Page 1

Page 2

Copyright
Information furnished by SMC Networks, Inc. (SMC) is believed to be accurate and reliable.
However, no responsibility is assumed by SMC for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or
other rights of third parties which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or
otherwise under any patent or patent rights of SMC. SMC reserves the right to change
specifications at any time without notice.
Copyright © 2003 by
SMC Networks, Inc.
38 Tesla
Irvine, California 92618
All rights reserved.
Trademarks
SMC is a registered trademark; and EliteConnect, EZ Connect and EZ Hub are trademarks of SMC
Networks, Inc. Other product and company names are trademarks or registered trademarks of
their respective holders.
Page 3

Compliances
FCC - Class B
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection
against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can
radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with instructions, may
cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that the
interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful
interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment
off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the interference by one or more of the
following measures:
• Reorient the receiving antenna
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which
the receiver is connected
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help
FCC Caution: To assure continued compliance, (example - use only shielded interface cables
when connecting to computer or peripheral devices). Any changes or modifications not expressly
approved by the party responsible for compliance could void the user’s authority to operate this
equipment.
This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions: (1) This device may not cause harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept
any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
CAUTION STATEMENT:
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled
environment. This equipment should be installed and operated with a minimum distance of 5
centimeters between the radiator and your body. This transmitter must not be co-located or
operating in conjunction with any other
antenna or transmitter. Note: In order to maintain compliance with the limits of a Class B digital
device, SMC requires that you use a quality interface cable when connecting to this device.
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by SMC could void the user’s authority to
operate this equipment.
Attach unshielded twisted-pair cable (UTP) to the RJ-45 port and shielded USB cable to the USB
port.
Industry Canada - Class B
This digital apparatus does not exceed the Class B limits for radio noise emissions from digita l
apparatus as set out in the interference-causing equipment standard entitled “Digital Apparatus,”
ICES-003 of Industry Canada.
Cet appareil numérique respecte les limites de bruits radioélectriques applicables aux appareils
numériques de Classe B prescrites dans la norme sur le matérial brouilleur: “Appareils
Numériques,” NMB-003 édictée par l’Industrie.
EC Conformance Declaration - Class B
SMC contact for these products in Europe is:
SMC Networks Europe,
Edificio Conata II,
Page 4

Calle Fructuós Gelabert 6-8, Planta 2,
08970 - Sant Joan Despí,
Barcelona, Spain.
This RF product complies with R&TTE Directive 99/5/EC (Annex IV) and with the requirements of
the Council Directive 89/336/EEC on the Approximation of the laws of the Member States relating
to Electromagnetic Compatibility and 73/23/EEC for electrical equipment used within certain
voltage limits and the Amendment Directive 93/68/
EEC. For the evaluation of the compliance with these Directives, the following standards were
applied:
• Electromagnetic compatibility and radio spectrum matters (ERM) EN300 328-1 (2001-12) and
EN300 328-2 (2001-12)
• Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Standard for radio equipment and services EN301 489-1
and EN301 489-17
• Safety Test EN60950
• Immunity to conducted disturbances, Induced by radio-frequency fields EN 61000-4- 6:1996
(0.15 - 80 MHz with 1 kHz AM 80% Modulation: 3 V/m)
• Power frequency magnetic field immunity test according to EN 61000-4-8:1993 (1 A/m at
frequency 50 Hz)
• Voltage dips, short interruptions and voltage variations immunity test according to EN 61000-411:1994 (>95% Reduction @10ms, 30% Reduction @500 ms, >95% Reduction @5000 ms)
• LVD: EN 60950 (A1/1992; A2/1993; A3/1993; A4/1995; A11/1997)
• MDD: IEC 60601-1
Wichtige Sicherheitshinweise (Germany)
1. Bitte lesen Sie diese Hinweise sorgfältig durch.
2. Heben Sie diese Anleitung für den späteren Gebrauch auf.
3. Vor jedem Reinigen ist das Gerät vom Stromnetz zu trennen. Verwenden Sie keine Flüssigoder Aerosolreiniger. Am besten eignet sich ein angefeuchtetes Tuch zur Reinigung.
4. Die Netzanschlußsteckdose soll nahe dem Gerät angebracht und leicht zugänglich sein.
5. Das Gerät ist vor Feuchtigkeit zu schützen.
6. Bei der Aufstellung des Gerätes ist auf sicheren Stand zu achten. Ein Kippen oder Fallen
könnte Beschädigungen hervorrufen.
7. Die Belüftungsöffnungen dienen der Luftzirkulation, die das Gerät vor Überhitzung schützt.
Sorgen Sie dafür, daß diese Öffnungen nicht abgedeckt werden.
8. Beachten Sie beim Anschluß an das Stromnetz die Anschlußwerte.
9. Verlegen Sie die Netzanschlußleitung so, daß niemand darüber fallen kann. Es sollte auch
nichts auf der Leitung abgestellt werden.
10. Alle Hinweise und Warnungen, die sich am Gerät befinden, sind zu beachten.
11.Wird das Gerät über einen längeren Zeitraum nicht benutzt, sollten Sie es vom Stromnetz
trennen. Somit wird im Falle einer Überspannung eine Beschädigung vermieden.
12. Durch die Lüftungsöffnungen dürfen niemals Gegenstände oder Flüssigkeiten in das Gerät
gelangen. Dies könnte einen Brand bzw. elektrischen Schlag auslösen.
13. Öffnen Sie niemals das Gerät. Das Gerät darf aus Gründen der elektrischen Sicherheit nur
von authorisiertem Servicepersonal geöffnet werden.
14. Wenn folgende Situationen auftreten ist das Gerät vom Stromnetz zu trennen und von einer
qualifizierten Servicestelle zu überprüfen:
a. Netzkabel oder Netzstecker sind beschädigt.
b. Flüssigkeit ist in das Gerät eingedrungen.
c. Das Gerät war Feuchtigkeit ausgesetzt.
Page 5

d. Wenn das Gerät nicht der Bedienungsanleitung entsprechend funktioniert oder Sie mit Hilfe
dieser Anleitung keine Verbesserung erzielen.
e. Das Gerät ist gefallen und/oder das Gehäuse ist beschädigt.
f. Wenn das Gerät deutliche Anzeichen eines Defektes aufweist.
15. Stellen Sie sicher, daß die Stromversorgung dieses Gerätes nach der EN60950 geprüft ist.
Ausgangswerte der Stromversorgung sollten die Werte von AC 7,5- 8V, 50-60Hz nicht über- oder
unterschreiten sowie den minimalen
Strom von 1A nicht unterschreiten. Der arbeitsplatzbezogene Schalldruckpegel nach DIN 45 635
Teil 1000 beträgt 70dB(A) oder weniger.
Page 6

1 | System Requirements
• Available 32-bit Cardbus PCMCIA Type II slot
• Windows 98SE/Me/2000/XP
• Minimum of 32MB RAM and 300 MHz CPU
• Minimum of 5 MB available hard disk space for utility and driver installation
• Another IEEE 802.11b, IEEE 802.11g or 802.11a compliant device installed in your
network, such as the SMC2804WBR Barricade™ g 2.4GHz 54 Mbps Wireless Cable/DSL
Broadband Router, or another PC with a wireless adapter, such as the SMC2662W EZ
Connect Wireless USB Adapter.
Page 7

2 | Package Contents
After unpacking the EliteConnect Universal 2.4GHz/5GHz High Power Wireless Cardbus Adapter,
check the contents of the box to be sure you have received the following components:
• 1 SMC2536W-AG 2.4GHz/5GHz Universal High Power Wireless Cardbus Adapter
• 1 EZ Installation Wizard and Documentation CD
• 1 Quick Installation Guide
Immediately inform your dealer in the event of any incorrect, missing or damaged parts. If
possible, please retain the carton and original packing materials in case there is a need to return
the product.
Please register this product and upgrade the product warranty at SMC's Web site:
http://www.smc.com
Page 8

3 | Getting Started…
Warning:
• Network cards are sensitive to static electricity. To protect the card, avoid touching its
electrical components and always touch the metal chassis of your computer before
handling the card
1. Turn on your computer and insert the EZ Installation Wizard, and Documentation
CD. Run the utility software and then reboot when requested.
2. Find an available Cardbus slot in your computer.
3. With the SMC2536W-AG 2.4GHz/5GHz Universal Hi gh Power Wireless Cardbus
Adapter's 68-pin connector facing the Cardbus slot, and the "EZ Connect g" label
facing up, slide the card completely into the Cardbus slot as shown below:
4. For Windows 98SE/Me/2000, Cardbus specification is required. Please check the
documents for your Cardbus adapter driver before installing the software driver
for the SMC2536W-AG.
5. The card will be automatically installed upon insertion. Once complete, you may
take advantage of the wireless functionality this adapter has to offer.
Page 9

