SMC Networks IP8000, IP8100 Installation And Maintenance Manual
IP80X14-TFJ21GB-B
Installation and Maintenance Manual
IP8000/IP8100 0#0 - # - X14 - L
Electropneumatic Positioner
1 Safety Instructions
• This manual contains essential information for the protection of users
and others from possible injury and/or equipment damage.
• Read this manual before using the product, to ensure correct handling,
and read the manuals of related apparatus before use.
• Keep this manual in a safe place for future reference.
• These instructions indicate the level of potential hazard by label of
"DANGER", "WARNING" or "CAUTION", followed by important safety
information which must be carefully followed.
• To ensure safety of personnel and equipment the safety instructions in
this manual and the product catalogue must be observed, along with
other relevant safety practices.
WARNING
• The compatibility of pneumatic equipment is the responsibility of
the person who designs the pneumatic system or decides its
specifications.
Since the products specified here can be used in various operating
conditions, their compatibility with the specific pneumatic system must
be based on specifications or after analysis and/or tests to meet
specific requirements.
• Only trained personnel should operate pneumatically operated
machinery and equipment.
• Compressed air can be dangerous if an operator is unfamiliar with it.
Assembly, handling or repair of pneumatic systems should be
performed by trained and experienced personnel.
• Do not service machinery/equipment or attempt to remove
components until safety is confirmed.
1) Inspection and maintenance of machinery/equipment should only
be performed after confirmation of safe locked-out control positions.
2) When equipment is to be removed, confirm the safety process as
mentioned above. Switch off air and electrical supplies and exhaust
all residual compressed air in the system.
3) Before machinery/equipment is re-started, ensure all safety
measures to prevent sudden movement of cylinders etc.
(Supply air into the system gradually to create back pressure, i.e.
incorporate a soft-start valve).
1 Safety Instructions (continued)
• Do not use this product outside of the specifications.
Contact SMC if it is to be used in any of the following conditions:
1) Conditions and environments beyond the given specifications, or if the
product is to be used outdoors.
2) Installations in conjunction with atomic energy, railway,
air navigation, vehicles, medical equipment, food and beverage,
recreation equipment, emergency stop circuits, press applications, or
safety equipment.
3) An application which has the possibility of having negative effects on
people, property, or animals, requiring special safety analysis.
CAUTION
• Ensure that the air supply system is filtered to 5 microns.
2 Specifications
Protect the unit from impact and dropping during installation and when
mounted. It may cause failure of the unit.
• Do not use the unit in places with high humidity & temperature. It may
cause malfunctions.
• Do not use this positioner outside of the range of it's specifications as this
can cause failure.
*1 : 1/2 split range is possible with the standard type (by adjusting the span)
*2 : The stroke is adjustable in 0~60° and 0~100°.
*3 : Standard air (JIS B0120): temp.20°C, absolute press. 760mmHg, ratio
humidity 65%.
2 Specifications (continued)
2.1 How to Order
3 Installation
WARNING
• Do not install unless the safety instructions have been read and
understood.
• Since zero-point varies depending on the mounting position, the zero point
should be adjusted after installation.
• Avoid hitting the product with metallic objects!
• Avoid using this product in non-explosive environments which can become
explosive due to air leakage!
• When using this product in hazardous areas, ensure that the operational
speed of the moving parts is less than 1m/s, and that the actuator is not
hunting!
3.1 Environment
WARNING
• Do not use in an environment where the product is directly exposed to
corrosive gases, chemicals, salt water, water or steam.
• The product should not be exposed to prolonged sunlight that can
generate a surface temperature higher than the value given for the
temperature classification. Use a protective cover.
• Do not mount the product in a location where it will be subject to strong
vibrations and/or shock.
• Do not mount the product in a location where it is exposed to radiant heat.
• Allow sufficient space for maintenance and adjustment around the product
when mounted.
3.2 Piping
CAUTION
• Before piping make sure to clean away all chips, cutting oil, dust etc.
• When installing piping or fitting into a port, ensure that sealant material
does not enter the port inside. When using seal tape, leave 1.5 to 2 threads
exposed on the end of the pipe/fitting.
4 Mounting
4.1 Type IP8000
4.1.1 Example of attaching to actuator
The type IP8000 positioner is compatible with Type IP6000 and IP600 in
the attaching pitch. If you are using IP600 and IP6000 already, the bracket
for these positioner can be used to attach IP8000 to the actuator.
