Page 1

Page 2

Page 3

EZ Connect™ g 2.4GHz 54 Mbps
Wireless Ethernet Adapter
User Guide
38 Tesla
Irvine, CA 92618
Phone: (949) 679-8000
October 2003
Revision Number: 1.0
Page 4

Copyright
Information furnished by SMC Networks, Inc. (SMC) is believed to be accurate and reliable.
Howev er , no responsib ility is assumed by SMC f or its use, nor f or an y infringements of patents
or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. No license is granted by
implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of SMC. SMC reserves the right to
change specifications at any time without notice.
Copyright © 2003 by
SMC Networks, Inc.
38 Tesla
Irvine, CA 92618
All rights reserved.
Trademarks:
SMC® is a registered trademark; and EZ-Stream, EZ Connect, Barricade and EZ Hub are
trademarks of SMC Networks, Inc. Other product and company names are trademarks or
registered trademarks of their respective holders.
Page 5

COMPLIANCES
FCC - Class B
The Federal Communication Commission Radio Frequency Interference
Statement includes the following paragraph:
The equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B
Digital Device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to
provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential
installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency
energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction, may
cause harmful interference to radio communication. However, there is no
guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this
equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which
can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to
try to overcome the interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the
receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
The equipment is for home or office use.
FCC ID INFORMATION
The product contains an approved FCC module ID: “QDWWN360G”.
CAUTION STATEMENT:
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement
FCC RF Radiation Exposure Statement: This equipment complies with FCC RF
radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled environment. This
equipment should be installed and operated with a minimum distance of 20cm
between the antenna and your body and must not be co-located or operating in
conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.
Caution: Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party
responsible for compliance could v oid the user's authority to operate the
equipment.
Industry Canada - Class B
This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class B limits f or radio noise emissions
from digital apparatus as set out in the interference-causing equipment standard
entitled "Digital Apparatus", ICES-003 of Industry Canada.
Cet appareil numerique respecte les limites de bruits radioelectriques applicables
aux appareils numeriques de Classe B prescrites dans la norme sur le material
brouilleur: "Appareils Numeriques," NMB-003 edictee par l'Industrie.
i
Page 6

COMPLIANCES
Low Power License-Exempt Radio communication Devices
(RSS-210)
1.
Warning Note:
2. Operation in 2.4GHz band: To prevent radio interference to the licensed service, this
device is intended to be operated indoors and away from windows to provide
maximum shielding. Equipment (or its transmit antenna) that is installed outdoors
is subject to licensing.
Exposure of Humans to RF Fields for Mobile Radios Equipment (RSS-102)
1. Mobile radios that are not body worn (e.g. mounted on vehicles or placed on desks,
shelves, etc.) and operated such that humans are normally separated from their
radiating element by at least 20cm are not subject to SAR tests, but must have an
RF evaluation
operation is subject to the following two conditions: (1) this device
may not cause interference, and (2) this device must accept any
interference, including interference that may cause undesired
operation of the device.
by the certification applicant, based on the calculated or measured field strength
value. SAR evaluation can be used if so desired in lieu of a RF evaluation of field
strength limits.
2. Exposures produced by such radios shall not exceed the exposure limits specified
in Health Canada's Safety Code 6. Health Canada’ s address is:
775 Brookfield Road, Ottawa, Ontario
Canada K1A 1C1; Tel: (613) 954 -6699 / Fax:(613) 941-1734 ;
e-mail: alice_mackinnon@hc-sc.gc.ca.
EC Conformance Declaration - Class B
SMC contact for these products in Europe is:
SMC Networks Europe,
Edificio Conata II,
Calle Fructuós Gelabert 6-8, 2
08970 - Sant Joan Despí,
Barcelona, Spain.
This RF product complies with all the requirements of the Directive 1999/5/EC of
the European parliament and the council of 9 March 1999 on radio equipment and
telecommunication terminal Equipment and the mutual recognition of their
conformity(R&TTE).
o
, 4a,
The R&TTE Directive repeals and replaces in the directive 98/13/EEC. As of April
8, 2000.
ii
Page 7

C
OMPLIANCES
Important Safety Notices
• Unplug this product from the AC power before cleaning. Do not use liquid clean-
ers or aerosol cleaners. Use a dry cloth for cleaning.
• Route the power supply cords so that they are not likely to be walked on or
pinched by items placed upon or against them. Pay particular attention to cords
at plugs, convenience receptacles, and the point where they exit from the product.
• Situate the product away from heat sources such as radiators, heat registers,
stoves, and other products that produce heat.
• To prevent fire or shock hazard, do not expose this unit to rain or moisture. Do
not allow water or any foreign objects to enter the interior. This may cause a fire
or electric shock. In the event that water or other foreign objects get into the
product, immediately unplug the AC adapter from the electrical outlet and contact Customer Service for inspection and/or repair/replacement options.
• Do not take apart the equipment. This may cause fire, electric shock or other in-
juries.
• Do not overload wall outlets and extension cords as this can result in a fire or
electric shock.
• This product is for use with the AC adapter that comes with it. Use with any other
AC power is strongly discouraged as it may cause fire, electric shock, or damage
to the equipment.
iii
Page 8

Page 9

T
ABLE OF
2.4GHz 54 Mbps Wireless Ethernet Bridge. . . . .1
System Requirements............ ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... .1
Equipment Checklist....................................................1
Hardware Description. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
Applications. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Understanding Wireless Security . . . . . . . . . . . .8
Hardware Installation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Using the EZ Installation Wizard . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
C
ONTENTS
Configuring Your Computer. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
Using IPCONFIG.......................................................20
Configuring Your IP Address.....................................21
Advanced Web Configuration (Wireless Bridge
mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Browser Configuration...............................................29
Internet Explorer in Windows ....................................29
Internet Explorer in Macintosh...................................30
Advanced Web Configuration (Access Point
mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Browser Configuration...............................................38
Advanced Telnet Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . .51
v
Page 10

Maximum Distance Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Important Notice ........ ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... .. 53
Troubleshooting. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Technical Specification. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Terminology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 60
vi
Page 11

2.4GHz 54 Mbps
Wireless Ethernet
System Requirements
• A web browser, such as Microsoft Internet Explorer 5.5 or
above installed on one PC at your site for configuring the
Wireless Ethernet Bridge
• CD-ROM drive
• An AC power outlet to supply power to the Wireless Ethernet
Bridge
Bridge
• Wired or Wireless Network Adapter
• An available RJ-45 (UTP) port on an Ethernet hub or switch
• TCP/IP network protocol installed on each PC that needs to
access the Internet.
Equipment Checklist
After unpacking the EZ Connect™ g 2.4GHz 54 Mbps Wireless
Ethernet Bridge, check the contents of the box to be sure you
have received the following components:
• 1 SMC2870W 2.4GHz 54 Mbps Wireless Ethernet Bridge
• 1 EZ Installation Wizard and Documentation CD
• 1 Quick Installation Guide
1
Page 12

2.4GHz 54 Mbps Wireless Ethernet Bridge
Immediately inform your dealer in the event of any incorrect,
missing or damaged parts. If possible, please retain the carton
and original packing materials in case there is a need to return
the product.
Please register this product and upgrade the product warranty at
SMC’s Web site: http://www.smc.com
2
Page 13

