Page 1

TigerSwitch 1000
Gigabit Ethernet Switch
◆
6 auto-MDIX 10/100/1000BASE-T ports
◆
Two slots for hot-swappable 1000BASE-X GBIC modules
◆ 16 Gbps of aggregate switch bandwidth
◆ Support for redundant power unit
◆ Up to four port trunks per switch
◆ Port mirroring for non-intrusive analysis
◆ QoS support for two-level priority
◆ Full support for IEEE 802.1Q VLANs
◆ IGMP multicast filtering and snooping
◆ Manageable via console, Web, SNMP/RMON
Management Guide
SMC8606T
Page 2

Page 3

TigerSwitch 1000
Management Guide
From SMC’s Tiger line of feature-rich workgroup LAN solutions
6 Hughes
Irvine, CA 92618
Phone: (949) 707-2400
September 2001
Pub. # 150000004900A R02
Page 4

Information furnished by SMC Networks, Inc. (SMC) is believed to
be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by
SMC for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights
of third parties which may result from its use. No license is granted
by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of
SMC. SMC reserves the right to change specifications at any time
without notice.
Copyright © 2001 by
SMC Networks, Inc.
6 Hughes
Irvine, CA 92618
All rights reserved. Printed in Taiwan
Trademarks:
SMC is a registered trademark; and EZ Switch, TigerStack and TigerSwitch are trademarks of
SMC Networks, Inc. Other product and company names are trademarks or registered
trademarks of their respective holders.
Page 5

L
IMITED
Limited Warranty Statement: SMC Networks, Inc. (“SMC”) warrants its products
to be free from defects in workmanship and materials, under normal use and
service, for the applicable warranty term. All SMC products carry a standard 90-day
limited warranty from the date of purchase from SMC or its Authorized Reseller.
SMC may, at its own discretion, repair or replace any product not operating as
warranted with a similar or functionally equivalent product, during the applicable
warranty term. SMC will endeavor to repair or replace any product returned under
warranty within 30 days of receipt of the product.
The standard limited warranty can be upgraded to a Limited Lifetime* warranty by
registering new products within 30 days of purchase from SMC or its Authorized
Reseller. Registration can be accomplished via the enclosed product registration
card or online via the SMC web site. Failure to register will not affect the standard
limited warranty. The Limited Lifetime warranty covers a product during the Life of
that Product, which is defined as the period of time during which the product is an
“Active” SMC product. A product is considered to be “Active” while it is listed on
the current SMC price list. As new technologies emerge, older technologies become
obsolete and SMC will, at its discretion, replace an older product in its product line
with one that incorporates these newer technologies. At that point, the obsolete
product is discontinued and is no longer an “Active” SMC product. A list of
discontinued products with their respective dates of discontinuance can be found
at:
http://www.smc.com/smc/pages_html/support.html.
All products that are replaced become the property of SMC. Replacement products
may be either new or reconditioned. Any replaced or repaired product carries
either a 30-day limited warranty or the remainder of the initial warranty, whichever
is longer. SMC is not responsible for any custom software or firmware,
configuration information, or memory data of Customer contained in, stored on, or
integrated with any products returned to SMC pursuant to any warranty. Products
returned to SMC should have any customer-installed accessory or add-on
components, such as expansion modules, removed prior to returning the product
for replacement. SMC is not responsible for these items if they are returned with the
product.
Customers must contact SMC for a Return Material Authorization number prior to
returning any product to SMC. Proof of purchase may be required. Any product
returned to SMC without a valid Return Material Authorization (RMA) number
clearly marked on the outside of the package will be returned to customers at
customer’s expense. For warranty claims within North America, please call our
toll-free customer support number at (800) 762-4968. Customers are responsible for
all shipping charges from their facility to SMC. SMC is responsible for return
shipping charges from SMC to customer.
WARRANTIES EXCLUSIVE: IF AN SMC PRODUCT DOES NOT OPERATE AS
WARRANTED ABOVE, CUSTOMER’S SOLE REMEDY SHALL BE REPAIR OR
W
ARRANTY
i
Page 6

L
IMITED WARRANTY
REPLACEMENT OF THE PRODUCT IN QUESTION, AT SMC’S OPTION. THE
FOREGOING WARRANTIES AND REMEDIES ARE EXCLUSIVE AND ARE IN LIEU
OF ALL OTHER WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, EITHER
IN FACT OR BY OPERATION OF LAW, STATUTORY OR OTHERWISE, INCLUDING
WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE. SMC NEITHER ASSUMES NOR AUTHORIZES ANY OTHER
PERSON TO ASSUME FOR IT ANY OTHER LIABILITY IN CONNECTION WITH
THE SALE, INSTALLATION, MAINTENANCE OR USE OF ITS PRODUCTS. SMC
SHALL NOT BE LIABLE UNDER THIS WARRANTY IF ITS TESTING AND
EXAMINATION DISCLOSE THE ALLEGED DEFECT IN THE PRODUCT DOES NOT
EXIST OR WAS CAUSED BY CUSTOMER’S OR ANY THIRD PERSON’S MISUSE,
NEGLECT, IMPROPER INSTALLATION OR TESTING, UNAUTHORIZED ATTEMPTS
TO REPAIR, OR ANY OTHER CAUSE BEYOND THE RANGE OF THE INTENDED
USE, OR BY ACCIDENT, FIRE, LIGHTNING, OR OTHER HAZARD.
LIMITATION OF LIABILITY: IN NO EVENT, WHETHER BASED IN CONTRACT OR
TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE), SHALL SMC BE LIABLE FOR INCIDENTAL,
CONSEQUENTIAL, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, OR PUNITIVE DAMAGES OF ANY KIND,
OR FOR LOSS OF REVENUE, LOSS OF BUSINESS, OR OTHER FINANCIAL LOSS
ARISING OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SALE, INSTALLATION,
MAINTENANCE, USE, PERFORMANCE, FAILURE, OR INTERRUPTION OF ITS
PRODUCTS, EVEN IF SMC OR ITS AUTHORIZED RESELLER HAS BEEN ADVISED
OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
SOME STATES DO NOT ALLOW THE EXCLUSION OF IMPLIED WARRANTIES OR
THE LIMITATION OF INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES FOR
CONSUMER PRODUCTS, SO THE ABOVE LIMITATIONS AND EXCLUSIONS MAY
NOT APPLY TO YOU. THIS WARRANTY GIVES YOU SPECIFIC LEGAL RIGHTS,
WHICH MAY VARY FROM STATE TO STATE. NOTHING IN THIS WARRANTY
SHALL BE TAKEN TO AFFECT YOUR STATUTORY RIGHTS.
* SMC will provide warranty service for one year following discontinuance from the
active SMC price list. Under the limited lifetime warranty, internal and external
power supplies, fans, and cables are covered by a standard one-year warranty from
date of purchase.
SMC Networks, Inc.
6 Hughes
Irvine, CA 92618
ii
Page 7

T
ABLE OF
C
ONTENTS
1 Switch Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
Configuration Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-1
Required Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
Console Port (Out-of-Band) Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
Remote Management via the Console Port . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
Configure the Switch Site . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
Configure the Remote Site . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-3
In-Band Connections . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-4
2 Console Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
Log-in Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-1
Main Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-2
System and Switch Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
Displaying System Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-6
Displaying Switch Version . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-7
Management Setup Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-8
Changing the Network Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-10
IP Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-11
IP Connectivity Test (Ping) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-13
HTTP Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-14
Configuring the Serial Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-15
Assigning SNMP Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-17
Configuring Community Names . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-18
Configuring IP Trap Managers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-19
Console Login Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-20
Downloading System Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-22
Using TFTP Protocol to Download Over
the Network . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-22
Saving the System Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-23
Configuring the Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-25
Configuring Port Parameters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-27
Viewing the Current Port Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-29
Using the Spanning Tree Algorithm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-30
Configuring Bridge STA . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-31
Configuring STA for Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-33
Viewing the Current Spanning Tree Information . . . . . 2-35
iii
Page 8

T
ABLE OF CONTENTS
Displaying the Spanning Tree Bridge State . . . . . . 2-35
Displaying the Spanning Tree Port State . . . . . . . . 2-37
Using a Mirror Port for Analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-39
Configuring Port Trunks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-40
IGMP Multicast Filtering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-42
Configuring IGMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-43
Configuring Broadcast Storm Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-44
Port Security Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-45
Configuring Bridge MIB Extensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-47
Configuring Traffic Classes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-49
Port Priority Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-50
802.1P Port Traffic Class Information . . . . . . . . . . 2-51
Configuring Virtual LANs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-52
802.1Q VLAN Base Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-52
802.1Q VLAN Current Table Information . . . . . . . 2-54
802.1Q VLAN Static Table Configuration . . . . . . . . 2-55
802.1Q VLAN Port Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-58
Monitoring the Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-60
Displaying Port Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-62
Displaying RMON Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-64
Displaying the Unicast Address Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-66
Displaying the IP Multicast Registration Table . . . . . . . 2-68
Configuring Static Unicast Addresses . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-69
Resetting the System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-71
Logging Off the System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-72
3 Web Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
Web-Based Configuration and Monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-1
Navigating the Web Browser Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
Home Page . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-2
Configuration Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
Panel Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
Port State Display . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
Configuring the Serial Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-6
Main Menu . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-7
System Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-9
Switch Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-10
iv
Page 9

T
ABLE OF CONTENTS
Main Board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-10
IP Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-11
SNMP Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-13
SNMP Community . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-13
Trap Managers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-14
Security Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-15
Change Password . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-15
Firmware Upgrade Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-16
Web Upload Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-16
TFTP Download Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-17
Configuration Save and Restore . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-18
Configuration Upload Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-18
Configuration Download Management . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-19
Address Table Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-20
STA (Spanning Tree Algorithm) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-22
Spanning Tree Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-22
Spanning Tree . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-22
Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-23
Spanning Tree Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-25
Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-25
When the Switch Becomes Root . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-26
STA Port Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-27
Configuring Bridge MIB Extensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-29
Bridge Capability . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-29
Bridge Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-30
Priority . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-31
Port Priority Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-31
Port Traffic Class Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-32
Configuring Virtual LANs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-33
VLAN Basic Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-33
VLAN Current Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-34
VLAN Static List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-35
VLAN Static Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-36
VLAN Static Membership by Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-38
VLAN Port Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-38
IGMP Multicast Filtering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-40
Configuring IGMP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-41
v
Page 10