4 | Driver Installation – Option 1 (Recommended)
Windows 98SE/Me/2000/XP
NOTE: Installation processes will require the use of your original, licensed copy of Windows.
Please have your Windows CD available BEFORE proceeding with the installation.
This installation method makes the process as simple and Plug-and-Play as possible. Simply run
the EZ Installation Wizard, reboot your machine and insert your EliteConnect Universal
SMC2536W-AG High Power Wireless Cardbus Adapter. It's as easy as 1- 2-3.
Step 1: Insert the EZ Installation Wizard and Documentation CD.
Step 2: Click the [Install Driver/Utility] button. Note: By default, the program will not install the
Boingo software. If you wish to install Boingo, please verify the checkbox is selected.
Step 3: Please shut down your machine and insert your SMC2536W-AG. Once the Windows
Operating System is booted up, it will find the new hardware and automatically install it.
Section 4.1 | Other Setup Processes
The following are Operating System-specific options that may appear during this installation
procedure:
Windows 98SE/Me: If you are using Windows 98SE, you must have your original Windows CD
on hand. In Windows Me, the installation process is fully Plug-and- Play.
Windows 2000/XP: Select [Install the software automatically]. If prompted, click [Next] to
complete the installation.
Continue to the Utility Configuration section for documentation on how to use the utility
application for your SMC2536W-AG.
Page 10
5 | Driver Installation – Option 2
Windows 98SE/Me/2000/XP
Section 5.1 | Windows 98SE
NOTE: Installation processes will require the use of your original, licensed copy of Windows.
Please have your Windows CD available BEFORE proceeding with the installation.
Step 1: After you have inserted the EliteConnect Universal SMC2536W-AG High Power Wireless
Cardbus Adapter in your machine, the Operating System will automatically recognize the adapter
and prompt you for the appropriate drivers. Click the [Next >] button to begin the installation.
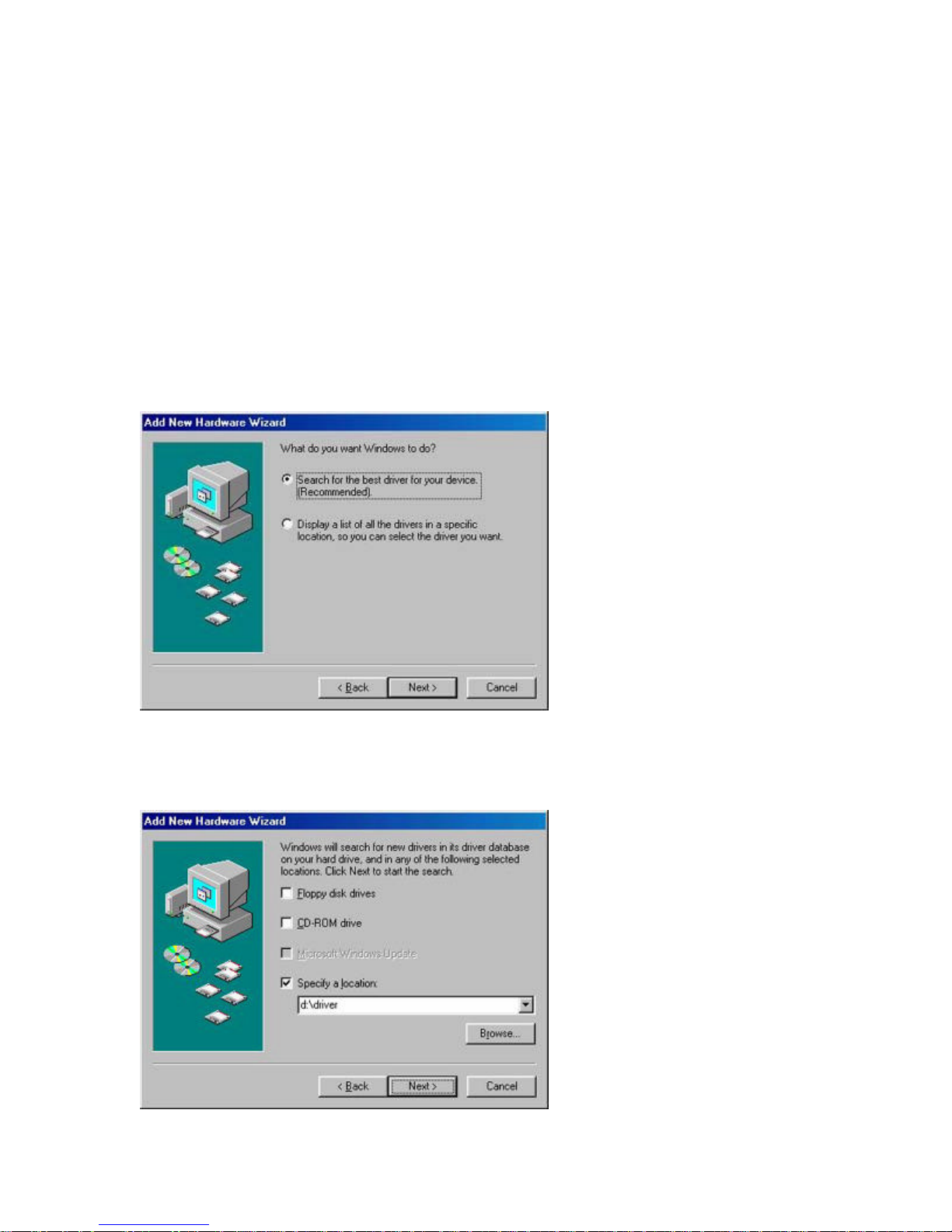
Step 2: Insert the Driver CD and select the [Search for the best driver for your device] option
and click [Next >].
Step 3: Clear all checkboxes except for [Specify a location:]. Then press the [Browse] button
