Škoda India 2015 Owner's Manual

SIMPLY CLEVER
OWNER'S MANUAL
OWNER'S MANUAL
ŠKODA Rapid

5J5012791AE

Preface
You have opted for a ŠKODA – our sincere thanks for your confidence in us.
The description of the vehicle operation, important information concerning safety, vehicle care, main-
tenance and support, as well as technical vehicle data, are given in this Owner's Manual.
Please read this Owner's Manual carefully, because the operation in accordance with these instruc-
tions is a prerequisite for proper use of the vehicle.
We hope you enjoy driving your ŠKODA, and wish you a pleasant journey at all times.
Your ŠKODA AUTO a.s. (hereinafter referred to only as ŠKODA or manufacturer)
5J5012791AE

Table of Contents
On-board literature 4
Notes 5
Design and further information to the Owner's
Manual 6
Abbreviations
Safety
Passive Safety 8
General information 8
Correct and safe seated position 8
Seat belts 11
Using seat belts 11
Inertia reels and belt tensioners 14
Airbag system 15
Description of the airbag system 15
Airbag overview 16
Deactivating airbags 17
Transporting children safely 18
Child seat 18
Usage
Cockpit
Overview
Instruments and Indicator Lights
Instrument cluster
Warning Lights
Information system
Driver information system
Multifunction display (MFA)
23
22
24
24
26
30
30
Unlocking and opening 34
Unlocking and locking 34
Luggage compartment lid 36
Window operation 37
Lights and visibility 40
Lights 40
Interior light 42
Visibility 43
Windscreen wipers and washers 43
Rear mirror 45
Seats and head restraints 47
Setting the seats and head restraints 47
Transporting and practical equipment 49
Transporting and practical equipment 49
Heating and ventilation 54
Manual air conditioning system, Climatronic 54
Communication and multimedia 58
Operating using the buttons on the
multifunction steering wheel 58
Mobile phone operation 58
Multimedia operation 59
Driving
Starting-off and Driving
Starting and turning off the engine 60
Brakes and parking 62
Manual gear changing and pedals 63
Automatic gearbox 64
Running-in and economical driving 67
Avoiding damage to your vehicle 68
Assist systems 69
Braking and stabilisation systems 69
31
Parking assistance (ParkPilot) 70
Cruise control system 71
General Maintenance
Care and maintenance 73
Service work, adjustments and technical
alterations 73
Washing the vehicle 76
Maintain vehicle exterior 78
Maintain interior 81
Inspecting and replenishing 84
Fuel 84
Engine compartment 86
Engine oil 89
Coolant 91
Brake fluid 92
Vehicle battery 93
Wheels 97
Tyres and wheel rims 97
Winter operation 101
Do-it-yourself
Emergency equipment and self-help
Emergency equipment 102
Changing a wheel 103
Jump-starting 106
Towing the vehicle 107
60
Remote control 109
Emergency unlocking/locking 110
Replacing windscreen wiper blades 110
Fuses and light bulbs 112
Fuses 112
Replacing bulbs 114
Technical data
Technical data 118
Basic vehicle data
Vehicle-specific details per engine type
102
118
122
2
Table of Contents
Index
Table of Contents
3

On-board literature
The on-board literature for your vehicle always consists of this Owner's Manual and a Service schedule.
Depending on the equipment the on-board literature can also include the radio instruction manual.
Owner's Manual
This Owner's Manual is valid for all body variants of the vehicle and for all related models and equipment levels.
This Owner's Manual describes all possible equipment variants without identifying them as special equipment, model variants or market-dependent equipment. Consequently, this vehicle does not contain all of the equipment com-
ponents described in this Owner's Manual.
The scope of equipment of your vehicle relates to your purchase contract for
the vehicle. With questions regarding the scope of equipment please call if
necessary a ŠKODA Partner.
The Pictures in these Owner's Manual are for illustrative purposes only. The illustrations can differ in minor details from your vehicle; they are only intended
to provide general information.
ŠKODA AUTO a.s. pursues a policy of constant product and model development. Changes in terms of supply scope are possible at any time with regard to
design, equipment and technology. The information listed in these Owner's
Manual corresponds to the information available at the time of going to press.
It is therefore not possible for legal claims to be made based on the technical
data, illustrations and information contained in these Owner's Manual.
Service schedule
The service schedule includes documentation for vehicle handover, information on warranty and service events.
The radio instruction manual
The operating manual for the radio contains a description of the operation of
the radio, and possibly also some functions and vehicle systems.
4
On-board literature
Notes
Terms used
The on-board literature contains the following terms relating to the service
work for your vehicle.
“Specialist garage”
ŠKODA vehicles. A specialist can be a ŠKODA partner, a ŠKODA service
partner, as well as an independent workshop.
“ŠKODA service partner”
by the manufacturer ŠKODA AUTO a.s. or its sales partner to perform
service tasks on ŠKODA vehicles and to sell ŠKODA Genuine Parts.
“ŠKODA partner”
ŠKODA AUTO a.s. or its sales partner to sell new ŠKODA vehicles and,
when applicable, to service them using ŠKODA Genuine Parts and to sell
ŠKODA Genuine Parts.
Explanation of symbols
An overview of the symbols used in the Owner's Manual and a brief explanation of their meaning.
Reference to the introductory module of a chapter with important infor-
mation and safety warnings
Continuation of the module on the next page
Situations in which the vehicle must be stopped as soon as possible
® Trademark
WARNING
Texts with this symbol draw attention to threats of a serious accident, injury or loss of life.
CAUTION
Texts with this symbol draw attention to the risk of vehicle damage or possible
inoperability of some systems.
For the sake of the environment
Texts with this symbol contain information on environmental protection and
tips for economical operation.
Notice
Texts with this symbol contain additional information.
- a workshop that carries out specialist service tasks for
- A Workshop that has been contractually authorized
- A company that has been authorized by the manufacturer
Notes
5

Design and further information to the Owner's Manual
Structure of the Owner's Manual
The Owner's Manual are hierarchically divided into the following areas.
■
Section (e.g. safety) - the title of the Section is always indicated at the lower
left side
■
Main chapters (e.g. Airbag system) - the title of the main chapter is always
indicated at the lower right side
■
Chapter (e.g. Airbag overview)
■
Introduction to the topic - Module overview within the chapter, in-
troductory information about the chapter content, if necessary, valid for
the entire chapter notes
■
Module (e.g. front airbags)
Information search
When searching for information in the Owner's Manual, we recommend using
the Index at the end of the Owner's Manual.
Direction indications
All direction indications such as “left”, “right”, “front”, “rear” relate to the forward direction of travel of the vehicle.
Units of measurement
The volume, weight, speed and length specifications are given in metric units,
unless otherwise stated.
6
Design and further information to the Owner's Manual
Abbreviations
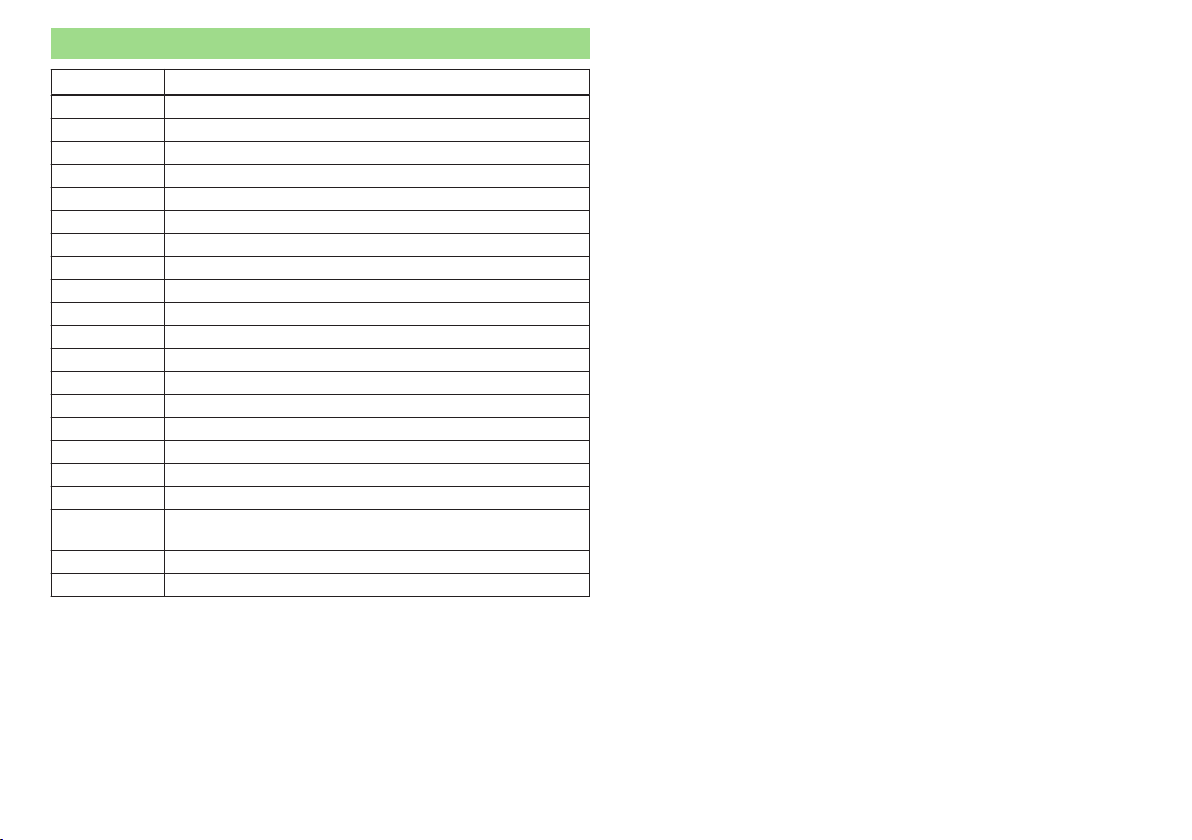
Abbreviation Meaning
rpm Engine revolutions per minute
ABS Anti-lock brake system
AG Automatic gearbox
TCS Traction control
CO
DSG automatic double clutch gearbox
EDL Electronic differential lock
ECE Economic Commission for Europe
EPC EPC fault light
ESC Electronic Stability Control
EU European Union
HBA Hydraulic brake assist
HHC Uphill start assist
kW Kilowatt, unit of power
MFD Multifunction display
MG Manual gearbox
MPI Petrol engine with multi-point fuel injection
Nm Newton meter, measuring unit for the engine torque
TDI CR
VIN Vehicle identification number
W Watt, unit of power
Carbon dioxide
2
Diesel engine with turbo charging and common rail injection
system
Abbreviations
7

Safety
Passive Safety
General information
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Before setting off
Driving safety 8
In this section of the instructions, you will find important information, tips and
notes on the subject of passive safety.