T
ABLE OF CONTENTS
IP Multicast Registration Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-42
Port Menus . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-43
Port Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-43
Port Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-44
Port Broadcast Storm Protect Configuration . . . . . . . . 3-45
Port Security Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-46
Using a Port Mirror for Analysis . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-47
Port Trunk Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-48
Port Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-50
Etherlike Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-50
RMON Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-52
4 Advanced Topics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
Layer 2 Switching . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-1
Spanning Tree Algorithm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
Virtual LANs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
Assigning Ports to VLANs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
Port Overlapping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-5
Forwarding Tagged/Untagged Frames . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-5
Connecting VLAN Groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-6
Multicast Filtering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-6
IGMP Snooping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-7
IGMP Protocol . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-7
Class-of-Service (CoS) Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-8
Port Trunks . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
SNMP Management Software . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-9
Remote Monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-10
A Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .A-1
Troubleshooting Chart . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-1
Upgrading Firmware via the Serial Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . A-2
B Pin Assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .B-1
Console Port Pin Assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-1
DB-9 Port Pin Assignments . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-2
Console Port to 9-Pin COM Port on PC . . . . . . . . . . . . . B-2
Console Port to 25-Pin DCE Port on Modem . . . . . . . . . B-2
vi
Page 11

T
ABLE OF CONTENTS
Console Port to 25-Pin DTE Port on PC . . . . . . . . . . . . .B-3
Glossary
Index
vii
Page 12

T
ABLE OF CONTENTS
viii
Page 13

C
HAPTER
S
WITCH
M
ANAGEMENT
Configuration Options
For advanced management capability, the TigerSwitch 1000
management agent provides a menu-driven system configuration
program. This program can be accessed by a direct or modem
connection to the serial port on the front panel (out-of-band), or
by a Telnet connection over the network (in-band).
The management agent is based on SNMP (Simple Network
Management Protocol). This SNMP agent permits the switch to be
managed from any PC in the network using in-band management
software (such as SMC’s EliteView).
The management agent also includes an embedded HTTP Web
agent. This Web agent can be accessed using a standard Web
browser from any computer attached to the network.
1
The system configuration program and the SNMP agent support
management functions such as:
• Enable/disable any port
• Set the communication mode for any port
• Configure SNMP parameters
• Configure VLANs or multicast filtering
• Display system information or statistics
• Configure the switch to join a Spanning Tree
• Download system firmware
• Restart the system
1-1
Page 14

S
WITCH MANAGEMENT
Required Connections
Console Port (Out-of-Band) Connections
Attach a VT100 compatible terminal or a PC running a terminal
emulation program to the serial port on the switch’s front panel.
Use the null-modem cable provided with this package, or use a
null modem connection that complies with the wiring assignments
shown in Appendix B of this guide.
When attaching to a PC, set terminal emulation type to VT100,
specify the port used by your PC (i.e., COM 1~4), and then set
communications to 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, no parity, and 19200 bps
(for initial configuration). Also be sure to set flow control to
“none.” (Refer to “Configuring the Serial Port” on page 2-17 for a
complete description of configuration options.)
Note: If the default settings for the switch’s serial port have been
modified and you are having difficulty making a console
connection, you can display or modify the current settings
using a Web browser as described under “Configuring the
Serial Port” on page 3-6.
1-2
Page 15

S
WITCH MANAGEMENT
Remote Management via the Console Port
Configure the Switch Site
Connect the switch’s DB9 serial port to the modem’s serial port
using standard cabling. For most modems which use a 25-pin port,
you will have to provide an RS-232 cable with a 9-pin connector on
one end and a 25-pin connector on the other end. Set the modem
at the switch’s site to force auto-answer mode. The following is a
sample initialization string: “ATQ1 S0=1&D0&K0&W” as defined
below:
Q1 : Inhibit result codes to DTE
S0=1 : Auto answer on first ring
D0 : Don’t care DTR
K0 : Disables DTE/DCE flow control
W : Write command to modem memory
Configure the Remote Site
At the remote site, connect the PC’s COM port (COM 1~4) to the
modem’s serial port. Set terminal emulation type to VT100, specify
the port used by your PC (i.e., COM 1~4), and then set
communications to 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, no parity, 19200 bps and
no flow control.
1-3
Page 16

S
WITCH MANAGEMENT
In-Band Connections
Prior to accessing the switch via a network connection, you must
first configure it with a valid IP address, subnet mask, and default
gateway using an out-of-band connection or the BOOTP protocol.
After configuring the switch’s IP parameters, you can access the
on-board configuration program from anywhere within the
attached network. The on-board configuration program can be
accessed using Telnet from any computer attached to the network.
The switch can also be managed by any computer using a Web
browser (Internet Explorer 4.0, or Netscape Navigator 4.0 or
above), or from a network computer using network management
software such as EliteView.
Notes: 1. By default BOOTP is disabled. To enable BOOTP, see
“IP Configuration” on page 2-13.
2. Use the Network Configuration menu to specify the
maximum number of simultaneous Telnet sessions that
are supported by the system (up to four).
3. The on-board program only provides access to basic
configuration functions. To access the full range of
SNMP management functions, you must use SNMPbased network management software, such as SMC’s
free EliteView software.
1-4
Page 17
C
HAPTER
C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Log-in Screen
Once a direct connection to the serial port or a Telnet connection
is established, the log-in screen for the onboard configuration
program appears as shown below.
SSSSSSSSSSSSSSS MMMMM MMMMM CCCCCCCCCCCCCC
SSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSS MM MM CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC
SS S MMM MMM CCC CC
SS MMMM MMMM CCC
SSSSSSSSSSSSSSSS MM MM MM MM CCC
SS MM MM MM MM CCC CC
S SS MM MM MM MM CCC CC
SSSSSSSSSSSSSSSSS MM MMM MM CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC
SSSSSSSSSSSSSSS MMMM MMMMM MMMM CCCCCCCCCCCCCC
TigerSwitch 1000 SMC8606T
V2.04.03.07 08-01-2001 (c)Copyright 2001, SMC Networks Inc.
User name :
Enter Password :
2
If this is your first time to log into the configuration program, then
the default user names are “admin” and “guest,” with no password.
The administrator has Read/Write access to all configuration
parameters and statistics. While the guest has Read Only access to
the management program.
You should define a new administrator password, record it and put
it in a safe place. Select Console Login Configuration from the
Management Setup Menu and enter a new password for the
administrator. Note that passwords can consist of up to 11
alphanumeric characters and are not case sensitive.
2-1
Page 18
C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Note: You are allowed three attempts to enter the correct
password; on the third failed attempt the current
connection is terminated.
Main Menu
The Main Menu is the first screen seen after successfully logging
into the system.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< Main Menu >
About this product
Management Setup Menu
Switch Configuration Menu
Network Monitor Menu
Reset System Menu
Quit Current Session
2-2
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select.
Selection Description
About this product
System Information Provides basic system description, including
contact information.
Switch Information Shows hardware/firmware version numbers
and power status of the switch.
Management Setup Menu
Network
Configuration
Includes IP setup, Ping facility, HTTP (Web
server) setup, Telnet configuration, and MAC
address.
Page 19

Selection Description
Serial Port
Configuration
Sets communication parameters for the serial
port, including management mode, baud rate,
console time-out, and screen data refresh
interval.
C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
SNMP Configuration Activates traps; and configures communities
Console Login
Configuration
TFTP Download
New Software
Configuration Save
and Restore
Switch Configuration
Menu
Port Configuration Enables any port, enables/disables flow
Port State Displays operational status, including link
Spanning Tree
Configuration
Spanning Tree
Information
and trap managers.
Sets user names and passwords for system
access, as well as the invalid password
threshold and lockout time.
Downloads new version of firmware to update
your system (in-band).
Saves the switch configuratin to a file on the
TFTP server. This file can be later downloaded
to restore the configuration.
control, and sets communication mode to
auto-negotiation, full duplex or half duplex.
state, flow control method, and duplex mode.
Enables Spanning Tree Algorithm; also sets
parameters for hello time, maximum message
age, switch priority, and forward delay; as well
as port priority and path cost.
Displays full listing of parameters for the
Spanning Tree Algorithm.
Mirror Port
Configuration
Port Trunking
Configuration
IGMP Configuration Configures IGMP multicast filtering.
Sets the source and target ports for mirroring.
Specifies ports to group into aggregate trunks.
2-3
Page 20

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Selection Description
BStorm Control
Configuration
Allows you to enable/disable broadcast storm
control on a per-port basis and set the
packet-per-second threshold.
Port Security
Configuration
Extended Bridge
Configuration
802.1P
Configuration
802.1Q VLAN
Base Information
802.1Q VLAN
Current Table
Information
802.1Q VLAN Static
Table Configuration
802.1Q VLAN
Port Configuration
Network Monitor
Menu
Port Statistics Displays statistics on network traffic passing
Allows you to enable and configure port
security for the switch.
Displays/configures extended bridge
capabilities provided by this switch, including
support for traffic classes, GMRP* multicast
filtering, and VLAN extensions.
Configures default port priorities and queue
assignments.
Displays basic VLAN information, such as
VLAN version number and maximum VLANs
supported.
Displays VLAN groups and port members.
Configures VLAN groups via static
assignments, including setting port members,
or restricting ports from being dynamically
added to a port by the GVRP* protocol.
Displays/configures port-specific VLAN
settings, including PVID, ingress filtering, and
GVRP*.
through the selected port.
2-4
RMON Statistics Displays detailed statistical information for the
Unicast Address
Table
selected port such as packet type and frame
size counters.
Provides full address listing, as well as search
and clear functions.
Page 21

