Socket CF RFID Reader Card 6, CF RFID Reader-Scan Card 6, CF RFID Reader-Scan Card 6P User Manual
Page 1

CF RFID Reader Card™
CF RFID Reader-Scan Card™
Series 6
User’s Guide
Page 2

9/2012 Document # 6410-00266 N
Copyright Notice
Copyright © 2012 Socket Mobile, Inc. All rights reserved.
Socket, the Socket logo and Mobility Friendly are registered trademarks of Socket Mobile,
Inc. CF RFID Reader Card, CF RFID Reader-Scan Card, SoMo, RFID Demo,
SocketScan Plug-in, and SocketScan Trigger are registered trademarks or trademarks of
Socket Mobile, Inc. All other brand and product names are trademarks of their respective
holders.
The CF RFID Reader Card and CF RFID Reader-Scan Card contains technology licensed
under United States Patent No. 5,902,991 and 7,003,627.
Reproduction of the contents of this manual without the permission of Socket Mobile is
expressly prohibited. Please be aware that the products described in this manual may
change without notice.
Feel free to contact Socket Mobile at:
Socket Mobile, Inc.
39700 Eureka Drive
Newark, CA 94560-4808
USA
Other than the above, Socket Mobile can assume no responsibility for anything resulting
from the application of information contained in this manual.
Please refrain from any applications of the CF RFID Reader Card or CF RFID ReaderScan Card that are not described in this manual. Please refrain from disassembling the
device. Disassembly of this device will void the product warranty.
You can track new product releases, software updates and technical bulletins by visiting
the Socket Mobile website at: http://www.socketmobile.com/
Page 3

Table of Contents
COPYRIGHT NOTICE 2
1 | INTRODUCTION 5
About the Software 6
Package Contents 6
System Compatibility Requirements 6
Accessory 6
Product Registration 7
2 | SETUP FOR THE SOMO® 8
STEP 1: Assign Trigger Button(s) 9
STEP 2: Start SocketScan Plug-in 13
STEP 3: Insert the Card 13
STEP 4: Open Your Application 14
STEP 5: Read Data into Your Application 15
3 | SETUP FOR NON-SOMO PDA 18
STEP 1: Uninstall Other Scanning Software 19
STEP 2: Install the Software 19
STEP 3: Assign Trigger Button(s) 21
STEP 4: Start SocketScan Plug-in 23
STEP 5: Insert the Card 23
STEP 6: Verify Card Mode 23
STEP 7: Open Application 24
STEP 8: Read Data 25
4 | SOCKETSCAN PLUG-IN SOFTWARE 28
RFID Settings 29
Symbology Selector 32
SocketScan Trigger 33
DUAL DEVICE SUPPORT 35
5 | RFID DEMO 36
Read an RFID Tag 37
Enable Inventory and Loop Modes 39
Select Tag Type 40
ADVANCED: Write to Tag 41
APPENDICES
A PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS 44
B HF RFID STANDARDS AND TAG DESCRIPTIONS 46
ISO15693 46
Tag-it HF 50
I·Code1 51
PicoTag 52
Page 4

ISO14443 53
C BARCODE LABEL SPECIFICATIONS 56
D ENABLING OR DISABLING SYMBOLOGIES 57
E LASER DECODE ZONE 59
F TROUBLESHOOTING 60
G TECHNICAL SUPPORT 61
LIMITED WARRANTY 62
REGULATORY COMPLIANCE 64
4
Page 5

1 | Introduction
Model
RFID Reader/Writer
Barcode Scanner
CF RFID Reader Card 6E
Yes
Not included
CF RFID Reader-Scan Card 6P
Yes
Class 2 laser (2D)
The Socket CF RFID Reader Card Series 6 enables you to can add high frequency RFID
read/write capability to your Socket SoMo
based device.
For applications that require both RFID and barcode reading functionality, the series
includes the dual-function CF RFID Reader-Scan Card 6P, which offers both capabilities
in the same compact form factor.
All three versions read and write to all ISO 15693 and many proprietary 13.56 MHz RFID
tags.
®
handheld computer or other Windows Mobile
The CF RFID Reader Card Series 6 includes three versions:
The CF RFID Reader Cards feature a sleek design with no cables or batteries. The
Battery Friendly
operation.
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION 5
®
product draws minimal power from the host device, allowing long-lasting
Page 6

About the Software
SocketScan Plug-in ™ software enters the RFID tag ID or barcode data
directly into any open Windows program, as if the data were manually typed.
Includes configuration utility.
The RFID Setup utility allows you configure what kinds of data are returned
after reading RFID tags, including tag ID, tag memory, tag types, tag type
prefix, etc.
Socket RFID Demo allows you to read memory blocks of selected RFID tags
in range in either Inventory Mode or a continuous Loop Mode. Advanced
users can write data to the RFID memory.
SocketScan Trigger places a software trigger on your screen that you can
tap to trigger the RFID reader or barcode scanner. Installation is optional.
The Socket Trigger Select program allows you to press a button to quickly
switch between the RFID and laser scanning modes of the CF RFID
Reader-Scan Card.
The Read Barcode program allows you to assign a button on your device to
triggering the barcode laser scanner.
The Read RFID program allows you to assign a button on your device to
trigger the RFID reader.
For software updates, please visit: http://www.socketmobile.com/support/downloads
Package Contents
• CF RFID Reader Card
• SocketScan Plug-in Installation CD
• Booklet with copyright and warranty information
System Compatibility Requirements
• Any of the following Windows Mobile versions:
− Windows Embedded Handheld
− Windows Mobile 2003, 2003SE or 5.0 for Pocket PC
− Windows Mobile 6 Classic/Professional
• Available CompactFlash slot
• Software installation requires a host PC with Microsoft ActiveSync or Windows Mobile
Device Center software
Accessory
FlexGuard is a protective silicone cover for the SoMo handheld computer and RFID card.
http://www.socketmobile.com/products/handheld-computer/accessories/flexguard-cf-card/
6
Page 7

Product Registration
Socket highly recommends that all customers register their products. Registered users receive
priority technical support and can opt to receive product updates, and special offers. Register
online at: http://support.socketmobile.com/
CHAPTER 1: INTRODUCTION 7
Page 8

2 | Setup for the SoMo®
This chapter shows how to install, configure, and use the CF RFID
Reader Card Series 6 on any version of the Socket SoMo handheld
computer.
Setup Summary
STEP 1: Assign a trigger button.
STEP 2: Start SocketScan Plug-in.
STEP 3: Insert the card.
STEP 4: Read tag IDs into your program.
Note: No software installation is required to use the CF RFID Reader Card on the SoMo.
However, you may choose to upgrade the SocketScan Plug-in software. The latest
software is available online at: http://www.socketmobile.com/support/downloads
8
Page 9
STEP 1: Assign Trigger Button(s)
You must set up a mechanism for triggering the CF RFID Reader Card. Hardware button(s)
are the best triggering method from a handheld device.
Note: If you do not want to assign a hardware button, you use SocketScan Trigger
software, which enables you to tap on a software icon to trigger SocketScan Plug-in and
the RFID reader/barcode scanner.
Windows Mobile 6
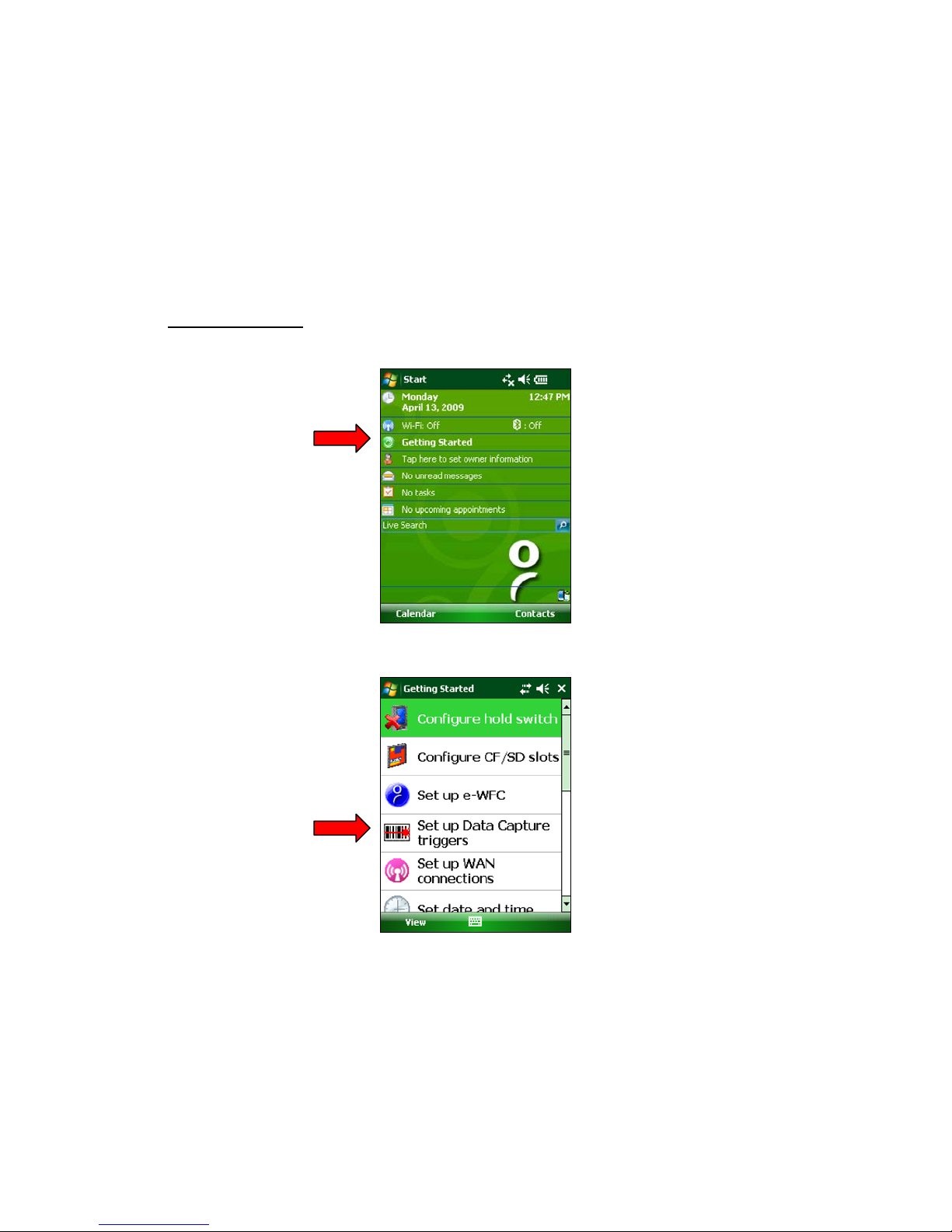
1. In the Today screen, tap Getting Started.
2. In the list, tap on Set up Data Capture triggers.
CHAPTER 2: SETUP FOR THE SOMO 9
Page 10

