net
SMTP mail host: smtp.prodigy.net
Quik Internet DNS: 204.182.160.1
http://www.quik.com
Alt DNS: 205.162.86.17
POP3 server: mail.quik.com
SMTP mail host: mail.quik.com
Southwestern Bell DNS: 151.164.1.8
http://www.swbell.net
Alt DNS: 151.164.1.7
POP3 server: postoffice.swbell.net
SMTP mail host: mail.swbell.net
Sympatico-British Columbia DNS: 204.174.64.1
http://www.bc.sympatico.ca
Alt DNS: 205.174.64.2
POP3 server: pop.bc.sympatico.ca
SMTP mail host: smtp.bc.sympatico.ca
UUNet DNS: 198.6.1.1
http://www.uu.net/
Alt DNS: 198.6.1.2
POP3 server: vpop1-alterdial.uu.net
SMTP mail host: vsmtp1-alterdial.uu.net
Note: Alternatives for POP3 and SMTP are:
vpop2-alterdial.uu.net and vsmtp0-alterdial.uu.net
46 | APPENDIX D: ISP RESOURCES
Page 49

Verio DNS: 129.250.35.250
http://www.verio.com
Alt DNS: 129.250.35.251
POP3 server: pop.veriomail.com
SMTP mail host: smtp.veriomail.com
Verizon Online DNS: 206.124.64.253
http://www.verizon.net
Alt DNS: 206.124.65.253
POP3 server: mail.gte.net
SMTP mail host: smtp.gte.net
Note: Requires GTE/ before user name.
APPENDIX D: ISP RESOURCES | 47
Page 50

Appendix E Technical Support
If you cannot resolve a technical problem with the Digital Phone Card,
contact Socket’s technical support department prepared with the following
information:
• The part number (including revision level) and serial number of your
DPC. Please see the diagram below.
• The manufacturer, model number, and Windows version of your mobile
computer
• If applicable, the Windows version of your host computer
• The manufacturer, model number and carrier of your GSM phone
• What you did to try to correct the problem
• What you do to consistently replicate the problem
To reach Socket’s technical support department:
• Visit www.socketcom.com/phone.htm
• Email techsupport@socketcom.com
• Phone 510-744-2720
• Fax 510-744-2727
Please refrain from disassembling the Digital Phone Card. Disassembly of
this device will void the product warranty.
48 | APPENDIX E: TECHNICAL SUPPORT
Page 51

Limited Warranty
Socket Communications Incorporated (Socket) warrants this product against defects
in material and workmanship, under normal use and service, for the following
periods from the date of purchase:
Plug-in card: Lifetime (Three years if not registered)
Non-removable cable: Lifetime (Three years if not registered)
Incompatibility is not a defect covered by Socket’s warranty. During the warranty
period, Socket will, at its option, repair or replace the defective product at no charge
when furnished with proof of retail purchase, provided that you deliver the product
to Socket or to an authorized Socket Service Center.
The returned product must be accompanied by a return material authorization
(RMA) number issued by Socket or by Socket's Authorized Service Center. If you
ship the product, you must use the original container or equivalent and you must pay
the shipping charges to Socket. Socket will pay shipping charges back to any
location in the contiguous United States. This warranty applies only to the original
retail purchaser and is not transferable.
Socket may, at its option, replace or repair the product with new or reconditioned
parts and the returned product becomes Socket's property. Socket warrants the
repaired or replaced products to be free from defects in material or workmanship for
ninety (90) days after the return shipping date, or for the duration of the original
warranty period, whichever is greater.
This warranty does not cover the replacement of products damaged by abuse,
accident, misuse or misapplication, nor as a result of service or modification other
than by Socket.
SOCKET IS NOT RESPONSIBLE FOR INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL
DAMAGES RESULTING FROM BREACH OF ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
WARRANTY, INCLUDING DAMAGE TO PROPERTY AND, TO THE EXTENT
PERMITTED BY LAW, DAMAGES FOR PERSONAL INJURY. THIS
WARRANTY IS IN LIEU OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES INCLUDING
IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
Some states do not allow limitation of implied warranties, or the exclusion or
limitation of incidental or consequential damages, so that the above limitations or
exclusions may not apply to you. This warranty gives you specific legal rights and
you may also have other rights which vary from state to state.
This product may contain fully tested, recycled parts, warranted as if new.
For warranty information, phone (510) 744-2700.
To register your product online, visit: www.socketcom.com/prodreg.htm
Page 52

