Page 1
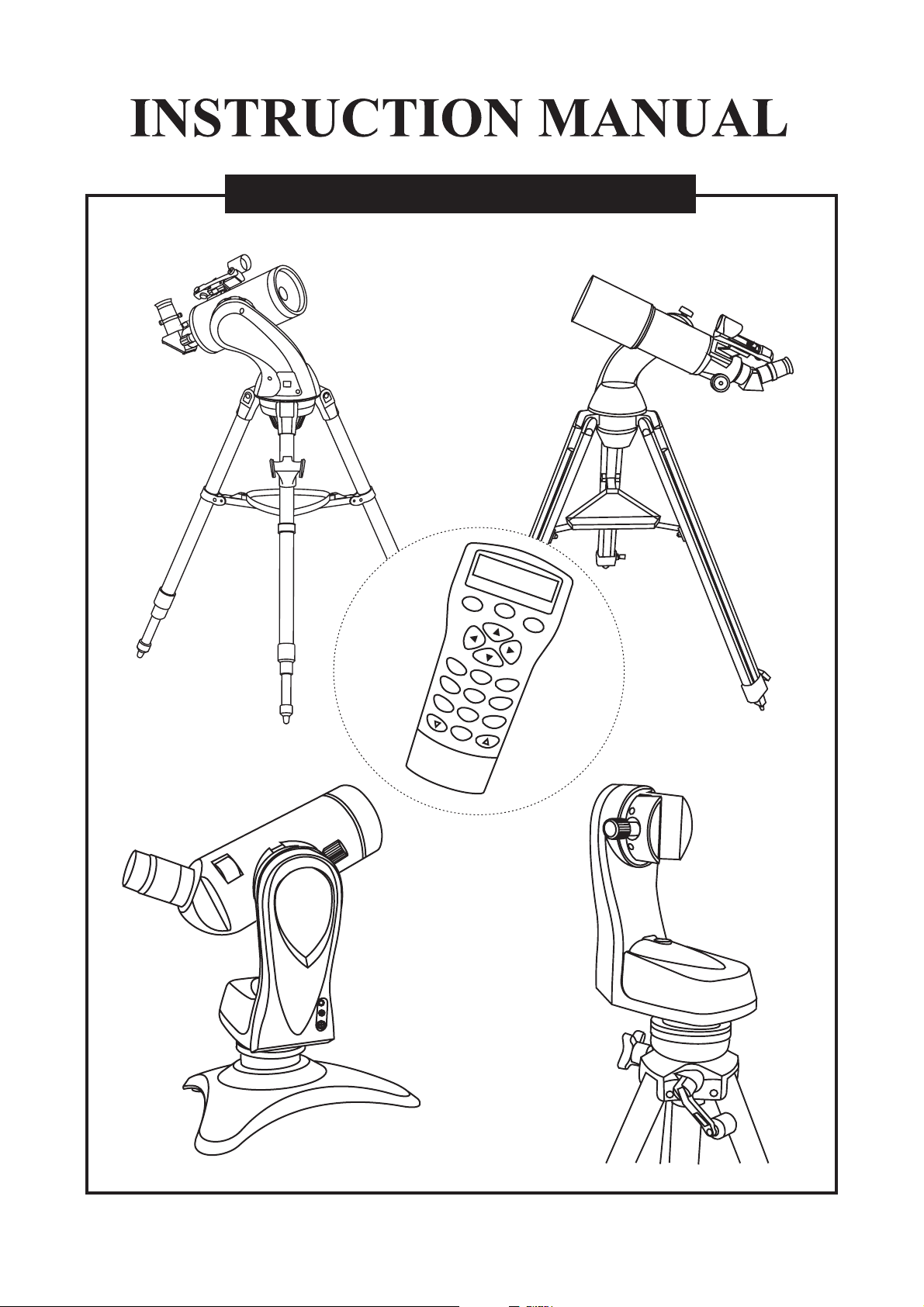
AZ GOTO TELESCOPES
ESC
SETUP
ENTER
T
OUR
1
R
A
TE
2
M
4
PLANET
7
UTILITY
3
NGC
5
IC
6
OBJECT
8
USER
9
ID
0
GT020609V3-03.05
Page 2