3. CF RFID Reader Card 6E:
Tap LEFT or RIGHT in the first set of links. The SoMo will automatically set up the
trigger button and send a confirmation message to your inbox.
CF RFID Reader-Scan Card 6P
• In the second set of links, tap LEFT or RIGHT for your barcode scanner trigger.
The SoMo will automatically set up the trigger button and send a confirmation
message to your inbox.
• You will return to the list of Getting Started tutorials. Tap Set up Data Capture
triggers.
• For the RFID reader trigger, tap on the link for the side you did not choose for the
barcode scanner trigger. The SoMo will automatically set up the trigger button and
send a confirmation message to your inbox.
10
Page 11
Windows Mobile 5
If SocketScan Plug-in is not open, SocketScan Plug-in will launch.
SocketScan Plug-in by manually tapping through menus.
Please refer to the chart below to determine which SocketScan Plug-in functions you would
like to assign to buttons on your device.
Note: If you have the CF RFID Reader-Scan Card 6P, SocketScan Plug-in allows you to
configure up to four buttons for launching SocketScan Plug-in and/or triggering the RFID
reader or barcode scanner.
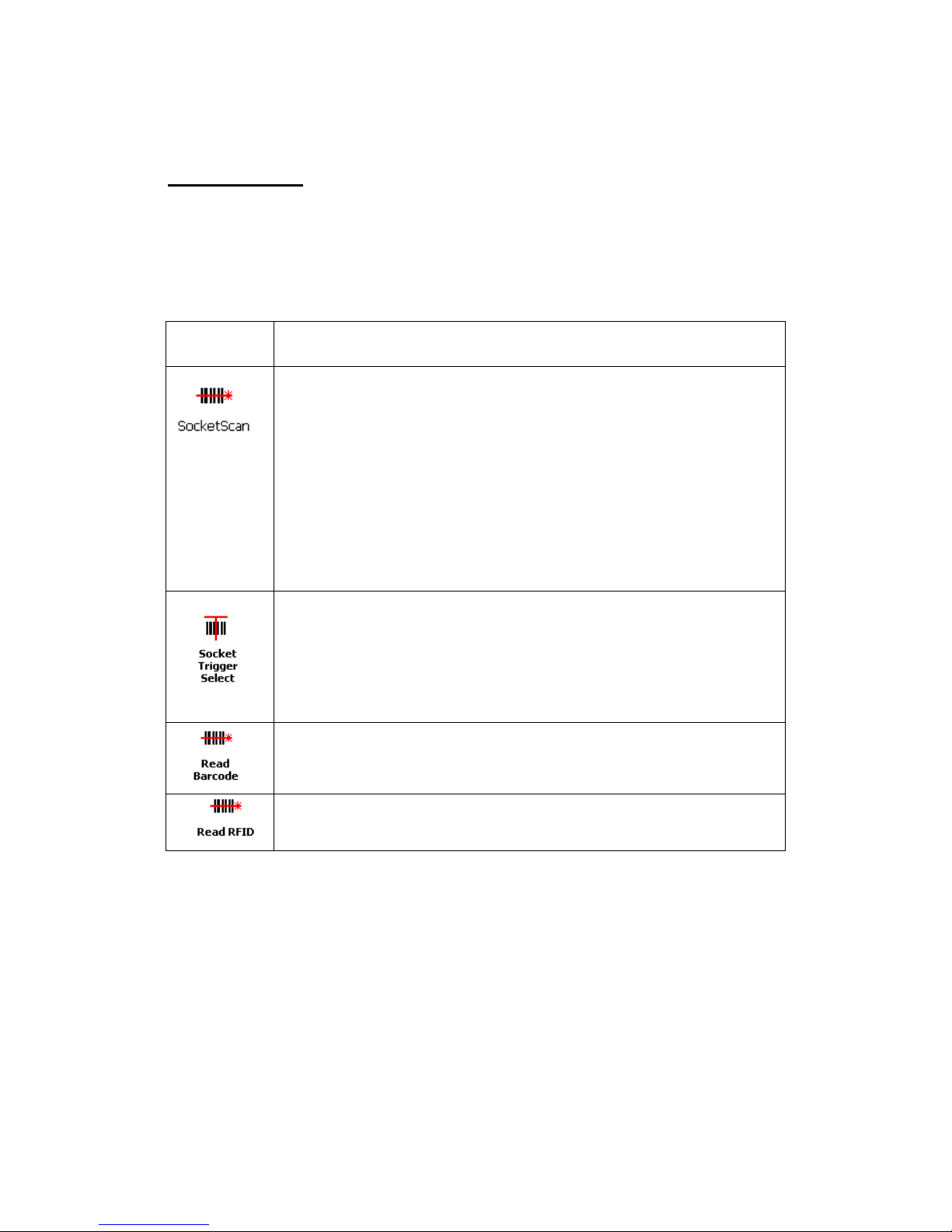
Program What happens when you press a button assigned to this program?
If SocketScan Plug-in is open and you have the CF RFID Reader Card 6E, the
RFID reader will activate.
If SocketScan Plug-in is open and you have the CF RFID Reader-Scan Card
6P, either the RFID reader or the laser scanner will activate, depending on
which mode the card is in.
If you assign only one hardware button for use with the CF RFID Reader
Card, this is the program that should be assigned.
If you do not assign a button to SocketScan Plug-in, you can only start
If you are using the CF RFID Reader-Scan Card 6P, this program will switch
the device from RFID mode to barcode scanning mode, or vice versa. This is
designed to be used with a trigger button assigned to SocketScan Plug-in. You
can also use Socket Trigger Select to toggle to other Socket Mobile barcode
scanners that use a software trigger.
The laser bar ode scanner will activate. SocketScan Plug-in must be running.
The RFID reader will activate. SocketScan Plug-in must be running.
CHAPTER 2: SETUP FOR THE SOMO 11
Page 12
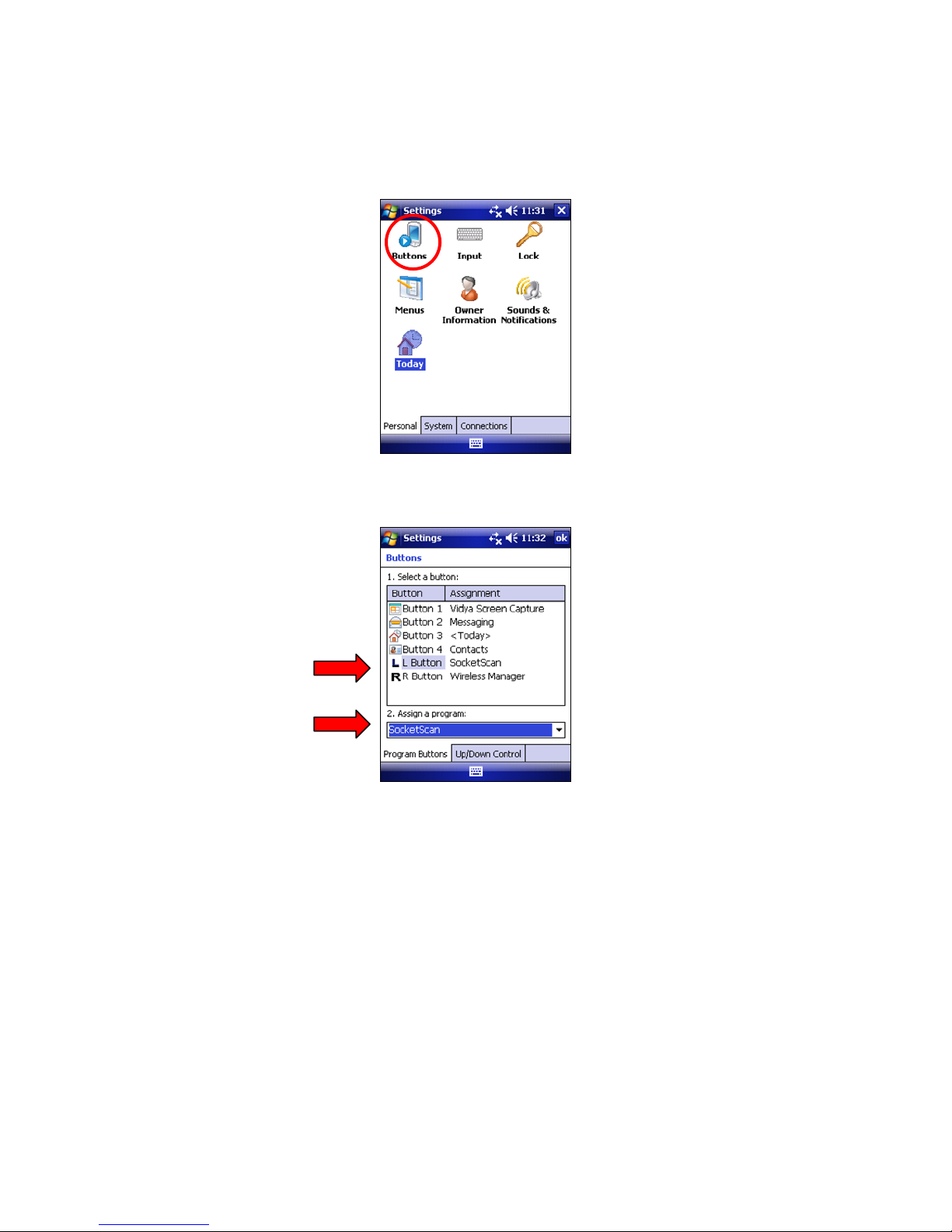
1. Tap Start | Settings | Buttons.
2. In the Button list, select a button. In the drop-down menu, select the program. If
desired, repeat to assign additional trigger buttons. When done, tap ok.
Note: For best ergonomics, choose the left or right buttons.
12
Page 13