Hardware Description
Hardware Description
The EZ Connect™ g Wireless Ethernet Bridge supports high
speed communication up to 54 Mbps. It incorporates support for
PRISM Nitro which provides enhanced throughput and range.
This device is fully compliant with 2.4 GHz DSSS and OFDM
CSMA/CA wireless networking as defined in IEEE 802.11b and
802.11g. It can be connected via an RJ-45 conn ection to d evices
such as Nintendo GameCube, Microsoft Xbox, Sony PlayStation
II, and Ethernet ready embedded devices. It can also function as
an IEEE 802.11g Access Point, giving you the capability of
creating a new 802.11g wireless netw ork. In addition, this product
supports Wireless Distribution System (WDS) for repeater
functionality to extend the range of your wireless network.
3
Page 14

Hardware Description
The EZ Connect™ g 54 Mbps Wireless Ethernet Bridge has three
types of LED indicators. Please check the following picture – the
front view of the Bridge and the table below, which displays the
current state the specific LED signifies.
LED Status Function
Power (PWR) On (Green) Power on
Off No power.
Wireless LAN (TX/RX) Blinking (Green) Wireless LAN connection is
transmitting.
On (Green) Wireless LAN connection is
active.
Off Wireless LAN connection is
not active.
LAN (LINK/ACT) Blinking (Green) Wired LAN connection is
transmitting.
On (Green) Wired LAN connection is
active.
Off Wired LAN connection is not
active.
4
Page 15
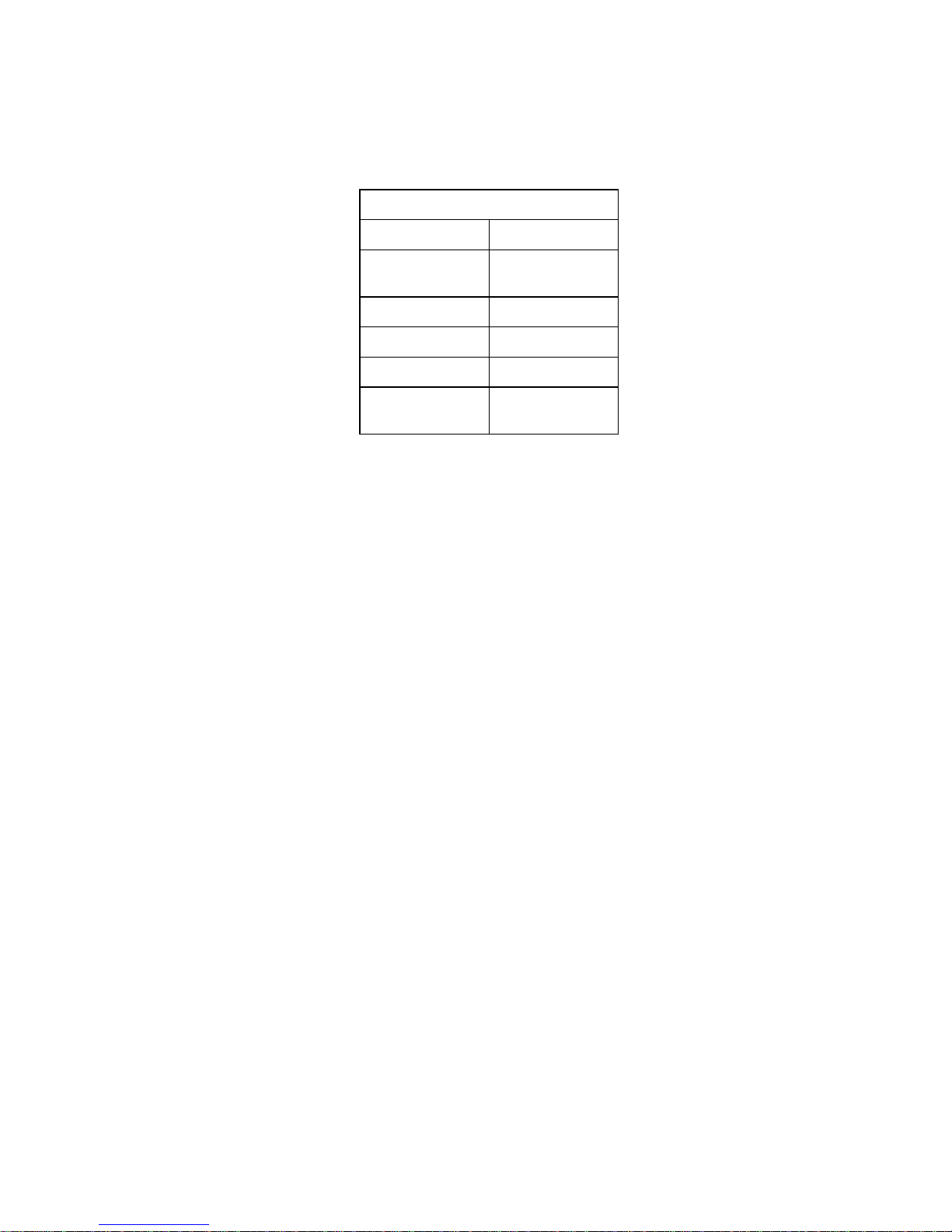
Default Settings
SSID SMC
Hardware Description
Wireless
Adapter Name
IP Address 192.168.2.25
Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0
Gateway 192.168.2.1
Mode Wireless
SMC2870W
Bridge
5
Page 16

Applications
SMC’s EZ Connect 2.4GHz 54 Mbps Wireless Ethernet Bridge
(SMC2870W) can function as:
• an Ethernet to Wireless Bridge, providing a wireless
connection via an RJ-45 connection to devices such as
Microsoft Xbox and Ethernet ready embedded devices
• standard IEEE 802.11g access point
• a wireless repeater, allowing you to effectively extend the
cover age of another SMC2870W that is configured to oper ate
in Access Point mode
Applications
This solution offers fast, reliable wireless connectivity with
considerable cost savings over wired LANs (eliminates long-term
maintenance overhead for cabling). Just install enough wireless
access points to cov er your network area, plug wireless cards into
your notebooks or install wireless adapters into your desktops,
and start networking.
Use this device in conjunction with SMC’ s EZ Connect™ Wireless
Cards to create an instant network that integrates seamlessly
with Ethernet LANs. Moreover , mo ving or expanding y our network
is as easy as moving or installing additional access points – no
wires!
EZ Connect wireless products offer a fast, reliable, cost-effective
solution for wireless Ethernet client access to the networ k in
applications such as:
• Video Game Systems
Provides wireless Internet access for users of video game
systems such as Nintendo GameCube, Microsoft Xbox and
Sony PlayStation II
6
Page 17