We have combined everything here with which you should be familiar regarding seat belts, airbags, safety of children and anything similar.
You can find further information on safety concerning you and those travelling
with you in the following chapters of this Owner's Manual.
The complete on-board literature should therefore always be in the vehicle.
This applies in particular, if you rent out or sell the vehicle.
Before setting off
For your own safety and the safety of the people travelling with you, please
pay attention to the following points before setting off.
▶
Ensure that the lighting and the turn signal system are functioning properly.
▶
Make sure that the function of the wipers and the condition of the wiper
blades are perfect.
▶
Ensure that all of the windows offer good visibility to the outside.
▶
Adjust the rear-view mirror so that viewing to the rear is assured.
▶
Ensure that the mirrors are not covered.
▶
Check the tyre inflation pressure.
▶
Check the engine oil, brake fluid and coolant level.
▶
Secure all items of luggage.
▶
Do not exceed the permissible axle loads and permissible gross weight of the
vehicle.
▶
Close all doors and the engine compartment and luggage compartment lid.
▶
Ensure that no objects can obstruct the pedals.
▶
Protect children in suitable child seats with correctly fastened seat belts
» page 18, Transporting children safely.
▶
Adopt the correct seated position » page 8, Correct and safe seated position. Tell your passengers to assume the correct seated position.
Driving safety
The driver is fully responsible for himself and passengers, especially children. If
your driving safety is effected, you place yourself and the oncoming traffic at
risk.
8
The following guidelines must therefore be observed.
▶
Do not become distracted from concentrating on the traffic situation, (e.g. by
your passengers or mobile phone calls, etc.).
▶
Never drive when your driving ability is impaired, (e.g. due to medication, alcohol or drugs).
▶
Keep to the traffic regulations and the permissible speed limit.
▶
Always adjust the driving speed to the road, traffic and weather conditions.
▶
Take regular breaks on long journeys (at least every two hours).
The following list contains instructions for the front passenger which, if not
observed, may cause serious injuries or death.
▶
Do not lean against the dash panel.
▶
Do not put your feet on the dash panel.
The following list contains instructions for all passengers which, if not observed, may cause serious injuries or death.
▶
Do not sit only on the front part of the seat.
▶
Do not sit facing to the side.
▶
Do not lean out of the window.
▶
Do not put your limbs out of the window.
▶
Do not put your feet on the seat cushion.
Correct and safe seated position
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Correct seat position of the driver 9
Adjusting the steering wheel position
Correct seated position for the front passenger
Correct seated position for the passengers in the rear seats
9
10
10
8
Safety
WARNING
■
The front seats and head restraints must be adjusted to match the body
size at all times and the seat belt must always be fastened properly to provide the most effective levels of protection to the passengers.
■
Each occupant must correctly fasten the seat belt belonging to the seat.
Children must be fastened » page 18, Transporting children safely with a
suitable restraint system.
■
By sitting incorrectly, the passenger is risking life-threatening injuries.
■
The seat backrests must not be angled too far back when driving, otherwise this will affect proper operation of the seat belts and of the airbag
system – risk of injury!
Correct seat position of the driver
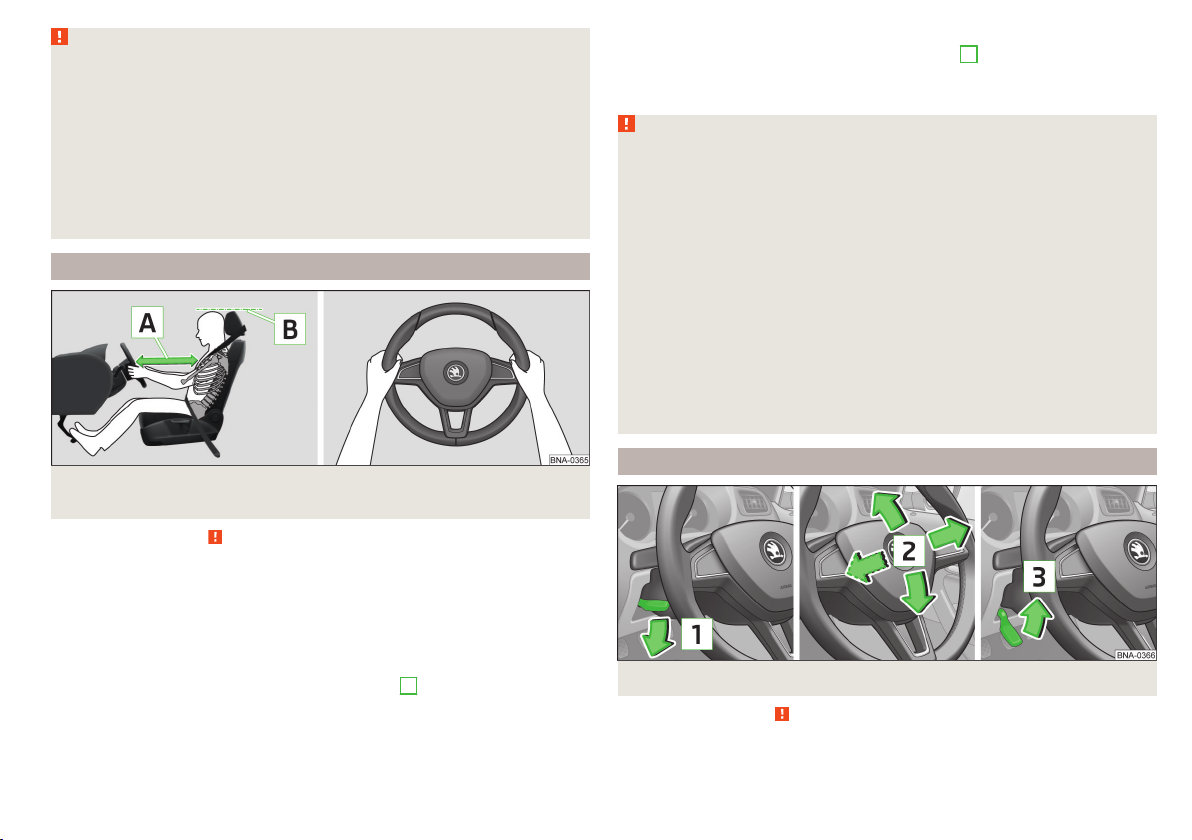
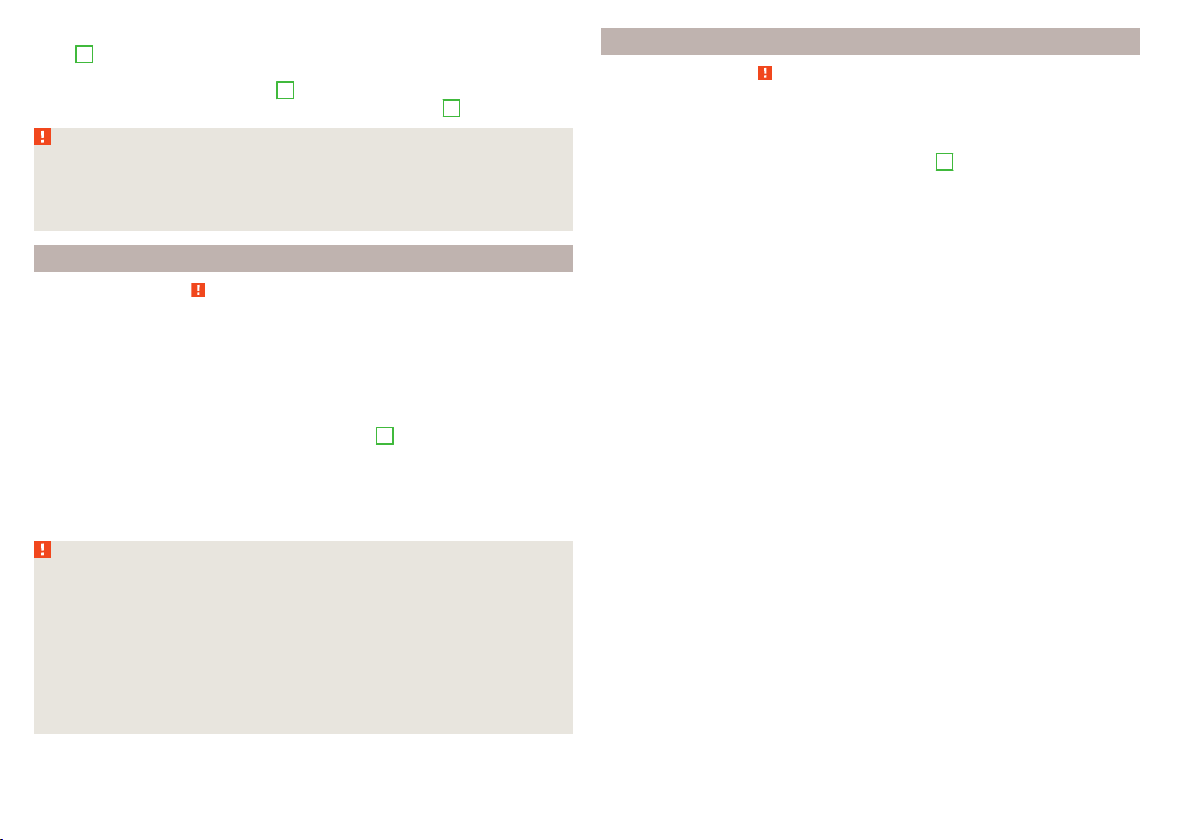
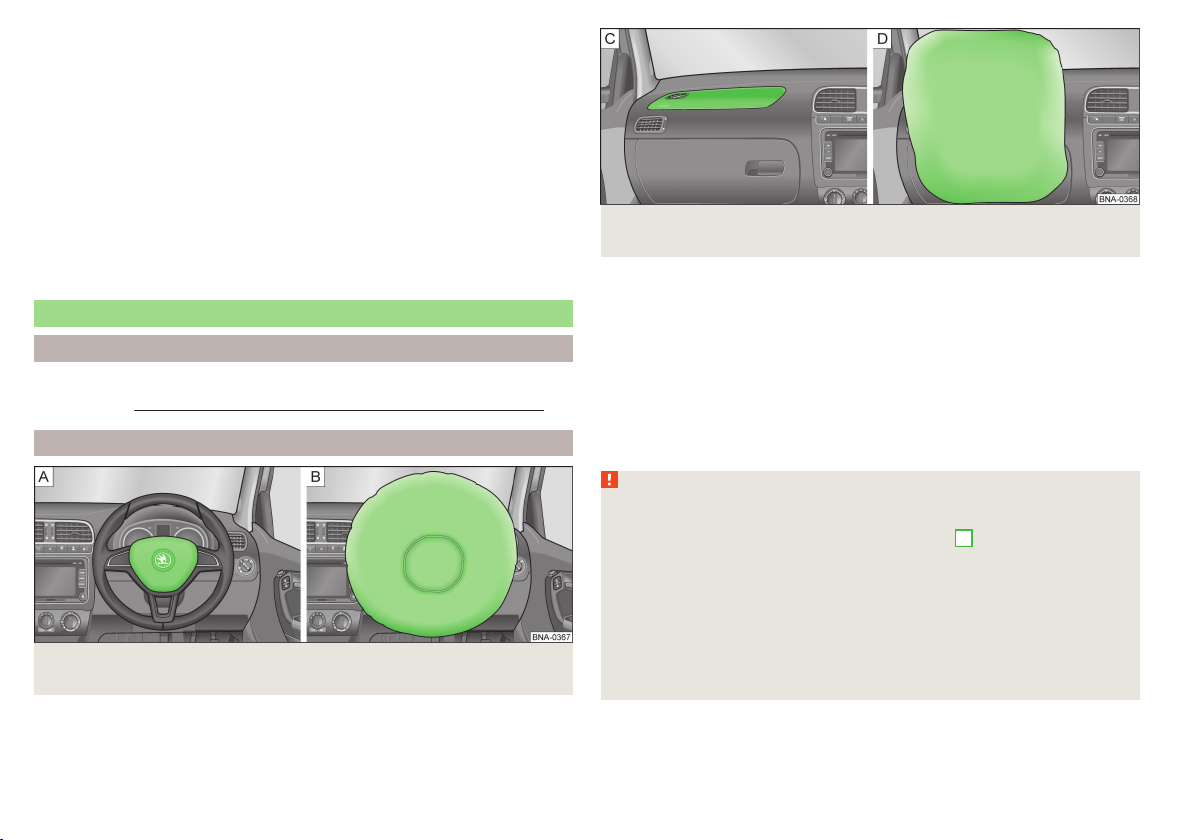
Fig. 1
Correct seated position for the driver/correct steering wheel posi-
tion
Read and observe on page 9 first.
For your own safety and to reduce the risk of injury in the event of an accident,
we recommend the following setting.
Adjust the driver’s seat in the forward/back direction so that the pedals
can be fully depressed with slightly bent legs.
Adjust the seat backrest so that the highest point of the steering wheel
can be reached with your arms at a slight angle.
Adjust the steering wheel so that the distance A between the steering
wheel and your chest is at least 25 cm » fig. 1.
Adjust the head restraint so that the top edge of the head restraint is at
the same level as the upper part of your head B » fig. 1 (not for seats with
integrated head restraint).
Correctly fasten the seat belt » page 11, Using seat belts.
WARNING
■
Always assume the correct seated position before setting off and do not
change this position while driving. Also advise your passengers to adopt
the correct seated position and not to change this position while the car is
moving.
■
Keep a distance of at least 25 cm from the steering wheel. Not maintaining this minimum distance will mean that the airbag system will not be able
to properly protect you - hazard!
■
When driving, hold the steering wheel with both hands firmly on the outer edge in the “9 o'clock” and “3 o'clock” position » fig. 1. Never hold the