STEP 2: Start SocketScan Plug-in
Icon
Meaning.
1. If you assigned a hardware button to SocketScan Plug-in, you can press
the button to quickly launch the program. Otherwise, tap Start |
Programs | SocketScan Plug-in folder | SocketScan Plug-in.
2. An icon will appear in the task tray of the Today screen indicating that the system
does not detect the RFID reader.
When SocketScan Plug-in is running, any of the following icons will appear in the task
tray of the Today screen:
Card detected, RFID mode. SocketScan Plug-in detects the card and is ready to
read RFID tags.
Card detected, scanning mode. SocketScan Plug-in detects the card and is
ready to read barcodes.
No RFID Reader Card detected. The reader card is either missing or improperly
inserted.
STEP 3: Insert the Card
1. Open the card slot cover on top of the SoMo.
2. Insert the card into the CompactFlash slot. Make sure the card is right-side up, with the
blue label on top. Push the card all the way into the slot.
CHAPTER 2: SETUP FOR THE SOMO 13
Page 14
Windows Mobile 5: If you have the CF RFID Reader-Scan Card 6P, and you did not
assign buttons to Trigger ISC or Trigger RFID, make sure the card is in the correct mode
you wish to use. The SocketScan Plug-in icon at the bottom of the Today screen indicates
your current mode.
To switch modes, do either of the following:
• If you assigned a button to Trigger Select, press the button.
• Tap on the SocketScan Plug-in icon. In the pop-up menu, tap to select the card
mode you want.
STEP 4: Open Your Application
Open the application that you want to receive the data (e.g., Excel, Notepad, etc.). Place
the cursor where you want to enter data.
Note: If reading RFID tags into Excel, you may want to widen the cells to fit the full tag
ID, which may exceed 20 characters.
14
Page 15
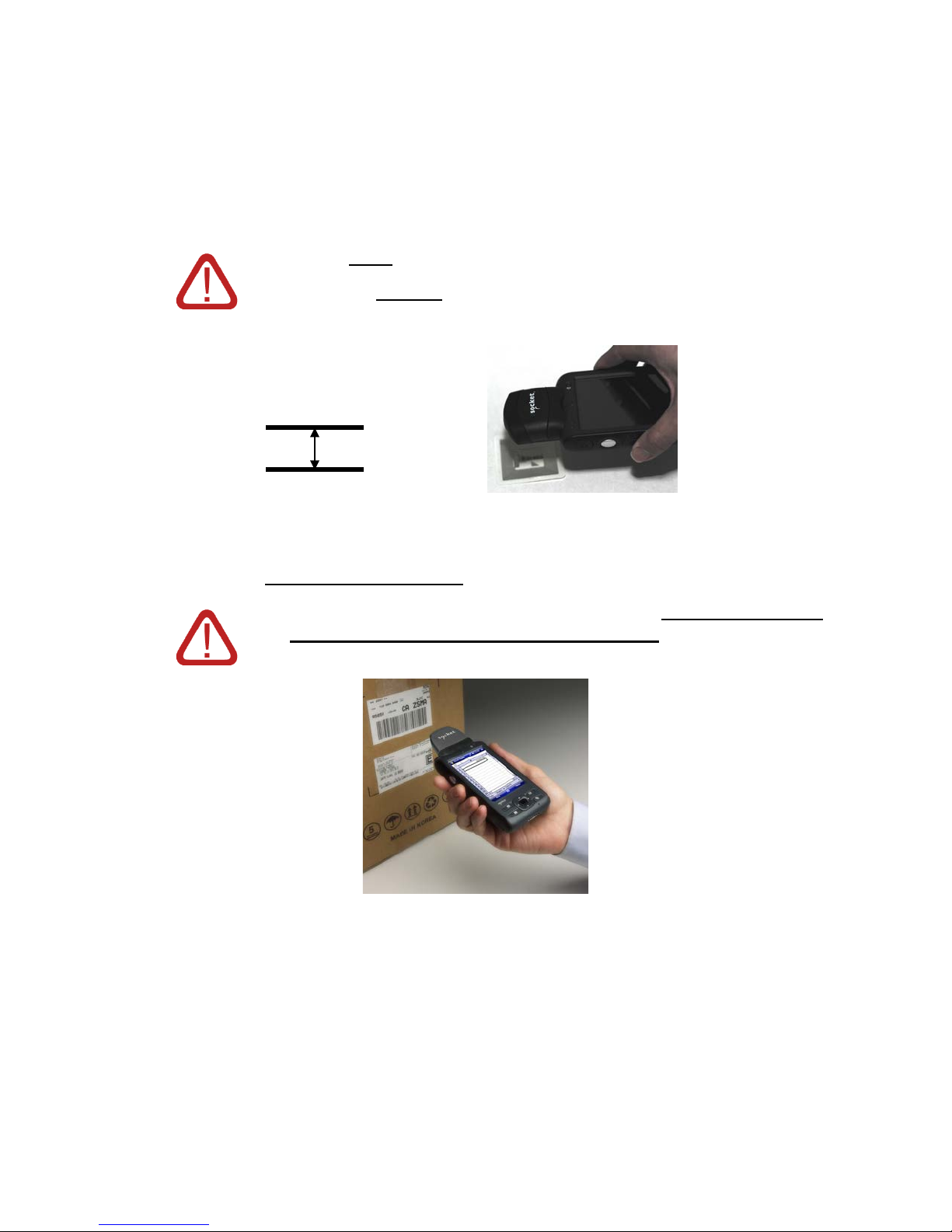
STEP 5: Read Data into Your Application
Parallel,
Please note that the correct positions for RFID reading and barcode scanning are
very different!
CORRECT RFID POSITION:
Hold the card parallel to and directly above the tag, at most 3.0
inches above the tag.
3.0 inches (7.6 cm)
maximum
Note: The LED will turn amber to indicate that the card is reading tag IDs.
CORRECT BARCODE SCANNING POSITION:
Hold the card so that the lens is angled about 45° to the barcode
and at least 2.0 inches away from the barcode. The red laser line
should cover the entire width of the barcode.
Note: The proper scanning distance and angle vary depending on the size, type, quality,
and print surface of the barcode.
CHAPTER 2: SETUP FOR THE SOMO 15
Page 16

DO NOT direct the RFID Reader-Scan Card at an angle
towards the tag.
WRONG RFID POSITION:
WRONG RFID POSITION:
DO NOT hold the RFID Reader-ScanCard perpendicular to the
tag.
16
Page 17