Applications
• Remote access to corporate network information
E-mail, file transfer, and terminal emulation
• Difficult-to-wire environments
Historical or old buildings, asbestos installations, and open
areas where wiring is difficult to employ
• Frequently changing environments
Retailers, manufacturers, and banks which frequently
rearrange the workplace or change locations
• Temporary LANs for special projects or peak periods
Trade shows, exhibitions, and construction sites that need a
temporary setup. Retailers, airline, and shipping companies
that need additional workstations for peak periods. Auditors
who require workgroups at customer sites
• Access to databases for mobile workers
Doctors, nurses, retailers, or white-collar work ers who need
access to databases while being mobile in a hospital, retail
store, in an office, or on a campus
• SOHO users
SOHO (Small Office and Home Office) users who need easy
and quick installation of a small computer network
7
Page 18

Understanding Wireless Security
Understanding
Wireless Security
Anyone within range of your wireless network is a potential
security risk. Without wireless security options configured on your
network, a person outside of your physical location, but within
your wireless range may be able to access the network and any
data that is being transmitted over it. SMC Networks’ wireless
devices support the wireless security standard called Wired
Equivalent Privacy (WEP) to prevent unauthorized users from
accessing your network over a wir eless connection. This security
feature uses a secure network key, called a WEP key. The WEP
key encrypts wireless data so that it is only readable by other
computers that have the matching WEP key. The WEP key is
stored on each wireless device, so that data can be encrypted
and decrypted as it is transmitted over the network.
While the Institute of Electrical & Electronics Engineers (IEEE)
802.11i standard is being finalized, an interim solution called
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) has been introduced. The EZ
Connect™ g Wireless Ethernet Bridge is the first device of its
kind to support this new wireless security specification. WPA
defines a set of interoperable se curity enhancements tha t gr eatly
improve upon the level of data encryption and au th e ntic at i on or
access control for e xisting and future wireless LAN systems . WPA
includes Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP), Temporal Ke y
Integrity Protocol (TKIP) and 802.1X for authentication and
dynamic key exchange. In the WPA-enabled network, the client
first associates with the Access Point. The Access P oint does not
allow network access until the user can be successfully
authenticated. If the client shows the correct credentials to the
8
Page 19

Understanding Wireless Security
Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) server, the
client is allowed to join the network. If not, the client stays b loc ked
from joining the LAN. Once the client joins the network, the
authentication server distributes a TKIP encryption key to both
the client and the Access Point. The client can then begin
communicating on the network and maintain the connection,
encrypting data back and forth with the Access Point. Note that
for environments without a Remote A uthentication Dial-In User
Service (RADIUS) infrastructure, WPA supports the use of a
pre-shared key (PSK). WPA-PSK specifies that encryption keys
be dynamically changed (called rekeying) and authenticated
between devices after a specified period of time, or after a
specified number of packets has been transferred.
If you are transferring private information over this wireless
connection, it is recommended to enable WEP or WPA for your
EZ Connect™ g Wireless Ethernet Bridge.
9
Page 20

Hardware Installation
Hardware Installation
1. Select the Site – Choose a location f or your Wireless Ethernet
Bridge. Usually, the best location is at the center of your
wireless coverage area, if possible within line-of-sight of all
wireless devices.
2. Place the Wireless Ethernet Bridge in a position that gives it
maximum coverage. Normally, the higher you place the
antenna, the better the performance.
3. Position the antennas in the desired positions. For more
effectiv e cov erage, positio n the antennas along diff erent ax es.
For example, try positioning the antennas arou nd 45 to 90
degrees apart. (The antennas emit signals along the toroidal
plane – and thus provide more effective coverage when
positioned along different axes.)
4. If used in Wireless Bridge mode, connect the Ethernet cable
to the RJ-45 socket of the device will communicate wirelessly
with an access point.
5. If used in Access Point mode, connect the Ethernet cable –
The SMC2870W can be wired to an Ethernet network through
an Ethernet device such as a hub or a switch using category
3, 4, or 5 UTP Ethernet cable and an RJ-45 connector.
6. Connect the power cable – Connect the power adapter cable
to the 5 VDC power socket on the rear panel. Warning: Use
only the power adapter supplied with the SMC2870W.
7. Check the LED’s on the front of the unit to make sure the
adapter is turned on properly and the status is okay.
10
Page 21

Using the EZ Installation Wizard
Using the EZ
Installation Wizard
The installation method makes the process as simple and
Plug-and-Play as possible. Please be sure that you have
successfully completed the steps shown in Section 6 before
proceeding.
1. Insert the EZ Installation Wizard and Documentation CD.
2. Click the [NEXT] button to continue.
11
Page 22

Using the EZ Installation Wizard
3. The wizard will scan for available SMC2870W’s and then list
them on the left column. Click [NEXT] to continue.
4. You will be asked to enter the password to modify the current
configuration settings. By default, the username is “admin”
and the password is “smcadmin”. Please enter this
information and press [NEXT].
12
Page 23

Using the EZ Installation Wizard
5. You will then be given the option to enable either “Wireless
Bridge” or “Access Point” mode. If you are trying to create a
new 802.11g network for your wireless clients to connect up
to, please select “Access Point” and click [NEXT]. If you are
trying to give an Ethernet-equipped device wireless
connectivity, please select “Wireless Bridge” and click
[NEXT]. If you selected “Wireless Bridge ”, ple as e go to Ste p
6. If you selected “Access Point”, go to Step 10.
13
Page 24

Using the EZ Installation Wizard
6. Wireless Bridge configuration: If you are connecting to an
existing wireless network, select “Infrastructure” and enter the
SSID of your network.
14
Page 25

Using the EZ Installation Wizard
7. Now you will be asked to configure the Network Settings. If
you are connecting to a network with a DHCP server, select
“Use DHCP server” and click [NEXT]. If you do not have a
DHCP server on your network, input a static IP address and
click [NEXT].
15
Page 26

Using the EZ Installation Wizard
8. If you have enabled Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) or Wi-Fi
Protected Access (WPA) on your wireless network, please
enter the private security key settings now. Select the drop
down menus of “Security Mode” to choose between WEP a nd
WPA. Select the drop down me nus of “Key Length” to ch oo se
between 64 or 128-bit encryption.
16
Page 27

Using the EZ Installation Wizard
9. Finally, please verify all the settings you have entered. If any
configuration changes still need to be made, please click
[BACK] and make them now. Otherwise, click [NEXT] to make
the settings take effect. This will take a few seconds. Please
go to Step 14.
10. Access Point configuration: To disable SSID broadcast,
select “Invisible”. Plea se enter your desired SSID, Channel
and Wireless Mode settings and click [NEXT] to continue.
17
Page 28

Using the EZ Installation Wizard
11. Now you will be asked to configure the Network Settings. If
you are connecting to a network with a DHCP server, select
“Use DHCP server” and click [NEXT]. If you do not have a
DHCP server on your network, input a static IP address and
click [NEXT].
12. If you would like to enab le Wired Equiv a lent Privacy (WEP) or
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) on your wireless network,
please enter the private security key settings now. Select the
drop down menus of “Security Mode” to choose between
WEP and WPA. Select the drop down menus of “Key Length”
to choose between 64 or 128-bit encryption.
18
Page 29

Using the EZ Installation Wizard
13. Finally, please verify all the settings you have entered. If any
configuration changes still need to be made, please click
[BACK] and make them now. Otherwise, click [NEXT] to make
the settings take effect.
14. You have now completed the configuration. You can now
begin to use your EZ Connect ™ g Wireless Ethernet Bridge.
19
Page 30