steering wheel in the “12 o'clock” position or in any other way (e.g. in the
middle, inner edge of the steering wheel or similar). In such cases, you
could severely injure your arms, hands and head if the driver airbag is deployed.
■
Ensure that there are no objects in the driver's footwell as they may get
caught behind the pedals when driving or applying the braking. You would
then no longer be able to operate the clutch, brake or accelerate.
Adjusting the steering wheel position
Fig. 2 Setting the steering wheel position
Read and observe
The height and forward/back position of the steering wheel can be adjusted.
on page 9 first.
Passive Safety
9
Swivel the safety lever underneath the steering wheel in the direction of ar-
›
row 1» fig. 2.
Adjust the steering wheel to the desired position. The steering wheel can be
›
adjusted in the direction of arrow 2.
Pull the safety lever until it stops in the direction of arrow 3.
›
WARNING
■
Never adjust the steering wheel when the vehicle is moving, only do so
when the vehicle is stationary!
■
The safety lever must be locked so that the steering wheel cannot acci-
dentally change position – risk of accident!
Correct seated position for the front passenger
Read and observe on page 9 first.
For passenger safety and to reduce the risk of injury in an accident, the following instructions must be observed.
Position the front passenger seat back as far as possible. The front passenger must maintain a distance of at least 25 cm to the dash panel so
that the airbag offers the greatest possible safety if it is deployed.
Adjust the head restraint so that the top edge of the head restraint is at
the same level as the upper part of your head B » fig. 1 on page 9 (not for
seats with integrated head restraint).
Correctly fasten the seat belt » page 11, Using seat belts.
In exceptional cases, you can turn off the front passenger airbag » page 17,
Deactivating airbags.
WARNING
■
Maintain a distance of at least 25 cm to the dash panel. Not maintaining
this minimum distance will mean that the airbag system will not be able to
properly protect you – risk of death!
■
Always keep your feet in the footwell when the car is being driven – never place your feet on the instrument panel, out of the window or on the
surface of the seats. You will be exposed to increased risk of injury if it becomes necessary to apply the brake or in the event of an accident. If an airbag is deployed, you may suffer fatal injuries when adopting an incorrect
seated position!
Correct seated position for the passengers in the rear seats
Read and observe on page 9 first.
To reduce the risk of injury in the event of a sudden braking manoeuvre or an
accident, the occupants on the rear seats must observe the following.
Adjust the head restraint such that the top edge of the head restraint is at
the same level as the upper part of the head B » fig. 1 on page 9.
Correctly fasten the seat belt » page 11, Using seat belts.
Use a suitable child restraint system if transporting children in the vehicle
» page 18, Transporting children safely.
10
Safety
Seat belts
Using seat belts
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
The physical principle of a frontal collision 12
Correct routing of seat belt 12
Fastening and unfastening seat belts 13
Two-point safety belt 13
Seat belts that are fastened correctly offer good protection in the event of an
accident. They reduce the risk of an injury and increase the chance of survival
in the event of a major accident.
Properly fastened seat belts hold occupants to correctly set seats in the right
seat position.
Particular safety aspects must be observed when transporting children in the
vehicle » page 18.
The national legal requirements must be observed when using seat belts.
WARNING
■
Fasten your seat belt before each journey - even when driving in town!
This also applies to other passengers - there is a risk of injury!
■
Maximum seat belt protection is only achieved if you are correctly seated
» page 8, Correct and safe seated position.
■
The seat backrests of the front seats must not be tilted too far to the rear
otherwise the seatbelts can lose their effectiveness.
WARNING
Information on the correct routing of the belt
■
Always ensure that the webbing of the seat belts is properly routed. Seat
belts which are not correctly adjusted can themselves cause injuries even
in minor accidents.
■
Adjust the height of the belt in such a way that the shoulder part of the
belt is roughly positioned across the middle of your shoulder - on no account across your neck.
WARNING (Continued)
■
A seat belt which is hanging too loose can result in injuries as your body is
moved forward by the kinetic energy produced in an accident and is then
suddenly held firm by the belt.
■
The belt webbing must not run across solid or fragile objects (e.g. spectacles, ball-point pens, bunches of keys etc.). Such objects can cause injury.
WARNING
Information on dealing with the safety belts
■
The belt webbing must not be jammed in-between at any point or twisted, or chafe against any sharp edges.
■
Make sure you do not catch the seat belt in the door when closing it.
WARNING
Information on the proper use of safety belts
■
No two persons (including children) should ever use a single seat belt together.