When data is read, a beep should sound indicating a good read, and data should appear
in your application.
For example, in an Excel Mobile spreadsheet, data should appear in the cell you
highlighted. The next cell should now be highlighted, ready for the next scan/read.
If the card fails to read data within a few seconds, you must try again.
Note: By default, the RFID reader will return the tag ID. The RFID Setup utility can be
used so that the RFID Reader-Scan Card returns only the tag data, or the tag ID plus
the tag data. (See the next page for instructions.)
CHAPTER 2: SETUP FOR THE SOMO 17
Page 18

3 | Setup for Non-SoMo PDA
This chapter shows how to install, configure, and use the CF RFID Reader Card
Series 6 on a Windows Mobile pow ered devi ce.
Setup Summary
STEP 1: Uninstall other scanning software.
STEP 2: Install the software.
STEP 3: Assign a trigger button.
STEP 4: Start SocketScan Plug-in.
STEP 5: Insert the card.
STEP 6: Read tag IDs into a Windows program.
18
Page 19

STEP 1: Uninstall O t he r Scanning Software
Uninstall any barcode scanning software already in your computer, including
previous versions of SocketScan Plug-in ™ software.
1. Make sure the software is not running.
2. Tap Start | Settings | System tab | Remove Programs.
3. Use the utility to delete the software.
STEP 2: Install the Software
ADVANCED USERS: Refer to the README file for CAB file installation
instructions.
Follow these instructions to install SocketScan Plug-in. Afterwards, you can use
the same process to install RFID Demo and/or Floating Trigger.
1. Use a serial/USB cable or cradle and the appropriate Microsoft
synchronization software to make an active connection between your device
and a host PC.
2. Insert the installation CD into your host PC.
3. Use My Computer or Windows Explorer to access your CD-ROM drive. In
the CD, click on SETUP.EXE.
4. The SocketScan Setup Center will appear in your web browser. Read the first
page and click Installation in the left margin.
5. In the SocketScan Installation page, in the Windows CE section, click Install
In the first paragraph.
CHAPTER 3: SETUP FOR NON-SOMO PDAS 19
Page 20
6. Your web browser will present a series of dialogs.
Internet Explorer:
• In the File Download –Security Warning dialog, click Run.
• In the second warning dialog, click Run.
• Internet Explorer will download the file.
Firefox:
• In the file opening dialog, click Save File.
• Firefox will download the file.
• In the Downloads list, next to SocketScanCE.exe, click Open.
• In the warning dialog, click OK to continue.
7. The InstallShield Wizard for SocketScan Plug-in Software will automatically
launch. Follow the wizard to install the software.
8. If your device warns that the software comes from an unknown publisher, tap
Yes to continue installation.
9. When software installation is complete, remove the device from the cradle.
Soft reset the device by pressing the reset button.
Note: After software installation, several new icons will appear in the Programs
screen.
20
Page 21

STEP 3: Assign Trigger Button(s)
If SocketScan Plug-in is not open, SocketScan Plug-in will
menus.
You must set up a mechanism for triggering the CF RFID Reader Card. Hardware
button(s) are the best triggering method from a handheld device.
If you have the CF RFID Reader-Scan Card 6P, SocketScan Plug-in allows you to
configure up to four buttons for launching SocketScan Plug-in and/or triggering the
RFID reader or barcode scanner.
Please refer to the chart below to determine which SocketScan Plug-in functions
you would like to assign to buttons on your device.
Program
What happens when you press a button assigned to
this program?
launch.
If SocketScan Plug-in is open and you have the CF RFID
Reader Card 6E, the RFID reader will activate.
If SocketScan Plug-in is open and you have the CF RFID
Reader-Scan Card 6P, either the RFID reader or the laser
scanner will activate, depending on which mode the card is in.
If you assign only one hardware button for use with the CF
RFID Reader Card, this is the program that should be
assigned.
If you do not assign a button to SocketScan Plug-in, you can
only start SocketScan Plug-in by manually tapping through
If you are using the CF RFID Reader-Scan Card 6P, this
program will switch the device from RFID mode to barcode
scanning mode, or vice versa. This is designed to be used with
a trigger button assigned to SocketSca Plug-in n. You can also
use Socket Trigger Select to toggle to other Socket Mobile
barcode scanners that use a software trigger.
The laser barcode scanner will activate. SocketScan Plug-in
must be running.
The RFID reader will activate. SocketScan Plug-in must be
running.
Note: If you do not want to assign a hardware button, you can install and use
SocketScan Trigger software from the installation CD, which enables you to tap
on a software icon to trigger SocketScan Plug-in and the RFID reader/barcode
scanner.
CHAPTER 3: SETUP FOR NON-SOMO PDAS 21
Page 22

Refer to your device manual for specific instructions.
1. Tap Start | Settings | Personal | Buttons.
2. In the Button list, select a button. In the drop-down menu, select the program.
If desired, repeat to assign additional trigger buttons. When done, tap ok.
Note: For best ergonomics, choose a button located beneath your thumb or
forefinger when you hold the device.
22
Page 23

STEP 4: Start SocketScan Plug-in
Icon
Meaning.
1. If you assigned a hardware button to SocketScan Plug-in, you
can press the button to quickly launch the program. Otherwise,
tap Start | Programs | SocketScan Plug-in folder |
SocketScan Plug-in.
2. An icon
will appear in the task tray of the Today screen indicating that the
system does not detect the RFID reader.
When SocketScan Plug-in is running, any of the following icons will appear in
the task tray of the Today screen:
Card detected, RFID mode. SocketScan Plug-in detects
the reader-scan card and is ready to read RFID tags.
Card detected, scanning mode. SocketScan Plug-in
detects the reader-scan card and is ready to read
barcodes.
No RFID Reader Card detected. The reader card is either
missing or improperly inserted.
STEP 5: Insert the Card
Insert the card into the CompactFlash slot of your device. Make sure the card is
right-side up, with the blue label on top. Push the card all the way into the slot.
STEP 6: Verify Card Mode
If you are using the dual-function CF RFID Reader-Scan Card 6P, and you did not
assign buttons to Trigger ISC or Trigger RFID, make sure the card is in the
correct mode you wish to use. The SocketScan Plug-in icon at the bottom of the
Today screen indicates your current mode.
To switch modes, do either of the following:
• If you assigned a button to Trigger Select, press the button.
• Tap on the SocketScan Plug-in icon. In the pop-up menu, tap to select the
card mode you want.
CHAPTER 3: SETUP FOR NON-SOMO PDAS 23
Page 24

STEP 7: Open Application
Start the application that you want to receive the data (e.g., Excel, Notepad, etc.).
Make sure a document or spreadsheet is open. Place the cursor where you want
to enter data.
Note: If reading RFID tags into Excel Mobile, you may want to widen the cells to
fit the full tag ID, which may exceed 20 characters.
24
Page 25

STEP 8: Read Data
Parallel,
Please note that the correct positions for RFID reading and barcode
scanning are very different!
CORRECT RFID POSITION:
Hold the card parallel to and directly above the tag, at most
3.0 inches above the tag.
3.0 inches (7.6 cm)
maximum
Note: The LED will turn amber to indicate that the card is reading tag IDs.
CORRECT BARCODE SCANNING POSITION:
Hold the card so that the lens is angled about 45° to the
barcode and at least 2.0 inches away from the barcode. The
red laser line should cover the entire width of the barcode.
Note: The proper scanning distance and angle vary depending on the size, type,
quality, and print surface of the barcode.
CHAPTER 3: SETUP FOR NON-SOMO PDAS 25
Page 26

DO NOT direct the RFID Reader-Scan Card at an angle
towards the tag.
WRONG RFID POSITION:
WRONG RFID POSITION:
DO NOT hold the RFID Reader-ScanCard perpe ndi cular
to the tag.
26
Page 27

When data is read, a beep should sound indicating a good read, and data should
appear in your application.
For example, in an Excel Mobile spreadsheet, data should appear in the cell you
highlighted. The next cell should now be highlighted, ready for the next scan/read.
If the card fails to read data within a few seconds, you must try again.
Note: By default, the RFID reader will return the tag ID. The RFID Setup utility
can be used so that the RFID Reader-Scan Card returns only the tag data, or
the tag ID plus the tag data. (See the next page for instructions.)
CHAPTER 3: SETUP FOR NON-SOMO PDAS 27
Page 28

4 | SocketScan Plug-in Software
This chapter shows how to install, configure, and use the CF
RFID Reader Card Series 6 on a Windows Mobile powered
device.
Application Features
RFID settings
Symbology selector
SocketScan Trigger.
Version information.
28
Page 29

RFID Settings
Note: Only printable
Note: These settings are only used with the SocketScan Plug-in keyboard wedge
programs and Scan Demo.
1. Tap on the SocketScan Plug-in icon. In the pop-up menu, tap Settings.
2. In the Prefix/Suffix screen, enter the characters you would like added to each
read/scan of data (128 character maximum).
ASCII characters
can be used as
prefixes or suffixes.
Note:
• The default suffix is a carriage return.
• If in the RFID Setup utility you selected Tag ID & Read Data, the prefix/suffix is
added to both the tag ID and the read data fields.
3. Tap on the Sound tab.
CHAPTER 4: SOCKETSCAN PLUG-IN SOFTWARE 29
Page 30