Configuring Your Computer
Configuring Your
Using IPCONFIG
1. Click the “Start” button, click “Run” and type “command”.
2. Press “OK” and a black command prompt will appear.
3. Type “ipconfig” and press enter
Computer
4. Verify that your IP Address is 192.168.2.xxx. If so, you can
now use the web interface of the SMC2870W to configure
additional advanced settings . If y our IP Add ress is comple tely
differen t, please go to the “Configure Your IP Addr ess” section
below.
20
Page 31

Configuring Your IP Address
Configuring Your IP Address
Windows 98/ME
Note: Some Windows 9x/ME systems will request that you
insert your Windows CD in order to complete the
following configuration. Please have this CD ready.
1. Click the "Start" button, choose "Settings", and then click
"Control Panel".
2. Double-click the "Network" icon.
21
Page 32

Configuring Your Computer
3. Select the TCP/IP that is bound to the network adapter that
you are currently using to configure your SMC2870W. Click
"Properties".
22
Page 33

Configuring Your IP Address
4. Select the Specify an IP option and insert 192.168.2.x (where
x is 2 ~ 24, 26 ~ 254). Then insert 255.255.255.0 for the
subnet mask.
5. Press OK and reboot the machine when prompted to do so.
23
Page 34

Configuring Your Computer
Windows 2000
1. Right-click the "Network Places" icon on your desktop and
click "Properties".
2. Right-click your Local Area Connection and click "Properties".
24
Page 35

Configuring Your IP Address
3. Click “Internet Protocol TCP/IP” and click “Properties”. Select
the "Use the following IP Address" option and insert
192.168.2.x (where x is 2 ~ 24, 25 ~254). If requested to
enter a gateway and DNS, you can enter 192.168.2.1.
4. Click "OK" and click "Close" to continue and save the
changes.
25
Page 36

Configuring Your Computer
Windows XP
1. Right-click the "Network Places" icon on your desktop and
click "Properties".
2. Right-click your "Local Area Connection" and click
"Properties".
26
Page 37

Configuring Your IP Address
3. Click “Internet Protocol TCP/IP” and click “Properties”. Select
the "Use the following IP Address" option and insert
192.168.2.x (where x is 2 ~ 24, 26 ~ 254) f or the IP address. If
requested to enter a gateway and DNS, you can type in
192.168.2.1.
27
Page 38

Configuring Your Computer
4. Click "OK" and click "Close" to continue and save the
changes.
28
Page 39

Advanced Web Configuration (Wireless Bridge mode)
Advanced Web
Configuration (Wireless
Bridge mode)
Use the web management interface to define advanced system
parameters, manage and control the Wireless Ethernet Bridge
and its ports, or monitor network conditions. (Note: You MUST
press [Save] and then [Reboot] for changes to take effect.)
Browser Configuration
Confirm your browser is configured for a direct connection to the
Internet using the Ethernet cable that is installed in the computer.
This is configured through the options/preference section of your
browser.
You will also need to verify that the HTTP Proxy feature of your
web browser is disabled. This is so that your web browser will be
able to view the SMC2870W configuration pages. The following
steps are for Internet Explorer. Determine which browser yo u use
and follow the appropriate steps.
Internet Explorer in Windows
1. Open Internet Explorer. Clic k Tools, and then select Internet
Options.
2. In the Internet Options window, click the Connections tab.
29
Page 40

Advanced Web Configuration (Wireless Bridge mode)
3. Click the LAN Settings button.
4. Clear all the check boxes and click OK to save these LAN
settings changes.
5. Click OK again to close the Internet Options window.
Internet Explorer in Macintosh
1. Open Internet Explorer. Click Explorer/Preferences.
2. In the Internet/Explorer/Preferences window, under Network,
select Proxies.
3. Uncheck all check boxes and click OK.
To access the SMC2870W’s web management interface, enter
the Wireless Ethernet Bridge IP address in your web browser as
follows: http://192.168.2.25 Then enter the username and
password and then click LOGIN.
Default username: admin
Default password: smcadmin
30
Page 41

Internet Explorer in Macintosh
After logging into the SMC2870W, all the System Information will
be displayed. You can proceed to another configuration page
using the navigational menu on the left.
Note: If you know the SSID or BSSID of your desired network,
you can automatically connect to it b y moving your mouse
over the appropriate BSSID of the network and then click
the link.
31
Page 42

Advanced Web Configuration (Wireless Bridge mode)
Go to Wireless | Basic Settings to change the Wireless Bridge
mode from Infrastructure to Adhoc, or you can also change the
SSID, Channel, Transmission Rate and Wireless Mode.
Note that when configured as a Wireless Bridge, changing the
channel of the SMC2870W has no effect b ecause it must connect
to the network using the same channel as your Access Point. If
you wish to use a diff erent cha nnel, you m ust change th e channel
in your Access Point’s configuration.
32
Page 43

Internet Explorer in Macintosh
Go to Wireless | Advanced Settings in order to change the
Fragmentation and RTS thresholds. (Note: It is recommended to
leave these values at their default settings.)
RTS Threshold: Set the R TS (Request to Send) frame length . You
may configure the access p oint to initiate an RTS frame. If the
packet size is smaller than the preset RTS threshold size, the
RTS/CTS mechanism will NO T be enabled.
The access point sends Request to Send (R TS) frames to a
particular receiving station to negotiate the sending of a data
frame. After receiving an RTS, the station sends a CTS (Clear to
Send) frame to acknowledge the right of the sending sta tion to
send data frames. The access points contending for the medium
may not be aware of each other. The RTS/CTS mechanism can
solve this “Hidden Node Problem.”
Fragmentation Threshold: If the packet size is smaller than the
preset Fragment size, the packet will not be segmented.
Fr agmentation of the PDUs (P ac kage Data Unit) ca n increase the
reliability of transmissions because it increases the probability of
a successful transmission due to smaller frame size. If there is
significant interference present, or collisions due to high network
utilization, try setting the fragment size to send smaller fragments.
This will enable the retransmission of smaller frames much f aster .
33
Page 44

Advanced Web Configuration (Wireless Bridge mode)
However, it is more efficient to set the fragment size larger if very
little or no interf erence is prese nt because it r equires overhead to
send multiple frames.
Go to Wireless | Security to configure wireless security. If you
have Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) security enabled on your
wireless LAN, please click the [WPA enabled] checkb ox and en ter
your pre-shared key (PSK):
If you have Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) security enabled on
your wireless LAN, please click the [Enable WEP] checkbox.
Then enter your desired k e y length and def ault WEP k e y. You can
use the Passphrase function to automatically generate a WEP
key or you can enter the full 10-digit (64-bit WEP) or 26-digit
(128-bit WEP) manually in the “WEP key” field. Select your
“Authentication” method and press [Save].
34
Page 45

Internet Explorer in Macintosh
Note: A passphrase can contain up to 32 alphanumeric
characters.
When setting up WEP without using the Passphrase function,
only Hexadecimal char acters (r a nge: 0~9 and A~F) ca n b e used.
When encryption is set to 64-bit, a maximum of 10 Hex
characters can be entered in the K e y field. When encryption is set
to 128-bit, a maximum of 26 Hex characters can be used.
Go to System | Admin Settings to change additional advanced
settings. (Note: If yo u ar e not su re how to use a particular setting
35
Page 46

