Page 1

Wireless Broadband Router
User Guide
The information furnished by SMC Networks, Inc. (SMC) is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by SMC for its use, nor for any
infringements of patents or other rights of third parties which may result from its use.
No license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of
SMC. SMC reserves the right to change specifications at any time without notice.
Copyright © 2001 by
SMC Networks, Inc.
6 Hughes
Irvine, CA 92618
All rights reserved.
Page 2

Trademarks:
SMC is a registered trademark and Barricade is a registered trademark of SMC Networks,
Inc. Other products and company names are trademarks or registered trademarks of their
respective holders.
FCC Interference Statement:
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
device pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide
reasonable protection against radio interference in a commercial environment. This
equipment can generate, use and radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and
used in accordance with the instructions in this manual, may cause harmful interference to
radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause
interference, in which case the user, at his own expense, will be required to take whatever
measures are necessary to correct such interference.
CE Declaration of Conformity:
This equipment complies with the requirements relating to electromagnetic compatibility,
EN 55022/A1 Class B, and EN 50082-1. This meets the essential protection requirements
of the European Council Directive 89/336/EEC on the approximation of the laws of the
member states relative to electromagnetic compatibility.
-1-
Page 3

Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction...............................................................................4
1.1 Functions and Features...................................................................4
1.2 Packing List ....................................................................................5
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation................................................................6
2.1 Panel Layout...................................................................................6
2.2 Procedure for Hardware Installation..............................................8
Chapter 3 Network Settings and Software Installation ...........................10
3.1 Make Correct Network Settings of Your Computer .....................10
3.2 Install the Software Into Your Computers ....................................11
Chapter 4 Configuring Wireless Broadband Router ................................14
4.1 Startup and Login .........................................................................14
4.2 Status ............................................................................................16
4.3 Toolbox.........................................................................................17
4.4 Primary Setup ...............................................................................18
4.5 DHCP Server ................................................................................21
4.6 Virtual Server................................................................................23
4.7 Special AP ....................................................................................25
4.8 Access Control..............................................................................26
4.9 Misc. Items ...................................................................................28
4.10 Wireless Setting..........................................................................30
4.11 MAC Address Control................................................................32
Chapter 5 Print Server .............................................................................36
5.1 Configuring on Windows 95/98 Platforms ...................................36
5.2 Configuring on Windows NT Platforms.......................................38
5.3 Configuring on Windows 2000 Platforms....................................39
-2-
Page 4

5.4 Configuring on Unix-based Platforms..........................................40
Appendix A: TCP/IP Configuration for Windows 95/98 ...........................41
A.1 Install TCP/IP Protocol Into Your PC..........................................41
A.2 Set TCP/IP Protocol for Working With IP Sharer ........................42
-3-
Page 5

Chapter 1 Introduction
Congratulations on your purchase of this outstanding SMC Wireless Broadband Router.
This product is designed specifically for small office and home office needs. It provides a
complete SOHO solution for Internet access and is easy to configure and operate even for
non-technical users. Instructions for installing and configuring this product are included in
this manual. Before you install and use this product, please read the manual carefully so
you may take full advantage of its functions.
1.1 Functions and Features
l High speed for wireless LAN connection
11Mbps data rate by incorporating Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS).
l Roaming
Provides seamless roaming within the IEEE 802.11b WLAN infrastructure.
l IEEE 802.11b compatible
Allowing inter -operation among multiple vendors.
l Auto fallback
11Mbps, 5.5Mbps, 2Mbps, 1Mbps data rate with auto-fallback.
l Broadband modem and IP sharing
Connects multiple computers to a broadband (cable or DSL) modem or an
Ethernet router to surf the Internet.
l Auto-sens ing Ethernet Switch
Equipped with a 3-port auto-sensing Ethernet switch.
l VPN supported
Supports multiple PPTP sessions and allows you to set up VPN server and VPN
clients.
l Firewall
All unwanted packets from outside sources and other intruders are blocked to
protect your Intranet.
-4-
Page 6

