Page 1

Doc. No. CE
※-
OMP0016-A
OPERATION MANUAL
READ THIS OPERATION MANUAL CAREFULLY BEFORE USE IT.
NEVER INSTALL THE PRODUCT UNTIL FINISH READING THIS MANUAL.
KEEP THIS MANUAL ALL THE TIME FOR YOUR REFERENCE.
PRODUCT NAME
:
HYRODLESS MONOSASHI-KUN
MODEL :
ML2B Series
Page 2

2
Contents
Chapter 1: Read Before Use ·····························································4~9
Chapter 2: General Description/Features
2-1. General Description ··································································· 10
2-2. Features ·················································································· 10
Chapter 3: System Configuration
3-1. System Configuration ································································ 11
3-2. Example of System Configuration ········································ 11~12
3-3. Pneumatic Circuit ······························································· 13~14
Chapter 4: Operating Principle
4-1. Operating Principle of Brake ······················································· 15
Chapter 5: Selecting Procedure
5-1. Precaution················································································ 16
5-2. Selecting Procedure ·································································· 17
5-3. Selection Information ·························································· 18~19
5-4. Example of Selection ·························································· 20~21
Chapter 6: Specifications
6-1. Cylinder Specifications ······························································· 22
6-2. Sensor Specifications ································································ 22
Chapter 7: How to Order
7-1. Cylinder ··················································································· 23
7-2. Controller / 3 Points Preset Counter············································· 23
7-3. Extension Cable········································································ 24
7-4. Specifications of Made to Order ML2B ·································· 24~25
Chapter 8: External Dimension Drawing
8-1. Hyrodless Monosashi-kun (with Brake, scale) ······························· 26
8-2. Hyrodless Monosashi-kun (with Scale)········································· 27
8-3. Hyrodless Monosashi-kun (with Brake) ········································ 28
8-4. Hyrodless Monosashi-kun (with Shock Absorber) ·························· 29
8-5. Hyrodless Monosashi-kun (with Stroke Adjustment Unit, X416) ······· 30
8-6. Hyrodless Monosashi-kun (with Stroke Adjustment Unit, X417) ······· 31
Chapter 9: Construction / Parts List ······················································· 32
Chapter 10: Cushion Capacity
10-1. Cushion Selection ··································································· 33
10-2. Absorbing Capacity of Air Cushion, Stroke Adjustment Unit··········· 34
10-3. Adjusting Method····································································· 35
Page 3