Page 3
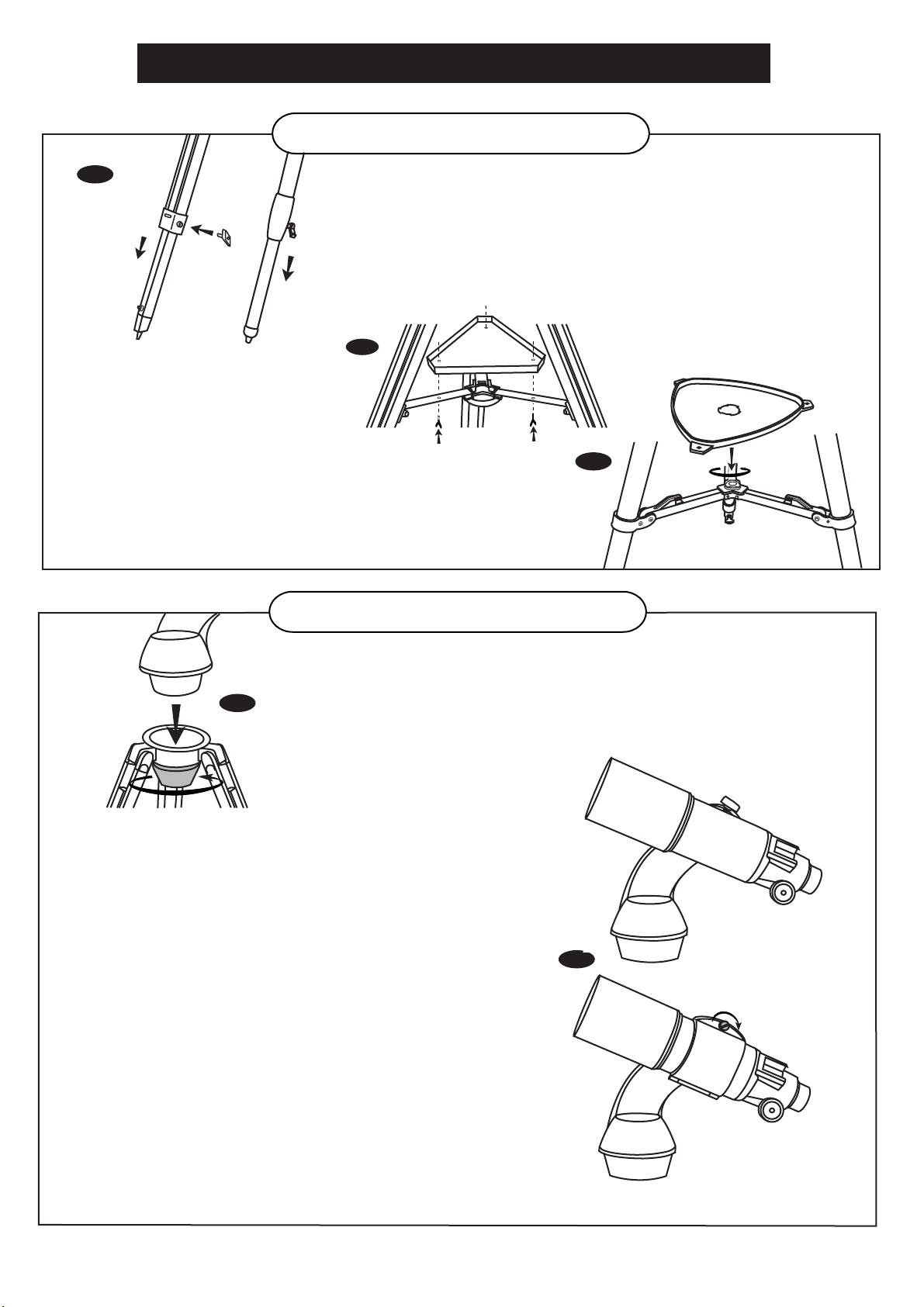
TELESCOPE ASSEMBLY - GT MOUNTS
TRIPOD SET UP
Fig.1
ADJUSTING TRIPOD LEGS (Fig.1)
1)
Slowly loosen the height adjustment clamp and gently pull out the lower
section of each tripod leg. Tighten the clamps to hold the legs in place.
2)
Spread the tripod legs apart to stand the tripod upright.
3)
Adjust the height of each tripod leg until the tripod head is properly leveled.
Note that the tripod legs may not be at same length when the mount is level.
Fig.2
ATTACHING THE TRIANGLE
ACCESSORY TRAY (Fig. 2)
1)
Place the accessory tray on top of
the bracket, and secure with the
locking knob from underneath.
ATTACHING THE QUICK-RELEASE ACCESSORY TRAY (Fig. 3)
1)
Hold the accessory tray directly above the bracket. Rotate the tray until the
shape of the hole matches the locking mechanism in the center of the bracket.
Place the tray on top of the bracket and rotate to lock the tray in place.
TELESCOPE ASSEMBLY
Fig.3
ATTACHING THE MOUNT TO THE TRIPOD (Fig.4)
Place the single arm mount into the tripod head.
Fig.4
1)
Push the large cup underneath the tripod head upward and
2)
turn counter-clock wise to secure the mount to the tripod.
ATTACHING THE TELESCOPE TUBE TO THE MOUNT (Fig.5)
The dovetail type
1)
Loosen the black screw on the top of the mount until it is not
protruding from the dovetail accepter.
2)
Find the approximate balance point on the telescope tube.
3)
Slide in the telescope tube until the balance point of the telescope falls
in the center of the mount head. Tighten the screw until the dovetail
bar on the telescope tube is securely fastened on the mount.
The clamp type
1)
Remove the black screw on the top of the cradle ring and
place it at a safe place for later use.
2)
Carefully open the cradle ring just enough so the telescope
tube can be slided in.
3)
Slide in the telescope tube. Close the cradle ring and insert the
black screw from the opposite side of the arm as shown in
Fig.4. Tighten the screw until the telescope tube is securely
fastened inside the cradle ring.
(Diagram applicable to
all telescope designs.)
Fig.5
(Diagram applicable to all
telescope designs.)
3
Page 4
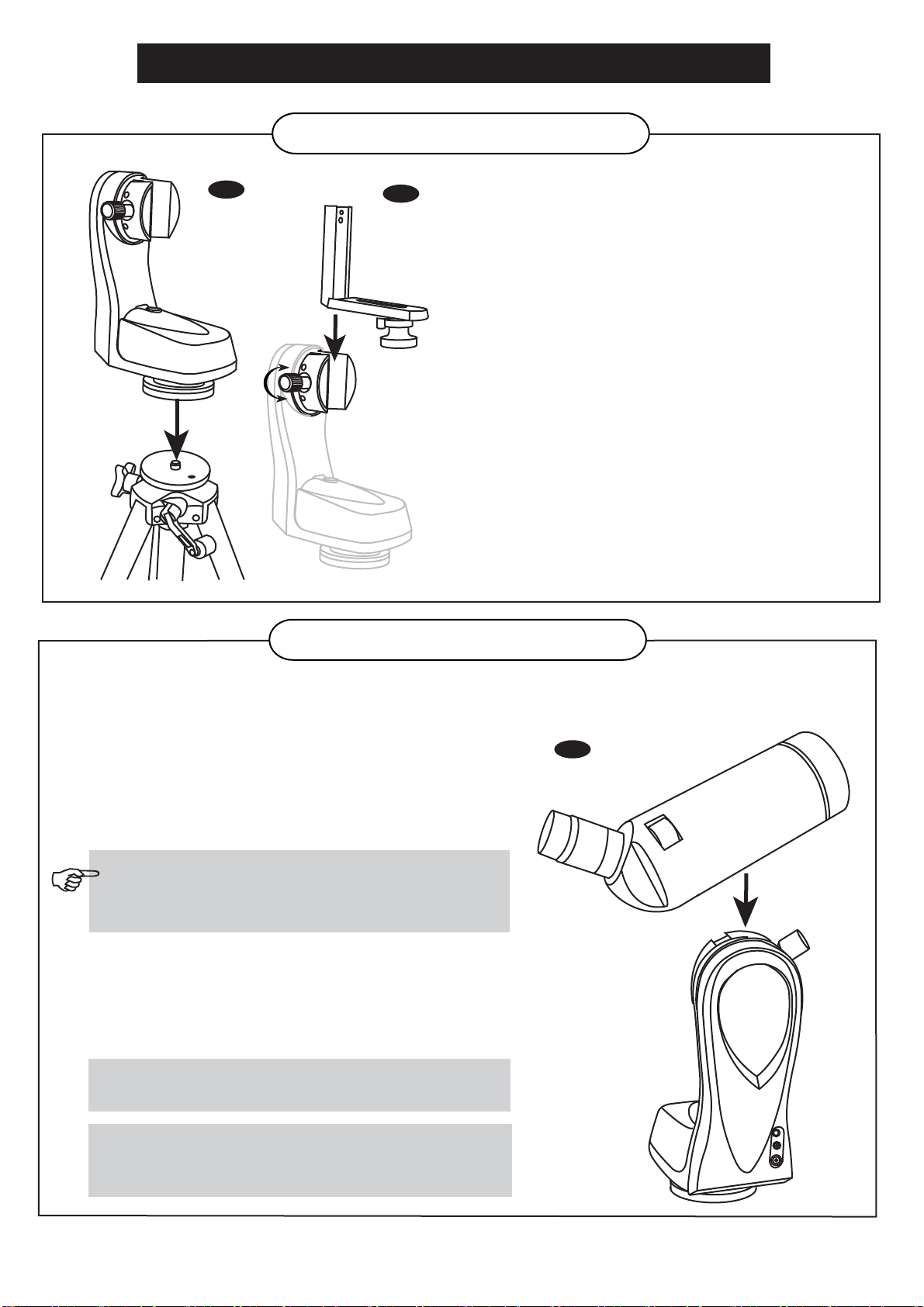
TELESCOPE ASSEMBLY - MULTIFUNCTION MOUNTS
TRIPOD & MOUNT SET UP
Fig.6
Fig.7
TRIPOD SET UP
Remove the tripod from the box and spread the
1.
legs apart until fully extended.
Adjust the desired height of the tripod before
2.
attaching the fork arm and your optical tube.
Minor adjustments can be made later. Loosen the
locking mechanisms on each leg and slide the
legs to the desired height and then retighten them.
MOUNT SET UP
Next you will attach your Multi-function mount to
1.
the tripod. Locate the 3/8" threaded bolt in the top
of the tripod platform. Then, find the mating 3/8"
threaded hole underneath the Fork Arm Base.
Thread the 3/8" bolt of the tripod platform into the
3/8" threaded hole in the fork arm base until it is
good and tight (Fig.6).
Locate the 1/4x20 Mounting Platform. Slide it down
2.
the slot on the Fork Arm as in dicated in Fig.7.
Secure by tightening the thumb screws.
TELESCOPE ASSEMBLY
ATTACHING THE TELESCOPE TUBE TO THE MOUNT
If you are using the telescope for tracking astronomical objects,
1.
attach the optical tube to the Mounting Platform so that the Fork
Arm is located on the right hand side (Fig.8). If the telescope is
installed incorrectly you will not be able to use the latitude scale
on the top of the Fork Arm. Thread the 1/4x20 Mounting Screw
into the 1/4x20 tripod adapter of the optical tube and make sure it
is tight. Do not overtighten the screw.
Telescopes with a dovetail bar attached can be installed
directly onto the Multi-function mount without using the
Mounting Platform.
ATTACHING A CAMERA TO THE MOUNT
For general terrestrial use, the camera can be secured on
1.
the Mounting Platform any way you wish. Thread the 1/4x20
Mounting Screw into the camera and make sure it is tight. Do
not overtighten the screw.
Do NOT overtighten the 1/4x20 Mounting Screw or it may
cause damage to the screw.
Fig.8
You must be careful not to use an optical tube that is too
heavy or too big as the motor assembly will not be able to
operate properly and you may damage the mount.
4
Page 5

