

54M Wireless Router
User
Manual
IP0489
Ver1.0.0.c

Sectionone:introduction ………………………………… ………… ……………1
1.1. About 54M Wirele Router……….………………….. …………………......1
1.2. Package contents……….………………….. …………………...................1
1.3. Features ………………………………………………………………………1
Section two:Hardware installation………………………………………………..2
2.1.Panel Layout…………………………………………………………………..2
2.11.The Front Panel………………………………………................................2
2.12.The Rear Panel………………………………………………………………3
2.2. The System Requirement…………………………..……………………….4
2.3. Installation Environment Requirement………………...............................4
2.4. Connectting The Router……………………………………………………..4
Section Three: Quick Installation Guide………………………………………….5
3.1. TCP/IP Configuration…………………………………………………………5
3.2. Quick Setup Wizard…………………………………………………………..6
3.3. Operation mode……………………………………………………………...12
Section four Configuration Guide…………………….…………………………..12
4.1. Login…………………………………………………………………………12
4.2. Wireless……………………………………………………………………..13
4.2.1. Wireless Basic settings……………………………………………………14
4.2.2. Wireless Advanced settings………………………………………………14
4.2.3. Wireless Security Setup…………………………………………………..15
4.2.4. Wireless Access Control……………………………...............................16
4.2.5. WDS Settings………………………………………………………………16
4.2.6. Wireless Site Survey …………………………......................................17

4.2 7.WPS Setting……………………………………………………...................17
4.3 .TCP/IP settings…………………………………………...............................18
4.3.1. LAN Interface…………………………………....................………………18
4.3.2. WAN Interface…………………………………………………………….....19
4.4 .Firewall………..………………………………………………………………..20
4.4.1. Port Filtering………………………………..........…..................................20
4.4.2. IP Filtering………………………………………........................................20
4.4.3.MAC Filtering……………………………………............... ………………..21
4.4.4. Port Forwarding ……………………………………..................................21
4.4.5. URL Filtering …………………………………….……...............................22
4.4.6. DMZ………………………………………..................................................22
4.4.7.AntiARP Cheating…………………………………………………………....23
4.5. Management……………………………………………………………………23
4.5.1 Status……………………………………..……………………………….......23
4.5.2. Statistics…………………………...………………….………………………24
4.5.3. Dynamic DNSSetting………………………………………………………..24
4.5.4. Time Zone Setting………………………………..………………………….25
4.5.5. Dneial of Service……………………………..…………..........................25
4.5.6. Log…………………………………………..………………………………...26
4.5.7. Upgrade Firmware…………………..……………………………………....26
4.5.8. Save/Reload settings……………….……………………………………....27
4.5.9. Password setup …………………….………………………………………27
Appendix 1 FAQ……………………………….……………………………………28
Appendix 2 Specification…………………………….…………………………….29
Appendix 3 Glossary……………………………….………………………………30

e
c
t
i
o
n
o
n
e
I
n
t
r
o
d
u
c
t
i
S
S
e
c
S
.1
1
54M
access into a single stand-alone unit. The device allows you take advantages of both mobility and
fast connection. All PCs whenever on wireless LAN or Ethernet LAN can share files, printers and
other network resource. Moreover, all users can share single account of Internet access by having
this device connect to a DSL/Cable modem.
1.
Ethernet is the most widely-u
(LAN) and is defined by the IEEE as the 802.3 standard. Normally, Ethernet is a shared media
LAN. All stations on the segment share the total bandwidth, which could be 10 Mbps (Ethernet),
100 Mbps (Fast Ethernet). With a switched Ethernet, each sender and receiver has the full
bandwidth.Fast Ethernet
with 100 Mbps transmission rate.
2.
Wireless Local Area
radio frequency (RF). This offers some advantages like mobility, ease of installation, and scalability
over traditional wired systems.
t
e
c
t
Thank you for purchasing 54M Wireless Broadband Router. This
user
About the
Wireless
Ethernet / Fast Ethernet
Wireless LAN
i
o
n
o
i
o
n
o
guide will assist you with the installation procedure.
Router is a hybrid design prod
n
e
I
n
t
r
o
d
n
e
I
n
t
r
54M Wireless Router
sed network access method, especially in a Local Area.Network
is defined by the IEEE 802.3u standard, a high-speed version of Ethernet
Network systems (WLANs) transmit and receive data through the air by using
o
d
u
u
o
c
c
t
i
o
t
i
o
uct which combines Ethernet technology and wireless
Mobility
WLANs combine data connectivity with user mobility. This provides users with access to network
anywhere in their organization. For example, users can roam from a conference room to their
office without being disconnected from the LAN. This is impossible with wired networks.
1.2 Package contents
1.3
:
g the shipping carton, check the contents listed below. After carefully unpackin
54M
If any ing, please contact the retailer from of the listed contents are damaged or miss
whom you purchased the
eatures
F
54M
The
connections.
Wireless Broadband Router Router
A power adapter
54M Wireless Broadband Router User Manual
Wireless Router
54M
Wireless Router for assistance.
the following features that make it excellent for network
has
- 1 -

Complies with IEEE802.11g, IEEE802.11b, IEEE802.3, IEEE802.3u standards
1 10/100M Auto-Negotiation WAN RJ45 port, 4 10/100M Auto-Negotiation LAN
RJ45 ports
MDI/MDIX Supports Auto
can move among different AP and no break Supports Wireless Roaming,
Supports 54/48/36/24/18/12/9/6/11/5.5/3/2/1Mbps wireless LAN data transfer
rates
64/128 bit WEP encryption security Provides
Supports wireless Relay/Bridging/WDS/WDS+AP mode
Provides WPA and WPA2 authentication and TKIP/AES encryption security
Provides wireless LAN ACL (Access Control List) filtering
Built-in NAT and DHCP server supporting static IP address distributing
Supports Virtual Server, Special Application, and DMZ host
Built-in firewall supporting IP address filtering, Domain Name filtering, and MAC
address filtering
PPoE, DHCP, ICMP, NAT Supports TCP/IP, P
Supports UPnP, Dynamic DNS, Static Routing,
Supports Flow Statistics
Supports ICMP-FLOOD, UDP-FLOOD, TCP-SYN-FLOOD filter
Supports firmware upgrade
Supports Remote and Web management
SSeeccttiioonn TTwwoo HHaarrddwwaarree IInnssttaallllaattiioonn
Section Two Hardware Installation
.1 Panel Layout
2
2.1.1 The Front Pa
The front panel of the
designed to indicate connections. Viewed from left to right. The table describes the LEDs
on the front panel of the router.
nel
54M W
ireless Router
- 2 -
consists of several LED indicators, which is