3
Chapter 11: Stopping Operation
11-1. Over run ················································································· 36
11-2. Dispersion of Stopping Position ················································· 36
Chapter 12: Manual Operating Procedure ·············································· 37
Chapter 13: Installation / Wiring
13-1. Installation of Cylinder ······················································· 38~39
13-2. Electrical Wiring ······································································ 40
13-3. Connection of Extension Cable ················································· 41
Specifications are subject to change without prior notice
Page 4
4
Chapter 1: Read before Use
These safety instructions are intended to prevent a hazardous situation and/or equipment damage.
These instructions indicate the level of potential hazard by label of “Caution”, ”Warning”, or ”Danger”.
To ensure safety, follow the instructions below as well as ISO/IEC, JIS
*1)
and other safety laws
*2)
.
Caution
Operator error could result in injury or equipment damage.
Warning
Operator error could result in serious injury or loss of life.
Danger
In extreme conditions, there is a possible result of serious injury or
loss of life.
*1) ISO 4414: Pneumatic fluid power - General rules relating to systems
ISO 10218-1: 2006: Robots for industrial environments - Safety requirements - Part 1: Robot
IEC 60204-1: Safety of machinery - Electrical equipment of machines - Part 1:General
requirements
JIS B 8370: General Rules for Pneumatic s ystems
JIS B 9960-1: Safety of machinery - Electrical equipment of machines - Part 1: General
requirements
JIS B 8433-1:2007: Robots for industrial environments - Safety requirements - Part 1: Robot
*2) Labor Safety and Sanitation Law etc.
Warning
1. The compatibility of pneumatic equipment is the responsibility of the person who designs the
pneumatic system or decides its specifications.
Since the products specified here are used in various operating conditions, their compatibility for
the specific pneumatic system must be based on specifications or after analysis and/or tests to
meet your specific requirements. Ensuring the initial performance and safety are the responsibility
of the person who decides the compatibility of the pneumatic system. Pneumatic systems should be
constructed after full review of the details of the products other than specifications and possibilities
of failures by checking the latest product information.
2. Only trained personnel should operate poneumaticallly operated machinery and equipment.
Assembly, handling, or repair of pneumatic systems should be performed by trained and
experienced operators.
3. Do not service machinery/equipment or attempt to remove component until safety is confirmed.
a. Inspection and maintenance of machinery/equipment should only be performed after confirmation
of safe locked-out control positions.
b. When equipment is to be removed, confirm the safety process as mentioned above. Cut the
supply pressure for this equipment and exhaust all residual compressed air in the system.
c. Before machinery/equipment is re-started, take measure to prevent shooting-out of cylinder piston
rod etc.
4. Contact SMC and take necessary safety measures if the products are to be used in any of the
following conditions:
a. Conditions and environments beyond the given specifications, or if products are used outdoors.
b. Installation on equipment in conjunction with atomic energy, railway, air navigation, vehicles,
medical equipment, food and beverages, recreation equipment, emergency stop circuits, press
applications, or safety equipment.
c. An application which has the possibility of having negative effects on people, property, or animals,
requiring special safety analysis.
d. When used in an interlock circuit, dual interlock such as mechanical protection is necessary in
case of accident. Periodical inspection is also necessary to confirm proper operation.
! ! !
!
Page 5
5
Operating and Storage Environments
Warning
1. Envionments to avoid
Avoid using or storing the products in the
following environments which may cause
failures.
If the products need to be used or stored in
those environments, take necessary measures.
a. Place where ambient temperature exceeds
the range of 5℃ to 60℃.
b. Place where ambient humidity exceeds the
range of 35% to 85% RH.
c. Place where condensation occurs due to
sudden temperature change.
d. Place where atmosphere containing corrosive
gas, flammable gas or organic solvent.
e. Place where atmosphere containing
con-ductive powder such as dust and iron
chips, oil mist, salt, or organic solvent, or
splashing cutting chips, dust and cutting oil
(water , liquid) over the products.
f. Place where the products are exposed to
direct sunlight or radiated heat.
g. Place where strong electromagnetic noise is
generated (place where strong electric field,
strong magnetic field or surge is generated).
h. Place where static electricity is discharged or
condition that the products have electrostatic
discharge.
i. Place where strong high frequency is
gene-rated.
j. Place where damages of thunder are
expected.
k. Place where vibration or impact is directly
given to the products.
l. Condition that the products are deformed by
force or weight applied.
2. Do not close any objects which are affected
by magnets.
Since magnets are built in cylinders, do not close
magnetic disks, magnetic cards or magnetic
tapes. The data may be destroyed.
Precaution on Design
Warning
1. There is a possibility of dangerous sudden
action by cylinders if sliding parts of
machi-nery are twisted due to external forces,
etc.
In such cases, human injury may occur; e. g., by
catching hands or feet in the machinery, or
damage to the machinery itself may occur.
2. Provide a cover to minimize the risk of
human injury.
When a driven object or moving parts of a
cylinder may cause the risk of human injury,
design a structure to avoid contact with human
body.
3. Securely tighten all stationary parts and
connected parts of cylinders so that they will
not become loose.
Tighten cylinders securely especially when they
are used in high frequency or in locations where
direct vibration or impact shock, etc. will be
applied to the body of the cylinder.
4. Deceleration circuits or shock absorbers are
needed in some cases.
If a driven object travels at a high speed or is
heavy, impact will not be sufficiently absorbed
only with the cylinder cushion. In such cases,
use a circuit to decelerate the cylinder speed
before the cushion becomes effective or use
external shock absorbers to reduce impact. At
this time, take the rigidity of machinery into
account.
5. Consider possible drop of pressure in circuit
due to power outage.
For cylinders used in clamping mechanism, a
work may become loose due to less clamping
force by pressure drop in circuit at the time of
power outage. Install safety devices to prevent
human injury and machinery damage. Measures
should be taken to prevent drop of hanging or
lifing equipment.
6. Consider possible loss of power sources.
Measures should be taken to protect against
human injury and machinery damage in the
event that there is a loss of air pressure,
electricity or hydraulic power.
7. Design circuit to prevent shooting out of a
driven object.
A driven object is quickly shot out when pressure
is supplied from one side of the piston after air in
the cylinder is exhausted in such cases that
cylinder is actuated by exhaust center type of
directional control valve or started after residual
air is exhausted from the circuit. At this time,
human injury may occur; e.g., by catching hands
or feet in the machinery, or damage to the
machinery itself may occur. Therefore, the
machine should be designed and constructed to
prevent shooting out.
!
!
Page 6
6
8. Consider emergency stops.
Design the machinery so that human injury
and/or damage to machinery and equipment will
not be caused when machinery is stopped by a
safety device under abnormal conditions, a
power outage or a manual emergency stop.
9. Consider actions when operation is restarted
after an emergency stop or abnormal stop.
Design the machinery so that human injury or
equipment damage will not occur upon restart of
operation. When the cylinder is required to return
to the initial position, provide the equipment with
a safe override.
10.Construct the machinery so that moving
objects and the moving parts of the cylinder
with brake do not come into direct contact with
the human body.
11.Use a balanced circuit in which lurching of the
cylinder is prevented. When operation is locked
in specified intermediate positions of the stroke,
and air pressure is applied to only one side of
the cylinder, the piston will lurch when the lock
is released. This might cause injury or damage
to machinery.
Selection
Warning
1. Confirm the specifications.
The product in this manual is designed to be
used only in industrial compressed air system.
The product should not be used with pressures
or temperatures outside the range of the
specifications, as this may cause damage or
malfunction, etc.
2. Intermediate stop
When cylinder piston is stopped intermediately
by 3-position closed center type of directional
control valve, intermediate stop positions may
not be as precise and exact as hydraulic
operation due to compressibility of air. Valves
and cylinders are not guaranteed for zero air
leakage, and stop position may not be held in a
long period of time. Consult SMC for long term
holding of stop positions.
