Page 1

SIMPLY CLEVER
ŠKODA Superb
Owner's Manual
Page 2
Layout of this Owner's Manual (explanations)
This Owner's Manual has been systematically designed to make it easy for you
to search for and obtain the information you require.
Chapters, table of contents and subject index
The text of the Owner's manual is divided into relatively short sections which
are combined into easy-to-read chapters. The chapter you are reading at any
particular moment is always specified on the bottom right of the page.
The Table of contents is arranged according to the chapters and the detailed
Subject index at the end of the Owner's Manual helps you to rapidly find the
information you are looking for.
Direction indications
All direction indications such as “left”, “right”, “front”, “rear” relate to the direction
of travel of the vehicle.
Units of measurement
All values are expressed in metric units.
Explanation of symbols
Denotes a reference to a section with important information and safety
advice in a chapter.
Denotes the end of a section.
Denotes the continuation of a section on the next page.
Indicates situations where the vehicle must be stopped as soon as
possible.
® Denotes a registered trademark.
Indicates the texts displayed in the MAXI DOT screen.
Indicates the texts shown in the segment display.
Display
In this owner's manual, the screen on the MAXI DOT display is used as the display illustration, provided it is not otherwise stated.
Notes
WARNING
The most important notes are marked with the heading WARNING. These
WARNING notes draw your attention to a serious risk of accident or injury.
CAUTION
A Caution note draws your attention to the possibility of damage to your vehicle
(e.g. damage to gearbox), or points out general risks of an accident.
For the sake of the environment
An Environmental note draws your attention to environmental protection aspects. This is where you will, for example, find tips aimed at reducing your fuel
consumption.
Note
A normal Note draws your attention to important information about the operation of your vehicle.
3T0012720AG
Page 3

Preface
You have opted for a ŠKODA – our sincere thanks for your confidence in us.
You have received a vehicle with the latest technology and range of amenities. Please read this Owner's Manual carefully, because the operation in accordance with these instructions is a prerequisite for
proper use of the vehicle.
If you have any questions about your vehicle, please contact a ŠKODA Partner.
We hope you enjoy driving your ŠKODA, and wish you a pleasant journey at all times.
Your ŠKODA AUTO a.s. (hereinafter referred to only as ŠKODA or manufacturer)
Page 4

Terms used
The on-board literature contains the following terms relating to the service
work for your vehicle.
“Specialist garage” - a workshop that carries out specialist service tasks for
›
ŠKODA vehicles A specialist garage can be a ŠKODA partner, a ŠKODA service
partner or an independent workshop.
“ŠKODA service partner” - A Workshop that has been contractually author-
›
ized by the manufacturer ŠKODA AUTO a.s. or its sales partner to perform
service tasks on ŠKODA vehicles and to sell ŠKODA Genuine Parts.
“ŠKODA partner” - A company that has been authorized by the manufacturer
›
ŠKODA AUTO a.s. or its sales partner to sell new ŠKODA vehicles and, when
applicable, to service them using ŠKODA Genuine Parts and sell ŠKODA Genuine Parts.
Owner's Manual
These operating instructions apply to all body variants of the vehicle and all
related models.
The manual describes all possible equipment variants without identifying
them as special equipment, model variants or market-dependent equipment.
Consequently, this vehicle does not necessarily contain all of the equipment
components described in this Owner's Manual.
The scope of equipment on your vehicle depends on your purchase contract
for the vehicle. More information is available from the ŠKODA Partner from
whom you bought the vehicle.
The illustrations can differ in minor details from your vehicle; they are only intended for general information.
Supplementary Information (applies to Russia)
The full licence number of the means of transport is indicated in the registration documents.
Page 5

Table of Contents
Abbreviations
Safety
Passive Safety 6
General information 6
Correct and safe seated position 7
Seat belts 10
Using seat belts 10
Inertia reels and belt tensioners 13
Airbag system
Description of the airbag system 14
Airbag overview 15
Deactivating airbags 19
Transporting children safely 21
Child seat 21
Fastening systems 23
Operation
Cockpit
Overview
Instruments and Indicator Lights
Instrument cluster
Warning lights
Information system
Driver information system
Multifunction display (MFD)
MAXI DOT display
Service interval display
Unlocking and opening
Unlocking and locking
Anti-theft alarm system
Luggage compartment lid
26
28
28
32
39
39
44
46
48
48
54
55
Electric boot lid (Superb Combi) 57
Electric power windows 59
Electric sliding/tilting roof 62
Panoramic sliding/tilting roof (Superb Estate) 63
Lights and visibility 65
Lights 65
Interior lights 71
Visibility 73
Windscreen wipers and washers 75
Rear mirror 77
Seats and useful equipment 79
Adjusting the seats 79
14
Seat features 83
Practical equipment 86
Luggage compartment 95
Removable light (Superb Combi) 101
Variable loading floor in the luggage
compartment (Estate) 102
Extending variable loading floor with
integrated aluminium rails and faseting
elements (Superb Combi) 103
Net partition (Superb Combi) 105
27
Roof rack system 106
Air conditioning system 108
Heating, ventilation, cooling 108
Air conditioning system (manual air
conditioning system) 110
Climatronic (automatic air conditioning
system) 113
Auxiliary heating (auxiliary heating and
41
ventilation) 116
Communication and multimedia 119
General information 119
Universal telephone preinstallation GSM II 122
Universal telephone preinstallation GSM IIl 124
WLAN 127
Voice control 129
Multimedia 131
Driving
Starting-off and Driving 135
Starting and stopping the engine using the
key 135
Starting and stopping the engine - KESSY 137
Brakes 140
Manual gear changing and pedals 141
Automatic gearbox 142
Running in 145
Economical driving and environmental
sustainability 146
Avoiding damage to your vehicle 149
Driving abroad 150
Assist systems 151
Brake assist systems 151
Parking aid 153
Park assist 154
Cruise Control System 158
START-STOP 159
Fatigue detection (break recommendation) 162
Towing a trailer 163
Towing device 163
Trailer 166
General Maintenance
Car care
Services, modifications, and technical
alterations 169
Washing your car 172
Taking care of your vehicle exterior 173
Taking care of the interior 176
169
Table of Contents
3
Page 6

Inspecting and replenishing 179
Fuel 179
Engine compartment 182
Engine oil 185
Coolant 187
Brake fluid 189
Vehicle battery 189
Wheels 193
Tyres and wheel rims 193
Winter operation 198
Do-it-yourself
Emergency equipment and self-help 200
Emergency equipment 200
Changing a wheel 201
Tyre repair 204
Jump-starting 207
Towing the vehicle 208
Radio remote control 210
Emergency unlocking/locking 212
Emergency operation of the sliding/tilting
roof 213
Replacing windscreen wiper blades 214
Fuses and light bulbs 215
Fuses 215
Bulbs 219
Technical data
Technical data
Vehicle data 224
224
Index
4
Table of Contents
Page 7
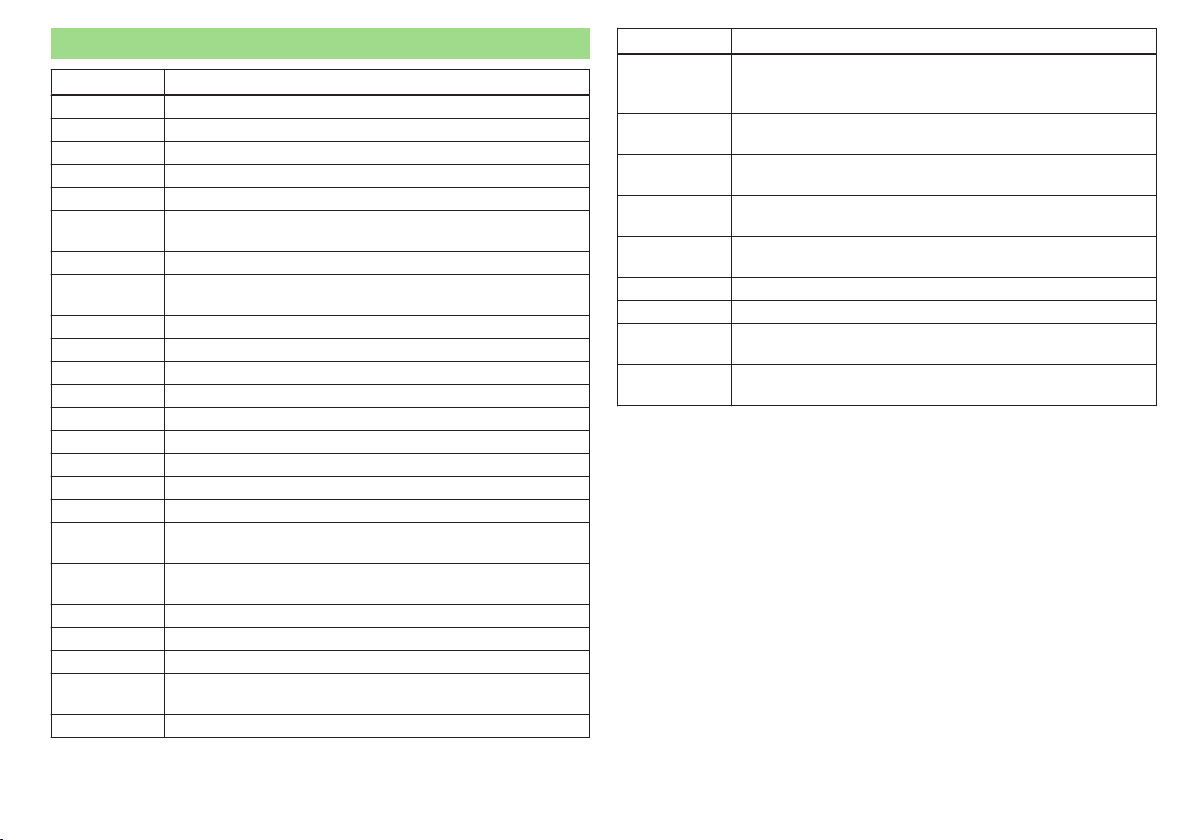
Abbreviations
Abbreviation Definition
rpm Engine revolutions per minute
ABS Anti-lock brake system
AF Multi-purpose vehicles
AHL Adaptive headlights
AG Automatic gearbox
APN
TCS Traction control
CO2 in g/km
DPF Diesel particle filter
DSG Automatic double clutch gearbox
DSR Active driver-steering recommendation
EDL Electronic differential lock
ECE Economic Commission for Europe
EPC EPC fault light
ESC Electronic Stability Control
EU European Union
FSI Stratified petrol direct injection
GSM
HFP
kW Kilowatt, measuring unit for the engine output
MG Manual gearbox
MFD Multifunction display
N1
Nm Newton meter, measuring unit for the engine torque
Access Point Name - the name of an access point for the WiFi network
discharged quantity of carbon dioxide in grams per driven
kilometer
Groupe Spécial Mobile - a digital network of mobile devices
for the transmission of voice and data
Hands-free profile - connection of a mobile device by means
of its Bluetooth® profile
Panel van intended exclusively or mainly for the transportation of goods
Abbreviation Definition
PIN
rSAP
SSP
TDI CR
TDI PD
TSA Trailer stabilisation
TSI Petrol engine with turbocharging and direct injection
UMTS
WLAN
Personal Identification Number - personal identification
number for the connection of electronic devices using Bluetooth® or WiFi
Remote SIM Access Profile - remote transmission of SIM data
Simple Security Pairing - connection of two devices using
Bluetooth® profile
Diesel engine with turbocharging and common rail injection
system
Diesel engine with injection system and unit injector injection system
Universal Mobile Telecommunication System - the next evolution of the GSM network (3G)
Wireless Local Area Network - wireless connection of electronic devices for data transfer (WiFi)
Abbreviations
5
Page 8
Safety
Passive Safety
General information
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Before setting off
Driving safety 6
Safety equipment 6
In this section you will find important information, tips and notes on the subject of passive safety in your vehicle.
We have combined everything here which you should be familiar with, for example, regarding seat belts, airbags, child seats and safety of children.
WARNING
■
This chapter contains important information on how to use the vehicle for
the driver and his occupants.
■
You can find further information on safety concerning you and those trav-
elling with you in the following chapters of this owner's manual.
■
The complete on-board literature should always be in the vehicle. This
applies in particular, if you rent out or sell the vehicle.
Before setting off
Read and observe on page 6 first.
For your own safety and the safety of the people travelling with you, please
pay attention to the following points before setting off.
Ensure that the lighting and the turn signal system are functioning proper-
ly.
Ensure that the function of the wiper and the condition of the wiper
blades are free of any defects.
Ensure that all of the windows offer good visibility to the outside.
Adjust the rear-view mirror so that vision to the rear is guaranteed.
Ensure that the mirrors are not covered.
Check the tyre inflation pressure.
Check the engine oil, brake fluid and coolant level.
Secure all items of luggage.
Do not exceed the permissible axle loads and permissible gross weight of
the vehicle.
Close all doors as well as the bonnet and boot lid.
Ensure that no objects can obstruct the pedals.
Protect children in suitable child seats with correctly fastened seat
6
belts » page 21, Transporting children safely.
Adopt the correct seated position » page 7, Correct and safe seated
position. Tell your passengers to assume the correct seated position.
Driving safety
Read and observe on page 6 first.
The driver is fully responsible for himself and his occupants. If your driving
safety is effected, you place yourself and the oncoming traffic at risk.
The following guidelines must therefore be observed.
Do not become distracted from concentrating on the traffic situation, e.g.
by your passengers or mobile phone calls.
Never drive when your driving ability is impaired, e.g. due to medication, al-
cohol or drugs.
Keep to the traffic regulations and the permissible speed limit.
Always adjust the driving speed to the road, traffic and weather condi-
tions.
Take regular breaks on long journeys – at least every two hours.
Safety equipment
Read and observe
The following list contains only part of the safety equipment in your vehicle.
Three-point seat belts for all the seats.
›
Belt force limiter for front and outer rear seats.
›
Belt tensioner for front and outer rear seats.
›
Seat belt height adjusters for the front seats.
›
Front airbag for the driver and the front passenger.
›
Driver’s knee airbag.
›
on page 6 first.
6
Safety
Page 9
Front side airbags.
›
Rear side airbags.
›
Head airbags.
›
Anchoring points for child seats using the ISOFIX system.
›
Anchoring points for child seats using the TOP TETHER system.
›
Head restraints adjustable for height.
›
Adjustable steering column.
›
The specified safety equipment works together, in order to optimally protect
you and those travelling with you in accident situations.
The safety equipment does not protect you or the people travelling with you, if
you or your occupants adopt an incorrect seated position or the equipment is
not correctly adjusted or used.
If the seat belt is not fastened properly, this may result in injuries if an airbag is
activated in the event of an accident.
Correct and safe seated position
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Correct seated position for the driver
Adjusting the steering wheel position 8
Correct seated position for the front passenger 8
Correct seated position for the passengers in the rear seats 9
Examples of incorrect seated positions 9
WARNING
■
The front seats and all head restraints must be adjusted to match the
body size at all times and the seat belt must always be fastened properly to
provide the most effective levels of protection to the passengers.
■
Each occupant must correctly fasten the seat belt belonging to the seat.
Children must be fastened » page 21, Transporting children safely with a
suitable restraint system.
■
If the occupant adopts an incorrect seated position, he is exposed to lifethreatening injuries, in case he is hit by a deployed airbag.
WARNING (Continued)
■
If the occupants on the rear seats are not sitting upright, the risk of injury
is increased due to incorrect routing of the seat belt.
■
The seat backrests must not be tilted too far back when driving, as this
will impair the function of the seat belts and of the airbag system – risk of
injury!
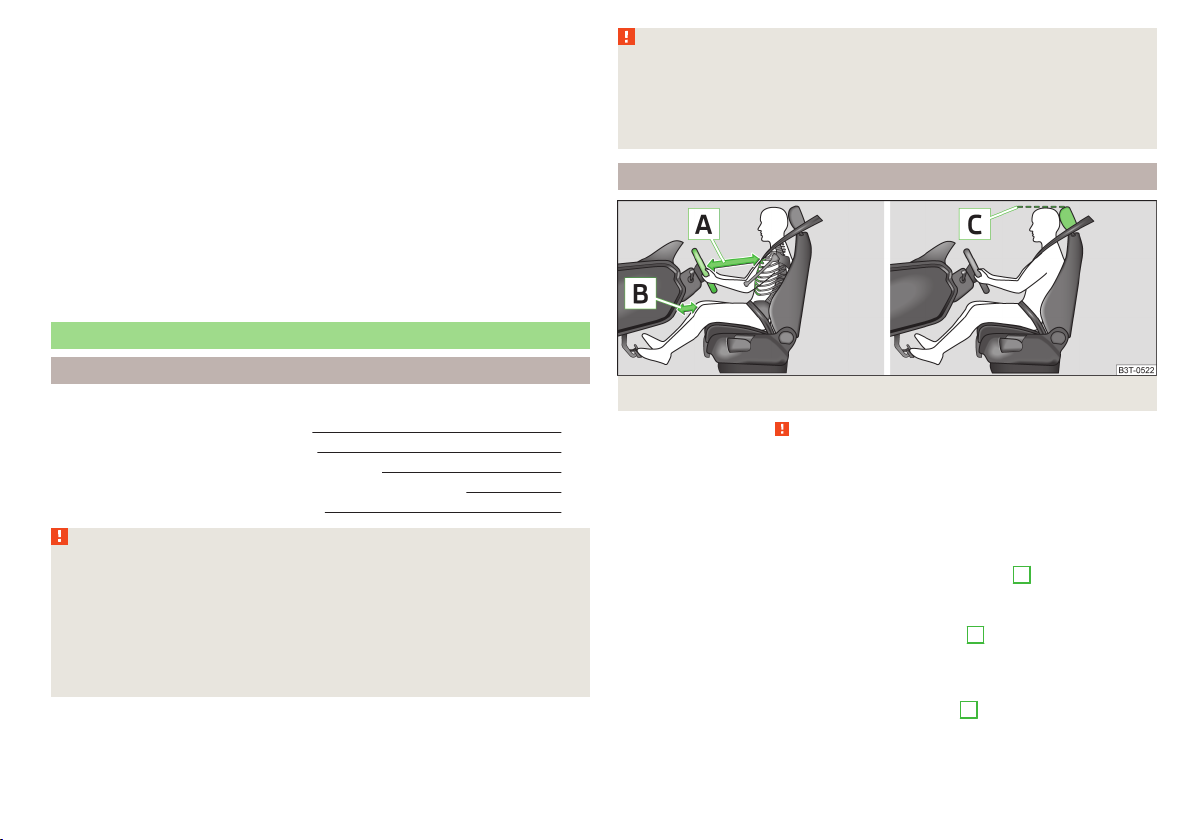
Correct seated position for the driver
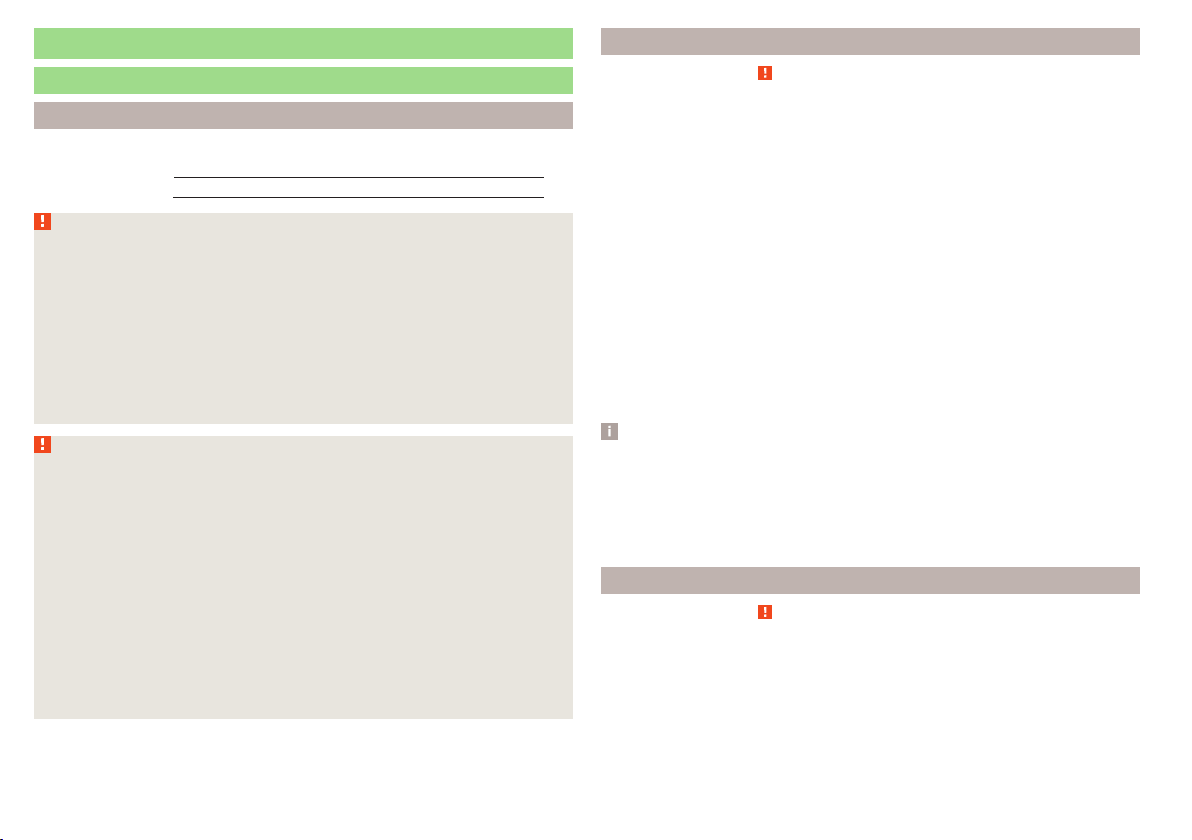
Fig. 1
Correct driver seating position / properly adjusted headrest
7
Read and observe on page 7 first.
For your own safety and to reduce the risk of injury in the event of an accident,
the following instructions must be observed.
Adjust the driver’s seat in the forward/back direction so that the pedals
can be fully depressed with slightly bent legs.
For vehicles with driver knee air-bag adjust the driver's seat in a forward/
back direction so that there is a gap of at least 10 cm between the legs
and the dash panel in the vicinity of the knee airbag - B » Fig. 1.
Adjust the seat backrest so that the highest point of the steering wheel
can be reached with your arms at a slight angle.
Adjust the steering wheel so that the distance A between the steering
wheel and your chest is at least 25 cm » Fig. 1. Adjust the steering
wheel » page 8, Adjusting the steering wheel position.
Adjust the head restraint so that the top edge of the head restraint is at
the same level as the upper part of your head C » Fig. 1.
Correctly fasten the seat belt » page 10.
Adjust the seats and head restraints » page 79.
Passive Safety
7
Page 10
WARNING
■
Always assume the correct seated position before setting off and do not
change this position while driving. Also advise your passengers to adopt
the correct seated position and not to change this position while the car is
moving.
■
Maintain a distance of at least 25 cm from the steering wheel, and a distance of at least 10 cm between the legs and the dash panel at the height
of the knee airbag. Not maintaining this minimum distance will mean that
the airbag system will not be able to properly protect you - hazard!
■
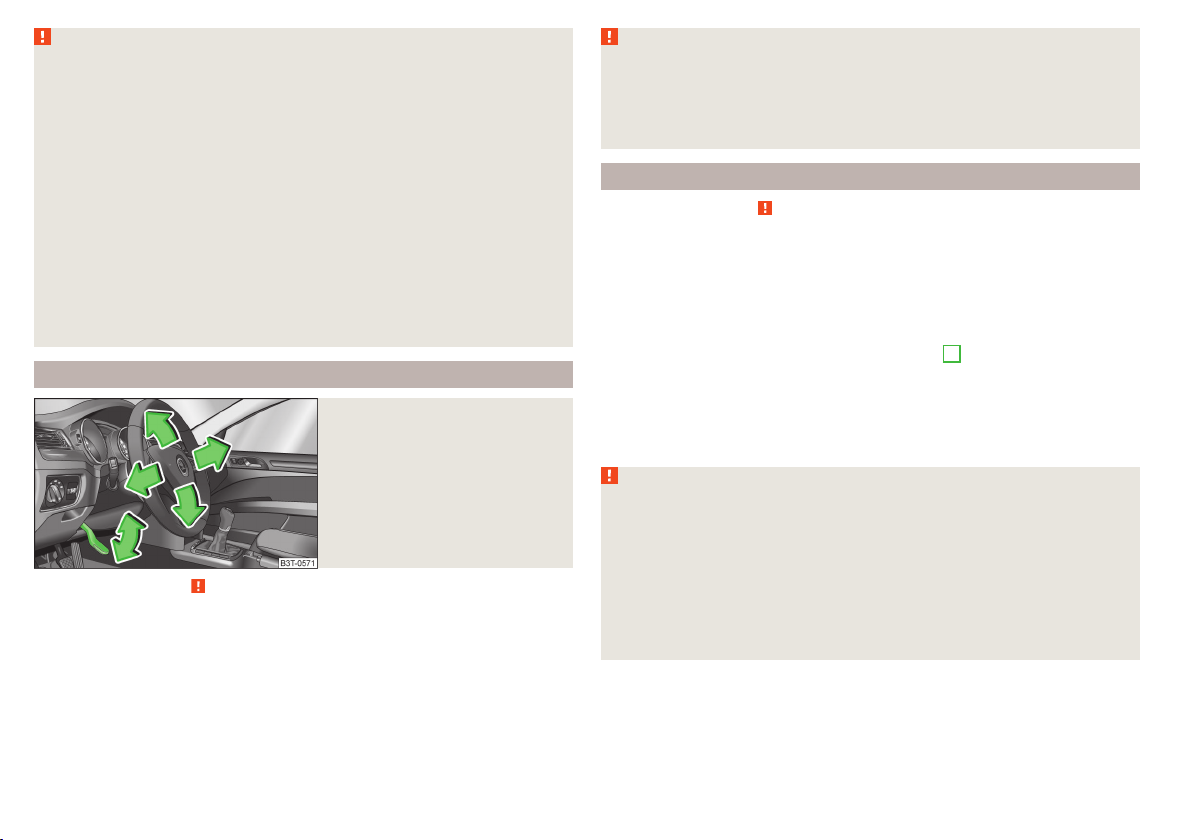
When driving, hold the steering wheel with both hands firmly on the outer edge in the “9 o'clock” and “3 o'clock” position. Never hold the steering
wheel in the “12 o'clock” position or in any other way (e.g. in the middle or
inner edge of the steering wheel). In such cases, you could severely injure
the arms, hands and head when the driver airbag is deployed.
■
Ensure that there are no objects in the driver's footwell as they may get
caught behind the pedals when driving or applying the braking. You would
then no longer be able to operate the clutch, brake or acceleration pedals.
Adjusting the steering wheel position
Fig. 2
Adjustable steering wheel: Lever
below steering wheel
Read and observe on page 7 first.
The height and forward/back position of the steering wheel can be adjusted.
Swivel the lever underneath the steering wheel downwards » Fig. 2.
›
Adjust the steering wheel to the desired position (with regard to the height
›
and forward/back position).
Push the lever upwards to the stop.
›
WARNING
■
The lever for adjusting the steering wheel must be locked whilst driving
so that the steering wheel cannot accidentally change position during the
journey – risk of accident!
■
Never adjust the steering wheel when the vehicle is moving only when
the vehicle is stationary!
Correct seated position for the front passenger
Read and observe
For passenger safety and to reduce the risk of injury in an accident, the following instructions must be observed.
Position the front passenger seat back as far as possible. The front pas-
senger must maintain a distance of at least 25 cm to the dash panel so
that the airbag offers the greatest possible safety if it is deployed.
Adjust the head restraint so that the top edge of the head restraint is at
the same level as the upper part of your head C » Fig. 1 on page 7.
Correctly fasten the seat belt » page 10.
Adjust the seats and head restraints » page 79.
In exceptional cases the front passenger airbag can be deactiva-
ted » page 19, Deactivating airbags.
WARNING
■
Maintain a distance of at least 25 cm to the dash panel. Not maintaining
this minimum distance will mean that the airbag system will not be able to
properly protect you - hazard!
■
Always keep your feet in the footwell when the car is being driven – never place your feet on the instrument panel, out of the window or on the
surfaces of the seats. You will be exposed to increased risk of injury if it becomes necessary to apply the brake or in the event of an accident. If an airbag is deployed, you could suffer fatal injuries by adopting an incorrect
seated position!
on page 7 first.
8
Safety
Page 11
Correct seated position for the passengers in the rear seats
Read and observe on page 7 first.
To reduce the risk of injury in the event of a sudden braking manoeuvre or an
accident, the occupants on the rear seats must observe the following.
Adjust the head restraint so that the top edge of the head restraint is at
the same level as the upper part of the head C » Fig. 1 on page 7.
Correctly fasten the seat belt » page 10.
Use a suitable child restraint system if transporting children in the vehicle » page 21, Transporting children safely.
Adjust the seats and head restraints » page 79.
Examples of incorrect seated positions
Read and observe
Maximum seat belt protection is only achieved if seat belts are fastened correctly.
Incorrect seated positions considerably reduce the protective functions of the
seat belts and therefore increase the risk of injury due to an incorrect routing
of the seat belt.
The driver is fully responsible for himself and passengers, especially children.
Never allow a passenger to adopt an incorrect seated position when the car is
moving.
The following list contains instructions which, if not observed, may cause serious injuries or death. This list is not complete, however we would like you to
familiarise yourself with this subject.
Observe the following instructions while driving.
Do not stand up.
Do not stand on the seats.
Do not kneel on the seats.
Do not tilt the seat backrest too far back.
Do not lean against the dash panel.
Do not lie on the rear seats.
Do not sit only on the front part of the seat.
Do not sit facing to the side.
on page 7 first.
Do not lean out of the window.
Do not put your feet out of the window.
Do not put your feet on the dash panel.
Do not put your feet on the seat cushion.
Do not allow anybody to travel in the footwell.
Do not drive without fastening your seat belt.
Do not delay in the luggage compartment.
Passive Safety
9
Page 12