■
The lock tongue should only be inserted into the lock which is the correct
one for your seat. Wrong use of the safety belt will reduce its capacity to
protect and the risk of injury increases.
■
The slot of the belt tongue must not be blocked, otherwise the belt
tongue will not lock in place properly.
■
Many layers of clothing and loose clothing (e. g. a winter coat over a jacket) do not allow you to be correctly seated and impairs proper operation of
the seat belts.
■
Do not use clamps or other objects to adjust seat belts (e.g. to shorten
the belts for smaller persons).
WARNING
Information on the care and maintenance of safety belts
■
The belt webbing must always be kept clean. Soiled belt webbing may impair proper operation of the inertia reel » page 83.
■
The seat belts must not be removed or changed in any way. Do not attempt to repair the seat belts yourself.
Seat belts
11
WARNING (Continued)
■
Check the condition of all the seat belts on a regular basis. If any damage
to the seat belts, seat belt connections, inertia reel or the lock is detected,
the relevant seat belt must be replaced by a specialist garage.
■
Damaged seat belts which have been subjected to stress in an accident
and were therefore stretched, must be replaced – this is best done by a
specialist garage. The anchorage points of the belts must also be inspected. The anchorage points for the belts should also be checked.
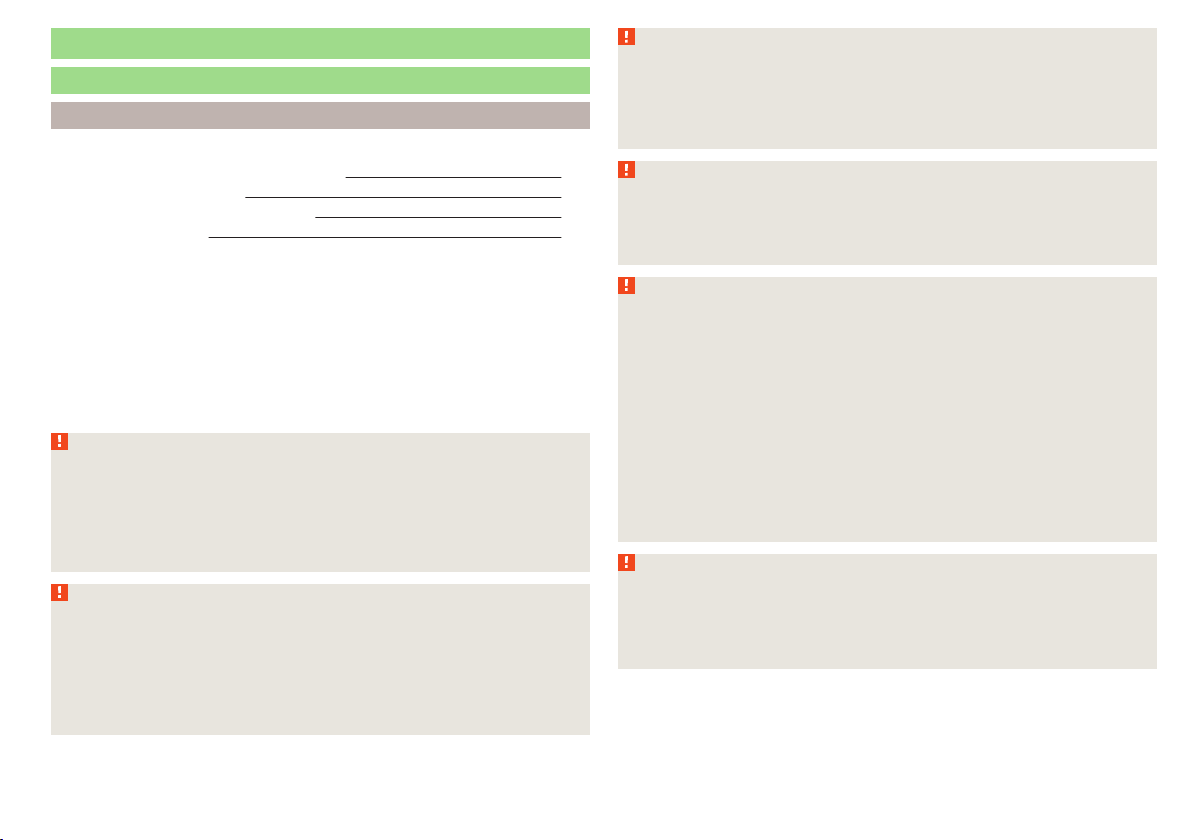
The physical principle of a frontal collision
Fig. 3 Driver without a fastened seat belt/rear seat passenger without a
fastened seat belt
Read and observe on page 11 first.
As soon as the vehicle is moving, so-called kinetic energy (the energy of motion) is produced both in terms of the car as well as in terms of the occupants.
The magnitude of this kinetic energy depends essentially on the speed at
which the vehicle is travelling and on the weight of the vehicle including the
occupants.
Doubling the speed of the vehicle from 25 km/h to 50 km/h increases the kinetic energy four times.
For example, a person's weight of 80 kg “increases” to 4.8 tons (4800 kg) at
50 km/h.
In the event of a frontal collision, occupants of the car not wearing a seat belt
are thrown forward and strike parts of the vehicle interior in an uncontrolled
manner, such as the steering wheel, dash panel or windscreen » fig. 3 – . In
certain circumstances you could even be thrown out of the vehicle, which
could cause life threatening or even fatal injuries.
Rear seat passengers who have not fastened their seat belts are a danger not
only to themselves but also to those seated at the front » fig. 3 – .
Correct routing of seat belt
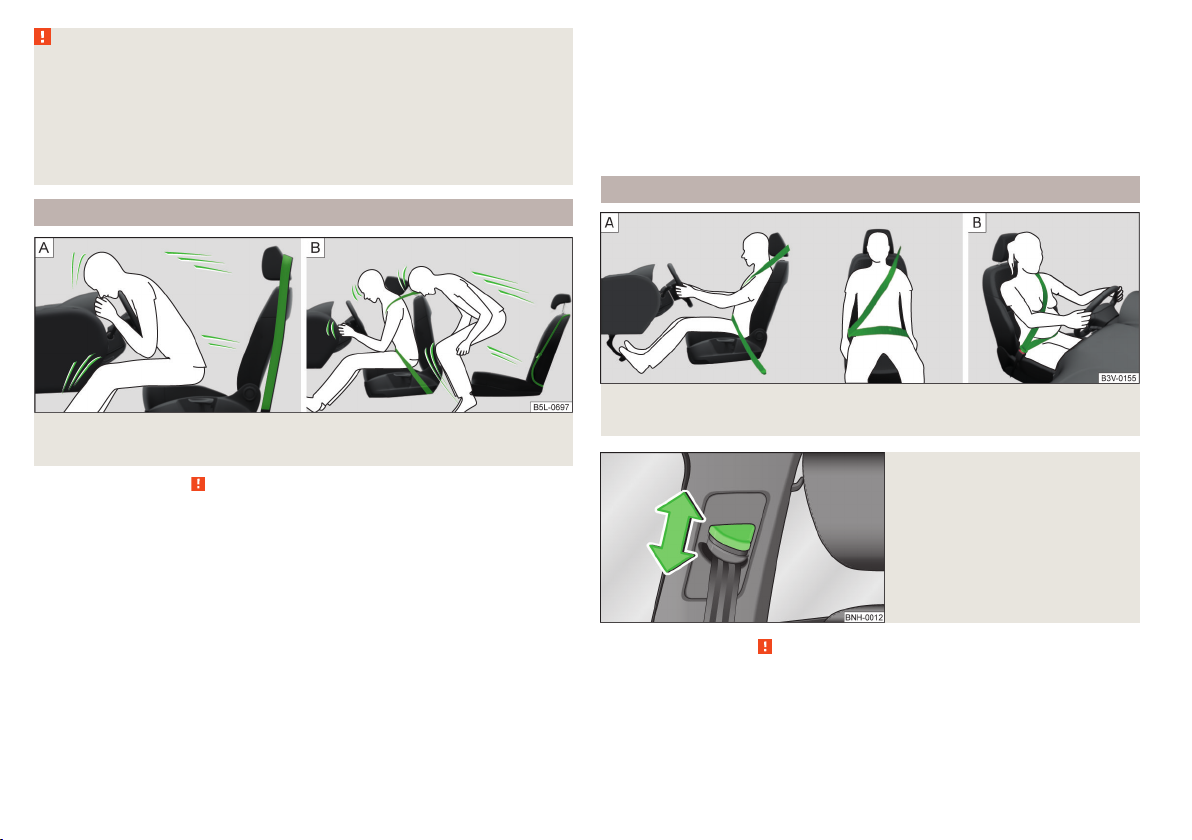
Fig. 4
Routing of belt webbing over the shoulders and the lap belt/Rout-
ing of belt webbing for an expectant mother
Fig. 5
Front seat: Seat belt height adjuster
Read and observe on page 11 first.
It is important that the belt is properly routed to ensure seat belts offer the
maximum protection.
12
Safety
The shoulder part of the seat belt must never run across the neck but must
roughly run over the middle of the shoulder and fit snugly against the chest.
The lap part of the belt must run across the pelvis, must not be positioned
across the stomach and must always fit snugly » fig. 4 – .
Seat belt height adjusters for front seats
The seat belt height adjuster makes it possible to adjust the routing of the
front seat belts in the area of the shoulder to the body size.
Press the height adjuster and move to the desired position » fig. 5.
›
Then pull firmly on the belt to ensure that the seat belt height adjuster has
›
correctly locked in place.
Seat belts for pregnant women
Expectant women must also always wear a seat belt. This is the only way of
ensuring optimal protection for the unborn child.