l DHCP server supported
All of the networked computers can retrieve TCP/IP settings automatically from
this product.
l Web-based configuring
Configurable through any networked computer’s web browser using Netscape
or Internet Explorer.
l MAC Address Access Control supported
Allows you to assign different access rights for different users.
l Virtual Server supported
Enables you to expose WWW, FTP and other services on your LAN for access
by Internet users.
l User-Definable Application Sensing Tunnel
User can define the attributes to support the special applications requiring
multiple connections, such as Internet gaming, videoconferencing, Internet
telephony, etc.. This product can then sense the application type and open the
correct multi-port tunnel for it.
l DMZ Host supported
Lets a networked computer be fully open to the Internet; this function is used
when the special application-sensing tunnel feature is insufficient to allow an
application to function correctly.
1.2 Packing List
l One wireless broadband router unit
l One installation CD -ROM
l One power adapter
l One CAT -5 UTP Fast Ethernet cable
-5-
Page 7
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation
2.1 Panel Layout
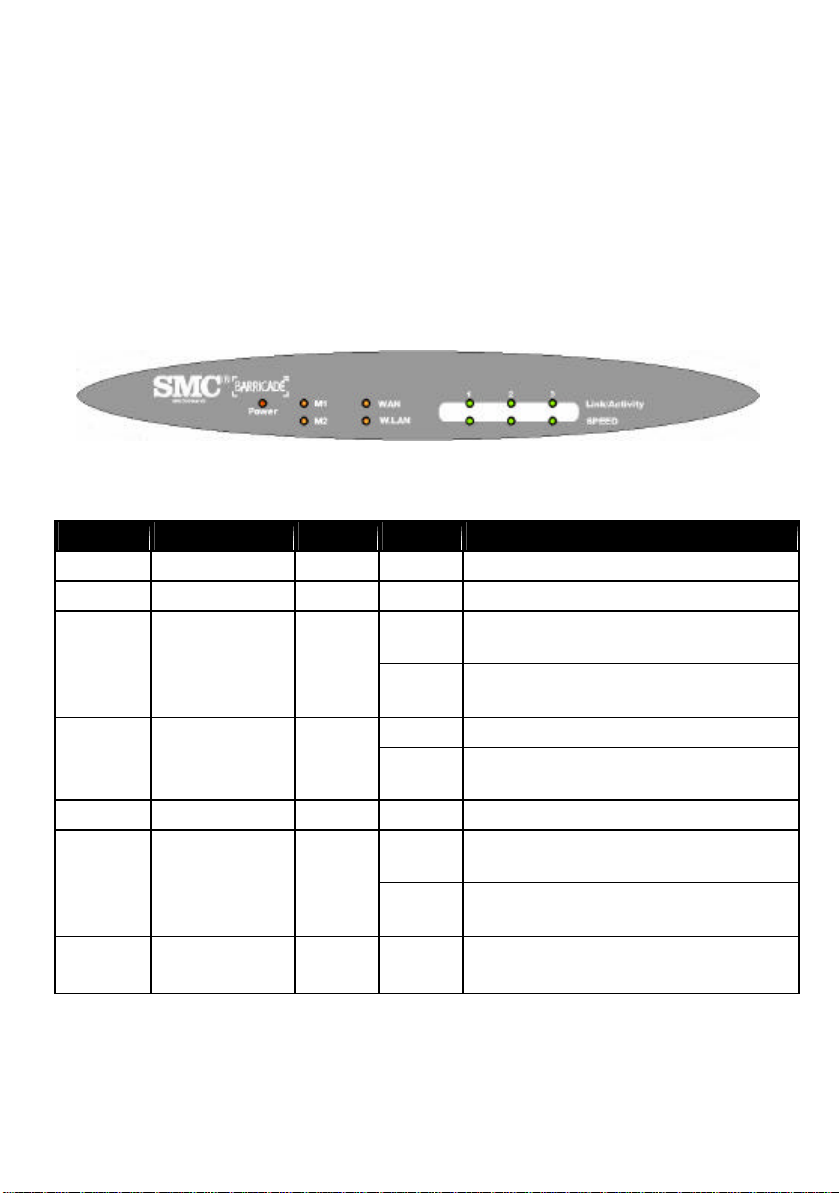
2.1.1. Front Panel
LEDs monitor the status of each port.
Figure 2-1 Front Panel
LED:
LED Function Color Status Description
POWER Power in dication Green On Power is being applied to this product.
M1 System status 1 Orange Blinking This product is functioning properly.
On
M2 System status 2 Orange
Blinking
WAN
W.LAN Wireless activity Green Blinking Sending or receiving data via wireless
Link/Act.
1~3
SPEED
1~3
WAN port
activity
Link status Green
Data Rate Green On
Green
On The WAN port is linked.
Blinking
On
Blinking
This product is working for a specific
service.
This product is being configured or
upgraded. Don’t turn it off !
The WAN port is sending or receiving
data.
An active station is connected to the
corresponding LAN port.
The corresponding LAN port is
sending or receiving data.
Data is transmitting in 100Mbps on the
corresponding LAN port.
-6-
Page 8