sing the Red Dot Finder
U
The Red Dot Finder is a zero magnification pointing tool that uses
a coated glass window to superimpose the image of a small red
dot onto the night sky. The Red Dot Finder is equipped with a
variable brightness control, azimuth adjustment control, and
altitude adjustment control (Fig.a). The Red Dot Finder is
powered by a 3-volt lithium battery located underneath at the
front. To use the Finder, simply look through the sight tube and
move your telescope until the red dot merges with the object.
Make sure to keep both eyes open when sighting.
Aligning the Red Dot Finder
Like all finderscopes, the Red Dot Finder must be properly
aligned with the main telescope before use. This is a simple
process using the azimuth and altitude control knobs.
1.
Open the battery cover by pulling it down (you can gently pry at
the 2 small slots) and remove the plastic shipping cover over
the battery (Fig.b).
2.
Turn on the Red Dot Finder by rotating the variable brightness
control clockwise until you hear a "click". Continue rotating the
control knob to increase the brightness level.
Insert a low power eyepiece into the telescope's focuser.
3.
Locate a bright object and position the telescope so that the
object is in the centre of the field of view.
With both eyes open, look through the sight tube at the object.
4.
If the red dot overlaps the object, your Red Dot Finder is
perfectly aligned. If not, turn its azimuth and altitude adjustment
controls until the red dot is merged with the object.
Fig.a
ON/OFF
Brightness
Control
Altitude
Adjustment
Control
Fig.b
Fig.c
Azimuth
adjustment
control
Sight Tube
Battery cover
Plastic
shipping
cover
ocusing
F
Slowly turn the focus knobs (Fig.c), one way or the other, until the
image in the eyepiece is sharp. The image usually has to be finely
refocused over time, due to small variations caused by
temperature changes, flexures, etc. This often happens with short
focal ratio telescopes, particularly when they haven't yet reached
outside temperature. Refocusing is almost always necessary
when you change an eyepiece or add or remove a Barlow lens.
alculating the m
C
The magnification produced by a telescope is determined by the focal length of the eyepiece that is used with it.
To determine a magnification for your telescope, divide its focal length by the focal length of the eyepieces you
are going to use. For example, a 10mm focal length eyepiece will give 80X magnification with an 800mm focal
length telescope.
magnification =
When you are looking at astronomical objects, you are looking through a column of air that reaches to the edge of
space and that column seldom stays still. Similarly, when viewing over land you are often looking through heat
waves radiating from the ground, house, buildings, etc. Your telescope may be able to give very high magnification
but what you end up magnifying is all the turbulence between the telescope and the subject. A good rule of thumb
is that the usable magnification of a telescope is about 2X per mm of aperture under good conditions.
agnication (power)
Focal length of the telescope
Focal length of the eyepiece
800mm
=
10mm
= 80X
5
Page 6
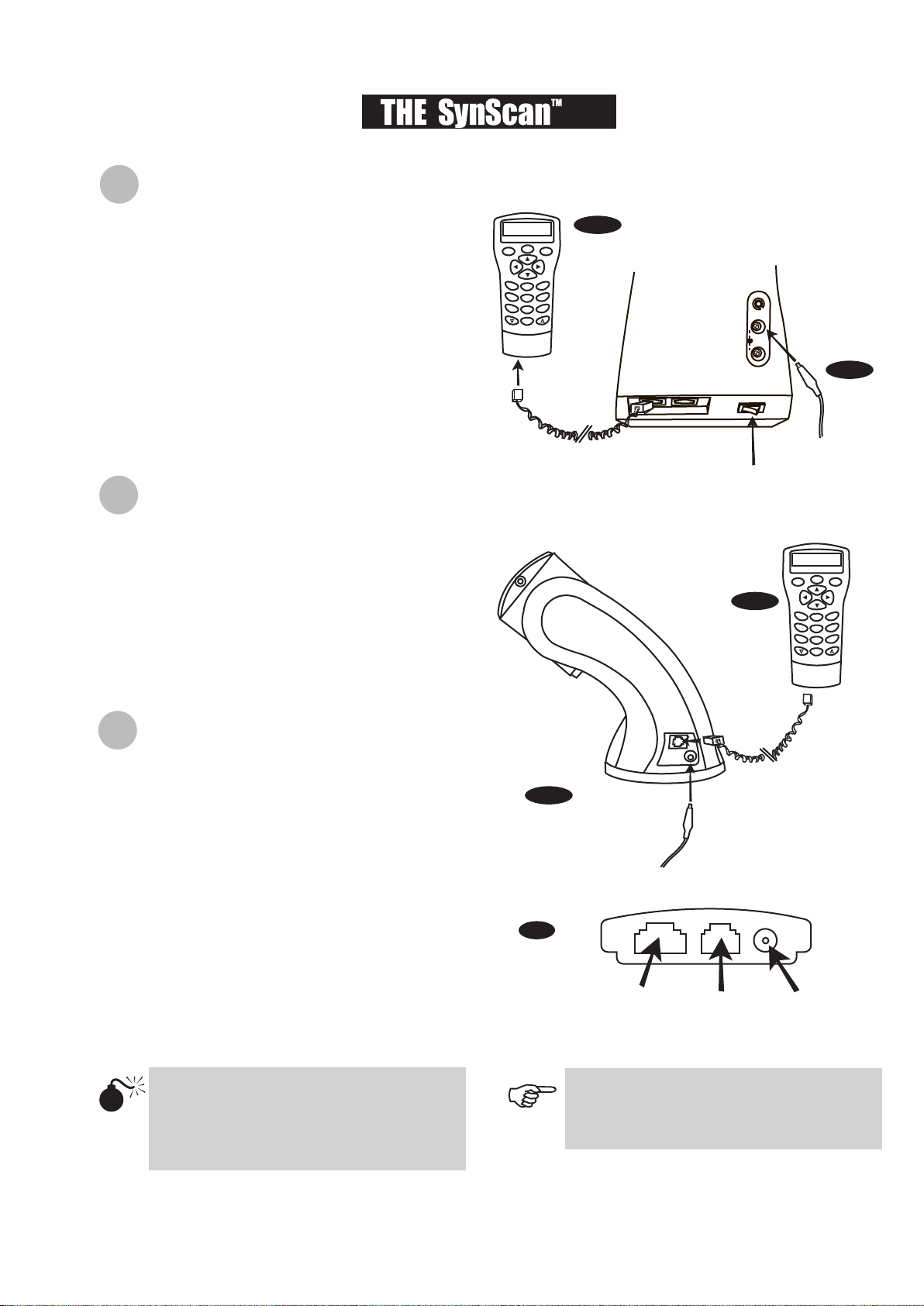
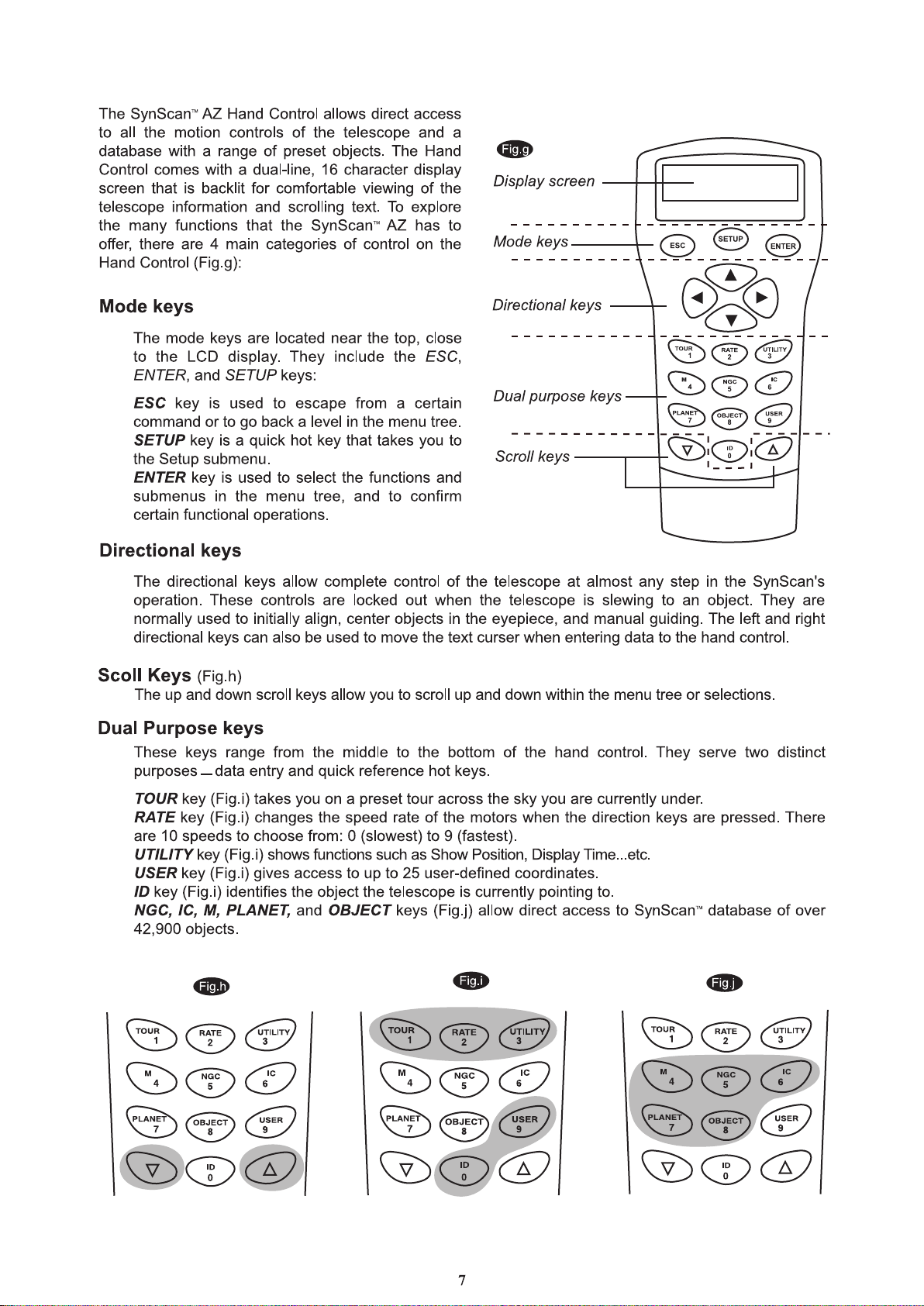
ntroduction to the SynScan
I
TM
AZ
AZ
The SynScanTM AZ is a precision-engineered
instrument that will allow you to easily find and enjoy
viewing night sky treasures, such as planets,
nebulea, star clusters, galaxies and much more. The
hand control allows you to point your telescope at a
specific object or even tour the skies at the touch of
a button. The user friendly menu system allows
automatic slewing to over 42,900 objects. Even an
inexperienced astronomer can master its variety of
features in a few observing sessions. Below is a brief
description of the individual components of the
SynScanTM AZ hand controller.
TM
Z
owering the SynScan
P
The SynScan
TM
AZ should be powered by 11-15V DC
A
power supply (tip-positive) capable of producing
continuous current of minimum 1 amps. Correctly plug
the power cord into the 12V DC outlet on the the
mount (See Fig.d-1 and d-2 for Multi-function
telescopes and Fig.e-1 and e-2 for AutoTracking
telescopes). For Multi-function telescopes, flip the
Power Switch to the "on" position to turn on the power.
ESC
TOUR
1
M IC
4
PLANET
OBJECT
7
Fig.d-2
SETUP
ENTER
EVENT
RATE
3
2
NGC
6
5
USER
9
8
ID
0
Multi-Function Mount
SNAP
IN
DC12V
OUT
Fig.d-2
AUX
HC
ON/OFF
power supply
power switch
AutoTracking Mount
SETUP
ESC
ENTER
Fig.e-1
TOUR
1
M IC
4
PLANET
OBJECT
7
EVENT
RATE
3
2
NGC
6
5
USER
9
8
ID
0
TM
AZ Hand Control
ynScan
S
The SynScanTM AZ hand control cable has a RJ-45 with
8 connecting pins on one end and a RJ-12 with 6
connecting pins on the other end. Plug the RJ-45 end
into the hand control (Fig.c) and the other end into the
outlet on the mount (Fig.b). On the bottom of the hand
control, the middle port is used for RS-232
communications between the SynScan
TM
AZ and a
computer or other devices. (See “Linking with a
Computer” for details.) The DC power port allows
independent use of the SynScanTM AZ hand control for
users who wish to browse the database or update the
firmware without connecting to the telescope (Fig.f).
The DC power port on the hand control is for
hand control stand-alone applications only.
For telescope applicaions, use the 12V DC
outlet on the mount.
Fig.e-2
Fig.f
power supply
RJ-45
RJ-12 DC power port
To connect the SynScanTM AZ to a PC, use
only the RS-232 cable provided with the
mount.
6
Page 7
Page 8