For pregnant women, the lap part of the belt must be positioned as low as
possible on the pelvis to avoid exerting any pressure on the lower abdomen
» fig. 4 – .
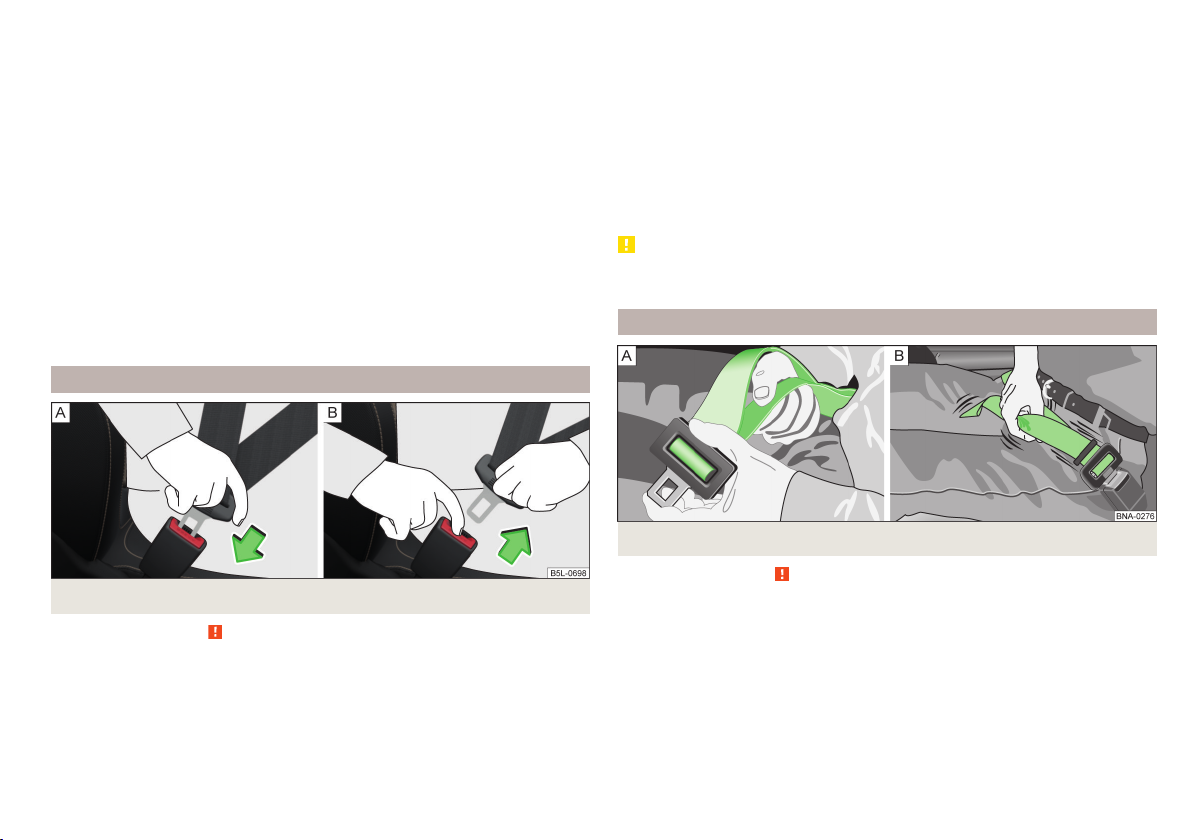
Fastening and unfastening seat belts
Fig. 6 Fastening/unfastening the seat belt
Read and observe on page 11 first.
Before using the seat belts, the following conditions must be met.
Correctly adjusted head restraint (not for seats with integrated head re-
straint).
Correctly adjusted seat (applies for the front seats).
Correctly adjusted steering wheel (applies to the driver's seat ).
Fasten
Use the lock tongue to slowly pull the webbing over your chest and pelvis.
›
Insert the lock tongue into the belt buckle » fig. 6 – that is part of the seat
›
until it clicks into place.
Pull on the belt to check that it has engaged correctly in the lock.
›
Release
Release the seat belt only when the vehicle is stationary.
Press the red button in the belt buckle » fig. 6 - , the lock tongue pops out.
›
Manually guide the belt back so that it is easier to fully roll up the webbing,
›
the seat belt does not twist.
CAUTION
When releasing the seatbelt ensure that the tongue of the lock does not damage the door trim or other parts of the interior.
Two-point safety belt
Two-point safety belt
Fig. 7
Read and observe
The middle rear seat is fitted with a two-point pelvic belt.
Extend lap
Hold the latch plate at a right angle to the strap and pull the strap to the de-
›
sired length » fig. 7 - .
Shorten lap
Pull on the free end of the strap » fig. 7 - .
›
Thread the excess strap length in the plastic slide.
›
on page 11 first.
Seat belts
13

Inertia reels and belt tensioners
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Inertia reels
Belt tensioners 14
WARNING
■
Any work on the belt tensioner system including removal and installation
of system components because of other repair work, must only be carried
out by a specialist garage.
■
The protective function of the system is only adequate for a single accident. If the belt tensioners have been deployed, it is then necessary to re-
14
place the entire system.
Inertia reels
Each three-point seat belt is equipped with an inertia reel. When pulling slowly
on the seat belt, the belt can move freely.
When pulling sharply on the seat belt, the movement is locked by the inertia
reel. The belts also lock when full braking, when the car accelerates, when
driving downhill and when cornering.
WARNING
If the seat belt does not lock when pulling sharply on it, have it inspected
immediately by a specialist garage.
Belt tensioners
Safety for the driver and front passenger wearing their seat belts is enhanced
by the belt tensioners fitted to the inertia reels of the front seat belts.
If there is a collision, the seat belts are tightened by the belt tensioner so that
unwanted body motion is prevented.
The three-point seat belts are automatically tensioned in the event of a frontal
collision of a certain severity.
The front seat belts are automatically tensioned in the event of a side collision
of a certain severity.
Belt tensioners are not activated in the event of minor frontal, side or rearend collisions, if the vehicle overturns and also not in accidents in which no
major forces are produced.
Notice
■
The belt tensioners can also be deployed if the seat belts are not fastened.
■
Smoke is generated when the belt tensioners are deployed. This is not an in-
dication of a fire in the vehicle.
■
When disposing of the vehicle or parts of the belt tensioner system, comply
with national legal requirements.
14
Safety
Airbag system
Description of the airbag system
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
System description 15
Airbag deployment 15
The airbag system supplements the fastened seat belts and provides additional occupant protection in severe frontal collisions.
The functional status of the airbag system is indicated by the indicator light
in the instrument cluster » page 29.
WARNING
■
An airbag can only offer you optimal protection in combination with a
fastened seat belt.
■
The airbag is not a substitute for the seat belt, but instead forms part of
the complete passive vehicle safety concept.
■
To ensure passengers are protected with the greatest possible effect
when the airbag is deployed, the front seats must be correctly adjusted to
match the body size » page 8, Correct and safe seated position.
■
If you do not fasten the seat belts when driving, lean too far forward or
adopt an incorrect seated position, you are exposing yourself to increased
risk of injury in the event of an accident.
WARNING
Information on the use of the airbag system
■
If there is a fault, have the airbag system checked immediately by a specialist garage. Otherwise, there is a risk of the airbag not being activated in
the event of an accident.
■
No modifications of any kind must be made to parts of the airbag system.
■
Any work on the airbag system including the installation and removal of
system components due to other repair work (e.g. removal of the steering
wheel) must only be carried out by a specialist garage.
■
Never make any changes to the front bumper or the bodywork.
WARNING (Continued)
■
Do not manipulate individual parts of the airbag system, as this might re-
sult in the airbag being deployed.
■
The protective function of the airbag system is sufficient for only one accident. The airbag system must then be replaced if the airbag has been deployed.
System description
Read and observe
The airbag inflates in a fraction of a second.
When the airbags are deployed, they fill with gas and inflate.
A grey white or red, non-harmful gas is released when the airbag is inflated.
This is perfectly normal and is not an indication of a fire in the vehicle.
Depending on the vehicle equipment, the airbag system consists of the
following parts.
▶
Front airbag for the driver and the front passenger » page 16.
▶
Airbag warning light in the instrument cluster » page 29.
Notice
When disposing of the vehicle or parts of the airbag system, comply with national legal requirements.
on page 15 first.
Airbag deployment
Read and observe on page 15 first.
The airbag system is only functional when the ignition is switched on.
Triggering conditions
It is not possible to generally determine which deployment conditions apply to
the airbag system in every situation. An important role is played by factors
such as the type of object that the vehicle hits (hard/soft), the impact angle,
vehicle speed etc.
A decisive factor for the deployment of the airbags is the deceleration which
occurs. If the vehicle deceleration which occurs and is measured during the
collision remains below the prescribed reference values specified in the control
unit, the airbags are not deployed although the vehicle may well suffer severe
damage to the bodywork as a consequence of the accident.
Airbag system
15
The following airbags will be deployed in the event of a severe frontal
collision.
▶
Driver’s front airbag.
▶
Front passenger airbag.
The following events occur when an airbag deploys.
▶
The interior light illuminates (if the automatic operation of the interior light is
switched on – switch ).
▶
The hazard warning lights are switched on.
▶
All the doors are unlocked.
▶
The fuel supply to the engine is cut off.
When is the airbag not deployed?
In the event of minor frontal and side collisions, rear-end collisions, the airbag
is not deployed, or if the vehicle overturns or rolls over.
Airbag overview
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Front airbags
Front airbags
Fig. 8 Driver front airbag in the steering wheel / gas-filled driver's front
airbag
Fig. 9
Front passenger airbag in the dashboard / gas-filled front passen-
ger airbag
In the event of a severe frontal collision, the front airbags offer additional protection for the head and chest area of the driver and front passenger.
