Singmai Electronics SM02 User Manual

1
SM02
High Definition Video Encoder
and
Pattern Generator
User Manual
Revision 0.1
15th March 2015

2
Contents
Contents ........................................................................................................ 2
Tables ........................................................................................................... 2
Figures .......................................................................................................... 3
1. Introduction ........................................................................................... 4
2. aCVi Overview ...................................................................................... 6
3. Connecting up the SM02 ...................................................................... 8
4. Quick Start Guide ............................................................................... 11
Switch On and Control ............................................................................ 11
Menu control ........................................................................................... 13
5. SM02 Patterns .................................................................................... 21
75% Colour bars ..................................................................................... 21
100% Colour bars ................................................................................... 21
SMPTE Colour bars ................................................................................ 22
Ramp ...................................................................................................... 24
5-step staircase ...................................................................................... 25
2T30T ..................................................................................................... 25
Multiburst ................................................................................................ 26
15MHzSw ............................................................................................... 27
30MHzSw ............................................................................................... 27
Black ....................................................................................................... 28
White ....................................................................................................... 28
50%Grey ................................................................................................. 29
Red ......................................................................................................... 29
Green ...................................................................................................... 29
Blue ......................................................................................................... 29
Xhatch ..................................................................................................... 29
SDI PLL .................................................................................................. 29
Matrix ...................................................................................................... 29
Zone Plate .............................................................................................. 30
5. SM02 Noise generator ............................................................................ 32
6. aCVi Data transfer protocol ................................................................ 33
Appendix A: Power supply specification ..................................................... 36
Tables
Table 1 aCVi output specification. ................................................................ 9
Table 2 Analogue Component output Specifications .................................. 10
Table 3 HD-SDI Output Specifications ....................................................... 10
Table 4 HD-SDI Input specification. ............................................................ 10
Table 5 SM02 Patterns. .............................................................................. 16
Table 6 aCVi Control words Transmitter > Receiver .................................. 34

3
Figures
Figure 1 aCVi Spectrum. ...............................................................................7
Figure 2 SM02 rear panel. .............................................................................8
Figure 3 SM02 AC-DC converter ...................................................................9
Figure 4 SM02 Front panel. ........................................................................ 11
Figure 5 SM02 Menu structure. .................................................................. 13
Figure 6 aCVi output, 30MHz sweep (Pre-emphasis = minimum). ............ 19
Figure 7 aCVi output, 30MHz sweep (Pre-emphasis = maximum). ........... 20
Figure 8 75% Component colour bar waveform. ........................................ 21
Figure 9 100% Colour bar waveform. ......................................................... 22
Figure 10 SMPTE Colour Bar component waveform. ................................ 23
Figure 11 SMPTE Reverse colour bars waveform. .................................... 23
Figure 12 SMPTE Pluge waveform. ........................................................... 24
Figure 13 Limit ramp waveform. ................................................................. 24
Figure 14 10-step waveform. ...................................................................... 25
Figure 15 2T30T pulse waveform. .............................................................. 26
Figure 16 Multiburst waveform. .................................................................. 26
Figure 17 15MHz frequency sweep waveform. .......................................... 27
Figure 18 30MHz sweep waveform. ........................................................... 28
Figure 19 30MHz sweep markers. .............................................................. 28
Figure 20 Matrix test signal......................................................................... 30
Figure 21 . Left side: The zone plate shows flickering colours at the
subcarrier frequency because of crosstalk between the luma and the
chroma. Right side: No crosstalk issues..................................................... 31
Figure 22 Hum generator............................................................................ 32
Figure 23 aCVi Data format. ....................................................................... 33