Selection Description
IP Multicast
Registration Table
Displays all the multicast groups active on this
switch, including multicast IP addresses and
corresponding VLAN IDs.
C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Static Unicast
Address Table
Configuration
Reset system menu Restarts system with options to use POST, or
Quit current session Exits the configuration program.
* Note that GMRP and GVRP are not implemented in the current
firmware release.
Used to manually configure host MAC
addresses in the unicast table.
to retain factory defaults, IP settings, or user
authentication settings.
2-5
Page 22
C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
System and Switch Information
Use the “About this product” menu to display a basic description
of the switch, including contact information, and hardware/
firmware versions.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< About this product >
System Information
Switch Information
<OK>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select.
Selection Description
System
Information
Switch
Information
Provides basic system description, including
contact information.
Shows hardware/firmware version numbers and
power status of the switch.
2-6
Page 23
C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Displaying System Information
Use the System Information screen to display descriptive
information about the switch, or for quick system identification as
shown in the following figure and table.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< System Information >
System Description : SMC TigerSwitch 1000 SMC8606T
System Object ID : 1.3.6.1.4.1.202.20.18
System Up Time : 8302069 (0 day 23 hr 3 min 40 sec)
Network Host Name :
System Contact :
System Location :
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, other keys to make changes.
Parameter Description
System
System hardware description.
Description
System Object ID MIB II object identifier for switch’s network
management subsystem.
System Up Time Length of time the current management agent has
been running. (Note that the first value is 1/100
seconds.)
Network Host
*
Name
System Contact
System Location
Name assigned to the switch system.
*
Contact person for the system.
*
Specifies the area or location where the system
resides.
*
Maximum string length is 255, but the screen only displays 45
characters. You can use the arrow keys to browse the whole string.
2-7
Page 24
C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Displaying Switch Version
Use the Switch Information screen to display hardware/firmware
version numbers for the switch, as well as the power status of the
system.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< Switch Information >
Main Board
Hardware Version : V1.0 (850 CPU)
Firmware Version : V2.04.03.08
POST ROM Version : V1.04
Serial Number : 00-E0-09-09-00-01
Port Number : 8
Internal Power Status : Active
Redundant Power Status : Inactive
<OK>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select.
Parameter Description
2-8
Hardware Version Hardware version of the main board.
Firmware Version System firmware version in Flash ROM.
POST ROM Version Power-On Self-Test version number.
Serial Number MAC address associated with the main board.
Port Number Number of ports on the switch.
Internal Power
Power status for the switch.
Status
Redundant Power
Redundant power status for the switch.
Status
Page 25
C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Management Setup Menu
After initially logging onto the system, adjust the communication
parameters for your console to ensure a reliable connection (Serial
Port Configuration). Specify the IP addresses for the switch
(Network Configuration / IP Configuration), and then set the
Administrator and User passwords (Console Login Configuration).
Remember to record them in a safe place. Also set the community
string which controls SNMP access to the switch via in-band
management software (SNMP Configuration). The items provided
by the Management Setup Menu are described in the following
sections.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< Management Setup Menu >
Network Configuration
Serial Port Configuration
SNMP Configuration
Console Login Configuration
TFTP Download New Software
Configuration Save & Restore
<OK>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select.
Selection Description
Network
Configuration
Serial Port
Configuration
Includes IP setup, Ping facility, HTTP (Web server)
setup, Telnet configuration, and MAC address.
Sets communication parameters for the serial port,
including management mode, baud rate, console
time-out, and screen data refresh interval.
2-9
Page 26

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
SNMP
Configuration
Console Login
Configuration
TFTP Download
New Software
Configuration
Save & Restore
Activates traps; and configures communities and
trap managers.
Sets user names and passwords for system access,
as well as the invalid password threshold and
lockout time.
Downloads new version of firmware to update
your system (in-band).
Saves the switch configuration to a file on a TFTP
server. This file can be later downloaded to restore
the configuration.
2-10
Page 27
C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Changing the Network Configuration
Use the Network Configuration menu to set the bootup option,
configure the switch’s Internet Protocol (IP) parameters, enable the
on-board Web server, or to set the number of concurrent Telnet
sessions allowed. The screen shown below is described in the
following table.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< Network Configuration >
IP Configuration
IP Connectivity Test(Ping)
HTTP Configuration
MAX Number of allowed Telnet sessions (1-4) : 4
Physical Address : 00-00-11-11-43-21
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select.
Parameter Description
IP Configuration Screen used to set the bootup option, or configure
the switch’s IP parameters.
IP Connectivity
Test
HTTP
Screen used to test IP connectivity to a (Ping)
specified device.
Screen used to enable the Web server.
Configuration
MAX Number of
Allowed Telnet
The maximum number of Telnet sessions allowed
to simultaneously access the switch.
Sessions
Physical Address MAC address of the switch.
2-11
Page 28
C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
IP Configuration
Use the IP Configuration screen to set the bootup option, or
configure the switch’s IP parameters. The screen shown below is
described in the following table.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< IP Configuration >
Interface Type : Ethernet
IP Address : 10.2.13.29
Netmask : 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway :
IP State : USER-CONFIG
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, other keys to make changes.
Parameter Default Description
2-12
Interface
Ethernet Indicates IP over Ethernet.
Type
IP Address 10.1.0.1 IP address of the switch you are
managing when accessing it over the
network. The switch supports SNMP over
UDP/IP transport protocol. In this
environment, all systems on the Internet,
such as network interconnection devices
and any PC accessing the switch must
have an IP address.
Valid IP addresses consist of four decimal
numbers, of 0 to 255, separated by
periods. Anything outside of this format
will not be accepted by the configuration
program.
Page 29

Parameter Default Description
Subnet
Mask
255.255.0.0 Subnet mask of the switch. This mask
identifies the host address bits used for
routing to specific subnets.
C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Default
Gateway
IP State USER-
CONFIG
The gateway that the switch’s agent uses
to pass data to the management station.
Note that the gateway must be defined if
the management station is located in a
different IP segment.
Specifies whether IP functionality is
enabled via manual configuration, or set
by Boot Protocol (BootP). Options
include:
USER-CONFIG -IP functionality is
enabled based on the default or user
specified IP configuration.
BOOTP-GET-IP - IP is enabled but will
not function until a BootP reply has been
received. BootP requests will be
broadcast 10 times, once every second, in
an effort to learn its IP address. If no
response is received, the switch will use
the default IP setting in NVRAM. (BootP
values can include the IP address, default
gateway, and subnet mask.)
2-13
Page 30
C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
IP Connectivity Test (Ping)
Use the IP Connectivity Test to see if another site on the Internet
can be reached. The screen shown below is described in the
following table.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< IP Connectivity Test(Ping) >
IP Address :
Test Times : 1 Interval : 3
Success : 0 Failure : 0
[Start]
<OK>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, other keys to make changes.
2-14
Parameter Description
IP Address IP address of the site you want to ping.
Test Times The number of ICMP echo requests to send to the
specified site.
Range: 1~9999
Interval The interval (in seconds) between pinging the
specified site.
Range: 1~10 seconds
Success/Failure The number of times the specified site has
responded or not to pinging.
Page 31

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
HTTP Configuration
Use the HTTP Configuration screen to enable/disable the on-board
Web server, and to specify the TCP port that will provide HTTP
service. The screen shown below is described in the following
table.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< HTTP Configuration >
HTTP Server : ENABLED
HTTP Port Number : 80
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, <Space> to scroll options.
Parameter Description
HTTP Server Enables/disables access to the on-board Web
server.
HTTP Port
Number
Specifies the TCP port that will provide HTTP
service.
Range : 0~65535
Default : Port 80
(Telnet Port 23 is prohibited.)
2-15
Page 32

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Configuring the Serial Port
You can access the on-board configuration program by attaching a
VT100 compatible device to the switch’s serial port. (For more
information on connecting to this port, see “Required
Connections” on page 1-2.) The communication parameters for
this port can be accessed from the Serial Port Configuration screen
shown below and described in the following table.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< Serial Port Configuration >
Management Mode : CONSOLE MODE
Baud rate : 19200
Data bits : 8
Stop bits : 1
Parity : NONE
Time-Out (in minutes) : 10
2-16
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, <Space> to scroll options.
Parameter Default Description
Management
Mode
Console
Mode
Indicates that the console port
settings are for direct console
connection.
Baud Rate 19200 The rate at which data is sent between
devices.
Options : 2400, 4800, 9600, 19200 bps,
and Auto detection
Data bits 8 bits Sets the data bits of the RS-232 port.
Options : 7, 8
Page 33

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Parameter Default Description
Stop bits 1 bit Sets the stop bits of the RS-232 port.
Options : 1, 2
Parity none Sets the parity of the RS-232 port.
Options : none/odd/even
Time-Out 10
minutes
If no input is received from the
attached device after this interval, the
current session is automatically
closed.
Range : 0 - 100 minutes; 0: disabled
2-17
Page 34

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Assigning SNMP Parameters
Use the SNMP Configuration screen to display and modify
parameters for the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP).
The switch includes an SNMP agent which monitors the status of
its hardware, as well as the traffic passing through its ports. A
computer attached to the network, called a Network Management
Station (NMS), can be used to access this information. Access
rights to the switch are controlled by community strings. To
communicate with the switch, the NMS must first submit a valid
community string for authentication. The options for configuring
community strings and related trap functions are described in the
following sections.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< SNMP Configuration >
Send Authentication Fail Traps : ENABLED
SNMP Security
IP Trap Managers
2-18
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, <Space> to scroll options.
Parameter Description
Send
Authentication
Fail Traps
SNMP Security Assigns SNMP access based on specified strings.
IP Trap Managers Specifies management stations that will receive
Issue a trap message to specified IP trap managers
whenever authentication of an SNMP request fails.
(The default is enabled.)
authentication failure messages or other trap
messages from the switch.
Page 35

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Configuring Community Names
The following figure and table describe how to configure the
community strings authorized for management access. Up to 5
community names may be entered.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< SNMP Security >
Community Name Access Status
1. public READ ONLY ENABLED
2.
3.
4.
5.
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, other keys to make changes.
Parameter Description
Community
Name
A community entry authorized for management
access.
Maximum string length : 19 characters
Access Management access is restricted to Read Only or
Read/Write.
Status Sets administrative status of entry to enabled or
disabled.
Note: The default community string is “public” with Read Only
access.
2-19
Page 36

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Configuring IP Trap Managers
The following figure and table describe how to specify
management stations that will receive authentication failure
messages or other trap messages from the switch. Up to 5 trap
managers may be entered.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< IP Trap Managers >
IP Address Community Name Status
1. 10.1.0.23 public DISABLED
2.
3.
4.
5.
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, <Space> to scroll options.
2-20
Parameter Description
IP Address IP address of the trap manager.
Community Name A community specified for trap management
access.
Status Sets administrative status of selected entry to
enabled or disabled.
Page 37

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Console Login Configuration
Use the Management Setup: Console Login Configuration to restrict
management access based on specified user names and
passwords, or to set the invalid password threshold and timeout.
There are only two user types defined, ADMIN (Administrator) and
GUEST, but you can set up to five different user names and
passwords. Only Administrators have write access for parameters
governing the switch. You should therefore assign a user name
and password to the default Administrator as soon as possible, and
store it in a safe place. (If for some reason your password is lost,
or you cannot gain access to the system configuration program,
contact SMC Technical Support for assistance.) The parameters
shown on this screen are indicated in the following figure and
table.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< Console Login Configuration >
Password Threshold : 3
Lock-out Time (in minutes) : 0
User Type User Name Password Confirm password
---------------------------------------------------------
1. ADMIN admin ****** ******
2. GUEST guest
3.
4.
5.
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, other keys to make changes.
Parameter Default Description
Password
Threshold
3 Sets the password intrusion threshold
which limits the number of failed logon
attempts. Range : 0~65535
2-21
Page 38

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Parameter Default Description
Lock-out
Time
Admin* name:
0 Time (in minutes) the management
console will be disabled, Range : 0~65535
Administrator has access privilege of
admin
password:
null
Read/Write for all screens.
Guest* name:
guest
password:
null
* Passwords can consist of up to 11 alphanumeric characters and are not
case sensitive.
Guest has access privilege of Read Only
for all screens.
2-22
Page 39