The driver's air bag is housed in the front wheel » fig. 8 – .
The front passenger airbag is housed in the dashboard above the glove com-
partment » fig. 9 – .
When the airbags are deployed, they inflate in front of the driver » fig. 8 –
16
and front passenger » fig. 9 - . The forward movement of the driver and of
the front passenger is cushioned when they make contact with the fully inflated airbag and the risk of injury to head and chest is thus reduced.
WARNING
Information on correct seating position
■
It is important that the driver and front passenger maintain a distance of
at least 25 cm to the steering wheel or dashboard A » fig. 1 on page 9. Not
maintaining this minimum distance will mean that the airbag system will
not be able to properly protect you - hazard! The front seats and the head
restraints must always also be correctly adjusted to match the body size of
the occupant.
■
The airbag develops enormous forces when triggered, which can lead to
injuries if the sitting position or seated position is not correct.
■
There must not by any further persons, animals or objects positioned between the front seated occupants and the deployment area of the airbag.
16
Safety

WARNING
Front airbag and transporting children
■
Never transport children on the front seat of a vehicle without using a
proper restraint system. If airbags are deployed in the event of an accident,
the child might suffer severe or even fatal injuries!
■
The front passenger airbag must be deactivated if using a rear-facing
child seat on the front passenger seat » page 17, Deactivating airbags. If
this is not done, there is a risk of the child suffering severe or even fatal
injuries if the front passenger airbag is deployed. When transporting a child
on the front passenger seat, pay attention to any relevant national regulations regarding the use of child safety seats.
WARNING
General information
■
The steering wheel and the surface of the airbag module in the dash panel on the passenger side must not have stickers attached, be covered or
modified in any other way. These parts should only be cleaned with a cloth
that is dry or has been moistened with water. No objects (such as cup holders, mobile phone mounts, etc.) are to be attached to the covers of the airbag modules or be located within their immediate vicinity.
■
Never place objects on the surface of the front passenger airbag module
in the dash panel.
Notice
■
In vehicles with head airbags, the lettering can be seen on the steering
wheel.
■
In vehicles with front passenger airbags, the lettering
can be seen on
the dash panel on the passenger side.
Deactivating airbags
If you sell your vehicle, provide the complete vehicle documentation to the
new owner. Please note that the information relating to the possibility of deactivating the front passenger airbag must be included!
If an airbag in the vehicle is to be switched off, the buyer must be informed of
this!
Deactivating an airbag should be considered in cases such as the ones below.
▶
If using a rear-facing child seat on the front passenger seat (due to different
legal regulations, the airbag must be deactivated if using a forwards-facing
child seat in some countries) » page 18, Transporting children safely.
▶
If it is not possible to maintain a distance of at least 25 cm between the middle of the steering wheel and chest, despite the driver's seat being correctly
adjusted.
▶
If special attachments are required in the area of the steering wheel because
of a physical disability.
▶
If different seats have been fitted (e.g. orthopaedic seats without side airbags).
We recommend that you ask a ŠKODA service partner to deactivate any other
airbags.
Notice
A ŠKODA service partner will be able to inform you which, if any, of your vehicle's airbags can or must be deactivated.
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Deactivating airbags 17
Deactivating airbags
The national regulations for switching off airbags must be observed.
Airbag system
17

Transporting children safely
Child seat
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Use of a child seat on the front passenger seat 19
Classification of child seats 19
Use of child seats fastened with a seat belt 19
To avoid serious injury or death, children must always be seated in an appropriate child safety seat taking height, weight and age into consideration.
For safety reasons, we recommend that you always transport children on the
rear seats.
The national legal requirements for transporting children and the use of a child
seat must be observed.
Child seats complying with the ECE-R 44 Economic Commission for Europe
standard must be used.
Child seats that comply with the ECE-R 44 standard have a test seal that cannot be removed: a large E within a circle with the test number below.
With child safety seats in groups 2 and 3, ensure that the loop-around fittings
attached to the child seat headrest are positioned in front of or at the same
height as the loop-around fittings on the B pillar on the passenger side.
WARNING
■
One should never carry children, and also not babies! - on one's lap.
■
Never leave children unattended in the vehicle. Certain outside climatic
conditions can cause life-threatening temperatures in the vehicle.
■
The child must be secured in the vehicle during the entire journey! Otherwise, the child would be thrown through the vehicle in the event of an accident, causing fatal injuries to both the child and other occupants.
■
Children are exposed to an increased risk of injury in the event of an accident if they lean forward or adopt an incorrect seated position when the
vehicle is moving. This particularly applies to children who are transported
on the front passenger seat as they can suffer severe, or even fatal injuries
if the airbag system is deployed!
WARNING (Continued)
■
Pay particular attention to the information provided by the manufacturer
of the child safety seat regarding the correct routing of the belt. Seat belts
which are not correctly adjusted can themselves cause injuries even in minor accidents.
■
Safety belts must be checked to ensure that they are running properly.
One should also ensure that the belt is not damaged by sharp-edged fittings.
■
The front passenger airbag must be deactivated if using a rear-facing
child seat on the front passenger seat. Further information » page 19, Use
of a child seat on the front passenger seat.
■
When installing the child seat on the back seat, the corresponding front
seat must be adjusted so that there is no contact between the front seat
and the child seat or the child being transported in a child seat.
CAUTION
■
When installing a child seat in which the child faces forward, adjust the head
restraints so that they are as high as possible.
■
If the head restraints still prevent the child seat from being installed, even in
the highest position, you will need to remove them » page 48. After removing
the child seat, refit the head restraints.
Notice
We recommend that you use child seats from ŠKODA Original Accessories.
These child seats were developed and also tested for use in ŠKODA vehicles.
They meet the ECE-R 44 standard.
18
Safety
Use of a child seat on the front passenger seat
Never use a backwards-facing child restraint system on a seat that is protected by an active airbag installed in front of it. This could cause the child severe
injury or even death.
Fig. 10
Sticker on the B column on the
front passenger side.
Read and observe and on page 18 first.
The following instructions must be followed when using a child seat on the
front passenger seat.
▶
The front passenger airbag must be deactivated if using a rear-facing child
seat » .
▶
If possible, adjust the front passenger seat backrest so that it is as vertical,
so as to ensure secure contact between the passenger seat backrest and the
back of the child seat.
▶
If possible, move the front passenger seat backwards so that there is no contact between the front passenger seat and the child seat behind it.
▶
Set the height-adjustable front passenger seat as high up as possible.
▶
Set the front passenger seat belt as high up as possible.
▶
When using a child seat where there is a height adjuster in the upper area,
the height of the passenger seat belt is to be set so that the belt is not
“kinked” in the height adjuster. In the event of an accident, the child's neck
may be injured by the seat belt!
WARNING
■
Never use a rear-facing child seat on the front passenger seat if the pas-
senger airbag is activated. This child safety seat is positioned in the deployment area of the front passenger airbag. The airbag may cause the child severe, or even fatal injuries, in the event of it being deployed.
■
This is also clearly stated on the sticker which is located on the B pillar on
the passenger side » fig. 10. The sticker is visible upon opening the front
passenger door.
■
With child safety seats in groups 2 or 3, make sure that the loop-around
fittings attached to the child seat headrest is positioned in front of or at
the same height as the loop-around fittings on the B pillar on the passenger side.
■
As soon as the rear-facing child seat is no longer being used on the passenger seat, the front passenger airbag should be re-activated again.
Classification of child seats
Read and observe
Classification of child seats according to the ECE-R 44 standard.
Group Weight of the child Approximate age
0 up to 10 kg up to 9 months
0+ up to 13 kg up to 18 months
1 9 - 18 kg up to 4 years
2 15 - 25 kg up to 7 years
3 22 - 36 kg over 7 years
and on page 18 first.
Use of child seats fastened with a seat belt
Read and observe and on page 18 first.
Overview of the usability of child seats fastened with a seat belt on each of
the seats in accordance with the ECE-R 16 standard.
Group Front passenger seat Outer rear seats
0
up to 10 kg
0+
up to 13 kg
U U
U U
Transporting children safely
19
Group Front passenger seat Outer rear seats
1
9-18 kg
2
15-25 kg
3
22-36 kg
“Universal” child seat category - a child seat designed to be attached to
U
the seat using the seat belt.