3 Installation (continued)
3.3 Lubrication
CAUTION
• The positioner has a fixed orifice and nozzle, which contain fine paths
in them. Use filtered, dehydrated air and avoid the use of lubricators as
this may cause malfunction of the positioner.Ensure that the air supply
system is filtered to 5 micron.
3.4 Handling
CAUTION
• Avoid applying impact to the body and torque motor of the positioner,
and avoid excessive force to the armature because this may lead to
failure. Handle with care during transport and operation.
• If you leave the positioner at the operation site for a long time without
using it, put the cover on it so that rain water does not enter the
positioner. If the atmosphere is of high temperature or humidity, take
measures to avoid condensation inside. The condensation control
measures must be taken thoroughly for export shipment.
• Avoid setting the positioner near magnetic fields because the
characteristics are effected.
In extreme conditions, there is a possibility of
serious injury or loss of life.
WARNING
If instructions are not followed there is a
possibility of serious injury or loss of life.
CAUTION
If instructions are not followed there is a
possibility of injury or equipment damage.
DANGER
II 2G Ex ib IIC T6 -40°C≤ Ta ≤60°C
ATEX marking description
II 2 G Ex ib IIC T6 -40°C≤Ta≤60°C
Equipment
Group
Category 2
Gas explosive
atmosphere
European
standards
Ambient temperature
Temperature
classification
Explosion Group
Ignition protection,
intrinsic safety
X
®
0344 II 2G Ex ib IIC T6
JISF8007 IP65 (IEC 60529)
-40°C ~ 60°C
IP8 0 0 - 0 0 - - X14 - L
ATEX EXPLOSION
PROTECTION
SPECIFICATION
LOW TEMPERATURE
SPECIFICATION
Fig.1 Example of
directly attaching
to diaphragm valve
Directly attach using the
screw hole at the side of
the positioner and the
screw hole at the yoke
side of the diaphragm
valve.
Fig.2 Example of
attaching using the
L-shape bracket
Attach by using screw
hole at the side of the
positioner and the screw
hole at the front mount
of diaphragm valve.
Fig.3 Example of
attaching using
front bracket
Attach by using screw
hole at the back of the
positioner and the screw
hole at the front mount
of diaphragm valve.
Positioner
Bracket
Bracket
Positioner
Positioner
Bracket
shape
Bracket
shape
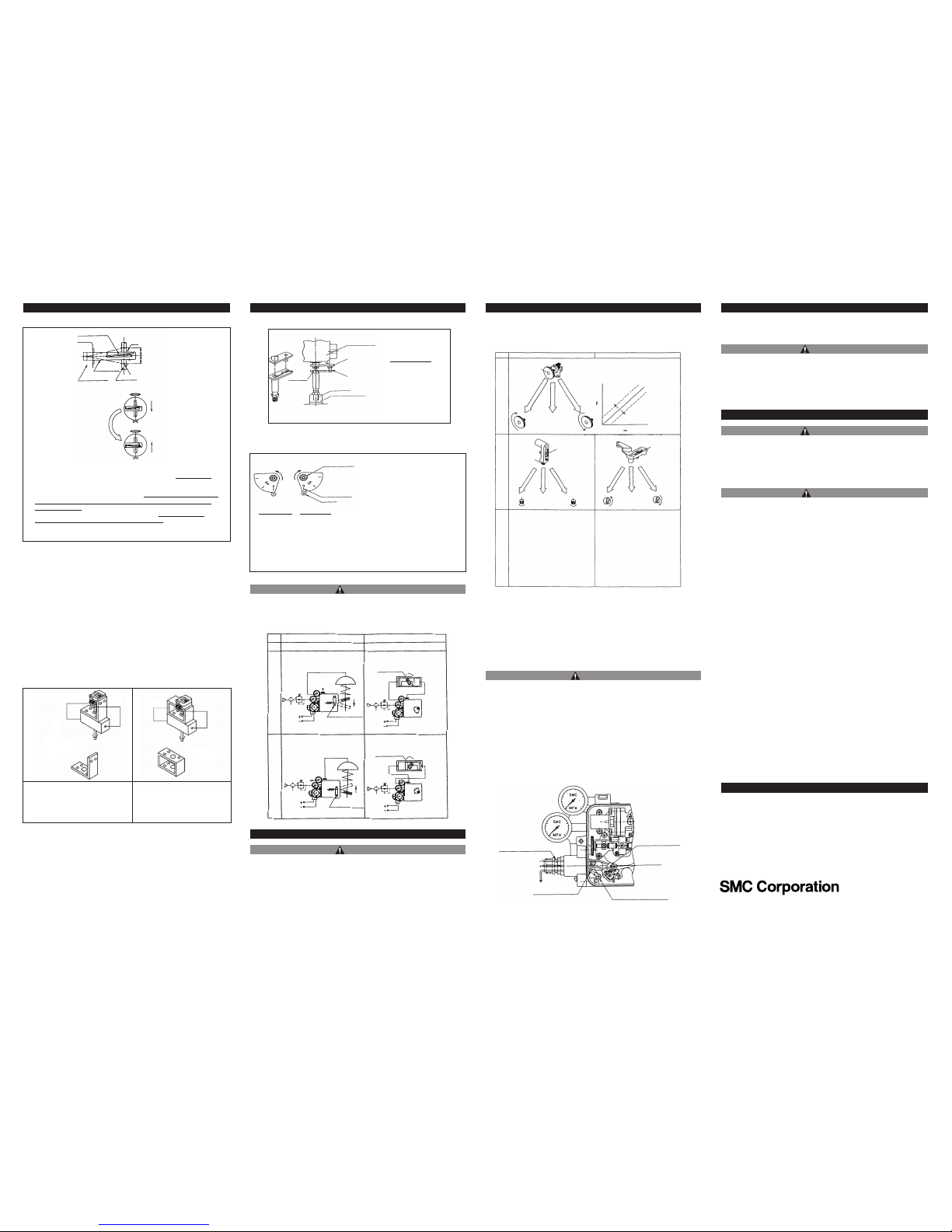
4 Mounting (continued)
4.1.2 Connection with external feedback lever
IP80X14-TFJ21GB-B
4.2 Type IP8100
4.2.1 Example of attaching to actuator
The type IP8000 positioner is compatible with type IP610 and IP6100 in