Name Action Description
Power
CPU
WL
1/2/3/4
OFF No Power
ON Power on
ON The router is initialising
Flashing The router is working properly
OFF The router has a hardware error
OFF The Wireless Radio function is disabled
Flashing The Wireless Radio function is enabled
OFF There is no device linked to the corresponding port
ON
There is a device linked to the corresponding port but no
activity
Flashing
There is an active device linked to the corresponding
2
.1.2 The Rear Panel
The rear panel contains the following features. (Viewed from left to right:)
1. Wireless antenna
2. WAN RJ45 port for
3. Four LAN 10/100Mbps RJ45 ports for connecting the router to the local PCs
4. AC power socket: only use the power adapter supplied with the 54M WIRELE
ROUTER 54Mbps Wireless Router, use of a different adapter may result in produc
damage.
Factory De
5. fault Reset button
connecting the router to a cable, DSL modem or Ethernet
SS
t
There is a way to reset the ro
uter's factory defaults
- 3 -

1.Use the Factory Default Reset button: First, turn on the router's power. Second, press
and hold the default reset button, until the system LED lights up(about 5 seconds). Last,
release the reset button and wait for the router to reboot.
Notice: Ensure the router is powered on before it restarts completely.
2.2 System Requirements
Broadband Internet Access Service (DSL/Cable/Ethernet)
One DSL/Cable modem that has an RJ45 connector (you do not
need it if you connect the router to Ethernet)
dapter and an Ethernet cable Each PC on the LAN needs a working Ethernet A
with RJ45 connectors
e installed on each PC TCP/IP protocol must b
Web browser, such as Microsoft Internet Explorer 5.0 or later, Netscape Navigator
6.0 or later
2.3 Inst vironment Requirements
allation En
Not in direct sunlight or near a heater or heating vent
Not cluttered or crowded. There should be at least 2 inches (5 cm) of clear space
on all sides of the router
if it is in a closet) Well ventilated (especially
Operating temperature: 0~40
Operating Humidity: 5%~90%RH, Non-condensing
.4 Connecting the Router
2
Before you install the router, you
broadband service successfully. If there is any problem, please contact your ISP. After that,
please install the router according to the following steps. Don't forget to pull out the power
plug and keep your hands dry.
Power off your PC(s), Cable/DSL modem, and the router.
Locate an optimum location for the router. The best place is usually near the
center of the area in which your PC(s) will wirelessly connect. The place mus
accord with the Installation Environment Requirements.
d direction. Adjust the direction of the antenna. Normally, upright is a goo
Connect the PC(s) and each Switch/Hub on your LAN to the LAN Ports on the
router.
t the DSL/Cable Modem to the WAN port on the router. Connec
should connect your PC to the Internet through your
t
Connect the AC power adapter to the AC power socket on the router, and the
other end into an electrical outlet. The router will start to work automatically.
Power on your PC(s) and Cable/DSL modem.
- 4 -

S
e
c
t
i
o
n
T
h
r
e
e
:
Q
u
i
c
k
I
n
s
t
a
l
l
a
t
i
o
n
G
u
i
d
e
S
e
c
t
i
o
n
T
h
r
e
e
:
Q
u
i
c
k
I
n
s
t
a
l
l
a
t
i
o
n
G
e
c
t
i
o
S
A figure it. This
er connecting the 54M Wireless Router into your network, you should conft
n
T
h
r
e
e
:
Q
u
i
c
k
I
n
s
t
a
l
l
a
t
i
o
n
G
u
u
i
d
e
i
d
e
chapter describes how to configure the basic functions of your 54M Wireless
Router. These procedures only take you a few minutes. You can access the Internet via the
router immediately after successfully configured.
3.1 TCP/IP configuration
The default IP address of the 54Mbps Wireless Router is 192.168.1.254, and the default
Subnet Mask is 255.255.255.0.
changed as you desire, as an example we use the default values for description in this
guide.
Connect the local PCs to the LAN ports on the router. There are then two means to
configu
C
onfigure the IP address manually
1 (s). If you need instructions as to how to do this.
. Set up the TCP/IP Protocol for your PC
2.Configure the network parameters.
254), Subnet Mask is 255.255.255.0, and Gateway is 192.168.1.254(The router
default IP address)
Obtain an IP address automatically
1.Set up the TCP/IP
PC(s). If you need instructions as to h
2.Power off the router and PC(s). Then turn on the router, and restart the PC(s). The bu
DHCP server will assign IP addresses for the PC(s).
Now, you can run the Ping command in the command prompt to verify the
network connection between your PC(s) and the
re the IP address for your PCs.
Protocol in "Obtain an IP address automatically" mode on your
These values can be seen from the LAN. They can be
The IP address is 192.168.1.xxx ("xxx" is from 2 to
's
ow to do this,
ilt-in
router.
- 5 -

Open a command prompt, and type ping 192.168.1.254, then press Enter.
If the result displayed is similar to that shown in the top of figure, the connection between
your PC and the router has been established.
If the result displayed is similar to that shown in the top of figure, it means that your PC has
not connected to the router. Please check it following these steps:
1. Is the connection between your PC and the router correct?
Notice: The 1/2/3/4 LEDs of LAN port on the router and LEDs o
should be lit.
. Is the TCP/
2 IP configuration for your PC correct?
Notice: If the router's IP address is 192.168.1.254, you
the range of 192.168.1.2 ~ 192.168.1.253, the gateway
3.2 Quick S etup wizard
With a Web-based (Internet Exp
Router is easy to configure and manage. The Web-based utility can be used on any
lorer or Netscape® Navigator) utility, the 54Mbps Wireless
r PC's IP address must be within
must be 192.168.1.254
n your PC's adapter
- 6 -