This section provides a step-by-step procedure on how to operate your SynScanTM AZ hand control.
up
nitial Se
I
Make sure the mount is level to the ground.
1.
Point the telescope roughly to one or a group of visible bright stars in the sky.
2.
Connect the hand control to the mount with the provided cable. For AutoTracking
3.
telescopes, plug the DC 12 volt power into the outlet of the mount to turn on the power.
For Multi-function telescopes, simply flip the power switch to the “on” position.
The initial screen displayed on the hand control is the Version Screen. You will hear a
4.
long beep indicating that the hand control is properly connected to the mount. The
directional keys are now activated. You can now move the telescope using the directional
keys on the hand control. The default speed rate at this point is Rate 9. Press ENTER to
proceed to the next Initial Setup step.
t
If the hand control is not properly connected to the mount, the screen will display “No
link to M.C. Stand-alone mode”. If you wish to use the hand control to control the
mount, unplug the connection cable and try again.
The hand control will display a warning concerning pointing the telescope at the sun without
5.
proper equipment. If you have read the message already, pressing ENTER will bypass the
message and skip to the next step.
The hand control's red light will become dimmer and the backlight of the key pads will
turn off if idle for 30 seconds. Pressing any key turns it back on.
6.
Enter the telescope's current latitudinal and longitudinal position using the numeric keypad.
First enter the longitudinal coordinate, followed by the latitudinal coordinate. Use the scroll
keys to choose between W or E, and N or S. Pressing the left or right directional keys will
move the cursor to the previous or next number. Press ENTER to confirm. The format you
enter should look like this: 123 04’ W 49 09’N.
7.
Enter your current time zone in hours and minutes (see Appendix C), using the scroll keys
and numeric key pad (+ for East, - for West). Press ENTER to confirm. The format you
enter should look like this if you are in Pacific Standard Time (PST): -08:00.
8.
Enter the date in the following format mm/dd/yyyy using the numeric keypad. Press ENTER
to confirm.
9.
Enter your current local time using the 24 hr time mode (e.g. 2:00PM=14:00). Press
ENTER to view the time you just entered. If it is incorrect, press ESC to go back to the
previous screen. If correct, press ENTER again to proceed to the daylight saving setting.
10.
After entering the current time, the SynScan
the scroll keys to make the selection and press ENTER to confirm.
After setting the daylight saving, SynScanTM will display "Begin alignment?". Press "1" or
ENTER to start the alignment procedure. Press "2" or ESC to skip the alignment and exit
to the Main Menu.
TM
AZ will prompt "DAYLIGHT SAVING?". Use
If a mistake was entered into the SynScanTM AZ hand control, press the ESC key to go
back to the previous menu, and press ENTER to start again.
8
Page 9