Advanced Web Configuration (Wireless Bridge mode)
or what it means, please review the Terminology section before
continuing. Any erroneous changes made here may cause
unwanted results.)
In the Device Name section, you can change the name of a
particular SMC2870W device. This is very useful if you have
more than one SMC2870W on your network.
In the IP Settings section, you can configure the unit with a static
IP or set it up to use Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol
(DHCP). Note: If you want to use DHCP, you must first make sure
that you ha ve a DHCP Server on your n etwork ready to distrib ute
additional IP Addresses.
36
Page 47

Internet Explorer in Macintosh
In the Security section, change the username and/or password
used to log into the SMC2870W. It is a good idea to write down
your username and password if you decide to change it. If you
forget this information in the future, you will need to reset the
SMC2870W to defaults.
In the Commands section, you can reboot your SMC2870W or
reset it to defaults.
As we add functionality and future enhancements are made,
firmware updates will be posted to SMC’s website. After
downloading the firmware, you need to update the SMC2870W
via the web interface under this Upgrade Firmware section.
Simply click the [Browse] button to locate and select the new
firmware and then press [Upload].
37
Page 48

Advanced Web Configuration (Access Point mode)
Advanced Web
Configuration (Access
Point mode)
Use the web management interface to define advanced system
parameters, manage and control the Wireless Ethernet Bridge
and its ports, or monitor network conditions.
Browser Configuration
Confirm your browser is configured for a direct connection to the
Internet using the Ethernet cable that is installed in the computer.
This is configured through the options/preference section of your
browser.
You will also need to verify that the HTTP Proxy feature of your
web browser is disabled. This is so that your web browser will be
able to view the SMC2870W configuration pages. The following
steps are for Internet Explorer. Determine which browser yo u use
and follow the appropriate steps.
Internet Explorer in Windows
1. Open Internet Explorer. Clic k Tools, and then select Internet
Options.
2. In the Internet Options window, click the Connections tab.
3. Click the LAN Settings button.
38
Page 49

4. Clear all the check boxes and click OK to save these LAN
settings changes.
5. Click OK again to close the Internet Options window.
Internet Explorer in Macintosh
1. Open Internet Explorer. Click Explorer/Preferences.
2. In the Internet/Explorer/Preferences window, under Network,
select Proxies.
3. Uncheck all check boxes and click OK.
To access the SMC2870W’s web management interface, enter
the Wireless Ethernet Bridge IP address in your web browser as
Browser Configuration
follows: http://192.168.2.25 Then enter the username and
password and then click LOGIN.
Default username: admin
Default password: smcadmin
39
Page 50

Advanced Web Configuration (Access Point mode)
After logging into the SMC2870W, all the System Information will
be displayed. You can proceed to another configuration page
using the navigational menu on the left.
Go to the Status | Associations page to view all the wireless
clients that are connected to your SMC2870W. The MAC
Addresses of the clients will be shown. This is helpful if you plan
to configure MAC Address Filtering in the future. You can simply
highlight the appropriate MAC Address, copy and paste it in the
section called Wireless | Access List.
Go to Wireless | Basic Settings to change parameters such as the
SSID, channel, and transmit rate. You can also change the
“Visibility Status”. Selecting [Visible] enables SSID broadcast
whereas selecting [Invisible] disables the SSID broadcast. The
“Wireless Mode” dictates what type of wireless client is allowed to
40
Page 51

Browser Configuration
associate to the SMC2870W. The supported modes are Mixed
(11b+11g), Long Range Mixed (11b+11g), 11g Only, and 11b
Only.
41
Page 52

Advanced Web Configuration (Access Point mode)
Go to Wireless | Access List to enter specific MAC Addresses
that are allowed to connect to the SMC2870W. This function
gives you added security without the ov erhead and increased
processing that WEP or WPA may require.
42
Page 53

Browser Configuration
Go to Wireless | Repeater to make use of the repeating
functionality to extend the wireless range of your network. (Note:
You need at least two SMC2870W units in order to successfully
enable repeating on your wireless LAN)
This function makes use of Wireless Distribution System (WDS)
technology. You can specify up to six WDS links, where each link
is defined by the MAC addresses of the other repeater capable
SMC2870W. (Note: The repeater function must be enabled on
both ends in order to function properly.)
43
Page 54

Advanced Web Configuration (Access Point mode)
Go to Wireless | Advanced Settings in order to change the
Fragmentation and RTS thresholds. (Note: It is recommended to
leave these values at their default settings.)
44
RTS Threshold: Set the R TS (Request to Send) frame length . You
may configure the access p oint to initiate an RTS frame. If the
packet size is smaller than the preset RTS threshold size, the
RTS/CTS mechanism will NO T be enabled.
The access point sends Request to Send (R TS) frames to a
particular receiving station to negotiate the sending of a data
frame. After receiving an RTS, the station sends a CTS (Clear to
Send) frame to acknowledge the right of the sending sta tion to
send data frames. The access points contending for the medium
may not be aware of each other. The RTS/CTS mechanism can
solve this “Hidden Node Problem.”
Page 55

Browser Configuration
Fragmentation Threshold: If the packet size is smaller than the
preset Fragment size, the packet will not be segmented.
Fr agmentation of the PDUs (P ac kage Data Unit) ca n increase the
reliability of transmissions because it increases the probability of
a successful transmission due to smaller frame size. If there is
significant interference present, or collisions due to high network
utilization, try setting the fragment size to send smaller fragments.
This will enable the retransmission of smaller frames much f aster .
However, it is more efficient to set the fragment size larger if very
little or no interf erence is prese nt because it r equires overhead to
send multiple frames.
Beacon Interval: Set the interval value of beacon between
synchronized frames. These synchronous frames also contain
indication of frames that need to transmit to the power-saved
stations.
DTIM: Set the Delivery Traffic Indication Message (DTIM) interval
value. The DTIM indicates how often the MAC layer forwards
multicast traffic. This parameter is necessary to accommodate
stations using Power Save mode. In order to maximize the
utilization of channels, broadcast data is not transmitted every
beacon for stations in Power Save mode. These power-saved
stations must wake up to receive broadcast data at the DTIM
interval. The DTIM is the interval between two synchronous
frames with broadcast information. If you set the value to 2, the
access point will save all mult icast frames for the BSS and
forward them after every second beacon. Having smaller DTIM
intervals delivers multicast frames in a more timely manner,
causing stations in Power Save mode to wake up more often an d
drain power faster. Having higher DTIM values, though, delays
the transmission of multicast frames.
Go to Wireless | Security to configure wireless security. Please
click the [WPA enabled] checkbox and enter your desired
45
Page 56

Advanced Web Configuration (Access Point mode)
pre-shared key (PSK) if you want to enable Wi-Fi Protected
Access (WPA) security on your wireless LAN. You can also set
the “WPA Group K ey Update Interval” value. This specifies how
often the wireless encryption keys are dynamically changed and
clients re-authenticate.
46
Page 57