Seat belts
Using seat belts
Introduction
Fig. 3
Driver wearing seat belt
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
The physical principle of a frontal collision 11
Fastening and unfastening seat belts 12
Belt height adjustment on the front seats 13
Seat belts that are fastened correctly offer good protection in the event of an
accident. They reduce the risk of an injury and increase the chance of survival
in the event of a major accident.
Correctly fastened seat belts hold occupants of the car in the correct seated
position » Fig. 3.
The seat belts reduce the kinetic energy (energy of motion) to a considerable
extent. They also prevent uncontrolled movements which, in turn, may well result in severe injuries.
Occupants of a vehicle who have correctly fastened their seat belts have the
major benefit of the fact that the kinetic energy is absorbed as effectively as
possible by the belts.
The structure of the front end of the vehicle and other passive safety measures, such as the airbag system, also contribute to the kinetic energy being reduced as effectively as possible. The energy produced is thus absorbed and
there is less risk of injury.
Particular safety aspects must be observed when transporting children in the
vehicle » page 21.
WARNING
■
Fasten your seat belt before each journey - even when driving in town!
This also applies to the passengers seated at the rear – risk of injury!
■
Expectant women must also always wear a seat belt. This is the only way
of ensuring optimal protection for the unborn child » page 12, Fastening
and unfastening seat belts.
■
Maximum seat belt protection is only achieved if you are correctly seated » page 7, Correct and safe seated position.
■
The seat backrests of the front seats must not be tilted too far to the rear
otherwise the seatbelts can lose their effectiveness.
WARNING
Information on the correct routing of the belt
■
Always ensure that the webbing of the seat belts is properly routed. Seat
belts which are not correctly adjusted can themselves cause injuries even
in minor accidents.
■
Adjust the height of the belt in such a way that the shoulder part of the
belt is roughly positioned across the middle of your shoulder - on no account across your neck.
■
A seat belt which is hanging too loose can result in injuries as your body is
moved forward by the kinetic energy produced in an accident and is then
suddenly held firm by the belt.
■
The belt webbing must not run across solid or fragile objects (e.g. spectacles, ball-point pens, bunches of keys etc.). Such objects can cause injury.
WARNING
Information on dealing with the safety belts
■
The belt webbing must not be jammed in-between at any point or twisted, or chafe against any sharp edges.
■
Make sure you do not catch the seat belt in the door when closing it.
WARNING
Information on the proper use of the safety belts
■
Never use one seat belt to secure two persons (including children). The
seatbelt must not be placed over a child who is sitting on the lap of another
passenger.
10
Safety
Page 13

WARNING (Continued)
■
The lock tongue should only be inserted into the lock which is the correct
one for your seat. Wrong use of the safety belt will reduce its capacity to
protect and the risk of injury increases.
■
The slot of the belt tongue must not be blocked, otherwise the belt
tongue will not lock in place properly.
■
Many layers of clothing and loose clothing (e. g. a winter coat over a jacket) do not allow you to be correctly seated and impairs proper operation of
the seat belts.
■
It is prohibited to use clamps or other objects to adjust seat belts (e. g. for
shortening the belts for smaller persons).
■
The seat belts for the rear seats can only fulfil their function reliably
when the seat backrests are correctly locked into position » page 85.
WARNING
Information on the care and maintenance of the safety belts
■
The belt webbing must always be kept clean. Soiled belt webbing may impair proper operation of the inertia reel » page 178.
■
The seat belts must not be removed or changed in any way. Do not attempt to repair the seat belts yourself.
■
Check the condition of all the seat belts on a regular basis. If any damage
to the seat belts, seat belt connections, inertia reel or the lock is detected,
the relevant seat belt must be replaced by a specialist garage.
■
Damaged seat belts which have been subjected to stress in an accident
and were therefore stretched, must be replaced – this is best done by a
specialist garage. The anchorage points of the belts must also be inspected. The anchorage points for the belts should also be checked.
Note
The national legal requirements must be observed when using seat belts.
The physical principle of a frontal collision
Fig. 4 Driver without a fastened seat belt/rear seat passenger without a
fastened seat belt
Read and observe
Motion energy, so-called kinetic energy, is produced as soon as the vehicle is
moving, both for the vehicle and its occupants.
The magnitude of this kinetic energy depends essentially on the speed at
which the vehicle is travelling and on the weight of the vehicle including the
occupants. The greater the speed and weight increase, the greater the
amount of energy which has to be absorbed in the event of an accident.
The speed of the vehicle is the most important factor. Doubling the speed of
the vehicle from 25 km/h up to 50 km/hour increases the kinetic energy four
times.
The idea that it is possible to support your body with your hands in a minor accident is incorrect. Even in a collision at only a low speed, the forces acting on
the body are such that it is no longer possible to support your body.
Even if you only drive at a speed of 30-50 km/h, the forces that your body is
exposed to in the event of an accident can exceed a metric ton (1000 kg).
For example, a person's weight of 80 kg “increases” to 4.8 tons (4800 kg) at
50 km/h.
In the event of a frontal collision, occupants of the car not wearing a seat belt
are thrown forward and strike parts of the interior of the car, such as the
steering wheel, dash panel, windscreen in ways which cannot be controlled » Fig. 4 - . In certain circumstances you could even be thrown out of the
vehicle, which could cause life threatening or even fatal injuries.
on page 10 first.
Seat belts
11
Page 14
It is also important that rear passengers fasten their seat belts, as they could
otherwise be thrown through the vehicle in an uncontrolled manner in the
event of an accident.
A rear seat passenger who has not fastened the seat belt is a danger not only
to himself but also for those seated in the front » Fig. 4 - .
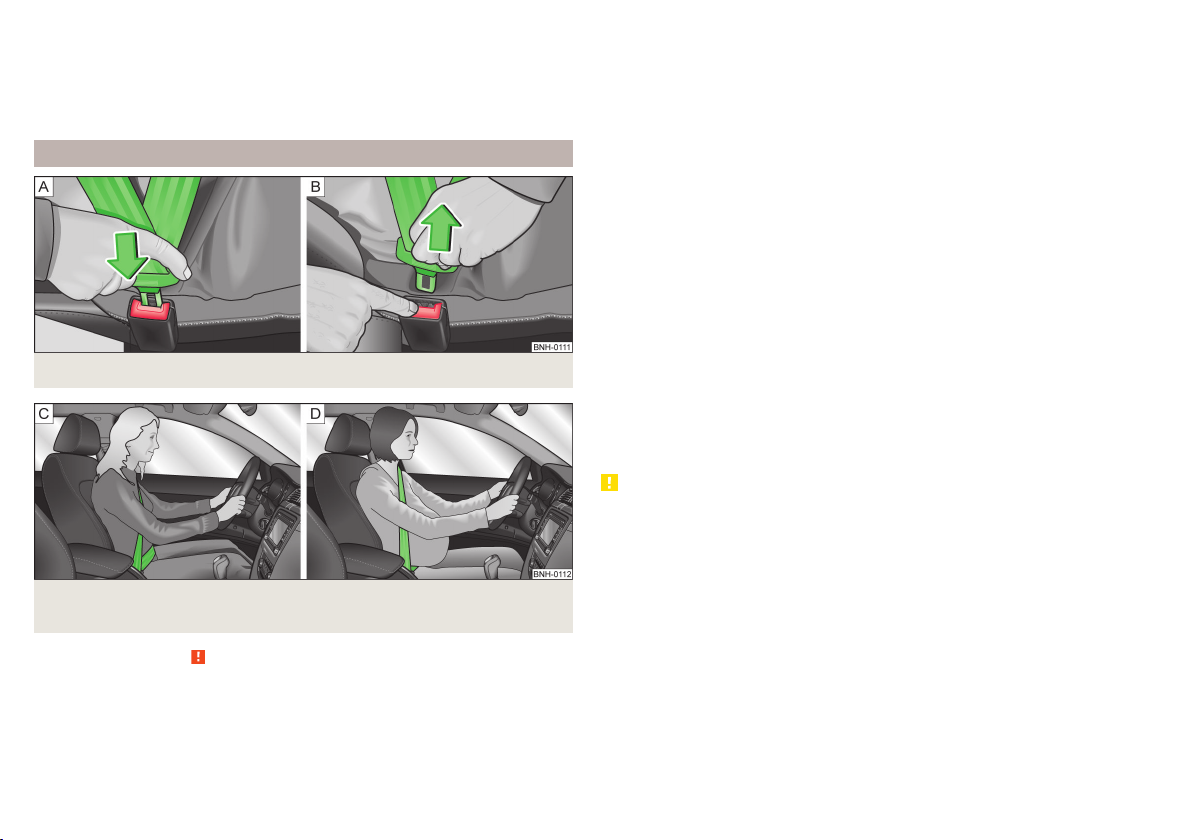
Fastening and unfastening seat belts
Fig. 5 Fastening/unfastening the seat belt
Fig. 6 Routing of belt webbing over the shoulders and the lap belt/Rout-
ing of belt webbing for an expectant mother
Insert the lock tongue into the belt buckle belonging to the seat » Fig. 5 –
›
until it you hear it click into place.
Pull on the belt to check that it has engaged correctly in the lock.
›
A plastic knob in the belt webbing holds the belt tongue in a position which is
easy to get hold of.
It is important that the belt is properly routed to ensure seat belts offer the
maximum protection.
The shoulder part of the seat belt must never run across the neck but must
roughly run over the middle of the shoulder and fit snugly against the chest.
The lap part of the belt must run across the pelvis, must not be lie across the
stomach and must always fit snugly » Fig. 6 - .
Expectant women must also always wear a seat belt. This is the only way of
ensuring optimal protection for the unborn child.
The lap part of the belt must be positioned as low as possible on the pelvis on
expectant mothers to avoid exerting any pressure on the lower abdomen » Fig. 6 - .
Release
Release the seat belt only when the vehicle is stationary.
Press the red button in the belt buckle » Fig. 5 - , the lock tongue pops out.
›
Manually guide the belt back so that it is easier to fully roll up the webbing,
›
the seat belt does not twist.
CAUTION
When releasing the seatbelt ensure that the tongue of the lock does not damage the door trim or other parts of the interior.
Read and observe on page 10 first.
Fasten
Correctly adjust the front seat and head restraint before fastening the seat
›
belt » page 7.
Use the lock tongue to slowly pull the webbing over your chest and pelvis.
›
12
Safety
Page 15
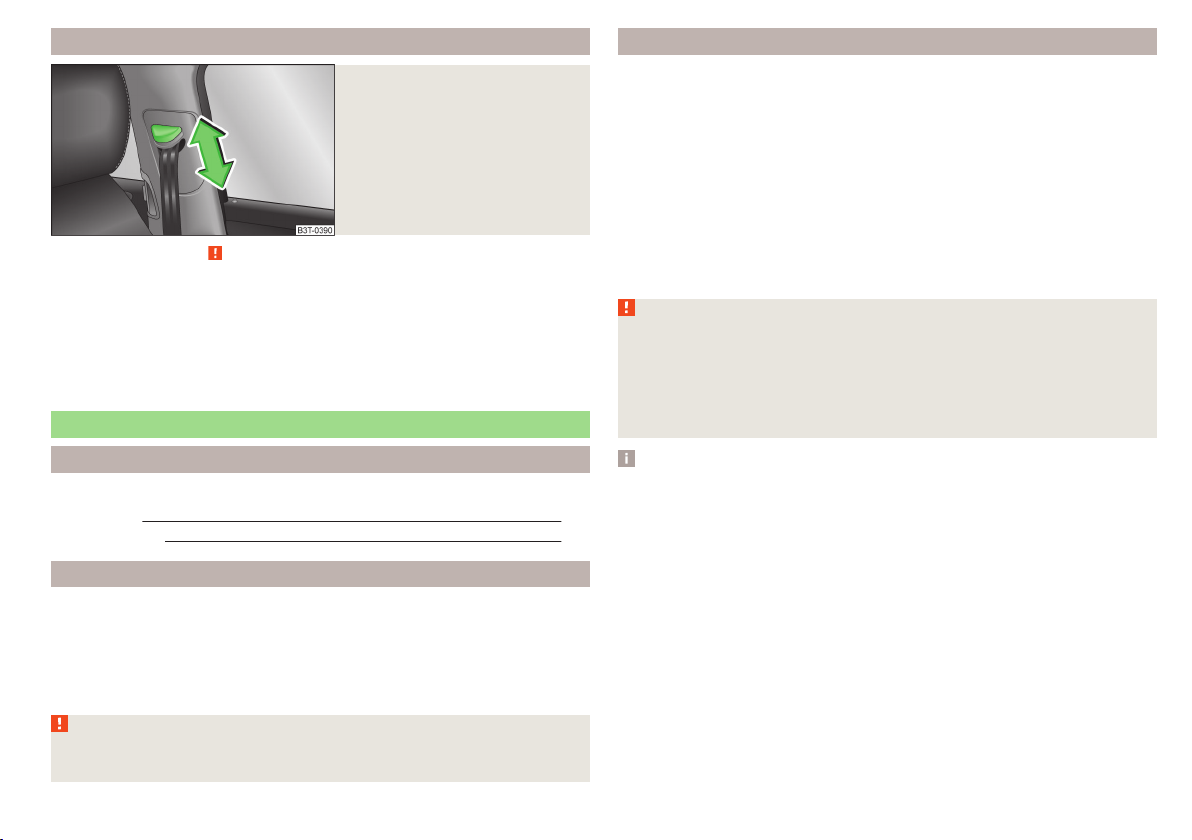
Belt height adjustment on the front seats
Fig. 7
Front seat: Seat belt height adjuster
Read and observe on page 10 first.
The seat belt height adjuster makes it possible to adjust the routing of the
front seat belts in the area of the shoulder to the body size.
Press the height adjuster and move up or down in the desired direc-
›
tion » Fig. 7.
Then pull firmly on the belt to ensure that the seat belt height adjuster has
›
correctly locked in place.
Inertia reels and belt tensioners
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Inertia reels
Belt tensioners
Inertia reels
Each seat belt is equipped with an inertia reel.
When pulling slowly on the seat belt, the belt can move freely. When pulling
sharply on the seat belt, the movement is locked by the inertia reel.
The belts also lock when full braking, when the car accelerates, when driving
downhill and when cornering.
WARNING
If the seat belt does not lock when pulling sharply on it, have it inspected
immediately by a specialist garage.
Belt tensioners
The safety for the driver, front passenger and passengers on the outer rear
seats who are wearing their seat belts, is enhanced by the belt tensioners fitted to the inertia reels on the front and rear external seat belts.
The three-point seat belts are automatically tensioned in the event of a frontal
collision of a certain severity. The belt tensioners can also be deployed if the
seat belts are not fastened.
The fastened three-point seat belts are automatically tensioned in the event
of a lateral collision of a certain severity.
Belt tensioners are not activated in the event of minor frontal collisions, side
and rear-end collisions, in the case of a rollover and also not in accidents in
which no major forces are produced from the front.
WARNING
■
Any work on the belt tensioner system including removal and installation
of system components because of other repair work, must only be carried
out by a specialist garage.
■
The protective function of the system is only adequate for a single accident. If the belt tensioners have been deployed, it is then necessary to replace the entire system.
Note
■
Smoke is generated when the belt tensioners are deployed. This is not an in-
dication of a fire in the vehicle.
■
13
When disposing of the vehicle or parts of the belt tensioner system, it is im-
portant to comply with national legal requirements. ŠKODA service partners
13
are familiar with these regulations and will be able to provide you with detailed information.
Seat belts
13
Page 16
Airbag system
Description of the airbag system
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
System description 14
Airbag deployment 14
WARNING
■
An airbag can only offer you optimal protection in combination with a
fastened seat belt.
■
The airbag is not a substitute for the seat belt, but instead forms part of
the complete passive vehicle safety concept.
■
To ensure passengers are protected with the greatest possible effect
when the airbag is deployed, the front seats must be correctly adjusted to
match the body size » page 7, Correct and safe seated position.
■
If you do not fasten the seat belts when driving, lean too far forward or
adopt an incorrect seated position, you are exposing yourself to increased
risk of injury in the event of an accident.
WARNING
Information on the use of the airbag system
■
If there is a fault, the airbag system must be checked by a specialist garage immediately. Otherwise, there is a risk of the airbag not being activated in the event of an accident.
■
No modifications of any kind must be made to parts of the airbag system.
■
Any work on the airbag system including the installation and removal of
system components due to other repair work (e.g. removal of the steering
wheel) must only be carried out by a specialist garage.
■
Never make any changes to the front bumper or bodywork.
■
It is prohibited to manipulate individual parts of the airbag system as this
might result in the airbag being deployed.
■
The protective function of the airbag system is sufficient for only one accident. The airbag system must then be replaced if the airbag has been deployed.
System description
Read and observe on page 14 first.
The functional status of the airbag system is indicated by the indicator light
in the instrument cluster » page 38.
When the airbags are deployed, they fill with gas and inflate.
A grey white or red, non-harmful gas is released when the airbag is inflated.
This is perfectly normal and is not an indication of a fire in the vehicle.
Depending on the vehicle equipment, the airbag system consists of the
following modules.
Electronic control unit.
›
Front airbag for the driver and the front passenger » page 15.
›
Driver’s knee airbag » page 16.
›
Side airbags » page 17.
›
Head airbags » page 18.
›
Airbag warning light in the instrument cluster » page 38.
›
Key switch for the front passenger airbag » page 20.
›
Warning light for the front passenger airbag deactivation/activation in the
›
middle of the dash panel » page 20.
Note
■
The airbag system needs no maintenance during its working life.
■
If you sell your vehicle, provide the complete vehicle documentation to the
new owner. Please note that the information relating to the possibility of deactivating the front passenger airbag must be included!
■
When disposing of vehicle or parts of the airbag system, it is important to
comply with the national legal requirements.
Airbag deployment
Read and observe
The airbags inflate in fractions of a second and at a high speed in order to be
able to offer additional protection in the event of an accident.
The airbag system is only functional when the ignition is switched on.
In certain accident situations, the several airbags may be deployed simultane-
ously.
on page 14 first.
14
Safety
Page 17
The airbags are not deployed in the case of minor frontal and side collisions,
rear-end collisions, tilting of the vehicle and vehicle rollover.
Deployment factors
It is not possible to generally determine which deployment conditions apply to
the airbag system in every situation. An important role is played by factors
such as the type of object that the vehicle hits (hard/soft), the impact angle,
vehicle speed etc.
A decisive factor for the deployment of the airbags is the deceleration which
occurs. The control unit analyses the nature of the collision and activates the
relevant restraint system.
If the vehicle deceleration which occurs and is measured during the collision
remains below the prescribed reference values specified in the control unit,
the airbags are not deployed although the vehicle may well suffer severe damage to the bodywork as a consequence of the accident.
The following airbags will be deployed in the event of a severe frontal
collision.
Driver’s front airbag.
›
Front passenger airbag.
›
Driver’s knee airbag.
›
The following airbags will be deployed in the event of a severe side collision.
Front side airbag on the side of the accident.
›
Rear side airbag on the side of the accident.
›
Head airbags on the side of the accident.
›
In the event of an accident in which the airbags are deployed:
the interior lighting comes on (if the switch for the interior light is in the door
›
contact position),
the hazard warning light is switched on;
›
all the doors are unlocked;
›
the fuel supply to the engine is interrupted.
›
Airbag overview
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Front airbags
Driver’s knee airbag 16
Side airbags 17
Head airbags 18
Front airbags
Fig. 8 Driver airbag in the steering wheel/front passenger airbag in the
dashboard
Fig. 9 Safe distance to steering wheel/gas-filled airbags
In the event of a severe frontal collision, the front airbag system offers additional protection for the head and chest area of the driver and front passenger.
The front airbag for the driver is housed in the steering wheel » Fig. 8 - .
The front airbag for the front seat passenger is located in the dash panel
above the glove compartment » Fig. 8 - .
The airbags inflate in front of the driver and front passenger when they are
deployed » Fig. 9 - . The forward movement of the driver and of the front
15
passenger is cushioned when they make contact with the fully inflated airbag
and the risk of injury to head and chest is thus reduced.
Airbag system
15
Page 18
WARNING
Information on correct seated position
■
For the driver and front passenger, it is important to maintain a distance
of at least 25 cm from the steering wheel or dashboard A » Fig. 9. Not
maintaining this minimum distance will mean that the airbag system will
not be able to properly protect you - hazard! The front seats and the head
restraints must always also be correctly adjusted to match the body size of
the occupant.
■
The airbag develops enormous forces when triggered, which can lead to
injuries if the sitting position or seated position is not correct.
■
There must not by any further persons, animals or objects positioned between the front seated occupants and the deployment area of the airbag.
WARNING
Front airbag and transporting children
■
Never transport children on the front seat of a vehicle without using a
proper restraint system. If airbags are deployed in the event of an accident,
the child might suffer severe or even fatal injuries!
■
The front passenger airbag must be deactivated if using a rear-facing
child seat on the front passenger seat » page 19, Deactivating airbags. If
this is not done, there is a risk of the child suffering severe or even fatal
injuries if the front passenger airbag is deployed. When transporting a child
on the front passenger seat, pay attention to any relevant national regulations regarding the use of child safety seats.
WARNING
General information
■
The steering wheel and the surface of the airbag module in the dash panel on the passenger side must not have stickers attached, be covered or
modified in any other way. These parts should only be cleaned with a cloth
that is dry or has been moistened with water. No objects such as cup holders, mobile phone mounts, etc. must be attached to the covers of the airbag modules or be located within their immediate vicinity.
■
Never place objects on the surface of the front passenger airbag module
in the dash panel.
Note
■
In vehicles with head airbags, the word AIRBAG can be seen on the steering
wheel.
■
In vehicles with front passenger airbags, the word AIRBAG is located on the
dash panel on the passenger side.
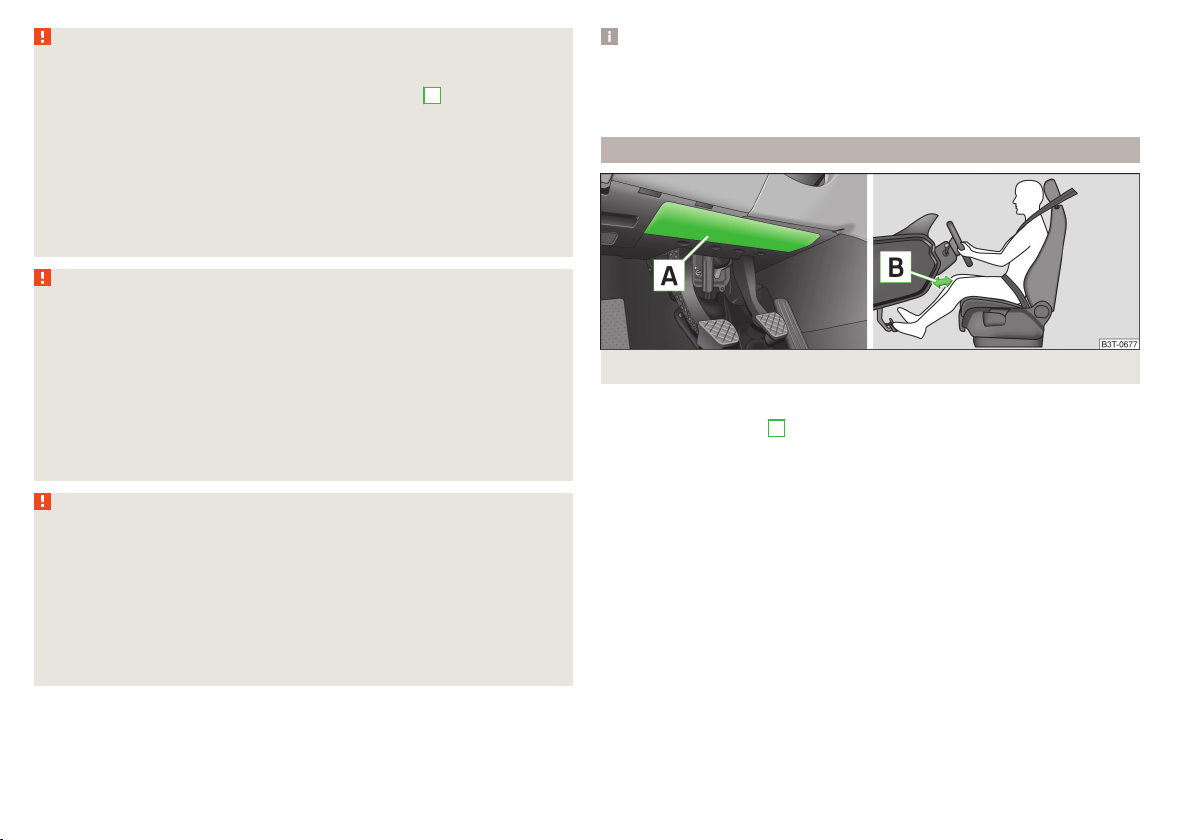
Driver’s knee airbag
Fig. 10 Installation of the airbag / Safe distance from the switching panel
The driver's knee airbag offers adequate protection for the driver's legs.
The driver's knee airbag A is located in the lower part of the dash panel below
the steering column » Fig. 10.
In the event of a severe frontal collision, the driver's knee airbag and front air-
bags are deployed.
The forward movement of the body is cushioned when it makes contact with
the fully inflated airbag and the risk of injury to the legs of the driver is thus
reduced.
16
Safety
Page 19
WARNING
■
Adjust the driver's seat in a forward/back direction so that there is a gap
of at least 10 cm between the legs B and the dash panel in the vicinity of
the knee airbag » Fig. 10. If it is not possible to meet this requirement due
to your body size, visit a specialist garage.
■
The surface of the airbag module in the lower part of the dash panel below the steering column not have stickers attached, be covered or modified
in any other way. This part should only be cleaned with a cloth that is dry or
has been moistened with water. No objects must be attached to the cover
of the airbag module or located within the immediate vicinity.
■
Do not attach any bulky and heavy objects (bunch of keys etc.) to the ignition key. These can be ejected by the knee airbag when it is deployed and
can cause injuries.
Note
In vehicles with a driver's knee airbag, a symbol with the word AIRBAG is located on the side panel on the driver's side.
Side airbags
Fig. 11 Location of the side airbag in the driver's seat/gas-filled side airbags
In the event of severe side collisions, the side airbag system provides additional protection for the upper body (chest, stomach and pelvis) of passengers in
the vehicle.
The front side airbags are housed in the upholstery of the seat backrests of
the front seats » Fig. 11 - .
The rear side airbags are located between the entrance area and the seat
backrest.
The head airbag and belt tensioner on the relevant side are also automatically
deployed when the side airbags » Fig. 11 - are deployed.
The load of the occupants is cushioned when plunging into the fully inflated
airbag and the risk of injury to the entire upper body (chest, stomach and pelvis) is reduced on the side facing the door.
WARNING
Information on correct seated position
■
Your head should never be positioned in the deployment area of the side
airbag. You might suffer severe injuries in the event of an accident. This applies in particular to children who are transported without using a suitable
child safety seat » page 22, Child safety and side airbag.
■
There must not be any further persons, animals or objects positioned between the occupants and the deployment area of the airbag. No accessories, such as cup holders, should be attached to the doors.
■
If children adopt an incorrect seated position when travelling, they may
be exposed to an increased risk of injury in the event of an accident. This
can result in serious injuries » page 21, Child seat.
WARNING
The airbag control unit operates using pressure sensors located in the front
doors. For this reason, no adjustments may be carried out to the doors or
door panels (e.g. installation of additional loudspeakers). Resulting damage
can have a negative impact on the function of the airbag system. Any work
on the front doors and door panels must be carried out by a specialist garage. The following guidelines must be observed.
■
Never drive with inner door panels removed.
■
Never drive if parts of the inner door panel have been removed and the
resulting openings have not been properly sealed.
■
Never drive if the loudspeakers in the doors have been removed, unless
the loudspeaker openings have been properly sealed.
■
Always make sure that the openings are covered or filled if additional
loudspeakers or other equipment parts have been installed in the inner
door panels.
■
Always have work carried out by a ŠKODA service partner or a professional specialist garage.
Airbag system
17
Page 20

WARNING
■
Only hang light items of clothing on the hooks fitted in the vehicle. Never
leave any heavy or sharp-edged objects in the pockets of the items of
clothing.
■
Ensure that there are no excessive forces, such as violent knocks, kicks
etc., impact on the backrests of the seats otherwise the system may be
damaged. The side airbags would not be deployed in such a case!
■
Any seat or protective covers which you fit to the driver or front passenger seats must only be of the type expressly authorized by ŠKODA. In view
of the fact that the airbag inflates out of the backrest of the seat, use of
non-approved seat or protective covers would considerably impair the protective function of the side airbag.
■
Any damage to the original seat covers in the area of the side airbag module must be repaired immediately by a specialist garage.
■
The airbag modules in the front seats must not display any damage,
cracks or deep scratches. It is not permissible to use force in order to open
the modules.
Note
■
In vehicles with side airbags at the front, a label with the word AIRBAG is lo-
cated on the front seat backrests.
■
In vehicles with rear side airbags, the word AIRBAG is located between the
entrance area and the rear seat rest.
Head airbags
The head airbags are positioned above the doors on both sides in the interior
of the car » Fig. 12 - .
In the event of a side collision the head airbag is deployed together with the
relevant side airbag and the belt tensioner on the side of the car on which the
accident occurs.
The airbag covers the windows of the front and rear doors, as well as the door
pillar when it is deployed » Fig. 12 - .
Head impact with interior parts is reduced by the inflated head airbag. The reduction in any impact to the head and the resultant minimizing of any movements of the head additionally reduce the risk of injuries to the neck area.
The head airbag also offers additional protection in the case of an offset impact by covering the front door pillar.
WARNING
General information
■
There must not be any objects in the deployment area of the head air-
bags which might prevent the airbags from inflating properly.
■
Only hang light items of clothing on the hooks fitted in the vehicle. Never
leave any heavy or sharp-edged objects in the pockets of the items of
clothing. Additionally, clothes hangers must not be used to hang up items
of clothing.
■
The installation of impermissible accessories in the vicinity of the head
airbags can considerably impair the protection offered by the head airbag in
the event of it being deployed. When the deployed head airbag is inflated,
parts of the accessories fitted could be thrown into the interior of the car
and injure the occupants » page 169.
■
The sun visors must not be swivelled towards the side windows in the
deployment area of the head airbags if any objects, such as ball-point pens,
etc. are attached to them. This might result in injuries to the occupants if
the head airbag is deployed.
■
There must not be any further persons, animals or objects positioned between the seated occupants and the deployment area of the airbag. In addition, none of the occupants should lean their head out of the window
when driving, or extend their arms and hands out of the window.
Fig. 12 Location of the head airbag/gas-filled head airbag
In the event of a severe side collision, the head airbag system offers additional
protection for the head and neck area of passengers.
18
Safety
Page 21