Alignment
Directional division
Span range in azimuth
The northern sky
°
The northeast sky
0 ° ~ 90
°
The eastern sky
45 ° ~ 135
°
The southeast sky
90 ° ~ 180
°
The southern sky
135 ° ~ 225
°
The southwest sky
180 ° ~ 270
°
The western sky
225 ° ~ 315
°
The northwest sky
270 ° ~ 360
°
tar
S
In order for the SynScanTM AZ to correctly point to objects in the sky, it must first be aligned to two to three
known positions (stars) in the sky. As the Earth rotates on its axis every 24 hours, astronomical objects
appear to move through the sky following an arc. With the supplied information, the telescope can replicate
a model of the sky and the movements of astronomical objects. Star alignment can be done anytime during
the observing session by choosing Alignment under Setup Mode, in the Main Menu.
There are two ways to align the SynScanTM AZ Brightest Star alignment and 2-Star alignment. If you are
using the SynScanTM AZ for the first time, and you are not familiar with the celestial object in the sky, we
recommend that you begin with the Brightest Alignment. The Brightest Star alignment will prompt and help
you find the brightest star of a specific direction in the sky at your current site. It is convenient for user to
identify the brightest star in the sky. Before performing the alignment method, make sure that your
finderscope is well aligned with the telescope tube. See the next page for tips on how to choose the
alignment stars. Below describes a step-by-step procedure on how to perform the Brightest Star Alignment:
Brightest Star Alignment
In the alignment screen, select Brightest-Star Align using the scroll keys. Press ENTER to confirm. The
1.
hand control will prompt "Select Region:" for you to select one of the eight directional divisions in azimuth
angle from the north, northeast, east, southeast to northwest etc. Each division covers 90-degree span in
azimuth. That means if you select the
northeast sky, the division will cover from
0 degree to 90 degrees in azimuth,
where North equals to 0 or 360 degree in
azimuth angle, East equals to 90 degree
in azimuth angle, South equals to 180
degree in azimuth angle, and West
equals to 270 degree in azimuth angle.
315 ° ~ 45
The table on the right is the range of
the eight directional divisions.
Once the directional division has been selected, the hand control will calculate and generate a list of the
2.
stars located within this region that are brighter than 1.5 in magnitudes. The stars and planets below 10
degrees, higher than 75 degrees in elevation or fainter than 1.4 in magnitudes will be filtered out.
The name and magnitude of the alignment star will be displayed on the first line of the LCD. The
3.
approximate position will be prompted on the second line. For example, if Arcturus is prompt as
alignment star, its magnitude is 0.0 and location is at 88.1 degree east and 24.1 degree above the
horizon. You will see the LCD display as shown in Fig.k.
For the first alignment star, the mount will not slew to the star automati-
4.
cally. Use the directional buttons to manually slew the telescope to point
to the object in the finder and then center it in the eyepiece. You may
change the slewing speed by pressing the RATE button, and then choose
a number between 0 (slowest) - 9 (fastest).
5.
Once the star has been centered in the eyepiece, if it is a planet the hand control will prompt you to reselect a star from the list as the first alignment star. Otherwise the hand control will prompt a list of objects
for you to choose as the second alignment star. Select an object from the list. The hand control will command the mount to slew the telescope to point to the object. Center the object in the eyepiece again. If
both alignment stars are properly aligned, "Alignment Successful" will display on the LCD. Otherwise,
the warning "Alignment Failed" will show and the alignment will have to be done again. You may exit the
alignment procedure by pressing the ESC key anytime during the procedure.
The slewing speed can be adjusted by
pressing on the RATE button. Then choose
a number between 0 (slowest) - 9 (fastest).
Fig.k
1. A r c t u r u s 0 . 0
E 88. 1° 24.1°
SynScanTMAZ
finished slewing to an object. Do not try to
adjust the telescope before you hear the beep.
SynScanTMAZ
key while slewing.
9
will beep once when it has
will only respond to the
ESC
Page 10

Two-Star Alignment
The two star alignment procedure is similar to the Brightest Star alignment, except that the hand control
will not prompt for you to select a directional region for a bright star. Below describes a step-by-step
procedure on how to perform the Two-Star Alignment:
1.
In the alignment screen, select 2-Star Align using the scroll keys. Press ENTER to confirm.
2.
The SynScan
first alignment star. Using the scroll keys, choose a star you are most familiar with and press
ENTER. The telescope will not automatically slew to the first selected alignment star. Use the
directional buttons to manually slew the telescope to point to the object. Now look through the
eyepiece and adjust the telescope so that the object is centered in the field of view of the
eyepiece. Press ENTER to confirm.
3.
SynScanTM AZ will now provide a list of objects for the second alignment star. Choose a star using
the scroll keys and press ENTER. The telescope will start slewing towards the chosen object.
When the slewing stops, adjust the telescope with the directional keys until the star is centered on
the crosshairs in the finder scope. Repeat the centering procedure to center the object in the field
of the eyepiece and press ENTER to confirm.
4.
If both alignment stars are properly aligned, "Alignment Successful" will display on the LCD.
Otherwise, the warning "Alignment Failed" will show and the alignment will have to be done again.
Following is some pointers on how to choose appropriate alignment stars:
Select two stars that are at least 60 degrees apart. The more distance between the two alignment
stars, the better accuracy the alignment will produce. Choosing two stars with the same altitude in
elevation will also create a better result.
TM
AZ will provide a list of stars available in your current sky for you to choose as the
AE)
Accuracy Enhancement (
ointing
P
Both the star alignment methods provide alignment adequate for any visual observing purpose. For
applications that require extra high precision in a particular part of the sky, the SynScan
Pointing Accuracy Enhancement (PAE) function to further improve the accuracy. The PAE can be
performed in up to 85 zones to cover the whole sky. The area(s) where the chosen alignment star(s) is located
should be already mapped out accurately by the SynScanTM AZ. Further accuracy enhancement is not
necessary. The following provides a step-by-step procedure on how to perform PAE:
1.
2.
3.
Use the direction keys to center the last go-to object, then go to the next step. (This step may be
skipped.)
Press and hold down the ESC key for 2 seconds. The hand control will display "Re-center" and
the name of the reference object will appear in a blinking mode (3 times). If the go-to command is
sent from the planetarium software, instead of the name of the object, the hand control will
display "Last goto object".
Make sure that the reference object is still in the center of the view and press ENTER. If you do
not wish to record the result, press ESC to abort the operation. After pressing ENTER, the
SynScan
Now the pointing accuracy of this particular part of the sky should be greatly improved.
TM
will record the amount of pointing inaccuracy and recalculate the model of the sky.
P
TM
AZ provides a
The result for the star alignments and PAE is stored in the hand control even after the power
has been shut off. You will only need to perform the star alignment once as long as these two
criteria are met: 1. The telescope is moved to its home position (Park the telescope) before
turning off the power. 2. The telescope setup, including the mount, has not been moved.
Accessory change is acceptable as long as it is done with great caution. When the hand control
is turned on for the next time, make sure that the time entered during initial setup is based on
the same source as last time. For example, if you enter the time on your watch during this
observing session, the time you enter next time should also be read from your watch.
10
Page 11