3. When a cylinder is in a no-load and locked state,
the holding force (maximum static load) is the
lock’s ability to hold a static load that does not
involve vibrations or shocks. To ensure braking
force, the maximum load must be set as
described below.
①For constant static loads, such as for drop
prevention:
35% or less of holding force (Maximum
static load)
Note) For applications such as drop prevention,
consider situations in which the air source
is shut off, and make selections based on
the holding force of the spring locked state.
Do not use the pneumatic lock for drop
prevention purposes.
②When kinetic energy acts upon the cylinder,
such as when effecting an intermediate stop,
there are constraints in terms of the allowable
kinetic energy that can be applied to the
cylinder in a locked state. Refer to the
allowable kinetic energy of the respective
series. Furthermore, during locking, the
mechanism must sustain the thrust of the
cylinder itself, in addition to absorbing the
kinetic energy. Therefore, even within a given
allowable kinetic energy level, there is an
upper limit to the amount of the load that can
be sustained.
- Maximum load for horizontal mounting: 70%
or less of the holding force (Maximum
static load) for spring lock
- Maximum load for vertical mounting: 35% or
less of the holding force (Maximum static
load) for spring lock
③ In a locked state, do not apply impact, strong
vibrations or rotational forces. Any impact,
strong vibrations or rotational forces from
external sources could damage or shorten
the life of the lock unit.
④ Although the cylinder can be locked in both
directions.
Caution
1. Mount speed controller and adjust cylinder
operation speed gradually from low speed to
a desired speed.
Air Supply
Warning
1. Do not use the product out of the specified
ranges for pressure and temperature to
pre-vent equipment damage and
mal-function.
!
!
!
Page 7
7
①Operating pressure:
Actuating part: 0.1 – 1.0MPa
Braking part
: 0.3 – 0.5MPa
②Fluid & ambient temperature: 5 to 60C
2. Use clean air.
Do not use the product with compressed air
includes chemicals, synthetic materials
(including organic solvents), salinity, corrosive
gases, etc., as this may cause damage or
malfunction.
Caution
1. Install air filter.
Install air filter before and in vicinity of valve. The
filter should be able to collect particles of 5
microns or smaller. A large quantity of drain may
cause malfunction of pneumatic components.
2. Install after cooler, air dryer, auto drain, etc.
Compressed air that includes excessive
condensate may cause malfunction of valve and
other pneumatic equipment. To prevent this,
install after cooler, air dryer, auto drain, etc.
Pneumatic circuit
Warning
1. Be certain to use a pneumatic circuit which will
apply balanced pressure to both sides of the
piston when in a locked stop. (Refer to Chapter 6
for recommended pneumatic circuit.)
In order to prevent the cylinder lurching after a
locked stop, use a circuit which applies balanced
pressure to both sides of the piston when restarting
or when manually releasing the lock, thereby
canceling the force generated by the load in the
direction of piston movement.
2. Use a solenoid valve for unlocking which has a
larger effective area, as a rule 50% or more of
the effective area of the cylinder drive solenoid
valve.
(Refer to Chapter 6 for recommended
pneumatic components.)
The larger the effective area is, the shorter
the locking time will be, and stopping
accuracy will be improved.
3. Place the solenoid for unlocking close to the
cylinder, and no farther than the cylinder drive
solenoid valve.
The shorter the distance from the cylinder, the
shorter the overrun amount will be, and stopping
accuracy will be improved.
4. Allow at least 0.5 seconds from a locked stop
(intermediate stop of the cylinder) until release of
the lock.
When the locked stop time is too short, the
piston rod may lurch at a speed greater than the
control speed of the speed controller.
5. When restarting, control the switching signal for
the unlocking solenoid valve so that it acts before
or at the same time as the cylinder drive solenoid
valve.
If the signal is delayed, the piston rod may lurch at
a speed greater than the control speed of the
speed controller.
Installation
Warning
1. Connect the slider end and the load with the lock
released.
2. Ensure that the equipment operates properly
before the use.
3. Operation manual
Do not install the products unless the safety
instruction have been read and understood.
Keep this operation manual on file for future
reference.
Caution
1. Maintenance space
When installing the products, allow space for
maintenance.
2. Do not give strong impact and/or excessive
moment when work is mounted.
External force other than allowable moment may
cause rattle at guide part and/or increase in
sliding resistance.
5. Be careful to avoid scratches or dents, etc. on
the sliding sections of the slider.
!
! ! !
Page 8
8
Wiring
Warning
1. Preparation for wiring
Shut off the power before wiring (including
insertion and removal of connectors). Mount a
protective cover on the terminal block after
wiring.
2. Check the power
Make sure the power has sufficient capacity and
voltages are within the specified range before
wiring.
3. Grounding
Ground terminal block F.G. (Frame Ground).
Do not ground it with devices generating strong
electromagnetic noise.
4. Check wiring
Incorrect wiring may cause damage or
malfunction of the products. Make sure the
wiring is correct before operation.
Caution
1. Separation of signal wires from power wire
Avoid common or parallel wiring of signal and
power wires to prevent malfunction due to noise.
2. Wiring arrangement and fixation
Avoid bending cables sharply at connector part
or electrical entry in wiring arrangement.
Inproper arrangement may cause disconnection
which in turn causes malfunction. Fix cables
close enough not to give excessive force to the
connector.
Piping
Caution
1. Before piping
Remove cutting chips, cutting oil, dust, etc. in
piping by flushing or cleaning before piping.
Care should be taken especially that any cutting
chips, cutting oil, dust, etc. do not exist after a
filter.
2. At piping
①Foreign matter should not enter. Entering of
foreign matter will cause malfunction.
②Cutting chips and sealing materials at piping
threads should not enter valves when piping
and fittings are screwed in. Leave 1.5 to 2
threads when seal tape is used.
Lubrication
Caution
1. Lubrication of cylinder
①This cylinder is pre-lubricated and can be used
without lubrication.
②In case of lubrication, use a equivalent of the
turbine oil type 1 ISO VG32. Once lubrication
is performed, it should be continued since the
initial lubricant flows out causing malfunction.
Adjustment
Caution
1. The locks are manually disengaged when the
cylinder is shipped from the factory. Be sure to
change them to the locked state before using
the cylinder.
2. Adjust the cylinder’s air balance. In the state in
which a load is attached to the cylinder,
disengage the lock and adjust the air pressure
on the rod side and the head side of the
cylinder to obtain a load balance. By
maintaining a proper air balance, the piston rod
can be prevented from lurching when the lock is
disengaged.
3. Adjust the mounting position of detection
devices such as autoswitches.
Sensor unit
Caution
1. Do not remove the sensor unit.
The position and sensitivity of the sensor is
adjusted properly before shipment.
Removing or replacing the sensor may cause
malfunction.
2. Operate the system with an external magnetic
field of 14.5mT or less.
Strong magnetic field in the vicinity may cause
malfunction, since ML2 sensor is magnetic
type.
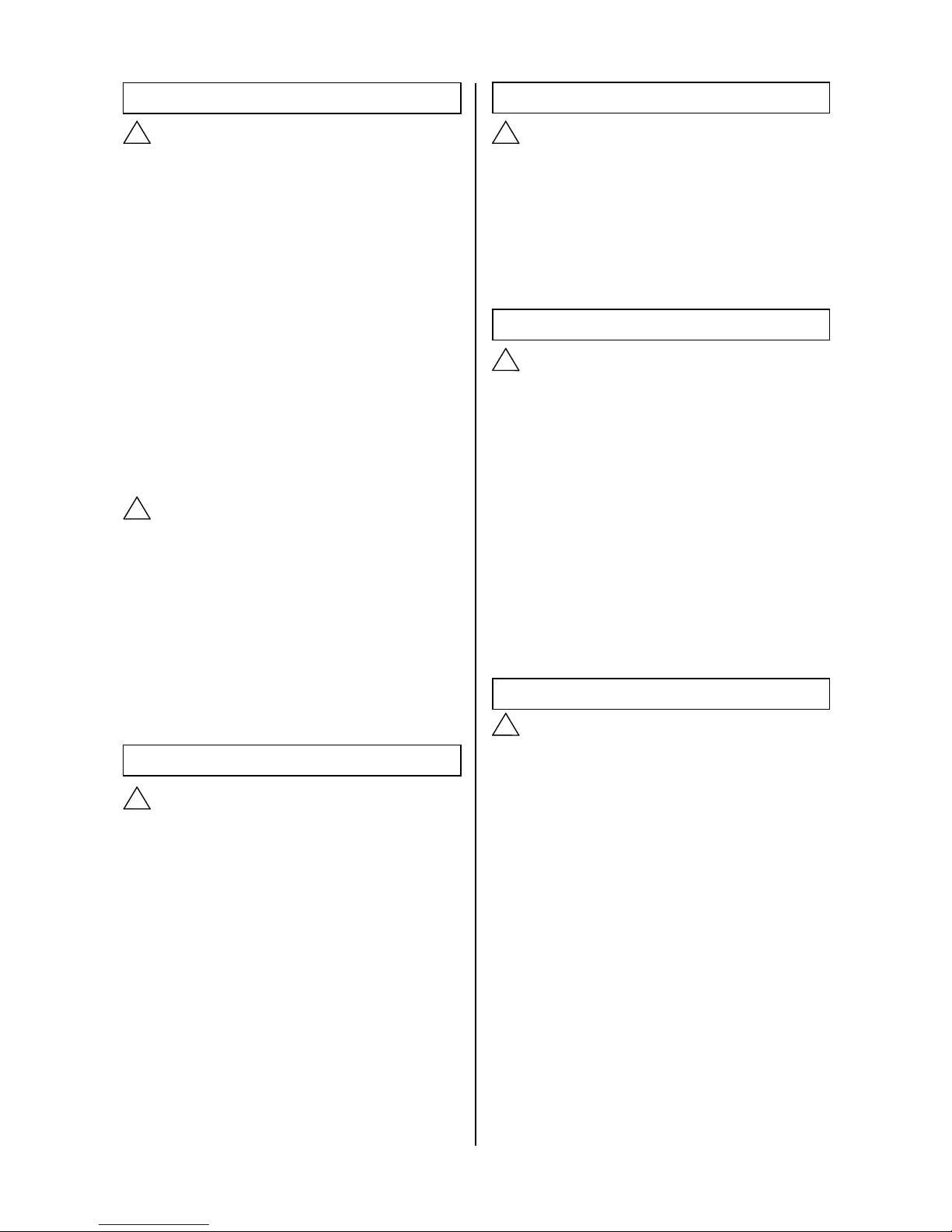
This is equivalent to a magnetic field of
approximately 18cm in radius from a welding
area using a welding current of almost 15,000
amperes. To use the system in a magnetic field
that exceeds this value, use a magnetic material
to shield the sensor unit
! ! ! ! !
!
Page 9
9
3. Do not pull sensor cable strongly.
Such action may cause failure.
4. Water shall be kept away from the sensor unit to
avoid failure.
5. Power supply line
Do not mount any switch or relay to power
supply line (12 VDC).
Measurement
Caution
SMC products are not intended for use as
instruments for legal metrology.
Measurement instruments that SMC manufactures
or sells have not been qualified by type approval
tests relevant to the metrology (measurement) laws
of each country. Therefore, SMC products cannot
be used for business or certification ordained by the
metrology (measurement) laws of each country.
Maintenance and Check
Warning
1. Performing regular check
Check regularly that the products do not operate
with failures unsolved. Check should be done
by trained and experienced operators.
2. Dismantling of product and supply/exhaust
of compressed air.
Before dismantling, ensure that drop preventing
and runaway preventing treatments are properly
provided, shut the power source of air supplied,
and exhausts compressed air in the system.
When starting operation again, operate the
product with care after ensuring that a treatment
for preventing extrusion is properly provided.
3. Prohibition of disassembly and modification
To prevent accidents such as failures and
electric shocks, do not remove the cover to
perform disassembly or modification. If the
cover has to be removed, shut off the power
before removal.
4. Disposal
Request a special agent for handling industrial
waste to dispose the products.
!
Operating
range
Welding machine
!
Page 10