2.1.2. Rear Panel
EDs, they will flash 8 times and then M1 flashes
The port where you will connect your cable (or DSL) modem or Ethernet
The rear panel features three 10/100 Mbps Ethernet ports and one Wide Area
network (WAN) port. The WAN port connects your DSL or cable modem to the router.
The LAN ports are used to connect to your computers or other network devices.
Figure 2-2 Rear Panel
Ports:
Port Description
RESET
PRINTER Printer Port (Optional)
COM Serial port (connect dial-up modem or console cable)
To reset system settings to factory defaults, please follow the steps:
1. Power off the device,
2. Press the reset button and hold,
3. Power on the device,
4. Keep the button pressed about 5 seconds,
5. Release the button,
6. Watch the M1 and M2 L
once per second.
WAN Port
router.
Port 1-3 The ports where you will connect networked computers and other devices.
DC IN Power inlet (DC 12V)
-7-
Page 9
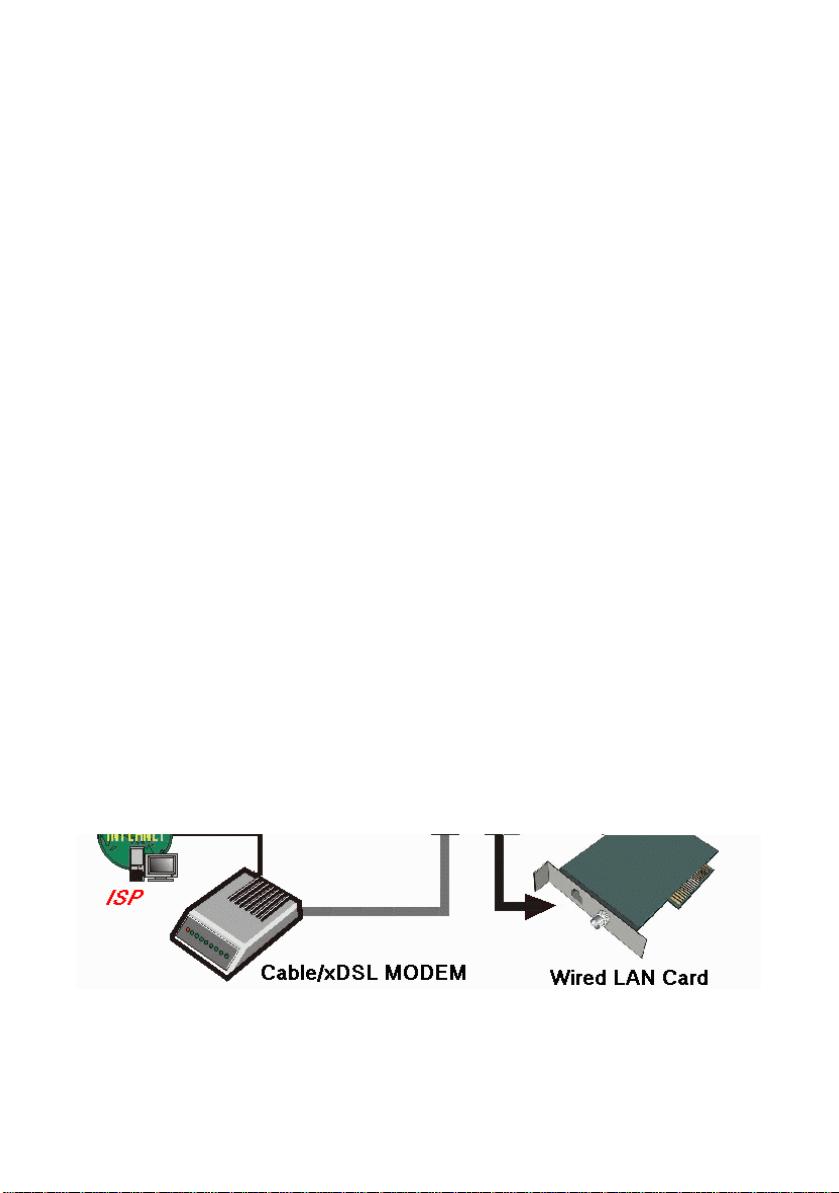
2.2 Procedure for Hardware Installation
1. Decide Where to Place Your Wireless Broadband Router:
You can place your Wireless Broadband Router on a desk or other flat surface, or you
can mount it on a wall. For optimal performance, place your Wireless Broadband Router
in the center of your office (or your home) in a location that is away from any potential
source of interference, such as a metal wall or microwave oven. This location must be
close to power and network connections.
2. Set up LAN connection:
a. Wired LAN connection: connect an Ethernet cable from your computer’s Ethernet
port to one of the LAN ports of this product.
b. Wireless LAN connection: make sure the antennas are in a vertical position.
Figure 2-3 Setup of LAN and WAN connections for this product
-8-
Page 10