TM
AZ
bject database in the SynScan
O
The SynScanTM AZ comes with a vast database with over 42,900 objects coordinates and
information all available in the palm of your hand. The database contains the following catalogs:
Solar System - The other 8 planets of our solar system, plus the Moon.
Named Star - A list of 212 best known stars from the SynScanTM AZ database.
*NGC - 7,840 of the brightest deep sky objects from the Revised New General Catalog.
IC - 5,386 of standard stars and deep sky objects from the Indexed Catalog.
Messier - Complete list of 110 Messier objects.
Caldwell - Complete list of 109 Caldwell objects.
Double Stars - Includes 55 well-known double stars.
Variable Stars - Includes 20 will-known variable stars.
SAO - Includes 29,523 stars.
electing an Object
S
Once the telescope has been aligned. You can now access and view the 42,900 different objects
in the SynScan
TOUR - Takes you on a preset tour across your current sky. It
(Fig.l)(Fig.l)
will automatically choose from the database the brightest and
most beautiful deep-sky objects for your viewing pleasure. Use
the down scroll key to view through the deep sky objects.
Choose the desired object by pressing ENTER. It will show the
coordinate of the chosen object. Pressing ENTER once more will
cause the telescope to slew to the object.
M, NGC, IC - These shortcut keys give you access to the most
popular celestial catalogues to date. Each Catalog has a set
number of objects to choose from. Use the numeric keys to
select an object by entering its number. Pressing ENTER will
display its coordinate. Primary information such as size,
magnitude, and constellation are obtained by pressing the scroll
keys. Pressing ENTER once more will cause the telescope to
slew to the object.
PLANET - This shortcut key takes you straight to the Planets
sub menu in the database. Use the scroll keys to scroll through
the list of planets in our solar system. Press ENTER to view its
coordinates, and ENTER once more to slew to the planet.
USER - This will take you to the database that you have defined
for yourself. You can enter a new location or recall the objects
that have been previously saved (see Using the User Defined
Database).
TM
database. There are three methods of selecting a celestial object to view:
Fig.l
Fig.m
(Fig.m)(Fig.m)
(Fig.n)(Fig.n)
The OBJECT key takes you to the Objects Catalogue, where
you have complete access to over 42,900 celestial objects in the
database. (See Object database in the S ynScan
menu tree.)
In the Main Menu, scroll down to OBJECT CATALOG and press
ENTER. Similar to the OBJECT key, this gives you the complete
access to all 42,900 celestial objects in the database. (See
Object database in the S ynScan
TM
AZ and the menu tree.)
11
TM
AZ and the
Fig.n
OBJECT CATALOG
Page 12

tility Functions
U
Utility Functions are useful tools that provide simple, one-step processes to your SynScanTM AZ.
Show Position - This displays the coordinates of the location where the telescope is
currently pointed.
Show Information - Under this submenu, you may check local time, local sidereal time,
hardware, firmware and database version of the SynScan hand control. If the hand control is
connected to the mount, this menu will also display the firmware of motor control board.
Park Scope - This moves the telescope to the Home position or parks the telescope at the
current or previously stored parking position.
PAE - Pointing Accuracy Enhancement function.
Clear PAE data - This allows you to clear all PAE data.
GPS - This allows you to obtain information from the SynScan GPS receiver.
etup Functions
S
The Setup functions allow you to change any system variable or information regarding location,
time, date, and alignment configurations. To access the Setup Functions, either press SETUP key
on the key pad or scroll to SETUP under menu option using the scroll keys. Below lists the
different types of functions available to you, and their purposes.
Date - Allows you to change the date entered at the initial setup.
Time - Allows you to change the current time.
Observing site - Allows you to change the current location.
Daylight Savings - Allows you to change the Daylight Savings option.
Alignment - Allows you to perform the star alignment.
Alignment Stars -
Auto Select - When this option is chosen, the hand control will filter out the star not
suitable for star alignment.
Sort by - This allows the hand control to generate a list of alignment stars and display
them alphabetically or by their magnitude.
Backlash - This feature allows you to insert a value for each axis to compensate for its
backlash. For better pointing accuracy, it is important that the backlash value is set to be
equal or greater than the real amount of backlash between the gears. The default setting of
the backlash is 0 d 00' 00" (0 degree, 0 arcmin. and 0 arcsec.). Use the numeric keys to
enter the desired value and press the RIGHT directional key to move the cursor to the next
digit. First set the value for R.A. Press ENTER to proceed to Dec.
Tracking
Auto Tracking - This feature allows for quick tracking of a celestial object while the hand
control displays the coordinates the telescope is curretnly pointed at. If the star alignment
procedure has already been performed, you can activate the AutoTracking mode any time. If
not, make sure that the location and time have been properly entered. Before choosing the
Auto Tracking mode, position the telescope so that the tube is level and pointed to the North.
Set Slew Limits - Allows you to set the slewing limits of the mount on altitude axis. Setting
the slew limit prevents the optical tube from colliding with mount. The slew limit range is
dependent on the mount and the optical tube installed on the mount.
Handset Setting - This submenu allows adjustments of the brightness of the LCD backlit,
the darkness of the LCD lettering, the brightness of the LED backlit and the beeper volume.
Press the RIGHT or LEFT directional key to increase or decrease the value.
Factory Setting - This submenu allows you to reset the hand control to its default setting.
Sid. Rate: This activates tracking in Sidereal rate (Dual Axes Tracking).
Lunar Rate: This activates tracking in Lunar rate (Dual Axes Tracking).
Solar Rate: This activates tracking in Solar rate (Dual Axes Tracking).
Stop Tracking: This stops the tracking instantly.
12
Page 13

sing the User Defined Database
U
SynScanTM AZ allows you to save up to 25 objects in the user
defined database.
Fig.o
Saving an object to the database
1.
In the Main Menu, use the scroll keys to scroll down the list until you
find Object Catalog. Press ENTER.
2.
Select User Defined in the Object Catalog scroll list and press ENTER.
The User Defined menu can also be accessed by pressing the quick reference hot key
"USER" (number 9). Fig.o
The first available selection in the Object Catalog is
3.
Recall Object. This is where you select previously-saved
objects to view. Use the scroll keys to scroll down to "Edit
Objects" and press ENTER.
The SynScanTM AZ stores the user-defined objects in two
4.
formats-R.A/Dec and Alt/Az. Press 1 for the R.A/Dec.
format and 2 for the Alt-Azimuth format.
By default the SynScanTM will display the R.A./Dec or
5.
Alt/Az coordinates where the telescope is currently
pointed. In the case of R.A/Dec format, the coordinate
readout will be similar to this: "22h46.1m +90 00'" (Fig.p) which means 22 hours and 46.1
minutes in R.A. and "+90 00'" in Dec. Change the coordinates using the numeric keypad
and scroll keys. Use the RIGHT or LEFT directional keys to move the cursor to the next
or previous digit. Press ENTER to save.
Fig.p
Enter RA-DEC:
22h46 .1m +90 00
If the R.A./Dec coordinate entered does not exist, the SynScanTM AZ hand control will not
respond when the ENTER key is pressed. Check the entry for mistake and re-enter the
correct coordinate.
To store an object/location in Alt/Az format, first point the
6.
telescope to the desired location to obtain the Alt/Az
value, then press ENTER to save.
After the coordinates have been saved, the SynScan
7.
will display an User Object number as shown in Fig.q. Use
the scroll keys to change to the number you wish to
represent the coordinates and press ENTER.
The SynScanTM AZ will display "View Object?" and the User
8.
Object number you just entered. Press ENTER to go to
the object or ESC to return to the Input Coordinate menu.
The User Object number displayed may not be a vacant one. If you are unsure which
numbers are vacant, it is recommended that you first check for the available numbers by
recalling the saved user objects.
Recalling an user defined object
1.
See Step 1-4 of "Saving an object to the database" for details on how to access to the User
Defined menu. Select Recall Object and press ENTER.
2.
Use the scroll keys to browse through the User Object number until the number
representing the object you wish to view is present. Press ENTER to show its coordinate.
Press ENTER again to slew to the object. The hand control will not respond if a vacant User
Object number is selected. Use the scroll keys to choose another number and try again.
TM
AZ
Fig.q
Save? <ENTER>
User o bj. # 03
If the recalled object is below horizon, the SynScanTM AZ hand control will display
"Below Horizon !!" and automatically return to the Recall Object menu.
13
Page 14