10
Chapter 2: General Description / Features
2-1 General Description
Positioning with high reproducibility has been realized by Hyrodless Monosashi-kun, which brake and
stroke sensor are installed in mechanical joint type rodless cylinder (MY1B Series). (Stopping
accuracy is ±0.5mm when specified controller. CEU2, is used.)
2-2 Features
Brake Structure
・Adoption of integrated pneumatic and spring
Slider stops instant due to quick response of brake. Also the current position is hold by spring lock
when the air pressure is lowered or the compressed air is stopped.
・Lock is possible for both directions
Lock is possible for reciprocation of cylinder stroke.
・Easy maintenance
Brake can be replaced and disassembled, and can be opened manually for its unit structure.
・Brake structure which does not give a load on cylinder
Slider can be stopped without losing its performance since brake does not give a load on cylinder
for its structure, which spring acts on brake shoe directly to put between upper and lower brake
plates.
Scale
・Minimum measuring unit : 0.1mm
This is measured by scale plate and detection head built-in body.
Page 11
11
Chapter 3: System Configuration
3-1 System Configuration
HYRODLESS MONOSASHI-KUN (ML2 Series) can be used for measurement or to prevent falling
besides positioning application.
Model
type
Function
Connected
equipment
Application
Brake
Scale
Keeping
Intermediate
stop
Measurement
Positioning
①
ML2B※
○
○
CEU1
○ ○ ○
②
ML2B※
○
○
CEU2
○
③
ML2B※S
○
CEU1
○
④
ML2B※B
○
Sequence, etc.
○ ○
3-2 Example of system Configuration
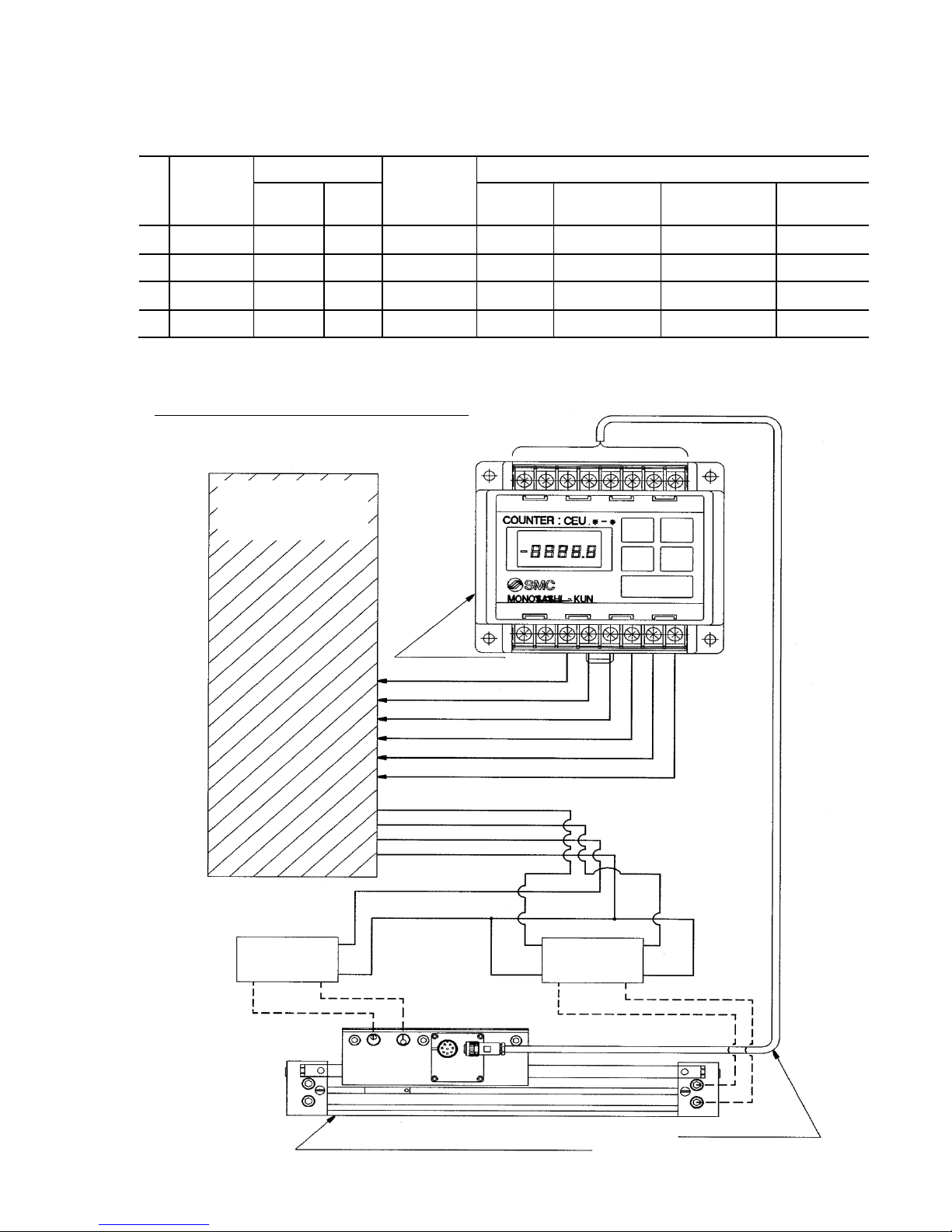
■For Keeping
Hyrodless Monosashi-kun + Counter
3 points preset counter : CEU1 Series
Brake valve
Solenoid
valve
Hyrodless Monosashi-kun (ML2※)
Extension cable
(CE1-R□□)
Counter
(CEU1)
External equipment
(Sequence
controller, etc.)
Page 12
12
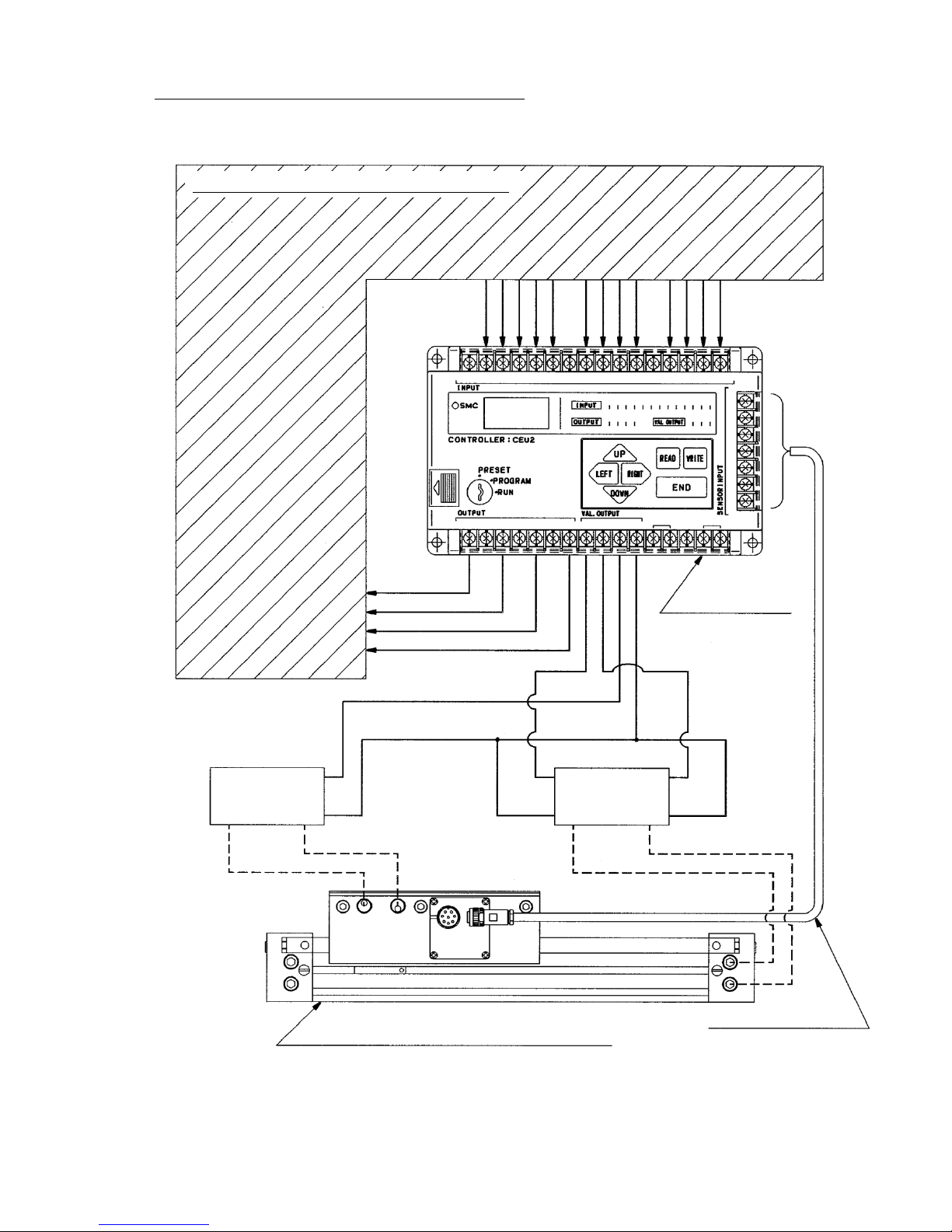
■For precise positioning (Stopping accuracy ±0.5mm)
Hyrodless Monosashi-kun + Controller
Controller : CEU2 Series
Brake valve
Solenoid
valve
Hyrodless Monosashi-kun (ML2※)
Extension cable
(CE1-R□□)
Controller
(CEU2)
External equipment (Sequence controller, etc.)
Page 13
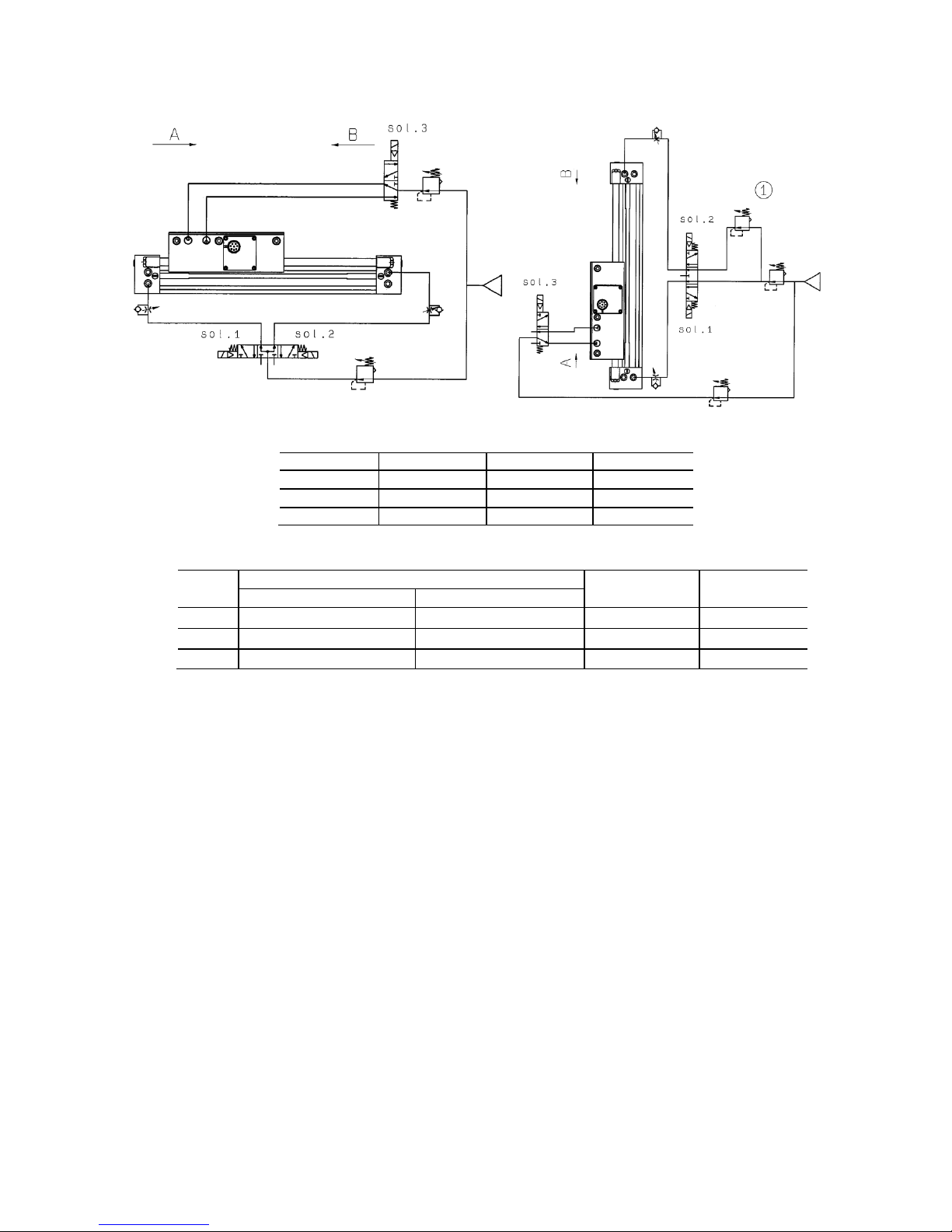
13
3-3 Pneumatic Circuit
Sol.1
Sol.2
Sol.3
A
ON
OFF
ON B OFF
ON
ON
Stop
OFF
OFF
OFF
Pneumatic Equipment
Bore
Size
Directional Valve
Brake Valve
Regulator
Horizontal Mounting
Vertical Mounting
25
VFS25□0
VFS24□0R
VFS21□0
AR425
32
VFS25□0
VFS24□0R
VFS21□0
AR425
40
VFS25□0
VFS24□0R
VFS21□0
AR425
・Air Balance
・ With the above circuit, maintaining the slider at center by balancing both sides (left & right) supply
pressure to achieve air balance state.
・ At the situation of vertical mounting, maintain the slider at the center and reduce the upper
portion’s supply pressure accordingly to counter for the weight due to gravity. If air balance is not
achieved, motion after center positioning will be either accelerating abnormally or false movement.
Hence, the accuracy of positioning will be affected.
・Tubing
・ Use larger diameter’s tube and reduce the tubing length between solenoid valve and cylinder, so
as to increase position determination’s precision.
・ Connect brake valve near to slider. If tubing between brake valve and slider is long, its motion
response time will be slower. Moreover, it may rush vigorously when brake is released.
・ During installation, connected tubing should be flushed thoroughly, and prevent dust and chips
from entering into cylinder.
・Supply Pressure
・ Set brake release port’s supply pressure as 0.3~0.5MPa. With supply pressure of below 0.3MPa,
brake’s release will not be activated. While with pressure of above 0.5MPa, brake’s life span will
be shortened.
・ Direct pressure supply from pressure line will cause pressure variation problem and thus, affect
cylinder performance. Hence, it is advisable to connect regulator before driving and brake
solenoid valve. Besides that, if there is a lot of cylinder activated and moving at the same time,
use regulator with larger flow characteristic and install air tank.
・ Connect head cover tubing wisely with consideration of surrounding conditions.
Horizontal Mounting
<Air Circuit Diagram>
Vertical Mounting
Page 14