and look for the drivers on your CD-ROM. Browse to ?:\driver. (Note: The "?" equals the letter of
your CD-ROM drive. In most cases, this is D.)
Page 11
Step 4: The system should find the drivers. Click the [Next >] button to continue the installation.
The wizard will show "SMC2536W-AG Universal High Power Wireless Adapter".
(Note: If the system could not find the drivers, click the [< Back] button, and select the [Display
a list of all the drivers...] option. Select [Network Adapters] from the list of devices, press [Have
Disk] and once again browse to the location of the drivers)
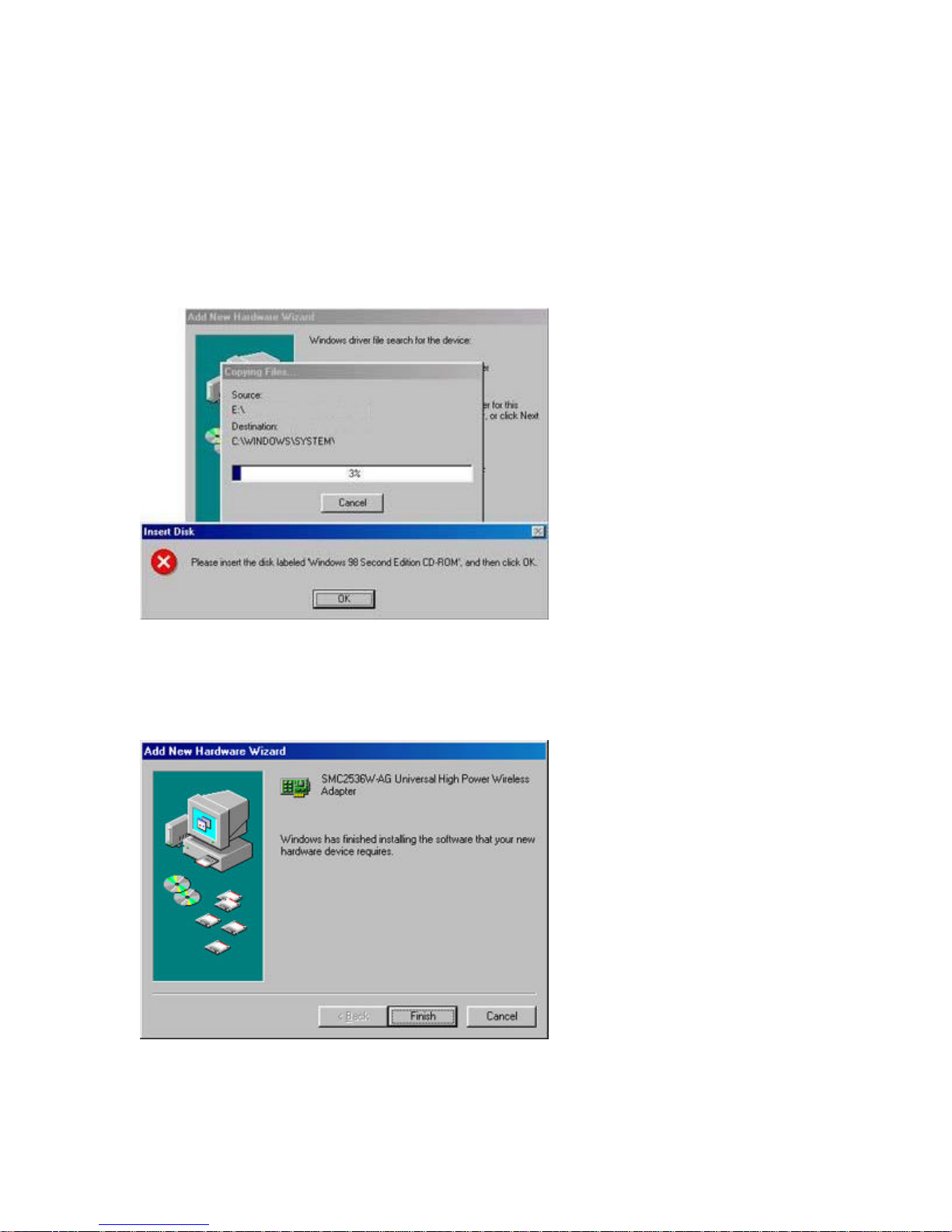
Step 5: Once the system has copied the SMC drivers from the CD, it may then request files from
your original Windows disk. Please insert the Windows CD at this time.
Step 6: The system will copy the files. Do NOT press [Cancel].
Step 7: Once all the necessary files are copied from the Windows CD, the driver install process
will be complete. Click [Finish] to exit the wizard.
Page 12
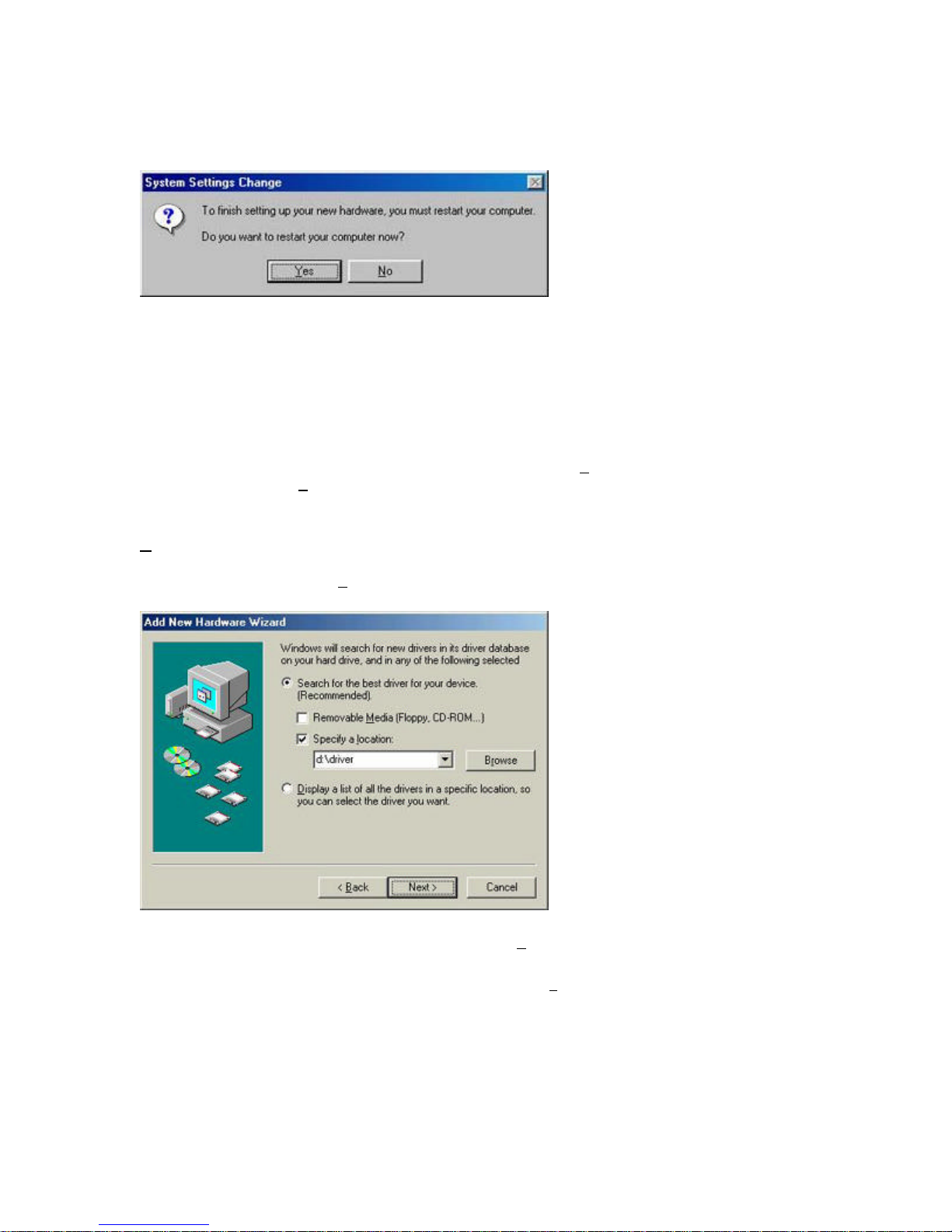
Step 8: You will then be prompted to reboot the machine. Press [Yes]. Upon reboot, the
SMC2536W-AG will be initialized and ready for use.
Section 5.2 |Windows Me
NOTE: Installation processes will require the use of your original, licensed copy of Windows.
Please have your Windows CD available BEFORE proceeding with the installation.
Step 1: After you have inserted the EliteConnect Universal SMC2536W-AG High Power Wireless
Cardbus Adapter in your machine and turned it back on, the OS will automatically recognize the
adapter and prompt you for the appropriate drivers. Select the [Specify the location of the driver]
option. Then click the [ Next >] button to begin the installation.
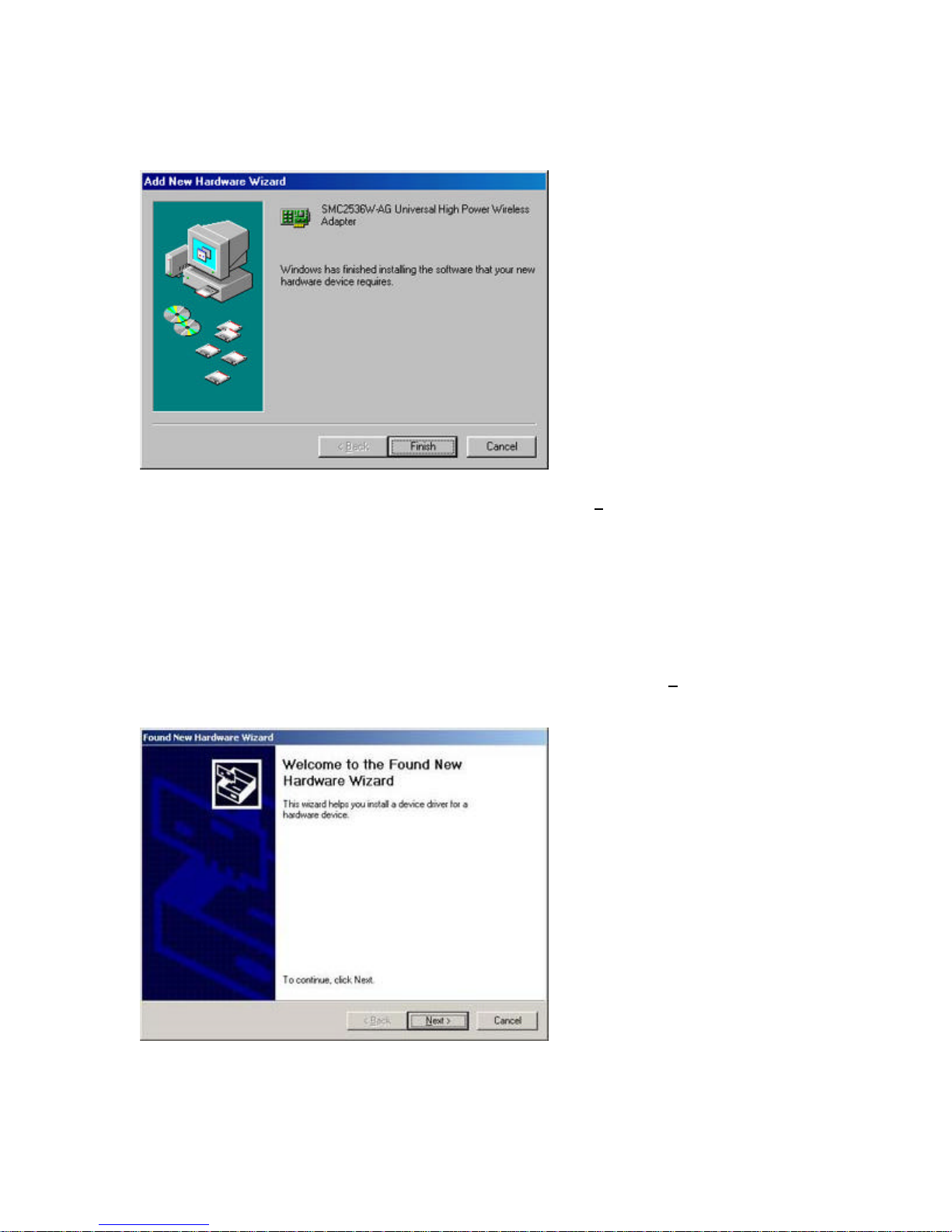
Step 2: Insert the Driver CD and select the [Specify a location:] option. Clear the [Removable
Media] checkbox. Then press the [Browse] button and look for the drivers on your CD. This
should be located in ?: \driver. (Note: The ? equals the letter of your CD-ROM drive. In most
cases, this is D.) Then click [Next >].
Step 3: The system should find the drivers. Click the [Next >] button to continue the installation.