WARNING
The airbag control unit operates using pressure sensors located in the front
doors. For this reason, no adjustments may be carried out to the doors or
door panels (e.g. installation of additional loudspeakers). Resulting damage
can have a negative impact on the function of the airbag system. Any work
on the front doors and door panels must be carried out by a specialist garage. The following guidelines must be observed.
■
Never drive with inner door panels removed.
■
Never drive if parts of the inner door panel have been removed and the
resulting openings have not been properly sealed.
■
Never drive if the loudspeakers in the doors have been removed, unless
the loudspeaker openings have been properly sealed.
■
Always make sure that the openings are covered or filled if additional
loudspeakers or other equipment parts have been installed in the inner
door panels.
■
Always have work carried out by a ŠKODA service partner or a professional specialist garage.
Note
In vehicles with head airbags, the word AIRBAG can be seen on the B column
cladding.
Deactivating airbags
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Deactivating airbags 19
Deactivating the front passenger airbag 20
Deactivating airbags
Deactivating an airbag should be considered in cases such as the ones below.
If using a rear-facing child seat on the front passenger seat (due to different
›
legal regulations, the airbag must be deactivated if using a forwards-facing
child seat in some countries) » page 21, Transporting children safely.
If it is not possible to maintain a distance of at least 25 cm between the mid-
›
dle of the steering wheel and chest, despite the driver's seat being correctly
adjusted.
If special attachments are required in the area of the steering wheel because
›
of a physical disability.
If different seats have been fitted (e.g. orthopaedic seats without side air-
›
bags).
The front passenger airbag can be switched off with the key-operated
switch » page 20, Deactivating the front passenger airbag.
We recommend that you ask a ŠKODA service partner to deactivate any other
airbags.
Monitoring the airbag system
The operational capability of the airbag system is monitored electronically, including when one of the airbags is switched off.
Airbag deactivated using diagnostic equipment
The warning light lights up for approximately 4 seconds after the ignition
›
is switched on and then flashes again for approximately 12 seconds.
Front passenger airbag deactivated using the key switch in the storage compartment
The warning light lights up for approximately 4 seconds after the ignition
›
is switched on.
The
›
tion is switched on.
Note
■
The national regulations for switching off airbags must be observed.
■
A ŠKODA service partner will be able to inform you which, if any, of your vehi-
cle's airbags can or must be deactivated.
3rd
» Fig. 13 on page 20 warning light comes on when the igni-
Airbag system
19
Page 22
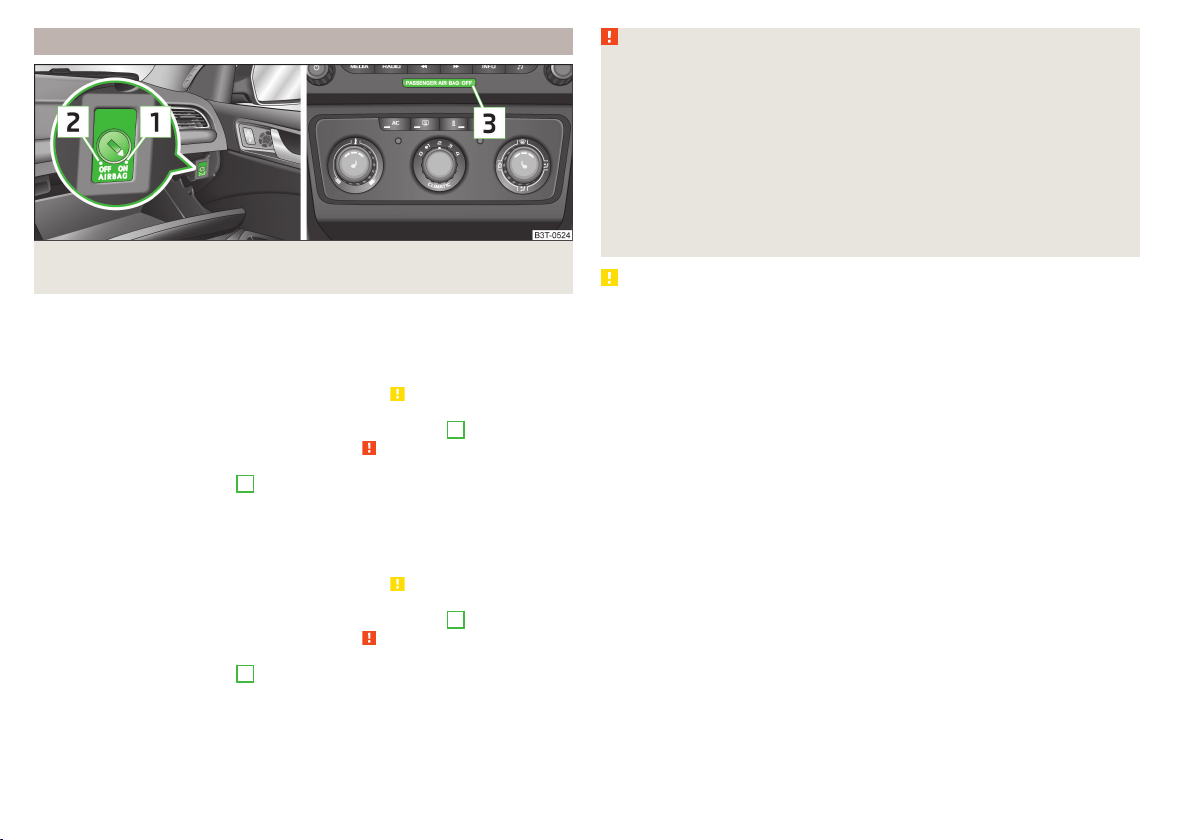
Deactivating the front passenger airbag
Fig. 13 Key switch for front passenger airbag/warning light for front passenger airbag activation/deactivation
Only the front passenger airbag is deactivated with the key switch.
Switching off
Switch off the ignition.
›
Open the storage box on the front passenger's side.
›
Fold the key bit out completely for the radio key » .
›
Carefully insert the key into the key slot in the key switch as far as the stop.
›
Use the key to turn the slot of the key switch into position 2 » Fig. 13 OFF.
›
Pull the key out of the slot in the key switch » .
›
Close the storage box on the front passenger's side.
›
Check that warning light
›
the ignition is switched on.
Switching on
Switch off the ignition.
›
Open the storage box on the front passenger's side.
›
Fold the key bit out completely for the radio key » .
›
Carefully insert the key into the key slot in the key switch as far as the stop.
›
Use the key to turn the slot of the key switch into position 1 » Fig. 13 ON.
›
Pull the key out of the slot in the key switch » .
›
Close the storage box on the front passenger's side.
›
Check that warning light
›
switched on.
3
3
in the text lights up after
lights up after the ignition is
WARNING
■
The driver is responsible for whether the airbag is switched on or switch-
ed off.
■
Only switch off the airbag when the ignition is switched off! Otherwise a
fault can occur in the system for deactivating the airbag.
■
If the warning light
deployed in an accident. Have the airbag system checked by a specialist garage immediately.
■
The key cannot be inserted in the key switch while driving.
■
Shocks can cause the key to turn in the slot and trigger the airbag!
■
The airbag could be triggered unexpectedly in an accident - it may result
in injury or death!
CAUTION
An insufficiently folded out key bit can damage the key switch!
is flashing, the front passenger airbag will not be
20
Safety
Page 23

Transporting children safely
Child seat
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Use of a child seat on the front passenger seat 21
Child safety and side airbag 22
Classification of child seats 23
Use of child seats fastened with a seat belt 23
Children are generally safer on the rear seats than on the front passenger
seat.
In contrast to adults, the muscles and bone structure of children are not yet
fully developed. Thus children are exposed to increased risk of injury.
Children should be transported in accordance with the relevant statutory provisions.
Child seats complying with the ECE-R 44 standard must be used. ECE-R stands
for: Economic Commission for Europe - Regulation.
Child seats that comply with the ECE-R 44 standard are identified with a test
mark that cannot be removed: a large E within a circle with the test number
below.
WARNING
■
The national legal requirements must be observed when using child
seats.
■
One should never carry children, and also not babies! - on one's lap.
■
Never leave children unattended in the vehicle. Certain outside climatic
conditions can cause life-threatening temperatures in the vehicle.
■
The child must be secured in the vehicle during the entire journey! Otherwise, the child would be thrown through the vehicle in the event of an accident, causing fatal injuries to both the child and other occupants.
■
Children are exposed to an increased risk of injury in the event of an accident if they lean forward or adopt an incorrect seated position when the
vehicle is moving. This particularly applies to children who are transported
on the front passenger seat as they can suffer severe, or even fatal injuries
if the airbag system is deployed!
WARNING (Continued)
■
Pay particular attention to the information provided by the manufacturer
of the child safety seat regarding the correct routing of the belt. Seat belts
which are not correctly adjusted can themselves cause injuries even in minor accidents.
■
Safety belts must be checked to ensure that they are running properly.
One should also ensure that the belt is not damaged by sharp-edged fittings.
■
The front passenger airbag must be deactivated if using a rear-facing
child seat on the front passenger seat. Further information » page 21, Use
of a child seat on the front passenger seat.
CAUTION
When installing a child seat in which the child faces forward, adjust the head
restraints so that they are as high as possible.
Note
We recommend that you use child seats from ŠKODA Original Accessories.
These child seats were developed and also tested for use in ŠKODA vehicles.
They meet the ECE-R 44 standard.
Use of a child seat on the front passenger seat
Never use a backwards-facing child restraint system on a seat that is protected by an active airbag installed in front of it. This could cause the child severe
injury or even death.
Fig. 14
Sticker on the B column on the
front passenger side.
Transporting children safely
21
Page 24
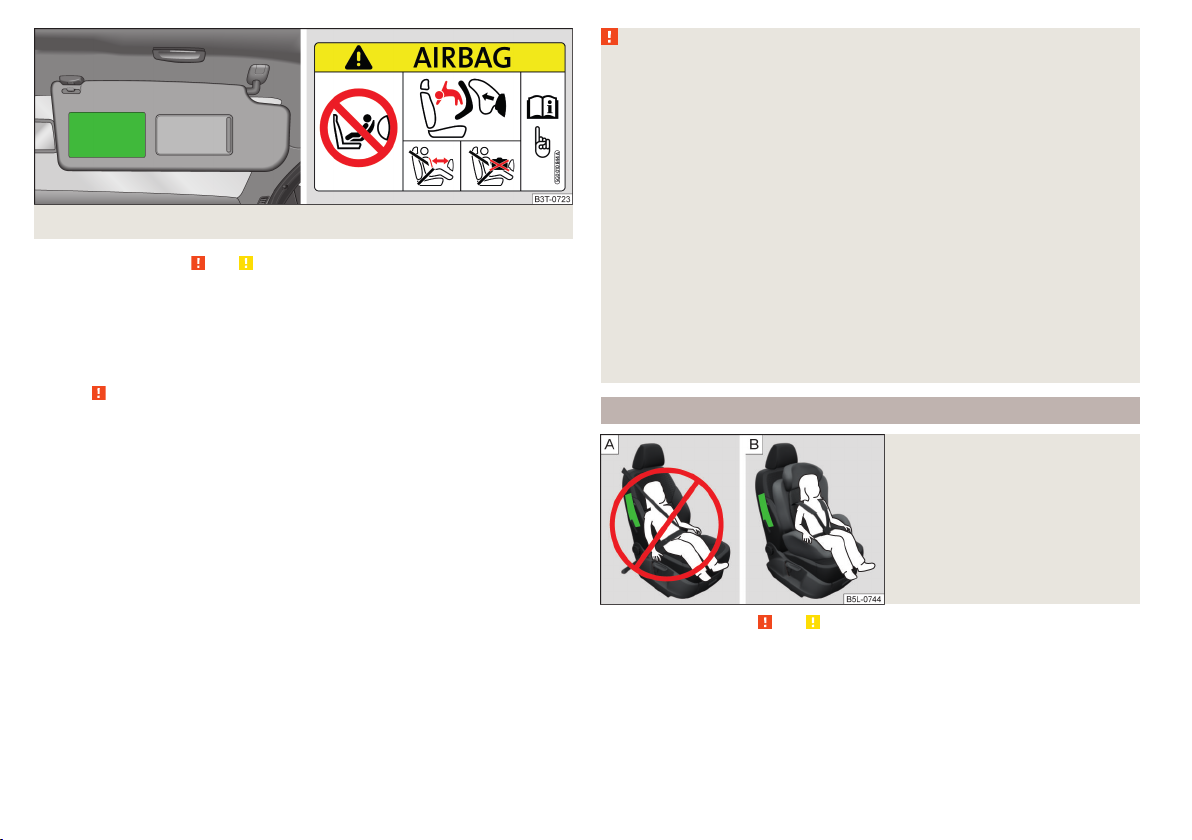
Fig. 15
Front passenger sun visor / sticker
Read and observe and on page 21 first.
For safety reasons, we recommend that you install child seats on the rear
seats whenever possible.
The following instructions must be followed when using a child seat on the
front passenger seat.
The front passenger airbag must be deactivated if using a rear-facing child
›
seat » .
If possible, adjust the front passenger seat backrest so that it is as vertical,
›
so as to ensure secure contact between the passenger seat backrest and the
back of the child seat.
If possible, move the front passenger seat backwards so that there is no con-
›
tact between the front passenger seat and the child seat behind it.
With child safety seats in groups 2 or 3, make sure that the loop-around fit-
›
tings attached to the child seat headrest is positioned in front of or at the
same height as the loop-around fittings on the B pillar on the passenger side.
Set the height-adjustable front passenger seat as high up as possible.
›
Set the front passenger seat belt as high up as possible.
›
Place and fasten the child seat on the seat and the child in the child seat ac-
›
cording to the specifications in the manufacturer's user manual of the child
seat .
WARNING
■
The front passenger airbag must be deactivated if using a rear-facing
child seat on the front passenger seat » page 19, Deactivating airbags.
■
Never use a rear-facing child seat on the front passenger seat if the passenger airbag is activated. This child safety seat is positioned in the deployment area of the front passenger airbag. The airbag may cause the child severe, or even fatal injuries, in the event of it being deployed.
■
This fact is also indicated by the sticker that can be found in one of the
following locations.
■
On the B-column on the front passenger side » Fig. 14. The sticker is
visible upon opening the front passenger door.
■
On the front passenger's sun visor. In some countries, the sticker is lo-
cated on the front passenger's sun visor » Fig. 15.
■
With child safety seats in groups 2 or 3, make sure that the loop-around
fittings attached to the child seat headrest is positioned in front of or at
the same height as the loop-around fittings on the B pillar on the passenger side.
■
As soon as the rear-facing child seat is no longer being used on the passenger seat, the front passenger airbag should be re-activated again.
Child safety and side airbag
Fig. 16
Incorrect seated position of a
child who is not properly secured
– risk from the side airbag/Child
properly protected by safety seat
Read and observe and on page 21 first.
The child must not be positioned in the area into which the side airbag will deploy » Fig. 16 - .
There must be sufficient room between the child and the area into which the
side airbag will deploy to allow the airbag to provide as much protection as
possible » Fig. 16 - .
22
Safety
Page 25
WARNING
■
Children must never be seated with their head in the deployment area of
the side airbag – risk of injury!
■
Do not place any objects within the deployment area of the side airbags –
risk of injury!
Classification of child seats
Read and observe and on page 21 first.
Classification of child seats according to the ECE-R 44 standard.
Group Weight of the child Approximate age
0 up to 10 kg up to 9 months
0+ up to 13 kg up to 18 months
1 9-18 kg up to 4 years
2 15-25 kg up to 7 years
3 22-36 kg over 7 years
Use of child seats fastened with a seat belt
Read and observe
Overview of the usability of child seats fastened with a seat belt on each of
the seats in accordance with the ECE-R 16 standard.
Group
0
up to 10 kg
0+
up to 13 kg
1
9-18 kg
2
15-25 kg
3
22-36 kg
Front passenger
and on page 21 first.
seat
U U U
U U U
U U U
U U U
U U U
Rear seats
outside
Rear seat
Center
“Universal” child seat category - a child seat designed to be attached to
U
the seat using the seat belt.
Fastening systems
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Anchor eyelets for the ISOFIX system 23
Use of child seats with the ISOFIX system 24
Anchor eyelets for the TOP TETHER system 24
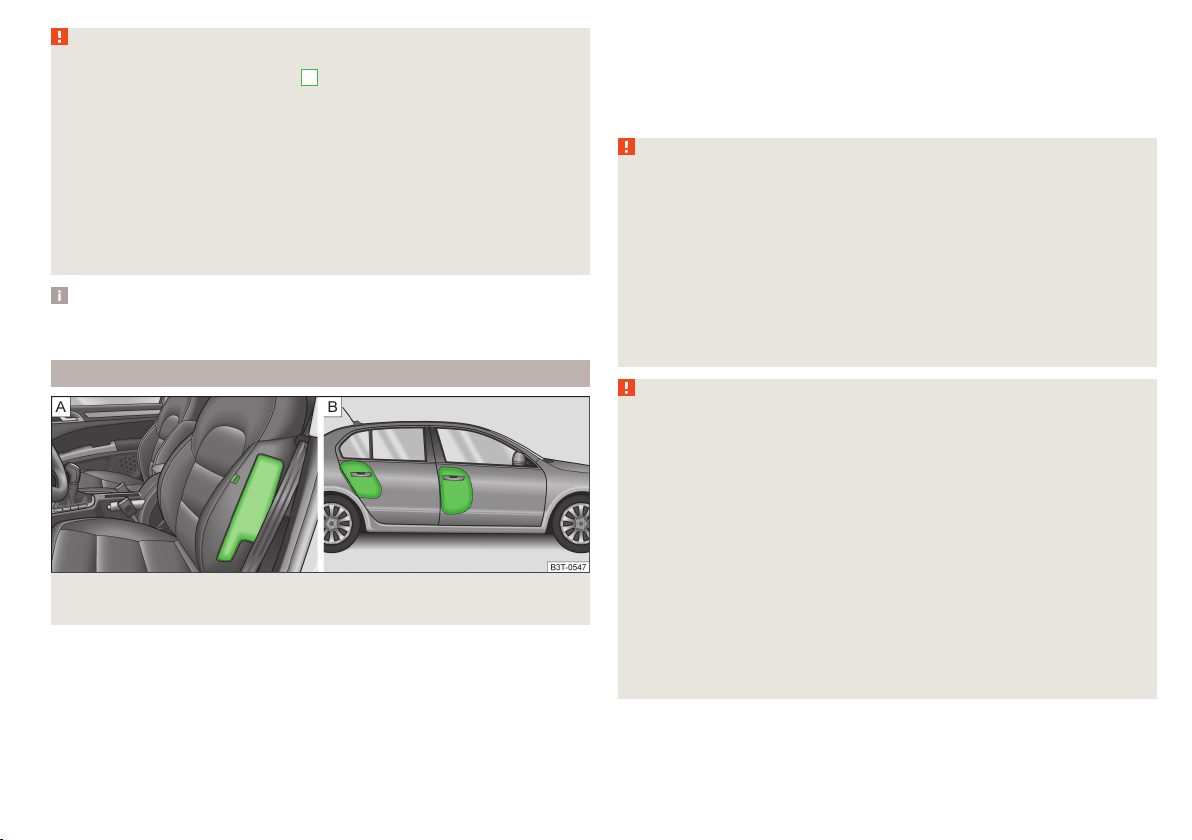
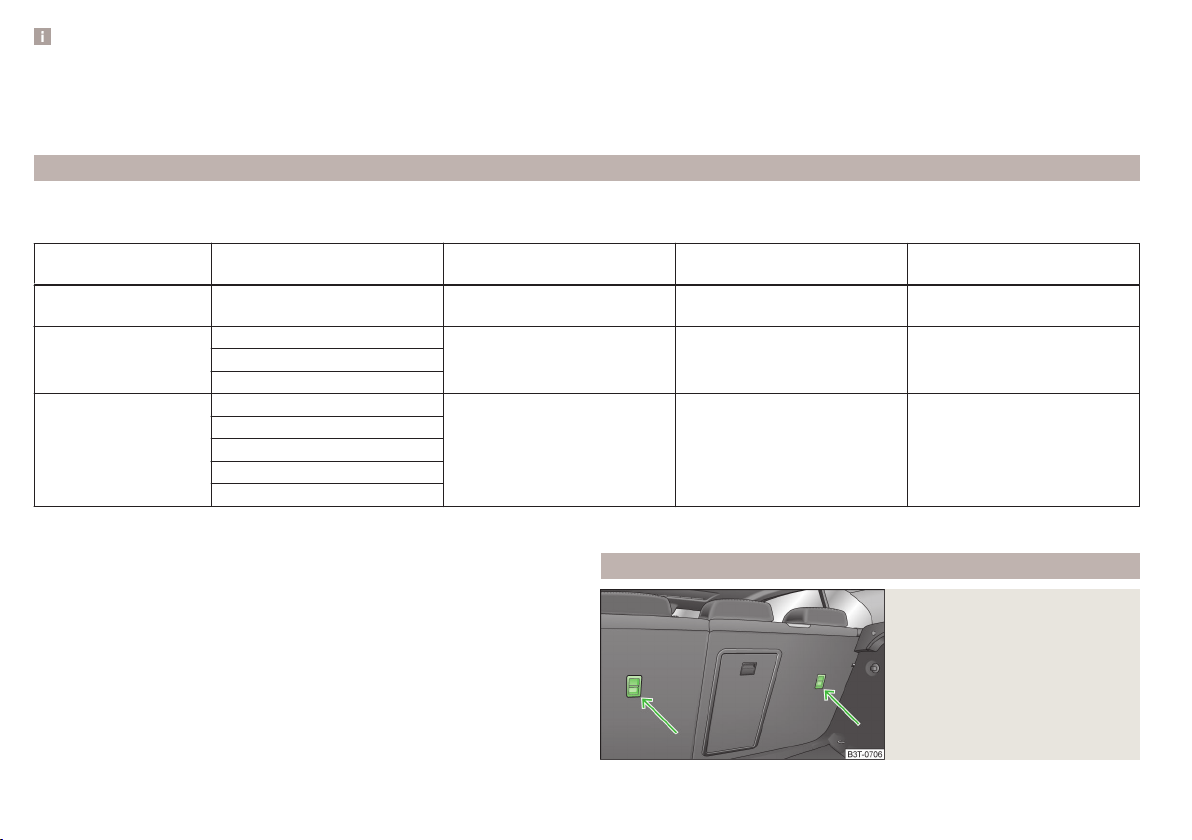
Anchor eyelets for the ISOFIX system
Fig. 17
Labels on the ISOFIX system
There are two locking eyes between the seat backrest and the seat cushion of
the outer rear seats and front passenger seat for fixing the ISOFIX system
child seat in place.
On the rear outside seats, the fixing eyes are located below the upholstery.
The places are marked with labels with the ISOFIX logo » Fig. 17.
WARNING
■
Always refer to the instructions from the manufacturer of the child seat
when installing and removing a child seat with the ISOFIX system.
■
Never attach other child seats, belts or objects to the anchor eyelets intended for the installation of a child seat with the ISOFIX system – risk to
life.
Transporting children safely
23
Page 26
Note
■
A child seat fitted with the ISOFIX system can only be mounted in a vehicle
fitted with an ISOFIX system if the child seat has been approved for this type
of vehicle. Further information is available from a ŠKODA Partner.
■
Child seats with the ISOFIX system can be purchased from ŠKODA Original
Accessories.
Use of child seats with the ISOFIX system
Overview of the usability of child seats with the ISOFIX system on each of the
seats in accordance with the ECE-R 16 standard.
Group
0
up to 10 kg
0+
up to 13 kg
Size class
of the child seat
a)
Front passenger seat
E X IL-SU X
E
X IL-SU XD
C
b)
Outer rear seats Rear seat middle
D
1
9-18 kg
C
B
X
B1
IL-SU
IUF
A
a)
The size category is shown on the label attached to the child seat.
b)
If the front passenger seat is fitted with the ISOFIX system attachment points, it is suited for the installation of an ISOFIX child seat with the “Semi-Universal” approval.
The seat is suited for installation of an ISOFIX child seat with “Semi-
IL-SU
Universal” approval. The “Semi-Universal” category means that the child
Anchor eyelets for the TOP TETHER system
seat with the ISOFIX system is approved for your vehicle. Observe the
list of vehicles that comes with the child seat.
The seat is suitable for the installation of an ISOFIX child seat with
IUF
“Universal” approval and attachment with the TOP TETHER belt.
The seat is not fitted with fixing eyes for the ISOFIX system.
X
24
Safety
X
Fig. 18
Anchor eyelets on the TOP
TETHER system
Page 27
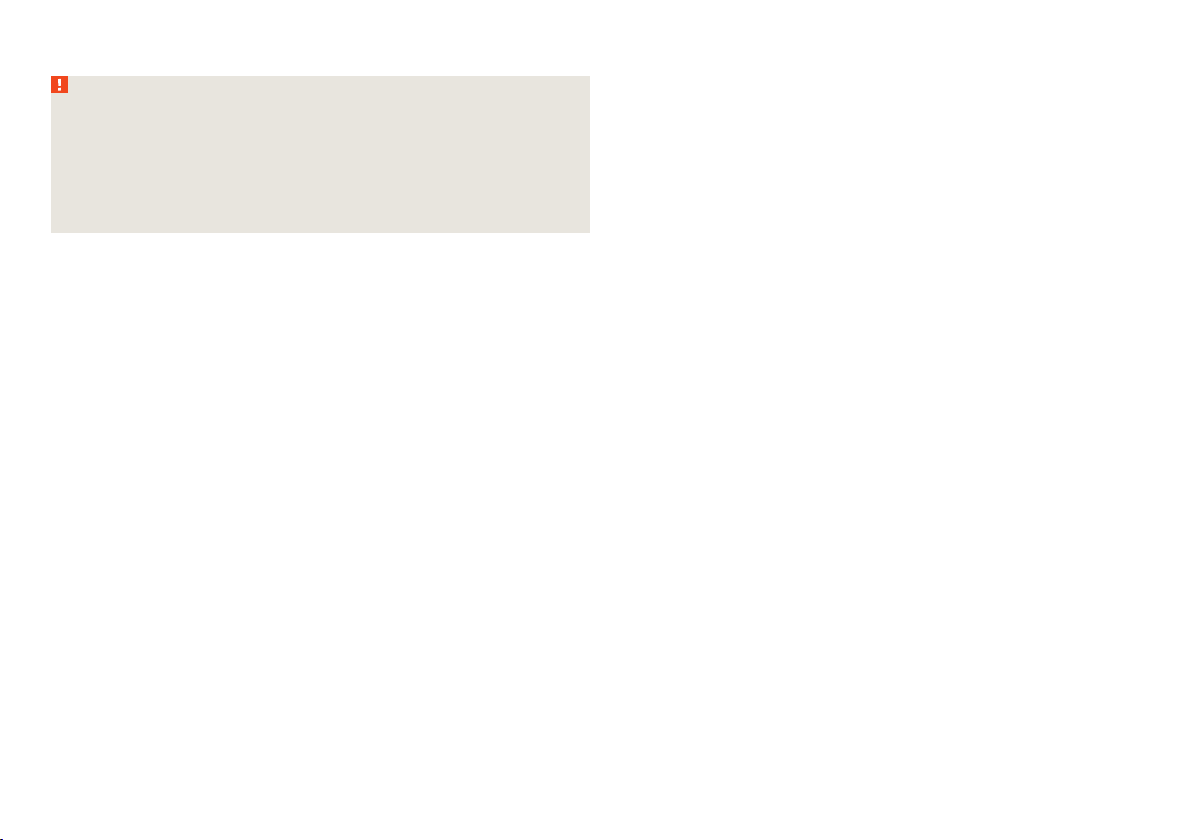
The anchor eyelets for attaching the belt for a child seat with the TOP TETHER
system are located on the rear side of the outer rear seat backrests » Fig. 18.
WARNING
■
Always refer to the instructions from the manufacturer of the child seat
when installing and removing a child seat with the TOP TETHER system.
■
Only use child seats with the TOP TETHER system on the seats with the
locking eyes.
■
Only ever attach one belt from the child seat to a locking eye.
■
On no account should you equip your vehicle, e.g. mount screws or other
anchorage points.
Transporting children safely
25
Page 28
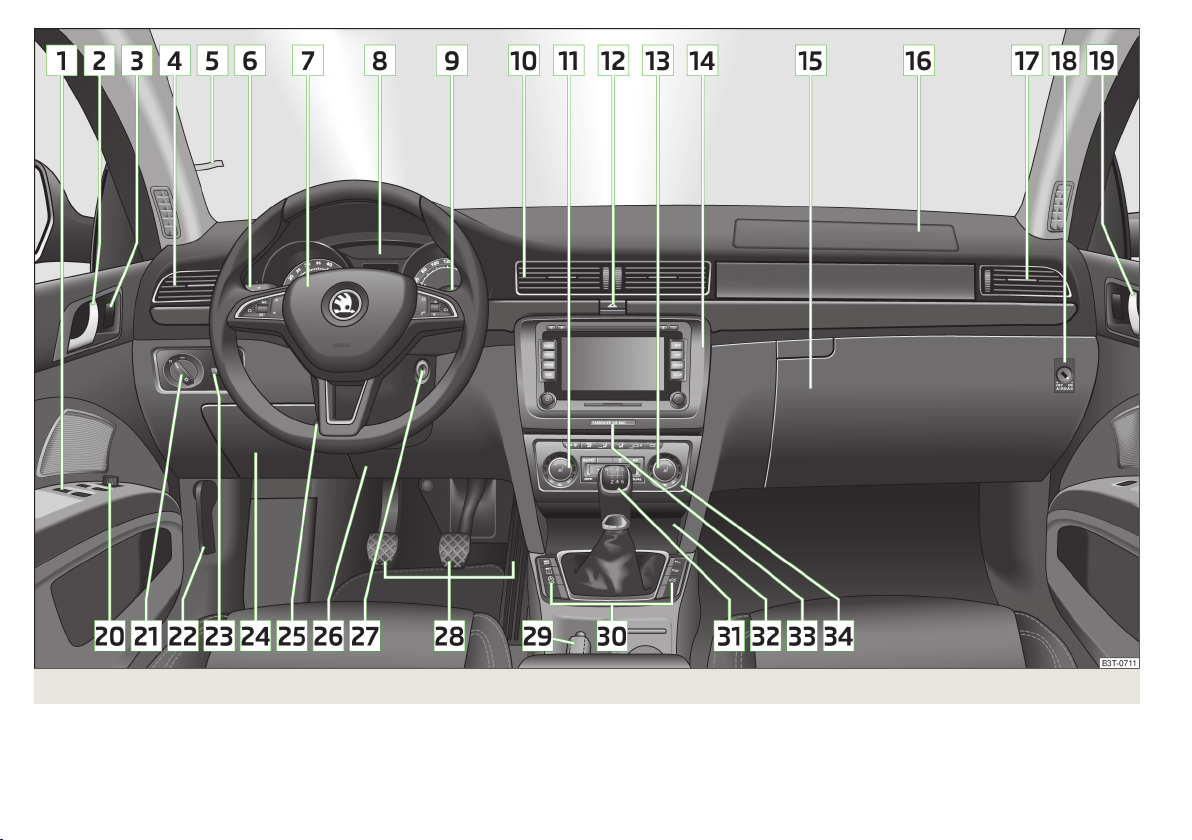
Fig. 19 Cockpit
26
Operation
Page 29