3. Set up WAN connection: Connect an Ethernet cable from the WAN port to your
cable/xDSL modem or Ethernet backbone. Figure 2-3 illustrates the WAN
connection.
4. Power on:
By connecting the power cord to the power inlet and turning the power switch on, this
product will automatically enter the self-test phase. When it is in the self -test phase,
the indicators M1 and M2 will be lighted ON for about 10 seconds, and then M1 and
M2 will be flashed 3 times to indicate that the self-test operation has finished. Finally,
the M1 will be continuously flashed once per second to indicate that this product is in
normal operation.
-9-
Page 11

Chapter 3 Network Settings and Software Installation
To use this product correctly, you have to properly configure the network settings of your
computers and install the attached setup program on your computer (Windows
95/98/ME/NT/2000).
3.1 Make Correct Network Settings of Your Computer
The default IP address of this product is 192.168.123.254 , and the default subnet mask is
255.255.255.0. These addresses can be changed as needed, but the default values are used
in this manual. If the TCP/IP environment of your computer has not yet been installed,
you can refer to Appendix A to configure it. Once TCP/IP is installed, configure it as
follows:
1. Configure IP as 192.168.123.1, subnet mask as 255.255.255.0 and gateway as
192.168.123.254, or, more easily,
2. Configure your computers to “Obtain an IP address automatically,” that is, via
DHCP server of this product.
After configuring the TCP/IP communication protocol, you can use the ping command
to check if your computer has successfully connected to this product. The following
example shows the ping procedure for Windows 95 platforms. First, execute the ping
command from a DOS window:
ping 192.168.123.254
If the following messages appear:
Pinging 192.168.123.254 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 192.168.123.254: bytes=32 time=2ms TTL=64
a communication link between your computer and this product has been successfully
established. Otherwise, if you get the following messages,
Pinging 192.168.123.254 with 32 bytes of data:
-10-
Page 12

Request timed out.
there must be something wrong in your installation procedure. You have to check the
following items in sequence:
1. Is the Ethernet cable correctly connected between this product and your computer?
Tip: The LAN LED of this product and the link LED of the network card on your
computer must be lit.
2. Is the TCP/IP environment of your computers properly configured?
Tip: If the IP address of this product is 192.168.123.254, the IP address of your
computer must be 192.168.123.X and the default gateway must be 192.168.123.254.
Now you can configure the Internet Sharer (refer to Chapter 4).
3.2 Install the Software Into Your Computers
Skip this section if you do not want to use the print server function of this product.
Step 1: Insert the installation CD-ROM into the CD-ROM drive. The following window
will be shown automatically. If it isn’t, please run “install.exe” on the CD -ROM.
-11-
Page 13
Step 2: Click on the INSTALL button. Wait until the following Welcome dialog appears,
and click on the Next button.
Step 3: Select the destination folder and click on the Next button. The setup program will
then begin to install the programs into the destination folder.
-12-
Page 14
Step 4: When the following window is displayed, click on the Finish button.
Step 5: Select the item to restart the computer, then click the OK button to reboot your
computer.
Step 6: After rebooting your computer, the software installation procedure is complete.
Now, you can configure the Internet Sharer (refer to Chapter 4) and set up the Print Server
(refer to Chapter 5).
-13-
Page 15
Chapter 4 Configuring Wireless Broadband Router
This product provides a Web-based configuration scheme, i.e., configuring by Netscape
Communicator or Internet Explorer. This approach can be adopted in any MS Windows,
Macintosh or UNIX based platform.
4.1 Startup and Login
Activate your browser, and disable the proxy or add the IP address of this product into
the exceptions. Then, type this product’s IP address in the Location (for Netscape) or
Address (for IE) field and press ENTER . For example: http://192.168.123.254.
After the connection is established, you will see the web user interface of this product.
-14-
Page 16

There are two appearances of web user interface: for general users and for system
administrator.
To log in as an administrator, enter the system password (the factory setting is ”admin”) in
the System Password field and click on the Log in button. If the password is correct, the
web appearance will be changed into administrator configure mode. As listed in its main
menu, there are several options for system administration.
-15-
Page 17