(Note: If the system could not find the drivers, click the [< Back] button, and select the [Display
a list of all the drivers] option. Select [Network Adapters] from the list of devices, press [Have
Disk] and once again browse to the location of the drivers)
Page 13
Step 4: Once all the necessary files have been copied, the driver installation is complete. Click
[Finish] to exit the wizard.
Step 5: You will then be prompted to reboot the machine. Press [Yes]. Upon reboot, the
SMC2536W-AG will be initialized and ready for use.
Section 5.3 | Windows 2000
Step 1: After you have inserted the EliteConnect Universal SMC2536W-AG High Power Wireless
Cardbus Adapter in your machine and turned it back on, the Operating System will automatically
recognize the adapter and prompt you for the appropriate drivers. Click the [Next >] button to
begin the installation.
Page 14
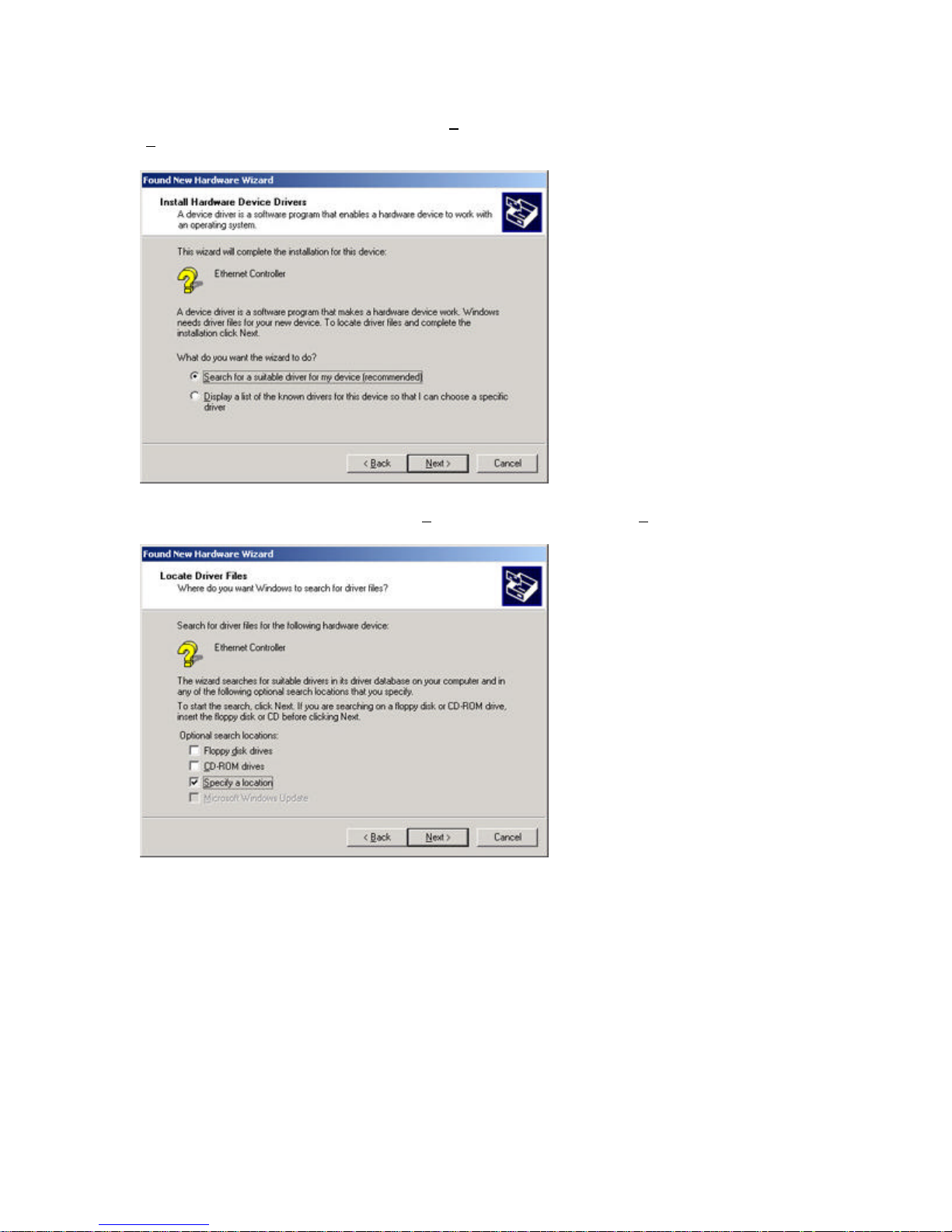
Step 2: Insert the Driver CD and select the [Search for a suitable driver...] option. Then click
[Next >].
Step 3: Clear all checkboxes except for [Specify a location]. Then click [Next >].
Page 15
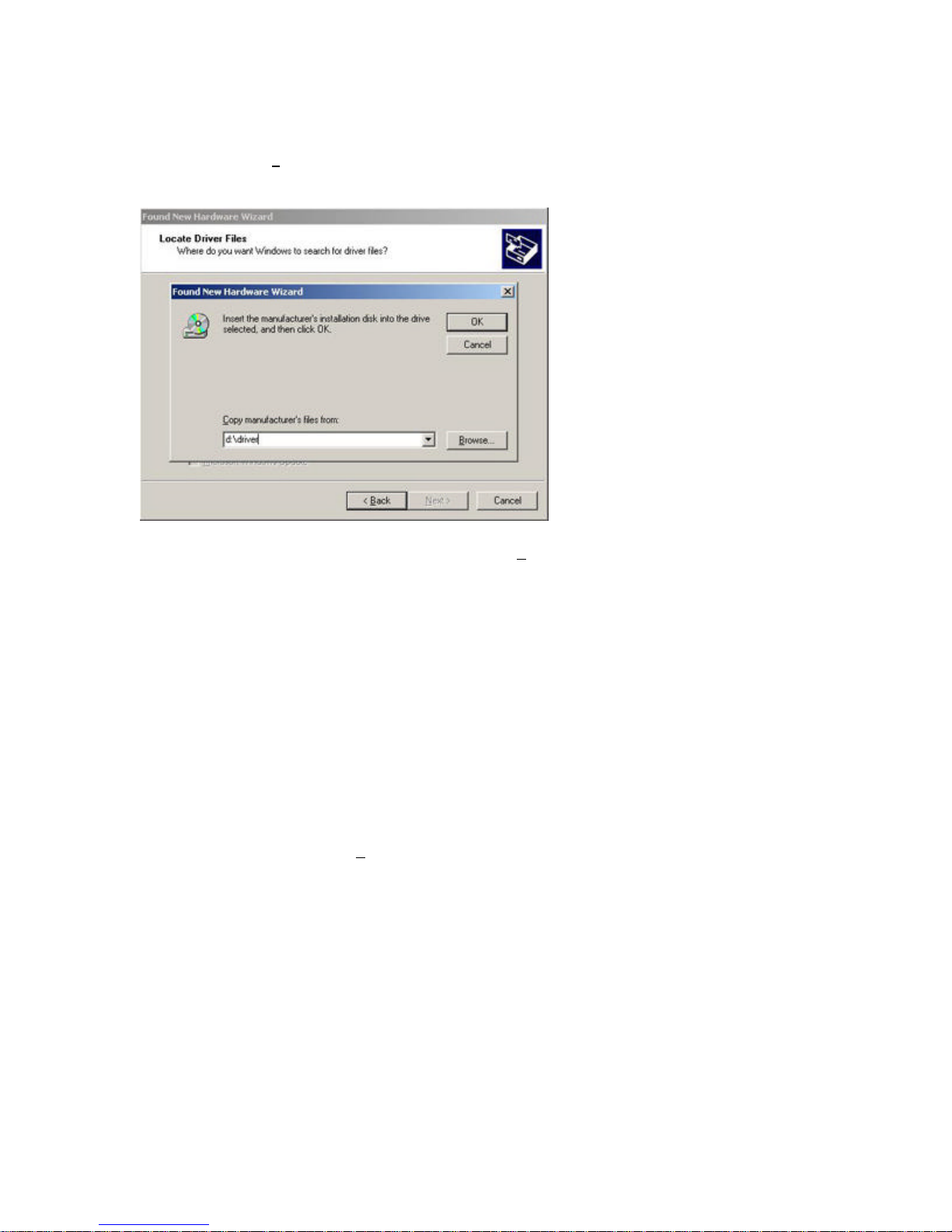
Step 4: You will then be prompted to enter the location of the drivers. This should be ?:\driver.
(Note: The ? equals the letter of your CD-ROM drive. In most cases, this is D.) Then click [OK].
You can also click [Browse] and browse to the location of the drivers on the CD for further
verification.
Step 5: The system should find the drivers. Click the [Next >] button to continue the installation.
(Note: If the system could not find the drivers, click the [< Back] button, and select the [Display
a list of the known drivers...] option. Select [Network Adapters] from the list of devices, press
[Have Disk] and once again browse to the location of the drivers.
Step 6: You have now completed the driver installation. Click [Finish] to initialize the adapter.
Section 5.4 | Windows XP
Step 1: After you have inserted the EliteConnect Universal SMC2536W-AG High Power Wireless
Cardbus Adapter in your machine and turned it back on, the Operating System will automatically
recognize the adapter and prompt you for the appropriate drivers. Select [Install from a list or
specific location] and click the [ Next >] button to begin the installation.
Page 16