Windows, Macintosh or UNIX OS with a web browser.
Connect to the router by typing http://192.168.1.25 in the address field of web browser.
After a moment, a login window will appear similar to that shown in Figure. Enter admin
4
for the User Name and Password, both in lower case le
press the Enter key.
tters. Then click the OK button or
NOTE:
If the above screen does not prompt, it means that your web-browser has been set to a
Configure the IP address manually
proxy. Go
appears, c
If the User Name and Password are correct, you can configure the router using the
web browser. Please click the Setup Wizard link on the left of the main menu and the
Setup Wizard screen will appear.
to Tools menu>Internet Options>Connections>LAN Settings, in the screen that
ancel the Using Proxy checkbox, and click OK to finish it.
Click SetupWizard, the SetupWizard will appear.
- 7 -
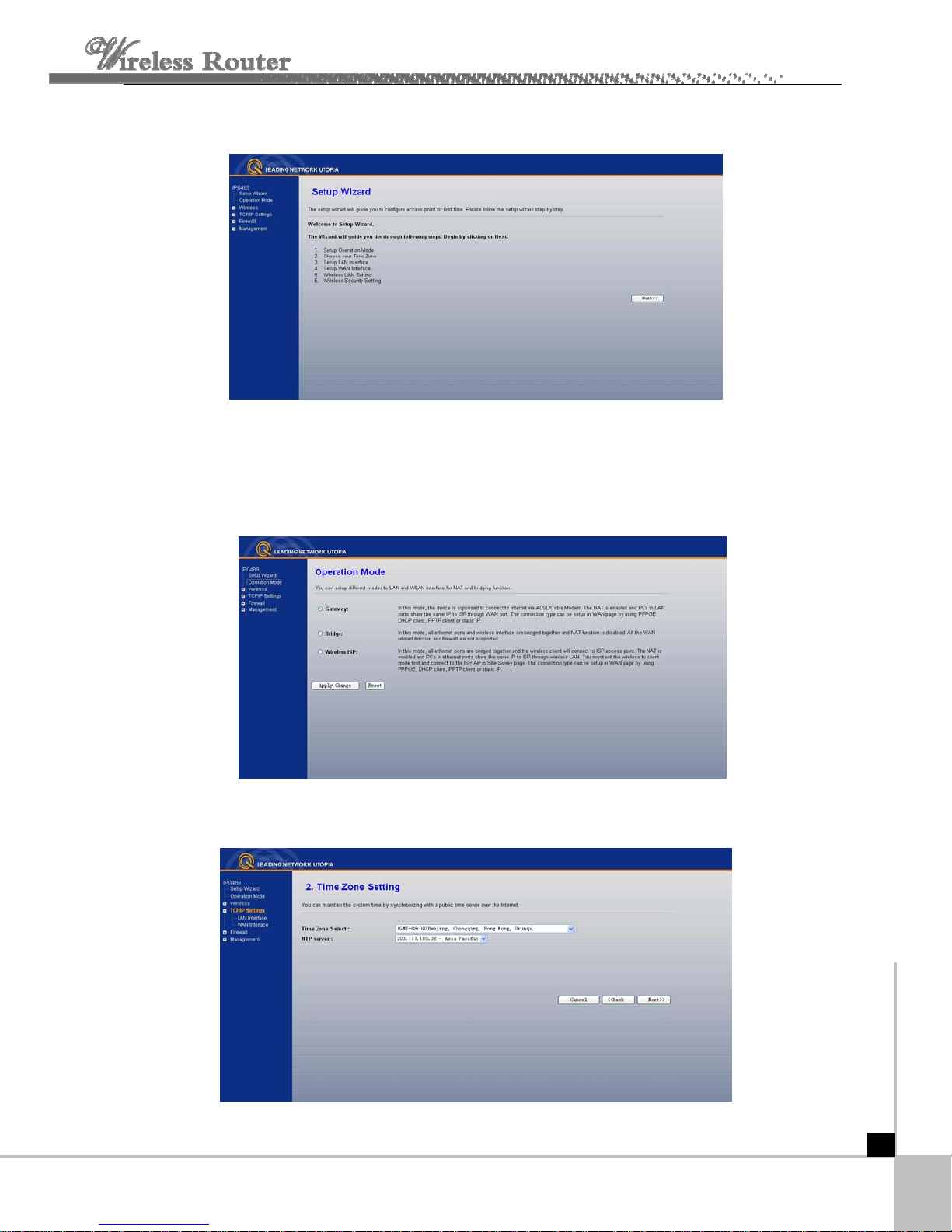
Click SetupWizard, the SetupWizard will appear.
The router supports three modes: gateway, bridge, wireless ISP. You can setup different
m
odes to LAN and WLAN interface for NAT and bridging function.
Click next, Time Zone Setting will appear. You can select the time zone what you need.
- 8 -