Operation
Cockpit
Overview
1
Electric windows 59
2
Door opening lever 53
3
Central locking system 52
4
Air jet 108
5
Parking ticket holder
6
Operating lever:
Turn signal light, headlight and parking light, headlight
›
flasher 67
Speed regulating system 158
›
7
Steering wheel:
With horn
›
With driver’s front airbag 15
›
with pushbuttons for radio, navigation system phone and in-
›
formation system 120, 132
8
Instrument cluster: Instruments, warning lights and display 28
9
Operating lever:
Information system 39
›
Windscreen wiper and wash system 75
›
10
Air outlets in the central part of the dash panel 108
11
Regulator for left seat heating 83
12
Button for hazard warning light system
13
Regulator for right seat heating 83
14
Depending on equipment fitted:
Radio
›
Navigation system
›
15
Storage compartment on the front passenger side 92
16
Front passenger airbag 15
17
Air jet 108
18
Key switch for switching off the front passenger airbag (in front
passenger storage compartment) 20
19
Door opening lever 53
20
Electric exterior mirror adjustment 78
21
Light switch 66
22
Bonnet release lever 183
23
Regulator for the instrument lighting and regulator for the headlight beam range adjustment 66, 66
24
Storage compartment on the driver's side 87
25
Lever for adjusting the steering wheel 8
26
Driver’s knee airbag 16
27
Ignition lock 136
28
Pedals 142
29
Handbrake 141
30
Bars with buttons depending on the equipment fitted:
START STOP 159
›
Tyre control display 38
›
Traction control TCS 152
›
Electronic Stability Control ESC 151
›
Park Assist 154
›
Parking aid 153
›
Tailgate operation (Superb Combi) 57
›
31
Depending on equipment fitted:
Gearshift lever (manual gearbox) 141
›
Selector lever (automatic gearbox) 142
›
32
Depending on equipment fitted:
Ashtrays 89
›
Storage compartment 88
›
33
Warning light for the deactivated front seat passenger airbag 20
34
Depending on equipment fitted:
70
Operating controls for the air conditioning system 110
›
Operating controls for Climatronic
›
Note
The arrangement of the controls right-hand drive models may differ from the
layout shown in » Fig. 19. The symbols on the controls and switches are the
same as for left-hand drive models.
113
Cockpit
27
Page 30
Instruments and Indicator Lights
Instrument cluster
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Overview 28
Revolutions counter 29
Speedometer 29
Coolant temperature gauge 29
Display 29
Fuel gauge 30
Counter for distance driven 30
30
Display of the second speed 31
Display in rear centre console 31
Auto Check Control 31
Fault display
If there is a fault in the instrument cluster, the Error message will appear in
the display. Have the fault rectified as soon as possible by a specialist garage.
WARNING
■
Concentrate fully at all times on your driving! As the driver you are fully
responsible for road safety.
■
Never operate the controls in the instrument cluster while driving - risk of
accident. Operate the controls only when the vehicle is at a standstill.
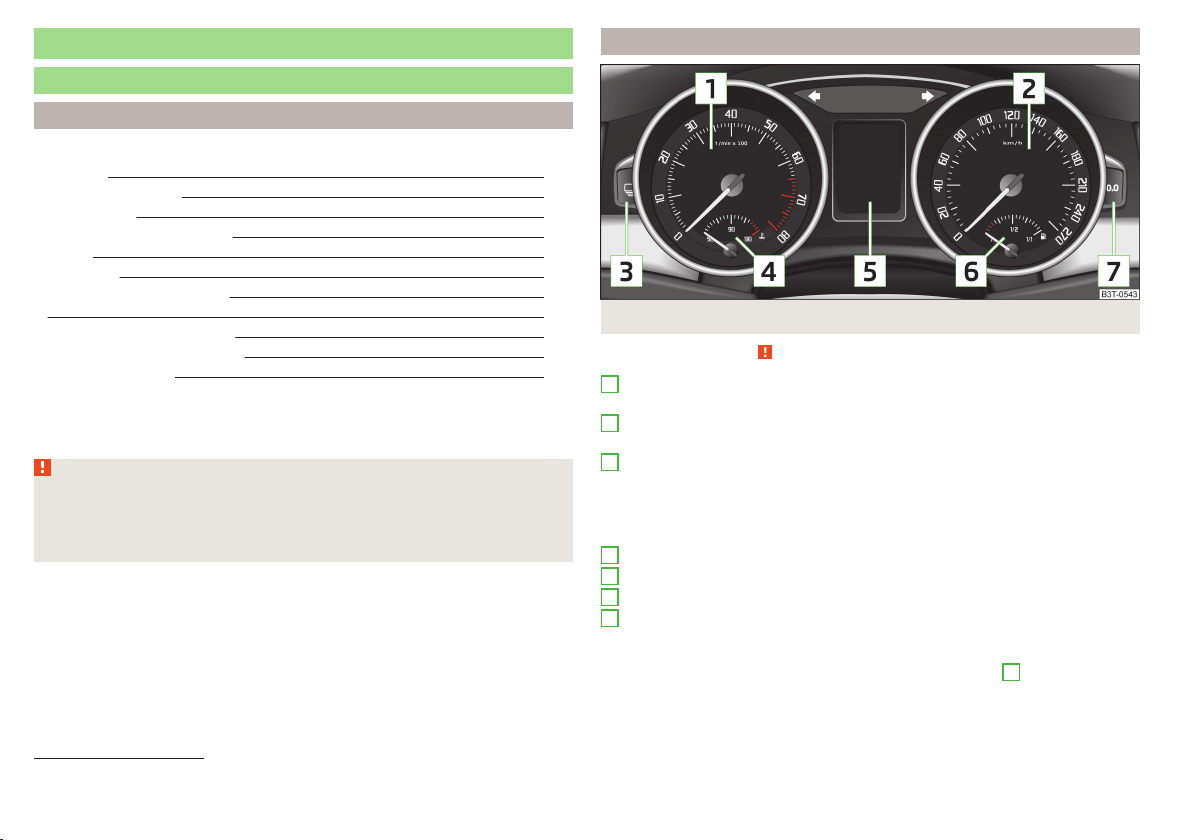
Overview
Fig. 20 Instrument cluster
Read and observe on page 28 first.
1
Engine revolutions counter » page 29
with warning lights » page 32
›
2
Speedometer » page 29
with warning lights » page 32
›
3
Button for display mode:
Time settings » page 30
›
Enable/disable the display of the second speed1) » page 31
›
Service intervals - Display of the number of days and kilometres remain-
›
ing until the next service1) » page 46
4
Coolant temperature gauge » page 29
5
Display » page 29
6
Fuel gauge » page 30
7
Button for:
Reset trip meter » page 30
›
Setting the time » page 30
›
enable / disable the mode selected by means of the 3 key
›
1)
Applies to vehicles with a segment display.
28
Operation
Page 31

Revolutions counter
Read and observe on page 28 first.
The red scale of the revolution counter 1 » Fig. 20 on page 28 indicates the
range in which the system begins to limit the engine speed. The system automatically restricts the engine speed to a steady limit.
You should shift into the next higher gear before the red scale of the revolution counter is reached, or select mode D on the automatic gearbox.
Follow the recommended gear to prevent engine speeds that are too high or
too low » page 40.
Speedometer
Read and observe
Warning against excessive speeds
An audible warning signal will sound when the vehicle speed exceeds 120 km/
h1). The audible warning signal is switched off when the vehicle speed falls below 120 km/h.
on page 28 first.
Coolant temperature gauge
Fig. 21
Coolant temperature gauge
Read and observe on page 28 first.
The coolant temperature gauge » Fig. 21 only operates when the ignitions is
switched on.
Cold range
The pointer in the left of the scale indicates that the engine has not yet
reached its operating temperature. Avoid high speeds, full throttle and high
engine loads. This prevents possible damage to the engine.
The operating range
The engine has reached its operating temperature as soon as the pointer
moves into the middle of the scale. At very high ambient temperatures or
heavy engine loads, the pointer may move even further to the right.
High temperature range
If the pointer reaches the red area of the scale, the coolant temperature is too
high. Further information » page 34.
CAUTION
■
Additional headlights and other attached components in front of the air inlet
impair the cooling efficiency of the coolant.
■
Never cover the radiator - there is a risk of the engine overheating.
Display
Fig. 22
Display types
Read and observe on page 28 first.
The following information will be displayed.
Distance travelled » page 30
›
Time » page 30
›
Details of the information system » page 39
›
Details of the service interval display » page 46
›
1)
This function is only valid for some countries.
Instruments and Indicator Lights
29
Page 32

Display types » Fig. 22.
Segment display
MAXI DOT display
CAUTION
Pull out the ignition key if coming in contact with the display (e.g. when cleaning) to prevent any possible damage. On vehicles with the KESSY system,
switch off the ignition and open the driver's door.
Fuel gauge
Counter for distance driven
Fig. 24
Segment display / MAXI DOT display
Fig. 23
Fuel gauge
Read and observe on page 28 first.
The fuel gauge » Fig. 23 only operates if the ignition is switched on.
The fuel tank has a capacity of about 60 litres. If the amount of fuel reaches
the reserve area (the pointer reaches the red scale range), the indicator symbol
is illuminated » page 37.
CAUTION
Never drive until the fuel tank is completely empty! The irregular supply of fuel
can cause misfiring. This can result in considerable damage to parts of the engine and the exhaust system.
Note
After filling up, it can occur that during dynamic driving (e.g. numerous curves,
braking, driving downhill and climbing a steep hill) the fuel gauge indicates approx. a fraction less. When stopping or during less dynamic driving, the fuel
gauge displays the correct fuel level again. This is not a fault.
30
Operation
Read and observe on page 28 first.
Display » Fig. 24
A
Trip odometer
B
Odometer
Daily trip counter (trip)
The counter indicates the distance you have driven since it was last reset - in
steps of 100 metres or 1/10 of a mile.
Reset trip meter
Press and hold the 7 » Fig. 20 on page 28 button.
›
Odometer
The odometer indicates the total distance which the vehicle has been driven.
Note
If the second speed display is enabled on vehicles with a segment display, this
speed will be shown instead of the odometer.
Read and observe on page 28 first.
Use buttons 3 and 7 to set the clock » Fig. 20 on page 28.
3
The choice to change the display (hours or minutes).
7
The change of the displayed value.
In vehicles equipped with the MAXI DOT display, it is also possible to set the
Time in the Time menu » page 45.
Page 33

Display of the second speed
Read and observe on page 28 first.
The display can show the current speed in mph1).
This feature is provided for driving in countries with different speed units.
Maxi DOT display
The display of the second speed can be set in the Alt. speed dis. menu
item » page 45, Settings.
Segment display
Press key 3 » Fig. 20 on page 28repeatedly, until the odometer display
›
flashes » page 30.
Press the 7 key while the display flashes.
›
The second speed is displayed instead of the odometer.
The display of the second speed can be disabled in the same way.
Display in rear centre console
Fig. 25
Centre console at rear: Display
Read and observe on page 28 first.
The time and the outside temperature is displayed on the display in the rear
centre console when the ignition is switched on » Fig. 25.
The values are taken over by the instrument cluster.
Auto Check Control
Read and observe on page 28 first.
Vehicle condition
Certain functions and conditions of individual vehicle systems are checked
continuously when the ignition is switched on.
Some error messages and other information are displayed in the MAXI DOT
display. The messages are displayed simultaneously with the icons in the MAXI
DOT display or with the warning lights in the instrument cluster » page 32,
Warning lights.
The menu item Vehicle status is shown in the main menu of the MAXI DOT
display whenever at least one fault message exists. After selecting this menu,
the first of the error messages is displayed. Several error messages are shown
on the display under the message e.g. 1/3. This indicates that the first of a total of three error messages is being displayed.
Warning symbols in the MAXI DOT display
Problem with the engine oil pressure
If the symbol is shown in the MAXI DOT display, you must have your vehicle
checked immediately by a specialist garage. The information about the maximum permissible engine speed is displayed together with this symbol.
Clutches of the automatic DSG gearbox are too hot
If the symbol appears in the MAXI DOT display, this indicates that the temperature of the automatic DSG gearbox clutched is too high.
Engine oil pressure too low » page 34
Clutches of the automatic DSG gearbox are
too hot
Check engine oil level,
engine oil sensor defective
Thickness of brake pads » page 38
Problem with engine oil pressure » page 31
» page 31
» page 35
1)
For models with the speedometer in mph, the second speed is displayed in km/h.
Instruments and Indicator Lights
31
Page 34

The following message is shown in the MAXI DOT display.
Gearbox overheated. Stop! Log book!
do not continue to drive! Stop the vehicle, switch off the engine, and wait
until the icon goes out – risk of gearbox damage! You can continue your
journey as soon as the symbol disappears.
WARNING
If you have to stop for technical reasons, then park the vehicle at a safe
distance from the traffic, switch off the engine and activate the hazard
warning lights system » page 70. The warning triangle must be set up at
the prescribed distance - observe the national legal provisions when doing
so.
Note
■
If the MAXI DOT display shows warning messages, these messages must be
confirmed in order to access the main menu » page 40 .
■
As long as the operational faults are not rectified, the symbols are always indicated again. After they are displayed for the first time, the symbols continue
to be indicated without any extra messages for the driver.
Warning lights
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Handbrake 33
Brake system 33
Seat belt warning light 33
Generator 33
Door open 34
Engine oil pressure 34
Coolant 34
Bonnet 34
Boot lid 34
Power steering / steering lock (system KESSY) 34
Engine oil level 35
Traction Control System (ASR) 35
Electronic Stability Control (ESC) 35
Antilock brake system (ABS) 36
Rear fog light 36
Lamp failure 36
Adaptive headlights (AFS) 36
Exhaust inspection system 36
Glow plug system (diesel engine) 36
Engine performance check (petrol engine)
Diesel particulate filter (diesel engine) 37
Fuel reserve 37
Airbag system 38
Tyre inflation pressure 38
Windscreen washer fluid level 38
Pads 38
Turn signal system 38
Low beam 39
Fog lights 39
Cruise control system 39
Selector lever lock / starter (system KESSY) 39
Main beam 39
The warning lights indicate certain functions or faults.
Some warning lights can be accompanied by acoustic signals and messages in
the display of the instrument cluster.
After switching on the ignition, some warning lights illuminate briefly as a
function test.
If the tested systems are OK, the corresponding warning lights go out a few
seconds after switching on the ignition or after starting the engine.
37
32
Operation
Page 35

WARNING
■
Ignoring illuminated warning lights and related messages or instructions
in the display of the instrument cluster may lead to serious personal injury
or damage to the vehicle.
■
If you have to stop for technical reasons, then park the vehicle at a safe
distance from the traffic, switch off the engine and activate the hazard
warning lights system » page 70. The warning triangle must be set up at
the prescribed distance - observe the national legal provisions when doing
so.
■
The engine compartment of your car is a hazardous area. The following
warning instructions must be followed at all times when working in the engine compartment » page 182, Engine compartment.
Handbrake
Read and observe
The warning light illuminates if the handbrake is applied.
An acoustic signal will sound if you drive the vehicle above 6 km/h for at least
3 seconds while the handbrake is applied.
The following message is shown in the MAXI DOT display.
Release parking brake!
on page 33 first.
WARNING
■
If the warning light is displayed simultaneously with warning light
» page 36, Antilock brake system (ABS), do not continue your
journey! Seek help from a specialist garage.
■
A fault to the ABS system or the braking system can increase the vehi-
cle's braking distance – risk of accident!
■
The following guidelines should be observed when opening the bonnet
and checking the brake fluid level » page 182, Engine compartment.
Seat belt warning light
Read and observe on page 33 first.
The warning light illuminates as a reminder for the driver and front passenger to fasten seat belts.
The indicator light goes off after the respective seat belt is fastened.
If the driver or front passenger has not fastened their seat belt and the vehicle
speed is more than 20 km/h, the warning light flashes and you will hear an
acoustic signal.
The warning signal is switched of and the indicator light is permanently lit if
the driver and front passenger have not fastened their seat belts within the
next 90 seconds.
Brake system
Read and observe
The indicator light illuminates if the brake fluid level in the braking system is
too low or there is a fault in the ABS.
The following message is shown in the MAXI DOT display.
Brake fluid: Log book!
Stop the vehicle, switch off the engine, and check the level of the brake flu-
›
id » page 189 » .
on page 33 first.
Generator
Read and observe
If the warning light illuminates when the engine is running, the vehicle battery is not being charged.
Seek assistance from a specialist garage immediately. The electrical system requires checking.
CAUTION
If the warning light (cooling system fault) lights up in addition to the
warning light while driving, do not continue to drive! Stop the engine there is a risk of engine damage! Seek help from a specialist garage.
on page 33 first.
Instruments and Indicator Lights
33
Page 36

Door open
Read and observe on page 33 first.
The indicator light illuminates if one or several doors are opened.
Engine oil pressure
Read and observe on page 33 first.
When the warning light is flashing , the engine oil pressure is too low.
The following message is shown in the MAXI DOT display.
Oil pressure: Log book!
Stop the vehicle, switch off the engine, and check the engine oil lev-
›
el » page 186.
If the warning light flashes, do not drive any further , even if the oil level is
correct! Also do not leave the engine running at an idling speed.
Seek help from a specialist garage.
Coolant
Read and observe on page 33 first.
If the warning light lights up or flashes, either the coolant temperature is
too high or the coolant level is too low.
The following message is shown in the MAXI DOT display.
Check coolant! Log book!
Stop the vehicle, switch off the engine, and check the coolant lev-
›
el » page 188.
If the coolant level is too low, add coolant to the reservoir » page 188.
›
If the indicator light does not illuminate after adding coolant and switching
on the ignition, you may continue your journey.
If the coolant level is within the specified range and the indicator light is still
illuminated, then there may be a malfunction of the cooling fan.
Check the fuse for the radiator fan, replace if necessary » page 217, Fuses in
›
the engine compartment.
If the coolant level and fan fuse are both OK but the indicator light is still
illuminated, do not continue your journey!
Seek help from a specialist garage.
WARNING
■
Carefully open the coolant expansion bottle. If the engine is hot, the cooling system is pressurized - risk of scalding! It is therefore best to allow the
engine to cool down before removing the cap.
■
Do not touch the radiator fan. The radiator fan may switch itself on automatically even if the ignition is off.
CAUTION
■
Additional headlights and other attached components in front of the air inlet
impair the cooling efficiency of the coolant.
■
Never cover the radiator - there is a risk of the engine overheating.
Bonnet
Read and observe on page 33 first.
The indicator light illuminates if the bonnet is unlocked.
Boot lid
Read and observe on page 33 first.
The indicator light illuminates if the boot lid is opened.
Power steering / steering lock (system KESSY)
Read and observe on page 33 first.
Power steering
If the indicator light illuminates, this indicates a partial failure of the power
steering and the steering forces can be greater.
If the indicator light illuminates, this indicates a complete failure of the
power steering and the steering assist has failed (significantly higher steering
forces).
Stop the car, turn the ignition off and on again.
›
The powered steering is fully functional again if the or warning light does
not illuminate after you switch the engine back on.
34
Operation
Page 37

If the warning light or illuminates again, then immediately obtain help
from an authorised dealer.
Steering lock (KESSY system)
As long as the warning light is flashing, the steering lock cannot be released.
If the warning light flashes, a signal tone sounds, and the following message appears in the MAXI DOT- display steering column lock. If Workshop! appears the electrical steering lock is faulty. Seek assistance from a specialist garage immediately.
If the warning light flashes, a beep sounds and in the MAXI DOT display the
message Steering lock defective appears, then the electric steering lock is
broken. Park the car, do not continue the journey. After switching off the
ignition, it is then no longer possible to lock the steering, to activate the electrical components (e.g. radio, navigation system), to switch on the ignition
again and to start the engine. Seek help from a specialist garage.
Note
The warning light illuminates after the ignition is switched on if the vehicle's battery has been disconnected and reconnected. If the warning light
does not go out after moving a short distance, this means there is an error in
the system. Seek assistance from a specialist garage immediately.
Engine oil level
Read and observe on page 33 first.
The indicator light lights up (oil quantity too low)
The following message is shown in the MAXI DOT display.
Check oil level!
Stop the vehicle, switch off the engine, and check the engine oil lev-
›
el » page 186.
The warning light will go out if the bonnet is left open for more than 30 seconds. If no engine oil has been replenished, the warning light will come on
again after driving about 100 km.
The indicator light flashes (engine oil level sensor faulty)
The following message is shown in the MAXI DOT display.
Oil sensor: Workshop!
If the engine oil level sensor is faulty, the warning light flashes several
times and an audible signal sounds when the ignition is turned on.
Seek assistance from a specialist garage immediately.
Traction Control System (ASR)
Read and observe on page 33 first.
The warning light flashes to show that the ASR is currently operating.
If the warning light illuminates, there is a fault in the ASR.
The following message is shown in the MAXI DOT display.
Error: Traction control (ASR)
Seek assistance from a specialist garage immediately.
If the warning light illuminates immediately after you start the engine, the
ASR might be switched off due to technical reasons.
Switch the ignition off and on again.
›
The ASR is fully functional again if the warning light no longer illuminates
after you switch the engine back on.
Further information » page 152.
Note
The warning light illuminates after the ignition is switched on if the vehicle's battery has been disconnected and reconnected. If the warning light
does not go out after moving a short distance, this means there is an error in
the system. Seek assistance from a specialist garage immediately.
Electronic Stability Control (ESC)
Read and observe
The warning light flashes to show that the ESC is currently operating.
If the warning light illuminates, there is a fault in the ESC.
The following message is shown in the MAXI DOT display.
Error: Electronic Stability Control (ESC)
Seek assistance from a specialist garage immediately.
on page 33 first.
Instruments and Indicator Lights
35
Page 38

If the warning light illuminates immediately after you start the engine, the
ESC might be switched off due to technical reasons.
Switch the ignition off and on again.
›
The ESC is fully functional again if the warning light no longer illuminates
after you switch the engine back on.
Further information » page 151.
Note
The warning light illuminates after the ignition is switched on if the vehicle's battery has been disconnected and reconnected. If the warning light
does not go out after moving a short distance, this means there is an error in
the system. Seek assistance from a specialist garage immediately.
Antilock brake system (ABS)
Read and observe on page 33 first.
If the warning light illuminates, there is a fault in the ABS.
The following message is shown in the MAXI DOT display.
Error: ABS
The vehicle will only be braked by the normal brake system without the ABS.
Seek assistance from a specialist garage immediately.
WARNING
■
If the warning light is displayed at the same time as the warning light
» page 33, Brake system, do not continue your journey! Seek help
from a specialist garage.
■
A fault to the ABS system or the braking system can increase the vehicle's braking distance – risk of accident!
Rear fog light
Read and observe
The warning light illuminates when the rear fog light is switched on.
on page 33 first.
Lamp failure
Read and observe on page 33 first.
The indicator light illuminates if a lamp is faulty.
The indicator light illuminates within a few seconds after switching on the
ignition or when a light with a faulty lamp is switched on.
The following message, for example, may be shown in the MAXI DOT display.
INFORMATION Check front right low beam!
Adaptive headlights (AFS)
Read and observe on page 33 first.
If the indicator light flashes for 1 minute while driving or after switching on
the ignition, there is a problem with the adaptive headlights.
The following message is shown in the MAXI DOT display.
Cornering light (AFS) has no function. Log book!
When the AFS mode “tourist light” (travel mode) is active » page 69, the
warning light flashes for 10 seconds each time the ignition is switched on.
Exhaust inspection system
Read and observe on page 33 first.
If the warning light illuminates, there is a fault in the exhaust inspection
system. The system allows the vehicle to run in emergency mode.
Seek assistance from a specialist garage immediately.
Glow plug system (diesel engine)
Read and observe on page 33 first.
The warning light illuminates after the ignition has been switched on . Once
the light has gone out, the engine can be started immediately.
There is a fault in the glow plug system if the indicator light does not come
on at all or lights up continuously.
If the warning light begins to flash while driving, a fault exists in the engine
control. The system allows the vehicle to run in emergency mode.
36
Operation
Page 39

Seek assistance from a specialist garage immediately.
Engine performance check (petrol engine)
Read and observe on page 33 first.
If the indicator light
system allows the vehicle to run in emergency mode.
Seek assistance from a specialist garage immediately.
Diesel particulate filter (diesel engine)
Read and observe on page 33 first.
The diesel particulate filter separates the soot particles from the exhaust. The
soot particles collect in the diesel particulate filter where they are burnt on a
regular basis.
If the indicator light illuminates, soot has accumulated in the filter.
To clean the filter, and where traffic conditions permit » , drive as follows for
at least 15 minutes or until the indicator light goes out.
4th or 5th gear selected (automatic gearbox: position S).
Vehicle speed at least 70 km/h.
Engine speed between 1800 - 2500 rpm.
If the filter is properly cleaned, the warning icon goes out.
If the filter is not properly cleaned, the warning light does not go out and
the warning light begins to flash.
The following message is shown in the MAXI DOT display.
Diesel particulate filter: Log book!
The system allows the vehicle to run in emergency mode. After switching the
ignition off and on again the indicator light, the indicator light also illumi-
nates.
Seek assistance from a specialist garage immediately.
illuminates, there is a fault in the engine control. The
WARNING
■
The diesel particulate filter reaches very high temperatures - there is a
fire hazard and serious injury could be caused. Therefore, never stop the
vehicle at places where the underside of your vehicle can come into contact
with flammable materials such as dry grass, undergrowth, leaves, spilled
fuel or such like.
■
Always adjust your speed to suit weather, road, region and traffic conditions. The recommendations indicated by the indicator light must not
tempt you to disregard the national regulations for road traffic.
CAUTION
■
As long as the indicator light lights up, one must take into account an in-
creased fuel consumption and in certain circumstances a power reduction of
the engine.
■
Using diesel fuel with an increased sulphur content can considerably reduce
the life of the diesel particle filter. A ŠKODA partner will be able to tell you
which countries use diesel fuel with a high sulphur content.
Note
■
To assist the combustion process of the soot particles in the filter, we recom-
mend that regularly driving short distances be avoided.
■
If the engine is turned off during the filter cleaning process or shortly after-
wards, the cooling fan may turn on automatically for a few minutes.
Fuel reserve
Read and observe
The warning light illuminates if the fuel level is less than 9 litres.
The following message is shown in the MAXI DOT display.
Please refuel. Range: ... km
CAUTION
Never drive until the fuel tank is completely empty! The irregular supply of fuel
can cause misfiring. This can result in considerable damage to parts of the engine and the exhaust system.
Note
The text in the display goes out only after refuelling and driving a short distance.
on page 33 first.
Instruments and Indicator Lights
37
Page 40

Airbag system
Read and observe on page 33 first.
If the warning light illuminates, there is a fault in the airbag system.
The following message is shown in the MAXI DOT display.
Error: Airbag
The functionality of the airbag system is monitored electronically even if one
of the airbags is switched off.
If a front, side or head airbag or belt tensioner has been switched off using
the vehicle system tester:
The warning illuminates for approx. 4 seconds after switching on the igni-
›
tion and then flashes again for approx. 12 seconds.
The following message is shown in the MAXI DOT display.
Airbag/belt tensioner deactivated.
If the air bag was switched off using the key-operated switch on the side of
the dash panel on the passenger side:
The indicator light illuminates for around 4 seconds after the ignition has
›
been switched on;
The deactivated air bag is indicated by the illumination of the warning
›
light » page 20
WARNING
When a fault in the airbag system occurs, there is a risk of the system not
being triggered in the event of an accident. Therefore, this must be
checked immediately by a specialized company.
in the middle of the dash panel .
Tyre inflation pressure
Read and observe on page 33 first.
The warning light illuminates, if there is a substantial drop in inflation pressure in one of the tyres.
An audible signal sounds as a warning signal.
Check and adjust the pressure in all tyres » page 194, Service life of tyres.
›
If the indicator light flashes, there is a fault in the tyre pressure monitoring
system.
Stop the car, turn the ignition off and on again.
›
If the warning light flashes again after re-starting the engine, then the help
of a professional service provider must be sought immediately.
Further information » page 196, Tyre pressure monitor.
Note
The warning light illuminates after the ignition is switched on if the vehicle's battery has been disconnected and reconnected. If the warning light
does not go out after moving a short distance, this means there is an error in
the system. Seek assistance from a specialist garage immediately.
Windscreen washer fluid level
Read and observe
If the windscreen washer fluid level is too low, the warning light illuminates.
The following message is shown in the MAXI DOT display.
Top up wash fluid!
Top up with liquid » page 184, Windscreen washer system.
Pads
Read and observe
If the indicator light is illuminated, the brake pads are worn.
The following message is shown in the MAXI DOT display.
Check brake wear!
Seek assistance from a specialist garage immediately.
on page 33 first.
on page 33 first.
Turn signal system
Read and observe on page 33 first.
Either the left or right warning light flashes depending on the position of
the turn signal lever.
If there is a fault in the turn signal system, the warning light flashes at twice
its normal rate.
38
Operation
Page 41

