Škoda Yeti 2014 Owner's Manual

SIMPLY CLEVER
ŠKODA Yeti
Owner's Manual

5L0012720AH


Preface
You have opted for a ŠKODA – our sincere thanks for your confidence in us.
This manual contains instructions about the vehicle operation, important information about safety,
vehicle care, maintenance and self-help and technical vehicle data.
Please read this Owner's Manual carefully, because operation in accordance with these instructions is
a prerequisite for proper use of the vehicle.
We hope you enjoy driving your ŠKODA, and wish you a pleasant journey at all times.
Your ŠKODA AUTO a.s. (hereinafter referred to only as ŠKODA or manufacturer)
5L0012720AH

Table of Contents
On board literature 4
Notes 5
Structure and more information about the
Owner's Manual 6
Abbreviations
Safety
Passive Safety 8
General information 8
Correct and safe seated position 9
Seat belts 12
Using seat belts 12
Inertia reels and belt tensioners 15
Airbag system 16
Description of the airbag system 16
Airbag overview 17
Deactivating airbags 21
Transporting children safely 23
Child seat 23
Fastening systems 26
Using the system
Cockpit 29
Overview
Instruments and Indicator Lights
Instrument cluster
Warning lights
Information system
Driver information system
Multifunction display (MFD)
28
30
30
34
42
42
44
MAXI DOT display 47
Service interval display 49
Unlocking and opening 51
Unlocking and locking 51
Anti-theft alarm system 56
Luggage compartment lid 57
Power windows 58
Mechanical windows 60
Panorama sliding/tilting roof 61
Lights and visibility 63
Lights 63
Interior lights 70
Visibility 71
Windscreen wipers and washers 72
Rear mirror 74
Seats and head restraints 77
Front seat 77
Front seat functions 80
Head restraints 82
Rear seats 83
Transporting and practical equipment 86
Useful equipment 86
Luggage compartment 96
Variable loading floor in the luggage
compartment (Estate) 102
Roof rack 103
Heating and air conditioning 104
Heating, ventilation, cooling 104
Auxiliary heating (auxiliary heating and
ventilation) 110
Communication and multimedia 113
General information 113
Universal telephone preinstallation (hands
free) 114
Universal telephone preinstallation GSM II 116
Universal telephone preinstallation GSM IIl 118
Wi-Fi 122
Voice control 123
Multimedia 125
SmartGate 129
Driving
Starting-off and Driving 131
Starting and stopping the engine using the
key 131
Start or stop the engine by pressing button 133
Brakes and parking 135
Manual gear changing and pedals 137
Automatic transmission 138
Running in and economical driving 140
Driving through water and driving off of
made-up roads 141
Assist systems 142
Braking and stabilisation systems 142
OFF ROAD-mode 144
Parking aid 146
Optical Parking Assistant (Rear view camera) 149
Park assist 150
Cruise Control System 154
START-STOP 155
Fatigue detection (break recommendation)
Tyre pressure monitoring 158
Hitch and trailer 159
Hitch 159
Trailer 163
157
General Maintenance
Care and maintenance
Service work, adjustments and technical
alterations 166
Washing vehicle 169
166
2
Table of Contents

Cleaning vehicle exterior 170
Interior care 174
Inspecting and replenishing 177
Fuel 177
Engine compartment 180
Engine oil 183
Coolant 184
Brake fluid 186
Vehicle battery 187
Wheels 191
Tyres and wheel rims 191
Manufacturer-approved tyre variants 193
Winter operation 195
Do-it-yourself
Emergency equipment and self-help 197
Emergency equipment 197
Reserve and temporary spare 199
Changing a wheel 200
Puncture repair kit 203
Jump-starting 206
Towing the vehicle 207
Remote control and removable light 209
Emergency unlocking/locking 211
Replacing windscreen wiper blades
Fuses and light bulbs 214
Fuses 214
Replacing bulbs 217
212
Technical data
Technical data
Vehicle data 222
Index
222
Table of Contents
3

On board literature
You will always find this Owner's Manual and the Service Plan included in the
on-board literature for your vehicle.
Depending on your vehicle equipment, the on-board literature may also include the Radio instruction manual, the Infotainment system manualand in
some countries also the On the road brochure.
Owner's Manual
These operating instructions apply to all body variants of the vehicle and all
related model versions as well as all equipment levels.
This owner's manual describes all possible equipment variants without identifying them as special equipment, model variants or market-dependent equipment. Consequently, this vehicle does not contain all of the equipment com-
ponents described in this Owner's Manual.
The level of equipment in your vehicle refers to your purchase contract for the
vehicle. For any questions regarding the scope of equipment, please contact a
ŠKODA Partner.
The Pictures in this manual are for illustrative purposes only. The illustrations
can differ in minor details from your vehicle; they are only intended to provide
general information.
ŠKODA AUTO a.s. pursues a policy of ongoing product and model development
with all vehicles. Changes in terms of supply scope are possible at any time
with regard to design, equipment and technology. The information listed in
this operating manual corresponds to the information available at the time of
going to press.
It is therefore not possible for legal claims to be made based on the technical
data, illustrations and information contained in this Owner's Manual.
Service schedule
The service schedule includes the documentation of the vehicle handover,
warranty information and service events.
The radio instruction manual
The radio instruction manual describes the operation of the radio, and in some
cases various functions and vehicle systems.
Infotainment operating instructions
The Infotainment manual contains a description of the Infotainment service
and possibly also some functions and vehicle systems.
On-the-road brochure
The On-the-road brochure contains phone numbers of importers and service
offices in individual countries, together with emergency numbers.
4
On board literature
Notes
Terms used
The on-board literature contains the following terms relating to the service
work for your vehicle.
“Specialist”
“ŠKODA service partner”
“ŠKODA partner”
Explanation of symbols
An overview of the symbols used in the instruction manual and a brief explanation of their meaning.
Continuation of the module on the next page.
Situations in which the vehicle must be stopped as soon as possible.
® Trademark.
Telephone operation in the MAXI DOT display .
Text display in the segment display.
Texts with this symbol draw attention to threats of a serious accident, injury or loss of life.
- Workshop - a workshop that carries out specialist service tasks
for ŠKODA vehicles. A specialist can be a ŠKODA Partner, a ŠKODA Service Partner, or an independent workshop.
- A Workshop that has been contractually authorized
by the manufacturer ŠKODA AUTO a.s. or its sales partner to perform
service tasks on ŠKODA vehicles and to sell ŠKODA Genuine Parts.
- A company that has been authorized by the manufacturer
ŠKODA AUTO a.s. or its sales partner to sell new ŠKODA vehicles and,
when applicable, to service them using ŠKODA Genuine Parts and sell
ŠKODA Genuine Parts.
Reference to the introductory module of a chapter with important information and safety warnings.
WARNING
Note
Texts with this symbol contain additional information.
CAUTION
Texts with this symbol draw attention to the risk of vehicle damage or possible
inoperability of some systems.
For the sake of the environment
Texts with this symbol contain information on environmental protection as
well as tips for economical operation.
Notes
5
Structure and more information about the Owner's Manual
Structure of the manual
The operating manual is hierarchically divided into the following areas.
■
Section (e.g. Safety) - the title of the Section is always indicated at the lower
left side
■
Main chapters (e.g. Airbag system) - the title of the main chapter is always
indicated at the lower right side
■
Chapter (e.g. Airbag overview)
■
Introduction to the topic - Module overview within the chapter, in-
troductory information about the chapter content, if necessary, applies
to all chapter notes
■
Module (e.g. Front airbags)
Information search
When searching for information in the operating instructions, we recommend
using the Index at the end of the Owner's Manual.
Direction indications
All direction indications such as “left”, “right”, “front”, “rear” relate to the forward direction of travel of the vehicle.
Units of measurement
The volume, weight, speed and length data are given in metric units, unless
otherwise indicated.
Display
In this owner's manual, the MAXI DOT display is used as the display in the instrument cluster unless otherwise stated.
6
Structure and more information about the Owner's Manual
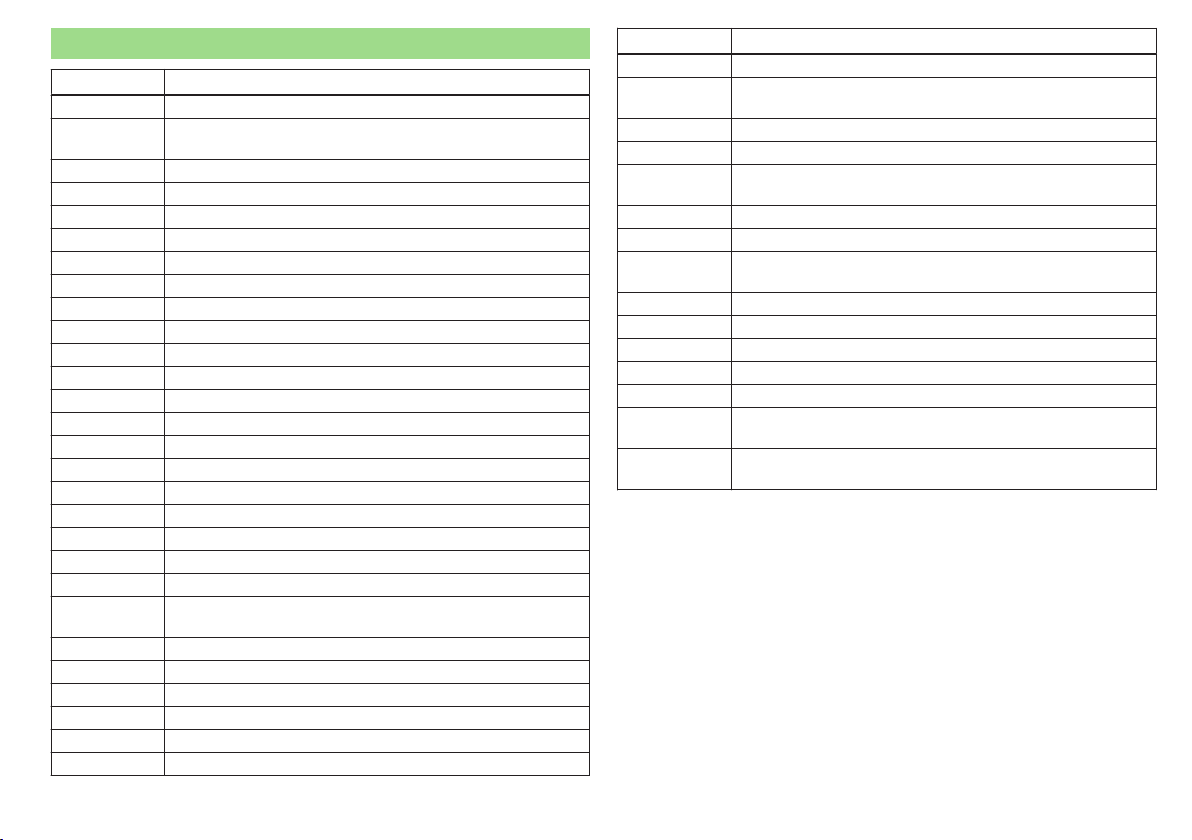
Abbreviations
Abbreviation Definition
rpm Engine revolutions per minute
A2DP
ABS Anti-lock brake system
AF Multi-purpose vehicles
AFS Adaptive headlights
AG Automatic gearbox
AGM Vehicle battery type
APN An access point name for the Wi-Fi connection
TCS Traction control
CO
DPF Diesel particle filter
DSG Automatic double clutch gearbox
DSR Active driver-steering recommendation
EDL Electronic differential lock
ECE Economic Commission for Europe
EPC EPC fault light
ESC Electronic Stability Control
D Rim depth
EU European Union
GSM Global system for mobile communications
HBA Hydraulic brake assist
HFP
HHC Uphill start assist
KESSY keyless unlocking, starting and locking
kW Kilowatt, measuring unit for the engine output
MDI Inputs for connecting external devices
MFD Multifunction display
MG Manual gearbox
a Bluetooth software profile for a one-way transfer of audio
data
Carbon dioxide
2
Connection of a mobile device by means of its Bluetooth
profile
Abbreviation Definition
MPI Gasoline engine with a multi-point fuel injection
N1
Nm Newton meter, measuring unit for the engine torque
PIN personal identification number
rSAP
SIM card a card for the identification of the mobile network operator
SSP Connect two devices using Bluetooth ® profile
TDI CR
TSA Trailer stabilisation
TSI Petrol engine with turbocharging and direct injection
UMTS the next generation of the GSM network (3G)
VIN Vehicle identification number
Wi-Fi wireless data network
WLAN
WPS
®
Panel van intended exclusively or mainly for the transportation of goods
a Bluetooth ® software profile for the remote transmission
of the SIM data
Diesel engine with turbo-charging and common rail injection
system
wireless connection of electronic devices for data transfer
(wireless)
wireless connection of devices for electronic data transfer
(WiFi) using an automatically generated key
Abbreviations
7