Click next, LAN Interface setup will appear. In this page, you can set IP address, Subnet
Mask.
IP Address - Enter the IP address of your router in dotted-decimal notation (factory default:
192.168.1.254).
Subnet Mask - An address code that determines the size of the network. Normally use
255.255.255.0 as the subnet mask.
Notice : The same to all PCs’ Subnet Mask with router in you LAN.
Click next, WAN Interface will appear. In this page is used to configure the parameters for
Internet network which connects to the WAN port of your Access Point.
WAN Access Type: Here you can select the access method to static IP, DHCP, PPPoE or
PPTP by click the item value of WAN Access type.
User Name and Password - Enter the User Name and Password provided by your ISP.
Services name: Default is blank.
- 9 -
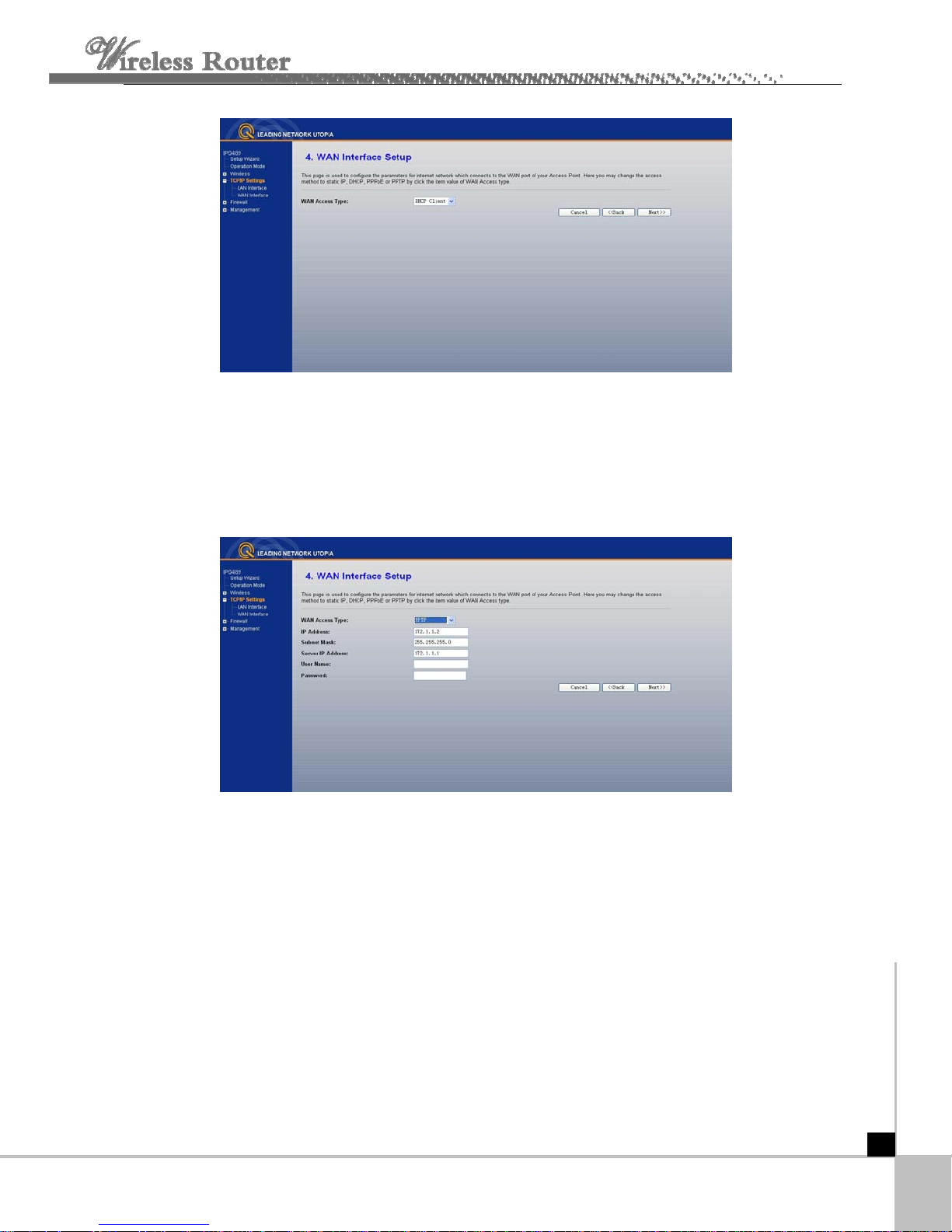
If you choose " DHCP Client", the router will automatically receive the IP parameters from
your ISP without needing to enter any parameters.
If you Choose "PPTP", the Static IP
settings page will appear, shown in the figure.
You can get IP Address Subnet Mask, server IP Address, User Name and Password from
your ISP
If
you Choose "Static IP", the Static IP settings page will appear, shown in figure.
- 10 -

Note: The IP parameters should have been provided by your ISP.
IP Ad
dress - This is the WAN IP address as seen by external users on the Internet
(including your ISP). Enter the IP address into the field.
Subnet Mask - The Subnet Mask is used for the WAN IP address, it is usually
255.255.255.0
efault Gateway - Enter the gateway into the box if required.
D
NS - Enter the DNS Server IP address into the boxes if required.
D
lick next, wireless basic setting will appear.
C
- 11 -
【This p gure these parameters】
B nd 2.4GHz(B)11Mbps
a - Indicates the current mode (2.4GHz(G)-54Mbps (802.11g),
(802.1 wireless stations to
conne
Mode-Default is AP,you can select Client,WDS,AP+WDS
Network Type-Default is Infrastructure,when mode is client,Network Type may be AD-HOC
SSID - Enter a value of up to 32 characters. The same name (SSID) must be ssigned to
all wireless devices in your network. The default SSID is Kingnet, but
it is recommended strongly that you change your networks name (SSID) to a different value.
This value is case-sensitive.
Channel – Fr om 1 to 13 .This field determines which operating frequency will be used. It
is not necessary to change the wireless channel unless you notice interference problems
with another nearby access point.
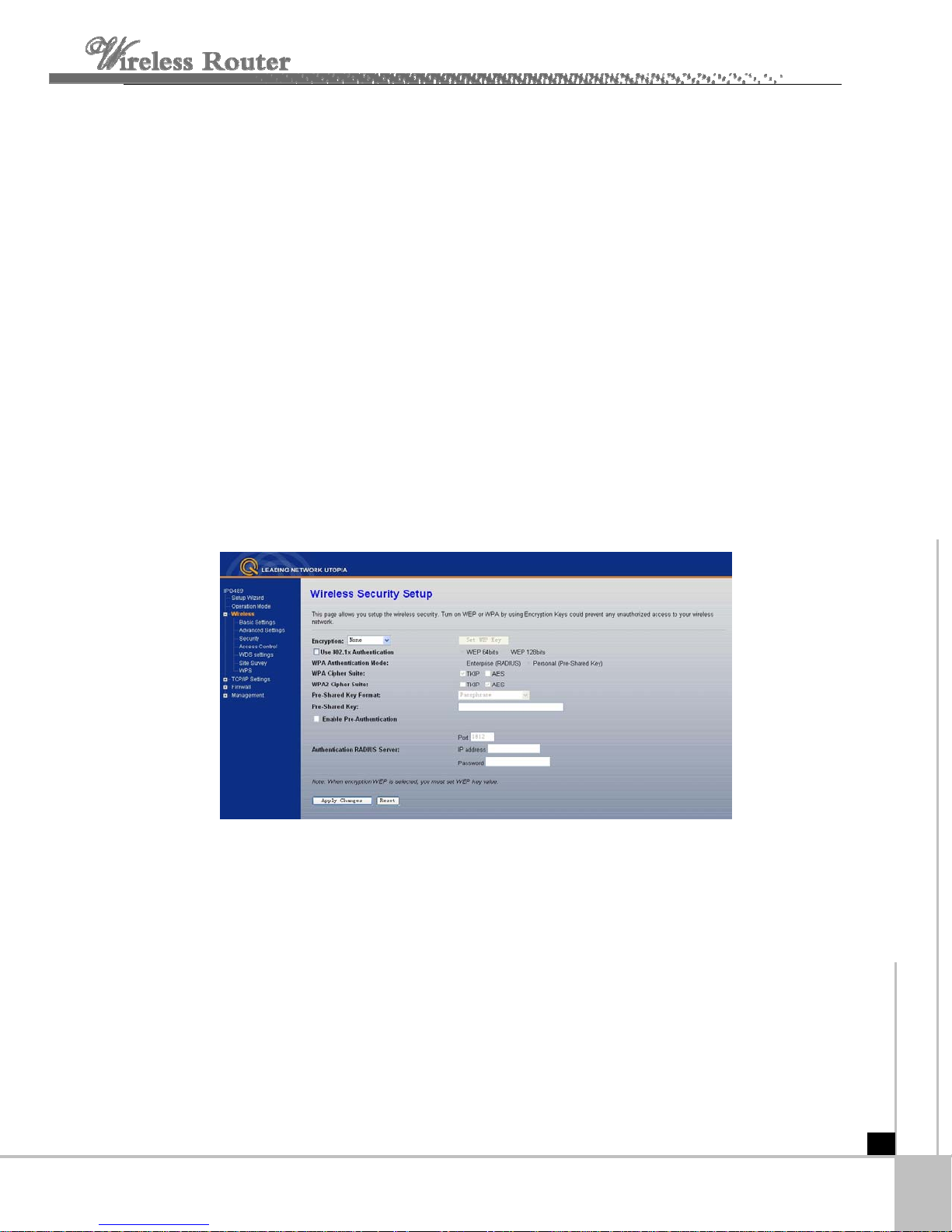
Click next, Wirelss Security Setup will appear.this page allow you setuo the security. You can
s
elect NoneWEP WPA(TKIP),WPA2(AES),WPA2 Mixed.
age is used to confi
1b)). 2.4GHz(G+B), which allows both 802.1
ct to the router.
1g and 802.11b
Click Apply Changes,you will find the page show set secceful.
Notice: If you change the param
eters of wireless, The router will reboot automatically.
- 12 -