Step 2: Insert the Driver CD and check the [Include this location in the search] option. Make
sure the [Search removable media] option is not checked. Click [Browse] and find the location of
the drivers. This should be ?:\driver. (Note: The ? equals the letter of your CD-ROM drive. In
most cases, this is D.) Then click [Next >].
Step 3: This process will be completed once the drivers are copied to the hard drive and
installed. Please click [Finish] to exit the wizard.
After clicking [Finish], you will see the following message in your system tray:
Page 17

6 | Driver Verification
Windows 98SE/Me/2000/XP
Section 6.1 | Windows 98SE/Me
Step 1: Right-click the My Computer icon on your desktop and click [Properties].
Step 2: Then go to the [Device Manager] tab and open the [Network adapters] section. You
should see your SMC2536W-AG Universal High Power Wireless Cardbus Adapter in this menu.
Highlight it and click [Properties].
Step 3: The Device Status shows that the "This device is working properly". If there are any
error messages displayed here, you will need to click the SMC adapter and click [Remove]. Then
reboot the machine and go through the installation process again.
Page 18

Section 6.2 | Windows 2000
Step 1: Right-click the My Computer icon on your desktop and click [Properties].
Step 2: Then go to the Hardware tab and click [Device Manager]. Open the [Network adapters]
section. You should see your SMC2536W-AG Universal High Power Wireless Cardbus Adapter in
this menu. Right-click your adapter and click [Properties].
Step 3: The Device Status shows that the "This device is working properly". If there are any
error messages displayed here, you will need to right-click the SMC adapter and click [Uninstall].
Then reboot the machine and go through the installation process again.
Page 19

Section 6.3 | Windows XP
Step 1: Click [Start] and click [Control Panel]. Then click the [Performance and Maintenance]
icon and select [System].
Step 2: Then go to the Hardware tab and click [Device Manager]. Open the [Network adapters]
section. You should see your SMC2536W-AG Universal High Power Wireless Cardbus Adapter in
this menu. Right-click the adapter and click [Properties].
Step 3: The Device Status shows that "This device is working properly". If there are any error
messages displayed here, you will need to right-click the SMC adapter and click [Uninstall]. Then
reboot the machine and go through the installation process again.
7 | Utility Installation
Windows 98SE/Me/2000/XP
This Installation method makes the process as simple and Plug-and-Play as possible. Simply run
the EZ Installation Wizard, reboot your machine and insert your EliteConnect Universal
SMC2536W-AG High Power Wireless Cardbus Adapter. It's as easy as 1- 2-3.
Step 1: Insert the EZ Installation Wizard and Documentation CD.
Page 20

Step 2: Click the [Install Driver/Utility] button (Note: If you completed the DRIVER
INSTALLATION OPTION #1 , you do NOT need to install the utility. Please skip to "Utility
Configuration").
Step 3: The installation wizard will begin. Click [Next >].
Step 4: You will be given the option to choose the location where the Configuration Utility will be
installed. It is recommended to leave this at the default value. Click [ Next >] to continue.
Page 21

You will also be given the option to choose the Folder name that will appear in the Start Menu. It
is recommended to leave this at the default value. Click [Next >] to continue.
Step 5: Click [Next] to begin copying the utility files to your computer.
Page 22

You have now completed the utility installation process. Click [Finish] to exit the wizard.
Step 6: Please shut down your machine. Then insert your SMC2536W-AG and boot up the
operating system.
8 | Utility Configuration
When the utility program is running, there will be a quick launch icon in the lower right- hand
corner of the taskbar. The icon will be GREE N if you have a good connection to a wireless
network. If it is red, you will need to verify the network settings and check to be sure that the
Wireless Access Point on your network is turned on. You may also need to re-position the Access
Point and place it in a higher position so that you are able to gain more wireless signal strength.
Double-click the quick launch icon in the system tray to bring up the Configuration Utility. This
provides quick access to management statistics and adapter settings.
The Configuration Utility includes the following tabs:
Profile Management: Allows you to implement Profile Management, edit SSID data, change
the Tx Rate and Operating mode, and enable 64/128/152-bit WEP or advanced security such as
LEAP, PEAP, TLS, or TTLS.
Link Information: Allows you to view/monitor network status, throughput, wireless channel,
and TCP/IP Information.
IP Information: Displays TCP/IP data.
Page 23

Site Survey: Displays all the Access Points within range of the wireless adapter's signal. Allows
you to select your desired WLAN.
Driver Information: Shows the driver and utility version information.
Section 8.1 | Configuration
The profile management window will show you the current selected profile of the wireless card.
Click [New] to create a new profile. Click [Modify] to modify the current settings in the selected
profile. Click [Remove] to delete the current profile. Click [Activate] to initialize a different profile.
Page 24

When you want to create a new network, you must enter the Profile Name. Also enter the SSID
of your network in any of the fields show under "Network Names". If you have more than one
Access Point in your local network with identical security settings, you can enter up to three
different SSID values - representing up to three different WLANs in your vicinity.
Then go to “Security” tab of the SMC2536W-AG Utility to configure various encryption options.
To configure WPA (Wi-Fi Protected Access), choose “WPA” under “Set Security Method”. After
selecting WPA, you will be given the option of using WAP EAP Type: TLS or PEAP.
Select TLS and then [Configure] to configure TLS options.
Page 25

You must have a digital certificate installed on your machine. If you do not, you will see the
following error message:
To configure PEAP, make sure WPA is selected. Then select PEAP and then [Configure].
Enter the User name and Password. After that click the [Advanced Configuration] button, you
can then specify the Server or Domain and Login Name information.
Page 26

For configuring 802.1x security method, select 802.1x under “Set Security Method”, you will be
given the option of using 802.1x EAP Type: TLS, PEAP, or LEAP.
Click TLS and then [Configure] to configure TLS options.
Page 27

You must have a digital certificate installed on your machine. If you do not, you will see the
following error message:
Click PEAP and then [Configure] to configure PEAP options.
Enter the User name and Password. After that click the [Advanced Configuration] button, you
can then specify the Server or Domain and Login Name information.
Page 28

Click LEAP and then [Configure] to configure LEAP options.
NOTE: PLEASE CONSULT YOUR NETWORK ADMINISTRATOR FOR ASSISTANCE IN
CONFIGURING THESE ADVANCED SECURITY OPTIONS.
Page 29

In addition to WPA and 802.1x, there are the options to enable WEP (Pre-Shared Key) or the new
Wi-Fi Protected Access Pre-Shared Key (WPA-PSK) on your wireless LAN. For WEP (Wired
Equivalent Privacy) security, the SMC2536W-AG Utility supports HEX and ASCII key entries.
For the HEX Key Format, the security is enabled by entering 10-digit keys for the 64-bit WEP
configuration, 26-digit keys for a 128-bit WEP configuration, and 32-digit keys for a 152-bit WEP
configuration. Allowed hex keys are 0-9 and A-F. For the ASCII Key Format, the security is
enabled by entering 5 characters for 64-bit WEP, 13 characters for 128-bit WEP and 16
characters for 152- bit WEP.
Click Pre-Shared Key and select the [Configure] button to enter in WEP keys.
Page 30