Safety
Passive Safety
General information
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Before setting off
Driving safety 8
Safety equipment 8
In this section you will find important information, tips and notes on the subject of passive safety in your vehicle.
We have combined everything here which you should be familiar with, for example, regarding seat belts, airbags, child seats and safety of children.
WARNING
■
This chapter contains important information on how to use the vehicle for
the driver and his occupants.
■
You can find further information on safety concerning you and those trav-
elling with you in the following chapters of this owner's manual.
■
The complete on-board literature should always be in the vehicle. This
applies in particular, if you rent out or sell the vehicle.
Before setting off
Read and observe on page 8 first.
For your own safety and the safety of the people travelling with you, please
pay attention to the following points before setting off.
Ensure that the lighting and the turn signal system are functioning proper-
ly.
Ensure that the function of the wipers and the condition of the wiper
blades are free of any defects.
Ensure that all of the windows offer good visibility to the outside.
Adjust the rear-view mirror so that vision to the rear is guaranteed.
Ensure that the mirrors are not covered.
Check the tyre inflation pressure.
Check the engine oil, brake fluid and coolant level.
Secure all items of luggage.
Do not exceed the permissible axle loads and permissible gross weight of
the vehicle.
Close all doors as well as the bonnet and boot lid.
Ensure that no objects can obstruct the pedals.
Protect children in suitable child seats with correctly fastened seat
8
belts » page 23, Transporting children safely.
Adopt the correct seated position » page 9, Correct and safe seated
position. Tell your passengers to assume the correct seated position.
Driving safety
Read and observe on page 8 first.
The driver is fully responsible for himself and his occupants. If your driving
safety is effected, you place yourself and the oncoming traffic at risk.
The following guidelines must therefore be observed.
Do not become distracted from concentrating on the traffic situation, e.g.
by your passengers or mobile phone calls.
Never drive when your driving ability is impaired, e.g. due to medication, al-
cohol or drugs.
Keep to the traffic regulations and the permissible speed limit.
Always adjust the driving speed to the road, traffic and weather condi-
tions.
Take regular breaks on long journeys – at least every two hours.
Safety equipment
Read and observe
The following list contains only part of the safety equipment in your vehicle.
Three-point seat belts for all the seats.
›
Belt force limiters for the front seats.
›
Belt tensioners for the front seats.
›
Seat belt height adjusters for the front seats.
›
Front airbag for the driver and the front passenger.
›
Driver’s knee airbag.
›
on page 8 first.
8
Safety
Front side airbags.
›
Rear side airbags.
›
Head airbags.
›
Anchoring points for child seats using the ISOFIX system.
›
Anchoring points for child seats using the TOP TETHER system.
›
Head restraints adjustable for height.
›
Adjustable steering column.
›
The specified safety equipment works together, in order to optimally protect
you and those travelling with you in accident situations.
The safety equipment does not protect you or the people travelling with you, if
you or your occupants adopt an incorrect seated position or the equipment is
not correctly adjusted or used.
If the seat belt is not fastened properly, this may result in injuries if an airbag is
activated in the event of an accident.
Correct and safe seated position
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Correct seated position for the driver
Adjusting the steering wheel position 10
Correct seated position for the front passenger 10
Correct seated position for the passengers in the rear seats 11
Examples of an incorrect seating position 11
WARNING
■
The front seats and all head restraints must be adjusted to match the
body size at all times and the seat belt must always be fastened properly to
provide the most effective levels of protection to the passengers.
■
Each occupant must correctly fasten the seat belt belonging to the seat.
Children must be fastened » page 23, Transporting children safely with a
suitable restraint system.
■
If the occupant adopts an incorrect seated position, he is exposed to lifethreatening injuries, in case he is hit by a deployed airbag.
WARNING (Continued)
■
If the occupants on the rear seats are not sitting upright, the risk of injury
is increased due to incorrect routing of the seat belt.
■
The seat backrests must not be tilted too far back when driving, as this
will impair the function of the seat belts and of the airbag system – risk of
injury!
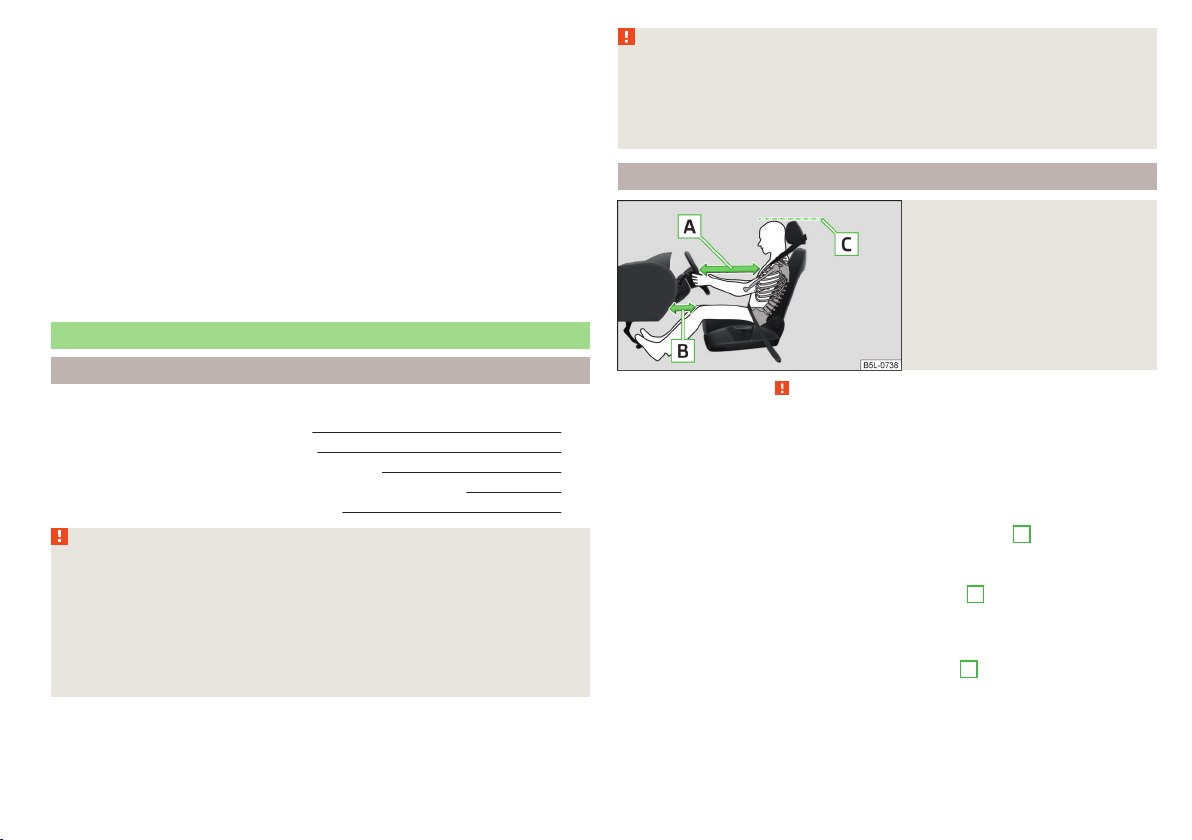
Correct seated position for the driver
Fig. 1
Correct seated position for the
driver
Read and observe on page 9 first.
For your own safety and to reduce the risk of injury in the event of an accident,
9
the following instructions must be observed.
Adjust the driver’s seat in the forward/back direction so that the pedals
can be fully depressed with slightly bent legs.
For vehicles with driver knee air-bag adjust the driver's seat in a forward/
back direction so that there is a gap of at least 10 cm between the legs
and the dash panel in the vicinity of the knee airbag - B » Fig. 1.
Adjust the seat backrest so that the highest point of the steering wheel
can be reached with your arms at a slight angle.
A
Adjust the steering wheel so that the distance
wheel and your chest is at least 25 cm » Fig. 1. Adjust the steering
wheel » page 10, Adjusting the steering wheel position.
Adjust the head restraint so that the top edge of the head restraint is at
the same level as the upper part of your head C » Fig. 1.
Correctly fasten the seat belt » page 12, Using seat belts.
Adjust the seats and head restraints » page 77.
between the steering
Passive Safety
9
WARNING
■
Always assume the correct seated position before setting off and do not
change this position while driving. Also advise your passengers to adopt
the correct seated position and not to change this position while the car is
moving.
■
Maintain a distance of at least 25 cm from the steering wheel, and a distance of at least 10 cm between the legs and the dash panel at the height
of the knee airbag. Not maintaining this minimum distance will mean that
the airbag system will not be able to properly protect you - hazard!
■
When driving, hold the steering wheel with both hands firmly on the outer edge in the “9 o'clock” and “3 o'clock” position. Never hold the steering
wheel in the “12 o'clock” position or in any other way (e.g. in the middle or
inner edge of the steering wheel). In such cases, you could severely injure
the arms, hands and head when the driver airbag is deployed.
■
Ensure that there are no objects in the driver's footwell, as these may get
caught in the pedal apparatus when driving or braking. You would then no
longer be able to operate the clutch, brake or acceleration pedals.
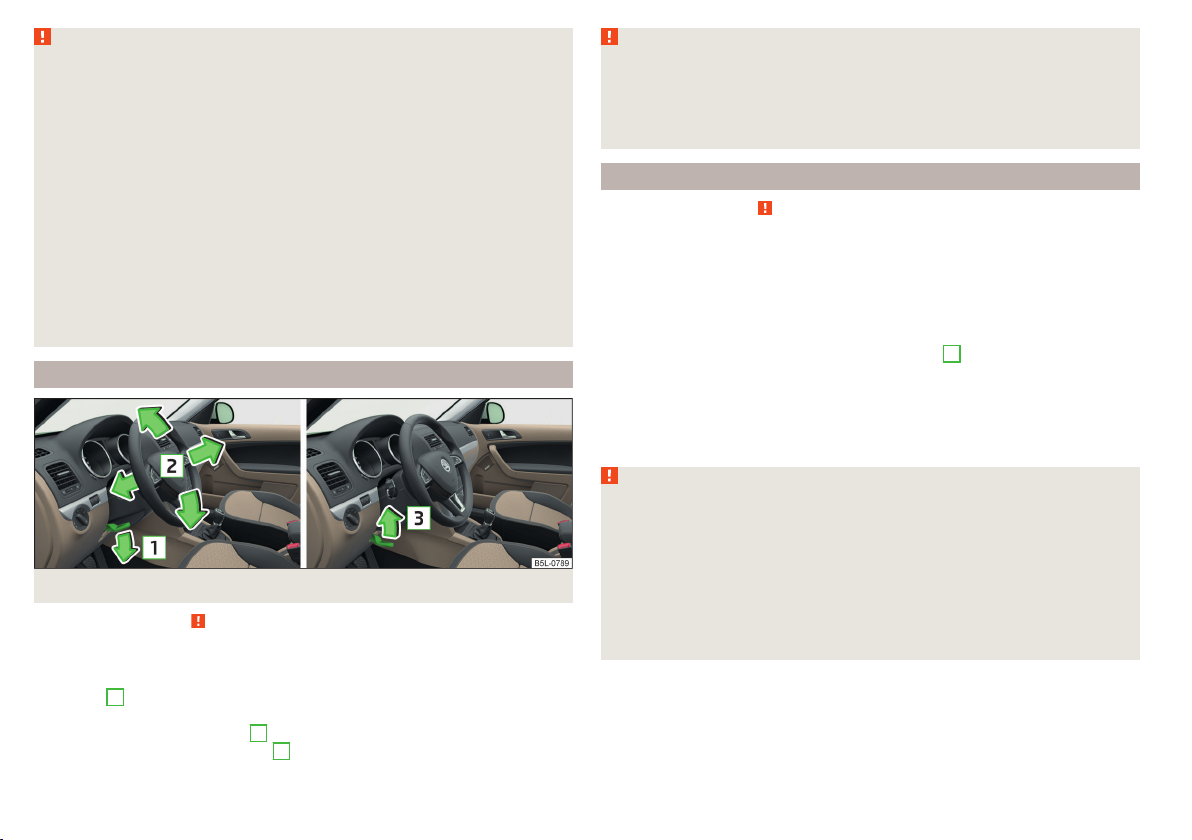
Adjusting the steering wheel position
Fig. 2 Adjusting the steering wheel position
Read and observe on page 9 first.
The height and forward/back position of the steering wheel can be adjusted.
Swivel the safety lever under the steering wheel downwards in the direction
›
of arrow 1 » Fig. 2.
Adjust the steering wheel to the desired position. The steering wheel can be
›
adjusted in direction of arrow 2.
Pull the holder in arrow direction 3 until the stop.
›
WARNING
■
The lever for adjusting the steering wheel must be locked while you are
driving so that the position of the steering wheel cannot accidentally
change during the journey – risk of accident!
■
Never adjust the steering wheel when the vehicle is moving only when
the vehicle is stationary!
Correct seated position for the front passenger
Read and observe
For passenger safety and to reduce the risk of injury in an accident, the following instructions must be observed.
Position the front passenger seat back as far as possible. The front pas-
senger must maintain a distance of at least 25 cm to the dash panel so
that the airbag offers the greatest possible safety if it is deployed.
Adjust the head restraint so that the top edge of the head restraint is at
the same level as the upper part of your head C » Fig. 1 on page 9.
Correctly fasten the seat belt » page 12.
Adjust the seats and head restraints » page 77.
In exceptional cases the front passenger airbag can be deactiva-
ted » page 21, Deactivating airbags.
WARNING
■
Maintain a distance of at least 25 cm to the dash panel. Not maintaining
this minimum distance will mean that the airbag system will not be able to
properly protect you – hazard!
■
Always keep your feet in the footwell when the car is being driven – never place your feet on the instrument panel, out of the window or on the
surfaces of the seats. You will be exposed to increased risk of injury if it becomes necessary to apply the brake or in the event of an accident. If an airbag is deployed, you could suffer fatal injuries by adopting an incorrect
seated position!
on page 9 first.
10
Safety