3.3 Operation mode
Gateway: (default) In this mode, the device is supposed to connect to internet via
DSL/Cable Modem. The NAT is enabled and PCs in LAN ports share the same IP to ISP
A
ugh WAN port. The connection type can be setup in WAN page by using PPPOE, DHCP
thro
client, PPTP client or static IP.
Bridge: In this mode, all ethernet ports and wireless interface are bridged together and
is disabled. All the WAN related function and firewall are not supported.
nction
fu
ireless ISP: In this mode, all ethernet ports are bridged together and the wireless client will
W
onnect to ISP access point. The NAT is enabled and PCs in ethernet ports share the same
c
to ISP through wireless LAN. You must set the wireless to client mode first and connect to
IP
e ISP AP in Site-Survey page. The connection type can be setup in WAN page by using
th
PPOE, DHCP client, PPTP client or static IP.
P
NAT
S
e
c
t
i
o
n
f
o
u
r
C
o
n
f
i
g
u
r
a
t
i
o
n
G
u
i
d
e
S
e
c
t
i
o
n
f
o
u
r
C
o
n
f
i
g
u
r
a
t
i
o
n
G
S
e
c
t
i
o
n
f
o
u
r
C
o
n
f
i
g
u
r
a
t
i
o
n
4.1 Login
After you login successful, Browser will show administrator WEB. on the left is contents. it
contains: Wireless setting, WAN Settings, LAN Settings, Network Security, System Services,
Management, Status Show, Exit Setting.
G
u
u
i
d
e
i
d
e
- 13 -

4.2 Wireless Setting
it contains Wireless Basic settings, Advance Settings, security, Access Control, WDS
Settings, Site Survey.
4.2.1 Wireless Basic settings
Band: Indicates the current mode (2.4GHz(G)-54Mbps (802.11g), 2.4GHz(B)11Mbps
(802.11b)). 2.4GHz(G+B), which allows both 802.11g and 802.11b wireless
stations to connect to the router.
Mode: Default is AP,you can select Client,WDS,AP+WDS
Network Type: Default is Infrastructure,when mode is client,Network Type should be
setting AD-HOC
SSID: Enter a value of up to 32 characters. The same name (SSID) must ssigned to
all wireless devices in your network. The default SSID is Kingnet, but
It is recommended strongly that you change your networks name (SSID) to a different
value. This value is
C
hannel: Fro m 1 to 1 3. This field determines which operating frequency will be used.
I change the wireless channel unless you notice interference
t is not necessary to
problems with another nea
case-sensitive.
rby access point.
Associated Client: click show active client, you can check the list of wireless client.
Enable MAC Clone: it only adapt to wireless client.
be
4.2.2 Wireless Advanced Settings
- 14 -

These settings are only for mo
re technically advanced users who have a sufficient
knowledge about wireless LAN. These settings should not be changed unless you know
what effect the changes will have on your Access Point.
4.2.3 Wireless security setup
This page allows you setup the wireless security. Turn on WEP or WPA by using
Encryption Keys could prevent any unauthorized access to your wireless network.
Encryption: you can select None,WEP,WPA,WPA2, WPA2 Mixed
WEP:Wired Equivalent Protoco.
WPA:(WI-FI Protected Access Wi-Fi) WPA is an intermediate solution for the security issues.
It uses Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) to replace WEP.
TKIP: TKIP is a compromise on strong security and possibility to use existing hardware. It still
uses RC4 for the encryption like WEP, but with per-packet RC4 keys. In addition, it
implements replay protection, keyed packet authentication mechanism (Michael MIC).
WPA Authentication Mode: Keys can be managed using two different mechanisms. WPA
- 15 -

can either use an external authentication server (e.g., RADIUS) and EAP just like IEEE
802.1X is using or pre-shared keys without need for additional servers. Wi-Fi calls these
"WPA-Enterprise" and "WPA-Personal", respectively. Both mechanisms will generate a
master session key for the Authenticator (AP) and Supplicant (client station).
802.1X: The original security mechanism of IEEE 802.11 standard was not designed to be
strong and has proven to be insufficient for most networks that require some kind of security.
Task group I (Security) of IEEE 802.11 working group
has worked to address the flaws of the
base standard and in practice completed its work in May 2004. The IEEE 802.11i amendment
to the IEEE 802.11 standard was approved in June 2004 and published in July 2004.
WPA Cipher suite/WPA2 Cipher suite:The encryption piece of WPA and WPA2 mandates
the use of TKIP
e
ncryption.
Pre-Shared Key Format: You can select PASSPHRASE or HEX(
Pre-Shared Key: You can input 1
or, because it's considered to be more secure than TKIP, preferably AES
64 CHARACTERS).
28 characters key.
Authentication RADIUS Server:input Port and IP Address and Password.
4.2.4 Wireless Access Control
If you choose 'Allowed Listed', only those clients whose wireless MAC addresses are in the
access control list will be able to connect to your Access Point. When 'Deny Lis
ted' is
selected, these wireless clients on the list will not be able to connect the Access Point.
4.2.5 WDS Settings
Wireless Distribution System uses wireless media to communicate with ot
Ethernet does. To do this, you must set these APs in the same channel and s
of other APs which you want to communicate with in the t
- 16 -
able and then enable the WDS
her APs, like the
et MAC address