Select the desired encryption strength from the drop-down menu on the right (64-, 128- or 152bit) and then enter the appropriate keys in Key 1, 2, 3, or 4. Remember to select the correct
radio button on the left. Then click [OK].
For WPA-PSK Security, select WPA-PSK under “Set Security Method”, and then click [Configure]
to enter your WPA key.
Page 31

After selecting the Configure option, you will be able to set your WPA Pre-Shared Key (WPAPSK). WPA- PSK supports both Passphrase (8-63 Characters) and Hexadecimal (64 Characters)
keys.
NOTE: WPA is currently available under Windows 2000 and Windows XP. Support for
Windows 98SE/ME will be available in Q1 of 2004.
Under the Profile Management Window, click on [Advanced] tab for advanced configurations.
Power Save Mode: Normal, Maximum, Off (Default Off)
Network Type: Access Point (Infrastructure) or Ad hoc (Peer to Peer)
802.11b Preamble : Short & Long or Long Only
Page 32

Transmit Power Level: Choose between 100%, 50%, 25%, 12.5%, Lowest.
Wireless Mode: Configure which 802.11 standard is used for each profile 802.11a 5GHz,
802.11b/g 2.4GHz .
Section 8.2 | Link Information
Associated BSS ID: Shows the MAC Address of the associated Access Point
Channel: Shows the current operating channel of your WLAN
Current Tx Rate: Current transmit rate value
Throughput: Number of packets sent and received
SSID: Workgroup name of the wireless network that you are connected to
Encryption: Displays the current Encryption used on the Network.
Link Quality: Shows the relative link quality (e.g., lack of frame errors) of the wireless
connection to the Access Point.
Page 33

Section 8.3 | IP Information
The IP Information screen displays network connection information.
Includes [Release] and [Renew] buttons to release and renew the IP address.
Section 8.4 | Site Survey
The Site Survey tab scans and displays all Access Points on the wireless LAN. The data is
organized by columns signifying the "SSID", "Channel", "Encryption" (a KEY symbol), "Signal",
and "Wireless Mode". If there is a key symbol in the Encryption column, the network is
encrypted. You will need to obtain the WEP information from the network administrator. To
choose a network, simply click the "SSID" and click the [Activate] button.
Page 34

Section 8.5 | Driver Information
The Driver Information screen displays the version information.
Page 35

9 | Disable Wireless Zero Configuration
in Windows XP
It is recommended that you use the SMC2536W-AG Configuration Utility to manage your wireless
connection. If you are using the SMC utility in Windows XP, you will need to disable the Wireless
Zero Configuration. Follow the instructions below.
Go to [Control Panel] and open [Network Connections]. Right-click the [Wireless Network
Connection], and select [Properties]. Select the "Wireless Networks" ta b and uncheck the [Use
Windows to configure my wireless network settings] check box.
NOTE: The Wireless Zero Configuration (WZC) and SMC2536W-AG Universal WLAN
Utility cannot be used simultaneously. If you are using the SMC2536W-AG Universal
WLAN Utilit y, you MUST disable the WZC (and vice versa).
Page 36

10 | SMC Networks EliteConnect Universal SMC2536W-AG Wireless
Cardbus Adapter Maximum Distance Table
Important Notice
Maximum distances posted below are actual tested distance thresholds. However, there are many
variables such as barrier composition and construction, as well as local environmental
interference that may impact your actual distances and cause you to experience distance
thresholds far lower than those posted below. If you have any questions or comments regarding
the features or performance of this product, or if you would like information regarding our full
line of wireless products, you can visit us at www.smc.com, or you can call us toll-free at
800.SMC.4YOU. SMC Networks stands behind every product sold with a 30-day satisfaction
guarantee and a limited-lifetime warranty.
802.11a Wireless Distance Table
Environmental
Condition
108 72 54 48 36 24 18 12 9 6
Outdoors: A lineof-sight
environment with
no interference or
obstruction
between the
Access Point and
users.
Indoors: A
typical office or
home
environment with
floor to ceiling
obstructions
between the
Access Point and
users.
45 m
(147
ft)
15 m
(49 ft)
75 m
(246
ft)
40 m
(131
ft)
150 m
(492 ft)
45 m
(148 ft)
Speed (Mbps) and Distance Ranges
305 m
(1000
ft)
55 m
(180 ft)
385 m
(1263
ft)
60 m
(197 ft)
435 m
(1427
ft)
62 m
(203 ft)
485 m
(1591
ft)
65 m
(213 ft)
500 m
(1640
ft)
70 m
(230 ft)
500 m
(1804
ft)
80 m
(262
ft)
650 m
(2145
ft)
95 m
(312
ft)
Page 37

Environmental
802.11g Wireless Distance Table
Environmental
Condition
54 48 36 24 18 12 11 9 6 5 2 1
Outdoors: A
line-of-sight
environment
with no
interference or
obstruction
between the
Access Point
and users.
Indoors: A
typical office or
home
environment
with floor to
ceiling
obstructions
between the
Access Point
and users.
150
m
(269
ft)
35
m
(115
ft)
205
m
(328
ft)
50
m
(164
ft)
350
m
(984
ft)
65
m
(213
ft)
Speed (Mbps) and Distance Ranges
395
m
(1082
ft)
85 m
(279
ft)
450
(1148
ft)
110
(361
ft)
m
m
500
(1475
ft)
120
(394
ft)
m
m
505
m
(1541
ft)
120
m
(394
ft)
515
m
(1590
ft)
125
m
(410
ft)
530
m
(1623
ft)
130
m
(426
ft)
535
m
(1672
ft)
135
m
(443
ft)
802.11b Wireless Distance Table
Speed and Distance Ranges
Condition
11 Mbps 5.5 Mbps 2 Mbps 1 Mbps
Outdoors: A
line-of-sight
environment
with no
interference or
obstruction
365 m
(1197 ft)
495 m
(1624 ft)
520 m
(1706 ft)
535 m
(1755 ft)
between the
Access Point
and users.
Indoors: A
typical office or
home
environment
with
floor to ceiling
obstructions
85 m
(279 ft)
95 m
(312 ft)
115 m
(377 ft)
125 m
(410 ft)
between the
Access Point
and users.
560
m
(1705
ft)
140
m
(459
ft)
565
m
(1853
ft)
145
m
(476
ft)
Page 38

11 | Troubleshooting
Common Installation Problems
Problems are often caused by conflicts with other devices installed in the same computer, or
software that has been configured incorrectly. If you encounter a problem with the EliteConnect
Universal SMC2536W-AG High Power Wireless Cardbus Adapter, use the following checklists to
identify and correct the problem.
• If your computer cannot find the Wireless Card, or the network driver does not install
correctly, check the following items before contacting SMC Technical Support
o Make sure the card is securely seated in the PCMCIA. Check for any hardware
problems, such as physical damage to the card.
o Try the card in another PCMCIA. If this fails, test the card in a completely
different system or try using a second Wireless Card in that particular slot.
o Check for resource conflicts
o Make sure your computer is using the latest BIOS available. Contact the
manufacturer of the laptop, motherboard for information on updating the BIOS
(e.g. – Dell, Toshiba, etc)
o If there are other network cards in the compute r, they may be causing conflicts.
Remove all other cards from the computer and test the Wireless Card separately.
Network Connection Problems
There may be a network connection problem if the LED on the card does not light, or if you
cannot access any network resources from the computer. Check the following items before
contacting SMC Technical Support.
• Make sure the correct network card driver is installed for your operating system. If
necessary, try uninstalling and reinstalling the driver. To do this, first shut down your
machine and remove your SMC adapter. Then boot up and open up your Start Menu, go
to Programs, click the "SMC2536W-AG Universal WLAN Utility" program folder and
choose "Uninstall". Reboot the machine when requested to do so. Then insert your Driver
CD and run the Setup.exe utility again. Then shut down the computer, reinsert your SMC
adapter and boot up the machine. The OS should properly reinstall the adapter during
this time.
• Make sure the computer and other network devices are receiving power. If you suspect a
power outlet to be faulty, plug another device into it to verify that it is working.
• If your wireless station cannot communicate with a computer on the Ethernet LAN when
configured for Infrastructure mode, try changing the wireless channel on the AP. Make
sure the SSID is the same as that used by the AP for a station with roaming disabled, or
the same as that used by the AP's in the extended service set (ESS).
• The Access Point you are trying to attach to is defective or may not be configured
properly to accept your signal. Check with the administrator of your wireless network for
more information on connecting to the LAN. Also run the necessary diagnostics on the AP
to make sure the unit is fully operational.
Page 39