Correct seated position for the passengers in the rear seats
Read and observe on page 9 first.
To reduce the risk of injury in the event of a sudden braking manoeuvre or an
accident, the occupants on the rear seats must observe the following.
Adjust the head restraint so that the top edge of the head restraint is at
the same level as the upper part of the head C » Fig. 1 on page 9.
Correctly fasten the seat belt » page 12, Using seat belts.
Use a suitable child restraint system if transporting children in the vehicle » page 23, Transporting children safely.
Adjust the seats and head restraints » page 77.
Examples of an incorrect seating position
Read and observe
Maximum seat belt protection is only achieved if seat belts are fastened correctly.
Incorrect seated positions considerably reduce the protective functions of the
seat belts and therefore increase the risk of injury due to an incorrect routing
of the seat belt.
The driver is fully responsible for himself and passengers, especially children.
Never allow a passenger to adopt an incorrect seated position when the car is
moving.
The following list contains instructions which, if not observed, may cause serious injuries or death. This list is not complete, however we would like you to
familiarise yourself with this subject.
Observe the following instructions while driving.
Do not stand up.
Do not stand on the seats.
Do not kneel on the seats.
Do not tilt the seat backrest too far back.
Do not lean against the dash panel.
Do not lie on the rear seats.
Do not sit only on the front part of the seat.
Do not sit facing to the side.
on page 9 first.
Do not lean out of the window.
Do not put your feet out of the window.
Do not put your feet on the dash panel.
Do not put your feet on the seat cushion.
Do not allow anybody to travel in the footwell.
Do not drive without fastening your seat belt.
Do not delay in the luggage compartment.
Passive Safety
11
Seat belts
Using seat belts
Introduction
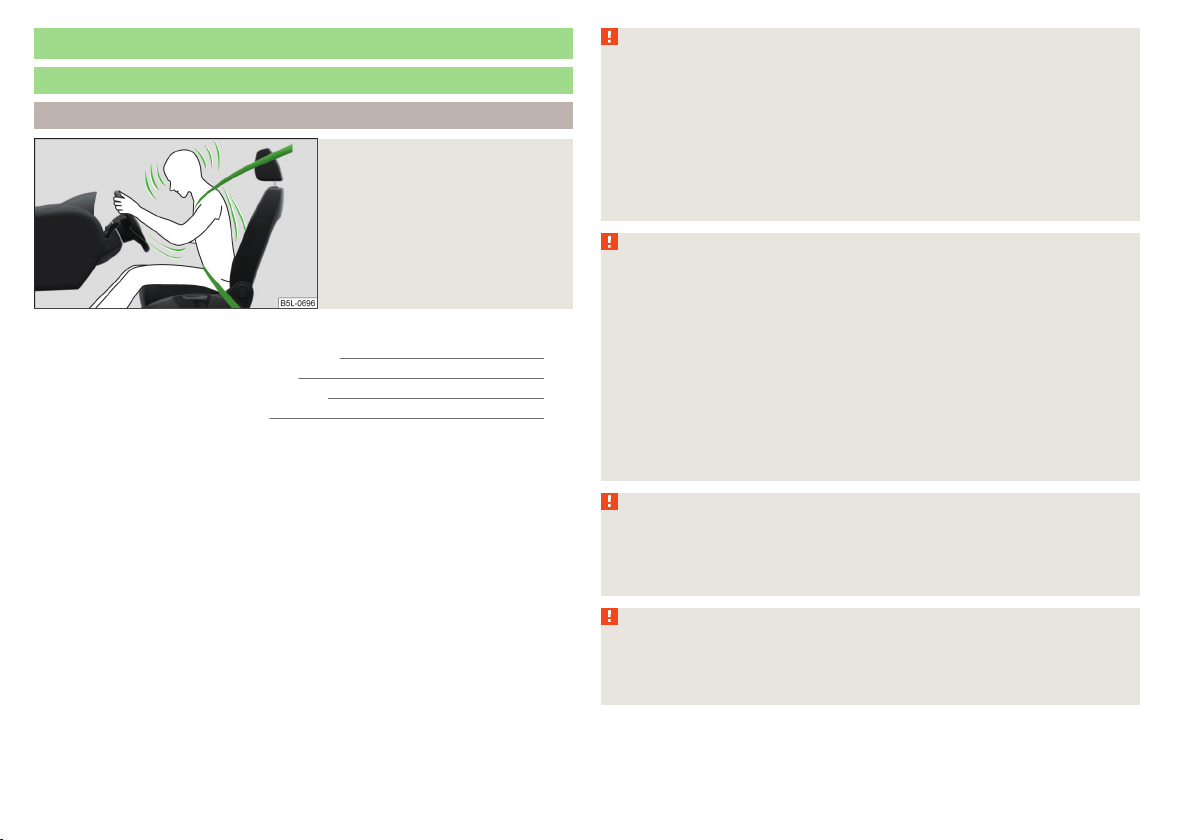
Fig. 3
Driver wearing seat belt
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
The physical principle of a head-on collision 13
Fastening and unfastening seat belts 14
Belt height adjustment on the front seats 15
Seat belt for the rear middle seat 15
Seat belts that are fastened correctly offer good protection in the event of an
accident. They reduce the risk of an injury and increase the chance of survival
in the event of a major accident.
Correctly fastened seat belts hold occupants of the car in the correct seated
position » Fig. 3.
The seat belts reduce the kinetic energy (energy of motion) to a considerable
extent. They also prevent uncontrolled movements which, in turn, may well result in severe injuries.
Occupants of a vehicle who have correctly fastened their seat belts have the
major benefit of the fact that the kinetic energy is absorbed as effectively as
possible by the belts.
The structure of the front end of the vehicle and other passive safety measures, such as the airbag system, also contribute to the kinetic energy being reduced as effectively as possible. The energy produced is thus absorbed and
there is less risk of injury.
Particular safety aspects must be observed when transporting children in the
vehicle » page 23.
WARNING
■
Fasten your seat belt before each journey - even when driving in town!
This also applies to the passengers seated at the rear – risk of injury!
■
Expectant women must also always wear a seat belt. This is the only way
of ensuring optimal protection for the unborn child » page 14, Fastening
and unfastening seat belts.
■
Maximum seat belt protection is only achieved if you are correctly seated » page 9.
■
The seat backrests of the front seats must not be tilted too far to the rear
otherwise the seatbelts can lose their effectiveness.
WARNING
Information on the correct routing of the belt
■
Always ensure that the webbing of the seat belts is properly routed. Seat
belts which are not correctly adjusted can themselves cause injuries even
in minor accidents.
■
Adjust the height of the belt in such a way that the shoulder part of the
belt is roughly positioned across the middle of your shoulder - on no account across your neck.
■
A seat belt which is hanging too loose can result in injuries as your body is
moved forward by the kinetic energy produced in an accident and is then
suddenly held firm by the belt.
■
The belt webbing must not run across solid or fragile objects (e.g. spectacles, ball-point pens, bunches of keys etc.). Such objects can cause injury.
WARNING
Information on dealing with the safety belts
■
The belt webbing must not be jammed in-between at any point or twisted, or chafe against any sharp edges.
■
Make sure you do not catch the seat belt in the door when closing it.
WARNING
Information on the proper use of safety belts
■
Never use one seat belt to secure two persons (including children). The
seatbelt must not be placed over a child who is sitting on the lap of another
passenger.
12
Safety