the attaching pitch. If you are using IP610 or IP6100 already, the bracket
can be used to attach IP8000 to the actuator. If you change from IP6100
to IP8100 and select accessory H (with external scale plate), fork lever
type fitting needs to be adjusted at lower position.
4 Mounting (continued)
4.2.2 Connection with feedback shaft
4.2.3 Cam attaching procedure
CAUTION
Table 2
5 Adjustment
CAUTION
Check the following prior to start the adjustment.
(1) Check that the pipeline is correctly connected with the pressure supply
port and OUT1 and OUT2 ports.
(2) Check that the actuator and positioner are sturdily connected.
(3) Check that the span adjusting lever of internal feed back (Type IP8000)
is attached to the correct (normal or reverse) position.
(Refer to Tables 2.)
(4) Check for locking of the auto/manual changeover screw of pilot valve
(fully tightened in the clockwise direction).
5 Adjustment (continued)
(5) Check for correct use of the cam face (normal or reverse) in Type
IP8100 and that the flange nut is firmly locked. (Refer to Table 2.)
(6) Check that the wires are connected correctly with the (+), (-) and
grounding terminals.
*¹ When the span adjusting screw is turned clock-wise with a slothead(-)
screwdriver, the span increases.When it is tur ned counter-clockwise, the
span decreases.
*² When the span adjusting screw is turned clock-wise with a slothead(-)
screwdriver, the span decreases.When it is turned counter-clockwise, the
span increases.
CAUTION
(1) For this positioner, span and zero point adjustment of each actuator is
necessary. Adjustment shall be done based on each actuator size.
(2) Keep in mind that span and zero point adjustment interfere in each
other.
(3) Characteristics changes due to change of mounting position, ambient
temperature and supply pressure.
(4) If it takes along time until the operation after initial adjustment, check
and adjust this product.
(5) Sensitive adjustment is effective for only double acting actuator.
(6) Manual change function is effective for single acting actuator which is
controlled by using OUT1.
5.1 Electrical wiring
residual air pressure is released from the piping.
(5) When the fixed orifice is clogged with carbon particles or other
material, remove the pilot valve Auto/Manual change over screw
(built in fixed aperture) and clean it by inserting a 0.3mm diameter
wire into the aperture.
(6) When you disassemble the pilot valve, coat the O-ring of the sliding
section with grease. (Use the Dow Corning Toray Company, Limited
SH45 grease.)