• If you cannot access the Internet, be sure to check with the ISP for further instructions
once the drivers for the Wireless Card are installed properly.
12 | Technical Specifications
Standards:
IEEE 802.11b / IEEE 802.11a / IEEE 802.11g
Wireless Data Rates (With Aut omatic Fall-back):
802.11b = 1/2/5.5/11 Mbps
802.11a = 6/9/12/18/24/36/48/54 Mbps
802.11a Turbo = 12/18/24/36/48/72/96/108 Mbps
802.11g = 1/2/5.5/6/9/11/12/18/24/36/48/54 Mbps
Data Modulation Techniques:
802.11b (DSSS) = BPSK, QPSK, CCK
802.11a (OFDM) = BPSK, QPSK, 16-QAM, 64- QAM
802.11g (OFDM) = BPSK, QPSK, 16-QAM, 64-QAM
Host Interface:
32-bit Cardbus interface
Operating Range:
Up to 2,145 ft
Network Configuration:
Ad-Hoc (Peer-to-Peer)
Infrastructure
Radio Signal Type:
Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS)
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM)
Media Access Protocol:
CSMA/CA (Collision Avoidance) with ACK architecture 32-bit MAC
Security:
802.11a mode = 64/128/152-bit Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP)
802.11b/g mode = 64/128-bit WEP
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP)
802.1x (EAP-MD5, LEAP, TLS, TTLS, PEAP)
WPA (WiFi Protected Access)
Channel Support (2.4GHz RF):
US/Canada - 1-11
Europe - 1-13
Spain – 2
China – 13
Japan – 14
France – 4
Page 40

RF Out put Power:
802.11a
20dBm +/- 2dBm @6-24Mbps
19dBm +/- 2dBm @36Mbps
17dBm +/- 2dBm @48Mbps
15dBm +/- 2dBm @54Mbps
802.11g
20dBm +/- 2dBm @6-24Mbps
19dBm +/- 2dBm @36Mbps
17dBm +/- 2dBm @48Mbps
15dBm +/- 2dBm @54Mbps
802.11b
21dBm +/- 2dBm
Channel Support (5GHz RF):
US/Canada
- 12 non-overlapping channels
- 5.15-5.35GHz, 5.725-5.825GHz
Europe
- 19 non-overlapping channels
- 5.15-5.35GHz, 5.47-5.725GHz
Japan
- 4 non-overlapping channels
- 5.15-5.25GHz
China – 5.725-5.85GHz
Operating Systems:
Windows 98SE/Me/2000/XP
Antenna Type:
Built-in
Power Voltage:
3.3 Volt + 5%
Power Consumption:
802.11a
Tx = 700mA
Rx = 300mA
802.11b/g
Tx = 850mA
Rx = 500mA
Dimensions:
0.30 x 2.13 x 4.65 in
Compliance:
USA: FCC Part 15 Class A & B
Page 41

Europe: CE-Mark & ETSI 300.328 & 300.826
Industry Canada
IEC 60950
IDA (Singapore)
WiFi Compliant
Temperature Range:
Operating: -10 C - +60 C
Storage: -40 C - +70 C
Receive Sensitivity:
11a:
-80 dBm at 6 Mbps
-80 dBm at 9 Mbps
-79 dBm at 12 Mbps
-78 dBm at 18 Mbps
-75 dBm at 24 Mbps
-73 dBm at 36 Mbps
-70 dBm at 48 Mbps
-67 dBm at 54 Mbps
11g:
-84 dBm at 6 Mbps
-84 dBm at 9 Mbps
-83 dBm at 12 Mbps
-82 dBm at 18 Mbps
-79 dBm at 24 Mbps
-77 dBm at 36 Mbps
-74 dBm at 48 Mbps
-71 dBm at 54 Mbps
11b:
-91 dBm at 1 Mbps
-89 dBm at 2 Mbps
-88 dBm at 5.5 Mbps
-87 dBm at 11 Mbps
Page 42

13 | Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Wireless LAN?
A local area network that transmits over the air typically in an unlicensed frequency such as the
2.4GHz band. A wireless LAN does not require lining up devices for line of sight transmission like
IrDA. Wireless access points (base stations) are connected to an Ethernet hub or server and
transmit a radio frequency over an area of several hundred to a thousand feet which can
penetrate walls and other non-metal barriers. Roaming users can be handed off from one access
point to another like a cellular phone system. Laptops use wireless network cards that plug into
an existing PCMCIA slot or that are self contained on PC cards, while stand-alone deskto ps and
servers use plug-in cards (ISA, PCI, etc.).
What is AD- HOC?
An AD- HOC network is a peer to peer network where all the nodes are wireless clients. As an
example, two PC’s with wireless adapters can communicate with each other as long as they are
within range. A wireless extension point can extend the range of an AD- HOC network.
What is the 802.11 standard?
A family of IEEE standards for wireless LANs first introduced in 1997. 802.11 provides 1 or 2
Mbps transmission in the 2.4GHz band using either a frequency hopping modulation (FHSS)
technique or direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS), which is also known as CDMA. The
802.11b standard defines an 11 Mbps data rate in the 2.4GHz band, 802.11g- draft standard
defines 54 Mbps in the 2.4GHz band, and the 802.11a standard defines 54 Mbps in the 5GHz
band.
What is Infrastructure?
In order for your wireless components to interact with traditional wired networks they need a
media bridge to translate for them. This is where INFRASTRUCTURE or Network mode comes
into play. An ACCESS POINT is attached to the network using CAT-5 Ethernet cable attaching to
a hub, switch or another PC. Wireless PC’s can then communicate to Wired Ethernet computers
through this access point. The total range of the network is limited to a radius around this Access
Point. To increase the range, extra Access Points may be wired into the network. These Access
Points talk to each other over the hard-wired Ethernet cables however, they cannot communicate
wirelessly to one another and they must be wired to the same network. Individual wireless PC’s
can move between Access Points on the same network seamlessly due to a feature called
ROAMING.
What is Tx Rate?
Page 43

Tx-Rate or TRANSFER RATE is the current speed at which the network component is operating.
SMC-802.11b products can operate at speeds of 1Mb, 2Mb, 5.5Mb, & 11Mbps. A wireless card set
to AUTO will attempt to connect at whatever speed will give the best throughput on the network.
What is RTS Threshold?
(Request To Send) An RS-232 signal sent from the transmitting station to the receiving station
requesting permission to transmit. RTS is a collision avoidance method used by all 802.11b
wireless networking devices. In most cases you will not need to activate or administer RTS. Only
if you find yourself in an Infrastructure environment where all nodes are in range of the Access
Point but may be out of range of each other. It is recommended to leave this setting at its
default value leaving this feature disabled.
What is Authentication Algorithm?
Authentication Algorithm is the means by which one station is authorized to communicate with
another. In an Open System, any station can request authorization in accordance with the WECA
standard. In a Shared key system, only stations that possess a secret encrypted key may
participate in the network. This is a low level security key which allows the equipment with the
shared key algorithm to see each other on the wireless lan.
What is DBI?
The ability of the antenna to shape the signal and focus it in a particular direction is called
Antenna Gain, and is expressed in terms of how much stronger the signal in the desired direction
is, compared to the worst possible antenna, which distributes the signal evenly in all directions
(an Isotropic Radiator). To express the relationship to the Isotropic reference, this is abbreviated:
"dBi". The typical omni- directional "stick" antenna is rated at 6-8 dBi, indicating that by
redirecting the signal that would have gone straight up or down to the horizontal level, 4 times as
much signal is available horizontally. A parabolic reflector design can easily achieve 24 dBi.
What is WEP?
Short for Wired Equivalent Privacy, WEP is a security protocol for wireless local area networks
(WLANs) defined in the 802.11b and 802.11a standards.
WEP is designed to provide the same level of security as that of a wired LAN. LANs are inherently
more secure than WLANs because LANs are somewhat protected by the physicalities of their
structure, having some or all part of the network inside a building that can be protected from
unauthorized access. WLANs, which are over radio waves, do not have the same physical
structure and therefore are more vulnerable to tampering.
WEP aims to provide security by encrypting data over radio waves so that it is protected as it is
transmitted from one end point to another. The Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP) feature uses the
RC4 PRNG algorithm developed by RSA Data Security, Inc.
If your wireless access point supports MAC filtering, it is recommended that you use this feature
in addition to WEP (MAC filtering is much more secure than encryption).
Page 44