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Downloading System Software
Using TFTP Protocol to Download Over the Network
Use the TFTP Download menu to load software updates into the
switch. The download file should be an SMC8606T binary file from
SMC; otherwise the switch will not accept it. The success of the
download operation depends on the accessibility of the TFTP
server and the quality of the network connection. After
downloading the new software, the switch will automatically
restart itself. Parameters shown on this screen are indicated in the
following figure and table.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< TFTP Download New Software >
Download Server IP :
Agent Software Upgrade : ENABLED
Download Filename :
Download Mode : PERMANENT
[Process TFTP Download]
Download status : Complete
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, other keys to make changes.
Parameter Description
Download Server IPIP address of a TFTP server.
Agent Software
Upgrade
Download
Indicates that the switch is enabled for software
upgrades.
The binary file to download to the switch.
Filename
Download Mode Downloads to permanent flash ROM.
[Process TFTP
Download]
Issues a request to the TFTP server to download
the specified file.
2-23
Page 40

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Parameter Description
Download Status Indicates if a download is “Complete” or “In
Progress.”
Saving the System Configuration
Use the Configuration Save & Restore menu to save the switch
configuration settings to a file on a TFTP server. The file can be
later downloaded to the switch to restore the switch’s settings. The
success of the operation depends on the accessibility of the TFTP
server and the quality of the network connection. Parameters
shown on this screen are indicated in the following figure and
table.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< Configuration Upload >
Upload Server IP :
Upload Filename :
[Process TFTP Upload]
Upload status : Complete
< Configuration Download >
Download Server IP :
Download Filename :
[Process TFTP Download]
Download status : Complete
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, other keys to make changes.
2-24
Parameter Description
Configuration Upload
Upload Server IP IP address of a TFTP server.
Upload Filename The name of the file to contain the switch
configuration settings.
Page 41

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Parameter Description
[Process TFTP
Upload]
Upload Status Indicates if an upload is “Complete” or “In
Issues a request to upload the configuration
settings to the specified file on the TFTP server.
Progress.”
2-25
Page 42

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Parameter Description
Configuration Download
Download Server IPIP address of a TFTP server.
Download
Filename
[Process TFTP
Download]
Download Status Indicates if a download is “Complete” or “In
The name of the file that contains the switch
configuration settings you wish to restore.
Issues a request to the TFTP server to
download the specified file.
Progress.”
2-26
Page 43

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Configuring the Switch
The Switch Configuration Menu is used to control a broad range of
functions, including port configuration, Spanning Tree support for
redundant switches, port mirroring, multicast filtering, and Virtual
LANs. Each of the setup screens provided by these configuration
menus is described in the following sections.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< Switch Configuration Menu >
Port Configuration Extended Bridge Configuration
Port State 802.1P Configuration
Spanning Tree Configuration 802.1Q VLAN Base Information
Spanning Tree Information 802.1Q VLAN Current Table Information
Mirror Port Configuration 802.1Q VLAN Static Table Configuration
Port Trunking Configuration 802.1Q VLAN Port Configuration
IGMP Configuration Port GARP Configuration
BStorm Control Configuration Port GMRP Configuration
Port Security Configuration
<OK>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select.
Selection Description
Port Configuration Sets communication parameters for ports.
Port State Displays current port settings and port status.
Spanning Tree
Configuration
Spanning Tree
Information
Mirror Port
Configures the switch and its ports to participate in
a local Spanning Tree.
Displays the current Spanning Tree configuration
for the switch and its ports.
Sets the source and target ports for mirroring.
Configuration
Port Trunking
Specifies ports to group into aggregate trunks.
Configuration
2-27
Page 44

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Selection Description
IGMP
Configuration
BStorm Control
Configuration
Configures IGMP multicast filtering.
Allows you to enable/disable broadcast storm
control on a per-port basis and set the
packet-per-second threshold.
Port Security
Configuration
Extended Bridge
Configuration
802.1P
Configuration
802.1Q VLAN
Base Information
802.1Q VLAN
Current Table
Information
802.1Q VLAN
Static Table
Configuration
802.1Q VLAN Port
Configuration
Port GARP
Configuration*
Port GMRP
Configuration*
* Not implemented in the current firmware release.
Allows you to enable and configure port security
for the switch.
Displays/configures extended bridge capabilities
provided by this switch, including support for
traffic classes, and VLAN extensions.
Configures default port priorities and queue
assignments.
Displays basic VLAN information, such as VLAN
version number and maximum VLANs supported.
Displays VLAN groups and port members.
Configures VLAN groups via static assignments,
including setting port members, or restricting ports
from being dynamically added to a port by the
GVRP protocol.
Displays/configures port-specific VLAN settings,
including PVID, ingress filtering, and GVRP.
Configures generic attribute settings used in the
Spanning Tree Algorithm, VLAN registration, and
multicast filtering.
Configures GMRP multicast filtering.
2-28
Page 45

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Configuring Port Parameters
Use the Port Configuration menus to set or display communication
parameters for any port on the switch.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< Port Configuration >
Flow Control mode of all ports : [Enable] [Disable]
Port Type Admin Flow Control Speed and Duplex
------------------------------------------------------------------ 1 1000T ENABLED DISABLED AUTO
2 1000T ENABLED DISABLED AUTO
3 1000T ENABLED DISABLED AUTO
4 1000T ENABLED DISABLED AUTO
5 1000T ENABLED DISABLED AUTO
6 1000T ENABLED DISABLED AUTO
7 GBIC ENABLED DISABLED AUTO
8 GBIC ENABLED DISABLED AUTO
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select
Parameter Default Description
Flow Control
mode of all ports
DISABLED Allows you to enable or disable flow
control for all ports on the switch.
Type Shows port types as:
1000T - 1000BASE-T
1000SX - 1000BASE-SX
GBIC - 1000BASE-SX or
1000BASE-LX transceiver
Admin ENABLED Allows you to disable a port due to
abnormal behavior (e.g., excessive
collisions), and then re-enable it
after the problem has been resolved.
You may also disable a port for
security reasons.
2-29
Page 46

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Parameter Default Description
Flow Control DISABLED Used to enable or disable flow
Speed and
Duplex
control. Flow control can eliminate
frame loss by “blocking” traffic from
end stations or segments connected
directly to the switch when its
buffers fill. Back pressure is used for
half duplex and IEEE 802.3x for full
duplex.
AUTO Used to set the current port speed,
duplex mode, and auto-negotiation.
2-30
Page 47

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Viewing the Current Port Configuration
The Port State screen displays the port type, status, link state, and
flow control in use, as well as the communication speed and
duplex mode. To change any of the port settings, use the Port
Configuration menu.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< Port State >
Port Type Operational Link FlowControl Speed and
InUse Duplex InUse
----------------------------------------------------------------- 1 1000T YES DOWN -------------- --------- 2 1000T YES DOWN -------------- --------- 3 1000T YES UP NONE 100_FULL
4 1000T YES DOWN -------------- --------- 5 1000T YES DOWN -------------- --------- 6 1000T YES DOWN -------------- --------- 7 GBIC YES DOWN -------------- --------- 8 GBIC YES DOWN -------------- ----------
<OK>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select.
Parameter Description
Type Shows port types as:
1000T - 1000BASE-T
1000SX - 1000BASE-SX
GBIC - 1000BASE-SX or 1000BASE-LX transceiver
Operational Shows if the port is functioning or not.
Link Indicates if the port has a valid connection to an
external device.
FlowControl
InUse
Shows the flow control type in use. Flow control
can eliminate frame loss by “blocking” traffic from
end stations connected directly to the switch. Back
pressure is used for half duplex and IEEE 802.3x
for full duplex.
2-31
Page 48

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Parameter Description
Speed and
Duplex InUse
Displays the current port speed and duplex mode
used.
2-32
Page 49
C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Using the Spanning Tree Algorithm
The Spanning Tree Algorithm can be used to detect and disable
network loops, and to provide backup links between switches,
bridges or routers. This allows the switch to interact with other
bridging devices (that is, an STA-compliant switch, bridge or
router) in your network to ensure that only one route exists
between any two stations on the network. For a more detailed
description of how to use this algorithm, refer to “Spanning Tree
Algorithm” on page 4-2.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< Spanning Tree Configuration Menu >
Spanning Tree Bridge Configuration
Spanning Tree Port Configuration
<OK>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select.
2-33
Page 50

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Configuring Bridge STA
The following figure and table describe Bridge STA configuration.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< Spanning Tree Bridge Configuration >
Spanning Tree Protocol : On
Bridge Priority : 32768
Hello Time (in seconds) : 2
Max Age (in seconds) : 20
Forward Delay (in seconds) : 15
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, <Space> to scroll options.
Parameter Default Description
2-34
Spanning
Tree
On Enable this parameter to participate in an
STA-compliant network.
Protocol
Priority 32,768 Device priority is used in selecting the root
device, root port, and designated port. The
device with the highest priority becomes the
STA root device. However, if all devices
have the same priority, the device with the
lowest MAC address will then become the
root device.
Enter a value from 0 - 65535.
Remember that the lower the numeric value,
the higher the priority.
Page 51

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Parameter Default Description
Hello Time 2 Time interval (in seconds) at which the root
device transmits a configuration message.
The minimum value is1.
The maximum value is
the lower of 10 or [(Max. Message Age / 2)
-1].
Max
(Message)
Age
Forward
Delay
20 The maximum time (in seconds) a device
can wait without receiving a configuration
message before attempting to reconfigure.
All device ports (except for designated
ports) should receive configuration
messages at regular intervals. Any port that
ages out STA information (provided in the
last configuration message) becomes the
designated port for the attached LAN. If it is
a root port, a new root port is selected from
among the device ports attached to the
network.
The minimum value is
the higher of 6 or [2 x (Hello Time + 1)].
The maximum value is
the lower of 40 or [2 x (Forward Delay - 1)].
15 The maximum time (in seconds) the root
device will wait before changing states (i.e.,
listening to learning to forwarding). This
delay is required because every device must
receive information about topology changes
before it starts to forward frames. In
addition, each port needs time to listen for
conflicting information that would make it
return to a blocking state; otherwise,
temporary data loops might result.
The maximum value is 30.
The minimum value is
the higher of 4 or [(Max. Message Age / 2) +
1].
2-35
Page 52

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Configuring STA for Ports
The following figure and table describe STA configuration for
ports.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< Spanning Tree Port Configuration >
Fast forwarding mode of all ports : [Enable] [Disable]
Port Type Priority Cost FastForwarding
------------------------------------------------------ 1 1000T 128 4 DISABLED
2 1000T 128 4 DISABLED
3 1000T 128 19 DISABLED
4 1000T 128 4 DISABLED
5 1000T 128 4 DISABLED
6 1000T 128 4 DISABLED
7 GBIC 128 4 DISABLED
8 GBIC 128 4 DISABLED
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select
Parameter Default Description
2-36
Fast forwarding
mode of all
DISABLED Allows you to enable or disable fast
forwarding for all ports on the switch.
ports
Type Shows port types as:
1000T - 1000BASE-T
1000SX - 1000BASE-SX
GBIC - 1000BASE-SX or 1000BASE-LX
transceiver
Page 53