Switching off the hazard warning light system is switched on will cause all of
the turn signal lights as well as both warning lights to flash.
Low beam
Read and observe on page 33 first.
The warning light illuminates when low beam is selected.
Fog lights
Read and observe on page 33 first.
The warning light illuminates when the fog lights are operating.
Cruise control system
Read and observe on page 33 first.
The warning light illuminates when the cruise control is active.
Selector lever lock / starter (system KESSY)
Read and observe on page 33 first.
If the warning light illuminates, operate the brake pedal. This is necessary
to move the selector lever from position P and N » page 143or to start the engine in vehicles with the KESSY system » page 139.
Main beam
Read and observe on page 33 first.
The warning light illuminates when the main beam is selected or when the
headlight flasher is operated.
Information system
Driver information system
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Using the information system 40
Display a low temperature 40
Gear recommendation 40
Door, boot or engine compartment warning 41
The information system provides the driver with alerts and messages about
individual vehicle systems. This information and advice is shown in the instru-
ment cluster display or indicated by the illumination of the corresponding indicator light in the instrument cluster.
The information system provides the following information and instructions
(depending on vehicle equipment).
Data relating to the multi-function display (MFD) » page 41.
›
Data relating to the Maxi DOT display » page 44.
›
Service interval display » page 46.
›
Auto Check Control » page 31.
›
Selector lever positions for an automatic gearbox » page 142.
›
WARNING
Concentrate fully at all times on your driving! As the driver, you are fully responsible for the operation of your vehicle.
Information system
39
Page 42

Using the information system
Fig. 26 Buttons / dial: on the operating lever / on the multifunction
steering wheel
Read and observe
Some functions of the information system can be operated using the buttons
on the multifunction steering wheel » Fig. 26.
Description of the operation
Button/
wheel
» Fig. 26
Briefly push up or down Select data / set data values
A
Press and hold button
B
C
Press button for a long
Turn upwards or down-
D
on page 39 first.
Action Operation
Main menu of the
MAXI DOT display » page 44
Press briefly View information / confirm specification
Press briefly
period of time
wards
Press briefly View information / confirm specification
return to go up one level in the menu
MAXI DOT display » page 44
Main menu of the
MAXI DOT display » page 44
Select data / set data values
Display a low temperature
Read and observe on page 39 first.
Prompt in the MAXI DOT display
If the outside temperature while driving drops to below +4°C, the following
icon appears on the display in front of the temperature display . An audible
signal is emitted.
If the outside temperature is already below +4°C when turning the ignition on,
the icon appears immediately.
Prompt in the segment display
If the outside temperature while driving drops to below +4°C, the temperature
display will show up with the following icon before this occurs . An audible
signal is emitted.
If the outside temperature is already below +4°C when turning the ignition on,
the temperature display and the icon appear immediately.
A
After pressing button
ta is shown.
WARNING
Even at temperatures of around +4 °C, there may still be black ice on the
road surface. You should therefore not rely solely on the outside temperature display for accurate information as to whether there is ice on the road.
» Fig. 26 on page 40, the most recently displayed da-
Gear recommendation
Fig. 27
Information on the selected
gear / Gear recommendation
40
Operation
Read and observe on page 39 first.
The function of the gear recommendation is to help reduce fuel consumption.
Page 43

Caption » Fig. 27
Optimal gear engaged
Recommended gear
Recommended gear
The gear recommendation is intended only for vehicles with a manual transmission or for vehicles with an automatic transmission in manual shift mode
(Tiptronic).
The recommended 1) gear and the arrow icon 2) is displayed.
Recommends that you shift to a higher gear.
›
Recommends that you shift to a lower gear.
›
If for example is shown in the display with vehicles that have a manual
gearboxes this indicates that it is better to shift from a lower gear to the 4th
gear.
If for example is shown in the display with vehicles that have an automatic
gearbox and are in the manual switching mode (Tiptronic), this indicates that it
is better to shift from the 4th gear to a higher gear.
WARNING
The driver is always responsible for selecting the correct gear in different
driving situations, such as overtaking.
For the sake of the environment
A suitably selected gear has the following advantages.
■
It helps to reduce fuel consumption.
■
It reduces the operating noise.
■
It protects the environment.
■
It benefits the durability and reliability of the engine.
Door, boot or engine compartment warning
Read and observe on page 39 first.
Vehicles with a MAXI DOT display
If at least one door, the boot or bonnet is open, the display indicates the relevant open door, boot or bonnet vehicle icon.
Vehicles with a segment display
If at least one door or the boot or bonnet is open, the indicator lights or
and come on in the instrument cluster » page 32, Warning lights .
An acoustic signal will also sound if you drive the vehicle above 6 km/h when a
door is open.
Multifunction display (MFD)
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Memory
Information overview 42
Warning at excessive speeds
The driving data is displayed on the multifunction display.
The multifunction display only operates if the ignition is switched on. After the
ignition is switched on, the function that was last selected before switching
off the ignition is displayed.
For vehicles with a MAXI DOT display, the menu item MFA must be selected
and confirmed in the main menu » page 44, MAXI DOT display.
On vehicles with a MAXI DOT display, there is an option to fade out some of
the information » page 45, Settings.
WARNING
■
Concentrate fully at all times on your driving! As the driver, you are fully
responsible for the operation of your vehicle.
■
Even at temperatures of around +4 °C, there may still be black ice on the
road surface. You should therefore not rely solely on the outside temperature display for accurate information as to whether there is ice on the road.
CAUTION
Pull out the ignition key if coming in contact with the display (e.g. when cleaning) to prevent any possible damage. On vehicles with the KESSY system,
switch off the ignition and open the driver's door.
42
43
1)
With vehicles that have an automatic gearbox and in the manual switching mode (Tiptronic) the current-
ly engaged gear is shown.
2)
For vehicles with segment display the arrow is displayed behind the gear indication.
Information system
41
Page 44

Note
■
In certain national versions the displays appear in the Imperial system of
measures.
■
If the display of the second speed is activated in mph, the current speed is
not indicated in km/h on the display.
■
The amount of fuel consumed will not be indicated.
Memory
Fig. 28
Multi-function display - memory display
Read and observe and on page 41 first.
The multifunction display is equipped with two automatic memories, 1 and 2.
Display of the selected memory in the display at the position A » Fig. 28 .
Single-trip memory
Total trip memory
Select memory
Select the corresponding element of the multifunction display » page 42.
›
Confirm the element again to switch between the individual memories.
Reseting
Select the corresponding element of the multifunction display » page 42.
›
Select the desired memory.
›
Press and hold button B or adjustment wheel D » Fig. 26 on page 40.
›
Single-trip memory (memory 1)
The single-trip memory collates the driving information from the moment the
ignition is switched on until it is switched off.
New data will also flow into the calculation of the current driving information if
the trip is continued within 2 hours after switching off the ignition.
If the trip is interrupted for more than 2 hours, the memory is automatically
erased.
Total-trip memory (memory 2)
The total trip memory collates the data from any number of individual trips up
to a total of 19 hours and 59 minutes or a 1999 km distance or, for vehicles
with a MAXI DOT display, 99 hours and 59 minutes, or a 9999 km distance.
The memory is deleted when either of these limits is reached and the calculation starts all over again.
Unlike the single-trip memory, the total-trip memory is not deleted after a period of interruption of driving of 2 hours.
The following values of the selected memory are set to zero.
Average fuel consumption.
›
Distance driven.
›
Average speed.
›
Driving time
›
Note
Disconnecting the vehicle battery will delete all memory data.
Information overview
Read and observe and on page 41 first.
Outside temperature
The current outside temperature is displayed.
For vehicles with a MAXI DOT display this information is always shown.
Driving time
The time travelled since the memory was last erased is displayed.
If you want to measure the time travelled from a particular moment in time on,
at this moment, reset the memory by setting the button to zero » page 42,
Memory.
The maximum time indicated in both memories is 19 hours and 59 minutes and
on vehicles which are fitted with a MAXI DOT display, it is 99 hours and 59 minutes. The indicator is set back to zero if this period is exceeded.
42
Operation
Page 45

Current fuel consumption
The current fuel consumption level is displayed in litres/100 km1). You can use
this information to adapt your driving style to the desired fuel consumption.
The display appears in litres/hour if the vehicle is stationary or driving at a low
speed2).
Average fuel consumption
The average fuel consumption since the memory was last erased is displayed
in litres/100 km
1 )
.
If you wish to determine the average fuel consumption over a certain period of
time, you must set the memory at the start of the new measurement to
zero » page 42, Memory. After erasing the memory, no value is displayed until
you have driven approx. 300 m.
The display is updated regularly while you are driving.
Range
The range indicates the distance you can still drive with your vehicle based on
the level of fuel in the tank and the same style of driving as before.
The display is shown in steps of 10 km. After lighting up of the indicator light
the display is shown in steps of 5 km.
The fuel consumption over the last 50 km is used to calculate the information.
The range will increase if you drive in a more economical manner.
If the memory is set to zero (after disconnecting the battery), a fuel consumption of 10 l./100 km is calculated for the range; afterwards the value is updated
according to the style of driving.
Distance travelled
The distance travelled since the memory was last erased is displayed.
If you want to measure the distance travelled from a particular moment in time
on, at this moment, reset the memory by setting the button to zero » page 42,
Memory.
The maximum distance indicated in both memories is 1 999 km or 9 999 km on
vehicles with a MAXI DOT display. The indicator is set back to zero if this period
is exceeded.
Average speed
The average speed since the memory was last erased is displayed in km/hour .
To determine the average speed over a certain period of time, set the memory
to zero at the start of the measurement » page 42, Memory.
After erasing the memory, no data will appear for the first 300 m driven.
The display is updated regularly while you are driving.
Current driving speed
The current speed displayed is identical to the display on the speedometer
2
» Fig. 20 on page 28.
Oil temperature
3)
If the engine oil temperature is in the range 80-110 °C, the engine operating
temperature is reached.
If the oil temperature is lower than 80 °C or above 110 °C, avoid high engine
revs, full throttle and high engine loads.
If the oil temperature is lower than 50 °C or if a fault in the system for checking the oil temperature is present, . symbols are displayed instead of the oil
temperature.
Warning against speeding
Set the speed limit, for example, for the maximum permissible speed in
town » page 43, Warning at excessive speeds.
Warning at excessive speeds
Read and observe and on page 41 first.
Adjust the speed limit while the vehicle is stationary
Select the menu item Speed warning (MAXI DOT display) or (segment dis-
›
play).
Activate the speed limit option by confirming this menu item4).
›
Set the desired speed limit, e.g. 50 km/h.
›
Store the speed limit by confirming the set value, or wait several seconds;
›
your settings will be saved automatically.
1)
On some models in certain countries, the display appears in kilometres/litre.
2)
On some models in certain countries, - -.- km/ltr. is displayed when the vehicle is stationary.
3)
Applies to vehicles using the MAXI DOT display.
4)
If no value is set the output value 30 km/h is automatically displayed.
Information system
43
Page 46

The speed limit can be adjusted from 30 km/h to 250 km/h in 5 km/h increments.
Adjusting the speed limit while the vehicle is moving
Select the menu item Speed warning (MAXI DOT display) or (segment dis-
›
play).
Drive at the desired speed, e.g. 50 km/h.
›
Confirm the current speed as the speed limit.
›
If you wish to adjust the set speed limit, you can do so in 5 km/h intervals (e.g.
the accepted speed of 47 km/h increases to 50 km/h or decreases to 45 km/h).
Store the speed limit, or wait several seconds; your settings will be saved au-
›
tomatically.
Change or disable speed limit
Select the menu item Speed warning (MAXI DOT display) or (segment dis-
›
play).
By confirming the stored value, the speed limit is disabled.
›
By reconfirming, the option to change the speed limit is activated.
›
If the set speed limit is exceeded, an audible signal will sound as a warning.
The menu item Speed warning (MAXI DOT display) or (Segment display) appears in the display at the same time as the set threshold.
The set driving mode is stored even after switching the ignition on and off.
MAXI DOT display
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Main menu
Settings 45
Compass point display 46
The MAXI DOT display provides you with information about the current operat-
ing state of your vehicle. Depending on the vehicle equipment, it also provides
you with data relating to the radio, multifunction display (MFD), mobile phone,
navigation system, automatic gearbox and devices connected via the MDI input. Furthermore, it allows the adjustment of some other features of your vehicle.
44
WARNING
Concentrate fully at all times on your driving! As the driver, you are fully responsible for the operation of your vehicle.
CAUTION
Pull out the ignition key if coming in contact with the display (e.g. when cleaning) to prevent any possible damage. On vehicles with the KESSY system,
switch off the ignition and open the driver's door.
Main menu
Read and observe
In order to activate the primary menu MAIN MENU, press and hold down But-
A
ton
or C » Fig. 26 on page 40. By briefly pressing the C button you will
reach one level higher.
Main menu items (depending on vehicle equipment)
■
MFD (Multifunction display) » page 41
■
Audio » Operating instructions for the radio
■
Navigation » Operating instructions for the navigation system
■
Phone » page 119;
■
Aux. heating » page 116
■
Assist systems » page 162
■
Vehicle status » page 31
■
Settings » page 45
The Audio and Navigation menu items are only displayed when the factory-fitted radio or navigation system is switched on.
Note
■
If warning messages are displayed, these messages must be verified to ac-
cess the main menu » page 40, Using the information system.
■
If the display is not activated at that moment, the menu always shifts to one
of the higher levels after approx. 10 seconds.
■
Using the factory-fitted radio or navigation system » Radio operating in-
structions or» navigation system operating instructions.
and on page 44 first.
44
Operation
Page 47

Settings
Read and observe and on page 44 first.
You can change certain settings by means of the MAXI DOT display. The current menu item is shown in the top of the display under a line.
The following information can be selected (depending on the equipment installed in the vehicle).
Language
You can set the language for the display texts here.
Automatic blind (Combi)
This is where the automatic roll-up function of the boot roll cover can be deactivated/activated when opening the boot lid.
MFD displays
Activate or deactivate certain displays of the multifunction display here.
Comfort
The following functions can be activated, deactivated or adjusted here:
Activate/deactivate the function for automatically
closing the window and the tilt/slide sunroof in a
Rain closing
ATA confirm
Central locking
Window op.
Mirror down
locked vehicle when it starts raininga). If the function
is activated and it is not raining, the windows including the panoramic tilt/slide sunroof will close automatically after approx. 12 hours.
Switch on/off the audible signal indicating activation
of the anti-theft alarm system. Further information » page 54.
Switch on/off the central locking and automatic locking function, also applies to the KESSY system. Further information » page 52, Individual settings.
Only convenience mode for the driver window or for
all of the windows can be adjusted here. Further information » page 61, Window convenience opera-
tion.
Activate/deactivate the function for mirror lowering
on the front passenger side when in the reverse
gearb). Further information » page 78, Fold in pas-
senger's mirror.
Activation / deactivation of the synchronous exterior
Mirror adjust.
mirror function settings. Further information » page 78, Synchronous adjustment of the mir-
ror.
Factory setting Restore the Convenience factory setting.
a)
This function is only available on vehicles with a rain sensor.
b)
This function is only available on vehicles with an electrically adjustable driver seat.
Lights and Visibility
The following functions can be activated, deactivated or adjusted here:
Activate/deactivate and adjust the light duration of
Coming Home
the COMING HOME function. Further information » page 70.
Switch on/off and adjust the light duration of the
Leaving Home
LEAVING HOME function. Further information » page 70.
Footwell light
Daytime running
lights
Activate/deactivate and adjust the footwell light intensity.
Activate/deactivate “DAY LIGHT” function. Further information » page 67, Daylight running lights (DAY
LIGHT).
Activate/deactivate the function of the automatic
Rear wiper
rear window wiping. Further information » page 76,
Automatic rear window wiper (Superb Combi).
Lane ch. flash
Travel mode
Activate/deactivate the lane ch. flash function. Further information » page 67.
Activate/deactivate the travel mode feature. Further
information » page 69, Tourist lights (Travel mode).
Factory setting Restore the factory setting for the lighting.
Time
The time, time format (12 or 24 hour indicator) and the changeover between
summer/winter time can be set here.
Winter tyres
Here, the speed and the switching on and off of the acoustic signals when exceeding this speed can be adjusted. This function is, for example, used for winter tyres where the maximum permissible speed is lower than the maximum
speed of the vehicle » page 193.
Information system
45
Page 48

As soon as the parking procedure is completed, an audible signal sounds and
the following message appears in the information display.
Winter tyres: maximum ... km/h.
Units of measurement
The units for the temperature, consumption and distance driven can be set
here.
Assistants
The tones of the audible signals for the parking aid can be adjusted here.
Alt. speed dis.
Here, the display of the second speed in mph1) can be activated.
Further information » page 31, Display of the second speed.
Service
The days and kilometres remaining until the next service can be displayed
here.
Further information » page 46, Service interval display.
Factory setting
The factory setting of the functions of the MAXI DOT display can be restored
here.
Compass point display
Read and observe and on page 44 first.
For vehicles with a factory fitted navigation system, an abbreviation for each
point of the compass (depending on the current direction of travel) is shown
on the top left-hand corner of the display.
The compass point display only operates when the ignition is switched on.
Service interval display
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Prompt in the MAXI DOT display
Prompt in the segment display 47
Resetting the service interval display 47
The service interval display shows the time and mileage to the next service
event.
The service due date is automatically displayed on the display and this information can be displayed manually if necessary.
The kilometre indicator or the days indicator reduces in steps of 100 km or,
where applicable, days until the service due date is reached.
The information regarding the service intervals can be found in the service
schedule.
Note
Information is retained in the Service Interval Display even after the vehicle
battery is disconnected.
Prompt in the MAXI DOT display
Oil change service
If an oil change service is due, the following message appears: Oil change in …
km or … days.
As soon as the service interval date has been reached, the message Oil
change now! appears once the ignition has been switched on!
Inspection
If an inspection is due, the following message appears: Inspection in ... km
or ... days.
As soon as the service interval date has been reached, the message Inspection now! appears once the ignition has been switched on!
46
1)
For models with the speedometer in mph, the second speed is displayed in km/h.
46
Operation
Page 49

Displaying the distance and days until the next service interval
You can view the remaining distance and days until the next service appointment at any time when the ignition is switched on by going to the Service
menu item » page 45, Settings or from the Vehicle status in the main menu of
the Maxi DOTdisplay. » page 44, Main menu .
The following message is displayed for 10 seconds.
Oil change ... km / ... days
Inspection ... km / ... days
Prompt in the segment display
Fig. 29
Segment display: Example of a
message
Explanation of a graphic » Fig. 29.
Service due
A
Differentiating between types of service
B
Days remaining until the next service interval
C
Kilometres remaining until the next service interval
Differentiating between types of service
The service type is determined by the number in position
Oil change service
Inspection
1)
A
» Fig. 29.
Service due
If a service becomes due, then the following information is displayed for about
10 seconds » Fig. 29.
The number 1 or 2 is displayed in position A.
›
The symbol and the number of days remaining until the next service inter-
›
val are displayed in position B.
The symbol and the number of kilometres remaining until the next service
›
interval are displayed in position C.
As soon as the due date for the service has been reached, the flashing icon
and the message OIL CHNG or INSPEC_ appear in the display for about 20 seconds after the ignition has been switched on.
Display the days and distance until the next service interval
You can press button 3 » Fig. 20 on page 28 repeatedly to display the remaining distance and time to until the next service whenever the ignition is switched on.
Information on the oil change service is displayed at first, followed by information on the inspection when button 3 is pressed again.
The number 1 or 2 is displayed in position A.
›
The symbol and the number of days remaining until the next service inter-
›
val are displayed in position B.
The symbol and the number of kilometres remaining until the next service
›
interval are displayed in position C.
Resetting the service interval display
We recommend that the display reset is completed by a specialist garage.
We recommend that you do not reset the service interval display yourself. Incorrectly setting the service interval display could cause problems to the vehicle.
Variable service interval
For vehicles with variable service intervals, after resetting the oil change service display, the values of a new service interval are displayed, which are based
on the previous operating conditions of the vehicle.
These values are then continuously matched according to the actual operating
conditions of the vehicle.
1)
The kilometres remaining until the next service interval are displayed instead of the odometer.
Information system
47
Page 50

Unlocking and opening
Unlocking and locking
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Vehicle key 49
Unlock/lock with remote control 49
Unlocking / locking - KESSY 50
Information message 51
Parking the vehicle 51
Safe securing 51
Individual settings 52
Locking/unlocking the vehicle from the inside 52
Child safety lock 53
Opening/closing a door 53
Your car is equipped with a central locking system.
The central locking system allows you to lock and unlock all doors, the fuel fill-
er flap and tailgate at the same time based on the current setting1).
The safe securing system » page 51 is integrated in the central locking sys-
tem. Once the car is locked from the outside, the door locks2) are automatically
blocked by the safe securing system » .
The following takes place after unlocking1).
The doors, the boot lid and the fuel filler flap are unlocked.
›
The interior light, which is switched by the door contact, comes on.
›
The safe securing system is switched off2).
›
The indicator light in the driver door stops flashing.
›
The anti-theft alarm system is deactivated.
›
The following takes place after locking1).
The doors, the boot lid and the fuel filler flap are locked.
›
The interior lights switched by the door contact come on.
›
The safe securing system is switched on2).
›
The indicator light in the driver door begins flashing.
›
The anti-theft alarm system is activated.
›
Displaying an error
If the indicator light in the driver's door initially flashes quickly for around 2
seconds, and then lights up for 30 seconds without interruption before flashing again slowly, you will need to seek the assistance of a specialist garage.
WARNING
■
Never leave the key in the vehicle when you exit the vehicle. Unauthorized persons, such as children, for example, could lock the car, turn on the
ignition or start the engine - there is a danger of injury and accidents!
■
When leaving the vehicle, never leave persons who are not completely independent, such as children, unattended in the vehicle. The children might,
for example, release the handbrake or take the vehicle out of gear. The vehicle could then start to move – risk of injury and accidents! These individuals might also not be able to leave the vehicle on their own or to help
themselves. Can be fatal at very high or very low temperatures!
■
If the car is locked from the outside and the safelock system is switched
on, there must not be any person in the car as it is then not possible to
open either a door or a window from the inside. The locked doors make it
more difficult for rescuers to get into the vehicle in an emergency – risk to
life.
Note
■
When leaving the vehicle, always check if it is locked.
■
In the event of an accident in which the airbags are deployed, the locked
doors are automatically unlocked in order to enable rescuers to gain access to
the vehicle.
■
Upon failure of the central locking system the key can be used only to unlock
and lock the driver's door. The other doors and the boot lid can be emergency
locked or released.
■
Emergency locking of the door » page 212.
■
Emergency unlocking of the boot lid » page 212.
1)
Depending on the individual setting » page 52 .
2)
This function is only enabled in certain countries.
48
Operation
Page 51

Vehicle key
Unlock/lock with remote control
Fig. 30
Remote control key
Read and observe on page 48 first.
Two remote control keys are provided with the vehicle» Fig. 30.
The transmitter with the battery is housed in the handle of the remote control
key. The receiver is located in the interior of the vehicle.
The operating range of the remote control key is approx. 30 m. But this range
of the remote control can be reduced if the batteries are weak.
The wireless key has a flip-out key bit.
The spare key must by initialised by a specialist garage after repair or replace-
ment of the receiver unit. Only then can the remote control key be used again.
CAUTION
■
Each key contains electronic components; therefore it must be protected
against moisture and severe shocks.
■
Keep the groove of the keys absolutely clean. Impurities (textile fibres, dust,
etc.) have a negative effect on the functionality of the locking cylinder and ignition lock.
■
The battery must be replaced if the central locking or anti-theft alarm system
does react to the remote control at less than approx. 3 metres
away » page 211.
Note
If you lose a key, please contact a specialist garage, who will be able to provide
you with a new one.
Fig. 31
Remote control key
Read and observe on page 48 first.
Image description » Fig. 31
Unlocking the vehicle
Locking the vehicle
Unlocking the boot lid
A
Folding out/folding up of the key bit
B
Warning light
Unlocking
The turn signal lights flash twice as confirmation that the vehicle has been unlocked.
If you unlock the vehicle and do not open a door or the boot lid within the next
30 seconds, the vehicle will lock again automatically and the safe lock system
or anti-theft alarm system will be switched on. This function is intended to
prevent the car being unlocked unintentionally.
The seat and mirror are adjusted after the vehicle is unlocked » page 82.
Locking
The turn signal lights flash once as confirmation that the vehicle has been
locked.
If the doors or the boot lid remain open after the vehicle has been locked, the
turn signal lights do not flash until they have been closed.
The current position of the seat and mirror after the vehicle is
locked » page 82.
1)
1)
This function is only enabled in certain countries.
Unlocking and opening
49
Page 52

Checking the battery condition
If the red indicator light B » Fig. 31 does not flash when you press a button on
the remote control key, the battery is empty. Replace the battery » page 211.
CAUTION
■
Only operate the remote control when the doors and boot lid are closed and
the vehicle is in your line of sight.
■
If the driver door is open, the vehicle cannot be locked using the remote con-
trol key.
■
The operation of the remote control may temporarily be affected by signal interference from transmitters close to the car and which operate in the same
frequency range (e.g. mobile phone, TV transmitter).
Note
For vehicles with anti-theft alarm the acoustic signals can also be activated/
deactivated by locking/unlocking » page 45.
Unlocking / locking - KESSY
Fig. 32 KESSY: Name of the zones/sensors in the handle of the front door
Read and observe on page 48 first.
The KESSY system (Keyless Entry Start Exit System) enables unlocking and
locking of the vehicle without actively using the remote control key.
Unlocking or locking areas » Fig. 32
A
Front door left
B
Front door right
C
Luggage compartment lid
D
Roof front
The KESSY system (Keyless Entry Start Exit System) enables unlocking and
locking of the vehicle without actively using the remote control key. The key
must be in one of the areas A, B or C » Fig. 32 (about 1.5 meters away from
the vehicle).
Unlocking
Grab the door handle of the front door or cover the sensor 2 » Fig. 32 with
›
the whole palm of your hand » .
Locking
Touch the sensor 1 » Fig. 32 with your fingers.
›
On vehicles fitted with automatic gearbox, the selector lever must be moved
into the position P before unlocking.
Unlocking the boot lid
Press the button in the handle of the boot lid » page 55.
›
Switching off the safelock system
Touch the sensor 1 » Fig. 32 twice within 2 seconds with your fingers.
›
If you cover the sensor 2 at the same time as the sensor 1 when unlocking
the vehicle, it is not unlocked.
If the vehicle is locked via the sensor 1, it will not be possible to unlock it
again in the following 2 seconds via the sensor 2 - prevents accidental unlocking.
The KESSY system can find the valid key, even if it was left in the front of the
vehicle's roof for example D » Fig. 32. It is therefore not always necessary to
know where the key is.
CAUTION
■
Do not use objects which might prevent direct contact between the hand
and the sensor.
■
Some types of gloves can impair the function of the grip sensor.
■
After leaving the vehicle, it does not lock automatically, the procedure for
locking the vehicle must therefore be observed.
■
If the battery in the key is weak or discharged, the vehicle may not be unlocked or locked via the KESSY system. In this case, use the emergency unlocking or emergency locking on the driver's door » page 212.
50
Operation
Page 53

Information message
Read and observe on page 48 first.
Key in the vehicle
The protection against inadvertently locking the key in the vehicle unlocks the
vehicle automatically if the following conditions are met.
The vehicle, including the boot lit, has been locked.
The key with which the vehicle has been locked remains in the vehicle in
the zone
The turn signal lights flash four times as confirmation that the vehicle has
been unlocked again.
The following message is shown in the information cluster display.
Key in vehicle.
KEY IN VEHICLE
Additionally, on vehicles which are fitted with the anti-theft alarm system, an
audible signal sounds.
The system has not found a key
If the system has not found a key in the vehicle, the following message appears in the display of the instrument cluster.
Key not found.
NO KEY
This can occur if the key is outside the vehicle, the battery in the key is discharged, the key is defective or the electromagnetic field is strongly disturbed.
Fault in KESSY system
If there is a fault in the KESSY system, the following message will appear in
the display of the instrument cluster.
Keyless access system faulty.
CHECK KEYLESS
Low voltage of the key battery
If the voltage of the battery in the remote control key is too low, the following
message appears in the display of the instrument cluster.
Change the key battery!
KEY BATTERY
Change the key battery » page 211!
D
» Fig. 32 on page 50.
Parking the vehicle
Read and observe on page 48 first.
If the vehicle is not unlocked within 60 or 90 hours, the sensors in the handle
of the driver or front passenger's door are deactivated automatically » Fig. 32
on page 50.
Activation after 60 hours
Unlock the driver's door using the sensor 2 » Fig. 32 on page 50.
›
Press the handle of the boot lid.
›
Unlock the vehicle using the symbol button on the remote control key.
›
Unlocking the driver's door in an emergency » page 212.
›
Activation after 90 hours
Unlock the vehicle using the symbol button on the remote control key.
›
Unlocking the driver's door in an emergency
›
» page 212.
Safe securing
Read and observe
The door locks are blocked automatically if the vehicle is locked from the outside. Afterwards, it is not possible to open the doors with the door handle either from the inside or from the outside.
This fact is pointed out by the following message on the display of the instrument cluster after switching out the ignition.
Check SAFELOCK! Log book!
CHECK SAFELOCK
Switching off
The safe lock can be switched off in one of the following ways.
By locking twice within 2 seconds.
›
By disabling the interior monitoring » page 54, Interior monitor and towing
›
protection.
If the vehicle is locked and the safe securing system is switched off, the door
can be opened separately from the inside by a single pull on opening lever.
Switching on
The safelock switches on automatically the next time the vehicle is locked and
unlocked.
on page 48 first.
Unlocking and opening
51
Page 54

Switch-on display
The indicator light flashes for around 2 seconds in quick succession, afterwards it begins to flash evenly at longer intervals.
Switch-off display
The indicator light in the driver door flashes for about 2 seconds fast, goes out
and starts to flash at longer intervals after about 30 seconds.
WARNING
If the car is locked and the safe securing system activated, no people must
remain in the car as it will then not be possible to either unlock a door or
open a window from the inside. The locked doors make it more difficult for
rescuers to get into the vehicle in an emergency – risk to life!
Note
This function is only enabled in certain countries.
Individual settings
Read and observe on page 48 first.
The following central locking functions can be set via the MAXI DOT display » page 45, Settings .
Opening a single door
This function makes it possible to only unlock the driver's door. The other
doors and the boot lid remain locked and are only unlocked after being opened
again.
Unlocking doors on one side of a vehicle
This function enables you to unlock both doors on the driver's side. The other
doors and the boot lid remain locked and are only unlocked after being opened
again.
Unlocking the vehicle with the KESSY system
This function enables you to unlock all the doors, individual doors, both doors
on the left or right vehicle side. The other doors and the boot lid remain locked
and are only unlocked after being opened again.
Automatic locking/unlocking
All doors are locked from a speed of around 15 km/h. The button in the handle
of the boot lid is deactivated.
If the ignition key is withdrawn, the car is then automatically unlocked again.
In addition, it is possible for the driver or front passenger to unlock the car by
pressing the central locking button .
The vehicle doors can be unlocked and opened at any time by pulling once on
the door opening lever.
WARNING
Locked doors prevent unwanted entry into the vehicle from outside, for ex-
ample at road crossings.
Locking/unlocking the vehicle from the inside
Fig. 33
Central locking button
Read and observe on page 48 first.
If the vehicle was not locked from the outside, it can also be unlocked and
locked with the rocker switch on the door opening lever of the driver or front
passenger door » Fig. 33 even without the ignition switched on. While a door is
opened, the vehicle cannot be locked.
Locking
Press the button / » Fig. 33 press.
›
The symbol in the button lights up.
Unlocking
Press the button / » Fig. 33 press.
›
The symbol in the button goes out.
52
Operation
Page 55