U U
U U
U U
20
Safety

Transporting children safely
21
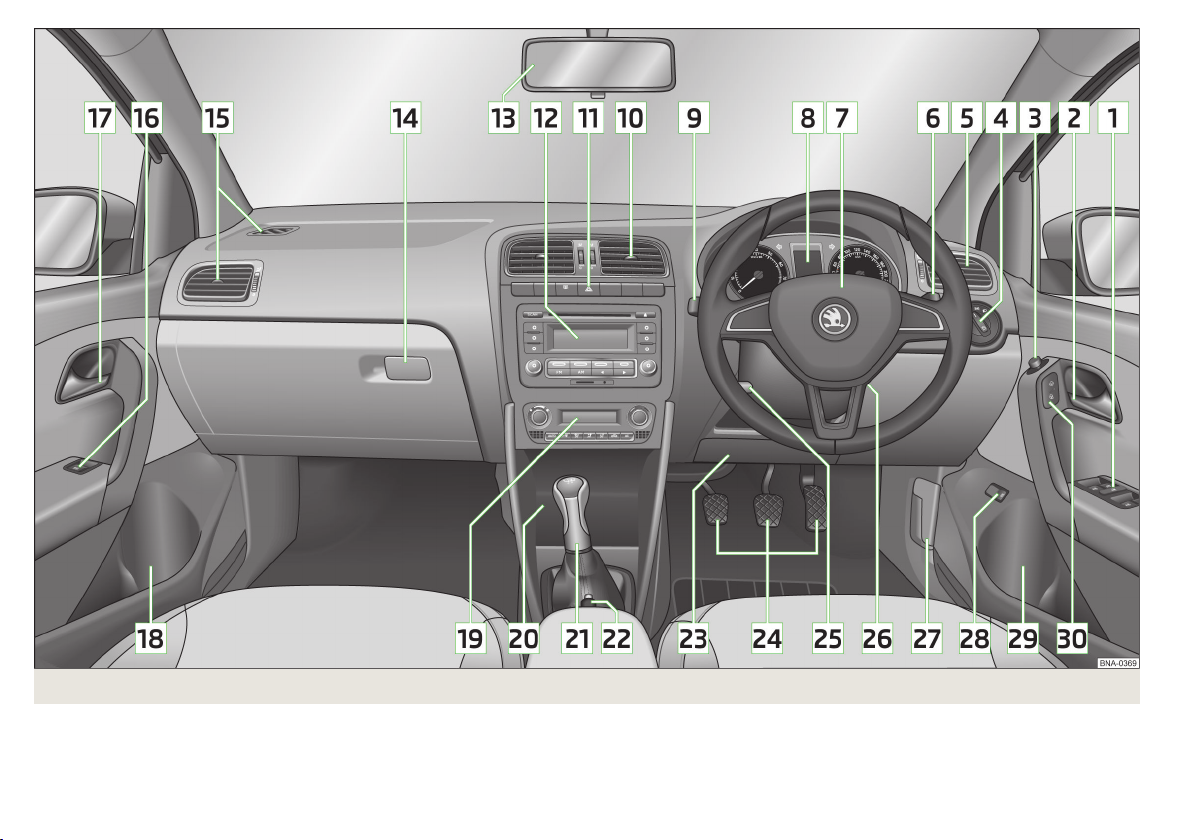
Fig. 11 Cockpit
22
Usage

Usage
Cockpit
Overview
1
Electrical power windows 37
2
Door opening lever 36
3
Electric exterior mirror adjustment 46
4
Light switch 40
5
Air outlet vents 57
6
Operating lever (depending on equipment):
▶
Windscreen wiper and wash system 44
▶
Information system
7
Multifunction steering wheel (depending on equipment):
▶
With horn
▶
With driver’s front airbag 16
8
Instrument cluster 24
9
Operating lever (depending on equipment):
▶
Turn signal lights and main beam, headlight flasher 41
▶
Speed regulating system
10
Air outlet vents 57
11
Bar with keys (depending on the equipment fitted):
▶
Traction control (TCS) 69
▶
Rear window heater
▶
Hazard warning lights system
12
Radio
13
Rear-view mirror 45
14
Storage compartment on the front passenger side 50
15
Air outlet vents 57
16
Power window in the front passenger door 37
17
Door opening lever 36
18
Storage compartments in the doors 51
19
Depending on equipment fitted:
▶
Operating the manual air conditioning system 55
▶
Operating controls for Climatronic 55
20
Storage compartment 52
30
43
42
21
Depending on equipment fitted:
▶
Gearshift lever (manual gearbox) 63
▶
Selector lever (automatic gearbox) 65
22
Handbrake lever 63
23
Fuse box 112
24
Pedals 64
25
Lever for adjusting the steering wheel 9
26
Ignition lock 61
27
Bonnet release lever 87
28
Push button to unlock the boot lid 36
29
Storage compartments in the doors 51
30
Central locking system 35
71
Cockpit
23
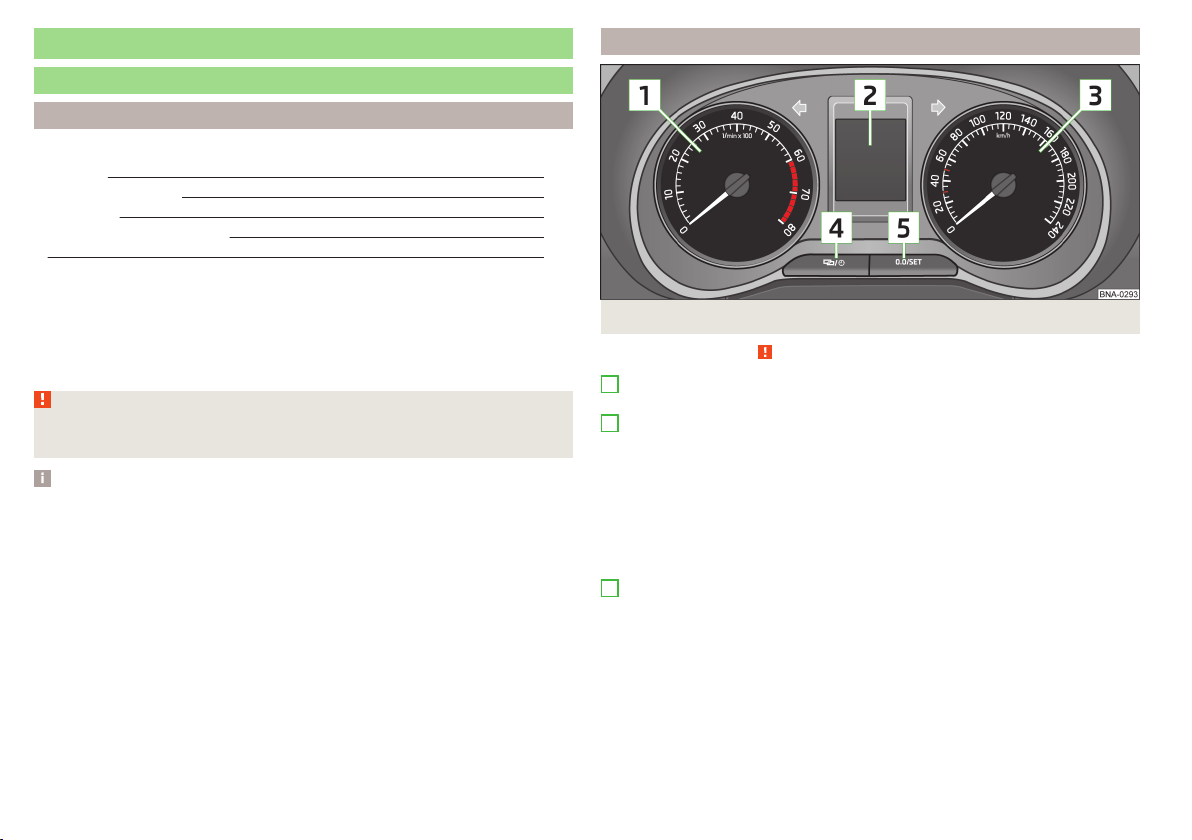
Instruments and Indicator Lights
Instrument cluster
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Overview 24
Revolutions counter 25
Fuel gauge 25
Counter for distance driven 25
26
The instrument cluster gives the driver basic information such as the current
speed, engine speed, the state of some vehicle systems and the like.
If there is a fault in the instrument cluster, the Error message will appear in
the display.
Seek help from a specialist garage.
WARNING
Concentrate fully at all times on your driving! As the driver you are fully responsible for road safety.
Notice
If appears in the display, then the system indicates that the ignition is
switched on.
Overview
Fig. 12 Instrument cluster
Read and observe on page 24 first.
1
Engine revolutions counter » page 25
▶
with warning lights » page 26
2
Display:
▶
with fuel gauge » page 25
▶
with counter for distance driven » page 25
▶
with clock display » page 26
▶
with warning lights » page 26
▶
with information system » page 30
▶
with multifunction display (MFA) » page 31
▶
with a display of the distance and the days until the next service appointment » page 31
3
Speedometer
▶
with warning lights » page 26
24
Usage
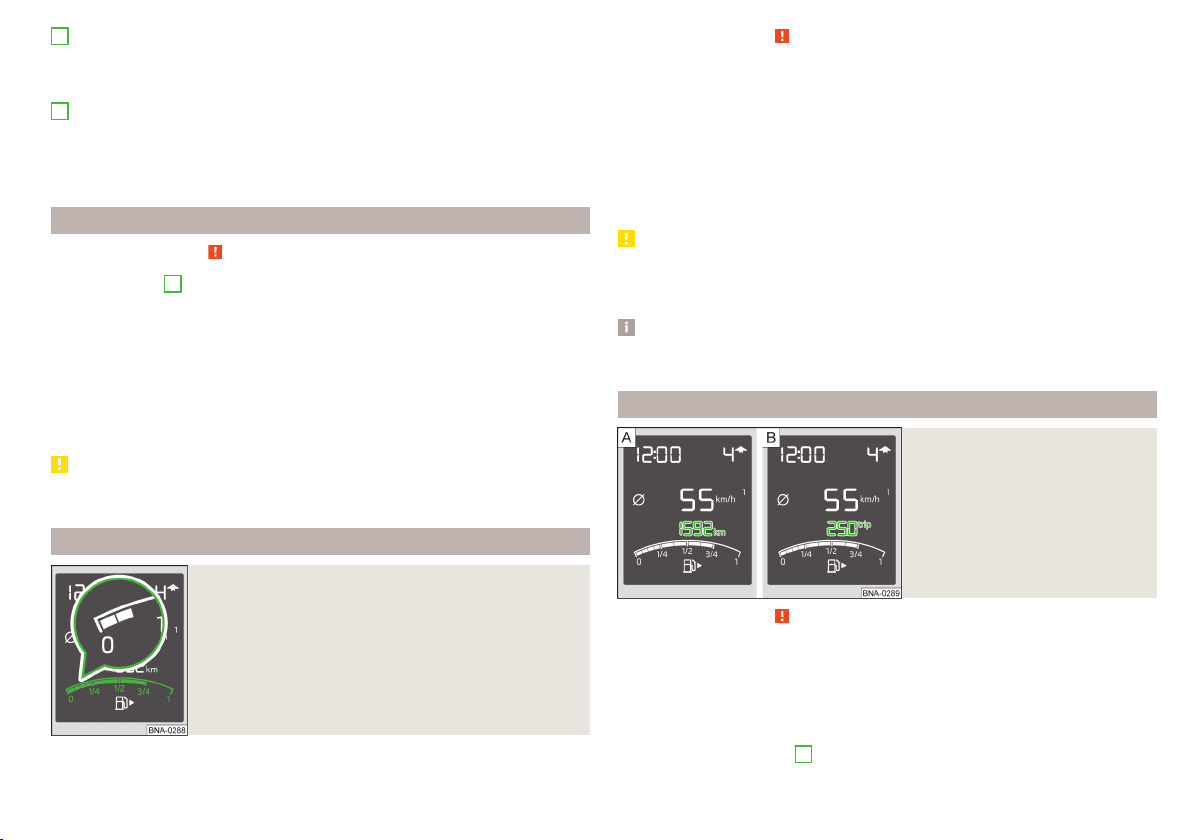
4
Button for display mode:
▶
Setting the clock » page 26
▶
Displaying the distance and days until the next service appointment
» page 31
5
Button for:
▶
switching between the odometer display and the counter for the distance driven (Trip) » page 25
▶
resetting the counter for distance driven (Trip) » page 25
▶
Setting the clock » page 26
Revolutions counter
Read and observe on page 24 first.