4.2.6 Wireless Site Survey
This page provides tool to scan the wireless network. If any Access Point or IBSS is found,
you could choose to connect it manually when client mode is enabled.
4.2.7 WPS Setting
This page allows you to change the setting for WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup). Using this
feature could let your wireless client automically syncronize its setting and connect to
the Access Point in a minute without any hassle.
- 17 -

4.3 TCP/IP Setting
4.3.1 LAN Setting Lan
Interface setup
This
page is used to configure the parameters for local area network which connects to the
LAN e the setting for IP addresss, subnet
port of your Access Point. Here you may chang
mask, DHCP, etc..
MAC Address - the physical address of the router, as seen from the LAN. The
value can't be changed.
IP Address - Enter the IP address of your router in dotted-decimal notation (factory default:
192.168.1.254).
Subnet Mask - An address code that
determines the size of the network. Normally use
255.255.255.0 as the subnet mask.
DHCP: You can select None,Client,Serve. The router is set up by default as a DHCP
(Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) server, which provides the TCP/IP configuration for
all the PCs that are connected to the router on the LAN.
DHCP Client Range: This field specifies the first of the addresses in the IP address pool.
802.1d Spanning Tree: The IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree Algorithm (STA) ,loop prevention
and redundant link configuration. You can select disable or enable.if your mode was set
WDS or AP+WDS, this item should be set “enable”
Clone MAC Address:you can enter a MAC,Then click clone.
- 18 -

4.3.2WAN Interface
This page is used to configure the parameters for Internet network which connects to the
WAN port of your Access Point. Here you may change the access method to static IP,
DHCP, PPPoE or PPTP by click the item value of WAN Access type.
W
AN Access Type,User name, password, Service:
you can refer to 3.2 Quick Installation Guide.
Connection Type:you can select continous o, connect on demand, manual.
Idle time: when connection type is connect on demand,you can set idle time.
MTU Size: The normal MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) value for most Ethernet networks
is 1492 Bytes. For some ISPs you need to reduce the MTU. But this is rarely required, and
should not be done unless you are sure it is necessary for your ISP connection.
DNS:You can select Attain DNS Automatically or Set DNS Manually
Clone MAC Address: if you wang clone, input MAC Address
Enable UpnP: The Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) feature allows the devices, such as
- 19 -

Internet computers, to access the local host resources or devices as needed. UPnP devices
can be automatically discovered by the UPnP service application on
the LAN.
Enable L2TP pass through on VPN connection:
Enable IPsec pass through on VPN connection:
Enable PPTP pass through on VPN connection:
4.4 Firewal
4.4.1 Port Filtering
Entries in this table are used to restrict certain types of data packets from your local network
to Internet through the Gateway. Use of such filters can be helpful in securing or restricting
your local network.
Enable Port filtering: select it, you can modify port filter.
Port range: input the filter port, for eaample 20-220
rotocol: you can select both,TCP,UDP
P
uurrent filter table: The list of port filter.
C
4.4.2 IP Filtering
Entries in this table are used to restrict certain types of data packets from your local network
to Internet through the Gateway. Use of such filters can be helpful in securing or restricting
your local network.
Enable IP Filtering:
Local IPAddress:input the IP Address,for example:192.16
select it, you can modify IP filter.
8.1.23.
Protocol: you can select both,TCP,UDP
Cuurrent Filter table: The list of IP filter.
- 20 -

4.4.3 MAC Filtering
Entries in this table are used to restrict certain types of data packets from your local network
to Internet through t
he Gateway. Use of such filters can be helpful in securing or restricting
your local network
Enable MAC Filtering: select it,you can modify MAC filter.
MACAddress:type the MACAddress,for
example:00:e0:4e:3f:2d:c5.
Cuurrent Filter table: The list of MAC filter.
4.4.4 Port Forwarding
Entries in this table allow you to automatically redirect common network services to a specific
- 21 -

machine behind the NAT firewall. These settings are only necessary if you wish to host some
sort of server like a web server or mail server on the private local network behind your
Gateway's NAT firewall.
Enable MAC Address:select it,you can modify MAC Address Filtering..
IP Address: The IP Address of the PC running the service application
Protocol - The protocol used for this application, either TCP, UDP, or both
(all protocols supported by the router).
P
ort Range- The numbers of External Ports. You can type a service port or a range of
s
ervice ports (the format is XXX – YYY, XXX is Start port, YYY is End port).
Current Port Forward Table
: port forward services already list.
4.4.5 URL Filtering
URL filter is used to deny LAN users from accessing the internet. Block those URLs which
contain keywords listed below.
Enable URL : select it, you can edit URL, For example:xxx.com
Click apply changes.
4.4.6 DMZ
The DMZ host feature allows one local host to be exposed to the In
special-purpose service such as Internet gaming or videoc
forwards all the ports at the same time. Any PC whose port is being forwarded must have its
DHCP client functio
n disabled and should have a new static IP Address assigned to it
because its IP Address may change when using the DHCP function.
DMZ Enable: Select it, DMZ ca
DMZ Host IP Address:input IP Address.for example 192.168.1.34.
ternet for a
onferencing. DMZ host
n be edit..
- 22 -

Click apply changes,complete set DMZ.
4
.4.7 AntiARP Cheating
This page can set the device to send packets to other hosts to refresh their ARP cache, and
can add static IP-MAC address entry to local ARP cache. Use of this function can be helpful
in preventing ARP virus or fake MAC address
4.5 Management
4.5.1 Status
T
his page shows the current status and some basic settings of the device. you can check
s
ystem Information, LAN Interface Information, WAN Interface Information.
- 23 -

4.5.2 Statistics
T
his page shows the packet counters for transmission and reception regarding to wireless
and Ethernet networks.
4.5.3 Dynamic DNS Setting
- 24 -