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Parameter Default Description
Priority 128 Defines the priority for the use of a
port in the STA algorithm. If the path
cost for all ports on a switch are the
same, the port with the highest
priority (i.e., lowest value) will be
configured as an active link in the
spanning tree. When more than one
port is assigned the highest priority,
the port with lowest numeric
identifier will be enabled.
The range is 0 - 255.
(Path) Cost 100/19/4 This parameter is used by the STA
algorithm to determine the best path
between devices. Therefore, lower
values should be assigned to ports
attached to faster media, and higher
values assigned to ports with slower
media.
(Path cost takes precedence over port
priority.)
The default and recommended range
is:
Ethernet: 100 (50~600)
Fast Ethernet: 19 (10~60)
Gigabit Ethernet: 4 (3~10)
The full range is 0 - 65535.
2-37
Page 54

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Parameter Default Description
FastForwarding DISABLED This parameter is used to enable/
disable the Fast Spanning Tree mode
for the port. In this mode, ports skip
the Blocked, Listening and Learning
states and proceed straight to
Forwarding.
FastForwarding enables end-node
workstations and servers to overcome
time-out problems when the
Spanning Tree Algorithm is
implemented in a network. Therefore,
FastForwarding should only be
enabled for ports that are connected
to an end-node device.
2-38
Page 55

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Viewing the Current Spanning Tree Information
The Spanning Tree Information screen displays a summary of the
STA information for the overall bridge or for a specific port. To
make any changes to the parameters for the Spanning Tree, use
the Spanning Tree Configuration menu.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< Spanning Tree Information Menu >
Spanning Tree Bridge State
Spanning Tree Port State
<OK>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select.
Displaying the Spanning Tree Bridge State
The parameters shown in the following figure and table describe
the current Bridge STA Information.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< Spanning Tree Bridge State >
Bridge Priority : 32768
Hello Time (in seconds) : 2
Max Age (in seconds) : 20
Forward Delay (in seconds) : 15
Hold Time (in seconds) : 1
Designated Root : 32768.00E009090001
Root Cost : 0
Root Port : 0
Configuration Changes : 1
Topology Up Time : 1221951 (0 day 3 hr 23 min 39 sec)
<OK>
<Enter> to select.
2-39
Page 56

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Parameter Description
Priority Device priority is used in selecting the root device, root
Hello Time The time interval (in seconds) at which the root device
Max Age The maximum time (in seconds) a device can wait
port, and designated port. The device with the highest
priority becomes the STA root device. However, if all
devices have the same priority, the device with the
lowest MAC address will then become the root device.
transmits a configuration message.
without receiving a configuration message before
attempting to reconfigure.
Forward
Delay
Hold Time The minimum interval between the transmission of
Designated
Root
Root Cost The path cost from the root port on this switch to the
Root Port The number of the port on this switch that is closest to
Configuratio
n Changes
Topology
Up Time
The maximum time (in seconds) the root device will
wait before changing states (i.e., listening to learning to
forwarding).
consecutive Configuration BPDUs.
The priority and MAC address of the device in the
spanning tree that this switch has accepted as the root
device.
root device.
the root. This switch communicates with the root device
through this port. If there is no root port, then this
switch has been accepted as the root device of the
spanning tree network.
The number of times the spanning tree has been
reconfigured.
The time since the spanning tree was last reconfigured.
2-40
Page 57

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Displaying the Spanning Tree Port State
The parameters shown in the following figure and table are for
port STA Information.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< Spanning Tree Port State >
Port Type Status Designated Designated Designated
Cost Bridge Port
------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 1000T NO LINK 0 32768.00E009090001 128.1
2 1000T NO LINK 0 32768.00E009090001 128.2
3 1000T FORWARDING 0 32768.00E009090001 128.3
4 1000T NO LINK 0 32768.00E009090001 128.4
5 1000T NO LINK 0 32768.00E009090001 128.5
6 1000T NO LINK 0 32768.00E009090001 128.6
7 GBIC NO LINK 0 32768.00E009090001 128.7
8 GBIC NO LINK 0 32768.00E009090001 128.8
<OK>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select.
Parameter Description
Type Shows port types as:
1000T - 1000BASE-T
1000SX - 1000BASE-SX
GBIC - 1000BASE-SX or 1000BASE-LX transceiver
2-41
Page 58

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Parameter Description
Status Displays the current state of this port within the spanning
tree:
Disabled Port has been disabled by the user or has
failed diagnostics.
No Link There is no valid link on the port.
Blocking Port receives STA configuration messages,
but does not forward packets.
Listening Port will leave blocking state due to
topology change, starts transmitting
configuration messages, but does not yet
forward packets.
Learning Has transmitted configuration messages for
an interval set by the Forward Delay
parameter without receiving contradictory
information. Port address table is cleared,
and the port begins learning addresses.
Forwarding The port forwards packets, and continues
learning addresses.
The rules defining port status are:
• A port on a network segment with no other
STA-compliant bridging device is always forwarding.
• If two ports of a switch are connected to the same
segment and there is no other STA device attached to
this segment, the port with the smaller ID forwards
packets and the other is blocked.
• All ports are blocked when the switch is booted, then
some of them change state to listening, to learning,
and then to forwarding.
2-42
Designated
Cost
Designated
Bridge (ID)
The cost for a packet to travel from this port to the root
in the current spanning tree configuration. The slower
the media, the higher the cost.
The priority and MAC address of the device through
which this port must communicate to reach the root of
the spanning tree.
Page 59

Parameter Description
Designated
Port (ID)
The priority and number of the port on the designated
bridging device through which this switch must
communicate with the root of the spanning tree.
C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
2-43
Page 60

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Using a Mirror Port for Analysis
You can mirror traffic from any source port to a target port for
real-time analysis. You can then attach a network sniffer or RMON
probe to the target port and study the traffic crossing the source
port in a completely unobtrusive manner. When mirroring port
traffic, note that the target port must be configured in the same
VLAN as the source port (see “Configuring Virtual LANs” on page
2-55).
You can use the Mirror Port Configuration screen to designate a
single port pair for mirroring as shown below:
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< Mirror Port Configuration >
Mirror Source Port : Port 1
Mirror Target Port : Port 2
2-44
Status : DISABLED
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, other keys to make changes.
Parameter Description
Mirror Source Port The port whose traffic will be monitored.
Mirror Target Port The port that will duplicate or “mirror” all the
traffic happening on the monitored port.
Status Enables or disables the mirror function.
Page 61

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Configuring Port Trunks
Port trunks can be used to increase the bandwidth of a network
connection or to ensure fault recovery. You can configure up to
four trunk connections (combining 2~4 ports into a fat pipe)
between any two TigerSwitch 1000 switches. However, before
making any physical connections between devices, use the Trunk
Configuration menu to specify the trunk on the devices at both
ends. When using a port trunk, note that:
• Ports can only be assigned to one trunk.
• The ports at both ends of a connection must be configured as
trunk ports.
• The ports at both ends of a trunk must be configured in an
identical manner, including duplex mode, and VLAN
assignments.
• None of the ports in a trunk can be configured as a mirror
source port or mirror target port.
• All the ports in a trunk have to be treated as a whole when
moved from/to, added or deleted from a VLAN.
• The Spanning Tree Algorithm will treat all the ports in a trunk
as a whole.
• Enable the trunk prior to connecting any cable between the
switches to avoid creating a loop.
• Disconnect all trunk port cables or disable the trunk ports
before removing a port trunk to avoid creating a loop.
2-45
Page 62

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
You can use the Port Trunking Configuration screen to set up port
trunks as shown
below. Remember that you must “Enable” a new
configuration before it will take effect.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< Port Trunking Configuration >
Trunk ID Status Member List
1 2 3 4
--------- -------- ----------- ----------- ----------- -----------
-- -------- Port : -- Port : -- Port : -- Port : --
-- -------- Port : -- Port : -- Port : -- Port : --
-- -------- Port : -- Port : -- Port : -- Port : --
Trunk ID : 1 Trunk ID : 1 Member Port : 1
[Show] [More]
[Enable] [Disable] [Add] [Delete]
<OK>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, other keys to make changes.
Parameter Description
Trunk ID Configure up to four trunks per switch (ID of 1~4).
Port Select from 2~4 ports per trunk.
2-46
[Show] Displays trunk settings, where the first trunk listed
is specified by “Sorted by Trunk ID.”
[More] Scrolls through the list of configured trunks.
[Enable] [Disable] Enables/disables the selected trunk.
Page 63

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
IGMP Multicast Filtering
Multicasting is used to support real-time applications such as video
conferencing or streaming audio. A multicast server does not have
to establish a separate connection with each client. It merely
broadcasts its service to the network, and any hosts which want to
receive the multicast register with their local multicast switch/
router. Although this approach reduces the network overhead
required by a multicast server, the broadcast traffic must be
carefully pruned at every multicast switch/router it passes through
to ensure that traffic is only passed on the hosts which subscribed
to this service.
This switch uses IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) to
query for any attached hosts who want to receive a specific
multicast service. The switch looks up the IP Multicast Group used
for this service and adds any port which received a similar request
to that group. It then propagates the service request on to any
neighboring multicast switch/router to ensure that it will continue
to receive the multicast service. (For more information, see “IGMP
Snooping” on page 4-7.)
2-47
Page 64

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Configuring IGMP
This protocol allows a host to inform its local switch/router that it
wants to receive transmissions addressed to a specific multicast
group. You can use the IGMP Configuration screen to configure
multicast filtering shown below:
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< IGMP Configuration >
IGMP Status : DISABLED
IGMP Query Count : 2
IGMP Report Delay (Seconds) : 10
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, <Space> to scroll options.
Parameter Description
IGMP Status If enabled, the switch will monitor network traffic
to determine which hosts want to receive multicast
traffic.
IGMP Query
Count
The maximum number of queries issued for which
there has been no response before the switch
takes action to solicit reports.
IGMP Report
Delay
The time (in seconds) between receiving an IGMP
Report for an IP multicast address on a port before
the switch sends an IGMP Query out of that port
and removes the entry from its list.
Note: The default values are indicated in the sample screen.
2-48
Page 65