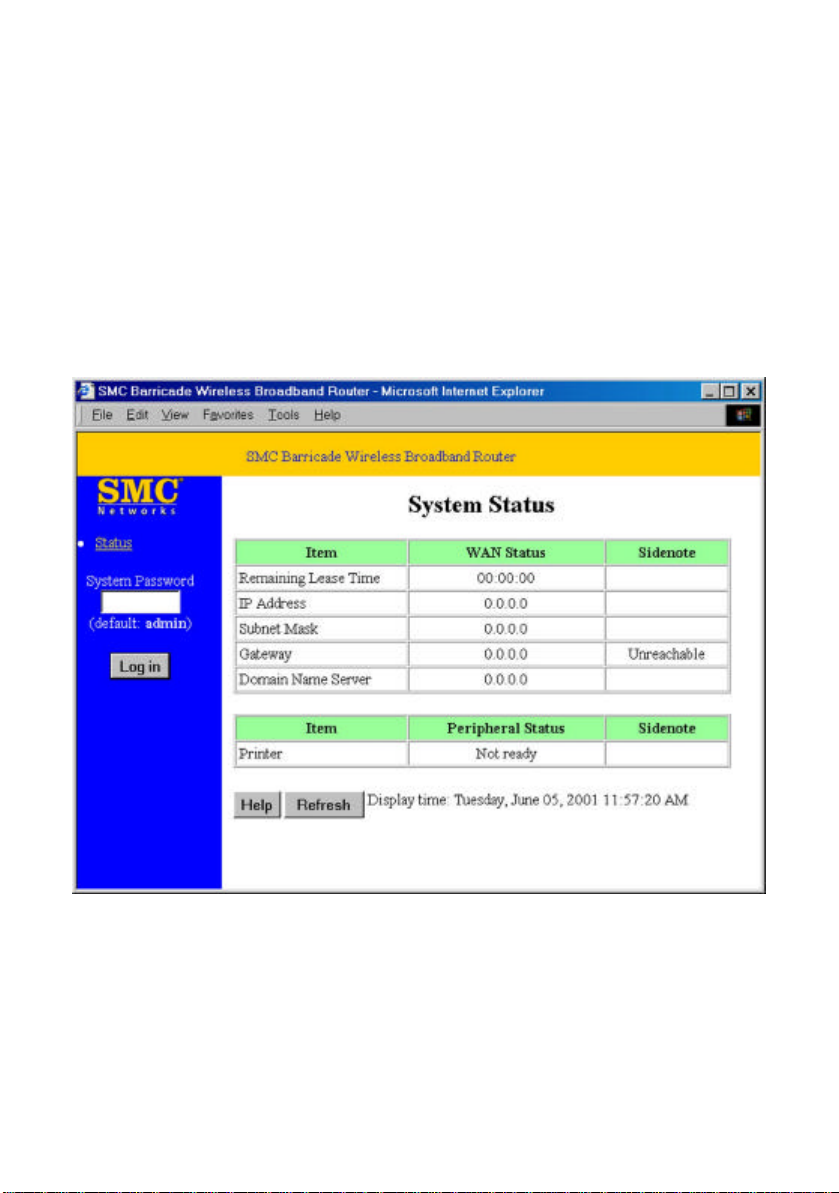
4.2 Status
This option provides the function for observing this product’s working status:
A. WAN Port Status.
If the WAN port is assigned a dynamic IP, there may appear a “Renew” or
“Release
-16-
Page 18

4.3 Toolbox
This option enables you change the administrator password. Besides, you can get the
information about Firmware version and WAN's MAC Address.
You can also reboot this product by clicking the Reboot button.
You can backup your settings by clicking the Backup Setting button and save it as a bin
file. Once you want to restore these settings , please click Firmware Upgrade button and
use the bin file you saved.
You can Clone MAC address by clicking Clone MAC button.
You can upgrade firmware by clicking Firmware Upgrade button.
Note: we strongly recommend that you change the system password for security reason.
-17-
Page 19

4.4 Primary Setup
This option is essential to enable this product to work properly. The setting items and the
web appearance depend on the WAN type. Choose the correct WAN type before you start.
1. LAN IP Address: the local IP address of this device. The computers on your network
must use the LAN IP address of your Barricade™ as their Default Gateway. You can
change it if necessary.
2. WAN Type: WAN connection type of your ISP. You can click Change… button to
choose a correct one from the following four options:
A. Static IP Address: ISP assigns you a static IP address.
B. Dynamic IP Address: Obtain an IP address from ISP automatically.
C. PPP over Ethernet: Some ISPs require the use of PPPoE to connect to their
services.
-18-
Page 20