4. In the Sound screen, select which sound you would like SocketScan Plug-in to
make to indicate a good read.
To you want to play a .WAV file, after selecting Play .wav file, you can search
through files by tapping the browse box. In the Open screen, tap on the file
you want:
Note: You can only select a WAV file from the My Documents folder. If
needed, copy the file you need to this folder.
5. After selecting your sound, tap on the RFID tab.
6. In the RFID screen, enter the following settings:
Trigger mode:
• Tag ID Only: Select to read only the tag ID.
• Read Data Only: Select to read only data from the tag memory.
• Tag ID & Read Data: Select to read both the tag ID and tag memory.
30
Page 31

Starting block: If you selected a Read Data option, enter the number of the
first block you want to begin reading.
Number of blocks: If you selected a Read Data option, enter the number of
blocks you want to read.
Read error string: Enter the string you want your application to display in case
the RFID reader cannot read the tag data.
Tag type: Select the type of RFID tag you want to read. The Auto Detect
setting enables all tag types to be read.
Note: Choosing a specific tag may result in a longer read range and faster read.
Inventory mode: Select for the RFID reader to read all tags present in an
RFID field, if supported by the tag type.
Display tag ID pr efix: Select to display the RFID tag ID prefix with each tag
ID. The prefix indicates the tag type.
Displayable characters only: Select for the RFID reader to read only
displayable characters while reading data from the tag memory. Otherwise,
the RFID reader will also read “filler” symbols used in memory blocks that
aren’t completely filled with data. This option is only available if you selected a
Read Data trigger mode.
7. After selecting all of your Prefix/Suffix, Sound and RFID settings, tap ok.
CHAPTER 4: SOCKETSCAN PLUG-IN SOFTWARE 31
Page 32

Symbology Selector
If you have the dual-function CF RFID Reader-Scan Card 6P, SocketScan Plug-in
provides an applet that makes it easy to modify which barcode symbologies the
scanner will recognize and attempt to decode. By default, the scanner is set to
recognize several of the most common symbologies.
1. Tap on the SocketScan Plug-in icon at the bottom of the Today screen.
2. In the pop-up menu, tap Symbology Selector. If SocketScan Plug-in is
currently configured for more than one scanner, then tap In-Hand
Scanner in the submenu that appears.
3. In the screen that appears, use the checkboxes to enable/disable
symbologies. Tap ok.
Note: Enabling all possible symbologies will make the decode process slightly
longer.
Note: If you want to read UPC-A barcodes disable GS1 DataBar (RSS) so that
UPC-A barcodes aren’t mistakenly read as GS1 DataBar.
Note: The RSS symbology is now known as GS1 DataBar.
32
Page 33

SocketScan Trigger
If you find it inconvenient or impossible to assign or use a hardware button to
trigger the reader, you can install this virtual trigger button that “floats” on top of
the active application.
1. Make sure to do all of the following before using SocketScan Trigger:
• Install SocketScan Trigger from the installation CD. The software must be
installed separately from SocketScan Plug-in.
• Start SocketScan. Tap Start | Programs | SocketScan Plug-in.
• Insert the CF RFID Reader Card into your device.
• Open the application that you want to receive data.
2. Start SocketScan Trigger. Tap Start | Programs | SocketScan Trigger.
3. The floating trigger button will appear on your screen on top of the active
application.
Drag from the title bar to move the trigger button to a convenient place on the
screen.
Tap the trigger button to activate the RFID reader/barcode scanner.
CHAPTER 4: SOCKETSCAN PLUG-IN SOFTWARE 33
Page 34

4. A SocketScan Trigger icon will also appear in the menu bar of the Today
screen. Tap on this icon to reveal a pop-up menu with the following options:
• Tap Scan Now to activate the scanner as if you had tapped the trigger
button.
• Tap Remove Floating Trigger to remove the trigger button from the
screen but keep the icon handy on the task bar. To restore the trigger
button, tap on the menu bar icon. In the pop-up menu, tap Launch
Floating Trigger.
• Tap About to view SocketScan Trigger version information.
• Tap Close SocketScan Trigger to close the application completely. From
this state, the SocketScan trigger can only be launched from the Programs
page.
34
Page 35

DUAL DEVICE SUPPORT
SocketScan v7.2.4.0 and later supports the simultaneous use of two Socket data
collection devices with the same computer. This enables you to use the CF RFID
Reader Card with a Socket Bluetooth barcode scanner on the same computer.
Note: SocketScan Plug-in can capture data from only one cordless scanner at a
time.
Simply connect or plug in each device you plan to use as you normally would.
The functionality of each device is the same, and no extra configuration is
required.
You can configure each device separately. In the SocketScan Plug-in menu, tap
on the appropriate device to configure its settings.
CHAPTER 4: SOCKETSCAN PLUG-IN SOFTWARE 35
Page 36

5 | RFID Demo
This chapter explains how to use the Socket Mobile RFID Demo
application with the CF RFID Reader Card to perform the
following:
• Read an RFID Tag.
• Enable Loop Mode.
• Select Tag Type.
• Advanced – Write to Tag.
Before you begin using the Socket Mobile RFID Demo application, make sure you
have done the following:
• Installed the RFID Demo application onto your device, following the same
software installation procedure described in Chapter 2.
• Inserted the CF RFID Reader Card into your device.
• When you use this application, you should only trigger the RFID Reader Card
by tapping on the Select Tags or Read Tag button on the RFID Demo screen.
36
Page 37

Read an RFID Tag
Parallel,
1. Start RFID Demo. Tap Start | Programs | RFID Demo.
2. The main screen of RFID Demo will appear with blank fields.
3. Hold the device in the correct position to read an RFID tag, as described in
Chapter 2. Hold the device so the CF RFID Reader Card is parallel to and
directly above the tag, at most 2.0 inches above the tag.
3.0 inches (7.6 cm)
maximum
4. Tap Select Tags.
CHAPTER 5: RFID DEMO 37
Page 38

5. Tag ID(s) should appear in the Available Tags field. Additionally, the bottom of
the screen will report the number of RFID tags found in range.
6. In the Available Tags field, tap to highlight the RFID tag you wish to read, then
tap Read Tag.
7. After the CF RFID Reader Card reads the tag, Tag Data will appear. If desired,
check Display as hex data to view the data in hexadecimal format.
38
Page 39

Enable Inventory and Loop Modes
Tag Select
Mode
Loop
Mode
Inventory
Mode
The CF RFID Reader Card has four reading modes, based on different
combinations of inventory mode and loop mode. The chart below shows the results
of enabling or disabling the modes.
Description
One tag Disabled Disabled Selects the first tag in RF fi eld
One tag
continuously
All tags
present
All tags
continuously
Enabled Disabled
Disabled Enabled
Enabled Enabled
Selects the first tag conti nuously (the same tag ID w ill
be returned as long as the tag remains in the RF field.
Inventory mode: returns the tag IDs of all tags in the
RF field and then report s when there are no more
tags.
Returns the tag IDs of all tags in t he R F field. It does
not repeat a tag ID unless the tag goes out and then
re-enters the RF field.
Note: Not all tag types are readable in Inventory Mode.
1. In the main screen of RFID Demo, tap RFID at the bottom of the screen. In the
pop-up menu, select adjust the Inventory Mode and/or Loop Mode settings as
desired.
2. After selecting the desired settings, tap Select Tags. The CF RFID Reader
Card will search for tags in range, according to your settings.
CHAPTER 5: RFID DEMO 39
Page 40

Select Tag Type
1. In the main screen of Socket Mobile RFID Demo, tap RFID at the bottom of
the screen. In the pop-up menu, tap Select Tag Type.
2. In the Select Tag Type dialog box, use the drop-down menu to select the tag
type. Tap ok.
Note:
• Tag selection response time is longer with Auto Detect than for specific tag
types. If Auto Detect is not selected, only the type of tags selected can be
read or written to.
• Auto Detect will search for tag types 01 to 04. Pico Tag (06) must be
selected in order to read tag ID.
40
Page 41

ADVANCED: Write to Tag
1. In the main screen of Socket Mobile RFID Demo, tap RFID at the bottom of
the screen. In the pop-up menu, tap Advanced.
2. Use the next screen to read and write data in specific blocks of an RFID tag.
Enter the number of the starting block and number of blocks you would like to
read.
3. Hold the Pocket PC in the correct position to read RFID tags — parallel to the
tag and directly above it, at most 2.0 inches above. Tap Read Tag.
CHAPTER 5: RFID DEMO 41
Page 42

4. RFID Demo will report any data saved to the RFID tag, as well as the type of
tag and number of bytes per block. The bottom of the screen will report the
read status and tag ID.
5. To write data to the tag, enter text into the bottom field. The type and amount
of text that can be written varies depending on your tag type. After entering
text, hold the Pocket PC in the correct reading/writing position and tap Write
Tag.
Note:
• The number of characters in the Write Tag field must match the number of
bytes per block multiplied by the number of blocks, or an error will occur.
• See Appendix B to find out the type and amount of text that can be written
to your tag.
• The most common cause of write failures is either an incorrect “start block”
or number of blocks.
42
Page 43