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Configuring Broadcast Storm Control
Use the Broadcast Storm Control Configuration screen to enable
broadcast storm control for any port on the switch, as shown
below.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< Broadcast Storm Control Configuration >
Broadcast control on all ports : [Enable] [Disable]
Port Threshold Broadcast Control
------------------------------------------------------ 1 500 ENABLED
2 500 ENABLED
3 500 ENABLED
4 500 ENABLED
5 500 ENABLED
6 500 ENABLED
7 500 ENABLED
8 500 ENABLED
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select
Parameter Description
Broadcast control on
all ports
Threshold The packet-per-second threshold for broadcast
Allows you to enable/disable broadcast storm
control for all ports on the switch.
packets on the port.
(Default is 500 pps.)
Broadcast Control Enables/disables broadcast control for the port.
When enabled, the switch will employ a
broadcast-control mechanism if the
packet-per-second threshold is exceeded. This
mechanism limits the amount of broadcasts passed
by the port to half of the received
packet-per-second count. The control mechanism
remains in effect until the number of received
broadcasts falls back below the packet-per-second
threshold. (Default is Enabled.)
2-49
Page 66

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Port Security Configuration
Use the Port Security Configuration screen to enable and configure
port security for the switch. Port Security allows you to configure
each port with a list of MAC addresses of devices that are
authorized to access the network through that port.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< Port Security Configuration >
MAC Address MAC Address
--------------------------------------------------
Secure address count : 0
Port : 1 MAC : 00-00-00-00-00-00
[Show] [More] [Add] [Delete]
Mode:DISABLE [Apply] [Clear]
<OK>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select
2-50
Parameter Description
MAC Address A list of the authorized MAC addresses that can
access the network through the specified port.
Secure address
count
The number of authorized MAC addresses for
the specified port.
Port Numeric identifier for switch port.
[Show] Displays authorized MAC addresses for the
specified port.
[More] Displays more MAC addresses for the port.
Page 67

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Parameter Description
Mode Port security can be set to three states; Static,
Disable, or Learning. When set to Static, the
switch will drop packets from the port if the
source MAC address does not match one of the
addresses in the MAC Address list. If set to
Learning, the switch will add the source MAC
address of all packets received on the port to the
authorized MAC Address list.
[Apply] Applies a change of Mode to the port.
MAC A specific MAC address to be added or deleted
[Add] Adds a new MAC address to the current list.
[Delete] Removes a MAC address from the current list.
[Clear] Clears all the MAC addresses for the current port.
from the list.
2-51
Page 68

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Configuring Bridge MIB Extensions
The Bridge MIB includes extensions for managed devices that
support Traffic Classes, Multicast Filtering and Virtual LANs. To
configure these extensions, use the Extended Bridge Configuration
screen as shown below:
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< Extended Bridge Configuration >
Bridge Capability : (Read Only)
Extended Multicast Filtering Services : NO
Traffic Classes : YES
Static Entry Individual Port : YES
VLAN Learning : SVL
Configurable PVID Tagging : YES
Local VLAN Capable : NO
Bridge Settings :
Traffic Classes : TRUE
GMRP : DISABLED
GVRP : DISABLED
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, <Space> to scroll options.
2-52
Parameter Description
Bridge Capability
Extended
Multicast
Filtering
Services
Indicates that the switch does not support the
filtering of individual multicast addresses based on
GMRP (GARP Multicast Registration Protocol).
Note that this function is not implemented for the
current firmware release.
Traffic Classes Indicates that the switch provides mapping of user
priorities to multiple traffic classes. (Refer to
802.1P Configuration.)
Page 69

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Parameter Description
Static Entry
Individual Port
VLAN Learning This switch uses Shared VLAN Learning (SVL),
Indicates that the switch allows static filtering for
unicast and multicast addresses. (Refer to Network
Monitor Menu / Static Unicast Address Table
Configuration and Static Multicast Address Table
Configuration.)
whereby all ports share the same VLAN filtering
database.
Configurable
PVID Tagging
Local VLAN
Capable
Bridge Settings
Traffic Class* Multiple traffic classes are supported by this switch
GMRP* GARP Multicast Registration Protocol (GMRP)
GVRP* GARP VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP) defines
* Not implemented in the current firmware release.
Indicates that the switch allows you to override the
default PVID setting (Port VLAN ID used in frame
tags) and its egress status (VLAN-Tagged or
Untagged) on each port. (Refer to 802.1Q VLAN
Port Configuration.)
This switch does not support multiple local
bridges (that is, multiple Spanning Trees).
as indicated under Bridge Capabilities. However,
you can disable this function by setting this
parameter to False.
allows network devices to register endstations
with multicast groups.
The Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP)
is currently used by this switch to provide
automatic multicast filtering.
a way for switches to exchange VLAN information
in order to register necessary VLAN members on
ports across the network. This function should be
enabled to permit VLANs groups which extend
beyond the local switch.
2-53
Page 70

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Configuring Traffic Classes
IEEE 802.1p defines up to 8 separate traffic classes. This switch
supports Quality of Service (QoS) by using two priority queues,
with Weighted Fair Queuing for each port. You can use the 802.1P
Configuration menu to configure the default priority for each port,
or to display the mapping for the traffic classes as described in the
following sections.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< 802.1P Configuration >
802.1P Port Priority Configuration
802.1P Port Traffic Class Information
<Ok>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select.
2-54
Page 71

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Port Priority Configuration
The default priority for all ingress ports is zero. Therefore, any
inbound frames that do not have priority tags will be placed in the
low priority output queue. Default priority is only used to
determine the output queue for the current port; no priority tag is
actually added to the frame. You can use the 802.1P Port Priority
Configuration menu to adjust default priority for any port as
shown below:
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< 802.1P Port Priority Configuration >
Port Default Ingress Number of Egress
User Priority Traffic Class
---------------------------------------------- 1 0 2
2 0 2
3 0 2
4 0 2
5 0 2
6 0 2
7 0 2
8 0 2
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, other keys to make changes.
Parameter Description
Port Numeric identifier for switch port.
Default Ingress
User Priority
Default priority can be set to any value from 0~7,
where 0~3 specifies the low priority queue and
4~7 specifies the high priority queue.
Number of Egress
Traffic Classes
Indicates that this switch supports two priority
output queues.
2-55
Page 72

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
802.1P Port Traffic Class Information
This switch provides two priority levels with weighted fair queuing
for port egress. This means that any frames with a default or user
priority from 0~3 are sent to the low priority queue “0” while those
from 4~7 are sent to the high priority queue “1” as shown in the
following screen:
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< 802.1P Port Traffic Class Information >
Port User Priority
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7
---------------------------------------------------- 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1
2 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1
3 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1
4 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1
5 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1
6 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1
7 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1
8 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1
<OK>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select.
2-56
Parameter Description
Port Numeric identifier for switch port.
User Priority Shows that user priorities 0~3 specify the low
priority queue and 4~7 specify the high priority
queue.
Page 73

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Configuring Virtual LANs
You can use the VLAN configuration menu to assign any port on
the switch to any of up to 256 LAN groups. In conventional
networks with routers, broadcast traffic is split up into separate
domains. Switches do not inherently support broadcast domains.
This can lead to broadcast storms in large networks that handle a
lot of IPX and NetBEUI traffic. By using IEEE 802.1Q compliant
VLANs and GARP VLAN Registration Protocol, you can organize
any group of network nodes into separate broadcast domains,
confining broadcast traffic to the originating group. This also
provides a more secure and cleaner network environment. For
more information on how to use VLANs, see “Virtual LANs” on
page 4-3. The VLAN configuration screens are described in the
following sections.
802.1Q VLAN Base Information
The 802.1Q VLAN Base Information screen displays basic
information on the VLAN type supported by this switch.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< 802.1Q VLAN Base Information >
VLAN Version Number : 1
MAX VLAN ID : 2048
MAX Supported VLANs : 256
Current Number of 802.1Q VLANs Configured : 1
<OK>
<Enter> to select.
2-57
Page 74

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Parameter Description
VLAN Version
Number
MAX VLAN ID Maximum VLAN ID recognized by this switch.
The VLAN version used by this switch as specified
in the IEEE 802.1Q standard.
MAX Supported
VLANs
Current Number
of VLANs
Configured
Maximum number of VLANs that can be
configured on this switch.
The number of VLANs currently configured on this
switch.
Note: All ports are assigned only to VLAN 1 by default.
2-58
Page 75

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
802.1Q VLAN Current Table Information
This screen shows the current port members of each VLAN and
whether or not the port supports VLAN tagging. Ports assigned to a
large VLAN group that crosses several switches should use VLAN
tagging. However, if you just want to create a small port-based
VLAN for one or two switches, you can assign ports to the same
untagged VLAN (page 2-61). The current configuration is shown in
the following figure.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< 802.1Q VLAN Current Table Information >
Deleted VLAN Entry Counts : 0
VID Creation Time Status
--------------------------------------------------------------- 1 0 (0 day 0 hr 0 min 0 sec) Permanent
Current Egress Ports Current Untagged Ports
11111111 11111111
Sorted by VID : 1
[Show] [More]
<OK>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select
Port 1 Port 8
Parameter Description
Deleted VLAN Entry
Counts
The number of times a VLAN entry has been
deleted from this table.
VID The ID for the VLAN currently displayed.
Creation Time The value of sysUpTime (System Up Time)
when this VLAN was created.
2-59
Page 76

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Parameter Description
Status Shows how this VLAN was added to the
switch:
Dynamic GVRP: Automatically learned via
GVRP.
Permanent: Added as a static entry.
Current Egress Ports Shows the ports which have been added to
Current Untagged
Ports
[Show] Displays the members for the VLAN indicated
[More] Displays any subsequent VLANs if configured.
the displayed VLAN group, where “1”
indicates that a port is a member and “0” that
it is not.
If a port has been added to the displayed
VLAN (see Current Egress Ports), its entry in
this field will be “1” if the port is untagged or
“0” if tagged.
by the “Sorted by VID” field.
802.1Q VLAN Static Table Configuration
Use this screen to create a new VLAN or modify the settings for an
existing VLAN. You can add/delete port members for a VLAN, or
prevent a port from being automatically added to a VLAN via the
GVRP protocol. (Also, note that all ports can only belong to one
untagged VLAN. This is set to VLAN 1 by default, but can be
changed via the 802.1Q VLAN Port Configuration screen on page
2-60
Page 77

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
2-61.)
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< 802.1Q VLAN Static Table Configuration >
VID VLAN Name Status
----------------------------- 1 Active
Egress Ports Forbidden Egress Ports
11111111 00000000
Untagged Ports
11111111 VID : 1
[Show]
[More]
[New]
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, other keys to make changes.
Parameter Description
VID The ID for the VLAN currently displayed.
Range: 1-2048
VLAN Name A user-specified symbolic name for this VLAN.
String length: Up to 8 alphanumeric characters
Status Sets the current editing status for this VLAN as:
Not in Service, Destroy, or Active.
Egress Ports Set the entry for any port in this field to “1” to add
it to the displayed VLAN, or “0” to remove it from
the VLAN.
Forbidden Egress
Ports
Prevents a port from being automatically added to
this VLAN via GVRP.
Untagged Ports Set the entry for any port in this field to “1” to add
it to the displayed VLAN as an untagged port.
[Show] Displays settings for the specified VLAN.
[More] Displays consecutively numbered VLANs.
2-61
Page 78