dentifying an Unknown Object
I
SynScanTM AZ has the ability to identify the unknown object the telescope
is currently pointing at. To do so, simply:
1.
Press the ID key (Fig.r) or scroll down to IDENTIFY in the main
menu and press ENTER to identify the object.
2.
The hand control will display a list containing the closest known
object in each M, IC, NGC, and Named Star catalogs and its
distance to the exact location where the telescope is pointed.
Use the scroll keys to view these objects.
3.
Press ESC to exit from this function.
Computer
inking with
L
Another feature of SynScanTM AZ is the ability to connect to a computer via a serial
communication cable. Many commercially available planetarium softwares can be used to
control SynScanTM AZ. SynScanTM AZ Version 3.00 and later is compatible with Celestron
NexStar 5i/8i, NexStar GPS, or Synta SkyWatcher Mount command protocol.
1.
Make sure that the telescope has been aligned.
2.
Connect the RS-232 cable to the RJ-11 connector on the
hand control and to the COM-port of your computer (Fig.s).
A
Fig.s
Fig.r
Hand Control
Do not use RS-232 cable other than the one provided to
connect between the hand control and your computer. It
may damage your computer or the hand control. If you are
RJ- 11
making your own cable based on the information provided
in Appendix B, make sure that only pin 2, 3 and 5 connect
RJ-11 Pin-outs
to the com connector on your computer.
3.
In the planetarium software of your choice, choose
"Celestron NexStar 5i", "Celestron NexStar 8/9/11 GPS",
or “Synta Skywatcher Mount” in the driver setup menu
and follow the instructions provided by your program to
establish the connection to the telescope. The SynScan
AZ should be under the full control of your computer once
the connection is successfully established.
4.
When you are finished, follow the instructions provided by
your software to close the connection to the telescope.
TM
6 5 43 2 1
See Appendix C for
more information on
RS-232 connection.
Do not disengage the SynScan AZ unit before you disengage the program. Doing so may
cause some programs to freeze.
1= EXP D+
2= TD
3= GND
4= EXP D5= RD
6= +12 V
14
Page 15

TM
pdating the SynScan
U
Firmware
From version 3.0 onward, the SynScanTM AZ firmware is user upgradeable. Users can download
the latest version of the SynScanTM AZ firmware from the Sky-Watcher web site and easily update
their hand controls.
System requirements
SynScanTM AZ Hand Control of version 3.0.or later.
Windows95 or later
An available RS-232C communication port on the PC.
PC link cable that comes with the SynScanTM AZ hand control.
DC power supply with 7.5~15V/100mA output. Power plug should be 2.1mm diameter,
tip positive.
Preparing your PC for the update
1.
Create a folder for all SynScan
2.
Visit the Support Page of the Sky-Watcher website at:
TM
AZ related files on your computer and name it SynScan.
http://www.SkywatcherTelescope.net/Support.html.
3.
Download and save the SynScanTM Firmware Loader to the SynScan folder on your
computer. You may create a shortcut on the desktop for quick access in the future. You
will only need to download this software once. Once it is saved on your computer, only
the firmware data file is needed for future updates.
4.
Download and save the firmware data file named SynScanVXXXXAZ.ssf to the SynScan
folder. (The XXXX indicates the version number of the firmware.)
Updating the SynScan
1.
Plug the RJ-11 end of the PC link cable into the
TM
AZ Hand Control
Fig.t
jack in the middle socket on the hand control
(Fig.c). Push the connector into the hand control
until it clicks into place. Plug the other end of the
SETUP
ESC
ENTER
cable, the DB9 connector, to the RS-232 port on
your PC.
2.
Press and hold down the key "0" and "8"
simutaniously, then plug the power cord into the
hand control, as shown in Fig.t.
3.
The hand control will give a beep, indicating a
successful start up. The SynScan
TM
AZ will display:
TOUR
RATE
1
2
M IC
NGC
4
5
PLANET
OBJECT
7
8
ID
0
UTILITY
USER
3
6
9
"SynScanTMUpdate Ver. x.x" on the LCD screen,
as seen in Fig.u.
4.
Run the SynScanFirmwareLoader software on
your PC. Once the program is launched, you
should see a window as Fig.v. The "HC.Version"
button provides the version number of the
hardware, firmware and database of your hand
control. It is for your reference only. You will not
need it for the update.
Fig.u
SynScan
ESC
Ver. 1.3
SETUP
Update
ENTER
15
Fig.v
SynScan Firmware Loader
Firmware File:
SynScan Firmware Loader
1.0
Update
Update
HC. Version
Browse
Page 16

Page 17
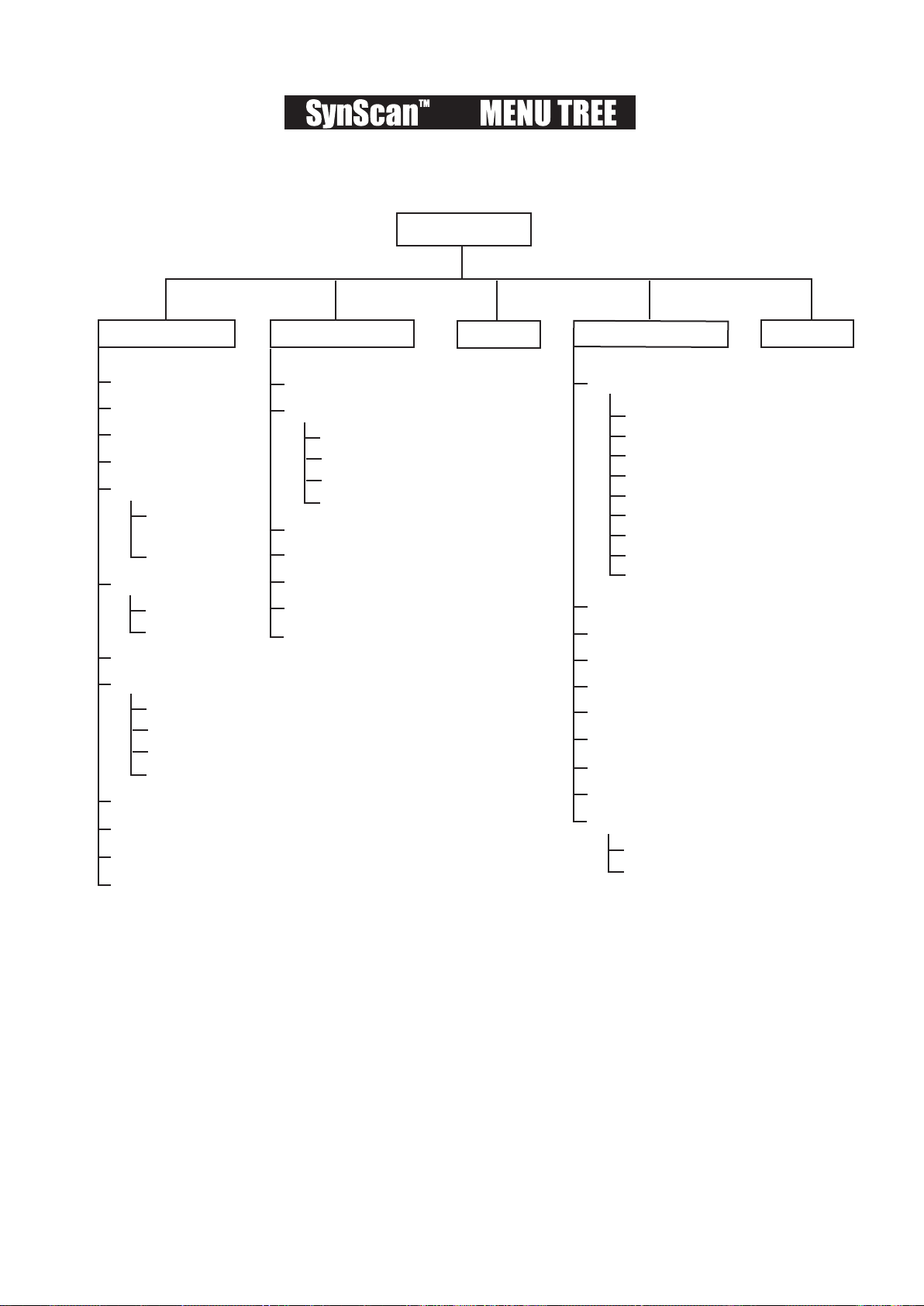
AZ
MAIN MENU
SETUP MODE
Date
Time
Observ. Site
Daylight Saving
Alignment
Brightest Star
Align.
2-Star Align
Alignment Stars
Auto Select
Sort By
Backlash
Tracking
Sidereal Rate
Lunar Rate
Solar Rate
Stop Tracking
Auto Tracking
Set Slew Limits
Handset Setting
Factory Setting
UTILITY FUNC. IDENTIFY
Show Position
Show Information
Time
Version
Temperature
Power Voltage
Park Scope
PAE
Clear PAE Data
GPS
PC Direct Mode
TOUR
OBJECT C
Solar System
Named Star
Messier Catalogue
IC Catalog
NGC Catalog
Caldwell Catalog
SAO Catalogue
Double Star
Variable Star
User Defined
A
T
ALOG
Mercury
Venus
Mars
Jupiter
Saturn
Uranus
Neptune
Pluto
Moon
Edit Object
Recall Object
17
Page 18