4
1. Introduction
SM02 is a video encoder and pattern generator supporting high definition
video standards.
As a video pattern generator, SM02 can generate 19 line based patterns
which are output as simultaneous HD-SDI (SMPTE-272M), YPbPr
component and aCVi.
Standards supported are:
720p/25Hz-30Hz-50Hz-59.94Hz-60Hz
1080p/24Hz-25Hz-29.97Hz-30Hz
1080i/50Hz-59.94Hz-60Hz
Patterns available include:
75%/100%/SMPTE colour bars
Black/White/50% Grey/Red/Green/Blue flat fields
2T, 30T and Pulse bar
Multiburst
15/7.5MHz and 30/15MHz luma/chroma frequency sweeps
5 step linearity
Crosshatch
5 pattern matrix pattern
Pathological (HD-SDI test)
Circular Zone Plate
In addition programmable amplitude white noise and/or 50Hz or 60Hz hum
may be added to the YPbPr (Y channel) and aCVi outputs.
As a video encoder SM02 accepts SMPTE-272M inputs at any of the above
standards which it encodes to simultaneous HD-SDI (SMPTE-272M),
YPbPr component and aCVi outputs. Again noise and/or hum may be
added to the YPbPr and aCVi outputs.
Controls provided include:
aCVi amplitude
aCVi Luma amplitude
aCVi Chroma amplitude
aCVi Burst amplitude

5
aCVi Sync amplitude
aCVi Black level
YPbPr Luma amplitude
YPbPr Pb/Pr amplitude
YPbPr Sync amplitude
YPbPr Black level
SM02 is powered by a universal input power supply and controlled with a
simple and intuitive selection menu.

6
2. aCVi Overview
The following is a brief overview of the aCVi interface.
The basic concept of the aCVi interface is to build on the proven and
reliable transport method of NTSC, (the advantages of PAL – v.v. multi-path
reception – is not relevant to a cable system so NTSC is used as the
model). NTSC transmissions are capable of transmitting more than 1km
across RG-59 cable but the bandwidth is limited to 5MHz. NTSC also has
chroma/luma crosstalk issues that are difficult to resolve at the receiver
end.
Because the cable system is a closed system, it is only necessary for the
transmitter and receiver to ‘understand’ each other so we can modify the
basic NTSC method to suit HD transmissions.
The first thing to overcome is the bandwidth restrictions of the cable. HD
video transmission requires a luma bandwidth of 30MHz according to the
SMPTE-296M specification. Because we have only a single coaxial cable
for the transport we have chosen to transmit luma and colour difference
signals (as opposed to component red, green blue) as the colour difference
signals, because of the visual perception of the eye being less acute to
colour, can be sent at half or less of the luma bandwidth: for aCVi the
chroma bandwidth is 7.5MHz (effectively aCVi is 4:1:1 transmission).
To further reduce the bandwidth of the transmission the colour difference
signals are modulated onto a carrier in quadrature so they effectively use
the same bandwidth. However, to minimise the signal recovery problems of
NTSC, (and as we have no backward compatibility issues), the lower
sideband of the chroma and the luma high frequencies overlap minimally;
the chroma subcarrier for aCVi is set to ~41.4MHz. (See Figure 1).
For 300m of RG-59 cable we can expect 18dB loss at this frequency
(6.2dB/100m @ 50MHz). However the synchronizing signals are at a much
lower frequency where the loss is only about 1-2dB so reliable rastering of
the received signal should always be assured.
To simplify the high frequency compensation of the transmission, preemphasis is used. The degree of pre-emphasis is programmable to allow
for different cable lengths. The maximum pre-emphasis is set at 30dB and
the frequency response of the pre-emphasis is set to approximate the cable
characteristics.

7
A further improvement in the SNR is achieved through transmitting a peak
to peak video level of 1.5V which maintains compatibility with any legacy
SD equipment on the network and also allows common low-power 5V
drivers to be used.
Figure 1 aCVi Spectrum.
ACVi also allows for the bidirectional transfer of data between receiver and
transmitter. One byte of data is transmitted in each direction per frame (i.e.
50bytes/second data rate for a 50Hz frame rate). The data rate is
deliberately kept low to reduce the effects of cable attenuation. Data is sent
using two dedicated lines in the vertical blanking interval.