WARNING (Continued)
■
The lock tongue should only be inserted into the lock which is the correct
one for your seat. Wrong use of the safety belt will reduce its capacity to
protect and the risk of injury increases.
■
The slot of the belt tongue must not be blocked, otherwise the belt
tongue will not lock in place properly.
■
Many layers of clothing and loose clothing (e. g. a winter coat over a jacket) do not allow you to be correctly seated and impairs proper operation of
the seat belts.
■
Do not use clamps or similar items, which inhibit the safety belt locking
function. A seat belt which is too loose can result in injuries as your body is
moved forward by the kinetic energy produced in an accident and is then
suddenly held firm by the belt.
■
The seat belts for the rear seats can only fulfil their function reliably
when the seat backrests are correctly locked into position » page 84.
WARNING
Information on the care and maintenance of safety belts
■
The belt webbing must always be kept clean. Soiled belt webbing may impair proper operation of the inertia reel » page 176, Safety belts.
■
The seat belts must not be removed or changed in any way. Do not attempt to repair the seat belts yourself.
■
Check the condition of all the seat belts on a regular basis. If any damage
to the seat belts, seat belt connections, inertia reel or the lock is detected,
the relevant seat belt must be replaced by a specialist garage.
■
Damaged seat belts which have been subjected to stress in an accident
and were therefore stretched, must be replaced – this is best done by a
specialist garage. The anchorage points of the belts must also be inspected. The anchorage points for the belts should also be checked.
Note
The national legal requirements must be observed when using seat belts.
The physical principle of a head-on collision
Fig. 4 Driver without a fastened seat belt/rear seat passenger without a
fastened seat belt
Read and observe on page 12 first.
Motion energy, so-called kinetic energy, is produced as soon as the vehicle is
moving, both for the vehicle and its occupants.
The magnitude of this kinetic energy depends essentially on the speed at
which the vehicle is travelling and on the weight of the vehicle including the
occupants. The greater the speed and weight increase, the greater the
amount of energy which has to be absorbed in the event of an accident.
The speed of the vehicle is the most important factor. Doubling the speed of
the vehicle from 25 km/h up to 50 km/hour increases the kinetic energy four
times.
The idea that it is possible to support your body with your hands in a minor accident is incorrect. Even in a collision at only a low speed, the forces acting on
the body are such that it is no longer possible to support your body.
Even if you only drive at a speed of 30-50 km/h, the forces that your body is
exposed to in the event of an accident can exceed a metric ton (1000 kg).
For example, a person's weight of 80 kg “increases” to 4.8 tons (4800 kg) at
50 km/h.
In the event of a frontal collision, occupants of the car not wearing a seat belt
are thrown forward and strike parts of the interior of the car, such as the
steering wheel, dash panel, windscreen in ways which cannot be controlled » Fig. 4 - . In certain circumstances you could even be thrown out of the
vehicle, which could cause life threatening or even fatal injuries.
Seat belts
13
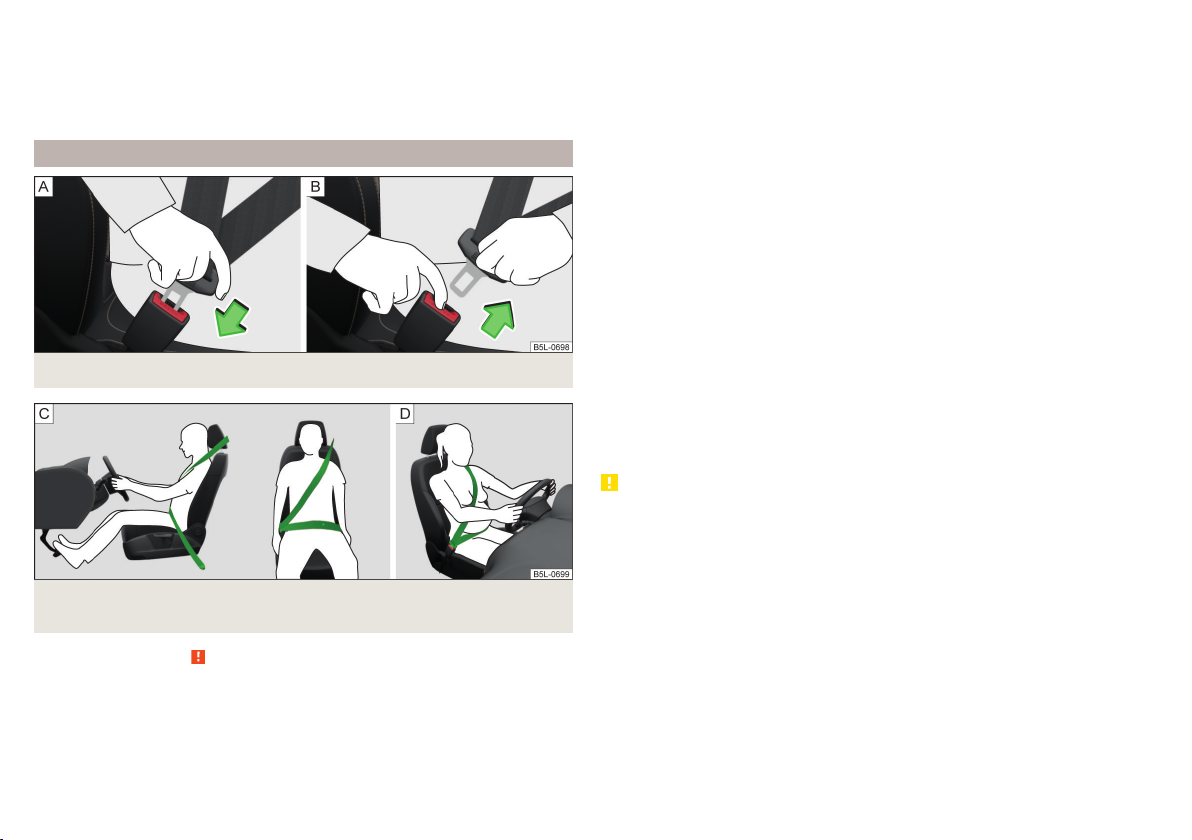
It is also important that rear passengers fasten their seat belts, as they could
otherwise be thrown through the vehicle in an uncontrolled manner in the
event of an accident.
Rear seat passengers who have not fastened their seat belts are a danger not
only to themselves but also to those seated at the front » Fig. 4 – .
Fastening and unfastening seat belts
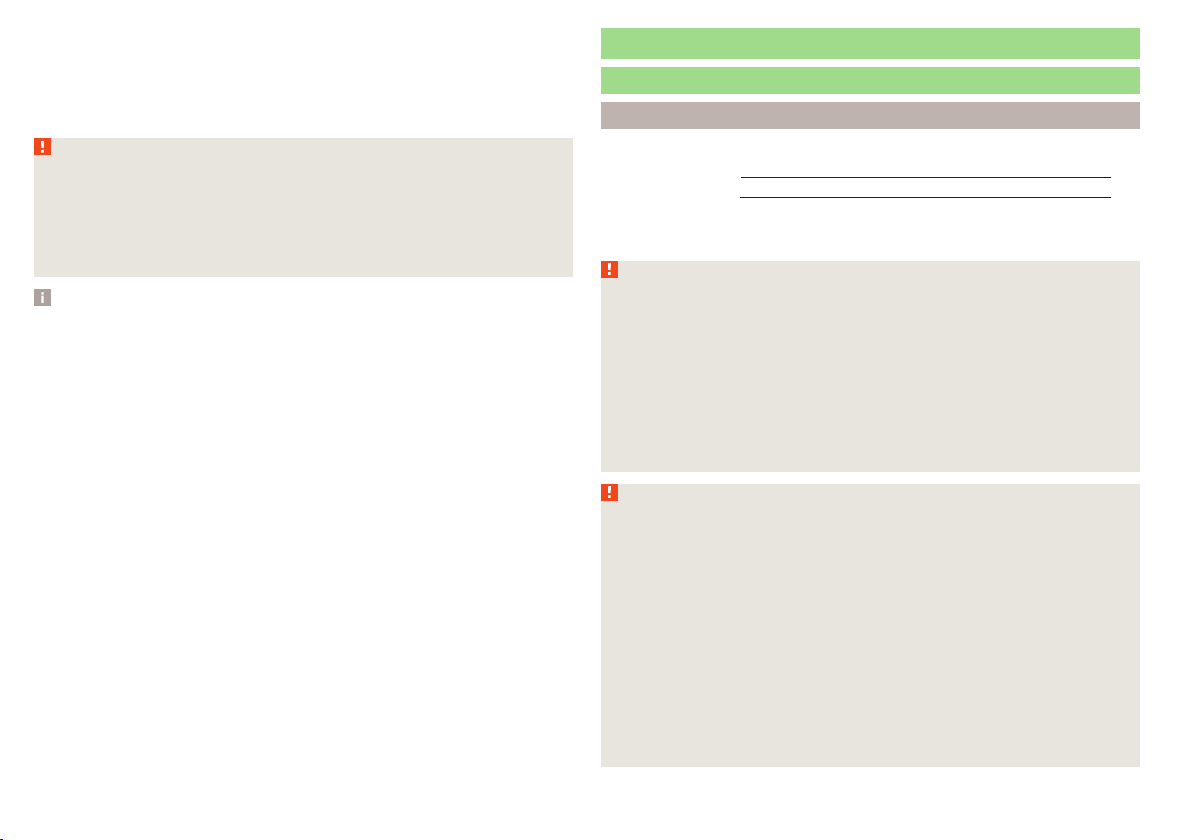
Fig. 5 Fastening/unfastening the seat belt
Fig. 6 Routing of belt webbing over the shoulders and the lap belt/Rout-
ing of belt webbing for an expectant mother
Insert the lock tongue into the belt buckle for the seat » Fig. 5 - until it
›
audibly clicks into place.
Pull on the belt to check that it has engaged correctly in the lock.
›
A plastic knob in the belt webbing holds the belt tongue in a position which is
easy to get hold of.
It is important that the belt is properly routed to ensure seat belts offer the
maximum protection.
The shoulder part of the seat belt must never run across the neck but must
roughly run over the middle of the shoulder and fit snugly against the chest.
The lap part of the belt must run across the pelvis, must not be positioned
across the stomach and must always fit snugly » Fig. 6 - .
Expectant women must also always wear a seat belt. This is the only way of
ensuring optimal protection for the unborn child.
With pregnant women, the lap part of the belt must be positioned as low as
possible on the pelvis to avoid exerting any pressure on the lower abdomen » Fig. 6 - .
Release
Release the seat belt only when the vehicle is stationary.
Press the red button in the belt buckle » Fig. 5 - ; the lock tongue pops out.
›
Manually guide the belt back so that it is easier to fully roll up the webbing,
›
the seat belt does not twist.
CAUTION
When releasing the seatbelt ensure that the tongue of the lock does not damage the door trim or other parts of the interior.
Read and observe on page 12 first.
Fasten
Correctly adjust the front seat and head restraint before fastening the seat
›
belt » page 9.
Use the lock tongue to slowly pull the webbing over your chest and pelvis.
›
14
Safety