Browser Configuration
If you have a RADIUS server on your network, you can configure
the SMC2870W to use it for the purpose of authenticating clients
to your wireless LAN. Simply click the [802.1x enabled] chec kbox
and enter your settings:
Please click the [Enable WEP] checkbox if you want to enable
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) security on your wireless LAN.
Then enter your desired k e y length and def ault WEP k e y. You can
use the Passphrase function to automatically generate a WEP
key or you can enter the full 10-digit (64-bit WEP) or 26-digit
(128-bit WEP) manually in the “WEP key” field. Select your
“Authentication” method and press [Save].
47
Page 58

Advanced Web Configuration (Access Point mode)
Note: A passphrase can contain up to 32 alphanumeric
characters.
When setting up WEP without using the Passphrase function,
only Hexadecimal char acters (r a nge: 0~9 and A~F) ca n b e used.
When encryption is set to 64-bit, a maximum of 10 Hex
characters can be entered in the K e y field. When encryption is set
to 128-bit, a maximum of 26 Hex characters can be used.
48
Page 59

Browser Configuration
Go to System | IP Settings to change additional advanced
settings. (Note: If yo u ar e not su re how to use a particular setting
or what it means, please review the Terminology section before
continuing. Any erroneous changes made here may cause
unwanted results.)
In the top portion, you can configure the unit with a static IP or set
it up to use Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). Note:
If you want to use DHCP, y ou must first mak e sure that you hav e a
DHCP Server on your network ready to distribute additional IP
Addresses.
In the Access P o int name section, you can change the name of a
particular SMC2870W device. This is very useful if you have
more than one SMC2870W on your network.
49
Page 60

Advanced Web Configuration (Access Point mode)
Change the username and/or password used to log into the
SMC2870W here. It is a good idea to write down your username
and password if you decide to change it. If you forget this
information in the future, you will need to reset the SMC2870W to
defaults.
In the Commands section, you can reboot your SMC2870W or
reset it to defaults.
As we add functionality and future enhancements are made,
firmware updates will be posted to SMC’s website. After
downloading the firmware, you need to update the SMC2870W
via the web interface under this Upgrade Firmware section.
Simply click the [Browse] button to locate and select the new
firmware and then press [Upload].
50
Page 61

Advanced Telnet Configuration
Advanced Telnet
Configuration
In addition to an EZ Installation Wizard and a Web-based
Management Utility, SMC Networks also gives y ou the ability to
manage the SMC2870W via Telnet.
All of the settings that are available via the Web-based
Management are also made available in the Telnet session. You
can use the standard Telnet or Hyperterminal programs built into
Windows to manage the SMC2870W. The setup below was done
with Hyperterminal:
1. Open Hyperterminal (if you do not have this program on your
PC, you can install it using your original Windows CD)
2. Choose [Connect using:] TCP/IP (Winsock), enter your
SMC2870W’s IP address and use 23 as the Port number.
Press [OK]
51
Page 62

Advanced Telnet Configuration
3. You will be asked to enter your Username and Password
before you can log in.
4. You are now successfully logged into you SMC2870W and
able to change settings. Note: Remember that an y e rron eous
changes here can cause unwanted operation and results.
52
Page 63

Maximum Distance
Important Notice
Maximum distances posted below are actual tested distance
thresholds. However, there are many variables such as barrier
composition and construction, as well as local environmental
interfer ence that ma y impact your actual dista nces and cause you
to experience distance thresholds far lower than those posted
Maximum Distance Table
Table
below. If you have any questions or comments regarding the
features or performance of this product, or if you would like
information regarding our full line of wireless products, visit us at
www.smc.com, or call us toll-free at 800.SMC.4YOU. SMC
Networks stands behind every product sold with a 30-day
satisfaction guarantee and a limited-lifetime warranty.
802.11g Wireless Distance Table
Environmental
Condition
Outdoors: A line-of-sight
environment with no
interference or
obstruction between the
Access Point and users.
Indoors: A typical office
or home environment
with floor to ceiling
obstructions between
the Access Point and
users.
54 48 36 24 18 12 9 6
25m
(82
ft)
10m
(33
ft)
Speed and Distance Ranges
30m
(99
ft)
13m
(43
ft)
38m
(125
ft)
20m
(66
ft)
70m
(230
ft)
28m
(92
ft)
110m
(361
ft)
36m
(118
ft)
150m
(492
ft)
42m
(138
ft)
220m
(722
ft)
50m
(164
ft)
320m
(1050
ft)
60m
(197
ft)
53
Page 64

Maximum Distance Table
802.11b Wireless Distance Table
Environmental
Condition
Outdoors: A
line-of-sightenvironment
with nointerference or
obstructionbetween the
Access Pointand users.
Indoors: A typical office
orhome environment
withfloor to ceiling
obstructionsbetween the
Access Pointand users.
Speed and Distance Ranges
11
Mbps
220m
(722 ft)
50m
(164 ft)
5.5
Mbps
340m
(1115
ft)
65m
(213 ft)
2 Mbps 1 Mbps
420m
(1378
ft)
80m
(263 ft)
520m
(1706
ft)
90m
(296 ft)
54
Page 65

Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting
1. My PC won’t communicate with a PC or printer connected to
the EZ Connect™ g Wireless Ethernet Bridge.
• Perform the following steps:
a)Verify if the PC or printer conn ec te d to th e Wire le ss
Ethernet Bridge is on the same wireless network by
checking the IP configuration.
b)Verify if the SSID and other settings are the same for
all devices connected to the same wireless network.
c)If the wireless LAN settings are correct, verify all the
devices are on the same IP network.
Check the Ethernet crossover cable and make sure it is properly
connected and that the LINK/ACT LED is lit. If this LED is not lit,
confirm you are using a crossover Ethernet cable.
2. I cannot get my Ethernet-equipped device online through the
EZ Connect™ g Wireless Ethernet Bridge
• Perform the following steps:
a)If using DHCP, verify that the DHCP server has two
availab le IP addresses – one f or the SMC2870W and
one for your Ethernet-equipped device
b)If you have MA C Filtering/Access Control enabled on
your Access P oint, y ou must put the MA C Address of
your SMC2870W into your AP’s list of allowed
clients. You can get the SMC2870W’s MAC Address
from the System Info page
55
Page 66

Troubleshooting
3. I cannot access the web based management.
c)Verify that the LINK/ACT LED is lit. If this LED is not
lit, confirm you are using a crossover Ethernet cable
a)Make sure that you have a network adapter installed
on the PC so you can access the web based
management
b)Verify that you are on the same IP network as your
SMC2870W. (See Section 9 for instructions)
56
Page 67

Technical Specification
Technical Specification
Standards:
IEEE 802.11b / IEEE 802.11g
Wireless Data Rates (With A utomatic Fall-back ):
802.11b = 1/2/5.5/11 Mbps
802.11g = 6/9/12/18/24/36/48/54 Mbps
Data Modulation Techniques:
802.11b (DSSS) = BPSK, QPSK, CCK
802.11g (OFDM) = BPSK, QPSK, 16-QAM, 64-QAM
Operating Range:
Up to 1,700 ft
Radio Signal Type:
Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS)
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)
Media Access Protocol:
CSMA/CA (Collision Avoidance) with ACK architecture 32-bit
MAC
Security:
64/128-bit Wired Equiva lent Privacy (WEP)
Temporal Key Integ rity Protocol (TKIP)
802.1x
WPA (WiFi Protected Access)
LED:
Power
Wireless Transmit/Receive
Wired Transmit/Receive
57
Page 68