14
The most suitable tubing can be selected according to the situation when tubing head cover.
Tube face No.
1 2 3 4 5 6 Type of head cover
Head Cover-WL
Head Cover-WR
Tubing face
Front
Side
Bottom
Front
Side
Bottom
Operating
direction
Left A C E G I K
Right B D F H J L
Note: 1)Tubing should be group according to the grouping in the table
above, 6 on each sides.
2)SMC’s one-touch speed controller can be mounted directly on
tubing No.1,2,4 and 5.
Installating dimension of bottom face
φ25,φ32
φ40
O-ring
C9
C11.2
φA
φ6
φ8
Driving Direction
Left
Right
<Back>
<Side>
<Front>
<Side>
<Back>
Brake Operating Port
Brake Release Port
Head Cover-WL
Head Cover-WR
Rz12.5
Head cover
O-ring
φA
Fixing plate
Speed
controller
Page 15

15
Chapter 4: Operating Principle
4-1 Operating principle of brake
Brake operation
Spring force caused by brake spring and the air pressure supplied from brake operating port work
on brake shoe 1 fixed with brake holder, bend brake plate fixed on head cover on both sides, and
stop slider by putting brake plate between brake shoe 1 and brake shoe 2 fixed on the slider side.
Brake release
The air pressure supplied from brake releasing port work on diaphragm, decline brake spring, and
cancel brake.
Brake operating port
Brake releasing port
Slider
Brake shoe 2
Diaphragm
Brake holder
Brake spring
Brake shoe 1
Brake plate
Page 16