6. After writing data to the tag, the bottom of the screen will report the write
status.
7. To verify that the data was written successfully to the tag, hold the device in
the correct reading/writing position, and tap Read Tag.
8. To close the advanced screen, tap ok.
CHAPTER 5: RFID DEMO 43
Page 44

Appendix A
Product Specifications
Physical Characteristics
CompactFlash Card Size: 1.4 x 1.68 x 0.20 inches (36 x 42.7 x 5.0 mm)
Reader/Scanner Head Size: 1.8 x 1.9 x 0.83 inches (45 x 49 x 21 mm)
Weight:
6E: 1.1 oz. (31 g)
6P: 1.3 oz (37 g)
Environmental:
Operating Temperature: -10 to +50°C (-4 to +122°F)
Storage Temperature: -40 to +70°C (-40 to +158°F)
Humidity: 5-95% RH non-condensing
Ambient Light for Barcode Scanning (6P only):
Sunlight: 10,000 ft candles (107,640 lux) Artificial light: 450 ft candles (4,844 lux)
Electrical Specifications:
Power Consumption (3.3 V):
6E: Standby: 11mA (36 mW),
Reading/Writing RFID: 52 mA (171 mW)
6P: Standby: 11 mA (36 mW) typical
Scanning barcodes: 72 mA (238 mW) typical
Reading/Writing RFID: 52 mA (171 mW)
Also operates at 5 V
Laser Power (6P): 1.7 mW (±0.2 mW)
Compatibility: Windows COM port
Operating System Support:
Windows Mobile 6 Classic/Professional
Windows Mobile 2003, 2003SE, 5.0 for Pocket PC
Certification: FCC: Part 15, Class B, CE: EN55024:1998, C-TICK: s.182
RFID Characteristics:
Frequency: 13.56 MHz (HF)
Maximum Read Range: ~ 3.0 inches for ISO15693 tags, depending on tag antenna size
44
Page 45

HF RFID Tags Supported
ISO15693: ICode SL2, LRI512, my-d, Tag-It HF-I
Proprietary: ICode SL1, PicoTag (no anti-collision), Tag-It HF
ISO14443A: Mifare (Tag ID only), Mifare Ultralight (no anti-collision)
Barcode Scanner Characteristics (6P only):
Symbology Support: Chinese 2 of 5, Codabar, Code 11, Code 128, Code 39, Code 93,
Discrete 2 of 5, GS1-128, GS1 DataBar (formerly RSS), Interleaved 2 of 5, MSI,
UPC/EAN
Scan Repetition Rate: 100 scans/sec (bidirectional)
Optical Resolution: 0.004 in. minimum/barcode element width (X Dimension)
Print Contrast: Minimum 25% absolute dark/light reflectance (MRD) measured at 650 MRD
Scan Angle: Wide (default): 47° ±3°, Narrow: 35° ±3°
Decode Zone: 1.5 to 45+ inches (3.8 to 144+ cm)
APPENDIX A: PRODUCT SPECIFICATIONS 45
Page 46

Appendix B
32 bits
(4 bytes per block)
0 (0x00)
1 (0x01)
2 (0x02)
.
.
.
.
.
62 (0x3E)
63 (0x3F)
TID
0xE0
0x07
Unique Tag ID - 48 bits (6 bytes)
HF RFID Standards and Tag Descriptions
ISO15693
The ISO/IEC 15693 standard was developed for “Contactless Vicinity Cards”. Adopted in
1998, ISO15693 has significantly enabled global acceptance of 13.56MHz RFID
technology. Based on contributions by Texas Instruments and Philips, ISO/IEC 15693 is
largely a superset of the features and specifications of the Tag-it HF and I·Code1
products, respectively.
• ISO15693-1: Defines the physical characteristics of a credit card transponder.
• ISO15693-2: Specifies the 13.56MHz air interface and modulation methods that
accommodate regulatory bodies worldwide.
• ISO15693-3: Specifies the command protocol and anti-collision method for data
exchange between tags and readers.
The ISO15693 “standard” permits tags to be manufactured that support optional and
custom commands, and that have custom memory structures, sizes and architectures.
The SkyeRead family of RFID readers fully supports all four (4) IC manufacturers that
offer ISO/IEC 15693 compatible tags.
Tag-It HF-I ISO15693 (Texas Instruments)
The complete Tag-It HF-I specification can be found in the Texas Instruments publication
titled “Tag-It HF-I Transponder Inlays Reference Guide”.
Figure 1 - Memory Structur e of the Tag-It HF-I
2K bits (256 bytes) of user memory is available for read/write.
Block #
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
The user can permanently lock any
block.
.
Once a block is locked, it can not be
.
unlocked.
A 64-bit ID (factory programmed) uniquely identifies each Tag-It HF-I chip.
46
Page 47

32 bits
(4 bytes per block)
0 (0x00)
1 (0x01)
2 (0x02)
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
26 (0x1A)
27 (0x1B)
TID
0xE0
0x04
0x01
Unique Tag ID 40 bits (5 bytes)
64 bits
(8 bytes per block)
3 (0x03)
4 (0x04)
5 (0x05)
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
30 (0x1E)
31 (0x1F)
I·Code SLI ISO15693 (Philips)
The complete I·Code SLI specification can be found in the Philips publication titled
“I·Code SLI Smart Label IC SL2 ICS20 Functional Specification”.
Figure 1 - Memory Structur e of the I·Code SLI (version SL2 ICS20)
896 bits (112 bytes) of user memory is available for read/write.
Block #
.
.
.
.
The user can permanently
lock any block.
.
Once a block is locked it can
not be unlocked.
A 64-bit ID (factory programmed) uniquely identifies each I·Code SLI chip (SL2 ICS20).
my-d SRF55VxxP ISO15693 (Infineon)
The complete my-d SRF55VxxP specification can be obtained from Infineon.
Figure 2 - Memory Structur e of the my-d SRF55V02P
29 blocks of 8 bytes = 232 bytes (1856 bits) of user memory is available for read/write.
Block #
.
.
APPENDIX B: HF RFID STANDARDS AND TAG DESCRIPTIONS 47
The user can
permanently lock
any block
Once a block is
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
locked it can not
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
be unlocked.
.
Page 48

TID
0x60
0x05
0x02
Unique Tag ID - 40 bits (5 bytes)
64 bits
(8 bytes per block)
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
TID
0x60
0x05
0x00
Unique Tag ID - 40 bits (5 bytes)
A 64-bit ID (factory programmed) uniquely identifies each my-d SRF55V02P chip.
Figure 4 - Memory Structur e of the my-d SRF55V10P
125 blocks of 8 bytes = 1000 bytes (8000 bits) of user memory is available for read/write.
Block #
3 (0x03)
4 (0x04)
5 (0x05)
.
.
126 (0x7E)
127 (0x7F)
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
The user can
permanently lock
any block
Once a block is
.
locked it can not
be unlocked.
.
A 64-bit ID (factory programmed) uniquely identifies each my-d SRF55V10P chip.
48
Page 49

32 bits
(4 bytes per block)
3 (0x03)
4 (0x04)
5 (0x05)
.
.
.
.
.
14 (0x0E)
15 (0x0F)
TID
0xE0
0x02
Unique Tag ID 48 bits (6 bytes)
LRI512 ISO15693 (ST Microelectronics)
The full LRI512 specification was included in “LRI512 Memory TAG IC 512 bit High
Endurance EEPROM 13.56MHz, ISO 15693 Standard Compliant with E.A.S.” by ST
Microelectronics.
Figure 5 - Memory Structur e of the STM LRI512
512 bits (64 bytes) of user memory is available for read/write.
Block #
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
The user can permanently lock any
block.
.
.
Once a block is locked it can not be
unlocked.
A 64-bit ID (factory programmed) uniquely identifies each STM LRI512 chip.
APPENDIX B: HF RFID STANDARDS AND TAG DESCRIPTIONS 49
Page 50

Tag-it HF
32 bits
(4 bytes per block)
0 (0x00)
1 (0x01)
2 (0x02)
.
.
.
.
.
6 (0x06)
7 (0x07)
TID
Unique Tag ID 32 bits (4 bytes)
The first 13.56MH z RFID IC that Texas Instrum ents developed was the Tag-it HF. Still in
high volume production, Tag-it HF is widely used in applications globally and has an
existing installed base of millions of tags . The Tag-it HF uses a protocol air interfac e that
is proprietary to Texas Instruments.
By contrast, the Tag-it HF-I was released by Texas Instruments in 2001 is compatible with
ISO/IEC 15693 parts -2 and -3. The host application developer s hould be aware of the
distinction between the Tag-it HF and the Tag-it HF-I.
Figure 7 - Memory Structur e of the Tag-it HF
256 bits (32 bytes) of user memory is available for read/write.
Block #
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
The user can permanently lock any
block.
.
.
Once a block is locked it can not be
unlocked.
A 32-bit ID (factory programmed) uniquely identifies each Tag-it HF chip.
The complete Tag-it HF specification can be obtained from Texas Instruments.
50
Page 51