Technical Specification
Channel Support:
US/Canada - 1-11
Europe - 1-13
Japan – 1-14
RF Output Power:
17dBm +/- 1dBm
Antenna Type:
Two External Dipole
Dimensions:
6.3 x 1.2 x 4.7 in
Compliance:
USA: FCC Part 15 subpart C and Class B
Europe: ETSI 300.328/301-489-17
Industry Ca na da
IDA (Singapore)
Operating System Support (EZ Install Wizard):
Windows 98SE/Me/2000/XP
Temperature Range:
Operating temperature: -20C to 40C (-4F to 104F)
Storage temperature: -25C to 70C (-13F to 158F)
Humidity: 10 to 90% (non-condensing)
Receive Sensitivity:
802.11b
8% FER@1Mbps?-91dBm
8% FER@2Mbps?-88dBm
8% FER@5.5Mbps?-85dBm
8% FER@11Mbps?-83dBm
58
Page 69

802.11g
10% PER@6Mbps?-88dBm
10% PER@9Mbps?-87dBm
10% PER@12Mbps?-84dBm
10% PER@18Mbps?-82dBm
10% PER@24Mbps?-79dBm
10% PER@36Mbps?-75dBm
10% PER@48Mbps?-69dBm
10% PER@54Mbps?-68dBm
Technical Specification
59
Page 70

Terminology
10BaseT - Physical Layer Specification for Twisted-Pair Ethernet
using Unshielded Twisted Pair wire at 10Mbps. This is the most
popular type of LAN cable used today because it is very cheap
and easy to install. It uses RJ-45 connectors and has a cable
length span of up to 100 meters. There are two versions, STP
(Shielded Twisted Pair) which is more expensive and UTP
(Unshielded Twisted Pair), the most popular cable. These cables
come in 5 different categories. However, only 3 are normally used
in LANs, Category 3, 4 and 5. CAT 3 TP (Twisted Pair) cable has
a network data transfe r rate of up to 10M bps. CAT 4 TP cable has
Terminology
a network data transfe r rate of up to 16M bps. CAT 5 TP cable has
a network data transfer rate of up to 100Mbps.
Access Point - A device that is able to receive wireless signals
and transmit them to the wired network, and vice versa - thereby
creating a connection between the wireless and wired networks.
Ad Hoc - An ad hoc wireless LAN is a group of computers, each
with LAN adapters, connected as an independent wireless LAN.
Adapter - A device used to connect end-user nodes to the
network; each contains an interfac e to a specific type of computer
or system bus, e.g. EISA, ISA, PCI, PCMCIA, CardBus, etc.
Auto-Negotiation - A signaling method that allows each node to
define its operational mode (e.g., 10/100 Mbps and half/full
duplex) and to detect the operational mode of the adjacent node.
Backbone - The core infrastructure of a network. The portion of
the network that transports information from one central location
to another central location where it is unloaded onto a local
system.
60
Page 71

Terminology
Base Station - In mobile telecommunications, a base station is
the central radio transmitter/receiver that maintains
communications with the mobile radiotelephone sets within its
range. In cellular and personal communications applications,
each cell or micro-cell has its o wn base station; each ba se station
in turn is interconnected with other cells' bases.
BSS - BSS stands for "Basic Service Set". It is an Access P oint
and all the LAN PCs that are associated with it.
CSMA/CA - Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision
Avoidance
DHCP - Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. This protocol
automatically configures the TCP/IP settings of every computer
on your home network.
DNS - DNS stands for Domain Name System, which allows
Internet host computers to have a domain name (such as
www.smc.com) and one or more IP addresses (such as
192.34.45.8). A DNS server keeps a database of host co mputers
and their respective domain names and IP addresses, so that
when a domain name is requested (as in typing " www.smc.com"
into your Internet browser), the user is sent to the proper IP
address. The DNS server address use d by the computers on y our
home network is the location of the DNS server your ISP has
assigned.
DSL - DSL stands for Digital Subscriber Line. A DSL modem
uses your existing phone lines to transmit data at high speeds.
EAP - (Extensible Authentication Protocol) This is a mode of
conv ersation between a Supplican t and an A uthentication Server.
Access Points or proxy servers do not take part in the
conversation. Their role is simply to forward EAP messages
between the parties performing the authentication. The EAP
61
Page 72

Terminology
messages are transported between a wireless station and an
802.1X Authenticator using EAPOL. The EAP messages are sent
between an 802.1X Authenticator and the Authentication Server
using RADIUS. The EAP framework supports the definition of
EAP-Type Authentication Methods. Today, the major EAP-Type
Authentication Methods include EAP-MD5, EAP-TLS , EAP-TTLS,
EAP-PEAP, and Cisco’s EAP-LEAP.
EAP-MD5 - This is the most basic EAP-Type, which must be
supported by all implementations of EAP. It is not a strong
authentication method and does not support dynamic WEP keys.
EAP-LEAP - (Lightweight Extensible Auth entication Protocol) It is
the type primarily used on Cisco WLAN access points. LEAP
provides security during credential exchange, encrypts using
dynamic WEP keys, and supports mutual authentication.
EAP-TLS - (Transpor t Layer Security) This us es th e TL S
handshake as the basis for authentication. TLS performs
authentication by exchanging digital certificates. The server
sends a certificate to the client and only after validating the
server's certificate does the client present a client certificate.
EAP-TTLS - (Tunneled TLS) This mode an advantage over
EAP-TLS that it only requires a certificate at the Authentication
Server.
Ethernet - A standard for computer networks. Ethernet networks
are connected by spe cial cables and hubs , and mov e data around
at up to 10 million bits per second (Mbps).
ESS - ESS (ESS-ID, SSID) stands for "Extended Service Set".
More than one BSS is configured to become an Extended
Service Set. LAN mobile users can roam between different BSSs
in an ESS (ESS-ID, SSID).
62
Page 73

Terminology
Fast Ethernet NIC - Network interface card that is in compliance
with the IEEE 802.3u standard. This card functions at the media
access control (MAC) layer, using carrier sense multiple access
with collision detection (CSMA/CD).
Fixed IP – (see Static IP)
Full-Duplex - Transmitting and receiving data simultaneously. In
pure digital networks, this is achieved with two pairs of wires. In
analog networks, or digital networks using carriers, it is achieved
by dividing the bandwidth of the line into two frequencies, one for
sending, one for receiving.
Hub - Central connection device for shared media in a star
topology. It may add nothing to the transmission (passive hub) or
may contain electronics that regenerate signals to boost strength
as well as monitor activity (active/intelligent hub). Hubs may be
added to bu s topo logies; for example, a hub can turn an Ethernet
network into a star topology to improve troubleshooting.
IP Address - IP stands for Internet Protocol. An IP address
consists of a series of four numbers separated by periods, that
identifies an single, unique Internet computer host. Example:
192.34.45.8.
ISP - Internet Service Provider. An ISP is a business that
provides connectivity to the Internet for individuals and other
businesses or organizations.
LAN - A communications network that serves users within a
confined geographical area. It is made up of servers,
workstations, a network operating system and a comm un ications
link. Servers are high-speed machines that hold programs and
data shared by network users. The workstations (clients) are the
users' personal computers, which perform stand-alone
processing and access the network servers as required.
63
Page 74