16
NO
NO
No particular problems for
operation.
YES
1. Is there any influence by
magneteic field?
YES
2. Is cylinder exposed to
coolant, oil, water and
power, etc?
YES
Start
NO
Is the total of moment of
each direction to cylinder
and load factor of movable
load within "1"?
(in the case of without
guide)
Is kinetic energy within
allowable kinetic energy?
(in the case of with guide)
Select cylinder size so that
load factor will become
less than "1"?
Select cylinder size so that
kinetic energy will become
within allowable kinetic
energy.
Is it possible to use at less
than 14.5mT?
NO
Do not use it since it will
cause miscount and
insufficient control.
YES
NO
Do not use it since it will
cause brekage of sensor
or degradation of
YES
Can the cable of
Hyrodless Monosashi-kun
be wired separate from
the other power cable?
Do not use it since it is
easily affected by noise
due to pulse output, which
will cause maloperation.
NO
YES
Can the cylinder be
protected with a cover,
etc?
Chapter 5: Selecting Procedure
5-1 Precaution
Be sure to check with the procedure below before using Hyrodless Monosashi-kun. For positioning
with CEU2, check with the procedure of “Operation Manual of Brake Positioning System (Rodless
type)”.
Page 17

17
W : Load (N) Mounting Direction :
Va : Average Speed (mm/s) Guide :
P : Operating Pressure (Mpa) Impact Absorption :
Autoswitch :
With Guide
NG
NG
OK OK
NG
OK OK
Operating Condition
Predetermined Cylinder Bore Size
With / Without Guide
Calculate Load,
W≦Wmax
Calculate Kinetic Energy
E≦Emax
Without Guide
Selection of Autoswitch
Determination of Model
Calculate Momentum
Σan≦1
Selection of Shock Absorption Unit
Air Cushion
Stroke Adjustment Unit
5-2 Selecting Procedure
Follow the procedure below to select the most suitable ML2 series.
As allowable moment, maximum movable load, and allowable kinetic energy vary with the conditions,
such as mounting position, piston speed, and with / without guide, ①maximum movable load, ②static
moment, ③dynamic moment (during impact with stopper and locking), and ④allowable kinetic energy
should be considered so that the total amount of load factor will not exceed 1 (∑an≦1) when
calculating allowable load. (In the case of ∑an>1, select a cylinder with larger bore size.)
When positioning is necessary, maximum speed should be not more than 500mm/s.
Page 18

18
5-3 Selection Information
W
(N)
: Load
We
(N)
: Impact loading (during locking or knocking of stopper)
V
(m/s)
: Impact speed (during locking or knocking of stopper)
Va
(m/s)
: Average speed
L
(m)
: Distance from C.G. of load
M
(Nm)
: Maximum moment
E
(J)
: Kinetic energy of load
g
(m/s)
: Gravity acceleration (9.8m/s2)
<Piston speed>
V=1.4xVa
<Maximum load>
We=1.4xVaxWx10
<Maximum allowable moment>
M=
WexL
=5xVaxWxL
3
<Load factor>
an=
F
Fmax
F ^ : Calculated load
Fmax : Maximum allowable load under the condition of allowable speed
(value obtained from graph)
<Allowable kinetic energy>
Ek=
W
V2
2g
・Allowable moment and maximum load
Model
Allowable moment N.m
Maximum load N
M1
M2
M3
W1
W2
W3
W4
ML2B25
10.0
1.2
3.0
200.0
58.0
65.0
100.0
ML2B32
20.0
2.4
6.0
300.0
80.0
96.0
150.0
ML2B40
40.0
4.8
12.0
500.0
106.0
140.0
250.0
・Allowable kinetic energy
ML2B25
ML2B32
ML2B40
Allowable kinetic energy J
0.43
0.68
1.21
Moment (N.m)
L
1
F
1
L
2
F
2
L
3
F
3
M1=F1x L
1
M2=F2x L
2
M3=F3x L
3
Load (N)
W1
W2
W3
W4
Page 19

19
Max. Allowable Momentum
Select cylinder accordingly with refer to the graph
below. Its momentum should not over the specified
range. However, selected cylinder may have larger
loading value than specified max. load. Counter
check with loading condition.
Max. Load
Select cylinder accordingly with refer to the graph
below. Its load should not over than specified
range. However, selected cylinder may have larger
momentum value than specified max. momentum.
Counter check with momentum condition.
Moment N・m
Piston speed m/s
Moment N・m
Piston speed m/s
Piston speed m/s
Moment N・m
Load N
Piston speed m/s
Allowable kinetic energy
Load N
Piston speed m/s
Piston speed m/s
Load N
Load N
Load N
Piston speed m/s
Piston speed m/s
horizontal Mounting
Vertical Mounting
Page 20

20
5-4 Example of selection
Ⅰ. Without Guide
① Operating Conditions
Loading
Static Load
Dynamic Load
①
Side load due to W
W3
-
②
Moment due to W
M2
-
③
Moment due to we when stopping
-
M
3
V
④
〃
-
M
1
V
② Static Load <normal load>
① W3max=60Nm (Checked from graph with Va)
Load factor a1=
W3
=
15
=0.25
W3max
60
② M2max=2N・ m (Checked from graph with Va)
M2=Wx L1=15x0.05=0.725N・m
Load factor a2=
M2
=
0.75
=0.375
M2max
2
③ Dynamic load <load applied during stopping)
Impact Loading, We=1.4x10xVaxW=1.4x10x0.25x15=52.2N
③ M3max=3.5N・m (Checked with V=1.4xVa)
M3=WexL2x
1
=52.5x0.05x
1
=0.88N・m
3
3
Load factor a3=
M3
=
0.88
=0.25
M3max
3.5
④ M1max=12N・m (Checked with V=1.4xVa)
M1=WexL1x
1
=52.5x0.05x
1
=0.88N・m
3
3
Load factor a4=
M1
=
0.88
=0.073
M1max
12
④ Examination of load factor
an ① 0.25
②
0.375
③
0.25
④
0.073
∑an
0.948
Decision
OK from ∑an≦1
Model : ML2B32 Load : 15N
Speed , Va : 0.25m/s Pressure : 0.5MPa
L1 : 0.05m L2 : 0.05m
W
L
1
W
L
1
ML2B32 is selected.
Page 21

21
Model : ML2B25 Load : 30N
Speed , Va : 350mm/s Mounting position : wall
Ⅱ. With Guide
① Operating conditions
② Allowable kinetic energy
E max=0.43 (J)
V=Vax1.4=350x1.4=490mm/s
Ev=
W
xV2=
30
x0.492=0.36 (J)
2g
2x9.8
Load factor a5=
E = 0.36
=0.84
Emax
0.43
③ Examination of load factor
a5 = 0.84 ≦ 1 OK
With above allowable value, there is no problem on the selection.
∴ If values are in the range of graph in page 19, there is no
problem on the operating conditions.
W
ML2B25 is selected.
∴ The weight of table is considered as 0 in this case.
However, during actual operation, the weight of table
should be taken into consideration.
Page 22