Limited Software Warranty
LIMITED WARRANTY. SOCKET warrants that the original disk or CD ROM is
free from defects for 90 days from the date of delivery of the SOFTWARE.
CUSTOMER REMEDIES. SOCKET’S entire liability and your exclusive remedy
shall be, at SOCKET’S option, either (a) return of the price paid or (b) replacement
of the SOFTWARE which does not meet SOCKET’S Limited Warranty and which
is returned to SOCKET with a copy of your receipt. Any replacement SOFTWARE
will be warranted for the remainder of the original warranty period or 30 days,
whichever is longer. THESE REMEDIES ARE NOT AVAILABLE OUTSIDE OF
THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA.
NO OTHER WARRANTIES. SOCKET disclaims all other warranties, either
express or implied, including but not limited to implied warranties of
merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose, with respect to the SOFTWARE
and the accompanying written materials. This limited warranty gives you specific
legal rights. You may have others which vary from state to state.
NO LIABILITY FOR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES. In no event shall SOCKET
or its suppliers be liable for any damages whatsoever (including, without limitation,
damages for loss of business profits, business interruption, loss of business
information, or other pecuniary loss) arising out of the use of or inability to use the
SOFTWARE, even if SOCKET has been advised of the possibility of such damages.
Because some states do not allow the exclusion or limitation of liability for
consequential or incidental damages, the above limitation may not apply to you.
EXPORT LAW ASSURANCES. You may not use or otherwise export or reexport
the SOFTWARE except as authorized by United States law and laws of the
jurisdiction in which the SOFTWARE was obtained. In particular, but without
limitation, none of the SOFTWARE may be used or otherwise exported or
reexported (a) into (or to a national or resident of) a United States embargoed
country or (b) to anyone on the U.S. Treasury Department’s list of Specially
Designated Nationals or the U.S. Department of Commerce’s Table of Denial
Orders. By using the SOFTWARE, you represent and warrant that you are not
located in, under control of, or a national or resident of any such country or on any
such list.
GOVERNMENT END USERS. If the SOFTWARE is supplied to the U. S.
Government, the SOFTWARE is classified as “restricted computer software” as
defined in clause 52.227-19 of the FAR. The U. S. Government ‘s rights to the
SOFTWARE are as provided in clause 52.227-19 of the FAR.
CONTROLLING LAW AND SEVERABILITY. This License shall be governed by
the laws of the United States and the State of California. If for any reason a court of
competent jurisdiction finds any provision, or portion thereof, to be unenforceable,
the remainder of this License shall continue in full force and effect.
Page 53

November 2001 Document # 6410-00144 I
Copyright Notice
Copyright © 2001 Socket Communications, Inc. All rights reserved.
Socket, the Socket logo and Battery Friendly are registered trademarks of
Socket Communications, Inc. Digital Phone Card is a trademark of Socket
Communications, Inc. All other brand and product names are trademarks of
their respective holders.
The Digital Phone Card includes technology licensed under United States
Patent Nos. 4,543,450, 4,603,320, 4,686,506, and 4,972,470.
Reproduction of the contents of this manual without the permission of
Socket Communications is expressly prohibited. Please be aware that the
products described in this manual may change without notice.
This manual has been prepared with the greatest care regarding its contents.
However, in the event that it contains omissions, errors or any other
misinformation, please contact SOCKET COMMUNICATIONS at:
Socket Communications, Inc.
37400 Central Court
Newark, CA 94560
Phone: (510) 744-2700
Fax: (510) 744-2727.
Technical support: (510) 744-2720.
Important! Before calling for technical support, please prepare yourself
with the information listed in Appendix E, “Technical Support”
Other than the above, Socket Communications can assume no responsibility
for anything resulting from the application of information contained in this
manual.
Socket Communications requests that you refrain from any applications of
the Socket Digital Phone Card that are not described in this manual. Socket
Communications also requests that you refrain from disassembling the
Digital Phone Card. Disassembly of this device will void the product
warranty.
You can track new product releases, software updates and technical
bulletins by visiting Socket’s web page at: www.DigitalPhoneCard.com.
Page 54

Regulatory Compliance
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a
Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC rules. This equipment
is also CE EN55024:1998 and C-TICK compliant. These limits are designed
to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the
equipment is operated in a commercial environment.
This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and,
if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may
cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this
equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in
which case the user will be required to correct the interference at his or her
own expense.
If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television
reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the
user may try to correct the interference by one or more of the following
measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna of the radio or television.
• Increase the distance separating the equipment and the receiver.
• Connect the equipment to an outlet on a different branch circuit than
that of the receiver.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
The user may find the following booklet helpful:
How to Identify and Resolve Radio-TV Interference Problems.
This booklet is available from the U.S. Government Printing Office,
Washington, D.C. 20402.
Page 55

© 2001 Socket Communications, Inc. Printed in U.S.A.
 Loading...
Loading...