SynScanTM AZ SPECIFICATIONS
Power Supply:
Motor type and resolution:
Slew speeds:
Tracking Rates:
Tracking Mode:
Alignment Method:
Database:
Pointing Accuracy:
11 to 15 V DC 1Amp (Tip positive)
DC Servo Motors
Resolution: GT mount: 1.3746 arc sec
Multifunction mount: 942,803 steps/rev
Rate 0 = 1.0X
Rate 1 = 2.0X
Rate 2 = 8X
Rate 3 = 16X
Rate 4 = 32X
Rate 5 = 200X
Rate 6 = 400X
Rate 7 = 600X
Rate 8 = 800X
Rate 9 = 1000X
Sidereal, Lunar, Solar
Dual Axes Tracking
Brightest-Star Alignment, Two-Star Alignment
25 user defined objects. Complete M, NGC, and IC and SAO
catalogues, total 42,900 objects
Up to 10 arc min
18
Page 19

The SynScanTM AZ telescopes are designed to receive control commands sent from a computer
Description
PC Command ASCII
Hand Control
Response
Notes
Echo
Kx
X#
Useful to check
communication
Goto Azm-Alt
B12AB, 4000
#
10 characters sent.
B=Command, 12AB=Azm,
comma, 4 000=Alt. If
command conflicts with slew
limits, there will be no action.
Goto Ra-Dec
R34B, 12CE
#
Scope must be aligned. If
command conflicts with slew
limits, there will be no action.
Get Azm-Alt
Z
12AB, 4000#
10 characters returned,
12AB=Azm, comma,
4000=Alt, #
Get RA-Dec
E
34AB, 12CE#
Scope must be a ligned.
Cancel Goto
M
#
Is Goto in Progress
L
0# or 1#
0=No, 1=Yes: “0” is ASCII
character zero
Is Alignment Complete
J
0# or 1#
0=No, 1=Yes
HC vers ion
V22Two bytes representing V2.2
Stop/Start Tracking
Tx
x= 0 (Tracking off)
x= 1 (Alt- Az on)
x= 2 (E Q -N)
x= 3 (E Q -S)
#
Alt-Az tracking requires
alignment
32-bit goto RA-Dec
r34AB0500,12CE0500
#
32-bit get RA-Dec
e
34AB0500,
12CE0500#
The last two characters will
always be zer o.
32-bit goto Azm-Alt
b34AB0500,12CE0500
#
32-bit get Azm-Alt
z
34AB0500,
12CE0500#
The last two characters will
always be zer o.
via the RS-232 port and RS-232 cable. Once connected, the SynScanTM AZ can be controlled by
most popular planetarium software program. The SynScanTM AZ will communicate with the
personal computer at 9600 bits/sec, no parity and stop bit. All angles are communicated with 16
bit angle and communicated using ASCII hexadecimal.
I
Page 20

Physical Connection Diagram
RJ-11 Connector
1
2
3
4
5
6
1= NC
2= RD
3= GND
4= NC
5= TD
6= NC
RD = 2
GND = 5
TD = 3
1 2
3 5
The Back of the DB9 Pinout
dditional RS232 Commands
A
Sending a track rate through RS232 to the hand control
1.
Multiply the desired tracking rate (arc seconds /second) by 4. For example: if the
desired track rate is 120 arc seconds/second (proximately 8 times of sidereal rate),
then the TRACKRATE = 480.
2.
Separate TRACKRATE into two bytes, such that (TRACKRATE =
3.
TrackRateHighByte*256 + TrackRateLowByte). For example TRACKRATE = 480,
then TrackRateHighByte = 1, TrackRateLowByte = 224.
To send a tracking rate, send the following 8 bytes:
a. Positive Azm tracking: 80, 3, 16, 6, TrackRateHighByte, TrackRateLowByte, 0, 0
b. Negative Azm tracking: 80, 3, 16, 7, TrackRateHighByte, TrackRateLowByte, 0, 0
c. Positive Alt tracking: 80, 3, 17, 6, TrackRateHighByte, TrackRateLowByte, 0, 0
d. Negative Alt tracking: 80, 3, 17, 7, TrackRateHighByte, TrackRateLowByte, 0, 0
The number 35 is returned from the hand control.
4.
Sending a slow-Goto command through RS232 to the hand control
1.
Convert the angle position to a 24bit number. Example: if the desired position is 220?,
then POSITION_24BIT = (220/360)*224 = 10,252,743
2.
Separate POSITION_24BIT into three bytes such that (POSITION_24BIT =
PosHighByte * 65536 + PosMedByte * 256 + PosLowByte). Example: PosHighByte =
156, PosMedByte = 113, PosLowByte = 199
3.
Send the following 8 bytes:
a. Azm Slow Goto: 80, 4, 16, 23, PosHighByte, PosMedByte, PosLowByte, 0
b. Alt Slow Goto: 80, 4, 17, 23, PosHighByte, PosMedByte, PosLowByte, 0
The number 35 is returned from the hand control.
4.
6
9
Reseting the position of Az or Alt
1.
Convert the angle position to a 24bit number, same as Slow-Goto example.\
2.
Send the following 8 bytes:
a. Azm Set Position: 80, 4, 16, 4, PosHighByte, PosMedByte, PosLowByte, 0
b. Alt Set Position: 80, 4, 17, 4, PosHighByte, PosMedByte, PosLowByte, 0
The number 35 is returned from the hand control.
3.
II
Page 21

III
Page 22

NEVER USE YOUR TELESCOPE TO LOOK DIRECTLY AT THE SUN.
PERMANENT EYE DAMAGE WILL RESULT. USE A PROPER SOLAR FILTER
FIRMLY MOUNTED ON THE FRONT OF THE TELESCOPE FOR VIEWING
THE SUN. WHEN OBSERVING THE SUN, PLACE A DUST CAP OVER YOUR
FINDERSCOPE OR REMOVE IT TO PROTECT YOU FROM ACCIDENTAL
EXPOSURE. NEVER USE AN EYEPIECE-TYPE SOLAR FILTER AND NEVER
USE YOUR TELESCOPE TO PROJECT SUNLIGHT ONTO ANOTHER
SURFACE, THE INTERNAL HEAT BUILD-UP WILL DAMAGE THE
TELESCOPE OPTICAL ELEMENTS.
 Loading...
Loading...