D. Dial-up Network: To surf the Internet via PSTN/ISDN.
4.4.1 Static IP Address
WAN IP Address, Subnet Mask, Gateway, Primary and Secondary DNS: enter the proper
setting provided by your ISP .
4.4.2 Dynamic IP Address
1. Host Name: optional, required by some ISPs, for example, @Home.
2. Renew IP Forever: this feature enables your Barricade to renew your IP address
automatically when the lease time is expiring-- even when the system is id le.
4.4.3 PPP over Ethernet
1. PPPoE Account and Password: the account and password your ISP assigned to you.
For security, this field appears blank. If you don't want to change the password, leave
it empty.
2. PPPoE Service Name : optional. Input the service name if your ISP requires it.
Otherwise, leave it blank.
3. Maximum Idle Time : the amount of time of inactivity before disconnecting your
PPPoE session. Set it to zero or enable Auto-reconnect to disable this feature.
4.4.4 Dial-up Network
1. Dial-up Telephone , Account and Password: assigned by your ISP. For security, this
field appears blank. If you don't want to change the password, leave it empty.
2. Primary and Secondary DNS: If they are configured as "0.0.0.0.", they will be
automatically assigned upon connection.
3. Maximum Idle Time : the amount of time of inactivity before disconnecting your
dial-up session.
4. Baud Rate: the communication speed between this product and your MODEM or
-19-
Page 21

ISDN TA.
5. Extra Setting: (initialization string) optional. Used to optimize the communication
quality between the ISP and your MODEM or ISDN TA.
-20-
Page 22

4.5 DHCP Server
The settings of a TCP/IP network include host IP, subnet mask, gateway, and DNS
configurations. It is not easy to manually configure all the computers and devices in your
network. Fortunately, the Barricade's DHCP Server provides a simple approach to handle
all these settings. If you enable this product’s DHCP server and configure your computers
as “automatic IP allocation” mode, when your computer is powered on it, will
automatically load the proper TCP/IP settings from this product. The settings of DHCP
server include the following items:
1. DHCP Server : Choose “Disable” or “Enable.”
2. Range of IP Address Pool: Whenever there is a request, the DHCP server will
automatically allocate an unused IP address from the IP address pool to the
requesting computer. You must specify the starting and ending address of the IP
-21-
Page 23

address pool.
the current mapping of the IP and MAC address for each
In general, DHCP server assigns an IP address chosen from the
IP addresses pool randomly. Fixed Mapping allows you to
3. Domain Name: Optional: this information will be passed to the client.
Function of buttons:
Client List... List
DHCP client.
Fixed Mapping...
assign a specific IP address to the specified MAC address.
-22-
Page 24

4.6 Virtual Server
This product’s NAT firewall filters out unrecognized packets to protect your Intranet, thus
all hosts behind this product are externally invisible. If you wish, you can make some of
them accessible by enabling the Virtual Server Mapping.
A virtual server is defined as a Service Port, and all requests to this port will be redirected
to the computer specified by the Server IP.
For example, if you have an FTP server (port 21) at 192.168.123.1, a Web server (port 80)
at 192.168.123.2, and a VPN server at 192.168.123.6, then you need to specify the
following virtual server mapping table:
-23-
Page 25

Service Port Server IP Enable
21 192.168.123.1 V
80 192.168.123.2 V
1723 192.168.123.6 V
-24-
Page 26

4.7 Special AP
Some applications require multiple connections, such as Internet games, video
conferencing, Internet telephony, etc. Because of the firewall function, these applications
cannot work with a pure NAT router. The Special Applications feature allows some of
these applications to work with your Barricade. If the mechanism of Special Applications
fails to make an application work, try setting your computer as the DMZ host instead.
1. Trigger: the outbound port number issued by the application.
2. Incoming Ports: when the trigger packet is detected, inbound packets sent to the
specified port numbers are allowed to pass through the firewall.
This product provides some predefined settings. Select your application and click Copy to
to add the predefined setting to your list.
Note: At any given time, only one PC can use each Special Application.
-25-
Page 27

4.8 Access Control
Can browse(80), receive(110)
Access Control allows you to assign different access rights to different users. First, you
have to divide users into different groups. Users are identified by their IP addresses. You
can assign the members of Group 1, 2 and 3. The others are all members of the Default
Group. Second, you have to assign the access rights for each group. Access rights can
allow or block for access specified TCP and UDP ports. For example:
Group Members Access Right Comments
Default - Allow 0 No access right (allow nothing)
Group 1 100-199 Allow (25,53,80,110)
Group 2
-26-
and send(25) email only
Page 28

Function of buttons:
The “Access Control” is based on IP addresses only. If a user
is able to change his/her IP address, then s/he will not be
controlled by this function. The “MAC level” access control
rol the mapping of MAC addresses and IP
addresses. You can also control which MAC address is allowed
MAC Level...
allows you to cont
to connect to this device.
-27-
Page 29