Belt height adjustment on the front seats
Fig. 7
Front seat: Seat belt height adjuster
Release
Take off the safety belt in the reverse order to how you fasten it.
›
Guide the belt back by hand so that the webbing rolls up easily, the seat belt
›
is not twisted and the trim panel is not damaged.
WARNING
■
After releasing the seat belt hold it tight and let it slowly reel up until
both lock tongues lock into the headliner mount and are secured with a
magnet - there is a risk of injury.
■
Never unlock both lock tongues simultaneously.
Read and observe on page 12 first.
The seat belt height adjuster makes it possible to adjust the routing of the
front seat belts in the area of the shoulder to the body size.
Press the seat belt height adjuster and move up or down in the desired di-
›
rection » Fig. 7.
Then pull firmly on the belt to ensure that the seat belt height adjuster has
›
correctly locked in place.
Seat belt for the rear middle seat
Read and observe
The seat belt for the rear middle seat is anchored in the area of the boot on
the left side of the headliner.
Fasten
Pull the belt with both lock tongues out of the headliner mount.
›
Insert the lock tongue at the end of the belt into the belt buckle on the left
›
side until it is heard to lock in place.
Pull the second lock tongue, which is moveable on the seat belt, over the
›
chest and insert it into the belt buckle on the right side until it is heard to
lock in place.
Pull on the seat belt to check that both lock tongues are securely engaged in
›
the locks.
The belt tongues for the rear middle seat are shaped differently so that they
only fit into the correct belt buckle. If you are not able to insert a lock tongue
into the wrong belt lock you probably tried to put it into the wrong buckle.
on page 12 first.
Inertia reels and belt tensioners
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Intertia reel
Belt tensioners 15
Intertia reel
Each seat belt is equipped with an inertia reel.
When pulling slowly on the seat belt, the belt can move freely. When pulling
sharply on the seat belt, the movement is locked by the inertia reel.
The belts also lock when full braking, when the car accelerates, when driving
downhill and when cornering.
WARNING
If the seat belt does not lock when pulling sharply on it, have it inspected
immediately by a specialist garage.
Belt tensioners
Safety for the driver and front passenger wearing their seat belts is enhanced
by the belt tensioners fitted to the inertia reels of the front three-point seat
belts.
The three-point seat belts are automatically tensioned in the event of a frontal
collision of a certain severity. The belt tensioners can also be deployed if the
seat belts are not fastened.
Seat belts
15
15
The fastened seat belts are automatically tensioned in the event of a collision
of a certain severity.
Belt tensioners are not activated in the event of minor frontal collisions, side
and rear-end collisions, in the case of a rollover and also not in accidents in
which no major forces are produced from the front.
WARNING
■
Any work on the belt tensioner system including removal and installation
of system components because of other repair work, must only be carried
out by a specialist garage.
■
The protective function of the system is only adequate for a single accident. If the belt tensioners have been deployed, it is then necessary to replace the entire system.
Note
■
Smoke is generated when the belt tensioners are deployed. This is not an in-
dication of a fire in the vehicle.
■
When disposing of the vehicle or parts of the belt tensioner system, it is im-
portant to comply with national legal requirements. ŠKODA service partners
are familiar with these regulations and will be able to provide you with detailed information.
Airbag system
Description of the airbag system
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
System description 17
Airbag deployment 17
The airbag system provides, as a supplement to the seat belts, additional occupant protection during severe frontal and side collisions.
WARNING
■
An airbag can only offer you optimal protection in combination with a
fastened seat belt.
■
The airbag is not a substitute for the seat belt, but instead forms part of
the complete passive vehicle safety concept.
■
To ensure passengers are protected with the greatest possible effect
when the airbag is deployed, the front seats must be correctly adjusted to
match the body size » page 9, Correct and safe seated position.
■
If you do not fasten the seat belts when driving, lean too far forward or
adopt an incorrect seated position, you are exposing yourself to increased
risk of injury in the event of an accident.
WARNING
Information on the use of the airbag system
■
If there is a fault, the airbag system must be checked by a specialist garage immediately. Otherwise, there is a risk of the airbag not being activated in the event of an accident.
■
No modifications of any kind must be made to parts of the airbag system.
■
Any work on the airbag system including the installation and removal of
system components due to other repair work (e.g. removal of the steering
wheel) must only be carried out by a specialist garage.
■
Never make any changes to the front bumper or bodywork.
■
It is prohibited to manipulate individual parts of the airbag system as this
might result in the airbag being deployed.
■
The protective function of the airbag system is sufficient for only one accident. The airbag system must then be replaced if the airbag has been deployed.
16
Safety
System description
Read and observe on page 16 first.
The functional status of the airbag system is indicated by the indicator light
in the instrument cluster » page 40.
When the airbags are deployed, they fill with gas and inflate.
A grey white or red, non-harmful gas is released when the airbag is inflated.
This is perfectly normal and is not an indication of a fire in the vehicle.
Depending on the vehicle equipment, the airbag system consists of the
following modules.
Electronic control unit.
›
Front airbag for the driver and the front passenger » page 18.
›
Driver’s knee airbag » page 19.
›
Side airbags » page 19.
›
Head airbags » page 20.
›
Airbag warning light in the instrument cluster » page 40.
›
Key switch for the front passenger airbag » page 22.
›
Warning light for the front passenger airbag deactivation/activation in the
›
middle of the dash panel » page 22.
Note
■
The airbag system needs no maintenance during its working life.
■
If you sell your vehicle, provide the complete vehicle documentation to the
new owner. Please note that the information relating to the possibility of deactivating the front passenger airbag must be included!
■
When disposing of vehicle or parts of the airbag system, it is important to
comply with the national legal requirements.
Airbag deployment
Read and observe
The airbags inflate in fractions of a second and at a high speed in order to be
able to offer additional protection in the event of an accident.
The airbag system is only functional when the ignition is switched on.
In certain accident situations, the several airbags may be deployed simultane-
ously.
on page 16 first.
The airbags are not deployed in the case of minor frontal and side collisions,
rear-end collisions, tilting of the vehicle and vehicle rollover.
Deployment factors
It is not possible to generally determine which deployment conditions apply to
the airbag system in every situation. An important role is played by factors
such as the type of object that the vehicle hits (hard/soft), the impact angle,
vehicle speed etc.
A decisive factor for the deployment of the airbags is the deceleration which
occurs. The control unit analyses the nature of the collision and activates the
relevant restraint system.
If the vehicle deceleration which occurs and is measured during the collision
remains below the prescribed reference values specified in the control unit,
the airbags are not deployed although the vehicle may well suffer severe damage to the bodywork as a consequence of the accident.
The following airbags will be deployed in the event of a severe frontal
collision.
Driver’s front airbag.
›
Front passenger airbag.
›
Driver’s knee airbag.
›
The following airbags will be deployed in the event of a severe side collision.
Front side airbag on the side of the accident.
›
Rear side airbag on the side of the accident.
›
Head airbags on the side of the accident.
›
When an airbag is deployed, the following events occur.
The interior lighting comes on (if the switch for the interior light is in the door
›
contact position).
The hazard warning lights are switched on.
›
All doors are unlocked.
›
The fuel supply to the engine is interrupted.
›
Airbag overview
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Front airbags
Driver’s knee airbag 19
18
Airbag system
17