22
Chapter 6: Specifications
6-1 Cylinder Specifications
Bore size
φ25
φ32
φ40
Fluid
Air
Operating method
Cylinder
Double acting type
Brake
Integrated pneumatic and spring
Operating pressure
range
Cylinder
0.1~0.8MPa
Brake
0.3~0.5MPa
Proof pressure
Cylinder
1.2MPa
Brake
0.75 MPa
Piston speed
100~1500mm/s (during positioning, 100~500mm/s)
Ambient and fluid temperature
5~50℃(No freezing)
Cushion
Both sides air cushion
Brake type
Integrated pneumatic and spring
Lubrication
Not required
Stroke tolerance mm
0~+1.8
Hardware
JIS B 0209
Port size
Front and side port
Rc1/8
Rc1/4
Bottom port
φ5
φ6
φ8
6-2 Sensor specifications
Cable
(Standard product with connector :
R04-R8M made by TAJIMI MUSEN DENKI CO.)
Max. transmission distance
20m (when using 6 core twist spare shield wire)
Position detection method
Magnetic scale rod, Detection head
(Incremental type)
Magnetic field resistance
14.5mT
Power supply
DC12V±10% (Power supply ripple : Less than 1%)
Current consumption
40mA
Resolution
0.1mm / pulse
Accuracy
±0.2mm (20℃) Note1)
Output method
Open collector (DC35V, 80mA)
Output signal
Phase A/B phase difference output
Max. response speed
500mm/s
Withstand voltage
AC500V, For one minute (Between case and 12E)
Insulation resistance
DC500V, 50MΩ (Between case and 12E)
Shock resistance
33.3Hz6.8G X,Y directions : For 2 hours, Z : 4 hours
In accordance with JIS D1061
Impact resistance
30G X,Y,Z directions : 3 times
Extension cable
(Option)
5m,10m,15m,20m
(Connector : R03-P8F made by TAJIMI MUSEN DENKI CO.)
Note1) Include digital error of the counter (CEU1,CEU5).
The accuracy as a whole unit after assembling to the device may vary depending on the mount
condition and environment. Please execute calibration of the device on customer ’s own
responsibility.
Page 23

23
Bore size
25 25mm
32 32mm
40 40mm
Control method
None
With brake and scale
S With scale only
B With brake only
No. of autoswitch
None 2
s 1
n n
No. of adjustment unit
None 2
S 1
L
Shock absorber + Adjust bolt
Stroke adjustment unit
Output method
None NPN open collector output
P PNP open collector output
Standard stroke
Standard stroke (mm)
25
32
40
1~2000
(It is possible to produce it at intervals of 1mm. )
Output method
None
NPN open collector
P
PNP open collector
Counter operating power supply
None
AC80~120V
D
DC24V±5%
Chapter 7: How to Order
7-1 Cylinder (Hyrodless Monosashi-kun)
ML2 B 25 ― 500 L - Z73
Option
Stroke adjustment unit Stroke adjustment unit
φ25
MY-A25L
φ25
MY-S25A
MY-S25B
φ32
MY-A32L
φ32
MY-S25A
MY-S25B
φ40
MY-A40L
φ40
MY-S32A
MY-S32B
7-2 Controller
CEU2
3 points preset counter
CEU1 -
Mounting
B Standard
Type of autoswitch
(See catalog)
Page 24

24
Stroke adjustment unit
None without adjustment unit
L Shock absorber + adjust bolt
Bracket
None One side only
W Both sides bracket
Z
The one for X417
is
No. of stroke adjustment unit
None 2
S 1
Length of cable
05 5m
10 10m
15 15m
20 20m
Additional symbol
None Extension cable
C Extensin cable + Connector
7-3 Extension cable
CE1-R
Connection of connector
Contact
A B C, D
E F G
Color of wire
White
Yellow
Brown, Blue
Red
Black
(Shield)
7-4 Specifications of Made to order ML2B
[Holder mounting bracket : ① ②]
Holder mounting bracket ① : -X416
Holder mounting bracket ② : -X417
Stroke fine adjustment range
Holder mounting bracket
X416
X417
Length of spacer
L (mm)
ML2B25
11.5
23
ML2B32
12
24
ML2B40
16
32
Stroke fine
adjustment range
(mm)
ML2B25
per one side
-11.5~-23
-23~-34.5
Both sides
-23~-46
-46~-69
ML2B32
per one side
-12~-24
-24~-36
Both sides
-24~-48
-48~-72
ML2B40
per one side
-16~-32
-32~-48
Both sides
-32~-64
-64~-96
How to order
1) When ordering stroke adjustment unit integrated into cylinder body.
ML2B25― 300 L - X416 Z
Note)This stroke shows
the stroke before
mounting stroke
adjustment unit.
Symbol of holder mounting bracket
X416
X417
Page 25

25
2) When ordering stroke adjustment unit only.
Add “X416” and “X417” at the end of part No. of unit.
Ex. MY-A25L-X416
3) When ordering holder mounting bracket only.
Add “N” at the end of part No. of unit.
Ex. MY-A25L-X416N
Page 26

26
Chapter 8: External Dimension Drawing
8-1 Hyrodless Monosashi-kun (with brake, scale)
Page 27

27
8-2 With scale
Page 28

28
8-3 With brake
Page 29

29
8-4 With shock absorber
Page 30

30
8-5 With stroke adjustment unit, X416
Page 31

31
8-6 With stroke adjustment unit, X417
Page 32

32
Chapter 9: Construction / Parts list
Page 33

33
Chapter 10: Cushion Capacity
10-1 Selection of cushion
<Air cushion>
Standard Hyrodless Monosashi-kun is equipped with an air cushion.
Air cushion is installed not to operate piston at low speed when piston approaches to stroke end, but
to avoid shock when piston with large kinetic energy stops at stroke end. The range of load and speed
absorbed by air cushion is within the limit line of air cushion in graph.
<Stroke adjustment unit with shock absorber>
This is used on the occasion when operating with load and speed of over the limit line of air cushion or
when cushion is needed out of the air cushion stroke range due to stroke adjustment.
<L-Unit>
This is used on the occasion when cushion is needed out of the air cushion stroke range although
load and speed are within the limit line of air cushion or when operating with the range of load and
speed of over the air cushion limit line and below the unit limit line.
<Note>
① Absorbing capacity of unit is for the occasion when all stroke of equipped shock absorber is used.
When effective stroke becomes shorter due to stroke adjustment, absorbing capacity becomes
extremely small. Therefore, fix adjustment bolt to project 0.5mm above shock absorber.
② When shock absorber is used in the range of air cushion stroke, air cushion needle shall be
almost full opened (about one and a half turn from the position of full close.)
Air cushion stroke
Unit : mm
Bore size (mm)
Cushion stroke
φ25
15
φ32
19
φ40
24
Shock absorber
Adjustment bolt
Page 34

34
10-2 Absorbing capacity of air cushion and stroke adjustment unit
Stroke adjustment unit with shock absorber
Calculation of absorbing energy
Type of collision
Horizontal collision
Vertical collision
(descent)
Vertical collision
(ascent)
Kinetic energy E1
1
m・v2
2
Thrust energy E2
F・s
F・s + m・g・s
F・s - m・g・s
Absorption energy E
E1 + E2
V: Speed of load (m/s) m: Weight of load (kg) F: Thrust of cylinder (N)
g: Gravitational acceleration (9.8m/s) s: Stroke of shock absorber (m)
Note) Speed of load is the speed of the moment when load collides with shock absorber.
Torque for bolt unit : N.m
Bore size (mm) Torque
25 3
32 5
40 10
Stroke adjustment unit lock plate
Torque for bolt unit : N.m
Bore size (mm) Torque
25 1.2
32 3.3
40 3.3
Stroke adjustment unit
Page 35