(7) Check for air leaks from the compressed air piping. Air leaks could
lower the performance characteristics of the positioner. Air is
normally discharged form a bleed port, but this is necessary air
consumption based on the construction of the positioner, and is not
an abnormality if the air consumption is within the specified range.
(8) If atmosphere is below freezing point, take measure to avoid
freezing the supply pressure and the actuator.
7 Contact
URL: http// www.smcworld.com (Global) http// www.smceu.com (Europe)
Specifications are subject to change without prior notice from the manufacturer.
© SMC Corporation All Rights Reserved.
5 Adjustment (continued)
Connect the (+) and (-) output terminal of positioner with the (+) and (-)
input terminal of positioner respectively. The input port of the electrical
connection is equiped with a (blue) cable connector M20 x 1.5.
WARNING
To use as explosion protection specification may only be connected to a
certified intrinsically safe electrical circuit with the following maximum
values.
Parameters (current circuit)
Ui ≤ 28V, Ii ≤ 125mA, Pi ≤ 1.2W, Ci ≤ 0nF, Li ≤ 0mH
6 Maintenance
WARNING
(1) After installation, repair and disassembly, connect compressed air
and perform a proper function test and leak test. If bleed noise is
louder than the initial state, or operation is abnormal, stop operation
and check if installation is correct or not.
(2) Modification of Electrical construction is prohibited to maintain
explosion proof certification.
CAUTION
(1) Check if supply air is clean or not. Inspect compressed air cleaning
system periodically so that dust, oil and humidity, which can cause
malfunction and failure of the unit, do not enter the equipment
(2) If handled improperly, compressed air can be dangerous.
Maintenance and replacement of unit parts should only be
performed by trained and experienced personnel for instrumentation
equipment , as well as following the product specifications.
(3) Check the positioner once a year. When an excessively worn
diaphragm, O-ring or other packing of any unit that has been
damaged is found, replace with new ones. Treatment at an early
stage is especially important if the positioner is used in a place of
severe environment, such as costal areas.
(4) Before removing the positioner for maintenance, or replacing unit
parts after installation, ensure the supply pressure is shut off and all
(1) Attach to the position that the valve stem and lever form the r
ight angle
when the input signal is 50% (distribute evenly with 50% input signal set as
the reference).
(2) Attach to the position of the runout angle is within the r
ange of 10° to 30°.
(3) To move the valve stem downward at the time of input current increase
(normal actuation), attach to the position at which the tightening spring
comes to the upper side of the connecting metal, as sho
wn in Fig 5.
To move the v
alve stem upw
ard (reverse actuation), turn-over the feedback
lever and attach to the position at which the tightening spring comes to the
lower side of connecting metal.
Tighening spring
Right angle
Input 0% (or 100%) position current
Input 100% (or 0%) position current
Input 50% position current
Connecting metal
Valve stem
Positioner body
Fedd back
lever
(The stem moves down as the input increases)
Stem direction
Stem direction
Turn over the feed
back lever
Fig.4 Attaching the feed back lever
Fig.6 Example of attaching using the
positioner side screw
Attaching using the screw hole of a side
of the positioner and the screw hole at
the actuator top.
Fig.7 Example of attaching using
the positioner back screw
Attaching using the screw hole at
the positioner back and the screw
hole at the actuator top.
OUT 1
OUT 2
Bracket shape
example
Bracket shape
example
OUT 1
OUT 2
(1) Attach to the position at
which the positioner feed
back shaft and the rotary
actuator main shaft are
almost concentr
ic (range
in which the spring pin of
feed back shaft edge
enters the hole of fork
lever assembly shaft
edge).
(2) If the seration joint type
for IP610 is made in a
special specification, it
can be used for this
connection.
Fork lever assembly
(P368010-36)
Positionery body
Fork pin unit
(P368010-23)
M6 x 1
Actuator main shaft
Spring pin
Fig.8 Attaching the feed back lever
(1) Use the DA face of the cam to turn the
actuator main shaft clockwise (viewed from
the positioner front cover side) at the time
of input signal increase. Use the RAface to
turn it counter-clockwise (reverse
actuation). Correctly attach the cam to the
flange part of feed back shaft.
(2) Attach the cam in the procedure of
loosening the hexagonal nut with flange
first, setting the using actuatorto the
starting position and then setting the cam
reference line and the bearing contact point
of span adjusting arm unit to the matching
position.