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Parameter Description
[New] Sets up the screen for configuring a new VLAN.
Note: No VLANs are statically configured by default.
2-62
Page 79

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
For example, the following screen displays settings for VLAN 2,
which includes tagged ports 1-4, and forbidden port 8.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< 802.1Q VLAN Static Table Configuration >
VID VLAN Name Status
----------------------------- 2 Active
Egress Ports Forbidden Egress Ports
11110000 00000001
Untagged Ports
00000000 VID : 2
[Show]
[More]
[New]
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, other keys to make changes.
2-63
Page 80

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
802.1Q VLAN Port Configuration
Use this screen to configure port-specific settings for IEEE 802.1Q
VLAN features.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< 802.1Q VLAN Port Configuration >
Port PVID Acceptable Ingress GVRP GVRP Failed GVRP Last
Frame Type Filtering Status Registrations PDU Origin
------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 1 All FALSE DISABLED 0 00-00-00-00-00-00
2 1 All FALSE DISABLED 0 00-00-00-00-00-00
3 1 All FALSE DISABLED 0 00-00-00-00-00-00
4 1 All FALSE DISABLED 0 00-00-00-00-00-00
5 1 All FALSE DISABLED 0 00-00-00-00-00-00
6 1 All FALSE DISABLED 0 00-00-00-00-00-00
7 1 All FALSE DISABLED 0 00-00-00-00-00-00
8 1 All FALSE DISABLED 0 00-00-00-00-00-00
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, other keys to make changes.
Parameter Description
2-64
PVID The VLAN ID assigned to untagged frames
received on this port. Use the PVID to assign ports
to the same untagged VLAN.
Acceptable Frame
1
Type
This switch accepts “All” frame types, including
VLAN tagged or VLAN untagged frames. Note that
all VLAN untagged frames received on this port are
assigned to the PVID for this port.
1
Ingress Filtering
If set to “True,” incoming frames for VLANs which
do not include this port in their member set will be
discarded at the inbound port.
Page 81

Parameter Description
GVRP Status
2
Enables or disables GVRP for this port. When
disabled, any GVRP packets received on this port
will be discarded and no GVRP registrations will
be propagated from other ports.
Note that GVRP must be enabled for the switch
before this setting can take effect. (See Switch
Configuration Menu / Extended Bridge
Configuration.)
C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
GVRP Failed
Registrations
2
GVRP Last PDU
2
Origin
The total number of failed GVRP registrations, for
any reason, on this port.
The Source MAC Address of the last GVRP
message received on this port.
1. This control does not affect VLAN independent BPDU frames, such as
GVRP or STP. However, it does affect VLAN dependent BPDU
frames, such as GMRP.
2. GVRP is not available for the current firmware release.
2-65
Page 82

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Monitoring the Switch
The Network Monitor Menu provides access to port statistics,
RMON statistics, IP multicast addresses, and the static (unicast)
address table. Each of the screens provided by these menus is
described in the following sections.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< Network Monitor Menu >
Port Statistics
RMON Statistics
Unicast Address Table
Multicast Address Registration Table
IP Multicast Registration Table
Static Unicast Address Table Configuration
Static Multicast Address Table Configuration
<OK>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select.
2-66
Parameter Description
Port Statistics Displays statistics on network traffic passing
through the selected port.
RMON Statistics Displays detailed statistical information for the
selected port such as packet type and frame size
counters.
Unicast
Address Table
Provides full listing of all unicast addresses stored
in the switch, as well as sort, search and clear
functions.
Multicast Address
Registration
Displays the ports that belong to each GMRP
Muticast group.
Table*
Page 83

Parameter Description
IP Multicast
Registration Table
Static Unicast
Address Table
Configuration
Displays the ports that belong to each IP Muticast
group.
Allows you to display or configure static unicast
addresses.
C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Static Multicast
Address Table
Configuration*
* Not implemented in the current firmware release.
Allows you to display or configure static GMRP
multicast addresses.
2-67
Page 84

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Displaying Port Statistics
Port Statistics display key statistics from the Ethernet-like MIB for
each port. Error statistics on the traffic passing through each port
are displayed. This information can be used to identify potential
problems with the switch (such as a faulty port or unusually heavy
loading). The values displayed have been accumulated since the
last system reboot.
Select the required port. The statistics displayed are indicated in
the following figure and table.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< Port Statistics > Port 1
Ether Like Counter :
Alignment Errors : 0 Late Collisions : 0
FCS Errors : 0 Excessive Collisions : 0
Single Collision Frames : 0 Internal Mac Transmit Errors: 0
Multiple Collision Frames: 0 Carrier Sense Errors : 0
SQE Test Errors : 0 Frame Too Longs : 0
Deferred Transmissions : 0 Internal Mac Receive Errors : 0
[Refresh Statistics] [Reset Counters]
2-68
<OK> <PREV PORT> <NEXT PORT>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select
Parameter Description
Alignment Errors The number of frames received that are not an
integral number of octets in length and do not pass
the FCS check.
FCS Errors The number of frames received that are an integral
number of octets in length but do not pass the FCS
check.
Page 85

Parameter Description
Single Collision
Frames*
The number of successfully transmitted frames for
which transmission is inhibited by exactly one
collision.
C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Multiple Collision
Frames*
SQE Test Errors* A count of times that the SQE TEST ERROR
Deferred
Transmissions*
Late Collisions The number of times that a collision is detected
Excessive
Collisions*
Internal Mac
Transmit Errors*
Carrier Sense
Errors*
Frame Too Longs The number of frames received that exceed the
Internal Mac
Receive Errors
* The reported values will always be zero because these statistics are not
supported by the internal chip set.
A count of successfully transmitted frames for
which transmission is inhibited by more that one
collision.
message is generated by the PLS sublayer.
A count of frames for which the first transmission
attempt on a particular interface is delayed
because the medium was busy.
later than 512 bit-times into the transmission of a
packet.
The number of frames for which transmission
failed due to excessive collisions.
The number of frames for which transmission
failed due to an internal MAC sublayer transmit
error.
The number of times that the carrier sense
condition was lost or never asserted when
attempting to transmit a frame.
maximum permitted frame size.
The number of frames for which reception failed
due to an internal MAC sublayer receive error.
2-69
Page 86

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Displaying RMON Statistics
Use the RMON Statistics screen to display key statistics for each
port from RMON group 1. (RMON groups 2, 3 and 9 can only be
accessed using SNMP management software.) The following
screen displays the overall statistics on traffic passing through each
port. RMON statistics provide access to a broad range of statistics,
including a total count of different frame types and sizes passing
through each port. Values displayed have been accumulated since
the last system reboot.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< RMON Statistics > Port 1
Drop Events : 4 Jabbers : 0
Received Bytes : 438387005 Collisions : 0
Received Frames : 2470786 64 Byte Frames : 715132
Broadcast Frames : 2180266 65-127 Byte Frames : 868284
Multicast Frames : 237352 128-255 Byte Frames : 502964
CRC/Alignment Errors : 0 256-511 Byte Frames : 379998
Undersize Frames : 172 512-1023 Byte Frames : 671
Oversize Frames : 0 1024-1518 Byte Frames : 3565
Fragments : 0
[Refresh Statistics] [Reset Counters]
2-70
<OK> <PREV PORT> <NEXT PORT>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select
Parameter Description
Drop Events The total number of events in which packets were
dropped due to lack of resources.
Received Bytes Total number of bytes of data received on the
network. This statistic can be used as a reasonable
indication of Ethernet utilization.
Received Frames The total number of frames (bad, broadcast and
multicast) received.
Page 87

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Parameter Description
Broadcast Frames The total number of good frames received that
were directed to the broadcast address. Note that
this does not include multicast packets.
Multicast Frames The total number of good frames received that
CRC/Alignment
Errors
Undersize Frames The total number of frames received that were less
Oversize Frames The total number of frames received that were
Fragments The total number of frames received that were less
Jabbers The total number of frames received that were
Collisions The best estimate of the total number of collisions
64 Byte Frames The total number of frames (including bad
were directed to this multicast address.
The number of frames received with CRC/
alignment errors (FCS or alignment errors).
than 64 octets long (excluding framing bits, but
including FCS octets) and were otherwise well
formed.
longer than 1518 octets (excluding framing bits,
but including FCS octets) and were otherwise well
formed.
than 64 octets in length (excluding framing bits,
but including FCS octets) and had either an FCS or
alignment error.
longer than 1518 octets (excluding framing bits,
but including FCS octets), and had either an FCS
or alignment error.
on this Ethernet segment.
packets) received and transmitted that were 64
octets in length (excluding framing bits but
including FCS octets).
65-127 Byte
Frames
The total number of frames (including bad
packets) received and transmitted that were
between 65 and 127 octets in length inclusive
(excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
2-71
Page 88

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Parameter Description
128-255 Byte
Frames
The total number of packets (including bad
packets) received and transmitted that were
between 128 and 255 octets in length inclusive
(excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
1024-1518 Byte
Frames
The total number of packets (including bad
packets) received and transmitted that were
between 1024 and 1518 octets in length inclusive
(excluding framing bits but including FCS octets).
2-72
Page 89

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Displaying the Unicast Address Table
The Address Table contains the MAC addresses and VLAN
identifier associated with each port (that is, the source port
associated with the address and VLAN), sorted by MAC address or
VLAN ID. You can search for a specific address, clear the entire
address table, or information associated with a specific address, or
set the aging time for deleting inactive entries. The information
displayed in the Address Table is indicated in the following figure
and table.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< Unicast Address Table >
Aging Time : 300 Dynamic Counts : 146 Static Counts : 0
MAC VID Port Status MAC VID Port Status
-------------------------------------------------------------------- 00-00-24-B3-28-83 1 8 D 00-00-E8-00-00-02 1 8 D
00-00-E2-12-F9-F8 1 8 D 00-00-E8-00-00-05 1 8 D
00-00-E2-16-C5-82 1 8 D 00-00-E8-00-00-96 1 8 D
00-00-E2-20-C3-D5 1 8 D 00-00-E8-00-01-01 1 8 D
00-00-E2-21-74-D0 1 8 D 00-00-E8-07-12-5E 1 8 D
00-00-E2-2A-59-9A 1 8 D 00-00-E8-11-03-51 1 8 D
00-00-E2-2E-FD-F6 1 8 D 00-00-E8-11-11-33 1 8 D
00-00-E8-00-00-00 1 8 D 00-00-E8-12-12-12 1 8 D
Sorted by : MAC + VID Cleared by : MAC + VID
VLAN ID : 1 VLAN ID : 1
MAC : 00-00-00-00-00-00 MAC : 00-00-00-00-00-00
[Show] [More] [Clear] [Clear Dynamic]
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, other keys to make changes.
Parameter Description
Aging Time Time-out period in seconds for aging out
dynamically learned forwarding information.
Range: 10 - 65534 seconds; Default: 300 seconds
Dynamic Counts The number of dynamically learned addresses in
the table.
Static Counts The number of static addresses in the table.
MAC The MAC address of a node.
VID The VLAN(s) associated with this address or port.
2-73
Page 90