32 bits
(4 bytes per block)
3 (0x03)
4 (0x04)
5 (0x05)
.
.
.
.
.
14 (0x0E)
15 (0x0F)
TID
Unique Tag ID 64 bits (8 bytes)
I·Code1
The first long range 13.56MHz RFID IC that Philips released was the I·Code1 ( SL1). Still
in high volume production, I·Code1 (SL1) is still widely used in applications globally and
has an existing installed base of millions of tags. The I· Code1 (SL1) uses a pr otocol and
air interface that is proprietary to Philips.
By contrast, the I·Code SLI (SL2), released by Philips in 2002, is fully compatible with
ISO/IEC 15693 parts -2 and -3. The host application developer should be explicitly aware
of the distinction between the I·Code1 (SL1) and the I·Code SLI (SL2).
Figure 8 - Memory Structur e of the I·Code1 (version SL1 ICS 30 01)
512 bits (64 bytes) of user memory is available for read/write.
Block #
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
The user can permanently lock
any block.
.
.
Once a block is locked it cannot
be unlocked.
A 64-bit ID (factory programmed) uniquely identifies each I·Code1 chip.
APPENDIX B: HF RFID STANDARDS AND TAG DESCRIPTIONS 51
Page 52

PicoTag
64 bits
(8 bytes per block)
3 (0x03)
4 (0x04)
5 (0x05)
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
30 (0x1E)
31 (0x1F)
TID
Unique Tag ID 64 bits (8 bytes)
Inside Contactless (formerly Inside Technologies) makes a contactless RFID product
series called the PicoTag. There ar e two different sizes of PicoTag memories, 2K and
16K. There are two different modes of operation, plain and secure.
Figure 9 - Memory Structur e of the PicoTag 2K
29 blocks of 8 bytes = 232 bytes (1856 bits) of user memory is available for read/write.
Block #
The user can
permanently lock
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
any block
Once a block is
.
locked it can not
be unlocked.
.
A 64-bit ID (factory programmed) uniquely identifies each PicoTag chip.
Note: Only the tag ID can be read by the CF RFID Reader-Scan Card.
52
Page 53

BYTE
15
14
13
12
11
10
09
08
07
06
05
04
03
02
01
00
Check
Byte
1
Data
2
Data
3
Key A
Lock Bits
Key B
4
Data
5
Data
6
Data
7
Key A
Lock Bits
Key B
.
.
.
.
.
.
60
Data
61
Data
62
Data
63
Key A
Lock Bits
Key B
ISO14443
ISO/IEC 14443 is a 4-part RFID standard for short-range “Contactless Proximity Cards”.
Adopted in 1999 and 2000, ISO14443 has become the worldwide standard for cashless
payment and contactless stored value applications.
• ISO14443-1 defines the physical characteristics of an RFID card.
• ISO14443-2 specifies two types (A and B) of 13.56MHz air interface and modulation
methods used for communication between tags and readers.
• ISO14443-3 specifies the anti-collision method for selecting one tag among many.
• ISO14443-4 defines the high-level protocol and method for data exchange between
tags and readers.
14443-A Mifare Standard 4K (Philips)
The Mif are chip from Philips is used in millions of secure contact less applications since it
was introduced in 1995.
Figure 10 - Memory Structure of the Mifare Standard 4K (MF1 IC S70)
BLOCK SECTOR
0
0
1
.
The complete Mifare specification can be obtained from the Philips publication “Mifare
Standard 4 kByte Card IC MF1 IC S70” dated October 2002.
Note: Only the tag serial number can be read by the CF RFID Reader Card.
.
15
Serial Number
Manufacturer Data
.
APPENDIX B: HF RFID STANDARDS AND TAG DESCRIPTIONS 53
Page 54

Mifare Ultralight (Philips)
System Area
User Area
The complete Mifare Ultr alight specification can be obtained from the Philips publication
“Mifare Ultralight Contactless Single-trip Ticket IC MF0 IC U1 Functional Specification”
dated March 2003.
Figure 11 - Memory Structure of the Mifare Ultralight (MF0 IC U1)
Byte
Block
00 01 02 03
0 SN0 SN1 SN2 BCC0
1 SN3 SN4 SN5 SN6
2 BCC1 Internal Lock 0 Lock 1
3 OTP 0 OTP 1 OTP 2 OTP 3
4 Data 0 Data 1 Data 2 Data 3
.
.
.
.
.
.
15 Data 44 Data 45 Data 46 Data 47
Note: Only the tag serial number can be read by the CF RFID Reader Card.
54
Page 55

LTO CM 14443-A (LTO) The LTO-CM is compliant with ISO14443-A air interface.
Figure 12 - Memory Structure of the LTO CM
128 blocks of 32 bytes = 4096 bytes (32768 bits) of user memory is available for read/write.
Note: Only the tag serial number can be read by the CF RFID Reader-Scan Card.
APPENDIX B: HF RFID STANDARDS AND TAG DESCRIPTIONS 55
Page 56

Appendix C
Barcode Label Specifications
All barcode symbols/labels should satisfy the appropriate AIM Uniform Symbology
Specification.
Background Substrate:
The barcode symbol should be printed on material (media) that is reflective and has a
matte (not glossy) finish. A background diffuse reflectance of at least 70% to 80% is
desirable for optimum contrast. Retro-reflective media should be used to obtain decode
distances greater than 36 inches.
Ink Color and Type:
The inked bars should not exceed 25% reflectance at the wavelength that is being used
for reading, whether printed with black ink or colored ink. The reflectance value should
not vary more than 5% within the same character.
Voids and Specks:
The code should be printed clearly, free of voids, specks, blemishes and lines that could
“fool” the scanner. Specks or blemishes in the white spaces, or false or missing bar
sections could be interpreted by the reading equipment as part of the code. Generally,
the width of such flaws is more serious than the height. Code symbols/ labels should be
rejected if these defects are present.
Definition:
The bars in the barcode symbol should be well defined. Their edges should not be rough
or fuzzy, so that the bars and spaces have the proper widths intended for the barcode
symbology used.
Contrast:
Background reflectance (that of the substrate on which the codes are printed) should
always provide a good contrast relative to the ink reflectance (that of the code bars). The
difference between the two should be at least 37.5% at the wavelength used for reading.
Tolerance:
The ratio of the widths of bars and spaces in a barcode symbol must conform to the
appropriate AIM barcode specifications and can cause problems if not correct throughout
the barcode. Problems can occur when bar edges are smeared or rough, or when they
exhibit voids.
56 | APPENDIX C: BARCODE LABEL SPECIFICATIONS
Page 57

Appendix D
Enabling or Disabling Symbologies
All Socket Mobile barcode scanning products are preset to automatically detect and
decode (autodiscriminate) the most common barcode symbologies. Refer to the table on
the next page to determine which symbologies and parameters are enabled by default. If
you would like to change your symbology settings, you can use either of two methods,
depending on which device you are using and which settings you want to change.
Note: If more symbologies are enabled, the scanner must work harder to search through
all possible combinations. This may make the decoding process slightly longer.
OPTION 1: Symbology Selector
If you are using a Windows Mobile-based device, you can quickly enable and disable any
of the seventeen most popular symbologies by using the SocketScan Symbology Selector.
Refer to Chapter 2 for instructions.
Note: The length of some symbologies will change after Symbology Selector is used. Refer
to the table on the next page.
OPTION 2: Scan Programming Barcodes
If you want to modify an option not included in Symbology Selector, you can scan
programming barcodes to configure your CF RFID Reader-Scan Card. There are a variety
of programming barcodes available that let you enable/disable symbologies as well as
configure special features (e.g., specify barcode lengths, transmit check digits, recognize
supplementals, etc.).
To obtain the programming barcodes, download the Programming Guide online from
http://www.socketmobile.com/support/downloads
WARNING!
When scanning programming barcodes with the CF RFID Reader-Scan
Card 6P, do not scan any barcodes that set communication protocols,
or the card will be disabled and must be returned to Socket Mobile for
reprogramming.
APPENDIX D: ENABLING/DISABLING SYMBOLOGIES | 57
Page 58

Table 1. Default Symbologies and Settings of the CF RFID Reader-Scan Card
UPC-A
Enabled
N/A
N/A
UPC-E
Enabled
N/A
N/A
UPC-E1
Disabled
N/A
N/A
EAN-8
Enabled
N/A
N/A
EAN-13
Enabled
N/A
N/A
• Supplementals
Disabled
N/A
N/A
• Transmit Check Digit
Enabled
N/A
N/A
Bookland EAN
Disabled
N/A
N/A
Code 128 - All
Enabled
Any
Any
Code 39
Enabled
2 to 55
2 to 55
Trioptic Code 39
Disabled
2 to 55
2 to 55
Code 39 Full ASCII
Disabled
2 to 55
2 to 55
• Transmit Check Digit
Disabled
N/A
N/A
Code 93
Disabled
4 to 55
2 to 55
Interleaved 2 of 5*
Enabled
14 Only
2 to 55
• Transmit Check Digit
Disabled
N/A
N/A
Discrete 2 of 5*
Disabled
12 Only
2 to 55
Codabar
Disabled
5 to 55
2 to 55
MSI Plessey*
Disabled
6 to 55
2 to 55
• Transmit Check Digit
Disabled
N/A
N/A
Length with
Symbology Default Length
Symbology
Selector
*WARNING: Setting the length to “Any” may lead to inaccurate decodes in these symbologies
58 | APPENDIX D: ENABLING OR DISABLING SYMBOLOGIES
Page 59