Side airbags 19
Head airbags 20
Front airbags
Fig. 8 Locations of the airbags / gas filled airbags
Fig. 9
Safe distance to steering wheel
In the event of a severe frontal collision, the front airbag system offers additional protection for the head and chest area of the driver and front passenger.
The driver's front airbag is located in the steering wheel, the front passenger
airbag is located in the instrument panel above the glove compartment » Fig. 8
- .
The airbags inflate in front of the driver and front passenger when they are
deployed » Fig. 8 - . The forward movement of the driver and of the front
passenger is cushioned when they make contact with the fully inflated airbag
and the risk of injury to head and chest is thus reduced.
WARNING
Information on correct seated position
■
It is important that the driver and front passenger maintain a distance of
at least 25 cm to the steering wheel or dashboard A » Fig. 9. Not maintaining this minimum distance will mean that the airbag system will not be able
to properly protect you - hazard! The front seats and the head restraints
must always also be correctly adjusted to match the body size of the occupant.
■
The airbag develops enormous forces when triggered, which can lead to
injuries if the sitting position or seated position is not correct.
■
There must not by any further persons, animals or objects positioned between the front seated occupants and the deployment area of the airbag.
WARNING
Front airbag and transporting children
■
Never transport children on the front seat of a vehicle without using a
proper restraint system. If airbags are deployed in the event of an accident,
the child might suffer severe or even fatal injuries!
■
The front passenger airbag must be deactivated if using a rear-facing
child seat on the front passenger seat » page 21, Deactivating airbags. If
this is not done, there is a risk of the child suffering severe or even fatal
injuries if the front passenger airbag is deployed. When transporting a child
on the front passenger seat, pay attention to any relevant national regulations regarding the use of child safety seats.
WARNING
General information
■
The steering wheel and the surface of the airbag module in the dash panel on the passenger side must not have stickers attached, be covered or
modified in any other way. These parts should only be cleaned with a cloth
that is dry or has been moistened with water. No objects such as cup holders, mobile phone mounts, etc. must be attached to the covers of the airbag modules or be located within their immediate vicinity.
■
Never place objects on the surface of the front passenger airbag module
in the dash panel.
18
Safety

Note
■
In vehicles with driver's airbag, the text can be found on the steering
wheel.
■
In vehicles with front passenger airbag, the text
is located on the dash
panel on the passenger side.
Driver’s knee airbag
Fig. 10 Position of the airbag / gas filled airbag
Fig. 11
Safe distance from the control
panel
WARNING
■
Adjust the driver's seat in a forward/back direction so that there is a gap
of at least 10 cm between the legs A and the dash panel in the vicinity of
the knee airbag » Fig. 11. If it is not possible to meet this requirement due
to your body size, visit a specialist garage.
■
The surface of the airbag module in the lower part of the dash panel below the steering column not have stickers attached, be covered or modified
in any other way. This part should only be cleaned with a cloth that is dry or
has been moistened with water. No objects must be attached to the cover
of the airbag module or located within the immediate vicinity.
■
Do not attach any bulky and heavy objects (bunch of keys etc.) to the ignition key. These can be ejected by the knee airbag when it is deployed and
can cause injuries.
Note
In vehicles with a driver's knee airbag, a symbol with the word AIRBAG is located on the side panel on the driver's side.
Side airbags
The driver's knee airbag offers adequate protection for the driver's legs.
The driver's knee airbag is located in the lower part of the dash panel below
the steering column » Fig. 10 - .
In the event of a severe frontal collision, the driver's knee airbag and front air-
bags are deployed.
The forward movement of the body is cushioned when it makes contact with
the fully inflated airbag » Fig. 10 - and the risk of injury to the legs of the
driver is thus reduced.
Fig. 12 Installation of airbags in front/rear seat
Airbag system
19

Fig. 13
Inflated airbags
In the event of severe side collisions, the side airbag system provides additional protection for the upper body (chest, stomach and pelvis) of passengers in
the vehicle.
The front side airbags are housed in the upholstery of the seat backrests of
the front seats » Fig. 12 - .
The rear side airbags are located between the entrance area and the seat
backrest » Fig. 12- .
When the side airbags are deployed, the head airbag and belt tensioner are also automatically deployed on the relevant side.
The load of the occupants is cushioned when plunging into the fully inflated
airbag » Fig. 13 and the risk of injury to the entire upper body (chest, stomach
and pelvis) is reduced on the side facing the door.
WARNING
Information on correct seating position
■
Your head should never be positioned in the deployment area of the side
airbag. You might suffer severe injuries in the event of an accident. This applies in particular to children who are transported without using a suitable
child safety seat » page 25, Child safety and side airbag.
■
There must not be any further persons, animals or objects positioned between the occupants and the deployment area of the airbag. No accessories, such as cup holders, should be attached to the doors.
■
If children adopt an incorrect seated position when travelling, they may
be exposed to an increased risk of injury in the event of an accident. This
can result in serious injuries » page 23, Child seat.
WARNING
■
The airbag control unit operates using pressure sensors located in the
front doors. For this reason, no adjustments may be carried out to the
doors or door panels (e.g. installation of additional loudspeakers). Further
information » page 168, Airbags.
■
Ensure that there are no excessive forces, such as violent knocks, kicks
etc., impact on the backrests of the seats otherwise the system may be
damaged. The side airbags would not be deployed in such a case!
■
Any seat or protective covers which you fit to the driver or front passenger seats must only be of the type expressly authorized by ŠKODA. In view
of the fact that the airbag inflates out of the backrest of the seat, use of
non-approved seat or protective covers would considerably impair the protective function of the side airbag.
■
Any damage to the original seat covers in the area of the side airbag module must be repaired immediately by a specialist garage.
■
The airbag modules in the front seats must not display any damage,
cracks or deep scratches. It is not permissible to use force in order to open
the modules.
Note
■
In vehicles with side airbags a label with the text is located on the front
seat backrests.
■
In vehicles with rear side airbags, the word AIRBAG is located between the
entrance area and the rear seat rest
.
Head airbags
Fig. 14 Location of the head airbag/gas-filled head airbag
In the event of a severe side collision, the head airbag system offers additional
protection for the head and neck area of passengers.
20
Safety

The head airbags are positioned above the doors on both sides of the vehicle
interior » Fig. 14 - .
In the event of a side collision the head airbag is deployed together with the
relevant side airbag and the front seat belt tensioner on the side of the car on
which the accident occurs.
When deployed, the airbag covers the window area of the front and rear doors,
as well as the area of the door pillar » Fig. 14 - .
Head impact with interior parts is reduced by the inflated head airbag. The reduction in any impact to the head and the resultant minimizing of any movements of the head additionally reduce the risk of injuries to the neck area.
WARNING
■
There must not be any objects in the deployment area of the head air-
bags which might prevent the airbags from inflating properly.
■
Only hang light items of clothing on the hooks fitted in the vehicle. Never
leave any heavy or sharp-edged objects in the pockets of the items of
clothing. Additionally, clothes hangers must not be used to hang up items
of clothing.
■
The installation of impermissible accessories in the vicinity of the head
airbags can considerably impair the protection offered by the head airbag in
the event of it being deployed. When the deployed head airbag is inflated,
parts of the fitted accessories could be thrown into the interior of the car
and injure the occupants.
■
The sun visors must not be swivelled towards the side windows in the
deployment area of the head airbags if any objects, such as ball-point pens,
etc. are attached to them. This might result in injuries to the occupants if
the head airbag is deployed.
■
There must not be any further persons, animals or objects positioned between the seated occupants and the deployment area of the airbag. In addition, none of the occupants should lean their head out of the window
when driving, or extend their arms and hands out of the window.
Note
In vehicles with head airbag, the word can be seen on the B and C column cladding.
Deactivating airbags
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Deactivating airbags
Deactivating the front passenger airbag 22
Deactivating airbags
Deactivating an airbag should be considered in cases such as the ones below.
If using a rear-facing child seat on the front passenger seat (due to different
›
legal regulations, the airbag must be deactivated if using a forwards-facing
child seat in some countries) » page 23, Transporting children safely.
If it is not possible to maintain a distance of at least 25 cm between the mid-
›
dle of the steering wheel and chest, despite the driver's seat being correctly
adjusted.
If special attachments are required in the area of the steering wheel because
›
of a physical disability.
If different seats have been fitted (e.g. orthopaedic seats without side air-
›
bags).
The front passenger airbag can be switched off with the key-operated
switch » page 22, Deactivating the front passenger airbag.
We recommend that you ask a ŠKODA service partner to deactivate any other
airbags.
Monitoring the airbag system
The operational capability of the airbag system is monitored electronically, including when one of the airbags is switched off.
Airbag deactivated using diagnostic equipment
The warning light lights up for approximately 4 seconds after the ignition
›
is switched on and then flashes again for approximately 12 seconds.
Front passenger airbag deactivated using the key switch in the storage compartment
The warning light lights up for approximately 4 seconds after the ignition
›
is switched on.
The warning light
›
has been switched on.
» Fig. 15 on page 22 - comes on after the ignition
21
Airbag system
21