4.9 Misc. Items
1. IP Address of DMZ Host: DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) Host is a host without the
protection of firewall. It allows a computer to be exposed to unrestricted 2-way
communication for Internet games, video conferencing, Internet telephony and other
special applications. (Note that this feature should be used only when needed.)
2. Remote Administrator Host: In general, only Intranet users can browse the built -in
web pages to perform administration task. If this feature is enabled, only the specified
IP address can perform remote administration. If the specified IP address is 0.0.0.0,
any remote host can connect to this product to perform administration tasks. When
this feature is enabled, the web port will be shifted to 88.
3. Administrator Time-out: The amount of inactive time after which the Barricade will
automatically close the Administrator session. Set this to zero to disa ble this feature.
-28-
Page 30

4. Discard PING from WAN side: When this feature is enabled, no host on the WAN
can ping the Barricade.
5. Non-standard FTP port: You have to configure this item if you want to access an
FTP server whose port number is not 21. This setting will be lost after rebooting.
-29-
Page 31

4.10 Wireless Setting
Wireless settings allow you to set the wireless configuration items.
1. Network ID (SSID): Network ID is used for identifying the Wireless LAN (WLAN).
Client stations can roam freely over this product and other Access Points that have the
same Network ID. (The factory setting is “default”)
2. Channel: The radio channel number. The permissible channels depends on the
Regulatory Domain: FCC/IC: 1-11, ETSI: 1-13, France: 10-13, Spain: 10-11,
MKK: 1-14 (The factory setting is channel 6)
3. WEP Security: Select the data privacy algorithm you want. Enabling the security can
protect your data while it is transferred from one station to another. The standardized
IEEE 802.11 WEP (128-bit or 64-bit) is used here.
4. WEP Key 1, 2, 3 & 4: When you enable the 128-bit or 64-bit WEP key security,
-30-
Page 32

please select one WEP key to be used and input 26 or 10 hexidecimal (0, 1, 2…8, 9,
ents
A, B…F) digits.
Function of buttons:
MAC Address Control... Setup MAC addresses to control which wireless cli
can associate to the wireless LAN.
-31-
Page 33

4.11 MAC Address Control
MAC Address Control
Every client that connects to the network has a unique MAC (Media Access Control)
address on his or her Ethernet adapter. An administrator can have more control —and more
security—over the network by specifying which MAC addresses are allowed to access the
Wireless Barricade. You can enable this feature by checking the “Enable” box.
Connection control
Connection control allows an administrator to allow or deny “connec tion” to clients trying
to access the Wireless Barricade and the Internet. Check "Connection control" to control
which of the wired AND wireless clients will be able to “connect” to the Wireless
-32-
Page 34

Barricade and to the Internet. If a client is denied “connection” to this device, it means
that the client can't access the Internet and some network resources . Choose "Allow" or
"Deny" to allow or deny clients whose MAC addresses are not listed in the "Control
table".
When a wired client CAN "Connect" to the Wireless Barricade, it means that it can have
full access to the Internet and Network Resources.
When a wired client CAN NOT "Connect" to the Wireless Barricade, it means that it
CAN:
1. Communicate with the other clients on the wired LAN
But CAN NOT:
1. Connect to the Internet
2. Use the Print Server function
3. Communicate with the clients on the wireless LAN
4. Use the Wireless Barricade’s Web configuration
Association control
The Association process is the exchange of information between wireless clients and a
wireless access point to establish a link between them. A wireless client is capable of
transmitting and receiving data to an access point only after the association process is
successfully completed.
Association control allows an administrator to allow or deny “association” to wireless
clients trying to link up to the Wireless Barricade. Check "Association control" to
control which of the wireless clients will be able to “associate” to the wireless LAN. If a
client is denied “association” to the wireless LAN, it means that the client can't send or
-33-
Page 35

receive any data through the Wireless Barricade. Choose "Allow" or "Deny" to allow or
deny clients whose MAC addresses are not listed in the "Control table"
When a wireless client CAN "Associate" to the wireless LAN, and CAN "Connect" to the
Wireless Barricade, that means it can have full access to the Internet and Network
Resources.
When a wireless client CAN NOT "Associate" to the wireless LAN, it means that it CAN
NOT:
1. Communicate with any others clients on the LAN (neither wired nor wireless)
2. Connect to the Internet
3. Use the Print Server function
4. Use the Wireless Barricade’s Web configuration
5. “Connect” to the Wireless Barricade
When a wireless client CAN "Associate" to the wireless LAN, but CAN NOT "Connect"
to the Wirel ess Barricade, it means that it CAN:
1. Communicate with others clients on the wireless LAN
But CAN NOT:
1. Communicate with any clients on the wired LAN
2. Connect to the Internet
3. Use the Print Server function
4. Use the Wireless Barricade’s Web configuration
Association control has no effect on wired clients.
Control table
"Control table" is at the bottom of the "MAC Address Control" page. Each row of this
-34-
Page 36

table indicates the MAC address and the mapped IP address of a client. There are four
columns in this table:
MAC Address Indicates a specific client’s MAC address.
IP Address Expected IP address of the corresponding client. Leave it blank if
you don't want a specified IP address.
C When "Connection control" is enabled, checking "C" will allow
the corresponding client to “Connect” to the Wireless Barricade.
A When "Association control" is enabled, checking "A" will allow
the corresponding client to “Associate” to the wireless LAN.
Previous page, Next page
To make this setup page simple and clear, we have divided the “Control table” into several
pages. You can use these buttons to navigate to different pages.
-35-
Page 37