14 | Terminology
10BaseT - Physical Layer Specification for Twisted- Pair Ethernet using Unshielded Twisted Pair
wire at 10Mbps. This is the most popular type of LAN cable used today because it is very cheap
and easy to install. It uses RJ-45 connectors and has a cable length span of up to 100 meters.
There are two versions, STP (Shielded Twisted Pair) which is more expensive and UTP
(Unshielded Twisted Pair), the most popular cable. These cables come in 5 different categories.
However, only 3 are normally used in LANs, Category 3, 4 and 5. CAT 3 TP (Twisted Pair) cable
has a network data transfer rate of up to 10Mbps. CAT 4 TP cable has a network data transfer
rate of up to 16Mbps. CAT 5 TP cable has a network data transfer rate of up to 100Mbps.
Access Point - A device that is able to receive wireless signals and transmit them to the wired
network, and vice versa - thereby creating a connection between the wireless and wired
networks.
Ad Hoc - An ad hoc wireless LAN is a group of computers, each with LAN adapters, connected as
an independent wireless LAN.
Adapter - A device used to connect end-user nodes to the network; each contains an interface to
a specific type of computer or system bus, e.g. EISA, ISA, PCI, PCMCIA, CardBus, etc.
Auto- Negotiation - A signaling method that allows each node to define its operational mode (e.g.,
10/100 Mbps and half/full duplex) and to detect the operational mode of the adjacent node.
Backbone - The core infrastructure of a network. The portion of the network that transports
information from one central location to another central location where it is unloaded onto a local
system.
Base Station - In mobile telecommunications, a base station is the central radio
transmitter/receiver that maintains communications with the mobile radiotelephone sets within its
range. In cellular and personal communications applications, each cell or micro-cell has its own
base station; each base station in turn is interconnected with other cells' bases.
BSS - BSS stands for "Basic Service Set". It is an Access Point and all the LAN PCs that are
associated with it.
CSMA/CA - Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance
DHCP - Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. This protocol automatically configures the TCP/IP
settings of every computer on your home network.
DNS - DNS stands for Domain Name System, which allows Internet host computers to have a
domain name (such as www.smc.com) and one or more IP addresses (such as 192.34.45.8). A
DNS server keeps a database of host computers and their respective domain names and IP
addresses, so that when a domain name is requested (as in typing " www.smc.com" into your
Page 45

Internet browser), the user is sent to the proper IP address. The DNS server address used by the
computers on your home network is the location of the DNS server your ISP has assigned.
DSL - DSL stands for Digital Subscriber Line. A DSL modem uses your existing phone lines to
transmit data at high speeds.
EAP - (Extensible Authentication Protocol) This is a mode of conversation between a Supplicant
and an Authentication Server. Access Points or proxy servers do not take part in the
conversation. Their role is simply to forward EAP messages between the parties performing the
authentication. The EAP messages are transported between a wireless station and an 802.1X
Authenticator using EAPOL. The EAP messages are sent between an 802.1X Authenticator and
the Authentication Server using RADIUS. The EAP framework supports the definition of EAP-Type
Authentication Methods. Today, the major EAP-Type Authentication Methods include EAP-MD5,
EAP-TLS, EAP-TTLS, EAP-PEAP, and Cisco’s EAP-LEAP.
EAP-MD5 - This is the most basic EAP-Type, which must be supported by all implementations of
EAP. It is not a strong authentication method and does not support dynamic WEP keys.
EAP-LEAP - (Lightweight Extensible Authentication Protocol) It is the type primarily used on Cisco
WLAN access points. LEAP provides security during credential exchange, encrypts using dynamic
WEP keys, and supports mutual authentication.
EAP-TLS - (Transport Layer Security) This uses the TLS handshake as the basis for
authentication. TLS performs authentication by exchanging digital certificates. The server sends a
certificate to the client and only after validating the server's certificate does the client present a
client certificate.
EAP-TTLS - (Tunneled TLS) This mode an advantage over EAP-TLS that it only requires a
certificate at the Authentication Server.
Ethernet - A standard for computer networks. Ethernet networks are connected by special cables
and hubs, and move data around at up to 10 million bits per second (Mbps).
ESS - ESS (ESS-ID, SSID) stands for "Extended Service Set". More than one BSS is configured to
become an Extended Service Set. LAN mobile users can roam between different BSSs in an ESS
(ESS-ID, SSID).
Fast Ethernet NIC - Network interface card that is in compliance with the IEEE 802.3u standard.
This card functions at the media access control (MAC) layer, using carrier sense multiple access
with collision detection (CSMA/CD).
Fixed IP – (see Static IP)
Full-Duplex - Transmitting and receiving data simultaneously. In pure digital networks, this is
achieved with two pairs of wires. In analog networks, or digital networks using carriers, it is
achieved by dividing the bandwidth of the line into two frequencies, one for sending, one for
receiving.
Hub - Central connection device for shared media in a star topology. It may add nothing to the
transmission (passive hub) or may contain electronics that regenerate signals to boost strength
Page 46

as well as monitor activity (active/intelligent hub). Hubs may be added to bus topologies; for
example, a hub can turn an Ethernet network into a star topology to improve troubleshooting.
IP Address - IP stands for Internet Protocol. An IP address consists of a series of four numbers
separated by periods, that identifies an single, unique Internet computer host. Example:
192.34.45.8.
ISP - Internet Service Provider. An ISP is a business that provides connectivity to the Internet for
individuals and other businesses or organizations.
LAN - A communications network that serves users within a confined geographical area. It is
made up of servers, workstations, a network operating system and a communications link.
Servers are high-speed machines that hold programs and data shared by network users. The
workstations (clients) are the users' personal computers, which perform stand-alone processing
and access the network servers as required.
Diskless and floppy-only workstations are sometimes used, which retrieve all software and data
from the server. Increasingly, "thin client" network computers (NCs) and Windows terminals are
also used. A printer can be attached locally to a workstation or to a server and be shared by
network users. Small LANs can allow certain workstations to function as a server, allowing users
access to data on another user's machine. These peer-to-peer networks are often simpler to
install and manage, but dedicated servers provide better performance and can handle higher
transaction volume. Multiple servers are used in large networks.
MAC Address - MAC (Media Access Control) A MAC address is the hardware address of a device
connected to a network.
MDI / MDI-X - Medium Dependent Interface - Also called an "uplink port," it is a port on a
network hub or switch used to connect to other hubs or switches without requiring a crossover
cable. The MDI port does not cross the transmit and receive lines, which is done by the regular
ports (MDI-X ports) that connect to end stations. The MDI port connects to the MDI-X port on
the other device. There are typically one or two ports on a device that can be toggled between
MDI (not crossed) and MDI-X (crossed).
Medium Dependent Interface – X (crossed) - A port on a network hub or switch that crosses the
transmit lines coming in to the receive lines going out.
NAT – (Network Address Translation) This process allows all of the c omputers on your home
network to use one IP address. The NAT capability of the Barricade, allows you to access the
Internet from any computer on your home network without having to purchase more IP
addresses from your ISP. Network Address Translation can be used to give multiple users access
to the Internet with a single user account, or to map the local address for an IP server (such as
Web or FTP) to a public address. This secures your network from direct attack by hackers, and
provides more flexible management by allowing you to change internal IP addresses without
affecting outside access to your network. NAT must be enabled to provide multi-user access to
the Internet or to use the Virtual Server function.
Packet Binary Convulational Code(tm) (PBCC) - A modulation technique developed by Texas
Instruments Inc. (TI) that offers data rates of up to 22Mbit/s and is fully backward compatible
with existing 802.11b wireless networks.
PCI - Peripheral Component Interconnect - Local bus for PCs from Intel that provides a highspeed data path between the CPU and up to 10 peripherals (video, disk, network, etc.). The PCI
bus runs at 33MHz, supports 32-bit and 64-bit data paths, and bus mastering.
Page 47

PPPoE - Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet. Point-to-Point Protocol is a method of secure data
transmission originally created for dial-up connections. PPPoE is for Ethernet connections.
Roaming - A function that allows your to move through a particular domain without losing
network connectivity.
Static IP - If your Service Provider has assigned a fixed IP address; enter the assigned IP
address, subnet mask and the gateway address provided by your service provider.
Subnet Mask - A subnet mask, which may be a part of the TCP/IP information provided by your
ISP, is a set of four numbers configured like an IP address. It is used to create IP address
numbers used only within a particular network (as opposed to valid IP address numbers
recognized by the Internet.
TKIP - (Temporal Key Integrity Protocol) The TKIP process begins with a 128- bit "temporal key"
which is shared among clients and access points. Then it combines the temporal key with the
client's MAC address and adds a 16-octet initialization vector to create the key that will encrypt
the data. This procedure ensures that each station uses different key streams to encrypt the
data.
TCP/IP - Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol. This is the standard protocol for data
transmission over the Internet.
TCP - Transmission Control Protocol - TCP and UDP (User Datagram Protocol) are the two
transport protocols in TCP/IP. TCP ensures that a message is sent accurately and in its entirety.
However, for real- time voice and video, there is really no time or reason to correct errors, and
UDP is used instead.
UDP - User Datagram Protocol - A protocol within the TCP/IP protocol suite that is used in place
of TCP when a reliable delivery is not required. For example, UDP is used for real-time audio and
video traffic where lost packets are simply ignored, because there is no time to retransmit. If
UDP is used and a reliable delivery is required, packet sequence checking and error notification
must be written into the applications.
Page 48

 Loading...
Loading...