35
10-2 Adjusting Method
<Travel and fix of unit body>
Unit body can be traveled by loosening 4 pieces of bolt. Unit body can be fixed by tightening unit
body evenly with 4 pieces of bolt at the specific position. The position, however, may got out of the
position depending on the energy size for collision. Mounting brackets for adjusting holder are
provided for –X416 and –X417. For the length of your request other than that, please consult with
us separately. (See bolt torque for fixing stroke adjusting unit.)
<Stroke adjustment of adjusting bolt>
Loosen lock nut for adjusting bolt and fix with lock nut after adjusting stroke with wrench from lock plate
side.
<Stroke adjustment of shock absorber>
After adjusting stroke by loosening two pieces of lock plate fixing bolt to turn shock absorber, fix shock
absorber by tightening lock plate fixing bolt evenly. On this occasion, care shall be taken so that bolts are
not tightened too much. (Please refer to torque for stroke adjustment unit lock plate bolt.)
Note) Although there are some cases where a little bend will be caused on lock plate due to tightening of
lock plate bolt, it does not affect on shock absorber and locking function.
Page 36

36
Chapter 11: Stopping Operation
11-1 Overrun (ML2 + Sequence controller)
The graph below shows the relation between piston speed and overrun.
(The length of overrun is changed by piston speed, load, tubing condition and control method. Be sure to
adjust the stop signal position, etc. by trial operation with the actual machine.)
11-2 Dispersion of stopping position
When cylinder is stopped intermediately, the stopping position is not fixed.
Dispersion of stopping position is changed by piston speed, load, tubing condition and control method,
etc. Please refer to the table below.
ML2 + Sequence controller
Piston speed
just
before stop
mm/s
100
300
500
800
1000
Stopping accuracy
mm
±0.5
±1.0
±2.0
±3.0
±4.0
ML2 + CEU2
Piston speed just
before stop
mm/s
500mm/s
Stopping accuracy
mm
±0.5
Start
Stop signal
Stop position
Idle
running
distance
Stop distance
(run)
(overrun)
Braking
distance
When cylinder is stopped intermediately, “idle running distance”
(from detection of stop signal to
beginning of brake operation)
and “braking distance “(from beginning
of brake operation to slider stop) are
occurred as shown in the figure left.
0.5
1.0
Piston speed just before stop m/s
No load
Load factor 50%
100
50
The length of
overrun
mm
Operating pressure 0.5MPa
Brake releasing pressure 0.3MPa
Mounting position Horizontal
Conditions
Operating pressure 0.5MPa
Brake releasing pressure 0.3MPa
Load factor 25%
Page 37

37
Chapter 12: Manual Operating Procedure
[Brake release]
①Supply brake releasing pressure of 0.3~0.5MPa from brake releasing port on slider side.
②Thread bolt into manual port on slider side.
③Exhaust brake releasing air.
[Brake operation]
①Supply brake releasing pressure of 0.3~0.5MPa from brake releasing port on slider side.
②Remove bolt threaded into manual port.
③Exhaust brake releasing air.
Bolt for manual release
ML2B25
M5×0.8
L=8
ML2B32
M6×1
L=10
ML2B40
M8×1.25
L=12
Page 38

38
Chapter 13: Installation & Wiring
13-1 Installation of Cylinder
1. It should be installed at high flatness surface. For uneven surface. Shim adjustment should be done
to achieve smooth operation of slider with a minimum operating pressure of 0.1MPa.
2. Installed with utilizing both sides head cover. Do not fix cylinder’s position through slider, as shown
in diagram (a). With overloading the bearing, operation error occurs.
Besides that, for the case of single sided fixing method (as refer in diagram (b), consultancy should
be made, due to bending of tube may occur and thus, lead to the occurs of operation error.
(a) Fixing through Slide (b) Single side’s Fixing
There are 2 ways, as shown in diagram below, to fix cylinder’s position.
Utilizing the installation method, with the consideration of mounting surface and situation.
(Side support, option, should be used for support purposes only.)
(c) Fastening through Upper Surface (d) Fastening through Lower Surface
3. With loading within allowable range of Hyrodless Monosashi-kun, supporting structure (LM Guide)
is still necessary to be installed as a support for the applied loading. Besides that, for the case of
long stroke, floating structure design should be brought in to overcome misalignment problem.
4. Cylinder has to be covered when it is used at environment that has chips, dust, oil mist and etc.
5. Be aware of not to harm (dented marks and etc.) the outer surface of cylinder tube, which will lead
to the damage of bearing and scraper. Consequently, disoperation will occur. Besies that, be aware
of not to apply too much of impact and momentum upon slider as slider is only supported by plastic
made bearing.
6. Do not apply load onto brake and scale plate, its bending will lead to operation error. Once, brake
and scale plate have been adjusted during installation state. Re-adjustment is not required and
should be advoided.
Page 39

39
Note:Grease used are lithium based grease with concentration class 1 or 2.
・Hyrodless Monosashi-kun uses magnetic sensor to detect position. Therefore, if strong magnetic field
appears nearby, operation error will occur.
Surrounding magnetic field should be below than 14.5mT.
Note: 14.5mT magnetic field will be just as the same as the resulted magnet field from 15,000A welding
current’s welding machine (within 18cm). To prevent from the effect of magnetic field, sensor should
be covered by magnetic material.
・Prevent sensor unit from contacting with water, oil and etc.
・Do not install Hyrodless Monosashi-kun near to motor, welding machine, and others facility which will
produce noise, which will cause counter malfunction.
Besides that, separate the power line from others.
The longest transmission distance for Hyrodless Monosashi-kun is 20m. Wiring above than the figure,
should be taken noted at.
Page 40

40
13-2 Electrical Wiring
Output method
Output signal of Hyrodless Monosashi-kun is phase difference output of A phase / B phase (open
collector output) as shown in the figure below.
1 pulse signal is sent to both output terminals A and B at every 0.1mm travel of Hyrodless
Monosahi-kun.
Also maximum response time of sensor for Hyrodless Monosashi-kun is maximum 1500 mm/sec
(15Kcps) in cylinder speed.
Input / Output
Input / Output of Hyrodless Monosashi-kun is performed by connector came from sensor.
Signal
Symbol of contact
Signal
A
A phase
B
B phase
C,D
COM (0V)
E
12V (Power supply)
F
0V (Power supply)
G
GND (Shield)
Reversed cylinder travelling direction
13432
Counter value
012
0.7
Cylinder
stroke mm
A phase output
pulse
B phase output
pulse
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
A phase
(white)
B phase
(yellow)
COM (0V)
(brown, blue)
Output circuit of Hyrodless Monosashi-kun
Page 41

41
13-3 Connection of Extension Cable
Use specified (SMC) extension cable. Cable length is 5m – 20m with interval of 5m. For the distance of
more than 20m, use specified transmission box (Model No.: CE1-H0374).
*Example of cable connection
*Note
①Clamp and fix the connector and sensor connection to reduce tension acting on them.
②Separate cable with power line or other lines which make noise.
③When cable is necessary to have U-shaped bend, set the bending radius to be above 25mm.
Bending performance: According to the drawing shown below, life span about 4 million cycle can
be achieved.
Extension cable
(CE1-R※※)
R25
Reciprocating with
bending speed 100times/min.
200mm
More than 20m
Receiving
Transmitter
Box
Receiver
Box
Sending
Less than 5m
100m
Less than 20m
Twisted pair shield wire
CE1-H0374
Page 42

42
 Loading...
Loading...