(3) Do not apply the supply pressure when attaching the cam as otherwise it is very
dangerous.
(4) When the positioner is shipped out of our plant, the cam is tentatively tightened to the
shaft. Be sure to firmly lock the cam to the lock nut [tightening torque 2.0 ~ 2.5 Nm.
Counterclockwise
(Re
verse actuation)
Clockwise
Cam reference
Bearing
(Nor
mal actuation)
Hex. nut with flange
Fig.9 Example of cam attaching
Single action
Reverse actuation
Normal actuation
Double action
IP8000 (Lever type)
IP8100 (Rotary type)
Actuation:The stem moves in the arrow
direction when the input current increases.
Actuation:The actuator main shaft tur ns
clockwise when the input signal increases.
Actuation:The stem moves in the arrow
direction when the input current increases.
(Reverse actuation using the normal
actuation drive unit).
Actuation:The actuator main shaft tur ns
counter-clockwise when the input signal
increases.
OUT 1
Span adjusting lever
normal position
IN
SUP
IN
IN
IN
OUT 1
Main shaft
Double action
actuator
The cam
should be
set to DA
surface.
Double action
actuator
Main shaft
The cam
should be
set to RA
surface.
OUT 2
OUT 1
OUT 2
OUT 2
Span adjusting lever
normal position
SUP
OUT 2:Plug
OUT 1:Plug
Span adjustment Zero point adjustment
Type IP8000
Zero adjusting knob
Move
clockwise
Move counterclockwise
When the zero adjusting knob is turned
clockwise, the starting point increases.When it
is turned counter-clockwise, the starting point
decreases.
Stroke
Input current
Decrease of starting points
Increase of
starting points
Counterclockwise
turn
Adjusting producre
(1) Set the input current to 0% (4mADC in the
standard specification) and turn the zero
adjusting knob by hand to set it to the actuator
starting point.
(2) Then set the input current to 100% (20mADC in
the standard specification) and check the actuator
stroke.At this point depending on the span is too
large or too small, loosen the lock screw and
adjust the span as shown in the illustration above.
(3) Set the input current to 0% and conduct the zero
point adjudtment, as done in Step (1) again.
(4) Repeat the above operations until the
predetermined stroke of the actuator is obtained
to the input current.
(1) Set the input current to 0% (4mADC in the
standard specification) and turn the zero
adjusting knob by hand to set it to the actuator
starting point.
(2) Then set the input current to 100% (20mADC in
the standard specification) and check the
actuator stroke.At this point depending on the
span is too large or too small, loosen the lock
screw and adjust the span as shown in the
illustration above.
(3) Set the input current to 0% and conduct the zero
point adjudtment, as done in Step (1) again.
(4) Repeat the above operations until the
predetermined stroke of the actuator is obtained
to the input current.
Too small starting point
Starting point OK
Too large starting point
to span adjustment
Span adjusting
screw
Lock screw
Span adjusting
screw
Move clockwise
Move counter-clockwise
Too large span
Spam OK
Too small span
Too large span
Spam OK
Too small span
Move counter-clockwise
Move clockwise
Type IP8100
*¹
*²
(blue) cable connector
M20 x 1.5
Input current
Mini-terminal unit
Twisted wire fixing screw
M4 screw for internal
grounding terminal connection
Terminal lug
(Use twisted wire of 2.63 to 6.64mm²)
Grounding
(Use twisted wire of
0.5 to 1.5mm²)
OUT2
AUSTRIA (43) 2262 62280 NETHERLANDS (31) 20 531 8888
BELGIUM (32) 3 355 1464 NORWAY (47) 67 12 90 20
CZECH REP. (420) 541 424 611 POLAND (48) 22 211 9600
DENMARK (45) 7025 2900 PORTUGAL (351) 21 471 1880
FINLAND (358) 207 513513 SLOVAKIA (421) 2 444 56725
FRANCE (33) 1 6476 1000 SLOVENIA (386) 73 885 412
GERMANY (49) 6103 4020 SPAIN (34) 945 184 100
GREECE (30) 210 271 7265 SWEDEN (46) 8 603 1200
HUNGARY (36) 23 511 390 SWITZERLAND (41) 52 396 3131
IRELAND (353) 1 403 9000 UNITED KINGDOM (44) 1908 563888
ITALY (39) 02 92711
Fig.5 Use position for feedback lever
 Loading...
Loading...