Dynamic DNS is a service, that provides you with a valid, unchanging, internet domain
name (an URL) to go with that (possibly everchanging) IP-address. DDNS lets you assign
a fixed host and domain name to a dynamic Internet IP Address. It is useful when you are
hosting your own website, FTP server, or other server behind the router. Before using this
feature, you need to sign up for DDNS service providers such as www.oray.net
www.comexe.cn
. The Dynamic DNS client service provider will give you a password or key.
or
To set up for DDNS, follow these instructions:
1. Type your dervice provider.
2. Type the User Name for your DDNS account.
3. Type the Password for your DDNS account.
4. Domain Name - the dom
the DDNS s
ervice.
ain names are displayed here. Click Apply Changes to logout
4.5.4 Time Zone Setting
You can maintain the system time by synchronizing with a public time server over the
Internet.
Current time: type the date and time.
Time Zone Select: Select your local time zone from this pull down list.
Enable NTP client update:select it, you can get the time from NTP.
NTP server :select a server from list.
Click the Apply changes get the time from Internet if you have connected toInternet.
4.5. 5 Denial of Service
A attack is characterized by an explicit attempt by hackers to
"denial-of-service" (DoS)
p
revent legitimate users of a service from using that service.
Enable D
OS Prevention:select it, you can modify DOS Prevention.
Enable Source IP Blocking: you can input source IP Blocking time
- 25 -
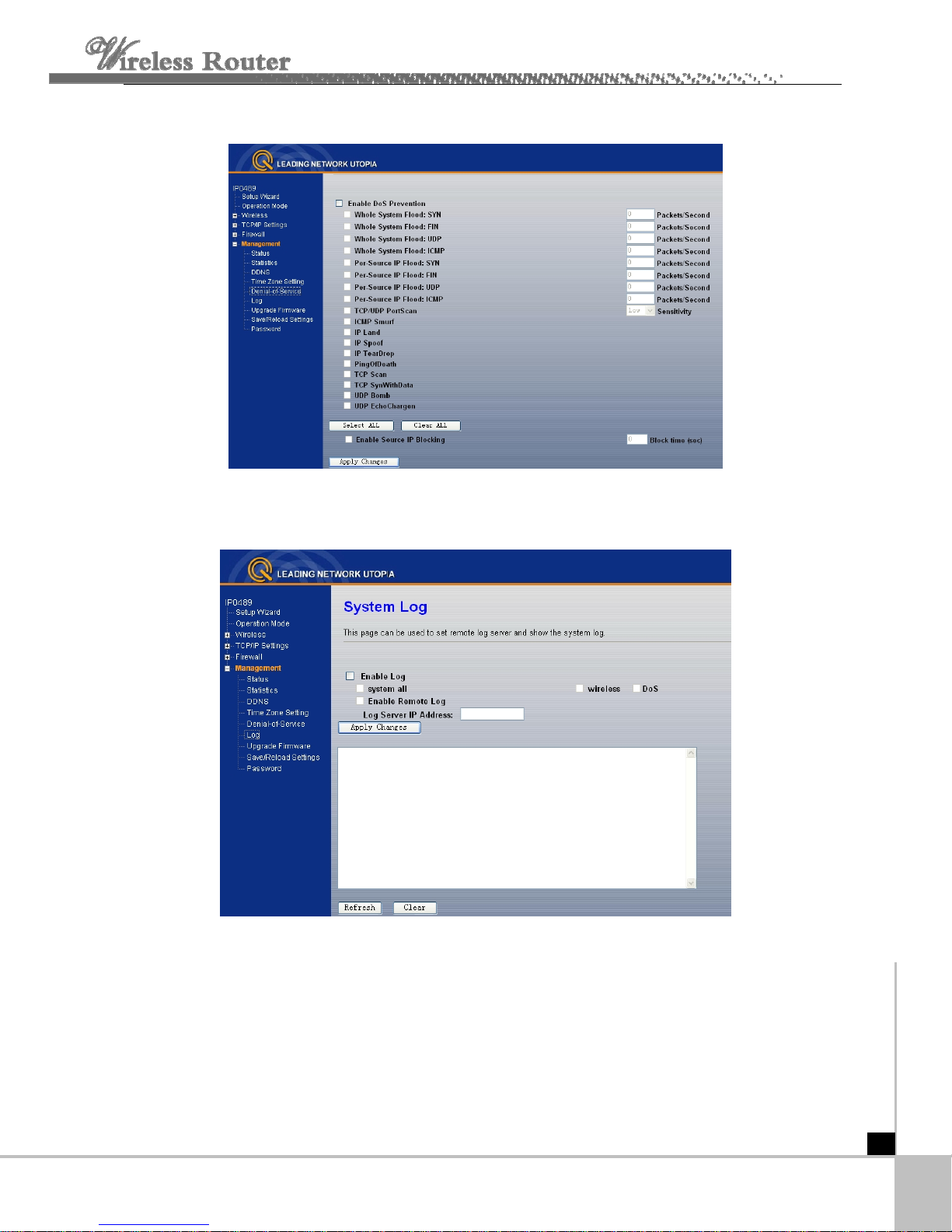
Click apply changes,DOS take effect.
4.5.6 Log
This page can be used to set remote log server and show the system log.
4.5.7 Upgrade Firmware
This page allows you upgrade the Access Point firmware to new version. Please note, do not
power off the
device during the upload because it may crash the system
- 26 -

4.5.8 Save/Reload settings
This page allows you save current settings to a file or reload the settings from the file which
was saved previously. Besides, you could reset the current configuration to factory default.
4.5.9 Password setup
This page is used to set the account to access the web server of Access Point. Empty user
name and password will disable the
- 27 -