The tachometer 1 » fig. 12 on page 24 shows the actual engine speed per minute.
The beginning of the red scale range of the tachometer indicates the maximum permitted engine speed of a driven-in and operating warm engine.
You should shift into the next higher gear before the red scale of the revolution counter is reached, or select mode D on the automatic gearbox.
The gear recommendation is important to note in order to maintain the optimum engine speed » page 30.
CAUTION
The pointer of the tachometer must reach the red area for only a short time there is a risk of engine damage!
Fuel gauge
Fig. 13
Fuel gauge
Read and observe on page 24 first.
The display provides information on the fuel level in the container.
The fuel gauge only operates if the ignition is switched on.
The fuel tank has a capacity of about 55 litres.
The reserve area is indicated by the display of only the last two segments
scale » fig. 13 .
The warning light illuminates when the amount of fuel reaches the reserve
zone » page 29.
CAUTION
Never drive until the fuel tank is completely empty! The irregular supply of fuel
can cause misfiring. This can result in considerable damage to parts of the engine and the exhaust system.
Notice
The arrow next to the icon within the fuel gauge displays the installation
location of the fuel filler on the right-hand side of the vehicle.
Counter for distance driven
Fig. 14
Counter for distance driven
Read and observe on page 24 first.
Display » fig. 14
Odometer
Counter for the distance driven since the last reset (Trip)
Select between the odometer display and the counter for the distance driven
(Trip)
Briefly press the button 5 » fig. 12 on page 24.
›
Instruments and Indicator Lights
25

Reset the counter for distance driven (Trip)
Select the counter for distance driven (Trip).
›
Press and hold the 5 button.
›
Read and observe on page 24 first.
The clock is set using the buttons 4 and 5 » fig. 12 on page 24.
4
The choice to change the display (hours or minutes).
5
The change of the displayed value.
Warning Lights
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the following subjects:
Handbrake 26
Braking system 26
Generator 27
Door open 27
Engine oil 27
Coolant 27
Power steering 28
Antilock brake system (ABS) 28
Electronic Stability Control (ESC) 28
Traction control system (ASR) off 28
Rear fog light 28
Exhaust inspection system
Glow plug system (diesel engine) 29
Engine performance check (petrol engine) 29
Fuel reserve 29
Airbag system 29
Water in the fuel filter (diesel engine)
Turn signal system 29
Cruise control system 29
Brake pedal (automatic gearbox) 29
Main beam 30
Display of a low temperature 30
Service 30
The warning lights in the instrument cluster indicate certain functions or
faults.
Some warning lights can be accompanied by acoustic signals.
After switching on the ignition, some warning lights illuminate briefly as a
function test.
If the tested systems are OK, the corresponding warning lights extinguish a
few seconds after switching on the ignition or leaving the vehicle.
WARNING
■
Ignoring illuminated warning lights and related messages or instructions
in the display of the instrument cluster may lead to serious personal injury
or damage to the vehicle.
■
If you have to stop for technical reasons, then park the vehicle at a safe
distance from the traffic, switch off the engine and activate the hazard
warning light system » page 42. The warning triangle must be set up at
the prescribed distance - observe the national legal provisions when doing
so.
■
The engine compartment of your car is a hazardous area. The following
warning instructions must be followed at all times when working in the engine compartment » page 86, Engine compartment.
Handbrake
Read and observe
illuminates – the hand brake is applied.
An audible warning is also given if you drive the vehicle for at least 3 seconds
29
at a speed of more than 6 km/h.
on page 26 first.
Braking system
Read and observe on page 26 first.
29
illuminates – the brake fluid level in the braking system is too low.
Stop the vehicle, switch off the engine and check the brake fluid level.
›
26
Usage
WARNING
■
If the warning light illuminates simultaneously with warning light
» page 28, Antilock brake system (ABS), stop driving! Seek help from
a specialist garage.
■
A fault to the ABS system or the braking system can increase the vehi-
cle's braking distance – risk of accident!
Generator
Read and observe
illuminates – while the engine is running, the battery is not being charged.
Seek help from a specialist garage.
CAUTION
If, in addition to light , light lights up while driving, stop driving – risk of
engine damage! Switch off the engine and seek assistance from a specialist
garage.
Door open
Read and observe on page 26 first.
illuminates – one or more doors are open.
Engine oil
Read and observe on page 26 first.
Low oil pressure
illuminates/flashes.
Stop the vehicle, switch off the engine and check the engine oil level.
›
If the warning light illuminates or flashes , stop driving, even if the oil
level is correct! Also do not leave the engine running at an idling speed.
Seek help from a specialist garage.
Engine oil level too low
illuminates.
Stop the vehicle, switch off the engine and check the engine oil level, top up
›
if necessary.
on page 26 first.
The warning light will go out if the bonnet is left open for more than 30 seconds. If no engine oil has been replenished, the warning light will illuminate
again after driving about 100 km.
Fault on the engine oil level sensor
flashes.
The warning light flashes several times after switching on the ignition and
there is an audible signal.
Seek help from a specialist garage.
Coolant
Read and observe on page 26 first.
illuminates or flashes – the coolant temperature is too high or the coolant
level is too low.
Stop the vehicle, switch off the engine, check the coolant level, and refill the
›
coolant if necessary.
If the coolant level is too low, add coolant to the reservoir » page 92.
›
If the coolant level is within the specified range and the warning light illuminates again after switching the ignition on, then there may be a malfunction of
the cooling fan.
Switch off the ignition.
›
Check the radiator fan fuse and replace if necessary » page 114, Fuses in the
›
engine compartment.
If the coolant level and the fan fuse are OK and the warning light illuminates
again after switching the ignition on , stop driving!
Seek help from a specialist garage.
WARNING
■
Carefully open the coolant expansion bottle. If the engine is hot, the cooling system is pressurized - risk of scalding! It is therefore best to allow the
engine to cool down before removing the cap.
■
Do not touch the radiator fan. The radiator fan may switch itself on automatically even if the ignition is off – risk of injury!
Instruments and Indicator Lights
27
Power steering
Read and observe on page 26 first.
illuminates – this indicates a complete failure of the power steering and the
steering assist has failed (significantly higher steering forces).
illuminates – this indicates a partial failure of the power steering and the
steering forces may be greater.
Stop the car, turn the ignition off and on again.
›
If the warning light or does not illuminate again after starting the engine
and driving a short distance, then the power steering is fully functional again.
If the warning light or illuminates again, then obtain assistance from an
authorised dealer.
Disconnecting the vehicle battery
If the vehicle's battery has been disconnected and reconnected, the warning
light illuminates after switching on the ignition.
The warning light should go out after driving a short distance.
If, after restarting the engine is restarted and driving a short distance, the
warning light does not go out, there is a system error.
Seek help from a specialist garage.
Antilock brake system (ABS)
Read and observe
illuminates – there is an ABS fault.
The vehicle will only be braked by the normal brake system without the ABS.
Seek help from a specialist garage.
WARNING
■
If the warning light illuminates simultaneously with warning light
» page 26, Braking system, stop driving! Seek help from a specialist
garage.
■
A fault to the ABS system or the braking system can increase the vehi-
cle's braking distance – risk of accident!
on page 26 first.
Electronic Stability Control (ESC)
Read and observe on page 26 first.
flashes – the ESC is now being activated.
ESC fault
illuminates.
Seek help from a specialist garage.
If the warning light illuminates immediately after you start the engine, the
ESC might be switched off for technical reasons.
Switch the ignition off and on again.
›
The ESC is fully functional again if the warning light does not illuminate after you switch the engine back on.
Disconnecting the vehicle battery
If the vehicle's battery has been disconnected and reconnected, the warning
light illuminates after switching on the ignition.
The warning light should go out after driving a short distance.
If, after driving a short distance, the warning light does not go out, there is a
system error.
Seek help from a specialist garage.
For more information about the ESC system » page 69, Stability Control
(ESC).
Traction control system (ASR) off
Read and observe
illuminates – the TCS system is deactivated » page 69, Stability Control
(ESC).
on page 26 first.
Rear fog light
Read and observe
illuminates – the rear fog light is switched on.
on page 26 first.
28
Usage
 Loading...
Loading...