Note
■
The national regulations for switching off airbags must be observed.
■
A ŠKODA service partner will be able to inform you which, if any, of your vehi-
cle's airbags can or must be deactivated.
Deactivating the front passenger airbag
Fig. 15 Key-operated switch for the front passenger airbag / warning
light for front passenger airbag
Only the front passenger airbag is deactivated with the key switch.
Switching off
Switch off the ignition.
›
Open the storage box on the front passenger's side.
›
Fold the key bit out completely for the radio key » .
›
Carefully insert the key into the key slot in the key switch as far as the stop.
›
Use the key to turn the slot of the key switch carefully into the position
›
OFF » Fig. 15 - .
Pull the key out of the slot in the key switch
›
Close the storage box on the front passenger's side.
›
Check that the warning light
›
lights up after the ignition is switched on.
Switching on
Switch off the ignition.
›
Open the storage box on the front passenger's side.
›
Fold the key bit out completely for the radio key » .
›
Carefully insert the key into the key slot in the key switch as far as the stop.
›
Use the key to turn the slot of the key switch carefully into the position
›
ON » Fig. 15 - .
Pull the key out of the slot in the key switch » .
›
under the text
» .
» Fig. 15 -
Close the storage box on the front passenger's side.
›
Check that the warning light under the text » Fig. 15 -
›
lights up after the ignition is switched on.
The warning light goes out 65 seconds after the key switch status has
changed or after the ignition is switched on.
WARNING
■
The driver is responsible for whether the airbag is switched on or switch-
ed off.
■
Only switch off the airbag when the ignition is switched off! Otherwise a
fault can occur in the system for deactivating the airbag.
■
If the
be deployed in the event of an accident! Have the airbag system checked
by a specialist garage immediately.
■
The key can not be inserted in the key switch while driving.
■
Shocks can cause the key to turn in the slot and trigger the airbag!
■
The airbag can be triggered unexpectedly in an accident - it may result
in injury or death!
CAUTION
An insufficiently folded out key bit can damage the key switch!
warning lights flash, the front passenger airbag will not
22
Safety

Transporting children safely
Child seat
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Use of a child seat on the front passenger seat 24
Use of the child seat in the front passenger seat 25
Child safety and side airbag 25
Classification of child seats 25
Use of child seats fastened with a seat belt 25
Children are generally safer on the rear seats than on the front passenger
seat.
In contrast to adults, the muscles and bone structure of children are not yet
fully developed. Thus children are exposed to increased risk of injury.
Children should be transported in accordance with the relevant statutory provisions.
Child seats complying with the ECE-R 44 standard must be used. ECE-R stands
for: Economic Commission for Europe - Regulation.
Child seats that comply with the ECE-R 44 standard are identified with a test
mark that cannot be removed: a large E within a circle with the test number
below.
WARNING
■
The national legal requirements must be observed when using child
seats.
■
One should never carry children, and also not babies! - on one's lap.
■
Never leave children unattended in the vehicle. Certain outside climatic
conditions can cause life-threatening temperatures in the vehicle.
■
The child must be secured in the vehicle during the entire journey! Otherwise, the child would be thrown through the vehicle in the event of an accident, causing fatal injuries to both the child and other occupants.
WARNING (Continued)
■
Children are exposed to an increased risk of injury in the event of an accident if they lean forward or adopt an incorrect seated position when the
vehicle is moving. This particularly applies to children who are transported
on the front passenger seat as they can suffer severe, or even fatal injuries
if the airbag system is deployed!
■
Pay particular attention to the information provided by the manufacturer
of the child safety seat regarding the correct routing of the belt. Seat belts
which are not correctly adjusted can themselves cause injuries even in minor accidents.
■
Safety belts must be checked to ensure that they are running properly.
One should also ensure that the belt is not damaged by sharp-edged fittings.
■
The front passenger airbag must be deactivated if using a rear-facing
child seat on the front passenger seat. Further information » page 24,
Use of a child seat on the front passenger seat.
CAUTION
■
When installing a child seat in which the child faces forward, adjust the head
restraints so that they are as high as possible.
■
If the head restraints still prevent the child seat from being installed, even in
the highest position, you will need to remove them » page 82. After removing the child seat, re-install the head restraints.
Note
We recommend that you use child seats from ŠKODA Original Accessories.
These child seats were developed and also tested for use in ŠKODA vehicles.
They meet the ECE-R 44 standard.
Transporting children safely
23