The following applies if your vehicle has been locked using the central locking
button.
It is not possible to open the doors or the boot lid from the outside (safety
›
feature, e.g. when stopping at traffic lights etc.).
The doors can be unlocked and opened from the inside by a single pull on the
›
opening lever of the respective door.
In the event of an accident in which the airbags are deployed, the locked
›
doors are automatically unlocked in order to enable rescuers to gain access
to the vehicle.
WARNING
■
Doors locked from the inside make it difficult for rescuers to get into the
vehicle in an emergency – risk to life!
■
If the safelock system is switched on » page 51, the door opening lever
and the central locking buttons do not operate.
Child safety lock
Fig. 34
Parental Control: Left rear door
Read and observe on page 48 first.
The child safety lock prevents the rear door from being opened from the inside. The door can only be opened from the outside.
You can switch the child safety lock on and off using the vehicle key.
Switching on
Turn the slot of the safety lock in the direction of the arrow » Fig. 34 (the
›
other way around on the right-hand door).
Switching off
Turn the slot of the safety lock in the opposite direction to the ar-
›
row » Fig. 34 (the other way around on the right-hand door).
Opening/closing a door
Fig. 35 Door handle/door opening lever:
Read and observe
Opening from the outside
Unlock the vehicle and pull the door handleA » Fig. 35 on the door you wish
›
to open.
Opening from the inside
Pull on door opening lever B of the respective door and push the door away
›
from you.
Closing from the inside
Grasp pull handle C and close the door.
›
WARNING
■
Make sure that the door has closed correctly as it can open suddenly
while driving – risk of death!
■
Only open and close the door when there is no one in the opening/closing
range – risk of injury!
■
An opened door can close automatically if there is a strong wind or the
vehicle is on an incline – risk of injury!
■
Never drive with the doors open - there is a risk of death!
on page 48 first.
Unlocking and opening
53
Page 56

Anti-theft alarm system
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Activating/deactivating
Interior monitor and towing protection 54
The anti-theft alarm system (hereinafter referred to only as alarm system) increases protection against break-in attempts into the vehicle.
The alarm system triggers audible and visual signals if an attempt is made to
break into the vehicle (hereafter referred to only as alarm).
An alarm is triggered when the following monitored areas of the vehicle have a
fault.
Bonnet.
›
Boot lid.
›
Doors.
›
Ignition lock.
›
Vehicle inclination » page 54.
›
Interior of car » page 54.
›
A drop in voltage of the on-board power supply.
›
Socket of the factory-fitted towing device » page 163, Towing a trailer.
›
An alarm is immediately triggered if either of the two battery terminals is disconnected while the anti-theft alarm system is activated.
The alarm is switched off by unlocking the vehicle or switching on the ignition.
CAUTION
Before leaving the vehicle, it must be checked that all of the windows, doors
and the sliding/tilting roof are locked in order to ensure the full functionality of
the anti-theft alarm system.
Note
The working life of the alarm siren is 5 years.
54
Activating/deactivating
Read and observe on page 54 first.
Activating
The anti-theft alarm system is activated automatically approximately 30 seconds after the vehicle is locked.
If you unlock the vehicle and do not open a door or the boot lid within the next
30 seconds, the vehicle will lock again automatically and the safelock system
or anti-theft alarm system will be switched on. This function is intended to
prevent the car being unlocked unintentionally.
Deactivating
The anti-theft alarm system is deactivated automatically after the vehicle is
unlocked. If the vehicle is not opened within 30 seconds, the anti-theft alarm
system is automatically activated again.
The alarm system is also deactivated if you unlock the driver door using the
key within 45 seconds of locking the vehicle.
Note
■
If the car is unlocked with the key in the driver door, insert the key into the
ignition and switch the ignition to deactivate the alarm system.
■
You can switch the audible signalling of the activation of the warning system
on and off in the Maxi DOT display in the menu item ATA confirm » page 45.
Interior monitor and towing protection
Fig. 36
Button for interior monitor and
towing protection
54
Operation
Read and observe on page 54 first.
The interior monitor detects movements inside the car and then triggers the
alarm.
Page 57

The tow-away protection triggers the alarm if a vehicle is registered as being
on an inclination.
Activating
The interior monitor and the towing protection are activated automatically after the vehicle is locked.
Deactivating
Switch off the ignition.
›
Open the driver door.
›
Press » Fig. 36 on the B-column on the driver's side. The symbol lighting in
›
the button changes from red to orange.
Lock the vehicle within 30 seconds.
›
Deactivate the interior monitor and the towing protection if there is a possibility of the alarm being triggered by movements (e.g. by children or animals)
within the vehicle interior or if the vehicle has to be transported (e.g. by train
or ship) or towed.
CAUTION
■
The opened glasses storage compartment reduces the effectiveness of the
interior monitor. To ensure the full functionality of the interior monitor, the
glasses storage compartment must always be closed before locking the vehicle.
■
The anti-theft alarm system is activated when the vehicle is locked even if
the safe securing system is deactivated. The interior monitor is however not
activated.
Luggage compartment lid
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Twindoor - open/close small boot lid 55
TwinDoor - open / close large boot
Open / close (Superb Combi)
Delayed locking of the boot lid
56
56
56
WARNING
■
Ensure that the lock is properly engaged after closing the boot lid. Otherwise, the lid might open suddenly while the vehicle is moving, even if the
lid was locked – risk of accident!
■
Never drive with the boot lid open or ajar, as otherwise exhaust gases
may get into the interior of the vehicle – risk of poisoning!
■
Do not press on the rear window when closing the luggage compartment
lid, as otherwise this could crack – risk of injury!
CAUTION
If the vehicle was locked before the boot lid was closed, the lid is immediately
locked automatically when closed » page 56.
Note
■
The function of the button in the grip above the licence plate is deactivated
when starting off or at a speed of 5 km/hour or more for vehicles with central
locking. The function is restored after the vehicle stops and the door is
opened.
■
Repeated opening and closing of the boot lid can lead to a temporary failure
of the function due to the overheating protection of the motors of the Twindoor system.
Twindoor - open/close small boot lid
Fig. 37 Handle of boot lid/opened small boot lid
Read and observe
After unlocking the vehicle, the boot lid can be opened with the button in the
handle above the number plate.
and on page 55 first.
Unlocking and opening
55
Page 58

Opening
Press the button in the handle at the lower edge of the boot lid 1 » Fig. 37
›
and lift the boot lid.
Closing
Pull down and strike the lid with the handle 2 » Fig. 37.
›
The small boot lid can also be opened by pressing the symbol button on the
remote control key » page 49.
TwinDoor - open / close large boot
Fig. 38 Handle of boot lid/opened large boot lid
Read and observe
After unlocking the vehicle, the boot lid can be opened with the button in the
handle above the number plate.
Opening
Press the button in the handle at the lower edge of the tailgate 1 » Fig. 38.
›
Wait until the brake light 2 in the rear window flashes twice and then lift
›
the lid.
Closing
Pull down and strike the lid with the handle 3 » Fig. 38.
›
and on page 55 first.
Open / close (Superb Combi)
Fig. 39 Boot lid handle/opening the boot lid
Fig. 40
Handle in the inner panelling of
the boot lid
Read and observe and on page 55 first.
After unlocking the vehicle, the boot lid can be opened with the button in the
handle above the number plate.
Opening
Press the handle A » Fig. 39 and raise the lid in the direction of the arrow
›
B
.
Closing
Pull the lid down with the handle C » Fig. 40 and close with a slight swing.
›
56
Operation
Delayed locking of the boot lid
Read and observe
If the boot lid is unlocked with the symbol button on the remote control
key, then the door is automatically locked after closing.
and on page 55 first.
Page 59

The period after which the boot lid is locked automatically can be extended by
a specialist garage.
After activation of delayed locking, the boot lid can be opened again after closing within a limited period.
Delayed locking can be deactivated by a specialist garage at any time.
CAUTION
There is a risk of unwanted entry into the vehicle before the boot lid is locked
automatically. We therefore recommend locking the vehicle with the symbol
button on the remote control key.
Electric boot lid (Superb Combi)
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Operating description 57
Acoustic signals
Adjusting/deleting the top lid position
Malfunctions
Force limiter
The electric luggage compartment lid (hereinafter referred to only as a lid) is
equipped with a force limiter. If the lid hits an obstacle when closing, it stops
and an audible signal sounds.
If you rapidly enter the vehicle during the opening or closing process of the
boot lid, the whole vehicle may jerk and as a result the movement of the lid
can be interrupted.
Manual operation
Manually opening and closing the lid is only possible in exceptional cases. It
must be completed slowly and without sudden movements as close to the
centre of the lid as possible » .
WARNING
■
Ensure that the lock is properly engaged after closing the lid. Otherwise,
the lid might open suddenly while the vehicle is moving, even if the lid was
locked – risk of accident!
■
Never drive with the lid open or unlatched, as otherwise exhaust gases
may get into the interior of the vehicle – risk of poisoning!
59
59
59
CAUTION
■
The movement of the lid can be stopped by applying an abrupt and quick
force against the lid.
■
Do not try to close the lid manually during the electrical closing process.
Damage can occur to the system of the electric boot lid.
■
If the lid is closed manually, it must be ensured that when moving the lid into
the lock, pressure is applied to the centre edge of the lid above the ŠKODA
logo. Handling the sides of the lid can damage the electric lid.
CAUTION
■
Before opening or closing the lid, check if there are any objects in the opening or closing range which could obstruct the movement (e.g. a load on the
roof rack or on the trailer, etc.) – risk of causing damage to the lid!
■
Ensure that there is at least 10 cm of clearance above the opened lid (e.g. distance from the garage ceiling). Otherwise, it may happen that the clearance
above the opened lid is no longer sufficient after relieving the vehicle of a load
(e.g. after unloading) – risk of causing damage to the lid.
■
In certain circumstances, if the lid is loaded (e.g by a thick layer of snow), the
opening process of the lid can be interrupted. Remove the load on the lid to reenable the electrical operation.
■
If the lid closes automatically (e.g. under load of snow), you will hear an intermittent beep.
Operating description
Fig. 41 Operation of the lid
Unlocking and opening
57
Page 60

Fig. 42
Lid operation/operating areas
Read and observe and on page 57 first.
Control elements
The lid can be operated with the following control elements.
With the symbol button on the remote control key (press for about 1 s).
›
With the button in the handle A on the outer part of the lid » Fig. 41.
›
With the button B on the inner part of the lid » Fig. 41.
›
With the button C in the centre console » Fig. 42.
›
Operating areas
The system distinguishes 3 operating areas where the function of the individual operating elements changes » Fig. 42. The end positions of the lid - fully
closed in the secured lock and fully opened - differ as well.
The range of the area 3 changes proportionally, depending on the setting of
the top position of the lid » page 59.
If the lid is set in the uppermost position in the area 2, the area 3 is not active. The range of the area 2 changes proportionally, depending on the setting of the top position of the lid.
Symbol explanation in the operating description
Feasible action
Non-feasible action
Movement in the opposite direction to the previous movement
Lid operation with the handle
Action
Opening
Stop
Closing
The operation of the lid using the handle A is only possible when the vehicle
is unlocked.
Lid operation with the button
Action
Opening
Stop
Closing
Operating the lid with the button B is only possible when the lid is open.
Lid operation with the symbol button on the remote control key and the
C
button
Action
Opening
Stop
Closing
When the ignition is switched on, the operation of the lid does not function using the remote control key.
Operating the lid with the button C does not work if the vehicle was locked
from the outside.
Operating the lid with the symbol button on the remote control key and the
button C does not work when a trailer is coupled to the vehicle.
Closed
Lid
Closed
Lid
Closed
Lid
A
Area
1 2 3
B
Area
1 2 3
Area
1 2 3
Open
Lid
Open
Lid
Open
Lid
58
Operation
Page 61

Acoustic signals
Read and observe and on page 57 first.
The acoustic signals serve as a safety function and provide information about
the success of a performed action.
Signals Status
Open (using the button on the remote control key
Interrupted tone
1 continuous tone Force limiter
3 rising tones Confirmation of the storage of the lid position
3 identical tones fault
or the button C » Fig. 42 on page 58 )
Automatic closing of the lid » page 57, in section In-
troduction
Adjusting/deleting the top lid position
Read and observe
Adjusting
Stop the lid in the desired position (electrically or manually).
›
Press and hold the button B » Fig. 41 on page 57 for longer than 3 seconds.
›
Storing the new position is confirmed with an audible signal.
Delete
Carefully lift up the lid manually to the maximum opening position.
›
Press and hold the button B » Fig. 41 on page 57 for longer than 3 seconds.
›
An audible signal sounds and the height which was originally set is deleted
from the memory, while the basic position of the top lid position is again set.
The top lid position is adjusted, for example, in the following situations.
When the space for opening the lid is limited (e.g. garage height).
›
For a more convenient operation, such as by a person's height.
›
The top position which is reached when the lid opens automatically, is always
lower than the maximum top position which can be reached when the lid is
opened manually.
The lid always opens to the height which was last stored.
and on page 57 first.
Malfunctions
Read and observe and on page 57 first.
If the battery is disconnected and reconnected while the lid is open, it is necessary to activate the system of the electric boot lid. Activation means closing
the lid by hand. Thus, the end position of the lid is stored under fully closed in
secured lock.
Examples of operational malfunctions
Description of the malfunction
The lid cannot be lifted out
of the lock.
The lid does not react to an
opening signal
The lid remains in the top
position
Possible solutions
Emergency unlocking of the lid » page 212
Removing a possible obstacle (e.g. snow), reopening the lid » page 57
Press handle A and pull the lid upwards
Manual closing of the lid
Electric power windows
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Opening/closing the window from the driver seat
Opening the windows in the front passenger door and in the rear doors
Force limit
Window convenience operation
Operational faults
60
61
61
61
62
Unlocking and opening
59
Page 62

WARNING
■
Ensure that no persons are still left in the vehicle when locking the vehicle. In an emergency, the windows will no longer be able to be opened from
the inside.
■
The system is fitted with a force limiter » page 61. If there is an obstacle, the closing process is stopped and the window goes down by several
centimetres. However, the windows should be closed carefully – risk of injury.
■
Deactivating the electrically operated power windows in the rear doors is
recommended (safety push button) S when children are being transported
in the rear seats » Fig. 43 on page 60.
CAUTION
■
Keep the windows clean to ensure the correct functionality of the electric
windows.
■
In the event that the windows are frozen, first of all eliminate the
ice » page 175, Windows and exterior mirrors and only then operate the electrical power windows. Otherwise, the window sealing and the electrical power
window mechanism could be damaged.
■
In the winter, ice accumulating on the surface of the window may cause
there to be more resistance when closing the window. The window will stop
and move back several centimetres.
■
It is necessary to deactivate the force limiter to close the win-
dow » page 61.
■
Make sure that the windows are closed whenever you leave the locked vehi-
cle.
For the sake of the environment
At high speeds, you should keep the windows closed to prevent unnecessarily
high fuel consumption.
Note
■
After switching the ignition off, it is still possible to open or close the windows for approx. 10 minutes. After the driver's or front passenger's door has
been opened, the windows can only be operated by using button A » Fig. 43
on page 60.
■
When driving always use the existing heating, air conditioning and ventilation system for ventilating the interior of the vehicle. If the windows are
opened, dust as well as other dirt can get into the vehicle and in addition the
wind noise is more at certain speeds.
■
The window lift system is equipped with protection against overheating. Repeated opening and closing of the window can cause this mechanism to overheat. If this happens, it will not be possible to operate the window for a short
time. You will be able to operate the window again as soon as the overheating
protection has cooled down.
Opening/closing the window from the driver seat
Fig. 43
Buttons on the driver's door
Read and observe and on page 60 first.
Power window buttons » Fig. 43.
A
Button for power window of the driver's door
B
Button for power window of the front passenger door
C
Button for power window of the rear right door
D
Button for power window at the rear left door
S
Safety pushbutton
Opening
Lightly press the appropriate button down and hold it until the window has
›
moved into the desired position. Releasing the button causes the window to
stop immediately.
60
Operation
Page 63

The window can be completely opened automatically by briefly pressing the
button as far as the stop. Renewed pressing of the button causes the window
to stop immediately.
Closing
Pull gently on the top edge of the corresponding button and hold until the
›
window has moved into the desired position. Releasing the button causes
the window to stop immediately.
The window can also be fully closed automatically by pulling the button up to
the stop. Renewed pulling of the button causes the window to stop immediately.
Safety pushbutton
The buttons for power windows in the rear doors can be deactivated by pressing the safety switch S » Fig. 43. The buttons for the electrical power windows in the rear doors are activated again by pressing the safety pushbutton
S
again.
If the buttons for the rear doors are deactivated, the indicator light in the
safety switch S lights up.
Opening the windows in the front passenger door and in the rear doors
Fig. 44
Button in the rear door
Read and observe and on page 60 first.
There is a button in the front passenger door and in the rear doors for that
window.
Opening
Lightly press the appropriate button down and hold it until the window has
›
moved into the desired position. Releasing the button causes the window to
stop immediately.
The window can be completely opened automatically by briefly pressing the
button as far as the stop. Renewed pressing of the button causes the window
to stop immediately.
Closing
Pull gently on the top edge of the corresponding button and hold until the
›
window has moved into the desired position. Releasing the button causes
the window to stop immediately.
The window can also be fully closed automatically by pulling the button up to
the stop. Renewed pulling of the button causes the window to stop immediately.
Force limit
Read and observe and on page 60 first.
The electrical power window system is fitted with a force limiter. It reduces
the risk of bruises or injuries when closing the windows.
If there is an obstacle, the closing process is stopped and the window goes
down by several centimetres.
If the obstacle prevents the window from being closed during the next 10 seconds, the closing process is interrupted once again and the window goes down
by several centimetres.
If you attempt to close the window again within 10 seconds of the window being moved down for the second time, even though the obstacle was not yet
been removed, the closing process is only stopped. During this time it is not
possible to automatically close the window. The force limiter is still switched
on.
The force limiter is only switched off if you attempt to close the window again
within the next 10 seconds - the window will now close with full force!
If you wait longer than 10 seconds, the force limiter is switched on again.
Window convenience operation
Read and observe
The convenience operation of the windows offers the possibility of opening or
closing all the windows at once.
Convenience operation can take place in one of the following ways.
and on page 60 first.
Unlocking and opening
61
Page 64

Opening
Press the button on the remote control key.
›
Hold the key in the driver's lock in the unlock position.
›
Press and hold the upper part of the central locking button in the driver's
›
door » page 52.
Hold button A » Fig. 43 on page 60 in the opening position.
›
Closing
Press button on the remote control key.
›
Hold the key in the driver's lock in the lock position.
›
Press and hold the lower part of the central locking button » page 52 in the
›
driver's door.
Hold button A » Fig. 43 on page 60 in the closing position.
›
In the KESSY system, hold a finger on the sensor 1 » Fig. 32 on page 50.
›
The speed limit for winter tyres can be set in the MAXI DOT display in the
menu item Window op. . » page 45.
The prerequisite for ensuring that the convenience operating feature correctly
is the automatic opening/closing of all windows is operational.
Convenience opening or closing the window using the key in the driver's lock
is only possible within 45 seconds after locking the vehicle.
The movement of the window is stopped immediately when the key or the respective button is released.
Operational faults
Read and observe and on page 60 first.
The automatic power windows do not work if the vehicle battery has been disconnected and connected again while a window was open. The system must
be activated.
Activation sequence:
Switch on the ignition.
›
Pull the top edge of the button and close the window.
›
Release the button.
›
Pull the relevant button upwards again for approx. 3 seconds, and keep it
›
pressed down.
Electric sliding/tilting roof
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Operation
Convenience operation of sliding / tilting roof 63
Electric sliding/tilting roof with solar cells 63
The electric sliding/tilting roof (abbreviated in the following as 'sliding/tilting
roof') can only be operated when the ignition is turned on and when the outdoor temperature is higher than -20 °C.
The sliding/tilting roof can still be operated for approx. 10 minutes after
switching the ignition off. However, as soon as the driver or front passenger's
door is opened it is no longer possible to operate the sliding/tilting roof.
CAUTION
■
Always close the sliding/tilting roof before disconnecting the battery.
■
If the battery has been disconnected and reconnected, it is possible that the
sliding/tilting roof does not operate correctly. In this case, turn the rotary
switch to the switch position A » Fig. 45 on page 62 and push forward for
about 10 seconds.
Operation
Fig. 45
Control dial for the sliding/tilting
roof
Read and observe on page 62 first.
Comfort position
Turn the switch to position C » Fig. 45.
›
When the sliding/tilting roof is in the comfort position, the intensity of the
wind noise is reduced.
62
62
Operation
Page 65

Open partially
Simply turn the knob to a point between A and
›
Open fully
Turn the switch to position B and hold it in this position (spring-tensioned
›
position).
Tilting roof
Turn the switch to position D.
›
Closing
Turn the switch to position A.
›
Sun screen
The sun screen is also opened automatically when the tilt/slide sunroof slides
open. When the tilt/slide sunroof is closed the sun screen can be manually operated » .
Force limiter
The sliding/tilting roof is fitted with a force limiter. If an obstacle (e.g. ice) prevents closing, the sliding/tilting roof stops and opens completely. The sliding/
tilting roof can be closed completely without the force limiter by pushing the
switch in position A » Fig. 45 forwards until the sliding/tilting roof is completely closed » .
WARNING
When operating the tilt/slide sunroof and the sunshade, proceed with caution to avoid causing crushing injuries – risk of injury!
CAUTION
During the winter it may be necessary to remove any ice and snow in the vicinity of the sliding/tilting roof before opening it to prevent any damage to the
opening mechanism.
C.
Convenience operation of sliding / tilting roof
Read and observe on page 62 first.
The sliding/tilting roof can be operated by locking/unlocking using the key or
using the KESSY system with the aid of the sensor 1 » Fig. 32 on page 50.
Press the button on the remote control key.
›
In the KESSY system, hold a finger on the sensor 1 » Fig. 32 on page 50.
›
By releasing the lock or lifting your finger off the sensor 1 when using the
KESSY system, the closing process is immediately interrupted.
WARNING
Close the sliding/tilting roof carefully – risk of injury. The force limiter does
not operate with the convenience closing.
Electric sliding/tilting roof with solar cells
Read and observe
If there is sufficient bright sunlight, the solar cells in the sliding/tilting roof deliver the electrical power for the fresh air blower. Further information » page 113, Climatronic (automatic air conditioning system).
The operation of the sliding/tilting roof with solar cells is the same as of a normal sliding/tilting roof.
on page 62 first.
Panoramic sliding/tilting roof (Superb Estate)
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Operation
Opening/closing the sun screen
Convenience operation of sliding / tilting roof
The panoramic sliding/tilting roof (abbreviated in the following as 'sliding/tilting roof') can only be operated when the ignition is turned on and when the
outdoor temperature is higher than -20 °C.
The sliding/tilting roof can still be operated for approx. 10 minutes after
switching the ignition off. However, as soon as the driver or front passenger's
door is opened it is no longer possible to operate the sliding/tilting roof.
CAUTION
■
Always close the sliding/tilting roof before disconnecting the battery.
■
If, for example, the battery has been disconnected and reconnected, it is possible that the sliding/tilting roof does not operate correctly. Next, move the rotary switch into position A » Fig. 46 on page 64 , pull the recess firmly
64
64
65
Unlocking and opening
63
Page 66

downwards and hold forwards firmly. The sliding/tilting roof opens and closes
again after around 10 seconds. Do not release the control dial until it has done
so.
■
If, for example, the battery has been disconnected and reconnected, it is possible that the sun screen does not operate correctly. Then turn the switch to
positionA » Fig. 46 on page 64and press and hold the button G » Fig. 47 on
page 64. The sun screen opens and closes again after around 10 seconds. Do
not release the control dial until it has done so.
Operation
Force limiter
The sliding/tilting roof is fitted with a force limiter. The sliding/tilting roof
stops and moves back several centimetres when it cannot be closed because
there is something in the way (e.g. ice). The sliding/tilting roof can be fully
closed without a force limiter by pressing the switch on the recess E down
and then pushing it forward until the sliding/tilting roof is fully closed » .
WARNING
When operating the sliding/tilting roof, proceed with caution to avoid causing crushing injuries – risk of injury!
Fig. 46
Control dial for the sliding/tilting
roof
Read and observe on page 63 first.
Comfort position
Turn the switch to position C » Fig. 46.
›
When the sliding/tilting roof is in the comfort position, the intensity of the
wind noise is reduced.
Open partially
Turn the switch to a position in area
›
Open fully
Turn the switch to position B and hold it in this position (spring-tensioned
›
position).
Tilting roof
Turn the switch to position A.
›
Press the switch in the region E towards the roof.
›
Closing
Turn the switch to position A.
›
Press the switch on the recess E down and pull forwards.
›
64
Operation
D
.
CAUTION
During the winter it may be necessary to remove any ice and snow in the vicinity of the sliding/tilting roof before opening it to prevent any damage to the
opening mechanism.
Opening/closing the sun screen
Fig. 47
Buttons for sun screen
Read and observe on page 63 first.
The sun screen can be closed or opened using the buttons » Fig. 47.
Opening
Briefly press the button F » Fig. 47 to open fully.
›
Press and hold the button F to open to the desired position.
›
The opening process stops when one releases the button.
Closing
Briefly press the button G » Fig. 47 to close fully.
›
Press and hold the button G to close in the desired position.
›
The closing process stops when one releases the button.
Page 67

WARNING
When operating the sunshade, proceed with caution to avoid causing
crushing injuries – risk of injury!
Convenience operation of sliding / tilting roof
Read and observe on page 63 first.
The sliding / tilting roof can be operated by locking or unlocking using the key
or using the KESSY system with the aid of the sensor 1 » Fig. 32 on page 50.
Closing
Press and hold the symbol button on the key or hold the key in the locking
›
cylinder of the driver's door in the lock position, or for the KESSY system,
keep your finger on the sensor 1 » Fig. 32 on page 50 » .
By releasing the lock or lifting your finger off the sensor 1 when using the
KESSY system, the closing process is immediately interrupted.
Tilting roof
Press the button on the remote control key.
›
WARNING
Close the sliding/tilting roof carefully – risk of injury. The force limiter does
not operate with the convenience closing.
Lights and visibility
Lights
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Parking and low beam lights 66
Daylight running lights (DAY LIGHT) 67
Turn signal and main beam 67
Automatic driving lamp control 68
Adaptive headlights (AFS) 68
Fog lights 69
Fog lights with the CORNER function 69
Rear fog light 69
COMING HOME / LEAVING HOME 70
Hazard warning light system 70
Parking lights 71
Unless otherwise stated, the lights only work when the ignition is switched
on.
The arrangement of the controls right-hand drive models may differ from the
layout shown in » Fig. 48 on page 66. The symbols which mark the positions
of the controls are identical.
Keep the headlights lenses clean. The following guidelines must be observed » page 175, Headlight lenses.
WARNING
■
The activation of the lights should only be undertaken in accordance with
national legal requirements.
■
The driver is always responsible for the correct settings and use of the
lights.
Lights and visibility
65
Page 68

WARNING (Continued)
■
The automatic driving lamp control only operates as a support and
does not release the driver from his responsibility to check the light and, if
necessary, to switch on the light depending on the given light conditions.
The light sensor cannot, for example, detect rain or snow. Under these conditions we recommend switching on the low beam or fog lights!
■
Never drive with only the side lights on! The side lights are not bright
enough to light up the road sufficiently in front of you or to be seen by other oncoming traffic. Therefore always switch on the low beam when it is
dark or if visibility is poor.
Note
The headlights may mist up temporarily. When the driving lights are switched
on, the light outlet surfaces are free from mist after a short period, although
the headlight lenses may still be misted up in the peripheral areas. This mist
has no influence on the life of the lighting system.
Parking and low beam lights
Fig. 48
Light switches, knobs for headlight beam adjustment and
brightness of instrument illumination
Read and observe on page 65 first.
Light switch positions - turning the switch A » Fig. 48
Switching off lights (except daytime running lights)
Automatic switching lights on and off » page 68
Switching on the parking light or parking lights » page 71
Turn on the low beam
Light switch positions - pulling the switch
Switch on the front fog lamp » page 69
Switching on the rear fog light » page 69
A
Turning the knob B » Fig. 48
Lights and visibility
Lights and visibility
By turning the rotary switch from the position in gradually adjusts the
headlight range control and thereby shortens the light cone.
The positions of the width of illumination correspond approximately to the following car load.
Front seats occupied, boot empty
All seats occupied, boot empty
All seats occupied, boot loaded
Driver seat occupied, boot loaded
Instrument lighting
Turning the rotary switch C when the lights are switched on adjusts the
brightness of the instrument lighting » Fig. 48 .
The instruments are also illuminated when the side light, low or high beam
light is switched on.
WARNING
Always adjust the headlight beam to satisfy the following conditions.
■
The vehicle does not dazzle other road users, especially oncoming vehi-
cles.
■
The beam range is sufficient for safe driving.
Note
■
We recommend you adjust the headlight beam when the low beam is switch-
ed on.
■
The Bi-Xenon bulbs adapt automatically to the load and driving state of the
vehicle when the ignition is switched on and when driving. Vehicles that are
equipped with Bi-Xenon headlights do not have a manual headlight range adjustment control.
■
The light switch is in position or
and the ignition is turned off, the low
beam is switched off automatically and the status light is lit. The side light
goes out after the ignition key is removed.
■
If there is a fault in the light switch, the low beam comes on automatically.
66
Operation
Page 69