Terminology
Diskless and floppy-only workstations are sometimes used, which
retrieve all software and data from the server. Increasingly, "thin
client" network computers (NCs) and Windows terminals are also
used. A printer can be attached locally to a workstation or to a
server and be shared by network users. Small LANs can allow
certain workstations to function as a server, allowing users
access to data on another user's machine. These peer-to-peer
networks are often simpler to install and manage, but dedicated
servers provide better performance and can handle higher
transaction volume. Multiple servers are used in large networks.
MAC Address - MAC (Media Access Control) A MAC address is
the hardware address of a device connected to a network.
MDI / MDI-X - Medium Dependent Interface - Also called an
"uplink port," it is a port on a network hub or switch used to
connect to other hubs or switches without requiring a crossover
cable. The MDI po rt does not cross the transmit and receive lines,
which is done by the regular ports (MDI-X ports) that connect to
end stations. The MDI port connects to the MDI-X port on the
other device . There are typically one or two ports on a device that
can be toggled between MDI (not crossed) and MDI-X (crossed).
Medium Dependent Interface – X (crossed) - A port on a
network hub or switch that crosses the transmit lines coming in to
the receive lines going out.
NAT – (Network Address Translation) This process allows all of
the computers on your home network to use one IP address. The
NAT capability of the Barricade, allows you to access the Internet
from any computer on your home network witho ut having to
purchase more IP addresses from your ISP. Network Address
Translation can be used to give multiple users access to the
Internet with a single user account, or to map the local address
for an IP server (such as Web or FTP) to a public address. This
secures your network from direct attack by hackers, and provides
64
Page 75

Terminology
more flexible management by allowing you to change internal IP
addresses without affecting outside access to your network. NAT
must be enabled to pro vide multi-user access to the Internet or to
use the Virtual Server function.
Packet Binary Con vulational Code(
tm
) (PBCC) - A modulation
technique developed b y Texas Instruments Inc. (TI) that offers
data rates of up to 22Mbit/s and is fully bac kw ard compatible with
existing 802.11b wirel ess networks.
PCI - Peripheral Component Interconnect - Local bus for PCs
from Intel that provides a high-spe ed data path betw een the CPU
and up to 10 peripherals (video , disk, netw ork, etc.). The PCI bus
runs at 33MHz, supports 32-bit and 64-bit data paths, and bus
mastering.
PPPoE - Point-to-P oint Protocol over Ethernet. Point-to-Point
Protocol is a method of secure data transmission originally
created for dial-up connections. PPPoE is for Ethernet
connections.
Roaming - A function that allows your to move through a
particular domain without losing network connectivity.
Static IP - If your Service Provider has assigned a fixed IP
address; enter the assigned IP address, subnet mask and the
gateway address provided by your service provider.
Subnet Mask - A subnet mask, which may be a part of the TCP/
IP information provided by your ISP, is a set of four numbers
configured like an IP address. It is used to create IP address
numbers used only within a particular network (as opposed to
valid IP address num bers recognized by the Internet.
TKIP - (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) The TKIP process
begins with a 128-bit "temporal key" which is shared among
65
Page 76

Terminology
clients and access points. Then it combines the tempor al ke y with
the client's MAC address and adds a 16-octet initialization vector
to create the key that will encrypt the data. This procedure
ensures that each station uses different key streams to encrypt
the data.
TCP/IP - Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol. This is
the standard protocol for data transmission over the Internet.
TCP - Transmission Control Protocol - TCP and UDP (User
Datagram Protocol) are the two transport protocols in TCP/IP.
TCP ensures that a message is sent accurately and in its entirety.
However, for real-time voice and video, there is really no time or
reason to correct errors , and UDP is used instead.
UDP - User Datagram Protocol - A protocol within the TCP/IP
protocol suite that is used in place of TCP when a reliable
delivery is not required. For example, UDP is used for real-time
audio and video traffic where lost packets are simply ignored,
because there is no time to retransmit. If UDP is used and a
reliable delivery is required, packet sequence checking and error
notification must be written into the ap plic at ion s.
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) – Wi-Fi Protected Access (WP A)
is a set of interoperable security improvements that greatly
increase the level of data encryption and authentication for
existing and future wireless LAN systems . It solves se veral issues
with the widely used WEP standard.
Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) - “Wired Equiv a lent Privacy” is
based on the use of 64-bit or 128-bit keys and the popular RC4
encryption algor ithm. Wireless devices without a valid WEP key
will be excluded from network traffic.
66
Page 77

FOR TECHNICAL SUPPORT, CALL:
From U.S.A. and Canada (24 hours a day, 7 days a week)
(800) SMC-4-YOU; Phn: (949) 679-8000;
Fax: (949) 679-1481
From Euro pe : Contact details can be found on
www.smc-europe.com o www.smc.com
INTERNET
E-mail addresses:
techsupport@smc.com
european.techsupport@smc-europe.com
Driver updates:
http://www.smc.com/
index.cfm?action=tech_support_drivers_downloads
World Wide Web:
http://www.smc.com
http://www.smc-europe.com
FOR LITERATURE OR ADVERTISING RESPONSE, CALL:
U.S.A. and Canada: (800) SMC-4-YOU; Fax (949) 679-1481
Spain: 34-91-352-00-40; Fax 34-93-477-3774
UK: 44 (0) 1932 866553; Fax 44 (0) 118 974 8701
France: 33 (0) 41 38 32 32; Fax 33 (0) 41 38 01 58
Italy: 39 (0) 335 5708602; Fax 39 02 739 14 17
Benelux: 31 33 455 72 88; Fax 31 33 455 73 30
Central Europe: 49 (0) 89 92861-0; Fax 49 (0) 89 92861-230
Nordic: 46 (0) 868 70700; Fax 46 (0) 887 62 62
Eastern Europe: 34 -93-477-4920; Fax 34 93 477 3774
Sub Saharian Africa: 216-712-36616; Fax 216-71751415
North West Africa: 34 93 477 4920; Fax 34 93 477 3774
CIS: 7 (095) 7893573; Fax 7 (095) 789 35 73
PRC: 86-10-6235-4958; Fax 86-10-6235-4962
Taiwan: 886-2-8797-8006; Fax 886-2-8797-6288
Asia Pacific: (65) 238 6556; Fax (65) 238 6466
Korea: 82-2-553-0860; Fax 82-2-553-7202
Japan: 81-45-224-2332 ; Fax 81-45-224-2331
Australia: 61-2-8875-7887; Fax 61-2-8875-7777
India: 91-22-8204437 ; Fax 91-22-8204443
If you are looking for further contact information, please visit
www.smc.com, www.smc-europe.com, or www.smc-asia.com.
38 Tesla
Irvine, CA 92618
Phone: (949) 679-8000
Model Number: SMC2870W-AG
Revision number: 1.0
 Loading...
Loading...