8
3. Connecting up the SM02
All connections to the SM02 are made via the rear panel: see Figure 2.
Figure 2 SM02 rear panel.
The AC-DC converter connects to the left hand jack. The SM02 input is
protected against reverse polarity and is fused against internal short circuits
or overloads. The converter supplied with the SM02 is a model MW173KB
manufactured by SL Power Electronics Corp. and provides 9VDC at 3A and
accepts AC inputs from 100-240VAC. Connect the supplied power cord to
the AC-DC converter and output DC of the converter to the 9VDC Power In
input of the SM02.

9
Figure 3 SM02 AC-DC converter
A full specification for the supplied AC-DC converter may be found in
Appendix A.
The SM02 provides both analogue and digital component outputs for
connecting to the equipment under test.
The aCVi output is connected to the BNC, ‘aCVi Out’. The specification for
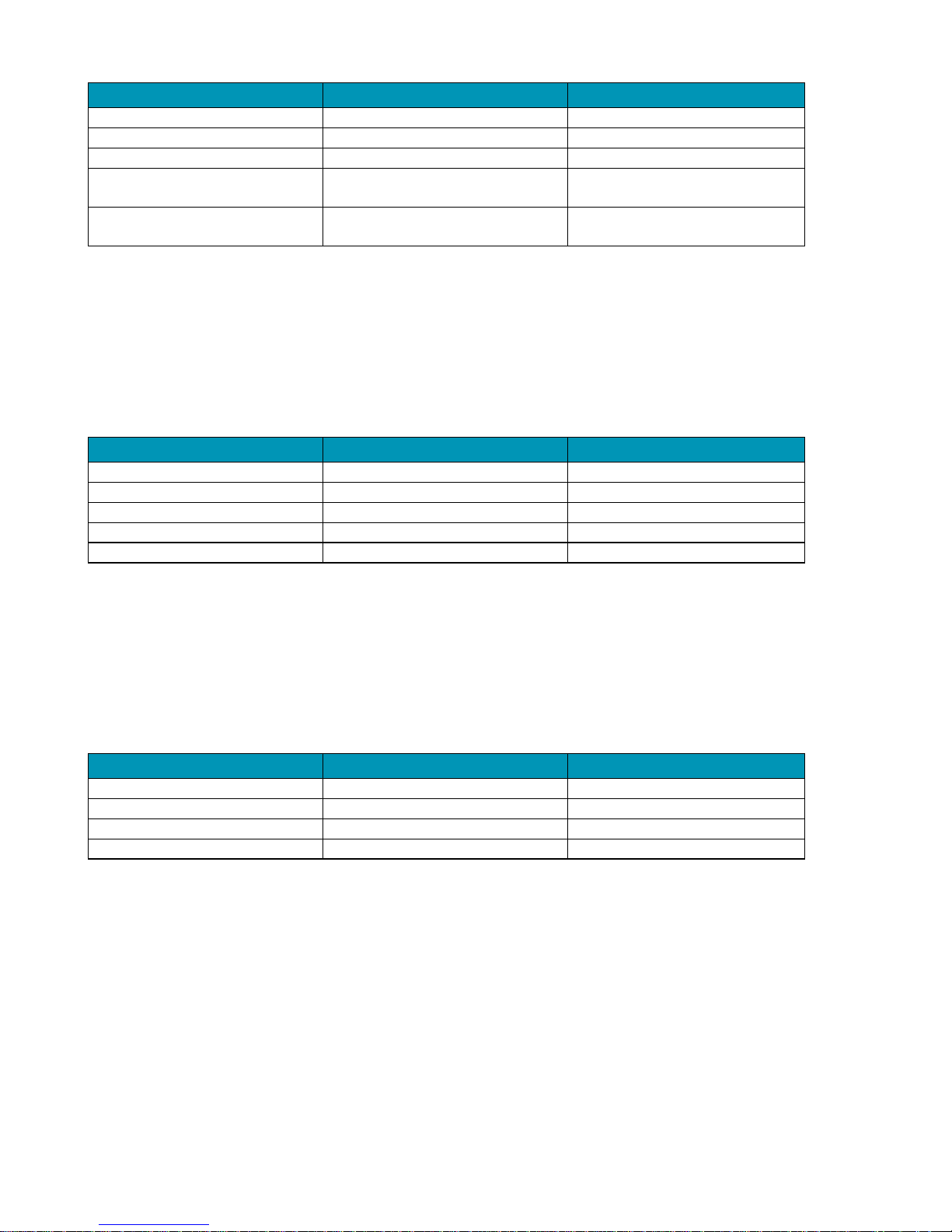
the output is shown in Table 1.
Parameter
Specification
Comments
Connector Type
BNC
Output impedance
75Ω
Output return loss
>30dB
0 - 37.125MHz
aCVi output level
1.5V pk.pk
Nominal peak Y to sync tip
for 100% colour bars input
Table 1 aCVi output specification.
The analogue component outputs are connected to the BNCs, ‘Y Out’, ‘Pb
Out’ and ‘Pr Out’. The specification for the outputs is shown in Table 2.
10
Parameter
Specification
Comments
Connector Type
BNC
Output impedance
75Ω
Output return loss
>30dB
0-5MHz
Y output level
1.0V pk.pk
Nominal 100% colour bars
input
Cb/Cr output levels
±350mV pk-pk
Nominal 100% colour bars
input
Table 2 Analogue Component output Specifications
The serial digital interface (HD-SDI) output is connected to the ‘HD SDI Out’
BNC and its specifications are shown in Table 3.
The HD-SDI output conforms to the SMPTE-272M specification.
Parameter
Specification
Comments
Connector Type
BNC
Output impedance
75Ω
Fixed termination
Output return loss
>15dB
50Hz-1.485GHz
Output level
800mV pk-pk ± 10%
Jitter
<0.2UI
Table 3 HD-SDI Output Specifications
The serial digital interface (HD-SDI) input (only used in encoder mode) is
connected to the ‘HD SDI In’ BNC and its specifications are shown in Table
4.
The HD-SDI input conforms to the SMPTE-272M specification.
Parameter
Specification
Comments
Connector Type
BNC
Input impedance
75Ω
Fixed termination
Input return loss
>15dB
50Hz-1.485GHz
Input level
800mV pk-pk
Nominal
Table 4 HD-SDI Input specification.