A
p
p
e
n
d
i
x
1
:
F
A
Q
A
p
p
e
n
d
i
x
1
:
A
p
p
e
n
d
i
x
1. How do I configure the router to access Internet by ADSL users?
(1) First, configure the ADSL modem configured in RFC1483 bridge model.
(2) Connect the Ethernet cable from your ADSL modem to the WAN port on the router.
The telephone cord plugs into the Line port of the ADSL modem.
(3) Login to the router, click the “TCP/IP settings” menu on the left of your browser,
and click "WAN Interface" submenu. On the WAN page, select “PPPoE” for WAN
Connection Type
“Password” field, finish by clicking “Connect”.
(4) If your ADSL lease is in “pay-according-time” mode, select “Connect on Demand”
or “Manual” for Interne
for Time to avoid wasting paid time. Otherwise, you can select “continous” for
Internet connection mode.
2. How do I configure the router to access Internet by Ethernet users?
(1) Login to the router, click the “TCP/IP Settings” menu on the left of your browser,
and click "LAN Interface" submenu. On the WAN page, select “DHCP” for "Client",
finish by clicking “apply changes”.
(2) Some ISPs require that you register the MAC Address of your adap r, which is
connected to your cable or DSL modem during installation. If your ISP requires
MAC register, login to the router and click the "TCP/IP Setting" menu link on the left
of your browser, and then click "LAN Interface", if your PC’s MAC address is
proper MAC address,type your PC’s MAC address will fill in the "Clone MAC
Address" field. Or else,The format for the MAC Address isXX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX.
Then click the "apply cha
3. I want to use Netmeeting, what do I need to do?
(1) If you start Netmeeting as a sponsor, you don’t need to do anything with the
(2) If you start as a responsor, you need configure Virtual Server or DMZ Host.
F
1
:
F
A
Q
A
Q
. Type user name in the “User Name” field and password in the
t connection mode. Type an appropriate number
te
nges" button. It will take effect after rebooting.
router.
ow to configure Virtual Server: Login to the router, click the “Forw
(3) H arding” menu on
the left of your browser, and click " port foward" submenu. On the "port forward " page,
nter “1720” into the blank below the “Service Port”, and your IP address below the
e
P Address, assuming 192.168.1.25469 for an example, remember to “supply
I
hanges”.
c
4) How to enable DMZ Host: Login to the router, click the “firewall settings” menu on
(
e left of your browser, and click " DMZ" submenu. On the "DMZ" page, click
th
nable DMZ” radio and type your IP address into the “DMZ Host IP Address” field,
“E
ing 192.168.1.25469 as an e
us xample, remember to click the "Apply changes” button.
4. he wireless stations cannot connect to the router.
T
- 28 -

(1) Make sure the "Disable Wireless LAN Interface " is not select.
(2)
Make sure that the wireless stations' SSID accord with the router's SSID.
(3) ve right KEY for encryption when the router is
Make sure the wireless stations ha
encrypted.
(4)
If the wireless connection is ready, but you can’t access the router, check the IP
Address of your wireless stations.
A
p
p
A
A
e
p
p
n
p
e
n
p
e
n
General
Standards IEEE 802.3, 802.3u, 802.11b and 802.11g
Protocols TCP/IP, PPPoE, DHCP, ICMP, NAT, SNTP
d
d
d
2
S
:
p
e
c
i
i
x
2
S
:
i
x
2
i
x
p
:
p
S
e
e
c
c
f
i
c
a
t
i
o
n
s
i
f
i
c
a
t
i
a
o
t
i
o
i
f
i
c
n
n
s
s
One 10/100M Auto-Negotiation WAN RJ45 port, Four
P 10/100M Auto-Negotiation LAN RJ45 ports supporting Auto orts
MDI/MDIX
10BASE-T :UTP category 3, 4, 5 cable (maximum 100m)
Cabling Type
100BASE-TX:UTP category 5, 5e cable (maximum 100m)
Radio Data Rae 54/48/36/24/18/12/9/6/11/5.5/3/2/1Mbps
Power Supply 9V~ 800mA
LE 1,2,3,4 Ds Power, M1, WLAN,
Environmental and Physical
Operating Temp.
Operating Humidity 10% - 95% RH, Non-condensing
EIA/TIA-568 100Ω STP (maximum 100m)
EIA/TIA-568 100Ω STP (maximum 100m)
0~40 (32
~104)
Dimensions (W×D×H) 7.9×4.7×1.2 in. (201×120×31.10 mm) (without antenna)
- 29 -

App : Glo
endix 3 ssary
802.11b - The 802.11 sing
d equence sp censed
irect-s
radio spectrum a and WEP encryption for security. 802.11b networks are
also referred to as Wi-Fi networks.
802.11g - specificatio e
spread-spect um (DSSS) tech rating in the
unlicensed rad
devices, and WEP encryption fo
DDNS (Dynamic Domain Name System) - The capability of assigning a fixed host and
domain name to a ynamic Internet IP Address.
DHCP st on Protocol) - A protocol that automatically
DMZ. arized Zone allows one local host to be exposed tothe
DNS. r) -
Domain Na
DoS(Denial of Service) - A
DSL
ISP(Internet Service Provider) - A company that provides access to the Internet
MTU
NAT(Network Address Translation) - NAT technology translates IP addresses of a local
P
. (Dynamic Ho Configurati
configure the TCP/ e PCs that are connected to a DHCP
serv
er.
(Demilitarized Zone) - A Demilit
Internet for a spec ervice such anternet gam
websites int
network from operating or communicating.
(Digital Subscriber Line) - A technology that allows data to be sent or received over
existing traditional phone lines.
(Maximum Transmission Unit) - The size in bytes of the largest packet that can be
transmitted.
area network to a different IP address for the Internet.
PPoE (Point to Point Protocol over Ethernet) - PPPoE is a protocol for connecting remote
hosts to the Internet over an always-on connection by simulating a dial-up
connection.
r
o IP addresses.
me - A descriptive name for an address or group of addresses on the Internet.
b standard specifies a wireless networking at 11 Mbps u
read- spectrum (DSSS) technolog and operating in the unli
t 2.4GHz,
n for wireless networking at 54 Mbps using direct-sequenc
io s
pectrum at 2.4GHz, and backward compatibility with IEEE 802.11b
d
IP parameters for the all th
ial-purpose s ing or videoconferencing.
nology, using OFDM modulation and ope
r security.
An Internet Service that translates the names of (Domain Name Serve
hacker attack designed to prevent your computer or
- 30 -

SSI Set Identification is a thirty-two character (maximum) alphanumeric key
D - A Service
identifying a wireless local area network. For the wireless devices in a network to
communicate with each other, all devices must be configured with the same SSID. This
i
s typically the configuration parameter for a wireless PC card. It corresponds to the
ESSID in the wireless Access Point and to the wireless network name.
P (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
WE - A data privacy mechanism based on a 64-bit or
128-bit or 152-bit shared key algorithm, as described in the IEEE 802.11 standard.
Wi-Fi - A trade name for the 802.11b wireless networking standard, given by
the Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance (WECA, see http://www.wi-fi.net), an
industry standards group promoting interope
rability among 802.11b devices.
WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) - A group of computers and associated devices
communicate with each oth
er wirelessly, which network serving
users are
limited in a local area.
- 31 -
 Loading...
Loading...