Chapter 5 Print Server
This product provides the function of the network print server for MS Windows
95/98/NT/2000 and Unix-based platforms.
You must configure each station individually to connect to your server printer.
5.1 Configuring on Windows 95/98 Platforms
After you complete the software installation procedure described in Chapter 3, your
computer possesses the network printing facility provided by this product. For
convenience, we call the printer connected to the printer port of this product as server
printer. On a Windows 95/98 platform, open the Printers window in the My Computer
menu:
Yon can now configure the print server of this product:
-36-
Page 38

1. Find out the corresponding icon of your server printer, for example, the HP LaserJet
6L. Click the mouse’s right button on that icon, and then select the Properties item:
2. Click the Details item:
-37-
Page 39

3. Choose the “PRTmate: (All-in-1)” from the list attached at the Print To item. Be sure
that the Printer Driver item is configured to the correct driver of your server printer.
4. Click on the button of Port Settings :
Type in the IP address of this product and then click the OK button.
5. Make sure that all the settings mentioned above are correct, and then click the OK
button.
5.2 Configuring on Windows NT Platforms
The configuration procedure for a Windows NT platform is similar to that of Windows
95/98 except the screen of printer Properties:
-38-
Page 40

Compared to the procedure in the previous section, the selection of Details is equivalent to
the selection of Ports, and Port Settings is equivalent to Configure Port.
5.3 Configuring on Windows 2000 Platforms
The configuration procedure for a Windows 2000 platform is similar to that of Windows
95/98, except for the screen of printer Properties:
Compared to the procedure in the previous section, the selection of Details is equivalent to
the selection of Ports, and Port Settings is equivalent to Configure Port.
-39-
Page 41

5.4 Configuring on Unix-based Platforms
Please follow the traditional configuration procedure on Unix platforms to set up the print
server of this product. The printer name is “lp.”
-40-
Page 42

Appendix A: TCP/IP Configuration for Windows 95/98
This section advises on how to install TCP/IP protocol into your personal computer. It
assumes you have successfully installed one network card on your personal computer. If
not, please refer to your network card manual. Also, Section A.2 tells you how to set
TCP/IP values for working with this IP Sharer correctly.
A.1 Install TCP/IP Protocol Into Your PC
1. Click Start button and choose Settings, then click Control Panel.
2. Double click Network icon and select Configuration tab in the Network window.
3. Click Add button to ad d network component into your PC.
4. Double click Protocol to add TCP/IP protocol.
-41-
Page 43

5. Select the Microsoft item in the manufacturers list. Choose TCP/IP in the Network
Protocols. Click OK button to return to Network window.
6. The TCP/IP protocol will be listed in the Network window. Click OK to complete the
install procedure and restart your PC to enable the TCP/IP protocol.
A.2 Set TCP/IP Protocol for Working With IP Sharer
1. Click Start button and choose Settings, then click Control Panel.
-42-
Page 44

2. Double click Network icon. Select the TCP/IP line that has been associated to your
network card in the Configuration tab of the Network window.
3. Click Properties button to set the TCP/IP protocol for this IP Sharer.
4. You now have two setting methods:
A. Get IP via DHCP server
-43-
Page 45

a. Select Obtain an IP address automatically in the IP Address tab.
-44-
Page 46

b. Do not input any value in the Gateway tab.
-45-
Page 47

c. Choose Disable DNS in the DNS Configuration tab.
-46-
Page 48

B. Configure IP manually
a. Select Specify an IP address in the IP Address tab. The defaul t IP address
of this product is 192.168.123.254. Therefore, please use
192.168.123.xxx (xxx is between 1 and 253) for IP Address field and
255.255.255.0 for Subnet Mask field.
-47-
Page 49

b. In the Gateway tab, add the IP address of this product (default IP is
192.168.123.254); in the New gateway field and click Add button.
-48-
Page 50

c. In the DNS Configuration tab, add the DNS values which are provided by
the ISP into DNS Server Search Order field and click Add button.
-49-
 Loading...
Loading...