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Parameter Description
Port The port whose address table includes this MAC
Status Indicates address status as:
[Show] Displays the address table based on specified
[More] Scrolls through the entries in the address table.
[Clear] Clears the specified MAC address.
address.
D: Dynamically learned, or
P: Fixed permanently by SNMP network
management software.
VLAN ID, and sorted by primary key MAC or VID.
[Clear Dynamic] Clears all dynamically learned MAC addresses in
the table.
2-74
Page 91

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Displaying the IP Multicast Registration Table
Use the IP Multicast Registration Table to display all the multicast
groups active on this switch, including multicast IP addresses and
the corresponding VLAN ID.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< IP Multicast Registration Table >
VID Multicast IP Dynamic Port Lists Learned by
------------------------------------------------------------------------
Sorted by : VID + Multicast IP
VID : 1
Multicast IP :
[Show] [More]
<OK>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select
Parameter Description
VID VLAN ID assigned to this multicast group.
Multicast IP IP address for specific multicast services.
Dynamic Port
Lists
The switch ports registered for the indicated
multicast service.
Learned by Indicates if the ports were learned dynamically or
via IGMP.
[Show] Displays the address table sorted on VID and then
Multicast IP.
[More] Scrolls through the entries in the address table.
2-75
Page 92

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Configuring Static Unicast Addresses
Use the Static Unicast Address Table Configuration screen to
manually configure host MAC addresses in the unicast table. You
can use this screen to associate a MAC address with a specific
VLAN ID and switch port as shown below.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< Static Unicast Address Table Configuration >
VID MAC Address Port Status
------------------------------------------------------------
Sorted by : VID + MAC VID : 1 MAC : 00-00-00-00-00-00
VID : 1 Port : 1
MAC : 00-00-00-00-00-00 Status : Permanent
[Show] [More] [Set]
<OK>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move. <Enter> to select
Parameter Description
2-76
VID The VLAN group this port is assigned to.
MAC Address The MAC address of a host device attached to this
switch.
Port The port the host device is attached to.
Page 93

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Parameter Description
Status The status for an entry can be set to:
Permanent: This entry is currently in use and
will remain so after the next reset of
the switch.
DeleteOnReset: This entry is currently in use and
Invalid: Removes the corresponding entry.
DeleteOnTimeOut:This entry is currently in use
Other: This entry is currently in use but the
will remain so until the next reset.
and will remain so until it is aged
out. (Refer to Address Table Aging
Time on page 2-70.)
conditions under which it will
remain so differ from the preceding
values.
[Show] Displays the static address table sorted on VID as
[More] Scrolls through entries in the static address table.
[Set] Adds the specified entry to the static address table,
the primary key and MAC address as secondary
key.
such as shown in the following example:
VID : 1 MAC : 00-00-00-e8-34-22
Port : : 1
Status : Permanent
2-77
Page 94

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Resetting the System
Select the Reset System Menu under the Main Menu to reset the
switch. The reset screen includes options as shown in the
following figure and table.
SMC TigerSwitch 1000 Local Management -- SMC8606T
< Reset System Menu >
Restart Option :
POST : YES
Reload Factory Defaults : NO
Keep IP Setting : NO
Keep User Authentication : NO
[Restart]
<APPLY> <OK> <CANCEL>
Use <TAB> or arrow keys to move, <Space> to scroll options.
2-78
Parameter Description
POST Runs the Power-On Self-Test
Reload Factory
Reloads the factory defaults
Defaults
Keep IP Setting Retains the settings defined in the IP Configuration
menu.
Keep User
Authentication
Retains the user names and passwords defined in
the Console Login Configuration menu.
Page 95

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
Logging Off the System
Use the Quit Current Session command under the Main Menu to
exit the configuration program and terminate communications with
the switch for the current session.
2-79
Page 96

C
ONSOLE INTERFACE
2-80
Page 97

C
HAPTER
W
EB INTERFACE
3
Web-Based Configuration and Monitoring
In addition to the menu-driven system configuration program, this
switch also provides an embedded HTTP Web agent. Using a Web
browser you can configure the switch and view statistics to monitor
network activity. The Web agent can be accessed by any computer on
the network using a standard Web browser (Internet Explorer 4.0 or
above, or Netscape Navigator 4.0 or above).
Prior to accessing the switch from a Web browser, be sure you have
first performed the following tasks:
1. Configure it with a valid IP address, subnet mask, and default
gateway using an out-of-band serial connection or BOOTP
protocol.
2. Set a user name and password using an out-of-band serial
connection. Access to the Web agent is controlled by the same
user name and password as the onboard configuration program.
3-1
Page 98
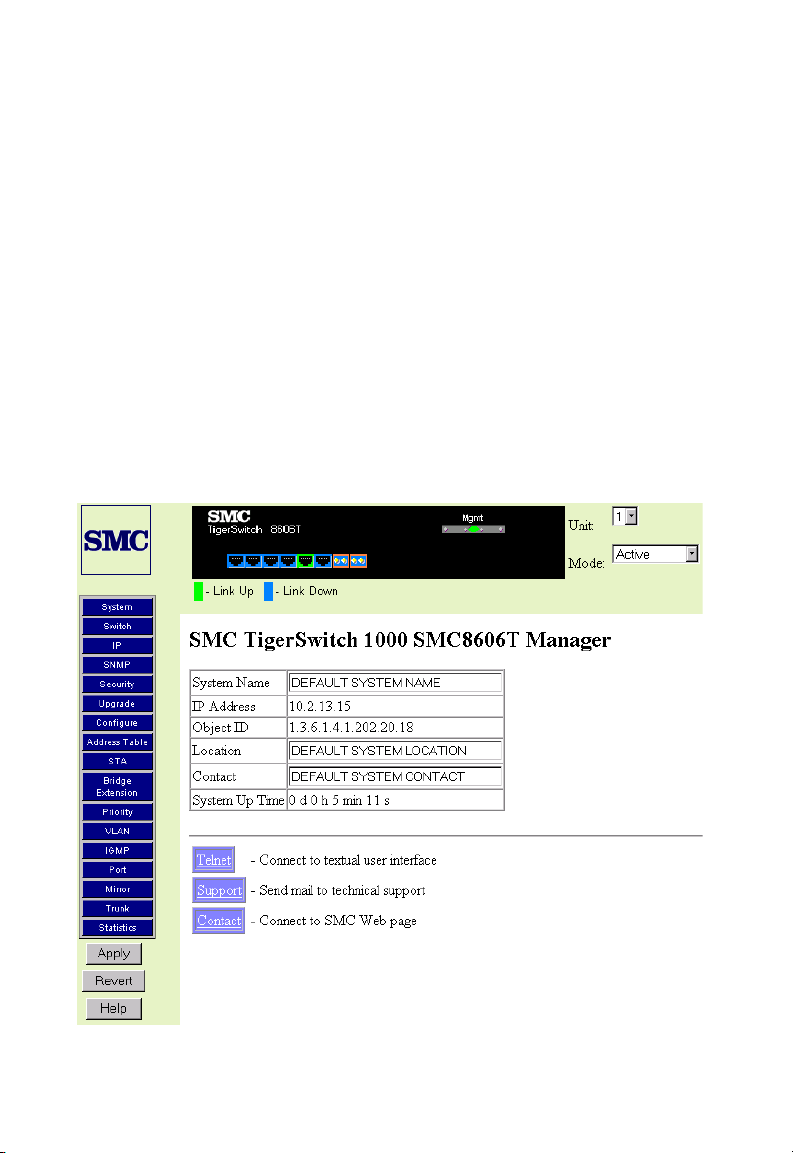
WEB I
NTERFACE
Navigating the Web Browser Interface
To access the Web-browser interface you must first enter a user name
and password. The administrator has Read/Write access to all
configuration parameters and statistics. The default user name for the
administrator is “admin,” with no password.
Home Page
When your Web browser connects with the switch’s Web agent, the
home page is displayed as shown below. The home page displays the
Main Menu on the left side of the screen and System Information on
the right side. The Main Menu links are used to navigate to other
menus and display configuration parameters and statistical data.
3-2
Page 99

WEB I
If this is your first time to access the management agent, you should
define a new Administrator password, record it and put it in a safe
place. From the Main Menu, select Security and enter a new password
for the Administrator. Note that passwords can consist of up to 11
alphanumeric characters and are not case sensitive.
Note: Based on the default configuration, a user is allowed three
attempts to enter the correct password; on the third failed
attempt the current connection is terminated. See “Console
Login Configuration” on page 2-22.
Configuration Options
Configurable parameters have a dialog box or a drop-down list. Once
a configuration change has been made on a page, be sure to click on
the “Apply” button at the bottom of the page to confirm the new
setting. The following table summarizes the Web page configuration
buttons.
Web Page Configuration Buttons
Button Action
Apply Sets specified values in the SNMP agent.
NTERFACE
Revert Cancels specified values prior to pressing the “Apply”
Refresh Immediately updates values from the SNMP agent.
button.
Notes: 1. To ensure proper screen refresh, be sure that Internet
Explorer 5.0 is configured as follows: Under the menu
“Tools / Internet Options / General / Temporary
Internet Files / Settings,” the setting for item “Check for
newer versions of stored pages” should be “Every visit to
the page.”
2. When using Internet Explorer 5.0, you may have to
manually refresh the screen after making configuration
changes by pressing the browser’s refresh button.
3-3
Page 100

WEB I
NTERFACE
Panel Display
The Web agent displays an image of the switch’s ports, showing port
links and activity. Clicking on the image of a port displays statistics
and configuration information for the port. Clicking on the image of
the serial port (labeled “Mgmt”) displays the Console Configuration
screen. Clicking on any other part of the front panel displays Switch
Information as described on page 3-9.
Port State Display
Click on any port to display a summary or port status as shown
below, as well as Etherlike statistics (page 3-53) and RMON
statistics (page 3-55).
Parameter Description
Type Shows port type as 1000Base-SX, 1000Base-T, or
1000Base-GBIC
Admin Status Shows if the port is enabled, or has been disabled due to
abnormal behavior or for security reasons. See “Port
Configuration” on page 3-46.
Link Status Indicates if the port has a valid connection to an external
Speed Status Indicates the current port speed.
device.
3-4
 Loading...
Loading...