Daylight running lights (DAY LIGHT)
Read and observe on page 65 first.
The daytime running lights (the only function) provides the lighting of the front
vehicle range.
The daytime running lights are switched on automatically if the following
conditions are met:
The light switch is in the position or
The ignition is switched on.
The parking aid is activated.
Deactivating the function
Switch off the ignition.
›
Pull the turning signal and main beam lever (
›
the steering wheel, push down and hold in this position.
Switch on the ignition.
›
Hold the lever in this position for at least 3 seconds after switching on the
›
ignition.
Activating the function
Switch off the ignition.
›
Pull the turning signal and main beam lever towards the steering wheel,
›
push it up and hold it in this position.
Switch on the ignition.
›
Hold the lever in this position for at least 3 seconds after switching on the
›
ignition.
On vehicles with MAXI DOT display, the function can be enabled or disabled in
the menu item Dayl. dri. light » page 45 .
WARNING
When the daytime running light is switched on, the side lights (neither at
the front or rear) and the number plate lights are not lit. Therefore always
switch on the low beam when the visibility is poor.
» Fig. 48 on page 66.
» Fig. 49 on page 67) towards
Turn signal and main beam
Fig. 49
Operating lever: Turn signal and
main beam operation
Read and observe on page 65 first.
Lever positions » Fig. 49
A
Switch on right turn signal
B
Switch on left turn signal
C
Switch on high beam (spring-loaded position)
D
Switch off main beam and headlamp flasher (spring-loaded position)
Main beam
The main beam can only be switched on when the low beam lights are on.
When the high beam or headlight flasher is on, the warning light lights up in
the instrument cluster.
Flashing
When the left or right turn signal is on, the warning light or flashes in the
instrument cluster.
The flashing light is turned on even before the upper and lower pressure point.
This is advantageous with some manoeuvres. For example, when changing
lanes hold the control lever of each pressure point.
The turn signal light switches itself off automatically when driving around a
curve or after making a turn.
The indicator light flashes at twice its normal rate if a bulb for the turn signal
light fails.
“Convenience turn signal”
If you only wish to flash three times, briefly push the lever to the upper or lower pressure point and release again.
Lights and visibility
67
Page 70

The “Intelligent turn signal” can be activated or deactivated via the Maxi DOT
display in the Intelligent turn signal» page 45 menu item.
WARNING
Only turn on the main beam or the headlight flasher if other road users will
not be dazzled.
Note
The headlight flasher can be operated even if the ignition is switched off.
Automatic driving lamp control
Fig. 50
Light switch: AUTO position
Read and observe on page 65 first.
If the light switch is in position
number plate lights are switched on or off automatically.
The light is regulated based on data gathered by the sensor fitted in the holder of the rear-view mirror below the windscreen.
If the light switch is in position
light switch. If the light is switched on automatically, the symbol next to the
light switch also lights up.
Automatic driving light control during rain
The daytime running lights are switched on automatically if the following conditions are met:
The light switch is in the position
Automatic wiping with rain - position
turned on » page 76, Windscreen wipers and washers.
The windscreen wipers are on for more than 15 s.
The light turns off about 4 minutes after turning off the wipers.
» Fig. 50, the parking lights, low beam and
, the lettering
illuminates next to the
» Fig. 50.
1
or wiping - position 2 or 3 is
CAUTION
Do not stick any stickers or similar objects in front of the light sensor on the
windscreen, so as not to cancel the function of automatic driving light control
or to impair its effectiveness.
Adaptive headlights (AFS)
Read and observe on page 65 first.
The AFS system makes sure the street remains lit up depending on the traffic
and weather situation.
The system automatically adjusts the cone of light in front of the vehicle to the
driving speed or the use of the wiper.
The AFS system works in tandem with automatic driving lamp control
please read the following » page 68.
The AFS system can only work if the following condition is met.
The light switch is in the position
The AHL system operates in the following modes.
Out of town mode
The cone of light in front of the vehicle is similar to the low beam. The mode is
active if none of the following modes are active.
City mode
The light cone in front of the vehicle is adjusted so that it also illuminates the
adjacent pavements, intersections and pedestrian crossings etc. The mode is
active at speeds of 15 - 50 km / h.
Motorway mode
The cone of light in front of the vehicle is adjusted so that the driver can respond in time to an obstruction or other hazard in time. The mode is activated
gradually from a speed of 90 km/h. It is most effective at speeds above
120 km/h.
Rain mode
The cone of light in front of the vehicle is adjusted so that the driver can reduce the glare from oncoming vehicles in rain.
The mode is active at speeds of 15 – 70 km/h and if the windscreen wipers
continuously operate for a period of time longer than 2 minutes. The mode is
deactivated when the windscreen wipers are switched off for longer than 8
minutes.
.
,
68
Operation
Page 71

Dynamic cornering lights
The cone of light in front of the vehicle is adjusted to the steering angle so
that the road in the curve is illuminated. This function is active at speeds
greater than 10 km.h and in all AFS modes.
Tourist lights (Travel mode)
This mode makes it possible to drive in countries with opposing traffic system
(driving on the left/right) without dazzling the oncoming vehicles.
When this mode is active, the above-mentioned modes and the side swivel of
the headlights is deactivated.
This mode can be enabled or disabled via the Maxi DOT display in the Travel
mode» page 45, Lights and Visibility menu option.
WARNING
If the AFS system is defective, the headlights are automatically lowered to
the emergency position, which prevents a possible dazzling of oncoming
traffic. This reduces the cone of light in front of the vehicle. Drive carefully
and visit a specialist garage as soon as possible.
Note
When the “tourist light” mode is active, the warning light flashes for 10 seconds each time the ignition is switched on.
Fog lights
Fig. 51
Light switch
Read and observe on page 65 first.
Switching on/off
Turn the light switch to position or » Fig. 51.
›
Pull the light switch to position 1.
›
The rear fog light is switched off in the reverse order.
The indicator light lights up in the instrument cluster when the fog lights
are switched on » page 32.
Fog lights with the CORNER function
Read and observe on page 65 first.
The CORNER function lights the front fog lamp on each side of the vehicle to
illuminate the area around the vehicle when turning, parking, etc.
The CORNER function is switched on automatically if the following conditions
are met.
The turn signal is switched on or the front wheels are turned sharply to
the right or left1).
The engine is running.
The vehicle is stopped or moves at a speed of no more than 40 km/h.
The low beam is switched on or the light switch is in the position
the low beam is switched on.
The daytime running lights are not switched on.
The fog lights are not switched on.
Note
The two fog lights are switched on when you shift into the reverse gear.
and
Rear fog light
Read and observe
Switching on/off
Turn the light switch to position or » Fig. 51 on page 69.
›
Pull the light switch to position 2.
›
on page 65 first.
1)
If both switch-on conditions are conflicting, for example, if the front wheels are turned to the left and
the right turn signal light is switched on, the turn signal light has the higher priority.
Lights and visibility
69
Page 72

The rear fog light is switched off in the reverse order.
The warning light lights up in the instrument cluster when the rear fog light
is switched on » page 32.
When in reverse gear only the rear fog lamp illuminates on the driver's side.
Only the rear fog light on the trailer lights up if the vehicle has a factory-fitted
towing device or a towing device from ŠKODA original accessories and it is
driven with a trailer.
COMING HOME / LEAVING HOME
Read and observe on page 65 first.
COMING HOME/LEAVING HOME (hereafter referred to only as function)
switches on the lights for a short time after leaving the vehicle or when approaching the vehicle.
The daytime running lights are switched on automatically if the following
conditions are met:
The light switch is in the position
The visibility in the vehicle environment is reduced.
The ignition is switched off.
The parking aid is activated.
The function switches on the following light, depending on the equipment
fitted.
Parking lights
›
Low beam
›
Entry lighting in the exterior mirrors
›
Licence plate light
›
The light is controlled on the basis of information that is collected from the
holder mounted in the rear-view mirror sensor » page 68 .
COMING HOME
The light turns on automatically when you open the driver's door on (within 60
seconds of turning off the ignition).
The light turns off 10 seconds after closing all the doors and the boot lid or after the pre-set time has expired.
If a door or the boot lid remains open, the light goes out after 60 seconds.
» Fig. 50 on page 68.
LEAVING HOME
The light turns on automatically after the vehicle is unlocked with the remote
control.
The light turns off after 10 seconds or after a pre-set time or after the vehicle
is locked.
Activate/deactivate the function
The functions and settings of the illumination time can be activated/deactivated via the MAXI DOT display in the menu items Coming Home or Leaving
Home » page 45.
CAUTION
■
Do not attach any stickers or similar objects in front of the light sensor on
the windscreen to avoid impairing the function or its reliability.
■
If this function is activated constantly, the battery will be heavily discharged
particularly in short-haul traffic.
Hazard warning light system
Fig. 52
Button for hazard warning light
system
Read and observe on page 65 first.
Switching on/off
Press the » Fig. 52 button.
›
All the turn signal lights on the vehicle flash at the same time when the hazard
warning light system is switched on. The warning light for the turn signals and
the warning light in the button also flash at the same time. The hazard warning light system can also be operated if the ignition is switched off.
If one of the airbags is deployed, the hazard warning light system will switch
on automatically.
70
Operation
Page 73

If the turn signal light is switched on when the hazard warning light and the
ignition are both switched on, then only the turn signal light on the corresponding vehicle side will flash.
WARNING
Switch on the hazard warning light system if, for example, the following occurs.
■
You encounter a traffic congestion.
■
The vehicle has broken down.
Parking lights
Read and observe on page 65 first.
Parking light switching on
Switch off the ignition.
›
Place the control lever into position A or B as far as it can go » Fig. 49 on
›
page 67 - the parking light on the right/left-hand side of the vehicle is
switched on.
If the right or left turn signal light has been switched on and the ignition is
switched off, the parking light is not automatically switched on.
Switching on the side light on both sides
Turn the light switch A to position » Fig. 48 on page 66 and lock the ve-
›
hicle.
Interior lights
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Front interior light 71
Rear interior light 72
Rear interior light 72
Front door warning light 72
Entry lighting 73
Front interior light
Fig. 53 Operation of the front interior light: Version 1/version 2
Rocker switch positions » Fig. 53
Switching on
Switching off
Control with the door contact switch (middle position)
For vehicles with interior monitoring, there is no icon for the center position
(operation with the door contact switch).
Switch for reading lights
Switching left reading lamp on/off
Switching right reading lamp on/off
If operating the light with the door contact switch is enabled the light will
come on when one of the following events occurs:
The vehicle is unlocked.
›
One of the doors or the tailgate is opened.
›
The ignition key is removed.
›
If operating the light with the door contact switch is enabled the light will go
off when one of the following events occurs:
The vehicle is locked.
›
The ignition is switched on.
›
About 30 seconds after all the doors have been closed.
›
Lights and visibility
71
Page 74

Note
■
If the interior light remains switched on when the ignition is switched off or
if one of the doors is open, the light will automatically go out after around 10
minutes.
■
Two diffuse lights are integrated in the front interior lighting, that illuminate
the gearshift lever and the middle of the dash panel. These are switched on
automatically when the parking light is activated. Also, after switching on the
ignition when the parking lights are switched on, the door handle lighting
comes on.
Rear interior light
Applies to vehicles without a panoramic sliding roof.
Fig. 54
Interior light and rear reading
lights
Switch for reading lights » Fig. 54
Switching left reading lamp on/off
Switching right reading lamp on/off
The rear interior light is operated together with the front interior
light » page 71.
Rear interior light
Applies to vehicles with a panoramic sliding roof.
Fig. 55
Interior lights at the rear
The light is operated by moving the lens into one of the following positions » Fig. 55.
Switching on
Control with the door contact switch (middle position)
Switching off
1)
Front door warning light
Fig. 56
Warning light
The warning light » Fig. 56 turns on when the front door is opened.
The warning light turns off when the front door is closed.
In vehicles without a warning light only a reflector is installed at this point.
1)
In this position, apply the same rules to the rear interior light as for the front interior light » page 71 .
72
Operation
Page 75

Note
If the door is open and the ignition switched off, the light extinguishes automatically after around 20 minutes.
Entry lighting
The lighting is positioned on the bottom edge of the exterior mirror and illuminates the entry area of the front door.
The light comes on after the vehicle has been unlocked or on opening the
front door. The lighting goes out about 30 seconds after the doors are closed
or if the ignition is switched on.
WARNING
If the entry light is on, do not touch its cover – risk of burns!
Note
If the door is open and the ignition switched off, the light will extinguish automatically after around 1 minutes.
Visibility
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Windscreen and rear window heater 73
Sun visors 74
Sun screen 74
Sun screen in the rear doors 74
Windscreen and rear window heater
Fig. 57 Buttons for the rear and front window heating Climatronic / manual air conditioning
Buttons in the centre console
Switching the rear window heater on/off
Switching the windscreen heater on/off
When the heater is switched on, a lamp lights up inside the button.
The heating only works when the engine is running.
The heater automatically switches off after approximately 10 minutes.
For the sake of the environment
The heating should be switched off as soon as the window is de-iced or free
from mist. The reduced current consumption will have a favourable effect on
fuel economy » page 148, Saving electrical energy.
Note
■
If the on-board voltage drops, the heater switches off automatically, in order
to provide sufficient electrical energy for the engine control » page 193, Auto-
matic load deactivation.
■
If the light is flashing inside the button the heater is off due to low battery.
Lights and visibility
73
Page 76

Sun visors
Sun screen
Fig. 60
Unroll the sun screen
Fig. 58 Sun visor: fold down / pivot to door
Fig. 59 Sun visor: Auxiliary panel fold down / makeup mirror
Operation of the sun visor » Fig. 58, » Fig. 59
1
Fold down the cover
2
Swivel cover towards the door
3
Fold down the auxiliary cover
A
Make-up mirror, the cover can be pushed in the direction of the arrow
B
Light - turns on automatically when the cover slides open
While sliding the cover A or when lifting the cover, the light turns off
WARNING
The sun visors must not be swivelled towards the side windows in the deployment area of the head airbags if any objects are attached to them. Initiation of the head airbags may cause injury.
74
Operation
The sun screen is located in the lower part of the boot cover.
Extending
Pull the sun screen on the handle
›
brackets B.
Retracting
Remove the sun screen from the magnetic brackets B and hold it on the
›
handle A so that it can slowly roll up into the housing on the boot cover
without being damaged.
Note
Do not place any objects that react sensitively to influences of magnetic fields
(watches, electronics, etc.) in the immediate vicinity of the magnetic brackets.
They can be damaged by the magnetic field.
A
» Fig. 60 and hang it in the magnetic
Sun screen in the rear doors
Fig. 61
Rear door: Sun screen
B.
Extending
Pull out the sun screen with the handle A » Fig. 61 and hang it in the brack-
›
et on the top edge of the door.
Page 77

Retracting
Remove the sun screen from the handle A » Fig. 61 and hold it in such a way
›
that it can roll up slowly without being damaged.
Windscreen wipers and washers
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Windscreen wipers and washers 76
Headlight cleaning system 77
The windscreen wipers and the wash system only operate if the ignition is
switched on and the bonnet is closed.
If the intermittent wipe is switched on, the intervals are also controlled depending on speed.
When automatic wiping in rain is active, the wiper intervals are regulated
based on the intensity of the rain.
The rear window is wiped once automatically if the windscreen wipers are on
when reverse gear is selected.
Top up with windscreen wiper fluid » page 184.
WARNING
■
Properly maintained windscreen wiper blades are essential for clear visi-
bility and safe driving » page 214.
■
Replace the windscreen wiper blades once or twice a year for safety rea-
sons. These can be purchased from a ŠKODA Partner.
■
Do not use the windscreen washer system at low temperatures, without
heating the windscreen beforehand. Otherwise the window cleaner could
freeze on the windscreen and restrict the view to the front.
■
Automatic wiping in rain only operates as a support. The driver is not released from the responsibility to set the function of the windscreen wipers
manually depending on the visibility conditions.
CAUTION
■
If the ignition is switched off while the windscreen wipers are switched on,
the windscreen wipers will continue wiping in the same mode after the ignition is turned back on. The windscreen wipers could freeze up in cold temperatures between the time the ignition was turned off and when it was turned
back on again.
■
In cold temperatures and during the winter, check before the journey or before switching on the ignition that the wiper blades are not frozen to the
windscreen. If the windscreen wipers are switched on when the blades are frozen to the windscreen, this may damage both the blades and windscreen wiper motor!
■
Carefully peel frozen wiper blades off the pane.
■
Remove snow and ice from the windscreen wipers before driving.
■
If the windscreen wipers are handled carelessly, there is a risk of damage to
the windscreen.
■
Do not switch on the ignition if the front wiper arms are retracted. The wiper
blades would move back into their rest position and while doing so damage
the paintwork of the bonnet.
■
If there is an obstacle on the windscreen, the wiper will try to push away the
obstacle. The wiper stops automatically after 5 attempts to eliminate the obstacle, in order to avoid a damage to the wiper. Remove the the obstacle and
switch the wiper on again.
Note
■
Each time the ignition switches off for the third time, the position of the
windscreen wipers changes. This counteracts an early fatigue of the wiper rubbers.
■
The rear window wiper only operates if the boot lid is closed.
■
The wiper blades should be cleaned on a regular basis with a windscreen
cleaner to avoid any smears. The wiper blades should be cleaned with a
sponge or cloth if they are heavily soiled by insect residues, for example.
■
Keep the wiper blades clean. They may become soiled, e.g., with wax residues after washing in automatic car wash systems » page 173.
■
The windscreen washer nozzles for the windscreen are heated when the engine is running and the outside temperature is less than approx. +10 °C.
Lights and visibility
75
Page 78

Windscreen wipers and washers
Fig. 62
Operating lever: Windscreen
wipers and washer settings
Read and observe and on page 75 first.
Lever positions
0
Wipers off
1
Periodic windscreen wiping/automatic wiping in rain
2
Slow windscreen wiping
3
Rapid windscreen wiping
4
Flick windscreen wiping, service position of the wiper
arms » page 214, (spring-loaded position)
5
Automatic wipe/wash for windscreen (spring-tensioned position)
6
Wiping the rear window pane (the windscreen wiper wipes at regu-
lar intervals after a few seconds)
7
Automatic wipe/wash for the rear window (spring-tensioned posi-
tion)
A
Switches for setting the required break between the individual
wiper strokes (1 periodic windscreen wiping) or the wiper speed in
rain (1 automatic windscreen wiping in rain)
Automatic wipe/wash for windscreen
The wash system operates immediately, the windscreen wipers wipe somewhat later. The wash system and the windscreen wiper operate simultaneously at a speed of more than 120 km/h.
Letting go of the lever will cause the windscreen wash system to stop and the
wiper to continue for another 3-4 wiper strokes (depending on the period of
spraying of the windscreen).
At a speed of more than 2 km/h, the wiper wipes once again 5 seconds after
the last wiper stroke in order to wipe the last drops from the windscreen. This
function can be activated/deactivated by a specialist garage.
Automatic wipe/wash for the rear window (Superb Combi)
The wash system operates immediately, the windscreen wiper wipes somewhat later.
Letting go of the lever will cause the windscreen wash system to stop and the
wiper to continue for another 2-3 wiper strokes (depending on the period of
spraying of the windscreen). The operating lever remains in position » Fig. 62
6
.
Automatic rear window wiper (Superb Combi)
If the lever is in position 2 » Fig. 62 or 3 the rear window is wiped every
30 or 10 seconds if the vehicle's speed exceeds 5 km/h.
If automatic windscreen wiping in rain is activated (the operating lever is in the
position 1) the function is only active if the windscreen wipers operate in
continuous mode (no break between each wiping process).
Automatic rear window wiping can be activated/deactivated via the MAXI DOT
display in the menu item Rear wiper » page 45.
Winter setting of the windscreen wiper
If the windscreen wipers are in rest position, they cannot be folded out from
the windscreen. For this reason we recommend adjusting the windscreen wipers in winter so that they can be folded out from the windscreen easily.
Switch on the windscreen wipers.
›
Switch off the ignition.
›
The windscreen wipers remain in the position in which they were when
switching off the ignition.
The service position can also be used as a winter position » page 214.
Note
If the operating lever is in the position 2 or 3 and the speed of the vehicle
drops below 4 km / h, the wiping speed is switched to a lower wiping level.
The original setting is restored step by step when the speed of the vehicle exceeds 8 km/h.
76
Operation
Page 79

Headlight cleaning system
Read and observe and on page 75 first.
After the ignition is switched on, the headlights are always cleaned at the first
and after every tenth spray of the windscreen (setting 5 » Fig. 62 on
page 76), when the low beam or main beam is switched on.
You should remove stubborn dirt (such as insect residues) from the headlight
lenses at regular intervals, for example when refuelling. The following guidelines must be observed » page 175, Headlight lenses.
To ensure the proper operation of the cleaning system during the winter, any
snow should be removed from the washer nozzle fixtures and ice should be
cleared with a de-icing spray.
CAUTION
Never remove the nozzles from the headlight cleaning system by hand – risk of
damage!
Rear mirror
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Interior mirror
Exterior mirrors 78
WARNING
■
Make sure that the mirror is not covered by ice, snow, mist or other ob-
jects.
■
Convex (curved outward) or aspheric exterior mirrors increase the field of
vision. They do, however, make objects appear smaller in the mirror. These
mirrors are therefore only of limited use for estimating distances to the following vehicles.
■
Whenever possible use the interior mirror for estimating the distances to
the following vehicles.
■
The illuminated display of an external navigation unit can lead to operational faults to the automatic dimming interior mirror – risk of accident.
WARNING
The mirrors with automatic dimming contain an electrolyte liquid which can
escape if mirror glass is broken.
■
The leaking electrolytic fluid can irritate the skin, eyes and breath apparatus. Immediately seek out fresh air and leave the vehicle. If this is not possible, at least open the window.
■
If you swallow electrolytic fluid, seek medical assistance immediately.
■
If your eyes or skin come into contact with the electrolytic fluid, immediately wash the affected area for a few minutes long with a lot of water.
Then consult a doctor immediately.
Interior mirror
Fig. 63
77
Mirrors with manual dimming » Fig. 63
1
2
Mirror with automatic dimming » Fig. 63
A
B
C
D
If the automatic dimming is enabled, the mirror dims automatically depending
on the light falling on the sensors.
Interior mirror: manual dimming / auto-darkening / light sensor
Read and observe on page 77 first.
Basic position of the mirror
Mirror blackout
Warning light - lights when dimming is activated
Switch for the activation of the automatic mirror dimming
Light sensor
Light sensor on the back of the mirror
Lights and visibility
77
Page 80

When the interior lights are switched on or the reverse gear is engaged, the
mirror always moves back into the basic position (not dimmed).
Do not attach external navigation devices on to the windscreen or in the vicinity of the automatic dimming mirror » page 77, in section Introduction.
Note
■
The automatic dimming mirror only functions smoothly if the light falling on
the sensors is not compromised (e.g. by the sun screen back).
■
If the automatic interior mirror dimming is switched off, the exterior mirror
dimming is also switched off.
Exterior mirrors
Fig. 64
Knob for the mirrors
Read and observe on page 77 first.
The knob can be moved into the following positions.
Adjust the left mirror
Adjust the right mirror
Switch off mirror control
Mirror heater
Folding in the exterior mirrors
Adjust the position
The mirror can be adjusted to the desired position by moving the knob in the
direction of the arrow » Fig. 64.
The movement of the mirror surface is identical to the movement of the rotary
knob.
Synchronous adjustment of the mirror
Activate the synchronous adjustment of the mirror above the MAXI DOT dis-
›
play in the menu item Mirror adjust. » page 45, Settings.
Turn the knob for the mirror control to the position for the driver mirror ad-
›
justment.
Adjust the mirror to the desired position.
›
Folding-in both of the exterior mirrors with the rotary knob
It is only possible to fold in both exterior mirrors when the ignition is switched
on and at a speed of up to 15 km/h.
The mirrors are folded out into the driving position after the rotary knob is
turned from the position to a different one.
Folding-in both of the exterior mirrors using the remote control key
Close all windows.
›
Press on the remote control key for about 2 seconds.
›
The exterior mirror is folded back into the driving position when the ignition is
switched on.
Mirror with automatic dimming
The exterior mirror blackout is controlled together with the automatic dimming
interior mirror » page 77.
Fold in passenger's mirror
The passenger-side mirror can tilt down to improve the view to the curb when
reversing.
The mirror will be folded if the following conditions are met.
The vehicle is equipped with the memory function for the driver's
seat » page 82.
The function is activated via the MAXI DOT display in the menu item Mirror
down. » page 45, Settings.
The knob for the mirror control is in the position for the passenger mirror
adjustment.
The reverse gear is engaged.
Memory function for mirrors
On vehicles fitted with a memory function for the driver seat, the relevant setting for the exterior mirrors can also be stored automatically when the seat
position is stored » page 82.
WARNING
Do not touch the exterior mirror surfaces, if the exterior mirror heating is
switched on - hazard of burning.
78
Operation
Page 81

CAUTION
■
The exterior mirrors with fold-in function never mechanically fold by hand
- there is a risk of damaging the electric mirror actuator!
■
When the mirror is swung by external influences (due to impact during manoeuvring, for example), then first fold-in the mirror by turning the knob and
wait for a loud clapping noise.
Note
■
The mirror heater only operates when the engine is running and up to an
outside temperature of +35 ℃.
■
If the electrical mirror setting fails at any time, the mirrors can be adjusted by
hand by pressing on the edge of the mirror surface.
Seats and useful equipment
Adjusting the seats
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Manually adjusting the front seats 80
Electric front seat adjustment 80
Head restraints 81
Memory function of the electrically adjustable seat 82
Memory function of the remote control key 82
The driver's seat should be adjusted in such a way that the pedals can be fully
pressed to the floor with slightly bent legs.
The seat backrest on the driver's seat should be adjusted in such a way that
the upper point of the steering wheel can be easily reached with slightly bent
arms.
Correct adjustment of the seats is particularly important for the following reasons.
Reaching the controls safely and quickly.
›
A relaxed and fatigue-free body position.
›
Achieving the maximum protection offered by the seat belts and the airbag
›
system.
WARNING
■
Only adjust the driver's seat when the vehicle is stationary – risk of acci-
dent!
■
Caution when adjusting the seat! You may suffer injuries or bruises as a
result of adjusting the seat without paying proper attention.
■
The electric front seat adjustment is still functional if the ignition is
switched off (even with the ignition key removed). Therefore, when leaving
the vehicle, never leave people who are not completely independent, such
as children, unattended in the vehicle - there is a danger of injury!
■
Never carry more people than the number of seats in the vehicle.
■
Do not carry any objects on the front passenger seat except objects designed for this purpose (e.g. child seats) – risk of accident!
Seats and useful equipment
79
Page 82

Note
■
After a certain time, play can develop within the adjustment mechanism of
the backrest angle.
■
For safety reasons, it is not possible to store the seat position in the electric
seat memory and remote control key memory if the inclination angle of the
seat backrest is more than 102° in relation to the seat cushion.
■
Each time you store the position of the electrically adjustable driver's seat
and exterior mirrors, the existing setting is deleted.
Manually adjusting the front seats
Fig. 65 Controls / setting
Read and observe on page 79 first.
Adjusting a seat in a forward/back direction
Pull the lever A » Fig. 65 in the direction of the arrow 1 and push the seat in
›
the required direction.
The lock must click into place after you release the lever.
Adjusting height of seat
Again push/pull the lever B » Fig. 65 in the direction of one of the arrows2.
›
Adjusting the angle of the seat backrest
Relieve any pressure from the seat backrest (do not lean on it) and turn the
›
handwheel C » Fig. 65 in the direction of the arrow 3.
Adjusting lumbar support
Push the lever D » Fig. 65 in the direction of one of the arrows4.
›
Electric front seat adjustment
Fig. 66 Adjusting controls / lumbar support
Fig. 67 Setting: Seat pad / backrest
Read and observe on page 79 first.
Adjusting a seat in a forward/back direction
Push the switch B » Fig. 66 in the direction of one of the arrows 3 » Fig. 67.
›
Set the height of the seat cushion
Push the switch B » Fig. 66 in the direction of one of the arrows 5 » Fig. 67.
›
Adjust the angle of the seat cushion
Push the switch B » Fig. 66 in the direction of one of the arrows 4 » Fig. 67.
›
Adjusting the angle of the seat backrest
Push the switch C » Fig. 66 in the direction of one of the arrows 6 » Fig. 67.
›
Reducing or increasing the curvature of the lumbar support
Push the switch A in the region of one of the arrows2 » Fig. 66.
›
80
Operation
Page 83

Raising or lowering the curvature of the lumbar support
Push the switch A in the region of one of the arrows1 » Fig. 66.
›
The adjusted driver's seat position can be set in the memory of the
seat » page 82 or the remote control key » page 82.
Note
If the setting procedure is interrupted, you will need to press the button again.
Head restraints
Fig. 68 Head restraints: setting / removing
Fig. 69
Rear centre head rests in vehicles with the TOP TETHER system
Read and observe
Best protection is achieved if the top edge of the head rest is at the same level
as the upper part of your head.
Setting height
Grasp the side of the head restraint with both hands and push it upwards as
›
required » Fig. 68 - .
on page 79 first.
To move the head restraint downwards, press and hold the safety but-
›
ton » Fig. 68 - with one hand and push the head restraint down with the
other hand.
The front seats and head rests must be adjusted to match the body size at all
times and the seat belt must always be fastened properly to provide the most
effective levels of protection to the passengers » page 7, Correct and safe
seated position.
Removing/installing
Pull the head restraint up out of the seat backrest as far as the stop (for the
›
rear head restraints fold the seat backrest forward).
Press the locking button in the direction of the arrow » Fig. 68 - and pull
›
the head restraint out.
To re-insert the head restraint, push it far enough down into the seat back-
›
rest until the locking button clicks into place.
Removing and installing rear middle head rest
Applies to vehicles using the TOP TETHER system.
Pull the head restraint out of the seat backrest as far as the stop.
›
Press the locking button in the direction of arrow 1 » Fig. 69 simultaneously
›
press the locking button into the opening 2 using a flat screwdriver with a
width of maximum 5 mm and pull out the head rest.
To re-insert the head restraint, push it far enough down into the seat back-
›
rest until the locking button clicks into place.
WARNING
■
The head rests must be correctly adjusted to avoid risk of injury.
■
Never drive with the head restraints removed - risk of injury.
■
If the rear seats are occupied, the rear head rests must not be in the low-
er position.
Note
The middle rear head restraint is adjustable in two positions.
Seats and useful equipment
81
Page 84