Use of a child seat on the front passenger seat
Does not apply to Taiwan
Fig. 16
Sticker on the B column on the
front passenger side.
Fig. 17 Front passenger sun visor / label
Read and observe
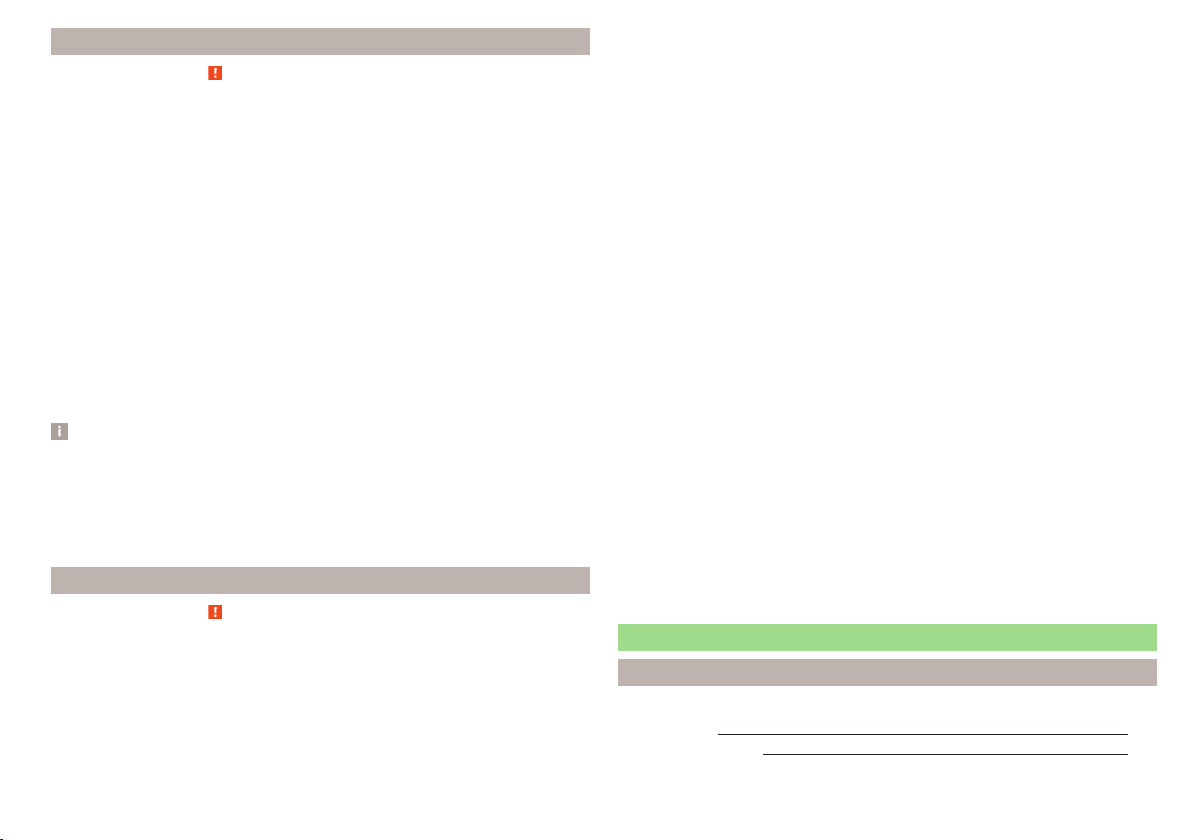
Never use a rearward-facing child restraint system on a seat which is protected by an active airbag. This could cause serious injury to the child, even
death.
For safety reasons, we recommend that you install child seats on the rear
seats whenever possible.
The following instructions must be followed when using a child seat on the
front passenger seat.
The front passenger airbag must be deactivated if using a rear-facing child
›
seat » .
If possible, adjust the front passenger seat backrest so that it is as vertical,
›
so as to ensure secure contact between the passenger seat backrest and the
back of the child seat.
and on page 23 first.
If possible, move the front passenger seat backwards so that there is no con-
›
tact between the front passenger seat and the child seat behind it.
With child safety seats in groups 2 or 3, make sure that the loop-around fit-
›
tings attached to the child seat headrest is positioned in front of or at the
same height as the loop-around fittings on the B pillar on the passenger side.
Set the height-adjustable front passenger seat as high up as possible.
›
Set the front passenger seat belt as high up as possible.
›
Place and fasten the child seat on the seat and the child in the child seat ac-
›
cording to the specifications in the manufacturer's user manual of the child
seat .
WARNING
■
The front passenger airbag must be deactivated if using a rear-facing
child seat on the front passenger seat » page 21, Deactivating airbags.
■
Never use a rear-facing child seat on the front passenger seat if the passenger airbag is activated. This child safety seat is positioned in the deployment area of the front passenger airbag. The airbag may cause the child severe, or even fatal injuries, in the event of it being deployed.
■
This fact is also indicated by the label that can be found in one of the following locations.
■
On the B-column on the front passenger side » Fig. 16. The sticker is
visible upon opening the front passenger door.
■
On the front passenger's sun visor. In some countries, the sticker is lo-
cated on the front seat passenger's sun visor » Fig. 17.
■
With child safety seats in groups 2 or 3, make sure that the loop-around
fittings attached to the child seat headrest is positioned in front of or at
the same height as the loop-around fittings on the B pillar on the passenger side.
■
As soon as the rear-facing child seat is no longer being used on the passenger seat, the front passenger airbag should be re-activated again.
24
Safety
Use of the child seat in the front passenger seat
Applies to Taiwan
Fig. 18 Front passenger sun visor / label
Read and observe
No babies, infants or children to be carried on the passenger seat.
Also indicated by the label on the passenger's sun visor » Fig. 18.
and on page 23 first.
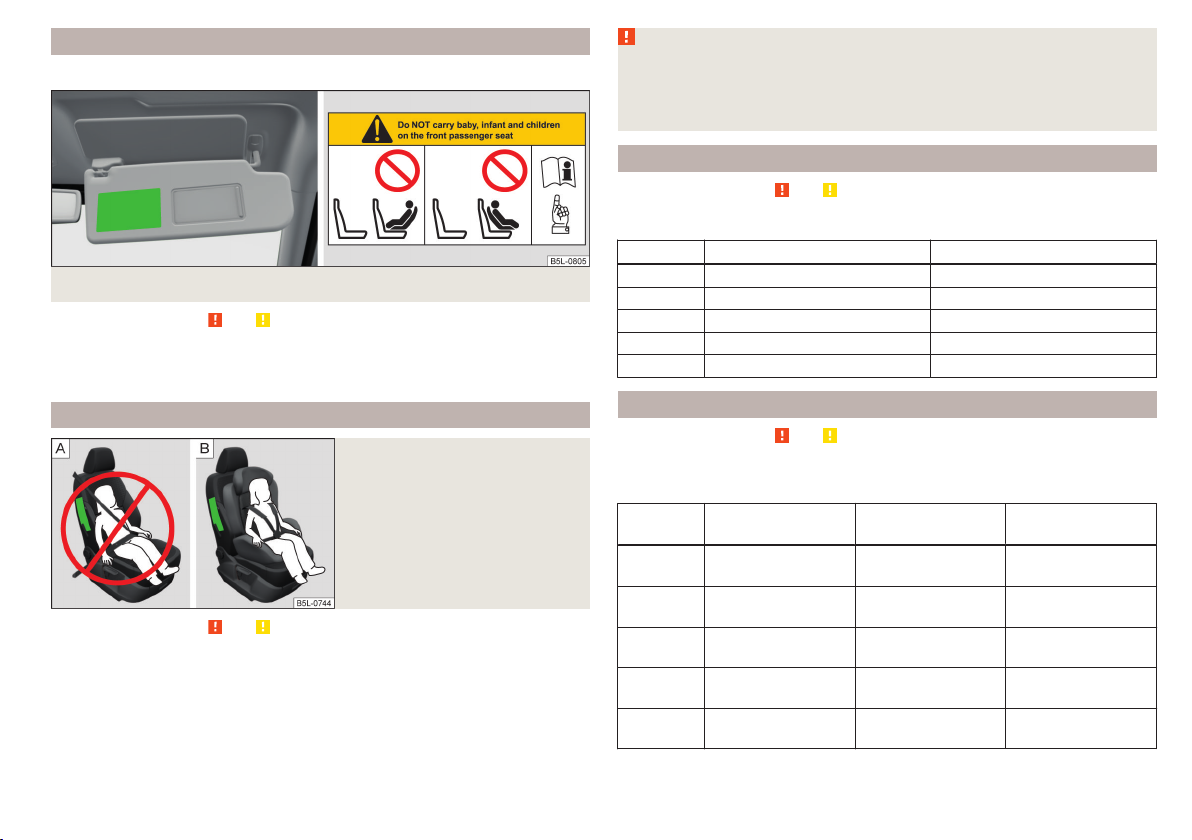
Child safety and side airbag
Fig. 19
Incorrect seated position of a
child who is not properly secured
– risk from the side airbag/Child
properly protected by safety seat
Read and observe and on page 23 first.
The child must not be positioned in the deployment area of the side airbag » Fig. 19 - .
There must be sufficient room between the child and the deployment area of
the side airbag » Fig. 19 , so that the airbag can provide as much protection
as possible.
WARNING
■
Children must never be seated with their head in the deployment area of
the side airbag – risk of injury!
■
Do not place any objects within the deployment area of the side airbags –
risk of injury!
Classification of child seats
Read and observe and on page 23 first.
Classification of child seats according to the ECE-R 44 standard.
Group Weight of the child Approximate age
0 up to 10 kg up to 9 months
0+ up to 13 kg up to 18 months
1 9-18 kg up to 4 years
2 15-25 kg up to 7 years
3 22-36 kg over 7 years
Use of child seats fastened with a seat belt
Read and observe
Overview of the usability of child seats fastened with a seat belt on each of
the seats in accordance with the ECE-R 16 standard.
Group
0
up to 10 kg
0+
up to 13 kg
1
9-18 kg
2
15-25 kg
3
22-36 kg
Front passenger
and on page 23 first.
seat
U U U
U U U
U U U
U U U
U U U
Rear seats
external
Rear seat
center
Transporting children safely
25
“Universal” child seat category - a child seat designed to be attached to
U is a system for a fast and secure child-seat mounting.
the seat using the seat belt.
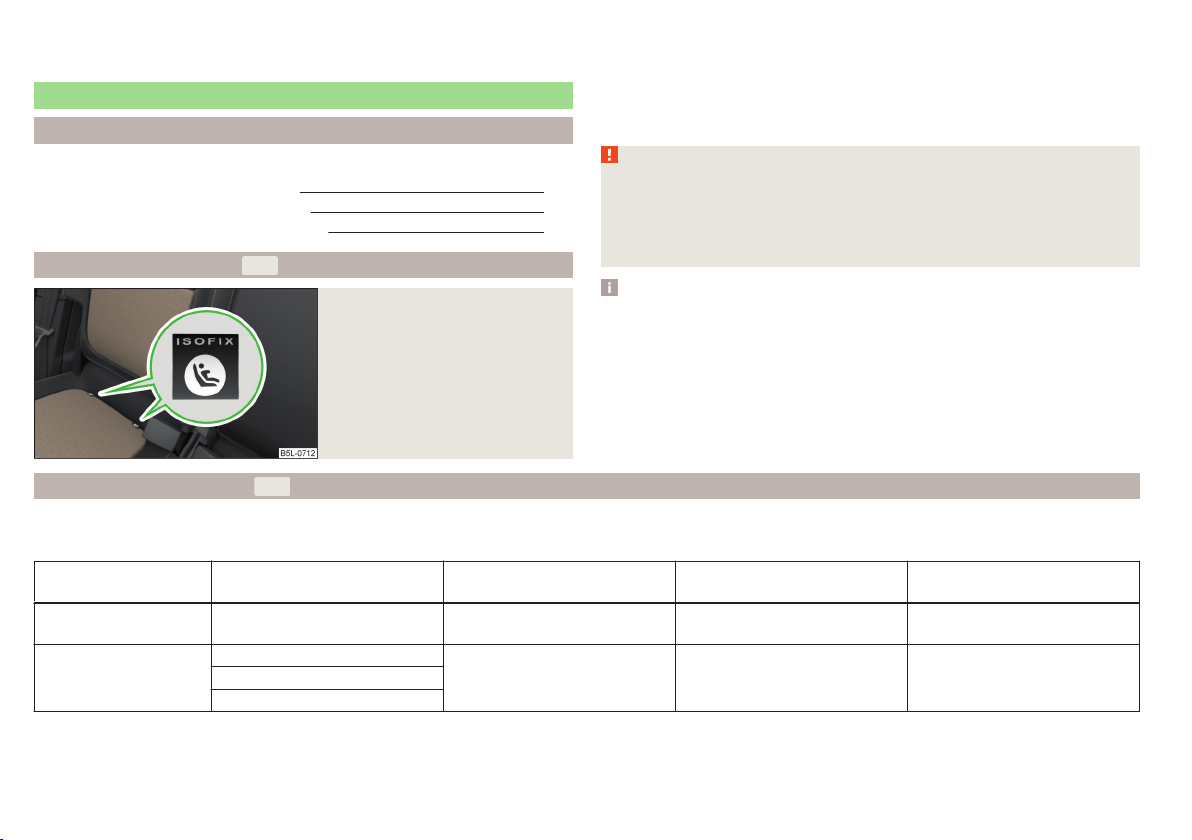
Fastening systems
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
attachment points of the
Use of child seats with the
Attachment points of the
system 26
system 26
system 27
There are two fixing eyes between the seat backrest and the seat cushion of
the front passenger seat for fixing a child seat with the
On the rear outside seats, the fixing eyes are located below the upholstery.
The places are marked with labels with the
logo » Fig. 20.
WARNING
■
Always refer to the instructions of the manufacturer of the child seat
when installing and removing a child seat with the system.
■
Never attach other child seats, belts or objects to the attachment points
intended for the installation of a child seat with the
death!
attachment points of the
system
Note
Fig. 20
Rear seat:
■
A child seat fitted with the system can only be mounted in a vehicle fitted with an system if the child seat has been approved for this type of vehicle. Further information is available from a ŠKODA Partner.
■
Child seats with the
system can be purchased from ŠKODA Original Ac-
cessories.
Use of child seats with the system
Overview of the use-ability of the child seats fastened with the system on
each of the seats in accordance with the ECE-R 16 standard.
system.
system – risk of
26
Group
0
up to 10 kg
0+
up to 13 kg
Safety
Size class of
the child seat
a)
Front passenger seat
b)
Outer rear seats Rear seat middle
E X IL-SU X
E
X IL-SU XD
C
Group
Size class of
the child seat
a)
D
1
9-18 kg
C
B
B1
A
2
15-25 kg
3
22-36 kg
a)
The size category is shown on the label attached to the child seat.
b)
If the front passenger seat is fitted with
The seat is suitable for the installation of a child seat with “Semi-
IL-SU
X IL-SU X
X IL-SU X
system attachment points, it is suitable for the installation of an
Universal” approval. The “Semi-Universal” category means that the child
seat with the
system is approved for your vehicle. Observe the list
of vehicles that comes with the child seat.
system
child seat with the
system belt.
The seat is suitable for the installation of a
IUF
“Universal” approval and attachment with the
The seat is not fitted with
X
Attachment points of the
system attachment points.
Front passenger seat
X
■
when installing and removing a child seat with the system.
■
tachment points.
■
■
anchorage points.
b)
child seat with “Semi-Universal” approval.
Outer rear seats Rear seat middle
IL-SU
IUF
X
WARNING
Always refer to the instructions from the manufacturer of the child seat
Only use child seats with the
system on the seats with the at-
Only ever attach one belt from the child seat to a locking eye.
On no account should you equip your vehicle, e.g. mount screws or other
Fig. 21
The attachment point of the
system
is a fastening system, which restricts the movement of the upper part
of the child seat.
The attachment points for attaching the belt for a child seat with the
system are located on the back of the outer rear seat backrests » Fig. 21.
Transporting children safely
27
 Loading...
Loading...