Appendix E
Laser Decode Zone
The decode zone for the Class 2 laser in the CF RFID Reader-Scan Card 6P is shown
below. The minimum element width (“X Dimension” or barcode “size”) is the width in
thousandths of an inch (mils) of the narrowest element (bar or space) in the symbol. The
figures shown are the typical scanning distances (depths of field) for selected barcode
sizes. The maximum usable length of a barcode symbol (Width of Field) at any given
range is also shown below.
Class 2 Laser Decode Zone
APPENDIX E: LASER DECODE ZONE | 59
Page 60

Appendix F
Your device does not recognize
the
Make sure the card is inserted properly. Push
it in all the way.
reinsert.
POSSIBLE REASON
SOLUTION
You are holding the RFID
Reader Card in the wrong
position.
Hold the device so the RFID Reader Card is
parallel to and directly above the RFID tag, at
most 2.5 inches above the tag.
The RFID tag antenna is broken
or incorrectly formatted.
Try reading another RFID tag that is correctly
formatted.
The tag type may be disabled.
Use RFID Demo to determine the tag type. If
needed, reconfigure the
the correct tag type.
POSSIBLE REASON
SOLUTION
You programmed the trigger
button incorrectly.
Test the button by assigning a different
program to it and make sure it works properly.
Troubleshooting
For help on SocketScan Plug-in on a Windows Mobile-based device, tap Start | Help.
SYMPTOM:
I get the “No Card Detected” icon in the task tray and can’t trigger the
RFID reader or scan any barcodes.
POSSIBLE REASON SOLUTION
card.
SYMPTOM:
If necessary, remove and
When I try to read an RFID tag, no data appears on my screen.
RFID Reader Card for
SYMPTOM:
When I press the trigger button, nothing happens.
60 | APPENDIX F: TROUBLESHOOTING
Page 61

Appendix G
Technical Support
If you have trouble installing or using the CF RFID Reader Card, Socket has different
support options to help you.
Online Knowledge Base: Search for articles, Frequently Asked Questions or Hot Topics
any time, day or night. http://support.socketmobile.com/faq
Online Requests: Register your product and submit a question to our Technical Support
Team. http://support.socketmobile.com/
By Phone: Contact our Tier 1 Technical Support by calling either:
• USA & Canada Toll-Free: 800-279-1390
• Direct: +1- 510-933-3020
Please refrain from disassembling the card. Disassembly of this device will void the
product warranty.
APPENDIX G: TECHNICAL SUPPORT | 61
Page 62

Limited Warra nt y
Socket Mobile, Inc. warrants this product against defects in material and workmanship, under normal use and
service, for one (1) year from the date of purchase.
EXCLUDES: Consumables such as batteries, removable cables, cases, straps, chargers, and CF-to-PC Card
adapters (90 day coverage only)
Incompatibility is not a defect covered by the Socket Mobile warranty. During the warranty period, Socket Mobile will,
at its option, repair or replace the defective product at no charge when furnished with proof of retail purchase,
provided that you deliver the product to Socket Mobile or to an authorized Socket Mobile Service Center.
The returned product must be accompanied by a return material authorization (RMA) number issued by Socket
Mobile or by an authorized Socket Mobile Service Center. If you ship the product, you must use the original container
or equivalent and you must pay the shipping charges to Socket. Socket Mobile will pay surface shipping charges
back to any location in the contiguous United States. This warranty applies only to the original retail purchaser and is
not transferable.
Socket Mobile may, at its option, replace or repair the product with new or reconditioned parts and the returned
product becomes the property of Socket Mobile. Socket Mobile warrants the repaired or replaced products to be free
from defects in material or workmanship for ninety (90) days after the return shipping date, or for the remainder of
the original warranty period, whichever is greater.
This warranty does not cover the replacement of products damaged by abuse, accident, misuse or misapplication,
nor as a result of service or modification other than by Socket Mobile.
SOCKET MOBILE IS NOT RESPONSIBLE FOR INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES RESULTING
FROM BREACH OF ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY, INCLUDING DAMAGE TO PROPERTY AND, TO
THE EXTENT PERMITTED BY LAW, DAMAGES FOR PERSONAL INJURY. THIS WARRANTY IS IN LIEU OF ALL
OTHER WARRANTIES INCLUDING IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
Some states do not allow limitation of implied warranties, or the exclusion or limitation of incidental or consequential
damages, so that the above limitations or exclusions may not apply to you. This warranty gives you specific legal
rights and you may also have other rights which vary from state to state.
This product may contain fully tested, recycled parts, warranted as if new.
For warranty information, please visit: http://support.socketmobile.com/
62
Page 63

Limited Software Warranty
LIMITED WARRANTY. SOCKET MOBILE warrants that the original disk or CD ROM is free from defects for 90 days
from the date of delivery of the SOFTWARE.
CUSTOMER REMEDIES. The entire liability of SOCKET MOBILE and your exclusive remedy shall be, at the option
of SOCKET MOBILE, either (a) return of the price paid or (b) replacement of the SOFTWARE which does not meet
the SOCKET MOBILE Limited Warranty and which is returned to SOCKET MOBILE with a copy of your receipt. Any
replacement SOFTWARE will be warranted for the remainder of the original warranty period or 30 days, whichever is
longer. THESE REMEDIES ARE NOT AVAILABLE OUTSIDE OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA.
NO OTHER WARRANTIES. SOCKET MOBILE disclaims all other warranties, either express or implied, including but
not limited to implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose, with respect to the
SOFTWARE and the accompanying written materials. This limited warranty gives you specific legal rights. You may
have others which vary from state to state.
NO LIABILITY FOR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES. In no event shall SOCKET MOBILE or its suppliers be liable for
any damages whatsoever (including, without limitation, damages for loss of business profits, business interruption,
loss of business information, or other pecuniary loss) arising out of the use of or inability to use the SOFTWARE,
even if SOCKET MOBILE has been advised of the possibility of such damages. Because some states do not allow
the exclusion or limitation of liability for consequential or incidental damages, the above limitation may not apply to
you.
EXPORT LAW ASSURANCES. You may not use or otherwise export or re-export the SOFTWARE except as
authorized by United States law and laws of the jurisdiction in which the SOFTWARE was obtained. In particular, but
without limitation, none of the SOFTWARE may be used or otherwise exported or re-exported (a) into (or to a
national or resident of) a United States embargoed country or (b) to anyone on the U.S. Treasury Department’s list of
Specially Designated Nationals or the U.S. Department of Commerce’s Table of Denial Orders. By using the
SOFTWARE, you represent and warrant that you are not located in, under control of, or a national or resident of any
such country or on any such list.
GOVERNMENT END USERS. If the SOFTWARE is supplied to the U. S. Government, the SOFTWARE is classified
as “restricted computer software” as defined in clause 52.227-19 of the FAR. The U. S. Government ‘s rights to the
SOFTWARE are as provided in clause 52.227-19 of the FAR.
CONTROLLING LAW AND SEVERABILITY. This License shall be governed by the laws of the United States and the
State of California. If for any reason a court of competent jurisdiction finds any provision, or portion thereof, to be
unenforceable, the remainder of this License shall continue in full force and effect.
63
Page 64

Regulatory Compliance
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant
to Part 15 of the FCC rules. This equipment is also CE EN55024:1998 and C-TICK compliant. These
limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is
operated in a commercial environment.
This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
Operation of this equipment in a residential area may cause harmful interference in which case the user
will be required to correct the interference at his or her own expense.
If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be
determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user may try to correct the interference by doing any
of the following:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna of the radio or television.
• Increase the distance separating the equipment and the receiver.
• Connect the equipment to an outlet on a different branch circuit than that of the receiver.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
The user may find the following booklet helpful: How to Identify and Resolve Radio-TV Interference
Problems. This booklet is available from the U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C. 20402
LASER DEVICES: The Socket barcode scanning product (version 6P) described in this User’s Guide
contains a Symbol SE955 laser scan engine.
For the Class 2 versio n o f th is engine, the following applies:
• Complies with 21CFR1040.10 and 1040.11 except for deviations pursuant to Laser Notice No. 50,
dated July 26, 2001.”
Caution: Use of controls, adjustments or performance of p rocedures other than those speci fied
herein may result in hazardous laser light exposure.
• Class 2 laser scanners use a low power, visible light diode. As with any very bright light source, such
as the sun, the user should avoid staring directly into the light beam. Momentary exposure to a Class 2
laser is not known to be harmful. A label such as the one below should appear on the end product.
PRODUCT DISPOSAL: Your device should not be placed in municipal waste. Please check local
regulations for disposal of electronic products.
64
Example of Class 2 Laser Warning Label
Page 65

1/2010 Printed in U.S.A.
 Loading...
Loading...