Memory function of the electrically adjustable seat
Fig. 70
Memory buttons and SET button
Read and observe on page 79 first.
The memory function for the driver's seat provides the option to store the positions of the driver's seat and the external mirrors. Each of the three memory
buttons B » Fig. 70 can be assigned a set position.
Storing seat and exterior mirror settings for driving forward
Switch on the ignition.
›
Adjust the seat to the desired position.
›
Adjust both of the exterior mirrors » page 78.
›
Press the button
›
Within 10 seconds after pressing the
›
button B.
An acknowledgment sound confirms the storage.
Saving front passenger mirror settings when reversing
Above the MAXI DOT display in the menu item Mirror down. The lowering function for the mirror on the passenger side when reversing must be enabled » page 45.
Switch on the ignition.
›
Press the required memory button B » Fig. 70.
›
Turn the knob for the external mirror control to the position for the passen-
›
ger side mirror adjustment » page 78.
Engage reverse gear.
›
Adjust the front passenger's mirror to the desired position » page 78.
›
Disengage reverse gear.
›
The set position of the exterior mirror is stored.
Retrieving the saved setting
Briefly press the desired memory button B » Fig. 70 with the ignition on.
›
SET
A » Fig. 70.
SET
button, press the desired memory
or
Press and hold the desired memory button B with the ignition off or when
›
the ignition is on and travelling at a speed of more than 5 km / h.
Stopping the ongoing adjustment
Press any button on the driver's seat or the button on the remote control
›
key.
Note
Each time new seat and exterior mirror settings for forward travel are saved,
the individual setting for the right exterior mirror for reverse travel must also
be saved again.
Memory function of the remote control key
Read and observe
The automatic storage of the driver's seat and exterior mirror positions when
locking the vehicle can be turned on in the memory of the remote control key
(afterwards only as function of automatic storage).
Enable automatic storage
Unlock the vehicle with the remote control key.
›
Press and hold any memory button B » Fig. 70 on page 82. After the seat
›
has assumed the position stored under this button, at the same time press
the button on the remote control key within 10 seconds.
The successful activation of the automatic storage function for each key is
confirmed by an acoustic signal.
Storing seat and exterior mirror settings for driving forward
Enable automatic storage.
›
on page 79 first.
82
Operation
Page 85

When automatic storage is activated, the current positions of the driver's seat
and the external mirrors are saved in the memory of the remote control key
each time the vehicle is locked. When the vehicle is next unlocked using the
same key, the driver's seat and the external mirrors assume the positions stored in the memory of this key1).
Saving front passenger mirror settings when reversing
Above the MAXI DOT display in the menu item Mirror down. The lowering function for the mirror on the passenger side when reversing must be enabled » page 45.
Unlock the vehicle with the remote control key.
›
Switch on the ignition.
›
Turn the knob for the external mirror control to the position for the passen-
›
ger side mirror adjustment » page 78.
Engage reverse gear.
›
Adjust the front passenger's mirror to the desired position » page 78.
›
Disengage reverse gear.
›
The adjusted position of the exterior mirror is stored in the remote control key
memory.
Disable the function of automatic storage
Unlock the vehicle with the remote control key.
›
Press and hold the
›
press the button on the remote control key within 10 seconds.
The successful deactivation of the automatic storage function for each key is
confirmed by an acoustic signal.
Stopping the ongoing adjustment
Press any button on the driver's seat or the button on the remote control
›
key.
SET
button A » Fig. 70 on page 82. At the same time,
Seat features
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Seat heaters
Ventilated front seats 84
83
Convenience features of passenger seat 85
Armrest, front 85
Armrest rear 85
Seat backrests 85
Rear seat folded forward (Superb Combi) 86
Seat heaters
Fig. 71 Heating: Front seats/ rear seats
The seat backrests and surfaces of the front seats and the two outer rear
seats can be heated electrically.
The seat heating can only be switched on when the engine is running.
Switching on the front seat heater
Press the controller in the area of the symbols and » Fig. 71 -
›
Switch on rear seat heater
Press the symbol button or » Fig. 71 - .
›
By pressing the button once, the heating is switched to the highest intensity level 3, which is indicated by all three of the indicator lights in the switch lighting up.
With repeated pressing of the switch, the heating is turned down until it goes
off.
The seat heating level is indicated by the number of illuminated warning lights
in the respective control.
1)
The vehicle must be locked and unlocked with the same key to save the seat and exterior mirror position
to the key.
Seats and useful equipment
83
Page 86

WARNING
If you have a subdued pain and/or temperature sensitivity, e.g. through
medication, paralysis or because of chronic illness (e.g. diabetes), we rec-
ommend not to use the seat heating. This can lead to burns on the back,
the posterior and the legs which are difficult to heal. If the seat heating is
used, we recommend to make regular breaks in your journey when driving
long distances, so that the body can recuperate from the stress of the jour-
ney. Please consult your doctor, who can evaluate your specific condition.
CAUTION
■
Do not kneel on the seats or otherwise apply concentrated pressure to them.
■
Do not turn on the seat heater if seats are not occupied.
■
Do not switch on the seat heating if the seats have objects attached to or
placed on them, for example a child seat, a bag, etc. A fault of the heating elements in the seat heating can occur.
■
If additional seat covers or protective covers are attached to the seats, do
not turn on the seat heater - there is a risk of damaging the seat covers and
seat heating.
■
Do not clean the seats using moisture » page 178, Seat covers.
Note
■
If the on-board voltage drops, the seat heating is switched off automatically,
in order to provide sufficient electrical energy for the engine control » page 193.
■
If the heaters for the rear seats are set to the highest intensity - level 3, they
are automatically switched over to level 2 after 10 minutes (two indicator lights
are illuminated on the switch).
Ventilated front seats
Fig. 72
Rocker switch for the seat ventilation
Heat and condensation can be removed from the seat cushions and seat
backrests on the front seats.
The ventilation is operated using the rocker switch » Fig. 72 in the front part of
the seat cushion, in front of the seat control elements for the electric front
seat adjustment.
Switching on
Switch the rocker switch to position 1 - lower intensity and to position 2 -
›
higher intensity.
Switching off
Switch the rocker switch to the centre position .
›
WARNING
If you or a passenger have limited pain and/or temperature sensitivity, e.g.
caused by medication, paralysis or because of chronic illness (e.g. diabetes),
we recommend that you consult your physician before using the ventilated
front seat.
CAUTION
■
Do not kneel on the seats or otherwise apply concentrated pressure to them.
■
The fan is located underneath the front seat cushion. Do not place any ob-
jects in this area - it may damage the fan.
■
Do not clean the seats using moisture » page 178, Seat covers.
Note
■
The ventilation should only be switched on when the engine is running. This
has a significant effect of saving on the battery capacity.
■
We do not recommend using the front seat ventilation and heating at the
same time. Using the ventilation to cool the seat surface considerably reduces
the heating capacity, at the same time affecting the ability of the control unit
to detect the right seat surface temperature.
84
Operation
Page 87

Convenience features of passenger seat
Fig. 73
Operating passenger seat from
the rear seat
The front passenger seat can also be operated from the rear seat.
Adjusting the angle of the seat backrest
Push the switch
›
Adjusting a seat in a forward/back direction
Push the switchB in the direction of one of the arrows 2 .» Fig. 73
›
A
in the direction of one of the arrows 1 » Fig. 73.
Armrest, front
Fig. 74
Adjusting armrest
The armrest is adjustable for height and length.
Setting height
First of all fold the cover downwards and then lift it in the direction of the
›
arrow 1 » Fig. 74 to one of the 4 fixed positions.
Move
Move the cover into the desired position in the direction of the arrow
›
2
» Fig. 74.
The armrest includes a storage compartment underneath » page 90.
Note
Push the armrest cover all the way back to the stop before applying the handbrake.
Armrest rear
Fig. 75
Fold the armrest forwards
Folding forward
Fold down the armrest in the direction of the arrow » Fig. 75.
›
A cup holder may be located in the armrest » page 88.
Seat backrests
Fig. 76 Seat back: unlock / lock
The luggage compartment can be increased in size by folding the seat backrests forward. The seat backrests can be folded forward individually on vehicles
with divided rear seats.
Seats and useful equipment
85
Page 88

Folding forward
Before folding the seat backrests forwards, adapt the position of the front
seats in such a way that they are not damaged by the folded seat backrests 1).
Push the lever A » Fig. 76 and fold the seat backrest completely forwards.
›
Folding backward
If you removed the head restraint, you need to reinsert it with the backrest
›
tilted slightly forwards » page 81.
Hold the rear outer seat belt C » Fig. 76 against the side trim panel.
›
Then push the seat backrest back into the upright position until the securing
›
knob A clicks into place – check by pulling on the seat backrest » .
Make sure that the red pin B is hidden.
›
WARNING
■
The seat belts and the belt locks must be in their original position after
folding back the seat backrests – they must be ready to use.
■
The seat backrests must be securely locked in position so that no objects
in the luggage compartment can slide into the passenger compartment on
sudden braking – risk of injury.
■
Ensure that the rear seat backrests are properly engaged. Only then can
the seat belt for the middle seat reliably fulfil its function.
CAUTION
Ensure that the seat belts are not damaged when operating the seat backrests. Under no circumstances must the rear seat belts be jammed by the folded back seat backrests.
Rear seat folded forward (Superb Combi)
Fig. 77
Folding the seat cushion forwards
Pull up the seat squab in the direction of the arrow 1 » Fig. 77 and fold for-
›
wards in the direction of the arrow 2.
Note
To achieve a loading space that is as horizontal as possible, the rear head restraints can be removed before folding the seat backrests forwards. Store the
removed head restraints in such a way that they are not be damaged or soiled.
Practical equipment
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Car park ticket holder
Storage compartment on the driver's side 87
Storage compartments in the doors 88
Storage compartment in the front centre console 88
Cup holders 88
Cigarette lighter 89
Ashtray 89
12-Volt power outlet 90
Storage compartment under the armrest, front 90
Storage net in the front centre console 91
Glasses storage box 91
87
1)
If the front seats are too far back, we recommend removing the rear head restraints before the seat
backrests are folded forward, to achieve a loading space that is as horizontal as possible. Store the removed head restraints in such a way that they are not be damaged or soiled.
86
Operation
Page 89

Storage compartment on the passenger side 92
Storage compartment under the passenger seat 92
Clothes hook 92
Storage pockets on the front seats 93
Storage compartment for umbrella 93
Storage compartment in rear centre console 93
Storage compartment in the rear armrest 94
Rear seat backrest with long-cargo channel 94
Removable ski bag 95
WARNING
■
Do not place anything on the dash panel. These objects might slide or fall
down when driving (when accelerating or cornering) and may distract you
from concentrating on the traffic – there is the risk of an accident.
■
When driving, ensure that no objects from the centre console or from other storage compartments can get into the driver's footwell. You would not
be able to brake, operate the clutch pedal or accelerate - danger of causing
an accident!
■
No objects should be placed in the storage compartments nor in the
drinks holders; the vehicle occupants could be endangered if there is sudden braking or the vehicle collides with something.
■
Ash and cigarette or cigar stubs must only be discarded in ashtrays!
Car park ticket holder
Fig. 78
Windscreen: Parking ticket holder
WARNING
The attached note has to always be removed before starting off in order
not to restrict the driver's vision.
Storage compartment on the driver's side
Fig. 79
Storage compartment on the
driver's side
Read and observe on page 87 first.
Opening
Raise the handle A » Fig. 79 and open out the compartment in the direction
›
of the arrow.
Closing
Swivel the lid against the direction of the arrow until it clicks into place.
›
WARNING
The storage compartment must always be closed when driving for safety
reasons.
Read and observe on page 87 first.
The note holder is designed e.g. for attaching car park tickets.
Seats and useful equipment
87
Page 90

Storage compartments in the doors
WARNING
The storage compartment must never be used as an ashtray or for the storage of combustible materials - fire hazard and risk of damage to the storage compartment!
Note
The storage compartment is equipped with an interior light which lights up
when the parking light is on.
Cup holders
Fig. 80 Storage compartment: in the front door/in the rear door
Read and observe
WARNING
Use the storage compartment only for storing objects which do not project
so that the effectiveness of the side airbag is not impaired.
on page 87 first.
Storage compartment in the front centre console
Fig. 81
Opening the storage compartment
Read and observe on page 87 first.
Open/close
Press on the edge of the roof A » Fig. 81 in the direction of the arrow.
›
Closing takes place in reverse order.
88
Operation
Fig. 82
Front centre console: Cup holder
Fig. 83 Rear armrest: Remove cup holder/insert cup holder
Read and observe on page 87 first.
Two beverage containers can be placed into the cup holder.
Cup holder at the front
On vehicles that are fitted with a cover for cup holders, you can cover the cup
holder by pulling on the handle A » Fig. 82 in the direction of the arrow.
Page 91

Rear cup holder
Press on the front end of the armrest in the direction of the arrow » Fig. 83 -
›
, the cup holder comes out.
To slide the cup holder in again, press the middle part of the cup hold-
›
er » Fig. 83 - and slide it into the armrest in the direction of the arrow.
WARNING
■
Never put hot beverage containers in the cup holder. If the vehicle moves,
they may spill – risk of scalding!
■
Do not use any cups or beakers which are made of brittle material (e.g.
glass, porcelain). This could lead to injuries in the event of an accident.
CAUTION
■
Do not leave open beverage containers in the cup holder during the journey.
There is a risk of spilling e.g. when braking which may cause damage to the
electrical components or seat upholstery.
■
Slide in the cup holder before raising the rear armrest.
Cigarette lighter
Fig. 84 Centre console: Cigarette lighter, front/rear
Read and observe on page 87 first.
Operation
Press the button of the cigarette lighter A or B » Fig. 84.
›
Wait until the button pops forward.
›
Remove the cigarette lighter immediately and use.
›
Place the cigarette lighter back into the socket.
›
WARNING
■
Take care when using the cigarette lighter! Improper usage can case
burns.
■
The cigarette lighter also operates when the ignition is switched off or
the ignition key withdrawn. Therefore, when leaving the vehicle, never
leave people who are not completely independent, such as children, unattended in the vehicle. They could operate the igniter and burn themselves.
Note
■
The cigarette lighter socket can also be used as a 12Volt socket for electrical
appliances » page 90, 12-Volt power outlet.
■
Further information » page 169, Services, modifications, and technical alter-
ations.
Ashtray
Fig. 85 Centre console: Ashtray at the front/rear
Read and observe on page 87 first.
The ashtray can be used for discarding ash, cigarettes, cigars and the like » .
Removing/inserting the front ash tray
Open the ashtray » Fig. 81 on page 88.
›
Grasp the ashtray insert in the area A » Fig. 85 and remove it in the direc-
›
tion of the arrow 1.
Insertion takes place in reverse order.
Removing/inserting the rear ashtray insert
Open the ashtray » Fig. 94 on page 93.
›
Seats and useful equipment
89
Page 92

Grasp the ashtray insert B » Fig. 85 in the area marked with the arrows and
›
remove it in the direction of the arrow 2.
Insertion takes place in reverse order.
WARNING
Never place flammable objects in the ashtray – risk of fire!
Note
The ashtrays are fitted with an interior light which lights up when the parking
light is on.
12-Volt power outlet
WARNING
■
Improper use of the power sockets and the electrical accessories can
cause fires, burns and other serious injuries. Therefore, when leaving the
vehicle, never leave people who are not completely independent, such as
children, unattended in the vehicle.
■
If the connected electric device becomes too hot, switch it off and disconnect it from the power supply immediately.
CAUTION
■
The power socket can only be used for connecting approved electrical acces-
sories with a power uptake of up to 120 watt.
■
Never exceed the maximum power consumption, otherwise the vehicle's
electrical system can be damaged.
■
Connecting appliances when the engine is not running will drain the battery
of the vehicle!
■
Only use matching plugs to avoid damaging the power sockets.
■
Only use accessories that have been tested for electromagnetic compatibility
in accordance with the applicable directives.
■
Switch off the devices connected to the power sockets before you switch
the ignition on or off and before starting the engine, to avoid damage from
voltage fluctuations.
■
Observe the operating instructions for the connected devices!
Fig. 86 Boot: Superb / Superb Combi socket
Read and observe on page 87 first.
The 12-volt power socket (hereinafter referred to only as a socket) is located in
the front center console A » Fig. 84 on page 89 in the rear center console
B
» Fig. 84 on page 89 and in the luggage compartment » Fig. 86.
Use
Remove the cover from power socket or cigarette lighter » Fig. 84 on
›
page 89or open the cover for the power socket » Fig. 86.
Connect the plug for the electrical appliance to the socket.
›
The power socket and any connected appliances can also be operated when
the ignition is switched off or the ignition key is withdrawn » .
90
Operation
Storage compartment under the armrest, front
Fig. 87
Armrest: Stowage compartment
Read and observe on page 87 first.
Opening
Pull and open the cover of the armrest using the handle A in the direction of
›
the arrow » Fig. 87.
Page 93

Closing
Open the lid to the stop, only then can it be folded downwards and against
›
the direction of the arrow » Fig. 87.
The sockets marked
storage compartment.
Note
The storage compartment is equipped with an interior light which lights up
when the parking light is on.
AUX-IN input and the MDI input are located in the
Storage net in the front centre console
Fig. 88
Front centre console: Storage
net
Read and observe on page 87 first.
WARNING
Only store soft objects with a total weight of 0.5 kg in the storage net.
Heavy objects are not secured sufficiently – risk of injury!
CAUTION
Do not place any sharp objects into the net – risk of net damage.
Glasses storage box
Fig. 89
Opening the glasses storage box
Read and observe on page 87 first.
Opening
Press the button
›
The box folds in the direction of the arrow.
Closing
Swivel the lid of the glasses storage box against the direction of the ar-
›
row » Fig. 89 until it audibly clicks into place.
WARNING
■
The compartment must only be opened when removing or inserting the
spectacles and otherwise must be kept closed!
■
The box must be closed before leaving and locking the vehicle – risk of
impairment to the functions of the anti-theft alarm system!
CAUTION
Do not put any heat-sensitive objects in the glasses storage box - they may be
damaged.
A
» Fig. 89.
Seats and useful equipment
91
Page 94

Storage compartment on the passenger side
Fig. 90 Tray open / operating air supply
Read and observe
A pen holder is provided in the stowage compartment.
Opening
Press the button » Fig. 90 - .
›
The flap folds down.
Closing
Lift the lid upwards until it clicks into place.
›
Air supply
Open the air supply by pulling the lever in the direction of the arrow » Fig. 90
›
- .
The air supply is closed by pressing the lever in the opposite direction to that
›
of the arrow.
Opening the air supply when the air conditioning system is switched on allows
cooled air to flow into the storage compartment.
Opening the air inlet when the air conditioning system is on causes fresh or interior air to flow into the storage compartment.
We recommend closing the air supply if it is operated in heating mode or the
cooling system for the storage compartment is not being used.
WARNING
The storage compartment must always be closed when driving for safety
reasons.
on page 87 first.
Note
When the stowage compartment is opened, a light lights up.
Storage compartment under the passenger seat
Fig. 91
Front passenger seat: Opening
the storage compartment
Read and observe on page 87 first.
Opening
Pull the handle to position 1 » Fig. 91 in the direction of the arrow.
›
The compartment opens in the direction of the arrow 2.
Closing
Grip the compartment by the handle and close in the opposite direction to
›
that of the arrow 2 » Fig. 91.
Hold onto the handle until the door is closed.
›
WARNING
The storage compartment must always be closed when driving for safety
reasons.
CAUTION
The storage compartment is designed for storing small objects of up to 1.5 kg.
in weight.
Clothes hook
Read and observe
The clothes hooks are located on the middle pillar of the vehicle and on the
handle of the headliner above each of the rear doors.
on page 87 first.
92
Operation
Page 95

WARNING
■
Only hang light items of clothing on the hooks. Never leave any heavy or
sharp-edged objects in the pockets of the items of clothing.
■
Do not use clothes hangers for hanging up items of clothing otherwise
this may reduce the effectiveness of head airbags.
■
Ensure that any clothes hanging from the hooks do not impair your vision
to the rear.
CAUTION
The maximum permissible load of the hooks is 2 kg.
Storage compartment for umbrella
Fig. 93
Left rear door: Stowage compartment for an umbrella
Storage pockets on the front seats
Fig. 92
Map pockets
Read and observe on page 87 first.
Pockets for storing maps, magazines etc. are provided on the back of the front
seat backrests » Fig. 92.
WARNING
Never put heavy items in the map pockets – risk of injury!
CAUTION
Never put large objects into the map pockets, e.g. bottles or objects with sharp
edges - risk of damaging the pockets and seat coverings.
Read and observe on page 87 first.
The storage compartment for an umbrella is located in the rear left
door » Fig. 93.
Note
An umbrella can be purchased from ŠKODA Original Accessories.
Storage compartment in rear centre console
Fig. 94
Opening the storage compartment
Read and observe on page 87 first.
The storage compartment is equipped with a removable insert.
Open/close
Pull the handle A » Fig. 94 on the upper section of the recess and open out
›
the compartment in the direction of the arrow.
Closing takes place in reverse order.
Seats and useful equipment
93
Page 96

WARNING
The storage compartment is not a substitute for the ashtray and must also
not be used for such purposes – risk of fire!
Storage compartment in the rear armrest
Fig. 95
Opening the storage compartment
Read and observe on page 87 first.
Opening
Lift button A on the front of the armrest and lift the storage compartment
›
cover in the direction of the arrow » Fig. 95.
Closing
Fold back the storage compartment lid in the opposite direction to that of
›
the arrow » Fig. 95 until it clicks.
Rear seat backrest with long-cargo channel
Read and observe on page 87 first.
After folding the rear armrest and cover up, an opening in the seat backrest
becomes visible through which the removable through-loading bag with skis
can be pushed. The armrest and cover can be folded forward from the passenger compartment or the boot.
Opening from the passenger compartment
Fold down the rear armrest » Fig. 75 on page 85.
›
Pull the handle A pull up to the stop in the direction of the arrow and fold
›
the cover down » Fig. 96 .
Opening from the boot
Push the unlock button B » Fig. 96 in the direction of the arrow and fold the
›
cover including the armrest forwards.
Closing
Fold the cover and rear armrest upwards to the stop - the cover must click
›
into place.
Ensure that the armrest is always locked into place after closing. This is apparent as the red field above the unlocking button B » Fig. 96 is not visible from
the boot.
WARNING
The through-loading channel is only intended for transporting skis that are
placed in a properly secured, removable through-loading bag » page 95.
Fig. 96 Rear seats: Cover handle/boot: Unlock button
94
Operation
Page 97

Removable ski bag
Fig. 97
Securing the through-loading
bag
Read and observe on page 87 first.
The removable through-loading bag (hereinafter referred to only as a throughloading bag) is used exclusively for transporting skis.
Loading
Open the tailgate.
›
Fold the rear armrest and the cover in the seat backrest down-
›
wards » page 94, Rear seat backrest with long-cargo channel.
Place the empty, through-loading bag in such a way that the end of the bag
›
with the zip is in the boot.
Push the skis into the through-loading bag from the boot » .
›
Close the through-loading bag.
›
Securing
Tighten the strap A on the free end around the skis in front of the bind-
›
ings» Fig. 97.
Fold the seat backrest a little forward.
›
Guide the securing strap
›
the upper part of the seat backrest.
Then push the seat backrest back into the upright position until the unlock-
›
ing button clicks into place - check by pulling on the seat backrest.
Insert the securing strap B into the lock C until it clicks into place.
›
On vehicles fitted with a luggage net partition, guide the securing strap
around the housing when the net partition is rolled up. After fixing the
through-loading bag in place, it is not longer possible to unroll the net partition.
B
through the opening in the seat backrest around
B
WARNING
■
After placing skis into the through-loading bag, you must secure the bag
with the securing strap B » Fig. 97.
■
The strap A must hold the skis tight.
■
Make sure that the strap A holds the skis in front of the binding (also re-
fer to imprint on the through-loading bag).
■
The total weight of the skis which are transported must not exceed 24
kg.
Note
■
The through-loading bag is foreseen for four pairs of skis.
■
Place the skis with the tips facing to the front and the sticks with the tips
facing to the rear. into the through-loading bag.
■
If there are several pairs of skis in the through-loading bag, ensure that the
bindings are positioned at the same height.
■
The through-loading bag must never be folded together or stowed when
moist.
Luggage compartment
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Class N1 vehicles 96
Fastening elements 97
Fixing nets 97
Folding hook 97
Floor covering 98
Luggage net 98
Luggage compartment cover 98
Roll-up boot cover (Superb Combi) 99
Automatic Retractable cargo cover (Superb Combi) 99
Side pockets in luggage compartment 99
Side compartment in boot with battery 100
Non-closable side pocket (Superb Combi) 100
Please observe the following for the purpose of maintaining good handling
characteristics of your vehicle:
Distribute loads as evenly as possible.
›
Seats and useful equipment
95
Page 98

Place heavy objects as far forward as possible.
›
Attach the items of luggage to the lashing eyes or using the
›
nets » page 97.
In the event of an accident, even small and light objects gain so much kinetic
energy that they can cause severe injuries.
The magnitude of the kinetic energy is dependent on the speed at which the
vehicle is travelling and the weight of the object.
Example: In the event of a frontal collision at a speed of 50 km/h, an object
with a weight of 4.5 kg produces an energy, which corresponds to 20 times its
own weight. This means that it results in a weight of approx. 90 kg “ ”.
Luggage compartment light
The light switches on/off when the luggage compartment lid is opened or
closed.
If the boot lid is open and the ignition switched off, the light will extinguish
automatically after around 10 minutes.
Boot light for Superb Combi vehicles » page 101.
WARNING
■
Store the objects in the boot and attach them to the lashing eyes.
■
Loose objects can be thrown forward during a sudden manoeuvre or in
case of an accident and can injure the occupants or other road users.
■
Loose objects could hit a deployed airbag and injure occupants – danger
of death!
■
Please note that transporting heavy objects alters the handling properties of the vehicle due to the displacement of the centre of gravity – risk of
accident! The speed and style of driving must be adjusted accordingly.
■
If the items of luggage or objects are attached to the lashing eyes with
unsuitable or damaged lashing straps, injuries can occur in the event of
braking manoeuvres or accidents. To prevent items of luggage from moving
around, always use suitable lashing straps which must be firmly attached
to the lashing eyes.
■
The transported items must be stowed in such a way that no objects are
able to slip forward on sudden driving or braking manoeuvres – risk of injury!
■
When transporting objects in the luggage compartment that has been enlarged by folding the rear seats forward, ensure the safety of the passengers transported on the other rear seats » page 9.
WARNING (Continued)
■
If the rear seat next to the folded forward seat is occupied, ensure maximum safety, e.g. by placing the goods to be transported in such a way that
the seat is prevented from folding back in case of a rear collision.
■
Do not drive with the luggage compartment lid fully opened or slightly
ajar otherwise exhaust gases may get into the interior of the vehicle – risk
of poisoning!
■
Do not exceed the permissible axle loads and permissible gross weight of
the vehicle – risk of accident!
■
Do not transport people in the boot!
CAUTION
Make sure that transported objects with sharp edges do not damage the following:
■
heating elements in the rear window;
■
elements of the aerial integrated in the rear window;
■
Aerial filaments integrated in the rear side windows (Superb Combi).
Note
Tyre pressure must be adjusted to the load » page 194.
Class N1 vehicles
Read and observe
On class N1 vehicles, which are not fitted with a protective grille, a lashing set
which complies with the standard EN 12195 (1 - 4) must be used for fastening
the load.
The proper functioning of the electrical system is essential for the safe operation of the vehicle. It is important to ensure that it is not damaged during modifications or when loading or unloading the luggage compartment.
and on page 96 first.
96
Operation
Page 99

Fastening elements
Read and observe and on page 96 first.
Examples for attaching the fixing nets » Fig. 99.
A
Vertical pocket
B
Horizontal pocket
C
Floor net
WARNING
Do not exceed the maximum permissible load of the fixing nets. Heavy objects are not secured sufficiently – risk of injury!
Fig. 98 Lashing eyes and fastening elements: Superb / Superb Combi
Read and observe
The following fastening elements are found in the luggage compartment » Fig. 98.
A
Lashing eyes for fastening items of luggage and fixing nets.
B
Fastening elements for fastening fixing nets.
CAUTION
The maximum permissible load of the lashing eyes is 3.5 kN (350 kg).
and on page 96 first.
Fixing nets
Fig. 99 Fastening examples for nets
CAUTION
■
The maximum permissible load of the fixing nets is 1.5 kg.
■
Do not place any sharp objects in the nets – risk of net damage.
Folding hook
Fig. 100
Folding hooks for attaching small items of luggage, such as bags etc., are provided on both sides of the boot.
Folding forward
Superb: Press on the lower portion of the hook A and fold down direction of
›
the arrow 1 » Fig. 100.
Superb Combi: Grip the hook B direction of the arrow and fold down in the
›
direction of arrow 2 » Fig. 100.
The maximum permissible load of the hook is 7.5 kg.
Folding hooks: Superb / Superb Combi
Read and observe and on page 96 first.
CAUTION
Seats and useful equipment
97
Page 100

Floor covering
Fig. 101 Fixing the floor covering: Superb / Superb Combi
Read and observe
The raised floor covering of the luggage compartment can be fixed (e.g. when
handling the spare wheel):
With the loop on a hook on the luggage compartment cover » Fig. 101 – .
›
With the hook on the frame of the luggage compartment lid » Fig. 101 - .
›
and on page 96 first.
Luggage net
Fig. 102
Luggage net
Read and observe and on page 96 first.
The luggage net is located on the underside of the luggage compartment cover.
The net is designed for transporting lighter objects.
WARNING
Only store soft objects with a total weight of 1.5 kg in the net. Heavy objects are not secured sufficiently – risk of injury!
CAUTION
Do not place any sharp objects into the net – risk of net damage.
Luggage compartment cover
Fig. 103
Removing/installing the luggage
compartment cover
Read and observe and on page 96 first.
Removing
Hook the support straps 1 » Fig. 103 onto the tailgate.
›
Place the cover in the horizontal position.
›
Pull the cover out of the holders 2 horizontally towards the rear.
›
The removed boot cover can be stowed behind the seat backrest.
Fitting
Push the boot cover into the brackets 2 » Fig. 103.
›
Hook the support straps
›
WARNING
No objects should be placed on the boot cover, the vehicle occupants could
be endangered if there is sudden braking or the vehicle collides with something.
CAUTION
Please ensure that the heating elements for the rear window heater are not
damaged as a result of objects placed in this area.
1
onto the tailgate.
98
Operation
 Loading...
Loading...