11
4. Quick Start Guide
Switch On and Control
Connect the AC-DC converter 9VDC cable into the rear panel power in
socket. Connect the AC supply to a local AC supply between 110-240VAC.
The Standby LED should light. Push the Adjust control and the unit will
switch on and the welcome message will be displayed (SingMai SM02).
To switch off the SM02 push the Adjust control again.
The front panel of the SM02 is shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4 SM02 Front panel.
There are just two controls for the SM01. The right hand control (Adjust)
switches the unit between On and Standby by pushing it whilst also
adjusting the value of parameters by rotating the knob left or right. The
central switch (Select) selects the chosen menu parameter and switches
preset parameters between, for example, on and off.
After the welcome message is displayed the LCD display will show the
available top level menus. A left hand arrow indicates which menu is
‘active’. Rotating the Adjust control will show all the available menus; after
the last of the menus an up arrow is shown.
To select a menu ensure the left arrow is by the side of the required top
level menu and press the Select button. Those menu options will then be
displayed.

12
To change a parameter within the lower menu choices choose the required
item by aligning the left arrow with it and press the Select button. The
parameter will either toggle between the available options (e.g. On or Off)
or will show a menu bar where to can select more options via the Adjust
control. Once you have chosen the setting you require press the Select
button to return to the menu choices.
The Adjust control is also used to set the parameter values. Once set the
required value, press the Select button to retain that value and return to the
menu.
To return to the top level menu scroll down the menu choices using the
Adjust control; the last one before the up arrow will show Exit. Select this
by pressing the Select button and you will return to the top level menus.
 Loading...
Loading...